⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-07 更新
Adaptive Few-shot Prompting for Machine Translation with Pre-trained Language Models
Authors:Lei Tang, Jinghui Qin, Wenxuan Ye, Hao Tan, Zhijing Yang
Recently, Large language models (LLMs) with in-context learning have demonstrated remarkable potential in handling neural machine translation. However, existing evidence shows that LLMs are prompt-sensitive and it is sub-optimal to apply the fixed prompt to any input for downstream machine translation tasks. To address this issue, we propose an adaptive few-shot prompting (AFSP) framework to automatically select suitable translation demonstrations for various source input sentences to further elicit the translation capability of an LLM for better machine translation. First, we build a translation demonstration retrieval module based on LLM’s embedding to retrieve top-k semantic-similar translation demonstrations from aligned parallel translation corpus. Rather than using other embedding models for semantic demonstration retrieval, we build a hybrid demonstration retrieval module based on the embedding layer of the deployed LLM to build better input representation for retrieving more semantic-related translation demonstrations. Then, to ensure better semantic consistency between source inputs and target outputs, we force the deployed LLM itself to generate multiple output candidates in the target language with the help of translation demonstrations and rerank these candidates. Besides, to better evaluate the effectiveness of our AFSP framework on the latest language and extend the research boundary of neural machine translation, we construct a high-quality diplomatic Chinese-English parallel