⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-07 更新
QuArch: A Question-Answering Dataset for AI Agents in Computer Architecture
Authors:Shvetank Prakash, Andrew Cheng, Jason Yik, Arya Tschand, Radhika Ghosal, Ikechukwu Uchendu, Jessica Quaye, Jeffrey Ma, Shreyas Grampurohit, Sofia Giannuzzi, Arnav Balyan, Fin Amin, Aadya Pipersenia, Yash Choudhary, Ankita Nayak, Amir Yazdanbakhsh, Vijay Janapa Reddi
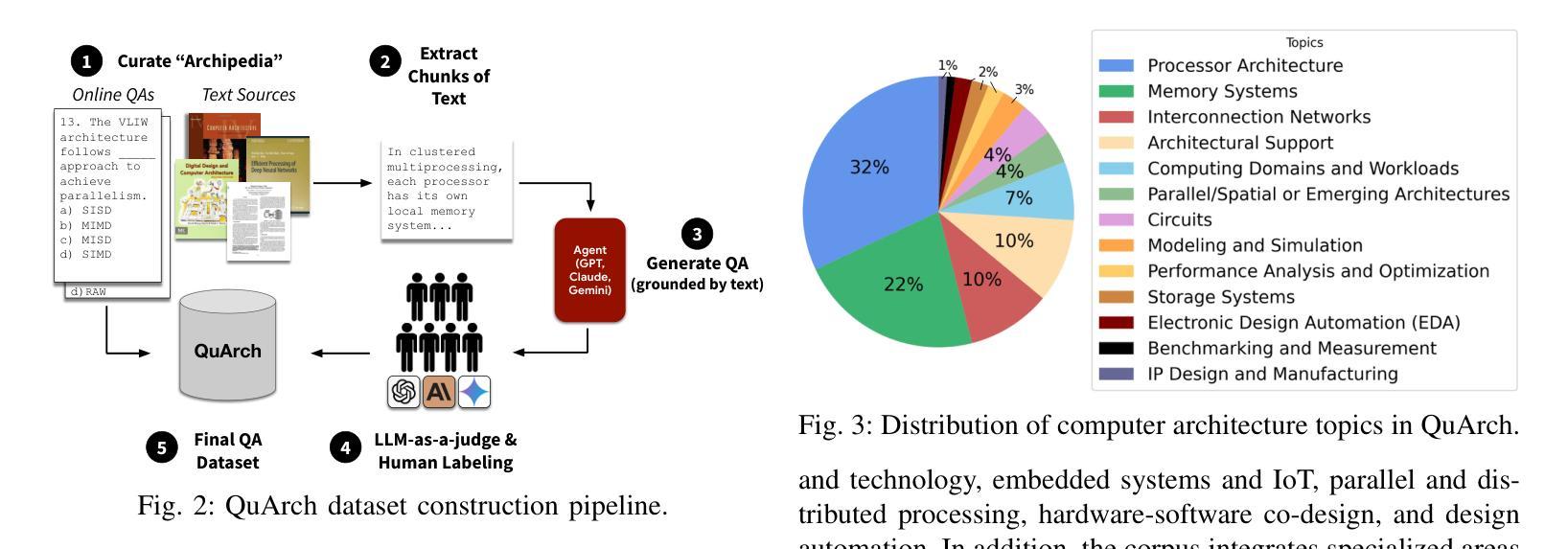
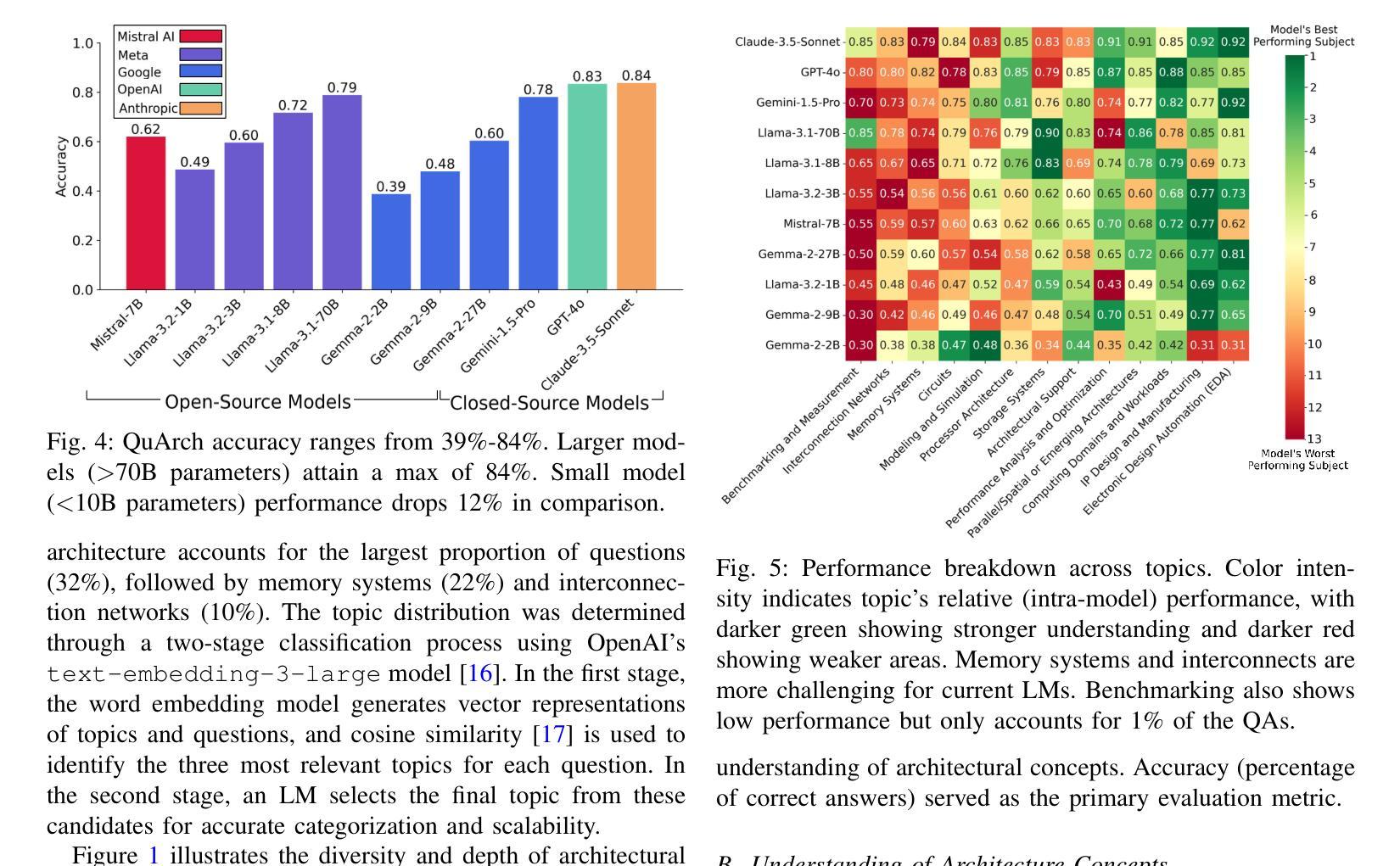
We introduce QuArch, a dataset of 1500 human-validated question-answer pairs designed to evaluate and enhance language models’ understanding of computer architecture. The dataset covers areas including processor design, memory systems, and performance optimization. Our analysis highlights a significant performance gap: the best closed-source model achieves 84% accuracy, while the top small open-source model reaches 72%. We observe notable struggles in memory systems, interconnection networks, and benchmarking. Fine-tuning with QuArch improves small model accuracy by up to 8%, establishing a foundation for advancing AI-driven computer architecture research. The dataset and leaderboard are at https://harvard-edge.github.io/QuArch/.
我们介绍了QuArch数据集,它包含1500组经过人工验证的问题答案对,旨在评估和增强语言模型对计算机架构的理解。该数据集涵盖了处理器设计、内存系统和性能优化等领域。我们的分析突显了显著的性能差距:最佳封闭源模型的准确率为84%,而顶尖的小型开源模型的准确率仅为72%。我们在内存系统、互联网络和基准测试方面遇到了明显的困难。使用QuArch进行微调可以提高小型模型的准确率,最高可提高8%,为推进AI驱动的计算机架构研究奠定了基础。数据集和排行榜位于https://harvard-edge.github.io/QuArch/。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
QuArch是一个包含人类验证的包含处理器设计、内存系统以及性能优化等领域的问题答案对的数据库。它旨在评估和增强语言模型对计算机架构的理解。分析显示,最好的闭源模型准确率可达百分之八十四,而表现最佳的小型开源模型准确率也达到百分之七十二,但在内存系统、互联网络和基准测试方面存在显著困难。使用QuArch微调可以提高小型模型的准确率至百分之八。该数据集和排行榜可访问https://harvard-edge.github.io/QuArch/。
关键见解
- QuArch数据集包含有人类验证的问题答案对,旨在评估和增强语言模型对计算机架构的理解。
- 数据集涵盖处理器设计、内存系统和性能优化等关键领域。
- 分析了语言模型在计算机架构方面的性能差距,最好的闭源模型与最佳小型开源模型的表现存在差异。
- 在内存系统、互联网络和基准测试方面存在挑战。
- 使用QuArch微调可以提高小型模型的准确率。
- QuArch数据集有助于推动AI驱动的计算机架构研究的发展。
点此查看论文截图

Multi-Agent Conversational Online Learning for Adaptive LLM Response Identification
Authors:Xiangxiang Dai, Yuejin Xie, Maoli Liu, Xuchuang Wang, Zhuohua Li, Huanyu Wang, John C. S. Lui
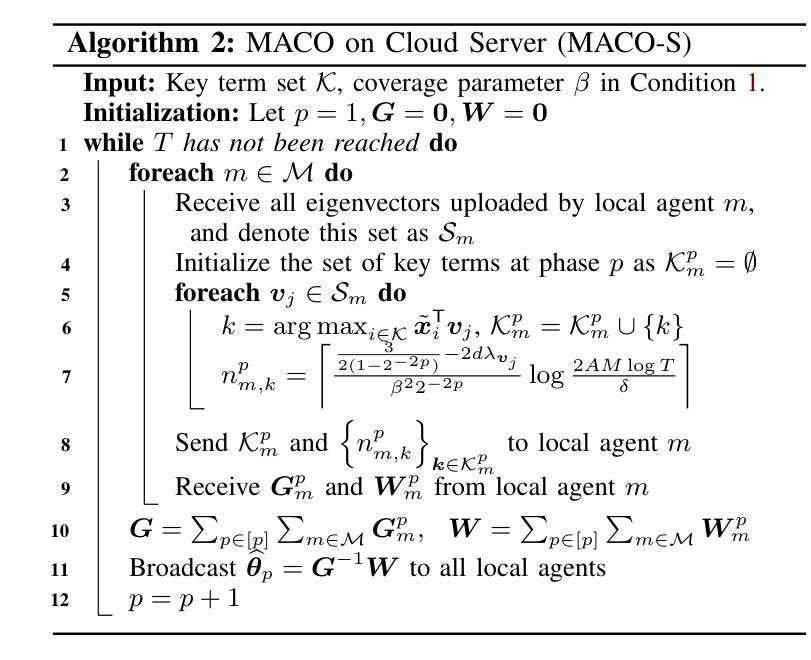
The remarkable generative capability of large language models (LLMs) has sparked a growing interest in automatically generating responses for different applications. Given the dynamic nature of user preferences and the uncertainty of LLM response performance, it is crucial to design efficient online learning algorithms to identify optimal LLM responses (i.e., high-quality responses that also meet user preferences). Most existing online algorithms adopt a centralized approach and fail to leverage explicit user preferences for more efficient and personalized LLM response identification. In contrast, this paper introduces \textit{MACO} (\underline{M}ulti-\underline{A}gent \underline{C}onversational \underline{O}nline Learning for Adaptive LLM Response Identification): 1) The online LLM response identification process is accelerated by multiple local agents (such as smartphones), while enhancing data privacy; 2) A novel conversational mechanism is proposed to adaptively conduct conversations for soliciting user preferences (e.g., a preference for a humorous tone over a serious one in generated responses), so to minimize uncertainty in preference estimation. Our theoretical analysis demonstrates that \cadi\ is near-optimal regarding cumulative regret. Additionally, \cadi\ offers reduced communication costs and computational complexity by eliminating the traditional, computing-intensive ``G-optimal design” found in previous works. Extensive experiments with the open LLM \textit{Llama}, coupled with two different embedding models from Google and OpenAI for text vector representation, demonstrate that \cadi\ significantly outperforms the current state-of-the-art in online LLM response identification.
