⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-06 更新
Leverage Cross-Attention for End-to-End Open-Vocabulary Panoptic Reconstruction
Authors:Xuan Yu, Yuxuan Xie, Yili Liu, Haojian Lu, Rong Xiong, Yiyi Liao, Yue Wang
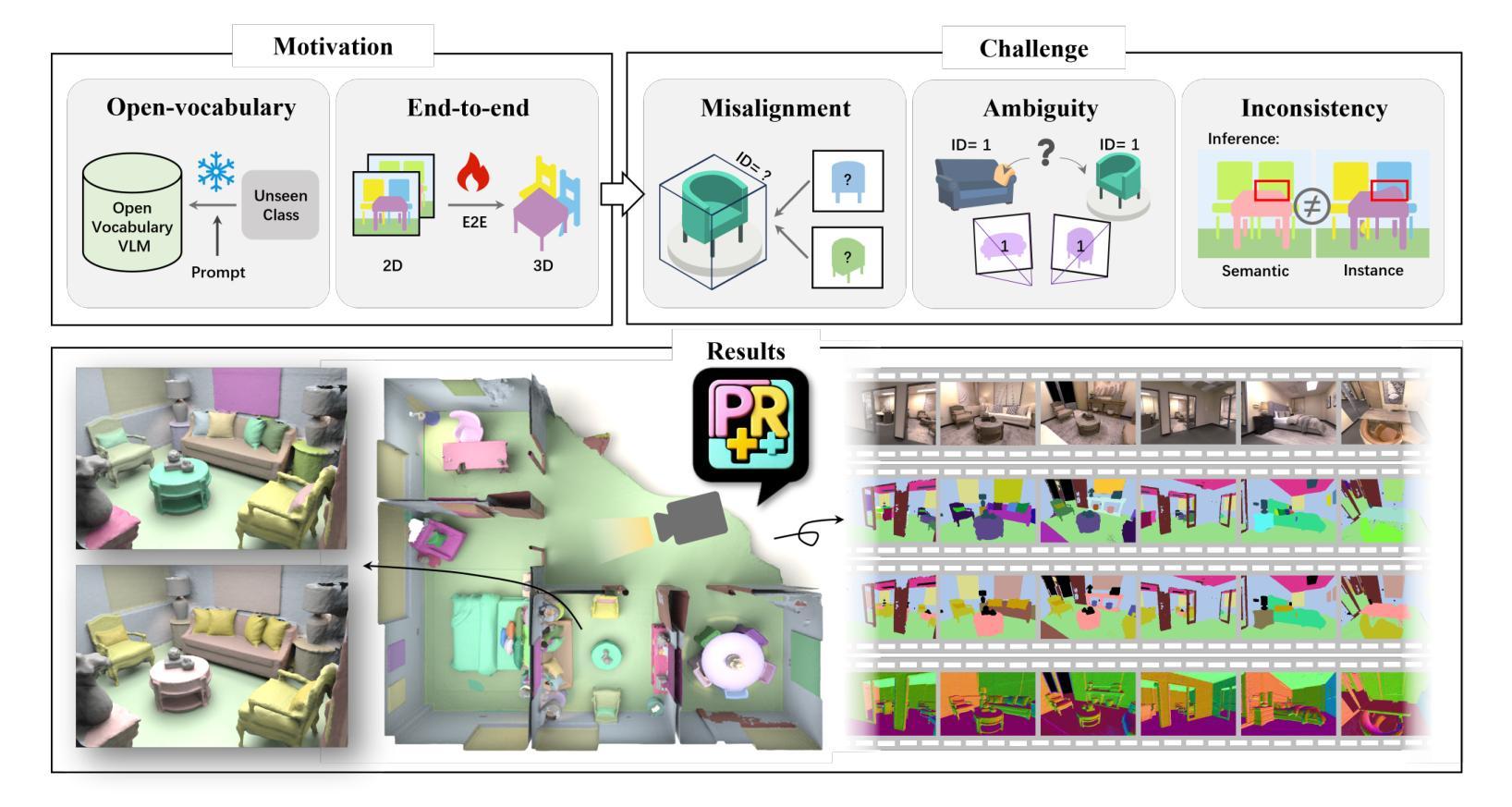
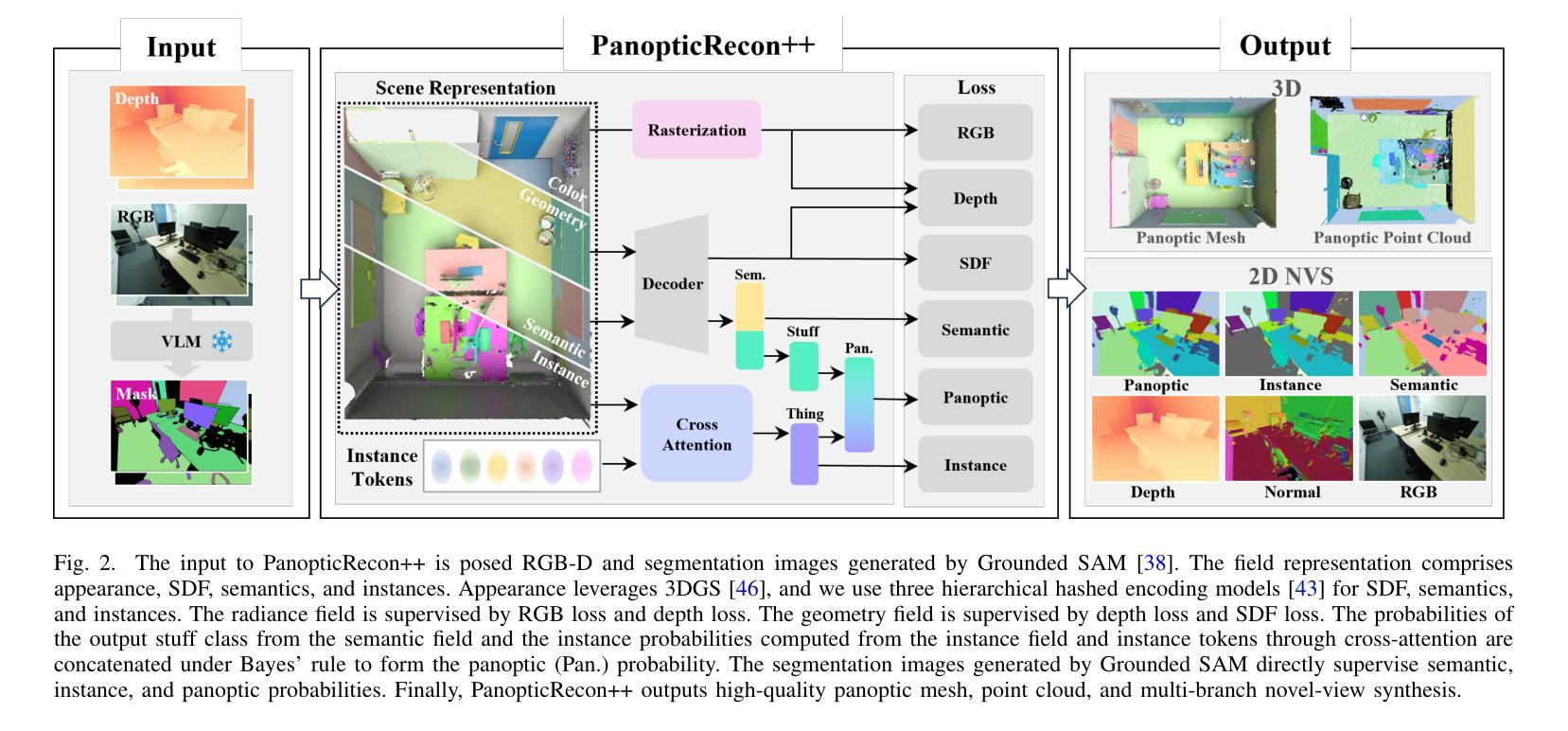
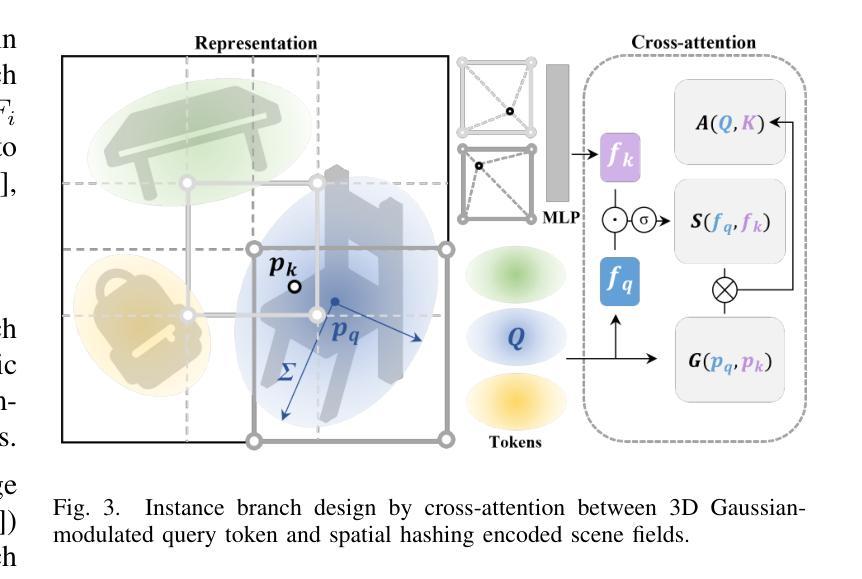
Open-vocabulary panoptic reconstruction offers comprehensive scene understanding, enabling advances in embodied robotics and photorealistic simulation. In this paper, we propose PanopticRecon++, an end-to-end method that formulates panoptic reconstruction through a novel cross-attention perspective. This perspective models the relationship between 3D instances (as queries) and the scene’s 3D embedding field (as keys) through their attention map. Unlike existing methods that separate the optimization of queries and keys or overlook spatial proximity, PanopticRecon++ introduces learnable 3D Gaussians as instance queries. This formulation injects 3D spatial priors to preserve proximity while maintaining end-to-end optimizability. Moreover, this query formulation facilitates the alignment of 2D open-vocabulary instance IDs across frames by leveraging optimal linear assignment with instance masks rendered from the queries. Additionally, we ensure semantic-instance segmentation consistency by fusing query-based instance segmentation probabilities with semantic probabilities in a novel panoptic head supervised by a panoptic loss. During training, the number of instance query tokens dynamically adapts to match the number of objects. PanopticRecon++ shows competitive performance in terms of 3D and 2D segmentation and reconstruction performance on both simulation and real-world datasets, and demonstrates a user case as a robot simulator. Our project website is at: https://yuxuan1206.github.io/panopticrecon_pp/
