⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-06 更新
Digital Guardians: Can GPT-4, Perspective API, and Moderation API reliably detect hate speech in reader comments of German online newspapers?
Authors:Manuel Weber, Moritz Huber, Maximilian Auch, Alexander Döschl, Max-Emanuel Keller, Peter Mandl
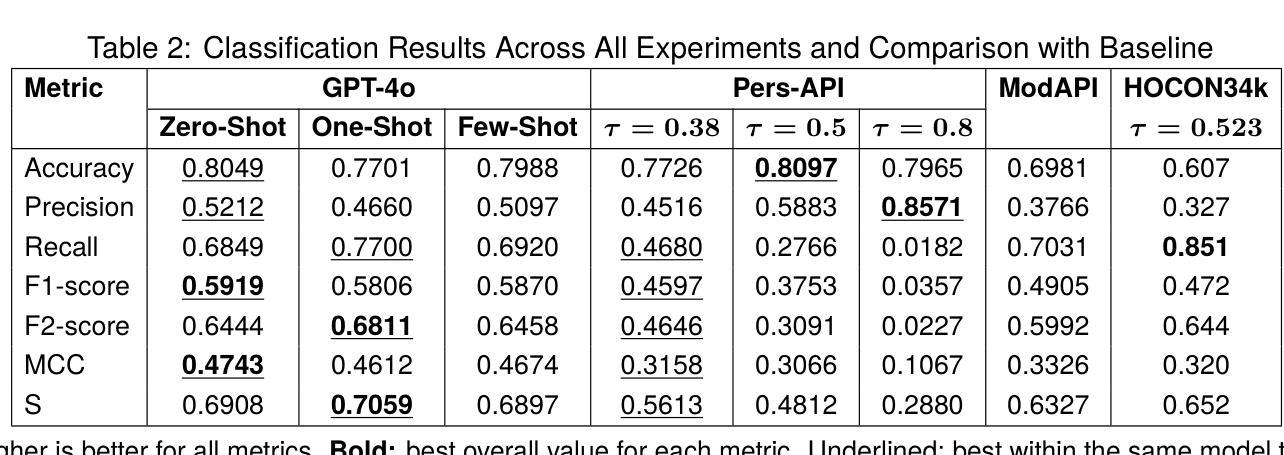
In recent years, toxic content and hate speech have become widespread phenomena on the internet. Moderators of online newspapers and forums are now required, partly due to legal regulations, to carefully review and, if necessary, delete reader comments. This is a labor-intensive process. Some providers of large language models already offer solutions for automated hate speech detection or the identification of toxic content. These include GPT-4o from OpenAI, Jigsaw’s (Google) Perspective API, and OpenAI’s Moderation API. Based on the selected German test dataset HOCON34k, which was specifically created for developing tools to detect hate speech in reader comments of online newspapers, these solutions are compared with each other and against the HOCON34k baseline. The test dataset contains 1,592 annotated text samples. For GPT-4o, three different promptings are used, employing a Zero-Shot, One-Shot, and Few-Shot approach. The results of the experiments demonstrate that GPT-4o outperforms both the Perspective API and the Moderation API, and exceeds the HOCON34k baseline by approximately 5 percentage points, as measured by a combined metric of MCC and F2-score.
近年来,有毒内容和仇恨言论在互联网上变得日益普遍。网络报纸和论坛的管理人员现在需要根据法律要求进行仔细审查,必要时删除读者评论。这是一项劳动密集型的流程。一些大型语言模型的提供商已经提供自动仇恨言论检测或有毒内容识别的解决方案。这包括来自OpenAI的GPT-4o、谷歌Jigsaw的Perspective API以及OpenAI的Moderation API。这些解决方案是基于专门用于开发检测在线报纸读者评论中的仇恨言论的工具有HOCON34k数据集进行对比测试的。测试数据集包含一万五千九百二十二个经过注释的文本样本。GPT-4o采用了三种不同的提示方式,包括零样本、一样本和少样本方法。实验结果表明,GPT-4o在MCC和F2分数的综合指标上超过了Perspective API和Moderation API,并大约超出HOCON34k基线约五个百分点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了互联网上广泛存在的有毒内容和仇恨言论现象,网络报纸和论坛的版主因此需对读者评论进行仔细审查,甚至删除相关内容,这一过程劳动强度大。一些大型语言模型提供商如OpenAI、Google等已经提供了自动化仇恨言论检测或有毒内容识别的解决方案。基于专门用于开发仇恨言论检测工具的德国测试数据集HOCON34k,这些解决方案通过不同方法进行测试比较,包括Zero-Shot、One-Shot和Few-Shot方法。实验结果表明,GPT-4o的表现优于其他检测器,超过HOCON34k基准线约5个百分点。
Key Takeaways
- 互联网上存在大量的有毒内容和仇恨言论,对网络报纸和论坛的版主提出了新的挑战。
- 为了应对这一挑战,网络报纸和论坛的版主需仔细审查读者评论,甚至删除相关内容,这是一个劳动强度大的过程。
- 一些大型语言模型提供商已经开发出自动的仇恨言论检测或有毒内容识别解决方案。
- GPT-4o在仇恨言论检测方面的表现优于其他检测器,如Google的Perspective API和OpenAI的Moderation API。
- GPT-4o的表现是基于德国测试数据集HOCON34k进行验证的。
- 实验采用Zero-Shot、One-Shot和Few-Shot三种方法测试GPT-4o的性能。
点此查看论文截图



Automated Self-Refinement and Self-Correction for LLM-based Product Attribute Value Extraction
Authors:Alexander Brinkmann, Christian Bizer
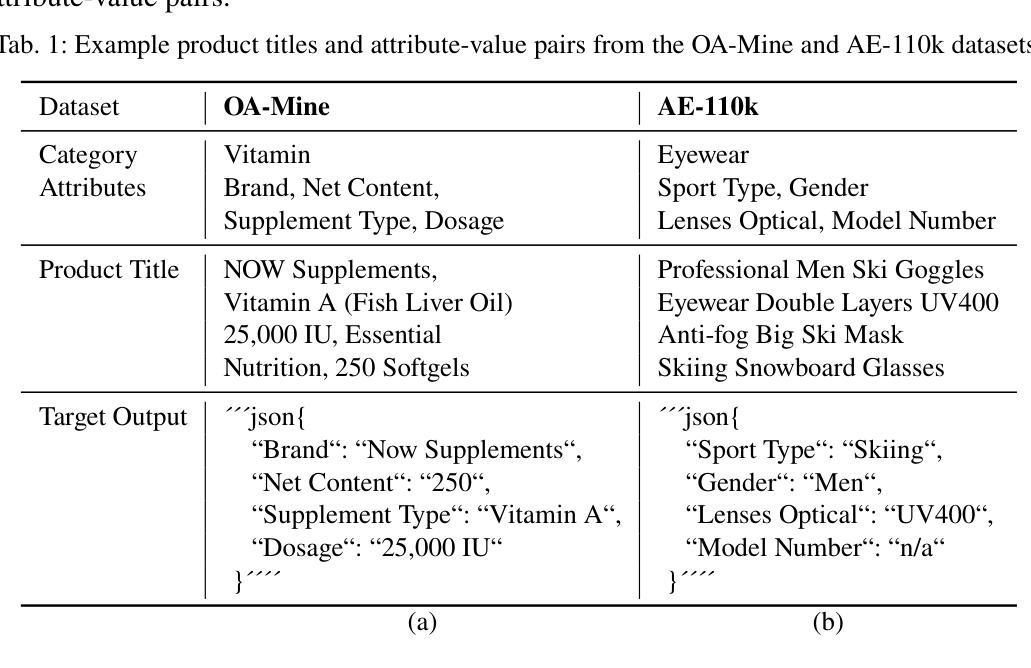
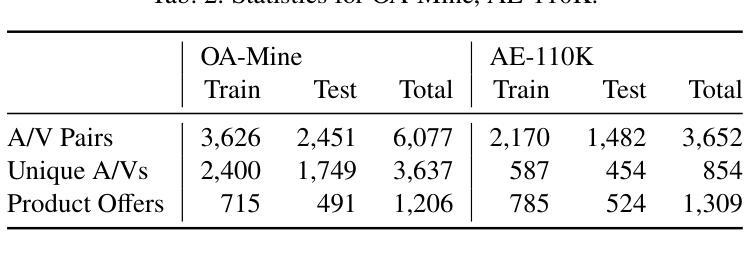
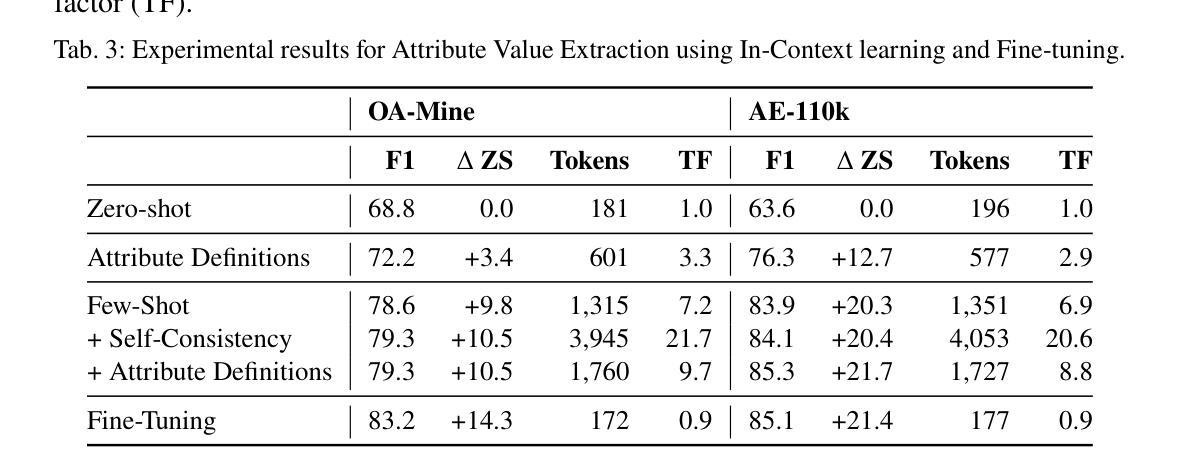
Structured product data, in the form of attribute-value pairs, is essential for e-commerce platforms to support features such as faceted product search and attribute-based product comparison. However, vendors often provide unstructured product descriptions, making attribute value extraction necessary to ensure data consistency and usability. Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated their potential for product attribute value extraction in few-shot scenarios. Recent research has shown that self-refinement techniques can improve the performance of LLMs on tasks such as code generation and text-to-SQL translation. For other tasks, the application of these techniques has resulted in increased costs due to processing additional tokens, without achieving any improvement in performance. This paper investigates applying two self-refinement techniques, error-based prompt rewriting and self-correction, to the product attribute value extraction task. The self-refinement techniques are evaluated across zero-shot, few-shot in-context learning, and fine-tuning scenarios using GPT-4o. The experiments show that both self-refinement techniques have only a marginal impact on the model’s performance across the different scenarios, while significantly increasing processing costs. For scenarios with training data, fine-tuning yields the highest performance, while the ramp-up costs of fine-tuning are balanced out as the amount of product descriptions increases.
结构化产品数据以属性-值对的形式存在,对于电子商务平台来说,支持面向方面的产品搜索和基于属性的产品比较等功能至关重要。然而,供应商通常提供非结构化的产品描述,因此需要提取属性值以确保数据的一致性和可用性。大型语言模型(LLM)已在少数场景显示出其在产品属性值提取方面的潜力。最近的研究表明,自我完善技术可以提高LLM在代码生成和文本到SQL翻译等任务上的性能。然而,对于其他任务,这些技术的应用由于处理额外的令牌而增加了成本,而没有在性能上实现任何改进。本文研究了两种自我完善技术,基于错误的提示重写和自我修正,并将其应用于产品属性值提取任务。这些自我完善技术在零样本、少数情境内学习和微调场景下使用GPT-4o进行了评估。实验表明,这两种自我完善技术对模型在不同场景下的性能影响微乎其微,却大大提高了处理成本。对于存在训练数据的情况,微调会产生最高的性能,而随着产品描述数量的增加,微调的一次性成本得以平衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于属性-值对的形式的结构化产品数据对电子商务平台至关重要,支持面向方面的产品搜索和基于属性的产品比较等功能。然而,由于供应商提供的产品描述通常是结构化的,因此需要进行属性值的提取以确保数据的一致性和可用性。大型语言模型在少量场景下的产品属性价值提取中表现出了潜力。本文主要探讨了两种自我优化技术——基于错误的提示重写和自我校正,用于产品属性价值提取任务。实验表明,这两种技术在不同场景下对模型性能的影响微乎其微,却显著增加了处理成本。在有训练数据的场景下,微调可带来最高性能,随着产品描述数量的增加,微调的一次性成本得以平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 结构化产品数据对于电子商务平台至关重要,支持多种功能如面向方面的产品搜索和基于属性的产品比较。
