⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-06 更新
OmniChat: Enhancing Spoken Dialogue Systems with Scalable Synthetic Data for Diverse Scenarios
Authors:Xize Cheng, Dongjie Fu, Xiaoda Yang, Minghui Fang, Ruofan Hu, Jingyu Lu, Bai Jionghao, Zehan Wang, Shengpeng Ji, Rongjie Huang, Linjun Li, Yu Chen, Tao Jin, Zhou Zhao
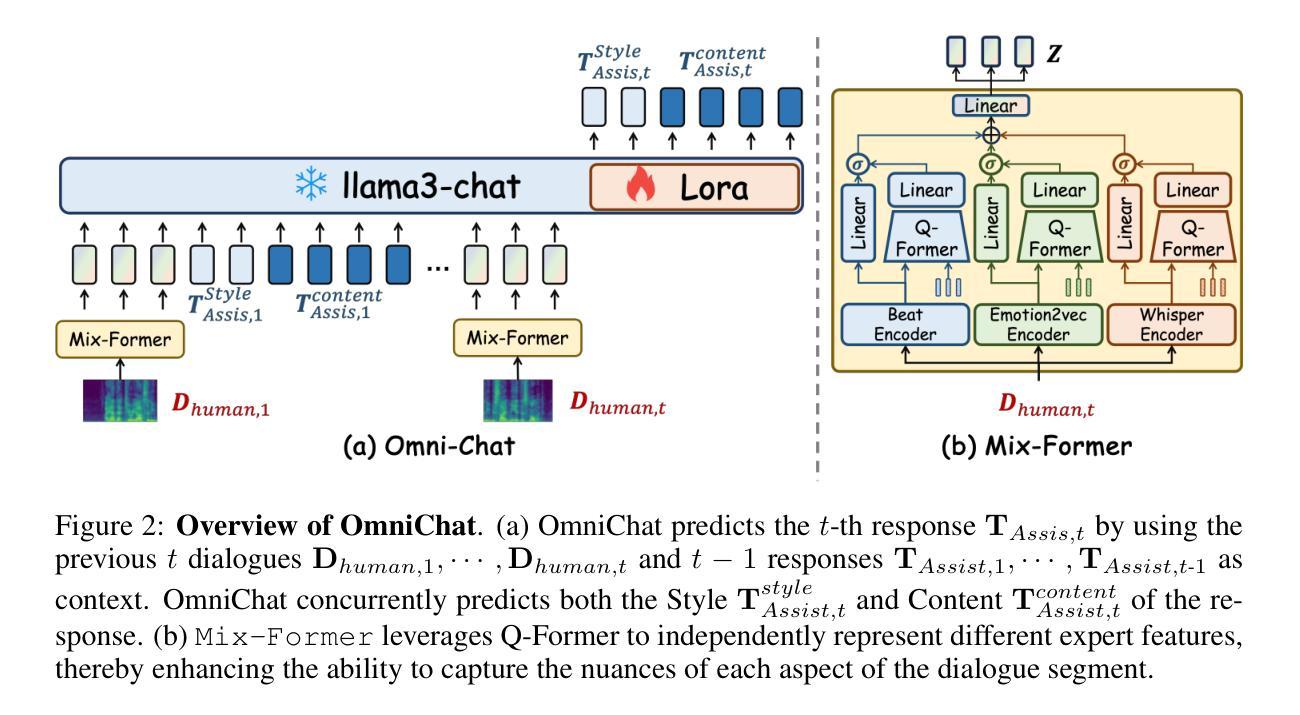
With the rapid development of large language models, researchers have created increasingly advanced spoken dialogue systems that can naturally converse with humans. However, these systems still struggle to handle the full complexity of real-world conversations, including audio events, musical contexts, and emotional expressions, mainly because current dialogue datasets are constrained in both scale and scenario diversity. In this paper, we propose leveraging synthetic data to enhance the dialogue models across diverse scenarios. We introduce ShareChatX, the first comprehensive, large-scale dataset for spoken dialogue that spans diverse scenarios. Based on this dataset, we introduce OmniChat, a multi-turn dialogue system with a heterogeneous feature fusion module, designed to optimize feature selection in different dialogue contexts. In addition, we explored critical aspects of training dialogue systems using synthetic data. Through comprehensive experimentation, we determined the ideal balance between synthetic and real data, achieving state-of-the-art results on the real-world dialogue dataset DailyTalk. We also highlight the crucial importance of synthetic data in tackling diverse, complex dialogue scenarios, especially those involving audio and music. For more details, please visit our demo page at \url{https://sharechatx.github.io/}.
