⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-07 更新
UAV-DETR: Efficient End-to-End Object Detection for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery
Authors:Huaxiang Zhang, Kai Liu, Zhongxue Gan, Guo-Niu Zhu
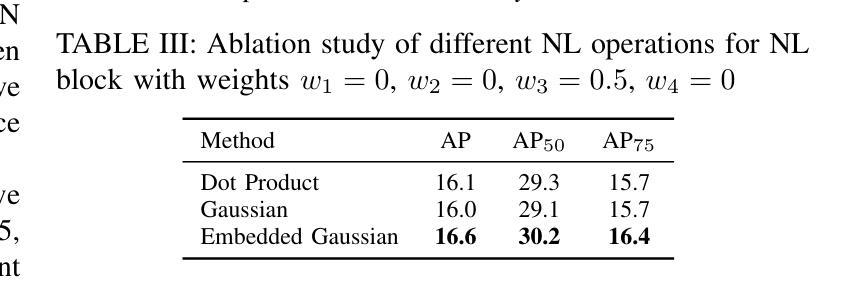
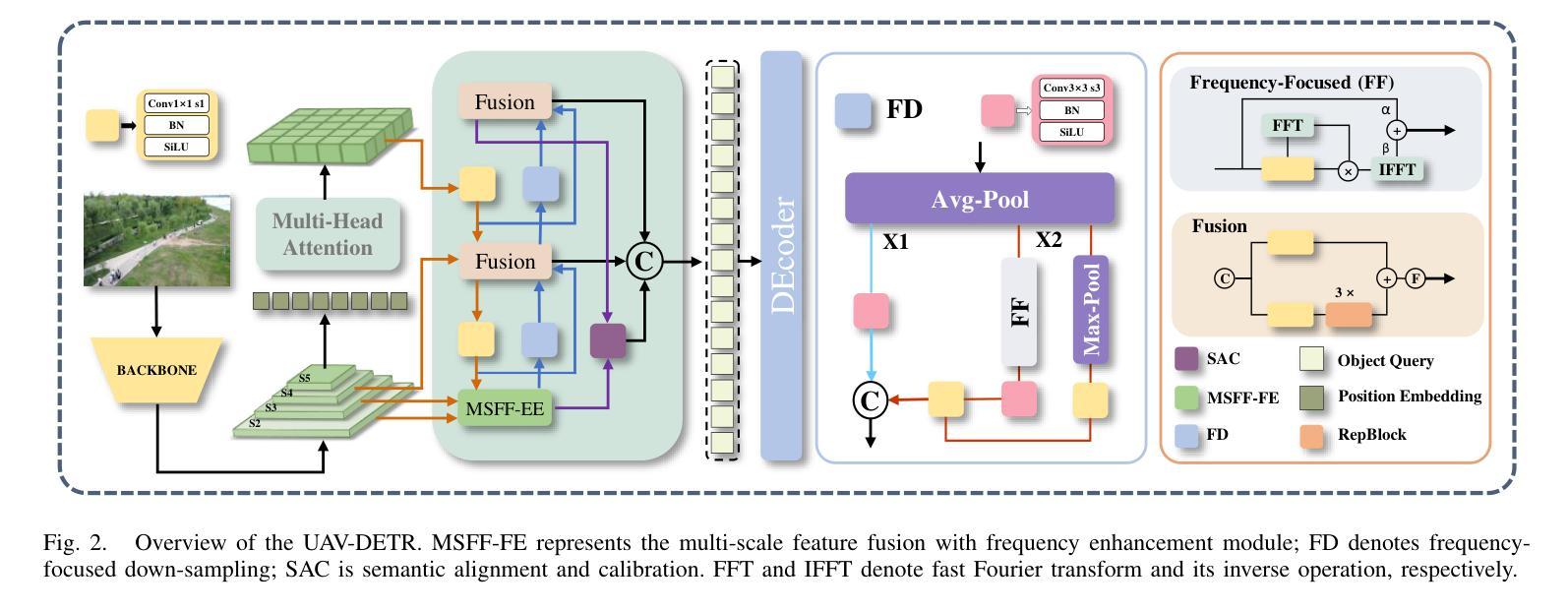
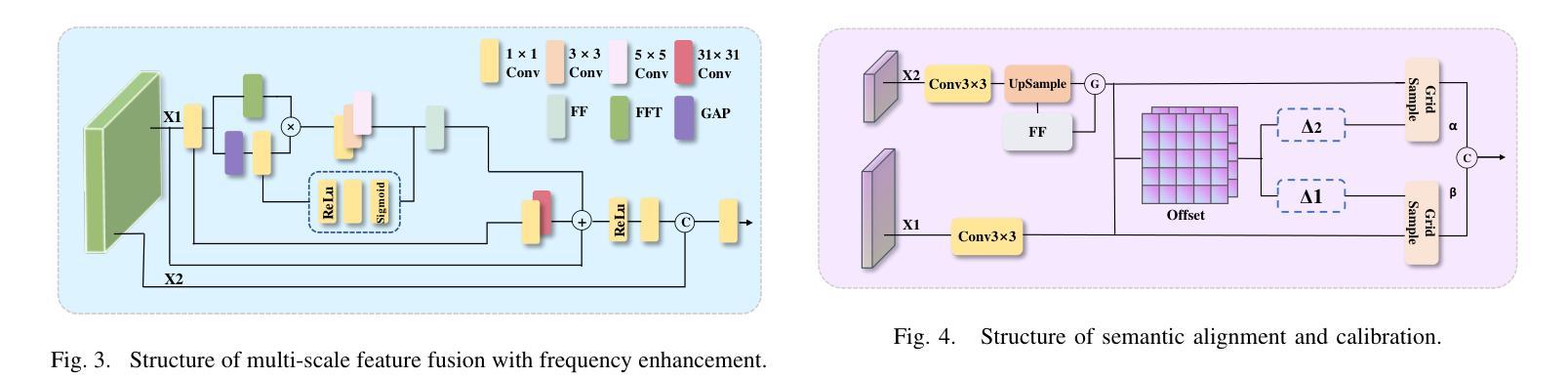
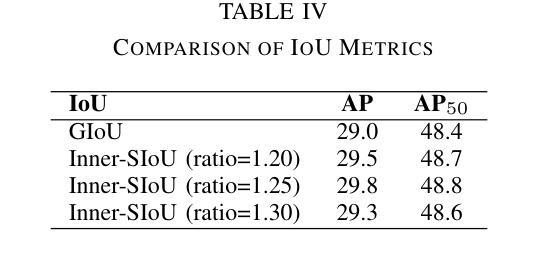
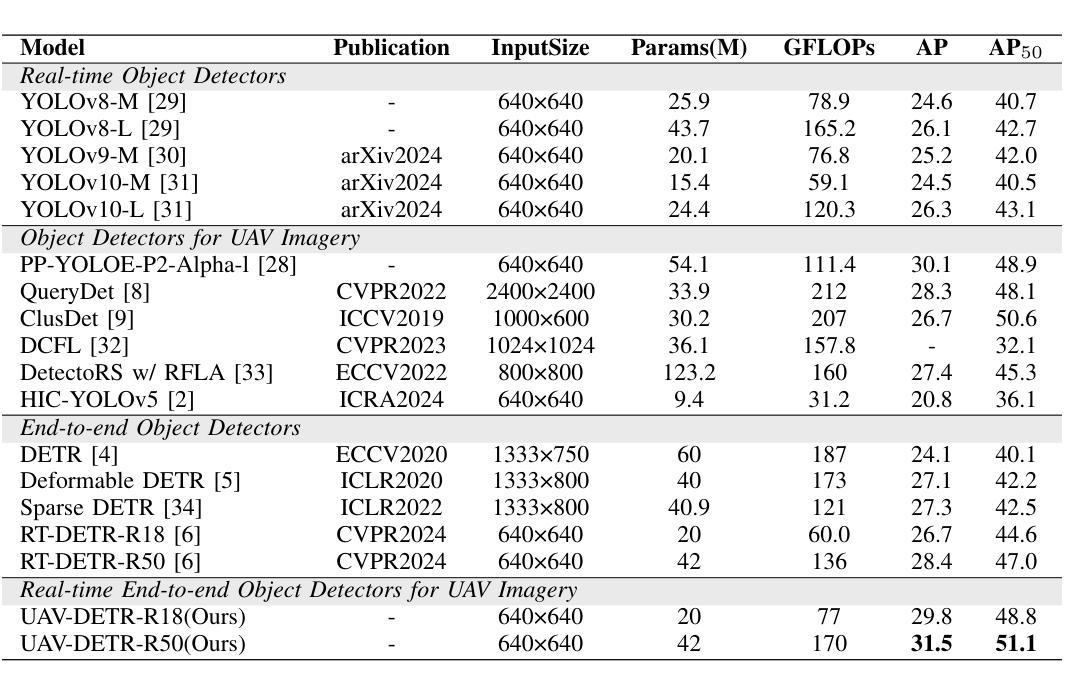
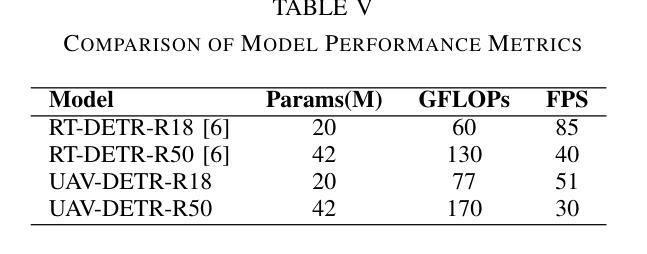
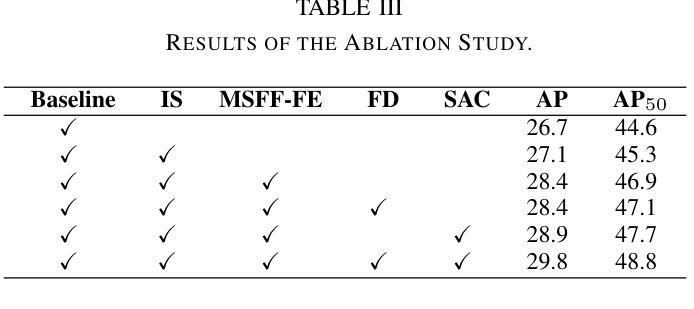
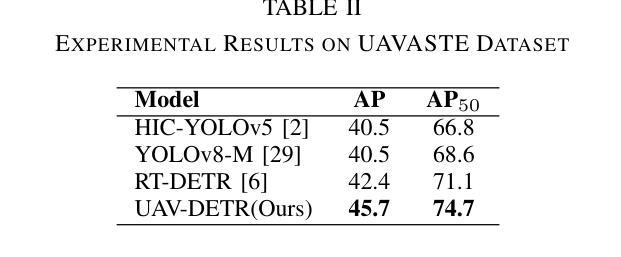
Unmanned aerial vehicle object detection (UAV-OD) has been widely used in various scenarios. However, most existing UAV-OD algorithms rely on manually designed components, which require extensive tuning. End-to-end models that do not depend on such manually designed components are mainly designed for natural images, which are less effective for UAV imagery. To address such challenges, this paper proposes an efficient detection transformer (DETR) framework tailored for UAV imagery, i.e., UAV-DETR. The framework includes a multi-scale feature fusion with frequency enhancement module, which captures both spatial and frequency information at different scales. In addition, a frequency-focused down-sampling module is presented to retain critical spatial details during down-sampling. A semantic alignment and calibration module is developed to align and fuse features from different fusion paths. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization of our approach across various UAV imagery datasets. On the VisDrone dataset, our method improves AP by 3.1% and $\text{AP}_{50}$ by 4.2% over the baseline. Similar enhancements are observed on the UAVVaste dataset. The project page: https://github.com/ValiantDiligent/UAV-DETR
无人机载体目标检测(UAV-OD)在各种场景中已得到广泛应用。然而,大多数现有的UAV-OD算法依赖于手动设计的组件,需要大量的调整。不依赖于此类手动设计组件的端到端模型主要设计用于自然图像,但对于无人机图像则效果较差。为了应对这些挑战,本文提出了一种针对无人机图像的的高效检测转换器(DETR)框架,即UAV-DETR。该框架包括一个具有频率增强模块的多尺度特征融合,能够捕获不同尺度的空间和时间频率信息。此外,还推出了一个专注于频率的下采样模块,以在下采样过程中保留关键的空间细节。开发了一个语义对齐和校准模块,以对齐和融合来自不同融合路径的特征。实验结果表明,我们的方法在各种无人机图像数据集上的有效性和通用性。在VisDrone数据集上,我们的方法较基线提高了3.1%的AP和4.2%的AP50。在UAVVaste数据集上也观察到了类似的改进。项目页面:https://github.com/ValiantDiligent/UAV-DETR
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文针对无人机图像的特点,提出了一种高效检测器Transformer(DETR)框架,即UAV-DETR。该框架融合了多尺度特征融合与频率增强模块,能够捕捉不同尺度的空间与频率信息。同时,它采用频率聚焦下采样模块保留关键空间细节,并开发了语义对齐与校准模块来融合不同融合路径的特征。实验结果表明,该方法在多种无人机图像数据集上具有良好的有效性和泛化性能,特别是对比基线方法显著提高了AP和AP50指标。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种针对无人机图像特点的DETR框架,即UAV-DETR。
- UAV-DETR采用多尺度特征融合与频率增强模块,捕捉不同尺度的空间与频率信息。
- 框架中包含频率聚焦下采样模块,旨在保留关键空间细节。
- 开发了语义对齐与校准模块,融合不同融合路径的特征。