开放词汇全景重建提供了全面的场景理解,促进了嵌入式机器人和真实感仿真技术的进展。在本文中,我们提出了PanopticRecon++,这是一种端到端的方法,通过新颖的跨注意力视角来进行全景重建。这个视角通过注意力图对3D实例(作为查询)和场景3D嵌入字段(作为键)之间的关系进行建模。与现有方法不同,这些方法要么将查询和键的优化分开,要么忽略了空间邻近关系,PanopticRecon++引入了可学习的3D高斯分布作为实例查询。这种表述注入了3D空间先验信息,以保留邻近关系并保持端到端的优化能力。此外,这种查询表述通过利用来自查询的实例掩膜进行最佳线性分配,促进了跨帧的2D开放词汇实例ID的对齐。通过融合基于查询的实例分割概率和语义概率在新型全景头中,由全景损失进行监管,我们还确保了语义实例分割的一致性。在训练过程中,实例查询令牌的数目会动态调整以适应对象的数量。PanopticRecon++在模拟和真实世界数据集上表现出具有竞争力的3D和2D分割和重建性能,并展示了作为机器人模拟器的用户案例。我们的项目网站是:[https://yuxuan1206.github.io/panopticrecon_pp/]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为PanopticRecon++的端到端方法,用于通过新型跨注意力视角进行全景重建。该方法建立3D实例(作为查询)与场景3D嵌入字段(作为键)之间的关系,通过注意力图模型实现。此方法采用可学习的3D高斯作为实例查询,注入3D空间先验信息以保留邻近性并保持端到端优化能力。此外,通过利用基于查询的实例掩膜渲染,该方法实现了跨帧的2D开放词汇实例ID对齐。结合查询基础上的实例分割概率与语义概率,该方法保证了语义实例分割的一致性。PanopticRecon++在模拟和真实数据集上的3D和2D分割以及重建性能具有竞争力,并展示了在机器人模拟器中的应用案例。
Key Takeaways
- PanopticRecon++是一种端到端的全景重建方法,通过新型跨注意力视角实现。
- 该方法建立3D实例与场景3D嵌入字段的关系,引入可学习的3D高斯作为实例查询。
- PanopticRecon++能保留邻近性并保持端到端优化能力,注入3D空间先验信息。
- 通过利用基于查询的实例掩膜渲染,实现了跨帧的2D开放词汇实例ID对齐。
- PanopticRecon++结合了查询基础上的实例分割概率与语义概率,确保语义实例分割的一致性。
- 该方法在模拟和真实数据集上的3D和2D分割以及重建性能具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图
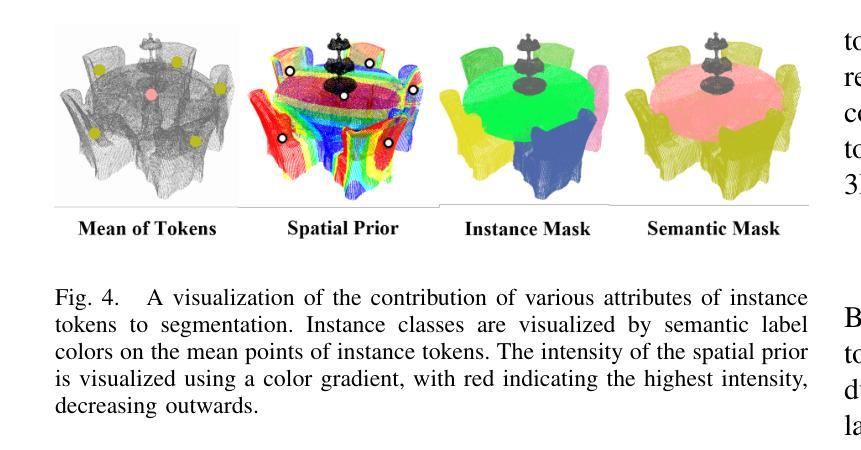
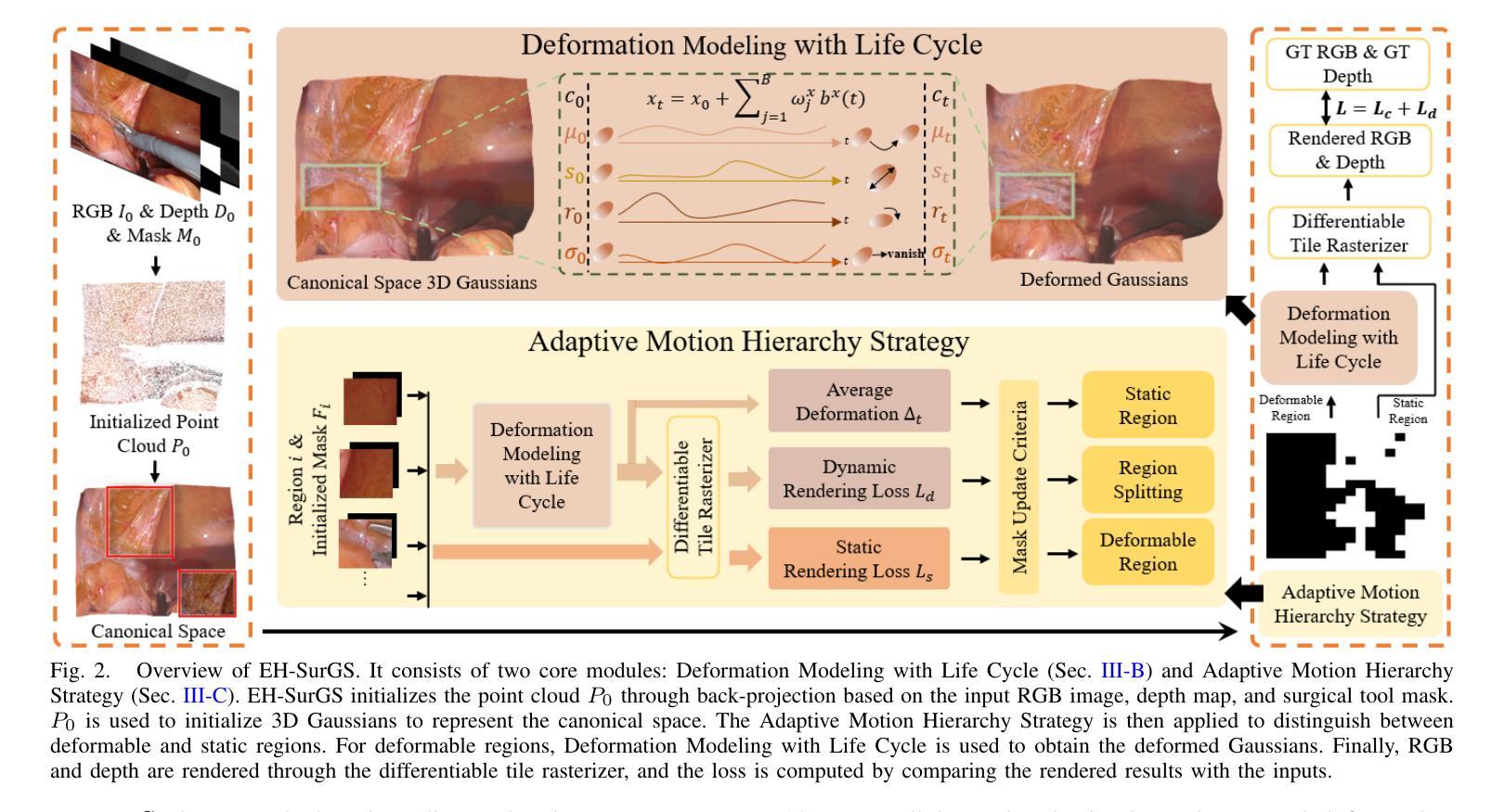
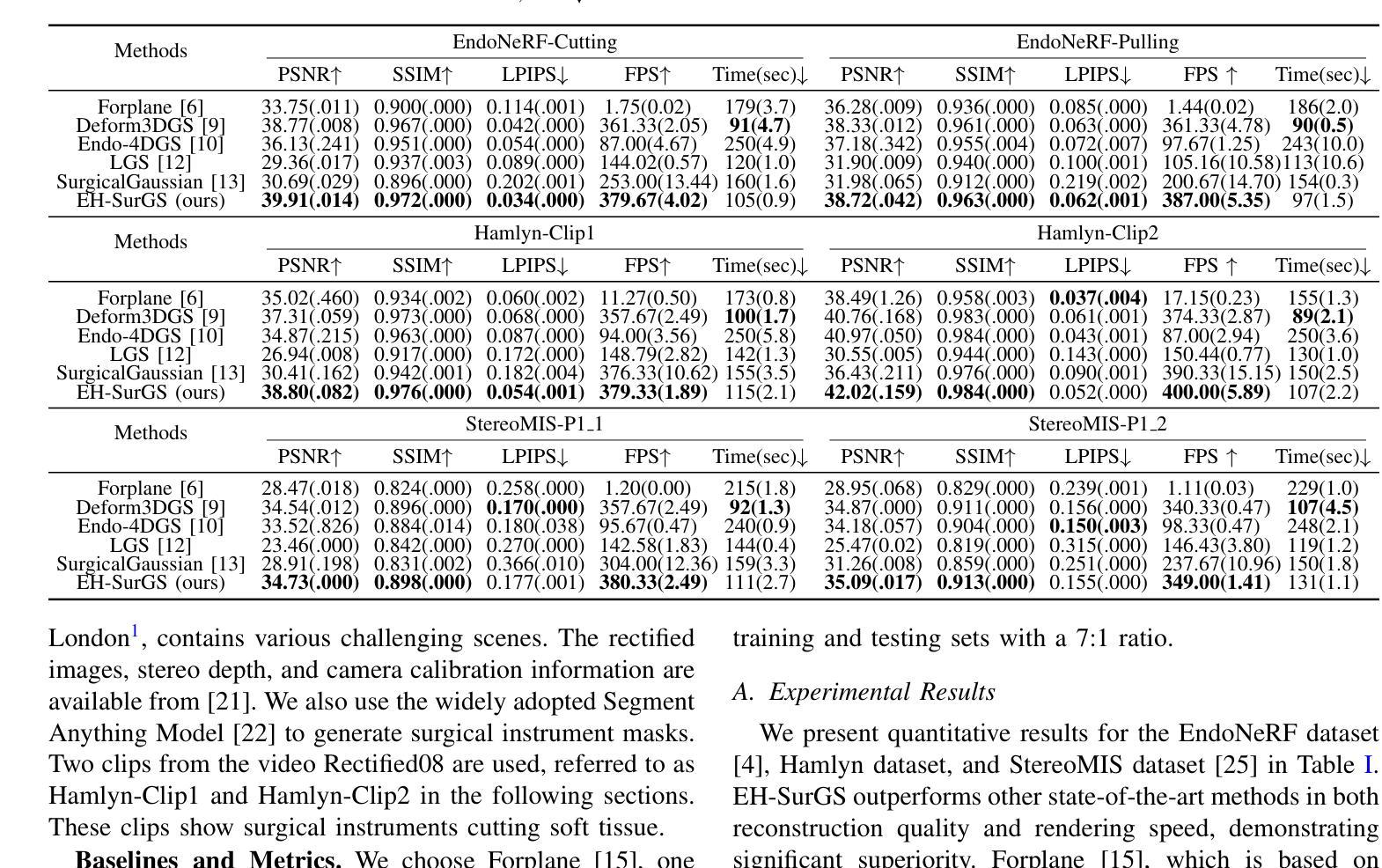
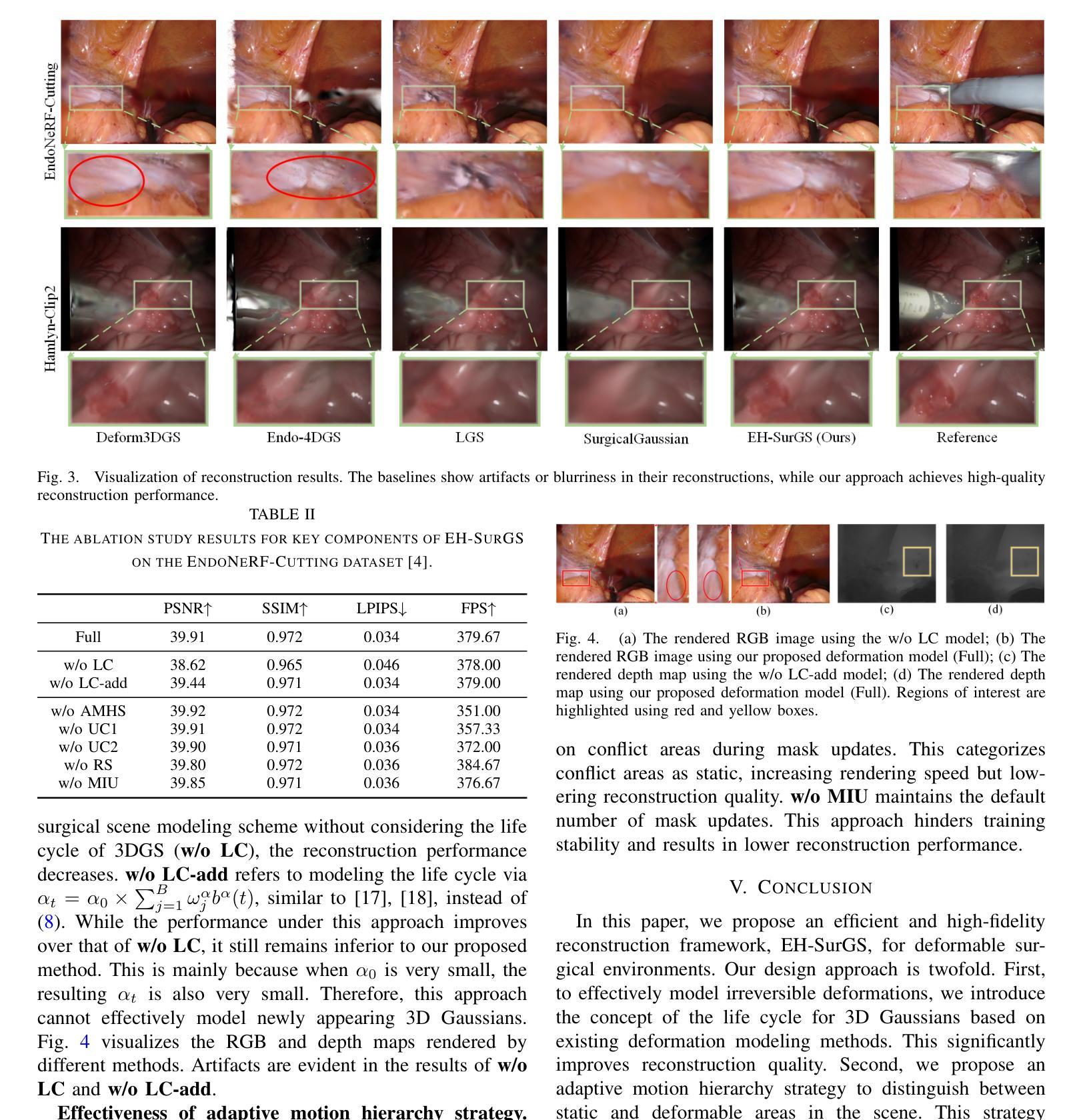
Deformable Gaussian Splatting for Efficient and High-Fidelity Reconstruction of Surgical Scenes
Authors:Jiwei Shan, Zeyu Cai, Cheng-Tai Hsieh, Shing Shin Cheng, Hesheng Wang
Efficient and high-fidelity reconstruction of deformable surgical scenes is a critical yet challenging task. Building on recent advancements in 3D Gaussian splatting, current methods have seen significant improvements in both reconstruction quality and rendering speed. However, two major limitations remain: (1) difficulty in handling irreversible dynamic changes, such as tissue shearing, which are common in surgical scenes; and (2) the