随着大型语言模型的快速发展,研究人员已经创建出越来越先进的口语对话系统,可以与人类进行自然对话。然而,这些系统在处理现实世界中对话的复杂性时仍然遇到困难,包括音频事件、音乐背景和情绪表达,这主要是因为当前对话数据集在规模和场景多样性方面存在限制。在本文中,我们提出利用合成数据来增强不同场景下的对话模型。我们介绍了ShareChatX,这是第一个全面、大规模的口语对话数据集,涵盖各种场景。基于此数据集,我们推出了OmniChat,这是一个多轮对话系统,配备有异质特征融合模块,旨在优化不同对话语境中的特征选择。此外,我们还探讨了使用合成数据训练对话系统的关键方面。通过全面的实验,我们确定了合成数据和真实数据之间的理想平衡,并在真实世界对话数据集DailyTalk上取得了最新结果。我们还强调了合成数据在处理多样、复杂的对话场景中的关键作用,特别是涉及音频和音乐的场景。想了解更多信息,请访问我们的演示页面:[https://sharechatx.github.io/]。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着大型语言模型的快速发展,研究者已创建出能够自然与人类对话的先进口语对话系统。然而,这些系统在处理真实世界的复杂对话时仍面临挑战,如音频事件、音乐背景和情绪表达等。主要原因是当前对话数据集在规模和场景多样性上的限制。本文提出利用合成数据增强对话模型在不同场景中的应用。我们引入了ShareChatX,第一个全面、大规模的口语对话数据集,涵盖各种场景。基于此数据集,我们推出了OmniChat,一个具有异质特征融合模块的多轮对话系统,旨在优化不同对话语境中的特征选择。此外,我们还探究了使用合成数据训练对话系统的关键方面。