dataset that consists of 5,528 parallel Chinese-English sentences. Finally, extensive experiments on the proposed diplomatic Chinese-English parallel dataset and the United Nations Parallel Corpus (Chinese-English part) show the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed AFSP.
最近,具有上下文学习功能的大型语言模型(LLM)在神经机器翻译方面展现出了巨大的潜力。然而,现有证据表明,LLM对提示很敏感,对于下游机器翻译任务,将固定提示应用于任何输入都是次优的。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种自适应少样本提示(AFSP)框架,该框架可以自动为各种源输入句子选择适合的翻译示例,以进一步激发LLM的翻译能力,实现更好的机器翻译。首先,我们基于LLM的嵌入构建了一个翻译示例检索模块,从对齐的平行翻译语料库中检索出语义上最相似的前k个翻译示例。我们并没有使用其他嵌入模型进行语义示范检索,而是构建了一个基于部署的LLM嵌入层的混合示范检索模块,以建立更好的输入表示,检索出更多语义相关的翻译示例。然后,为了确保源输入和目标输出之间的语义一致性,我们强制部署的LLM本身在翻译示例的帮助下生成多个目标语言输出候选,并对这些候选进行重新排序。此外,为了在我们的AFSP框架上评估最新的语言并扩展神经机器翻译的研究边界,我们构建了一个高质量的中英外交平行数据集,包含5528个平行的中英文句子。最后,在提出的外交中英平行数据集和联合国平行语料库(中英部分)上的大量实验证明了我们的AFSP框架的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF published to AAAI2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在神经机器翻译领域展现出显著潜力,但对固定提示的敏感性限制了其在下游任务中的表现。为此,本文提出了一种自适应少样本提示(AFSP)框架,能够自动为不同源输入句子选择适当的翻译示例,以激发LLM的翻译能力,实现更好的机器翻译。该框架建立了基于LLM嵌入的翻译示例检索模块,从对齐的平行翻译语料库中检索语义相似的前k个翻译示例。同时,为确保源输入与目标输出之间的语义一致性,LLM生成多个目标语言输出候选,借助翻译示例进行重排。此外,为评估AFSP框架在最新语言上的效果并拓展神经机器翻译的研究边界,构建了高质量的中英平行数据集,并在该数据集和联合国平行语料库(中英部分)上进行广泛实验,验证了AFSP的有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在神经机器翻译中展现出显著潜力。
- 现有证据显示大型语言模型对固定提示敏感,需要自适应少样本提示框架来改善机器翻译。
- 提出了一种自适应少样本提示(AFSP)框架,能够自动选择适当的翻译示例。
- 建立基于LLM嵌入的翻译示例检索模块,从平行翻译语料库中检索语义相似示例。
- LLM生成多个目标语言输出候选,借助翻译示例进行重排,确保语义一致性。
- 为评估AFSP框架效果,构建了高质量的中英平行数据集。
点此查看论文截图


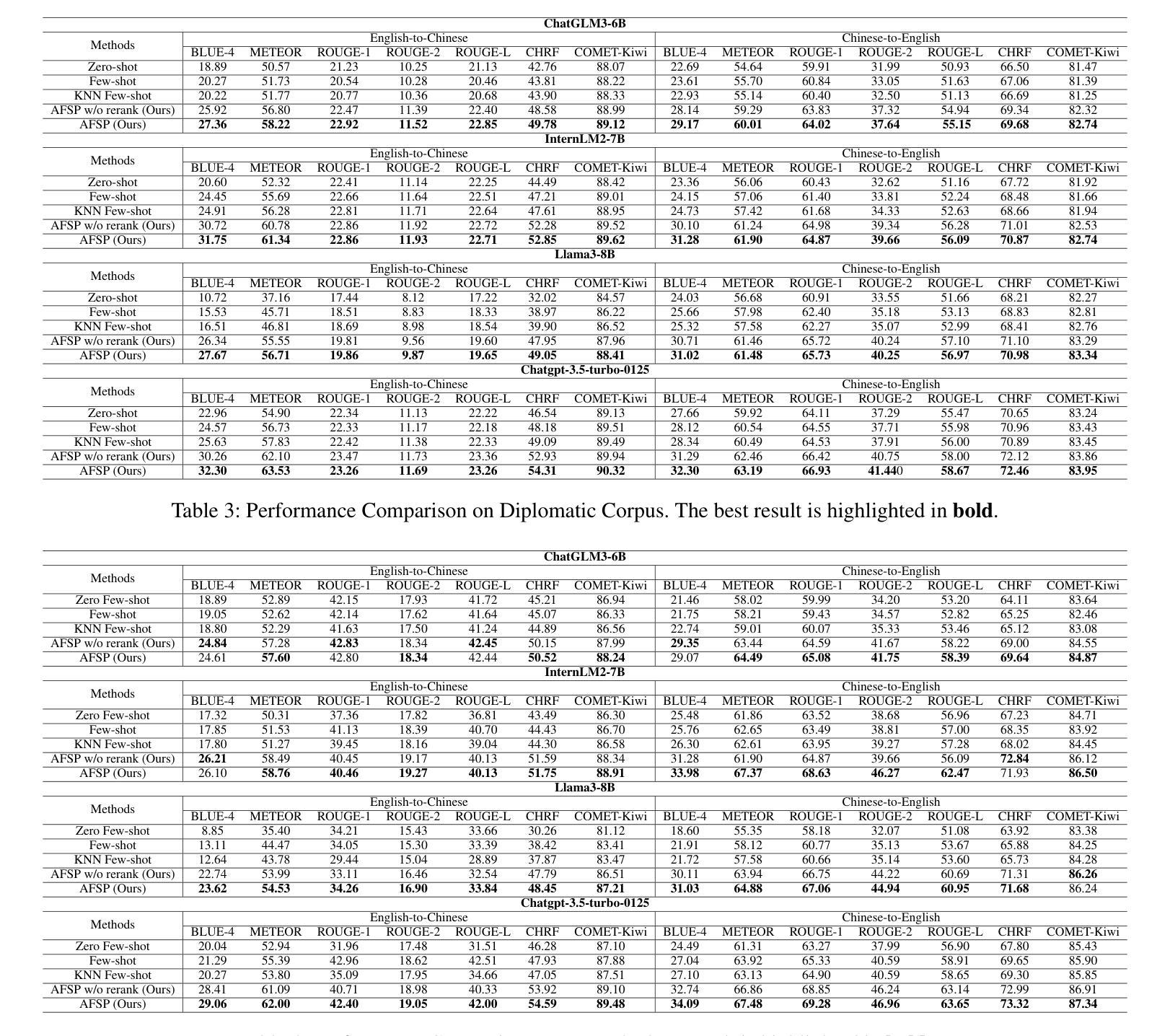
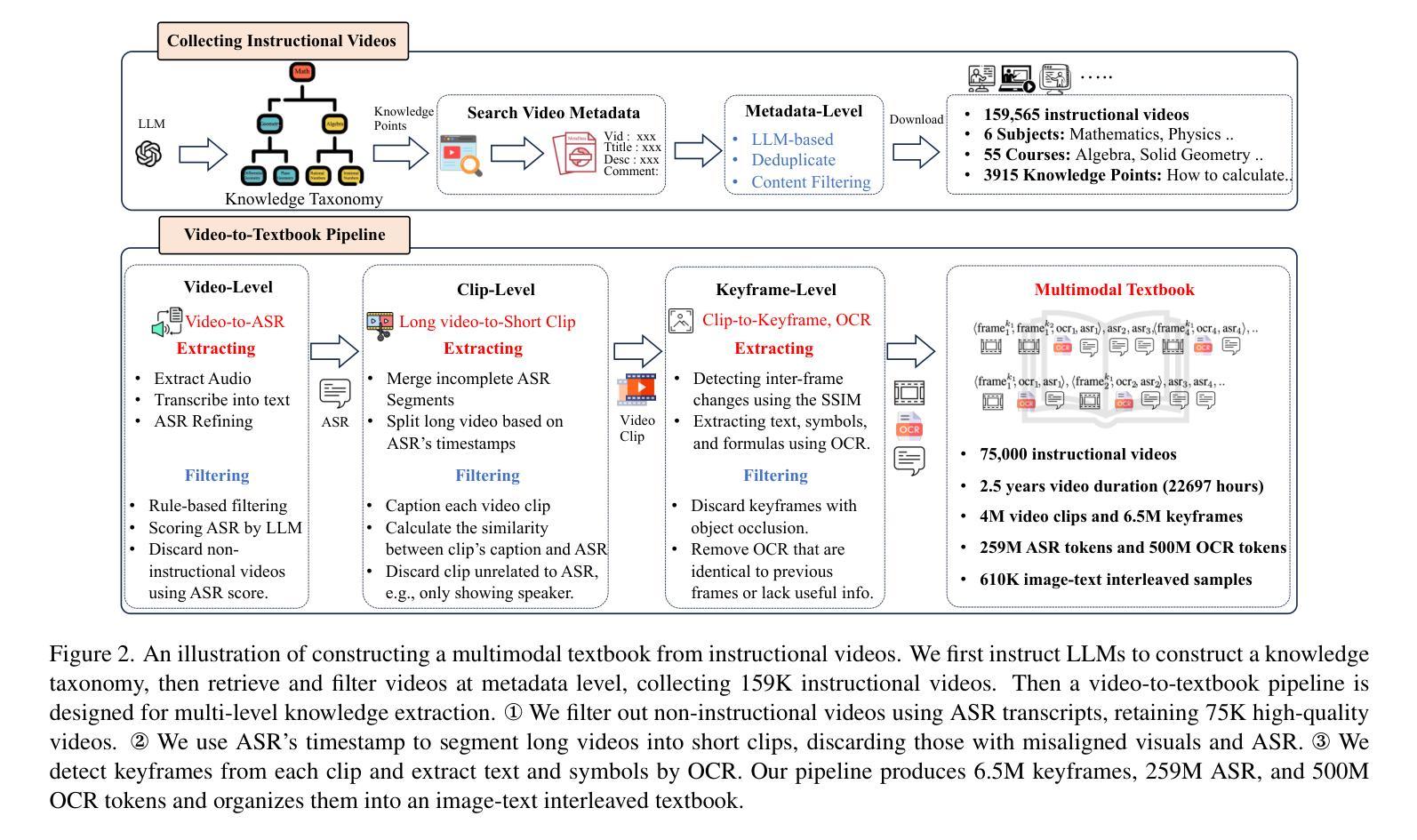
2.5 Years in Class: A Multimodal Textbook for Vision-Language Pretraining