lack of hierarchical modeling for surgical scene deformation, which reduces rendering speed. To address these challenges, we introduce EH-SurGS, an efficient and high-fidelity reconstruction algorithm for deformable surgical scenes. We propose a deformation modeling approach that incorporates the life cycle of 3D Gaussians, effectively capturing both regular and irreversible deformations, thus enhancing reconstruction quality. Additionally, we present an adaptive motion hierarchy strategy that distinguishes between static and deformable regions within the surgical scene. This strategy reduces the number of 3D Gaussians passing through the deformation field, thereby improving rendering speed. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method surpasses existing state-of-the-art approaches in both reconstruction quality and rendering speed. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness and necessity of our proposed components. We will open-source our code upon acceptance of the paper.
对于可变形手术场景的效率和高质量重建是一项至关重要但又充满挑战的任务。基于近年来对高斯二次积算法研究的最新进展,当前方法在重建质量和渲染速度方面都取得了重大进步。然而仍存在两大挑战:(1)处理不可逆的动态变化(如手术场景中常见的组织剪切)的难度;(2)缺乏手术场景变形的层次建模,这降低了渲染速度。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了EH-SurGS,这是一个针对可变形手术场景的高效且高质量重建算法。我们提出了一种结合高斯生命周期的变形建模方法,可以有效地捕捉常规和不可逆的变形,从而提高重建质量。此外,我们还提出了一种自适应运动层次策略,可以区分手术场景中的静态和可变形区域。这种策略减少了通过变形场的三维高斯数量,从而提高了渲染速度。大量实验表明,我们的方法在重建质量和渲染速度方面都超过了现有的最新方法。消融研究进一步验证了所提出组件的有效性和必要性。论文接受后,我们将公开我们的源代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 4 figures, submitted to ICRA 2025
摘要
高效且高保真地重建可变形手术场景是一项至关重要的任务,但具有挑战性。基于最近的三维高斯绘制技术的进展,当前的方法已在重建质量和渲染速度方面取得了显著改进。然而,仍存在两个主要挑战:一是难以处理手术场景中常见的不可逆动态变化,如组织剪切;二是缺乏手术场景变形的层次建模,这降低了渲染速度。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了EH-SurGS,这是一种高效且高保真地重建可变形手术场景的方法。我们提出了一种变形建模方法,该方法结合了三维高斯的生命周期,可以有效地捕捉常规和不可逆变形,从而提高重建质量。此外,我们提出了一种自适应运动层次策略,可以区分手术场景中的静态和可变形区域。该策略减少了通过变形场的三维高斯数量,从而提高了渲染速度。大量实验表明,我们的方法在重建质量和渲染速度方面都超越了现有的最新方法。消融研究进一步验证了我们所提出组件的有效性和必要性。论文被接受后,我们将公开源代码。
