⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-07 更新
VITA-1.5: Towards GPT-4o Level Real-Time Vision and Speech Interaction
Authors:Chaoyou Fu, Haojia Lin, Xiong Wang, Yi-Fan Zhang, Yunhang Shen, Xiaoyu Liu, Yangze Li, Zuwei Long, Heting Gao, Ke Li, Xiawu Zheng, Rongrong Ji, Xing Sun, Caifeng Shan, Ran He
Recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have typically focused on integrating visual and textual modalities, with less emphasis placed on the role of speech in enhancing interaction. However, speech plays a crucial role in multimodal dialogue systems, and implementing high-performance in both vision and speech tasks remains a significant challenge due to the fundamental modality differences. In this paper, we propose a carefully designed multi-stage training methodology that progressively trains LLM to understand both visual and speech information, ultimately enabling fluent vision and speech interaction. Our approach not only preserves strong vision-language capacity, but also enables efficient speech-to-speech dialogue capabilities without separate ASR and TTS modules, significantly accelerating multimodal end-to-end response speed. By comparing our method against state-of-the-art counterparts across benchmarks for image, video, and speech tasks, we demonstrate that our model is equipped with both strong visual and speech capabilities, making near real-time vision and speech interaction.
最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)通常专注于整合视觉和文本模态,较少强调语音在增强交互中的作用。然而,语音在多模态对话系统中扮演着至关重要的角色,由于在根本的模态差异,实现在视觉和语音任务中的高性能仍然是一个巨大的挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种精心设计的多阶段训练方法论,逐步训练LLM理解视觉和语音信息,最终实现流畅的视觉和语音交互。我们的方法不仅保留了强大的视觉语言功能,还实现了高效的语音对话能力,无需单独的ASR和TTS模块,从而显著加快了多模态端到端的响应速度。通过与图像、视频和语音任务的最新先进模型进行比较,我们证明了我们的模型具有强大的视觉和语音功能,可实现近乎实时的视觉和语音交互。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/VITA-MLLM/VITA
Summary:
近期多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在集成视觉和文本模态方面投入了大量关注,但忽视了语音在增强交互中的作用。本文提出了一种精心设计的多阶段训练方法,逐步训练LLM理解视觉和语音信息,最终实现流畅的视听觉交互。该方法不仅保留了强大的视觉语言功能,还能实现高效的语音对话能力,无需单独的ASR和TTS模块,显著提高了多模态端到端的响应速度。通过与图像、视频和语音任务的最新技术相比,证明该模型具有强大的视觉和语音功能,可实现近乎实时的视听觉交互。
Key Takeaways:
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在集成视觉和文本模态时忽视了语音的重要性。
- 语音在多模态对话系统中扮演重要角色。
- 实现视听觉任务的高性能是一个重大挑战,因为不同模态之间存在根本性差异。