大型语言模型(LLM)的出色生成能力引发了人们对不同应用自动生成响应的浓厚兴趣。考虑到用户偏好的动态性和LLM响应性能的不确定性,设计高效的在线学习算法来识别最佳的LLM响应(即高质量且符合用户偏好的响应)至关重要。现有的大多数在线算法采用集中式方法,未能充分利用明确的用户偏好来进行更高效、个性化的LLM响应识别。相比之下,本文介绍了\textit{MACO}(用于自适应LLM响应识别的多代理在线对话学习):1)在线LLM响应识别过程通过多个本地代理(如智能手机)加速,同时增强数据隐私;2)提出了一种新的对话机制,以自适应的方式进行对话,以征求用户偏好(例如,在生成的响应中更喜欢幽默的语调而不是严肃的语调),从而最小化偏好估计中的不确定性。我们的理论分析表明,\cadi\在累积遗憾方面接近最优。此外,\cadi\通过消除先前工作中的计算密集型“G最优设计”,降低了通信成本和计算复杂性。使用开源LLM“Llama”进行的广泛实验,结合谷歌和OpenAI的两个不同嵌入模型进行文本向量表示,表明\cadi\在在线LLM响应识别方面显著优于当前最新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的生成能力引起了广泛关注,并广泛应用于自动生成响应的不同应用。针对用户偏好动态性和LLM响应性能的不确定性,设计高效的在线学习算法至关重要。本文提出了一种基于多智能体的在线学习方法MACO,用于自适应LLM响应识别。MACO通过多个本地代理(如智能手机)加速在线LLM响应识别过程,提高数据隐私保护。它采用新颖的对话机制,通过对话了解用户偏好,降低偏好估计的不确定性。MACO具有近最优的累积遗憾值,并降低了通信成本和计算复杂性。实验表明,MACO在在线LLM响应识别方面显著优于当前最先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的生成能力在自动生成响应的不同应用中受到广泛关注。
- 设计和实施高效的在线学习算法对于识别符合用户偏好的高质量LLM响应至关重要。
- MACO方法通过多个本地代理(如智能手机)加速在线LLM响应识别,增强数据隐私保护。
- MACO采用新颖的对话机制了解用户偏好,降低偏好估计的不确定性。
- MACO具有理论上的近最优性能,在累积遗憾方面表现良好。
- MACO降低了通信成本和计算复杂性,优于传统的计算密集型方法。
点此查看论文截图


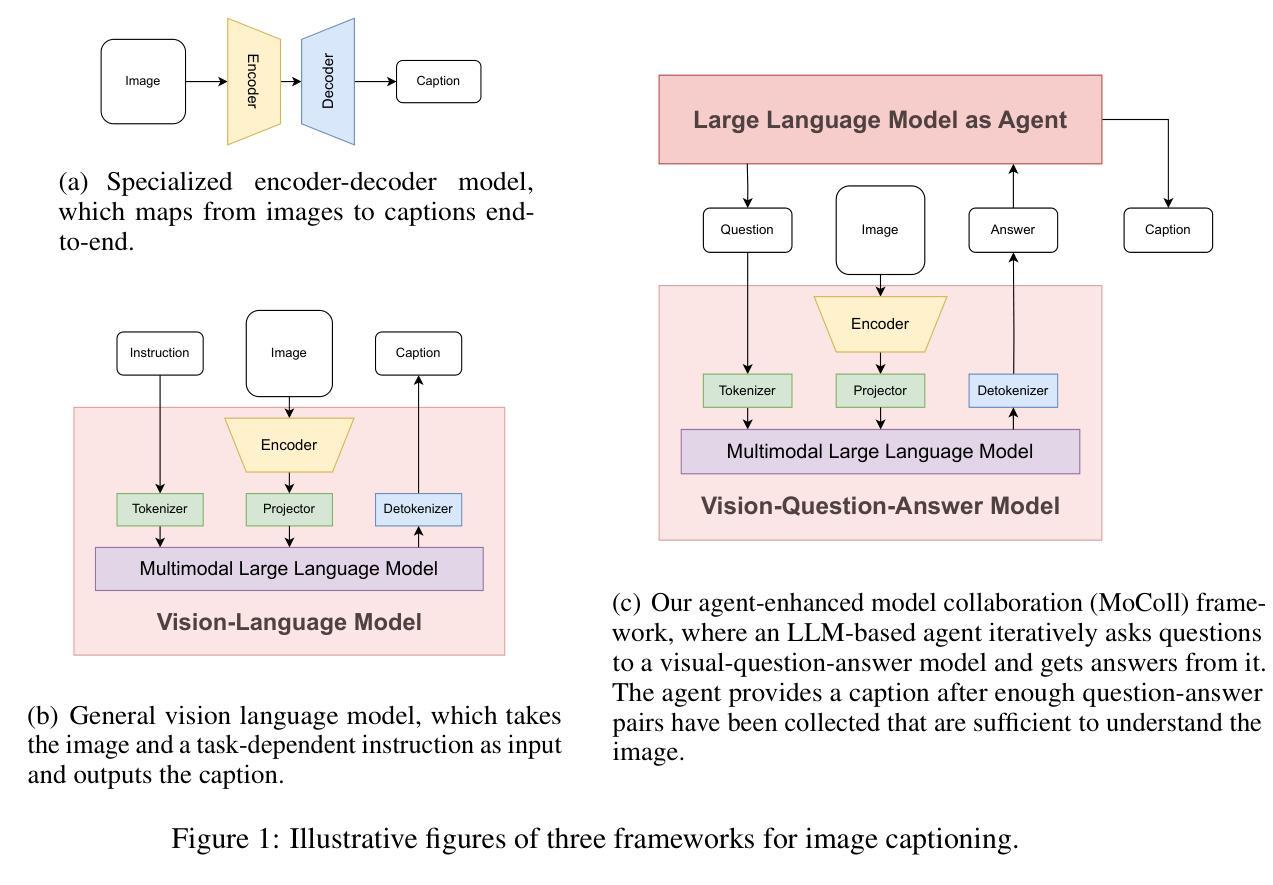
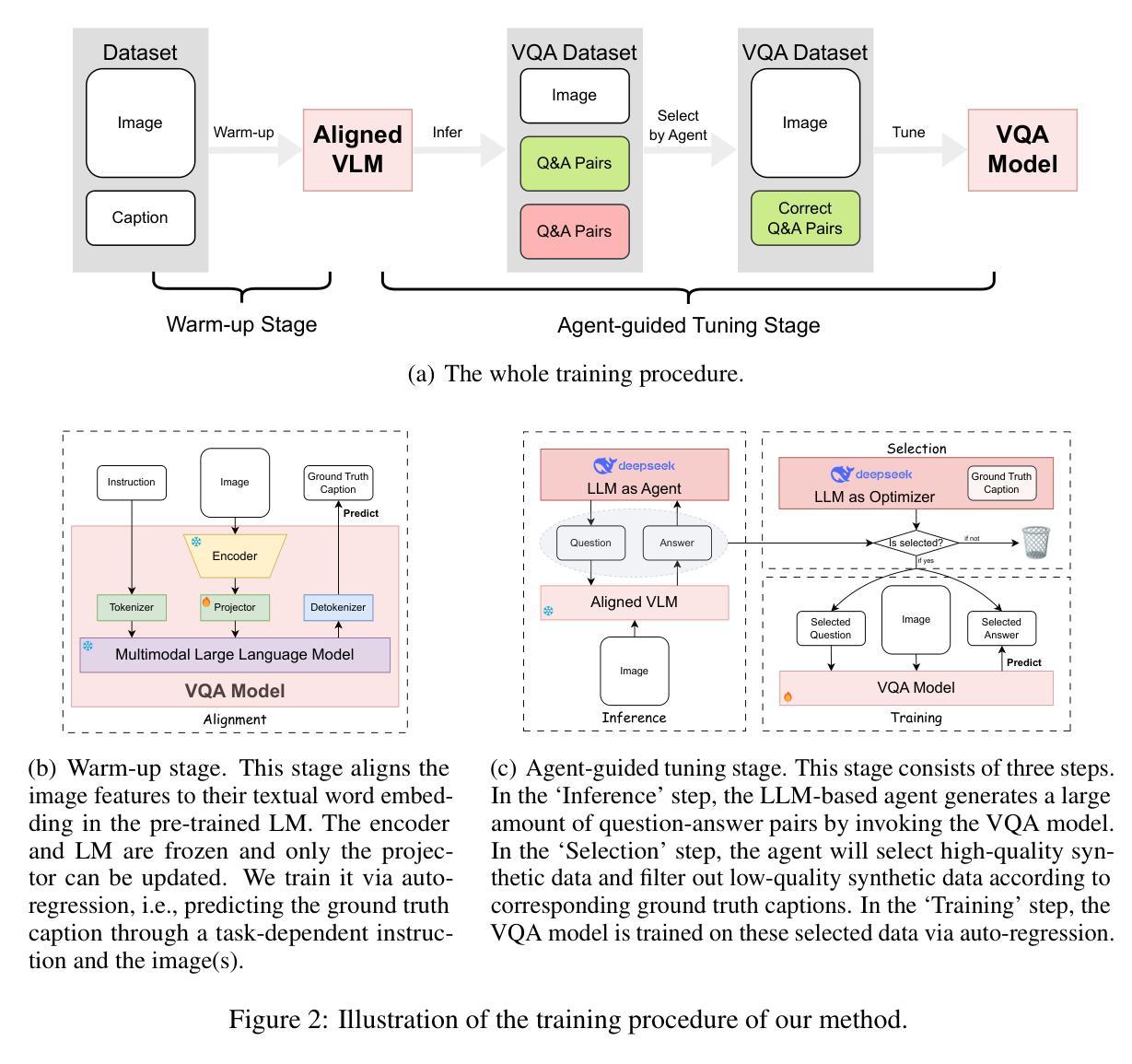
MoColl: Agent-Based Specific and General Model Collaboration for Image Captioning
Authors:Pu Yang, Bin Dong
Image captioning is a critical task at the intersection of computer vision and natural language processing, with wide-ranging applications across various domains. For complex tasks such as diagnostic report generation, deep learning models require not only domain-specific image-caption datasets but also the incorporation of relevant general knowledge to provide contextual accuracy. Existing approaches exhibit inherent limitations: specialized models excel in capturing domain-specific details but lack generalization, while vision-language models (VLMs) built on large language models (LLMs) leverage general knowledge but struggle with domain-specific adaptation. To address these limitations, this paper proposes a novel agent-enhanced model collaboration framework, which we called \textbf{MoColl}, designed to effectively integrate domain-specific and general knowledge. Specifically, our approach is to decompose complex image captioning tasks into a series of interconnected question-answer subtasks. A trainable visual question answering (VQA) model is employed as a specialized tool to focus on domain-specific visual analysis, answering task-specific questions based on image content. Concurrently, an LLM-based agent with general knowledge formulates these questions and synthesizes the resulting question-answer pairs into coherent captions. Beyond its role in leveraging the VQA model, the agent further guides its training to enhance its domain-specific capabilities. Experimental results on radiology report generation validate the effectiveness of the proposed framework, demonstrating significant improvements in the quality of generated reports.