要点提炼
- 当前方法在重建手术场景时面临处理不可逆动态变化和缺乏层次建模的挑战。
- 引入EH-SurGS方法,有效结合三维高斯的生命周期进行变形建模,提高重建质量。
- 提出自适应运动层次策略,区分静态和可变形区域,提高渲染速度。
- 相比现有方法,EH-SurGS在重建质量和渲染速度方面都有显著优势。
- 消融研究验证了方法的有效性,论文被接受后将公开源代码。
- EH-SurGS有助于更精确地模拟手术场景中的动态变化,为手术导航和模拟提供更强支持。
点此查看论文截图

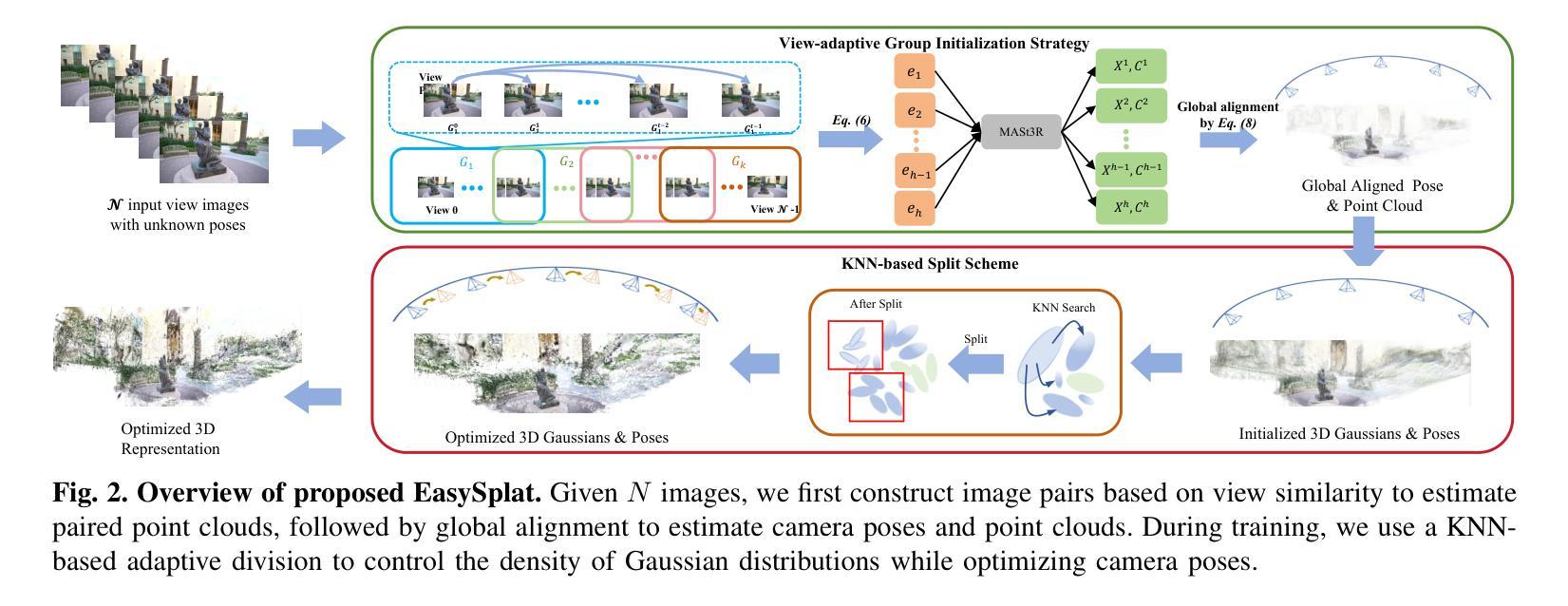
EasySplat: View-Adaptive Learning makes 3D Gaussian Splatting Easy
Authors:Ao Gao, Luosong Guo, Tao Chen, Zhao Wang, Ying Tai, Jian Yang, Zhenyu Zhang
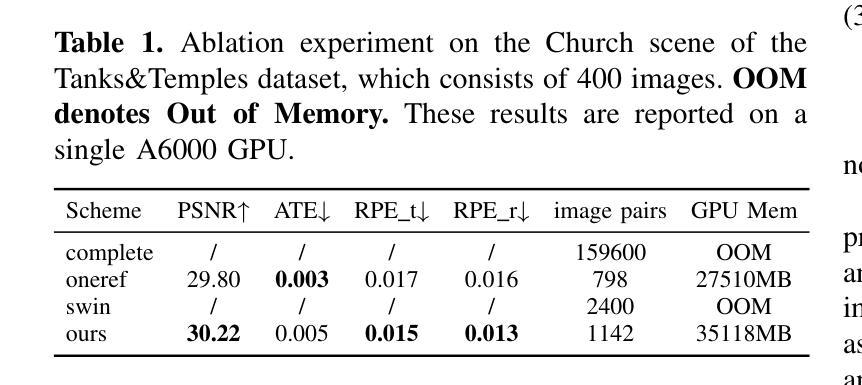
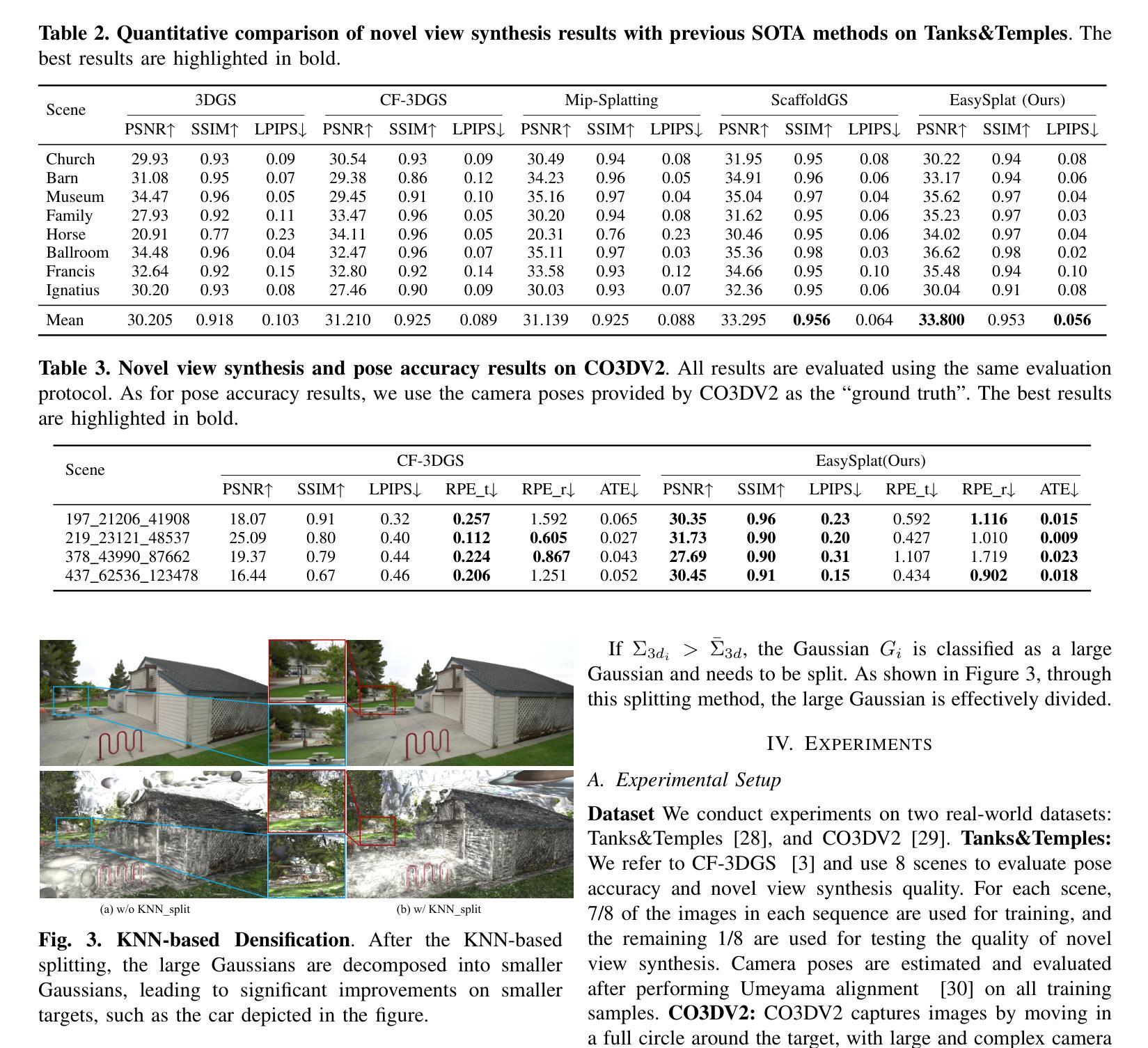
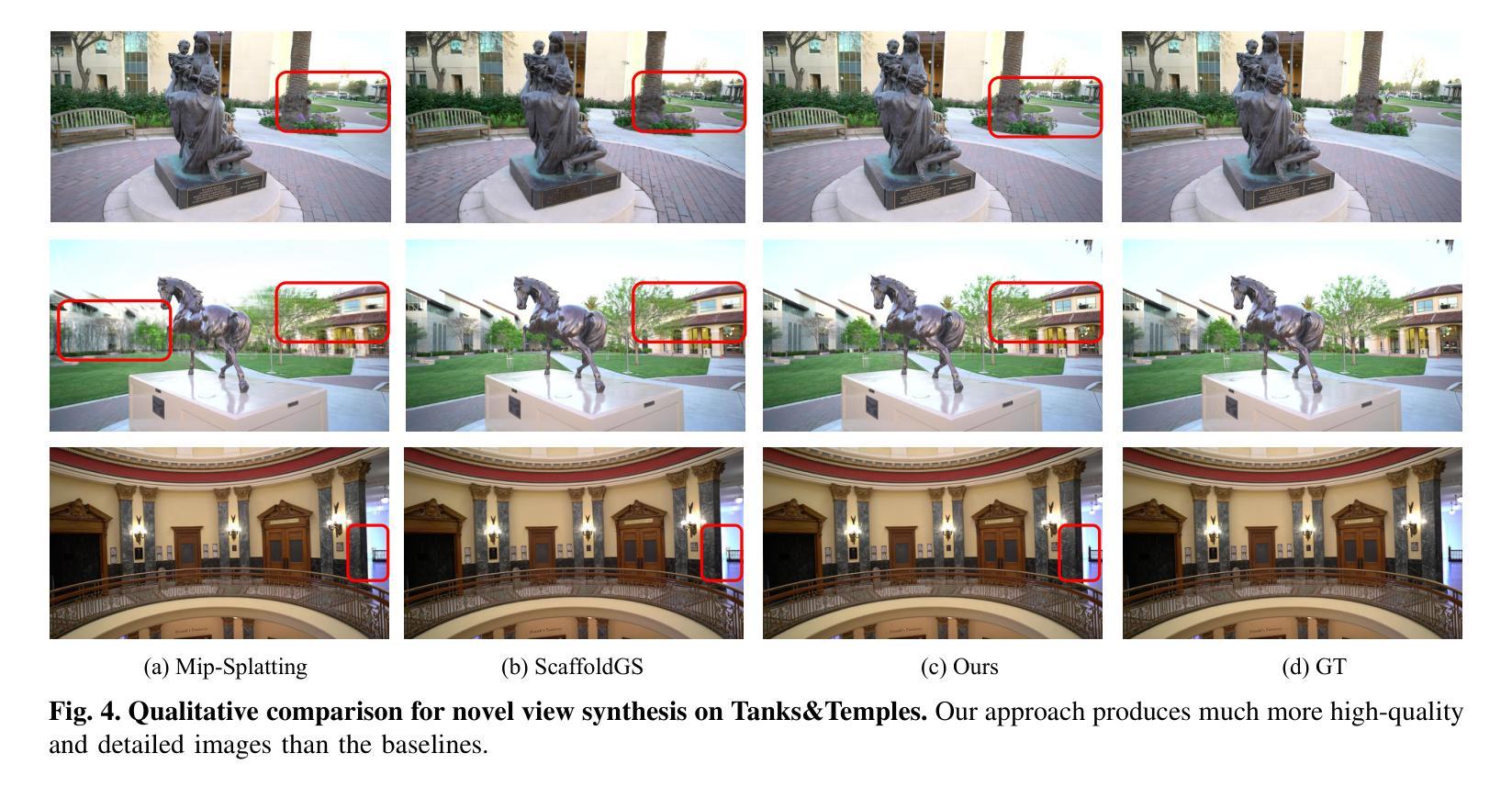
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) techniques have achieved satisfactory 3D scene representation. Despite their impressive performance, they confront challenges due to the limitation of structure-from-motion (SfM) methods on acquiring accurate scene initialization, or the inefficiency of densification strategy. In this paper, we introduce a novel framework EasySplat to achieve high-quality 3DGS modeling. Instead of using SfM for scene initialization, we employ a novel method to release the power of large-scale pointmap approaches. Specifically, we propose an efficient grouping strategy based on view similarity, and use robust pointmap priors to obtain high-quality point clouds and camera poses for 3D scene initialization. After obtaining a reliable scene structure, we propose a novel densification approach that adaptively splits Gaussian primitives based on the average shape of neighboring Gaussian ellipsoids, utilizing KNN scheme. In this way, the proposed method tackles the limitation on initialization and optimization, leading to an efficient and accurate 3DGS modeling. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EasySplat outperforms the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) in handling novel view synthesis.