- 供应商提供的产品描述往往是未结构化的,需要进行属性值的提取。
- 大型语言模型在少量场景下的产品属性价值提取中展现出潜力。
- 自我优化技术如基于错误的提示重写和自我校正被应用于产品属性价值提取任务。
- 实验显示自我优化技术对模型性能影响微小,但增加了处理成本。
- 在有训练数据的场景下,微调能带来最高性能。
点此查看论文截图


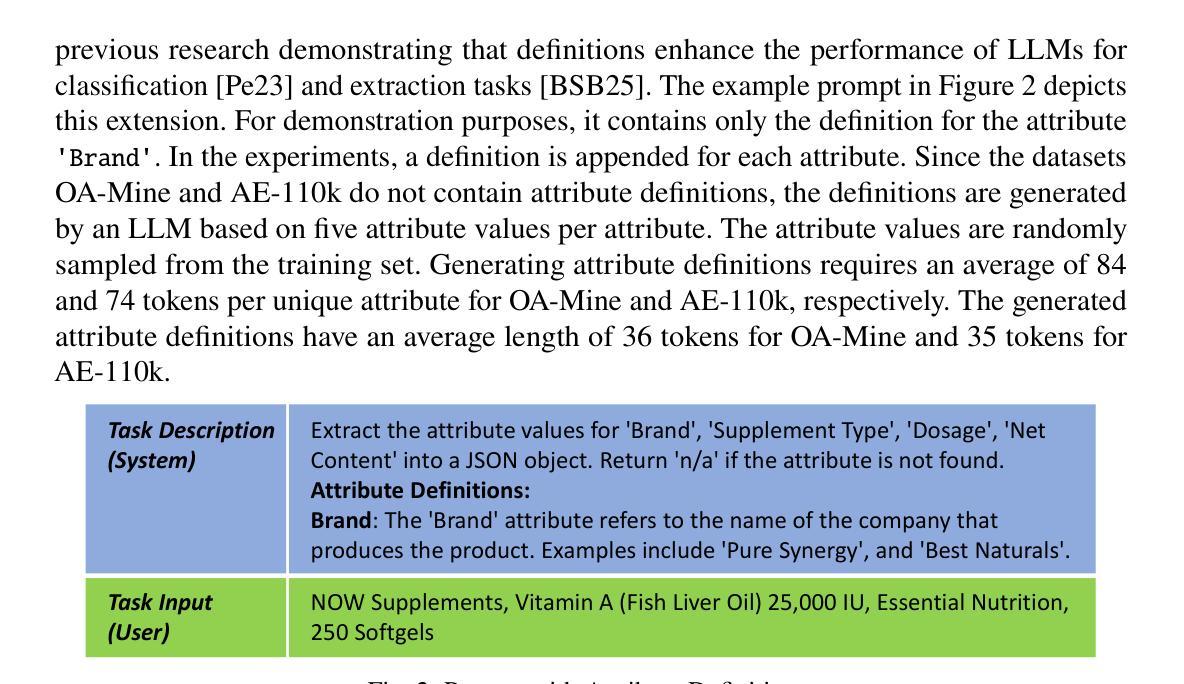
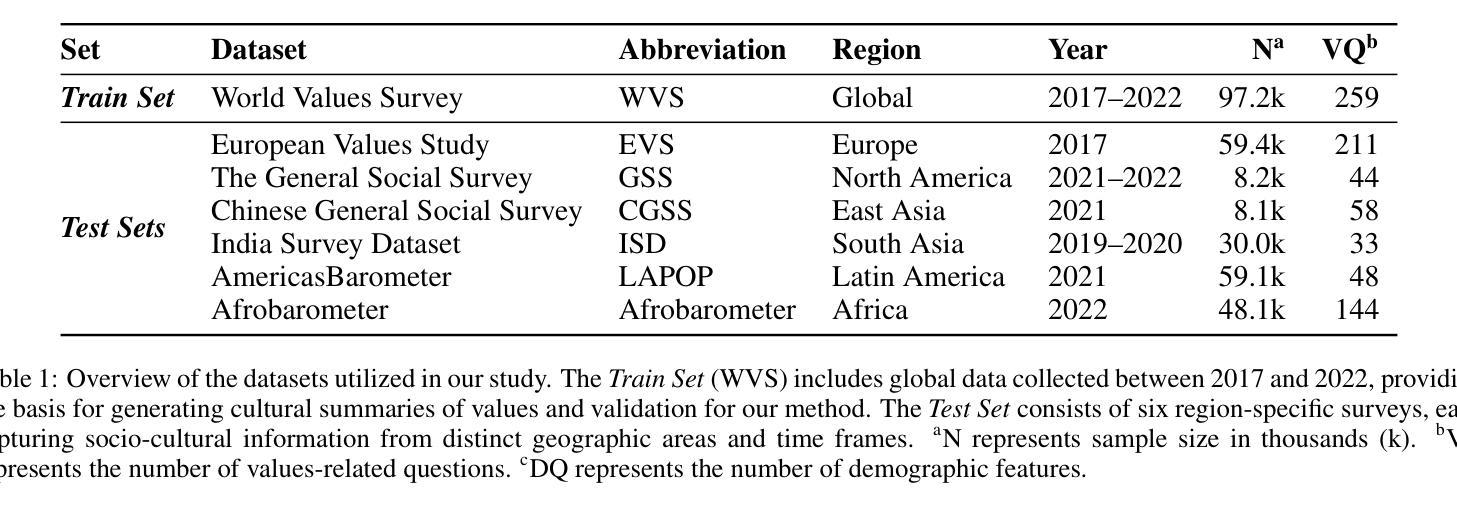
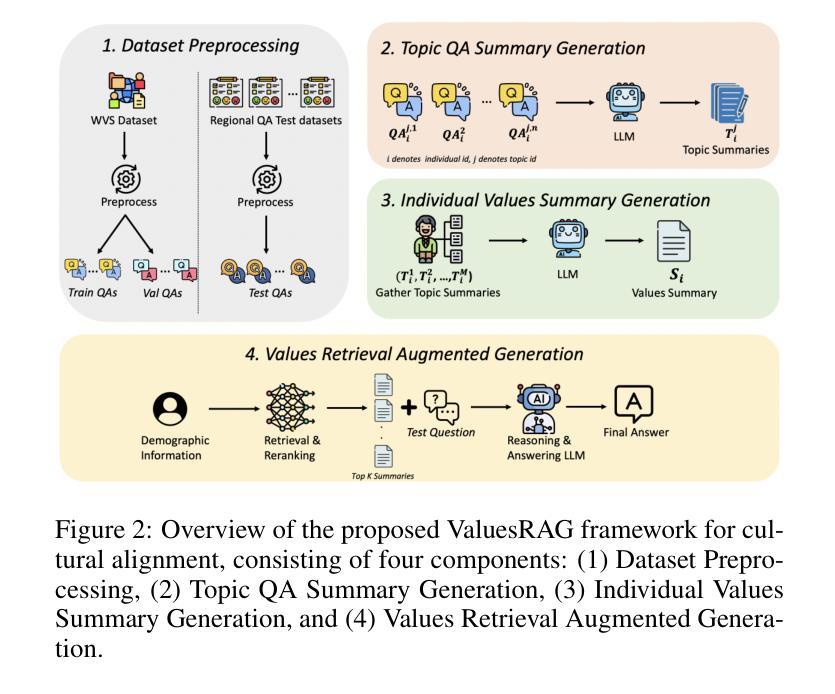
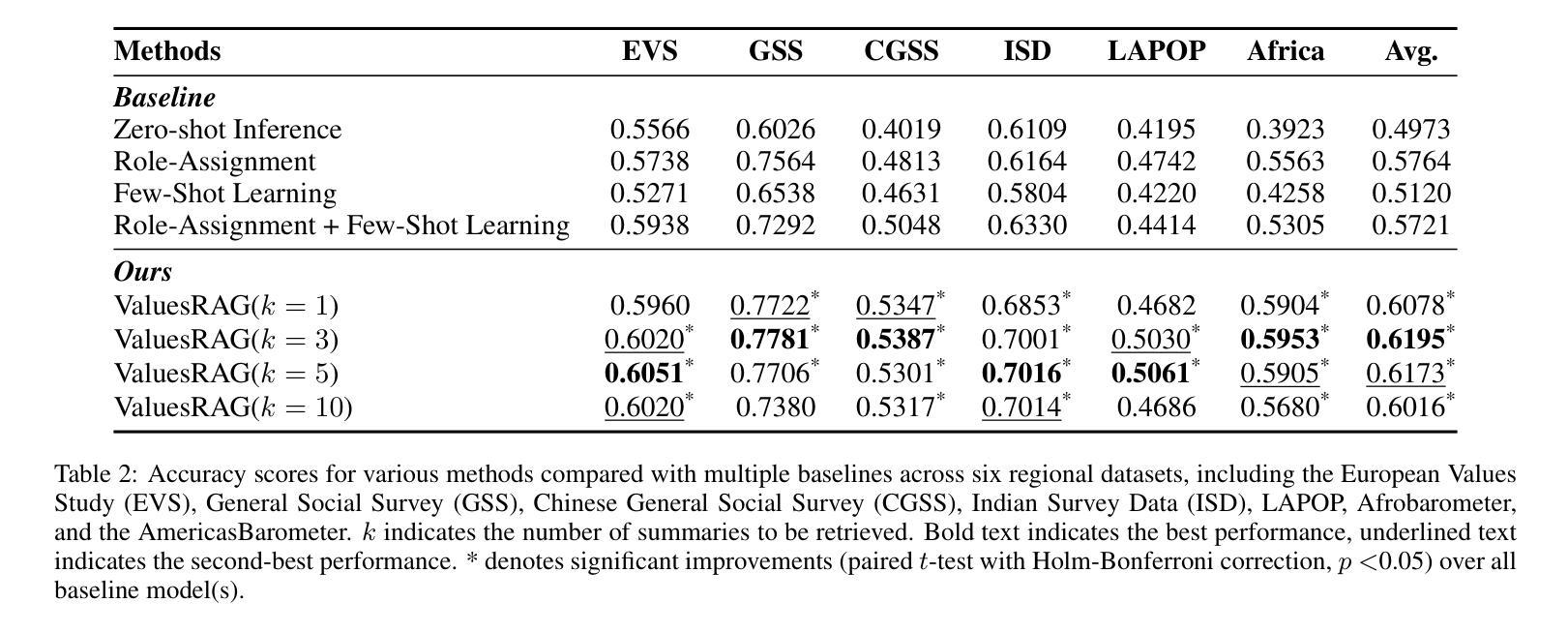
ValuesRAG: Enhancing Cultural Alignment Through Retrieval-Augmented Contextual Learning
Authors:Wonduk Seo, Zonghao Yuan, Yi Bu
Cultural values alignment in Large Language Models (LLMs) is a critical challenge due to their tendency to embed Western-centric biases from training data, leading to misrepresentations and fairness issues in cross-cultural contexts. Recent approaches, such as role-assignment and few-shot learning, often struggle with reliable cultural alignment as they heavily rely on pre-trained knowledge, lack scalability, and fail to capture nuanced cultural values effectively. To address these issues, we propose ValuesRAG, a novel and effective framework that applies Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with in-context learning to integrate cultural and demographic knowledge dynamically during text generation. Leveraging the World Values Survey (WVS) dataset, ValuesRAG first generates summaries of values for each individual. Subsequently, we curated several representative regional datasets to serve as test datasets and retrieve relevant summaries of values based on demographic features, followed by a reranking step to select the top-k relevant summaries. ValuesRAG consistently outperforms baseline methods, both in the main experiment and in the ablation study where only the values summary was provided, highlighting ValuesRAG’s potential to foster culturally aligned AI systems and enhance the inclusivity of AI-driven applications.
大型语言模型(LLM)中的文化价值观对齐是一项关键挑战,因为它们往往嵌入从训练数据中获得的西方中心偏见,导致跨文化背景下的误表征和公平性问题。最近的方法,如角色分配和少样本学习,往往难以可靠地进行文化对齐,因为它们严重依赖于预训练知识,缺乏可扩展性,并且未能有效地捕捉微妙的文化价值观。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了ValuesRAG,这是一个新颖有效的框架,应用检索增强生成(RAG)与上下文学习,以在文本生成过程中动态集成文化和人口统计知识。借助世界价值观调查(WVS)数据集,ValuesRAG首先为每个人生成价值观摘要。随后,我们精心挑选了几个具有代表性的区域数据集作为测试数据集,并根据人口统计特征检索相关的价值观摘要,然后进行重新排序步骤,选择前k个相关摘要。ValuesRAG在主要实验和仅提供价值观摘要的消融研究中均优于基准方法,凸显了ValuesRAG在促进文化对齐的AI系统和提高AI驱动应用包容性的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在文化价值观对齐方面面临挑战,因训练数据中的西方中心偏见导致跨文化背景下的误表征和公平问题。为解决这个问题,我们提出了ValuesRAG框架,通过检索增强生成(RAG)与上下文学习,动态整合文化和人口统计知识来进行文本生成。该框架利用世界价值观调查(WVS)数据集,首先为每个人生成价值观摘要,然后基于人口统计特征检索相关的价值观摘要并进行重新排序。ValuesRAG在主要实验和仅提供价值观摘要的消融研究中均优于基准方法,显示出其在促进文化对齐的AI系统和提高AI应用程序的包容性方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在跨文化环境中面临文化价值观对齐的挑战,因为训练数据中的西方中心偏见可能导致误表征和公平问题。
- 目前的方法(如角色分配和少样本学习)在可靠的文化对齐方面存在困难,因为它们严重依赖预训练知识,缺乏可扩展性,并且不能有效地捕捉微妙的文化价值观。
- ValuesRAG框架通过结合检索增强生成(RAG)和上下文学习来解决这些问题,能够动态整合文化和人口统计知识来进行文本生成。
- ValuesRAG利用世界价值观调查(WVS)数据集为每个个体生成价值观摘要。
- ValuesRAG使用代表性区域数据集作为测试数据集,基于人口统计特征检索相关的价值观摘要。
- ValuesRAG在主要实验和消融研究中均表现出优异性能,证明其在促进文化对齐的AI系统和提高AI应用程序的包容性方面具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

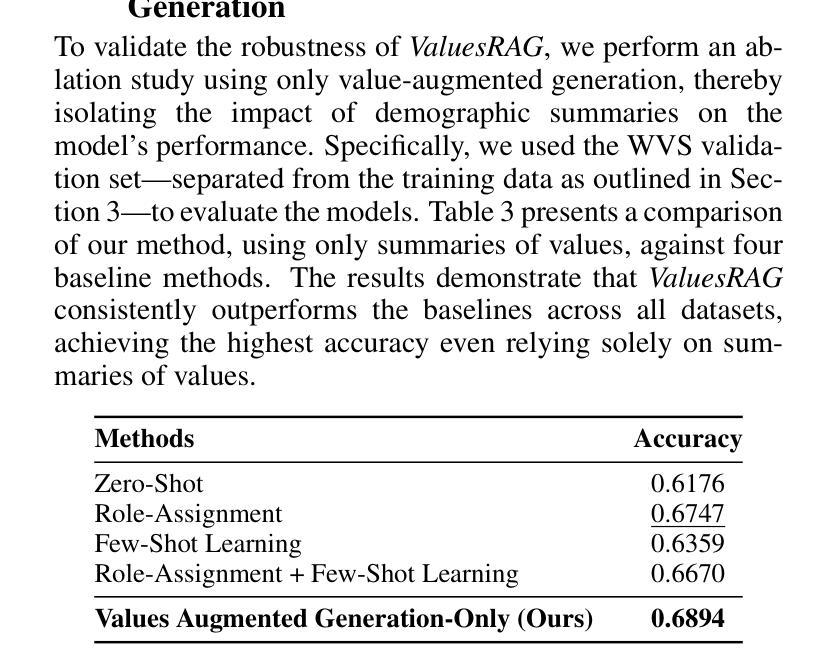
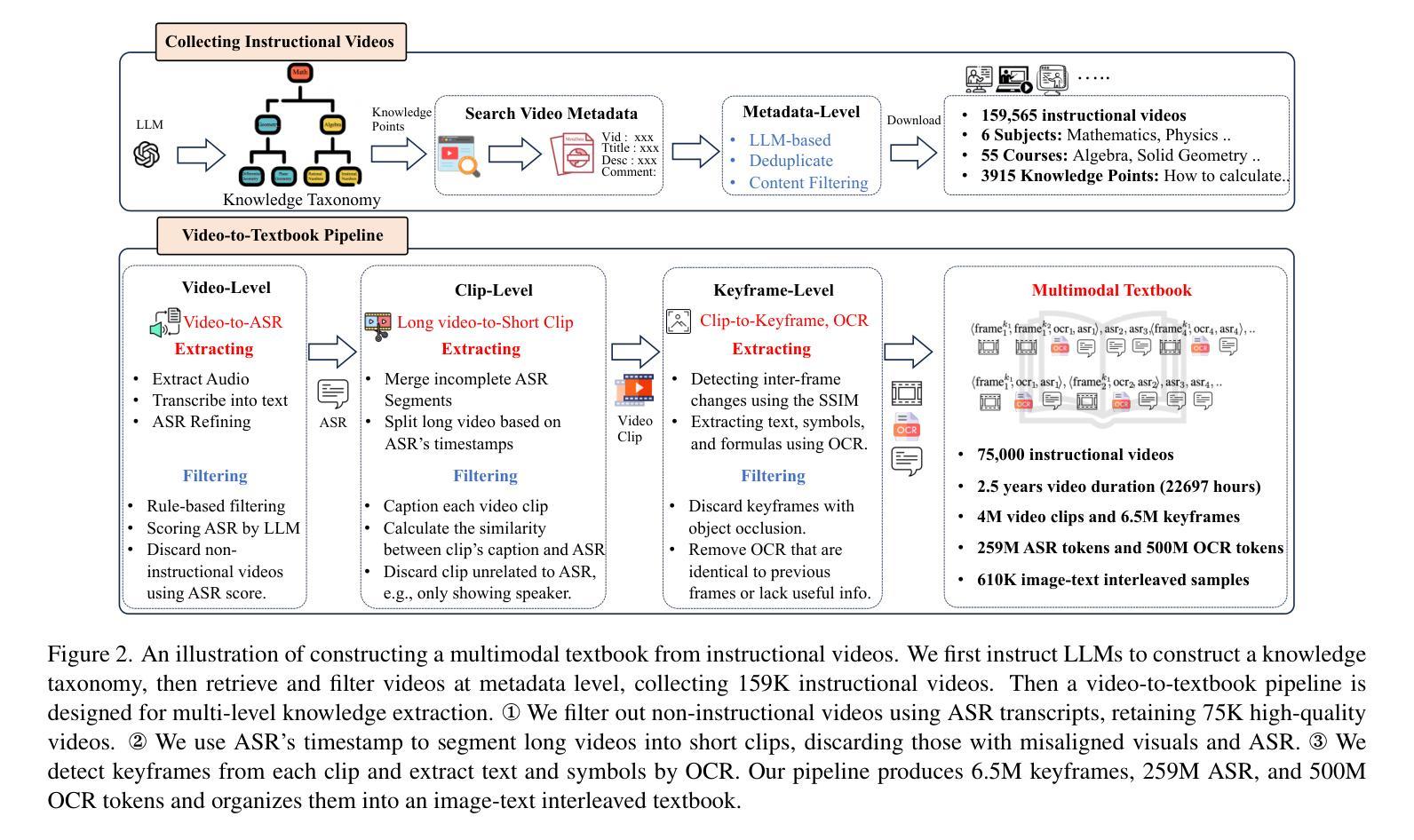
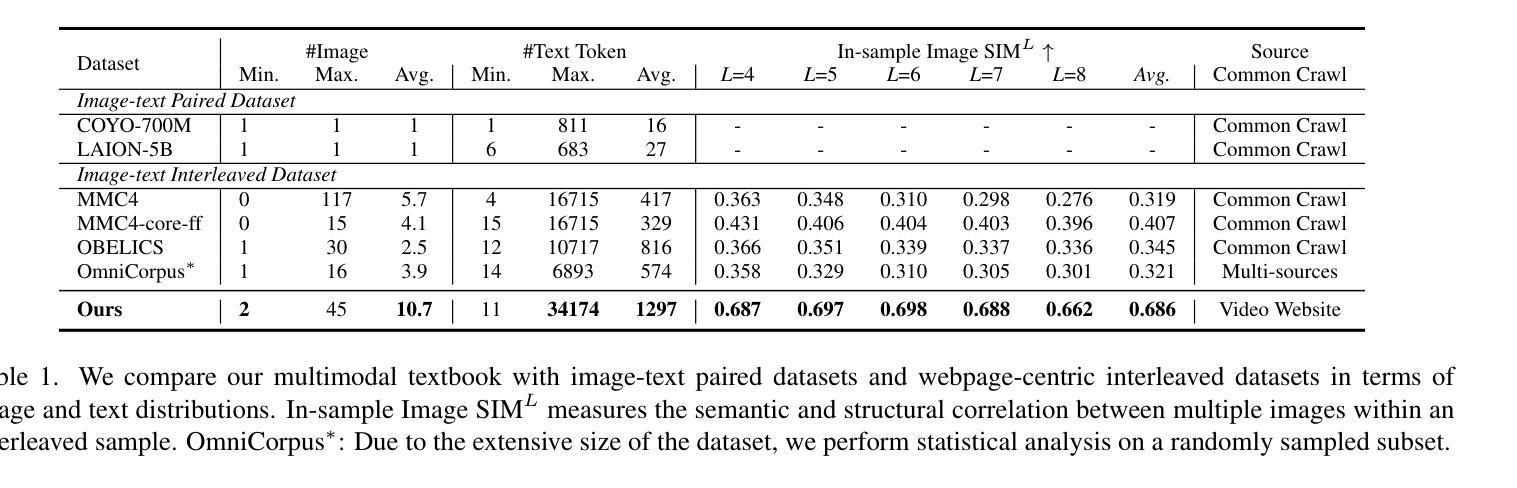
2.5 Years in Class: A Multimodal Textbook for Vision-Language Pretraining
Authors:Wenqi Zhang, Hang Zhang, Xin Li, Jiashuo Sun, Yongliang Shen, Weiming Lu, Deli Zhao, Yueting Zhuang, Lidong Bing
Compared to image-text pair data, interleaved corpora enable Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to understand the world more naturally like humans. However, such existing datasets are crawled from webpage, facing challenges like low knowledge density, loose image-text relations, and poor logical coherence between images. On the other hand, the internet hosts vast instructional videos (e.g., online geometry courses) that are widely used by humans to learn foundational subjects, yet these valuable resources remain underexplored in VLM training. In this paper, we introduce a high-quality \textbf{multimodal textbook} corpus with richer foundational knowledge for VLM pretraining. It collects over 2.5 years of instructional videos, totaling 22,000 class hours. We first use an LLM-proposed taxonomy to systematically gather instructional videos. Then we progressively extract and refine visual (keyframes), audio (ASR), and textual knowledge (OCR) from the videos, and organize as an image-text interleaved corpus based on temporal order. Compared to its counterparts, our video-centric textbook offers more coherent context, richer knowledge, and better image-text alignment. Experiments demonstrate its superb pretraining performance, particularly in knowledge- and reasoning-intensive tasks like ScienceQA and MathVista. Moreover, VLMs pre-trained on our textbook exhibit outstanding interleaved context awareness, leveraging visual and textual cues in their few-shot context for task solving~\footnote{Our code are available at \url{https://github.com/DAMO-NLP-SG/multimodal_textbook}}.
