⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-07 更新
CrossView-GS: Cross-view Gaussian Splatting For Large-scale Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Chenhao Zhang, Yuanping Cao, Lei Zhang
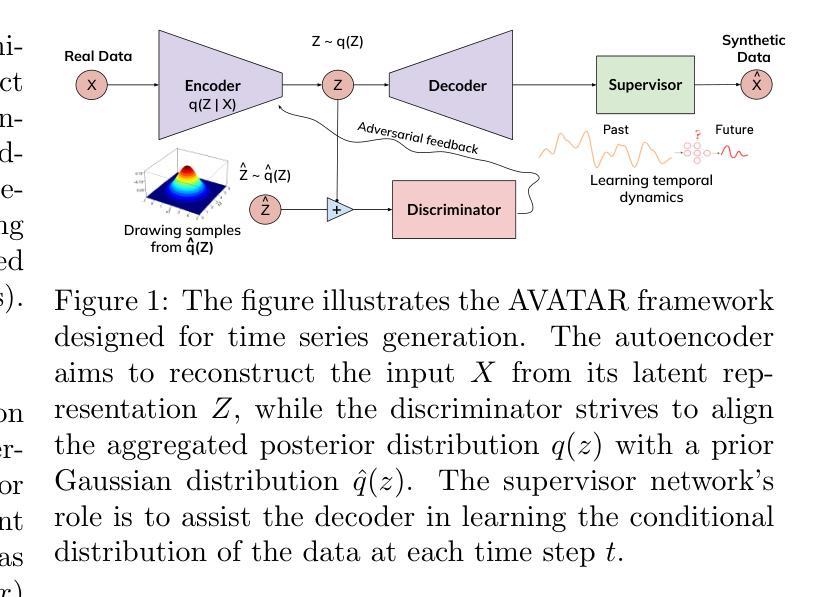
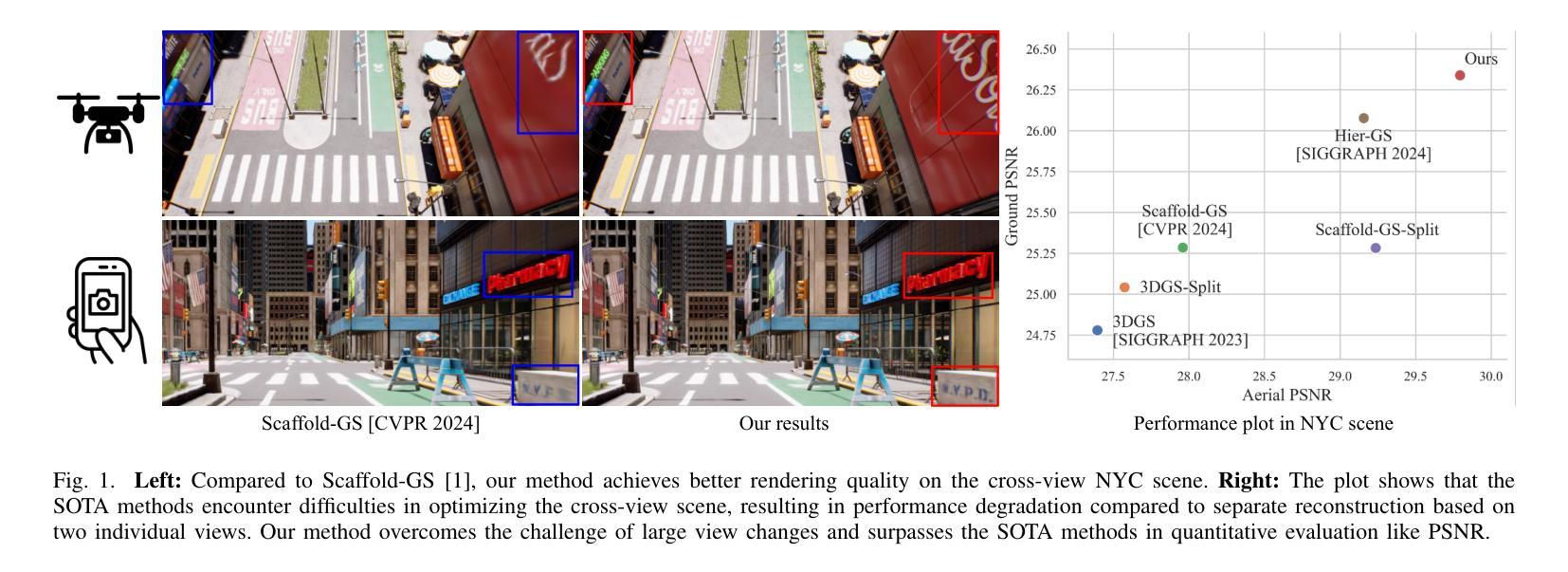
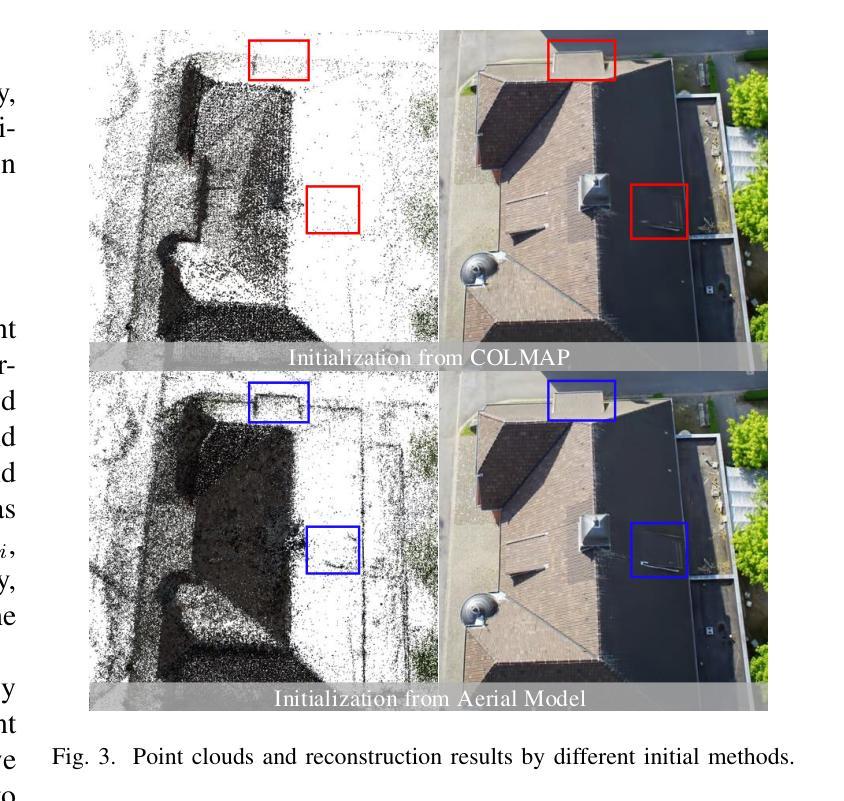
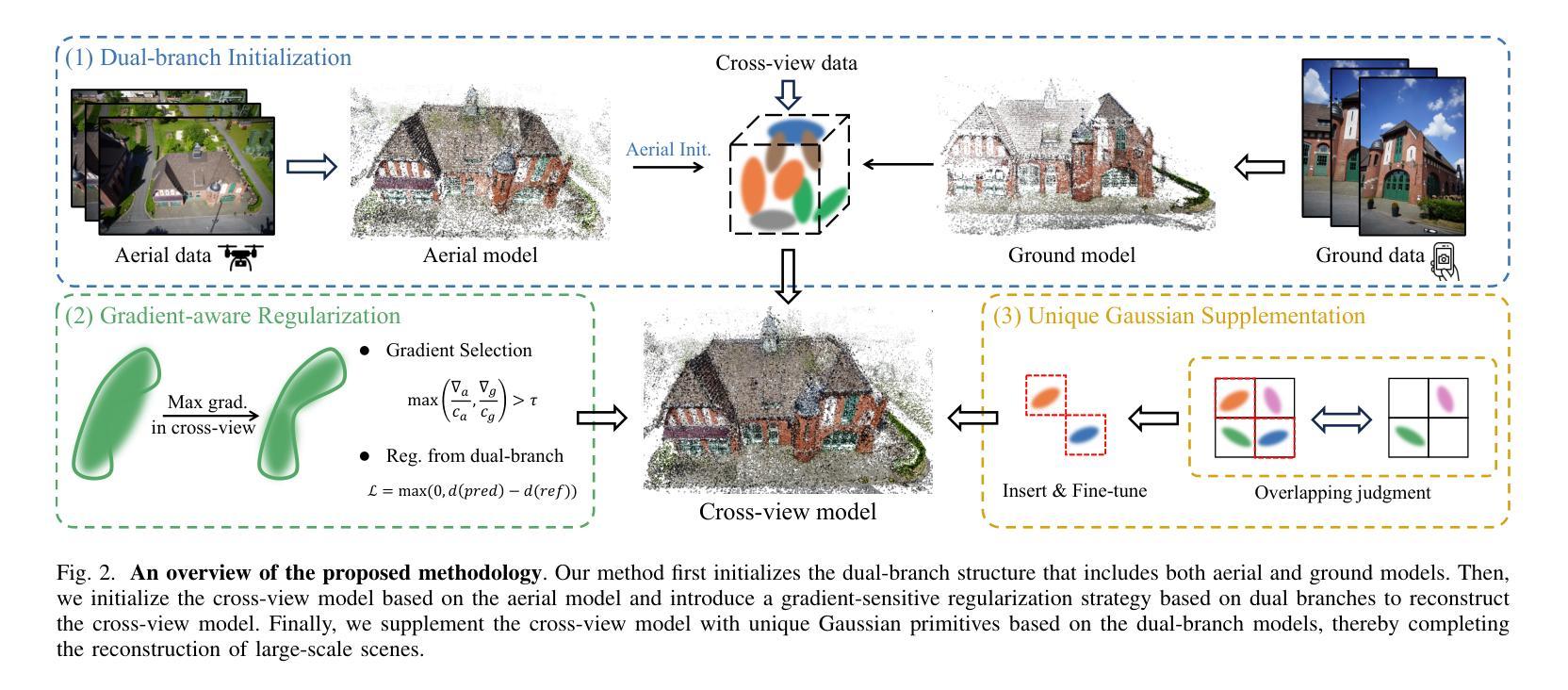
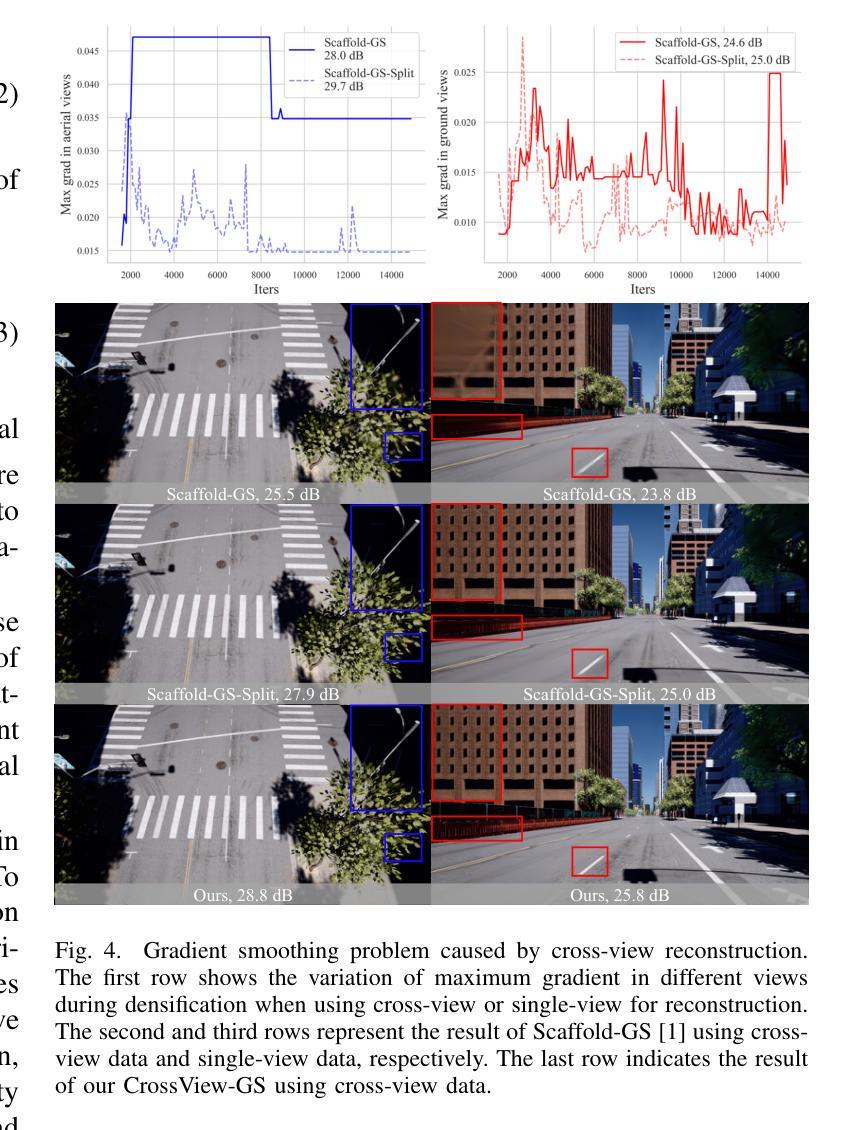
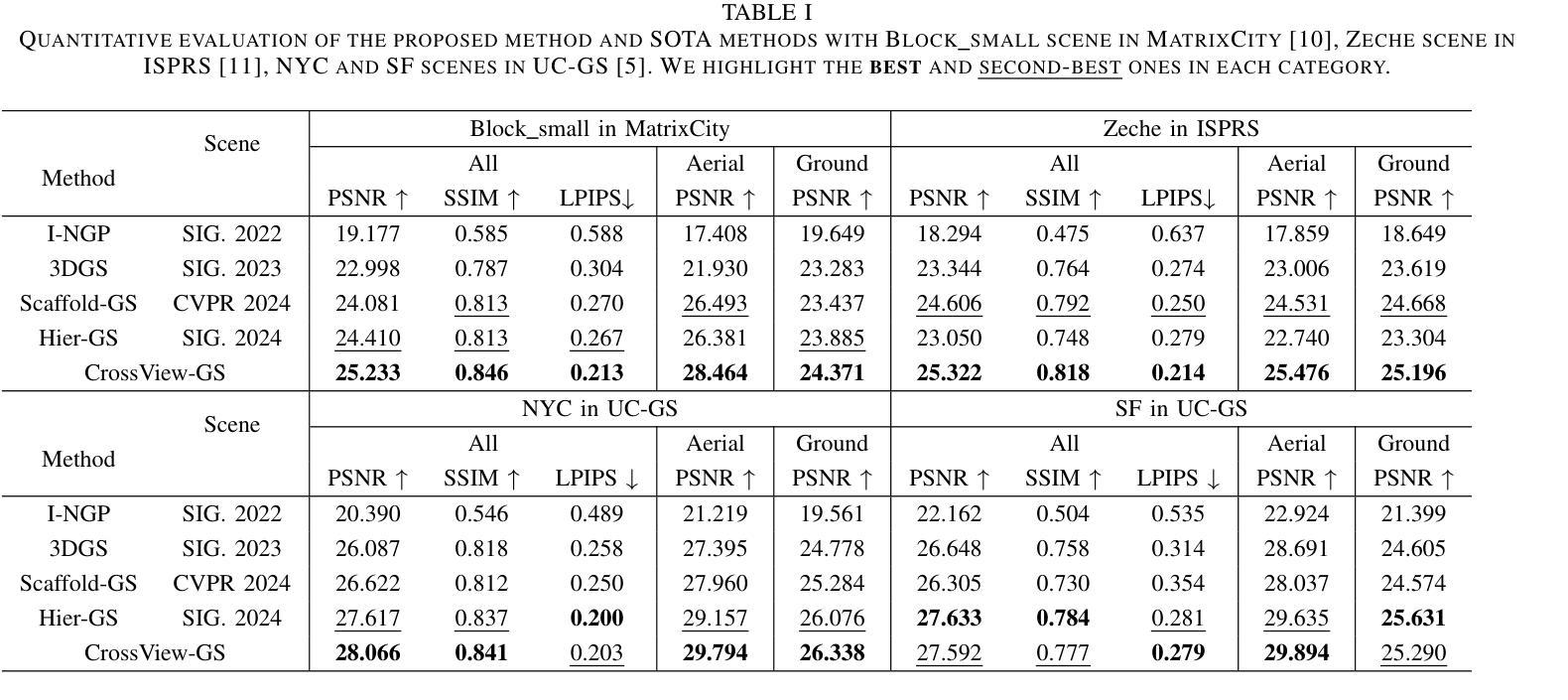
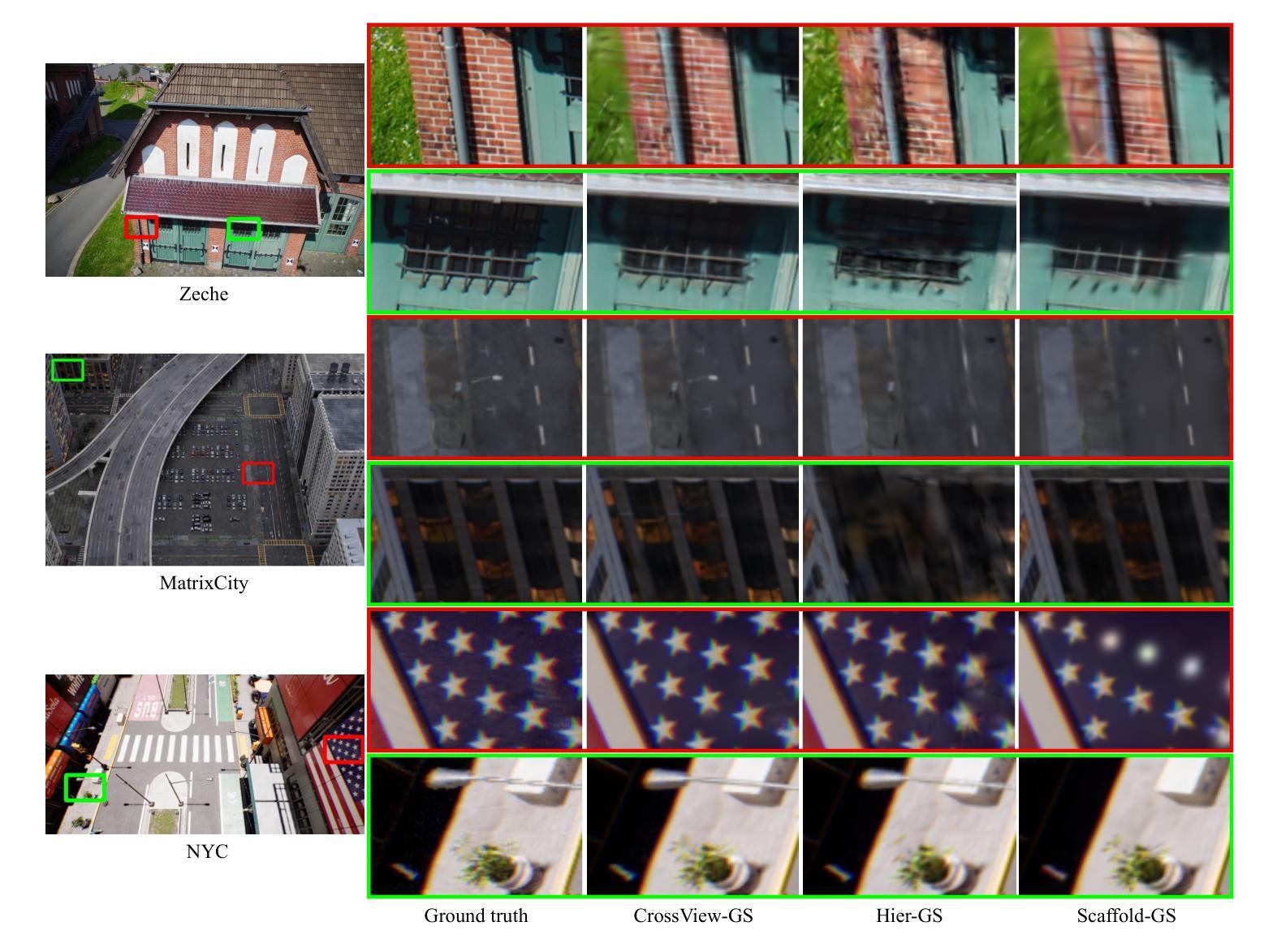
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a prominent method for scene representation and reconstruction, leveraging densely distributed Gaussian primitives to enable real-time rendering of high-resolution images. While existing 3DGS methods