Authors:Wenqi Zhang, Hang Zhang, Xin Li, Jiashuo Sun, Yongliang Shen, Weiming Lu, Deli Zhao, Yueting Zhuang, Lidong Bing
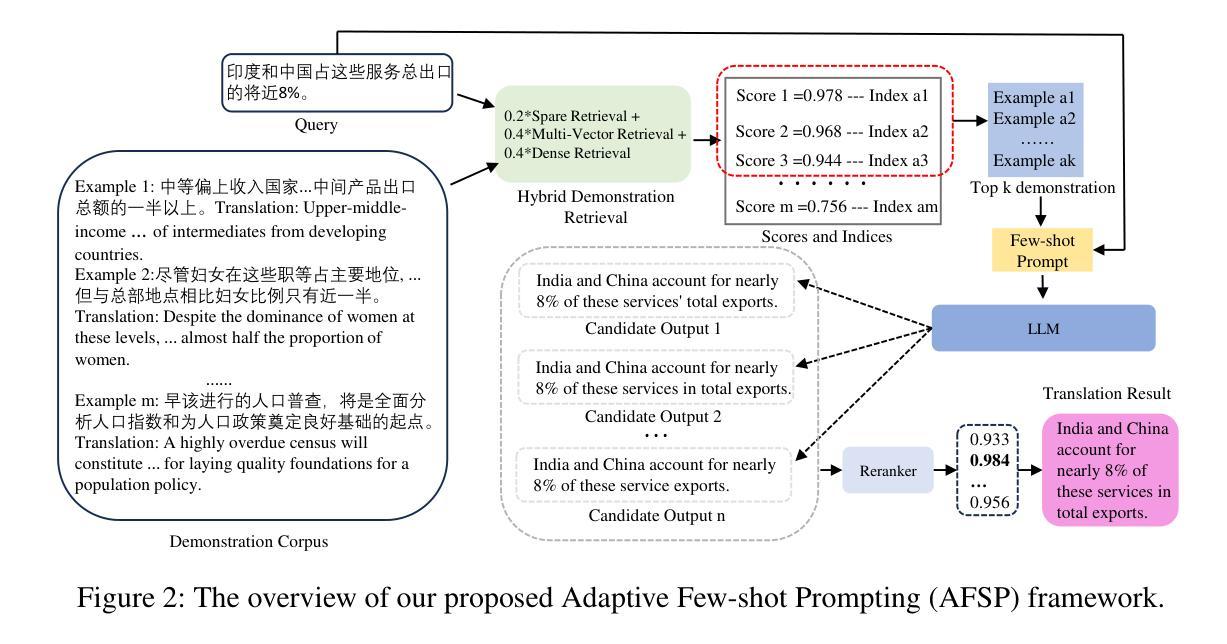
Compared to image-text pair data, interleaved corpora enable Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to understand the world more naturally like humans. However, such existing datasets are crawled from webpage, facing challenges like low knowledge density, loose image-text relations, and poor logical coherence between images. On the other hand, the internet hosts vast instructional videos (e.g., online geometry courses) that are widely used by humans to learn foundational subjects, yet these valuable resources remain underexplored in VLM training. In this paper, we introduce a high-quality \textbf{multimodal textbook} corpus with richer foundational knowledge for VLM pretraining. It collects over 2.5 years of instructional videos, totaling 22,000 class hours. We first use an LLM-proposed taxonomy to systematically gather instructional videos. Then we progressively extract and refine visual (keyframes), audio (ASR), and textual knowledge (OCR) from the videos, and organize as an image-text interleaved corpus based on temporal order. Compared to its counterparts, our video-centric textbook offers more coherent context, richer knowledge, and better image-text alignment. Experiments demonstrate its superb pretraining performance, particularly in knowledge- and reasoning-intensive tasks like ScienceQA and MathVista. Moreover, VLMs pre-trained on our textbook exhibit outstanding interleaved context awareness, leveraging visual and textual cues in their few-shot context for task solving~\footnote{Our code are available at \url{https://github.com/DAMO-NLP-SG/multimodal_textbook}}.