- 提出了一种多阶段训练方法,使LLM能够处理视觉和语音信息,促进流畅的视听觉交互。
- 该方法不仅保持强大的视觉语言功能,还具备高效的语音对话能力。
- 该模型无需额外的ASR和TTS模块,提高了多模态端到端的响应速度。
点此查看论文截图

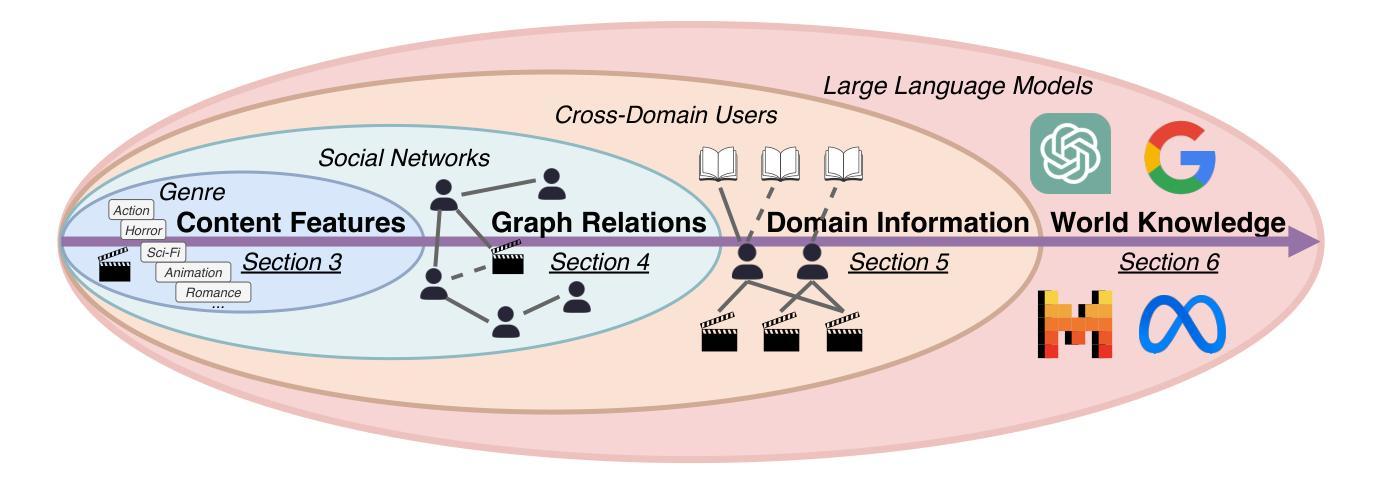
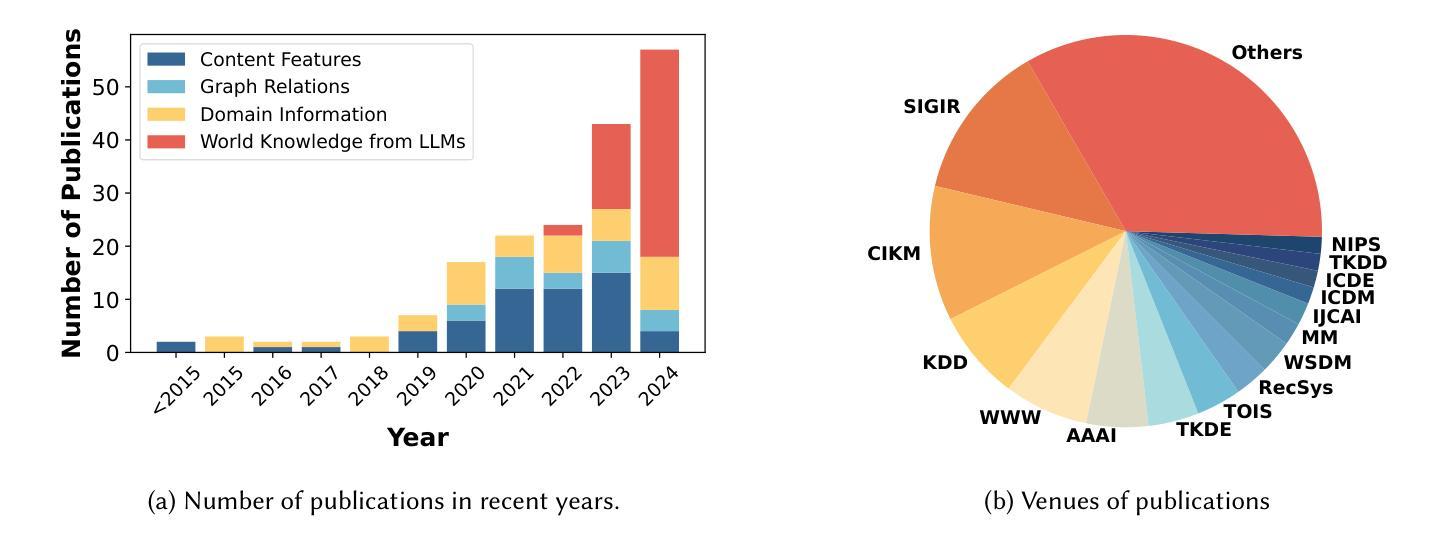
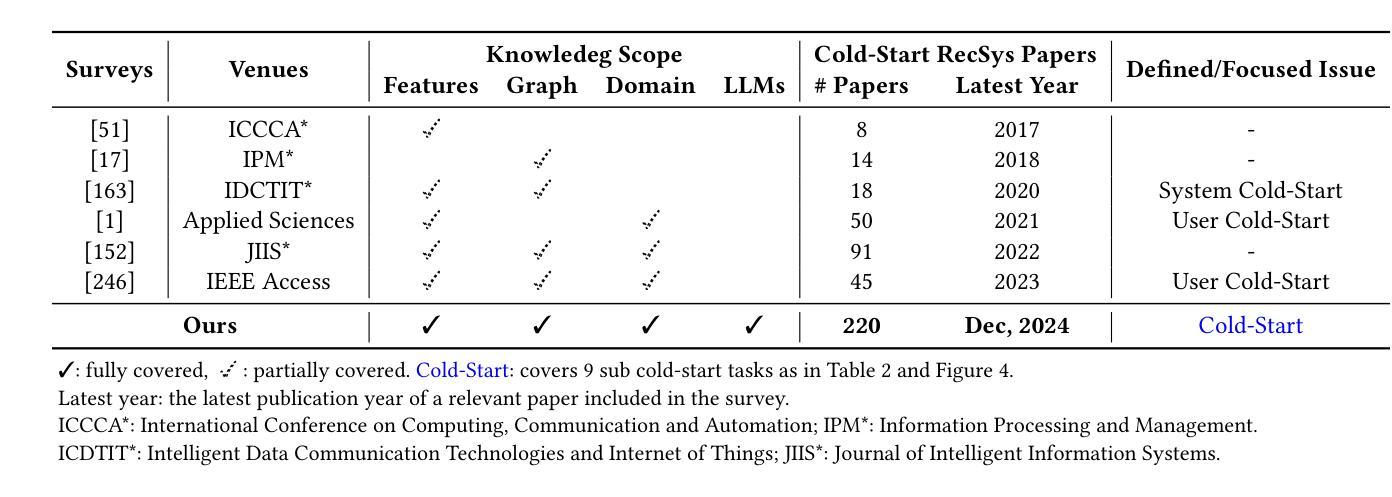
Cold-Start Recommendation towards the Era of Large Language Models (LLMs): A Comprehensive Survey and Roadmap
Authors:Weizhi Zhang, Yuanchen Bei, Liangwei Yang, Henry Peng Zou, Peilin Zhou, Aiwei Liu, Yinghui Li, Hao Chen, Jianling Wang, Yu Wang, Feiran Huang, Sheng Zhou, Jiajun Bu, Allen Lin, James Caverlee, Fakhri Karray, Irwin King, Philip S. Yu
Cold-start problem is one of the long-standing challenges in recommender systems, focusing on accurately modeling new or interaction-limited users or items to provide better recommendations. Due to the diversification of internet platforms and the exponential growth of users and items, the importance of cold-start recommendation (CSR) is becoming increasingly evident. At the same time, large language models (LLMs) have achieved tremendous success and possess strong capabilities in modeling user and item information, providing new potential for cold-start recommendations. However, the research community on CSR still lacks a comprehensive review and reflection in this field. Based on this, in this paper, we stand in the context of the era of large language models and provide a comprehensive review and discussion on the roadmap, related literature, and future directions of CSR. Specifically, we have conducted an exploration of the development path of how existing CSR utilizes information, from content features, graph relations, and domain information, to the world knowledge possessed by large language models, aiming to provide new insights for both the research and industrial communities on CSR. Related resources of cold-start recommendations are collected and continuously updated for the community in https://github.com/YuanchenBei/Awesome-Cold-Start-Recommendation.
