⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-06 更新
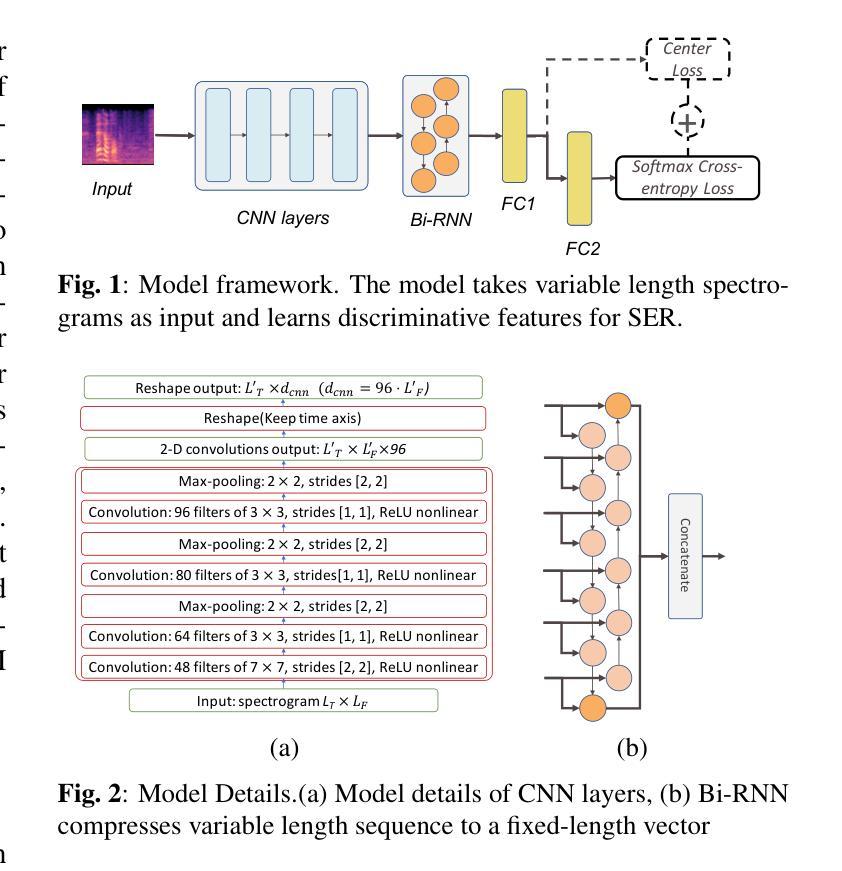
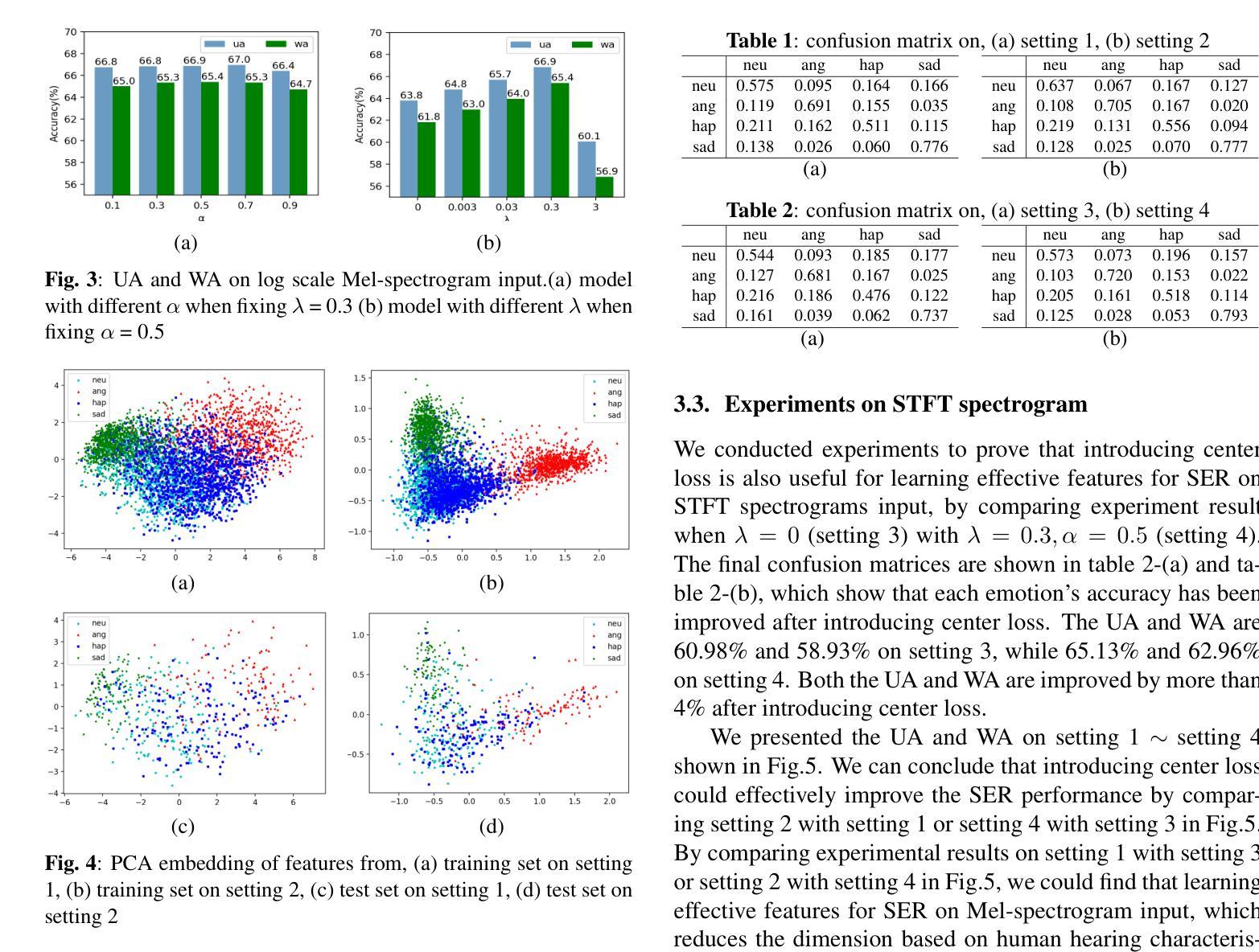
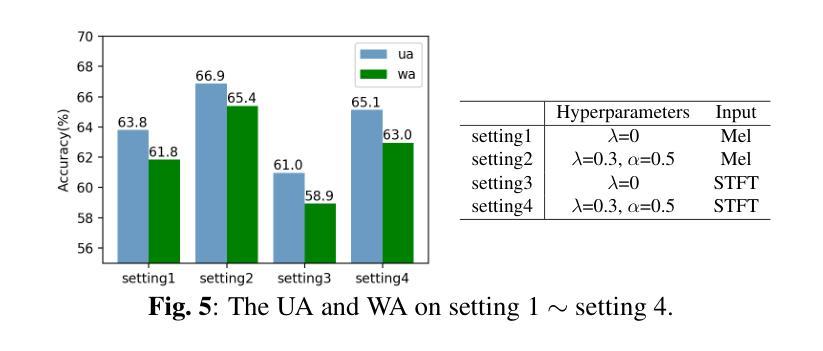
learning discriminative features from spectrograms using center loss for speech emotion recognition
Authors:Dongyang Dai, Zhiyong Wu, Runnan Li, Xixin Wu, Jia Jia, Helen Meng
Identifying the emotional state from speech is essential for the natural interaction of the machine with the speaker. However, extracting effective features for emotion recognition is difficult, as emotions are ambiguous. We propose a novel approach to learn discriminative features from variable length spectrograms for emotion recognition by cooperating softmax cross-entropy loss and center loss together. The softmax cross-entropy loss enables features from different emotion categories separable, and center loss efficiently pulls the features belonging to the same emotion category to their center. By combining the two losses together, the discriminative power will be highly enhanced, which leads to network learning more effective features for emotion recognition. As demonstrated by the experimental results, after introducing center loss, both the unweighted accuracy and weighted accuracy are improved by over 3% on Mel-spectrogram input, and more than 4% on Short Time Fourier Transform spectrogram input.
从语音中识别情感状态对于机器与说话人之间的自然交互至关重要。然而,由于情感具有模糊性,提取有效的情感识别特征是困难的。我们提出了一种通过合作softmax交叉熵损失和中心损失来从可变长度谱图中学习判别特征的新方法,以进行情感识别。softmax交叉熵损失使不同情感类别的特征可分离,而中心损失有效地将属于同一情感类别的特征拉向它们的中心。通过将这两种损失结合在一起,判别力将大大增强,这将导致网络学习更有效的情感识别特征。实验结果表明,在引入中心损失后,Mel光谱图输入的未加权准确率和加权准确率均提高了3%以上,短时傅里叶变换光谱图输入的准确率提高了4%以上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2019
Summary
本文提出一种结合softmax交叉熵损失和中心损失的方法,从可变长度谱图中学习情感识别判别特征。该方法能提高不同情感类别特征的分离度,并将同一情感类别的特征拉近其中心,从而提高判别能力。实验结果显示,引入中心损失后,Mel谱图输入的无权重准确率和加权准确率均提高了3%以上,短时傅里叶变换谱图输入提高了超过4%。
Key Takeaways
- 情感识别对于机器与人的自然交互至关重要。
- 提取有效的情感特征用于识别是困难的,因为情感具有模糊性。
- 提出了一种结合softmax交叉熵损失和中心损失的新方法,以提高情感识别的判别能力。
- softmax交叉熵损失使不同情感类别的特征可分离。
- 中心损失将同一情感类别的特征拉近其中心。
- 结合两种损失函数,增强了模型的判别能力。
点此查看论文截图

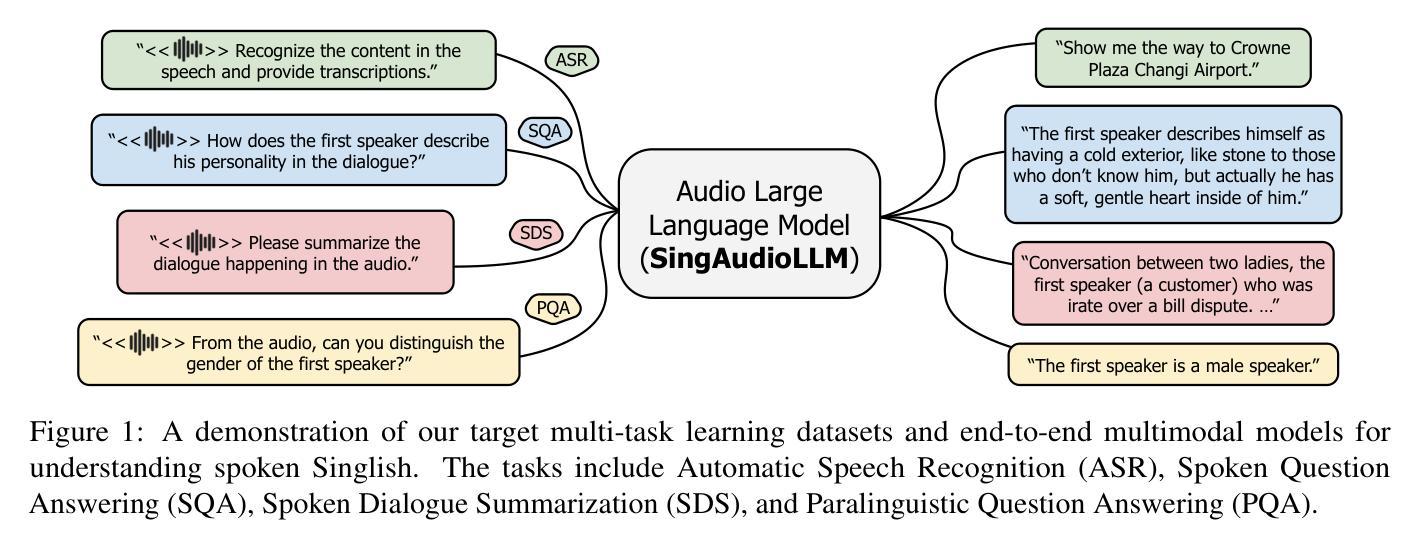
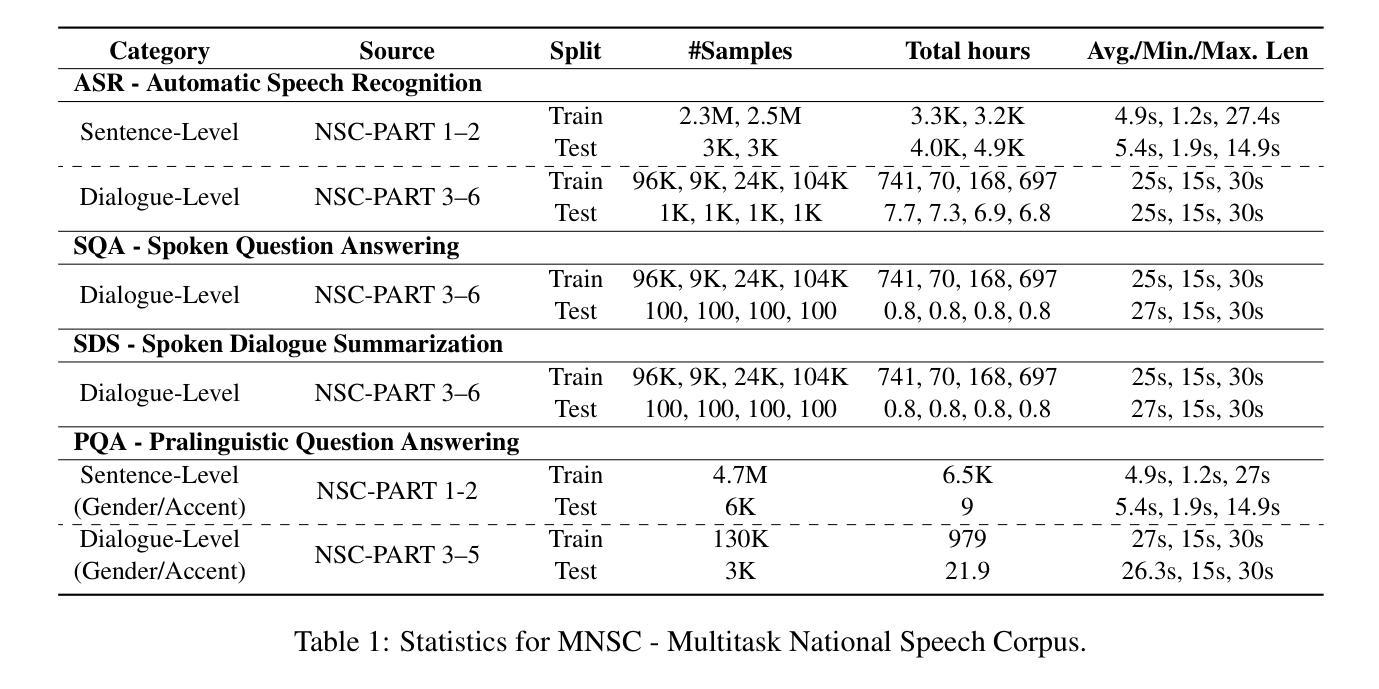
Advancing Singlish Understanding: Bridging the Gap with Datasets and Multimodal Models
Authors:Bin Wang, Xunlong Zou, Shuo Sun, Wenyu Zhang, Yingxu He, Zhuohan Liu, Chengwei Wei, Nancy F. Chen, AiTi Aw
Singlish, a Creole language rooted in English, is a key focus in linguistic research within multilingual and multicultural contexts. However, its spoken form remains underexplored, limiting insights into its linguistic structure and applications. To address this gap, we standardize and annotate the largest spoken Singlish corpus, introducing the Multitask National Speech Corpus (MNSC). These datasets support diverse tasks, including Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Spoken Question Answering (SQA), Spoken Dialogue Summarization (SDS), and Paralinguistic Question Answering (PQA). We release standardized splits and a human-verified test set to facilitate further research. Additionally, we propose SingAudioLLM, a multi-task multimodal model leveraging multimodal large language models to handle these tasks concurrently. Experiments reveal our models adaptability to Singlish context, achieving state-of-the-art performance and outperforming prior models by 10-30% in comparison with other AudioLLMs and cascaded solutions.