通过综合实验,我们确定了合成数据与真实数据之间的理想平衡,并在真实世界对话数据集DailyTalk上取得了最新结果。我们还强调了合成数据在处理多样化、复杂对话场景中的关键作用,特别是涉及音频和音乐的部分。更多详情,请访问我们的演示页面:ShareChatX官网链接。
Key Takeaways
- 口语对话系统虽然取得进展,但仍难以处理真实世界的复杂对话,如音频事件、音乐背景和情绪表达。
- 当前对话数据集在规模和场景多样性上存在限制。
- 提出了利用合成数据增强对话模型的方法,以改善其在各种场景中的表现。
- 引入了ShareChatX,一个全面、大规模的口语对话数据集。
- 基于ShareChatX数据集,推出了OmniChat多轮对话系统,具有异质特征融合模块。
- 综合实验表明,合成数据与真实数据之间存在理想平衡,且在真实世界对话数据集上取得最新成果。
点此查看论文截图

TED: Turn Emphasis with Dialogue Feature Attention for Emotion Recognition in Conversation
Authors:Junya Ono, Hiromi Wakaki
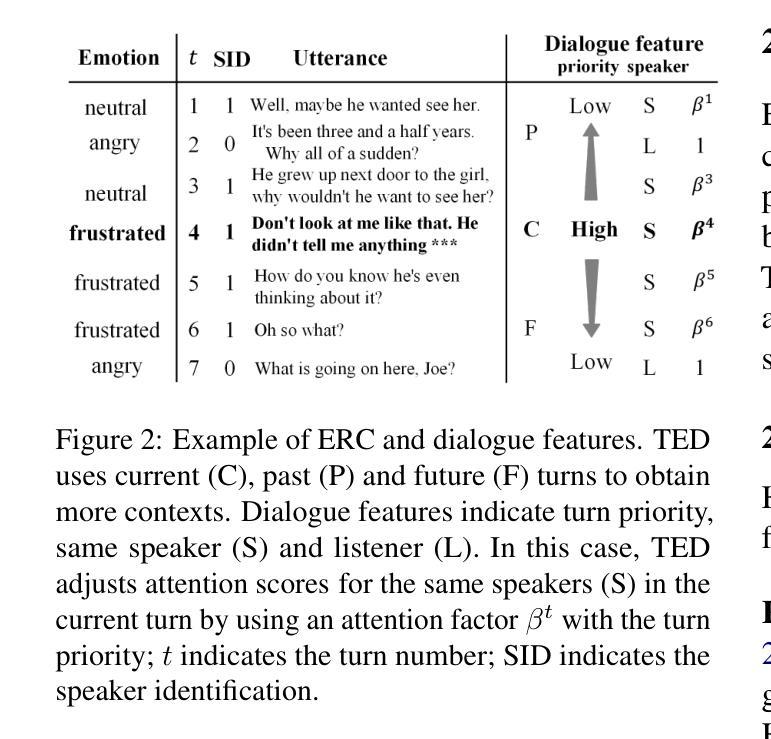
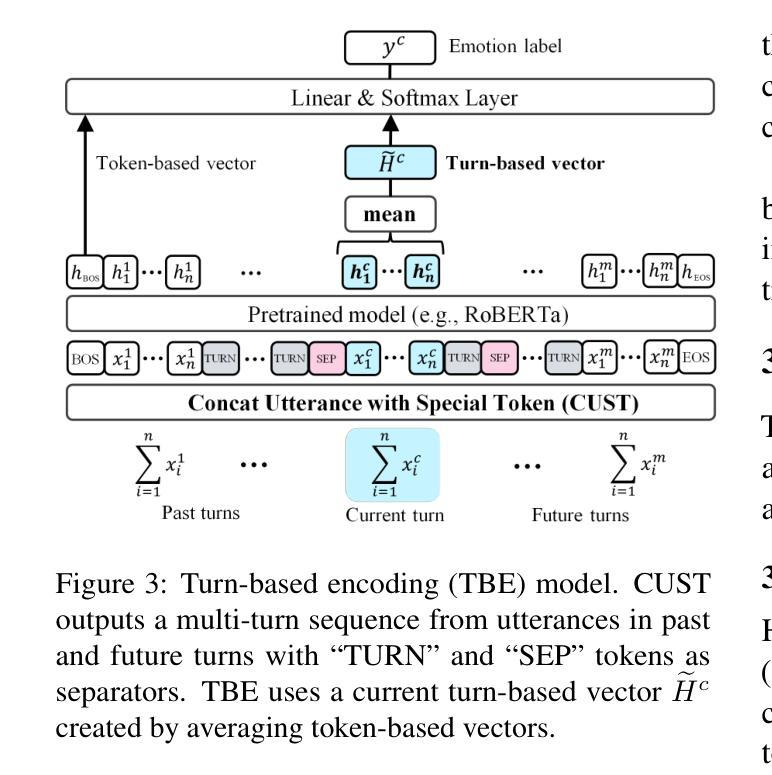
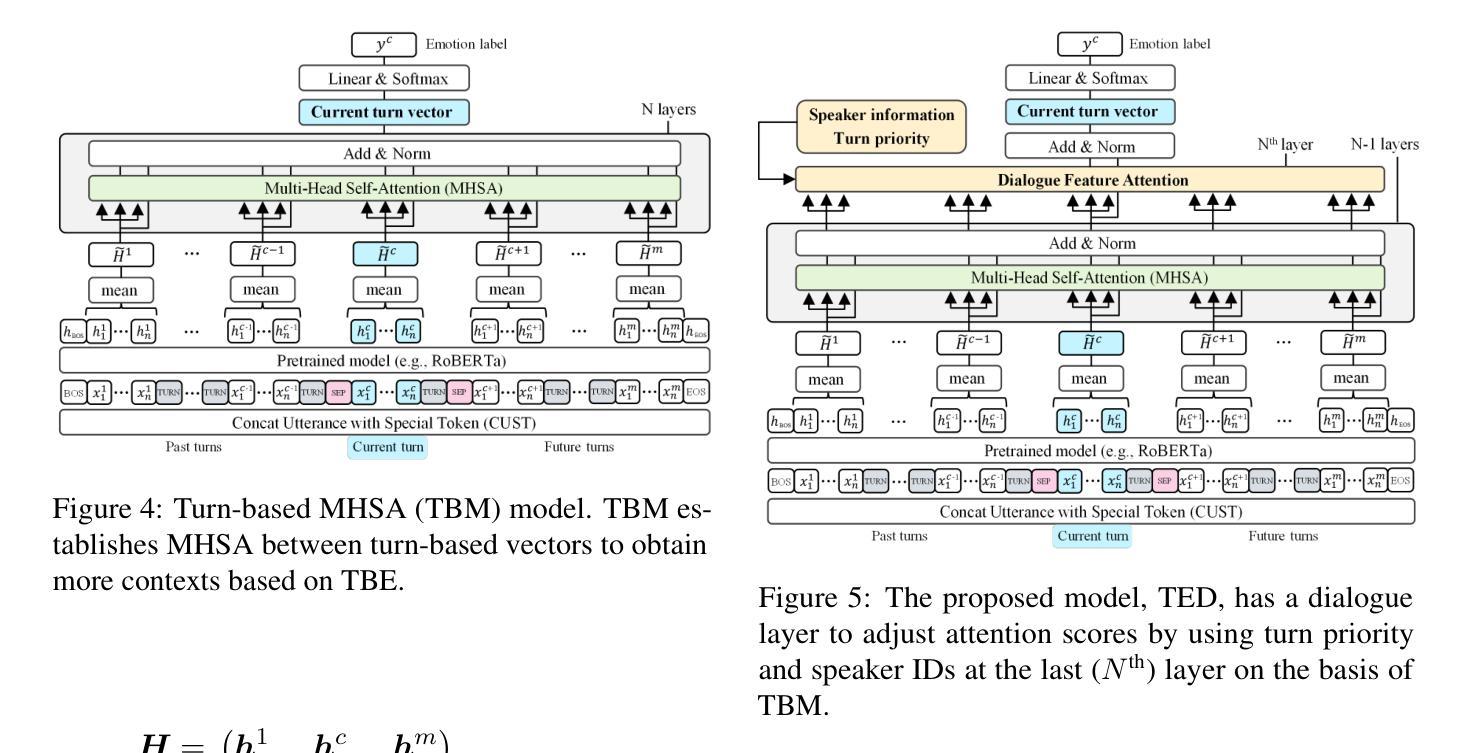
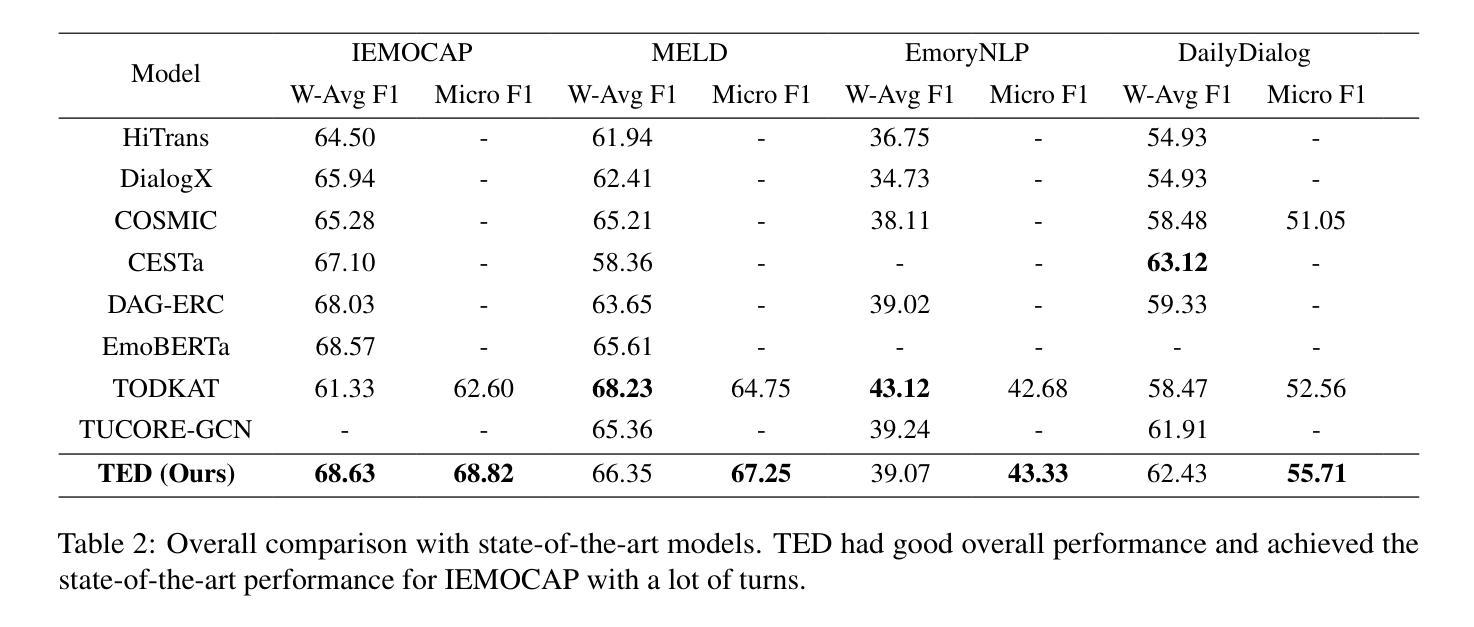
