⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-06 更新
A3: Android Agent Arena for Mobile GUI Agents
Authors:Yuxiang Chai, Hanhao Li, Jiayu Zhang, Liang Liu, Guozhi Wang, Shuai Ren, Siyuan Huang, Hongsheng Li
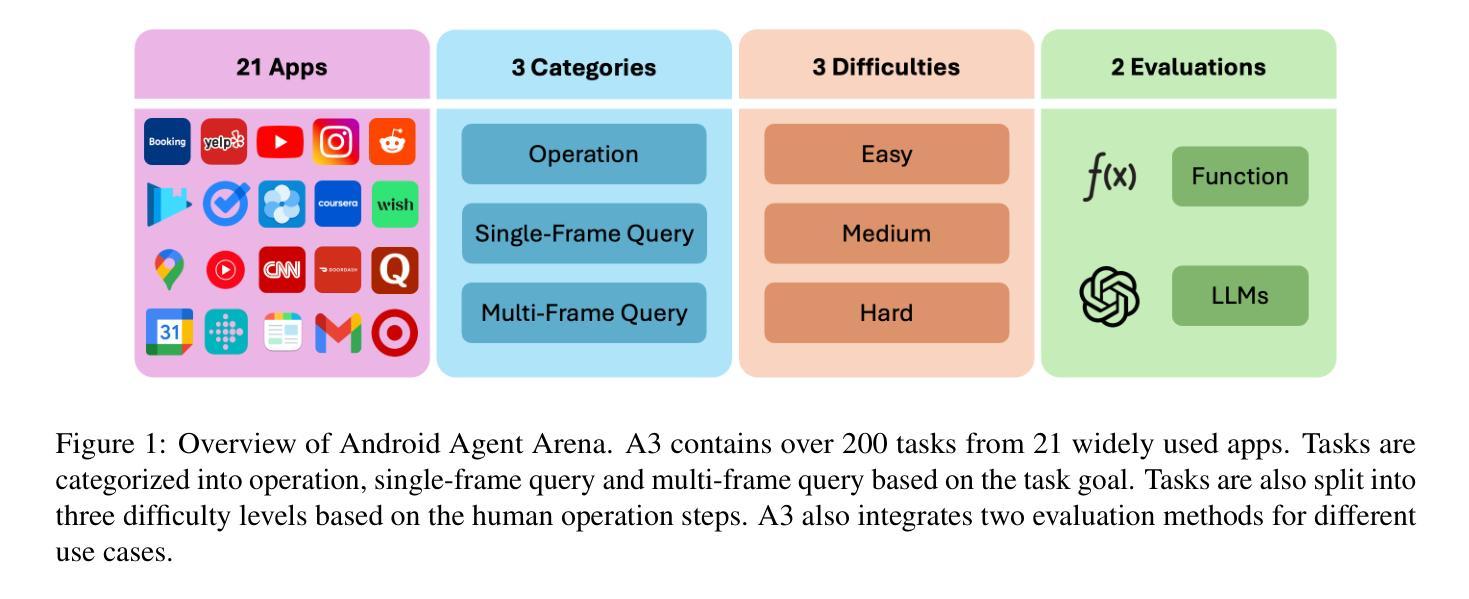
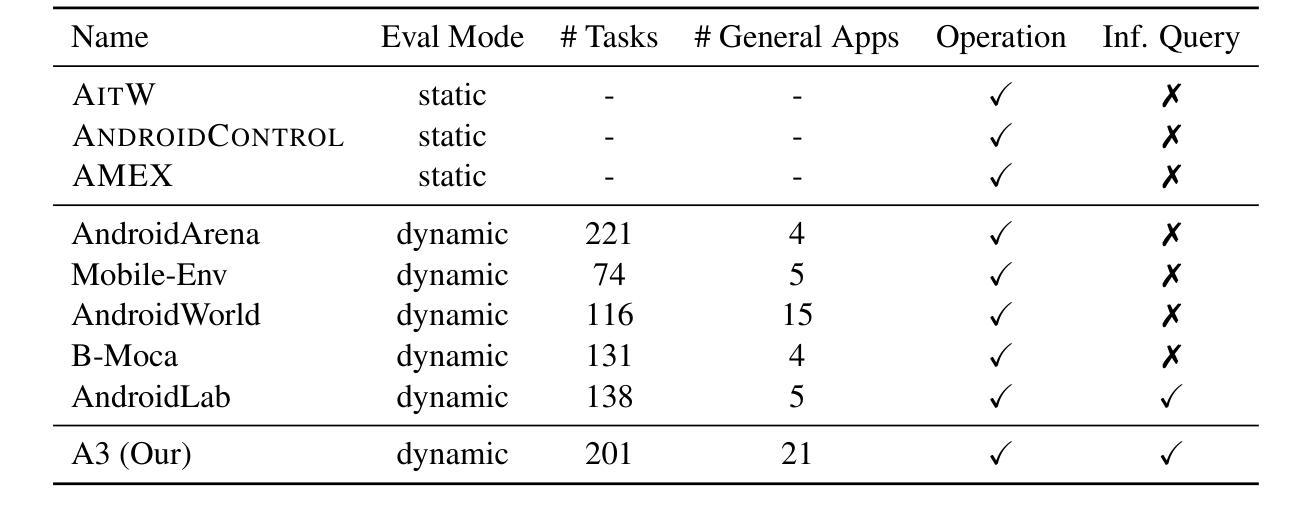
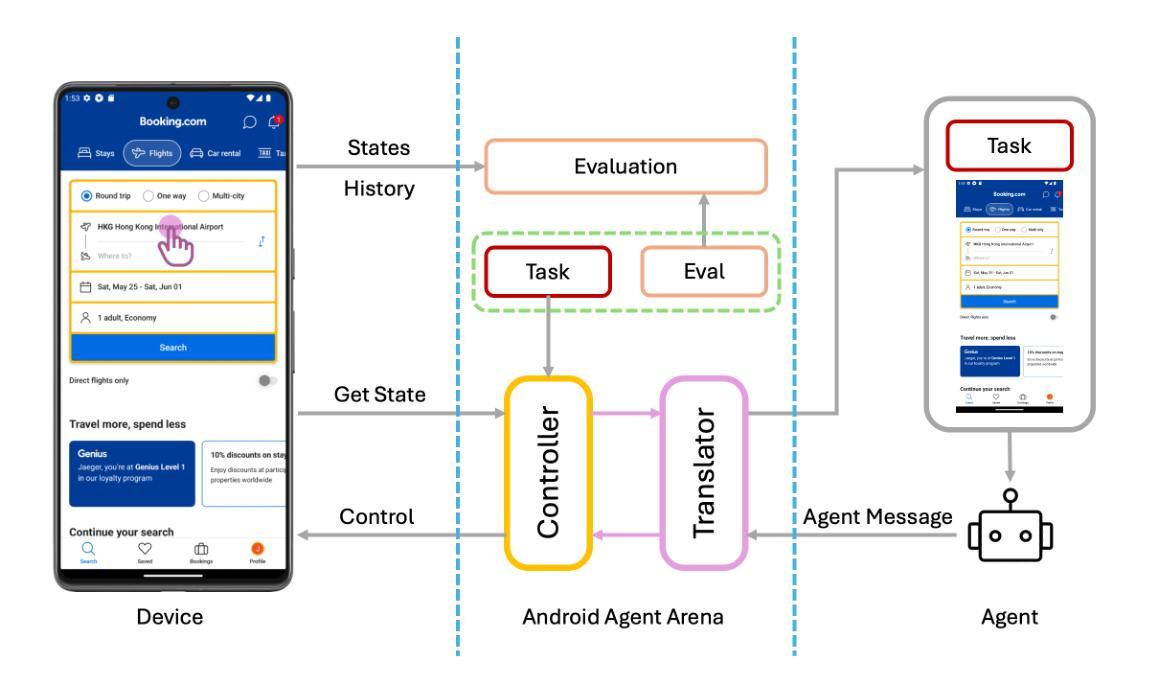
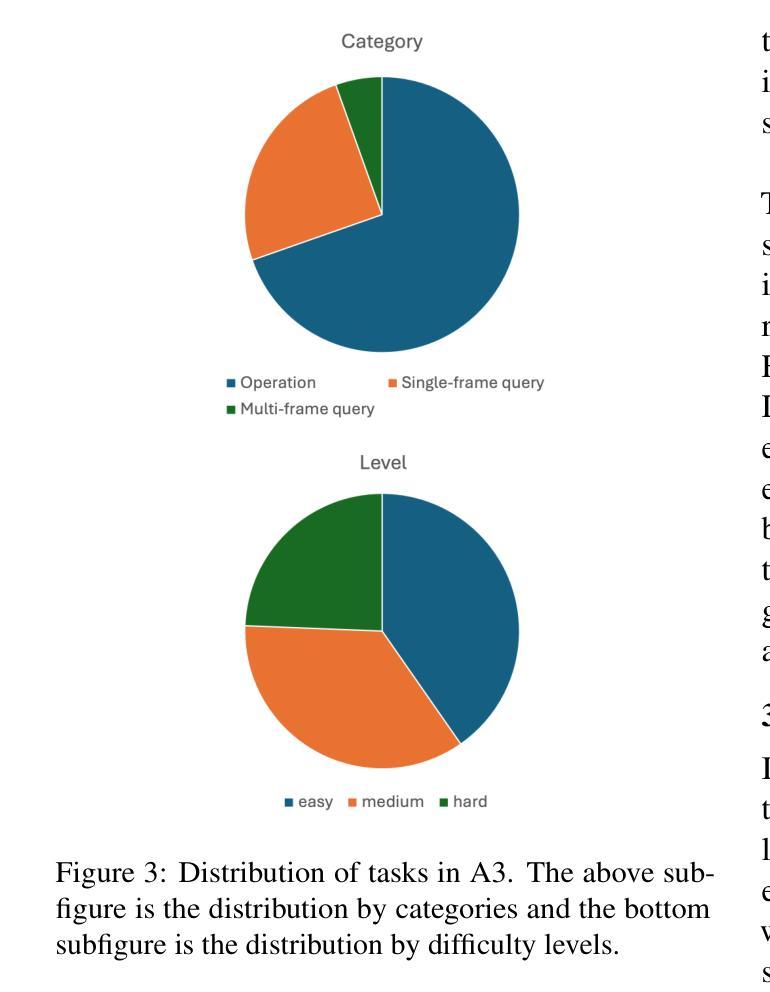
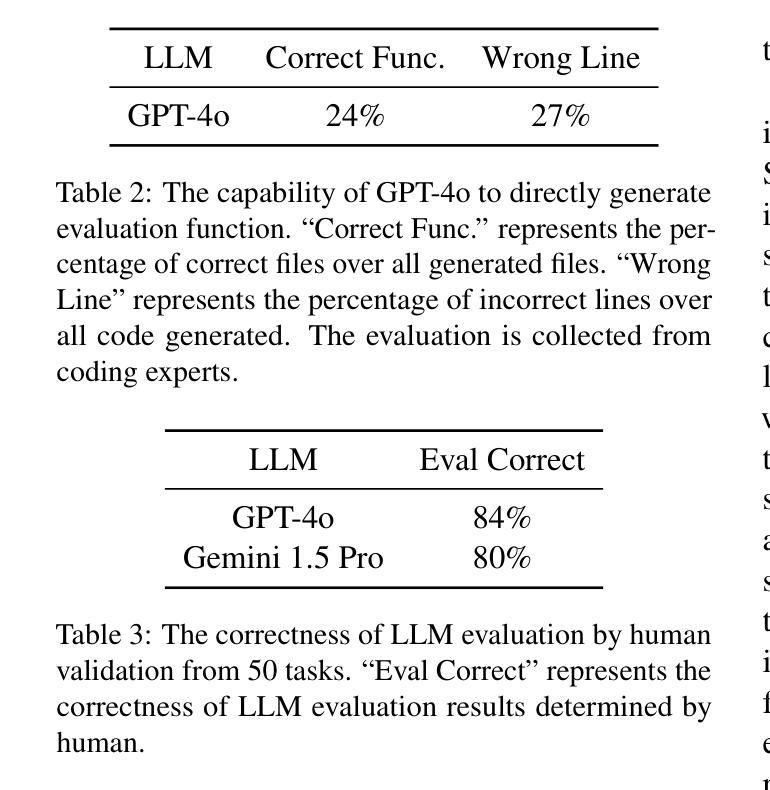
AI agents have become increasingly prevalent in recent years, driven by significant advancements in the field of large language models (LLMs). Mobile GUI agents, a subset of AI agents, are designed to autonomously perform tasks on mobile devices. While numerous studies have introduced agents, datasets, and benchmarks to advance mobile GUI agent research, many existing datasets focus on static frame evaluations and fail to provide a comprehensive platform for assessing performance on real-world, in-the-wild tasks. To address this gap, we present Android Agent Arena (A3), a novel evaluation platform. Unlike existing in-the-wild systems, A3 offers: (1) meaningful and practical tasks, such as real-time online information retrieval and operational instructions; (2) a larger, more flexible action space, enabling compatibility with agents trained on any dataset; and (3) automated business-level LLM-based evaluation process. A3 includes 21 widely used general third-party apps and 201 tasks representative of common user scenarios, providing a robust foundation for evaluating mobile GUI agents in real-world situations and a new autonomous evaluation process for less human labor and coding expertise. The project is available at \url{https://yuxiangchai.github.io/Android-Agent-Arena/}.
近年来,随着自然语言模型领域的重大进展,人工智能代理变得越来越普遍。移动GUI代理是人工智能代理的一个子集,旨在自主地在移动设备执行各种任务。尽管许多研究已经引入了代理、数据集和基准测试来推动移动GUI代理的研究,但许多现有数据集侧重于静态框架评估,未能提供一个全面平台来评估在现实世界中执行任务的表现。为了解决这一差距,我们推出了Android Agent Arena(A3)这一新型评估平台。不同于现有的野外系统,A3提供了:(1)有意义且实用的任务,如实时在线信息检索和操作规程;(2)一个更大、更灵活的动作空间,可与任何数据集上训练的代理兼容;(3)自动化的业务级基于LLM的评估流程。A3包括21个广泛使用的第三方通用应用程序和代表常见用户场景的201个任务,为在真实世界环境中评估移动GUI代理提供了稳健的基础和一个减少人力劳动和编码专业知识的新自主评估过程。该项目可在链接[https://yuxiangchai.github.io/Android-Agent-Arena/]中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着大型语言模型(LLMs)领域的显著进步,AI代理近年来变得越来越普遍。为解决现有移动GUI代理评估平台在真实世界任务评估方面的不足,提出了Android Agent Arena(A3)这一新型评估平台。A3提供了实用任务、更大的灵活动作空间以及自动化的业务级LLM评估流程。