冷启动问题是推荐系统长期以来的挑战之一,主要关注如何对新用户或交互受限的用户或项目进行准确建模,以提供更好的推荐。由于互联网平台的多样化和用户项目的指数级增长,冷启动推荐(CSR)的重要性变得越来越明显。同时,大型语言模型(LLM)已经取得了巨大的成功,在建模用户和项目信息方面拥有强大的能力,为冷启动推荐提供了新的潜力。然而,CSR研究领域仍然缺乏对该领域的全面回顾和反思。基于此,本文站在大型语言模型的时代背景下,全面回顾和讨论CSR的发展道路、相关文献和未来方向。具体来说,我们探索了现有CSR如何利用信息的发展路径,从内容特征、图关系到领域信息,再到大型语言模型所拥有的世界知识,旨在为CSR的研究和工业界提供新的见解。冷启动推荐的相关资源已收集并在https://github.com/YuanchenBei/Awesome-Cold-Start-Recommendation上持续更新,以供相关社区使用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型时代下的冷启动推荐挑战综述。本文全面回顾和讨论了冷启动推荐(CSR)的研究进展、相关文献和未来方向。文章探讨了现有CSR如何利用信息的发展路径,从内容特征、图关系到领域信息,再到大型语言模型所拥有的世界知识,为CSR的研究和工业界提供了新的见解。相关资源可通过https://github.com/YuanchenBei/Awesome-Cold-Start-Recommendation获取。
Key Takeaways
- 冷启动问题是推荐系统长期存在的挑战,主要针对新用户或交互受限的用户或项目进行准确建模,以提供更好的推荐。
- 随着互联网平台的多样化和用户项目的指数级增长,冷启动推荐(CSR)的重要性日益凸显。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在建模用户和项目信息方面取得了巨大成功,为冷启动推荐提供了新的潜力。
- 现有CSR的研究在如何利用信息方面进行了探索,包括内容特征、图关系和领域信息。
- CSR的研究进展和未来方向进行了全面回顾和讨论,为研究和工业界提供了新的见解。
- 可以通过https://github.com/YuanchenBei/Awesome-Cold-Start-Recommendation获取相关资源。
点此查看论文截图

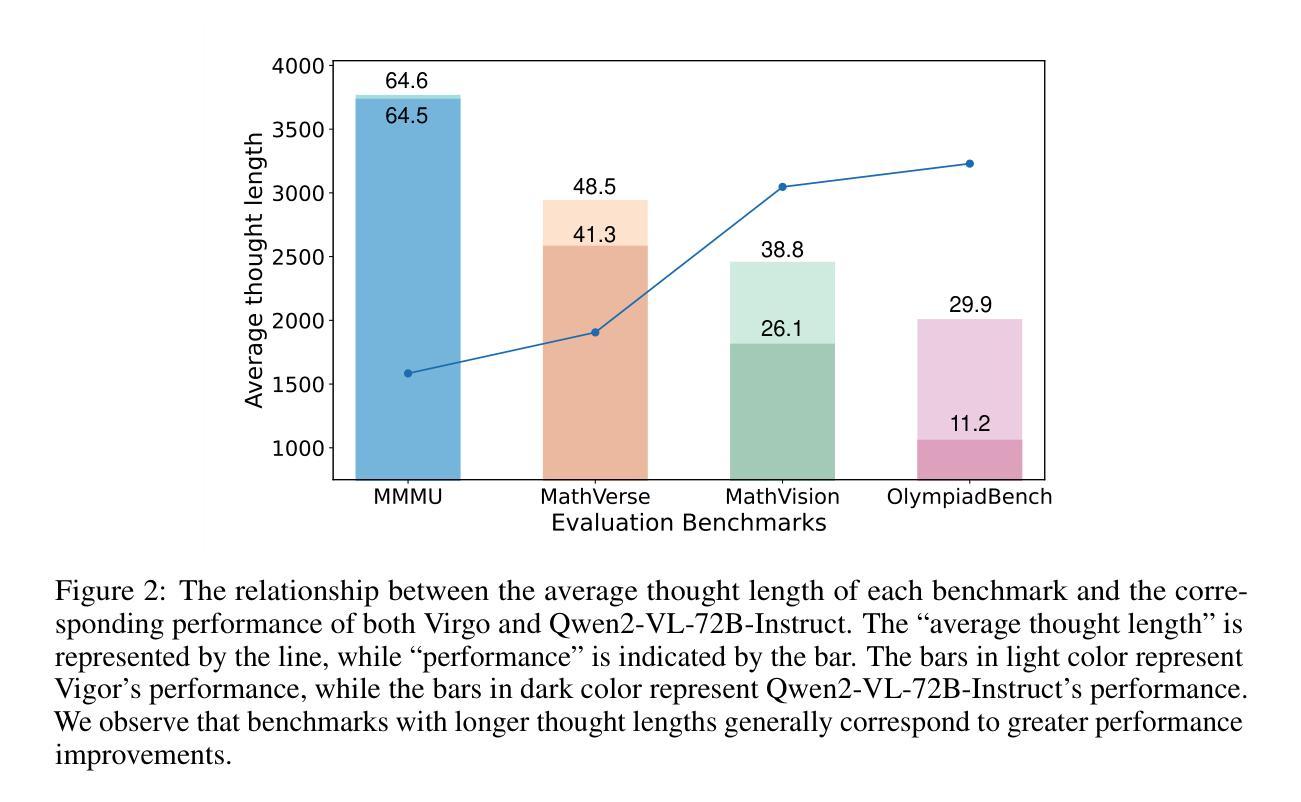
Virgo: A Preliminary Exploration on Reproducing o1-like MLLM
Authors:Yifan Du, Zikang Liu, Yifan Li, Wayne Xin Zhao, Yuqi Huo, Bingning Wang, Weipeng Chen, Zheng Liu, Zhongyuan Wang, Ji-Rong Wen
Recently, slow-thinking reasoning systems, built upon large language models (LLMs), have garnered widespread attention by scaling the thinking time during inference. There is also growing interest in adapting this capability to multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Given that MLLMs handle more complex data semantics across different modalities, it is intuitively more challenging to implement multimodal slow-thinking systems. To address this issue, in this paper, we explore a straightforward approach by fine-tuning a capable MLLM with a small amount of textual long-form thought data, resulting in a multimodal slow-thinking system, Virgo (Visual reasoning with long thought). We find that these long-form reasoning processes, expressed in natural language, can be effectively transferred to MLLMs. Moreover, it seems that such textual reasoning data can be even more effective than visual reasoning data in eliciting the slow-thinking capacities of MLLMs. While this work is preliminary, it demonstrates that slow-thinking capacities are fundamentally associated with the language model component, which can be transferred across modalities or domains. This finding can be leveraged to guide the development of more powerful slow-thinking reasoning systems. We release our resources at https://github.com/RUCAIBox/Virgo.