- 实验结果证明了该框架在各种无人机图像数据集上的有效性和泛化性能。
- 在VisDrone数据集上,相比基线方法,UAV-DETR提高了AP和AP50指标。
点此查看论文截图

Uncertainty and Energy based Loss Guided Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Rini Smita Thakur, Vinod K. Kurmi
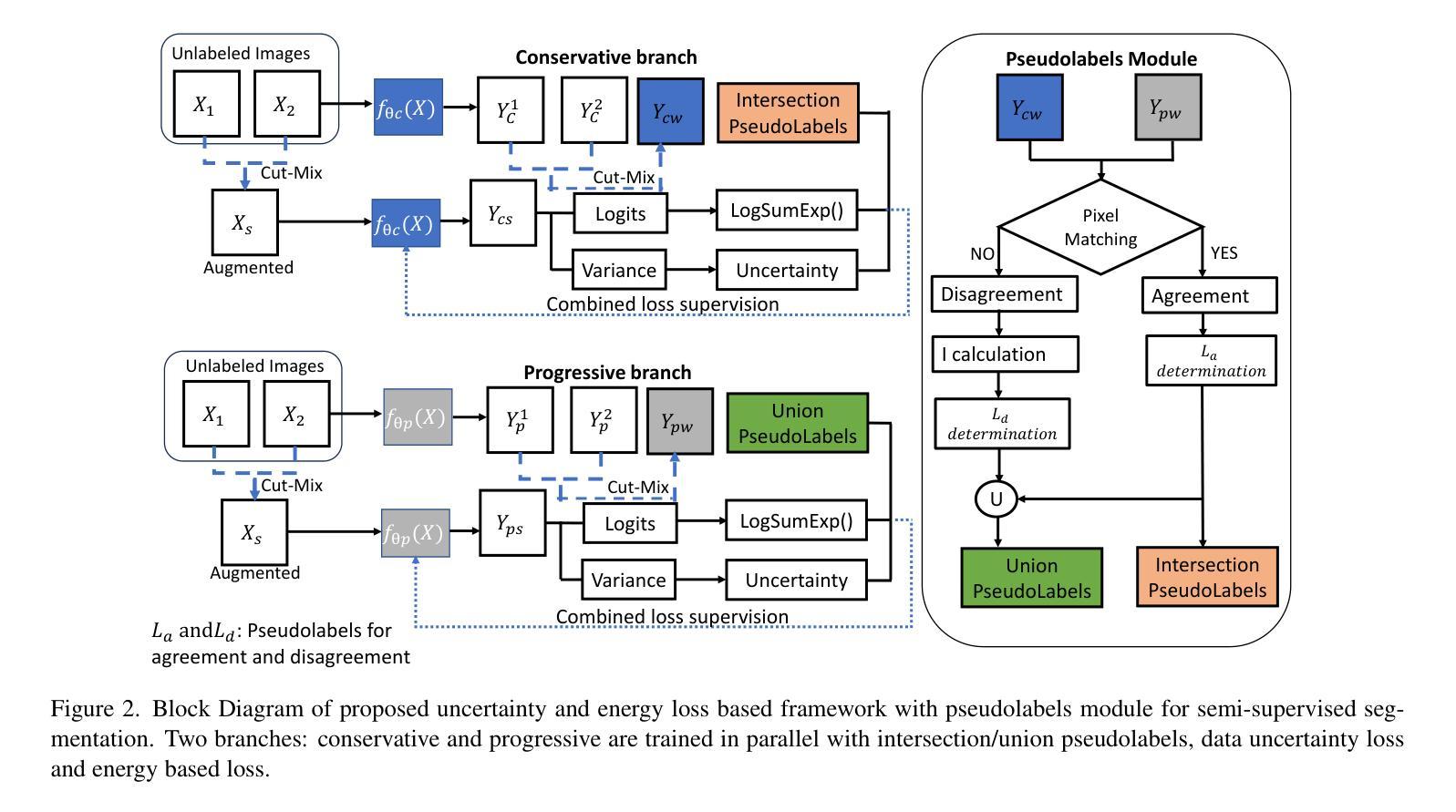
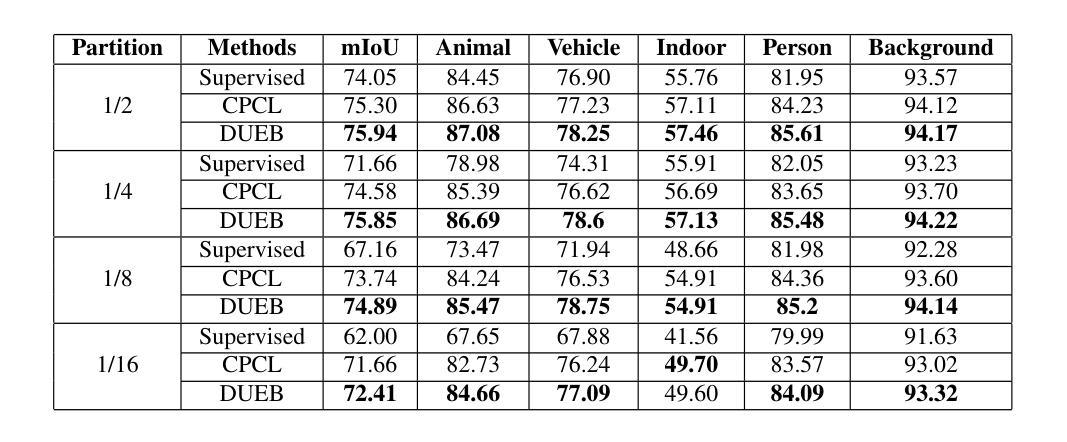
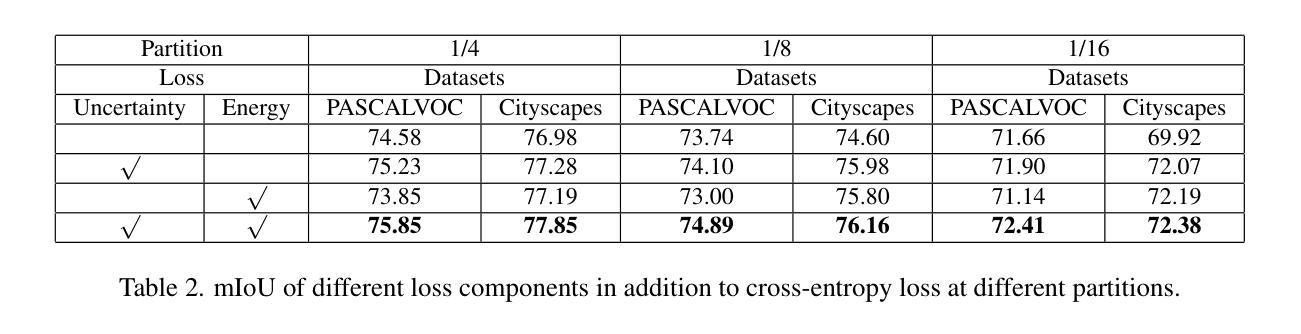
Semi-supervised (SS) semantic segmentation exploits both labeled and unlabeled images to overcome tedious and costly pixel-level annotation problems. Pseudolabel supervision is one of the core approaches of training networks with both pseudo labels and ground-truth labels. This work uses aleatoric or data uncertainty and energy based modeling in intersection-union pseudo supervised network.The aleatoric uncertainty is modeling the inherent noise variations of the data in a network with two predictive branches. The per-pixel variance parameter obtained from the network gives a quantitative idea about the data uncertainty. Moreover, energy-based loss realizes the potential of generative modeling on the downstream SS segmentation task. The aleatoric and energy loss are applied in conjunction with pseudo-intersection labels, pseudo-union labels, and ground-truth on the respective network branch. The comparative analysis with state-of-the-art methods has shown improvement in performance metrics.