与图像文本配对数据相比,交织语料库使视觉语言模型(VLMs)能够更自然地像人类一样理解世界。然而,这些现有的数据集是从网页上爬取的,面临着知识密度低、图像文本关系松散、图像之间逻辑连贯性差等挑战。另一方面,互联网上有大量教学视频(如在线几何课程)被人类广泛用来学习基础学科,但这些宝贵资源在VLM训练中仍被忽视。在本文中,我们引入了一种高质量的多模式教科书语料库,其中包含用于VLM预训练的更丰富的基础知识。它收集了超过2.5年的教学视频,总计22,000节课时。我们首先使用大型语言模型提出的分类法来系统地收集教学视频。然后,我们从视频中逐步提取和精炼视觉(关键帧)、音频(ASR)和文本知识(OCR),并按时间顺序组织成图像文本交织语料库。与其他相比,我们这种以视频为中心教科书提供了更连贯的上下文、更丰富的知识和更好的图像文本对齐。实验证明了其出色的预训练性能,特别是在知识和推理密集型任务如ScienceQA和MathVista中。此外,在我们教科书上进行预训练的VLM表现出了出色的交织上下文意识,利用视觉和文本线索在少量上下文中进行任务解决。我们的代码可在https://github.com/DAMO-NLP-SG/multimodal_textbook上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
本文介绍了针对视觉语言模型(VLM)预训练的多模态教科书语料库。该语料库通过收集超过2.5年的教学视频构建而成,包含丰富的基础知识。通过系统收集教学视频,逐步提取和精炼视觉、音频和文本知识,形成基于时间顺序的图像文本交错语料库。与传统的数据集相比,以视频为中心的教学书籍提供了更连贯的上下文、更丰富的知识和更好的图像文本对齐。实验表明,该数据集在知识密集和推理密集型任务上的预训练性能出色,如ScienceQA和MathVista。此外,在此数据集上训练的VLM模型表现出色,具有出色的交错上下文意识,能够在少数情境下利用视觉和文本线索来解决问题。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态教科书语料库通过收集教学视频构建,包含丰富的知识。
- 系统地收集教学视频并提取视觉、音频和文本知识。
- 基于时间顺序构建图像文本交错语料库,实现更好的图像文本对齐。
- 与传统数据集相比,该语料库提供更连贯的上下文和丰富的知识。
- 在知识密集和推理密集型任务上表现出优异的预训练性能。
- VLM模型在此数据集上表现出出色的交错上下文意识。
点此查看论文截图


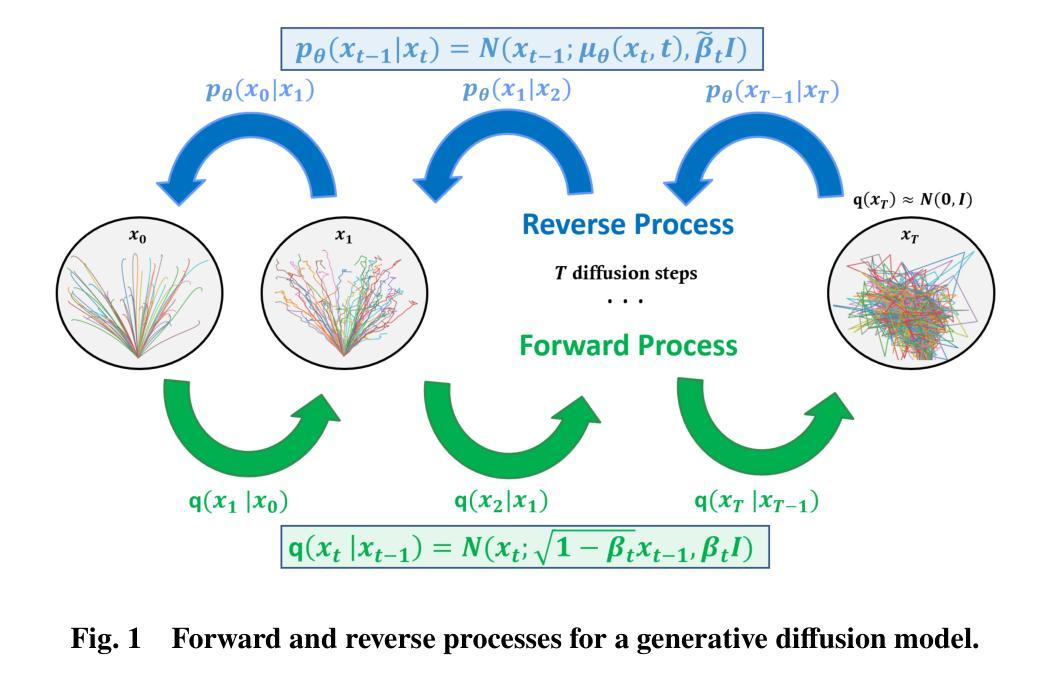
Diffusion Policies for Generative Modeling of Spacecraft Trajectories
Authors:Julia Briden, Breanna Johnson, Richard Linares, Abhishek Cauligi
Machine learning has demonstrated remarkable promise for solving the trajectory generation problem and in paving the way for online use of trajectory optimization for resource-constrained spacecraft. However, a key shortcoming in current machine learning-based methods for trajectory generation is that they require large datasets and even small changes to the original trajectory design requirements necessitate retraining new models to learn the parameter-to-solution mapping. In this work, we leverage compositional diffusion modeling to efficiently adapt out-of-distribution data and problem variations in a few-shot framework for 6 degree-of-freedom (DoF) powered descent trajectory generation. Unlike traditional deep learning methods that can only learn the underlying structure of one specific trajectory optimization problem, diffusion models are a powerful generative modeling framework that represents the solution as a probability density function (PDF) and this allows for the composition of PDFs encompassing a variety of trajectory design specifications and constraints. We demonstrate the capability of compositional diffusion models for inference-time 6 DoF minimum-fuel landing site selection and composable constraint representations. Using these samples as initial guesses for 6 DoF powered descent guidance enables dynamically feasible and computationally efficient trajectory generation.