3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)技术在3D场景表示方面取得了令人满意的成果。尽管其性能令人印象深刻,但它们仍然面临着由于运动结构(SfM)方法获取精确场景初始化的限制或密集化策略的效率低下所带来的挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了一个新型框架EasySplat,以实现高质量的3DGS建模。我们并不使用SfM进行场景初始化,而是采用了一种新方法,以释放大规模点云方法的潜力。具体来说,我们提出了一种基于视图相似性的高效分组策略,并使用稳健的点云先验知识来获得高质量的点云和用于3D场景初始化的相机姿态。在获得可靠的场景结构后,我们提出了一种新型的密集化方法,该方法根据相邻高斯椭圆体的平均形状自适应地拆分高斯原始数据,并利用KNN方案。通过这种方式,所提出的方法解决了初始化和优化方面的限制,实现了高效且准确的3DGS建模。大量实验表明,在处理新型视图合成方面,EasySplat的性能优于当前最先进的水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 5figures
Summary
本文提出了一种基于EasySplat框架的新型三维高斯映射(3DGS)建模方法。该方法通过基于视图相似性的分组策略和利用稳健的点图先验知识,实现了高质量的三维场景初始化。随后,提出了一种基于邻近高斯椭圆体平均形状的自适应分割密集化方法,克服了初始化和优化方面的局限性,实现了高效且准确的三维场景建模。实验结果证明,EasySplat在处理新型视图合成方面优于当前最先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 采用基于视图相似性的高效分组策略,结合点图先验实现高质量的三维场景初始化。
- 提出了一种新型自适应分割的密集化方法,根据邻近高斯椭圆体的平均形状进行自适应分割。
- 该方法克服了结构从运动(SfM)方法的局限性,提高了场景初始化的准确性。
- EasySplat框架在解决三维场景建模的优化问题方面表现出了优越性。
- 通过广泛的实验验证,证明了EasySplat在处理新型视图合成方面的性能优于当前最先进技术。
- 该方法提高了三维场景建模的质量和效率。
点此查看论文截图


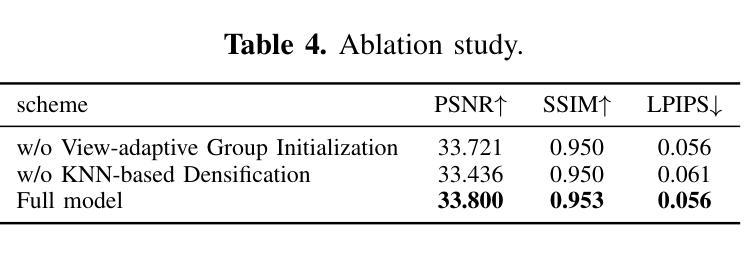
STORM: Spatio-Temporal Reconstruction Model for Large-Scale Outdoor Scenes
Authors:Jiawei Yang, Jiahui Huang, Yuxiao Chen, Yan Wang, Boyi Li, Yurong You, Apoorva Sharma, Maximilian Igl, Peter Karkus, Danfei Xu, Boris Ivanovic, Yue Wang, Marco Pavone
We present STORM, a spatio-temporal reconstruction model designed for reconstructing dynamic outdoor scenes from sparse observations. Existing dynamic reconstruction methods often rely on per-scene optimization, dense observations across space and time, and strong motion supervision, resulting in lengthy optimization times, limited generalization to novel views or scenes, and degenerated quality caused by noisy pseudo-labels for dynamics. To address these challenges, STORM leverages a data-driven Transformer architecture that directly infers dynamic 3D scene representations–parameterized by 3D Gaussians and their velocities–in a single forward pass. Our key design is to aggregate 3D Gaussians from all frames using self-supervised scene flows, transforming them to the target timestep to enable complete (i.e., “amodal”) reconstructions from arbitrary viewpoints at any moment in time. As an emergent property, STORM automatically captures dynamic instances and generates high-quality masks using only reconstruction losses. Extensive experiments on public datasets show that STORM achieves precise dynamic scene reconstruction, surpassing state-of-the-art per-scene optimization methods (+4.3 to 6.6 PSNR) and existing feed-forward approaches (+2.1 to 4.7 PSNR) in dynamic regions. STORM reconstructs large-scale outdoor scenes in 200ms, supports real-time rendering, and outperforms competitors in scene flow estimation, improving 3D EPE by 0.422m and Acc5 by 28.02%. Beyond reconstruction, we showcase four additional applications of our model, illustrating the potential of self-supervised learning for broader dynamic scene understanding.