半监督(SS)语义分割利用有标签和无标签的图像,克服了繁琐且成本高昂的像素级标注问题。伪标签监督是同时使用伪标签和真实标签训练网络的核心方法之一。本工作使用基于偶然性或数据不确定性和能量建模的交集伪监督网络。偶然性不确定性是对网络数据中固有噪声变化进行建模,通过两个预测分支实现。从网络获得的每个像素的方差参数提供了关于数据不确定性的定量信息。此外,基于能量的损失实现了生成模型在下游SS分割任务中的潜力。偶然性损失和能量损失与伪交集标签、伪联合标签和真实标签一起应用于相应的网络分支。与最新技术的比较分析表明,性能指标有所提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) 2025
Summary
半监督(SS)语义分割利用带标签和不带标签的图像来解决繁琐且成本高昂的像素级标注问题。伪标签监督是训练网络和伪标签及真实标签网络的核心方法之一。本文采用基于数据不确定性和能量建模的交并集伪监督网络。数据的不确定性通过两个预测分支的网络建模固有噪声变化。从网络中获得的像素方差参数可以定量地了解数据的不确定性。此外,基于能量的损失实现了生成模型在下游SS分割任务上的潜力。数据不确定性和能量损失与伪交集标签、伪联合标签和真实标签一起应用于相应的网络分支。与最新方法的对比分析显示,性能有所提升。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督语义分割利用带标签和不带标签的图像来减轻标注工作量并降低成本。
- 伪标签监督是训练网络的核心方法之一,涉及伪标签和真实标签的使用。
- 文章中引入了一种基于数据不确定性和能量建模的交并集伪监督网络。
- 数据的不确定性通过两个预测分支的网络进行建模,能够定量表示像素方差参数。
- 基于能量的损失在下游SS分割任务中展现出生成模型的潜力。
- 数据不确定性和能量损失与伪交集标签、伪联合标签以及真实标签结合应用在网络中。
点此查看论文截图

FGAseg: Fine-Grained Pixel-Text Alignment for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Bingyu Li, Da Zhang, Zhiyuan Zhao, Junyu Gao, Xuelong Li
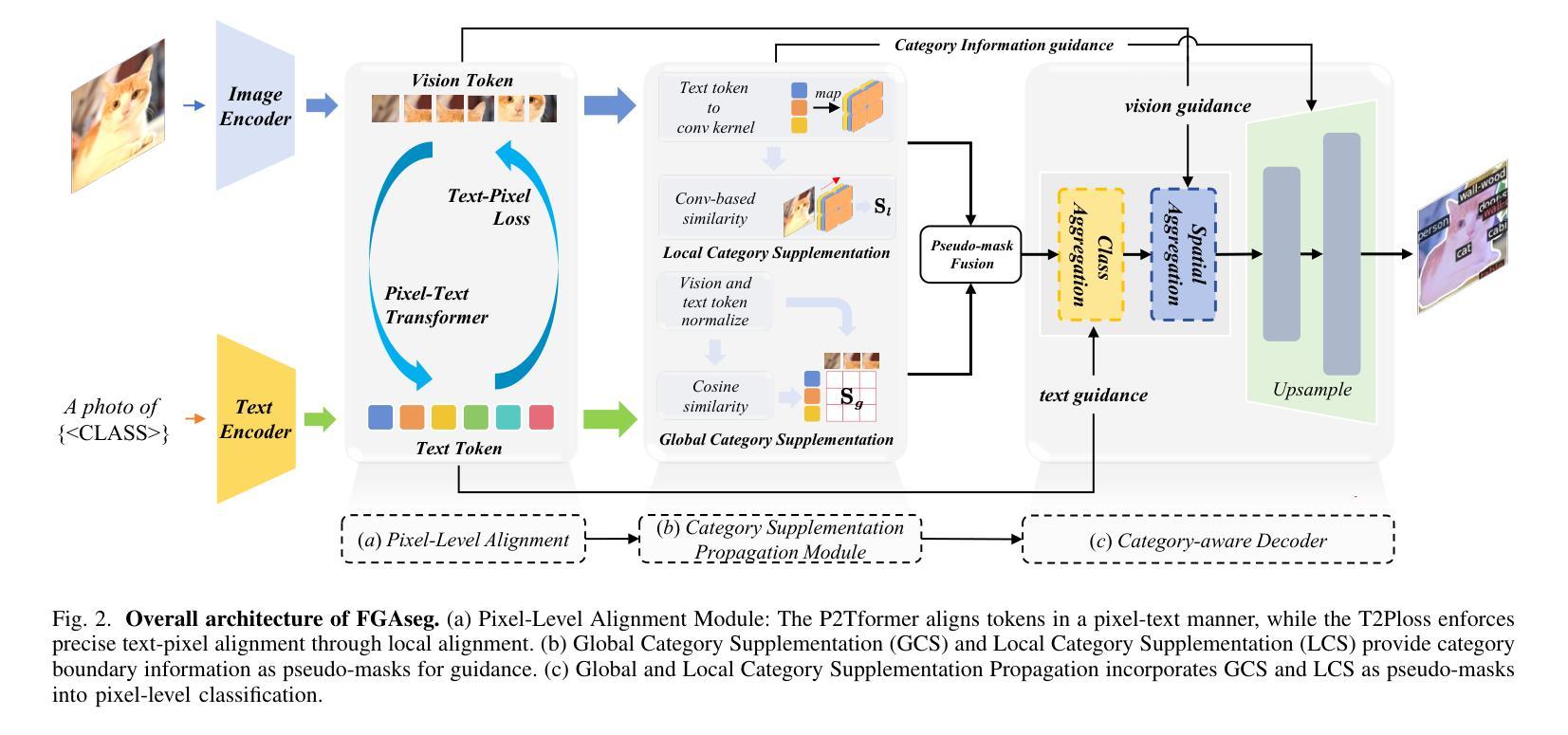
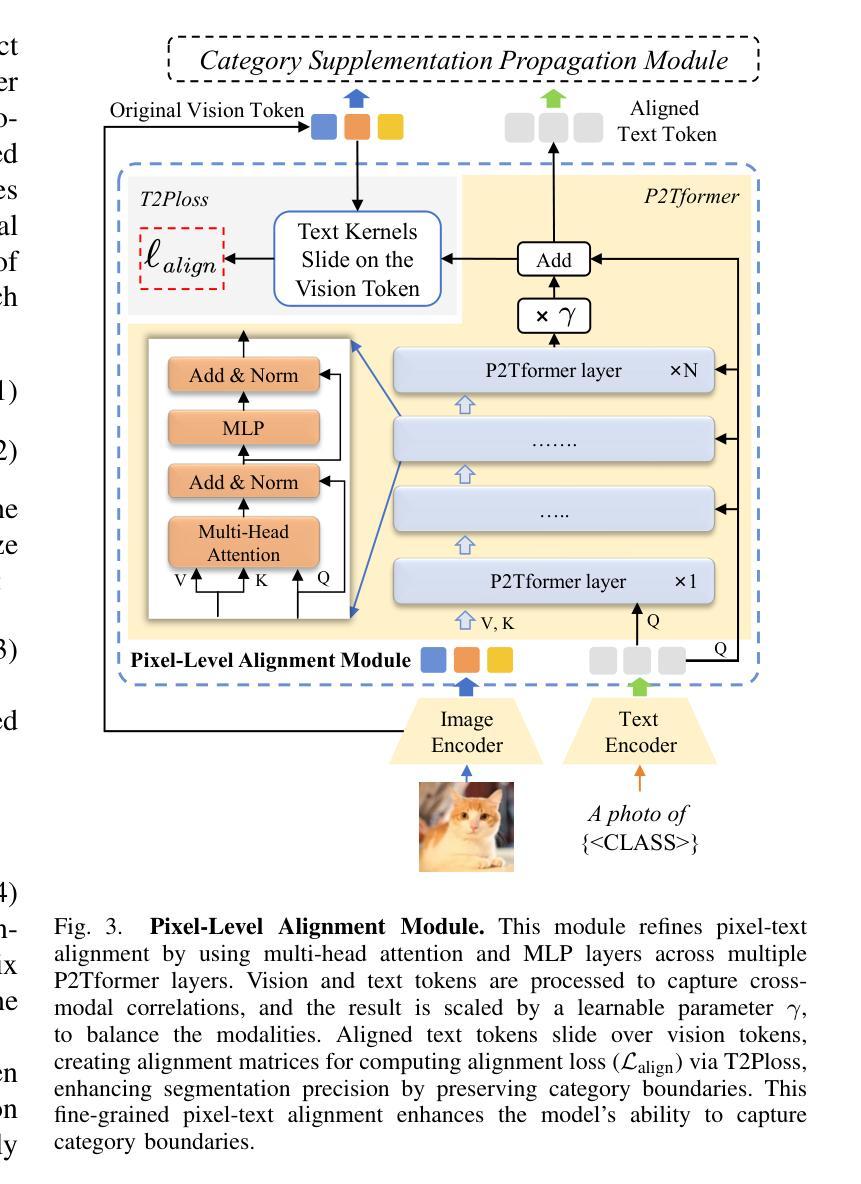
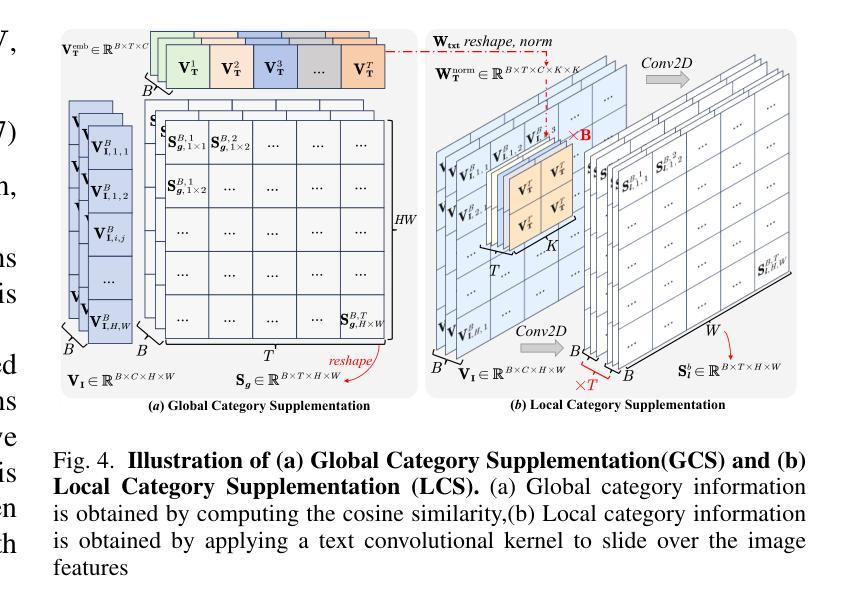
Open-vocabulary segmentation aims to identify and segment specific regions and objects based on text-based descriptions. A common solution is to leverage powerful vision-language models (VLMs), such as CLIP, to bridge the gap between vision and text information. However, VLMs are typically pretrained for image-level vision-text alignment, focusing on global semantic features. In contrast, segmentation tasks require fine-grained pixel-level alignment and detailed category boundary information, which VLMs alone cannot provide. As a result, information extracted directly from VLMs can’t meet the requirements of segmentation tasks. To address this limitation, we propose FGAseg, a model designed for fine-grained pixel-text alignment and category boundary supplementation. The core of FGAseg is a Pixel-Level Alignment module that employs a cross-modal attention mechanism and a text-pixel alignment loss to refine the coarse-grained alignment from CLIP, achieving finer-grained pixel-text semantic alignment. Additionally, to enrich category boundary information, we introduce the alignment matrices as optimizable pseudo-masks during forward propagation and propose Category Information Supplementation module. These pseudo-masks, derived from cosine and convolutional similarity, provide essential global and local boundary information between different categories. By combining these two strategies, FGAseg effectively enhances pixel-level alignment and category boundary information, addressing key challenges in open-vocabulary segmentation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FGAseg outperforms existing methods on open-vocabulary semantic segmentation benchmarks.