图像标注是计算机视觉和自然语言处理领域的交叉任务,具有广泛的应用范围。对于生成诊断报告等复杂任务,深度学习模型不仅需要特定领域的图像标注数据集,还需要融入相关的通用知识来提供上下文准确性。现有方法存在固有的局限性:特定领域的模型擅长捕捉特定领域的细节,但缺乏泛化能力;而基于大型语言模型的视觉语言模型(VLMs)则利用通用知识,但在特定领域的适应性方面遇到困难。为了解决这些局限性,本文提出了一种新型代理增强模型协作框架,我们称之为MoColl,旨在有效地整合特定领域知识和通用知识。具体来说,我们的方法是将复杂的图像标注任务分解为一系列相互关联的问答子任务。我们采用可训练的视觉问答(VQA)模型作为专用工具,专注于特定领域的视觉分析,根据图像内容回答特定任务的问题。同时,一个基于大型语言模型的代理利用通用知识来制定这些问题,并将结果的问题答案对综合成连贯的标注。除了引导VQA模型的作用外,代理还能进一步引导其训练以增强其特定领域的能力。在放射学报告生成方面的实验验证了所提框架的有效性,显示出生成的报告质量显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像描述是计算机视觉和自然语言处理领域的核心任务之一,广泛应用于多个领域。针对诊断报告生成等复杂任务,深度学习模型不仅需要特定的图像描述数据集,还需要融入相关的通用知识以提高语境准确性。现有方法存在局限性:特定模型擅长捕捉特定领域的细节,但缺乏通用性;而基于大型语言模型的视觉语言模型(VLMs)虽然可以利用通用知识,但在特定领域的适应性上却遇到困难。为解决这些问题,本文提出了一种新型代理增强模型协作框架(MoColl),旨在有效整合特定领域和通用知识。该框架通过将复杂的图像描述任务分解为一系列相互关联的问答子任务来发挥作用。一个训练有素的视觉问答(VQA)模型作为专用工具,专注于特定领域的视觉分析,根据图像内容回答特定任务的问题。同时,具有通用知识的LLM代理负责提出问题和整合问答对形成连贯的描述。除了引导VQA模型的应用外,代理还能进一步提升其特定领域的技能。在放射学报告生成方面的实验验证了该框架的有效性,显著提高了生成报告的质量。
Key Takeaways
- 图像描述是计算机视觉和自然语言处理领域的交叉任务,具有广泛的应用领域。
- 深度学习模型在复杂任务如诊断报告生成中需要特定的图像描述数据集和通用知识。
- 现有方法存在局限性:特定模型缺乏通用性,而基于大型语言模型的视觉语言模型在特定领域适应性上存在问题。
- 提出了一种新型的代理增强模型协作框架(MoColl),整合特定领域和通用知识。
- 通过将复杂的图像描述任务分解为一系列相互关联的问答子任务来发挥作用。
- 采用视觉问答(VQA)模型作为专用工具,回答特定任务的问题,而LLM代理则负责提出问题和整合问答对。
点此查看论文截图


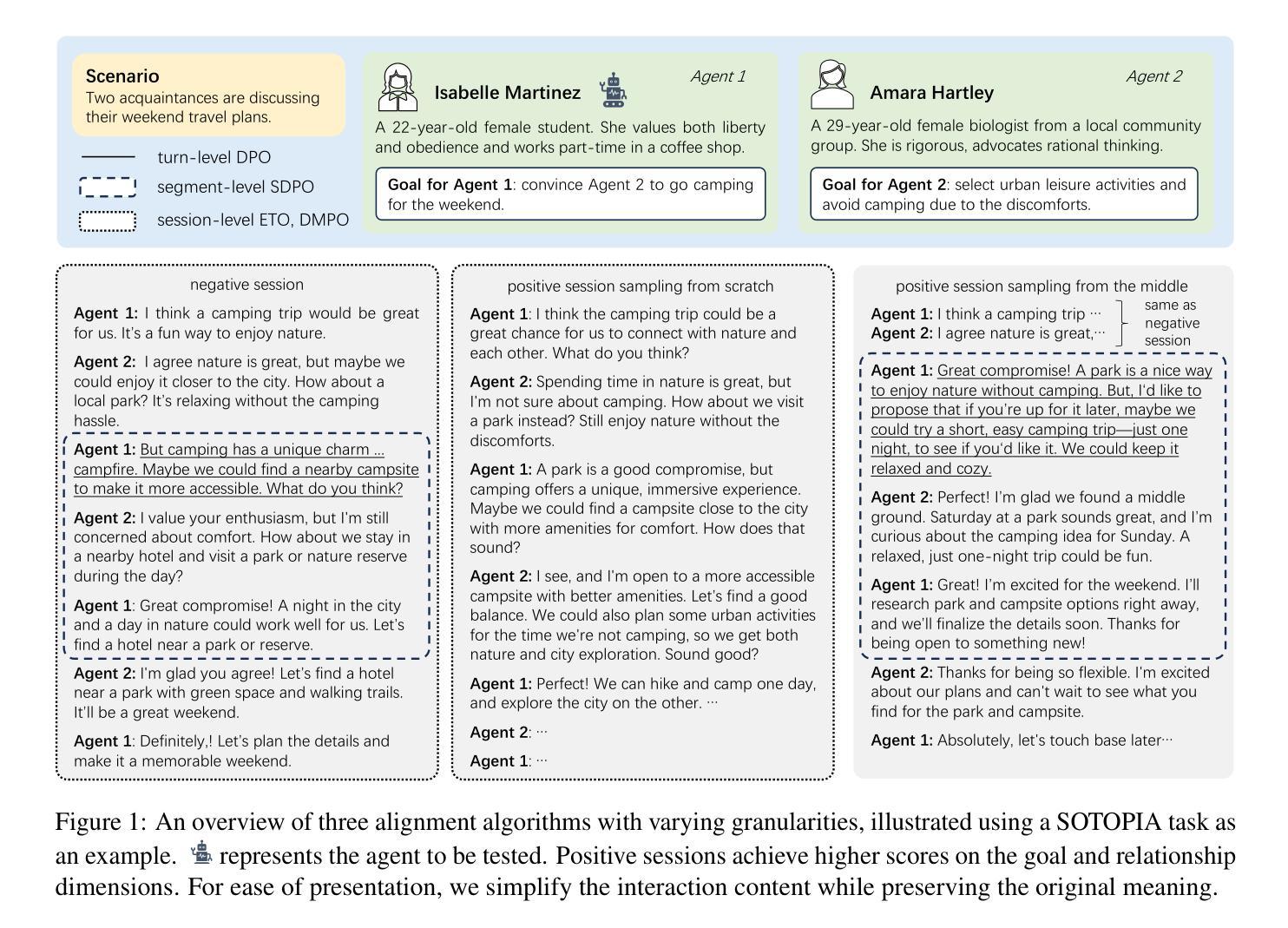
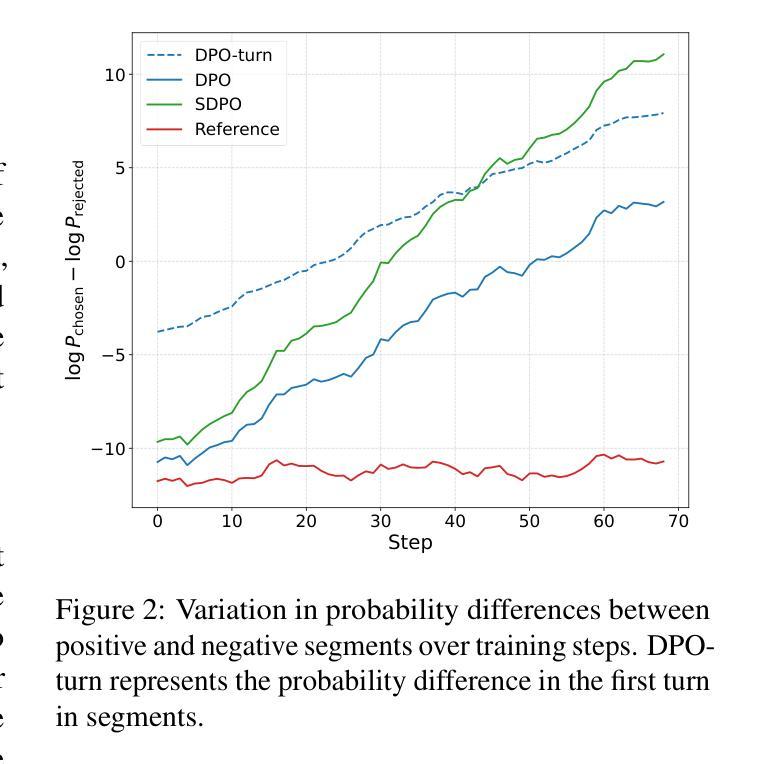
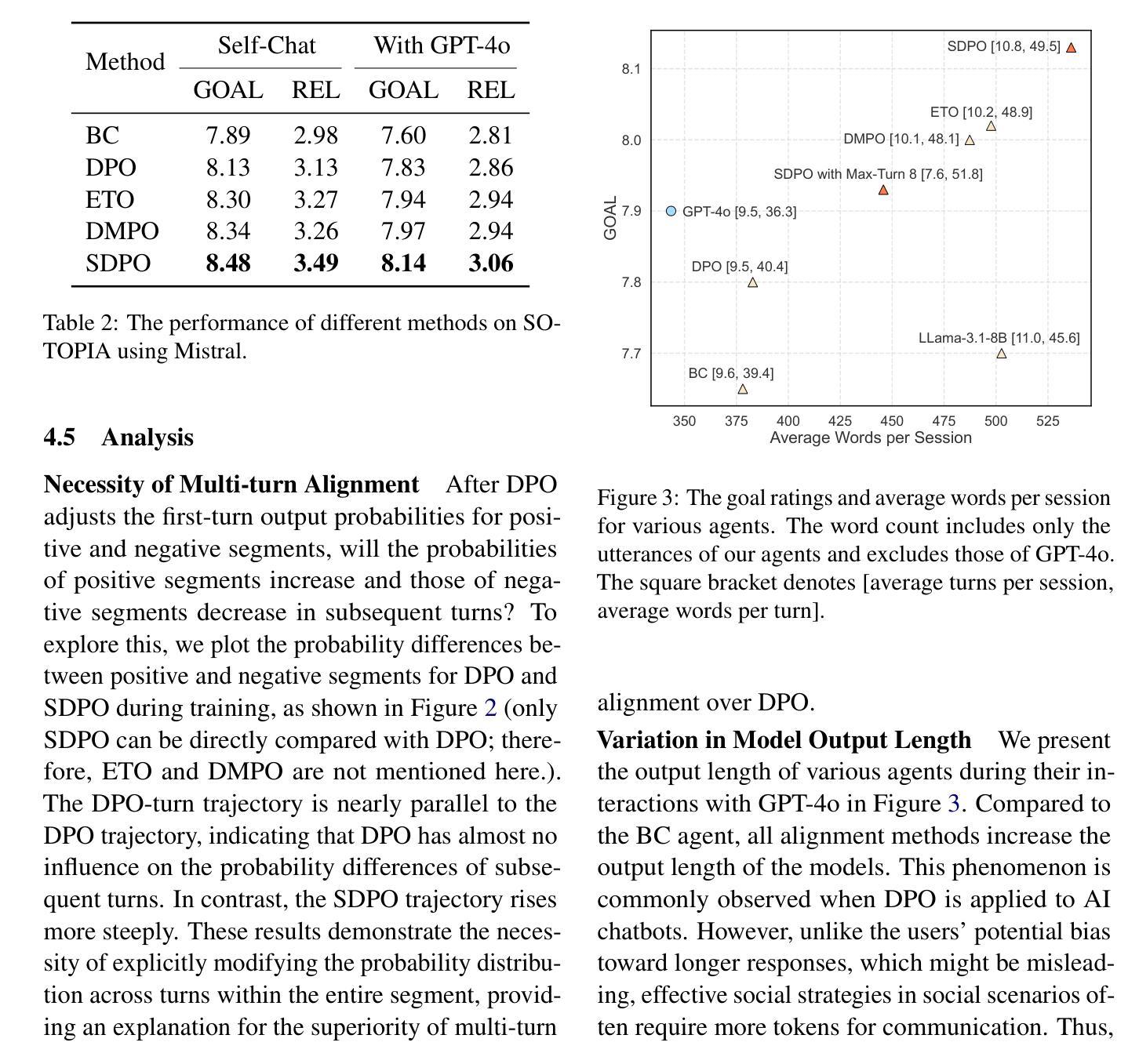
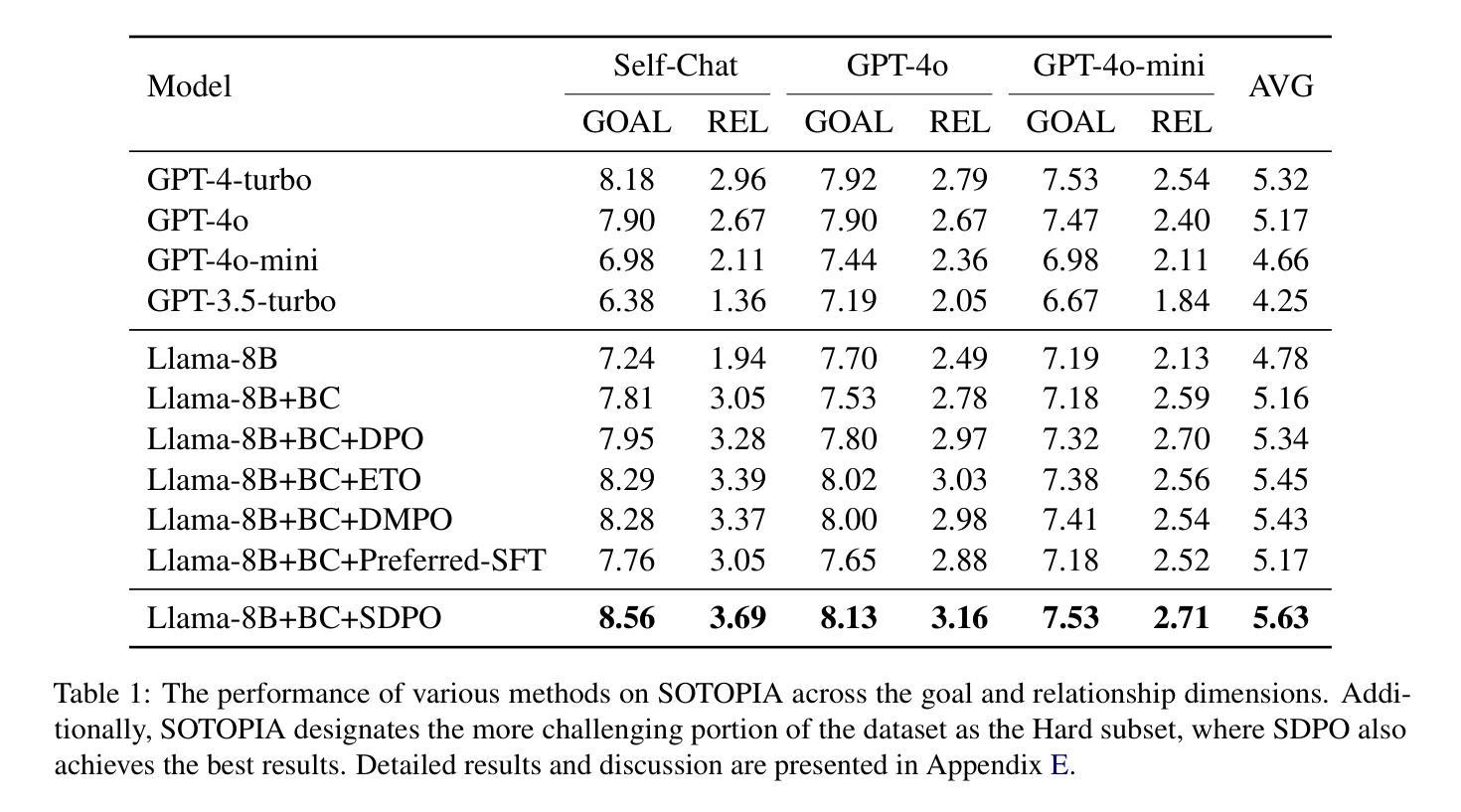
SDPO: Segment-Level Direct Preference Optimization for Social Agents
Authors:Aobo Kong, Wentao Ma, Shiwan Zhao, Yongbin Li, Yuchuan Wu, Ke Wang, Xiaoqian Liu, Qicheng Li, Yong Qin, Fei Huang
Social agents powered by large language models (LLMs) can simulate human social behaviors but fall short in handling complex goal-oriented social dialogues. Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has proven effective in aligning LLM behavior with human preferences across a variety of agent tasks. Existing DPO-based approaches for multi-turn interactions are divided into turn-level and session-level methods. The turn-level method is overly fine-grained, focusing exclusively on individual turns, while session-level methods are too coarse-grained, often introducing training noise. To address these limitations, we propose Segment-Level Direct Preference Optimization (SDPO), which focuses on specific key segments within interactions to optimize multi-turn agent behavior while minimizing training noise. Evaluations on the SOTOPIA benchmark demonstrate that SDPO-tuned agents consistently outperform both existing DPO-based methods and proprietary LLMs like GPT-4o, underscoring SDPO’s potential to advance the social intelligence of LLM-based agents. We release our code and data at https://github.com/AlibabaResearch/DAMO-ConvAI/tree/main/SDPO.