最近,基于大型语言模型(LLM)的慢思考推理系统已经引起了广泛关注,它们通过扩展推理时间来扩大规模。将这一能力适应于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的兴趣也在日益增长。考虑到MLLM处理不同模态下更复杂的数据语义,实现多模态慢思考系统更具挑战性。为了解决这个问题,本文探索了一种简单的方法,即通过少量文本长思考数据对功能强大的MLLM进行微调,从而构建了一个多模态慢思考系统Virgo(视觉推理与长思考)。我们发现,用自然语言表达的长思考过程可以有效地转移到MLLM上。而且,似乎这种文本推理数据在激发MLLM的慢思考能力方面甚至比视觉推理数据更有效。虽然这项工作只是初步的,但它证明了慢思考能力从根本上与语言模型组件相关联,可以跨模态或领域进行转移。这一发现可用于指导开发更强大的慢思考推理系统。我们在https://github.com/RUCAIBox/Virgo上发布了我们的资源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report on Slow Thinking with LLMs: Visual Reasoning
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的慢思考推理系统通过扩展推理时间获得了广泛关注。为适应多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的这一能力,研究者们正不断探索。本文探索了一种简单的方法,即通过微调具备能力的MLLM与少量文本长形式思维数据,实现多模态慢思考系统——维京(Visual reasoning with long thought)。研究结果表明,自然语言表达的长期推理过程可以有效地转移到MLLM上,并且这种文本推理数据似乎比视觉推理数据更能激发MLLM的慢思考能力。这为开发更强大的慢思考推理系统提供了重要启示。
Key Takeaways
- 慢思考推理系统通过扩展大型语言模型的推理时间而受到广泛关注。
- 多模态大型语言模型的慢思考能力适应是一个新兴的研究方向。
- 通过微调具备能力的多模态大型语言模型与少量文本长形式思维数据,可以实现多模态慢思考系统——维京(Virgo)。
- 自然语言的长期推理过程可以有效地转移到多模态大型语言模型上。
- 文本推理数据比视觉推理数据更能激发多模态大型语言模型的慢思考能力。
- 维京系统的发现表明慢思考能力根本上与语言模型组件相关,可跨模态或领域进行转移。
点此查看论文截图


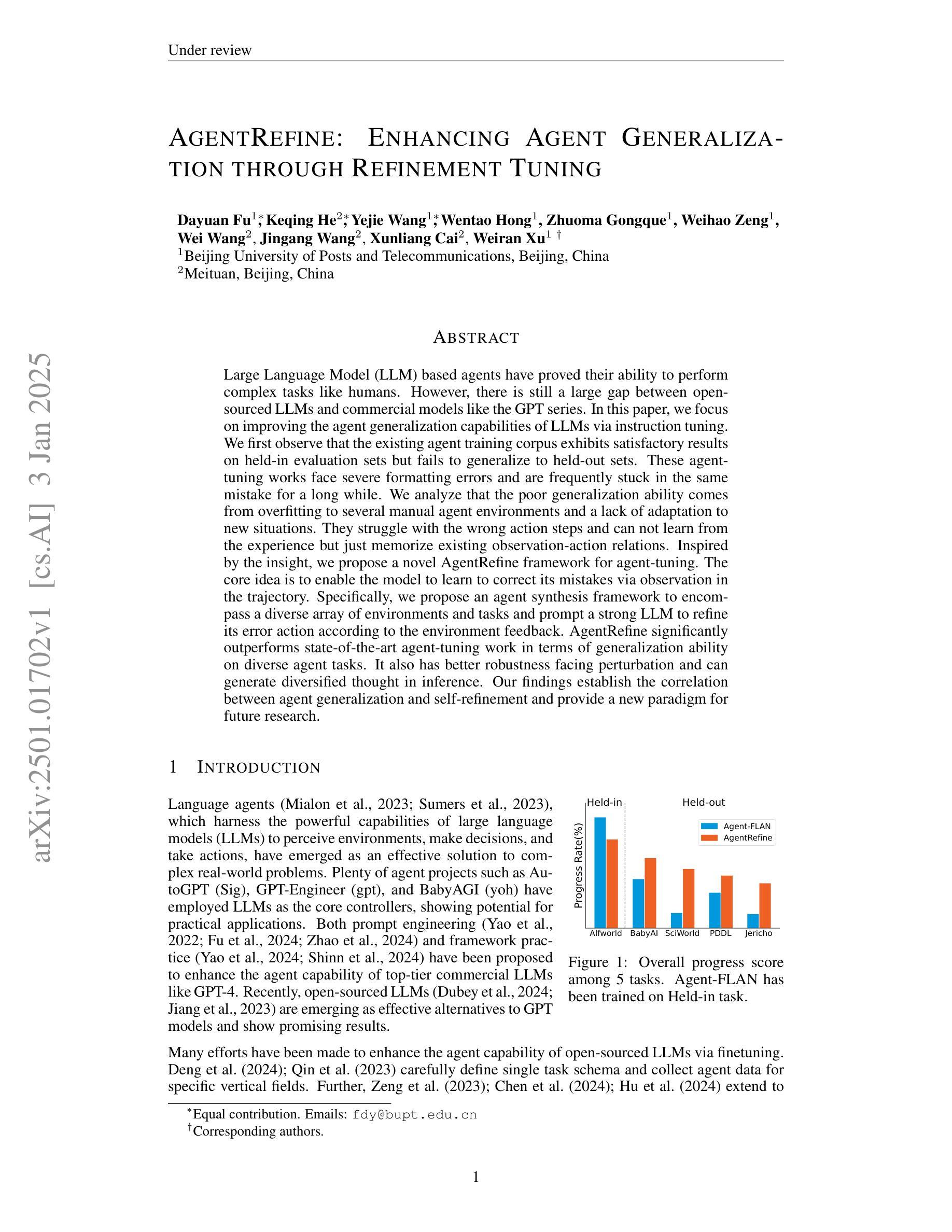
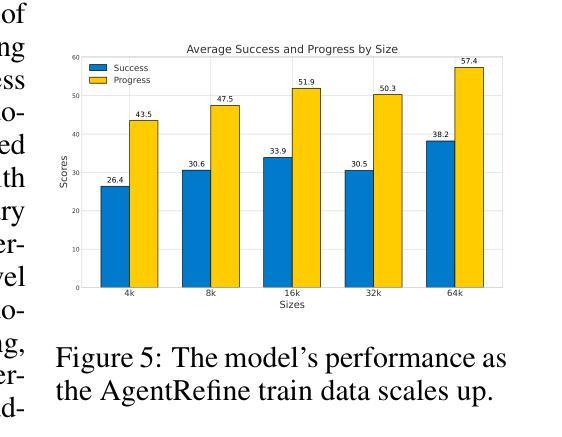
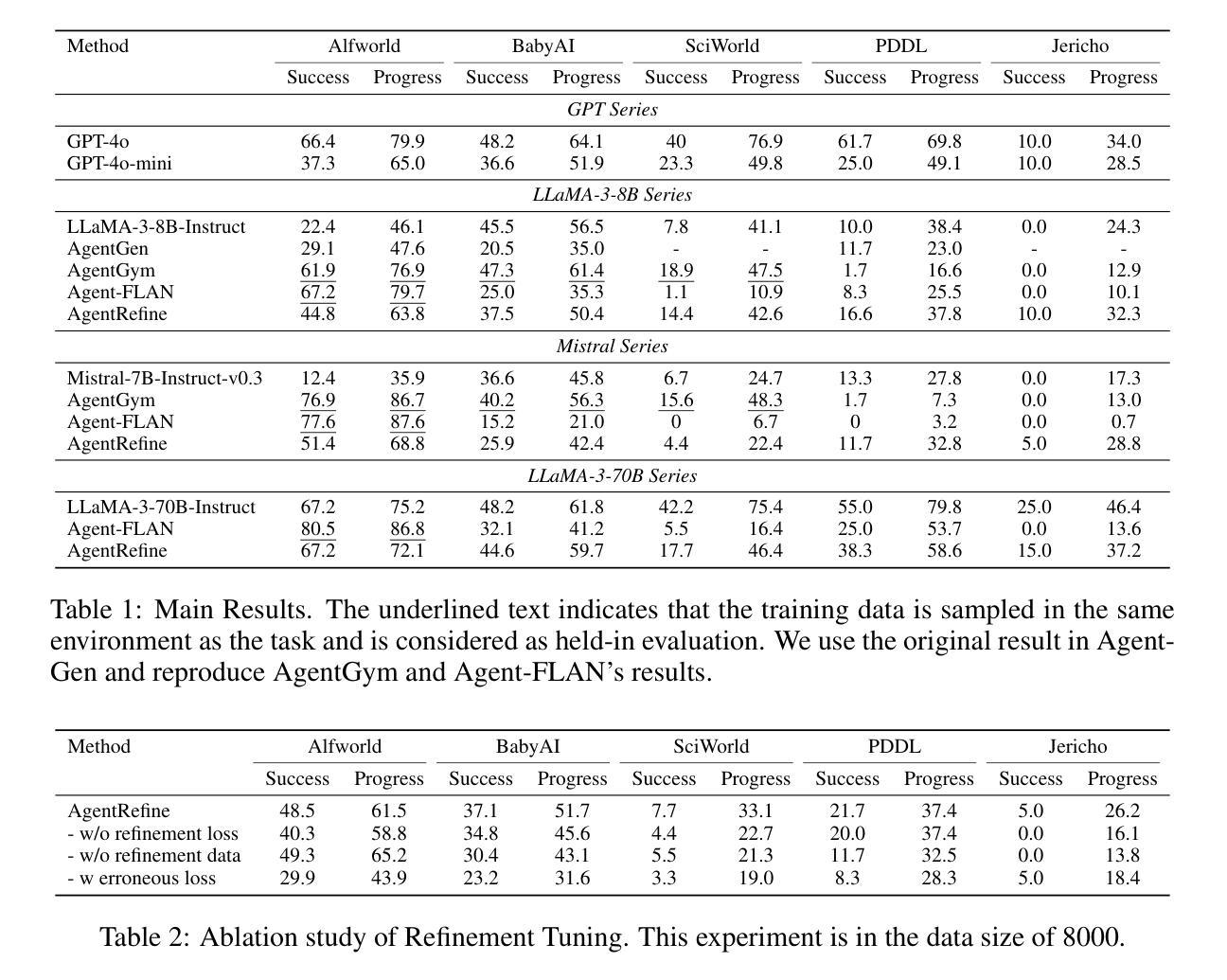
AgentRefine: Enhancing Agent Generalization through Refinement Tuning
Authors:Dayuan Fu, Keqing He, Yejie Wang, Wentao Hong, Zhuoma Gongque, Weihao Zeng, Wei Wang, Jingang Wang, Xunliang Cai, Weiran Xu
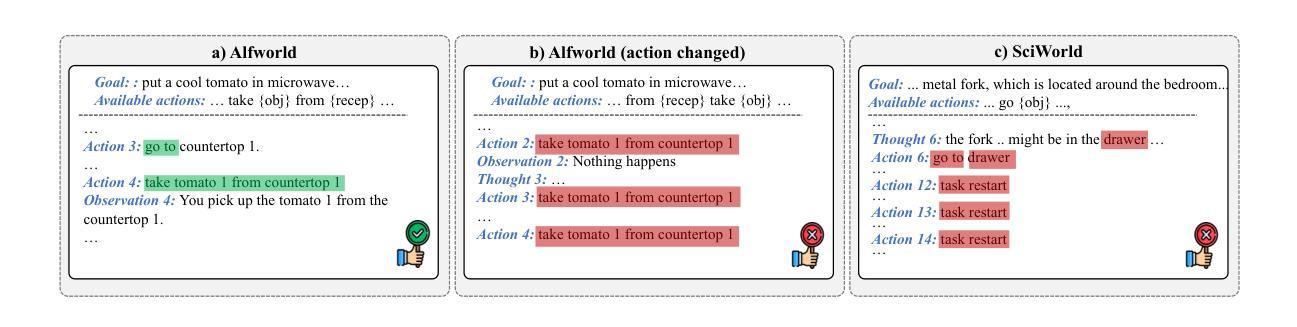
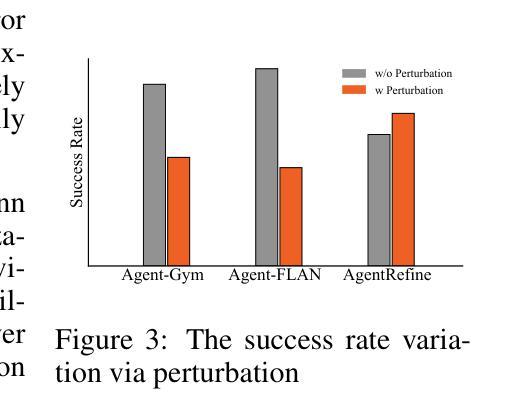
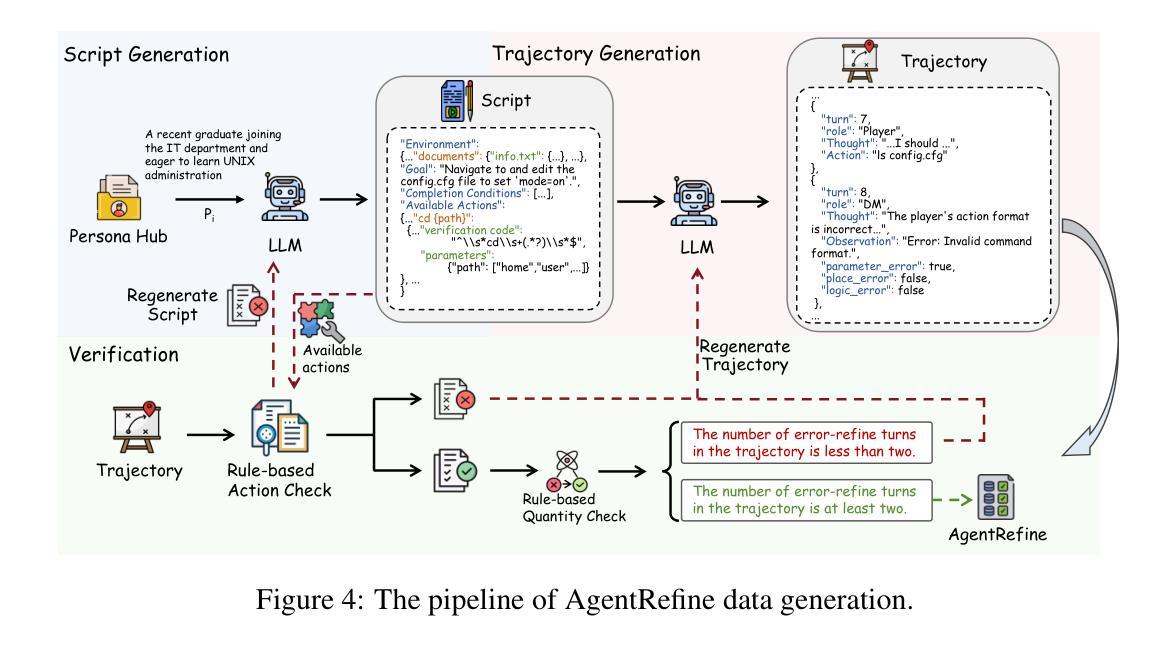
Large Language Model (LLM) based agents have proved their ability to perform complex tasks like humans. However, there is still a large gap between open-sourced LLMs and commercial models like the GPT series. In this paper, we focus on improving the agent generalization capabilities of LLMs via instruction tuning. We first observe that the existing agent training corpus exhibits satisfactory results on held-in evaluation sets but fails to generalize to held-out sets. These agent-tuning works face severe formatting errors and are frequently stuck in the same mistake for a long while. We analyze that the poor generalization ability comes from overfitting to several manual