与图像文本配对数据相比,交错语料库使视觉语言模型(VLMs)能够更自然地像人类一样理解世界。然而,这些现有的数据集是从网页上爬取的,面临着知识密度低、图像文本关系松散、图像之间逻辑连贯性差等挑战。另一方面,互联网上拥有大量教学视频(如在线几何课程),人类广泛利用这些视频来学习基础学科,但这些宝贵资源在VLM训练中却被忽视。在本文中,我们引入了一个高质量的多模态教科书语料库,其中包含用于VLM预训练的更丰富的基础知识。它收集了超过2.5年的教学视频,总计22,000节课时。我们首先使用大型语言模型(LLM)提出的分类法来系统地收集教学视频。然后,我们逐步从视频中提取和精炼视觉(关键帧)、音频(ASR)和文本知识(OCR),并按时间顺序组织成图像文本交错语料库。与同类产品相比,我们这种以视频为中心教科书提供了更连贯的上下文、更丰富的知识和更好的图像文本对齐。实验证明其在预训练方面的卓越性能,特别是在知识密集和推理密集的任务(如ScienceQA和MathVista)中。此外,在我们教科书上进行预训练的VLM表现出卓越的错误上下文感知能力,能够利用视觉和文本线索解决少量上下文中的任务。我们的代码可在https://github.com/DAMO-NLP-SG/multimodal_textbook访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
本文介绍了针对视觉语言模型(VLM)预训练的一种新型多媒体教材库。该库通过收集超过2.5年的教学视频,以时间顺序组织成图像与文本交替出现的数据集。该数据集相比传统数据集,拥有更丰富的基础知识和更连贯的上下文环境,以及更好的图像与文本对齐效果。实验证明,该数据集在知识密集和推理密集型任务上的预训练性能卓越,特别是在如ScienceQA和MathVista的任务中。此外,在此教材库上预训练的VLM模型表现出强大的交替上下文意识,能够在少量情境下利用视觉和文本线索解决问题。
Key Takeaways
- 多媒体教材库结合了教学视频、图像和文本,为VLM预训练提供了更丰富、更连贯的上下文环境。
- 与传统图像-文本对数据集相比,该多媒体教材库提供了更好的图像与文本对齐效果。
- 该数据集通过系统收集教学视频、逐步提取和精炼视觉、音频和文本知识,组织成基于时间顺序的图像-文本交替出现的数据集。
- 实验证明,该数据集在知识密集和推理密集型任务上的预训练性能卓越。
- 在此教材库上预训练的VLM模型展现出强大的交替上下文意识,能在少情境下利用视觉和文本线索解决问题。
- 该研究提供的代码可在公开代码库中找到。
点此查看论文截图


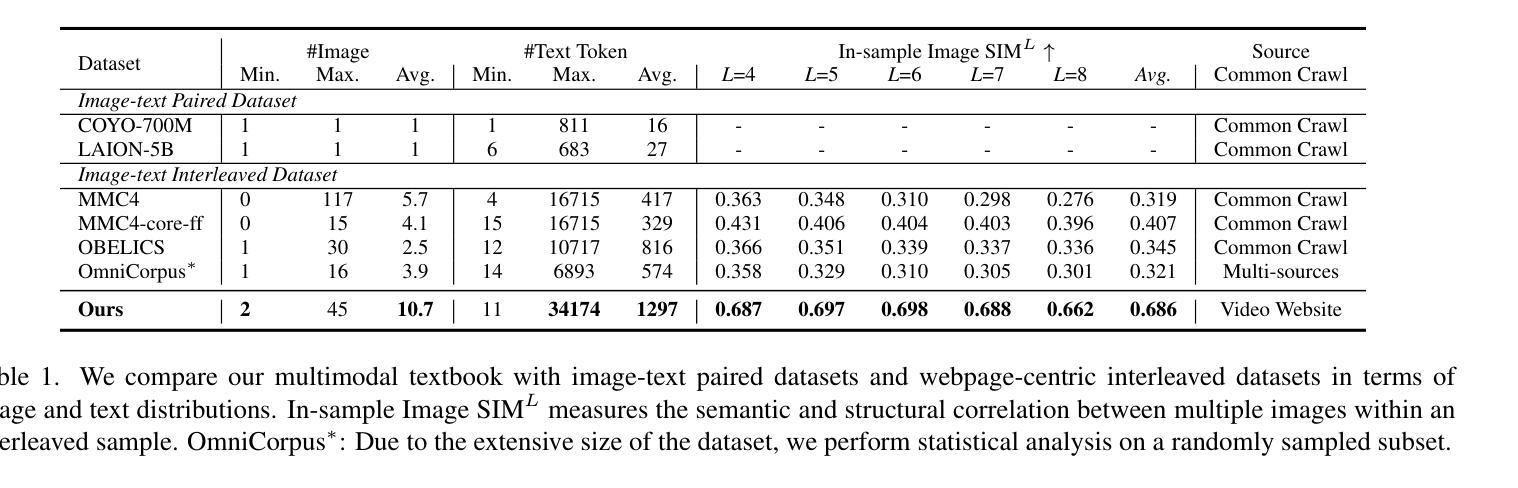
Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Multi-Path Collaborative Reactive and Reflection agents
Authors:Chengbo He, Bochao Zou, Xin Li, Jiansheng Chen, Junliang Xing, Huimin Ma
Agents have demonstrated their potential in scientific reasoning tasks through large language models. However, they often face challenges such as insufficient accuracy and degeneration of thought when handling complex reasoning tasks, which impede their performance. To overcome these issues, we propose the Reactive and Reflection agents with Multi-Path Reasoning (RR-MP) Framework, aimed at enhancing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Our approach improves scientific reasoning accuracy by employing a multi-path reasoning mechanism where each path consists of a reactive agent and a reflection agent that collaborate to prevent degeneration of thought inherent in single-agent reliance. Additionally, the RR-MP framework does not require additional training; it utilizes multiple dialogue instances for each reasoning path and a separate summarizer to consolidate insights from all paths. This design integrates diverse perspectives and strengthens reasoning across each path. We conducted zero-shot and few-shot evaluations on tasks involving moral scenarios, college-level physics, and mathematics. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms baseline approaches, highlighting the effectiveness and advantages of the RR-MP framework in managing complex scientific reasoning tasks.
