⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-06 更新
GPT4Scene: Understand 3D Scenes from Videos with Vision-Language Models
Authors:Zhangyang Qi, Zhixiong Zhang, Ye Fang, Jiaqi Wang, Hengshuang Zhao
In recent years, 2D Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have made significant strides in image-text understanding tasks. However, their performance in 3D spatial comprehension, which is critical for embodied intelligence, remains limited. Recent advances have leveraged 3D point clouds and multi-view images as inputs, yielding promising results. However, we propose exploring a purely vision-based solution inspired by human perception, which merely relies on visual cues for 3D spatial understanding. This paper empirically investigates the limitations of VLMs in 3D spatial knowledge, revealing that their primary shortcoming lies in the lack of global-local correspondence between the scene and individual frames. To address this, we introduce GPT4Scene, a novel visual prompting paradigm in VLM training and inference that helps build the global-local relationship, significantly improving the 3D spatial understanding of indoor scenes. Specifically, GPT4Scene constructs a 3D Bird’s Eye View (BEV) image from the video and marks consistent object IDs across both frames and the BEV image. The model then inputs the concatenated BEV image and video frames with markers. In zero-shot evaluations, GPT4Scene improves performance over closed-source VLMs like GPT-4o. Additionally, we prepare a processed video dataset consisting of 165K text annotation to fine-tune open-source VLMs, achieving state-of-the-art performance on all 3D understanding tasks. Surprisingly, after training with the GPT4Scene paradigm, VLMs consistently improve during inference, even without visual prompting and BEV image as explicit correspondence. It demonstrates that the proposed