agent environments and a lack of adaptation to new situations. They struggle with the wrong action steps and can not learn from the experience but just memorize existing observation-action relations. Inspired by the insight, we propose a novel AgentRefine framework for agent-tuning. The core idea is to enable the model to learn to correct its mistakes via observation in the trajectory. Specifically, we propose an agent synthesis framework to encompass a diverse array of environments and tasks and prompt a strong LLM to refine its error action according to the environment feedback. AgentRefine significantly outperforms state-of-the-art agent-tuning work in terms of generalization ability on diverse agent tasks. It also has better robustness facing perturbation and can generate diversified thought in inference. Our findings establish the correlation between agent generalization and self-refinement and provide a new paradigm for future research.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理已经证明了它们执行复杂任务的能力,类似于人类。然而,开源LLM和商业模型(如GPT系列)之间仍存在很大差距。在本文中,我们专注于通过指令微调提高LLM的代理泛化能力。我们首先观察到,现有的代理训练语料库在保留的评价集上取得了令人满意的结果,但未能推广到保留外的数据集。这些代理调整工作面临着严重的格式错误,并且经常长时间陷入同样的错误。我们分析认为,泛化能力差的根源在于对几种手动代理环境的过度适应以及对新情况的适应不足。他们难以执行错误的行动步骤,无法从经验中学习,而只是记住现有的观察-行动关系。受此启发,我们提出了一种新型的AgentRefine框架用于代理调整。核心思想是使模型能够通过轨迹中的观察来纠正自己的错误。具体来说,我们提出了一个代理合成框架,以涵盖各种环境和任务,并提示强大的LLM根据环境反馈细化其错误行动。AgentRefine在多种代理任务上的泛化能力方面显著优于最新的代理调整工作。它还具有更好的抗扰动性,并能在推理中产生多样化的想法。我们的发现建立了代理泛化和自我完善之间的关联,并为未来的研究提供了新的范式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)已展现出类似人类处理复杂任务的能力。但开源LLM与商业模型如GPT系列间仍存在差距。本文聚焦于通过指令微调提升LLM的代理泛化能力。研究发现,现有代理训练语料库在内部评估集上表现良好,但在外部评估集上泛化失败。本文分析了其源于过度适应手动代理环境以及难以适应新情境的问题。为此,本文提出了新颖的AgentRefine框架进行代理调整,其核心在于让模型通过轨迹观察学习纠正错误。AgentRefine显著提升了现有代理调整工作在多样化代理任务上的泛化能力,并具有更好的抗扰动性和推理多样性。
Key Takeaways
- LLM已展现出处理复杂任务的能力,但与商业模型如GPT系列相比仍有差距。
- 现有LLM代理训练存在过度适应特定环境的问题,导致在新情境下泛化能力弱。
- AgentRefine框架旨在提升LLM的代理泛化能力,通过让模型学习纠正错误来提高性能。
- AgentRefine框架包含多样化的环境任务,并提示强LLM根据环境反馈修正错误行动。
- AgentRefine在多样化代理任务上的泛化能力显著优于现有工作。
- AgentRefine具有更好的抗扰动性,能在推理过程中产生多样化思考。
点此查看论文截图
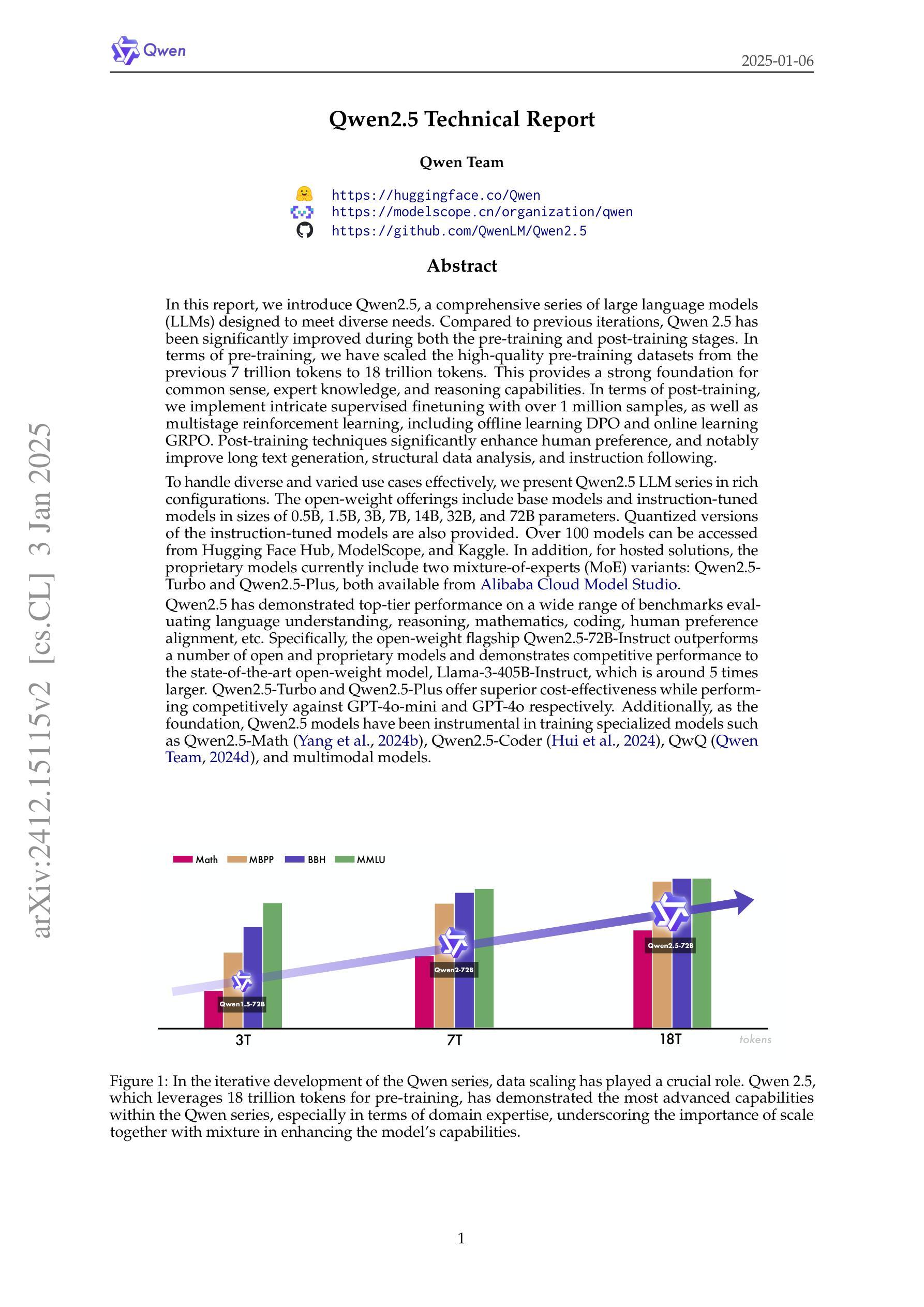
Qwen2.5 Technical Report
