⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-06 更新
MalCL: Leveraging GAN-Based Generative Replay to Combat Catastrophic Forgetting in Malware Classification
Authors:Jimin Park, AHyun Ji, Minji Park, Mohammad Saidur Rahman, Se Eun Oh
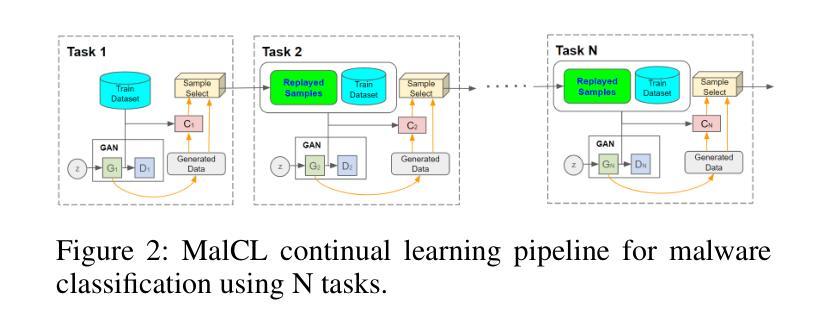
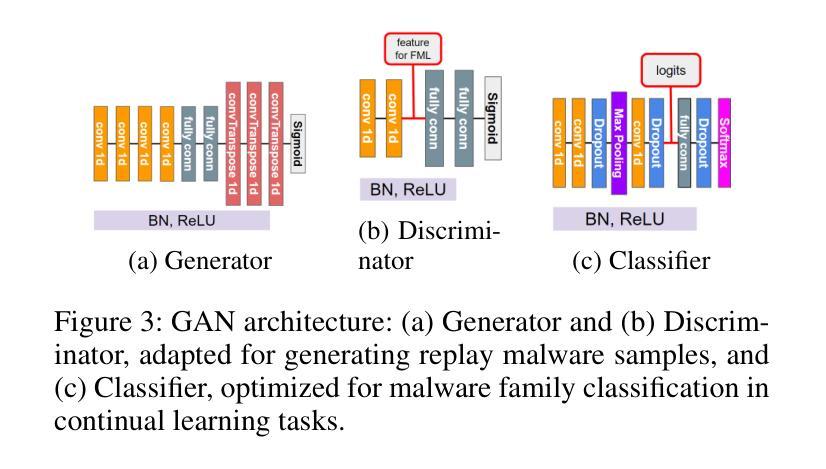
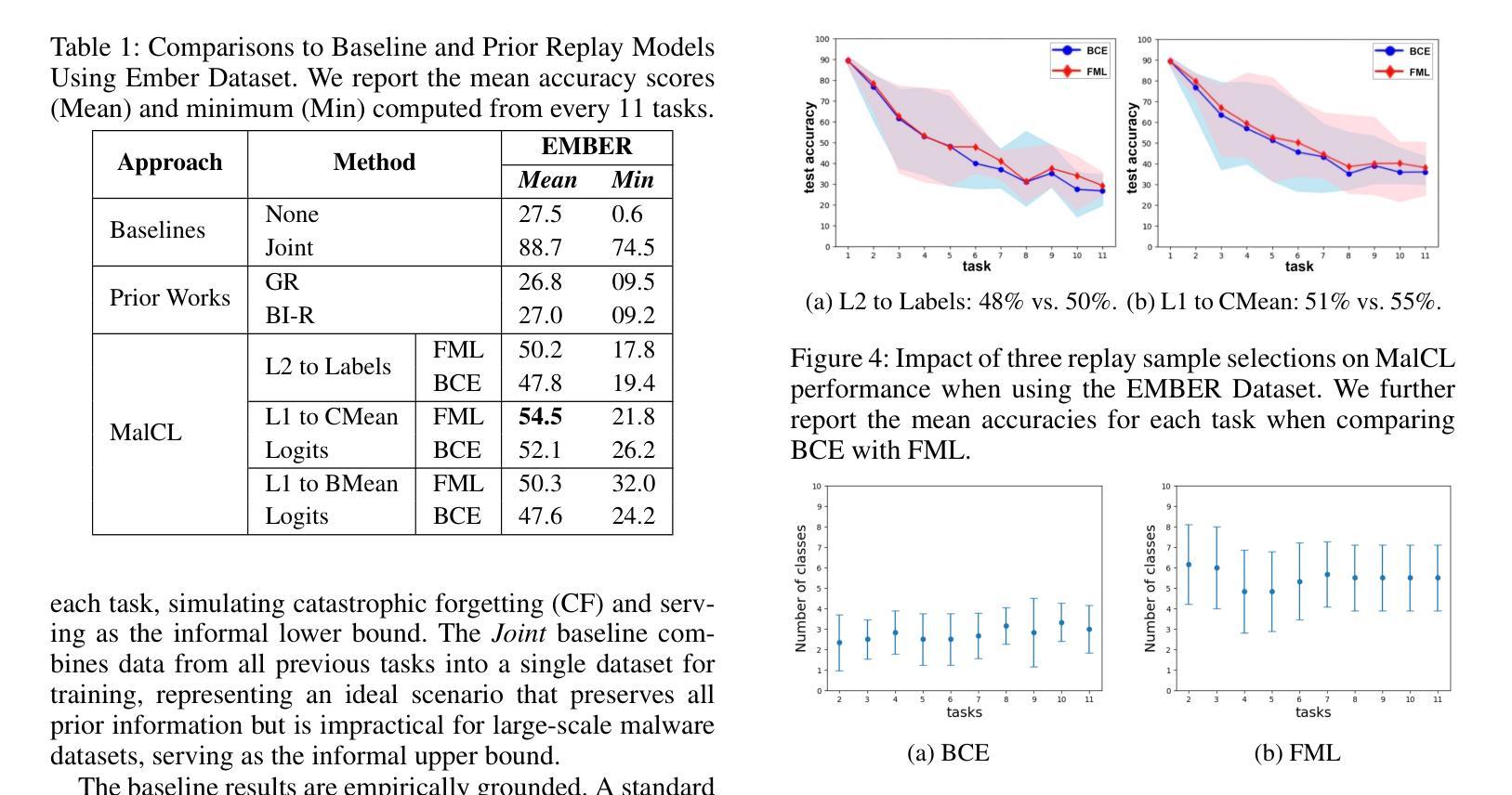
Continual Learning (CL) for malware classification tackles the rapidly evolving nature of malware threats and the frequent emergence of new types. Generative Replay (GR)-based CL systems utilize a generative model to produce synthetic versions of past data, which are then combined with new data to retrain the primary model. Traditional machine learning techniques in this domain often struggle with catastrophic forgetting, where a model’s performance on old data degrades over time. In this paper, we introduce a GR-based CL system that employs Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) with feature matching loss to generate high-quality malware samples. Additionally, we implement innovative selection schemes for replay samples based on the model’s hidden representations. Our comprehensive evaluation across Windows and Android malware datasets in a class-incremental learning scenario – where new classes are introduced continuously over multiple tasks – demonstrates substantial performance improvements over previous methods. For example, our system achieves an average accuracy of 55% on Windows malware samples, significantly outperforming other GR-based models by 28%. This study provides practical insights for advancing GR-based malware classification systems. The implementation is available at \url {https://github.com/MalwareReplayGAN/MalCL}\footnote{The code will be made public upon the presentation of the paper}.