代理在大规模语言模型中已经在科学推理任务中表现出了潜力。然而,在处理复杂的推理任务时,它们经常面临准确性不足和思维退化等挑战,这阻碍了它们的性能。为了克服这些问题,我们提出了具有多路推理能力的反应与反思代理(RR-MP)框架,旨在增强大规模语言模型的推理能力。我们的方法采用多路推理机制来提高科学推理的准确性,每条路径包含一个反应代理和一个反思代理,它们协同工作,防止单一代理依赖导致的固有思维退化。此外,RR-MP框架不需要额外的训练;它为每条推理路径利用多个对话实例和一个单独的摘要器来整合所有路径的见解。这种设计融合了不同的观点,加强了每条路径的推理能力。我们对涉及道德场景、大学物理和数学的任务进行了零样本和少样本评估。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于基准方法,突出了RR-MP框架在管理复杂的科学推理任务中的有效性和优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大语言模型的智能体在科技推理任务中展现出了巨大潜力,但在处理复杂推理任务时面临准确性不足和思维退化等挑战。为解决这些问题,提出了反应与反思多路径推理框架(RR-MP),旨在提升大语言模型的推理能力。通过采用多路径推理机制,结合反应智能体和反思智能体的协作,有效防止单一智能体依赖导致的思维退化问题。此外,该框架无需额外训练,通过对话实例和独立总结者来巩固所有路径的见解,促进多样化视角的整合和每条路径的推理能力。在道德场景、大学物理和数学任务上的零样本和少样本评估结果表明,该方法优于基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 智能体在科技推理任务中有巨大潜力,但处理复杂任务时存在准确性不足和思维退化的问题。
- 提出了反应与反思多路径推理框架(RR-MP)来解决这些问题。
- 该框架采用多路径推理机制,结合反应智能体和反思智能体的协作,防止思维退化。
- RR-MP框架不需要额外训练,利用对话实例和独立总结者来整合多样视角和加强每条路径的推理能力。
- 评估结果显示,该框架在科技推理任务上的表现优于基线方法。
- 该框架具有潜在的应用价值,特别是在处理涉及道德、物理和数学等复杂科技推理任务时。
点此查看论文截图


FUSED-Net: Detecting Traffic Signs with Limited Data
Authors:Md. Atiqur Rahman, Nahian Ibn Asad, Md. Mushfiqul Haque Omi, Md. Bakhtiar Hasan, Sabbir Ahmed, Md. Hasanul Kabir
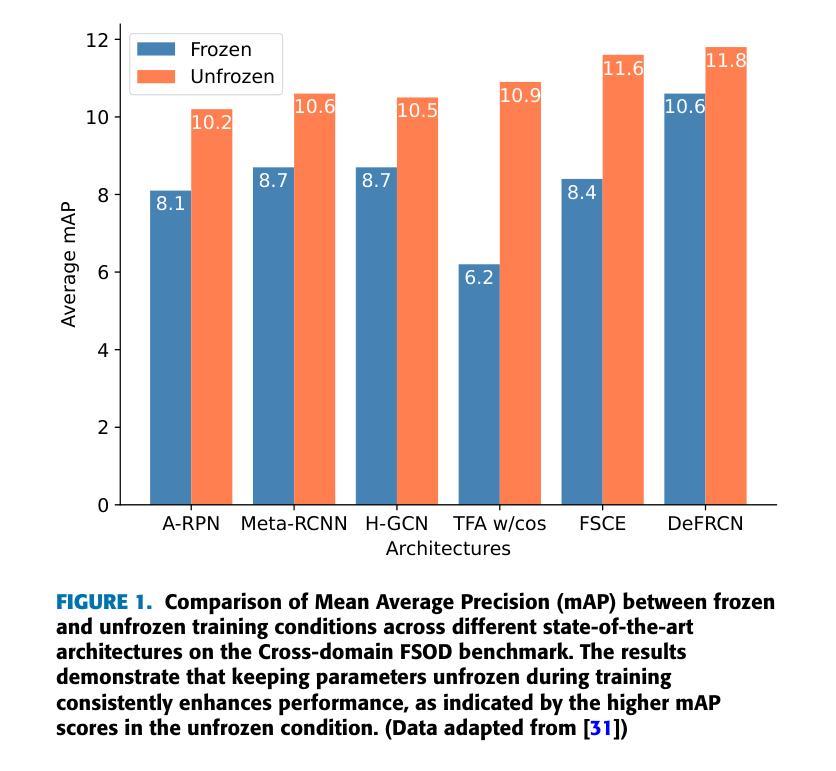
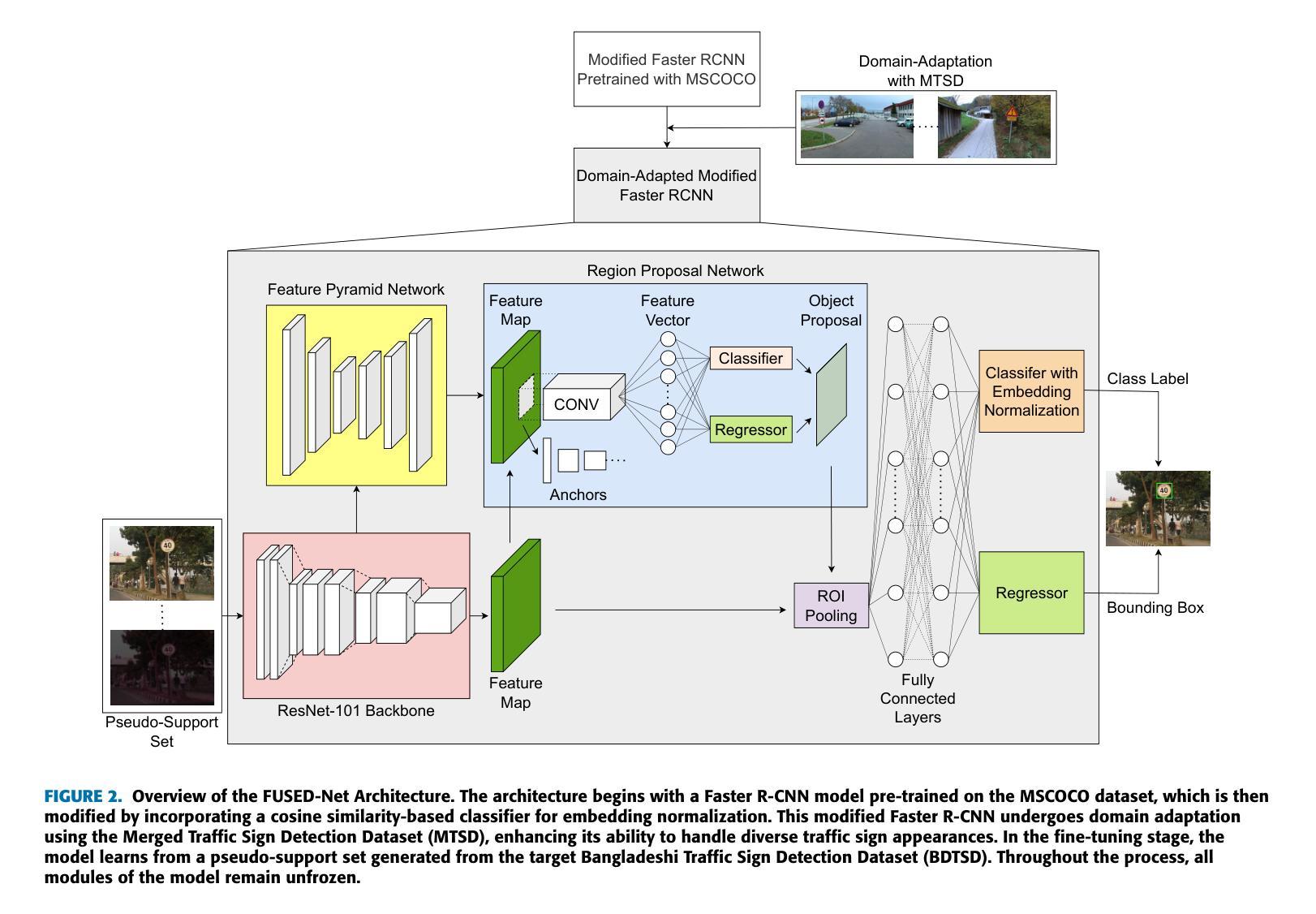