新加坡式英语是一种根植于英语的克里奥尔语言,在多语言和多元文化背景下,它是语言研究的一个重要焦点。然而,其口语形式仍被低估,对其语言结构和应用的了解有限。为了弥补这一空白,我们对最大的新加坡式英语口语语料库进行了标准化和注释,推出了多任务国家语音语料库(MNSC)。这些数据集支持多种任务,包括自动语音识别(ASR)、口语问答(SQA)、口语对话摘要(SDS)和副语言问答(PQA)。我们发布了标准化分割和人工验证的测试集,以促进进一步研究。此外,我们提出了SingAudioLLM,这是一个多任务多模式模型,利用多模式大型语言模型同时处理这些任务。实验表明,我们的模型能够适应新加坡式英语的语境,取得了最先进的性能表现,与其他音频LLM和级联解决方案相比,性能提高了10%-30%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Open-Source: https://github.com/AudioLLMs/Singlish
Summary
本文介绍了针对新加坡英语(Singlish)口语形式的研究不足问题,创建了多任务的全国语音语料库(MNSC),支持自动语音识别(ASR)、口语问答(SQA)、口语对话摘要(SDS)和副语言问答(PQA)等任务。此外,提出了多模态大语言模型SingAudioLLM,能同时处理这些任务,实验证明该模型适应新加坡语境,性能优于其他AudioLLMs和级联解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- Singlish作为英语的一种克里奥尔语,在多语言和文化背景下是语言研究的重要焦点。
- 现有的研究对Singlish口语形式探索不足,限制了对其语言结构和应用的理解。
- 创建了多任务的全国语音语料库(MNSC),以支持多种任务,包括自动语音识别(ASR)、口语问答(SQA)等。
- 发布了标准化的数据集分割和人工验证的测试集,以促进进一步研究。
- 提出了多模态大语言模型SingAudioLLM,能同时处理多个任务。
- 实验显示SingAudioLLM模型适应Singlish语境,性能优于其他模型。
点此查看论文截图

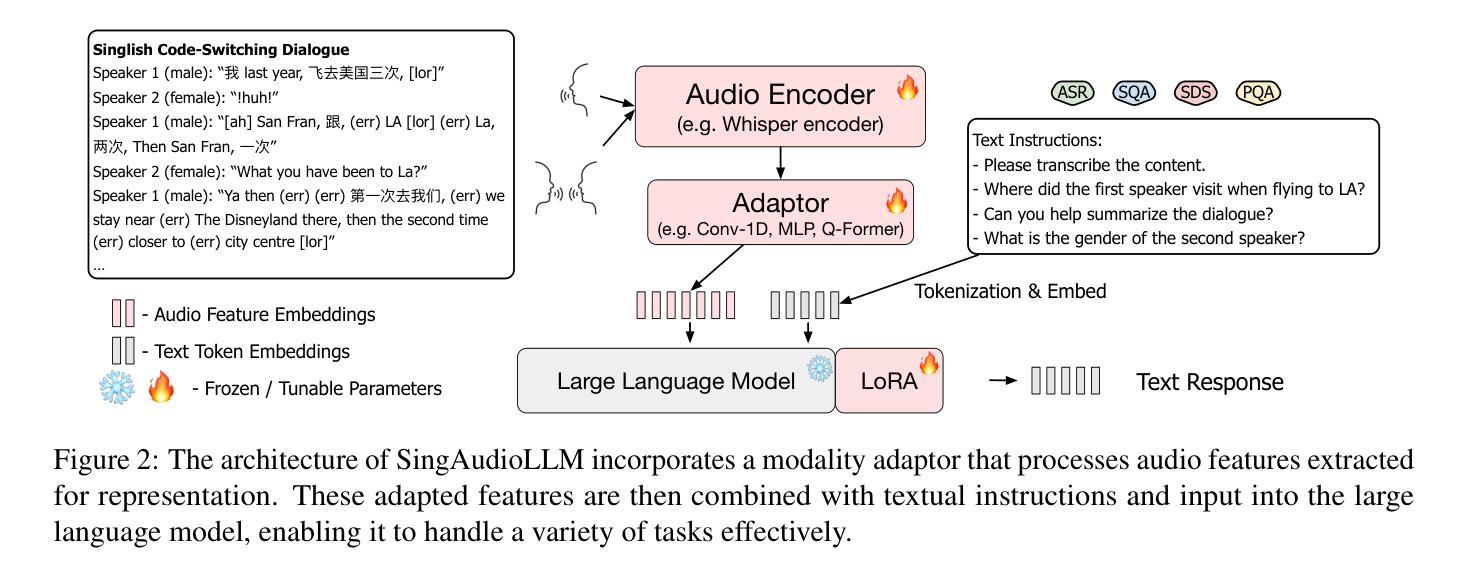
U-GIFT: Uncertainty-Guided Firewall for Toxic Speech in Few-Shot Scenario
Authors:Jiaxin Song, Xinyu Wang, Yihao Wang, Yifan Tang, Ru Zhang, Jianyi Liu, Gongshen Liu
With the widespread use of social media, user-generated content has surged on online platforms. When such content includes hateful, abusive, offensive, or cyberbullying behavior, it is classified as toxic speech, posing a significant threat to the online ecosystem’s integrity and safety. While manual content moderation is still prevalent, the overwhelming volume of content and the psychological strain on human moderators underscore the need for automated toxic speech detection. Previously proposed detection methods often rely on large annotated datasets; however, acquiring such datasets is both costly and challenging in practice. To address this issue, we propose an uncertainty-guided firewall for toxic speech in few-shot scenarios, U-GIFT, that utilizes self-training to enhance detection performance even when labeled data is limited. Specifically, U-GIFT combines active learning with Bayesian Neural Networks (BNNs) to automatically identify high-quality samples from unlabeled data, prioritizing the selection of pseudo-labels with higher confidence for training based on uncertainty estimates derived from model predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that U-GIFT significantly outperforms competitive baselines in few-shot detection scenarios. In the 5-shot setting, it achieves a 14.92% performance improvement over the basic model. Importantly, U-GIFT is user-friendly and adaptable to various pre-trained language models (PLMs). It also exhibits robust performance in scenarios with sample imbalance and cross-domain settings, while showcasing strong generalization across various language applications. We believe that U-GIFT provides an efficient solution for few-shot toxic speech detection, offering substantial support for automated content moderation in cyberspace, thereby acting as a firewall to promote advancements in cybersecurity.