由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的社会代理能够模拟人类的社会行为,但在处理复杂的以目标为导向的社会对话方面表现不足。直接偏好优化(DPO)在各种代理任务中,已被证明在将LLM行为与人的偏好对齐方面非常有效。现有的基于DPO的多轮交互方法分为轮级和会话级方法。轮级方法过于精细,只关注个别轮次,而会话级方法则过于粗糙,经常引入训练噪声。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了分段级直接偏好优化(SDPO),它专注于交互中的特定关键段,以优化多轮代理行为,同时最小化训练噪声。在SOTOPIA基准测试上的评估表明,SDPO调优的代理始终优于现有的DPO方法和专有LLM,如GPT-4o,这突显了SDPO在推进基于LLM的代理的社会智能方面的潜力。我们的代码和数据已在https://github.com/AlibabaResearch/DAMO-ConvAI/tree/main/SDPO发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型驱动的社会代理能够模拟人类社交行为,但在处理复杂的、以目标为导向的社会对话方面存在不足。为解决现有直接偏好优化(DPO)方法在处理多轮交互时的局限性,我们提出了分段级别直接偏好优化(SDPO),专注于交互中的特定关键段落,以优化多轮代理行为并减少训练噪声。评估表明,SDPO调优的代理在SOTOPIA基准测试中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的社会代理可以模拟人类社交行为,但在处理目标导向的社会对话时存在不足。
- 直接偏好优化(DPO)对于对齐LLM行为和人类偏好在各种代理任务中已被证明是有效的。
- 现有DPO方法在处理多轮交互时存在局限性,分为轮级和会话级方法。轮级方法过于精细,专注于个别轮次;会话级方法则过于粗糙,常引入训练噪声。
- 为解决上述问题,提出了分段级别直接偏好优化(SDPO),专注于交互中的特定关键段落进行优化,以减少训练噪声。
- SDPO在SOTOPIA基准测试中的表现优于现有的DPO方法和GPT-4o等专有LLM,显示出其在提高LLM基础代理的社会智能方面的潜力。
- 我们已在指定链接公开了相关代码和数据,以便进一步研究和应用。
点此查看论文截图

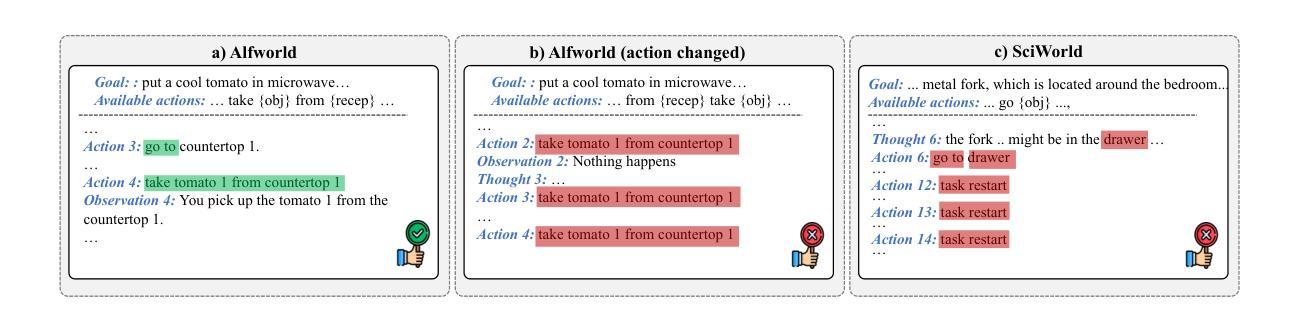
AgentRefine: Enhancing Agent Generalization through Refinement Tuning
Authors:Dayuan Fu, Keqing He, Yejie Wang, Wentao Hong, Zhuoma Gongque, Weihao Zeng, Wei Wang, Jingang Wang, Xunliang Cai, Weiran Xu
Large Language Model (LLM) based agents have proved their ability to perform complex tasks like humans. However, there is still a large gap between open-sourced LLMs and commercial models like the GPT series. In this paper, we focus on improving the agent generalization capabilities of LLMs via instruction tuning. We first observe that the existing agent training corpus exhibits satisfactory results on held-in evaluation sets but fails to generalize to held-out sets. These agent-tuning works face severe formatting errors and are frequently stuck in the same mistake for a long while. We analyze that the poor generalization ability comes from overfitting to several manual agent environments and a lack of adaptation to new situations. They struggle with the wrong action steps and can not learn from the experience but just memorize existing observation-action relations. Inspired by the insight, we propose a novel AgentRefine framework for agent-tuning. The core idea is to enable the model to learn to correct its mistakes via observation in the trajectory. Specifically, we propose an agent synthesis framework to encompass a diverse array of environments and tasks and prompt a strong LLM to refine its error action according to the environment feedback. AgentRefine significantly outperforms state-of-the-art agent-tuning work in terms of generalization ability on diverse agent tasks. It also has better robustness facing perturbation and can generate diversified thought in inference. Our findings establish the correlation between agent generalization and self-refinement and provide a new paradigm for future research.