Automatic Traffic Sign Recognition is paramount in modern transportation systems, motivating several research endeavors to focus on performance improvement by utilizing large-scale datasets. As the appearance of traffic signs varies across countries, curating large-scale datasets is often impractical; and requires efficient models that can produce satisfactory performance using limited data. In this connection, we present ‘FUSED-Net’, built-upon Faster RCNN for traffic sign detection, enhanced by Unfrozen Parameters, Pseudo-Support Sets, Embedding Normalization, and Domain Adaptation while reducing data requirement. Unlike traditional approaches, we keep all parameters unfrozen during training, enabling FUSED-Net to learn from limited samples. The generation of a Pseudo-Support Set through data augmentation further enhances performance by compensating for the scarcity of target domain data. Additionally, Embedding Normalization is incorporated to reduce intra-class variance, standardizing feature representation. Domain Adaptation, achieved by pre-training on a diverse traffic sign dataset distinct from the target domain, improves model generalization. Evaluating FUSED-Net on the BDTSD dataset, we achieved 2.4x, 2.2x, 1.5x, and 1.3x improvements of mAP in 1-shot, 3-shot, 5-shot, and 10-shot scenarios, respectively compared to the state-of-the-art Few-Shot Object Detection (FSOD) models. Additionally, we outperform state-of-the-art works on the cross-domain FSOD benchmark under several scenarios.