perform well in scenes with minor view variation, large view changes in cross-view scenes pose optimization challenges for these methods. To address these issues, we propose a novel cross-view Gaussian Splatting method for large-scale scene reconstruction, based on dual-branch fusion. Our method independently reconstructs models from aerial and ground views as two independent branches to establish the baselines of Gaussian distribution, providing reliable priors for cross-view reconstruction during both initialization and densification. Specifically, a gradient-aware regularization strategy is introduced to mitigate smoothing issues caused by significant view disparities. Additionally, a unique Gaussian supplementation strategy is utilized to incorporate complementary information of dual-branch into the cross-view model. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance in novel view synthesis compared to state-of-the-art methods.
3D高斯延展(3DGS)作为一种突出的场景表示和重建方法,利用密集分布的高斯基本体来实现高分辨率图像实时渲染。虽然现有的3DGS方法在轻微视角变化的场景中表现良好,但在跨视角场景中视角的大变化给这些方法带来了优化挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种基于双分支融合的新型跨视角高斯延展方法,用于大规模场景重建。我们的方法独立地从空中和地面视角建立两个独立分支重建模型,以建立高斯分布基线,为初始化和密集化过程中的跨视角重建提供可靠的先验信息。具体来说,引入了一种梯度感知正则化策略,以缓解由于显著视角差异导致的平滑问题。此外,还采用了一种独特的高斯补充策略,将双分支的互补信息融入跨视角模型中。在基准数据集上的大量实验表明,与最先进的方法相比,我们的方法在新型视角合成方面取得了优越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了三维高斯平铺(3DGS)方法在场景表示和重建中的新兴应用。针对现有方法在跨视角场景中存在的大视角变化优化挑战,提出了一种基于双分支融合的新跨视角高斯平铺方法。该方法通过独立重建空中和地面视角的模型,建立高斯分布的基线,为跨视角重建提供可靠的先验信息。