paradigm helps VLMs develop an intrinsic ability to understand 3D scenes, which paves the way for a noninvasive approach to extending pre-trained VLMs for 3D scene understanding.
近年来,二维视觉语言模型(VLMs)在图文理解任务中取得了显著进展。然而,它们在三维空间理解方面的表现,对于体现智能至关重要,仍然有限。最近的进展利用三维点云和多视角图像作为输入,取得了令人瞩目的结果。然而,我们提出探索一种纯粹基于视觉的解决方案,该方案受到人类感知的启发,仅依赖视觉线索进行三维空间理解。本文经验性地研究了VLMs在三维空间知识方面的局限性,发现它们的主要短板在于场景与单个帧之间缺乏全局局部对应关系。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了GPT4Scene,这是一种新型的视觉提示范式,有助于建立全局局部关系,显著提高了对室内场景的三维空间理解。具体而言,GPT4Scene从视频中构建三维鸟瞰图(BEV),并在帧和BEV图像上标记一致的对象ID。然后,模型将标记后的BEV图像和视频帧作为输入。在零样本评估中,GPT4Scene改进了封闭源VLMs(如GPT-4o)的性能。此外,我们还准备了一个包含16.5万条文本注释的处理过的视频数据集,以微调开源VLMs,在所有三维理解任务上均达到最新性能水平。令人惊讶的是,经过GPT4Scene范式的训练后,即使在推理过程中没有明确的视觉提示和BEV图像作为对应关系,VLMs的表现也持续提高。这表明所提出的范式帮助VLMs形成了对三维场景理解的内在能力,这为扩展预训练的VLMs以进行三维场景理解提供了无创方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://gpt4scene.github.io/
摘要