持续学习(CL)在恶意软件分类中的应用解决了恶意软件威胁的快速演变和新类型频繁出现的问题。基于生成回放(GR)的CL系统利用生成模型产生过去数据的合成版本,然后将其与新的数据结合,重新训练主要模型。在这个领域,传统的机器学习技术经常面临灾难性遗忘的问题,即模型对旧数据的性能随时间推移而下降。在本文中,我们介绍了一个基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的GR系统,采用特征匹配损失来生成高质量的恶意软件样本。此外,我们根据模型的隐藏表示实现了创新的回放样本选择方案。我们在Windows和Android恶意软件数据集上进行了全面的评估,在一个类增量学习场景中——新类不断在多个任务中引入——表明与以前的方法相比,我们的系统实现了显著的性能提升。例如,我们的系统在Windows恶意软件样本上实现了55%的平均准确率,显著优于其他基于GR的模型,高出28%。这项研究为推进基于GR的恶意软件分类系统提供了实际见解。实现细节可在\url{https://github.com/MalwareReplayGAN/MalCL}\footnote{代码将在论文发表后公开}中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted paper at AAAI 2025. 9 pages, Figure 6, Table 1
Summary
这篇论文介绍了基于生成回放(GR)的持续学习(CL)系统在恶意软件分类中的应用。该系统采用生成对抗网络(GANs)和特征匹配损失来生成高质量的恶意软件样本,并基于模型的隐藏表示实现了回放样本的创新选择方案。在Windows和Android恶意软件数据集上的综合评估表明,该系统在类增量学习场景中实现了显著的性能改进,平均准确率达到了55%,相较于其他GR基模型提高了28%。
Key Takeaways
- 持续学习(CL)在恶意软件分类中用于应对不断进化的恶意软件威胁和新兴类型。