引入梯度感知正则化策略以缓解因视角显著差异造成的平滑问题,并采用独特的高斯补充策略将双分支的互补信息融入跨视角模型中。实验证明,该方法在新视角合成方面较现有方法性能更优。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS已用于场景表示和重建。
- 现有方法在跨视角场景中存在大视角变化的优化挑战。
- 提出了一种基于双分支融合的跨视角高斯平铺方法。
- 独立重建空中和地面视角的模型,建立高斯分布基线。
- 引入梯度感知正则化策略解决视角差异导致的平滑问题。
- 采用独特的高斯补充策略融合双分支的互补信息。
点此查看论文截图



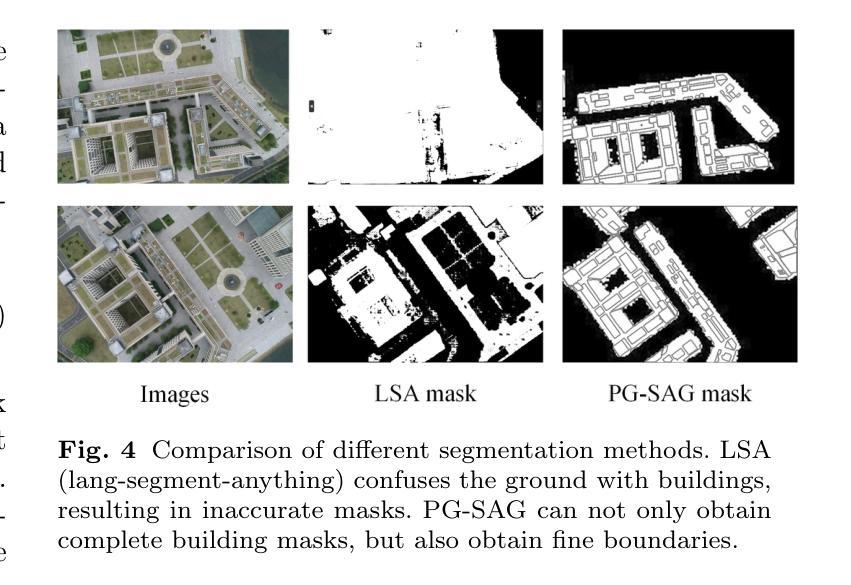
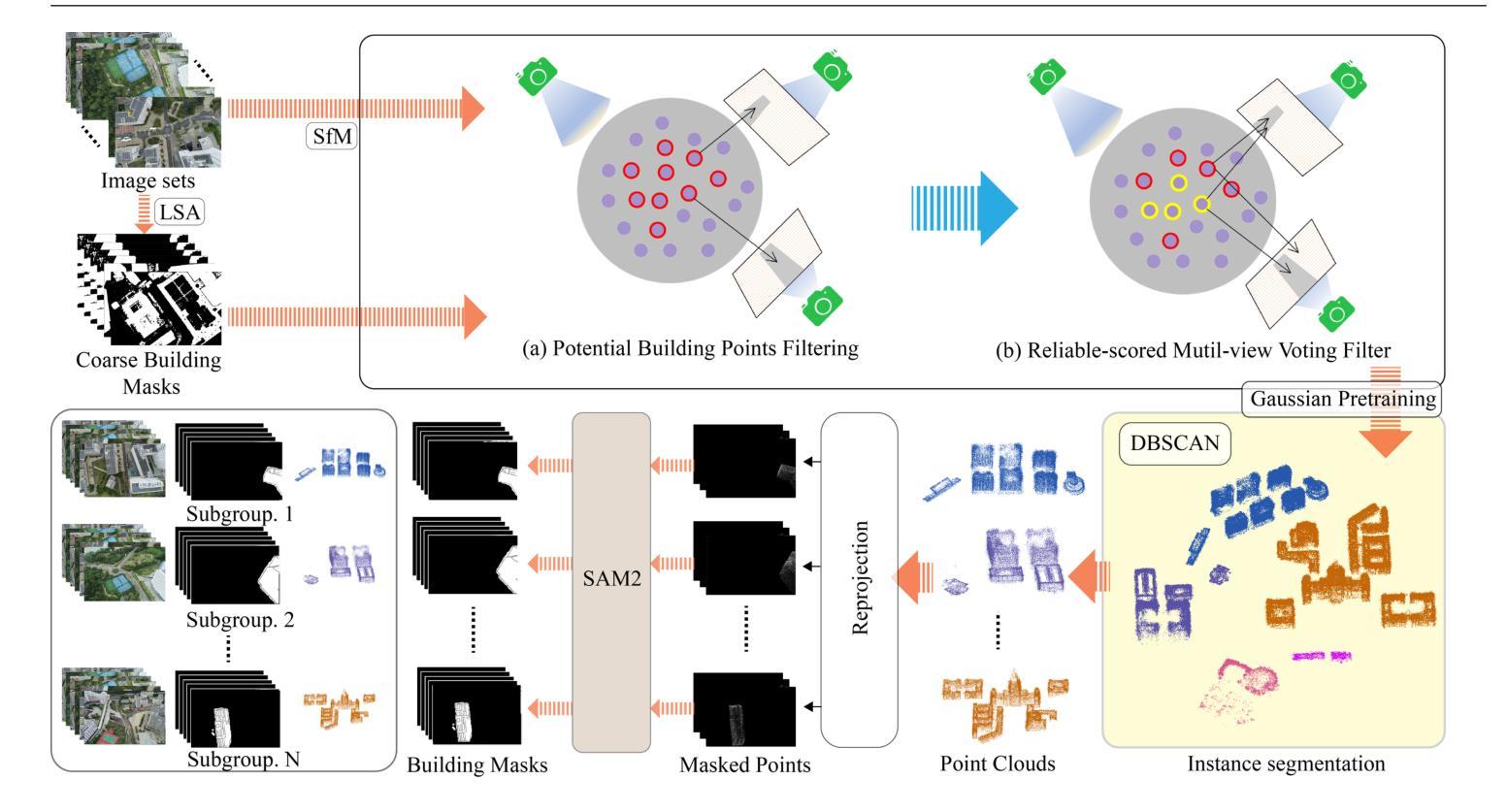
PG-SAG: Parallel Gaussian Splatting for Fine-Grained Large-Scale Urban Buildings Reconstruction via Semantic-Aware Grouping
Authors:Tengfei Wang, Xin Wang, Yongmao Hou, Yiwei Xu, Wendi Zhang, Zongqian Zhan
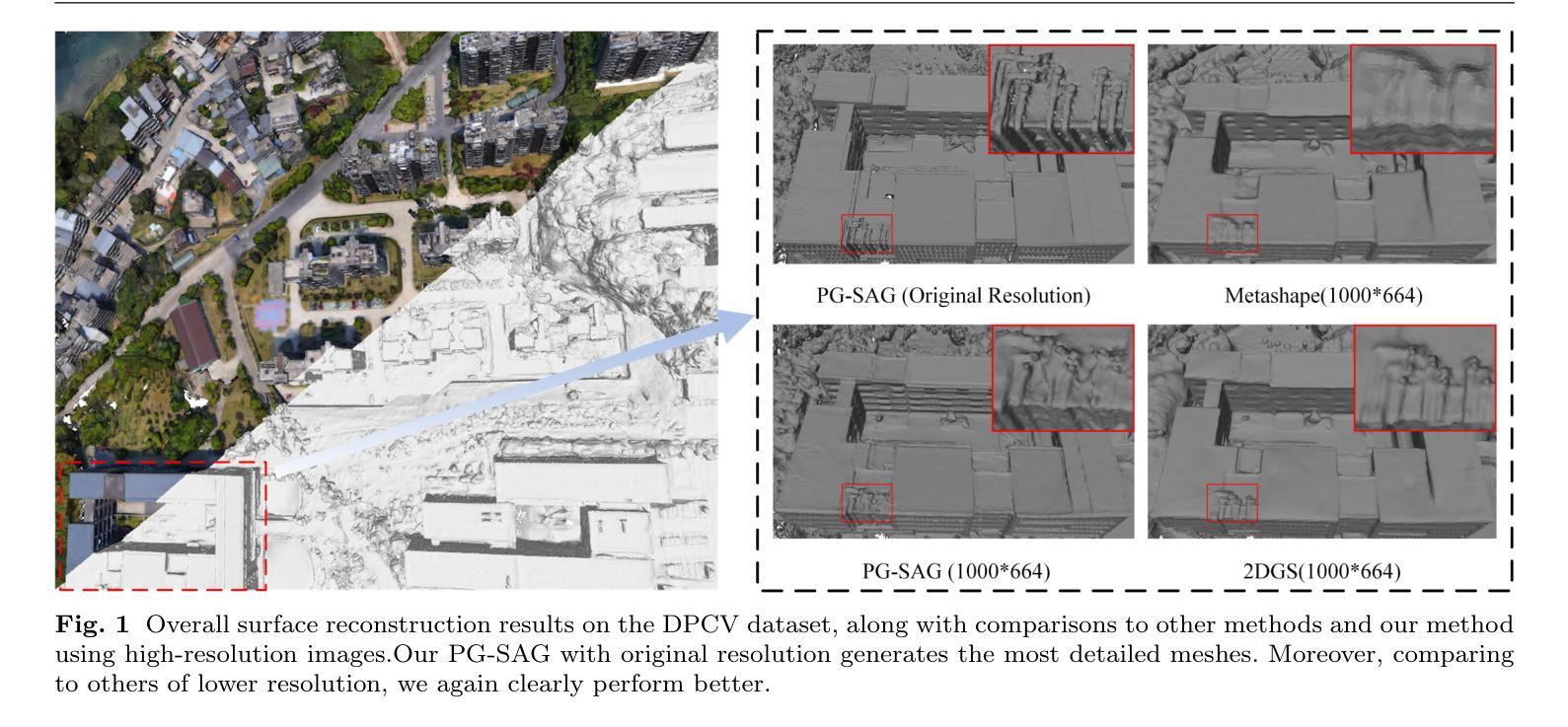
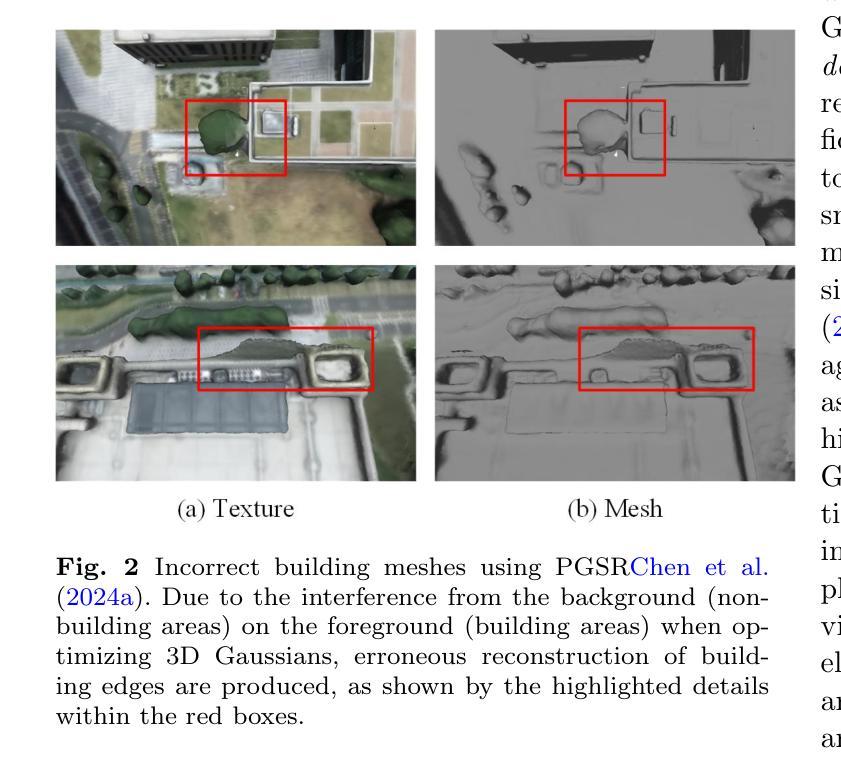
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a transformative method in the field of real-time novel synthesis. Based on 3DGS, recent advancements cope with large-scale scenes via spatial-based partition strategy to reduce video memory and optimization time costs. In this work, we introduce a parallel Gaussian splatting method, termed PG-SAG, which fully exploits semantic cues for both partitioning and Gaussian kernel optimization, enabling fine-grained building surface reconstruction of large-scale urban areas without downsampling the original image resolution. First, the Cross-modal model - Language Segment Anything is leveraged to segment building masks. Then, the segmented building regions is grouped into sub-regions according to the visibility check across registered images. The Gaussian kernels for these sub-regions are optimized in parallel with masked pixels. In addition, the normal loss is re-formulated for the detected edges of masks to alleviate the ambiguities in normal vectors on edges. Finally, to improve the optimization of 3D Gaussians, we introduce a gradient-constrained balance-load loss that accounts for the complexity of the corresponding scenes, effectively minimizing the thread waiting time in the pixel-parallel rendering stage as well as the reconstruction lost. Extensive experiments are tested on various urban datasets, the results demonstrated the superior performance of our PG-SAG on building surface reconstruction, compared to several state-of-the-art 3DGS-based methods. Project Web:https://github.com/TFWang-9527/PG-SAG.