近年来,二维视觉语言模型(VLMs)在图像文本理解任务上取得了显著进展,但在三维空间理解上的表现仍然有限,这对智能提出了更高需求。本研究探讨了VLMs在三维空间知识方面的局限性,发现其主要短板在于场景与个体帧之间缺乏全局-局部对应关系。为解决这一问题,本文提出了GPT4Scene,一种新型视觉提示范式,在VLM训练和推理过程中构建全局-局部关系,显著提高室内场景的三维空间理解能力。GPT4Scene构建三维鸟瞰图(BEV),在帧和BEV图像之间标记一致的对象ID。模型输入拼接的BEV图像和视频帧带有标记。在零样本评估中,GPT4Scene改进了封闭源VLMs如GPT-4o的性能。此外,使用处理过的包含16.5万文本注释的视频数据集微调开源VLMs,在所有三维理解任务上达到最佳性能。令人惊讶的是,采用GPT4Scene范式训练后,即使在无需视觉提示和BEV图像作为明确对应的情况下,VLMs的推理能力持续提高。这表明所提范式帮助VLMs发展了对三维场景的内在理解能力,为扩展预训练VLMs进行三维场景理解提供了无创方法。
关键见解
- 二维视觉语言模型(VLMs)在三维空间理解方面存在局限性。
- VLMs的主要短板在于缺乏场景与帧之间的全局-局部对应关系。
- GPT4Scene是一种新型视觉提示范式,旨在解决VLMs的这一短板。
- GPT4Scene通过构建三维鸟瞰图(BEV)和标记对象ID来建立全局-局部关系。
- GPT4Scene能提高零样本评估中VLMs的性能。
- 使用处理过的视频数据集微调VLMs,可在三维理解任务上达到最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

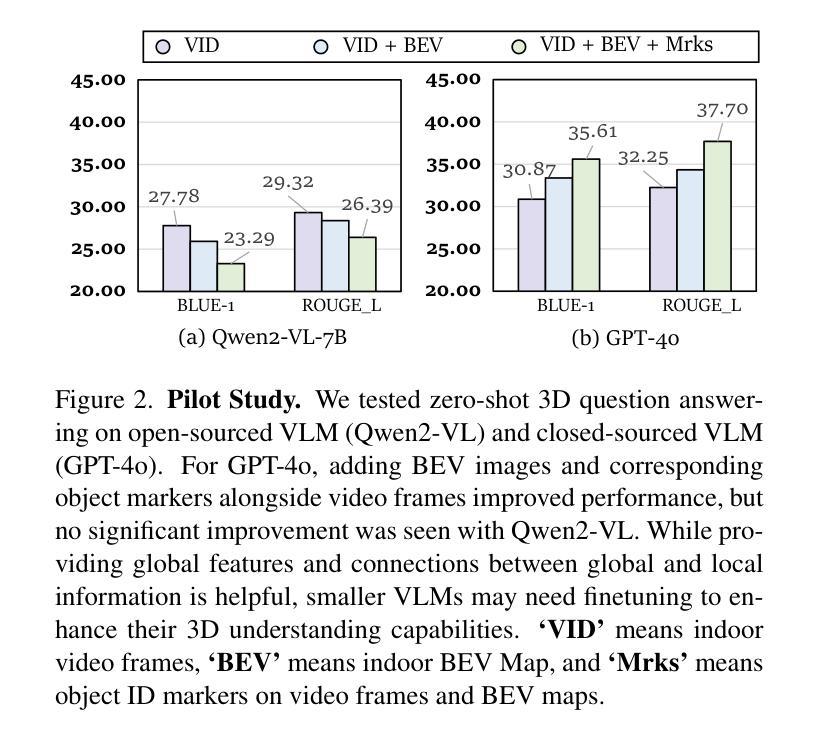
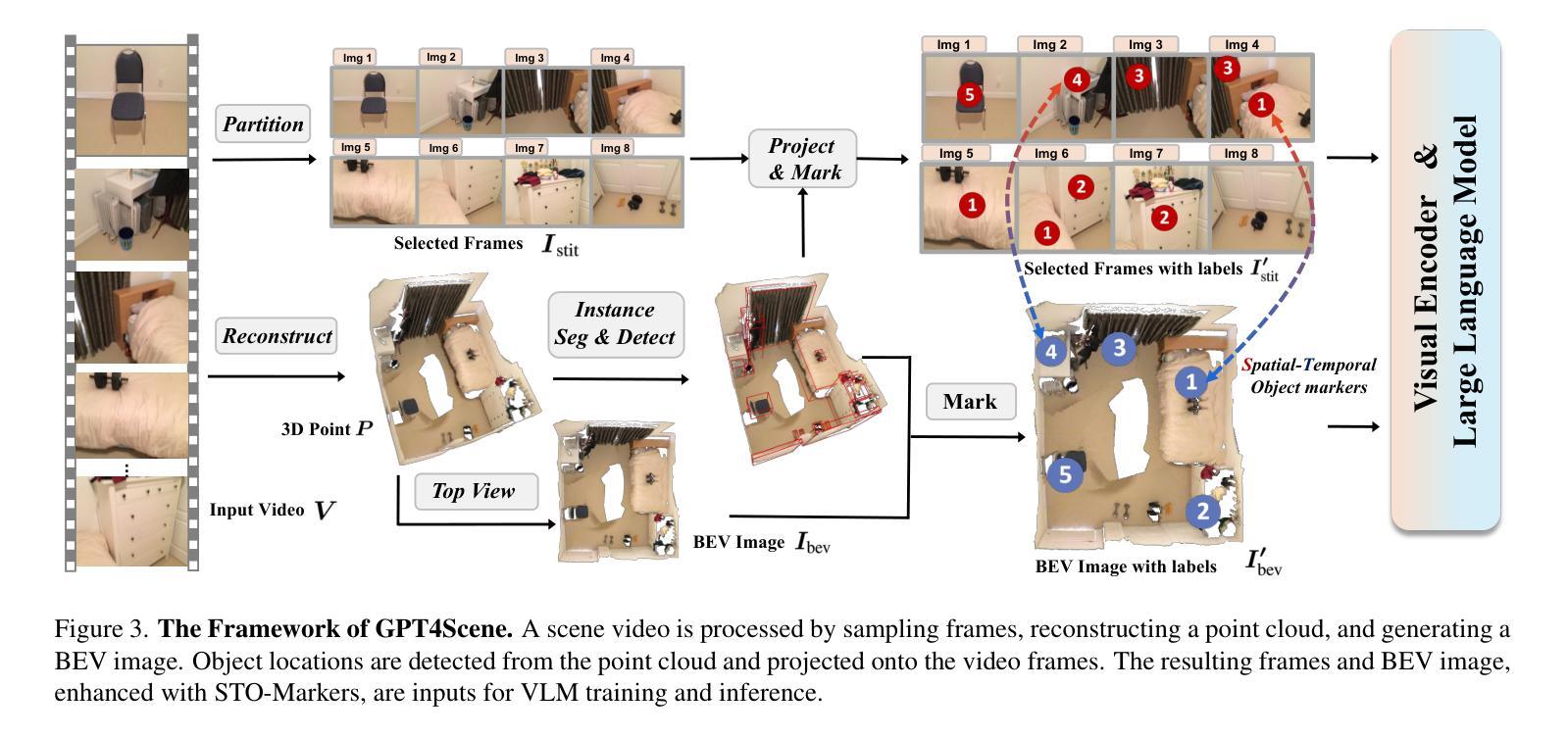

Online Video Understanding: A Comprehensive Benchmark and Memory-Augmented Method
Authors:Zhenpeng Huang, Xinhao Li, Jiaqi Li, Jing Wang, Xiangyu Zeng, Cheng Liang, Tao Wu, Xi Chen, Liang Li, Limin Wang