随着社交媒体广泛使用,用户生成内容已在网上平台激增。当此类内容包含仇恨、侮辱、冒犯或网络欺凌行为时,它就被归类为有毒言论,对在线生态系统的完整性和安全构成重大威胁。虽然手动内容管理仍然普遍,但内容的大量涌现以及人类管理者承受的心理压力凸显了自动化有毒言论检测的需求。之前提出的检测方法往往依赖于大量标注数据集;然而,在实践中获取这样的数据集既昂贵又具有挑战性。为解决此问题,我们针对小样本场景下的有毒言论,提出了一个不确定性引导防火墙U-GIFT。它利用自我训练来提高检测性能,即使在标记数据有限的情况下也能发挥作用。具体来说,U-GIFT结合主动学习与贝叶斯神经网络(BNNs),从未标记数据中自动识别高质量样本,并根据模型预测产生的不确定性估计,优先选择和培训具有更高自信的伪标签样本。大量实验表明,在少量检测场景中,U-GIFT显著优于竞争基线。在5次射击的场景中,其性能比基本模型提高了14.92%。重要的是,U-GIFT友好且易于适应各种预训练语言模型(PLMs)。它在样本不平衡和跨域场景中表现出稳健的性能,并在各种语言应用中展现出强大的泛化能力。我们相信U-GIFT为小样有毒言论检测提供了有效的解决方案,为网络空间的自动化内容管理提供了强有力的支持,从而作为防火墙促进了网络安全的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 6 figures and 10 tables. Comments are welcome
摘要
社交媒体广泛普及导致用户生成内容大量涌现于网络平台。当中包含仇恨、滥用、冒犯或网络欺凌行为的言论被视为有毒言论,对在线生态系统的完整性和安全性构成严重威胁。虽然人工内容管理仍然普遍,但内容的巨大数量和人类管理者面临的压力突显了自动检测有毒言论的必要性。先前提出的检测方法往往依赖于大型注释数据集,但在实践中获取这些数据集既昂贵又具有挑战性。为解决这一问题,我们提出了用于低资源场景的有毒言论防火墙U-GIFT,它利用自我训练即使在标记数据有限的情况下也能提高检测性能。具体来说,U-GIFT结合了主动学习与贝叶斯神经网络(BNNs),自动从未标记的数据中识别高质量样本,并根据模型预测得出的不确定性估计,优先筛选具有较高置信度的伪标签用于训练。大量实验表明,在小型检测场景中,U-GIFT显著优于其他基线模型。在5次射击的场景下,它的性能比基本模型提高了14.92%。重要的是,U-GIFT易于用户使用且适应多种预训练语言模型(PLMs)。在样本不均衡和跨域设置中,它表现出稳健的性能,并在各种语言应用中展现出强大的泛化能力。我们相信U-GIFT为低资源有毒言论检测提供了有效的解决方案,为网络安全中的自动内容管理提供了坚实的支持。
要点总结
- 随着社交媒体的普及,用户生成内容中包含的有毒言论对在线生态系统构成威胁。
- 传统检测方法依赖大量标注数据,但获取成本高昂且挑战重重。
- U-GIFT结合了主动学习与贝叶斯神经网络,有效应对低资源场景下的有毒言论检测。
- U-GIFT在少量样本情况下性能卓越,相较于基础模型有显著提升。
- U-GIFT适应多种预训练语言模型,表现出稳健的跨域和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

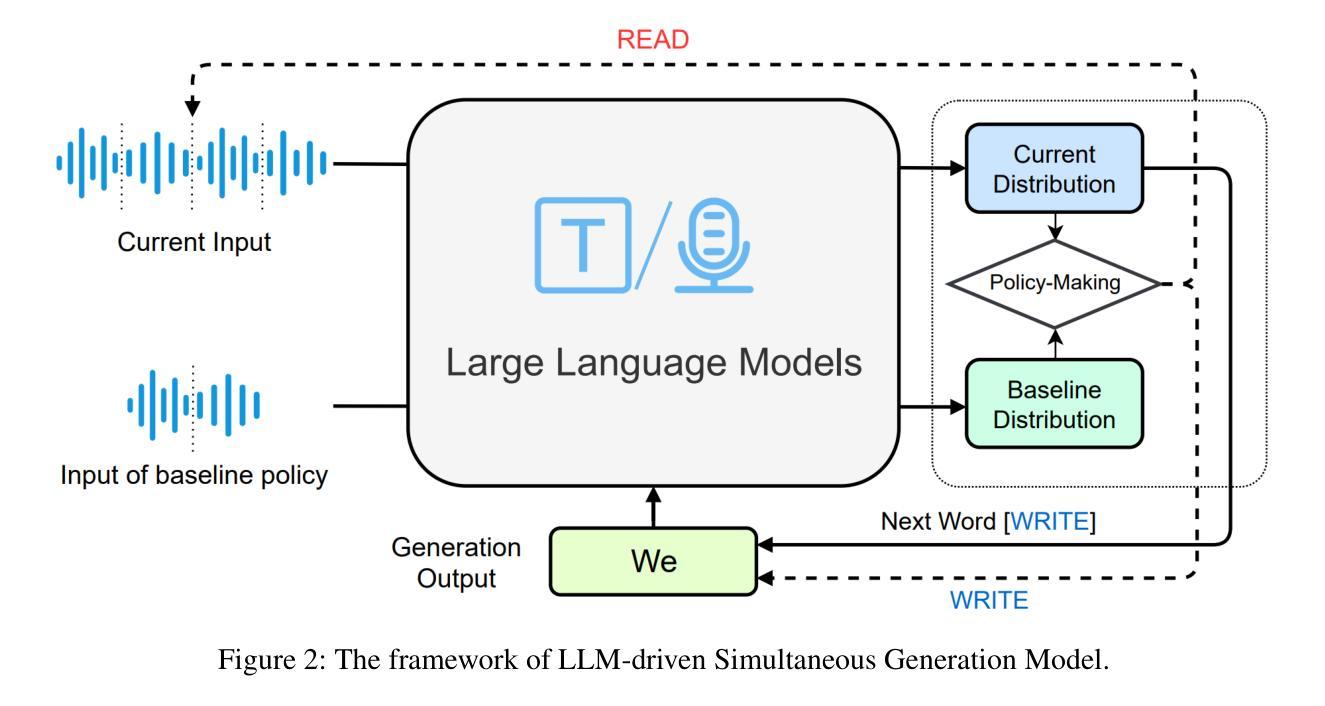
Large Language Models Are Read/Write Policy-Makers for Simultaneous Generation
Authors:Shoutao Guo, Shaolei Zhang, Zhengrui Ma, Yang Feng
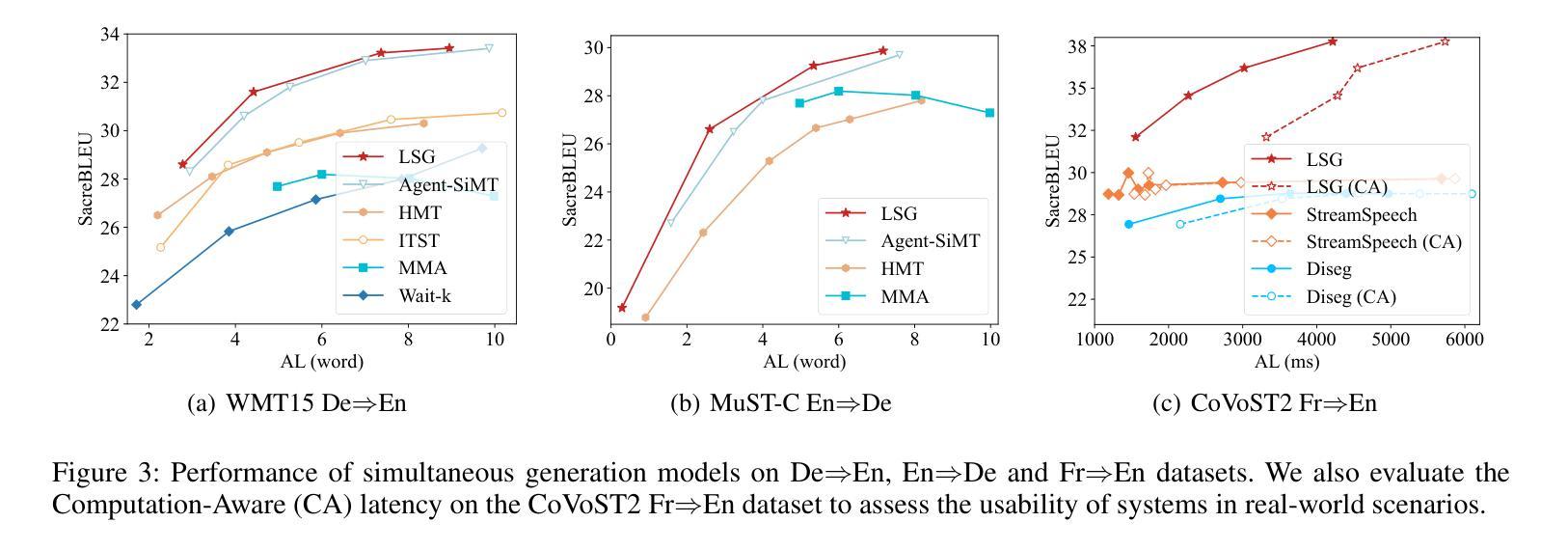
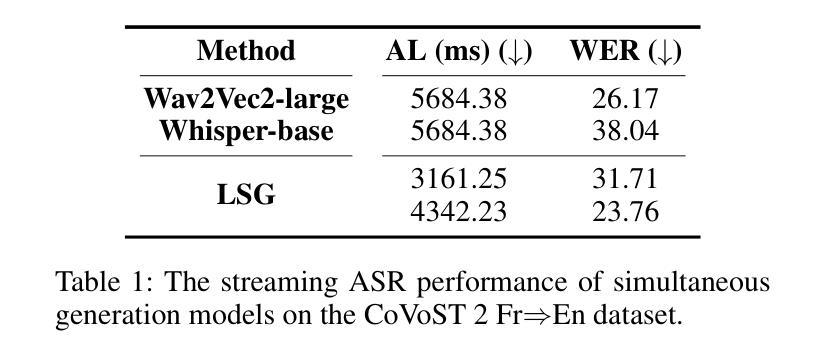
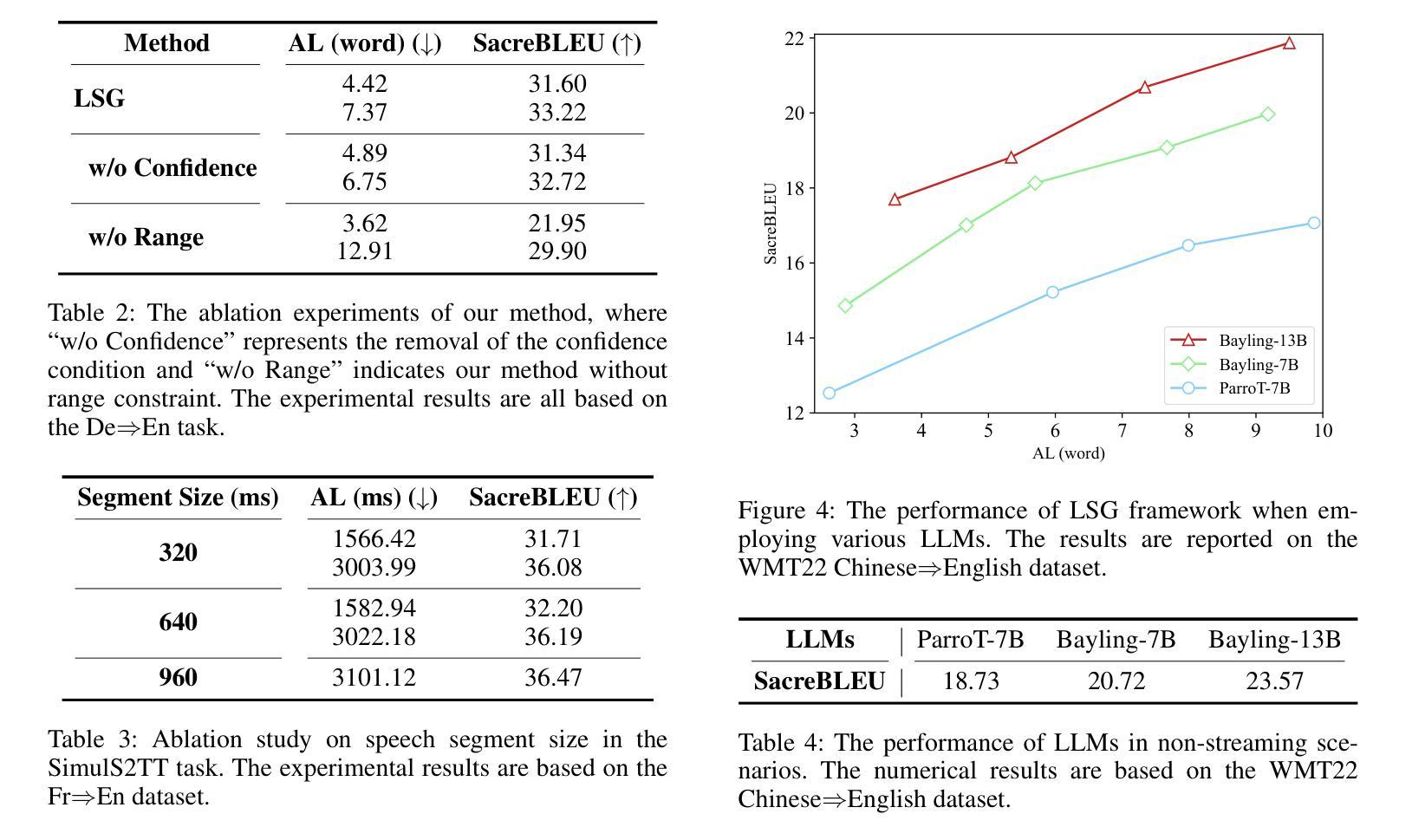
Simultaneous generation models write generation results while reading streaming inputs, necessitating a policy-maker to determine the appropriate output timing. Existing simultaneous generation methods generally adopt the traditional encoder-decoder architecture and learn the generation and policy-making capabilities through complex dynamic programming techniques. Although LLMs excel at text generation, they face challenges in taking on the role of policy-makers through traditional training methods, limiting their exploration in simultaneous generation. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel LLM-driven Simultaneous Generation (LSG) framework, which allows the off-the-shelf LLM to decide the generation timing and produce output concurrently. Specifically, LSG selects the generation policy that minimizes latency as the baseline policy. Referring to the baseline policy, LSG enables the LLM to devise an improved generation policy that better balances latency and generation quality, and writes generation results accordingly. Experiments on simultaneous translation and streaming automatic speech recognition tasks show that our method can achieve state-of-the-art performance utilizing the open-source LLMs and demonstrate practicality in real-world scenarios.
