⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-07 更新
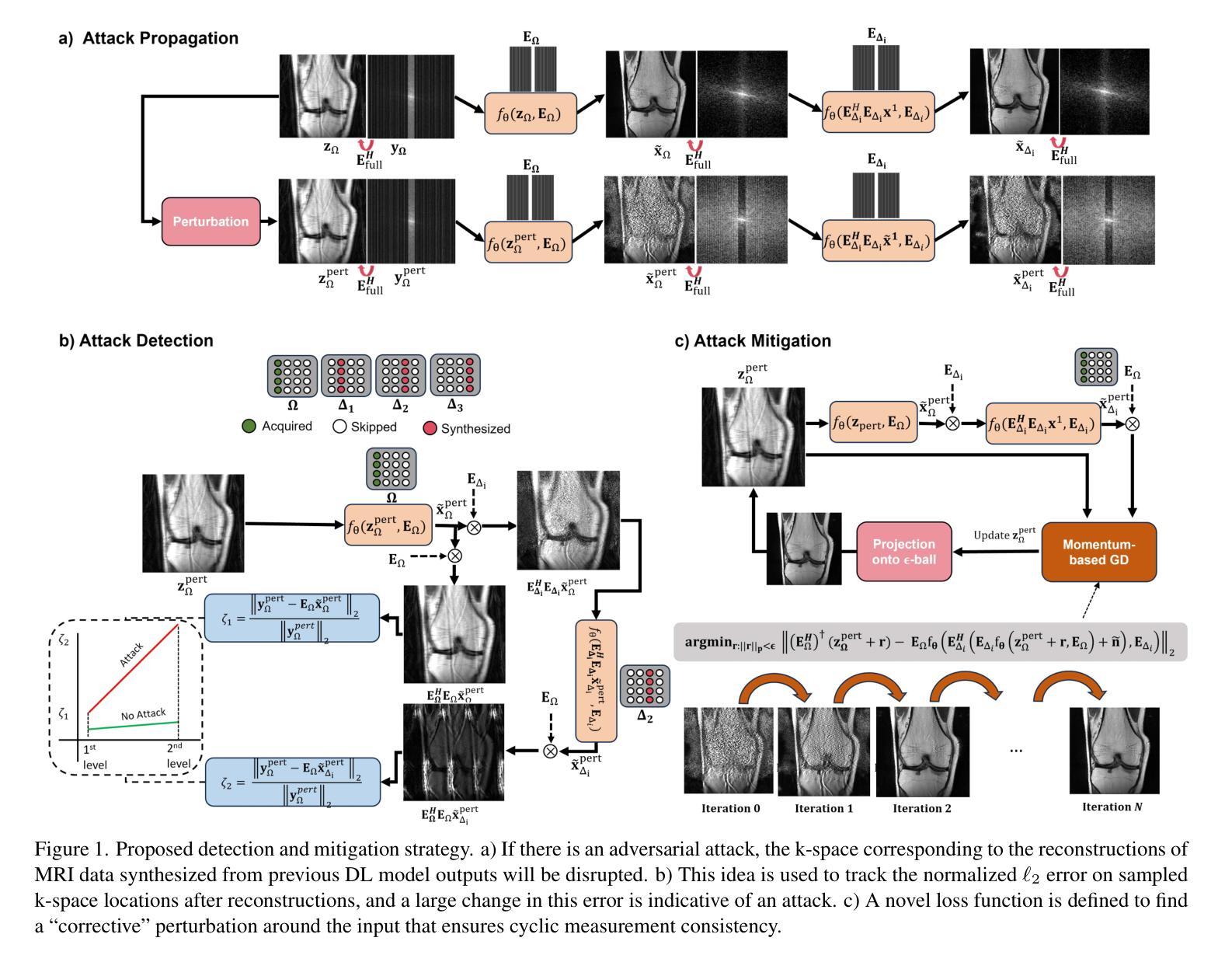
Detecting and Mitigating Adversarial Attacks on Deep Learning-Based MRI Reconstruction Without Any Retraining
Authors:Mahdi Saberi, Chi Zhang, Mehmet Akcakaya
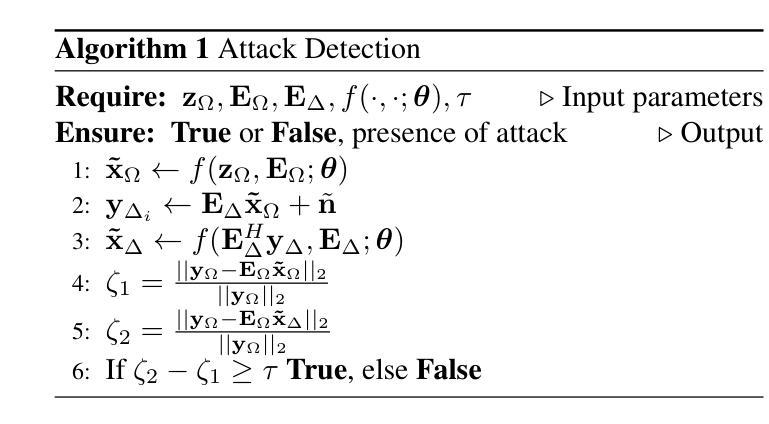
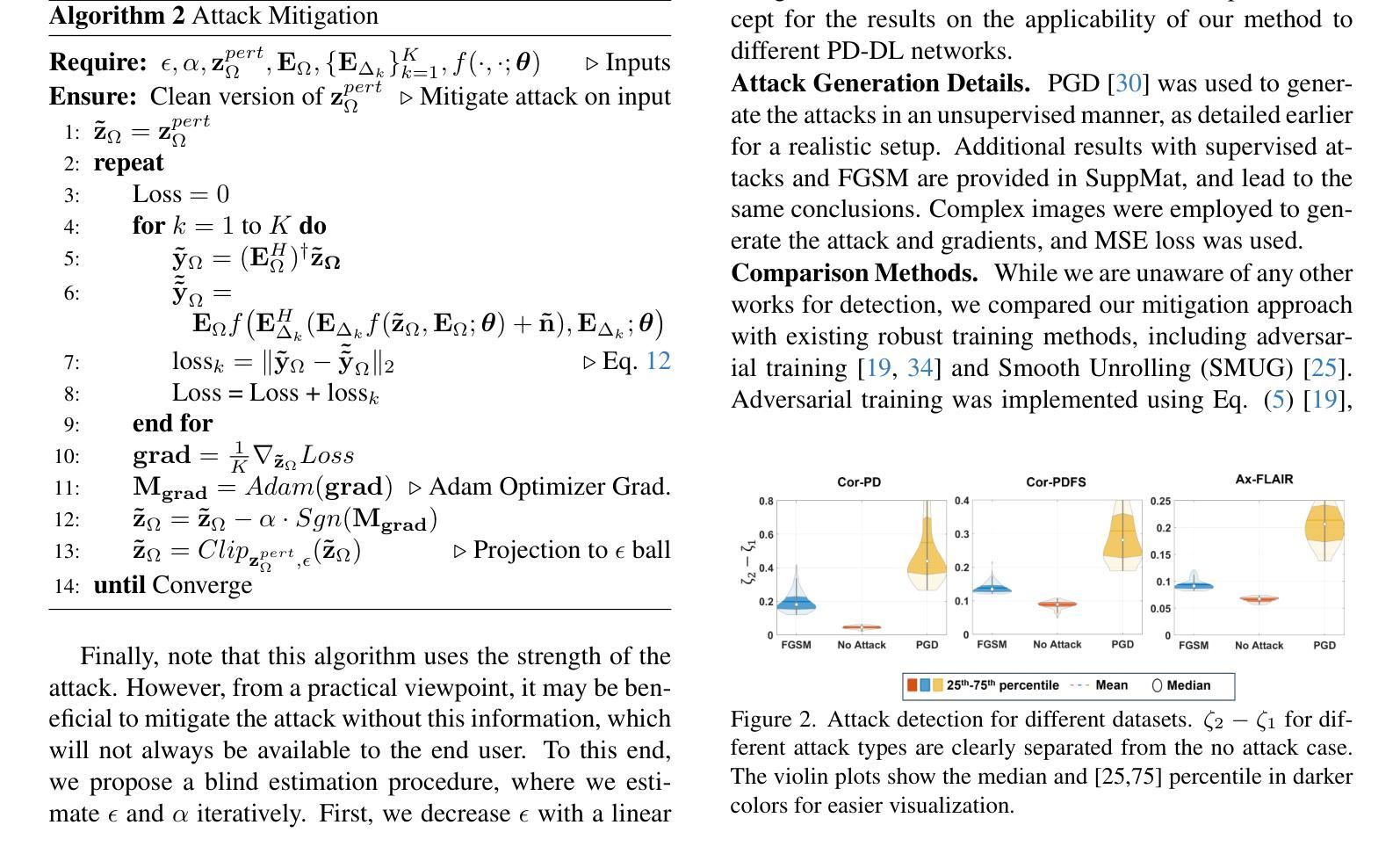
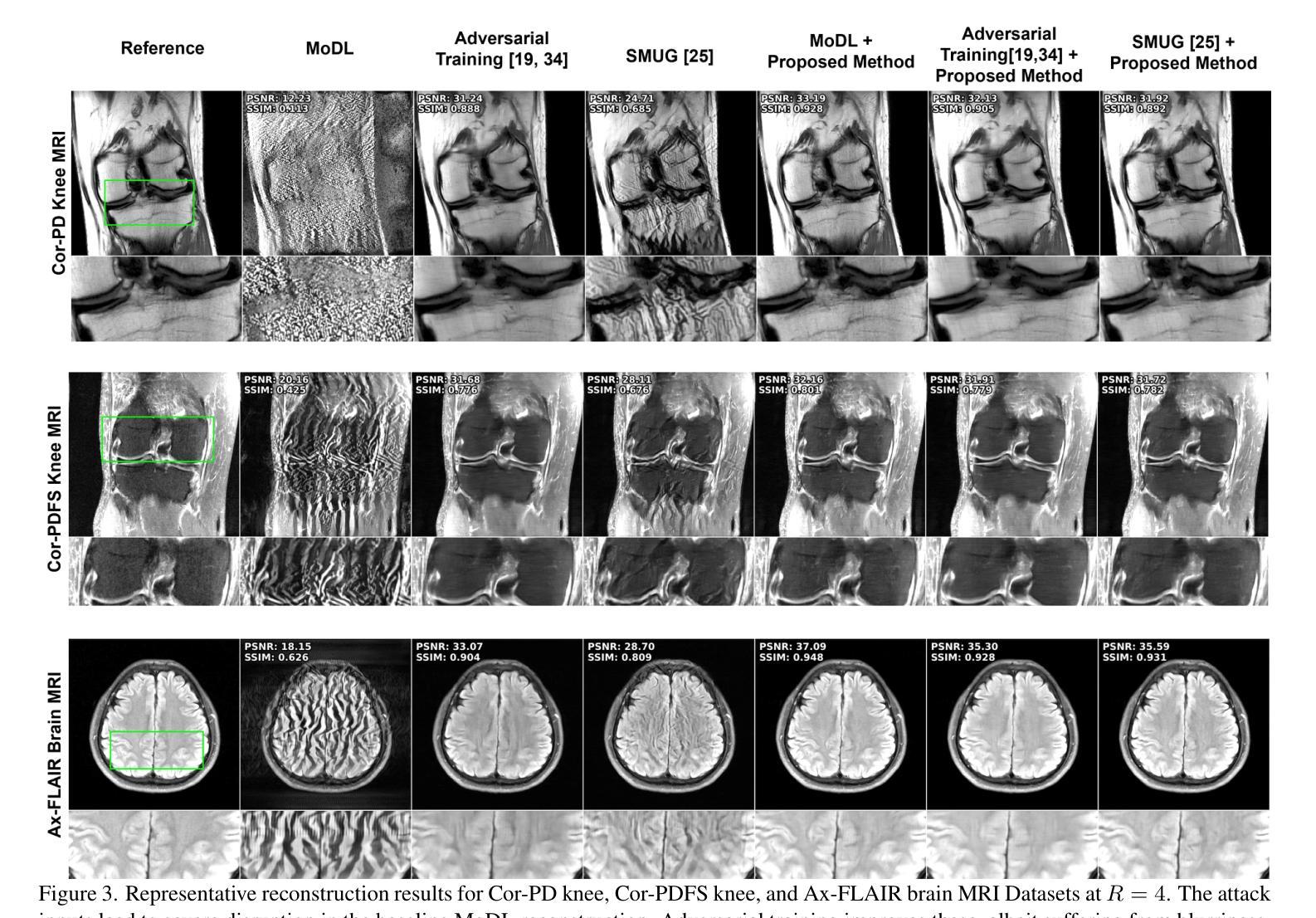
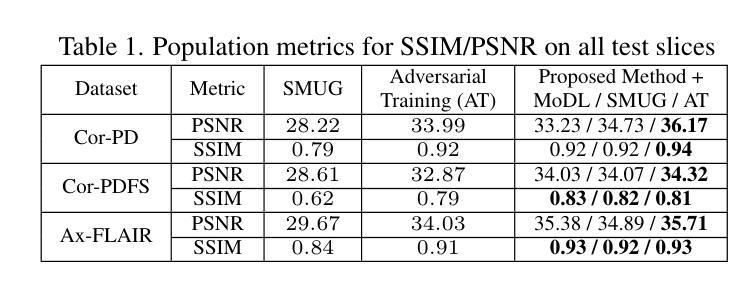
Deep learning (DL) methods, especially those based on physics-driven DL, have become the state-of-the-art for reconstructing sub-sampled magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data. However, studies have shown that these methods are susceptible to small adversarial input perturbations, or attacks, resulting in major distortions in the output images. Various strategies have been proposed to reduce the effects of these attacks, but they require retraining and may lower reconstruction quality for non-perturbed/clean inputs. In this work, we propose a novel approach for detecting and mitigating adversarial attacks on MRI reconstruction models without any retraining. Our detection strategy is based on the idea of cyclic measurement consistency. The output of the model is mapped to another set of MRI measurements for a different sub-sampling pattern, and this synthesized data is reconstructed with the same model. Intuitively, without an attack, the second reconstruction is expected to be consistent with the first, while with an attack, disruptions are present. Subsequently, this idea is extended to devise a novel objective function, which is minimized within a small ball around the attack input for mitigation. Experimental results show that our method substantially reduces the impact of adversarial perturbations across different datasets, attack types/strengths and PD-DL networks, and qualitatively and quantitatively outperforms conventional mitigation methods that involve retraining.