我们提出了名为STORM的时空重建模型,该模型旨在从稀疏观测中重建动态室外场景。现有的动态重建方法通常依赖于针对每个场景的优化、跨越时空的密集观测和强烈的运动监督,这导致了优化时间长、对新颖视图或场景的概括能力有限,以及由动态伪标签噪声引起的质量下降。为了应对这些挑战,STORM利用数据驱动的Transformer架构,在单次前向传递中直接推断动态3D场景表示——通过3D高斯及其速度进行参数化。我们的关键设计是通过自监督场景流汇聚所有帧的3D高斯,并将其转换为目标时间步长,以实现从时间上任意的视点进行完整的(即“非模态”)重建。作为一个附加属性,STORM能够自动捕获动态实例,并仅使用重建损失生成高质量蒙版。在公共数据集上的广泛实验表明,STORM实现了精确的动态场景重建,超越了最先进的按场景优化方法(提高4.3至6.6 PSNR),并超越了现有的前馈方法(提高2.1至4.7 PSNR)在动态区域。STORM在200毫秒内重建大规模室外场景,支持实时渲染,并在场景流估计方面超越竞争对手,3D EPE提高0.422米,Acc5提高28.02%。除了重建之外,我们还展示了模型的其他四个应用,说明了自我监督学习在更广泛的动态场景理解中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page at: https://jiawei-yang.github.io/STORM/
Summary
本文提出一种名为STORM的时空重建模型,用于从稀疏观测中重建动态户外场景。该模型采用数据驱动的Transformer架构,直接推断动态的三维场景表示,通过一次前向传递即可完成。模型通过聚合所有帧的3D高斯分布并利用自监督场景流进行转换,实现任意时刻任意视角的完整重建。此外,STORM还能自动捕获动态实例并仅通过重建损失生成高质量掩膜。实验表明,STORM在公共数据集上实现了精确的动态场景重建,超越了基于场景优化的方法和现有的前馈方法。
Key Takeaways
- STORM是一种用于重建动态户外场景的时空重建模型。
- 该模型采用数据驱动的Transformer架构,可快速推断动态的三维场景表示。
- 通过聚合所有帧的3D高斯分布并利用自监督场景流进行转换,实现任意时刻和视角的完整重建。
- STORM能够自动捕获动态实例并生成高质量掩膜。
- 实验表明,STORM在动态场景重建上超越了现有的方法和竞争对手。
- STORM具有实时渲染能力,处理速度较快。
点此查看论文截图

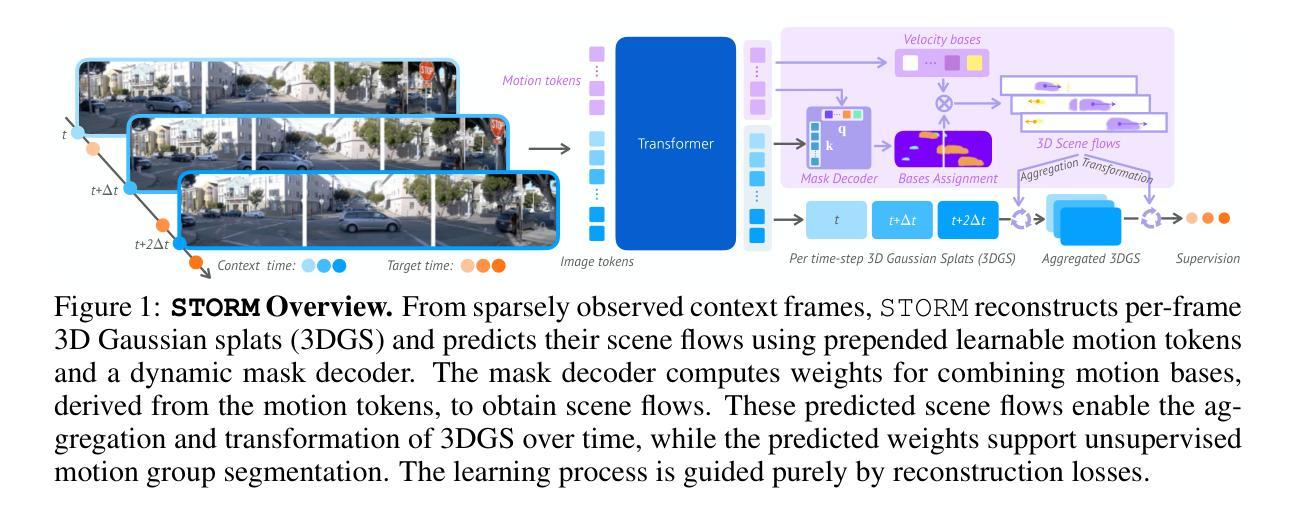


PanoSLAM: Panoptic 3D Scene Reconstruction via Gaussian SLAM
Authors:Runnan Chen, Zhaoqing Wang, Jiepeng Wang, Yuexin Ma, Mingming Gong, Wenping Wang, Tongliang Liu
Understanding geometric, semantic, and instance information in 3D scenes from sequential video data is essential for applications in robotics and augmented reality. However, existing Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) methods generally focus on either geometric or semantic reconstruction. In this paper, we introduce PanoSLAM, the first SLAM system to integrate geometric reconstruction, 3D semantic segmentation, and 3D instance segmentation within a unified framework. Our approach builds upon 3D Gaussian Splatting, modified with several critical components to enable efficient rendering of depth, color, semantic, and instance information from arbitrary viewpoints. To achieve panoptic 3D scene reconstruction from sequential RGB-D videos, we propose an online Spatial-Temporal Lifting (STL) module that transfers 2D panoptic predictions from vision models into 3D Gaussian representations. This STL module addresses the challenges of label noise and inconsistencies in 2D predictions by refining the pseudo labels across multi-view inputs, creating a coherent 3D representation that enhances segmentation accuracy. Our experiments show that PanoSLAM outperforms recent semantic SLAM methods in both mapping and tracking accuracy. For the first time, it achieves panoptic 3D reconstruction of open-world environments directly from the RGB-D video. (https://github.com/runnanchen/PanoSLAM)
从连续的视频数据中理解三维场景中的几何、语义和实例信息,对于机器人技术和增强现实应用至关重要。然而,现有的同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)方法通常只关注几何或语义重建。在本文中,我们介绍了PanoSLAM,这是第一个在同一框架内集成几何重建、三维语义分割和三维实例分割的SLAM系统。我们的方法基于三维高斯贴图技术,通过几个关键组件的修改,可以从任意视角高效地呈现深度、颜色、语义和实例信息。为了实现从连续RGB-D视频进行的全景三维场景重建,我们提出了一种在线时空提升(STL)模块,该模块将视觉模型的二维全景预测转化为三维高斯表示。STL模块通过精炼多视角输入的伪标签,解决了标签噪声和二维预测中的不一致性挑战,创建了一个连贯的三维表示,提高了分割精度。我们的实验表明,PanoSLAM在映射和跟踪精度上均优于最新的语义SLAM方法。它首次实现了直接从RGB-D视频进行全景三维重建开放世界环境。(https://github.com/runnanchen/PanoSLAM)
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了PanoSLAM系统,该系统首次在一个统一框架中集成了几何重建、3D语义分割和3D实例分割。该系统基于3D高斯拼贴技术构建,通过在线时空提升模块实现从连续RGB-D视频进行全景3D场景重建。PanoSLAM解决了标签噪声和二维预测不一致的问题,提高了分割精度,并在映射和跟踪准确性方面优于最近的语义SLAM方法。