Emotion recognition in conversation (ERC) has been attracting attention by methods for modeling multi-turn contexts. The multi-turn input to a pretraining model implicitly assumes that the current turn and other turns are distinguished during the training process by inserting special tokens into the input sequence. This paper proposes a priority-based attention method to distinguish each turn explicitly by adding dialogue features into the attention mechanism, called Turn Emphasis with Dialogue (TED). It has a priority for each turn according to turn position and speaker information as dialogue features. It takes multi-head self-attention between turn-based vectors for multi-turn input and adjusts attention scores with the dialogue features. We evaluate TED on four typical benchmarks. The experimental results demonstrate that TED has high overall performance in all datasets and achieves state-of-the-art performance on IEMOCAP with numerous turns.
对话中的情感识别(ERC)已经引起了通过建模多轮上下文的方法的注意。预训练模型的多轮输入隐含地假设在训练过程中通过向输入序列插入特殊令牌来区分当前轮次和其他轮次。本文提出了一种基于优先级的注意力方法,通过向注意力机制中添加对话特征来明确区分每一轮,称为“以对话为重点的回合”(TED)。它根据回合位置和说话者信息作为对话特征为每一回合设置优先级。它在基于回合的向量之间采用多头自注意力,用于多回合输入,并用对话特征调整注意力分数。我们在四个典型基准上对TED进行了评估。实验结果表明,TED在所有数据集上表现出较高的整体性能,在轮次较多的IEMOCAP上实现了最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF past activity in 2021
Summary
对话中的情感识别(ERC)正受到采用多轮上下文建模方法的关注。本文提出一种基于优先级的注意力方法,通过向注意力机制中添加对话特征来显式区分每一轮对话,称为带有对话的转向强调(TED)。它根据轮次位置和说话者信息为每轮设定优先级作为对话特征。通过调整基于轮次向量的多轮输入之间的多头自注意力,并与对话特征相结合,TED取得了良好的效果。在四个典型基准测试上的实验结果表明,TED在所有数据集上的总体性能较高,并在具有众多轮次的IEMOCAP上实现了最新技术性能。
Key Takeaways