深度学习(DL)方法,尤其是基于物理驱动的DL方法,已成为重建子采样磁共振成像(MRI)数据的最新技术。然而,研究表明,这些方法容易受到微小敌对输入扰动或攻击的影响,导致输出图像出现重大失真。虽然已提出各种策略来减少这些攻击的影响,但它们需要重新训练,并可能降低对非扰动/清洁输入的重建质量。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种无需重新训练即可检测和减轻MRI重建模型遭受敌对攻击的新方法。我们的检测策略基于循环测量一致性的理念。模型的输出被映射到另一组MRI测量值,用于不同的子采样模式,然后用同一模型重建这些合成数据。直观地说,在没有攻击的情况下,第二次重建应与第一次重建一致,而受到攻击时则会出现干扰。随后,将这个理念扩展到一个新的目标函数中,通过最小化攻击输入周围小范围内的该函数来减轻攻击影响。实验结果表明,我们的方法大大减少了不同数据集、攻击类型和强度以及PD-DL网络中的敌对扰动的影响,并且在定性和定量上均优于涉及重新训练的传统缓解方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习(DL)在重建子采样磁共振成像(MRI)数据方面表现出卓越性能,尤其是基于物理驱动的DL方法。然而,研究表明这些方法容易受到小型的对抗性输入扰动或攻击的影响,导致输出图像出现重大失真。本研究提出了一种无需重新训练即可检测和减轻MRI重建模型对抗性攻击的新方法。该方法基于循环测量一致性检测策略,并通过实验验证其能有效减少不同数据集、攻击类型和强度以及部分物理驱动DL网络中的对抗性扰动影响,并在定性和定量上优于涉及重新训练的常规缓解方法。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在MRI数据重建中表现优异,尤其是物理驱动DL方法。
- DL方法容易受到对抗性输入扰动或攻击的影响,导致输出图像失真。
- 本研究提出了一种无需重新训练的新方法,用于检测和减轻MRI重建模型的对抗性攻击。
- 该方法基于循环测量一致性检测策略。
- 实验证明该方法能有效减少不同数据集、攻击类型和强度中的对抗性扰动影响。
- 与常规需要重新训练的缓解方法相比,该方法在定性和定量上表现更优。
- 该方法具有广泛的应用前景,可应用于不同的MRI重建模型和情境。
点此查看论文截图

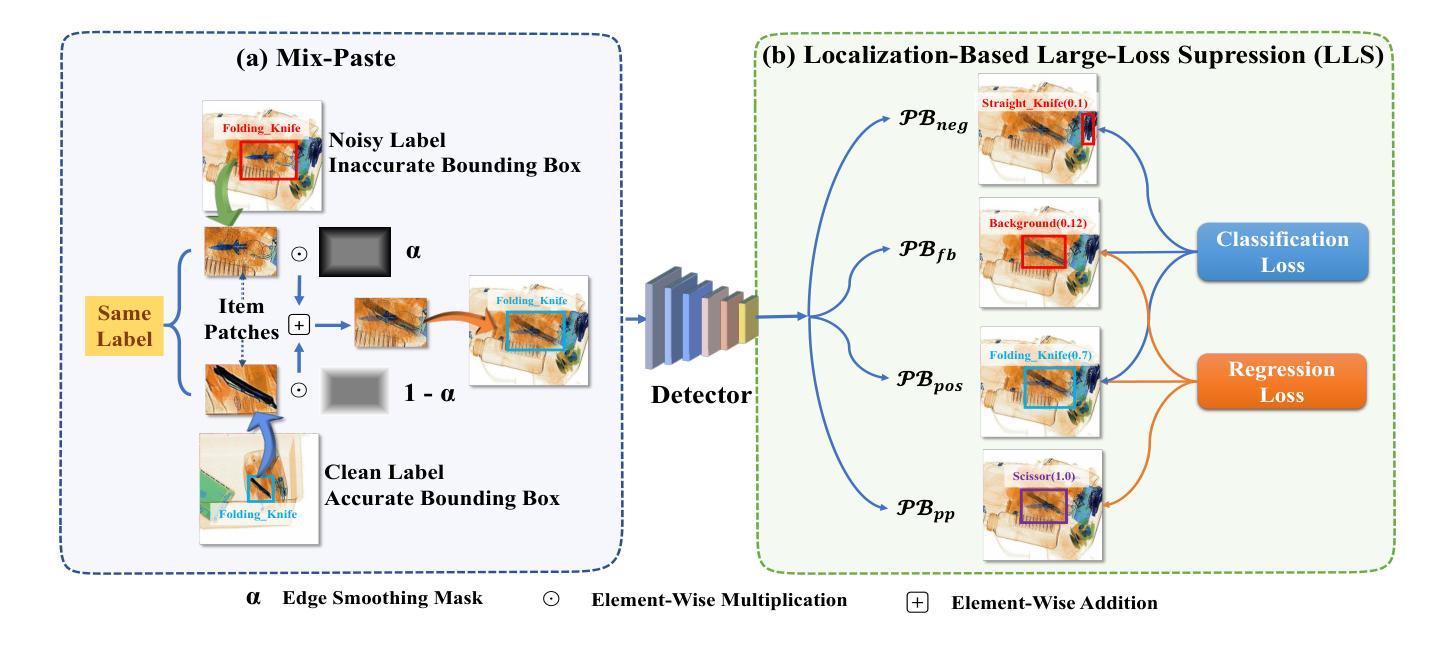
Augmentation Matters: A Mix-Paste Method for X-Ray Prohibited Item Detection under Noisy Annotations
Authors:Ruikang Chen, Yan Yan, Jing-Hao Xue, Yang Lu, Hanzi Wang
Automatic X-ray prohibited item detection is vital for public safety. Existing deep learning-based methods all assume that the annotations of training X-ray images are correct. However, obtaining correct annotations is extremely hard if not impossible for large-scale X-ray images, where item overlapping is ubiquitous.As a result, X-ray images are easily contaminated with noisy annotations, leading to performance deterioration of existing methods.In this paper, we address the challenging problem of training a robust prohibited item detector under noisy annotations (including both category noise and bounding box noise) from a novel perspective of data augmentation, and propose an effective label-aware mixed patch paste augmentation method (Mix-Paste). Specifically, for each item patch, we mix several item patches with the same category label from different images and replace the original patch in the image with the mixed patch. In this way, the probability of containing the correct prohibited item within the generated image is increased. Meanwhile, the mixing process mimics item overlapping, enabling the model to learn the characteristics of X-ray images. Moreover, we design an item-based large-loss suppression (LLS) strategy to suppress the large losses corresponding to potentially positive predictions of additional items due to the mixing operation. We show the superiority of our method on X-ray datasets under noisy annotations. In addition, we evaluate our method on the noisy MS-COCO dataset to showcase its generalization ability. These results clearly indicate the great potential of data augmentation to handle noise annotations. The source code is released at https://github.com/wscds/Mix-Paste.
自动X射线违禁品检测对公共安全至关重要。现有的基于深度学习的方法都假设训练X射线图像的注释是正确的。然而,对于大规模的X射线图像,由于物品重叠普遍存在,获取正确的注释极其困难甚至不可能。因此,X射线图像很容易受到带有噪声的注释的污染,导致现有方法的性能下降。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The manuscript has been ACCEPTED for publication as a regular paper in the IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics & Security
Summary
基于深度学习的自动X射线违禁物品检测在存在噪声标注的情况下性能会下降。本文创新性地从数据增强角度解决这一难题,提出一种标签感知混合补丁粘贴增强方法(Mix-Paste),通过混合相同类别标签的物品补丁,增加生成图像中包含正确违禁物品的概率,同时模仿物品重叠情况,使模型学习X射线图像的特性。此外,设计了一项基于物品的较大损失抑制策略,以抑制因混合操作产生的其他潜在阳性预测物品的较大损失。该策略在处理带有噪声标注的X射线数据集上表现卓越,并在噪声MS-COCO数据集上评估展示其泛化能力。数据增强在应对噪声标注方面具有巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 自动X射线违禁物品检测对公共安全至关重要。
- 现有深度学习方法假设训练X光图像的注释是正确的,但在大规模图像中获得正确注释极其困难。
- Mix-Paste方法通过数据增强解决噪声标注问题,提高模型对X光图像中违禁物品的识别能力。
- Mix-Paste方法混合相同类别标签的物品补丁,增加生成图像的正确率并模仿物品重叠情况。
- 提出一种基于物品的较大损失抑制策略,以处理因混合操作产生的潜在阳性预测物品。
- 方法在带有噪声标注的X射线数据集上表现优越,并在噪声MS-COCO数据集上评估具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

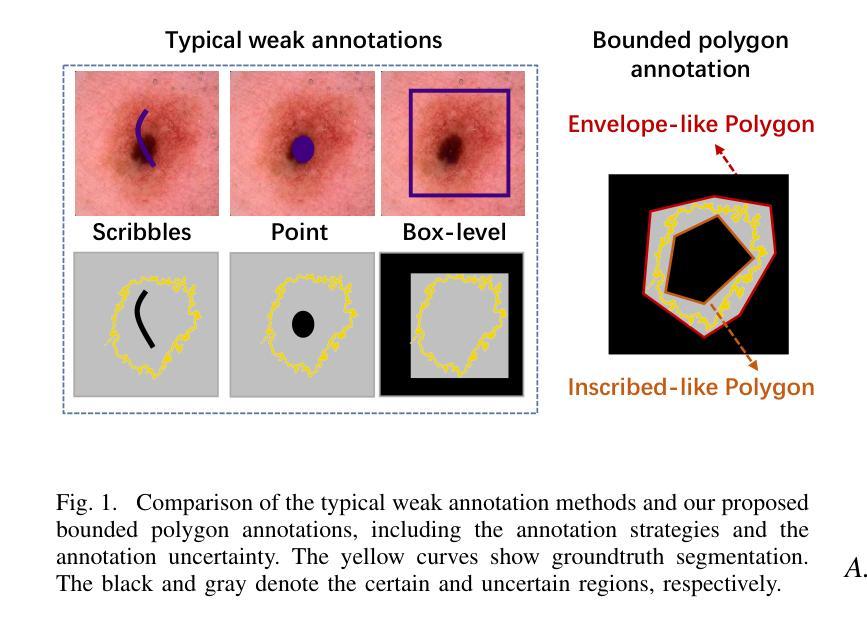
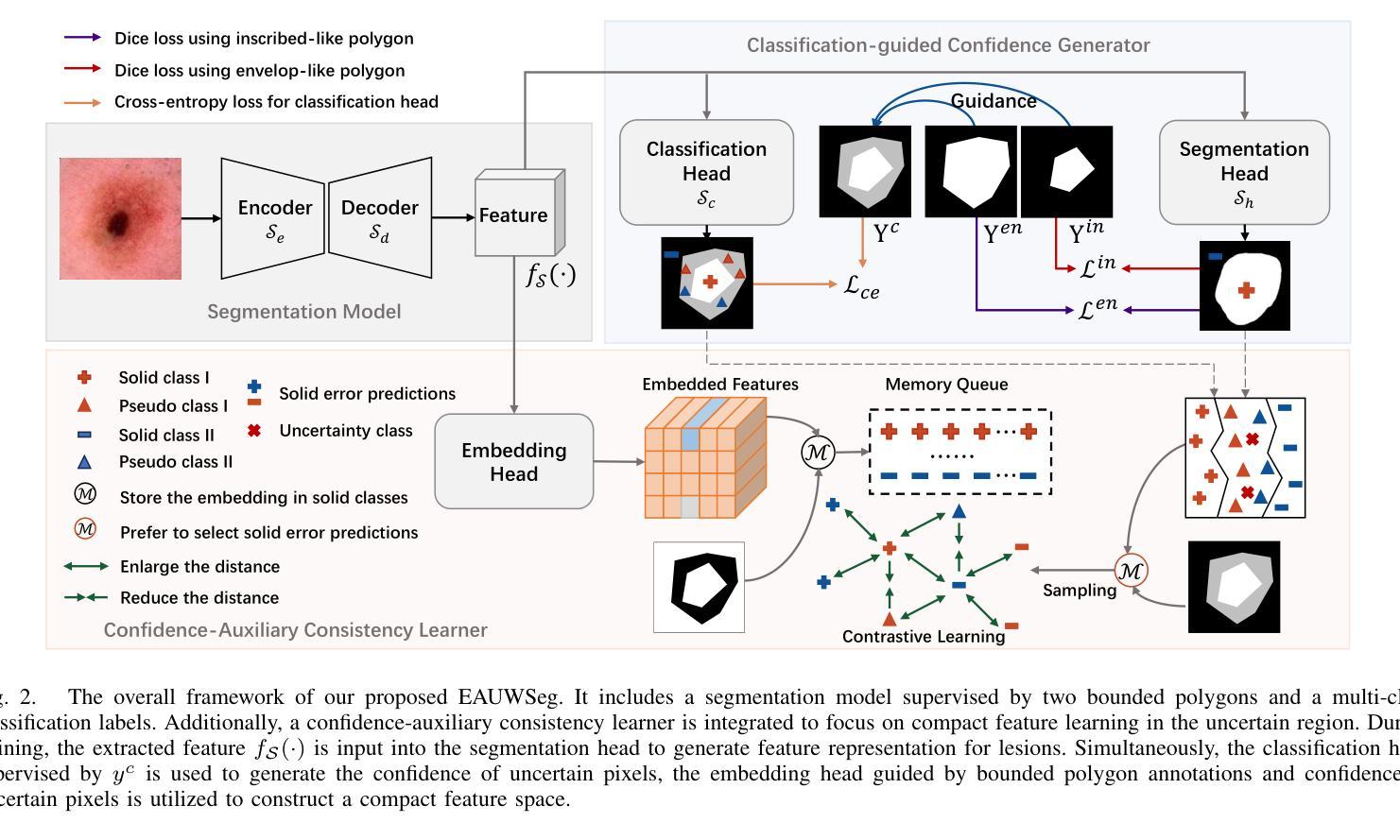
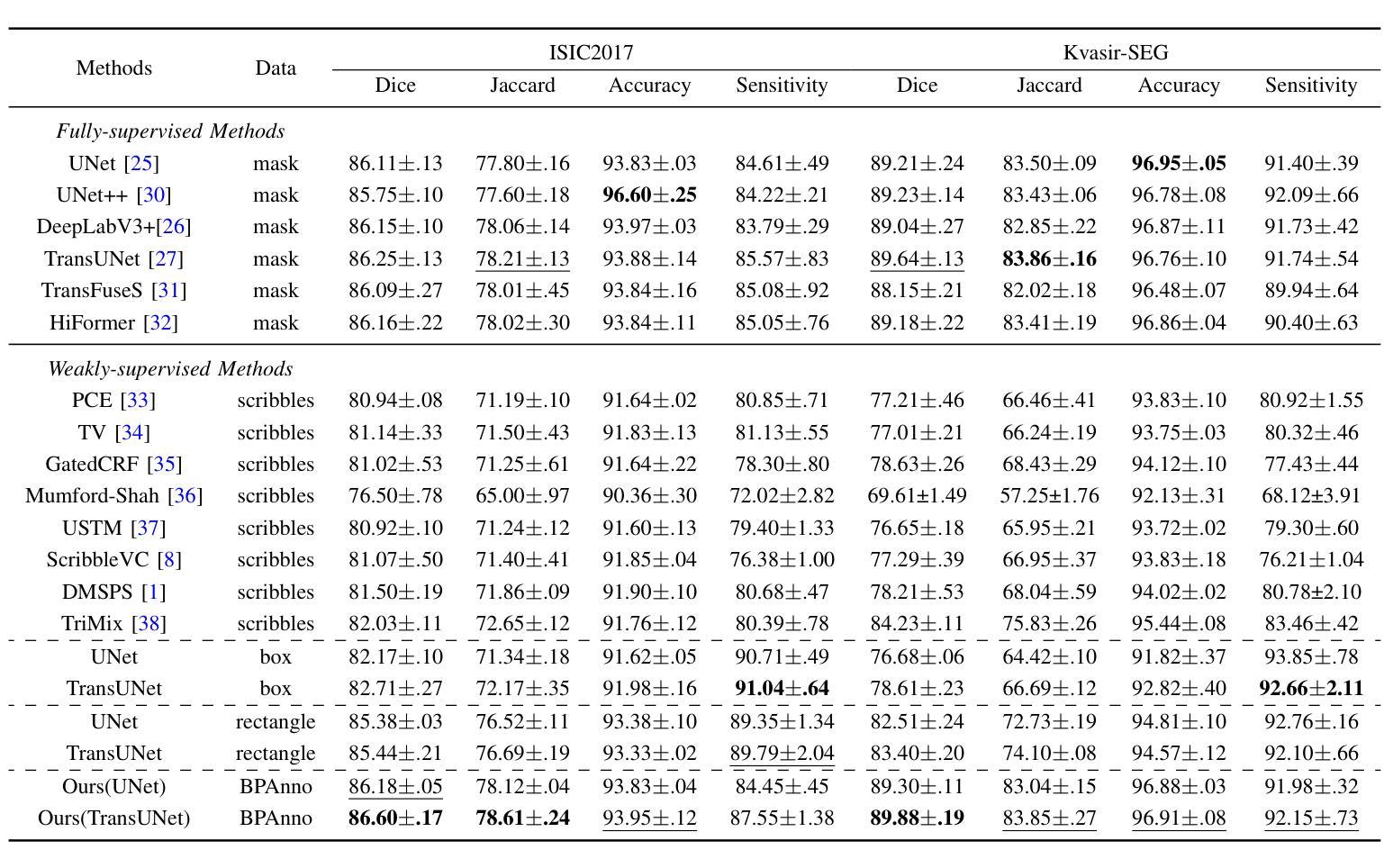
EAUWSeg: Eliminating annotation uncertainty in weakly-supervised medical image segmentation
Authors:Wang Lituan, Zhang Lei, Wang Yan, Wang Zhenbin, Zhang Zhenwei, Zhang Yi
Weakly-supervised medical image segmentation is gaining traction as it requires only rough annotations rather than accurate pixel-to-pixel labels, thereby reducing the workload for specialists. Although some progress has been made, there is still a considerable performance gap between the label-efficient methods and fully-supervised one, which can be attributed to the uncertainty nature of these weak labels. To address this issue, we propose a novel weak annotation method coupled with its learning framework EAUWSeg to eliminate the annotation uncertainty. Specifically, we first propose the Bounded Polygon Annotation (BPAnno) by simply labeling two polygons for a lesion. Then, the tailored learning mechanism that explicitly treat bounded polygons as two separated annotations is proposed to learn invariant feature by providing adversarial supervision signal for model training. Subsequently, a confidence-auxiliary consistency learner incorporates with a classification-guided confidence generator is designed to provide reliable supervision signal for pixels in uncertain region by leveraging the feature presentation consistency across pixels within the same category as well as class-specific information encapsulated in bounded polygons annotation. Experimental results demonstrate that EAUWSeg outperforms existing weakly-supervised segmentation methods. Furthermore, compared to fully-supervised counterparts, the proposed method not only delivers superior performance but also costs much less annotation workload. This underscores the superiority and effectiveness of our approach.