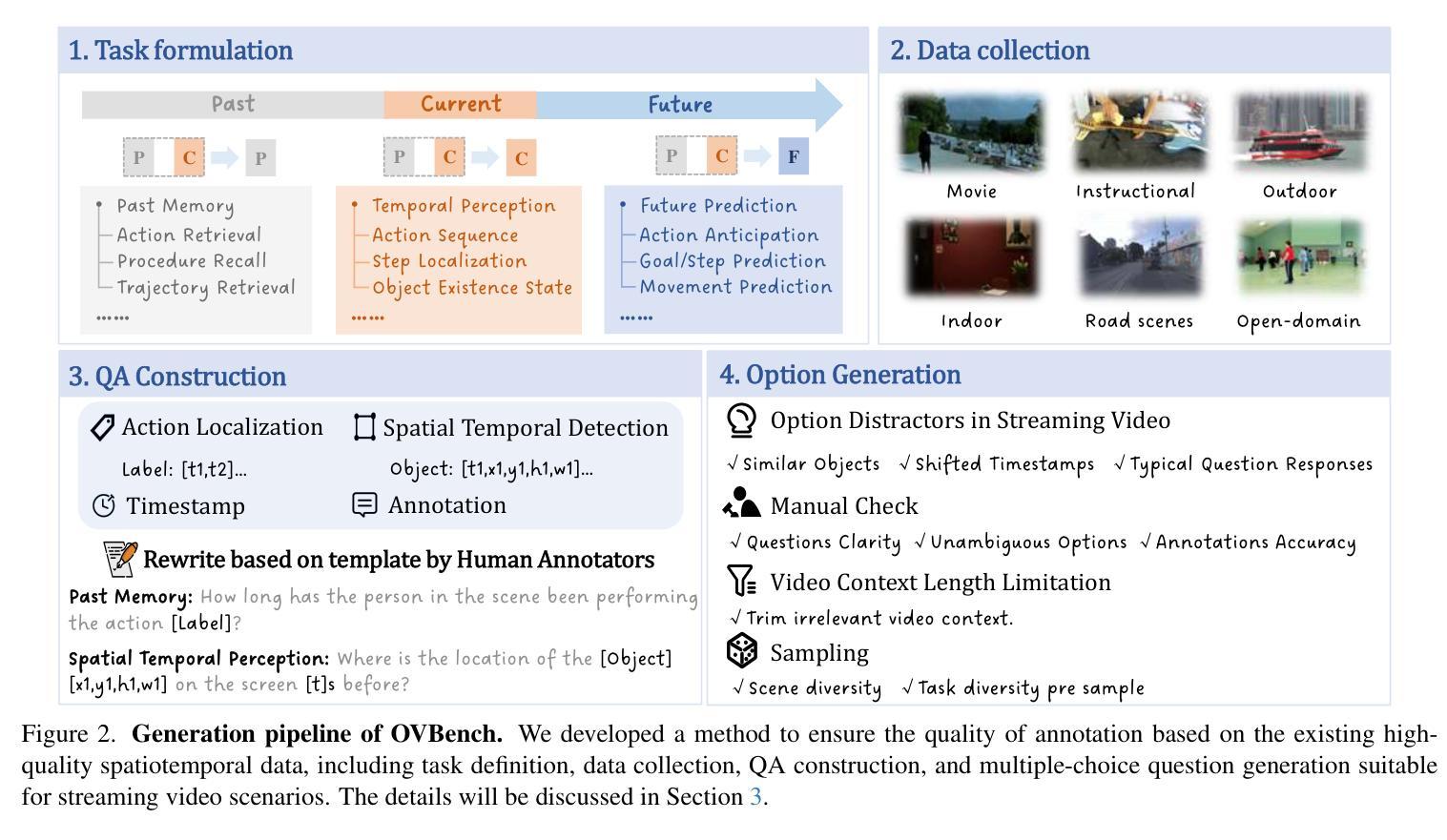
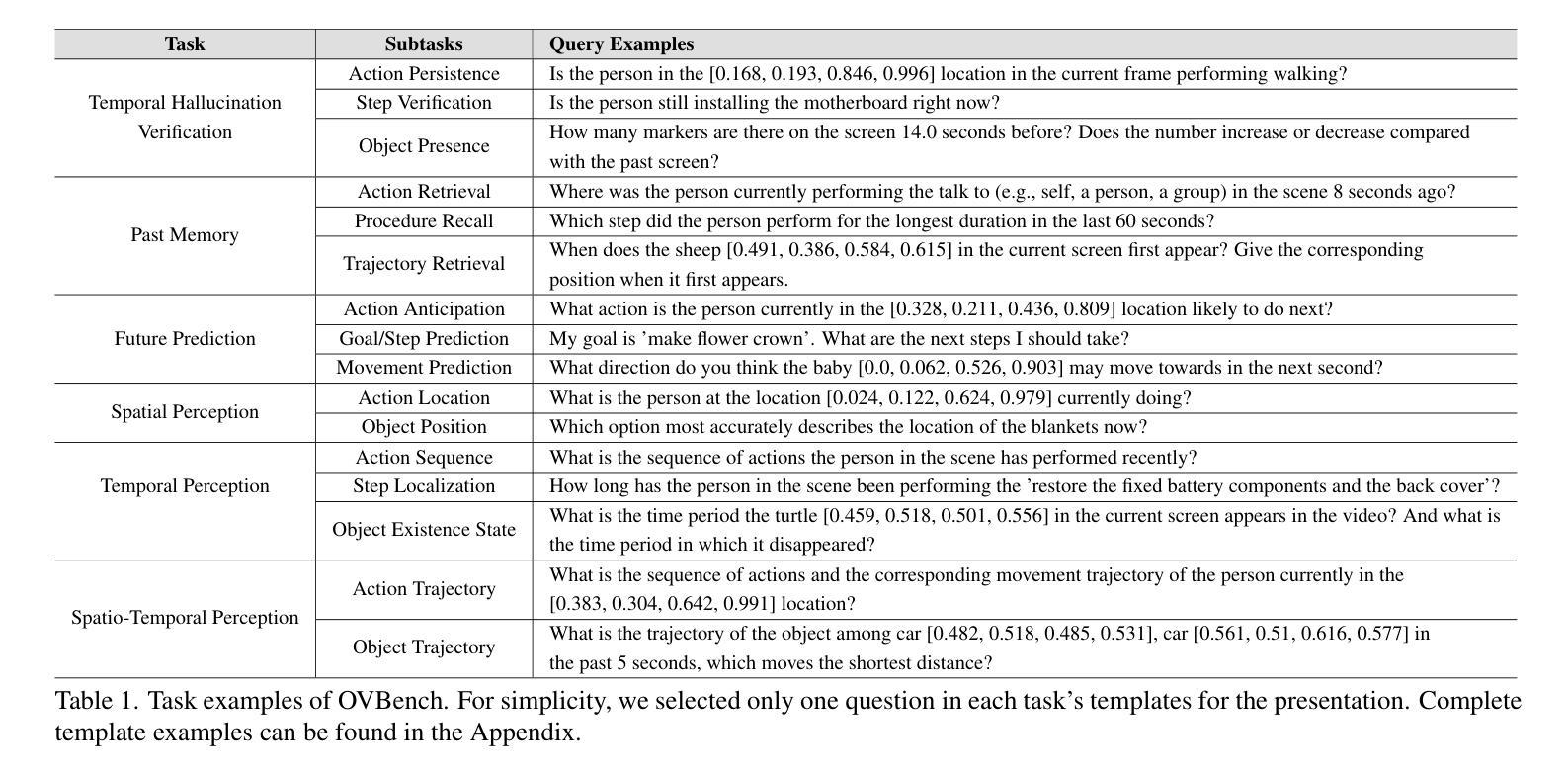
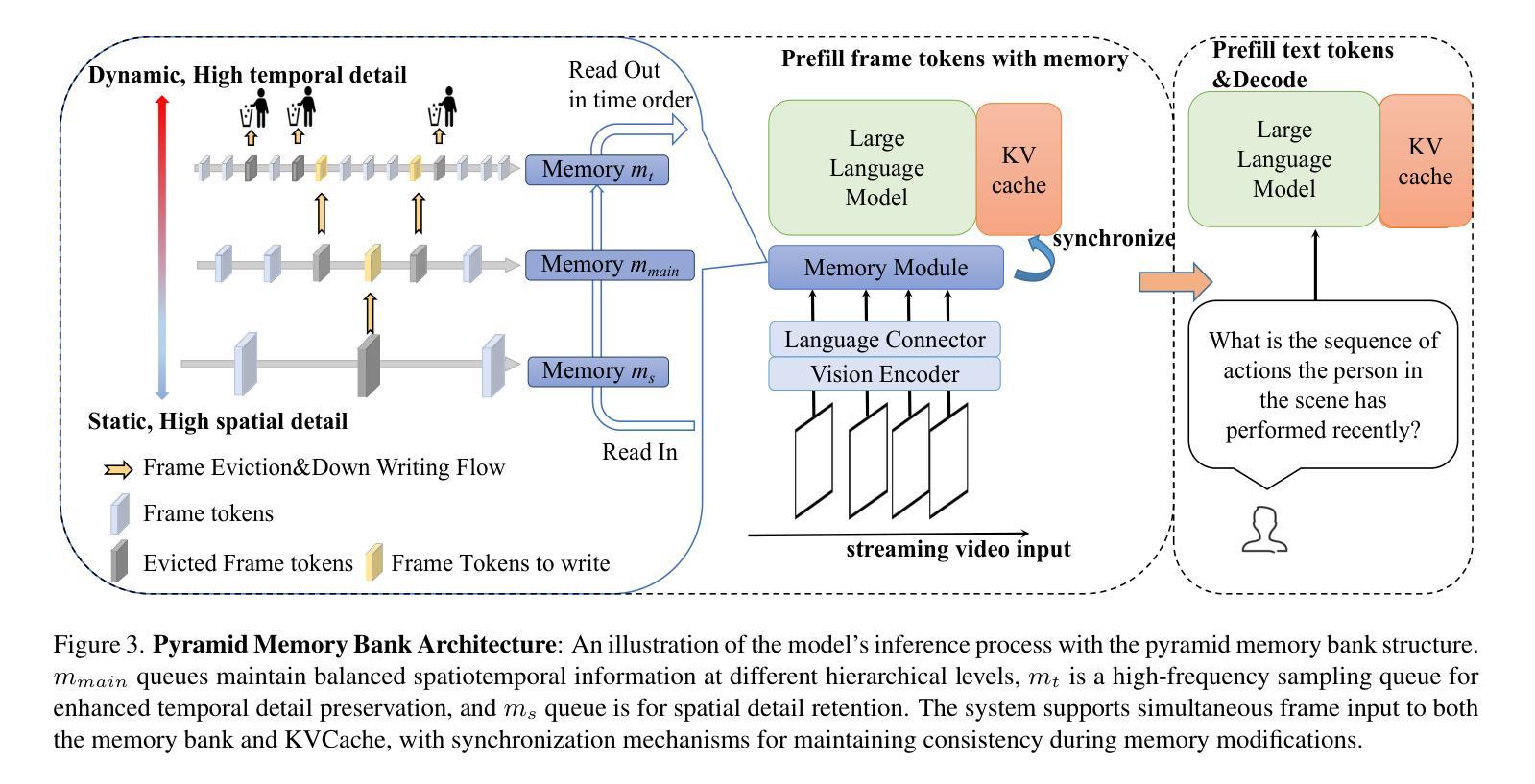
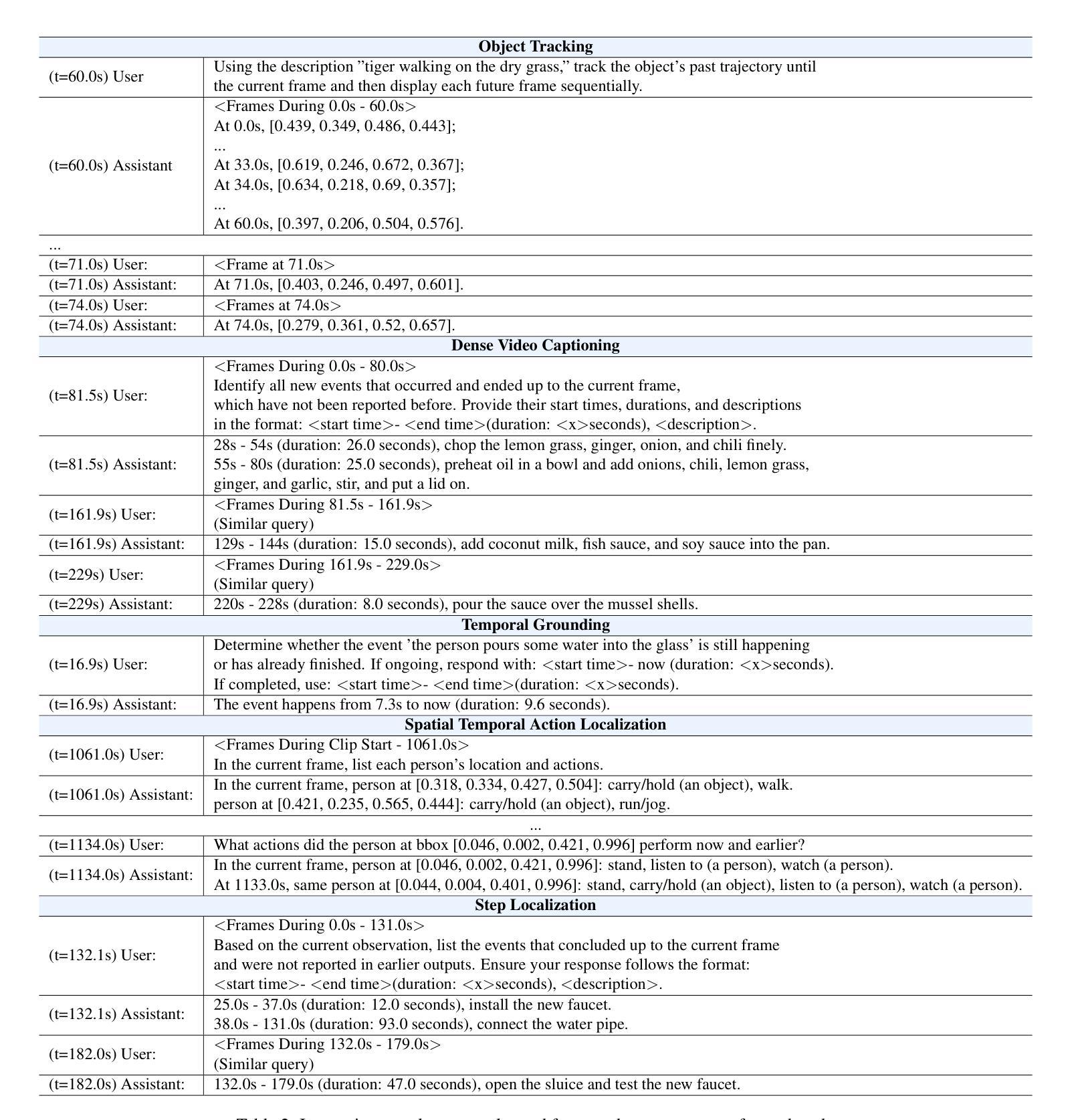
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown significant progress in offline video understanding. However, applying these models to real-world scenarios, such as autonomous driving and human-computer interaction, presents unique challenges due to the need for real-time processing of continuous online video streams. To this end, this paper presents systematic efforts from three perspectives: evaluation benchmark, model architecture, and training strategy. First, we introduce OVBench, a comprehensive question-answering benchmark specifically designed to evaluate models’ ability to perceive, memorize, and reason within online video contexts. It features six core task types across three temporal contexts-past, present, and future-forming 16 subtasks from