- ERC(对话中的情感识别)正受到关注,多轮上下文建模方法成为研究热点。
- 当前的研究通过插入特殊令牌来区分对话中的当前轮次和其他轮次。
- TED(转向强调与对话)是一种基于优先级的注意力方法,通过添加对话特征来显式区分每轮对话。
- TED根据轮次位置和说话者信息设定每轮的优先级。
- TED采用多轮输入的多头自注意力机制,结合对话特征。
- 在四个基准测试上的实验表明,TED在所有数据集上表现出良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

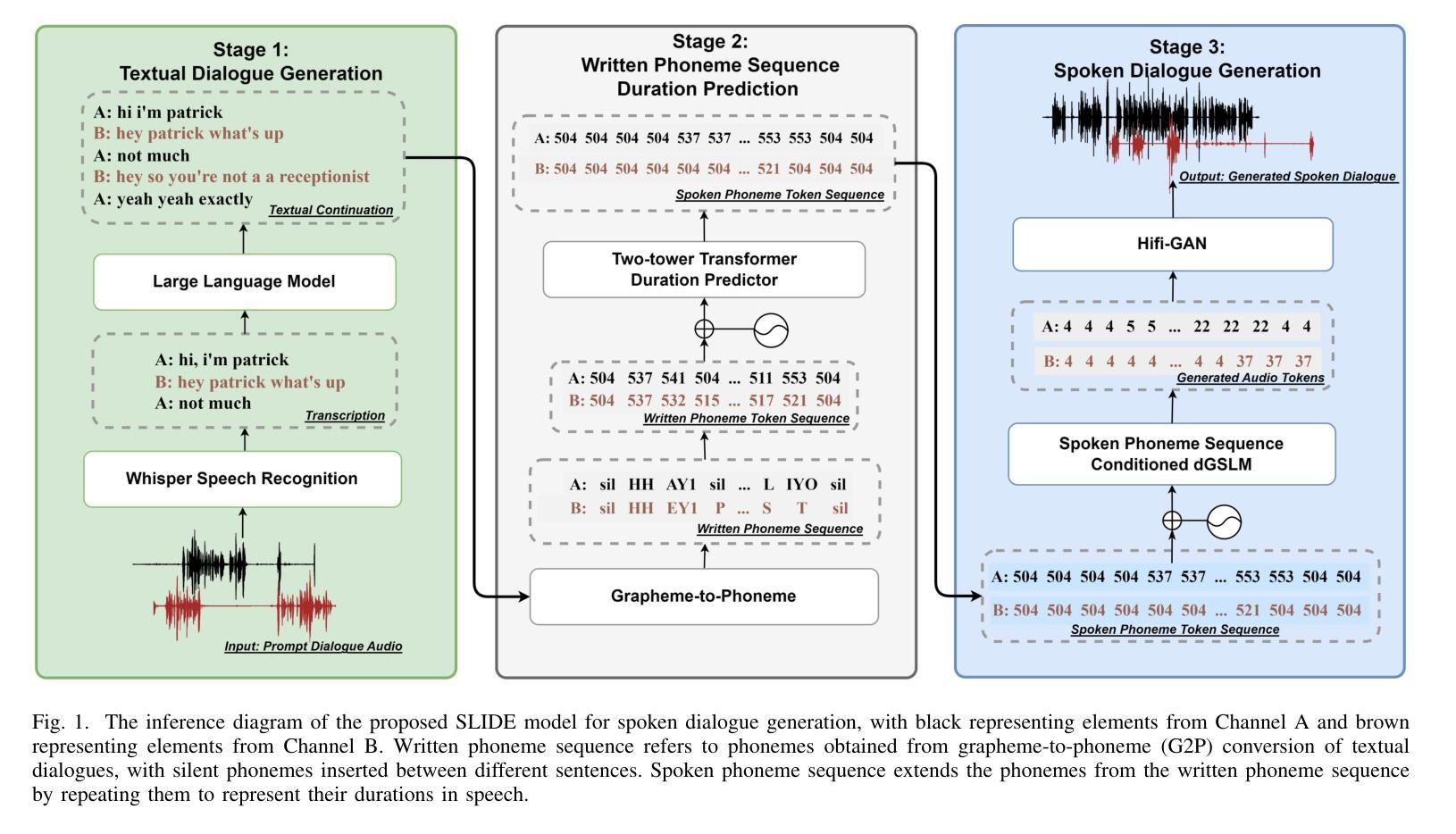
SLIDE: Integrating Speech Language Model with LLM for Spontaneous Spoken Dialogue Generation
Authors:Haitian Lu, Gaofeng Cheng, Liuping Luo, Leying Zhang, Yanmin Qian, Pengyuan Zhang
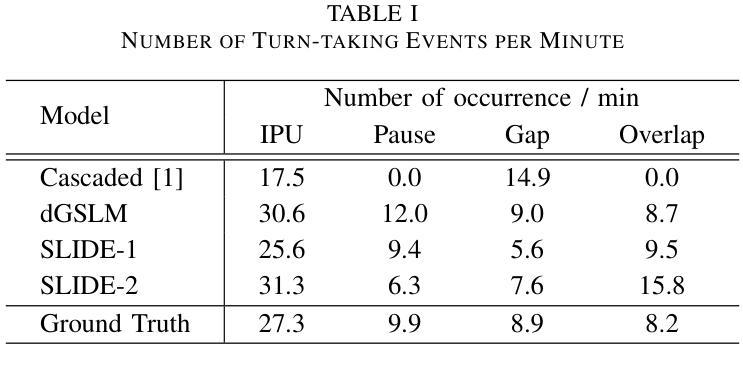
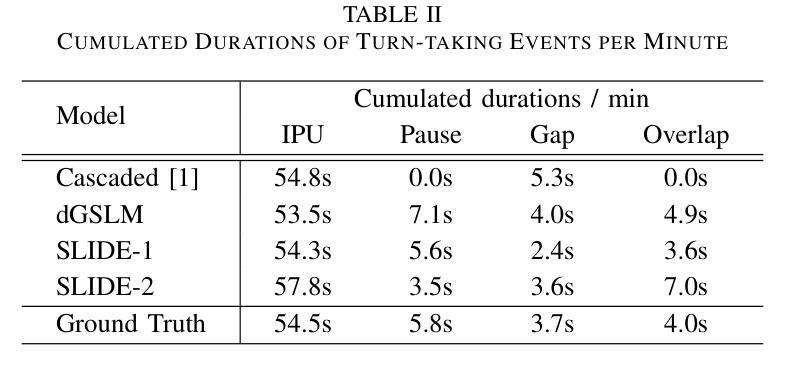
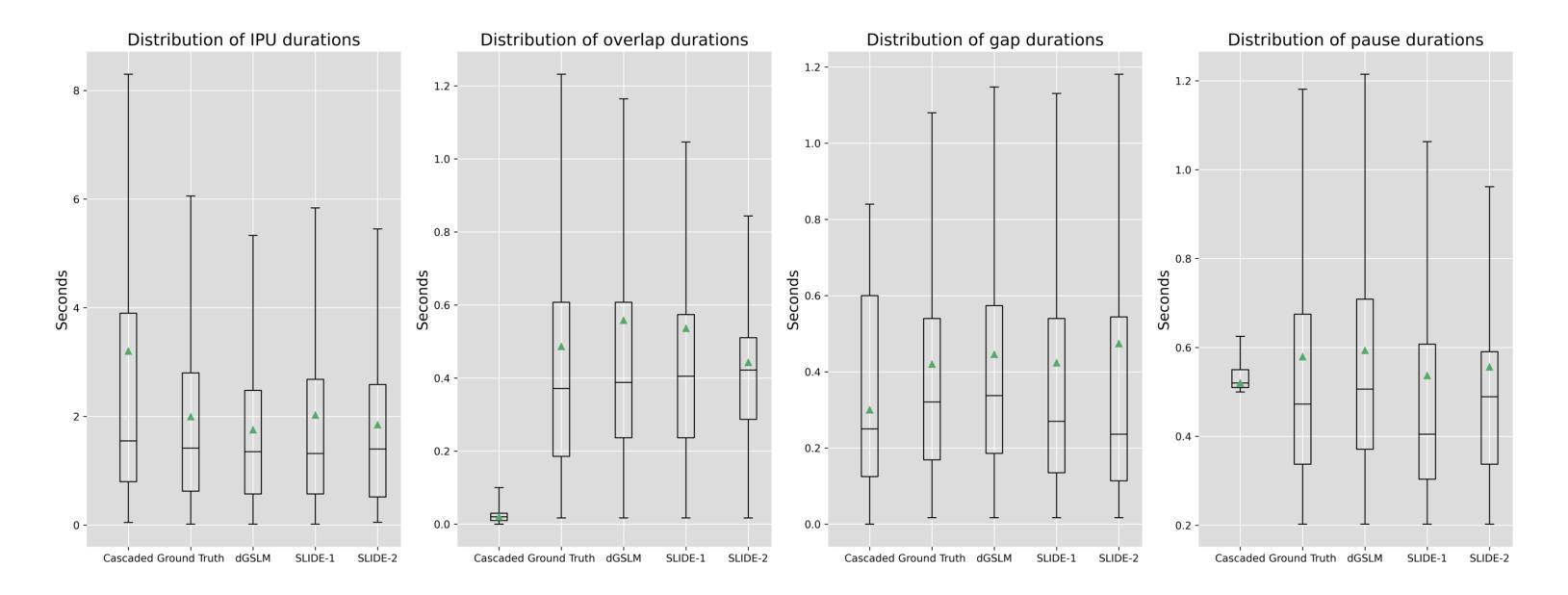
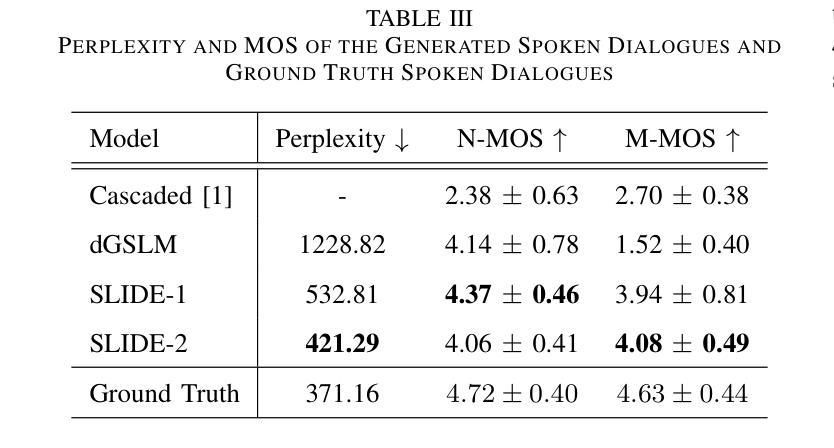
Recently, ``textless” speech language models (SLMs) based on speech units have made huge progress in generating naturalistic