弱监督医学图像分割正受到越来越多的关注,因为它只需要粗略的注释,而不需要精确的像素到像素的标签,从而减少了专家的工作量。虽然已取得了一些进展,但标签效率高的方法与全监督方法之间的性能差距仍然很大,这可以归因于这些弱标签的不确定性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的弱标注方法及其学习框架EAUWSeg,以消除标注的不确定性。具体来说,我们首先提出有界多边形注释(BPAnno),只需为病变标注两个多边形。然后,我们提出了一种定制的学习机制,将多边形明确地视为两个单独的注释进行处理,通过为模型训练提供对抗性监督信号来学习不变特征。随后,设计了一个与分类引导置信度生成器相结合的置信辅助一致性学习者,通过利用同一类别内像素之间的特征表示一致性以及包含在边界多边形注释中的类别特定信息,为不确定区域的像素提供可靠的监督信号。实验结果表明,EAUWSeg优于现有的弱监督分割方法。此外,与全监督方法相比,该方法不仅性能优越,而且大大减少了标注工作量。这凸显了我们方法的优越性和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割中,弱监督方法因仅需粗略标注而备受关注,但存在性能差距。为此,提出一种新型弱标注方法与学习框架EAUWSeg,通过Bounded Polygon Annotation(BPAnno)和对抗性监督信号消除标注不确定性,设计信心辅助一致性学习者,提供可靠监督信号。实验显示,EAUWSeg优于现有弱监督方法,与全监督方法相比,性能优越且标注工作量更少。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督医学图像分割因减少专家工作量而受关注。
- 现有方法存在性能差距,主要源于弱标注的不确定性。
- 提出新型弱标注方法BPAnno和学习框架EAUWSeg。
- BPAnno通过仅标注两个多边形来代表病灶。
- EAUWSeg利用对抗性监督信号学习不变特征。
- 信心辅助一致性学习者提供可靠监督信号,尤其针对不确定区域。
点此查看论文截图

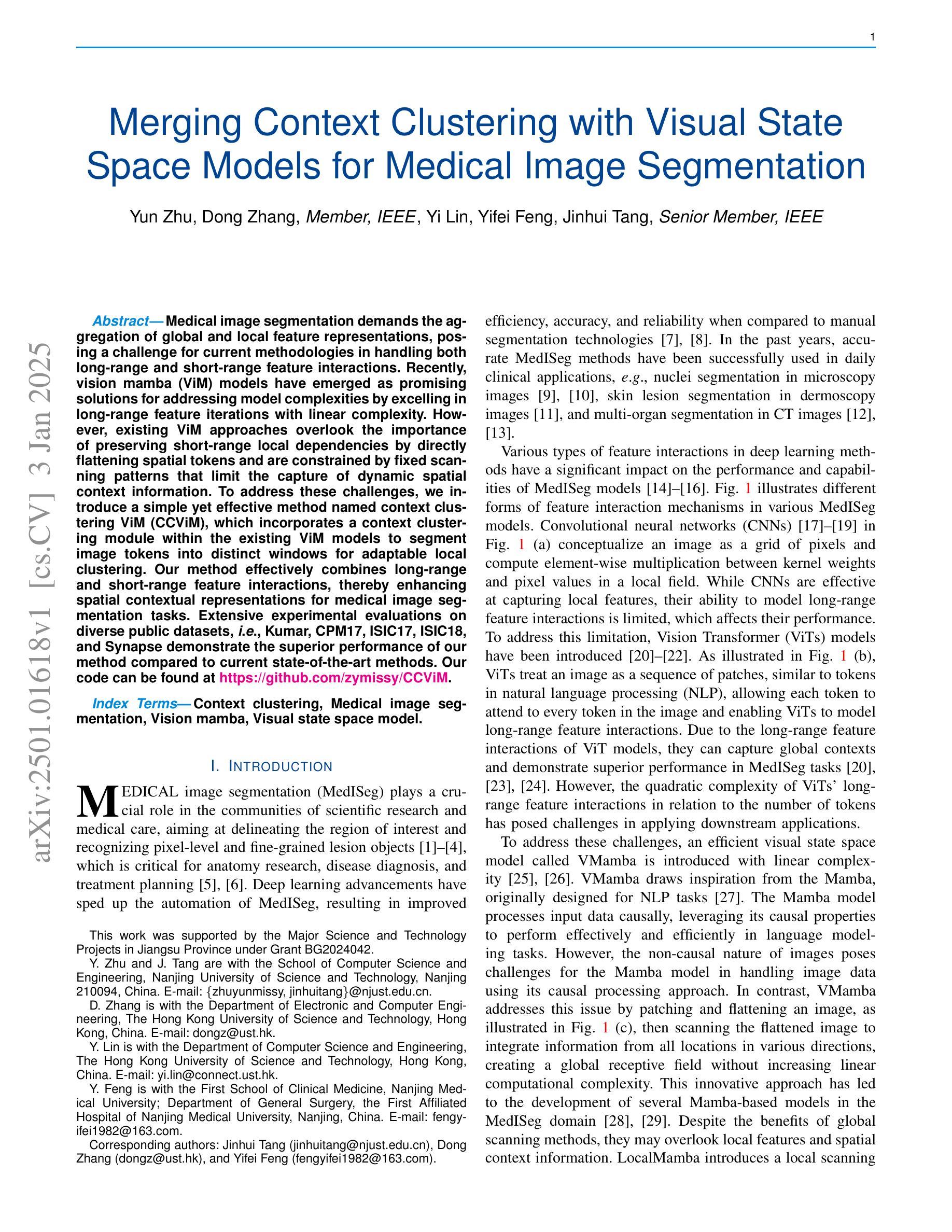
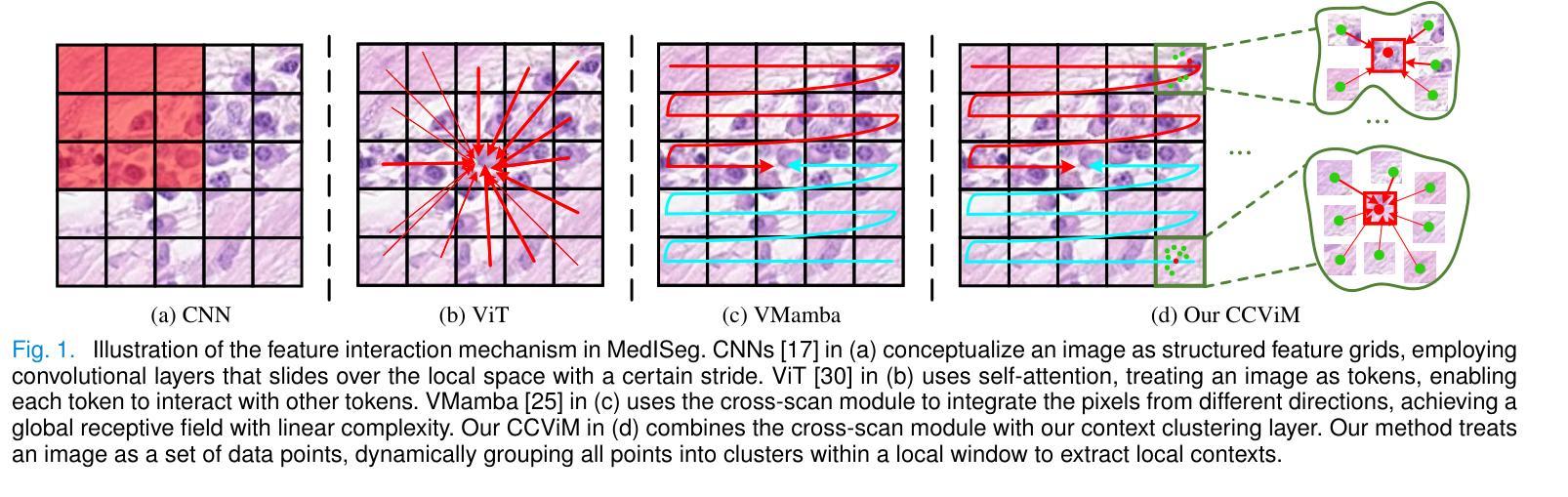
Merging Context Clustering with Visual State Space Models for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yun Zhu, Dong Zhang, Yi Lin, Yifei Feng, Jinhui Tang
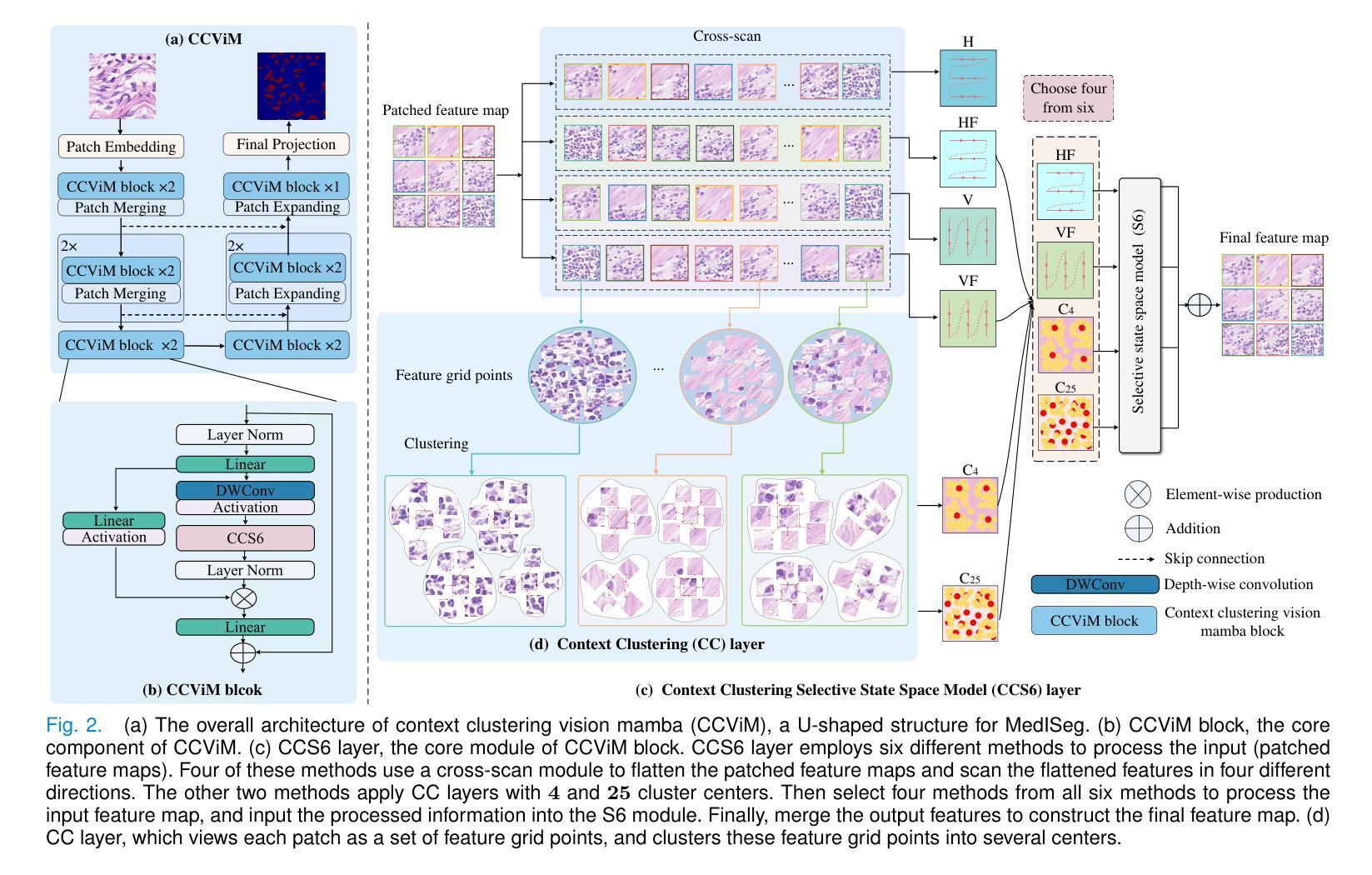
Medical image segmentation demands the aggregation of global and local feature representations, posing a challenge for current methodologies in handling both long-range and short-range feature interactions. Recently, vision mamba (ViM) models have emerged as promising solutions for addressing model complexities by excelling in long-range feature iterations with linear complexity. However, existing ViM approaches overlook the importance of preserving short-range local dependencies by directly flattening spatial tokens and are constrained by fixed scanning patterns that limit the capture of dynamic spatial context information. To address these challenges, we introduce a simple yet effective method named context clustering ViM (CCViM), which incorporates a context clustering module within the existing ViM models to segment image tokens into distinct windows for adaptable local clustering. Our method effectively combines long-range and short-range feature interactions, thereby enhancing spatial contextual representations for medical image segmentation tasks. Extensive experimental evaluations on diverse public datasets, i.e., Kumar, CPM17, ISIC17, ISIC18, and Synapse demonstrate the superior performance of our method compared to current state-of-the-art methods. Our code can be found at https://github.com/zymissy/CCViM.