同时生成模型在阅读流式输入时生成结果,这需要决策者来确定适当的输出时间。现有的同时生成方法通常采用传统的编码器-解码器架构,通过复杂的动态编程技术来学习生成和决策能力。尽管大型语言模型在文本生成方面表现出色,但它们通过传统训练方法担任决策者的角色时面临挑战,限制了它们在同时生成方面的探索。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种新型的大型语言模型驱动的同时生成(LSG)框架,该框架允许现成的大型语言模型自行决定生成时间并同时产生输出。具体来说,LSG选择以最小化延迟为基准的生成策略作为基准策略。参照基准策略,LSG使大型语言模型能够制定改进的生成策略,更好地平衡延迟和生成质量,并据此编写生成结果。针对同声传译和流式语音识别任务的实验表明,我们的方法可以利用开源的大型语言模型实现最新技术性能,并在实际场景中展示实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAAI 2025. 13 pages, 7 tables, 10 figures
Summary
基于流式输入的实时生成模型需要在阅读过程中即时输出生成结果,这需要决策者确定适当的输出时间。传统的同时生成方法通常采用编码器-解码器架构,通过复杂的动态规划技术学习生成和决策能力。大型语言模型(LLM)虽擅长文本生成,但难以通过传统训练方式承担决策角色,限制了其在实时生成领域的应用。为克服这些限制,我们提出了新型LLM驱动的同时生成(LSG)框架,允许即插即用的LLM决定生成时间并实现实时输出。LSG选择最小化延迟的生成策略作为基准策略,并据此使LLM制定改进生成策略,更好地平衡延迟和生成质量。在同时翻译和流式语音识别任务上的实验表明,利用开源LLM的方法能达到业界最佳性能并在实际场景中展现实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 同时生成模型需要确定适当的输出时间,以处理流式输入并即时生成结果。
- 传统的同时生成方法依赖于编码器-解码器架构和复杂的动态规划技术。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在文本生成方面表现出色,但在承担决策角色时面临挑战。
- 提出的LLM驱动的同时生成(LSG)框架允许LLM决定生成时间并实现实时输出。
- LSG通过选择最小化延迟的生成策略作为基准,并在此基础上改进策略,以平衡延迟和生成质量。
- LSG框架利用开源LLM实现业界最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

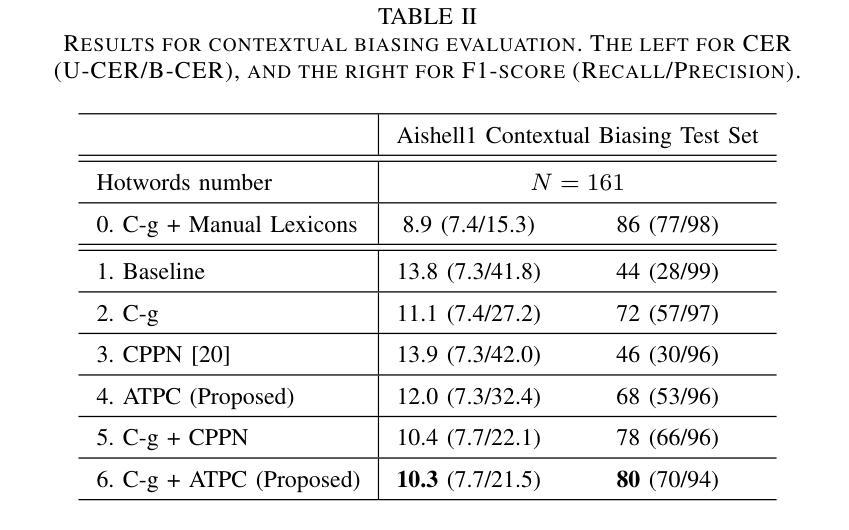
Automatic Text Pronunciation Correlation Generation and Application for Contextual Biasing
Authors:Gaofeng Cheng, Haitian Lu, Chengxu Yang, Xuyang Wang, Ta Li, Yonghong Yan
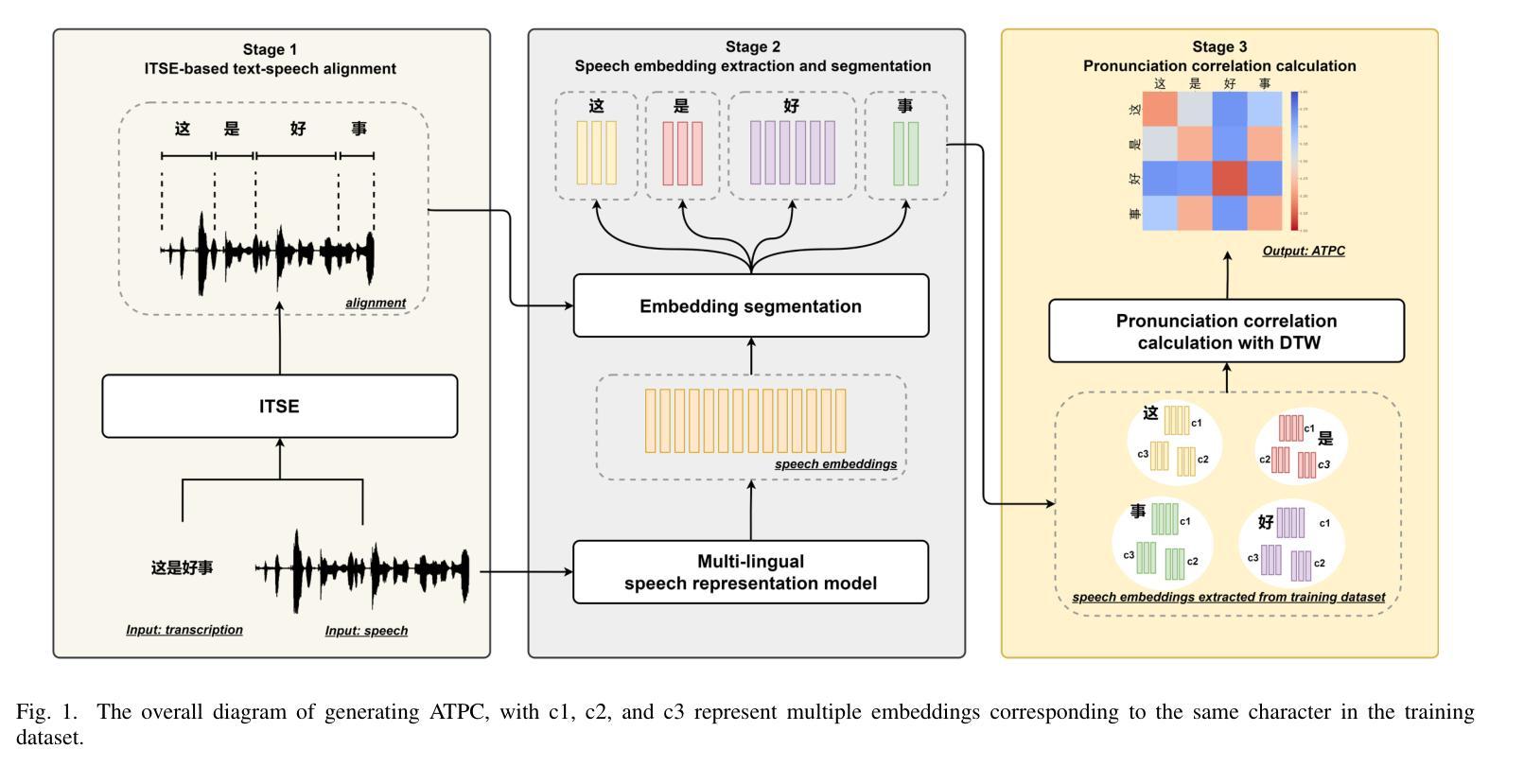
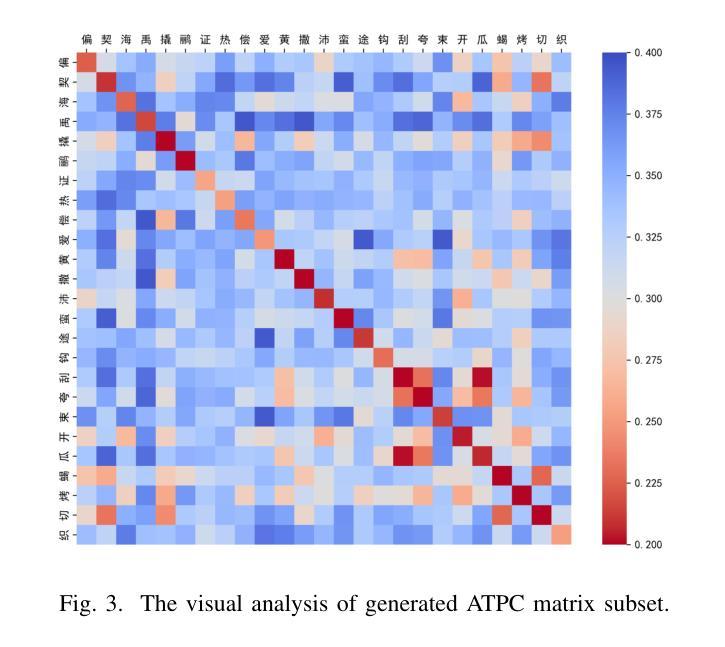
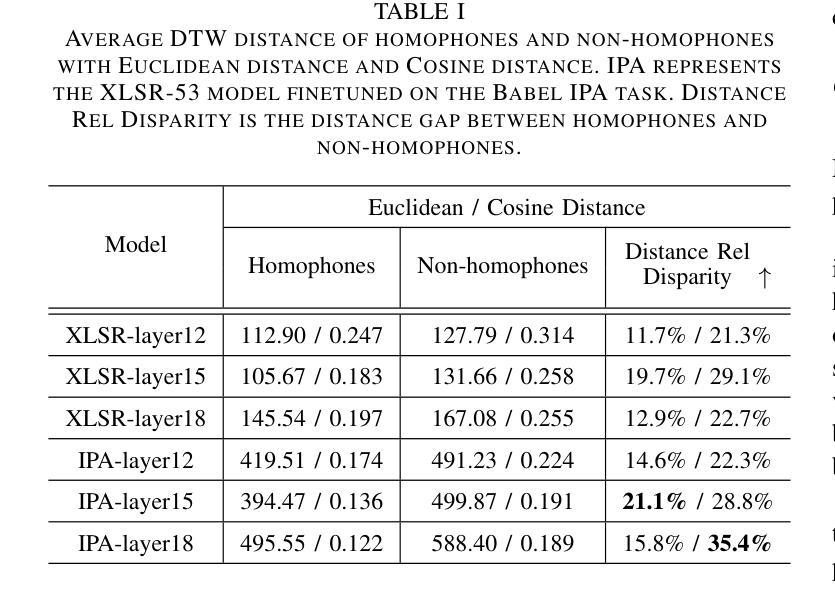
Effectively distinguishing the pronunciation correlations between different written texts is a significant issue in linguistic acoustics. Traditionally, such pronunciation correlations are obtained through manually designed pronunciation lexicons. In this paper, we propose a data-driven method to automatically acquire these pronunciation correlations, called automatic text pronunciation correlation (ATPC). The supervision required for this method is consistent with the supervision needed for training end-to-end automatic speech recognition (E2E-ASR) systems, i.e., speech and corresponding text annotations. First, the iteratively-trained timestamp estimator (ITSE) algorithm is employed to align the speech with their corresponding annotated text symbols. Then, a speech encoder is used to convert the speech into speech embeddings. Finally, we compare the speech embeddings distances of different text symbols to obtain ATPC. Experimental results on Mandarin show that ATPC enhances E2E-ASR performance in contextual biasing and holds promise for dialects or languages lacking artificial pronunciation lexicons.