Key Takeaways
- AI代理近年来因大型语言模型的进步而日益普及。
- 移动GUI代理旨在在移动设备上自主完成任务。
- 现有数据集大多关注静态框架评估,缺乏针对真实世界任务的全面评估平台。
- Android Agent Arena (A3)是一个新型评估平台,提供实际任务并扩大灵活动作空间。
- A3兼容任何数据集训练的代理。
- A3采用自动化的业务级LLM评估流程,减少人工和编码专业知识需求。
点此查看论文截图

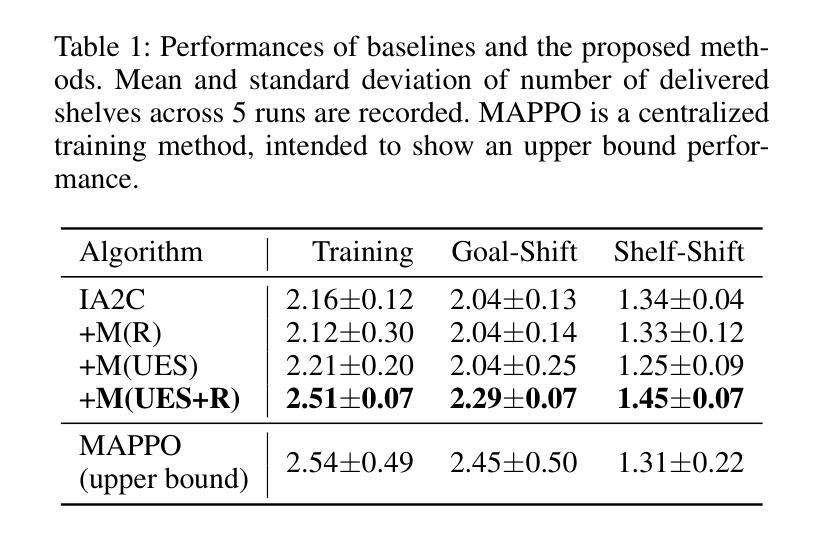
Communicating Unexpectedness for Out-of-Distribution Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Min Whoo Lee, Kibeom Kim, Soo Wung Shin, Minsu Lee, Byoung-Tak Zhang
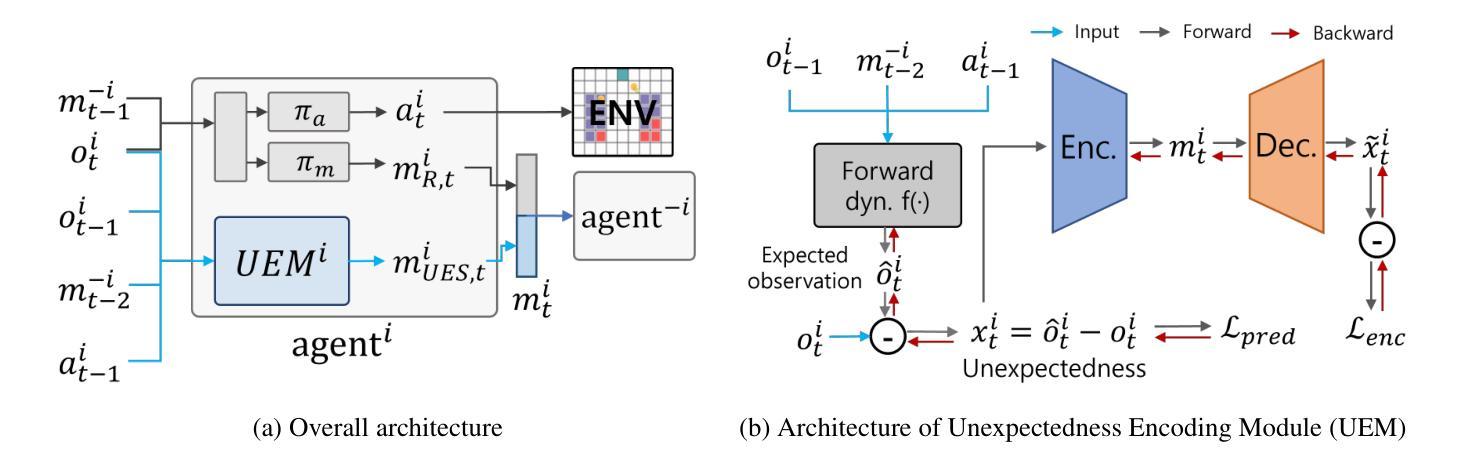
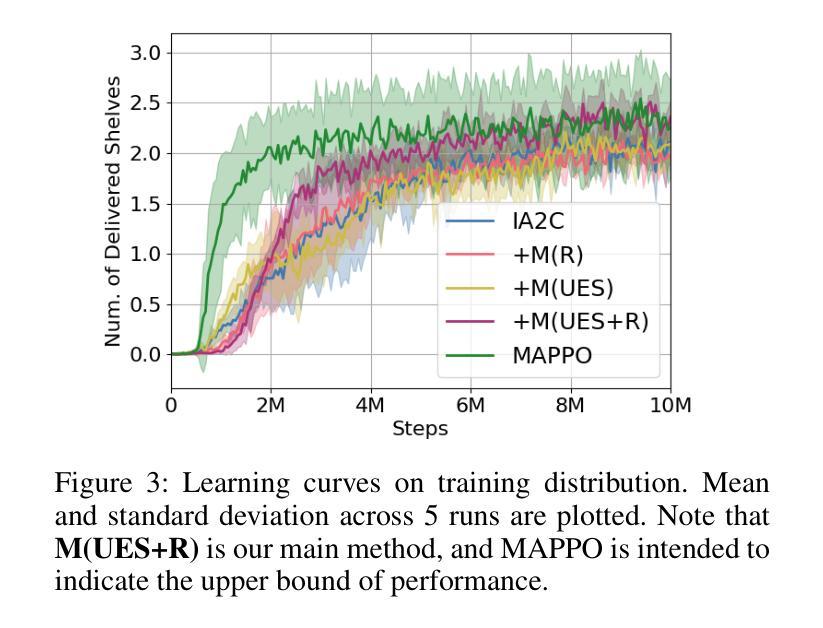
Applying multi-agent reinforcement learning methods to realistic settings is challenging as it may require the agents to quickly adapt to unexpected situations that are rarely or never encountered in training. Recent methods for generalization to such out-of-distribution settings are limited to more specific, restricted instances of distribution shifts. To tackle adaptation to distribution shifts, we propose Unexpected Encoding Scheme, a novel decentralized multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithm where agents communicate “unexpectedness,” the aspects of the environment that are surprising. In addition to a message yielded by the original reward-driven communication, each agent predicts the next observation based on previous experience, measures the discrepancy between the prediction and the actually encountered observation, and encodes this discrepancy as a message. Experiments on multi-robot warehouse environment support that our proposed method adapts robustly to dynamically changing training environments as well as out-of-distribution environment.