医学图像分割要求全局和局部特征表示的聚合,这对当前方法处理长程和短程特征交互提出了挑战。最近,视觉妈妈(ViM)模型以线性复杂度的长程特征迭代能力突出,成为解决模型复杂性的有前途的解决方案。然而,现有的ViM方法通过直接平铺空间令牌而忽略了保持短程局部依赖关系的重要性,并且受到固定扫描模式的约束,限制了动态空间上下文信息的捕获。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种简单有效的方法,称为上下文聚类ViM(CCViM),该方法在现有的ViM模型内引入了一个上下文聚类模块,用于将图像令牌分割成不同的窗口进行自适应局部聚类。我们的方法有效地结合了长程和短程特征交互,从而增强了医学图像分割任务的上下文空间表示。在Kumar、CPM17、ISIC17、ISIC18和Synapse等多个公共数据集上的广泛实验评估表明,我们的方法与当前最先进的方法相比具有优越的性能。我们的代码位于https://github.com/zymissy/CCViM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our paper has been accepted by the IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. Our code can be found at https://github.com/zymissy/CCViM
Summary
医学图像分割需要融合全局和局部特征表示,这对当前方法处理长程和短程特征交互提出了挑战。新型的视觉mamba(ViM)模型以处理长程特征交互的线性复杂度为优势,应对模型复杂性。然而,现有ViM方法忽略了保持短程局部依赖性的重要性,通过直接扁平化空间令牌受到固定扫描模式的约束,限制了动态空间上下文信息的捕获。为解决这些问题,我们提出了一种简单有效的方法——上下文聚类ViM(CCViM),在现有ViM模型中引入上下文聚类模块,对图像令牌进行可适应的局部聚类。我们的方法有效地结合了长程和短程特征交互,从而提升医学图像分割任务的空间上下文表示。在Kumar、CPM17、ISIC17、ISIC18和Synapse等多个公共数据集上的广泛实验评估表明,我们的方法优于当前最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割需要兼顾全局和局部特征表示,存在挑战。
- 视觉mamba(ViM)模型能处理长程特征交互,但忽视短程局部依赖性。
- 现有ViM方法通过直接扁平化空间令牌受到固定扫描模式的约束。
- 上下文聚类ViM(CCViM)结合长程和短程特征交互。
- CCViM通过引入上下文聚类模块,对图像令牌进行可适应的局部聚类。
- CCViM在多个公共数据集上的表现优于当前最先进的方法。
- 相关代码已上传至GitHub(https://github.com/zymissy/CCViM)。
点此查看论文截图
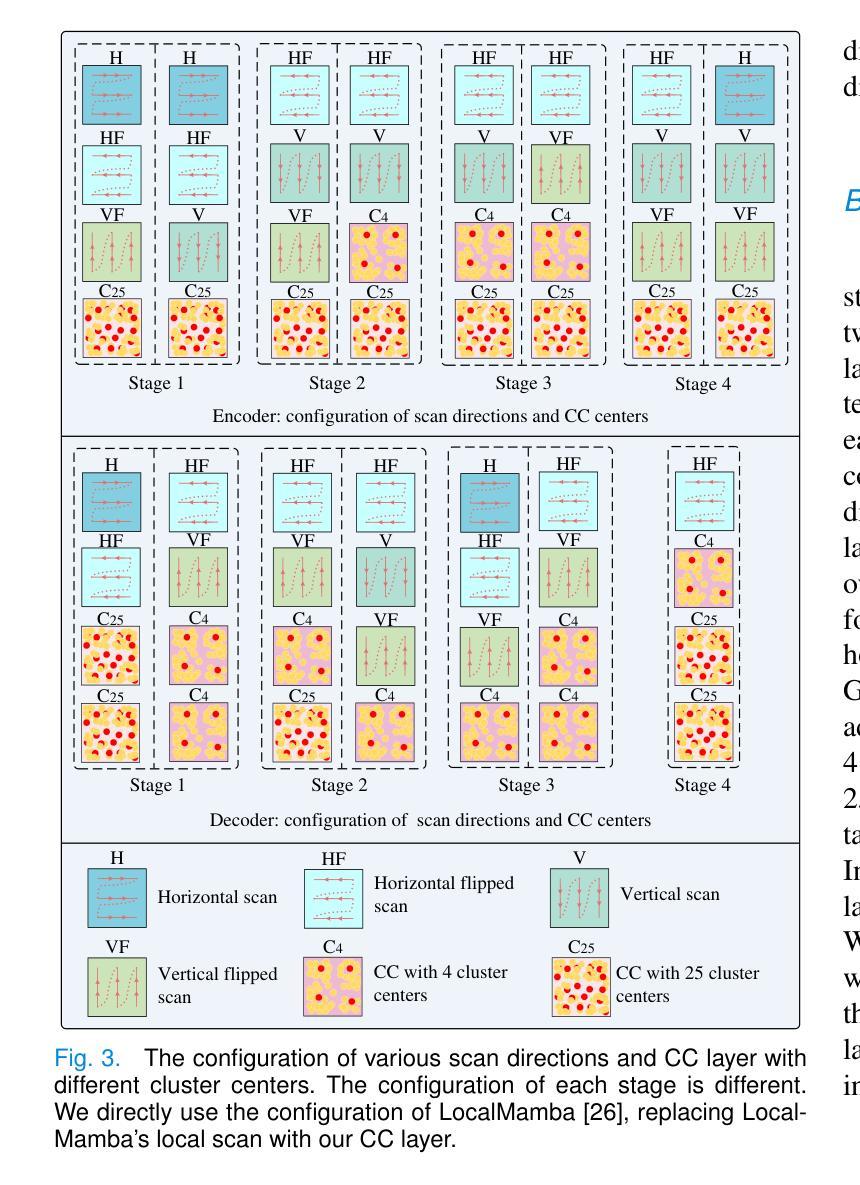
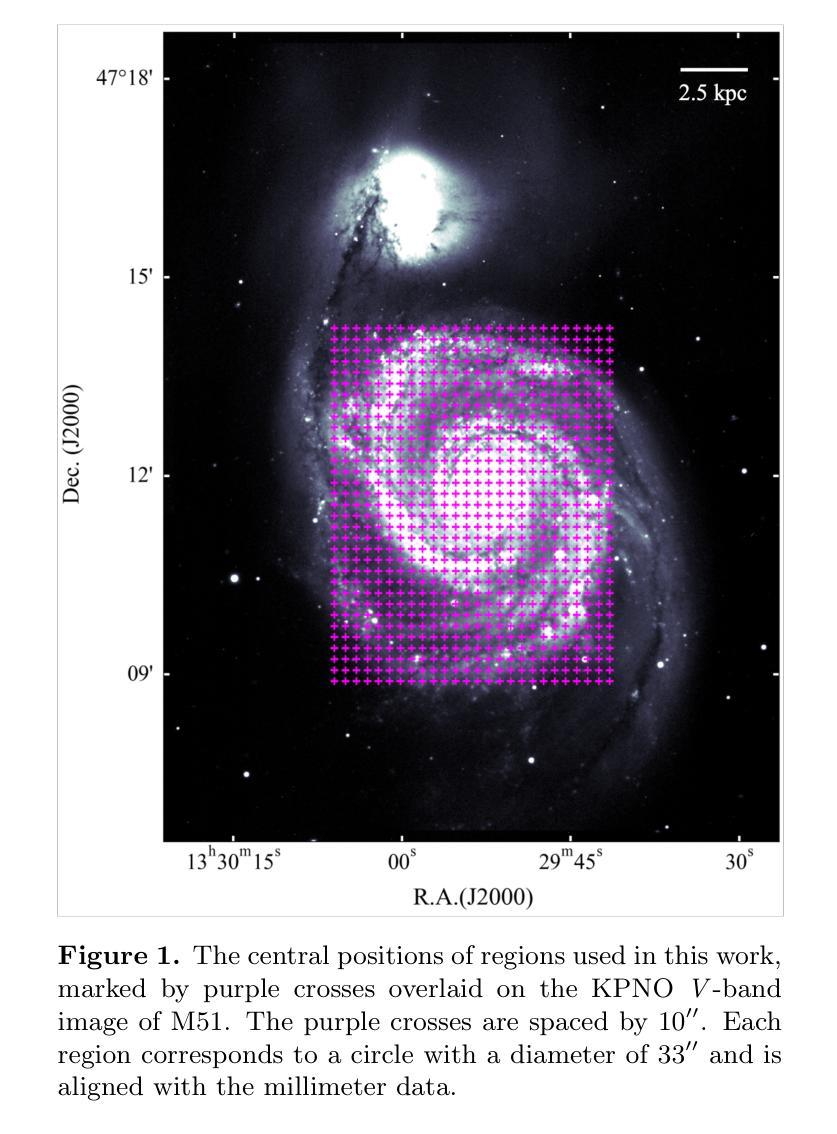
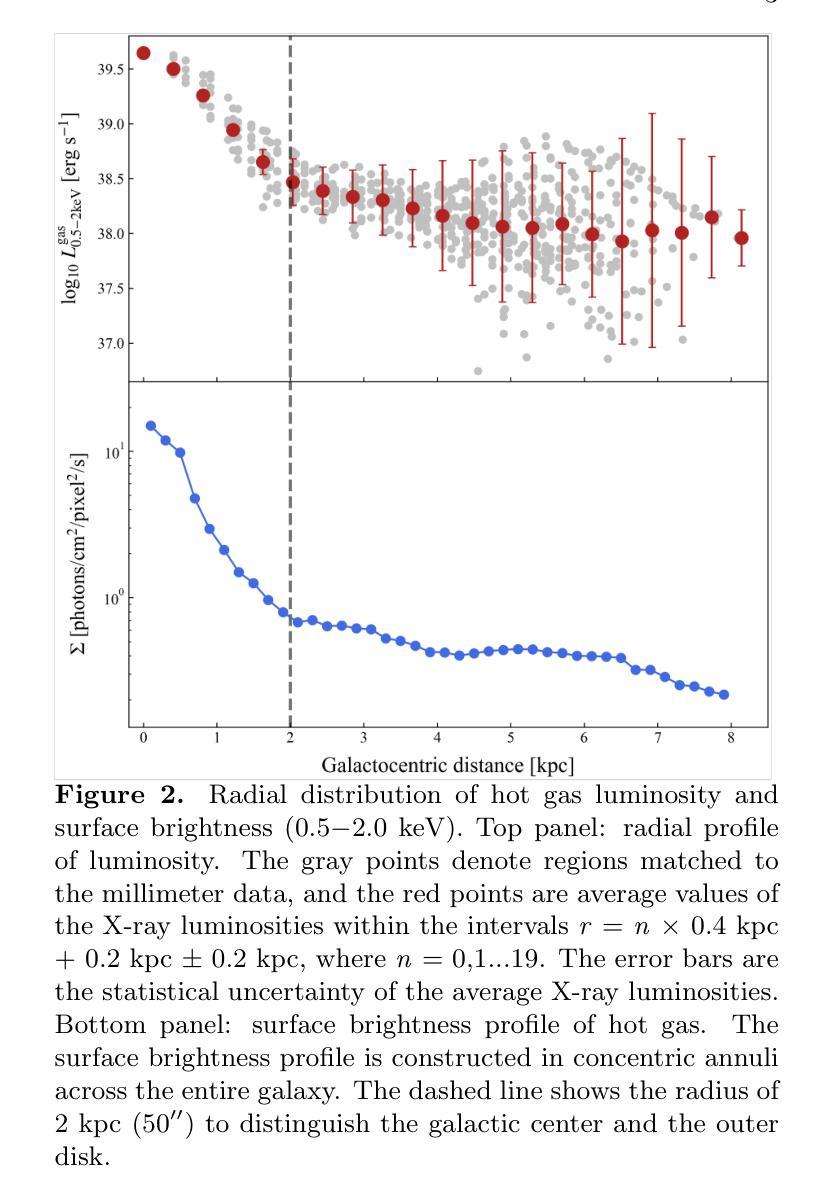
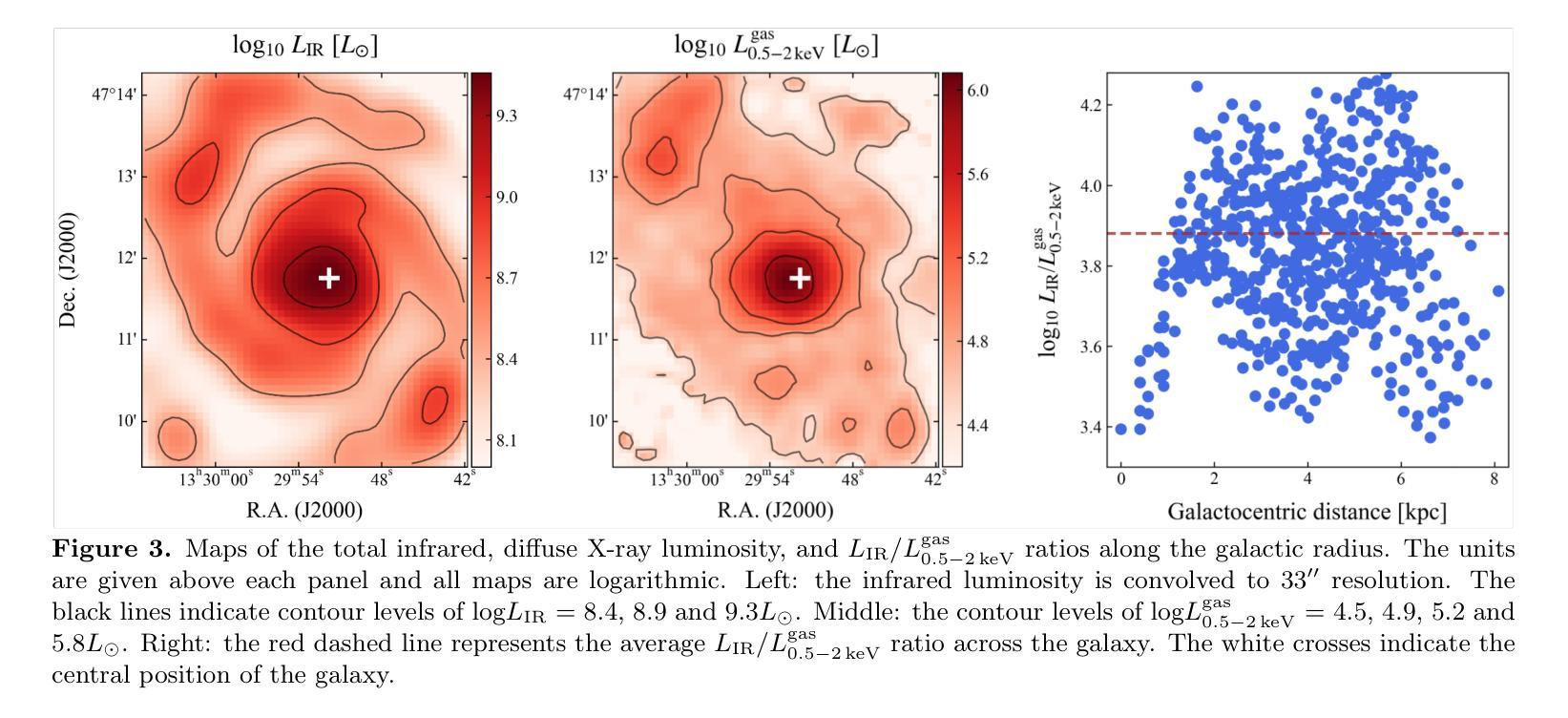
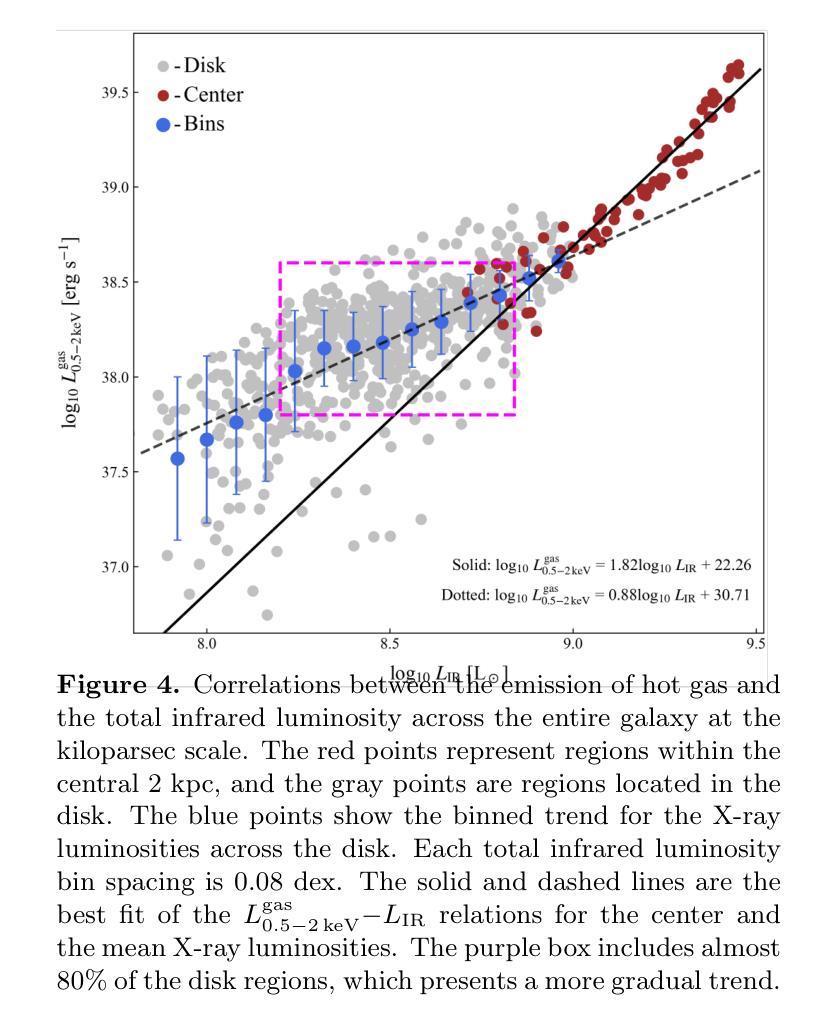
Fire and Ice in the Whirlpool: Spatially Resolved Scaling Relations between X-ray Emitting Hot Gas and Cold Molecular Gas in M51
Authors:Chunyi Zhang, Junfeng Wang, Tian-Wen Cao
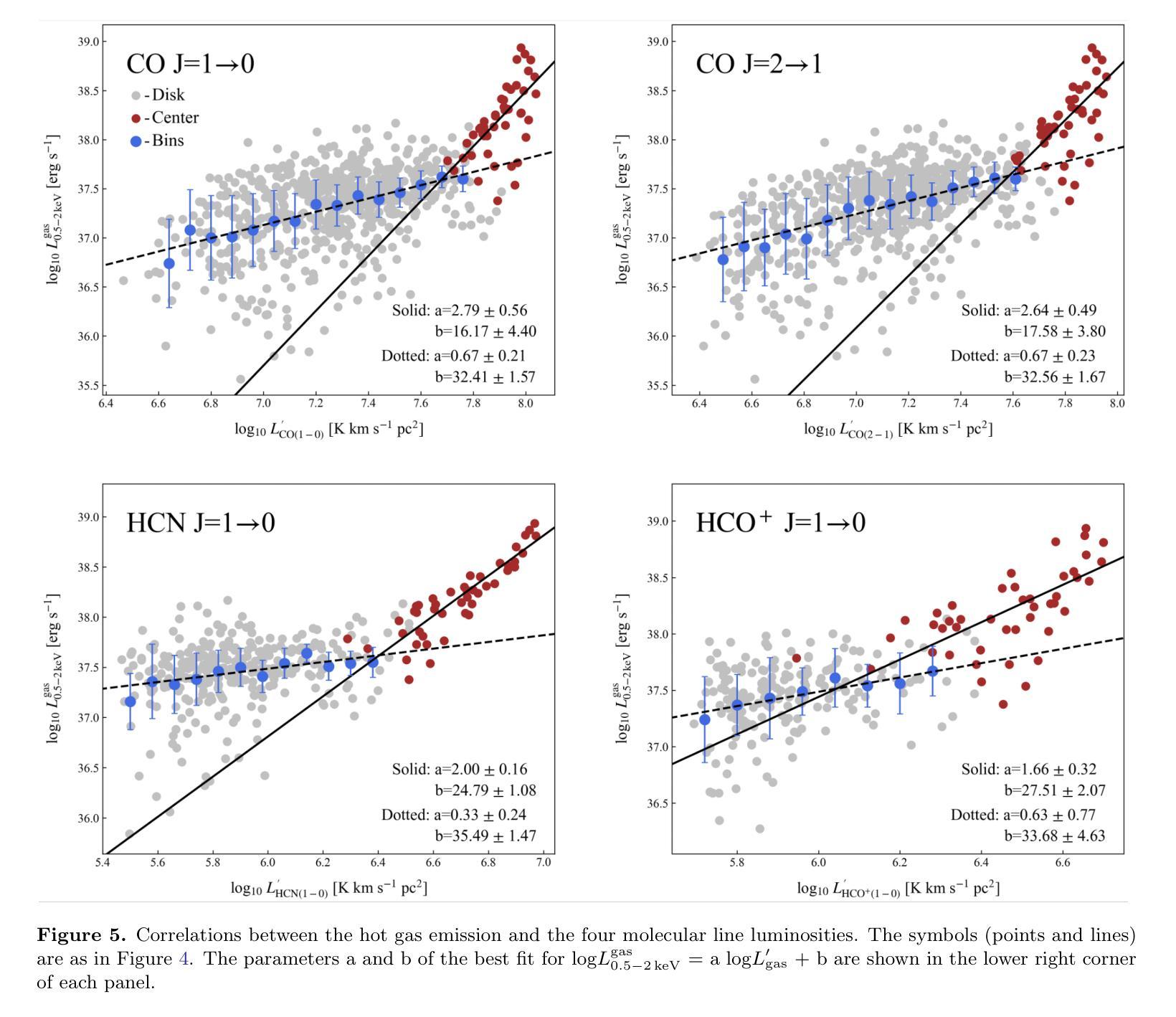
The cold and hot interstellar medium (ISM) in star forming galaxies resembles the reservoir for star formation and associated heating by stellar winds and explosions during stellar evolution, respectively. We utilize data from deep $Chandra$ observations and archival millimeter surveys to study the interconnection between these two phases and the relation to star formation activities in M51 on kiloparsec scales. A sharp radial decrease is present in the hot gas surface brightness profile within the inner 2 kpc of M51. The ratio between the total infrared luminosity ($L_{\rm IR}$) and the hot gas luminosity ($L_{\rm 0.5 - 2,keV}^{\rm gas}$) shows a positive correlation with the galactic radius in the central region. For the entire galaxy, a twofold correlation is revealed in the $L_{\rm 0.5 - 2,keV}^{\rm gas}$${-}$$L_{\rm IR}$ diagram, where $L_{\rm 0.5 - 2,keV}^{\rm gas}$ sharply increases with $L_{\rm IR}$ in the center but varies more slowly in the disk. The best fit gives a steep relation of ${\rm log}(L_{\rm 0.5-2,keV}^{\rm gas} /{\rm erg,s^{-1}})=1.82,{\rm log}(L_{\rm IR} /{L_{\rm \odot}})+22.26$ for the center of M51. The similar twofold correlations are also found in the $L_{\rm 0.5 - 2,keV}^{\rm gas}$${-}$molecular line luminosity ($L^\prime_{\rm gas}$) relations for the four molecular