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理已经证明了它们执行复杂任务的能力,如同人类。然而,开源LLM和商业模型(如GPT系列)之间仍存在巨大差距。在本文中,我们专注于通过指令调整提高LLM的代理泛化能力。我们首先观察到,现有的代理训练语料库在内部评估集上表现良好,但却无法泛化到外部集。这些代理调整工作面临着严重的格式错误,并经常长时间陷入同样的错误。我们分析认为,泛化能力差的根源在于对多种手动代理环境的过度适应以及对新情况的适应能力不足。他们无法采取正确的行动步骤,无法从经验中学习,而只是记忆现有的观察-行动关系。在此基础上,我们提出了新颖的AgentRefine框架用于代理调整。核心思想是使模型能够通过轨迹中的观察来纠正其错误。具体来说,我们提出了一个代理合成框架,以涵盖各种环境和任务,并提示强大的LLM根据环境反馈来纠正其错误行动。AgentRefine在多种代理任务的泛化能力方面显著优于最新的代理调整工作。它还具有更好的抗扰动性,并在推理过程中能产生多样化的思想。我们的发现建立了代理泛化和自我完善之间的关联,为未来研究提供了新的范式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂任务上的表现已接近人类水平,但开源LLM与商业模型如GPT系列之间仍存在差距。本文聚焦于通过指令微调提升LLM的代理泛化能力。研究发现,现有代理训练语料库在封闭测试集上表现良好,但在开放测试集上泛化能力较差。为解决这一问题,本文提出了新型的AgentRefine框架,该框架旨在让模型通过观察轨迹学习纠正错误。AgentRefine显著提升了现有代理调整工作在多样化代理任务上的泛化能力,并展现出更好的鲁棒性和推理多样性。本文的发现为代理泛化与自我修正之间的关联提供了新的视角和研究范式。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在复杂任务上的表现已接近人类水平,但存在开源与商业模型间的差距。
- 现有LLM代理训练存在泛化能力不足的问题,无法适应新情境。
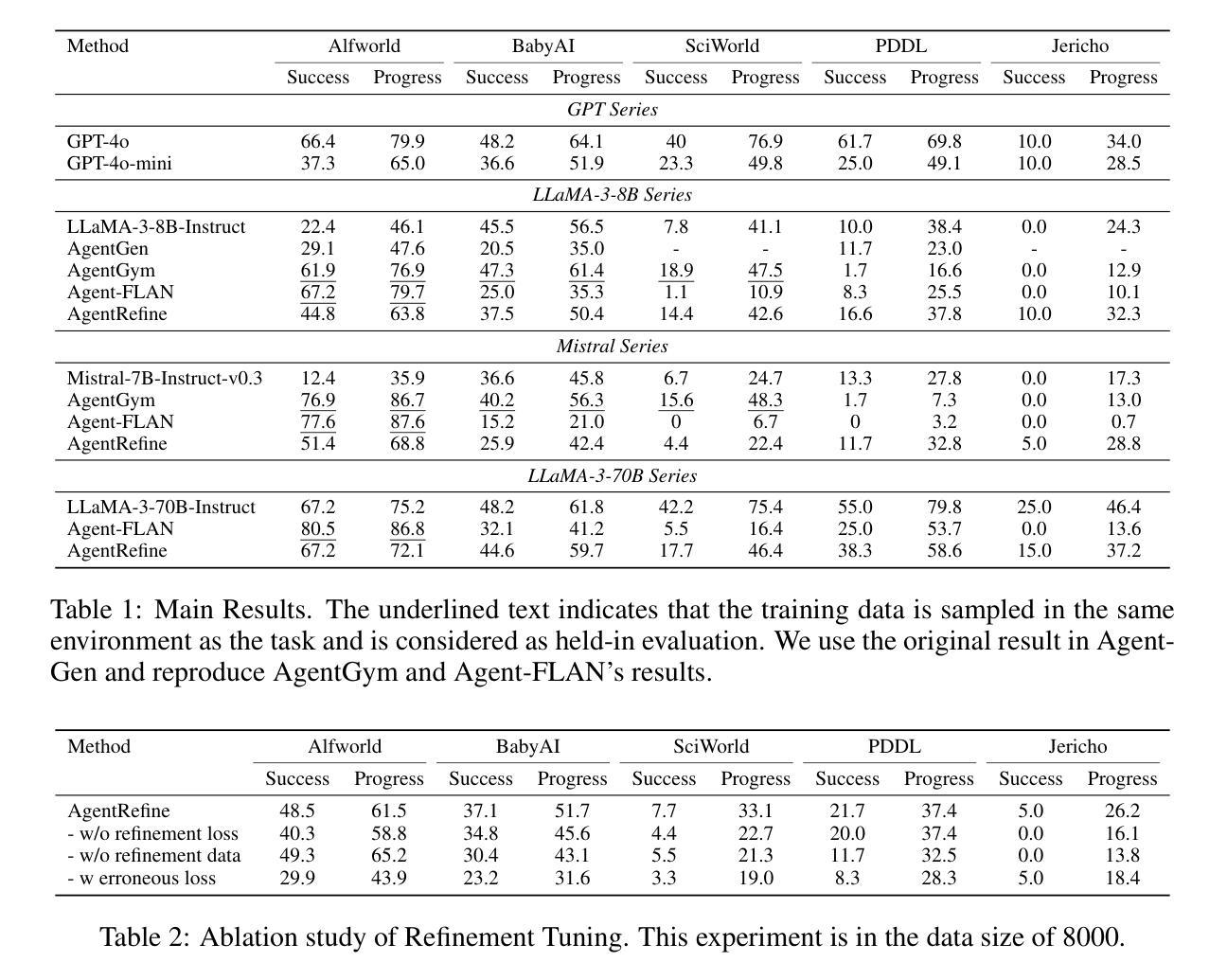
- AgentRefine框架被提出用于提升LLM的代理泛化能力,通过自我修正学习来纠正错误。
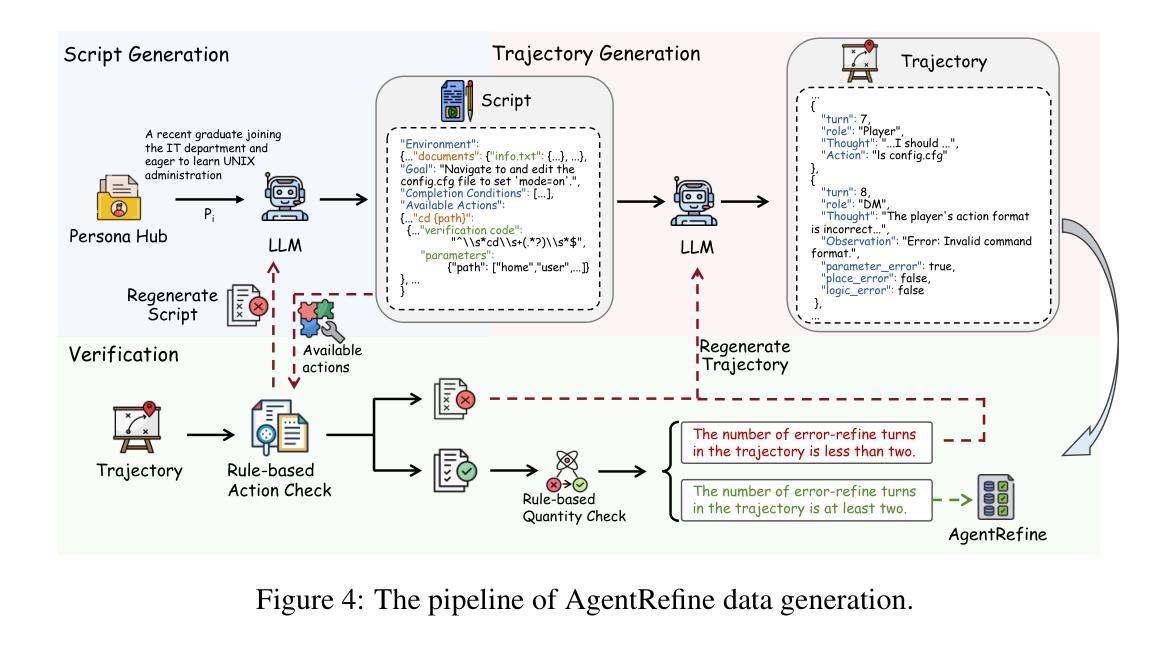
- AgentRefine框架包含多样化的环境和任务,并成功引导LLM根据环境反馈修正错误动作。
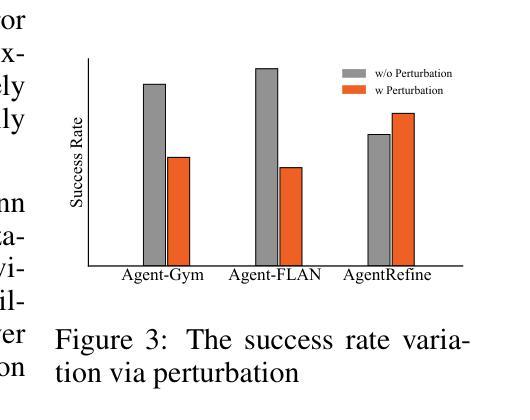
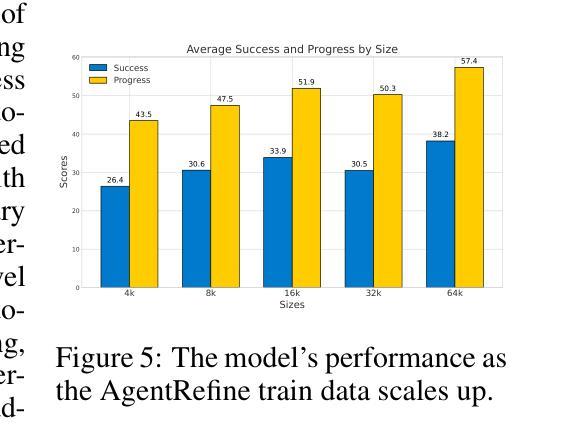
- AgentRefine显著提升了在多样化代理任务上的泛化能力,展现更好的鲁棒性和推理多样性。
- 本文发现代理泛化与自我修正之间的关联为未来研究提供了新的视角。
点此查看论文截图
Large Language Model Based Multi-Agent System Augmented Complex Event Processing Pipeline for Internet of Multimedia Things
Authors:Talha Zeeshan, Abhishek Kumar, Susanna Pirttikangas, Sasu Tarkoma
This paper presents the development and evaluation of a Large Language Model (LLM), also known as foundation models, based multi-agent system framework for complex event processing (CEP) with a focus on video query processing use cases. The primary goal is to create a proof-of-concept (POC) that integrates state-of-the-art LLM orchestration frameworks with publish/subscribe (pub/sub) tools to address the integration of LLMs with current CEP systems. Utilizing the Autogen framework in conjunction with Kafka message brokers, the system demonstrates an autonomous CEP pipeline capable of handling complex workflows. Extensive experiments evaluate the system’s performance across varying configurations, complexities, and video resolutions, revealing the trade-offs between functionality and latency. The results show that while higher agent count and video complexities increase latency, the system maintains high consistency in narrative coherence. This research builds upon and contributes to, existing novel approaches to distributed AI systems, offering detailed insights into integrating such systems into existing infrastructures.