3D高斯平滑技术(3DGS)已成为实时新合成领域的变革性方法。基于3DGS,最近的进展通过基于空间的分区策略来处理大规模场景,以减少视频内存和优化时间成本。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种并行高斯平滑方法,称为PG-SAG。它充分利用了语义线索来进行分区和高斯内核优化,能够在不下采样原始图像分辨率的情况下,实现对大规模城市区域的精细建筑表面重建。首先,利用跨模态模型——语言分割任何事物(Language Segment Anything)来分割建筑掩膜。然后,根据已注册图像之间的可见性检查,将分割的建筑区域分组为子区域。这些子区域的高斯核与掩像素并行进行优化。此外,为了减轻边缘法线上存在的歧义,对检测到的掩边进行了法线损失的重新计算。最后,为了优化三维高斯函数,我们引入了一种梯度约束平衡损失,考虑到相应场景的复杂性,有效地减少了像素并行渲染阶段的线程等待时间以及重建损失。在各种城市数据集上进行了广泛实验,结果表明我们的PG-SAG在建筑表面重建方面优于其他先进的基于3DGS的方法。项目网站:https://github.com/TFWang-9527/PG-SAG。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于3D高斯展平(3DGS)技术的并行高斯展平方法PG-SAG。该方法充分利用语义线索进行分区和高斯核优化,实现了大规模城市区域的精细建筑表面重建,无需降低原始图像分辨率。通过跨模态模型分割建筑掩膜,并采用可见性检查对分割的建筑区域进行子区域分组。优化子区域的高斯核与掩码像素并行进行。同时,针对掩码边缘的检测,重新定义了法线损失,以减轻边缘法线向量的歧义性。为提高3D高斯优化的效果,引入梯度约束平衡负载损失,以应对相应场景的复杂性,最小化像素并行渲染阶段的线程等待时间和重建损失。在多个城市数据集上的实验表明,PG-SAG在建筑表面重建方面表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS已成为实时新数据合成领域的变革性方法。
- PG-SAG方法利用语义线索进行分区和高斯核优化,实现大规模城市区域的精细建筑表面重建。
- PG-SAG方法无需降低原始图像分辨率。
- 跨模态模型用于分割建筑掩膜,基于可见性检查对分割区域进行子区域分组。
- 高斯核优化与掩码像素并行进行。
- 重新定义法线损失以减轻边缘法线向量的歧义性。
点此查看论文截图

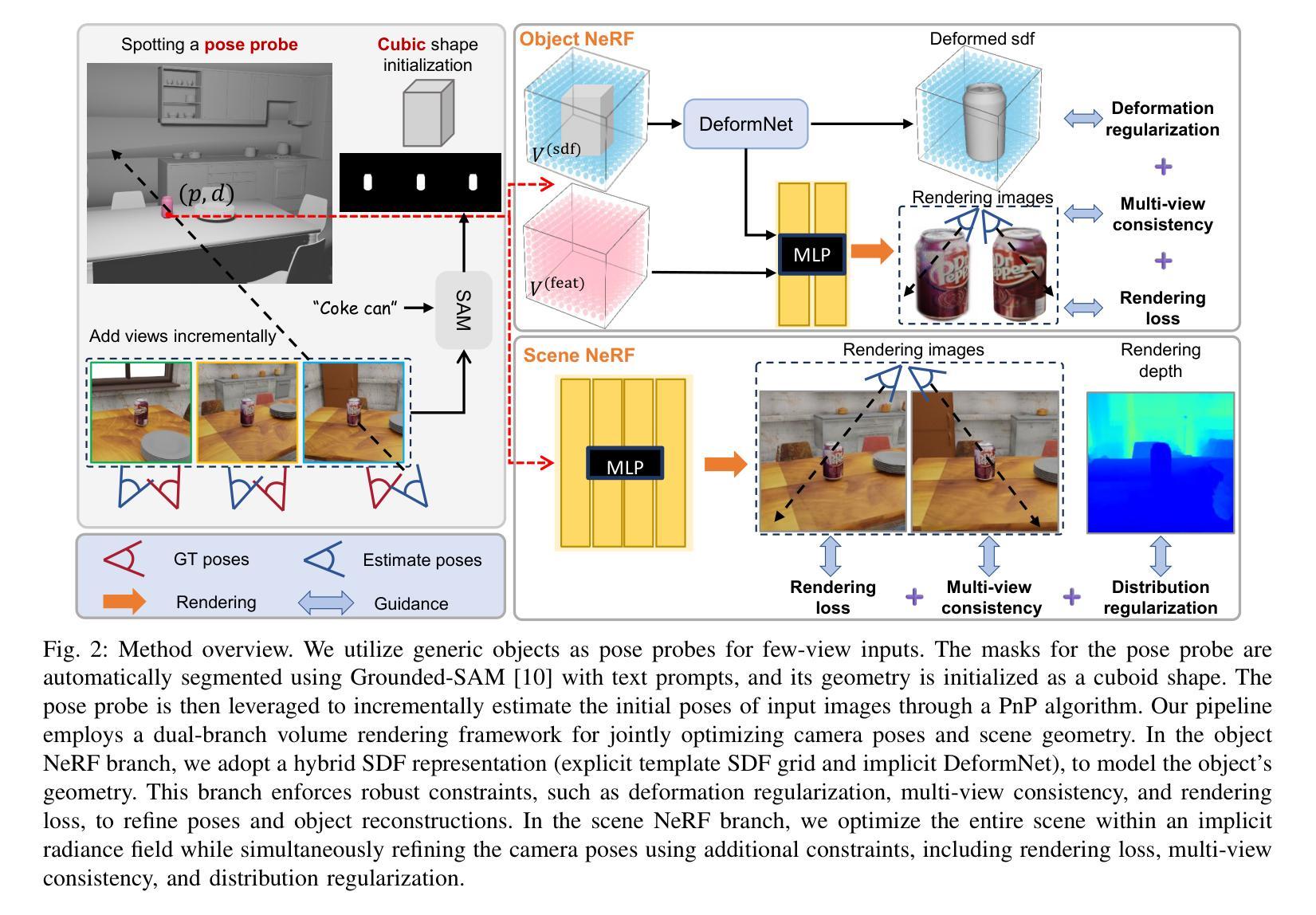
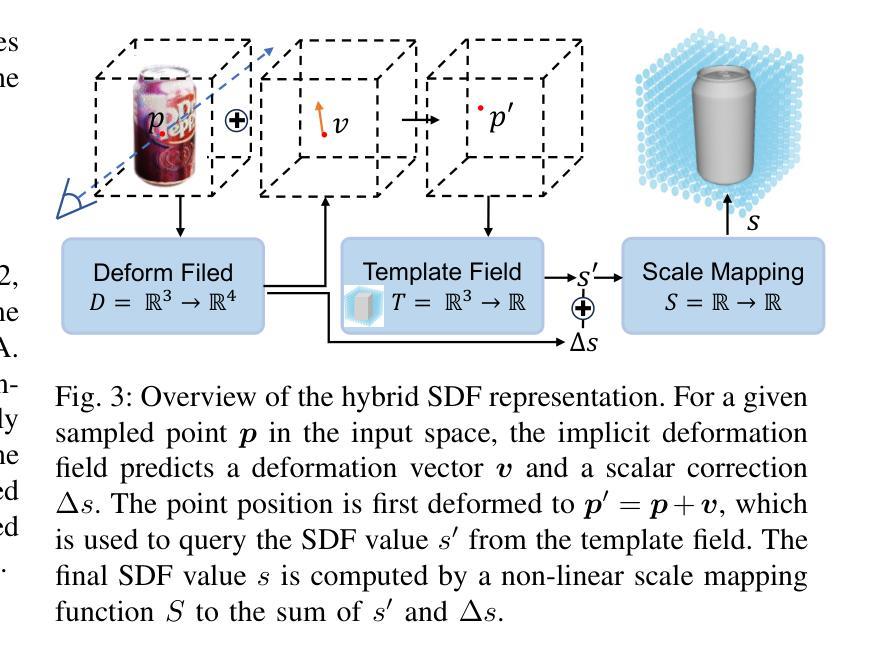
Generic Objects as Pose Probes for Few-shot View Synthesis
Authors:Zhirui Gao, Renjiao Yi, Chenyang Zhu, Ke Zhuang, Wei Chen, Kai Xu
Radiance fields including NeRFs and 3D Gaussians demonstrate great potential in high-fidelity rendering and scene reconstruction, while they require a substantial number of posed images as inputs. COLMAP is frequently employed for preprocessing to estimate poses, while it necessitates a large number of feature matches to operate effectively, and it struggles with scenes characterized by sparse features, large baselines between images, or a limited number of input images. We aim to tackle few-view NeRF reconstruction using only 3 to 6 unposed scene images. Traditional methods often use calibration boards but they are not common in images. We propose a novel idea of utilizing everyday objects, commonly found in both images and real life, as “pose probes”. The probe object is automatically segmented by SAM, whose shape is initialized