emission lines CO(1-0), CO(2-1), HCN(1-0), and HCO$^+$(1-0). We demonstrate that the core-collapse supernovae (SNe) are the primary source of energy for heating gas in the galactic center of M51, leading to the observed steep $L_{\rm 0.5 - 2,keV}^{\rm gas}$${-}$$L_{\rm IR}$ and $L_{\rm 0.5 - 2,keV}^{\rm gas}$${-}$$L^\prime_{\rm gas}$ relations, as their X-ray radiation efficiencies ($\eta$ $\equiv$ $L_{\rm 0.5 - 2,keV}^{\rm gas}$/$\dot{E}_\mathrm{SN}$) increase with the star formation rate surface densities, where $\dot{E}_\mathrm{SN}$ is the SN mechanical energy input rate.
星际介质(ISM)在星系形成中起到重要作用,冷热交替状态反映了恒星形成及其演化过程中恒星风和爆炸产生的热量变化。我们利用深度钱德拉观测数据和存档毫米波调查数据来研究这两个阶段之间的联系以及与M51中星形成活动的关系,在千秒尺度上。在M51的2kpc内部区域中,热气体表面亮度分布呈现出明显的径向减少趋势。红外总辐射亮度($L_{\rm IR}$)和热气体辐射亮度($L_{\rm 0.5 - 2,keV}^{\rm gas}$)的比率在中心区域与星系半径呈现正相关。对于整个星系而言,在$L_{\rm 0.5 - 2,keV}^{\rm gas}$${-}$$L_{\rm IR}$图上呈现双倍的关联性,其中热气体辐射亮度在中心随红外总辐射亮度而急剧增加,但在盘状区域则变化较慢。最佳拟合给出中心区域的陡峭关系为${\rm log}(L_{\rm 0.5-2,keV}^{\rm gas} /{\rm erg,s^{-1}})=1.82{\rm log}(L_{\rm IR} /{L_{\rm \odot}})+22.26$。在四种分子发射线CO(1-0)、CO(2-1)、HCN(1-0)和HCO+(1-0)的辐射中,也发现了类似的气体辐射亮度和分子线辐射亮度的双倍关联关系。我们证明核心坍缩超新星(SNe)是M51星系中心气体加热的主要能量来源,导致了观察到的陡峭的$L_{\rm 0.5 - 2,keV}^{\rm gas}$${-}$$L_{\rm IR}$和$L_{\rm 0.5 - 2,keV}^{\rm gas}$${-}$$L^\prime_{\rm gas}$关系,因为随着恒星形成率表面密度的增加,其X射线辐射效率($\eta$)也相应增长,其中$\dot{E}_\mathrm{SN}$为超新星的机械能量输入率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures, accepted for publication in the ApJ Letters
Summary
研究发现在星系M51中,冷热气相交介质与恒星形成活动密切相关。利用深度$Chandra$观测数据和毫米波档案调查数据,发现M51内2kpc的热气体表面亮度急剧下降。红外辐射与热气体亮度存在正相关关系,中心区域的关联性尤为显著。中心区域的热气体光度与红外光度之间存在陡峭关系,表明核心崩溃超新星是M51中心气体加热的主要能源来源。
Key Takeaways
- M51星系中的冷热气相交介质与恒星形成活动紧密相关。
- 在M51内2kpc区域观察到热气体表面亮度急剧下降。
- 红外辐射与热气体亮度存在正相关性,这种关系在M51的中心区域尤为显著。
- M51中心区域的热气体光度与红外光度之间存在陡峭关系。
- 核心崩溃超新星是M51中心气体加热的主要能源来源。
- 超新星的X射线辐射效率随着恒星形成率表面密度的增加而增加。
点此查看论文截图

PB-UAP: Hybrid Universal Adversarial Attack For Image Segmentation
Authors:Yufei Song, Ziqi Zhou, Minghui Li, Xianlong Wang, Hangtao Zhang, Menghao Deng, Wei Wan, Shengshan Hu, Leo Yu Zhang
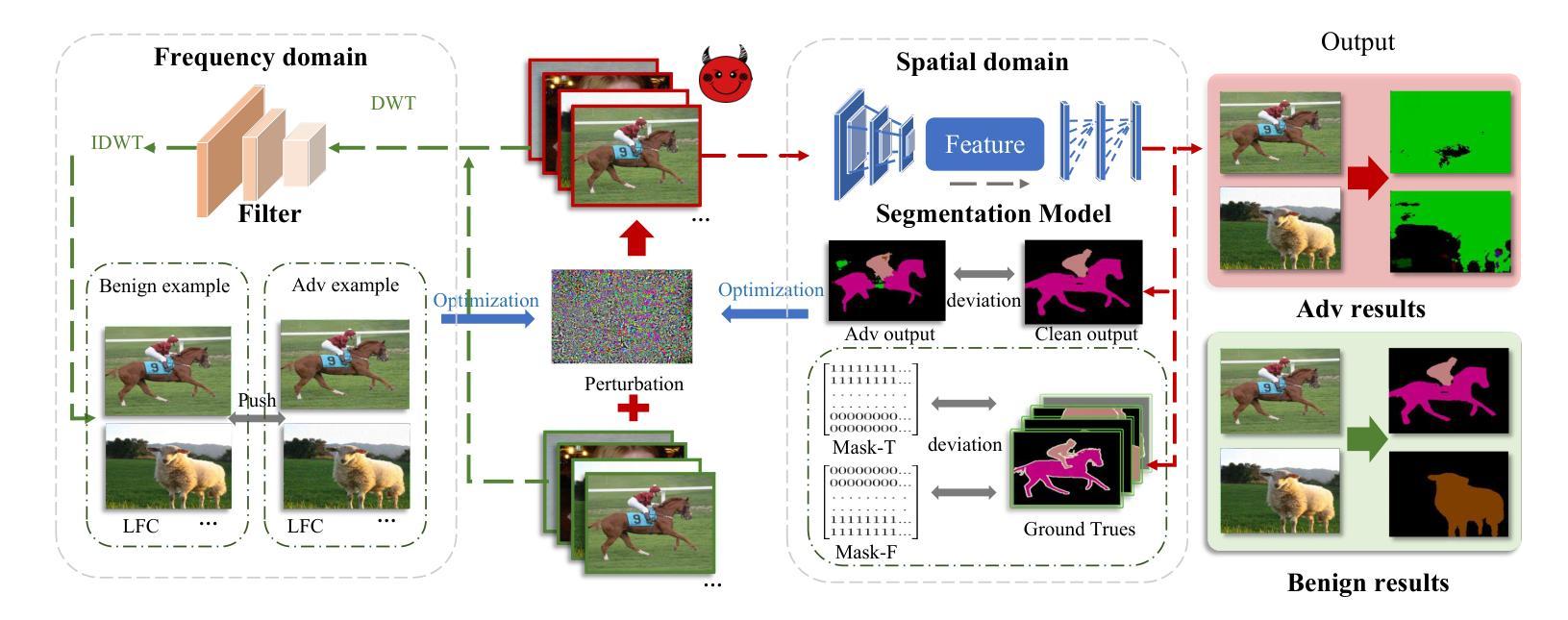
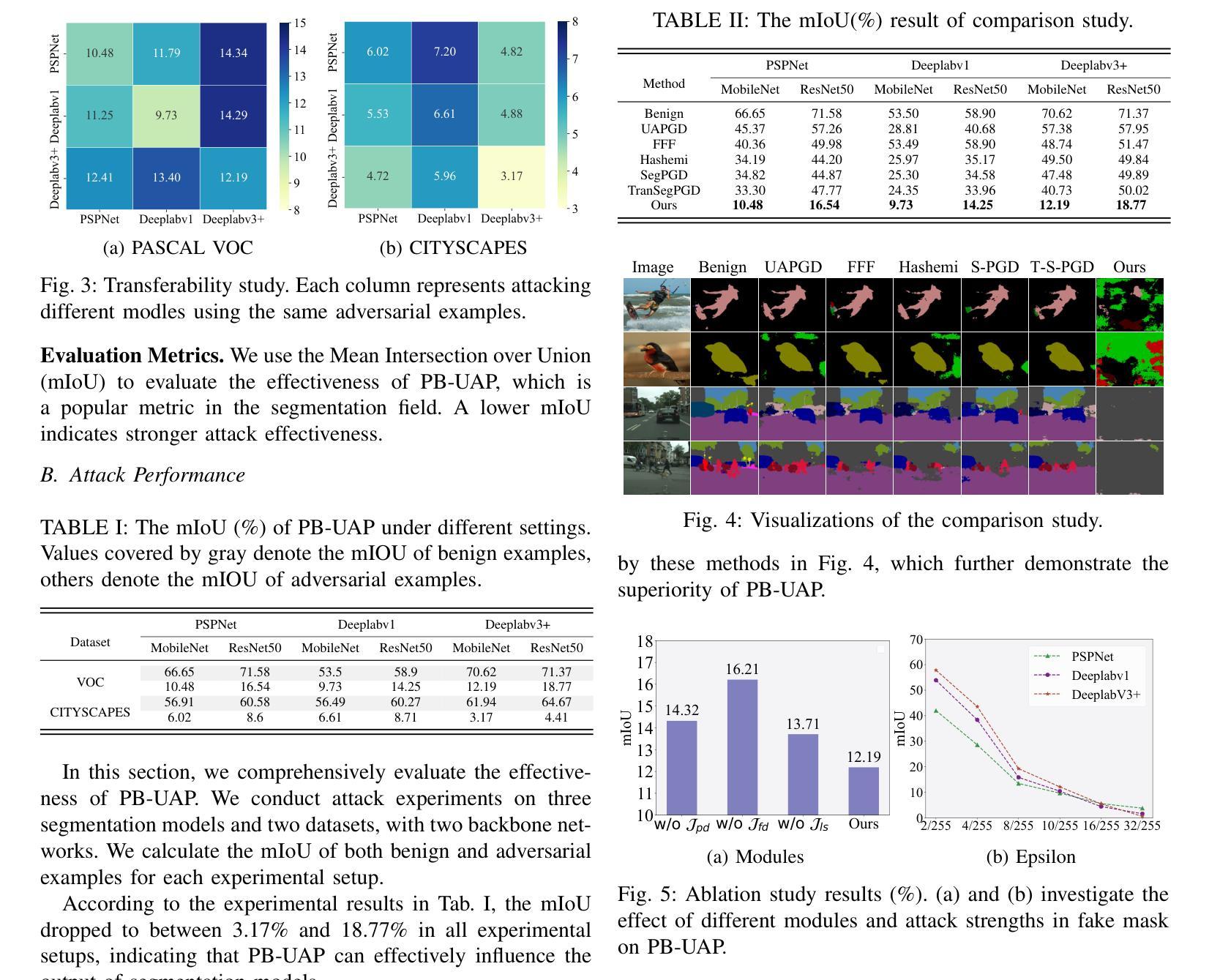
With the rapid advancement of deep learning, the model robustness has become a significant research hotspot, \ie, adversarial attacks on deep neural networks. Existing works primarily focus on image classification tasks, aiming to alter the model’s predicted labels. Due to the output complexity and deeper network architectures, research on adversarial examples for segmentation models is still limited, particularly for universal adversarial perturbations. In this paper, we propose a novel universal adversarial attack method designed for segmentation models, which includes dual feature separation and low-frequency scattering modules. The two modules guide the training of adversarial examples in the pixel and frequency space, respectively. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves high attack success rates surpassing the state-of-the-art methods, and exhibits strong transferability across different models.