将多智能体强化学习方法应用于现实场景具有挑战性,因为它可能需要智能体快速适应在训练中很少遇到或从未遇到过的意外情况。最近泛化到这类离分布设置的方法仅限于分布转移的更具特异性、受限的实例。为了解决适应分布转移的问题,我们提出了意外编码方案(Unexpected Encoding Scheme),这是一种新型的去中心化多智能体强化学习算法,智能体在其中交流“意外性”,即环境中令人惊讶的方面。除了由原始奖励驱动通信产生的信息外,每个智能体还根据之前的经验预测下一个观察结果,测量预测与实际观察到的结果之间的差异,并将这种差异编码为信息。在多机器人仓库环境的实验支持我们的方法稳健地适应动态变化的训练环境以及离分布环境。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 3 figures, Published in AAAI 2024 Workshop (Cooperative Multi-Agent Systems Decision-Making and Learning: From Individual Needs to Swarm Intelligence)
Summary
在面临分布转移时,应用多智能体强化学习方法面临挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种名为Unexpected Encoding Scheme的新算法,该算法通过智能体之间的“意外性”交流来适应环境变化。智能体会预测下一个观察结果并衡量预测与实际观察之间的差异,将差异编码为信息。实验证明,该方法在多机器人仓库环境中可以适应动态变化的训练环境和未知分布环境。
Key Takeaways
- 应用多智能体强化学习于实际场景面临分布转移的挑战。
- 传统方法在处理此类分布转移问题上有所局限。
- Unexpected Encoding Scheme是一种新型的多智能体强化学习算法,解决了智能体在面临分布转移时的适应性问题。
- 该算法通过智能体间的“意外性”交流来适应环境变化。
- 智能体会预测下一个观察结果并衡量预测与实际观察之间的差异。
- 这种差异被编码为信息,有助于智能体适应动态变化的训练环境和未知分布环境。
点此查看论文截图

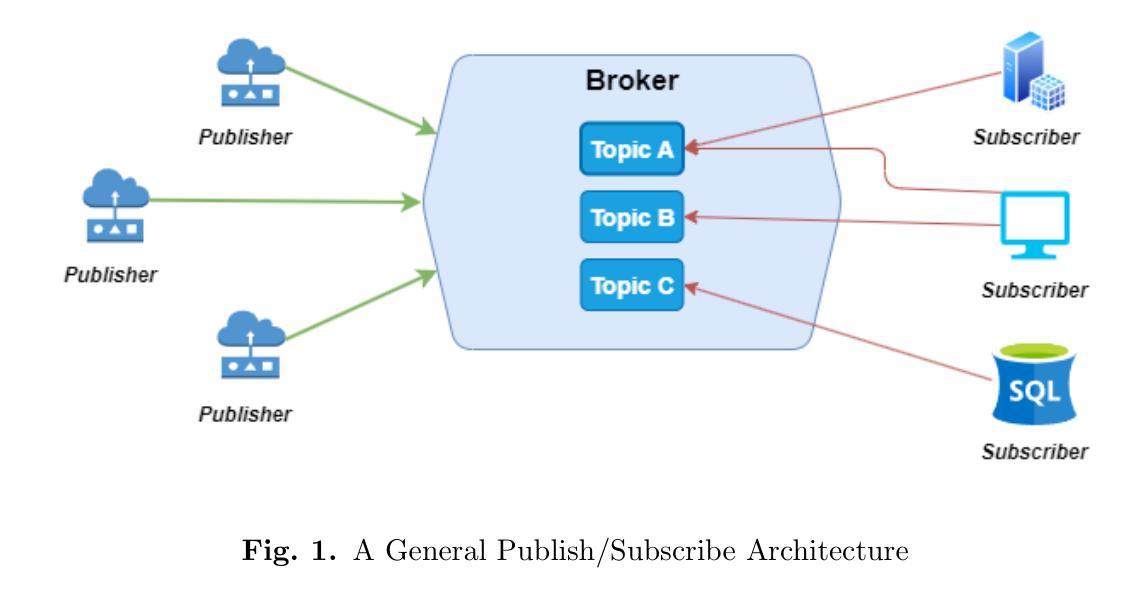
Large Language Model Based Multi-Agent System Augmented Complex Event Processing Pipeline for Internet of Multimedia Things
Authors:Talha Zeeshan, Abhishek Kumar, Susanna Pirttikangas, Sasu Tarkoma
This paper presents the development and evaluation of a Large Language Model (LLM), also known as foundation models, based multi-agent system framework for complex event processing (CEP) with a focus on video query processing use cases. The primary goal is to create a proof-of-concept (POC) that integrates state-of-the-art LLM orchestration frameworks with publish/subscribe (pub/sub) tools to address the integration of LLMs with current CEP systems. Utilizing the Autogen framework in conjunction with Kafka message brokers, the system demonstrates an autonomous CEP pipeline capable of handling complex workflows. Extensive experiments evaluate the system’s performance across varying configurations, complexities, and video resolutions, revealing the trade-offs between functionality and latency. The results show that while higher agent count and video complexities increase latency, the system maintains high consistency in narrative coherence. This research builds upon and contributes to, existing novel approaches to distributed AI systems, offering detailed insights into integrating such systems into existing infrastructures.