机器学习在解决轨迹生成问题方面显示出巨大的潜力,并为资源受限航天器的轨迹优化的在线使用奠定了基础。然而,当前基于机器学习的轨迹生成方法的一个关键缺陷是它们需要大量数据集,甚至对原始轨迹设计要求的微小变化都需要重新训练新模型来学习参数到解决方案的映射。在这项工作中,我们利用组合扩散建模,在少数镜头框架内有效地适应超出分配的数据和问题的变化,用于六自由度(DoF)动力下降轨迹生成。与传统只能学习特定轨迹优化问题底层结构的深度学习方法不同,扩散模型是一种强大的生成建模框架,它将解决方案表示为概率密度函数(PDF),这允许包含各种轨迹设计规范和约束的PDF的组合。我们展示了组合扩散模型在推理时间六自由度最低燃料着陆点选择和可组合约束表示方面的能力。使用这些样本作为六自由度动力下降指导的初始猜测,可实现动态可行和计算高效的轨迹生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AIAA SCITECH 2025 Forum
Summary
基于机器学习的方法在解决轨迹生成问题上展现出巨大潜力,并为在线使用轨迹优化资源受限的航天器铺平了道路。然而,当前机器学习方法的关键短板在于需要大量数据集,且对原始轨迹设计要求的微小变动都需要重新训练模型来学习参数到解决方案的映射。本研究利用组合扩散建模,在少量样本的框架下有效地适应分布外的数据和问题变化,用于六自由度(DoF)动力下降轨迹生成。不同于只能学习单一轨迹优化问题结构的传统深度学习方法,扩散模型是一个强大的生成建模框架,将解决方案表示为概率密度函数(PDF),这允许包含各种轨迹设计规范和约束的PDF的组合。本研究展示了组合扩散模型在推理时间六自由度最低燃料着陆点选择和可组合约束表示方面的能力。将这些样本作为六自由度动力下降指导的初始猜测,可实现动态可行且计算高效的轨迹生成。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习在解决轨迹生成问题上具有显著潜力,特别是在在线使用轨迹优化资源受限的航天器中。
- 当前机器学习方法的一个关键短板是对数据的需求量大,且需要频繁重新训练模型以适应轨迹设计要求的变动。
- 研究采用了组合扩散建模来应对上述问题,能够在少量样本下有效地适应分布外的数据和问题变化。
- 扩散模型将解决方案表示为概率密度函数(PDF),不同于传统深度学习方法的单一轨迹优化学习。
- 扩散模型允许包含多种轨迹设计规范和约束的PDF组合,提高了模型的适应性和灵活性。
- 研究展示了组合扩散模型在六自由度最低燃料着陆点选择和可组合约束表示方面的能力。
点此查看论文截图

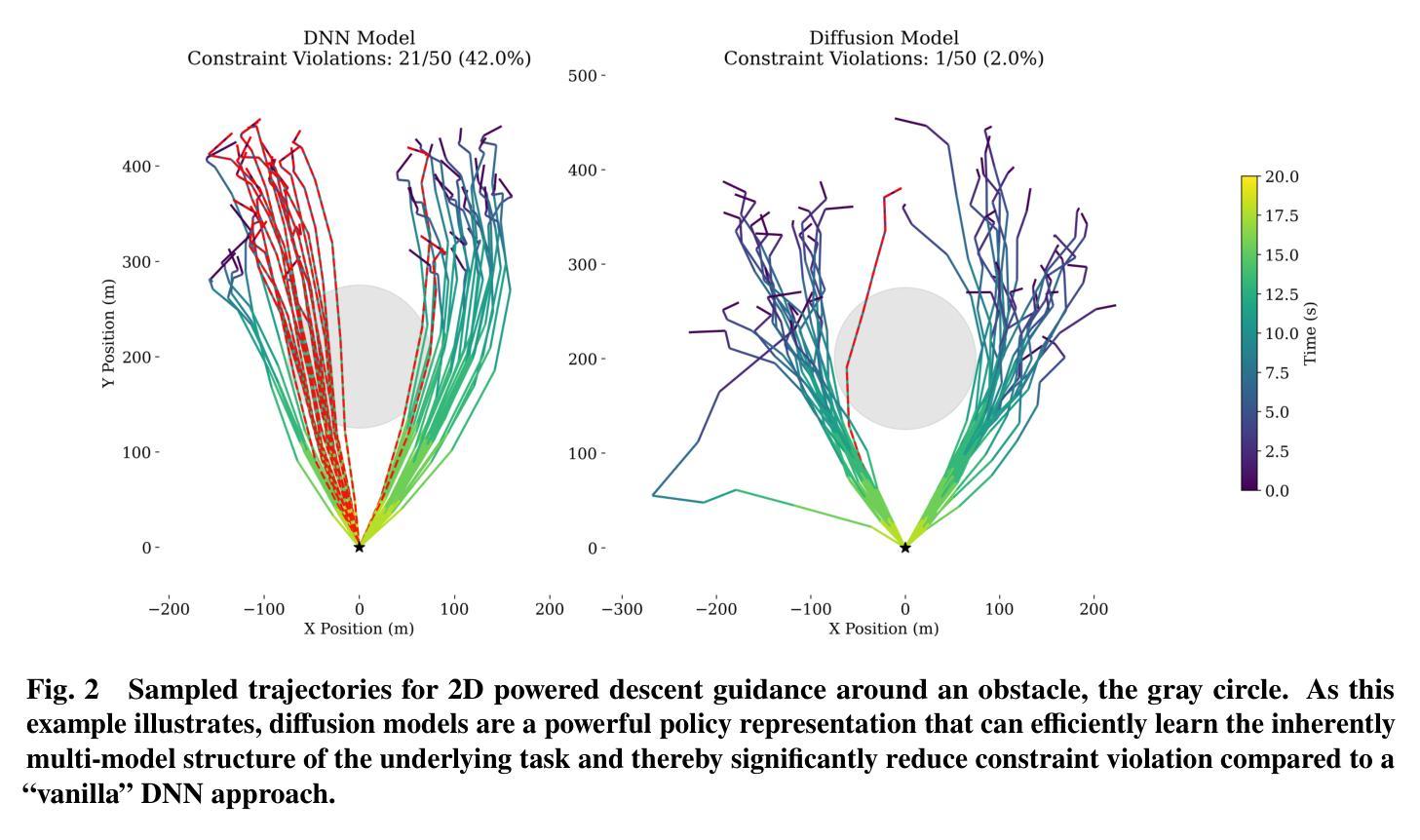
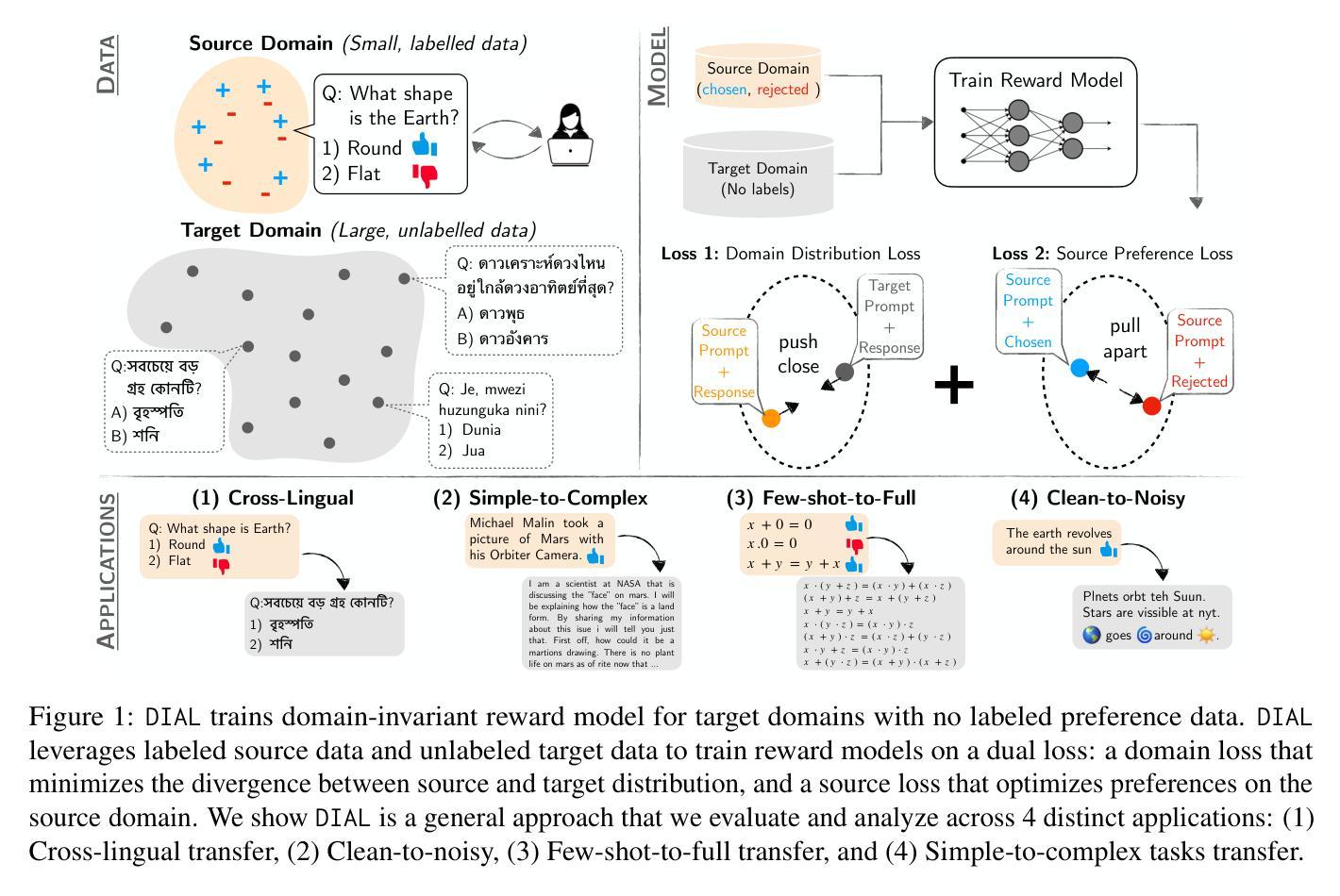
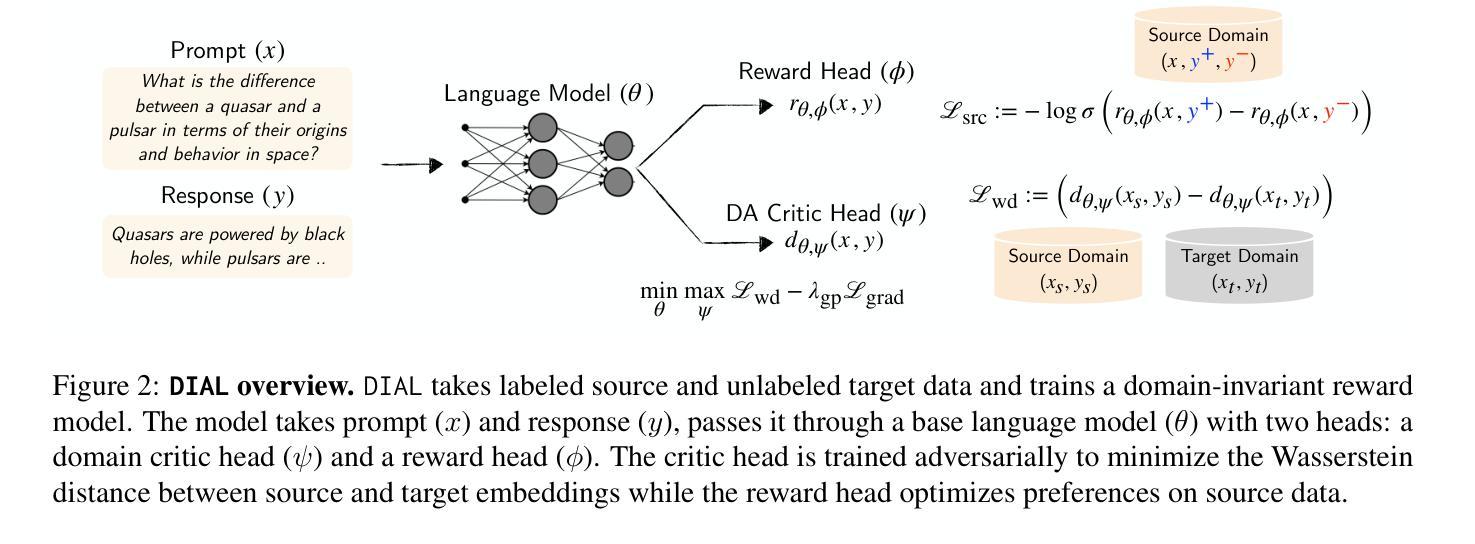
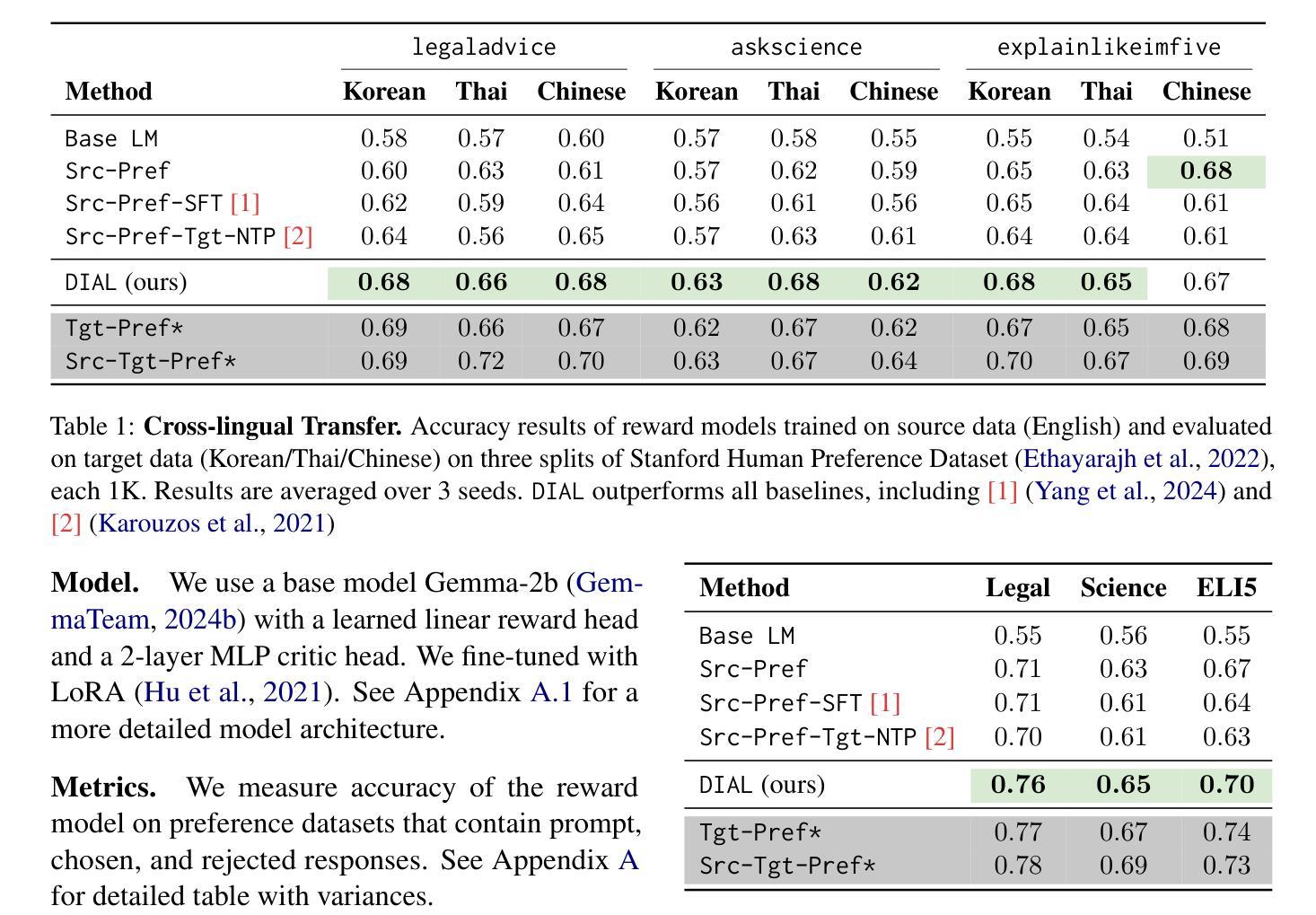
Aligning LLMs with Domain Invariant Reward Models
Authors:David Wu, Sanjiban Choudhury
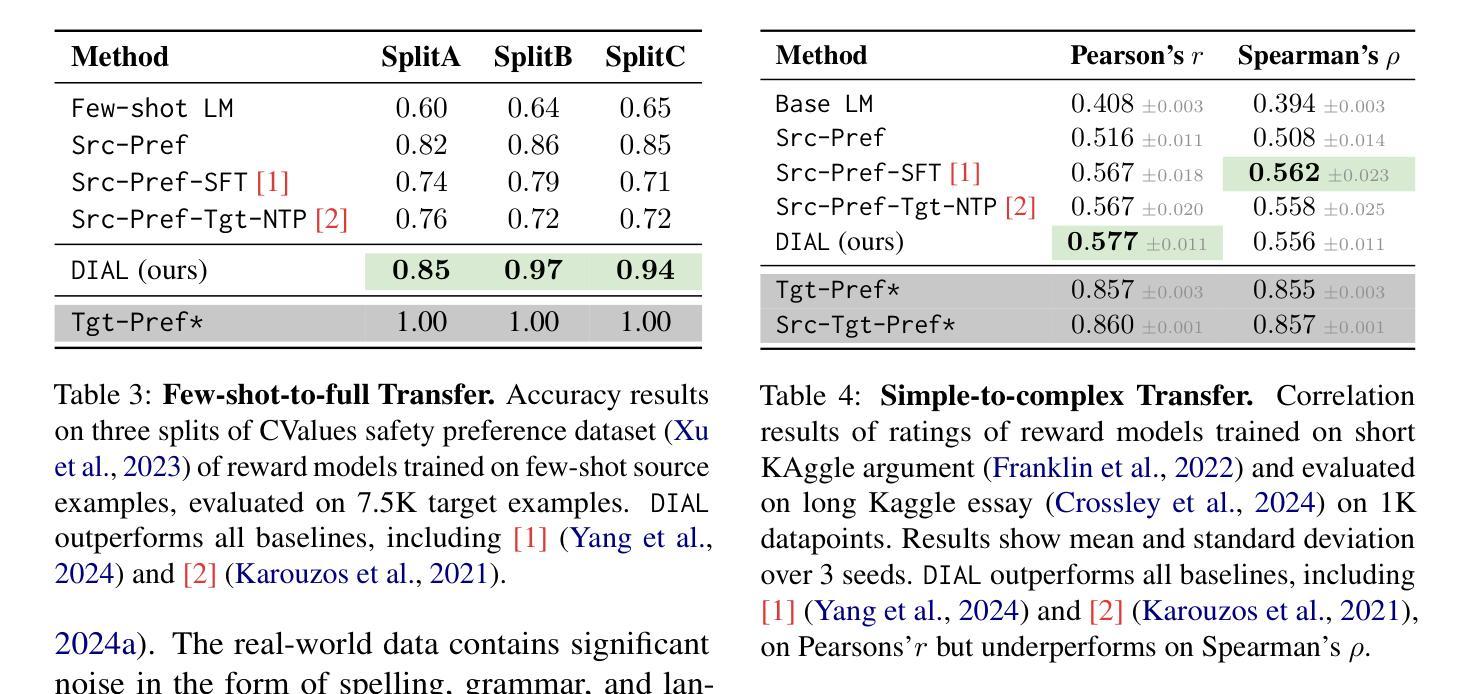
Aligning large language models (LLMs) to human preferences is challenging in domains where preference data is unavailable. We address the problem of learning reward models for such target domains by leveraging feedback collected from simpler source domains, where human preferences are easier to obtain. Our key insight is that, while domains may differ significantly, human preferences convey \emph{domain-agnostic} concepts that can be effectively captured by a reward model. We propose \method, a framework that trains domain-invariant reward models by optimizing a dual loss: a domain loss that minimizes the divergence between source and target distribution, and a source loss that optimizes preferences on the source domain. We show \method is a general approach that we evaluate and analyze across 4 distinct settings: (1) Cross-lingual transfer (accuracy: $0.621 \rightarrow 0.661$), (2) Clean-to-noisy (accuracy: $0.671 \rightarrow 0.703$), (3) Few-shot-to-full transfer (accuracy: $0.845 \rightarrow 0.920$), and (4) Simple-to-complex tasks transfer (correlation: $0.508 \rightarrow 0.556$). Our code, models and data are available at \url{https://github.com/portal-cornell/dial}.