随着深度学习的快速发展,模型的稳健性已成为一个重要的研究热点,即对深度神经网络的对抗性攻击。现有工作主要集中在图像分类任务上,旨在改变模型的预测标签。由于输出复杂和网络架构更深,针对分割模型的对抗性示例研究仍然有限,特别是通用对抗性扰动的研究。在本文中,我们提出了一种针对分割模型的新型通用对抗性攻击方法,包括双特征分离和低频散射模块。这两个模块分别在像素和频率空间引导对抗性示例的训练。实验表明,我们的方法实现了高攻击成功率,超越了最先进的方法,并在不同模型之间表现出强大的可迁移性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
随着深度学习技术的飞速发展,模型的稳健性逐渐成为研究热点,特别是针对深度神经网络的对抗性攻击。目前的研究主要关注图像分类任务,旨在改变模型的预测标签。然而,由于输出复杂性和更深的网络架构,针对分割模型的对抗性示例研究仍然有限,特别是通用对抗性扰动的研究。本文提出了一种新型的针对分割模型的通用对抗性攻击方法,包括双特征分离和低频散射模块。这两个模块分别在像素和频率空间指导对抗性示例的训练。实验表明,该方法实现了高攻击成功率,超越了最先进的方法,并在不同模型之间表现出强大的迁移性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型的稳健性成为研究热点,对抗性攻击是其中的重要研究方向。
- 当前研究主要关注图像分类任务的对抗性攻击,改变模型的预测标签。
- 针对分割模型的对抗性示例研究仍然有限,尤其是通用对抗性扰动的研究。
- 本文提出了一种新型的通用对抗性攻击方法,包括双特征分离和低频散射模块。
- 双特征分离模块在像素空间指导对抗性示例的训练。
- 低频散射模块在频率空间指导对抗性示例的训练。
点此查看论文截图

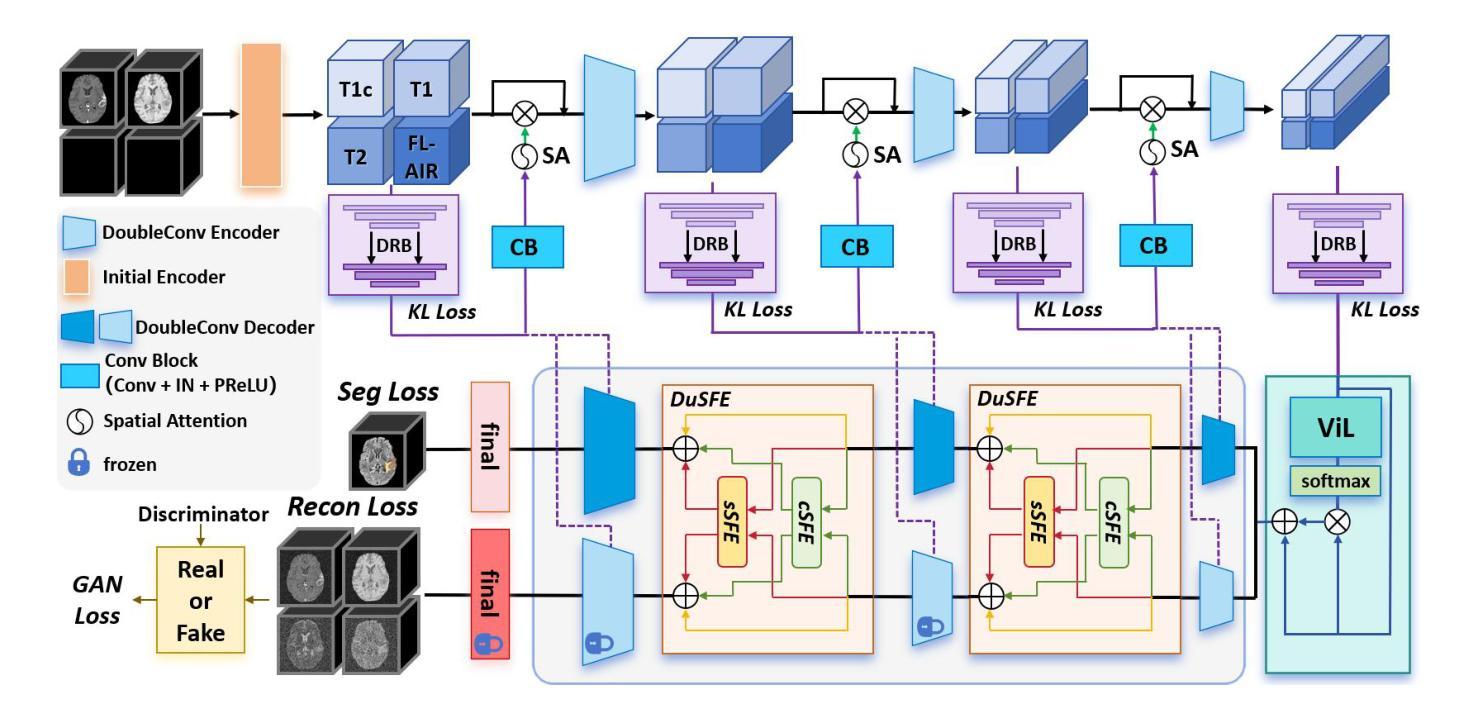
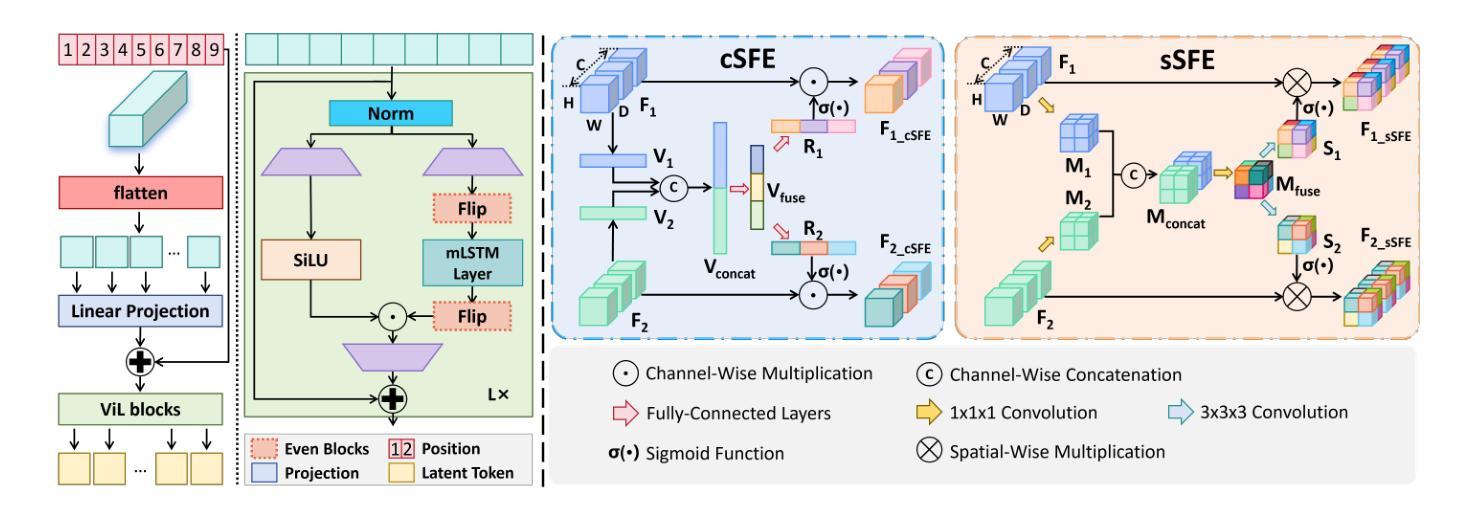
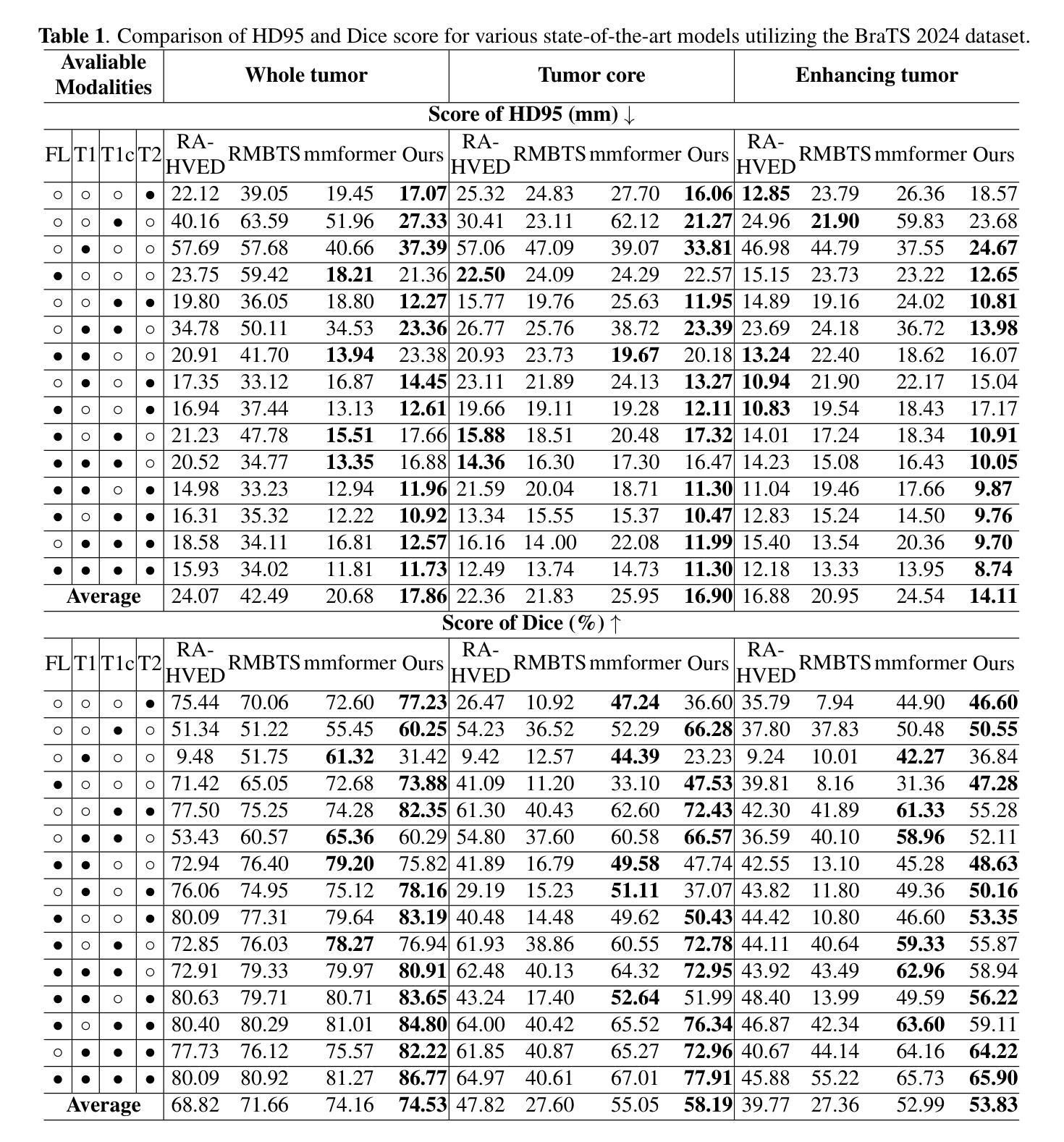
XLSTM-HVED: Cross-Modal Brain Tumor Segmentation and MRI Reconstruction Method Using Vision XLSTM and Heteromodal Variational Encoder-Decoder
Authors:Shenghao Zhu, Yifei Chen, Shuo Jiang, Weihong Chen, Chang Liu, Yuanhan Wang, Xu Chen, Yifan Ke, Feiwei Qin, Changmiao Wang, Zhu Zhu
Neurogliomas are among the most aggressive forms of cancer, presenting considerable challenges in both treatment and monitoring due to their unpredictable biological behavior. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is currently the preferred method for diagnosing and monitoring gliomas. However, the lack of specific imaging techniques often compromises the accuracy of tumor segmentation during the imaging process. To address this issue, we introduce the XLSTM-HVED model. This model integrates a hetero-modal encoder-decoder framework with the Vision XLSTM module to reconstruct missing MRI modalities. By deeply fusing spatial and temporal features, it enhances tumor segmentation performance. The key innovation of our approach is the Self-Attention Variational Encoder (SAVE) module, which improves the integration of modal features. Additionally, it optimizes the interaction of features between segmentation and reconstruction tasks through the Squeeze-Fusion-Excitation Cross Awareness (SFECA) module. Our experiments using the BraTS 2024 dataset demonstrate that our model significantly outperforms existing advanced methods in handling cases where modalities are missing. Our source code is available at https://github.com/Quanato607/XLSTM-HVED.