本文介绍了一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统框架的开发与评估,用于复杂事件处理(CEP),重点关注视频查询处理用例。主要目标是创建一个概念验证(POC),将最新的LLM编排框架与发布/订阅(pub/sub)工具集成,以解决LLM与当前CEP系统的集成问题。该系统利用Autogen框架和Kafka消息代理,展示了一个能够处理复杂工作流程的自主CEP管道。通过广泛的实验,对系统在不同配置、复杂度和视频分辨率下的性能进行了评估,揭示了功能与延迟之间的权衡。结果表明,虽然较高的智能体数量和视频复杂度会增加延迟,但系统在叙事连贯性方面保持高度一致性。该研究建立在现有的分布式人工智能系统的新颖方法之上,并为其做出贡献,为将此类系统融入现有基础设施提供了详细的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出并评估了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统框架,主要应用于复杂事件处理(CEP)。其专注于视频查询处理用例,旨在创建一种将先进的LLM编排框架与发布/订阅工具结合的原型概念,以解决LLM与当前CEP系统的集成问题。通过结合Autogen框架和Kafka消息代理,该系统展示了能够处理复杂工作流程的自主CEP管道。实验结果显示,尽管在智能体数量增加和视频复杂度提高的情况下,系统延迟有所增加,但在叙事连贯性方面保持高度一致性。本研究对分布式AI系统的集成进行了深入的探索和改进,提供了现有基础设施中集成的深入见解。
Key Takeaways
以下是关键要点总结:
- 大型语言模型在多智能体系统框架中被用来进行复杂事件处理,特别是视频查询处理。
- 该系统旨在整合先进的LLM编排框架与发布/订阅工具,以解决LLM与当前CEP系统的集成问题。
- 利用Autogen框架和Kafka消息代理技术实现了自主CEP管道。
- 实验评估了系统在不同配置、复杂度和视频分辨率下的性能表现。
- 智能体数量和视频复杂度的增加会增加系统延迟。
- 系统在叙事连贯性方面表现良好,即使在较高的复杂度和延迟下。
点此查看论文截图

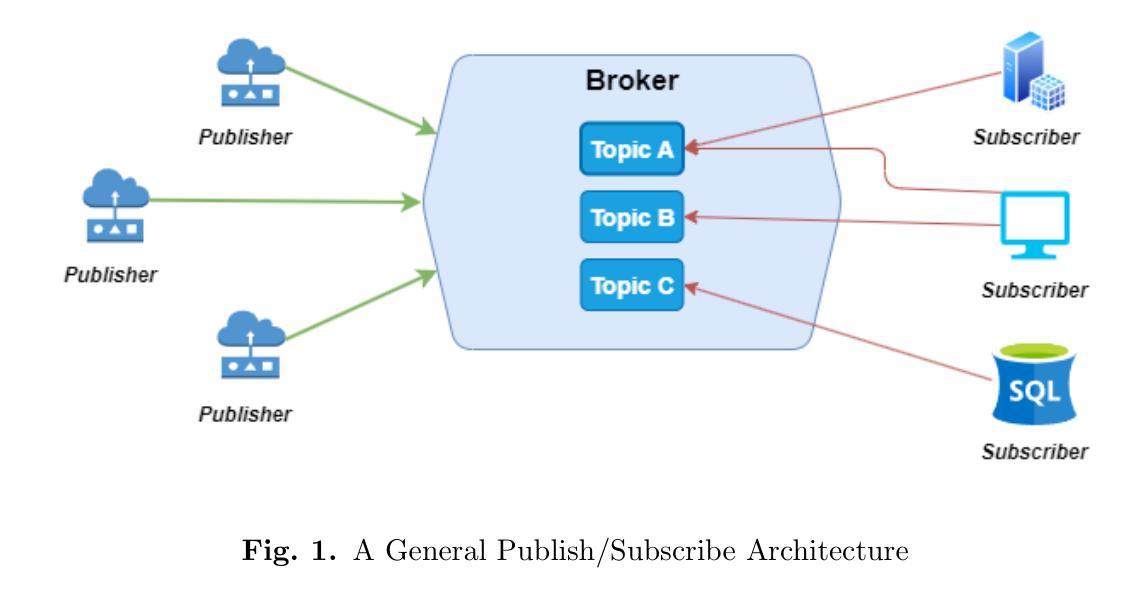
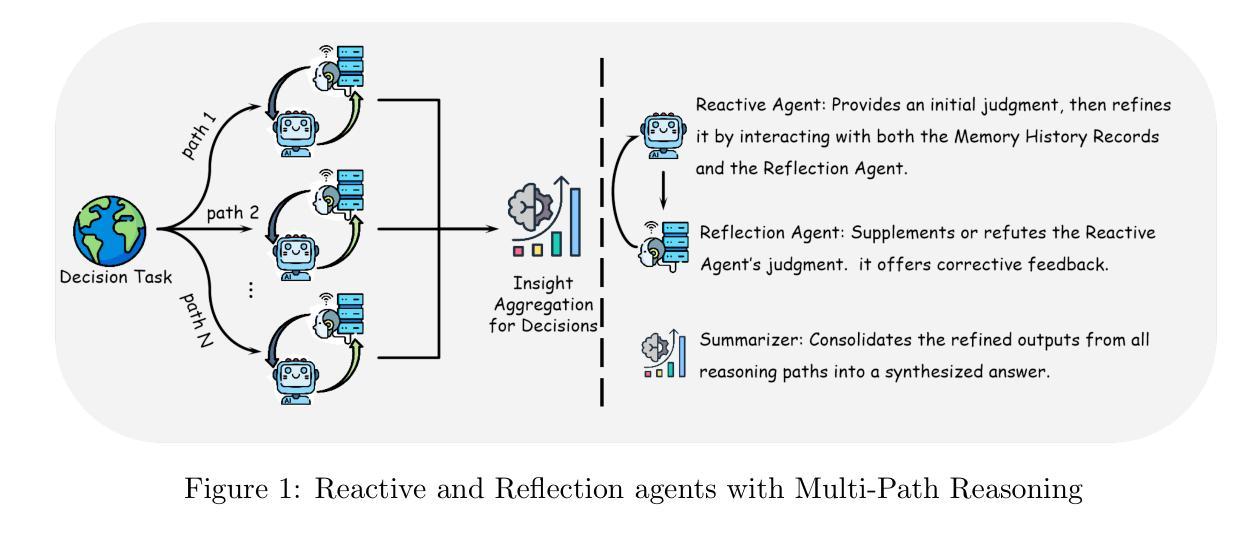
Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Multi-Path Collaborative Reactive and Reflection agents
Authors:Chengbo He, Bochao Zou, Xin Li, Jiansheng Chen, Junliang Xing, Huimin Ma
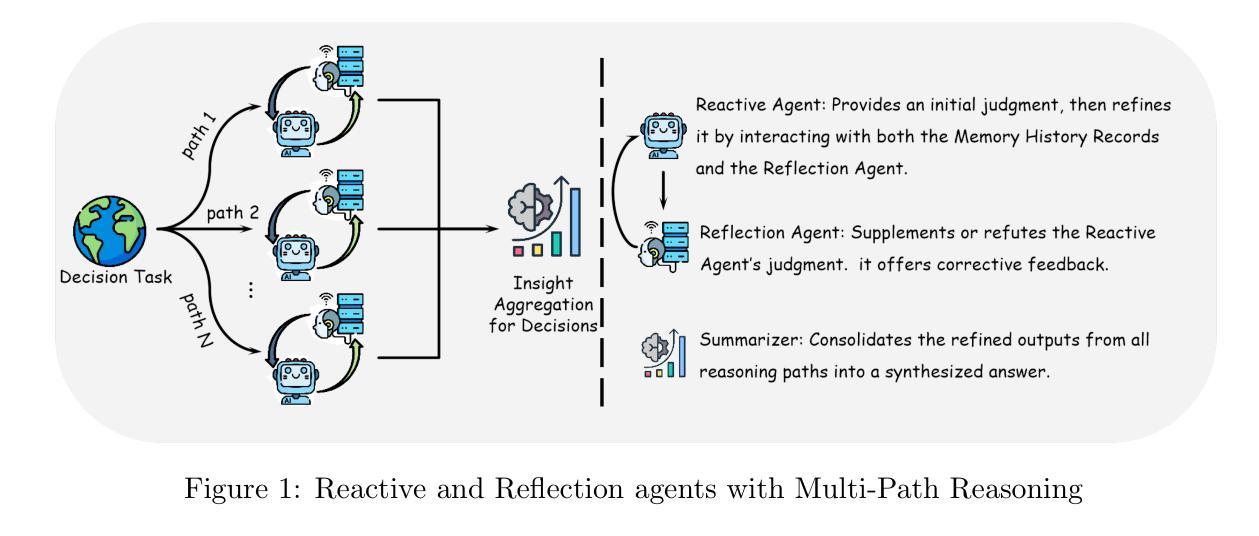
Agents have demonstrated their potential in scientific reasoning tasks through large language models. However, they often face challenges such as insufficient accuracy and degeneration of thought when handling complex reasoning tasks, which impede their performance. To overcome these issues, we propose the Reactive and Reflection agents with Multi-Path Reasoning (RR-MP) Framework, aimed at enhancing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Our approach improves scientific reasoning accuracy by employing a multi-path reasoning mechanism where each path consists of a reactive agent and a reflection agent that collaborate to prevent degeneration of thought inherent in single-agent reliance. Additionally, the RR-MP framework does not require additional training; it utilizes multiple dialogue instances for each reasoning path and a separate summarizer to consolidate insights from all paths. This design integrates diverse perspectives and strengthens reasoning across each path. We conducted zero-shot and few-shot evaluations on tasks involving moral scenarios, college-level physics, and mathematics. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms baseline approaches, highlighting the effectiveness and advantages of the RR-MP framework in managing complex scientific reasoning tasks.
人工智能代理通过大规模语言模型在科学推理任务中展示了其潜力。然而,在处理复杂的推理任务时,它们经常面临准确性不足和思想退化等挑战,这阻碍了它们的性能。为了克服这些问题,我们提出了具有多路径推理的响应与反思代理(RR-MP)框架,旨在增强大型语言模型的推理能力。我们的方法采用多路径推理机制来提高科学推理的准确性,每条路径包含一个响应代理和一个反思代理,它们协同工作以防止单一代理依赖所导致的思想退化。此外,RR-MP框架不需要额外的训练;它利用每个推理路径的多个对话实例和一个单独的摘要器来整合所有路径的见解。这种设计融合了不同的观点,加强了每条路径的推理能力。我们在涉及道德场景、大学物理和数学的任务上进行了零样本和少样本评估。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于基准方法,突显了RR-MP框架在处理复杂科学推理任务中的有效性和优势。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