diverse datasets. Second, we propose a new Pyramid Memory Bank (PMB) that effectively retains key spatiotemporal information in video streams. Third, we proposed an offline-to-online learning paradigm, designing an interleaved dialogue format for online video data and constructing an instruction-tuning dataset tailored for online video training. This framework led to the development of VideoChat-Online, a robust and efficient model for online video understanding. Despite the lower computational cost and higher efficiency, VideoChat-Online outperforms existing state-of-the-art offline and online models across popular offline video benchmarks and OVBench, demonstrating the effectiveness of our model architecture and training strategy.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在离线视频理解方面取得了显著进展。然而,将这些模型应用于自动驾驶和人机交互等现实场景,由于需要对连续的在线视频流进行实时处理,面临着独特的挑战。为此,本文从评估基准、模型架构和训练策略三个方面进行了系统的努力。首先,我们介绍了OVBench,这是一个专门设计用于评估模型在线视频语境中的感知、记忆和推理能力的综合问答基准。它涵盖了过去、现在和未来的三个时间语境中的六种核心任务类型,从各种数据集中形成了16个子任务。其次,我们提出了一种新的Pyramid Memory Bank(PMB),它能有效地保留视频流中的关键时空信息。第三,我们提出了从离线到在线的学习范式,为在线视频数据设计了一种交替对话格式,并构建了一个适用于在线视频训练的指令调整数据集。这一框架催生了VideoChat-Online,一个用于在线视频理解的稳健高效的模型。尽管计算成本较低,效率较高,VideoChat-Online在流行的离线视频基准测试和OVBench上的表现都超过了现有的最先进的离线和在线模型,这证明了我们的模型架构和训练策略的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文从评估基准、模型架构和训练策略三个方面对在线视频理解进行了深入研究。构建了专门针对在线视频理解的问答基准测试OVBench,覆盖了过去、现在和未来三个时间维度的16个子任务。同时,提出了金字塔记忆库(PMB)以有效保存视频流中的关键时空信息。此外,建立了针对在线视频的离线到在线学习范式,设计了针对在线视频数据的交互对话格式,并构建了针对在线视频训练的指令调整数据集。基于这些研究,开发了适用于在线视频理解的稳健高效模型VideoChat-Online。该模型在主流离线视频基准测试和OVBench上的表现优于现有最先进的离线及在线模型,验证了其模型架构和训练策略的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 论文构建了新的在线视频理解问答基准测试OVBench,涵盖了三个时间维度的16个子任务。
- 引入了金字塔记忆库(PMB),用于有效保存视频流中的关键时空信息。
- 提出了离线到在线的学习范式,为在线视频理解建立了新的模型训练框架。
- 设计了针对在线视频数据的交互对话格式,增强了模型的实时互动能力。
- 构建了针对在线视频训练的指令调整数据集,提升了模型的适应性和性能。
- VideoChat-Online模型在多个基准测试中表现优越,证明了其架构和训练策略的有效性。
点此查看论文截图