神经胶质瘤是最具侵袭性的癌症形式之一,由于其不可预测的生物行为,为治疗和监测带来了相当大的挑战。目前,磁共振成像(MRI)是诊断和监测胶质瘤的首选方法。然而,缺乏特定的成像技术往往会影响成像过程中肿瘤分割的准确性。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了XLSTM-HVED模型。该模型结合了异模式编码器-解码器框架和Vision XLSTM模块,以重建缺失的MRI模式。通过深度融合空间和时间特征,提高了肿瘤分割的性能。我们的方法的关键创新点是自注意力变分编码器(SAVE)模块,它改进了模式特征的融合。此外,它通过挤压-融合-兴奋交叉意识(SFECA)模块优化了分割和重建任务之间的特征交互。我们使用BraTS 2024数据集进行的实验表明,我们的模型在处理缺失模式的情况时显著优于现有的高级方法。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/Quanato607/XLSTM-HVED找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 2 figures
Summary
神经胶质瘤是最具侵袭性的癌症之一,其生物行为不可预测,为治疗和监测带来重大挑战。当前,磁共振成像(MRI)是诊断和监测胶质瘤的首选方法,但缺乏特定的成像技术,影响肿瘤分割的准确性。为解决这一问题,我们引入了XLSTM-HVED模型。该模型结合异模编码器-解码器框架与Vision XLSTM模块,重建缺失的MRI模式。通过深度融合空间和时间的特征,提高了肿瘤分割的性能。我们的方法的关键创新在于自注意力变分编码器(SAVE)模块,它改进了模态特征的融合。此外,它通过挤压-融合-兴奋交叉意识(SFECA)模块优化了分割和重建任务之间的特征交互。使用BraTS 2024数据集的实验表明,我们的模型在处理缺失模态的情况下显著优于现有高级方法。
Key Takeaways
- 神经胶质瘤治疗与监测存在挑战,因其生物行为不可预测。
- 磁共振成像(MRI)是当前诊断和监测胶质瘤的主要手段。
- 缺乏特定的成像技术会影响肿瘤分割的准确性。
- 引入的XLSTM-HVED模型通过结合异模编码器-解码器框架与Vision XLSTM模块,旨在解决这一问题。
- XLSTM-HVED模型通过深度融合空间和时间的特征,提高了肿瘤分割的性能。
- 自注意力变分编码器(SAVE)模块是该方法的关键创新点,改进了模态特征的融合。
点此查看论文截图

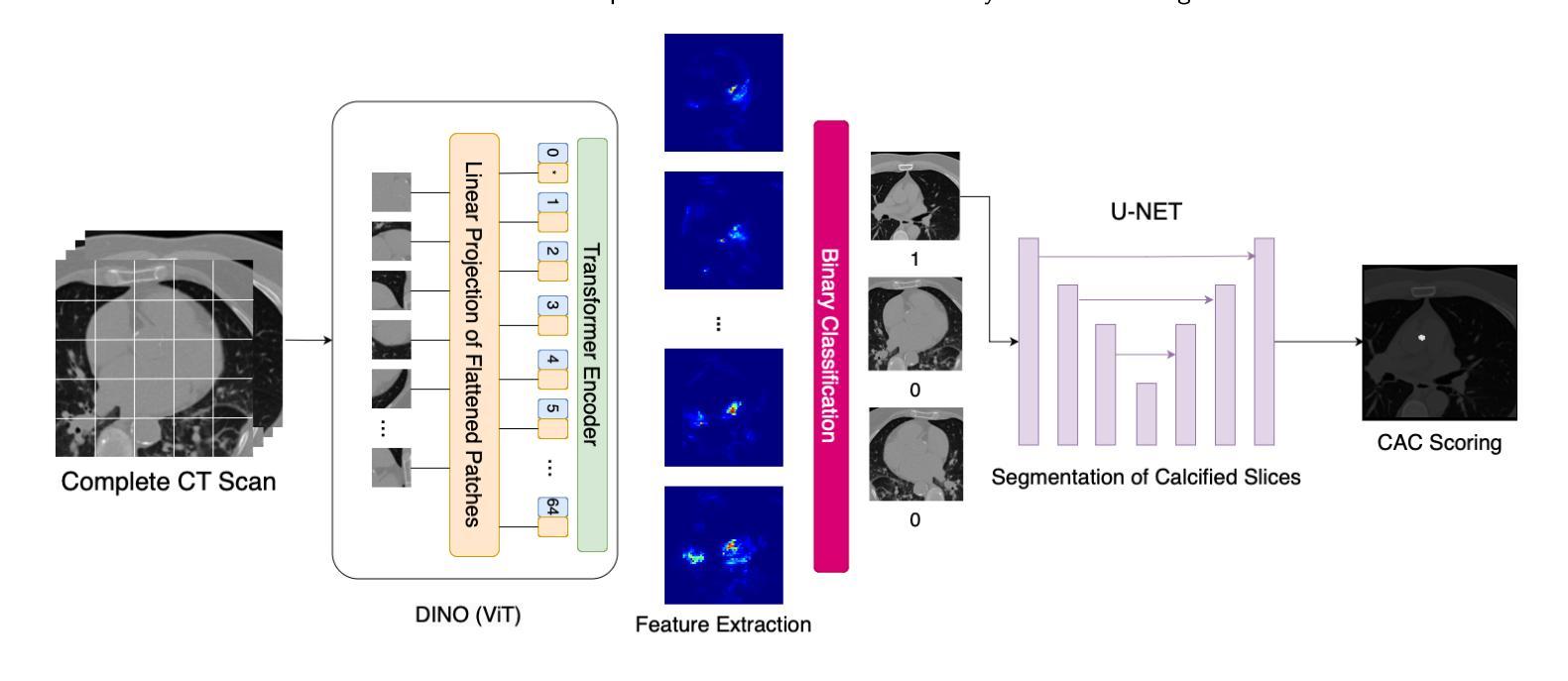
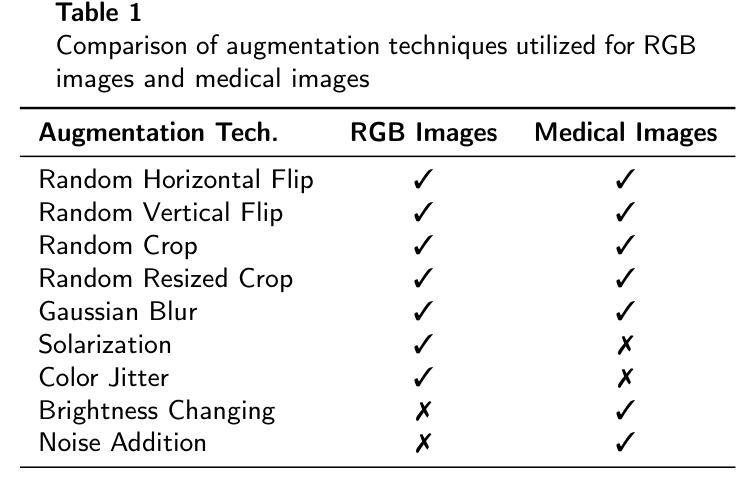
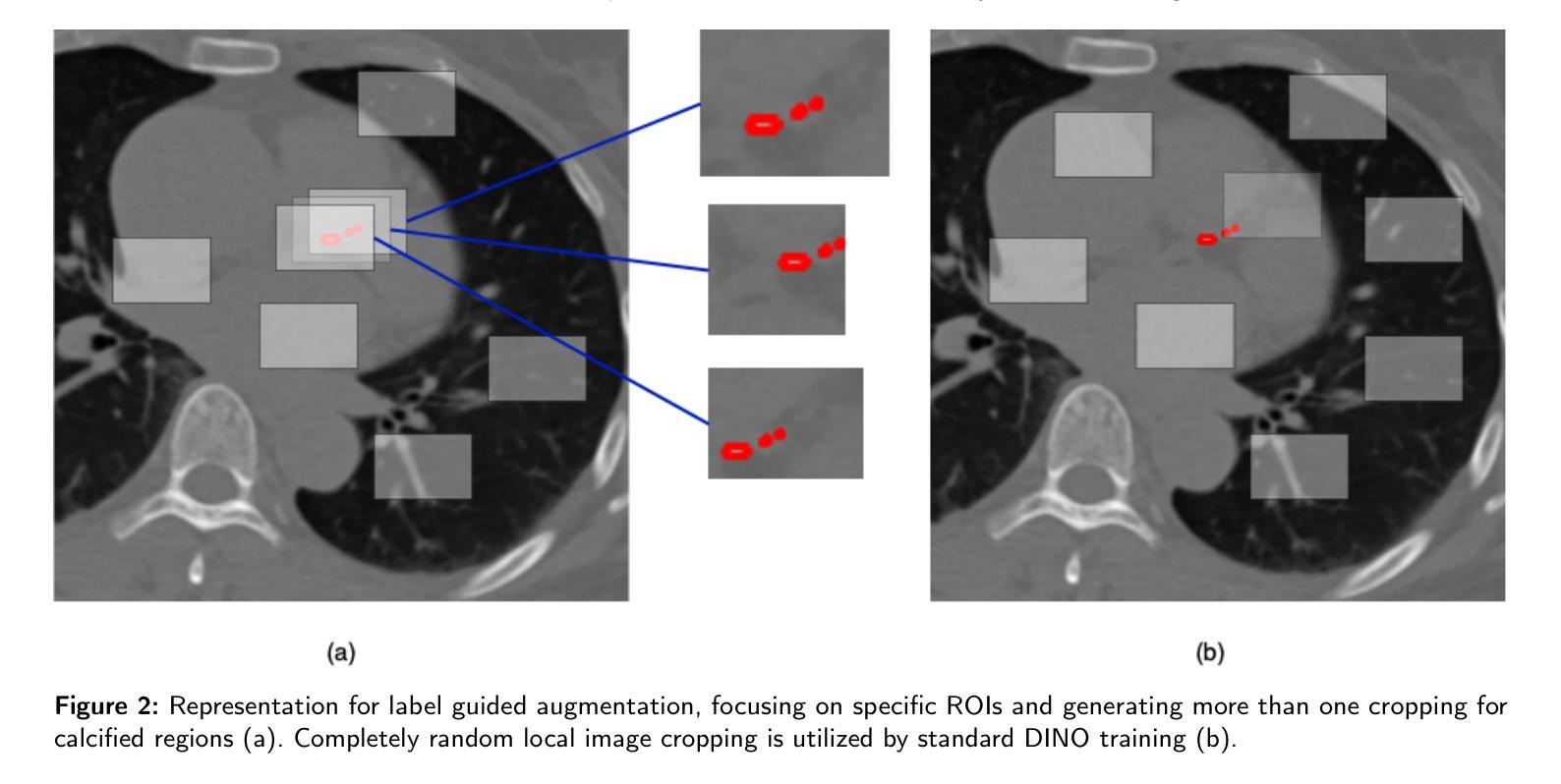
DINO-LG: A Task-Specific DINO Model for Coronary Calcium Scoring
Authors:Mahmut S. Gokmen, Caner Ozcan, Moneera N. Haque, Steve W. Leung, C. Seth Parker, W. Brent Seales, Cody Bumgardner
Coronary artery disease (CAD), one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, necessitates effective risk assessment strategies, with coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring via computed tomography (CT) being a key method for prevention. Traditional methods, primarily based on UNET architectures implemented on pre-built models, face challenges like the scarcity of annotated CT scans containing CAC and imbalanced datasets, leading to reduced performance in segmentation and scoring tasks. In this study, we address these limitations by incorporating the self-supervised learning (SSL) technique of DINO (self-distillation with no labels), which trains without requiring CAC-specific annotations, enhancing its robustness in generating distinct features. The DINO-LG model, which leverages label guidance to focus on calcified areas, achieves significant improvements, with a sensitivity of 89% and specificity of 90% for detecting CAC-containing CT slices, compared to the standard DINO model’s sensitivity of 79% and specificity of 77%. Additionally, false-negative and false-positive rates are reduced by 49% and 59%, respectively, instilling greater confidence in clinicians when ruling out calcification in low-risk patients and minimizing unnecessary imaging reviews by radiologists. Further, CAC scoring and segmentation tasks are conducted using a basic UNET architecture, applied specifically to CT slices identified by the DINO-LG model as containing calcified areas. This targeted approach enhances CAC scoring accuracy by feeding the UNET model with relevant slices, significantly improving diagnostic precision, reducing both false positives and false negatives, and ultimately lowering overall healthcare costs by minimizing unnecessary tests and treatments, presenting a valuable advancement in CAD risk assessment.