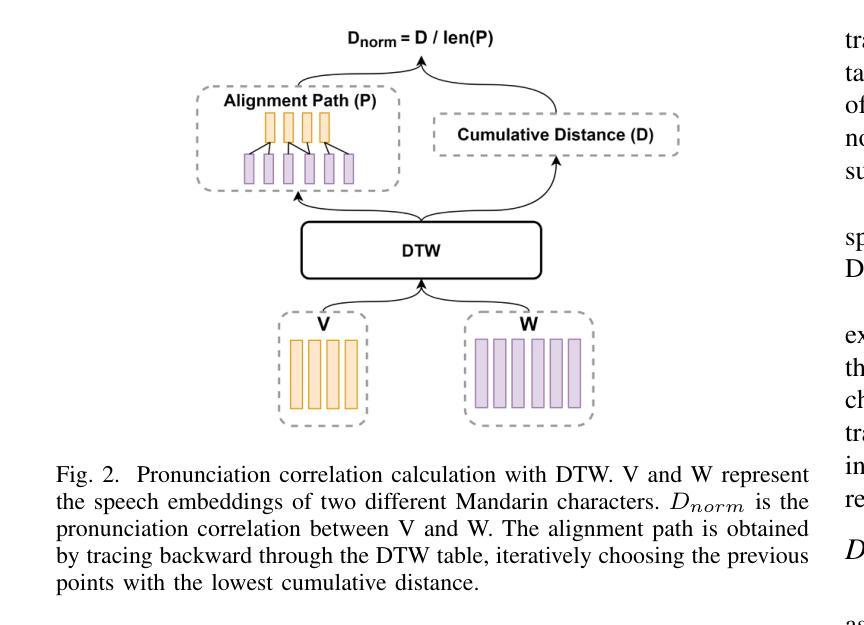
在语言声学领域,有效地区分不同书面文本之间的发音关联是一个重要问题。传统上,这种发音关联是通过人工设计的发音词典获得的。在本文中,我们提出了一种数据驱动的方法,自动获取这些发音关联,称为自动文本发音关联(ATPC)。该方法所需的监督与训练端到端自动语音识别(E2E-ASR)系统所需的监督一致,即语音和相应的文本注释。首先,采用迭代训练的时间戳估计(ITSE)算法将语音与相应的注释文本符号对齐。然后,使用语音编码器将语音转换为语音嵌入。最后,我们比较不同文本符号的语音嵌入距离,以获得ATPC。在普通话上的实验结果表明,ATPC提高了E2E-ASR在上下文偏向方面的性能,并有望应用于缺乏人工发音词典的方言或语言。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
摘要
本研究提出一种数据驱动方法——自动文本发音关联(ATPC),以自动获取不同文本间的发音关联,解决了传统手动设计发音词典的问题。该方法采用与端到端自动语音识别(E2E-ASR)系统训练相同的监督方式,即语音和对应文本的注释,用于获取一致的发音。通过使用迭代训练的timestamp估算器算法,实现语音与对应文本符号的对齐。随后使用语音编码器将语音转换为语音嵌入,通过比较不同文本符号的语音嵌入距离获得ATPC。在普通话上的实验结果表明,ATPC能提高E2E-ASR在语境偏向方面的性能,并对缺乏人工发音词典的方言或语言具有应用前景。
要点归纳
- 自动文本发音关联(ATPC)方法提出,用于数据驱动地获取不同文本的发音关联。
- 采用与端到端自动语音识别(E2E-ASR)系统相同的监督方式来获取发音关联的一致性。
- 利用迭代训练的timestamp估算器算法实现语音与对应文本符号的精准对齐。
- 使用语音编码器将语音转换为语音嵌入。
- 通过比较不同文本符号的语音嵌入距离来获取发音关联。
- 在普通话的实验中,ATPC能提高E2E-ASR系统的语境偏向性能。
- ATPC方法对缺乏人工发音词典的方言或语言具有应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

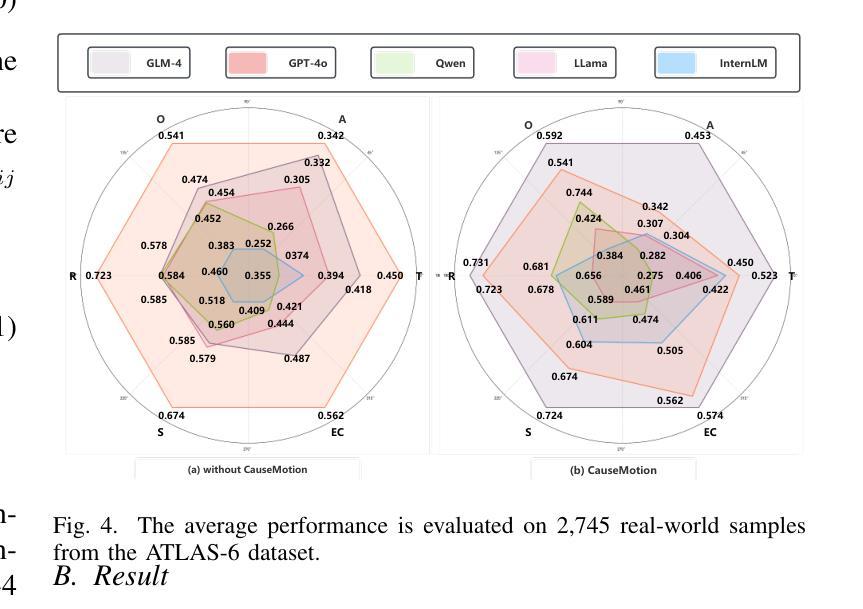
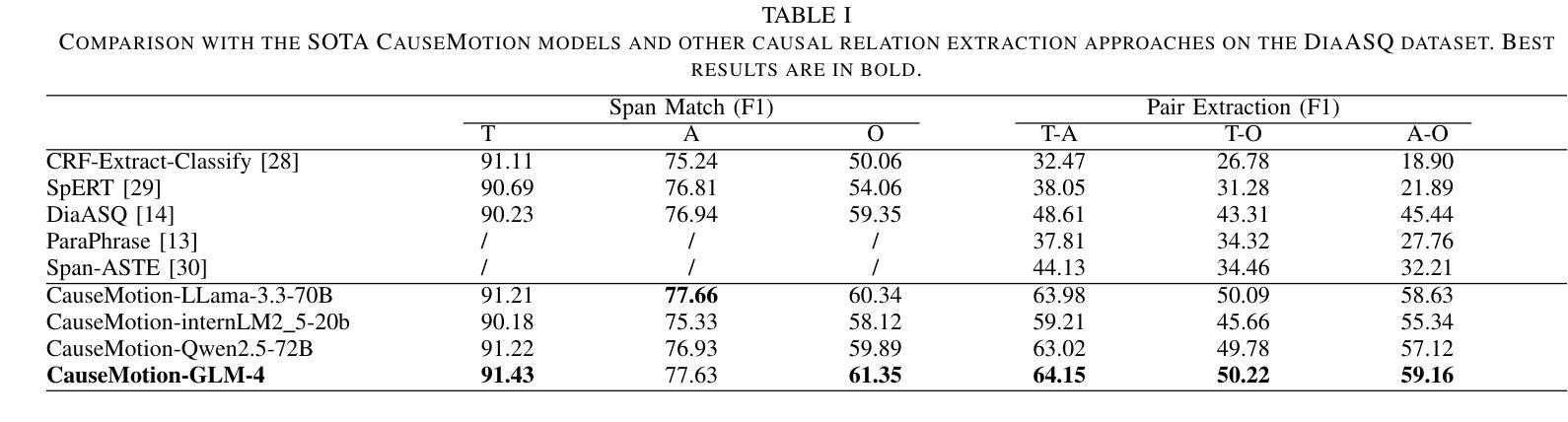
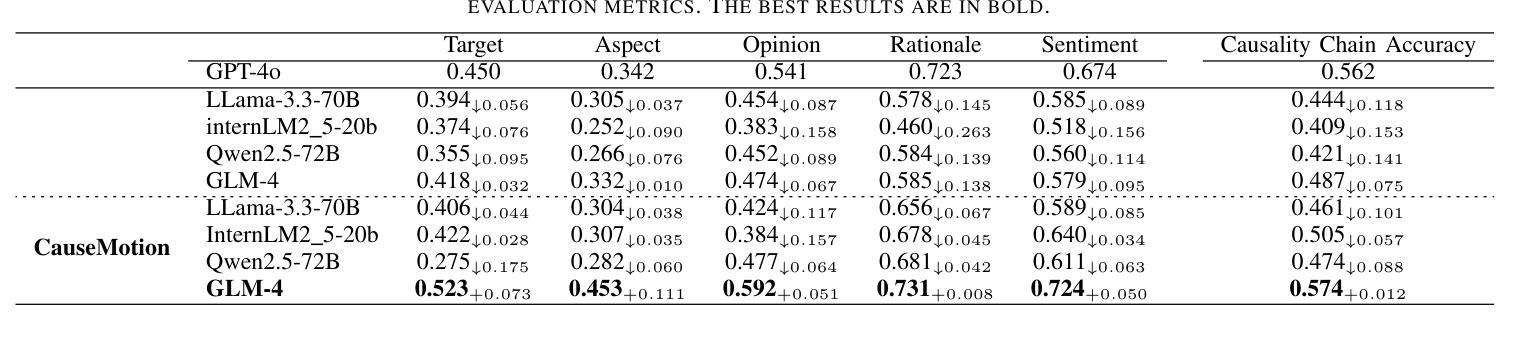
Decoding the Flow: CauseMotion for Emotional Causality Analysis in Long-form Conversations
Authors:Yuxuan Zhang, Yulong Li, Zichen Yu, Feilong Tang, Zhixiang Lu, Chong Li, Kang Dang, Jionglong Su
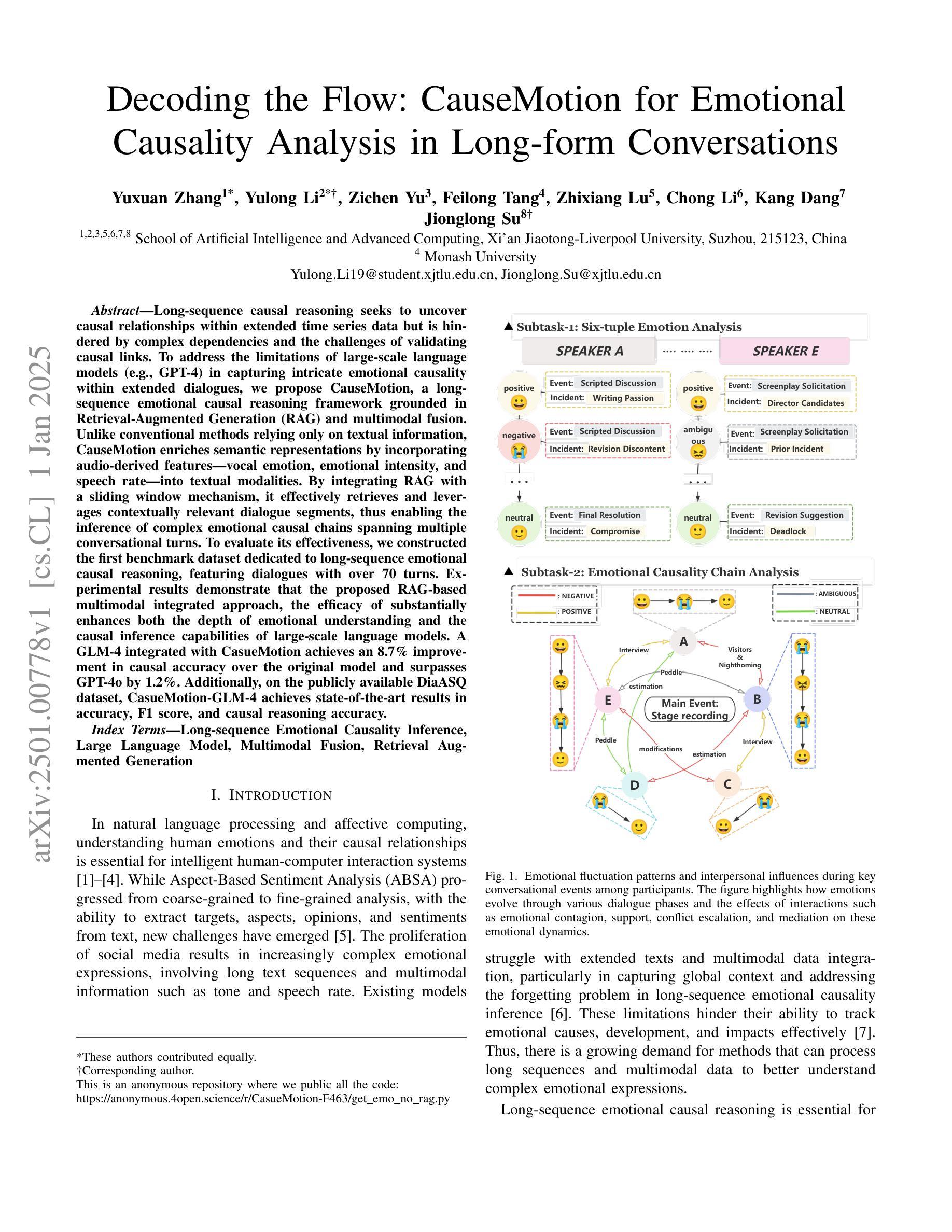
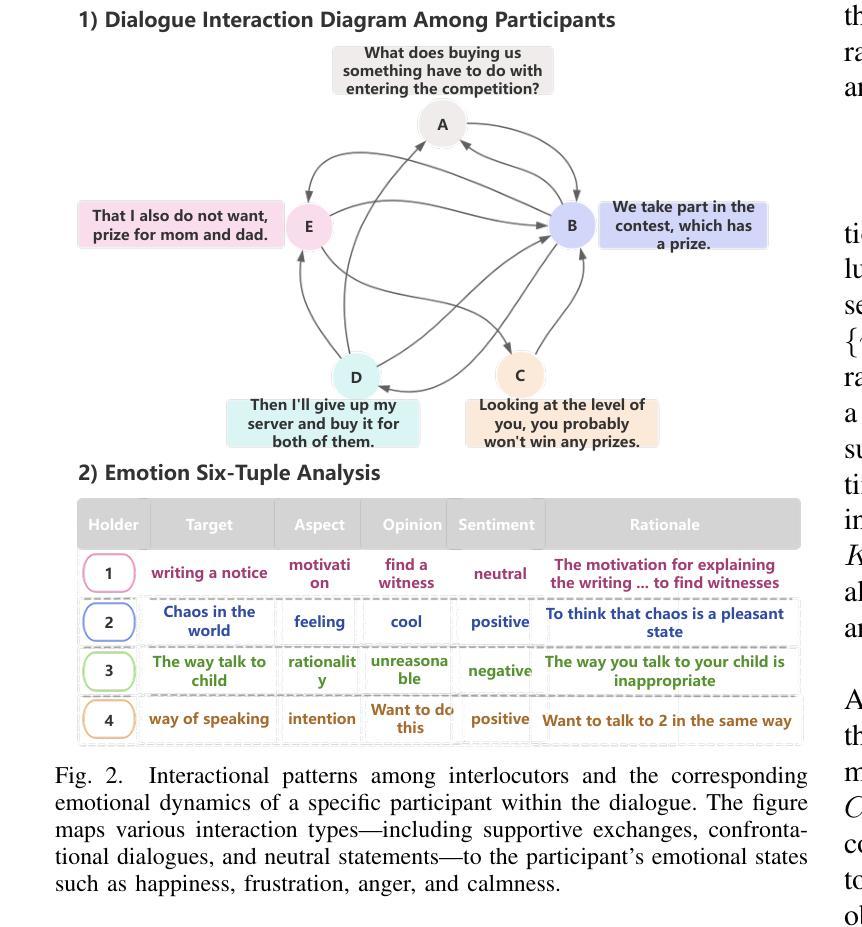
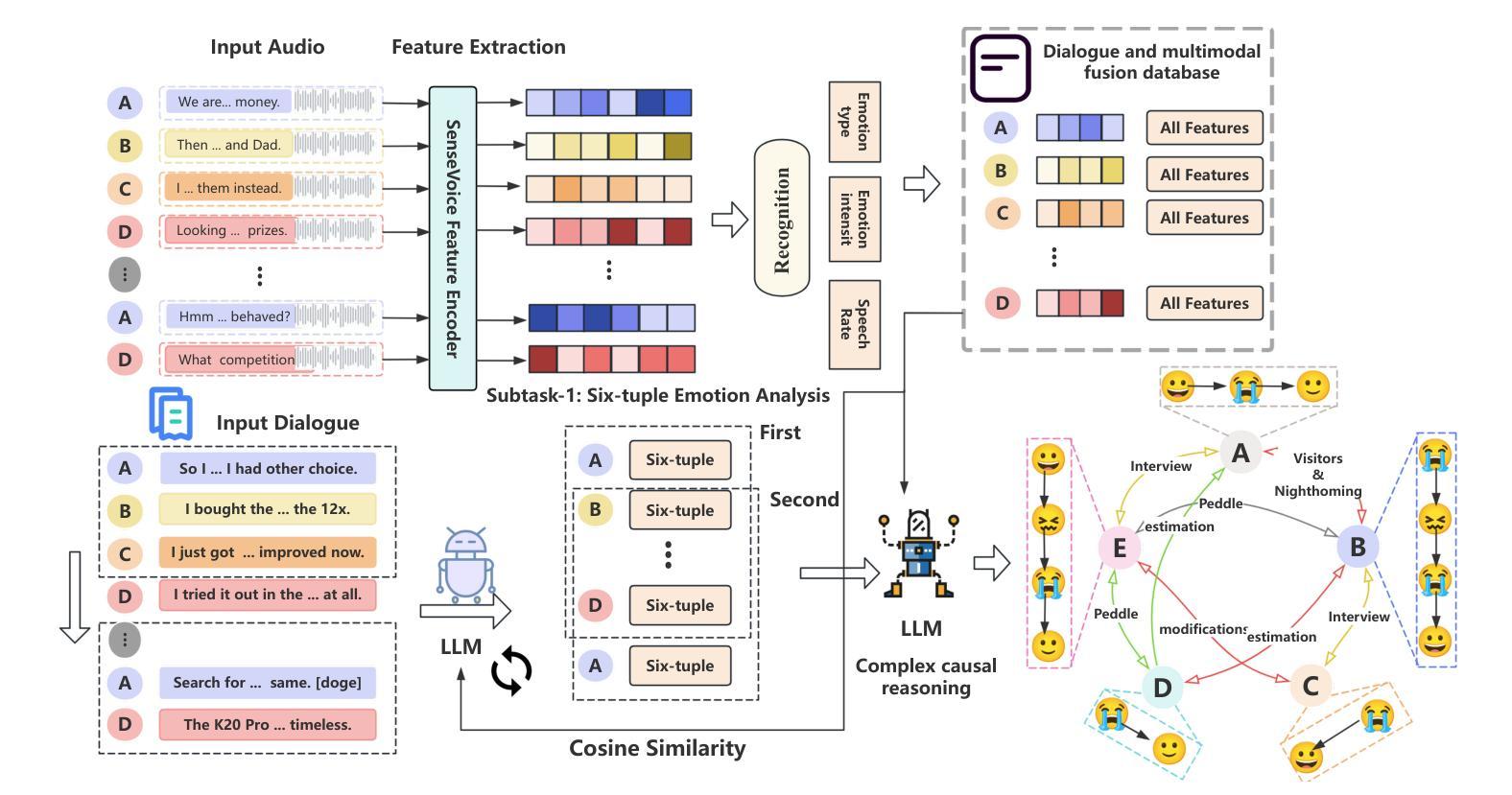
Long-sequence causal reasoning seeks to uncover causal relationships within extended time series data but is hindered by complex dependencies and the challenges of validating causal links. To address the limitations of large-scale language models (e.g., GPT-4) in capturing intricate emotional causality within extended dialogues, we propose CauseMotion, a long-sequence emotional causal reasoning framework grounded in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and multimodal fusion. Unlike conventional methods relying only on textual information, CauseMotion enriches semantic representations by incorporating audio-derived features-vocal emotion, emotional intensity, and speech rate-into textual modalities. By integrating RAG with a sliding window mechanism, it effectively retrieves and leverages contextually relevant dialogue segments, thus enabling the inference of complex emotional causal chains spanning multiple conversational turns. To evaluate its effectiveness, we constructed the first benchmark dataset dedicated to long-sequence emotional causal reasoning, featuring dialogues with over 70 turns. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed RAG-based multimodal integrated approach, the efficacy of substantially enhances both the depth of emotional understanding and the causal inference capabilities of large-scale language models. A GLM-4 integrated with CauseMotion achieves an 8.7% improvement in causal accuracy over the original model and surpasses GPT-4o by 1.2%. Additionally, on the publicly available DiaASQ dataset, CauseMotion-GLM-4 achieves state-of-the-art results in accuracy, F1 score, and causal reasoning accuracy.