- 生成回放(GR)基于CL系统使用生成模型产生过去数据的合成版本。
- 传统机器学习方法在此领域常遭遇灾难性遗忘问题,即模型对旧数据性能随时间下降。
- 论文引入基于GANs和特征匹配损失的GR-CL系统,生成高质量恶意软件样本。
- 实现了基于模型隐藏表示的回放样本创新选择方案。
- 在Windows和Android恶意软件数据集上的评估显示,该系统在类增量学习场景中显著优于其他方法,平均准确率55%。
点此查看论文截图

Text-to-Image GAN with Pretrained Representations
Authors:Xiaozhou You, Jian Zhang
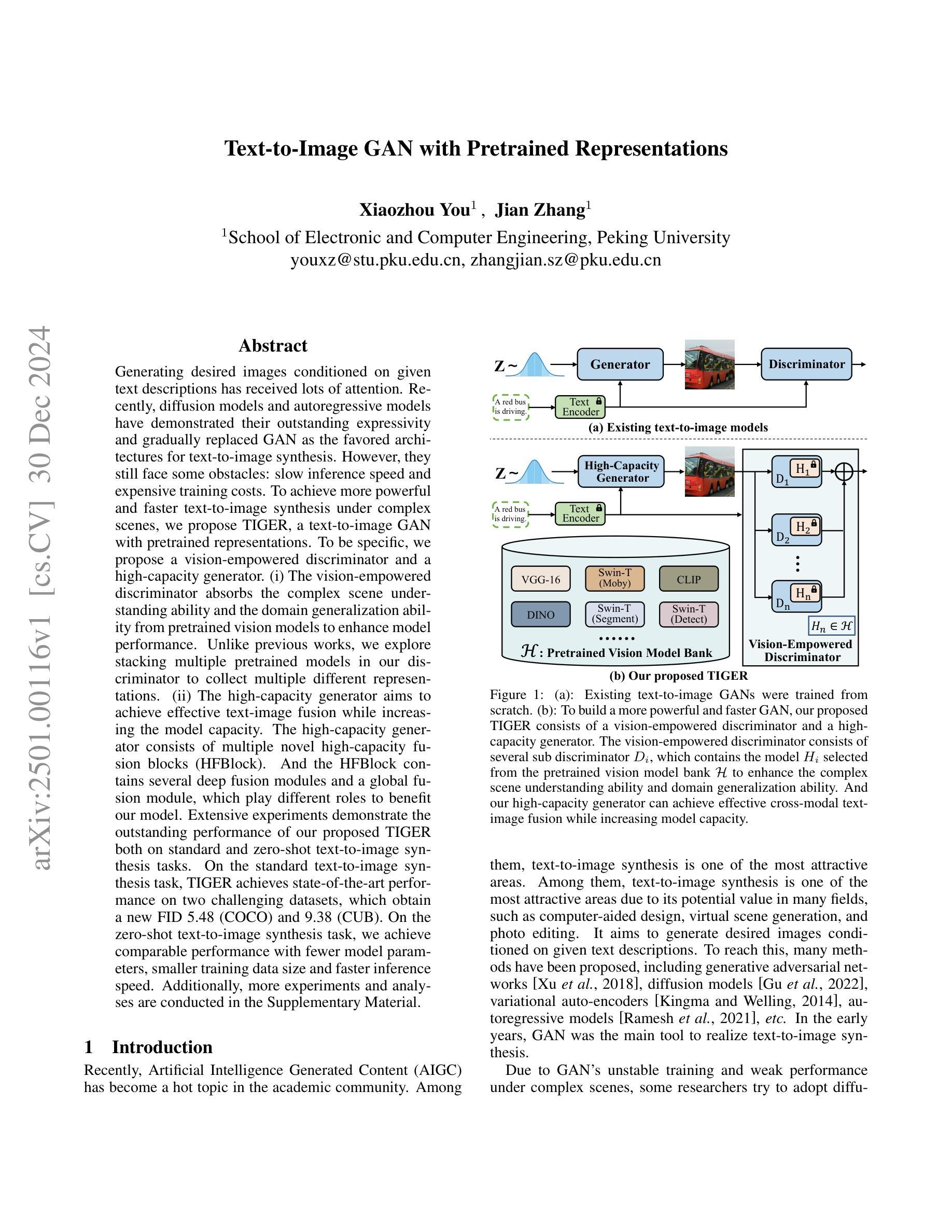
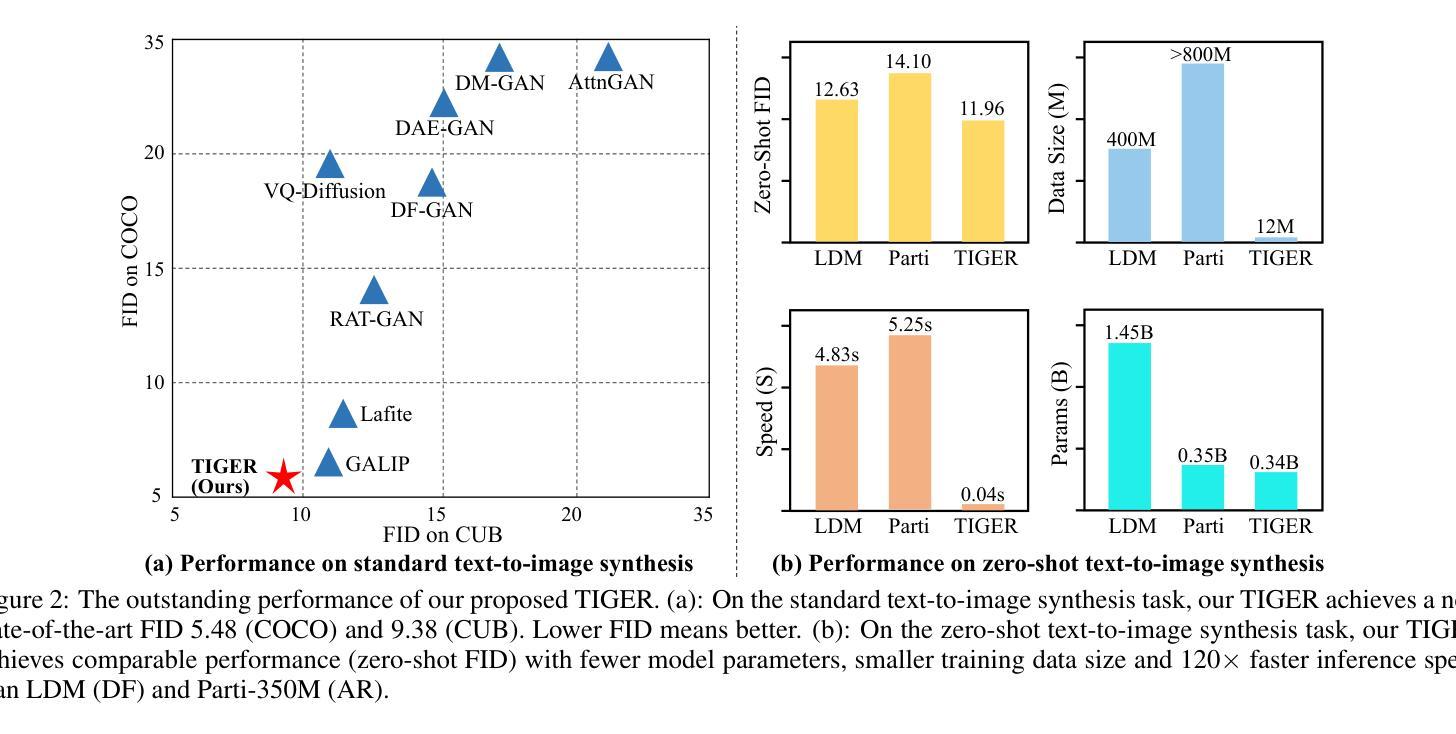
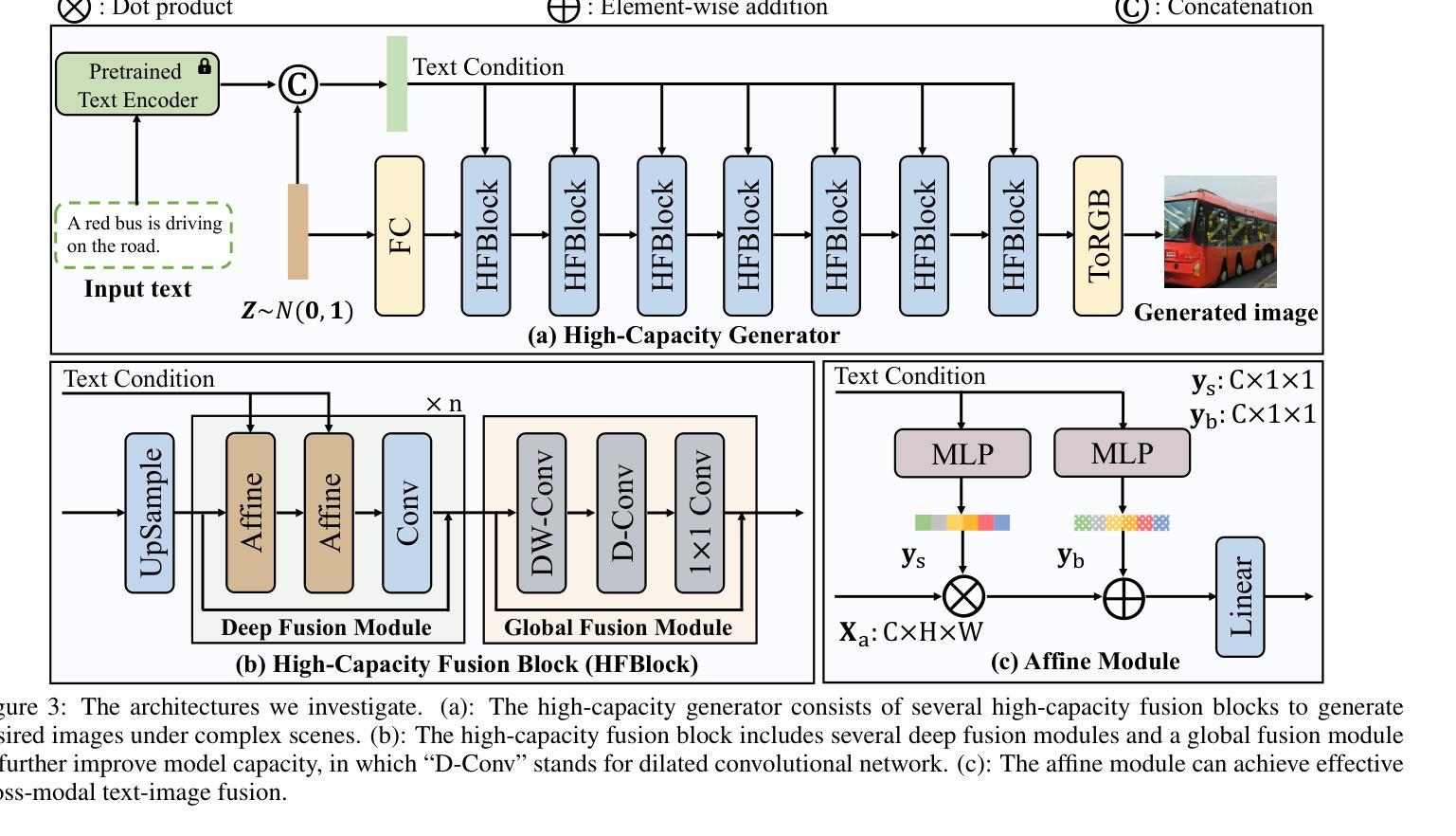
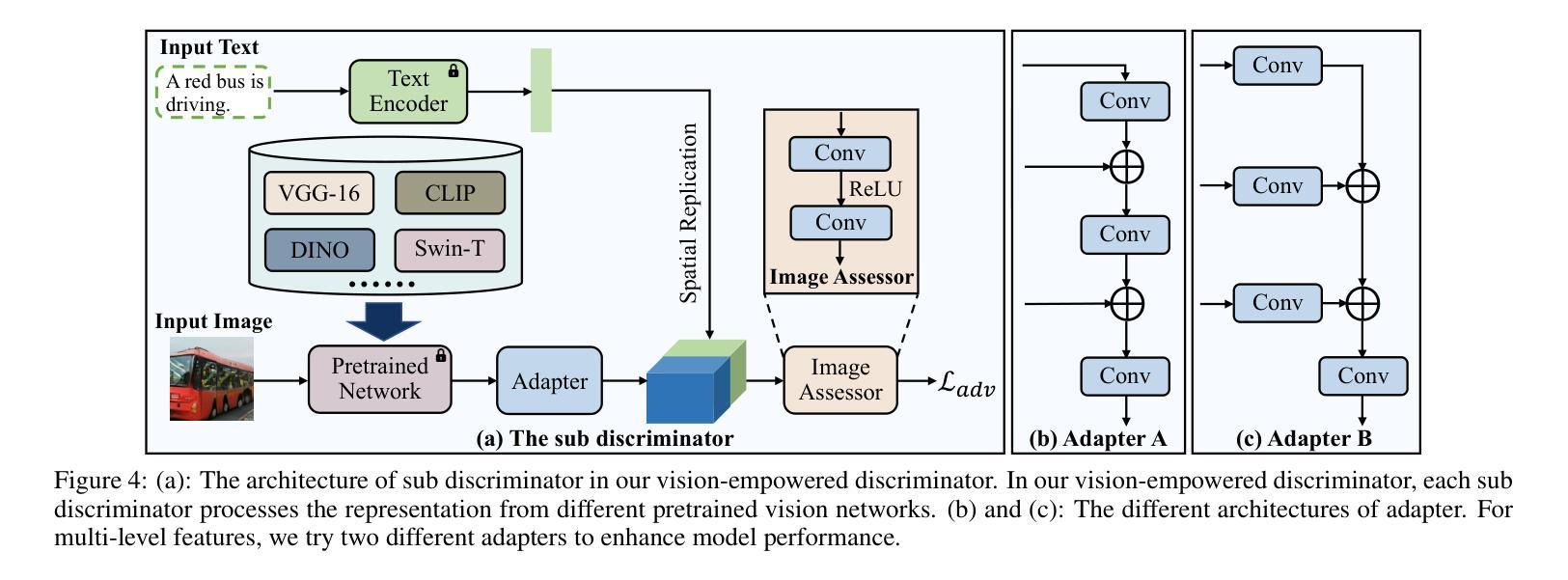
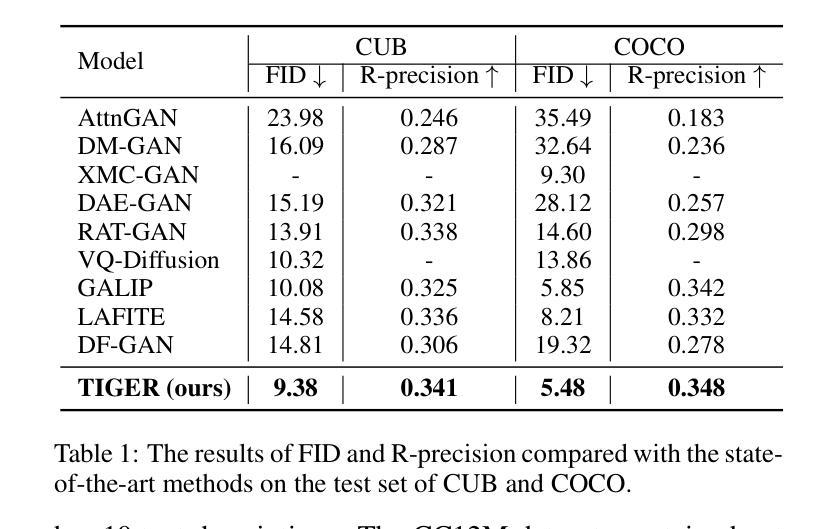
Generating desired images conditioned on given text descriptions has received lots of attention. Recently, diffusion models and autoregressive models have demonstrated their outstanding expressivity and gradually replaced GAN as the favored architectures for text-to-image synthesis. However, they still face some obstacles: slow inference speed and expensive