基于多路径推理机制的反应与反思智能体(RR-MP)框架增强了语言大模型在科学推理任务中的能力。通过采用包含反应智能体和反思智能体的多路径推理机制,RR-MP框架能有效防止单一智能体推理过程中的思维退化问题。无需额外训练,该框架利用不同推理路径的对话实例和汇总器来整合观点,加强每条路径的推理能力。在道德情境、大学物理和数学任务上的零样本和少样本评估表明,该方法优于基准方法,突显了RR-MP框架在处理复杂科学推理任务时的优势和效果。
关键见解
- Agents在科研推理任务中具有巨大潜力,但仍面临准确性不足和应对复杂任务时思维退化等挑战。
- 提出的RR-MP框架旨在增强语言大模型(LLMs)的推理能力。
- RR-MP框架采用多路径推理机制,包含反应智能体和反思智能体,以克服单一智能体的思维退化问题。
- 该框架利用不同推理路径的对话实例,通过汇总器整合观点,加强了每条路径的推理能力。
- RR-MP框架设计灵活,不需要额外训练。
- 实验结果表明,RR-MP框架在复杂科学推理任务上的表现优于基准方法。
点此查看论文截图


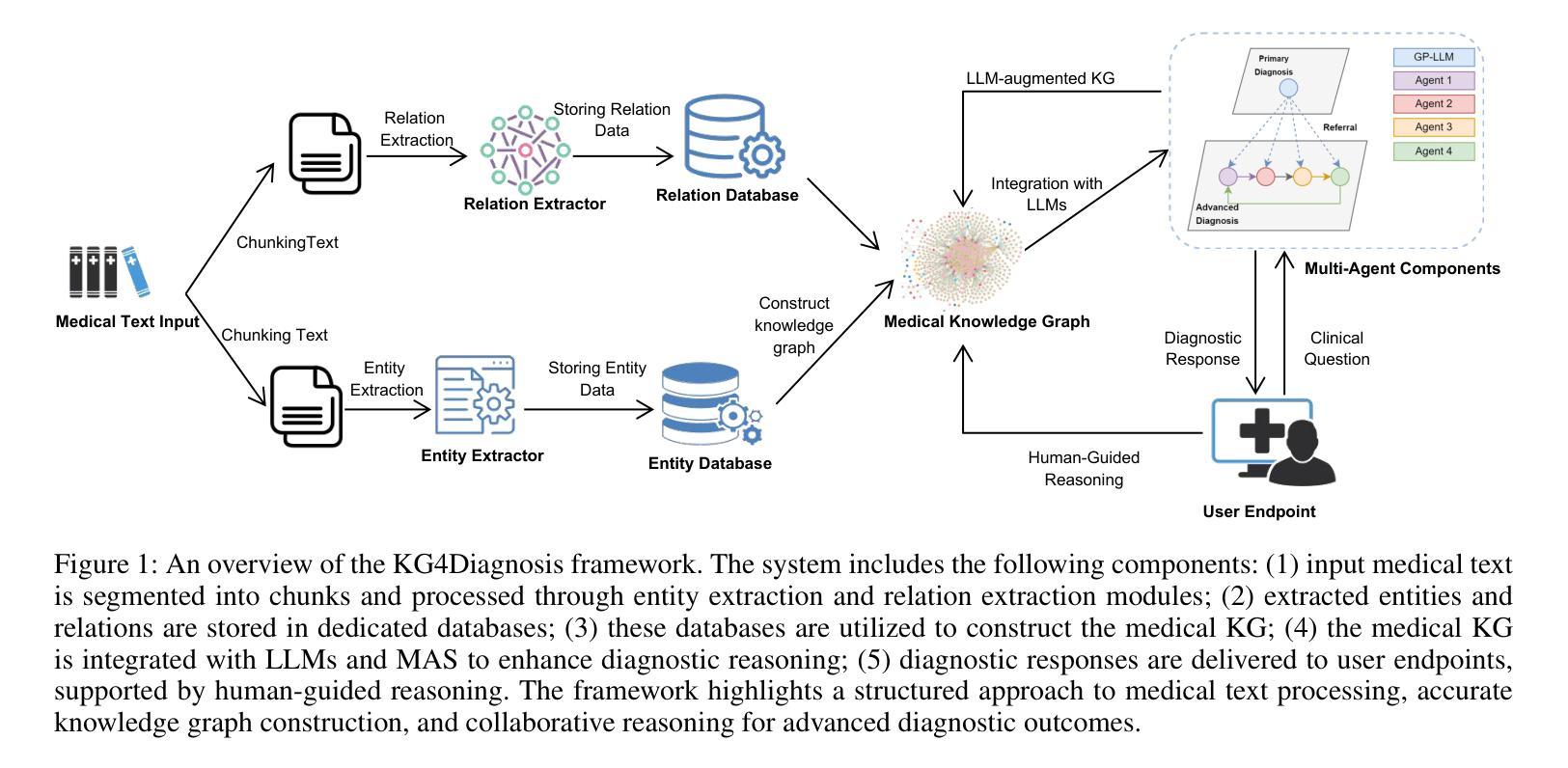
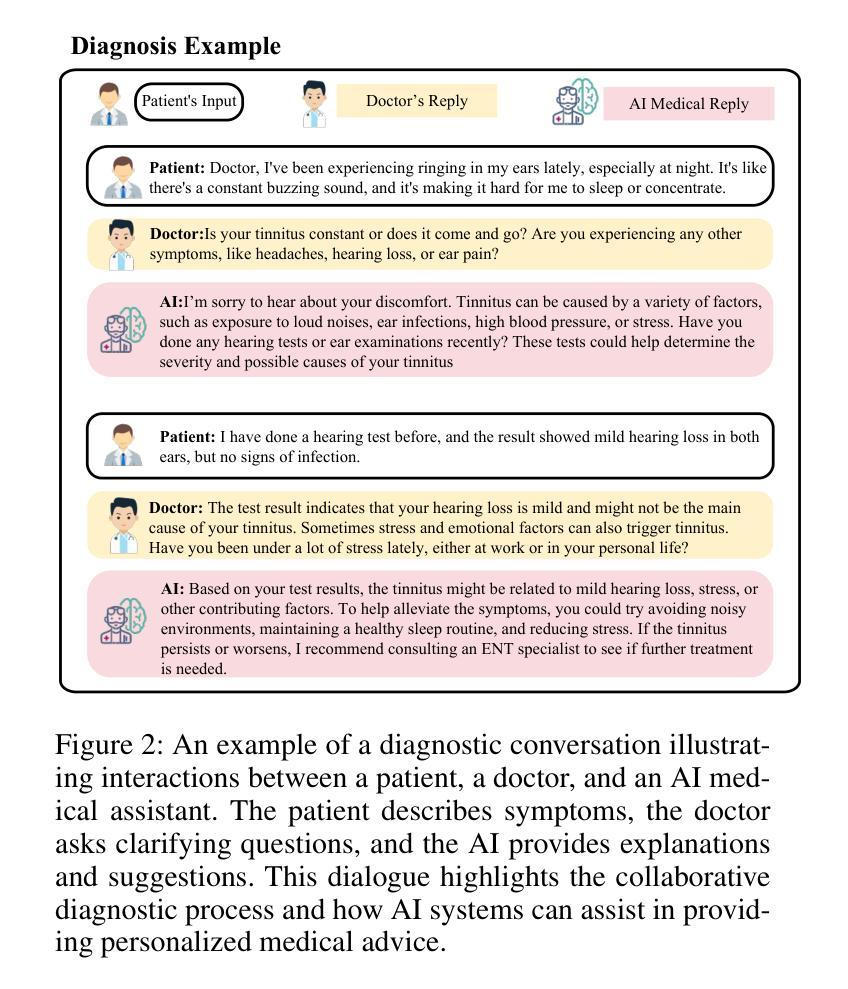
KG4Diagnosis: A Hierarchical Multi-Agent LLM Framework with Knowledge Graph Enhancement for Medical Diagnosis
Authors:Kaiwen Zuo, Yirui Jiang, Fan Mo, Pietro Lio
Integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) in healthcare diagnosis demands systematic frameworks that can handle complex medical scenarios while maintaining specialized expertise. We present KG4Diagnosis, a novel hierarchical multi-agent framework that combines LLMs with automated knowledge graph construction, encompassing 362 common diseases across medical specialties. Our framework mirrors real-world medical systems through a two-tier architecture: a general practitioner (GP) agent for initial assessment and triage, coordinating with specialized agents for in-depth diagnosis in specific domains. The core innovation lies in our end-to-end knowledge graph generation methodology, incorporating: (1) semantic-driven entity and relation extraction optimized for medical terminology, (2) multi-dimensional decision relationship reconstruction from unstructured medical texts, and (3) human-guided reasoning for knowledge expansion. KG4Diagnosis serves as an extensible foundation for specialized medical diagnosis systems, with capabilities to incorporate new diseases and medical knowledge. The framework’s modular design enables seamless integration of domain-specific enhancements, making it valuable for developing targeted medical diagnosis systems. We provide architectural guidelines and protocols to facilitate adoption across medical contexts.
将大型语言模型(LLMs)整合到医疗诊断中,需要能够处理复杂医疗场景并保持专业知识的系统性框架。我们提出了KG4Diagnosis,这是一种新型分层多智能体框架,它将LLMs与自动化知识图谱构建相结合,涵盖362种常见疾病,涉及医学各个专业。我们的框架通过两层架构反映现实医疗系统:全科医师(GP)智能体进行初步评估和分级,并与针对特定领域的专业智能体协调进行深入诊断。核心创新在于我们端到端的知识图谱生成方法,包括:(1)针对医学术语优化的语义驱动实体和关系提取,(2)从非结构化医疗文本中重建多维决策关系,(3)用于知识扩展的人机协同推理。KG4Diagnosis是一个可扩展的基础,用于专业医疗诊断系统,有能力融入新的疾病和医学知识。该框架的模块化设计使其能够无缝集成特定领域的增强功能,对于开发有针对性的医疗诊断系统非常有价值。我们提供架构指南和协议,以推动其在医疗环境中的采用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages,5 figures,published to AAAI-25 Bridge Program
Summary:KG4Diagnosis框架结合大型语言模型与知识图谱构建技术,为医疗保健诊断提供了系统化解决方案。该框架采用分层多智能体架构,包括初级评估与协调的智能体及专业领域的深度诊断智能体,覆盖362种常见疾病。其核心创新在于端到端的知识图谱生成方法,包括针对医学术语优化的语义驱动实体和关系提取、从非结构化医学文本中重建的多维度决策关系以及人类引导的知识扩展推理。KG4Diagnosis框架为开发专业医疗诊断系统提供了可扩展的基础,并能轻松集成领域特定增强功能。
Key Takeaways:
- KG4Diagnosis是一个整合大型语言模型的系统化医疗诊断框架。
- 该框架采用分层多智能体架构,包括初级评估与协调的智能体及专业领域智能体。
- KG4Diagnosis覆盖362种常见疾病,并具备扩展能力以纳入新的疾病和医学知识。