长序列因果推理旨在揭示扩展时间序列数据中的因果关系,但由于复杂的依赖关系和验证因果联系所面临的挑战而受到阻碍。为了解决大规模语言模型(如GPT-4)在捕捉扩展对话中复杂情绪因果关系方面的局限性,我们提出了CauseMotion,这是一个基于检索增强生成(RAG)和多模态融合的长序列情绪因果推理框架。不同于仅依赖文本信息的传统方法,CauseMotion通过融入音频衍生特征(如语音情绪、情绪强度和语速)来丰富语义表示,丰富文本模式。通过结合RAG和滑动窗口机制,它能够有效地检索和利用语境相关的对话片段,从而推断跨越多个对话回合的复杂情绪因果链。为了评估其有效性,我们构建了首个专注于长序列情绪因果推理的基准数据集,包含超过70回合的对话。实验结果表明,所提出的基于RAG的多模态集成方法大大提高了大规模语言模型对情绪的理解和因果推理能力。与原始模型相比,集成了CauseMotion的GLM-4在因果准确性方面提高了8.7%,并超越了GPT-4o 1.2%。此外,在公开的DiaASQ数据集上,CauseMotion-GLM-4在准确性、F1分数和因果推理准确性方面达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7pages
Summary
本文介绍了针对长序列因果推理中的情感因果关系的挑战,提出了CauseMotion框架。该框架结合了检索增强生成(RAG)和多模态融合技术,将音频衍生特征(如语音情感、情感强度和语速)融入文本模态,以丰富语义表示。通过RAG与滑动窗口机制的集成,CauseMotion能有效检索和利用相关的对话片段,从而推断跨越多个对话回合的复杂情感因果关系链。实验结果表明,该框架显著提高了大型语言模型对情感理解和因果推理的能力。
Key Takeaways
- CauseMotion框架旨在解决长序列因果推理中的情感因果关系问题,结合了检索增强生成(RAG)和多模态融合技术。
- 该框架将音频衍生特征(如语音情感、情感强度和语速)融入文本模态,以丰富语义表示。
- 通过RAG与滑动窗口机制的集成,CauseMotion能有效处理复杂的情感因果关系链,并推断跨多个对话回合的因果关系。
- 构建了专门用于长序列情感因果推理的基准数据集,包含超过70轮对话。
- 实验结果表明,CauseMotion框架显著提高大型语言模型的情感理解和因果推理能力。
- 与原始模型相比,集成了CauseMotion的GLM-4在因果准确性方面提高了8.7%,并在DiaASQ数据集上实现了最先进的准确性、F1分数和因果推理准确性。
点此查看论文截图
Whisper Turns Stronger: Augmenting Wav2Vec 2.0 for Superior ASR in Low-Resource Languages
Authors:Or Haim Anidjar, Revital Marbel, Roi Yozevitch
Approaching Speech-to-Text and Automatic Speech Recognition problems in low-resource languages is notoriously challenging due to the scarcity of validated datasets and the diversity of dialects. Arabic, Russian, and Portuguese exemplify these difficulties, being low-resource languages due to the many dialects of these languages across different continents worldwide. Moreover, the variety of accents and pronunciations of such languages complicate ASR models’ success. With the increasing popularity of Deep Learning and Transformers, acoustic models like the renowned Wav2Vec2 have achieved superior performance in the Speech Recognition field compared to state-of-the-art approaches. However, despite Wav2Vec2’s improved efficiency over traditional methods, its performance significantly declines for under-represented languages, even though it requires significantly less labeled data. This paper introduces an end-to-end framework that enhances ASR systems fine-tuned on Wav2Vec2 through data augmentation techniques. To validate our framework’s effectiveness, we conducted a detailed experimental evaluation using three datasets from Mozilla’s Common Voice project in Arabic, Russian, and Portuguese. Additionally, the framework presented in this paper demonstrates robustness to different diacritics. Ultimately, our approach outperforms two previous baseline models, which are the pre-trained Wav2Vec2 and the well-known Whisper ASR model, resulting in an average relative improvement of 33.9% in Word Error Rate and a 53.2% relative improvement in Character Error Rate.