training costs. To achieve more powerful and faster text-to-image synthesis under complex scenes, we propose TIGER, a text-to-image GAN with pretrained representations. To be specific, we propose a vision-empowered discriminator and a high-capacity generator. (i) The vision-empowered discriminator absorbs the complex scene understanding ability and the domain generalization ability from pretrained vision models to enhance model performance. Unlike previous works, we explore stacking multiple pretrained models in our discriminator to collect multiple different representations. (ii) The high-capacity generator aims to achieve effective text-image fusion while increasing the model capacity. The high-capacity generator consists of multiple novel high-capacity fusion blocks (HFBlock). And the HFBlock contains several deep fusion modules and a global fusion module, which play different roles to benefit our model. Extensive experiments demonstrate the outstanding performance of our proposed TIGER both on standard and zero-shot text-to-image synthesis tasks. On the standard text-to-image synthesis task, TIGER achieves state-of-the-art performance on two challenging datasets, which obtain a new FID 5.48 (COCO) and 9.38 (CUB). On the zero-shot text-to-image synthesis task, we achieve comparable performance with fewer model parameters, smaller training data size and faster inference speed. Additionally, more experiments and analyses are conducted in the Supplementary Material.
基于给定文本描述生成所需图像已引起广泛关注。最近,扩散模型和自回归模型表现出出色的表现力,并逐步取代了GAN在文本到图像合成中的首选架构。然而,它们仍面临一些障碍:推理速度慢和训练成本高。为了实现更复杂场景下的更强大、更快的文本到图像合成,我们提出了TIGER,这是一种具有预训练表示的文本到图像GAN。具体来说,我们提出了一个视觉赋能判别器和一个高性能生成器。(一)视觉赋能判别器从预训练的视觉模型中吸收复杂场景理解能力和领域泛化能力,以增强模型性能。