本文介绍了一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统框架的开发与评估,用于复杂事件处理(CEP),重点关注视频查询处理用例。主要目标是创建一个概念验证(POC),将最新的LLM编排框架与发布/订阅(pub/sub)工具集成,以解决LLM与当前CEP系统的集成问题。利用Autogen框架和Kafka消息代理,系统展示了一个能够处理复杂工作流程的自主CEP管道。通过广泛的实验,对系统在不同配置、复杂性和视频分辨率下的性能进行了评估,揭示了功能与延迟之间的权衡。结果表明,虽然较高的智能体数量和视频复杂性会增加延迟,但系统在叙事连贯性方面保持高度一致性。这项研究建立在现有的分布式人工智能系统的新颖方法之上,并为这些方法提供了详细的见解,有助于将这些系统集成到现有基础设施中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文开发并评估了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统框架,主要用于复杂事件处理(CEP),重点研究视频查询处理用例。论文旨在创建集成最新LLM协同框架与发布/订阅工具的原型,解决LLM与当前CEP系统的集成问题。通过结合Autogen框架和Kafka消息代理,系统展示了一条能够处理复杂工作流程的自主CEP管道。通过广泛的实验,论文评估了系统在不同配置、复杂程度和视频分辨率下的性能,揭示了功能延迟之间的权衡。结果表明,虽然较高的智能体数量和视频复杂度会增加延迟,但系统在叙事连贯性方面保持高度一致性。该研究为分布式AI系统的现有新颖方法提供了发展并作出了贡献,并为将此类系统集成到现有基础设施中提供了深入的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统框架,用于复杂事件处理(CEP)。
- 论文重点关注视频查询处理用例,旨在集成LLM协同框架与发布/订阅工具来解决LLM与当前CEP系统的集成问题。
- 系统利用Autogen框架和Kafka消息代理,展示了自主CEP管道的处理能力。
- 实验表明,虽然智能体数量和视频复杂度增加会导致延迟上升,但系统保持了高叙事连贯性。
- 研究在分布式AI系统领域有所发展和贡献,为集成此类系统到现有基础设施提供了深入见解。
- 论文详细探讨了大型语言模型在复杂事件处理中的应用及其优势。
点此查看论文截图

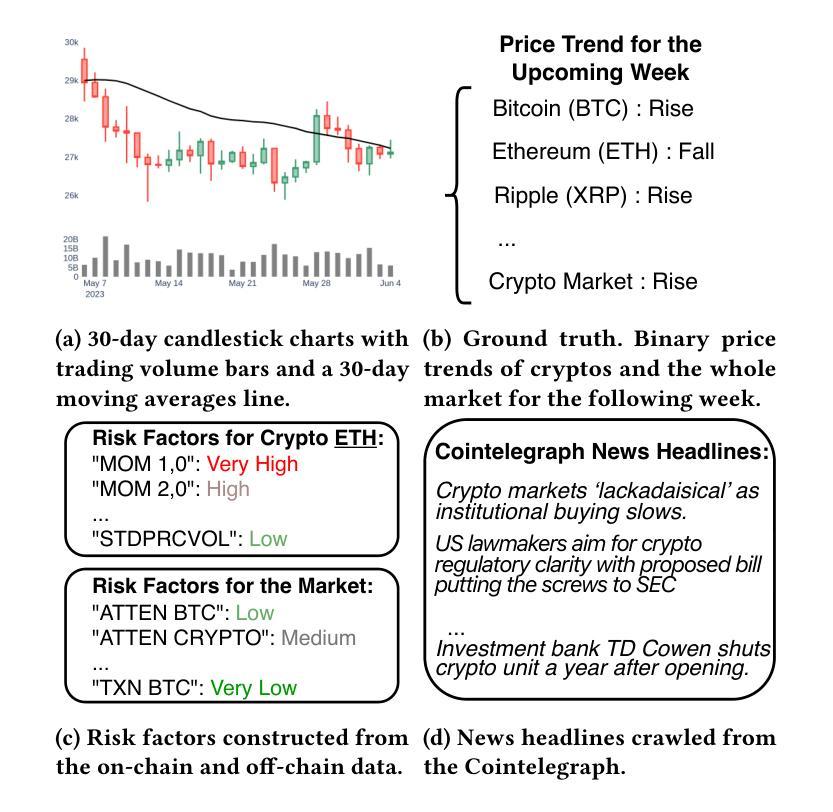
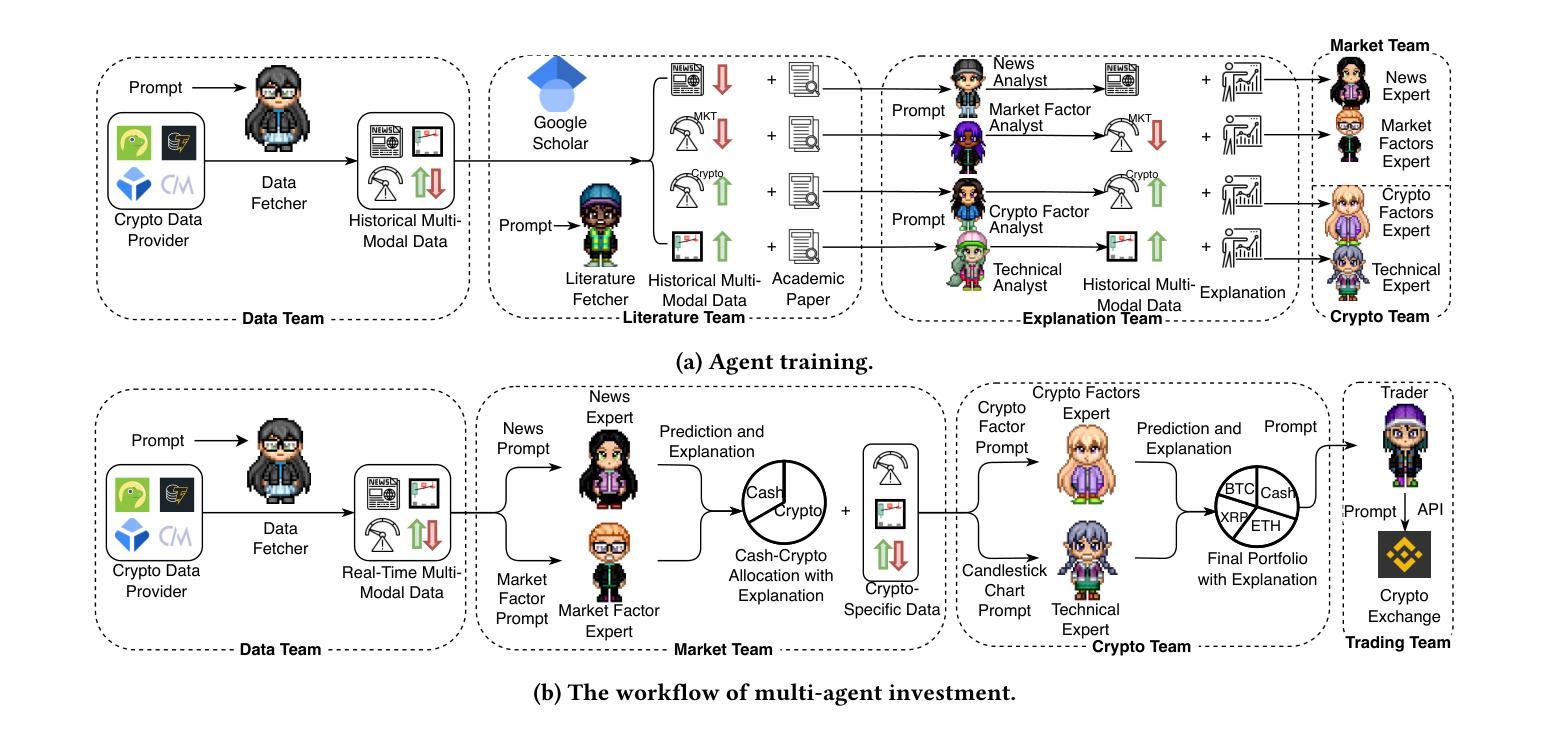
LLM-Powered Multi-Agent System for Automated Crypto Portfolio Management
Authors:Yichen Luo, Yebo Feng, Jiahua Xu, Paolo Tasca, Yang Liu
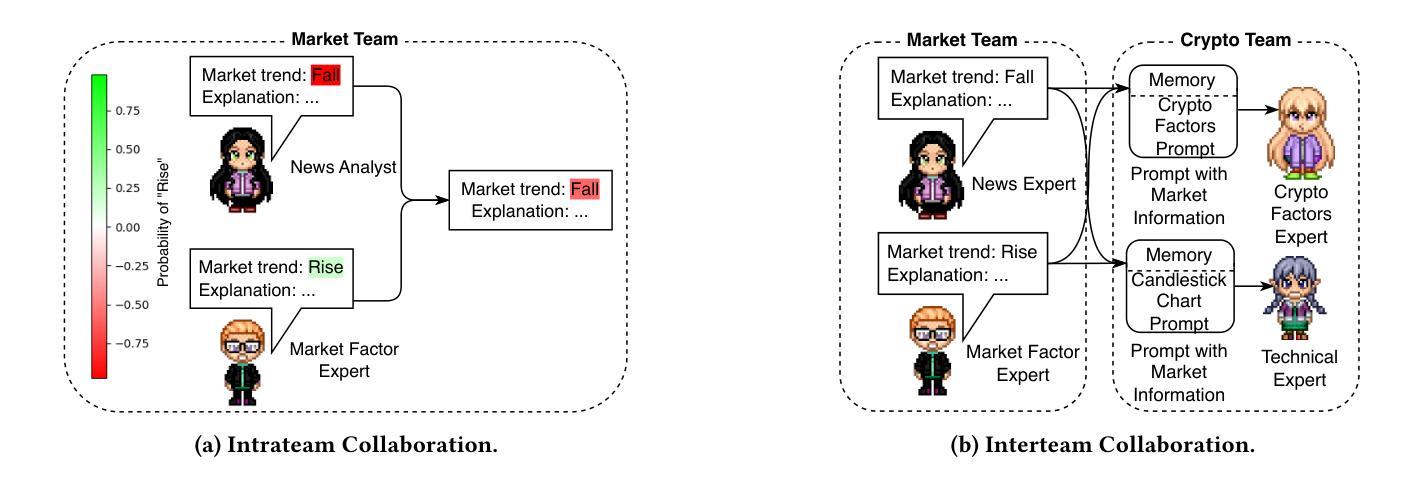
Cryptocurrency investment is inherently difficult due to its shorter history compared to traditional assets, the need to integrate vast amounts of data from various modalities, and the requirement for complex reasoning. While deep learning approaches have been applied to address these challenges, their black-box nature raises concerns about trust and explainability. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have shown promise in financial applications due to their ability to understand multi-modal data and generate explainable decisions. However, single LLM faces limitations in complex, comprehensive tasks such as asset investment. These limitations are even more pronounced in cryptocurrency investment, where LLMs have less domain-specific knowledge in their training corpora. To overcome these challenges, we propose an explainable, multi-modal, multi-agent framework for cryptocurrency investment. Our framework uses specialized agents that collaborate within and across teams to handle subtasks such as data analysis, literature integration, and investment decision-making for the top 30 cryptocurrencies by market capitalization. The expert training module fine-tunes agents using multi-modal historical data and professional investment literature, while the multi-agent investment module employs real-time data to make informed cryptocurrency investment decisions. Unique intrateam and interteam collaboration mechanisms enhance prediction accuracy by adjusting final predictions based on confidence levels within agent teams and facilitating information sharing between teams. Empirical evaluation using data from November 2023 to September 2024 demonstrates that our framework outperforms single-agent models and market benchmarks in classification, asset pricing, portfolio, and explainability performance.