针对低资源语言中的语音到文本和自动语音识别问题,由于缺乏验证过的数据集和方言多样性,解决起来极为具有挑战性。阿拉伯语、俄语和葡萄牙语就是这些困难的例证,这些语言在世界各地的大陆上都有许多方言,因此是低资源语言。此外,这些语言的发音和语调变化使得ASR模型的成功变得复杂。随着深度学习和Transformer的日益普及,如著名的Wav2Vec2等声学模型在语音识别领域取得了相比最新技术方法的卓越表现。然而,尽管Wav2Vec2相较于传统方法在效率上有所提升,但对于代表性不足的语言,其表现却大幅下降,尽管它需要的标注数据要少得多。本文介绍了一个端到端的框架,该框架通过数据增强技术改进了基于Wav2Vec2的ASR系统。为了验证我们框架的有效性,我们使用Mozilla的Common Voice项目中的阿拉伯语、俄语和葡萄牙语的三个数据集进行了详细的实验评估。此外,本文介绍的框架显示出对不同音标的稳健性。最终,我们的方法超越了先前的两个基准模型,即预训练的Wav2Vec2和著名的Whisper ASR模型,在单词错误率方面实现了平均相对改进33.9%,在字符错误率方面实现了相对改进53.2%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pagesm 3 figures
摘要
针对低资源语言(如阿拉伯语、俄语和葡萄牙语)的语音识别和文字识别问题具有诸多挑战,原因在于缺乏验证过的数据集以及方言多样性。虽然深度学习(如著名的Wav2Vec2模型)在语音识别领域取得了显著进展,但对于代表性不足的语种来说,其性能依然有所受限。本文提出一种端到端的框架,利用数据增强技术提升Wav2Vec2微调后的语音识别系统性能。通过Mozilla的Common Voice项目中的阿拉伯语、俄语和葡萄牙语的三个数据集进行详尽的实验评估,验证了框架的有效性。此外,该框架对不同语种的书写变体展现出稳健性,最终超越了Wav2Vec2预训练模型和著名的Whisper语音识别模型,在单词错误率上平均相对提高了33.9%,字符错误率上提高了53.2%。
关键见解
- 低资源语言在语音转文字与自动语音识别方面面临诸多挑战,主要由于缺乏验证过的数据集和方言多样性。
- Wav2Vec2模型虽在语音识别领域取得显著进步,但在低资源语种中表现仍有限制。
- 本研究引入一种端到端的框架,通过数据增强技术提升ASR系统性能。
- 框架在Mozilla的Common Voice项目的阿拉伯语、俄语和葡萄牙语数据集上进行了实验验证。
- 框架对不同语种的书写变体表现出稳健性。
- 对比实验显示,该框架在单词错误率和字符错误率上显著超越了基线模型Wav2Vec2和Whisper模型。
- 该研究为低资源语言的语音识别提供了有效的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

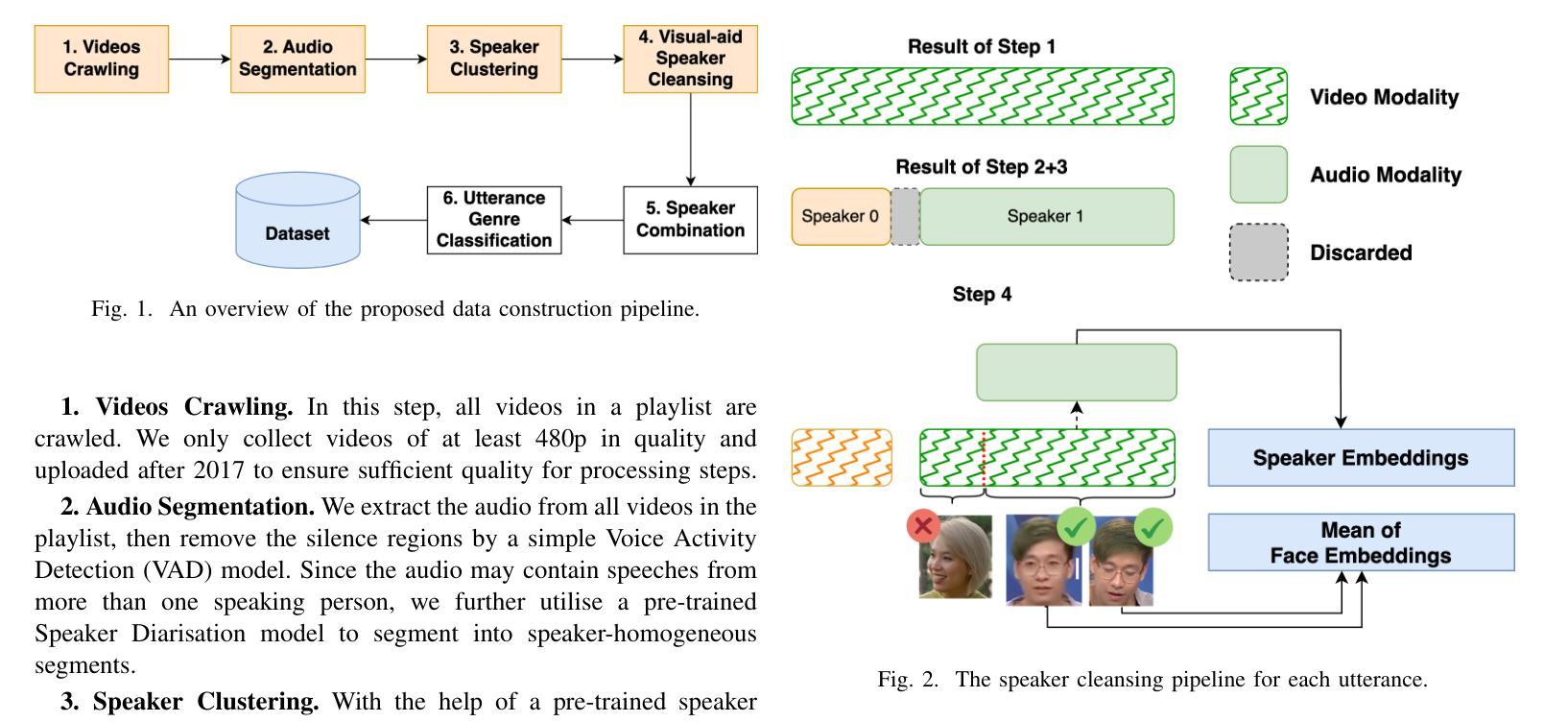
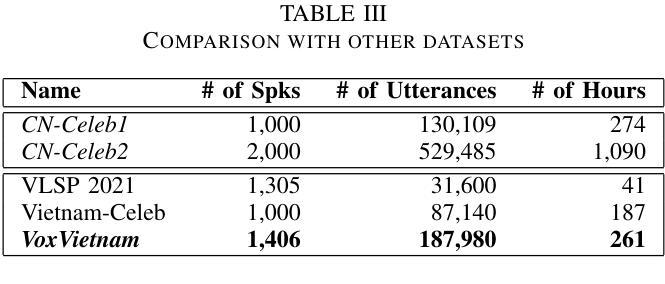
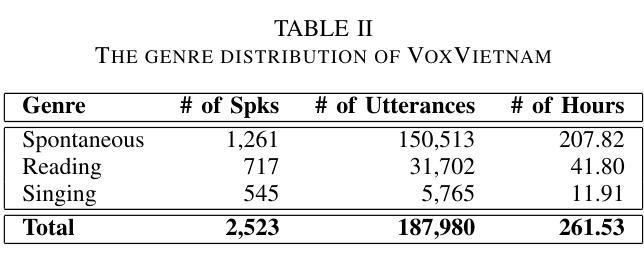
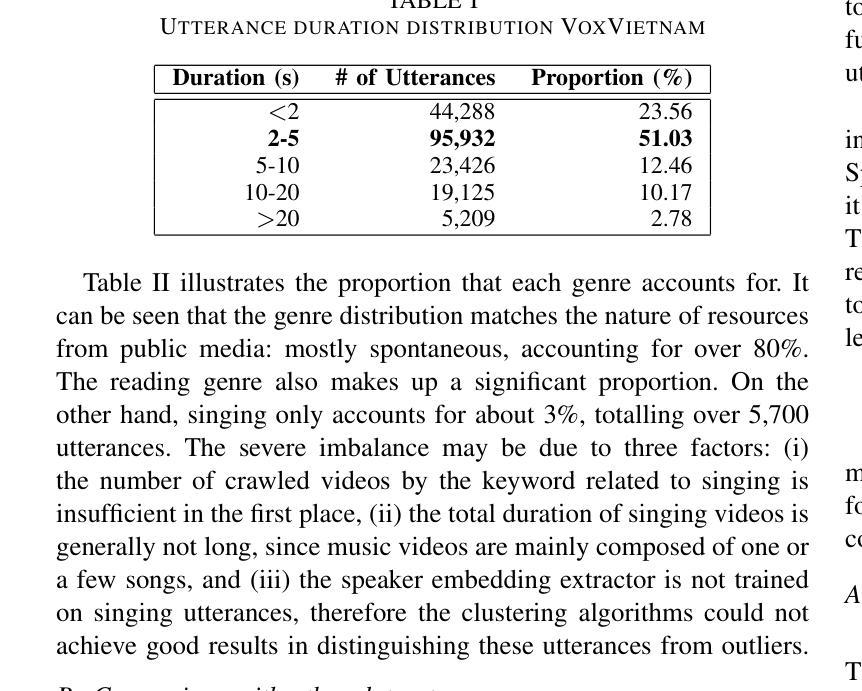
VoxVietnam: a Large-Scale Multi-Genre Dataset for Vietnamese Speaker Recognition
Authors:Hoang Long Vu, Phuong Tuan Dat, Pham Thao Nhi, Nguyen Song Hao, Nguyen Thi Thu Trang
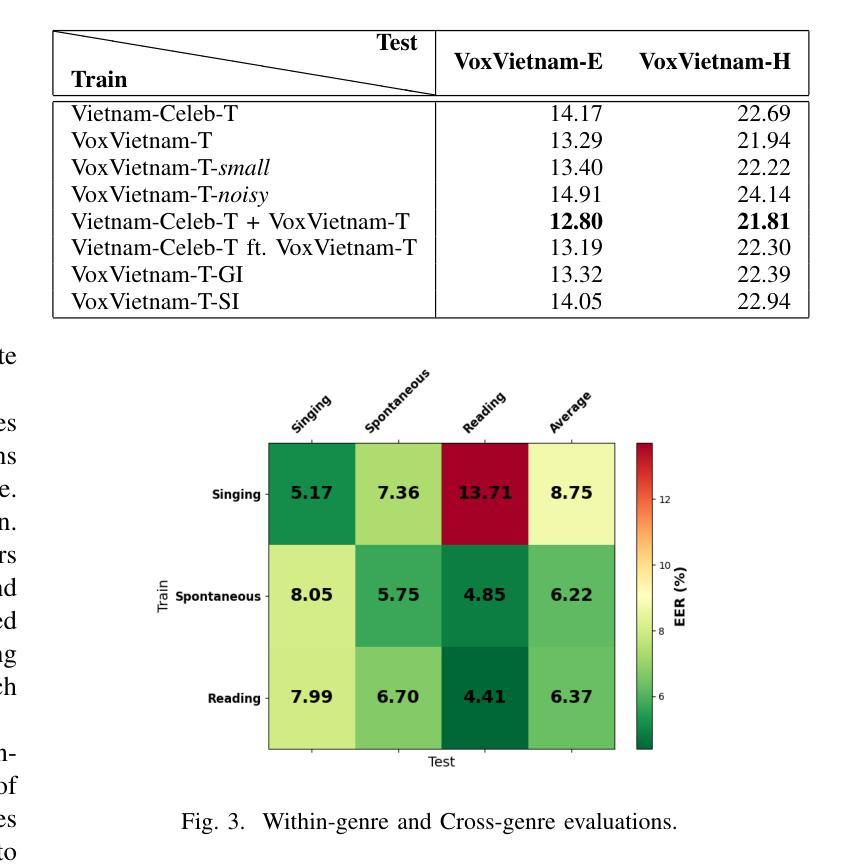
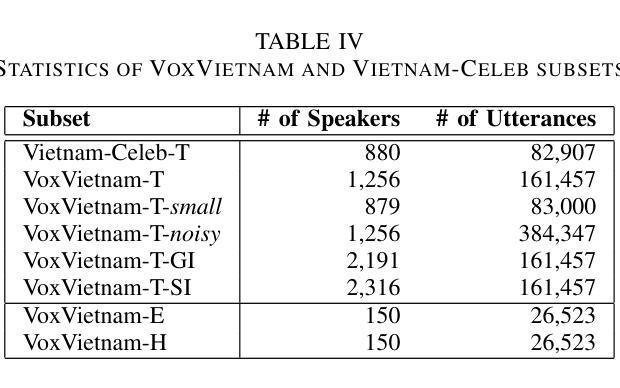
Recent research in speaker recognition aims to address vulnerabilities due to variations between enrolment and test utterances, particularly in the multi-genre phenomenon where the utterances are in different speech genres. Previous resources for Vietnamese speaker recognition are either limited in size or do not focus on genre diversity, leaving studies in multi-genre effects unexplored. This paper introduces VoxVietnam, the first multi-genre dataset for Vietnamese speaker recognition with over 187,000 utterances from 1,406 speakers and an automated pipeline to construct a dataset on a large scale from public sources. Our experiments show the challenges posed by the multi-genre phenomenon to models trained on a single-genre dataset, and demonstrate a significant increase in performance upon incorporating the VoxVietnam into the training process. Our experiments are conducted to study the challenges of the multi-genre phenomenon in speaker recognition and the performance gain when the proposed dataset is used for multi-genre training.