Key Takeaways
- PanoSLAM系统是首个在一个框架内整合几何重建、3D语义分割和3D实例分割的SLAM系统。
- 它基于3D高斯拼贴技术构建,能够从任意视角高效渲染深度、颜色、语义和实例信息。
- 通过在线时空提升模块,PanoSLAM实现了从连续RGB-D视频进行全景3D场景重建。
- 该系统解决了标签噪声和二维预测不一致的问题,提高了分割精度。
- PanoSLAM在映射和跟踪准确性方面优于最近的语义SLAM方法。
- 它首次实现了直接从RGB-D视频进行开放世界环境的全景3D重建。
- PanoSLAM具有广泛的潜在应用,如机器人技术和增强现实。
点此查看论文截图

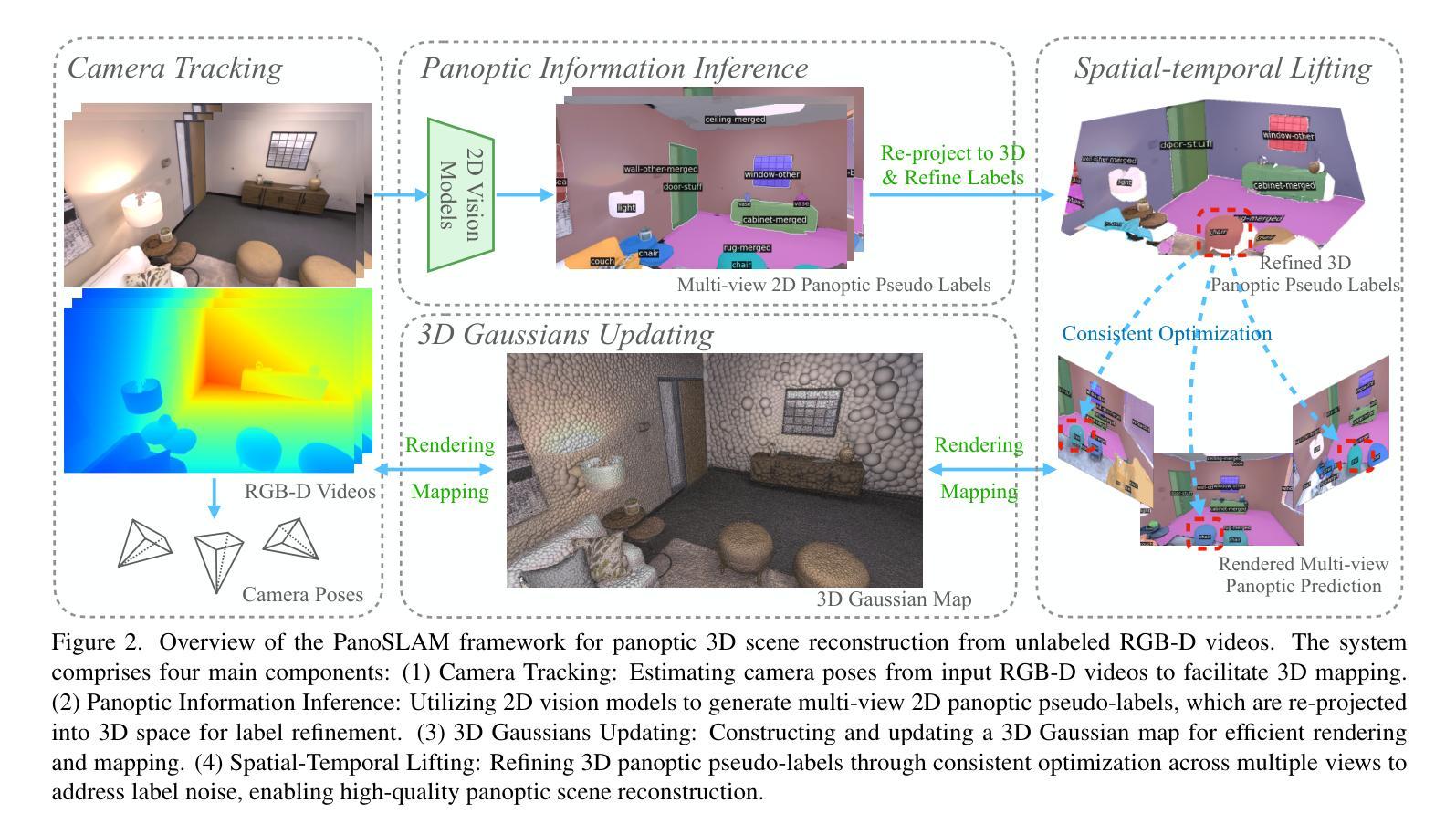
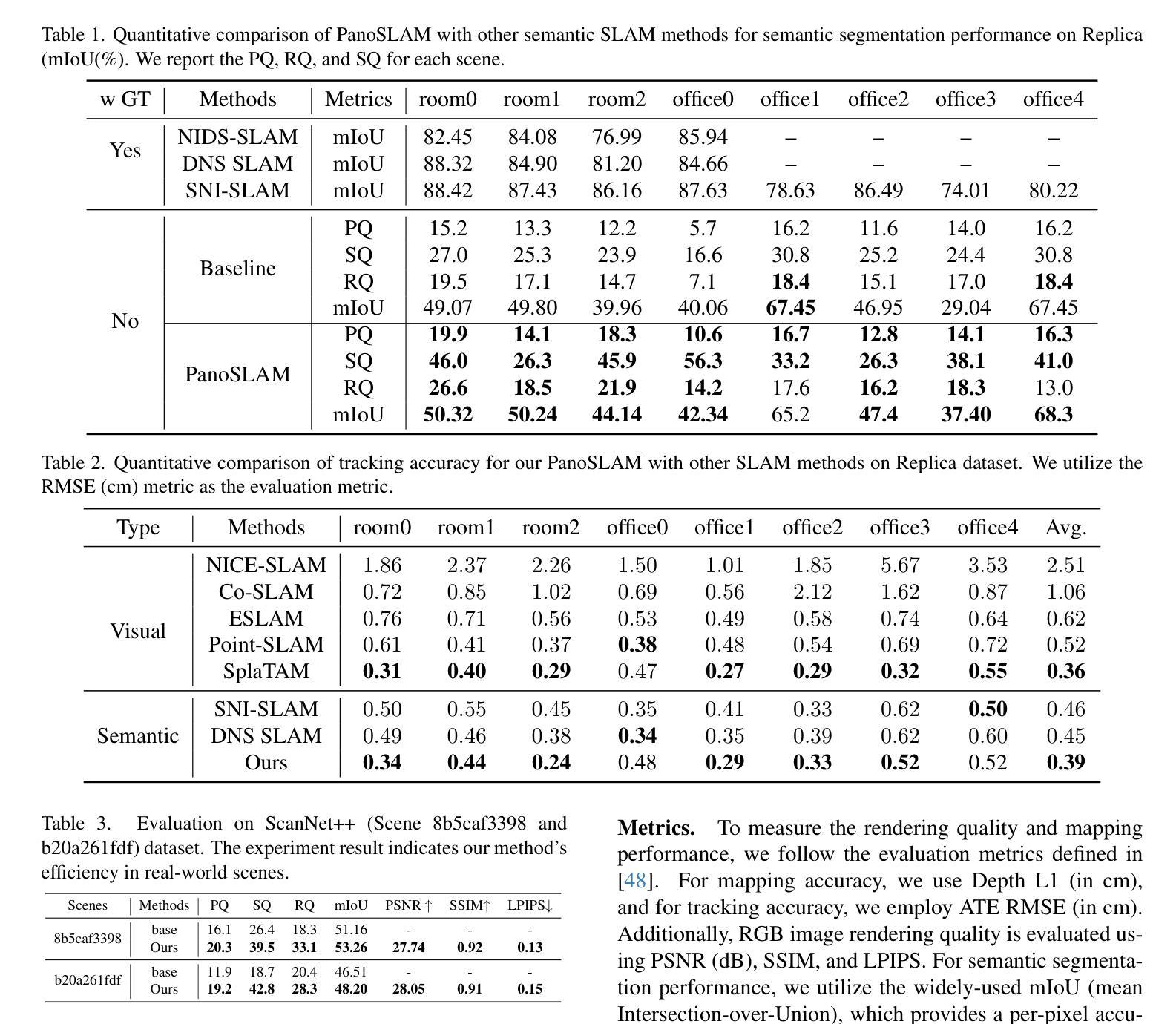
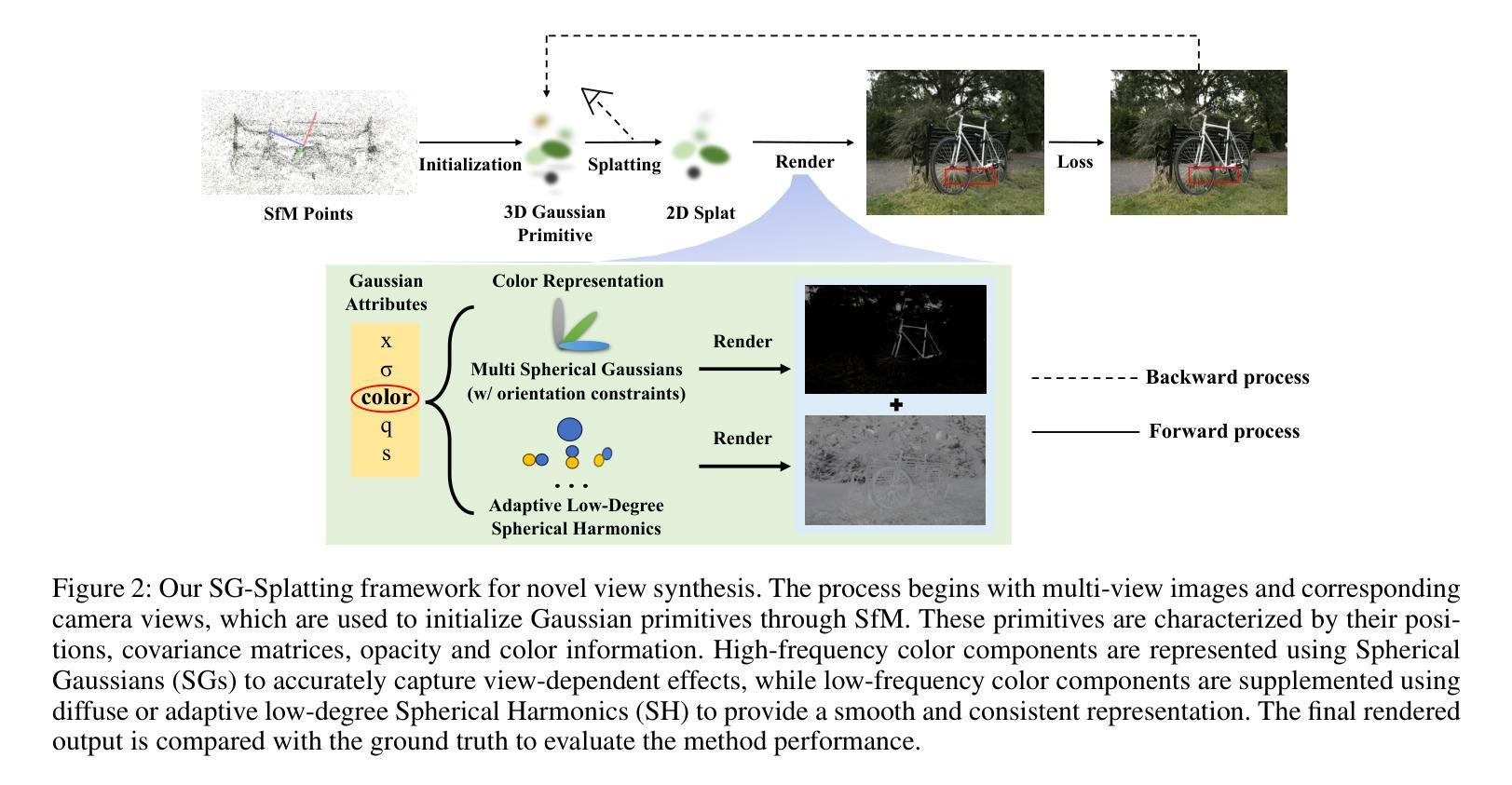
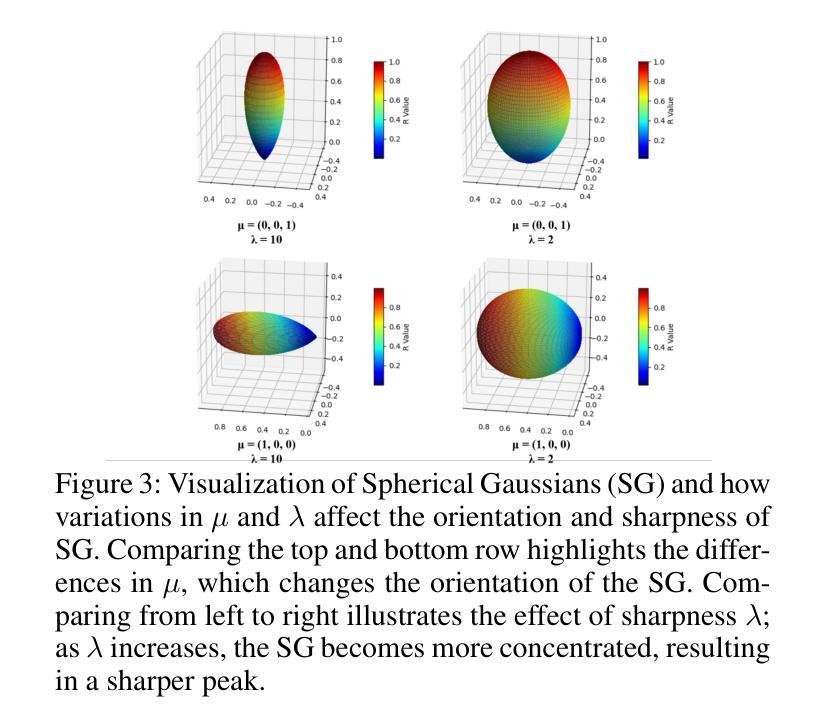
SG-Splatting: Accelerating 3D Gaussian Splatting with Spherical Gaussians
Authors:Yiwen Wang, Siyuan Chen, Ran Yi
3D Gaussian Splatting is emerging as a state-of-the-art technique in novel view synthesis, recognized for its impressive balance between visual quality, speed, and rendering efficiency. However, reliance on third-degree spherical harmonics for color representation introduces significant storage demands and computational overhead, resulting in a large memory footprint and slower rendering speed. We introduce SG-Splatting with Spherical Gaussians based color representation, a novel approach to enhance rendering speed and quality in novel view synthesis. Our method first represents view-dependent color using Spherical Gaussians, instead of three degree spherical harmonics, which largely reduces the number of parameters used for color representation, and significantly accelerates the rendering process. We then develop an efficient strategy for organizing multiple Spherical Gaussians, optimizing their arrangement to achieve a balanced and accurate scene representation. To further improve rendering quality, we propose a mixed representation that combines Spherical Gaussians with low-degree spherical harmonics, capturing both high- and low-frequency color information effectively. SG-Splatting also has plug-and-play capability, allowing it to be easily integrated into existing systems. This approach improves computational efficiency and overall visual fidelity, making it a practical solution for real-time applications.
3D高斯模糊技术作为一种先进的视图合成技术正逐渐崭露头角,以其视觉质量、速度和渲染效率之间的出色平衡而受到认可。然而,该技术使用三次球面谐波进行颜色表示,产生了巨大的存储需求和计算开销,导致内存占用较大且渲染速度较慢。我们引入了基于球面高斯颜色表示的SG模糊技术,这是一种提高视图合成中渲染速度和质量的新方法。我们的方法首先使用球面高斯而不是三次球面谐波来表示视图相关的颜色,这大大降低了用于颜色表示的参数数量,并大大加快了渲染过程。然后,我们开发了一种有效的策略来组织多个球面高斯,优化它们的排列以实现平衡和准确的场景表示。为了进一步提高渲染质量,我们提出了一种混合表示法,它将球面高斯与低阶球面谐波相结合,有效地捕捉了高低频颜色信息。SG模糊还具有即插即用功能,可轻松集成到现有系统中。这种方法提高了计算效率和总体视觉保真度,使其成为实时应用的实用解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了新兴的3D高斯展平技术及其在新型视图合成中的应用。该技术采用基于球面高斯的颜色表示法,提高了渲染速度和品质。通过优化球面高斯排列策略,实现了场景表示的平衡和准确性。结合低阶球面谐波,有效捕捉了高低频颜色信息,提高了渲染质量。SG-Splatting技术还具有易于集成现有系统的特点,计算效率高,视觉效果好,适合实时应用。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯展平技术已成为最新视图合成的先进技术,其在视觉质量、速度和渲染效率之间取得了平衡。
- 原技术使用三度球面谐波进行颜色表示,存在存储需求大、计算量大、内存占用高和渲染速度慢的问题。
- 引入SG-Splatting技术,采用球面高斯进行颜色表示,大幅度减少了颜色表示所需的参数数量,加速了渲染过程。
- 优化了多个球面高斯的排列策略,实现了场景表示的平衡和准确性。
- 结合低阶球面谐波,提出了混合表示方法,有效捕捉高低频颜色信息,提高了渲染质量。
- SG-Splatting技术具有易于集成现有系统的特点,具有插件和播放功能。
点此查看论文截图


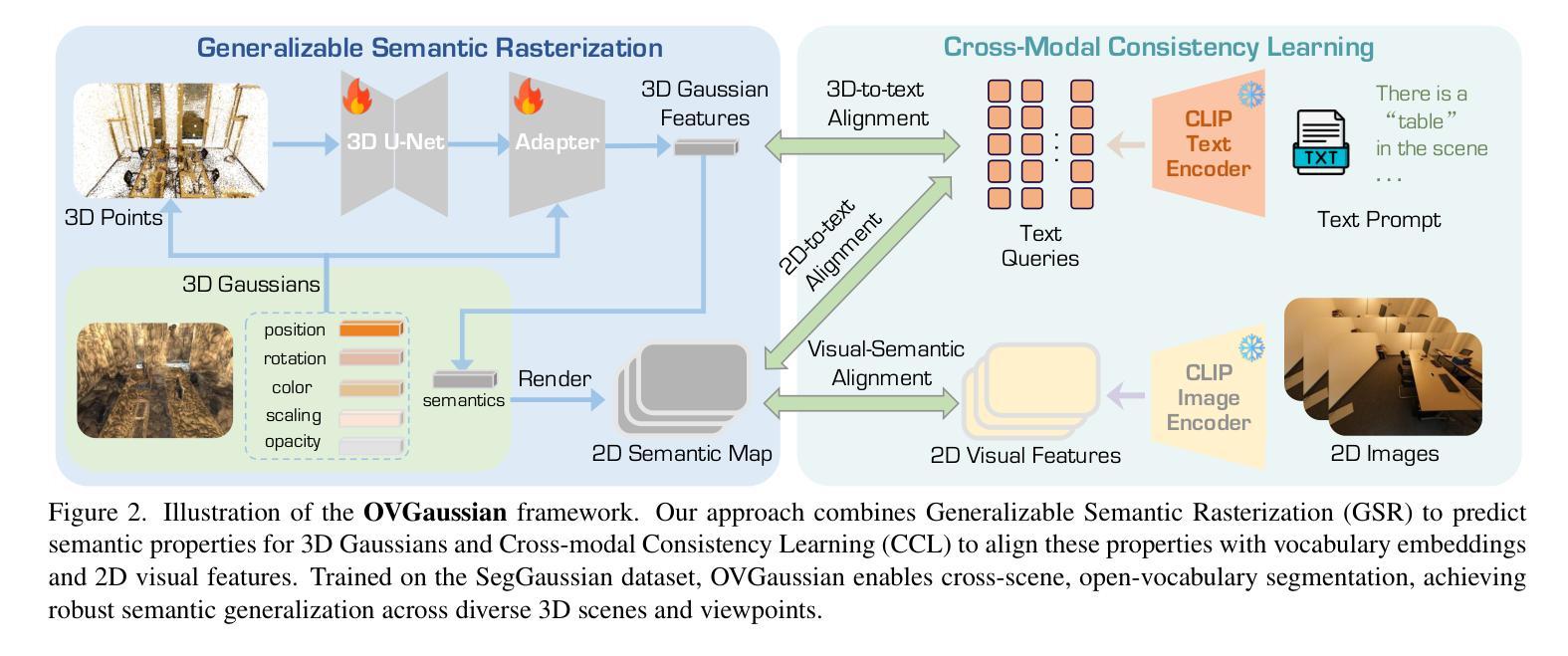
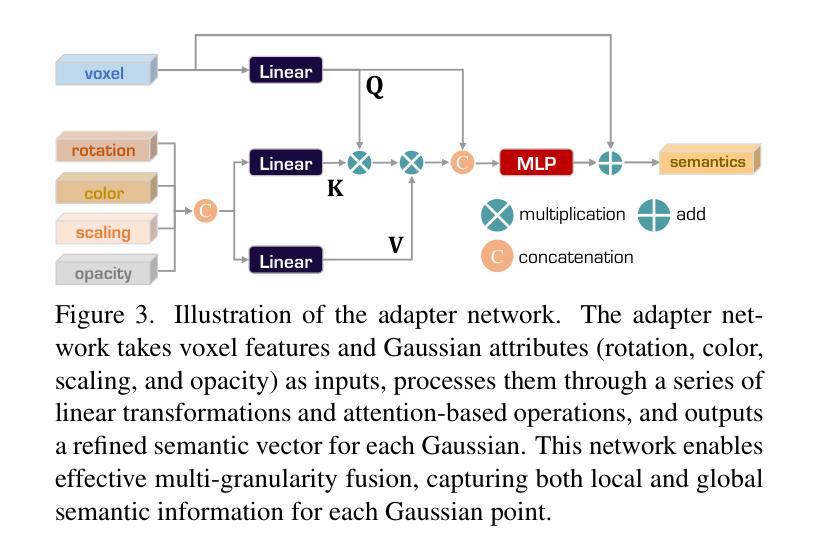
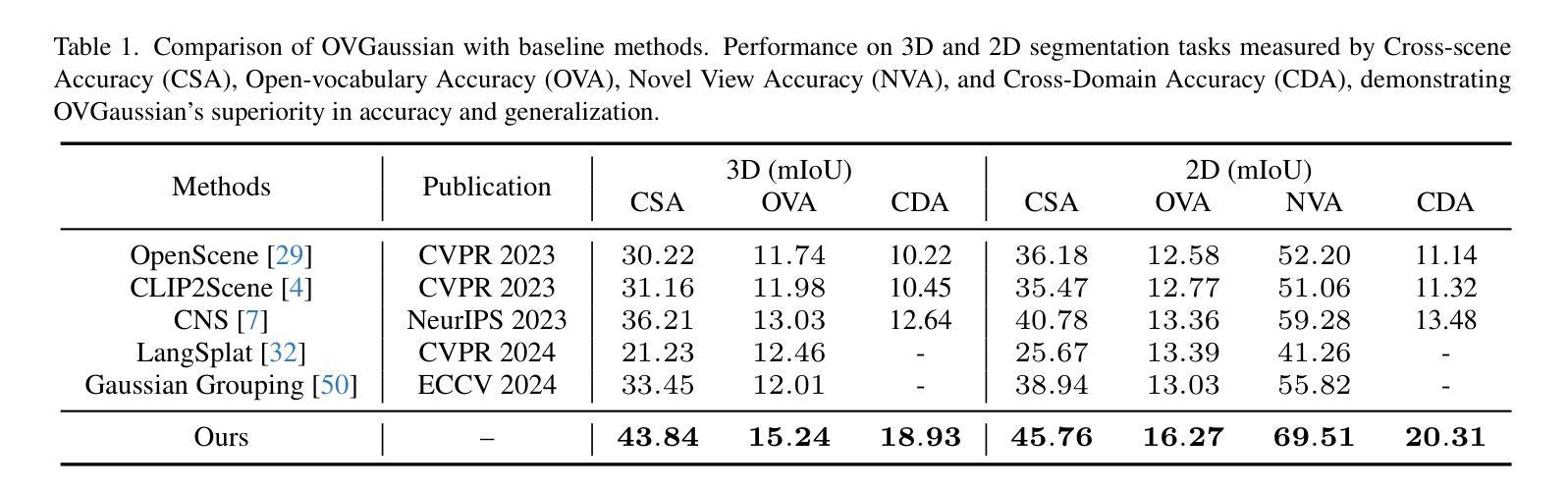
OVGaussian: Generalizable 3D Gaussian Segmentation with Open Vocabularies