Authors: Qwen, :, An Yang, Baosong Yang, Beichen Zhang, Binyuan Hui, Bo Zheng, Bowen Yu, Chengyuan Li, Dayiheng Liu, Fei Huang, Haoran Wei, Huan Lin, Jian Yang, Jianhong Tu, Jianwei Zhang, Jianxin Yang, Jiaxi Yang, Jingren Zhou, Junyang Lin, Kai Dang, Keming Lu, Keqin Bao, Kexin Yang, Le Yu, Mei Li, Mingfeng Xue, Pei Zhang, Qin Zhu, Rui Men, Runji Lin, Tianhao Li, Tianyi Tang, Tingyu Xia, Xingzhang Ren, Xuancheng Ren, Yang Fan, Yang Su, Yichang Zhang, Yu Wan, Yuqiong Liu, Zeyu Cui, Zhenru Zhang, Zihan Qiu
In this report, we introduce Qwen2.5, a comprehensive series of large language models (LLMs) designed to meet diverse needs. Compared to previous iterations, Qwen 2.5 has been significantly improved during both the pre-training and post-training stages. In terms of pre-training, we have scaled the high-quality pre-training datasets from the previous 7 trillion tokens to 18 trillion tokens. This provides a strong foundation for common sense, expert knowledge, and reasoning capabilities. In terms of post-training, we implement intricate supervised finetuning with over 1 million samples, as well as multistage reinforcement learning. Post-training techniques enhance human preference, and notably improve long text generation, structural data analysis, and instruction following. To handle diverse and varied use cases effectively, we present Qwen2.5 LLM series in rich sizes. Open-weight offerings include base and instruction-tuned models, with quantized versions available. In addition, for hosted solutions, the proprietary models currently include two mixture-of-experts (MoE) variants: Qwen2.5-Turbo and Qwen2.5-Plus, both available from Alibaba Cloud Model Studio. Qwen2.5 has demonstrated top-tier performance on a wide range of benchmarks evaluating language understanding, reasoning, mathematics, coding, human preference alignment, etc. Specifically, the open-weight flagship Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct outperforms a number of open and proprietary models and demonstrates competitive performance to the state-of-the-art open-weight model, Llama-3-405B-Instruct, which is around 5 times larger. Qwen2.5-Turbo and Qwen2.5-Plus offer superior cost-effectiveness while performing competitively against GPT-4o-mini and GPT-4o respectively. Additionally, as the foundation, Qwen2.5 models have been instrumental in training specialized models such as Qwen2.5-Math, Qwen2.5-Coder, QwQ, and multimodal models.