加密货币投资由于其相较于传统资产的历史较短、需要整合来自不同模态的大量数据以及需要进行复杂推理,因此本质上具有挑战性。虽然深度学习的方法已经被用来应对这些挑战,但其黑箱性质引发了关于信任和解释性的担忧。最近,大型语言模型(LLM)在金融应用中显示出潜力,因为它们能够理解多模态数据并产生可解释的决定。然而,单一的大型语言模型在处理复杂的综合任务时面临局限性,例如在加密货币投资方面。这些局限性在加密货币投资中尤为突出,因为大型语言模型在训练语料库中的领域特定知识较少。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了一种用于加密货币投资的解释性、多模态、多智能体框架。我们的框架使用专门设计的智能体,它们在团队内部和团队之间进行协作,以处理诸如数据分析、文献整合和基于市值前30名的加密货币的投资决策等子任务。专家训练模块使用多模态历史数据和专业投资文献对智能体进行微调,而多智能体投资模块则利用实时数据做出明智的加密货币投资决策。独特的团队内部和团队之间的协作机制通过根据智能体团队内的置信水平调整最终预测并促进团队之间的信息共享,从而提高预测准确性。使用2 0 2 3 年 1 1 月至 2 0 2 4 年 9 月的数据进行的实证评估表明,我们的框架在分类、资产定价、投资组合和解释性能方面优于单智能体模型和基准市场。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习在解决数字货币投资难题上的挑战及其自身缺陷,例如缺少足够的域知识、黑盒性质等,本文提出了一种可解释的多模态多智能体框架。该框架通过精细化智能体训练和实战化投资策略协作机制,能够有效提高数字货币投资预测精度并提升模型透明度。实证结果表明,该框架在分类、资产定价、投资组合和解释性能等方面均优于单智能体模型和市场预期。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在数字货币投资领域面临诸多挑战,包括数据集成、复杂推理和信任度问题。
- 大型语言模型在理解多模态数据和生成可解释决策方面展现出潜力,但在复杂任务中面临局限。
- 提出的多模态多智能体框架旨在解决单一模型在数字货币投资中的局限性,包括数据分析、文献整合和决策制定等子任务。
- 专家训练模块利用多模态历史数据和专业投资文献对智能体进行微调。
- 多智能体投资模块采用实时数据做出明智的数字货币投资决策。
- 智能体团队内部的协作机制和团队间的信息共享机制提高了预测精度。
点此查看论文截图

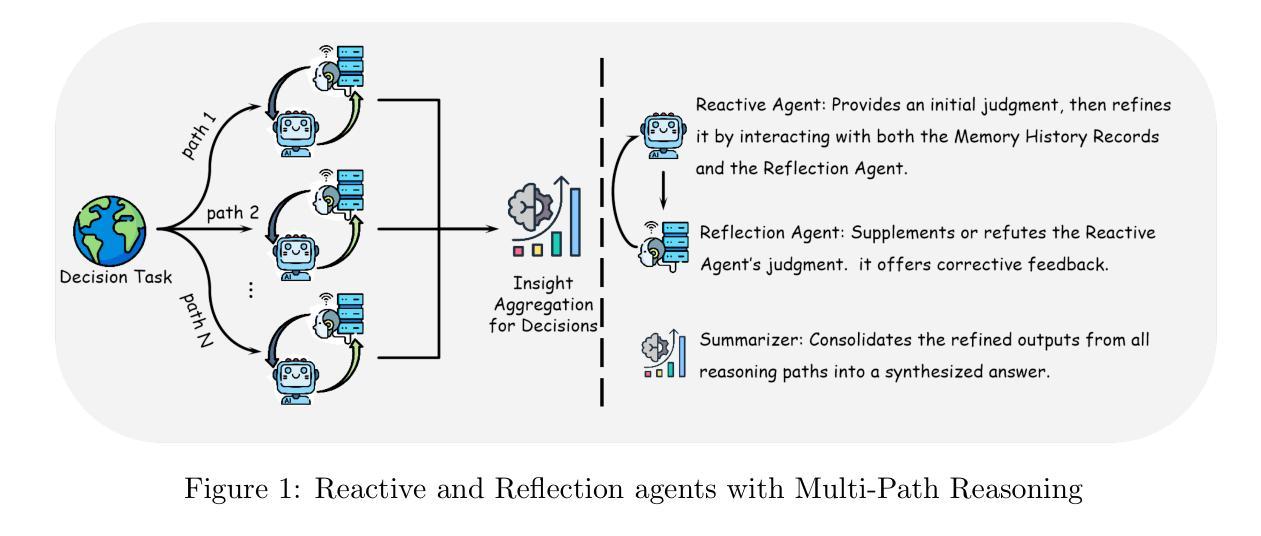
Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Multi-Path Collaborative Reactive and Reflection agents
Authors:Chengbo He, Bochao Zou, Xin Li, Jiansheng Chen, Junliang Xing, Huimin Ma
Agents have demonstrated their potential in scientific reasoning tasks through large language models. However, they often face challenges such as insufficient accuracy and degeneration of thought when handling complex reasoning tasks, which impede their performance. To overcome these issues, we propose the Reactive and Reflection agents with Multi-Path Reasoning (RR-MP) Framework, aimed at enhancing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Our approach improves scientific reasoning accuracy by employing a multi-path reasoning mechanism where each path consists of a reactive agent and a reflection agent that collaborate to prevent degeneration of thought inherent in single-agent reliance. Additionally, the RR-MP framework does not require additional training; it utilizes multiple dialogue instances for each reasoning path and a separate summarizer to consolidate insights from all paths. This design integrates diverse perspectives and strengthens reasoning across each path. We conducted zero-shot and few-shot evaluations on tasks involving moral scenarios, college-level physics, and mathematics. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms baseline approaches, highlighting the effectiveness and advantages of the RR-MP framework in managing complex scientific reasoning tasks.