冠状动脉疾病(CAD)是全球主要的死亡原因之一,必须进行有效的风险评估策略。计算机断层扫描(CT)中的冠状动脉钙化(CAC)评分是预防的关键方法。传统方法主要基于预构建模型上实施的UNET架构,面临挑战,如含有CAC的标注CT扫描稀缺和数据集不平衡,导致分割和评分任务性能下降。本研究通过融入无监督学习(SSL)技术来解决这些问题,即无需CAC特定标注进行训练的DINO(无标签自我蒸馏)技术,增强了其在生成独特特征方面的稳健性。利用标签指导聚焦于钙化区域的DINO-LG模型,与标准DINO模型相比,检测含有CAC的CT切片的敏感度和特异性分别达到了89%和90%(DINO模型为79%和77%),取得了显著改进。此外,假阴性和假阳性率分别降低了49%和59%,使临床医生在排除低风险患者的钙化情况时有更大的信心,并减少了对放射科医生进行不必要的影像复查的需求。此外,使用基本UNET架构进行CAC评分和分割任务,该架构特定应用于DINO-LG模型识别为含有钙化区域的CT切片。这种有针对性的方法通过向UNET模型提供相关的切片,提高了CAC评分的准确性,从而显著提高了诊断的精确度,减少了假阳性和假阴性结果,并最终通过减少不必要的测试和治疗来降低整体医疗保健成本,为CAD风险评估提供了宝贵的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Developed by Center for Applied Artificial Intelligence (CAAI), University of Kentucky
Summary
本摘要以汉语简洁表述论文主要内容:针对冠状动脉疾病的风险评估,研究采用无标签自监督学习方法DINO结合标签引导(DINO-LG模型)提升对含钙化区域CT切片的检测性能,通过精准定位钙化区域,提高冠状动脉钙化(CAC)评分和分割任务的准确性,为临床医生提供更可靠的诊断依据,降低误诊率和不必要的影像复查,进而降低整体医疗保健成本。
Key Takeaways
- 冠状动脉疾病(CAD)是全球主要的死亡原因之一,需要有效的风险评估策略。
- 冠状动脉钙化(CAC)评分是预防CAD的关键方法,但传统方法面临数据标注不足和数据不平衡的挑战。
- 研究采用无标签自监督学习(SSL)技术中的DINO方法,无需CAC特定标注进行训练,提高了特征生成的稳健性。
- DINO结合标签引导(DINO-LG模型)显著提高了检测CAC含钙化区域CT切片的敏感性和特异性。
- DINO-LG模型降低了误诊率和不必要的影像复查,增强了医生对低危患者钙化排除的信心。
- 研究采用基本UNET架构进行CAC评分和分割任务,针对DINO-LG模型识别出的含钙化区域CT切片进行,提高了诊断精度。
点此查看论文截图

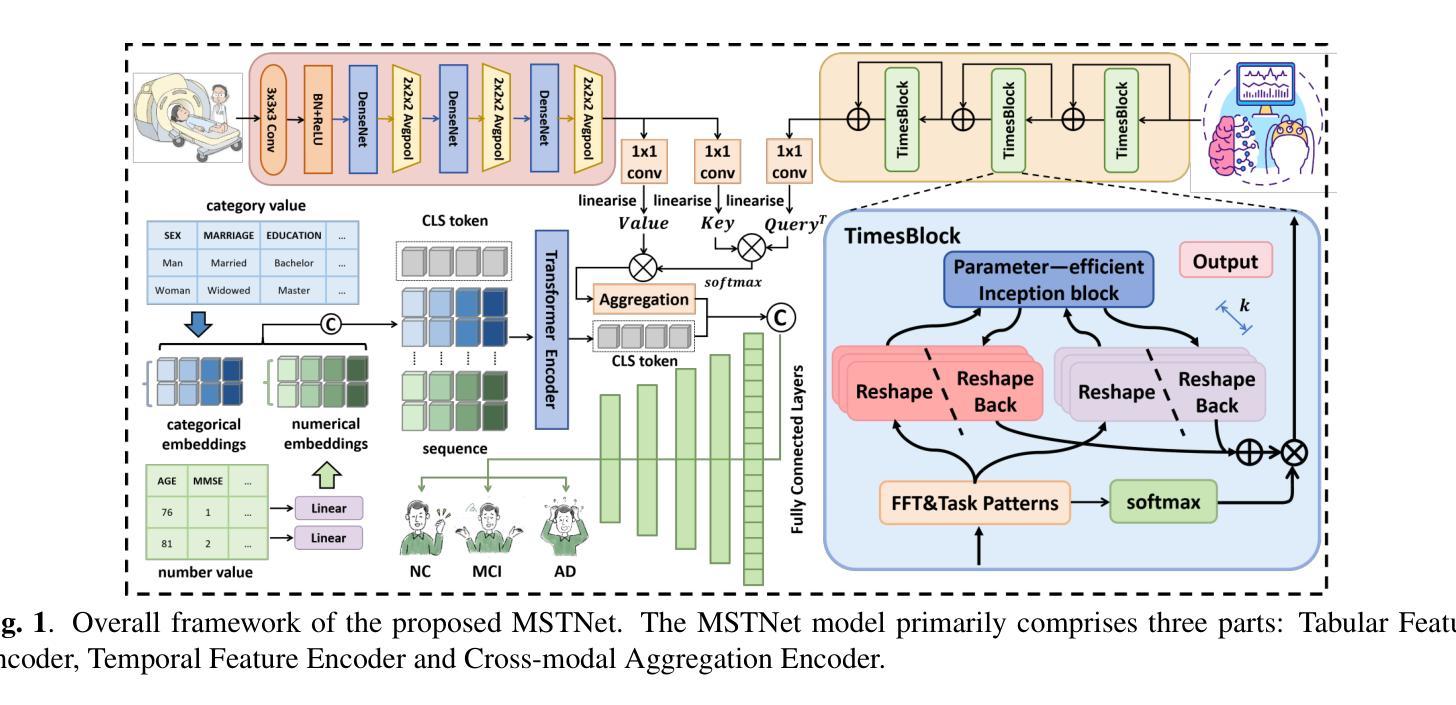
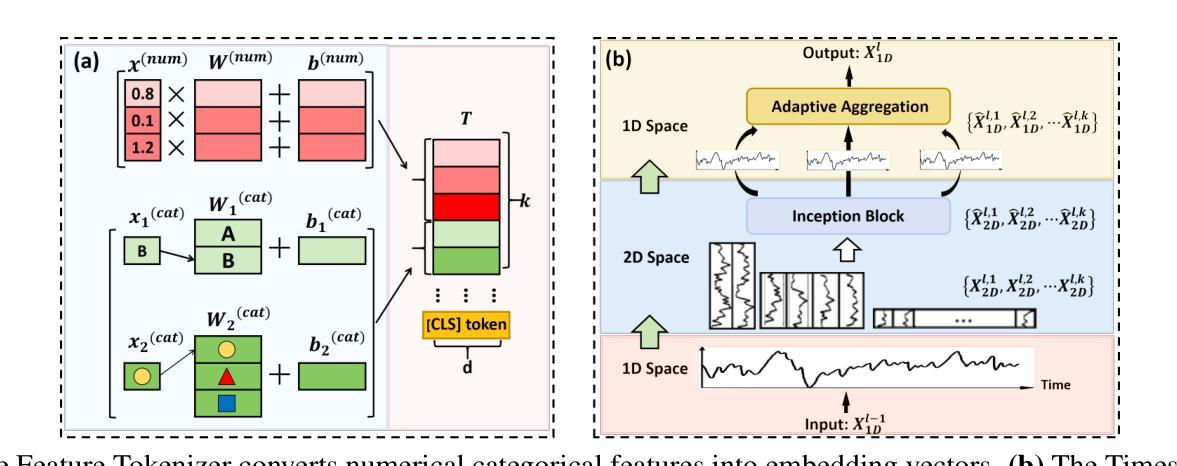
Toward Robust Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease via an Integrated Multimodal Learning Approach
Authors:Yifei Chen, Shenghao Zhu, Zhaojie Fang, Chang Liu, Binfeng Zou, Yuhe Wang, Shuo Chang, Fan Jia, Feiwei Qin, Jin Fan, Yong Peng, Changmiao Wang
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a complex neurodegenerative disorder marked by memory loss, executive dysfunction, and personality changes. Early diagnosis is challenging due to subtle symptoms and varied presentations, often leading to misdiagnosis with traditional unimodal diagnostic methods due to their limited scope. This study introduces an advanced multimodal classification model that integrates clinical, cognitive, neuroimaging, and EEG data to enhance diagnostic accuracy. The model incorporates a feature tagger with a tabular data coding architecture and utilizes the TimesBlock module to capture intricate temporal patterns in Electroencephalograms (EEG) data. By employing Cross-modal Attention Aggregation module, the model effectively fuses Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) spatial information with EEG temporal data, significantly improving the distinction between AD, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Normal Cognition. Simultaneously, we have constructed the first AD classification dataset that includes three modalities: EEG, MRI, and tabular data. Our innovative approach aims to facilitate early diagnosis and intervention, potentially slowing the progression of AD. The source code and our private ADMC dataset are available at https://github.com/JustlfC03/MSTNet.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种复杂的神经退行性疾病,以记忆丧失、执行功能障碍和个性改变为特征。由于早期症状细微且表现各异,早期诊断具有挑战性,往往使用传统的单一诊断方法会导致误诊,因为它们的应用范围有限。本研究引入了一种先进的跨模态分类模型,该模型融合了临床、认知、神经影像学和脑电图数据,以提高诊断的准确性。该模型采用特征标签器和表格数据编码架构,并使用TimesBlock模块捕捉脑电图(EEG)数据中复杂的时间模式。通过采用跨模态注意力聚合模块,该模型有效地融合了磁共振成像(MRI)的空间信息与EEG的时间数据,显著提高了对阿尔茨海默病、轻度认知障碍和正常认知的区分能力。同时,我们构建了首个包含三种模式(EEG、MRI和表格数据)的AD分类数据集。我们的创新方法旨在促进早期诊断和干预,可能有助于减缓阿尔茨海默病的进展。源代码和我们的私有ADMC数据集可在https://github.com/JustlfC03/MSTNet获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本研究引入了一种先进的多模式分类模型,该模型集成了临床、认知、神经成像和脑电图数据,以提高对阿尔茨海默病(AD)的诊断准确性。通过采用跨模态注意力聚合模块,模型有效融合了磁共振成像(MRI)的空间信息与脑电图(EEG)的时间数据,显著提高了对AD、轻度认知障碍和正常认知的区分能力。
Key Takeaways
- 阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种复杂的神经退行性疾病,早期确诊具有挑战性。
- 传统的一维诊断方法由于局限性,常常导致误诊。
- 本研究提出了一种多模式分类模型,集成了临床、认知、神经成像和EEG数据,以提高诊断准确性。
- 模型采用特征标签器和表格数据编码架构。
- TimesBlock模块用于捕捉EEG数据中复杂的时间模式。
- Cross-modal Attention Aggregation模块有效融合了MRI的空间信息和EEG的时间数据,提高了对AD和其他认知状态的区分能力。
点此查看论文截图

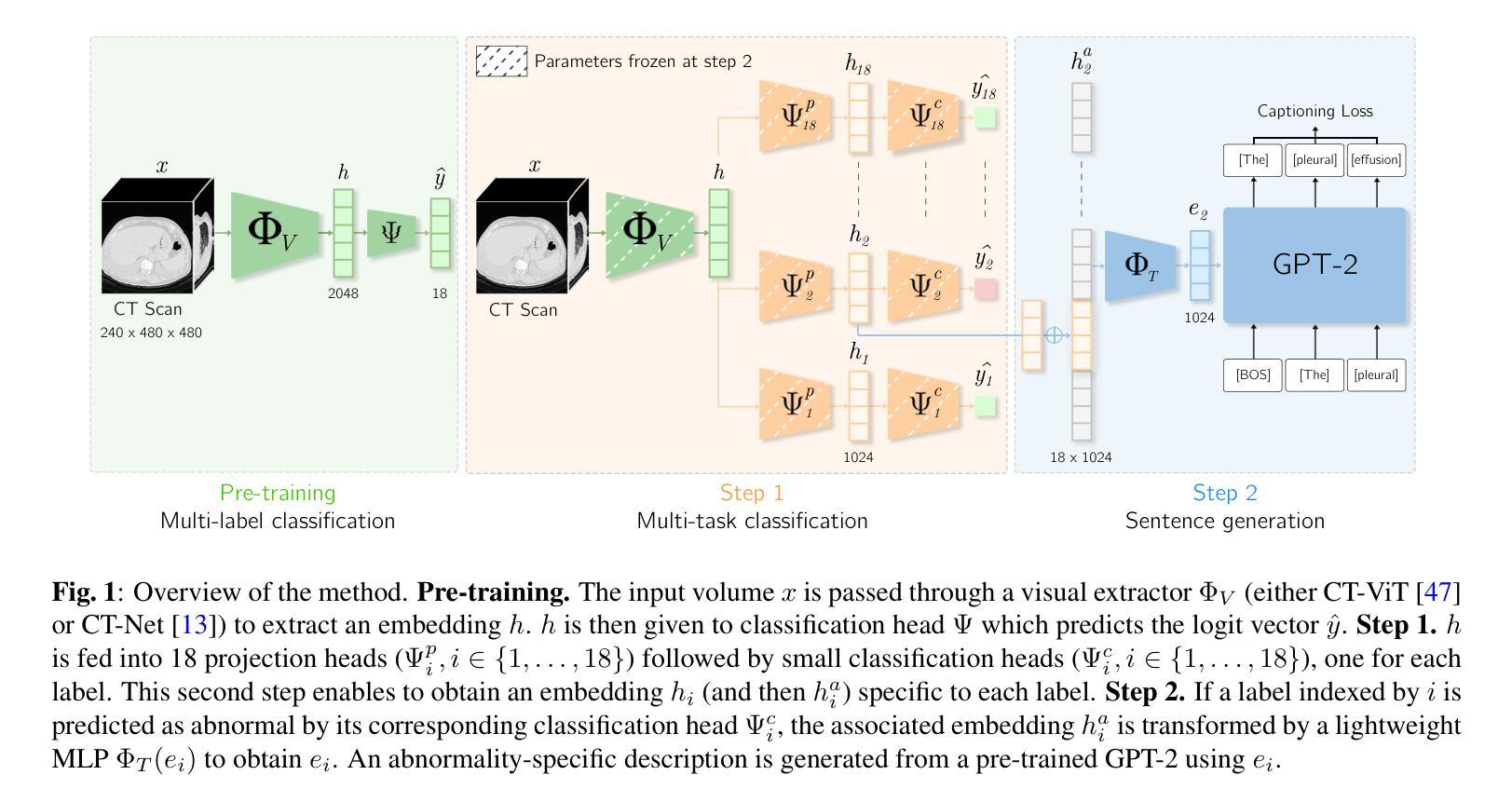
CT-AGRG: Automated Abnormality-Guided Report Generation from 3D Chest CT Volumes
Authors:Theo Di Piazza
The rapid increase of computed tomography (CT) scans and their time-consuming manual analysis have created an urgent need for robust automated analysis techniques in clinical settings. These aim to assist radiologists and help them managing their growing workload. Existing methods typically generate entire reports directly from 3D CT images, without explicitly focusing on observed abnormalities. This unguided approach often results in repetitive content or incomplete reports, failing to prioritize anomaly-specific descriptions. We propose a new anomaly-guided report generation model, which first predicts abnormalities and then generates targeted descriptions for each. Evaluation on a public dataset demonstrates significant improvements in report quality and clinical relevance. We extend our work by conducting an ablation study to demonstrate its effectiveness.
计算机断层扫描(CT)扫描的迅速增加及其耗时的人工分析,为临床环境中稳健的自动化分析技术创造了迫切的需求。这些技术的目标是帮助放射科医生处理他们日益增长的工作量。现有方法通常直接从3D CT图像生成整个报告,而没有明确关注观察到的异常情况。这种无导向的方法常常导致内容重复或报告不完整,无法优先提供异常情况的描述。我们提出了一种新的异常导向的报告生成模型,该模型首先预测异常情况,然后为每一个异常情况生成有针对性的描述。在公共数据集上的评估表明,该模型在报告质量和临床相关性方面都有显著提高。我们通过进行消融研究来进一步证明其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 9 figures, accepted to ISBI 2025
Summary
文中指出CT扫描数量的迅速增加及其手动分析的耗时性,临床环境中对稳健的自动化分析技术有着迫切的需求。现有方法通常直接从3D CT图像生成整个报告,没有特别强调观察到的异常。本文提出了一种新的异常引导报告生成模型,该模型首先预测异常,然后为每个异常生成有针对性的描述。在公共数据集上的评估证明了该模型在报告质量和临床相关性方面的显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- CT扫描数量增加,手动分析耗时,需要自动化分析技术辅助放射科医生处理大量工作。
- 现有方法直接从3D CT图像生成报告,缺乏重点关注异常。
- 新的异常引导报告生成模型首先预测异常,然后为每个异常生成描述。
- 在公共数据集上的评估证明了新模型在报告质量和临床相关性方面的显著提高。
- 新模型通过生成针对异常的描述,能够减少重复性内容和提高报告的完整性。
- 该研究通过进行消融研究来展示其模型的有效性。
点此查看论文截图