与以前的工作不同,我们在判别器中探索堆叠多个预训练模型,以收集多种不同的表示。(二)高性能生成器的目标是实现有效的文本图像融合,同时增加模型容量。高性能生成器由多个新型的高性能融合块(HFBlock)组成。HFBlock包含多个深度融合模块和一个全局融合模块,它们扮演着不同的角色来有益于我们的模型。大量实验表明,我们提出的TIGER在标准和零样本文本到图像合成任务上均表现出卓越的性能。在标准文本到图像合成任务上,TIGER在两个具有挑战性的数据集上达到了最新性能,获得了新的FID 5.48(COCO)和9.38(CUB)。在零样本文本到图像合成任务上,我们的性能相当,但使用了更少的模型参数、更小的训练数据集和更快的推理速度。此外,更多的实验和分析将在补充材料中进行。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于预训练表示的文本到图像生成模型TIGER,旨在实现更强大和更快的复杂场景下的文本到图像合成。通过引入视觉赋能判别器和高容量生成器,模型性能得以提升。在标准文本到图像合成任务和零样本任务上都表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
以下是对文章主要内容的概括和关键洞察:
1. 提出一种文本到图像生成模型TIGER,结合了预训练表示的优势。
2. 采用视觉赋能判别器,利用预训练视觉模型的复杂场景理解能力和领域泛化能力来提升模型性能。
3. 在判别器中探索堆叠多个预训练模型,以获取多种不同的表示。
4. 高容量生成器旨在实现有效的文本-图像融合,同时增加模型容量。
5. 高容量生成器包含多个新颖的高容量融合块(HFBlock),其中含有深度融合模块和全局融合模块,对模型有益。
6. 在标准文本到图像合成任务上,TIGER在两个具有挑战性的数据集上取得了最新技术性能。在零样本任务上取得了优异的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图