from a cube. We apply a dual-branch volume rendering optimization (object NeRF and scene NeRF) to constrain the pose optimization and jointly refine the geometry. Specifically, object poses of two views are first estimated by PnP matching in an SDF representation, which serves as initial poses. PnP matching, requiring only a few features, is suitable for feature-sparse scenes. Additional views are incrementally incorporated to refine poses from preceding views. In experiments, PoseProbe achieves state-of-the-art performance in both pose estimation and novel view synthesis across multiple datasets. We demonstrate its effectiveness, particularly in few-view and large-baseline scenes where COLMAP struggles. In ablations, using different objects in a scene yields comparable performance. Our project page is available at: \href{https://zhirui-gao.github.io/PoseProbe.github.io/}{this https URL}
NeRF和三维高斯等辉度场在高保真渲染和场景重建方面显示出巨大潜力,但它们需要大量的定位图像作为输入。COLMAP常被用于估计位置进行预处理,但它需要大量特征匹配才能有效运行,且在特征稀疏、图像间基线较大或输入图像数量有限的场景中表现挣扎。我们的目标是仅使用三到六张未定位的场景图像来解决少视角NeRF重建问题。传统方法通常使用校准板,但在图像中并不常见。我们提出了一种利用在图像和现实生活中都能找到的常见物体作为“定位探针”的新颖想法。探针对象通过SAM自动分割,其形状从立方体初始化。我们采用双分支体积渲染优化(对象NeRF和场景NeRF)来约束定位优化并共同优化几何结构。具体来说,首先通过PnP匹配在SDF表示中估计两个视角的物体位置,作为初始位置。PnP匹配仅需要几个特征,适用于特征稀疏的场景。额外的视角将逐渐融入以根据先前视角优化位置。在实验上,PoseProbe在多数据集上的姿态估计和新颖视角合成方面都达到了最新技术水平。我们证明了其有效性,特别是在COLMAP表现挣扎的少视角和大基线场景中。在研究中,使用场景中的不同对象会产生相当的性能。我们的项目页面可通过以下网址访问:[https://zhirui-gao.github.io/PoseProbe.github.io/]
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
高保真渲染和场景重建中,NeRFs和3D Gaussians等辉光场技术潜力巨大,但需大量定位图像作为输入。COLMAP常用于预处理估计定位,但需大量特征匹配才能有效运行,对特征稀疏、图像基线大或输入图像数量有限的场景应对困难。本研究旨在仅使用3至6张未定位的场景图像解决少量视图NeRF重建问题。我们提出利用常见物体作为“定位探针”的新理念,通过SAM自动分割探针对象,以立方体初始化其形状。我们采用双分支体积渲染优化(对象NeRF和场景NeRF)来约束定位优化并共同优化几何结构。PoseProbe实现了多个数据集上的最佳定位估计和新型视角合成性能。在少量视图和大基线场景中,PoseProbe尤其有效,而COLMAP在这些场景中表现困难。在不同场景中使用不同物体进行消融实验表现相当。我们的项目页面可在此URL找到。
关键见解
- 辉光场技术如NeRFs和3D Gaussians在高保真渲染和场景重建中具有巨大潜力,但需要大量定位图像。
- COLMAP在特征稀疏、图像基线大或输入图像有限的场景中应对困难。
- 提出利用常见物体作为“定位探针”的新方法,解决少量视图NeRF重建问题。
- 通过SAM自动分割探针对象,采用双分支体积渲染优化进行定位优化和几何优化。
- PoseProbe在多个数据集上实现最佳定位估计和新型视角合成性能。
- PoseProbe在少量视图和大基线场景中表现尤其出色。
- 在不同场景中使用不同物体进行消融实验,表现稳定。
点此查看论文截图