Authors:Runnan Chen, Xiangyu Sun, Zhaoqing Wang, Youquan Liu, Jiepeng Wang, Lingdong Kong, Jiankang Deng, Mingming Gong, Liang Pan, Wenping Wang, Tongliang Liu
Open-vocabulary scene understanding using 3D Gaussian (3DGS) representations has garnered considerable attention. However, existing methods mostly lift knowledge from large 2D vision models into 3DGS on a scene-by-scene basis, restricting the capabilities of open-vocabulary querying within their training scenes so that lacking the generalizability to novel scenes. In this work, we propose \textbf{OVGaussian}, a generalizable \textbf{O}pen-\textbf{V}ocabulary 3D semantic segmentation framework based on the 3D \textbf{Gaussian} representation. We first construct a large-scale 3D scene dataset based on 3DGS, dubbed \textbf{SegGaussian}, which provides detailed semantic and instance annotations for both Gaussian points and multi-view images. To promote semantic generalization across scenes, we introduce Generalizable Semantic Rasterization (GSR), which leverages a 3D neural network to learn and predict the semantic property for each 3D Gaussian point, where the semantic property can be rendered as multi-view consistent 2D semantic maps. In the next, we propose a Cross-modal Consistency Learning (CCL) framework that utilizes open-vocabulary annotations of 2D images and 3D Gaussians within SegGaussian to train the 3D neural network capable of open-vocabulary semantic segmentation across Gaussian-based 3D scenes. Experimental results demonstrate that OVGaussian significantly outperforms baseline methods, exhibiting robust cross-scene, cross-domain, and novel-view generalization capabilities. Code and the SegGaussian dataset will be released. (https://github.com/runnanchen/OVGaussian).
使用基于三维高斯(3DGS)表示进行开放词汇场景理解已经引起了相当大的关注。然而,现有的方法大多基于场景对场景的方式将大型二维视觉模型的知识提升到三维高斯表示中,这限制了其在训练场景内开放词汇查询的能力,并缺乏泛化到新场景的能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了基于三维高斯表示的通用开放词汇三维语义分割框架,名为“OVGaussian”。我们首先构建了一个基于三维高斯表示的大规模三维场景数据集,称为“SegGaussian”,它为高斯点和多视图图像提供了详细的语义和实例注释。为了促进场景之间的语义泛化,我们引入了可泛化语义渲染(GSR),该渲染利用三维神经网络来学习和预测每个三维高斯点的语义属性,其中语义属性可以呈现为多视图一致的二维语义地图。接下来,我们提出了跨模态一致性学习(CCL)框架,该框架利用SegGaussian中的二维图像和三维高斯点的开放词汇注释来训练能够在基于高斯的三维场景上进行开放词汇语义分割的三维神经网络。实验结果表明,OVGaussian在基线方法上表现出显著的优势,展现出强大的跨场景、跨域和新视角的泛化能力。代码和SegGaussian数据集将公开发布。(https://github.com/runnanchen/OVGaussian)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于三维高斯(3DGS)表示进行开放词汇场景理解已经引起了广泛关注。现有方法主要在场景基础上将二维视觉模型的知识迁移到三维场景上,限制了其在训练场景内的开放词汇查询能力,并且缺乏对新场景的泛化能力。本研究提出了基于三维高斯表示的通用开放词汇三维语义分割框架OVGaussian。首先构建了大规模三维场景数据集SegGaussian,为高斯点和多视角图像提供了详细的语义和实例注释。为了促进跨场景的语义泛化,我们引入了可泛化的语义栅格化(GSR),利用三维神经网络学习和预测每个三维高斯点的语义属性,并将其渲染为多视角一致性的二维语义图。随后,我们提出了跨模态一致性学习(CCL)框架,利用SegGaussian中的二维图像和三维高斯值的开放词汇注释来训练三维神经网络,实现对基于高斯的三维场景的开放词汇语义分割。实验结果表明,OVGaussian显著优于基准方法,具有强大的跨场景、跨域和新颖视角泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 现有方法大多将二维视觉模型的知识迁移到三维场景上,限制了开放词汇查询能力。
- 研究提出了基于三维高斯表示的通用开放词汇三维语义分割框架OVGaussian。
- 构建了大规模三维场景数据集SegGaussian,包含高斯点和多视角图像的详细语义和实例注释。
- 通过引入可泛化的语义栅格化(GSR),利用三维神经网络预测每个高斯点的语义属性。
- 提出了跨模态一致性学习(CCL)框架,用于训练能够执行开放词汇语义分割的三维神经网络。
- OVGaussian显著优于基准方法,具有强大的跨场景、跨域和新颖视角泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图