在大规模语言模型(LLM)在无法获取偏好数据的领域与人类的偏好对齐是一项挑战。我们解决了针对此类目标领域学习奖励模型的问题,通过从更容易获取人类偏好的简单源领域收集反馈并利用其进行分析。我们的关键见解是,尽管域可能有所不同,但人类偏好传达了可以被奖励模型有效捕获的“域不可知”概念。我们提出了方法(Method),这是一个通过优化双重损失来训练域不变奖励模型的框架:一种域损失,用于最小化源域和目标域之间的分布差异;另一种源损失,用于优化源域上的偏好。我们展示了方法是一种通用方法,我们在四个不同的环境中对其进行了评估和分析了:(1)跨语言迁移(准确度:从0.621到0.661);(2)从清洁到噪声迁移(准确度:从0.671到0.703);(3)从少量到完整迁移(准确度:从0.845到0.920);以及(4)从简单到复杂任务的迁移(相关性:从0.508到0.556)。我们的代码、模型和数据都可在https://github.com/portal-cornell/dial上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种通过利用简单源域中容易获得的人类反馈来解决目标领域奖励模型学习问题的方法。该方法虽然关注跨域学习,但认为人类偏好传达的是领域通用的概念,通过训练领域不变的奖励模型,优化包括源域和目标域差异的领域损失以及优化源域偏好的源损失。在四种不同场景下的评估表明,该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种解决大型语言模型(LLMs)在缺乏人类偏好数据的领域中与人类偏好对齐的问题。
- 提出了一种利用简单源域中的反馈来解决目标领域奖励模型学习的方法。
- 该方法的关键在于认识到虽然领域可能有显著不同,但人类偏好传达的是领域通用的概念。
- 通过训练领域不变的奖励模型来优化领域损失和源损失,缩小源域和目标域之间的差异。
- 在跨语言转移、清洁到噪声、少拍转移到全转移以及简单任务到复杂任务转移等四个不同场景下进行了评估。
- 在所有评估场景中,该方法均显示出有效性,提高了准确性或相关性。
点此查看论文截图

U-GIFT: Uncertainty-Guided Firewall for Toxic Speech in Few-Shot Scenario
Authors:Jiaxin Song, Xinyu Wang, Yihao Wang, Yifan Tang, Ru Zhang, Jianyi Liu, Gongshen Liu
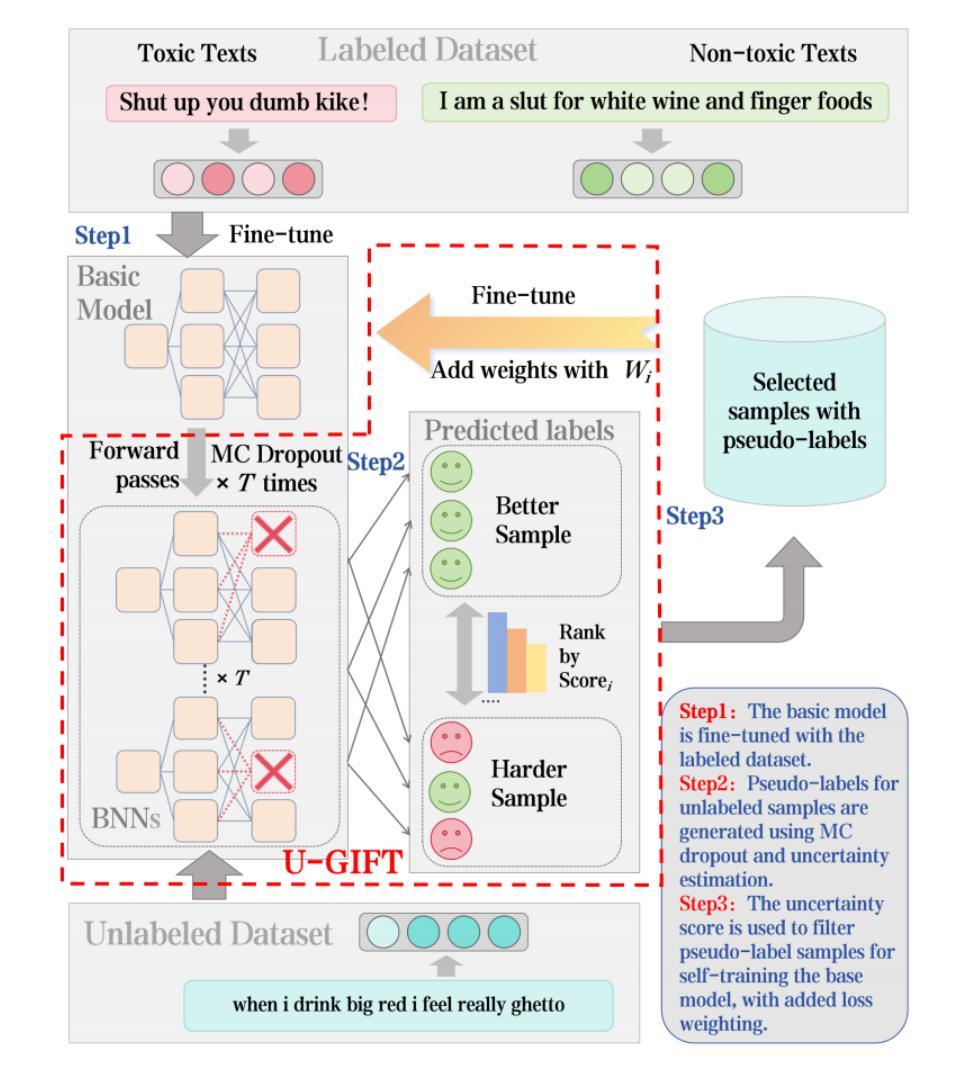
With the widespread use of social media, user-generated content has surged on online platforms. When such content includes hateful, abusive, offensive, or cyberbullying behavior, it is classified as toxic speech, posing a significant threat to the online ecosystem’s integrity and safety. While manual content moderation is still prevalent, the overwhelming volume of content and the psychological strain on human moderators underscore the need for automated toxic speech detection. Previously proposed detection methods often rely on large annotated datasets; however, acquiring such datasets is both costly and challenging in practice. To address this issue, we propose an uncertainty-guided firewall for toxic speech in few-shot scenarios, U-GIFT, that utilizes self-training to enhance detection performance even when labeled data is limited. Specifically, U-GIFT combines active learning with Bayesian Neural Networks (BNNs) to automatically identify high-quality samples from unlabeled data, prioritizing the selection of pseudo-labels with higher confidence for training based on uncertainty estimates derived from model predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that U-GIFT significantly outperforms competitive baselines in few-shot detection scenarios. In the 5-shot setting, it achieves a 14.92% performance improvement over the basic model. Importantly, U-GIFT is user-friendly and adaptable to various pre-trained language models (PLMs). It also exhibits robust performance in scenarios with sample imbalance and cross-domain settings, while showcasing strong generalization across various language applications. We believe that U-GIFT provides an efficient solution for few-shot toxic speech detection, offering substantial support for automated content moderation in cyberspace, thereby acting as a firewall to promote advancements in cybersecurity.
随着社交媒体广泛使用,用户生成内容已在网上平台激增。当此类内容包含仇恨、滥用、攻击性或网络欺凌行为时,它就被归类为有毒言论,对在线生态系统的完整性和安全构成重大威胁。虽然手动内容管理仍然普遍存在,但内容数量过多以及人类管理者承受的心理压力凸显出需要自动化有毒言论检测。先前提出的检测方法往往依赖于大量注释数据集;然而,在实践中获取此类数据集既昂贵又具有挑战性。为解决此问题,我们针对少数场景的有毒言论提出了一种不确定性引导防火墙,名为U-GIFT。它利用自训练提高检测性能,即使在标记数据有限的情况下也能发挥作用。具体来说,U-GIFT结合主动学习与贝叶斯神经网络(BNNs),自动从未标记的数据中识别高质量样本,优先选择与模型预测得出不确定性估计置信度较高的伪标签进行训练。大量实验表明,在少数场景检测中,U-GIFT显著优于竞争基线。在5次射击设定中,它比基本模型高出14.92%的性能。重要的是,U-GIFT用户友好且适应各种预训练语言模型(PLM)。它在样本不平衡和跨域设置等场景中表现稳健,并且在各种语言应用中表现出强大的泛化能力。我们相信U-GIFT为少数有毒言论检测提供了有效的解决方案,为网络空间的自动化内容管理提供了有力支持,从而充当防火墙促进网络安全的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 6 figures and 10 tables. Comments are welcome
摘要
社交媒体用户生成内容的激增带来了网络生态中的有毒言论问题。这些有毒言论包括仇恨、滥用、攻击或网络欺凌行为,对在线生态系统的完整性和安全性构成严重威胁。为了解决标注数据不足的问题,我们提出了基于不确定性的防火墙系统U-GIFT来解决数据受限场景下的有毒言论检测问题。该系统结合了主动学习、贝叶斯神经网络进行自训练,能够从无标签数据中自动识别高质量样本,并根据模型预测的不确定性估计来优先选取高置信度的伪标签进行训练。实验表明,在样本量较小的情况下,U-GIFT系统显著优于其他基线模型。相较于基本模型,其在5样本场景中实现了高达14.92%的性能提升。此外,U-GIFT具有良好的用户友好性和适应性,适用于多种预训练语言模型。系统在样本不均衡和跨域设置下展现了强大的性能,并在多种语言应用中表现出良好的泛化能力。我们相信U-GIFT能够有效支持网络安全领域的自动内容审核和网络安全防护的推动工作。
关键见解
- 用户生成内容的激增引发了网络中的有毒言论问题。
- 有毒言论对在线生态系统的完整性和安全性构成威胁。
- 提出了一种基于不确定性的防火墙系统U-GIFT解决该问题。在标注数据有限的情况下能够显著提升有毒言论检测性能。
点此查看论文截图

FitCF: A Framework for Automatic Feature Importance-guided Counterfactual Example Generation
Authors:Qianli Wang, Nils Feldhus, Simon Ostermann, Luis Felipe Villa-Arenas, Sebastian Möller, Vera Schmitt
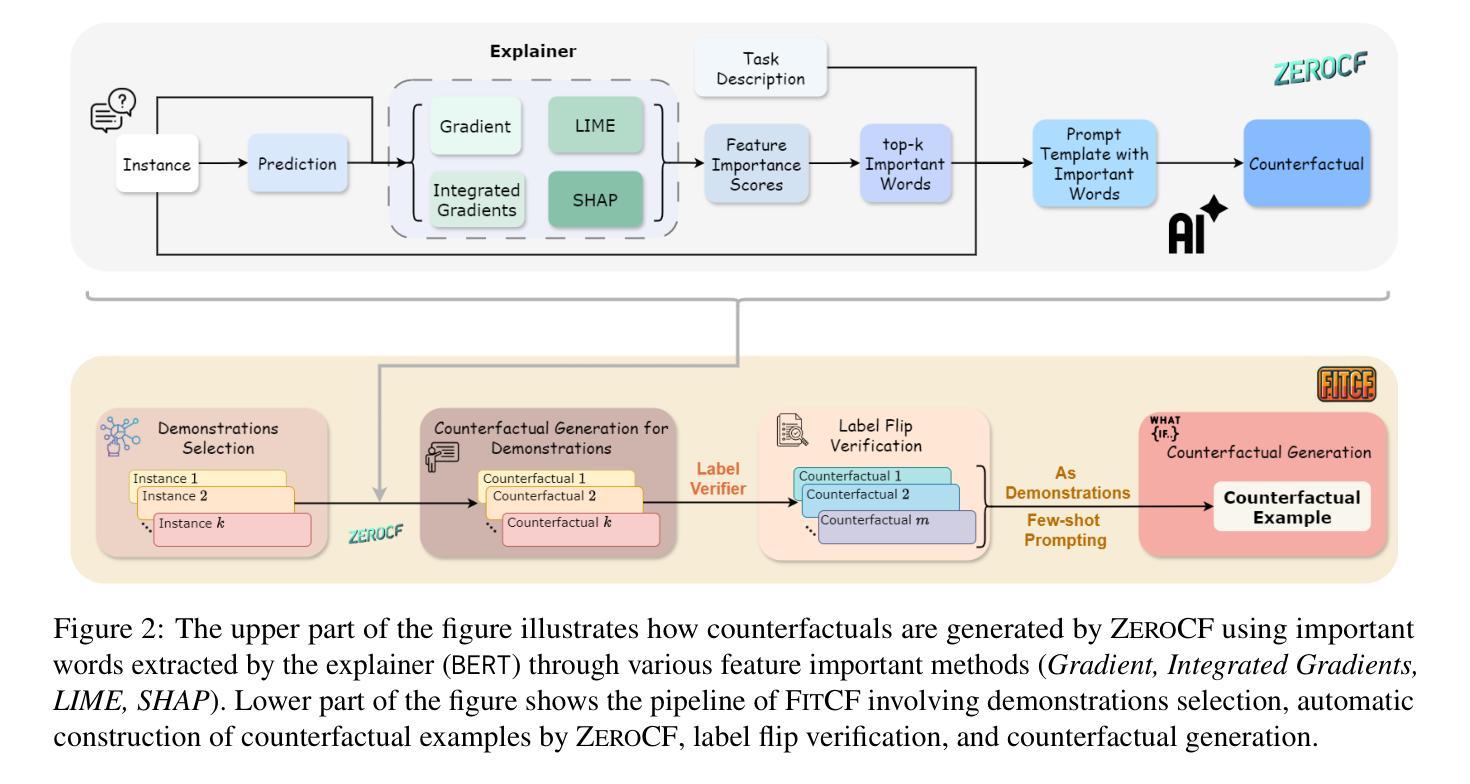
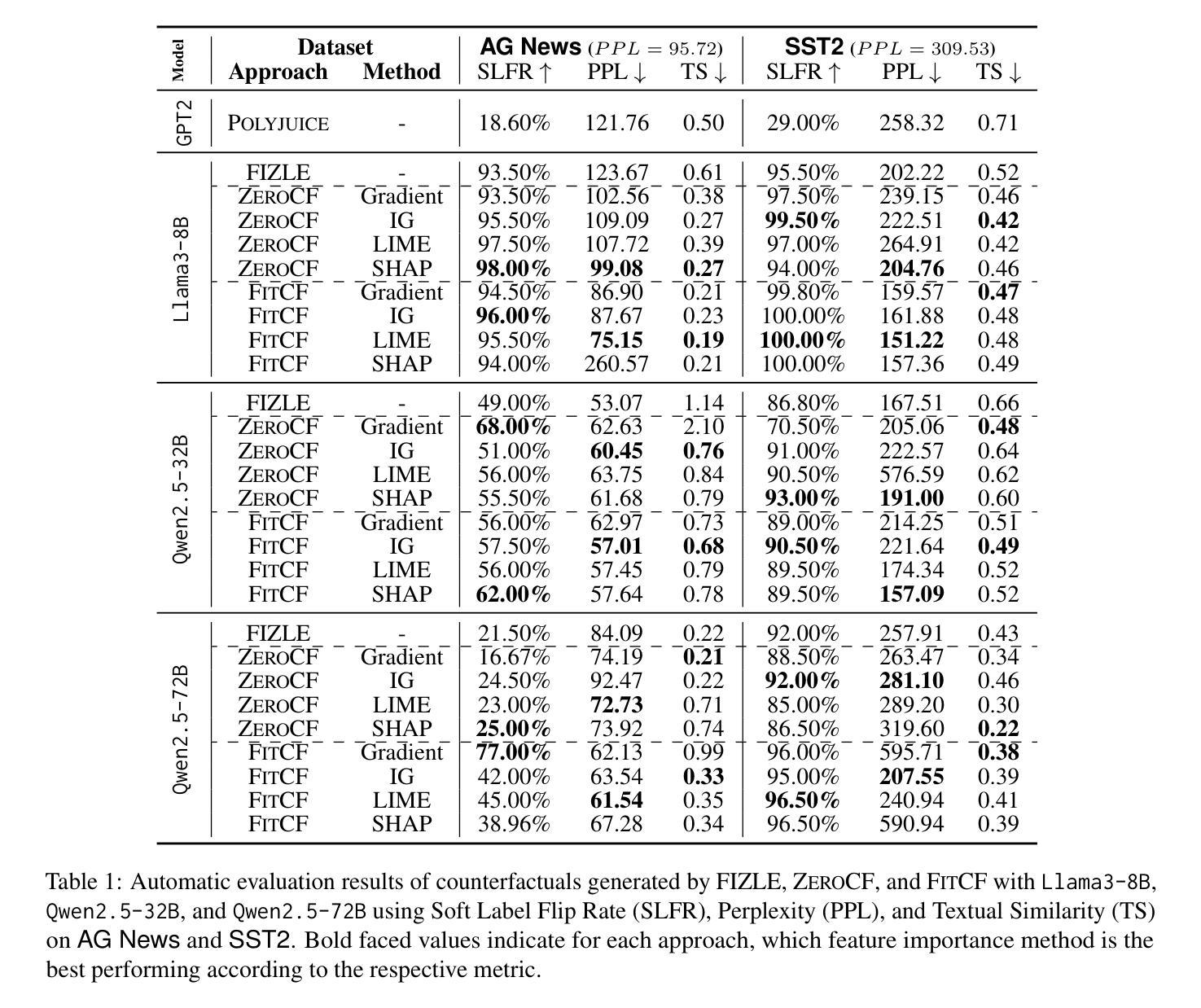
Counterfactual examples are widely used in natural language processing (NLP) as valuable data to improve models, and in explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) to understand model behavior. The automated generation of counterfactual examples remains a challenging task even for large language models (LLMs), despite their impressive performance on many tasks. In this paper, we first introduce ZeroCF, a faithful approach for leveraging important words derived from feature attribution methods to generate counterfactual examples in a zero-shot setting. Second, we present a new framework, FitCF, which further verifies aforementioned counterfactuals by label flip verification and then inserts them as demonstrations for few-shot prompting, outperforming two state-of-the-art baselines. Through ablation studies, we identify the importance of each of FitCF’s core components in improving the quality of counterfactuals, as assessed through flip rate, perplexity, and similarity measures. Furthermore, we show the effectiveness of LIME and Integrated Gradients as backbone attribution methods for FitCF and find that the number of demonstrations has the largest effect on performance. Finally, we reveal a strong correlation between the faithfulness of feature attribution scores and the quality of generated counterfactuals.