在这份报告中,我们介绍了Qwen2.5,这是一系列为了满足不同需求而设计的大型语言模型(LLM)。相较于之前的版本,Qwen 2.5在预训练和后训练阶段都得到了显著提升。在预训练方面,我们将高质量的预训练数据集从之前的7万亿标记扩展到18万亿标记。这为常识、专业知识和推理能力提供了坚实的基础。在后训练方面,我们实施了复杂的监督微调,使用了超过1百万个样本,以及多阶段强化学习。后训练技术提高了人类偏好,并显著改善了长文本生成、结构化数据分析和指令遵循能力。为了有效地处理各种用例,我们推出了丰富的Qwen2.5 LLM系列。开放权重产品包括基础版和指令调优模型,也有量化版本可供选择。此外,对于托管解决方案,专有模型目前包括两个混合专家(MoE)变体:Qwen2.5-Turbo和Qwen2.5-Plus,两者都可在阿里云模型工作室中使用。Qwen2.5已在广泛的语言理解、推理、数学、编码、人类偏好对齐等基准测试中表现出卓越性能。特别是开放权重的旗舰产品Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct,在多个公开和专有模型中表现出色,与最先进的开放权重模型Llama-3-405B-Instruct相比具有竞争力,尽管后者规模大约是前者的5倍。Qwen2.5-Turbo和Qwen2.5-Plus提供了出色的性价比,与GPT-4o-mini和GPT-4o相比表现良好。此外,作为基石,Qwen2.5模型在训练专业模型如Qwen2.5-Math、Qwen2.5-Coder、QwQ和多模态模型中发挥了重要作用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了Qwen2.5系列大型语言模型(LLMs),该系列模型旨在满足不同的需求。相较于之前的版本,Qwen 2.5在预训练和后训练阶段都有显著的提升。在预训练方面,高质量预训练数据集从之前的7万亿标记扩展到了18万亿标记,为常识、专业知识和推理能力提供了坚实的基础。后训练方面,采用复杂的监督微调技术,使用超过1百万样本进行训练,并采用多阶段强化学习。这些后训练技术提高了对人类偏好的符合度,并显著改善了长文本生成、结构化数据分析和指令遵循能力。为了有效应对各种用例,我们推出了丰富的Qwen2.5 LLM系列。开放权重产品包括基础版和指令调优模型,还有量化版本。此外,对于托管解决方案,还包括两个专有模型MoE(混合专家)变体:Qwen2.5-Turbo和Qwen2.5-Plus,两者均可在阿里云模型工作室通过阿里巴巴云获得。Qwen2.5系列模型在多种评估基准测试中表现优异,如语言理解、推理、数学、编码、人类偏好对齐等。特别是开放权重的旗舰产品Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct在多个公开和专有模型中表现出色,与当前先进的开放权重模型Llama-3-405B-Instruct相比也具有竞争力。而Qwen2.5-Turbo和Qwen2.5-Plus在成本效益方面表现优异。此外,Qwen2.5系列模型还为训练专业模型和多模态模型提供了基础。
要点总结
- Qwen2.5系列大型语言模型(LLMs)为满足不同需求而设计。
- 相较于之前版本,Qwen 2.5在预训练数据集、后训练技术和性能上有所提升。
- Qwen 2.5系列包括多种规模和类型的模型,如基础版、指令调优版、量化版等。
- Qwen2.5在后训练方面采用了复杂的监督微调技术和多阶段强化学习,提高了长文本生成、结构化数据分析和指令遵循能力。
- Qwen2.5系列在多种基准测试中表现优异,包括语言理解、推理、数学、编码等。
- 旗舰产品Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct在公开和专有模型中表现出色,与当前最先进的模型具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图
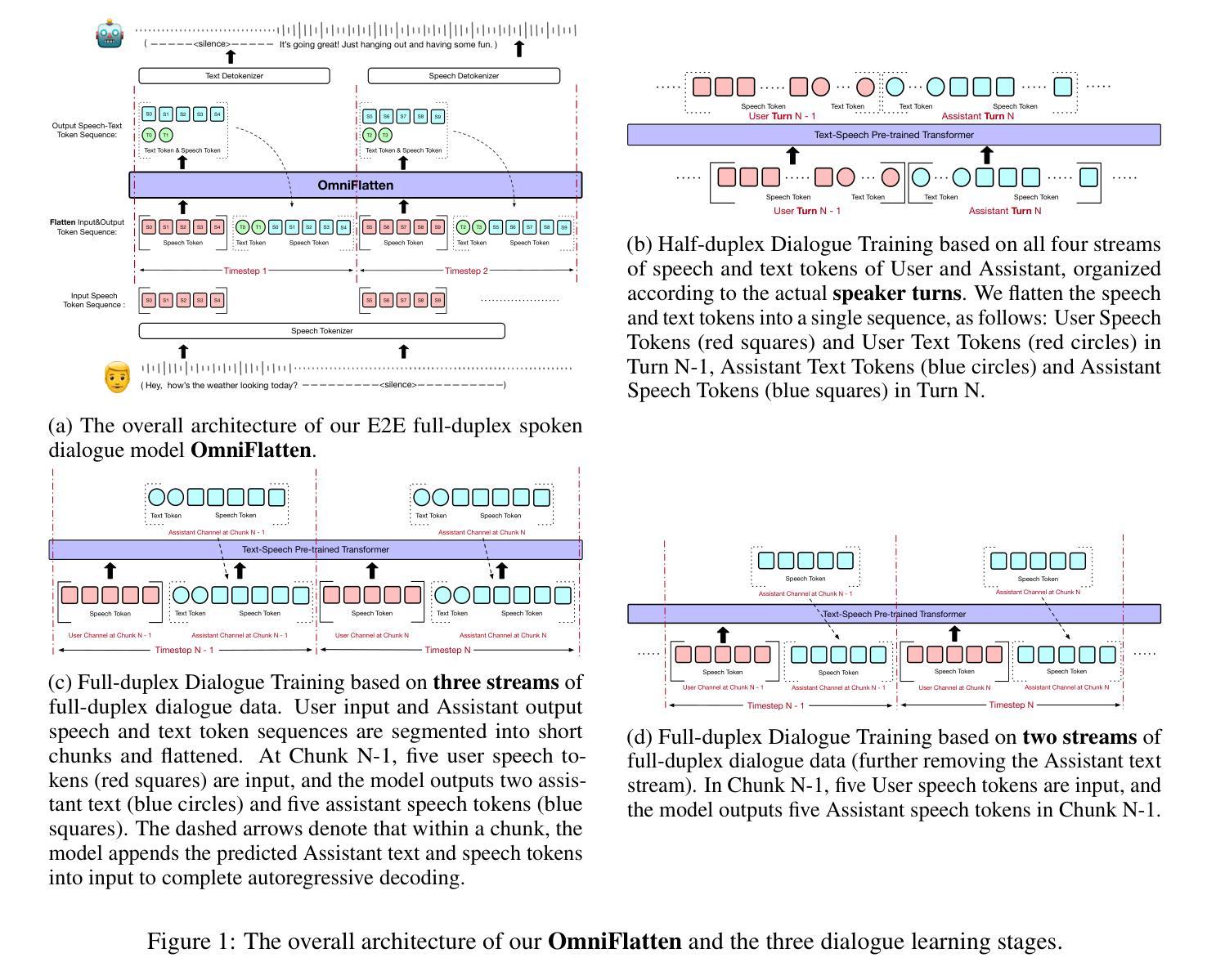
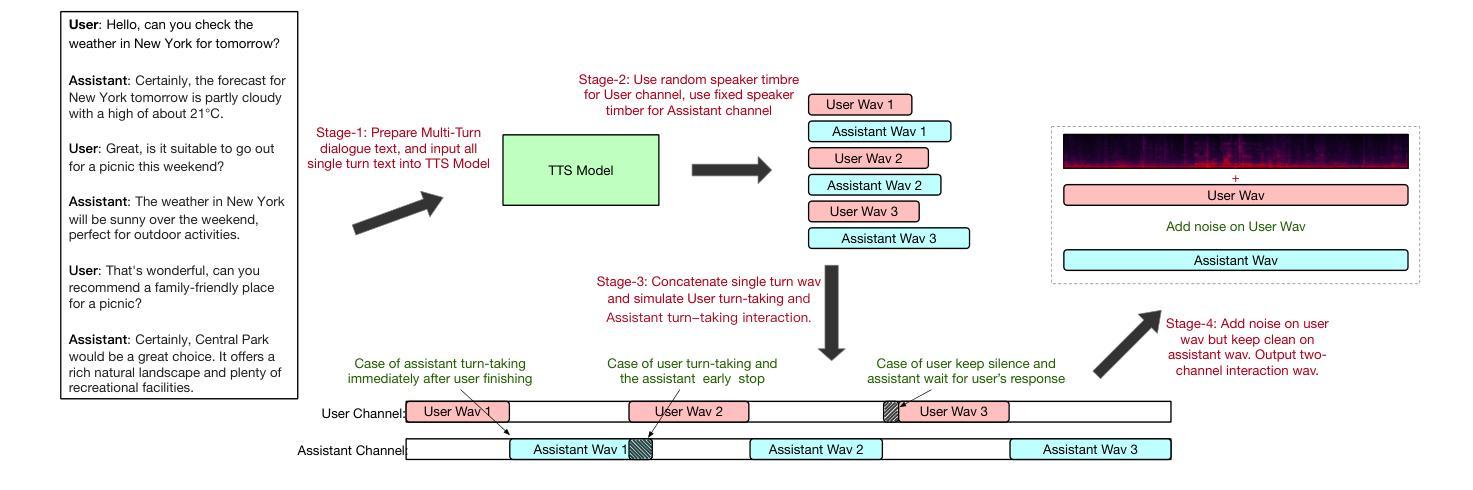
OmniFlatten: An End-to-end GPT Model for Seamless Voice Conversation
Authors:Qinglin Zhang, Luyao Cheng, Chong Deng, Qian Chen, Wen Wang, Siqi Zheng, Jiaqing Liu, Hai Yu, Chaohong Tan, Zhihao Du, Shiliang Zhang
Full-duplex spoken dialogue systems significantly surpass traditional turn-based dialogue systems, as they allow simultaneous bidirectional communication, closely mirroring human-human interactions. However, achieving low latency and natural interactions in full-duplex dialogue systems remains a significant challenge, especially considering human conversation dynamics such as interruptions, backchannels, and overlapping speech. In this paper, we introduce a novel End-to-End GPT-based model OmniFlatten for full-duplex conversation, capable of effectively modeling the complex behaviors inherent to natural conversations with low latency. To achieve full-duplex conversation capabilities, we propose a multi-stage post-training scheme that progressively adapts a text large language model (LLM) backbone into a speech-text dialogue LLM, capable of generating text and speech in real time, without modifying the architecture of the backbone LLM. The training process comprises three stages: modality alignment, half-duplex dialogue learning, and full-duplex dialogue learning. In all training stages, we standardize the data using a flattening operation, which enables unifying the training methods and the GPT backbone across different modalities and tasks. Our approach offers a simple modeling technique and a promising research direction for developing efficient and natural end-to-end full-duplex spoken dialogue systems. Audio samples of dialogues generated by OmniFlatten can be found at this web site (https://omniflatten.github.io/).