人工智能代理在大规模语言模型的支持下,已在科学推理任务中展现出巨大潜力。然而,在处理复杂的推理任务时,它们常常面临准确性不足和思想退化等挑战,阻碍了其性能的提升。为了克服这些问题,我们提出了带有多路推理的反应与反思代理(RR-MP)框架,旨在增强大型语言模型的推理能力。我们的方法采用多路推理机制来提高科学推理的准确性,其中每条路径包含一个反应代理和一个反思代理,它们协同工作,防止单一代理依赖所带来的思想退化。此外,RR-MP框架无需额外训练;它为每条推理路径利用多个对话实例和一个单独的总结器来整合所有路径的见解。这种设计融合了各种观点,加强了每条路径的推理能力。我们对涉及道德情景、大学物理学和数学的任务进行了零样本和少样本评估。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于基准方法,突出了RR-MP框架在处理复杂科学推理任务中的有效性和优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型的智能体在科学推理任务中已展现潜力,但面临处理复杂推理任务时准确不足与思维退化等挑战。为解决这些问题,提出采用反应与反思多路径推理框架(RR-MP),旨在增强语言模型的推理能力。通过多路径推理机制提升科学推理准确性,其中每条路径包含反应与反思智能体,协作防止单一智能体依赖导致的思维退化。此外,RR-MP框架无需额外训练,利用每个推理路径的多个对话实例和独立总结者来整合不同视角和加强每条路径的推理能力。实验结果显示,在涉及道德场景、大学物理和数学的零样本和少样本评估中,该方法优于基准方法,突显RR-MP框架在处理复杂科学推理任务中的有效性和优势。
Key Takeaways
- 智能体在科学推理任务中具有潜力,但仍面临准确性和思维退化挑战。
- 提出反应与反思多路径推理框架(RR-MP)以增强语言模型的推理能力。
- RR-MP框架采用多路径推理机制,每条路径包含反应和反思智能体,以预防思维退化。
- RR-MP框架不需要额外训练,利用多个对话实例来整合不同视角和加强推理能力。
- 反应与反思智能体的协作有助于提升科学推理的准确性。
- 实验结果显示RR-MP框架在处理复杂科学推理任务时表现优于基准方法。
点此查看论文截图


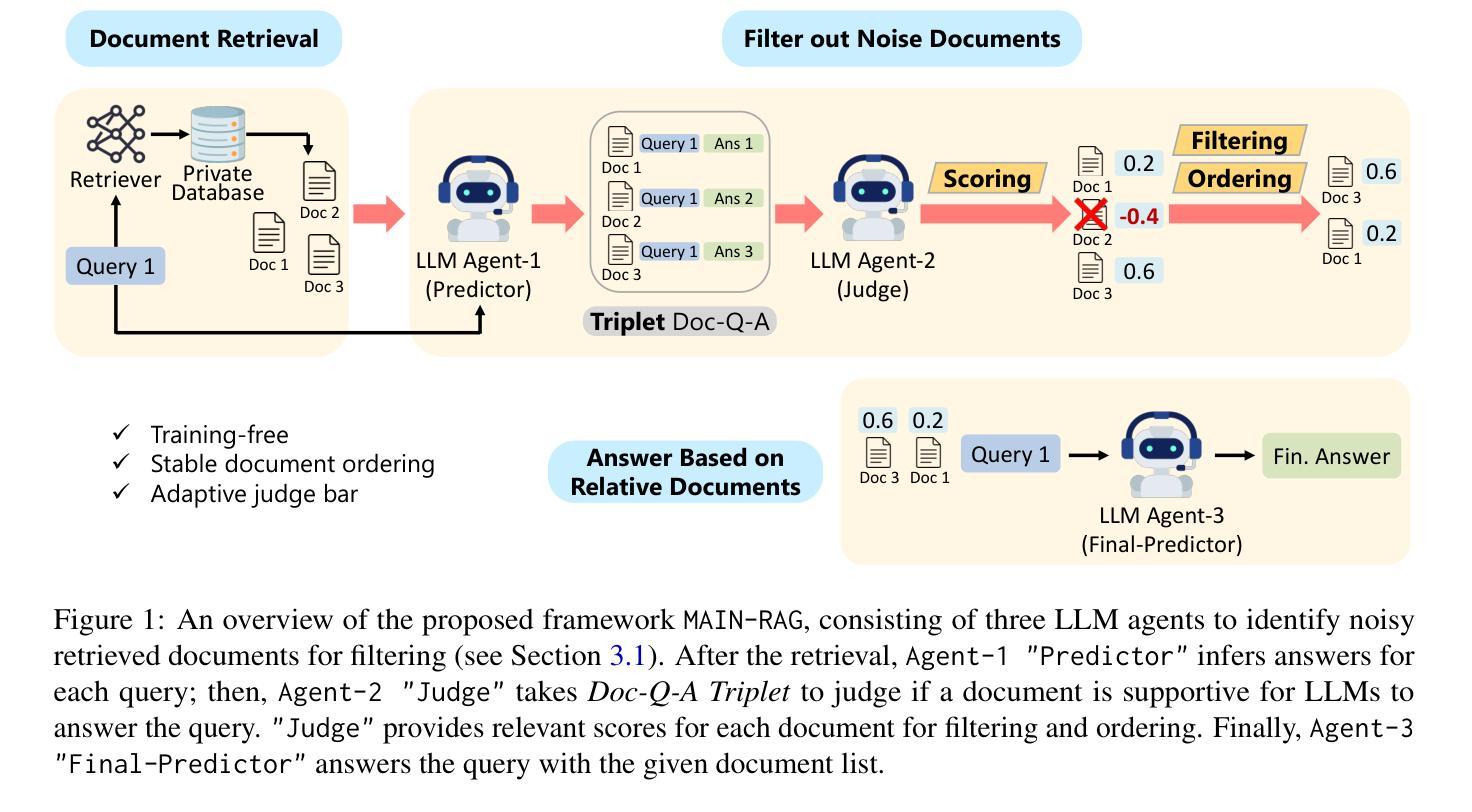
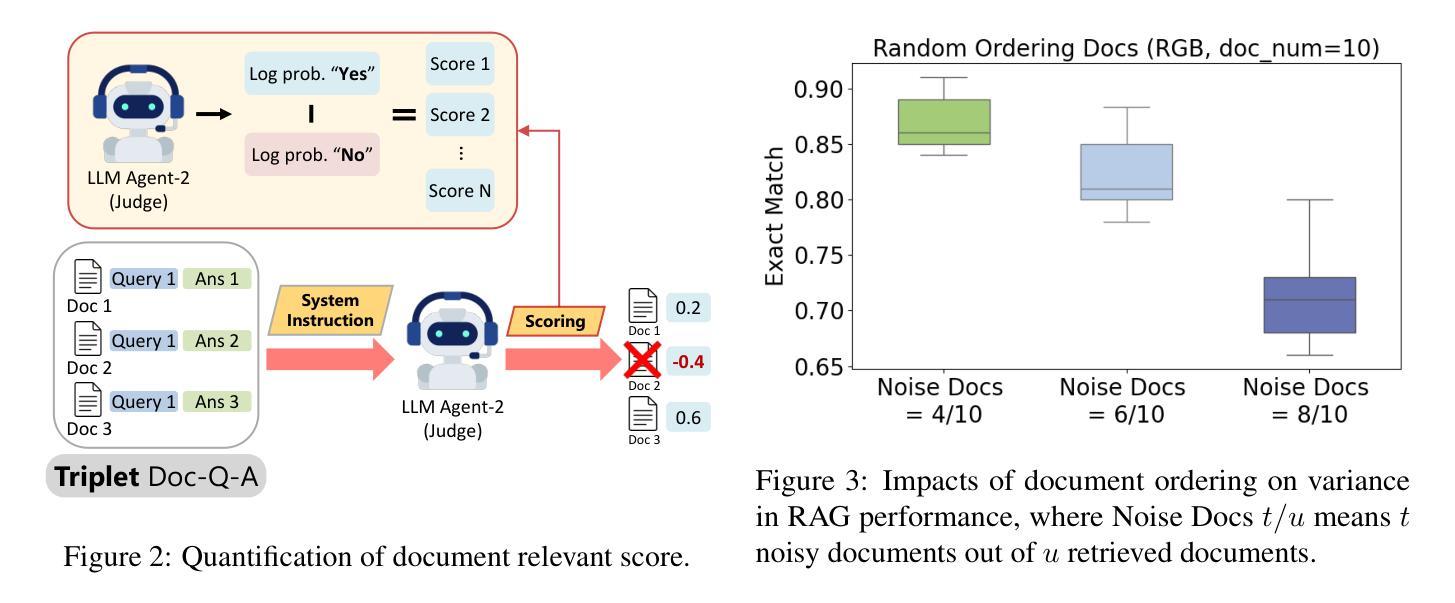
MAIN-RAG: Multi-Agent Filtering Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Chia-Yuan Chang, Zhimeng Jiang, Vineeth Rakesh, Menghai Pan, Chin-Chia Michael Yeh, Guanchu Wang, Mingzhi Hu, Zhichao Xu, Yan Zheng, Mahashweta Das, Na Zou
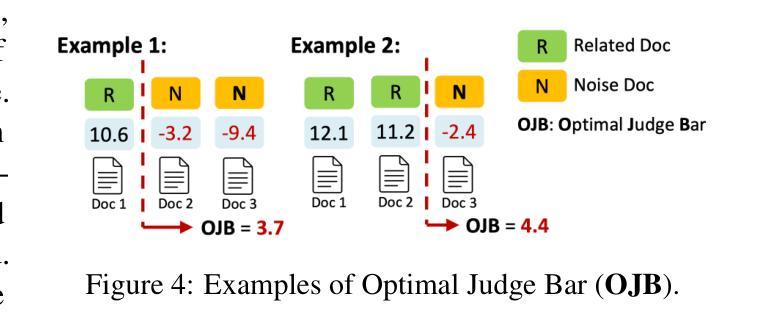
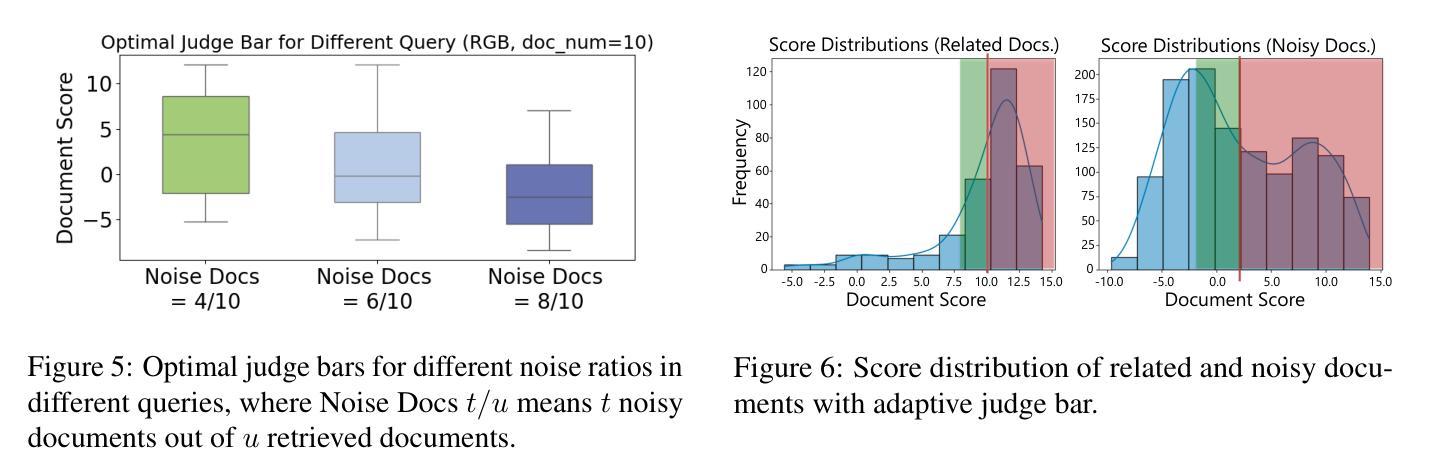
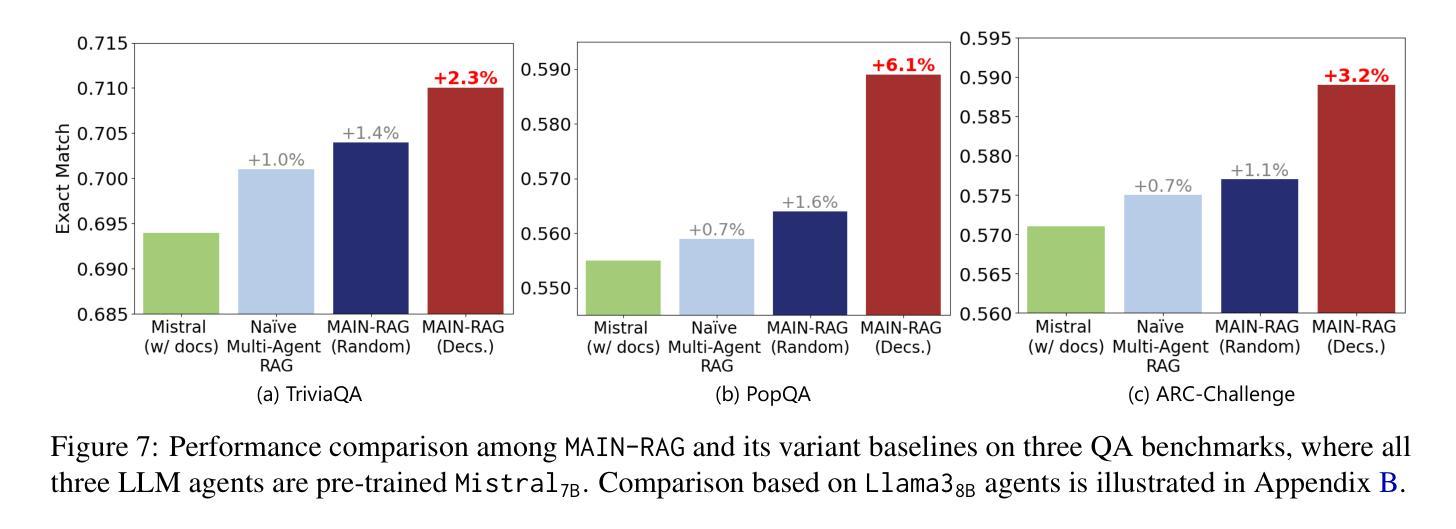
Large Language Models (LLMs) are becoming essential tools for various natural language processing tasks but often suffer from generating outdated or incorrect information. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) addresses this issue by incorporating external, real-time information retrieval to ground LLM responses. However, the existing RAG systems frequently struggle with the quality of retrieval documents, as irrelevant or noisy documents degrade performance, increase computational overhead, and undermine response reliability. To tackle this problem, we propose Multi-Agent Filtering Retrieval-Augmented Generation (MAIN-RAG), a training-free RAG framework that leverages multiple LLM agents to collaboratively filter and score retrieved documents. Specifically, MAIN-RAG introduces an adaptive filtering mechanism that dynamically adjusts the relevance filtering threshold based on score distributions, effectively minimizing noise while maintaining high recall of