近期关于语音识别的研究旨在解决由于注册和测试语音之间的变化造成的漏洞,特别是在不同语音类型的多类型现象中。越南语音识别的先前资源规模有限,或者并不专注于类型多样性,这使得多类型影响的研究尚未被探索。本文介绍了VoxVietnam数据集,它是越南语音识别领域的首个多类型数据集,包含来自1406名发言人的超过18万条语音记录,并有一个从公共来源大规模构建数据集的自动化管道。我们的实验显示了在单类型数据集上训练的模型面临的多类型现象带来的挑战,并证明了在训练过程中引入VoxVietnam后性能的显著提高。我们的实验旨在研究语音识别中多类型现象的挑战以及使用所提出数据集进行多类型训练时的性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to 2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2025)
Summary:
此论文针对越南语语音识别中的多风格现象进行了深入研究,并介绍了VoxVietnam数据集。该数据集为越南语语音识别提供了首个多风格数据集,包含超过187,000个说话人的发音片段。研究发现多风格现象给单一风格训练模型带来的挑战,以及使用VoxVietnam数据集进行多风格训练带来的性能提升。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究针对越南语语音识别中的多风格现象。
- 介绍了VoxVietnam数据集,该数据集为越南语语音识别提供了首个多风格数据集。
- 数据集包含超过187,000个说话人的发音片段,规模较大。
- 多风格现象对单一风格训练模型带来挑战。
- 使用VoxVietnam数据集进行多风格训练可以显著提高性能。
- 该研究通过实验验证了多风格现象在语音识别中的挑战以及使用所提出数据集的收益。
点此查看论文截图

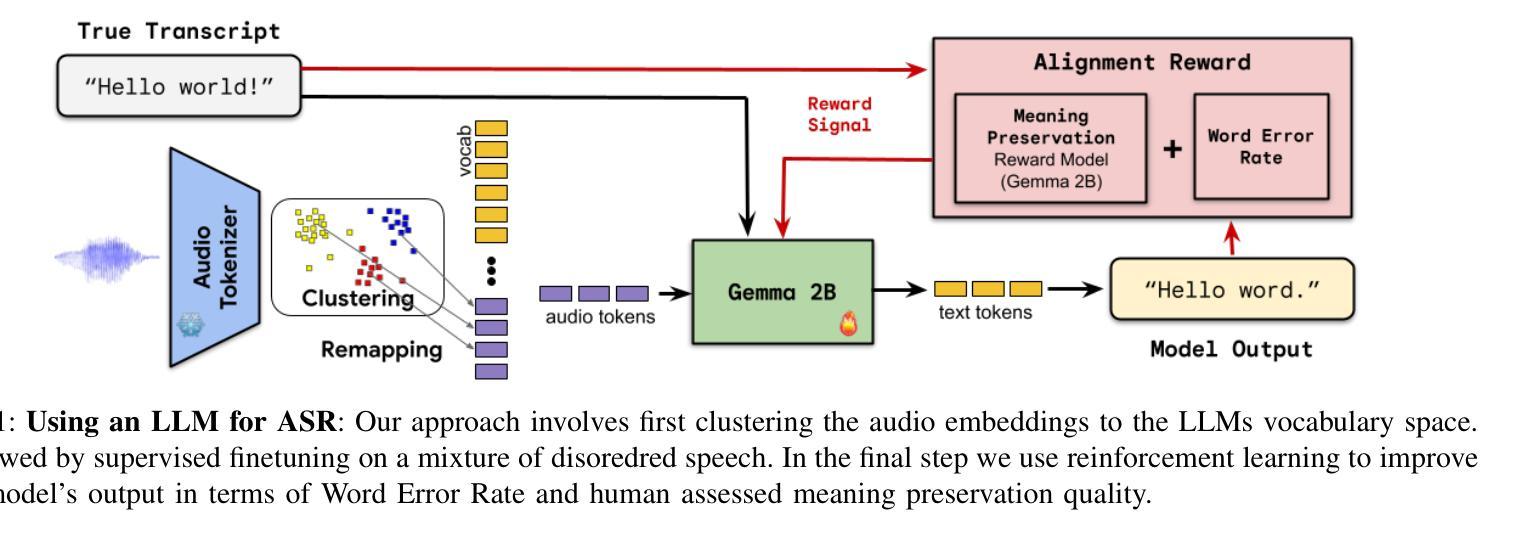
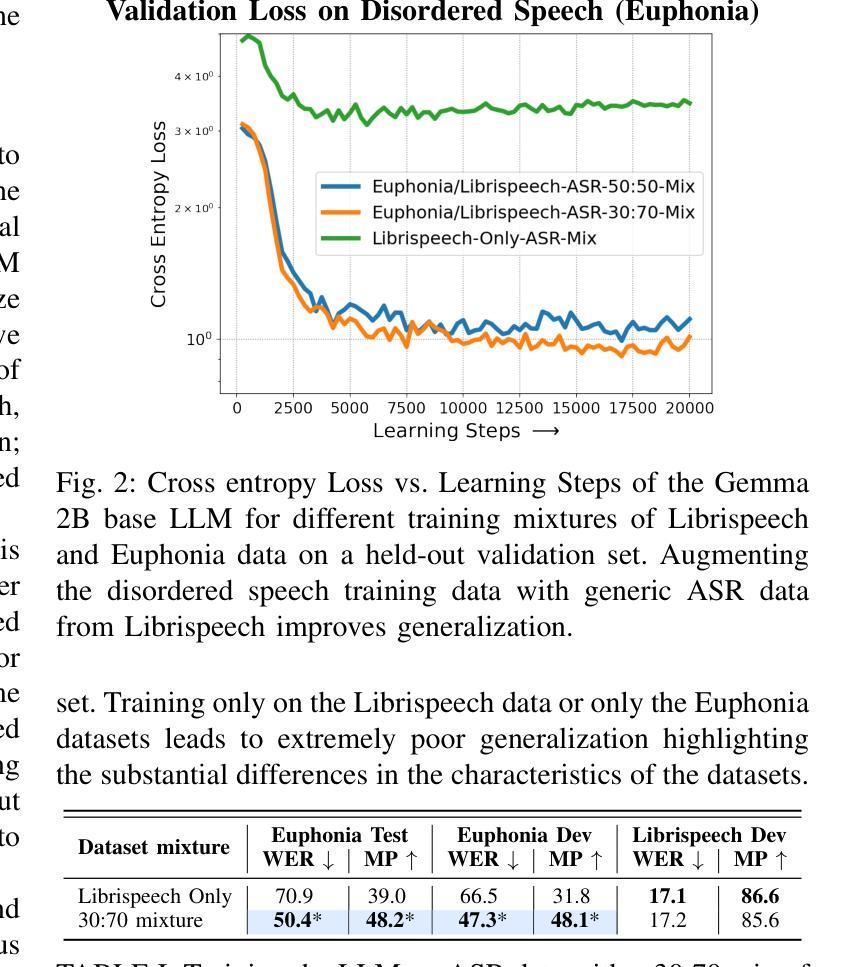
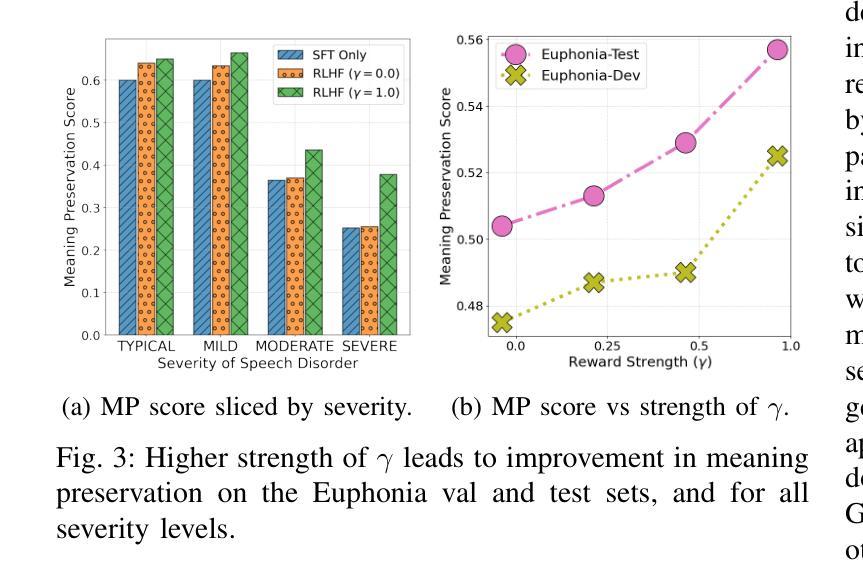
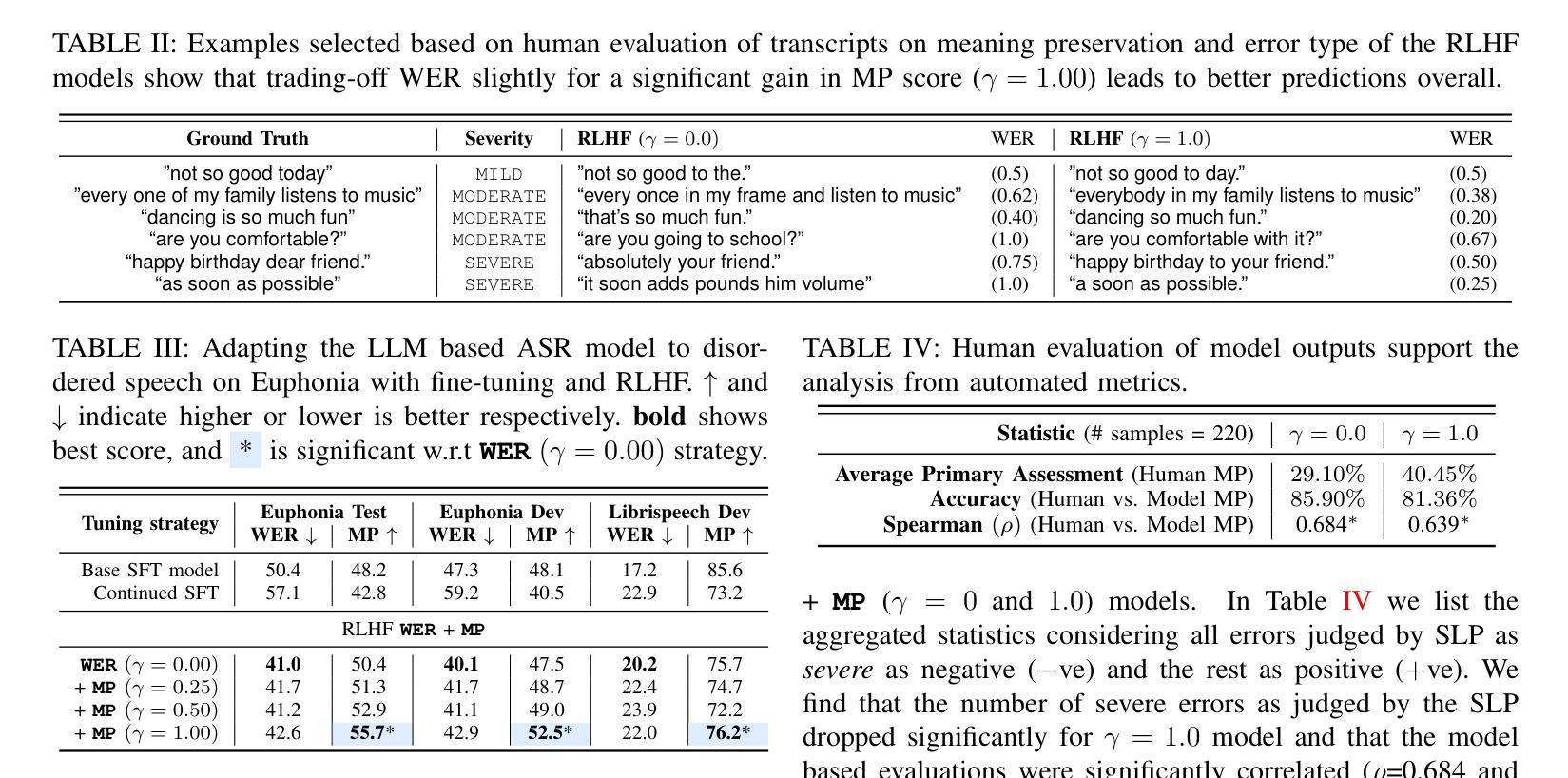
Speech Recognition With LLMs Adapted to Disordered Speech Using Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Chirag Nagpal, Subhashini Venugopalan, Jimmy Tobin, Marilyn Ladewig, Katherine Heller, Katrin Tomanek
We introduce a large language model (LLM) capable of processing speech inputs and show that tuning it further with reinforcement learning on human preference (RLHF) enables it to adapt better to disordered speech than traditional fine-tuning. Our method replaces low-frequency text tokens in an LLM’s vocabulary with audio tokens and enables the model to recognize speech by fine-tuning it on speech with transcripts. We then use RL with rewards based on syntactic and semantic accuracy measures generalizing the LLM further to recognize disordered speech. While the resulting LLM does not outperform existing systems for speech recognition, we find that tuning with reinforcement learning using custom rewards leads to substantially better performance than supervised fine-tuning of the language model, specifically when adapting to speech in a different setting. This presents a compelling alternative tuning strategy for speech recognition using large language models.
我们引入了一种能够处理语音输入的大型语言模型(LLM),并展示通过基于人类偏好的强化学习(RLHF)进一步调整它,可以比传统微调更好地适应乱序语音。我们的方法用音频令牌替换LLM词汇表中的低频文本令牌,并通过在带有转录的语音上对模型进行微调,使其能够识别语音。然后,我们使用基于句法和语义准确性度量的奖励来使用强化学习,进一步将LLM推广以识别乱序语音。虽然所得LLM在语音识别方面并未超越现有系统,但我们发现使用自定义奖励进行强化学习调整,在适应不同环境下的语音时,其性能明显优于对语言模型的监督微调。这为使用大型语言模型的语音识别提供了一个吸引人的替代调整策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)经强化学习对人类偏好(RLHF)的进一步调整,能更好地适应紊乱语音的处理。方法是用音频令牌替换LLM词汇表中的低频文本令牌,使模型通过微调语音和转录本来识别语音。然后,使用基于句法语义准确性的奖励来强化学习,使LLM进一步泛化,以识别紊乱语音。虽然结果不如现有的语音识别系统,但使用自定义奖励的强化学习调整策略相较于监督微调语言模型,性能显著提升,尤其在适应不同场景的语音时更是如此。这为使用大型语言模型的语音识别提供了有吸引力的替代策略。
Key Takeaways
- LLM可以通过处理语音输入进行训练和调整。
- 强化学习(RL)用于调整LLM以更好地适应紊乱语音。
- 用音频令牌替换LLM中的低频文本令牌,使其能够识别语音。
- 基于句法语义准确性的奖励用于强化学习。
- 虽然LLM在语音识别方面的表现尚未超越现有系统,但强化学习策略相较于传统微调方法性能更优。
- 强化学习策略在适应不同场景的语音时表现出优势。
点此查看论文截图