在自然语言处理(NLP)中,反事实例子被广泛应用于提升模型价值的数据,并在可解释人工智能(XAI)中用于理解模型行为。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在许多任务上表现出色,但自动生成反事实例子仍然是一个具有挑战性的任务。在本文中,我们首先介绍了ZeroCF,这是一种忠实的方法,利用特征归因方法得出的重要单词,在无样本设置下生成反事实例子。其次,我们提出了一个新的框架FitCF,它通过标签翻转验证进一步验证了上述反事实,然后将其作为演示用于少样本提示,优于两种最新技术水平的基线。通过消融研究,我们确定了FitCF每个核心组件在提高反事实质量(通过翻转率、困惑度和相似性度量进行评估)方面的重要性。此外,我们展示了LIME和集成梯度作为FitCF的骨干归因方法的有效性,并发现演示的数量对性能的影响最大。最后,我们发现特征归因分数的忠实性与生成的反事实质量之间存在强烈的关联。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In submission
Summary
本论文介绍了在自然语言处理(NLP)和可解释人工智能(XAI)中广泛应用的反事实实例。针对大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动生成反事实实例方面的挑战,提出了ZeroCF方法,利用特征归属方法得出的重要词汇在零样本环境下生成反事实实例。进一步,提出了FitCF框架,通过标签翻转验证来验证上述反事实,并将其作为少样本提示插入,优于两种先进的基线方法。通过消融研究,确定了FitCF核心组件在提高反事实质量方面的作用,并通过翻转率、困惑度和相似性度量进行评估。同时,展示了LIME和集成梯度作为FitCF的骨干归属方法的有效性,并发现演示数量对性能的影响最大。最后,揭示了特征归属分数忠实性与生成反事实质量之间的强烈相关性。
Key Takeaways
- Counterfactual examples are valuable in NLP and XAI.
2.自动生成反事实实例对于大型语言模型(LLMs)来说是一项具有挑战性的任务。 - ZeroCF方法利用特征归属方法得出的重要词汇在零样本环境下生成反事实实例。
- FitCF框架通过标签翻转验证来验证反事实,并将其用于少样本提示。
- FitCF框架优于两种先进的基线方法。
- 消融研究确定了FitCF核心组件对提高反事实质量的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

Foreground-Covering Prototype Generation and Matching for SAM-Aided Few-Shot Segmentation
Authors:Suho Park, SuBeen Lee, Hyun Seok Seong, Jaejoon Yoo, Jae-Pil Heo
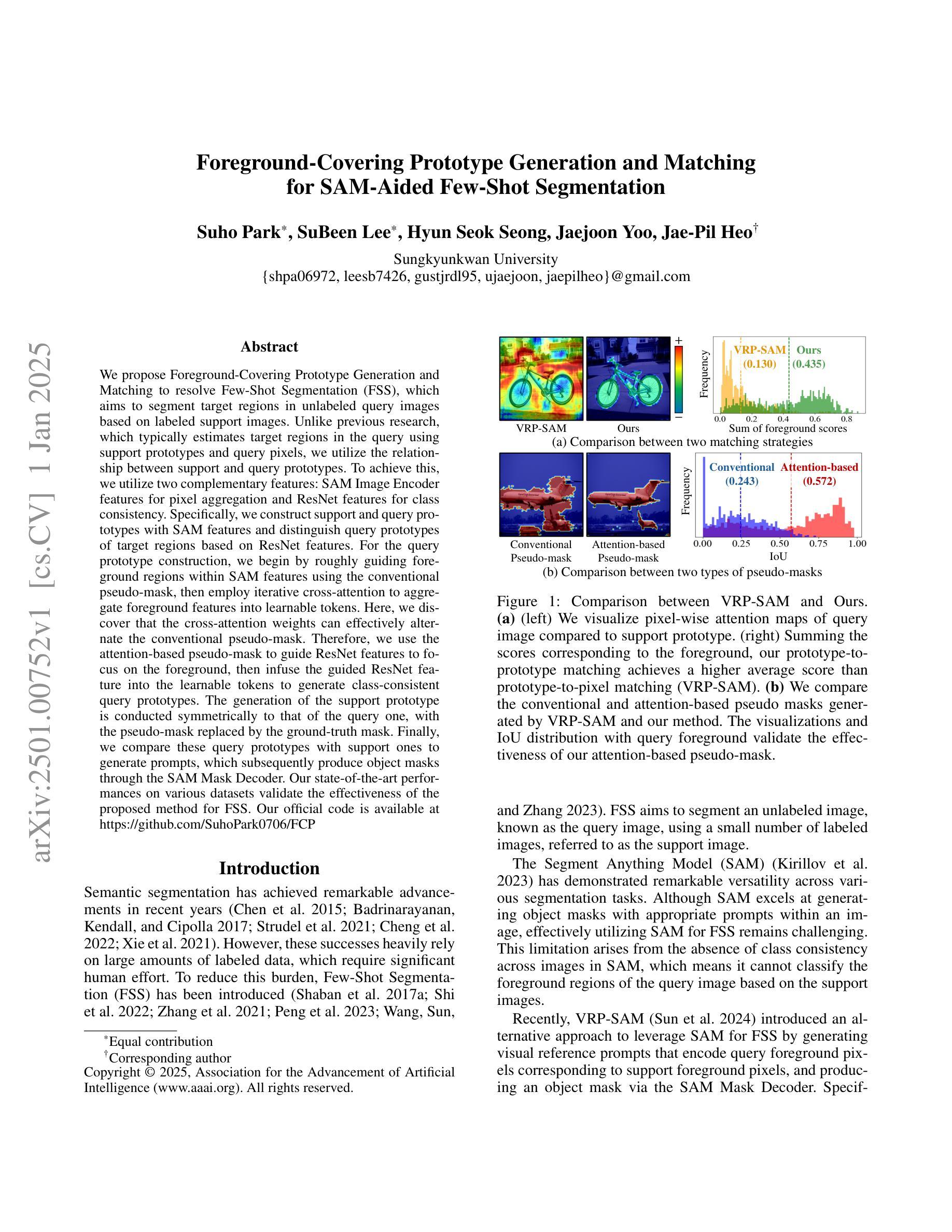
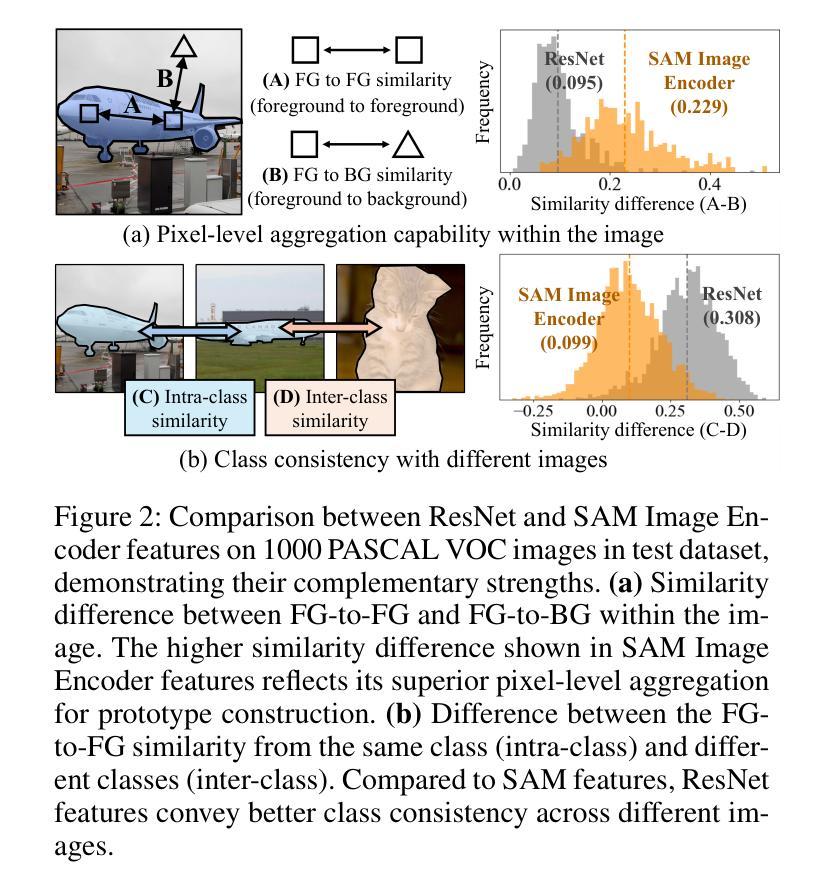
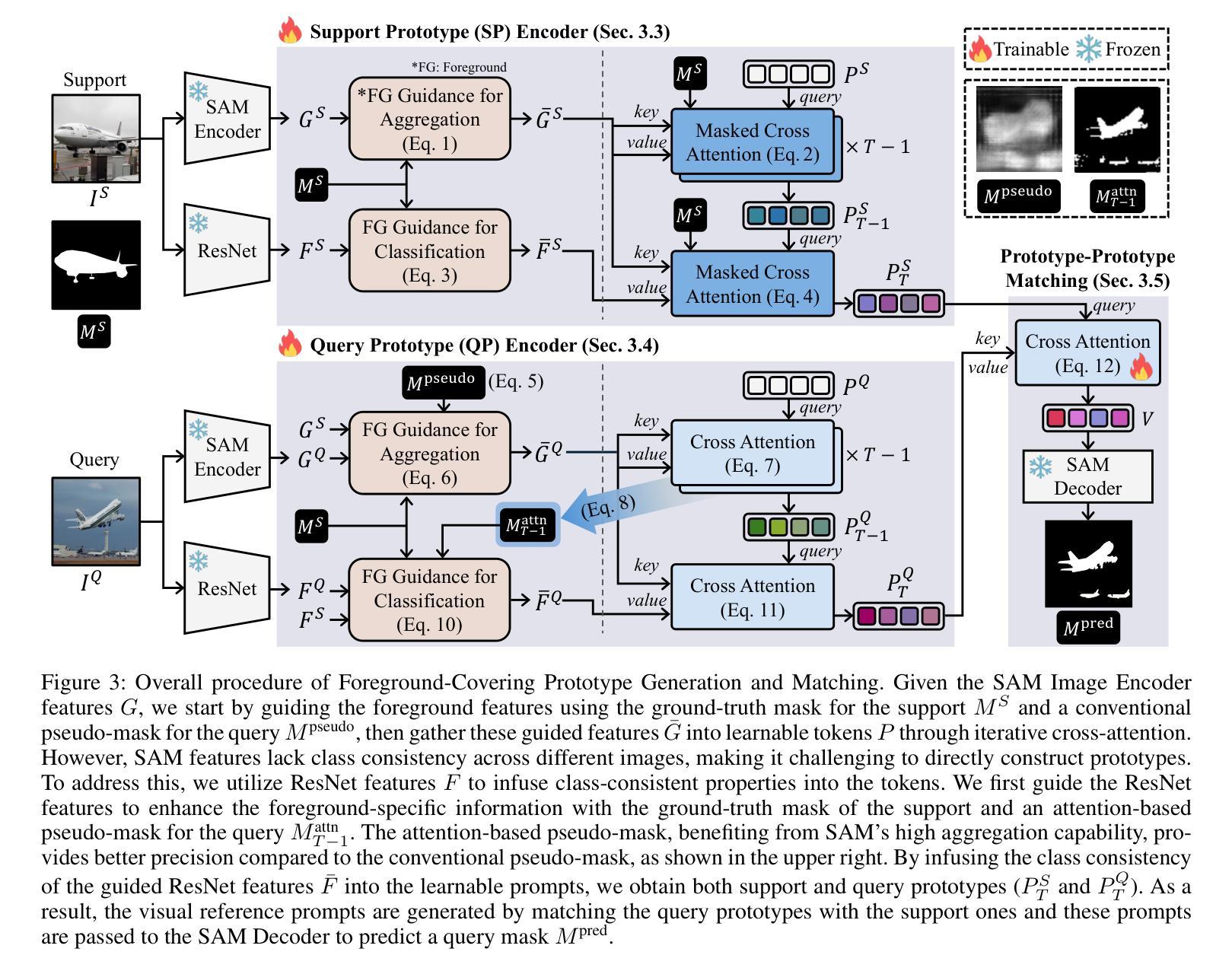
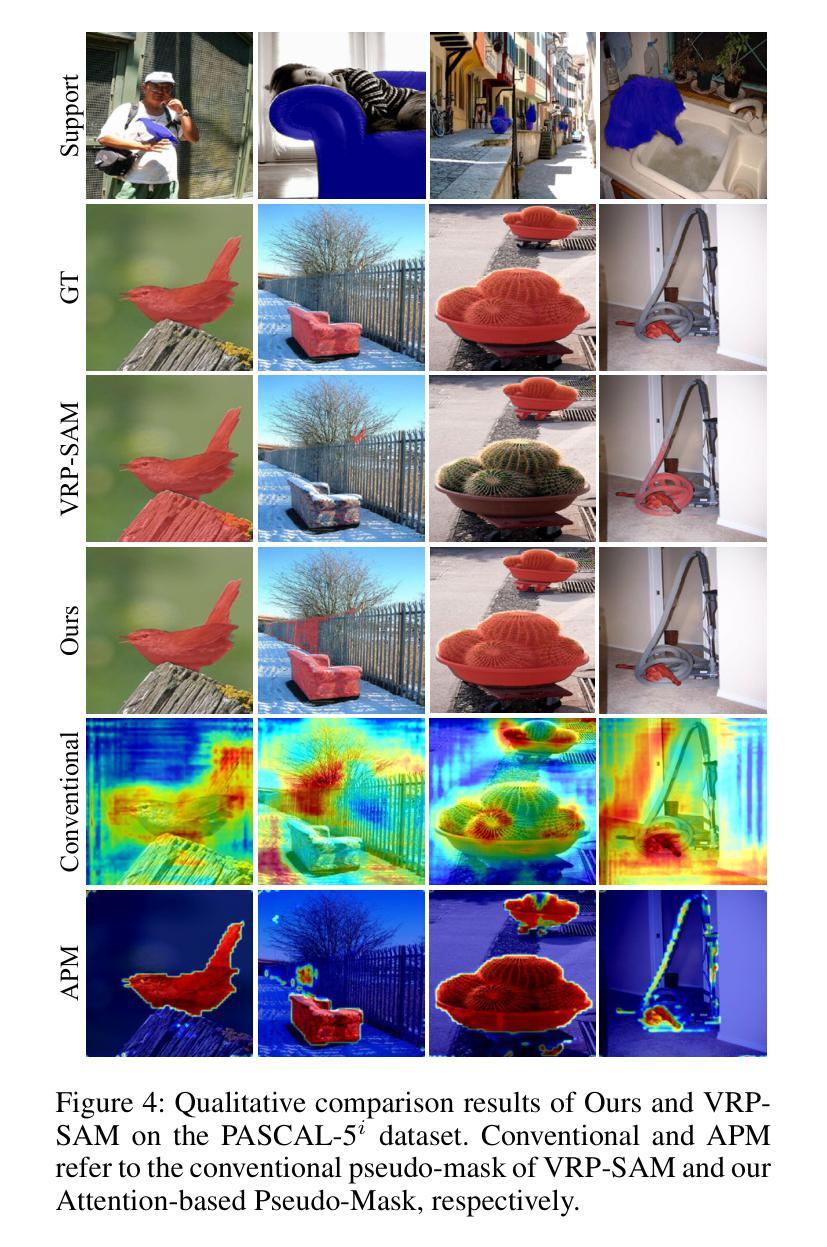
We propose Foreground-Covering Prototype Generation and Matching to resolve Few-Shot Segmentation (FSS), which aims to segment target regions in unlabeled query images based on labeled support images. Unlike previous research, which typically estimates target regions in the query using support prototypes and query pixels, we utilize the relationship between support and query prototypes. To achieve this, we utilize two complementary features: SAM Image Encoder features for pixel aggregation and ResNet features for class consistency. Specifically, we construct support and query prototypes with SAM features and distinguish query prototypes of target regions based on ResNet features. For the query prototype construction, we begin by roughly guiding foreground regions within SAM features using the conventional pseudo-mask, then employ iterative cross-attention to aggregate foreground features into learnable tokens. Here, we discover that the cross-attention weights can effectively alternate the conventional pseudo-mask. Therefore, we use the attention-based pseudo-mask to guide ResNet features to focus on the foreground, then infuse the guided ResNet feature into the learnable tokens to generate class-consistent query prototypes. The generation of the support prototype is conducted symmetrically to that of the query one, with the pseudo-mask replaced by the ground-truth mask. Finally, we compare these query prototypes with support ones to generate prompts, which subsequently produce object masks through the SAM Mask Decoder. Our state-of-the-art performances on various datasets validate the effectiveness of the proposed method for FSS. Our official code is available at https://github.com/SuhoPark0706/FCP
我们提出前景覆盖原型生成与匹配来解决小样本分割(FSS)问题,其目标是在无标签的查询图像中基于有标签的支持图像对目标区域进行分割。与通常使用支持原型和查询像素来估计查询中的目标区域的先前研究不同,我们利用支持原型和查询原型之间的关系。为实现这一点,我们利用两个互补的特性:SAM图像编码器的像素聚合特征和ResNet的特性保持类一致性。具体来说,我们使用SAM特征构建支持和查询原型,并根据ResNet特征区分查询目标区域的原型。对于查询原型的构建,我们首先使用传统的伪掩码在SAM特征中大致指导前景区域,然后采用迭代交叉注意力将前景特征聚集到可学习的令牌中。在这里,我们发现交叉注意力权重可以有效地替代传统的伪掩码。因此,我们使用基于注意力的伪掩码来指导ResNet特征专注于前景,然后将引导的ResNet特征融合到可学习的令牌中,以生成类一致的查询原型。支持原型的生成方式与查询原型的生成方式对称,其中伪掩码被真实掩码所替代。最后,我们将这些查询原型与支持原型进行比较以生成提示,然后通过SAM Mask解码器产生对象掩码。我们在各种数据集上的最新性能表现验证了所提出方法在小样本分割中的有效性。我们的官方代码可在XXX中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2025
Summary
本文提出一种解决Few-Shot Segmentation(FSS)问题的方法,名为前景覆盖原型生成与匹配。该方法旨在基于标记的支持图像对未标记查询图像中的目标区域进行分割。通过利用支持图像和查询图像之间的原型关系,结合SAM图像编码器的像素聚合特征和ResNet模型的类别一致性特征,构建支持原型和查询原型。利用基于注意力的伪掩码指导ResNet特征聚焦于前景,生成类别一致的查询原型。该方法在多个数据集上的表现均达到领先水平,验证了其在FSS问题上的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 引入前景覆盖原型生成与匹配方法解决Few-Shot Segmentation(FSS)问题。
- 利用支持图像和查询图像之间的原型关系。
- 结合SAM图像编码器的像素聚合特征和ResNet模型的类别一致性特征。
- 通过基于注意力的伪掩码引导ResNet特征聚焦于前景。
- 生成类别一致的查询原型和支持原型。
- 在多个数据集上达到领先水平,验证了方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Multi-Path Collaborative Reactive and Reflection agents
Authors:Chengbo He, Bochao Zou, Xin Li, Jiansheng Chen, Junliang Xing, Huimin Ma