开放词汇分割旨在基于文本描述来识别和分割特定区域和对象。一种常见解决方案是利用强大的视觉语言模型(VLMs),如CLIP,来弥合视觉和文本信息之间的差距。然而,VLMs通常进行图像级别的视觉文本对齐预训练,侧重于全局语义特征。相比之下,分割任务需要精细的像素级对齐和详细的类别边界信息,这是仅凭VLMs无法提供的。因此,直接从VLMs中提取的信息不能满足分割任务的要求。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了FGAseg模型,该模型旨在实现精细像素文本对齐和类别边界补充。FGAseg的核心是像素级对齐模块,该模块采用跨模态注意力机制和文本像素对齐损失来优化CLIP的粗略对齐,实现更精细的像素文本语义对齐。此外,为了丰富类别边界信息,我们引入了对齐矩阵作为前向传播过程中的可优化伪掩码,并提出了类别信息补充模块。这些伪掩码来源于余弦和卷积相似性,提供了不同类别之间重要的全局和局部边界信息。通过结合这两种策略,FGAseg有效地增强了像素级对齐和类别边界信息,解决了开放词汇分割中的关键挑战。大量实验表明,在开放词汇语义分割基准测试中,FGAseg的性能超过了现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对开放词汇语义分割问题,提出了一种名为FGAseg的模型。它通过精细像素级别的文本对齐和类别边界补充来解决现有视觉语言模型(VLMs)如CLIP在分割任务上的局限性。模型包括像素级对齐模块和类别信息补充模块,可有效提高像素级对齐和类别边界信息丰富度,在开放词汇语义分割基准测试中表现优异。
Key Takeaways:
- 开放词汇分割旨在基于文本描述来识别和分割特定区域和对象。
- 常用的方法是利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)来缩小视觉和文本信息之间的差距。
- VLMs通常是为图像级别的视觉文本对齐进行预训练的,侧重于全局语义特征。
- 分割任务需要精细的像素级对齐和详细的类别边界信息,这是VLMs无法单独提供的。
- FGAseg模型通过像素级文本对齐和类别边界补充来解决VLMs在分割任务上的局限性。
- FGAseg模型包括像素级对齐模块,采用跨模态注意力机制和文本像素对齐损失来优化粗粒度的CLIP对齐,实现更精细的像素文本语义对齐。
点此查看论文截图
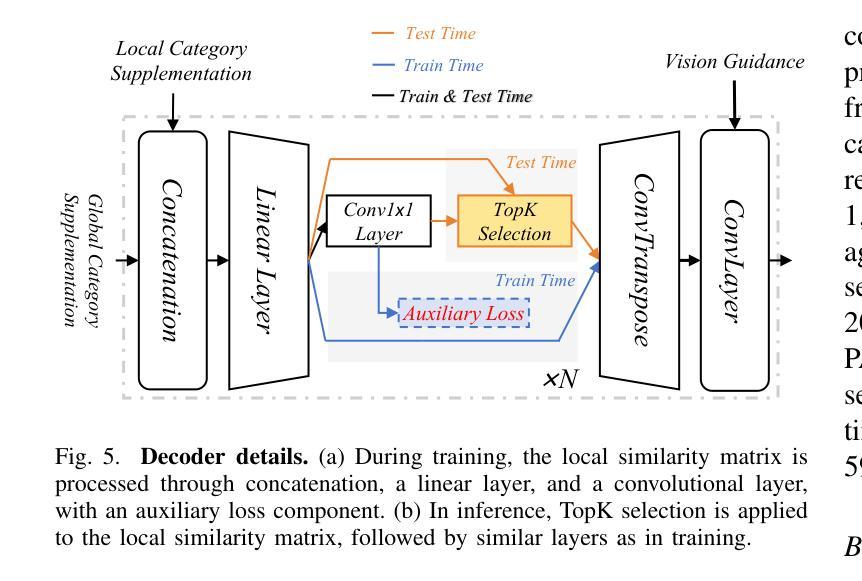
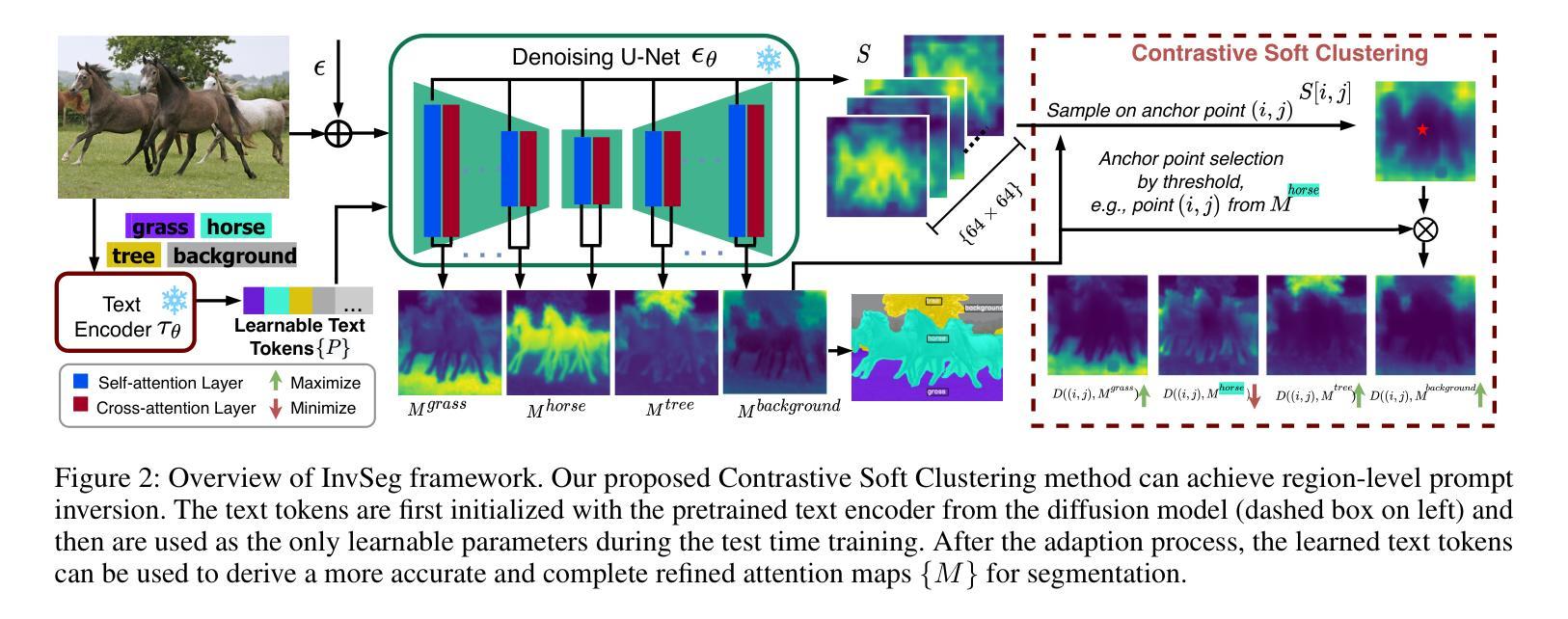
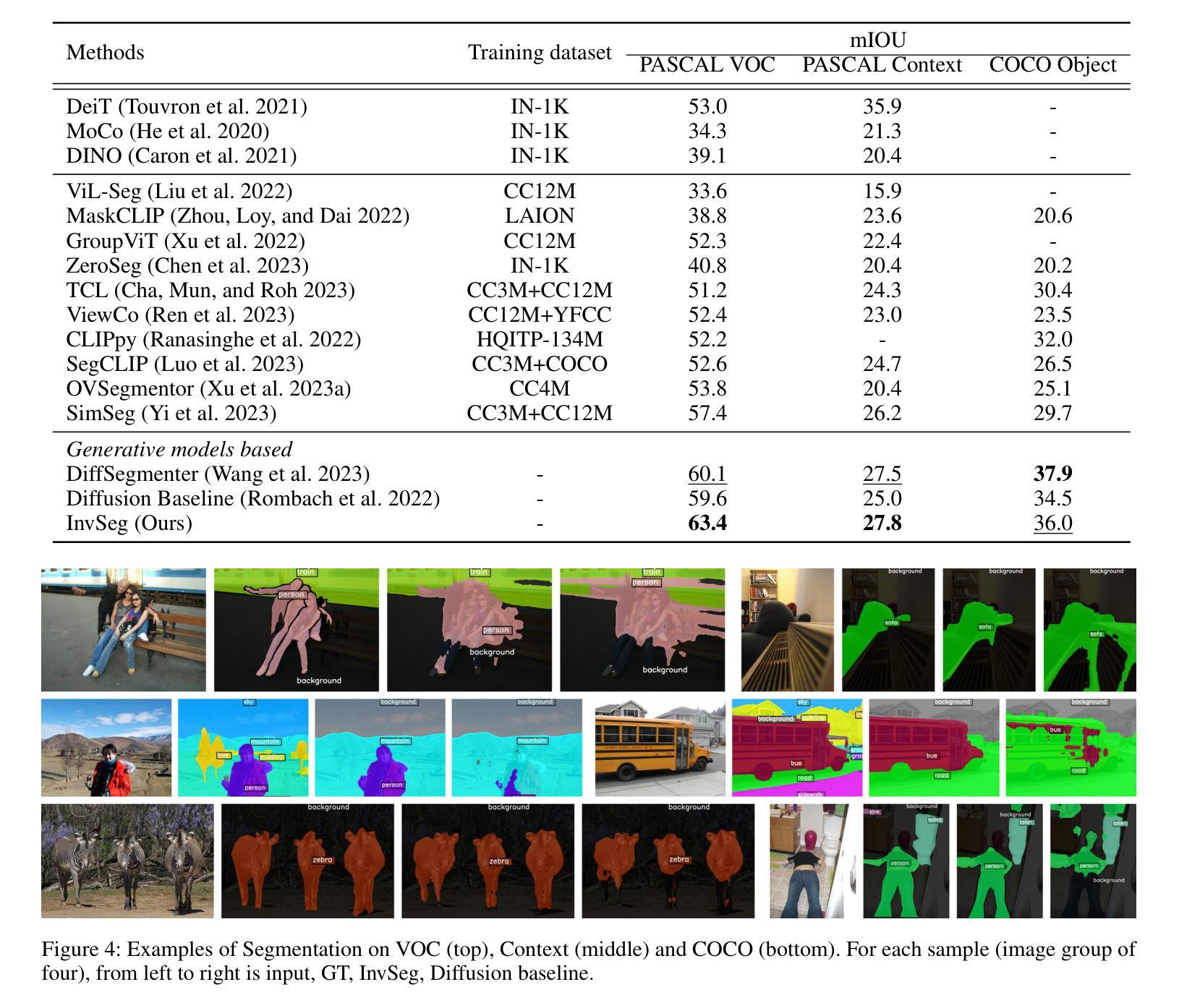
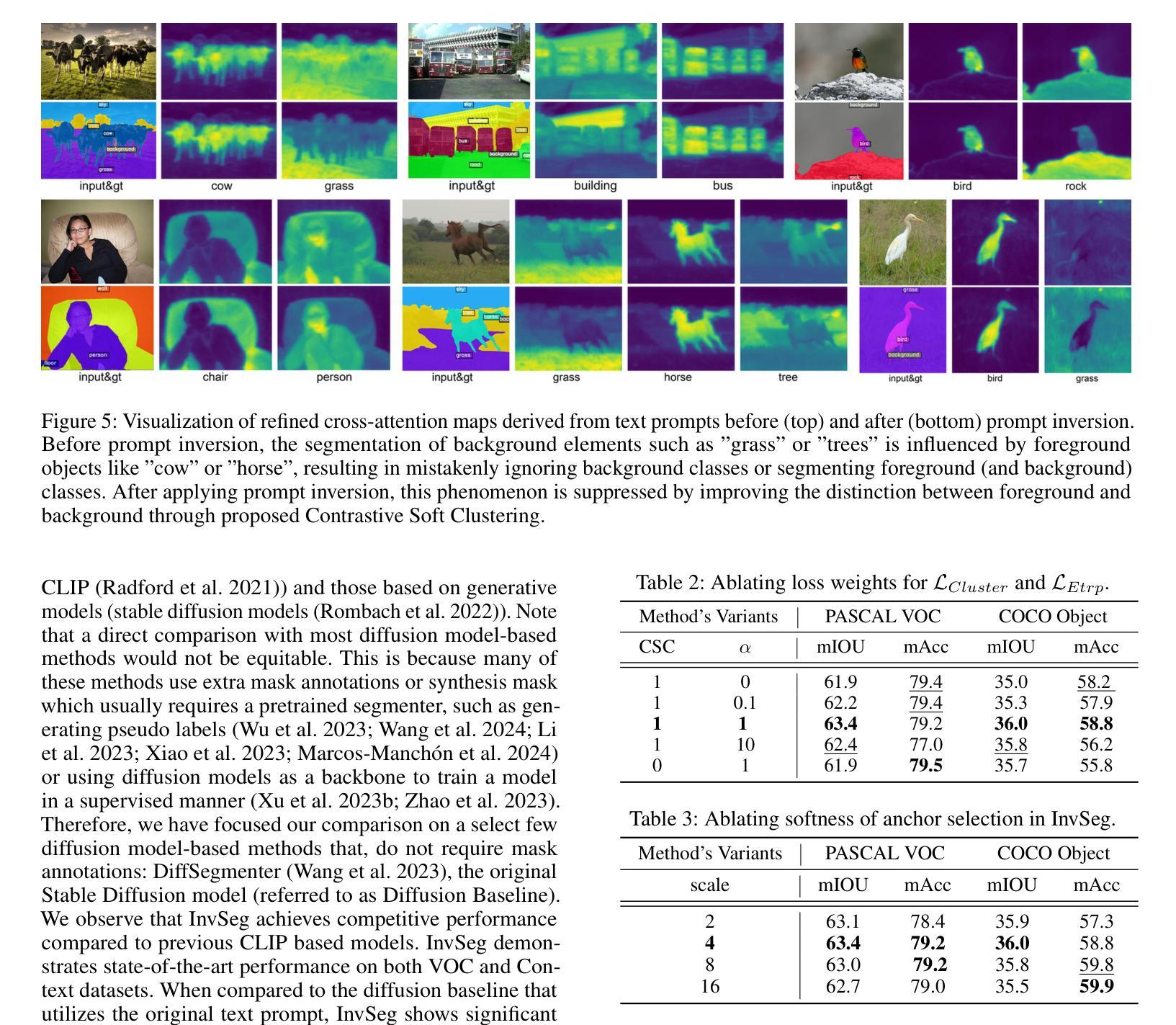
InvSeg: Test-Time Prompt Inversion for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Jiayi Lin, Jiabo Huang, Jian Hu, Shaogang Gong
Visual-textual correlations in the attention maps derived from text-to-image diffusion models are proven beneficial to dense visual prediction tasks, e.g., semantic segmentation. However, a significant challenge arises due to the input distributional discrepancy between the context-rich sentences used for image generation and the isolated class names typically used in semantic segmentation. This discrepancy hinders diffusion models from capturing accurate visual-textual correlations. To solve this, we propose InvSeg, a test-time prompt inversion method that tackles open-vocabulary semantic segmentation by inverting image-specific visual context into text prompt embedding space, leveraging structure information derived from the diffusion model’s reconstruction process to enrich text prompts so as to associate each class with a structure-consistent mask. Specifically, we introduce Contrastive Soft Clustering (CSC) to align derived masks with the image’s structure information, softly selecting anchors for each class and calculating weighted distances to push inner-class pixels closer while separating inter-class pixels, thereby ensuring mask distinction and internal consistency. By incorporating sample-specific context, InvSeg learns context-rich text prompts in embedding space and achieves accurate semantic alignment across modalities. Experiments show that InvSeg achieves state-of-the-art performance on the PASCAL VOC, PASCAL Context and COCO Object datasets.