自动交通标志识别在现代交通系统中至关重要,这促使多项研究致力于通过利用大规模数据集来提高性能。由于交通标志的外观因国家而异,因此需要建立大规模数据集是不切实际的;同时还需要能使用有限数据产生满意性能的模型。在这方面,我们提出了基于Faster RCNN构建的交通标志检测器’FUSED-Net’,并通过解冻参数、伪支持集、嵌入归一化和域适应等手段强化,同时降低了对数据的需求。与传统方法不同,我们在训练期间保持所有参数未冻结,使FUSED-Net能够从有限的样本中学习。通过数据增强生成伪支持集进一步提高了性能,弥补了目标域数据的稀缺性。此外,通过嵌入归一化来减少类内差异,标准化特征表示。通过在不同于目标域的多样化交通标志数据集上进行预训练实现的域适应提高了模型的泛化能力。在BDTSD数据集上评估FUSED-Net时,与最新的Few-Shot对象检测(FSOD)模型相比,我们在单次射击、三次射击、五次射击和十次射击场景中分别实现了mAP的2.4倍、2.2倍、1.5倍和1.3倍改进。此外,在跨域FSOD基准测试中,我们在多种场景下均超过了最新技术成果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 8 figures, 5 tables, submitted to IEEE Access for review
Summary
交通标志识别在现代交通系统中至关重要,研究者们利用大型数据集来提高性能。针对交通标志外观在不同国家之间的差异,提出一种名为FUSED-Net的新方法,它基于Faster RCNN构建,通过未冻结参数、伪支持集、嵌入归一化和域适应等技术增强,降低了对数据的要求。在BDTSD数据集上评估,与最新的Few-Shot目标检测模型相比,FUSED-Net在1-shot、3-shot、5-shot和10-shot场景中的mAP分别提高了2.4倍、2.2倍、1.5倍和1.3倍。此外,在跨域FSOD基准测试中,我们的方法也优于现有最佳工作。
Key Takeaways
- 自动交通标志识别是现代交通系统的关键。
- 研究者努力利用大型数据集提高性能,但跨国交通标志外观差异使大数据集难以实现。
- FUSED-Net基于Faster RCNN构建,通过多项技术增强,降低对数据的要求。
- FUSED-Net采用未冻结参数训练,能从有限样本中学习。
- 伪支持集通过数据增强生成,进一步提高了性能。
- 嵌入归一化用于减少类内方差,标准化特征表示。
点此查看论文截图

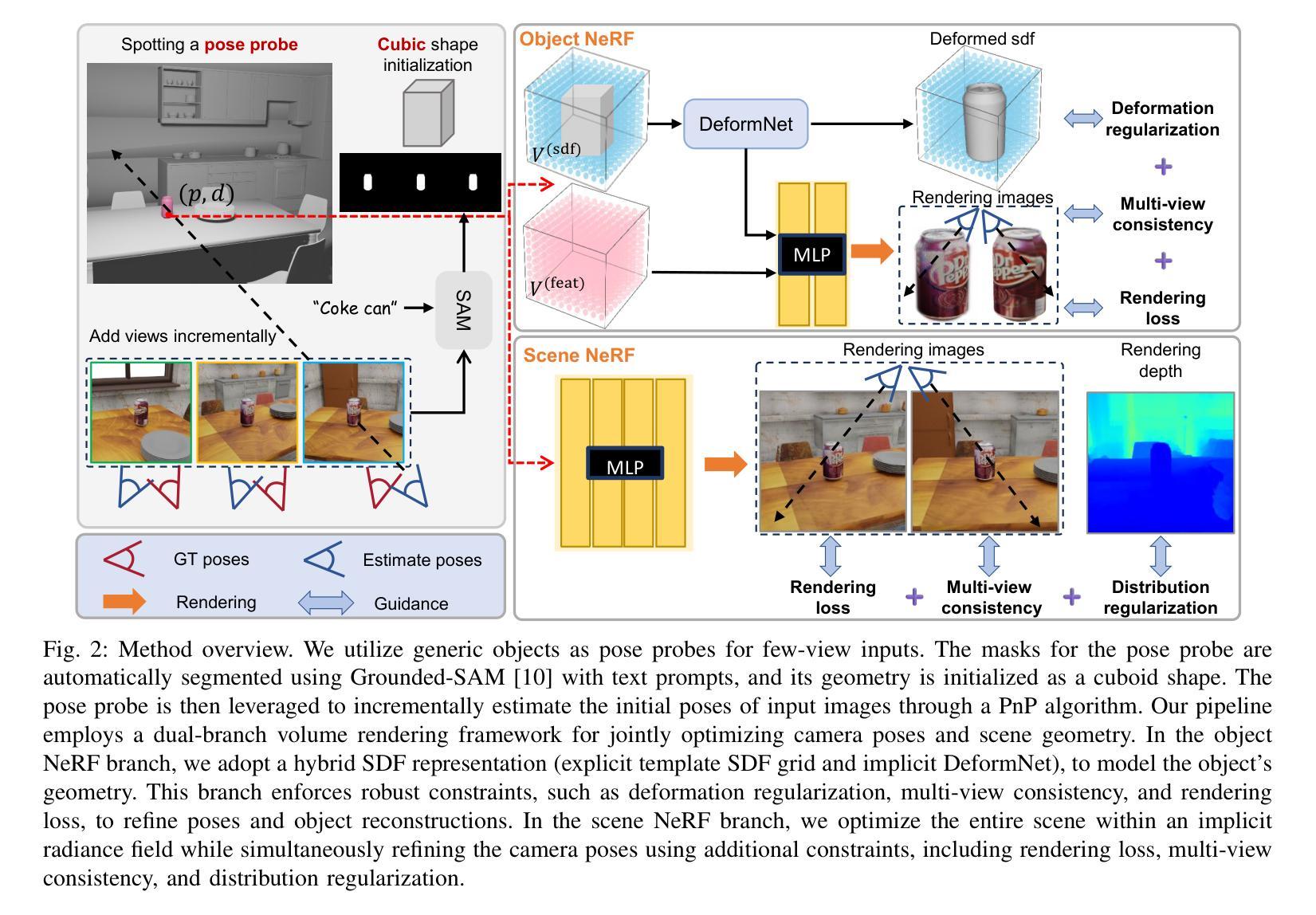
Generic Objects as Pose Probes for Few-shot View Synthesis
Authors:Zhirui Gao, Renjiao Yi, Chenyang Zhu, Ke Zhuang, Wei Chen, Kai Xu
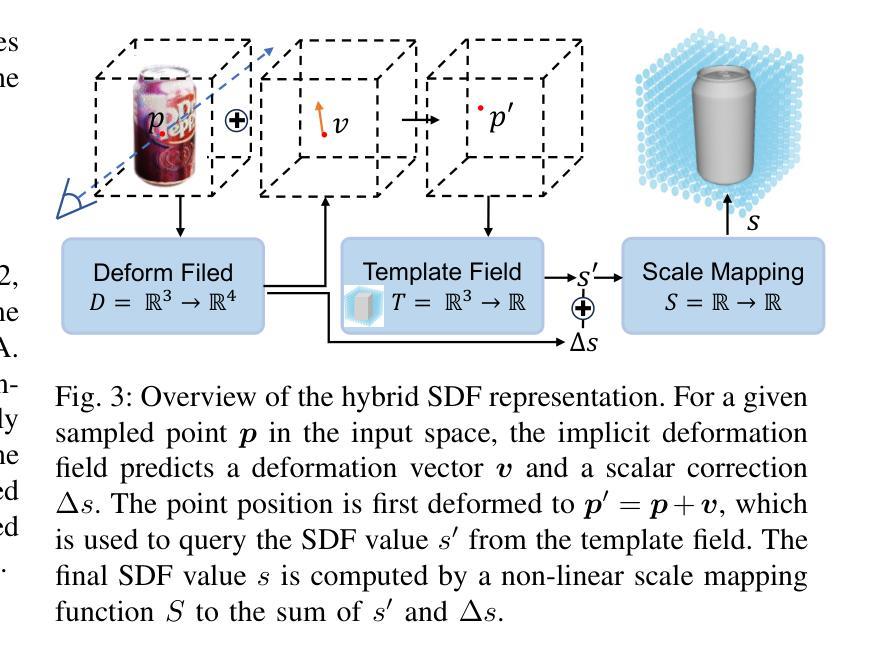
Radiance fields including NeRFs and 3D Gaussians demonstrate great potential in high-fidelity rendering and scene reconstruction, while they require a substantial number of posed images as inputs. COLMAP is frequently employed for preprocessing to estimate poses, while it necessitates a large number of feature matches to operate effectively, and it struggles with scenes characterized by sparse features, large baselines between images, or a limited number of input images. We aim to tackle few-view NeRF reconstruction using only 3 to 6 unposed scene images. Traditional methods often use calibration boards but they are not common in images. We propose a novel idea of utilizing everyday objects, commonly found in both images and real