Agents have demonstrated their potential in scientific reasoning tasks through large language models. However, they often face challenges such as insufficient accuracy and degeneration of thought when handling complex reasoning tasks, which impede their performance. To overcome these issues, we propose the Reactive and Reflection agents with Multi-Path Reasoning (RR-MP) Framework, aimed at enhancing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Our approach improves scientific reasoning accuracy by employing a multi-path reasoning mechanism where each path consists of a reactive agent and a reflection agent that collaborate to prevent degeneration of thought inherent in single-agent reliance. Additionally, the RR-MP framework does not require additional training; it utilizes multiple dialogue instances for each reasoning path and a separate summarizer to consolidate insights from all paths. This design integrates diverse perspectives and strengthens reasoning across each path. We conducted zero-shot and few-shot evaluations on tasks involving moral scenarios, college-level physics, and mathematics. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms baseline approaches, highlighting the effectiveness and advantages of the RR-MP framework in managing complex scientific reasoning tasks.
人工智能在科研推理任务中展现出了巨大的潜力,这主要得益于大型语言模型的应用。然而,在处理复杂的推理任务时,它们常面临诸如准确度不足和思维退化等挑战,制约了其性能表现。为了克服这些问题,我们提出了带有多路推理的反应与反思代理(RR-MP)框架,旨在增强大型语言模型的推理能力。我们的方法采用多路推理机制来提升科学推理的准确度,每条路径包含一名反应代理和一名反思代理,他们协同工作,防止单一代理依赖导致的思维退化。此外,RR-MP框架无需额外训练,它利用每个推理路径的多个对话实例和一个单独的摘要器来整合所有路径的见解。这种设计融合了不同的观点,加强了每条路径的推理能力。我们对涉及道德情景、大学物理和数学的任务进行了零样本和少样本评估。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于基准方法,突显了RR-MP框架在处理复杂科学推理任务中的有效性和优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
反应与反思多路径推理框架(RR-MP)旨在增强大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,解决其在处理复杂推理任务时面临的准确性不足和思维退化问题。该框架通过采用多路径推理机制,每个路径包含反应和反思两个代理,协作防止单一代理依赖导致的思维退化。RR-MP框架无需额外训练,利用每个推理路径的多个对话实例和单独的总结者来整合不同观点,加强各路径的推理能力。在道德场景、大学物理和数学任务上的零样本和少样本评估表明,该方法优于基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 反应与反思多路径推理框架(RR-MP)旨在增强大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂科学推理任务中的性能。
- RR-MP框架采用多路径推理机制,通过反应和反思代理的协作,解决思维退化问题。
- 该框架通过整合多个对话实例和不同观点,提高科学推理的准确性。
- RR-MP框架设计独特,无需额外训练,通过单独的总结者模块来巩固各路径的见解。
- 实验结果表明,RR-MP框架在道德场景、大学物理和数学任务上的表现优于基线方法。
- RR-MP框架能够管理复杂的科学推理任务,显示出其有效性和优势。
点此查看论文截图

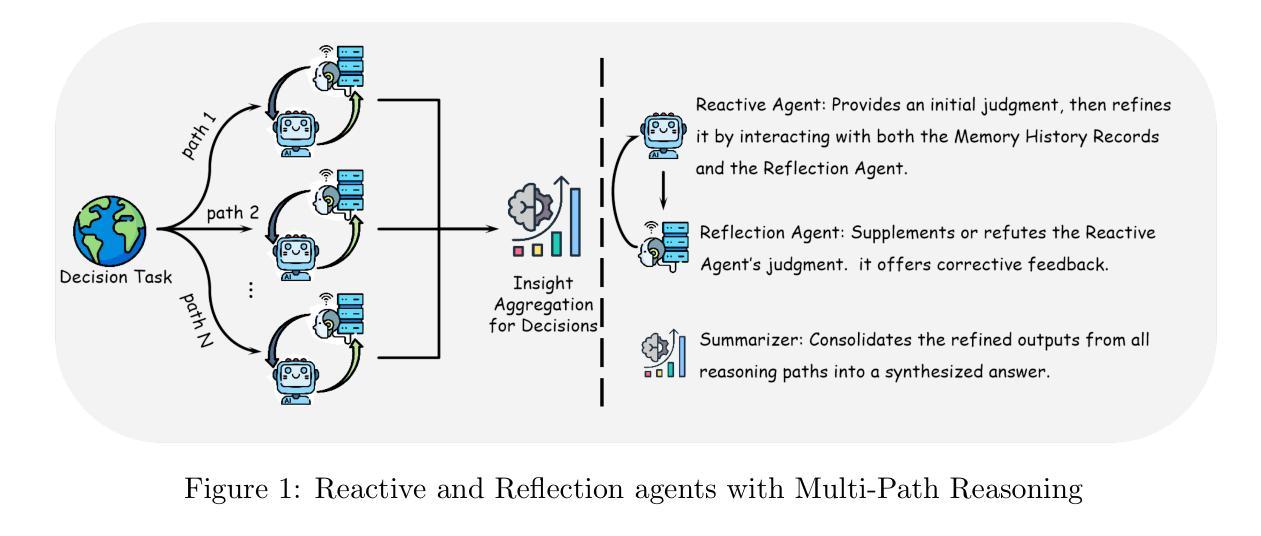

SAM-Aware Graph Prompt Reasoning Network for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation
Authors:Shi-Feng Peng, Guolei Sun, Yong Li, Hongsong Wang, Guo-Sen Xie
The primary challenge of cross-domain few-shot segmentation (CD-FSS) is the domain disparity between the training and inference phases, which can exist in either the input data or the target classes. Previous models struggle to learn feature representations that generalize to various unknown domains from limited training domain samples. In contrast, the large-scale visual model SAM, pre-trained on tens of millions of images from various domains and classes, possesses excellent generalizability. In this work, we propose a SAM-aware graph prompt reasoning network (GPRN) that fully leverages SAM to guide CD-FSS feature representation learning and improve prediction accuracy. Specifically, we propose a SAM-aware prompt initialization module (SPI) to transform the masks generated by SAM into visual prompts enriched with high-level semantic information. Since SAM tends to divide an object into many sub-regions, this may lead to visual prompts representing the same semantic object having inconsistent or fragmented features. We further propose a graph prompt reasoning (GPR) module that constructs a graph among visual prompts to reason about their interrelationships and enable each visual prompt to aggregate information from similar prompts, thus achieving global semantic consistency. Subsequently, each visual prompt embeds its semantic information into the corresponding mask region to assist in feature representation learning. To refine the segmentation mask during testing, we also design a non-parameter adaptive point selection module (APS) to select representative point prompts from query predictions and feed them back to SAM to refine inaccurate segmentation results. Experiments on four standard CD-FSS datasets demonstrate that our method establishes new state-of-the-art results. Code: https://github.com/CVL-hub/GPRN.