由文本到图像扩散模型生成的注意力图中的视觉文本相关性已被证明对密集视觉预测任务(例如语义分割)有益。然而,由于用于图像生成的丰富上下文句子与通常在语义分割中使用的孤立类名之间的输入分布差异,出现了一个重大挑战。这种差异阻碍了扩散模型捕捉准确的视觉文本相关性。
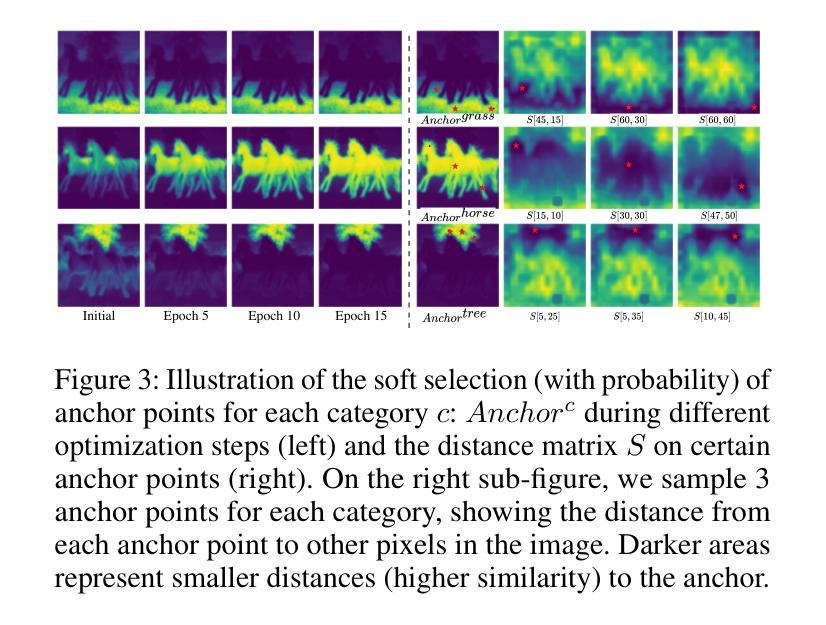
为了解决这一问题,我们提出了InvSeg,这是一种测试时提示反转方法,通过反转图像特定的视觉上下文到文本提示嵌入空间,解决开放词汇语义分割问题。InvSeg利用从扩散模型的重建过程中获得的结构信息来丰富文本提示,从而使每个类与结构一致的掩膜相关联。具体来说,我们引入了对比软聚类(CSC),以将派生掩膜与图像的结构信息对齐,为每个类轻柔地选择锚点,并计算加权距离,以推动同类像素彼此接近,同时分离不同类像素,从而确保掩膜的区别和内部一致性。通过融入样本特定上下文,InvSeg在嵌入空间中学习丰富的上下文文本提示,并在多个模式之间实现准确的语义对齐。实验表明,InvSeg在PASCAL VOC、PASCAL Context和COCO Object数据集上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
视觉文本关联在文本到图像扩散模型生成的注意力图上对密集视觉预测任务(如语义分割)有益。然而,由于用于图像生成的丰富语境与语义分割中常用的孤立类名之间的输入分布差异,产生了挑战。此差异阻碍了扩散模型捕捉准确的视觉文本关联。为解决此问题,我们提出InvSeg方法,这是一种测试时提示反转法,通过反转图像特定视觉上下文到文本提示嵌入空间来解决开放词汇语义分割问题。此方法利用扩散模型的重建过程获得的结构信息来丰富文本提示,从而将每个类别与结构一致的掩膜相关联。具体来说,我们引入对比软聚类(CSC)来对齐生成的掩膜与图像的结构信息,为每个类别轻柔地选择锚点,计算加权距离来拉近类内像素并分离类间像素,确保掩膜的区别和内部一致性。通过结合样本特定上下文,InvSeg在嵌入空间中学习丰富的语境文本提示,并在不同模态之间实现准确的语义对齐。实验表明,InvSeg在PASCAL VOC、PASCAL Context和COCO对象数据集上达到了最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型的视觉文本关联对密集视觉预测任务如语义分割有益。
- 上下文丰富句子与孤立类名间的输入分布差异给扩散模型带来挑战。
- 提出InvSeg方法,利用图像特定视觉上下文反转至文本提示嵌入空间来解决此问题。
- InvSeg利用扩散模型的重建过程的结构信息来丰富文本提示,并与图像结构信息对齐。
- 对比软聚类(CSC)用于确保生成的掩膜与图像结构一致,实现类内像素的聚集和类间像素的分离。
- InvSeg结合样本特定上下文,在嵌入空间中学习丰富的语境文本提示。
点此查看论文截图


Multi-Scale Denoising in the Feature Space for Low-Light Instance Segmentation
Authors:Joanne Lin, Nantheera Anantrasirichai, David Bull
Instance segmentation for low-light imagery remains largely unexplored due to the challenges imposed by such conditions, for example shot noise due to low photon count, color distortions and reduced contrast. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end solution to address this challenging task. Our proposed method implements weighted non-local blocks (wNLB) in the feature extractor. This integration enables an inherent denoising process at the feature level. As a result, our method eliminates the need for aligned ground truth images during training, thus supporting training on real-world low-light datasets. We introduce additional learnable weights at each layer in order to enhance the network’s adaptability to real-world noise characteristics, which affect different feature scales in different ways. Experimental results on several object detectors show that the proposed method outperforms the pretrained networks with an Average Precision (AP) improvement of at least +7.6, with the introduction of wNLB further enhancing AP by upto +1.3.
针对低光照图像的实例分割仍然是一个未被充分研究的领域,主要由于这些条件所带来的挑战,例如由于光子计数低导致的拍摄噪声、色彩失真和对比度降低。在本文中,我们提出了一种端到端的解决方案来解决这一具有挑战性的任务。我们提出的方法在特征提取器中实现加权非局部块(wNLB)。这种集成使特征级的固有去噪过程成为可能。因此,我们的方法在训练过程中不需要对齐的真实图像,从而支持在真实世界的低光照数据集上进行训练。为了增强网络对真实世界噪声特性的适应性,我们在每一层引入了可学习的权重,不同的特征尺度会受到不同方式的影响。在多个目标检测器上的实验结果表明,该方法优于预训练网络,平均精度(AP)至少提高+7.6,引入wNLB后AP进一步提高,最多可提高+1.3。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary:针对低光照图像实例分割的挑战,本文提出了一种端到端的解决方案。通过特征提取器中加权非局部块(wNLB)的集成,实现了特征级的固有去噪过程。该方法无需对齐的真实图像进行训练,可在真实世界的低光照数据集上进行训练。通过引入可学习的权重,增强了网络对真实世界噪声特性的适应性,提高了平均精度(AP)。
Key Takeaways:
- 低光照图像实例分割是一个未被充分研究的领域,面临如光子计数少导致的噪声、颜色失真和对比度降低等挑战。
- 本文提出了一种端到端的解决方案,通过集成加权非局部块(wNLB)在特征提取器中实现去噪。
- wNLB的集成使得模型能够在没有对齐的真实低光照图像数据集上进行训练。
- 引入可学习的权重,增强了网络对真实世界噪声的适应性。
- 实验结果表明,该方法优于预训练网络,平均精度(AP)至少提高7.6%。
- wNLB的引入进一步提高了平均精度,最多可提高1.3%。
点此查看论文截图