relevant documents. The proposed approach leverages inter-agent consensus to ensure robust document selection without requiring additional training data or fine-tuning. Experimental results across four QA benchmarks demonstrate that MAIN-RAG consistently outperforms traditional RAG approaches, achieving a 2-11% improvement in answer accuracy while reducing the number of irrelevant retrieved documents. Quantitative analysis further reveals that our approach achieves superior response consistency and answer accuracy over baseline methods, offering a competitive and practical alternative to training-based solutions.
大型语言模型(LLM)已成为各种自然语言处理任务中不可或缺的工具,但它们常常会出现生成过时或错误信息的问题。检索增强生成(RAG)通过结合外部实时信息检索来解决这个问题,使LLM响应更具实际性。然而,现有的RAG系统经常面临检索文档质量的问题,不相关或嘈杂的文档会降低性能,增加计算开销,并破坏响应的可靠性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了多代理过滤检索增强生成(MAIN-RAG),这是一种无需训练即可使用的RAG框架,它利用多个LLM代理协同过滤和评分检索到的文档。具体来说,MAIN-RAG引入了一种自适应过滤机制,该机制根据评分分布动态调整相关性过滤阈值,在尽量减少噪音的同时保持对相关文档的高召回率。该方法利用代理间的共识来确保稳健的文档选择,无需额外的训练数据或微调。在四个问答基准测试上的实验结果表明,MAIN-RAG持续优于传统的RAG方法,在提高答案准确性的同时减少了不相关检索文档的数量。定量分析进一步表明,我们的方法在响应一致性和答案准确性方面优于基准方法,为基于训练的方法提供了一个有竞争力的实用替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)对于多种自然语言处理任务至关重要,但存在生成过时或错误信息的问题。检索增强生成(RAG)通过融入外部实时信息检索来解决这一问题。然而,现有RAG系统常面临检索文档质量不佳的挑战,不相关或嘈杂的文档会降低性能、增加计算负担并影响响应可靠性。为解决此问题,我们提出无需训练的多智能体过滤检索增强生成(MAIN-RAG)框架,利用多个LLM智能体协同过滤和评分检索到的文档。MAIN-RAG引入自适应过滤机制,根据评分分布动态调整相关度过滤阈值,既有效减少噪声又保持高相关文档召回率。该框架利用智能体间共识,确保稳健的文档选择无需额外的训练数据或微调。实验结果显示,MAIN-RAG在四个问答基准测试上持续优于传统RAG方法,答案准确性提高2-11%,同时减少不相关检索文档数量。定量分析进一步证明,我们的方法在响应一致性和答案准确性上优于基线方法,提供基于训练的解决方案的竞争性和实用替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理任务中表现出色,但存在信息时效性和准确性问题。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)通过融入外部实时信息提高LLM响应的准确度。
- 现有RAG系统面临检索文档质量挑战,如文档的不相关性和噪声。
- MAIN-RAG框架通过多智能体协同过滤和评分检索文档,提高性能并减少噪声。
- MAIN-RAG引入自适应过滤机制,根据评分分布动态调整过滤阈值,保持高相关文档召回率。
- 该框架利用智能体间共识,确保稳健的文档选择,无需额外的训练数据或微调。
点此查看论文截图

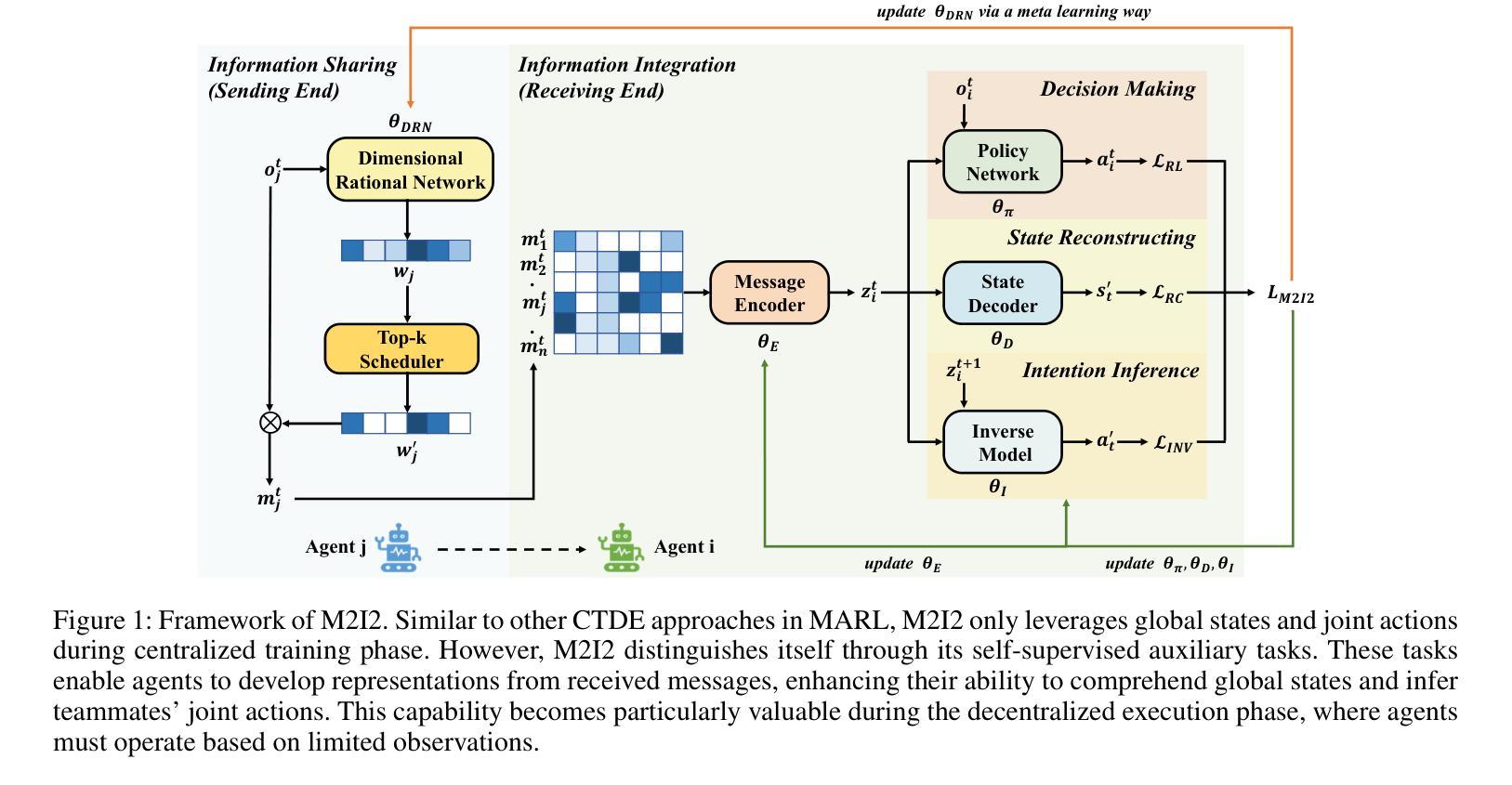
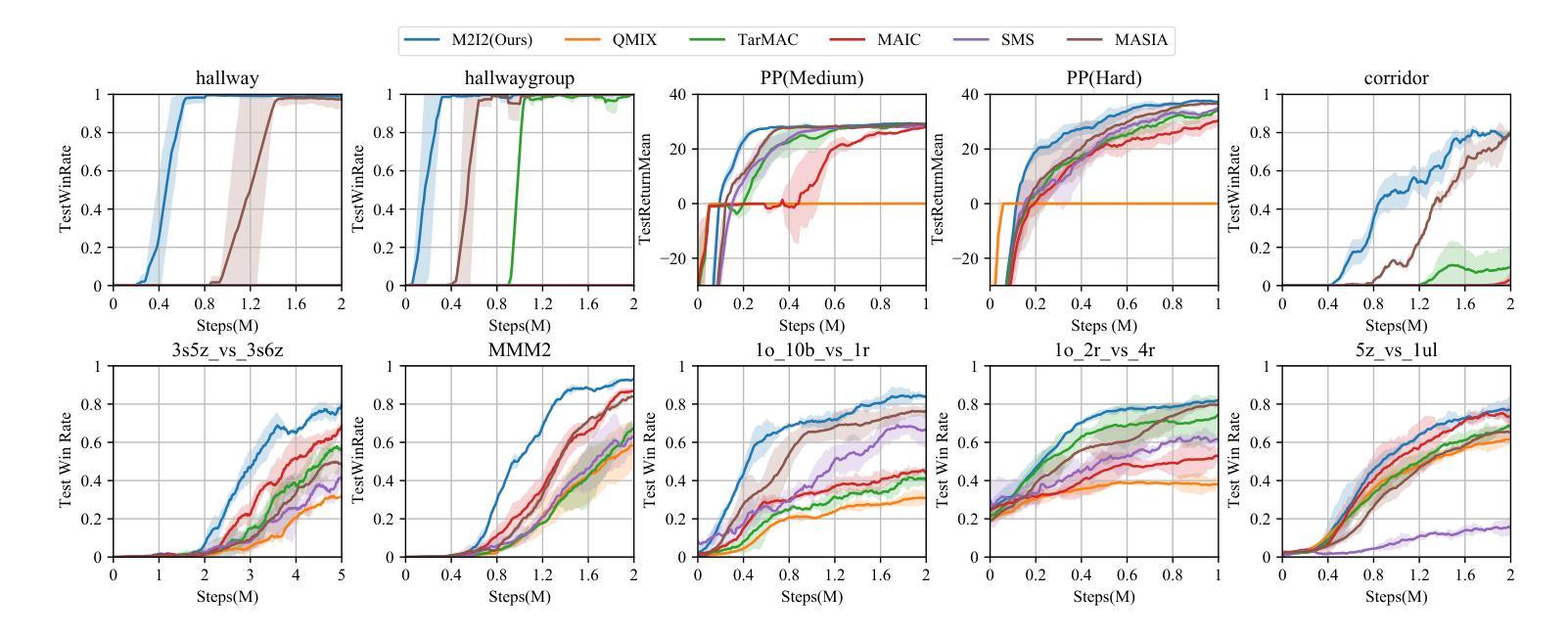
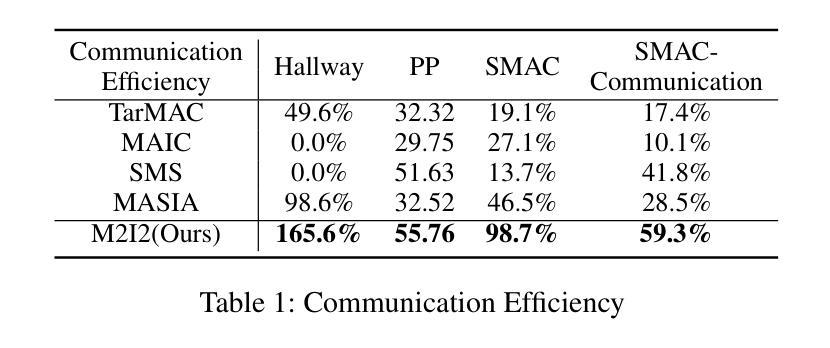
M2I2: Learning Efficient Multi-Agent Communication via Masked State Modeling and Intention Inference
Authors:Chuxiong Sun, Peng He, Qirui Ji, Zehua Zang, Jiangmeng Li, Rui Wang, Wei Wang