- 框架的核心创新在于其端到端的知识图谱生成方法,包括语义驱动的实体和关系提取、多维度决策关系重建和人类引导的知识扩展。
- 该框架能够从非结构化医学文本中提取信息,并据此进行诊断决策。
- KG4Diagnosis的模块化设计使无缝集成特定领域的增强功能成为可能。
点此查看论文截图

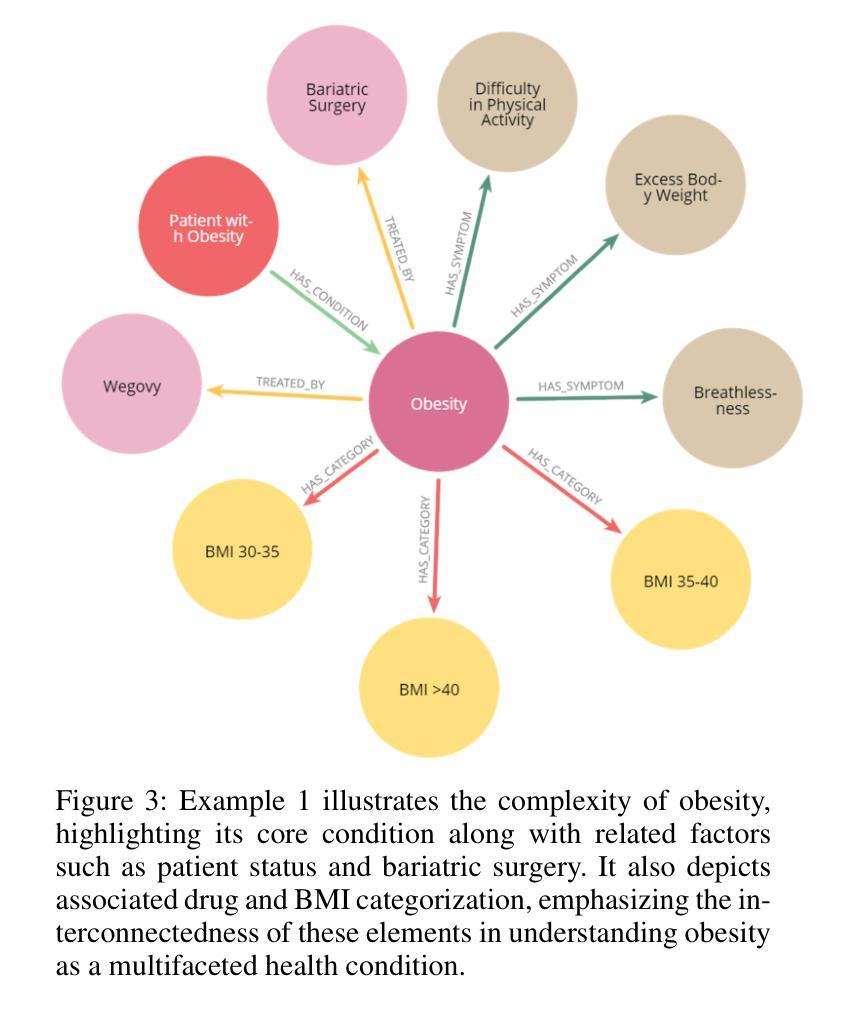
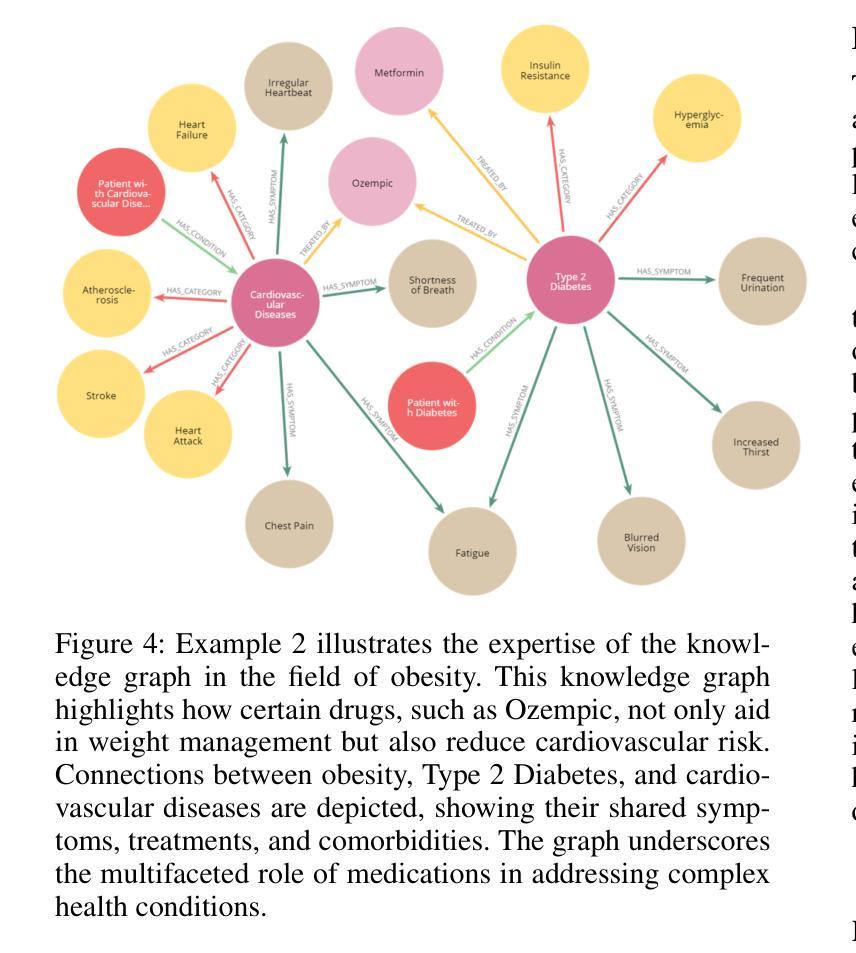
Agent Planning with World Knowledge Model
Authors:Shuofei Qiao, Runnan Fang, Ningyu Zhang, Yuqi Zhu, Xiang Chen, Shumin Deng, Yong Jiang, Pengjun Xie, Fei Huang, Huajun Chen
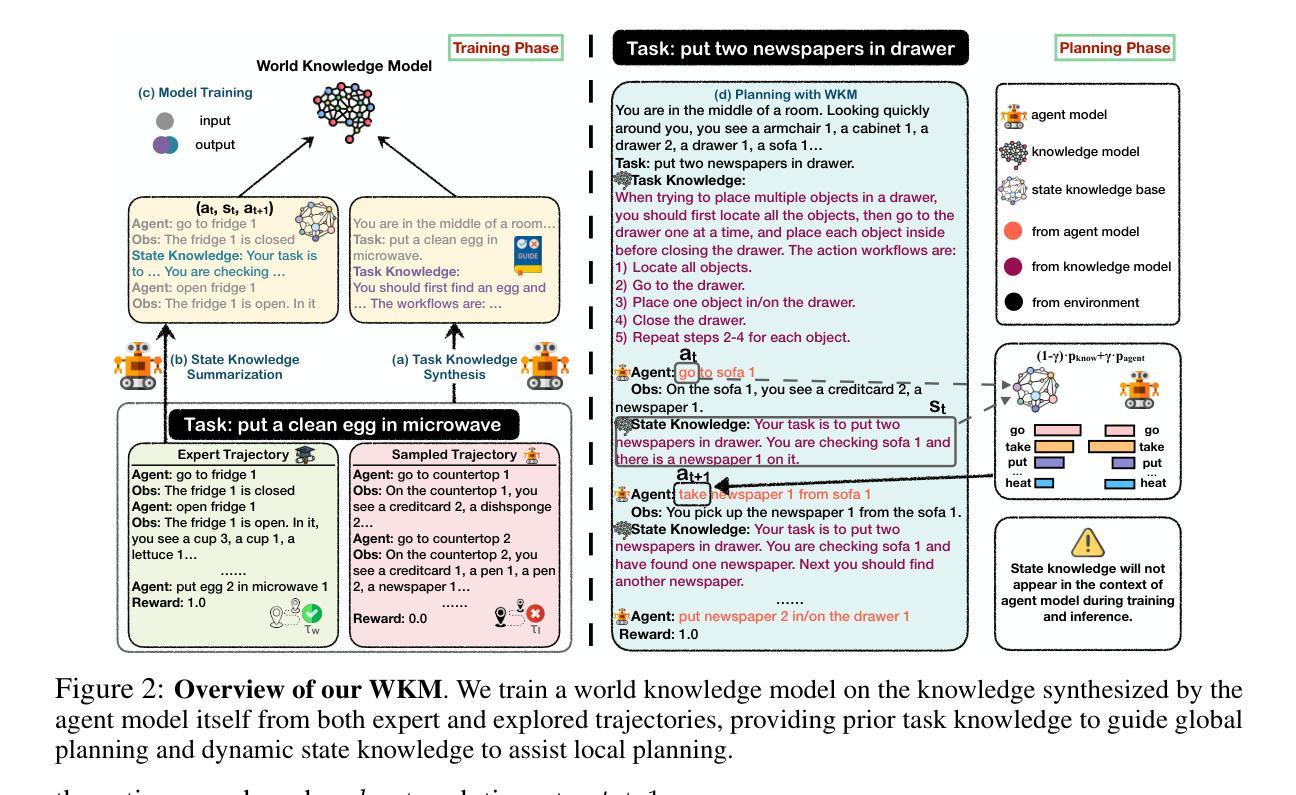
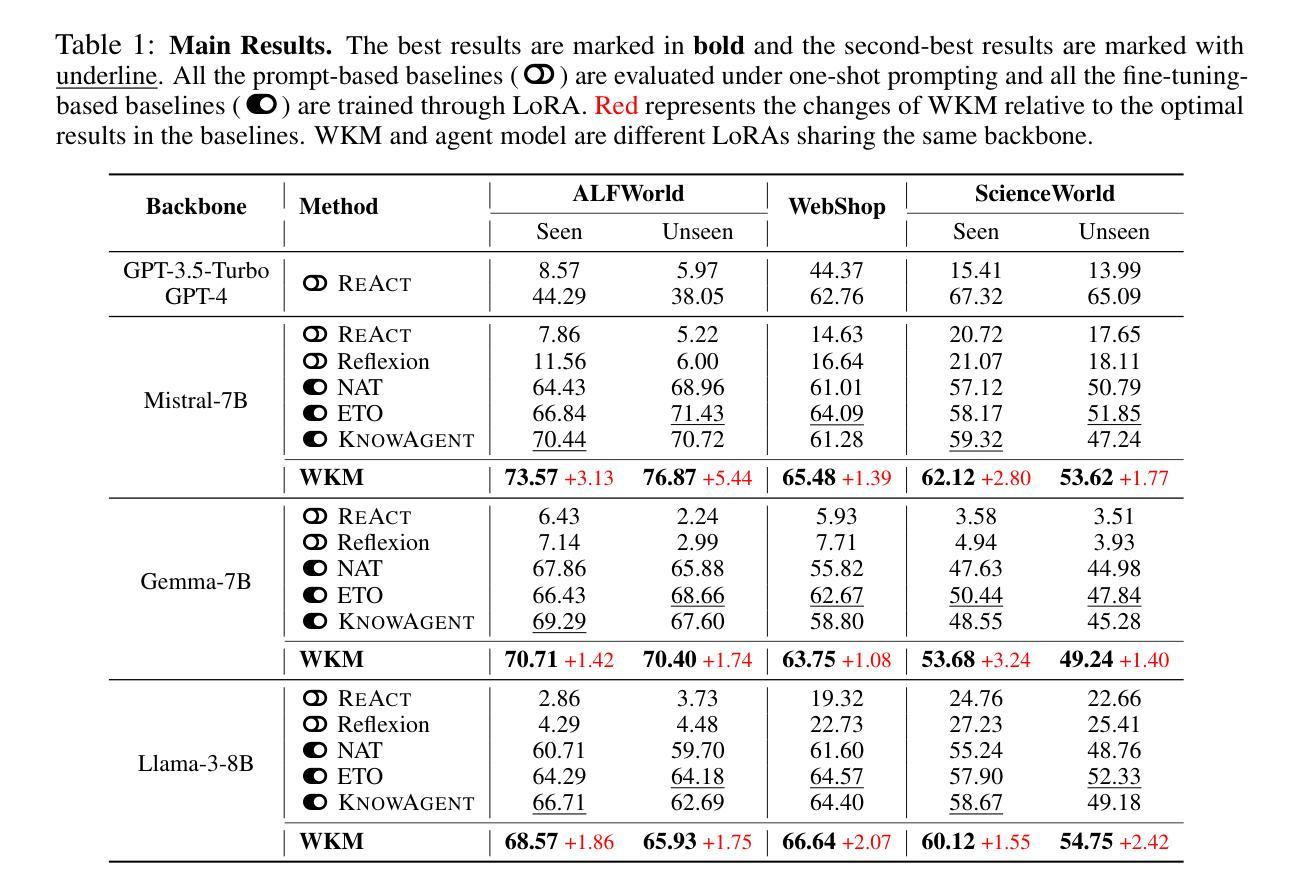
Recent endeavors towards directly using large language models (LLMs) as agent models to execute interactive planning tasks have shown commendable results. Despite their achievements, however, they still struggle with brainless trial-and-error in global planning and generating hallucinatory actions in local planning due to their poor understanding of the ``real’’ physical world. Imitating humans’ mental world knowledge model which provides global prior knowledge before the task and maintains local dynamic knowledge during the task, in this paper, we introduce parametric World Knowledge Model (WKM) to facilitate agent planning. Concretely, we steer the agent model to self-synthesize knowledge from both expert and sampled trajectories. Then we develop WKM, providing prior task knowledge to guide the global planning and dynamic state knowledge to assist the local planning. Experimental results on three complex real-world simulated datasets with three state-of-the-art open-source LLMs, Mistral-7B, Gemma-7B, and Llama-3-8B, demonstrate that our method can achieve superior performance compared to various strong baselines. Besides, we analyze to illustrate that our WKM can effectively alleviate the blind trial-and-error and hallucinatory action issues, providing strong support for the agent’s understanding of the world. Other interesting findings include: 1) our instance-level task knowledge can generalize better to unseen tasks, 2) weak WKM can guide strong agent model planning, and 3) unified WKM training has promising potential for further development. The code is available at https://github.com/zjunlp/WKM.
近期,直接使用大型语言模型(LLM)作为代理模型执行交互式规划任务的研究取得了值得赞扬的成果。然而,尽管取得了成就,它们仍然在全球规划方面存在盲目试错的问题,并在局部规划生成幻觉行为,这是因为它们对“真实”物理世界的理解不足。
本文中,我们引入参数化世界知识模型(WKM)来促进代理规划,模仿人类的精神世界知识模型,在任务前提供全局先验知识,并在任务期间保持局部动态知识。具体地,我们引导代理模型从专家轨迹和采样轨迹中自我合成知识。然后,我们开发WKM,提供任务先验知识来指导全局规划,以及动态状态知识来辅助局部规划。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)作为代理模型直接执行交互式规划任务取得了可喜的成果,但仍存在全球规划中的盲目试错和本地规划中的幻想行为问题。为了解决这个问题,本文引入了参数化世界知识模型(WKM),使代理模型能够从专家轨迹和采样轨迹中自我合成知识。实验结果表明,该方法在三个复杂现实世界的模拟数据集上,使用三种最先进的开源LLM(Mistral-7B、Gemma-7B和Llama-3-8B)时,相比各种强大的基线方法具有优越的性能。此外,本文分析了WKM能有效减轻盲目试错和幻想行为问题,为代理模型理解世界提供有力支持。还发现实例级任务知识能更好地推广到未见过的任务,弱WKM能指导强代理模型规划,统一WKM训练有进一步开发的潜力。代码可在https://github.com/zjunlp/WKM获取。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在执行交互式规划任务时虽然取得显著成果,但在全球规划和本地规划中仍存在盲目试错和幻想行为问题。
- 引入参数化世界知识模型(WKM)以增强代理模型对现实世界理解的缺乏的问题。该模型能够结合专家轨迹和采样轨迹进行自我合成知识。
- 在三个复杂现实世界的模拟数据集上进行的实验表明,使用WKM的方法相较于基线方法具有优越性能。
- WKM能有效减轻盲目试错和幻想行为问题,改善代理模型的世界理解力。此外,它能够推广实例级任务知识到未见过的任务。
点此查看论文截图