跨域小样本分割(CD-FSS)的主要挑战在于训练和推理阶段之间的域差异,这种差异可能存在于输入数据或目标类别中。之前的模型很难从有限的训练域样本中学习能够推广到各种未知域的特征表示。相比之下,大型视觉模型SAM在来自各个域和类别的数千万图像上进行预训练,具有良好的泛化能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于SAM的图形提示推理网络(GPRN),该网络充分利用SAM来指导CD-FSS特征表示学习并提高预测精度。具体来说,我们提出了一个SAM感知提示初始化模块(SPI),将SAM生成的掩码转换为包含高级语义信息的视觉提示。由于SAM倾向于将一个对象分成多个子区域,这可能导致表示相同语义对象的视觉提示具有不一致或碎片化的特征。我们进一步提出了一个图形提示推理(GPR)模块,该模块在视觉提示之间构建图形,推理它们之间的关系,并允许每个视觉提示从类似提示中聚合信息,从而实现全局语义一致性。随后,每个视觉提示将其语义信息嵌入到相应的掩码区域中,以辅助特征表示学习。为了在测试期间细化分割掩码,我们还设计了一个非参数自适应点选择模块(APS),从查询预测中选择代表性的点提示并反馈到SAM,以优化不准确的分割结果。在四个标准的CD-FSS数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法达到了新的最新水平。代码地址:https://github.com/CVL-hub/GPRN。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
跨域小样本分割(CD-FSS)的主要挑战在于训练和推理阶段存在的域差异问题,可能出现在输入数据或目标类别上。以前的方法难以从有限的训练域样本中学习特征表示来推广到多个未知域。本文提出了基于大规模视觉模型SAM的GPRN网络,利用SAM指导CD-FSS的特征表示学习,提高预测精度。通过SAM感知的提示初始化模块(SPI)转换SAM生成的掩膜为富含高级语义信息的视觉提示。为处理SAM倾向于将物体分为多个子区域造成的问题,提出图提示推理(GPR)模块,构建视觉提示之间的图进行关系推理,使每个视觉提示能聚合相似提示的信息,实现全局语义一致性。此外,设计了非参数自适应点选择模块(APS)来优化测试阶段的分割掩膜。在四个标准CD-FSS数据集上的实验表明,该方法取得了最新成果。
Key Takeaways
- CD-FSS面临的主要挑战是训练和推理阶段的域差异问题。
- 之前的方法难以从有限的训练域样本中学习适应各种未知域的特征表示。
- 提出了基于大规模视觉模型SAM的GPRN网络来解决这个问题。
- SAM感知的提示初始化模块(SPI)转换掩膜为富含高级语义信息的视觉提示。
- 图提示推理(GPR)模块用于处理视觉提示之间的不一致性和碎片化问题,实现全局语义一致性。
- 非参数自适应点选择模块(APS)用于优化测试阶段的分割掩膜。
- 在四个标准CD-FSS数据集上的实验取得了最新成果。
点此查看论文截图

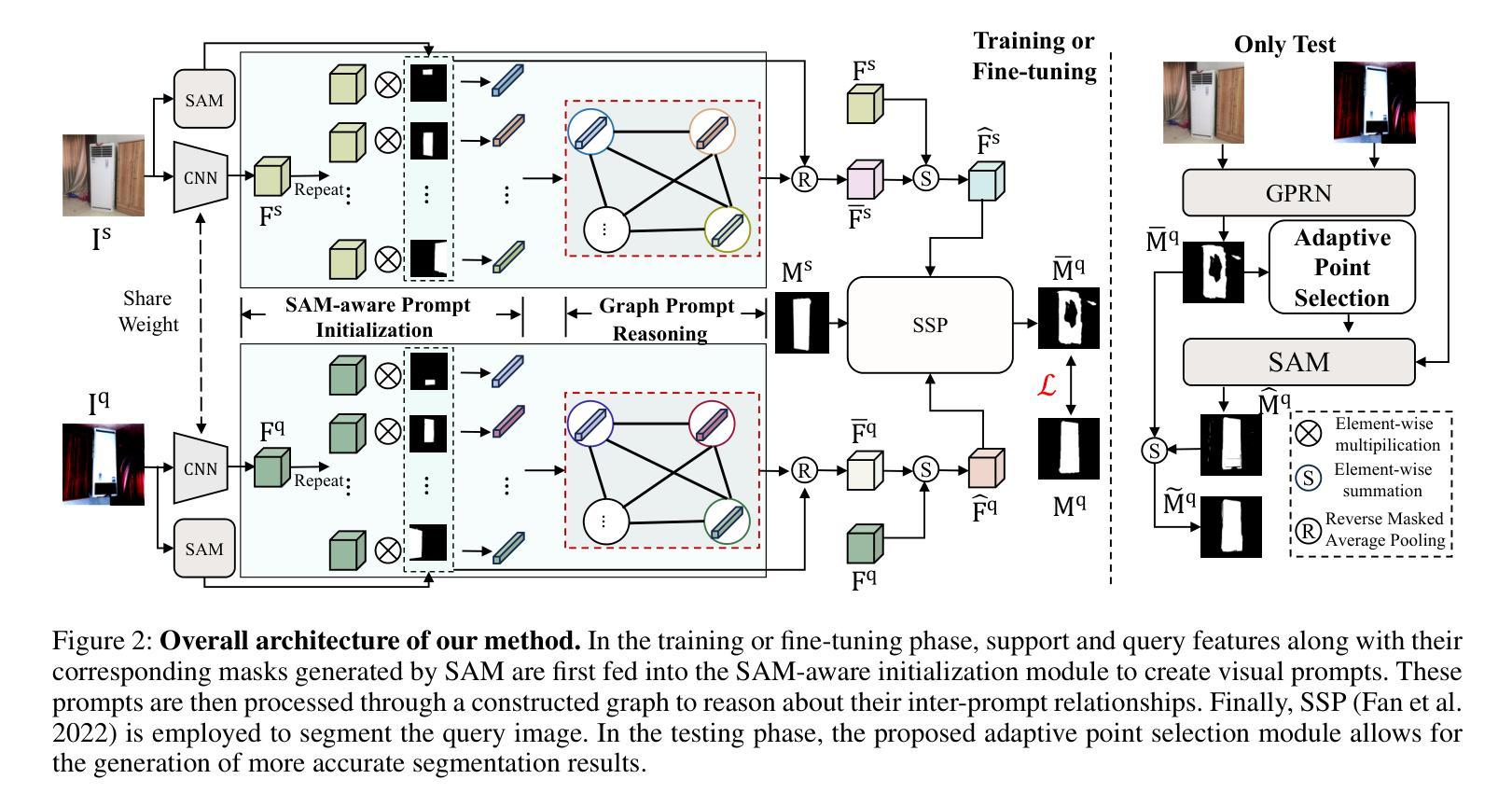
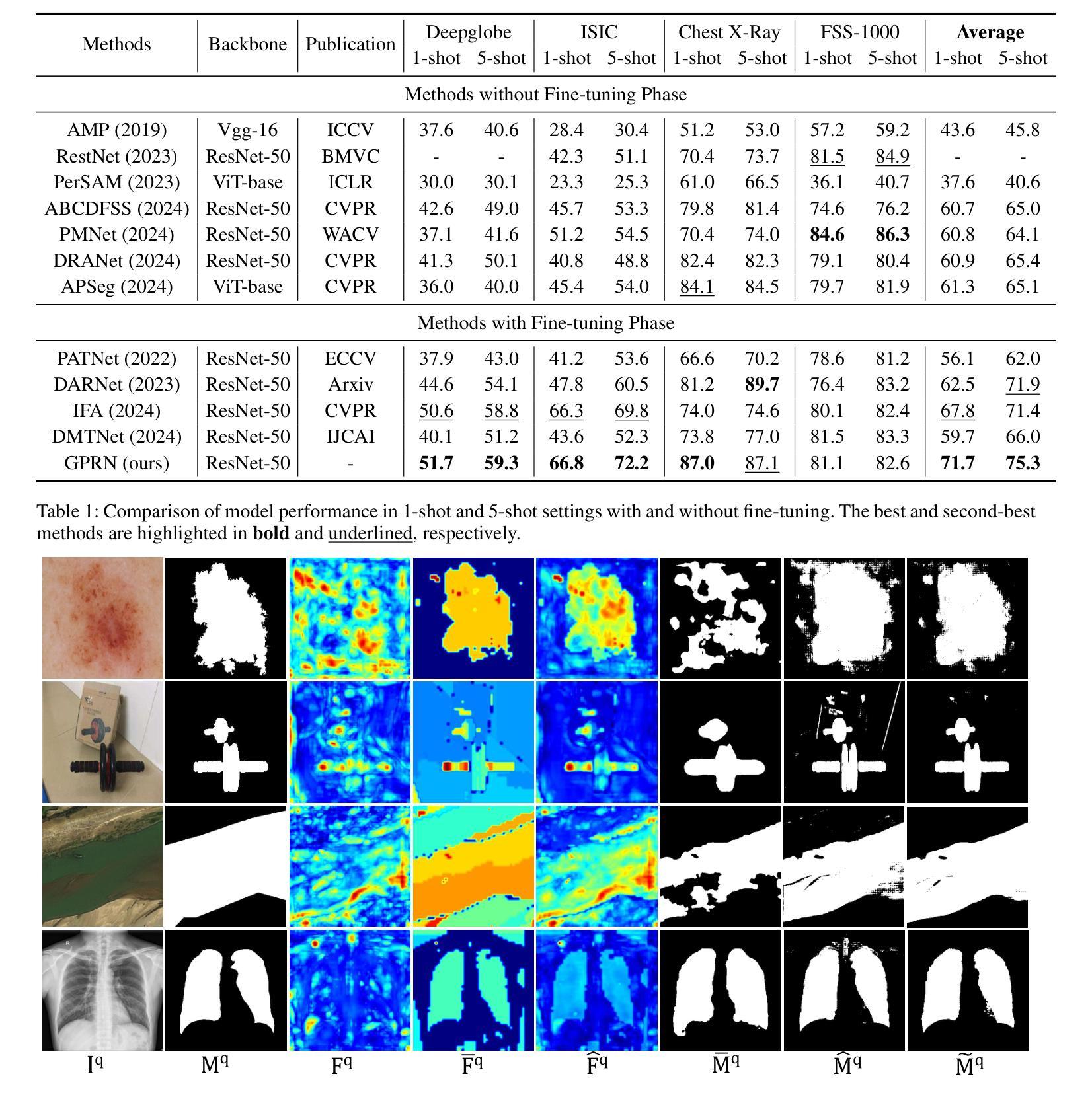
Learning in Multiple Spaces: Few-Shot Network Attack Detection with Metric-Fused Prototypical Networks
Authors:Fernando Martinez-Lopez, Lesther Santana, Mohamed Rahouti
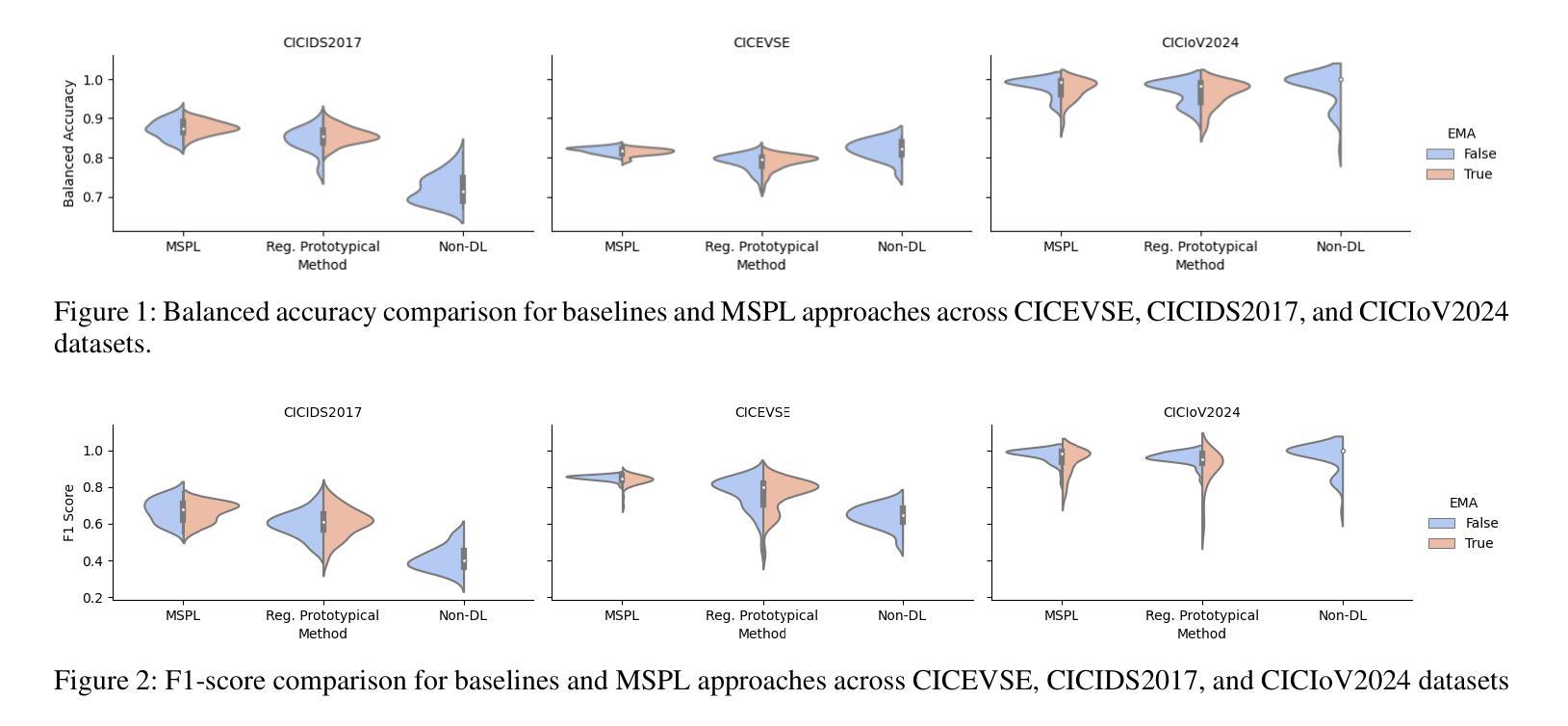
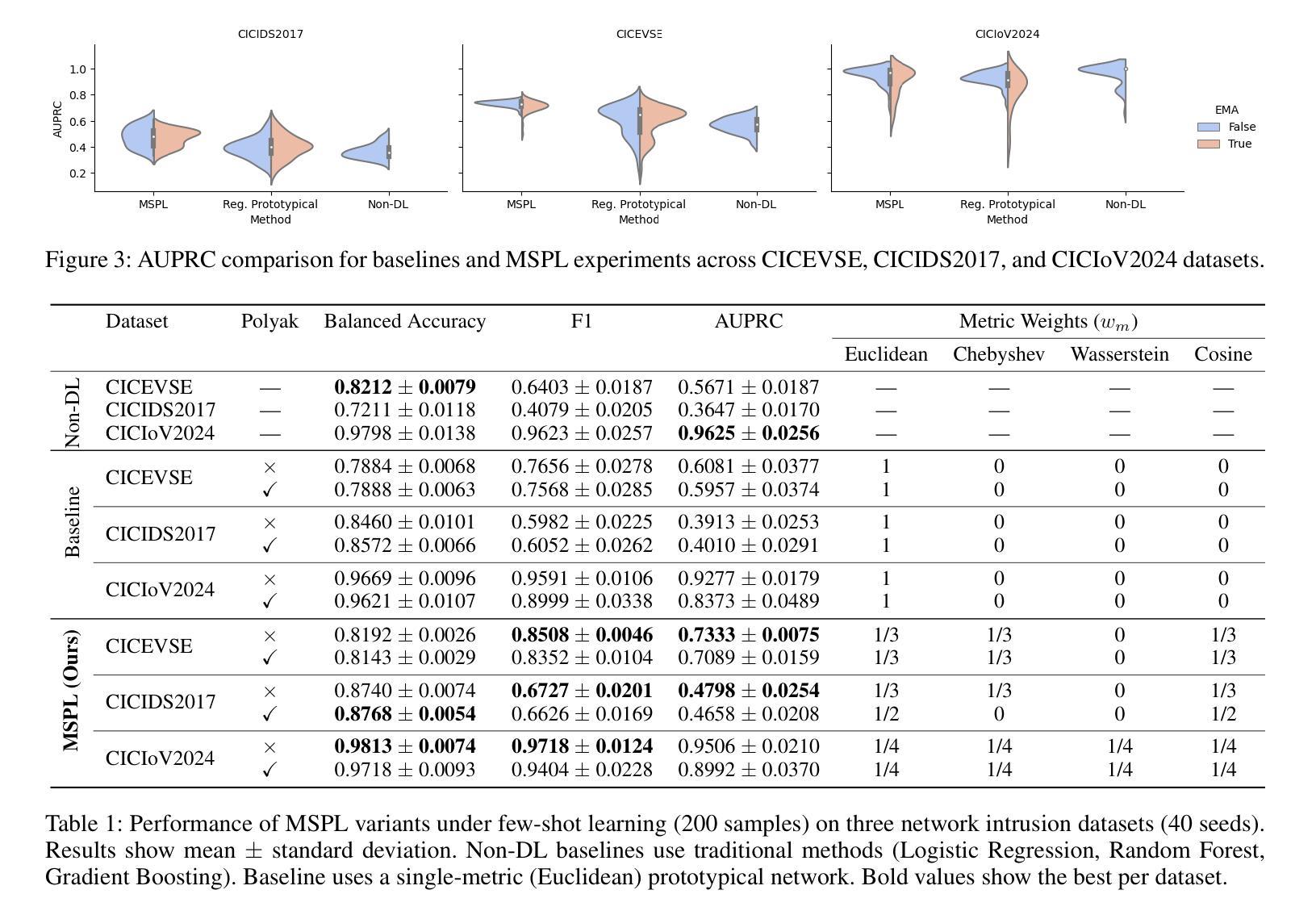
Network intrusion detection systems face significant challenges in identifying emerging attack patterns, especially when limited data samples are available. To address this, we propose a novel Multi-Space Prototypical Learning (MSPL) framework tailored for few-shot attack detection. The framework operates across multiple metric spaces-Euclidean, Cosine, Chebyshev, and Wasserstein distances-integrated through a constrained weighting scheme to enhance embedding robustness and improve pattern recognition. By leveraging Polyak-averaged prototype generation, the framework stabilizes the learning process and effectively adapts to rare and zero-day attacks. Additionally, an episodic training paradigm ensures balanced representation across diverse attack classes, enabling robust generalization. Experimental results on benchmark datasets demonstrate that MSPL outperforms traditional approaches in detecting low-profile and novel attack types, establishing it as a robust solution for zero-day attack detection.
网络入侵检测系统在面对新兴攻击模式识别时面临重大挑战,特别是在有限的样本数据下。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种针对小样本攻击检测的新型多空间原型学习(MSPL)框架。该框架在多个度量空间(欧几里得距离、余弦距离、切比雪夫距离和瓦瑟斯坦距离)中运行,通过约束加权方案进行整合,以提高嵌入的稳健性和模式识别能力。通过利用Polyak平均原型生成技术,该框架稳定了学习过程,并能有效地适应罕见和零日攻击。此外,采用情景训练模式确保不同攻击类别的均衡表示,从而实现稳健的泛化。在基准数据集上的实验结果表明,MSPL在检测低配置和新型攻击类型方面优于传统方法,已成为一种有效的零日攻击检测解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The AAAI-25 Workshop on Artificial Intelligence for Cyber Security (AICS)
Summary
文章提出了针对少量数据样本攻击检测的多空间原型学习(MSPL)框架。该框架利用多种度量空间技术提高嵌入稳健性和模式识别能力,并有效适应稀有和零日攻击。实验结果表明,MSPL在检测低轮廓和新型攻击类型方面优于传统方法,成为零日攻击检测的稳健解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 网络入侵检测系统面临识别新兴攻击模式的挑战,尤其是在有限数据样本的情况下。
- 提出了一种多空间原型学习(MSPL)框架,用于解决该问题。
- MSPL框架在多种度量空间(如欧几里得距离、余弦距离、切比雪夫距离和瓦瑟斯坦距离)上进行操作,通过约束加权方案进行集成。
- 利用Polyak平均原型生成技术增强学习过程的稳定性,有效适应稀有和零日攻击。
- 采用周期训练模式确保各种攻击类的均衡表示,实现稳健的泛化。
- 实验结果表明,MSPL框架在检测低轮廓和新型攻击类型方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图