Communication is essential in coordinating the behaviors of multiple agents. However, existing methods primarily emphasize content, timing, and partners for information sharing, often neglecting the critical aspect of integrating shared information. This gap can significantly impact agents’ ability to understand and respond to complex, uncertain interactions, thus affecting overall communication efficiency. To address this issue, we introduce M2I2, a novel framework designed to enhance the agents’ capabilities to assimilate and utilize received information effectively. M2I2 equips agents with advanced capabilities for masked state modeling and joint-action prediction, enriching their perception of environmental uncertainties and facilitating the anticipation of teammates’ intentions. This approach ensures that agents are furnished with both comprehensive and relevant information, bolstering more informed and synergistic behaviors. Moreover, we propose a Dimensional Rational Network, innovatively trained via a meta-learning paradigm, to identify the importance of dimensional pieces of information, evaluating their contributions to decision-making and auxiliary tasks. Then, we implement an importance-based heuristic for selective information masking and sharing. This strategy optimizes the efficiency of masked state modeling and the rationale behind information sharing. We evaluate M2I2 across diverse multi-agent tasks, the results demonstrate its superior performance, efficiency, and generalization capabilities, over existing state-of-the-art methods in various complex scenarios.
沟通对于协调多个代理人的行为至关重要。然而,现有方法主要关注信息共享的内容、时机和伙伴,往往忽视了整合共享信息的至关重要的方面。这一差距会显著影响代理人在理解和应对复杂、不确定的互动方面的能力,从而影响整体的沟通效率。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了M2I2,这是一个旨在增强代理人有效同化并利用所接收信息能力的新型框架。M2I2为代理人提供了先进的掩态建模和联合行动预测能力,丰富了他们对环境不确定性的感知,并促进了对队友意图的预测。这种方法确保了代理人们拥有全面且相关的信息,从而支持更加明智和协同的行为。此外,我们提出了一种称为“维度理性网络”的创新网络,通过元学习范式进行训练,以识别信息维度的重要性,评估其对决策和辅助任务的贡献。接着,我们基于重要性启发实施选择性信息掩蔽和共享。这一策略优化了掩态建模的效率以及信息共享的合理性。我们在多种多代理任务中评估了M2I2的性能,结果表明,在各种复杂场景中,其性能、效率和泛化能力均优于现有最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文强调信息整合在协调多智能体行为中的重要性,并提出了M2I2框架来解决智能体在信息同化与利用方面的不足。M2I2框架包含状态建模和联合行动预测能力,增强智能体对环境不确定性的感知和对队友意图的预测。此外,通过元学习范式训练维度理性网络,提出基于重要性的启发式选择性信息掩蔽和共享策略,优化建模效率和信息共享合理性。在多智能体任务中的评估表明,M2I2框架在性能、效率和泛化能力方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 信息整合对于多智能体行为的协调至关重要,现有方法往往忽视这一关键方面。
- M2I2框架旨在增强智能体在信息同化与利用方面的能力。
- M2I2包含状态建模和联合行动预测能力,丰富智能体对环境不确定性的感知和对队友意图的预测。
- 采用维度理性网络,通过元学习范式训练,评估信息决策中的贡献。
- 提出基于重要性的启发式选择性信息掩蔽和共享策略,优化信息利用效率。
- M2I2框架在多种多智能体任务中表现出卓越的性能、效率和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图