speech, including non-verbal vocalizations. However, the generated speech samples often lack semantic coherence. In this paper, we propose SLM and LLM Integration for spontaneous spoken Dialogue gEneration (SLIDE). Specifically, we first utilize an LLM to generate the textual content of spoken dialogue. Next, we convert the textual dialogues into phoneme sequences and use a two-tower transformer-based duration predictor to predict the duration of each phoneme. Finally, an SLM conditioned on the spoken phoneme sequences is used to vocalize the textual dialogue. Experimental results on the Fisher dataset demonstrate that our system can generate naturalistic spoken dialogue while maintaining high semantic coherence.
最近,基于语音单元的“无文本”语音语言模型(SLM)在生成自然语音方面取得了巨大进展,包括非言语性发声。然而,生成的语音样本通常缺乏语义连贯性。在本文中,我们提出了用于自发口语对话生成的SLM和LLM集成(SLIDE)方法。具体来说,我们首先将LLM用于生成口语对话的文本内容。接下来,我们将文本对话转换为音素序列,并使用基于双塔变压器的持续时间预测器来预测每个音素的持续时间。最后,以口语音素序列为条件的SLM被用于将文本对话发声出来。在Fisher数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的系统可以生成具有自然性的口语对话,同时保持高语义连贯性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
文本无监督的语音语言模型(SLM)通过语音单位生成自然语音,包括非言语发声,但生成的语音样本常缺乏语义连贯性。本文提出SLM与大型语言模型(LLM)融合的自发口语对话生成方法(SLIDE)。首先利用LLM生成文本对话内容,然后将文本对话转换为音素序列,使用双塔变压器结构的持续时间预测器预测每个音素的持续时间。最后,以语音音素序列为条件的SLM用于将文本对话语音化。在Fisher数据集上的实验结果表明,该系统能够生成自然口语对话,同时保持高语义连贯性。
Key Takeaways
- 文本无监督的语音语言模型(SLM)可以基于语音单位生成自然语音。
- SLM生成的语音样本常缺乏语义连贯性。
- 提出SLM与大型语言模型(LLM)融合的口语对话生成方法(SLIDE)。
- LLM用于生成文本对话内容。
- 文本对话被转换为音素序列,并使用双塔变压器预测每个音素的持续时间。
- SLM以语音音素序列为条件,用于将文本对话语音化。
点此查看论文截图