life, as “pose probes”. The probe object is automatically segmented by SAM, whose shape is initialized from a cube. We apply a dual-branch volume rendering optimization (object NeRF and scene NeRF) to constrain the pose optimization and jointly refine the geometry. Specifically, object poses of two views are first estimated by PnP matching in an SDF representation, which serves as initial poses. PnP matching, requiring only a few features, is suitable for feature-sparse scenes. Additional views are incrementally incorporated to refine poses from preceding views. In experiments, PoseProbe achieves state-of-the-art performance in both pose estimation and novel view synthesis across multiple datasets. We demonstrate its effectiveness, particularly in few-view and large-baseline scenes where COLMAP struggles. In ablations, using different objects in a scene yields comparable performance. Our project page is available at: \href{https://zhirui-gao.github.io/PoseProbe.github.io/}{this https URL}
辐射场,包括NeRF和3D高斯分布,在高保真渲染和场景重建方面表现出巨大潜力,但它们需要大量的姿态图像作为输入。COLMAP常用于预处理以估计姿态,但需要大量特征匹配才能有效运行,对于特征稀疏、图像间基线大或输入图像数量有限的场景,它表现困难。我们的目标是解决仅使用3到6张未定位的场景图像进行少量视图NeRF重建的问题。传统方法通常使用校准板,但在图像中并不常见。我们提出了一种利用日常物体的新颖想法,这些物体在图像和现实生活中都很常见,作为“姿态探针”。探针物体通过SAM自动分割,其形状从立方体初始化。我们应用双分支体积渲染优化(对象NeRF和场景NeRF)来约束姿态优化并共同改进几何。具体来说,首先通过PnP匹配在SDF表示中估计两个视图的对象姿态,作为初始姿态。PnP匹配仅需要几个特征,适用于特征稀疏的场景。然后逐步加入额外的视图,从前视图修正姿态。在实验中,PoseProbe在多数据集上实现了姿态估计和新型视图合成的最先进的性能。我们证明了其在少量视图和大基线场景中的有效性,这正是COLMAP表现困难的地方。在消融实验中,使用场景中的不同物体可以获得相当的性能。我们的项目页面可在以下网址找到:此HTTPS链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在仅有3到6个未经定位的场景图像的情况下,NeRF重建面临挑战。本研究提出利用日常物体作为“姿态探针”,通过自动分割、双分支体积渲染优化(对象NeRF和场景NeRF)进行姿态估计和优化。研究在多个数据集上的表现均达到业界领先,尤其在稀疏特征、大基线或有限输入图像的场景下表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF和3D高斯等辉光场在高保真渲染和场景重建方面具有巨大潜力,但需要大量定位图像作为输入。
- COLMAP在预处理中常被用于估计姿态,但在特征稀疏、大基线间隔或输入图像数量有限的场景中表现不佳。
- 研究旨在解决仅使用少量(3到6张)未经定位的场景图像进行NeRF重建的问题。
- 提出利用常见物体作为“姿态探针”,自动分割并优化姿态。
- 采用双分支体积渲染优化(对象NeRF和场景NeRF)来约束姿态优化并共同改进几何结构。
- 在多个数据集上实现业界领先的姿态估计和新型视角合成效果,特别是在具有挑战性的场景中表现尤为出色。
点此查看论文截图