全双工对话系统显著超越了传统的基于轮转的对话系统,因为它们允许同时双向通信,紧密地模拟了人与人之间的互动。然而,在全双工对话系统中实现低延迟和自然交互仍然是一个重大挑战,尤其是在考虑人类对话动态(如中断、反馈通道和重叠语音)时。在本文中,我们引入了一种基于GPT的新型端到端全双工对话模型OmniFlatten,它能够有效地对自然对话中固有的复杂行为进行建模,实现低延迟。为了实现全双工对话功能,我们提出了一种多阶段后训练方案,该方案逐步将一个文本大型语言模型(LLM)主干改造为一个语音文本对话LLM,能够实时生成文本和语音,无需修改主干LLM的架构。训练过程包括三个阶段:模态对齐、半双工对话学习和全双工对话学习。在所有训练阶段中,我们使用展平操作来标准化数据,这使我们能够在不同的模态和任务中使用统一的训练方法和GPT主干。我们的方法提供了一种简单的建模技术,并为开发高效、自然的端到端全双工对话系统提供了一个有前景的研究方向。OmniFlatten生成对话的音频样本可以在这个网站找到(https://omniflatten.github.io/)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
全双工对话系统允许同时双向通信,更贴近人与人之间的交流。本文提出了一种基于GPT的OmniFlatten模型,用于全双工对话,有效建模自然对话的复杂行为并实现低延迟。通过多阶段后训练方案,将文本大型语言模型(LLM)改编为语音文本对话LLM,实现实时生成文本和语音,无需修改架构。此方法为开发高效、自然的端到端全双工对话系统提供了简单建模技巧和具有前景的研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 全双工对话系统模拟人类交流,允许同时双向通信。
- OmniFlatten模型用于全双工对话,有效建模自然对话的复杂行为。
- 提出多阶段后训练方案,使文本LLM具备语音文本对话能力。
- 训练过程中采用数据标准化操作,统一不同模态和任务下的训练方法。
- OmniFlatten模型可实现低延迟对话。
- 模型在多种对话模态下具有通用性。
- 音频样本可在指定网站找到。
点此查看论文截图

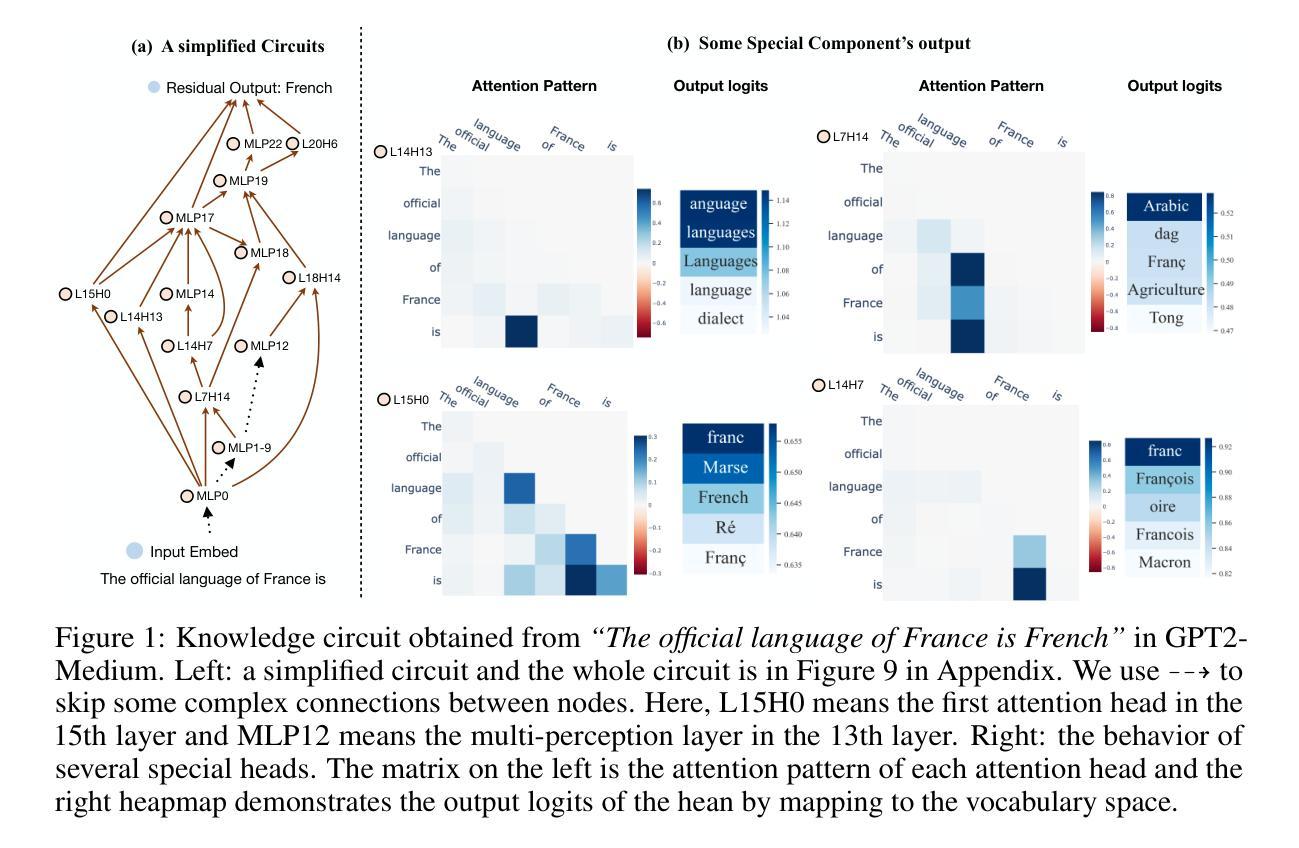
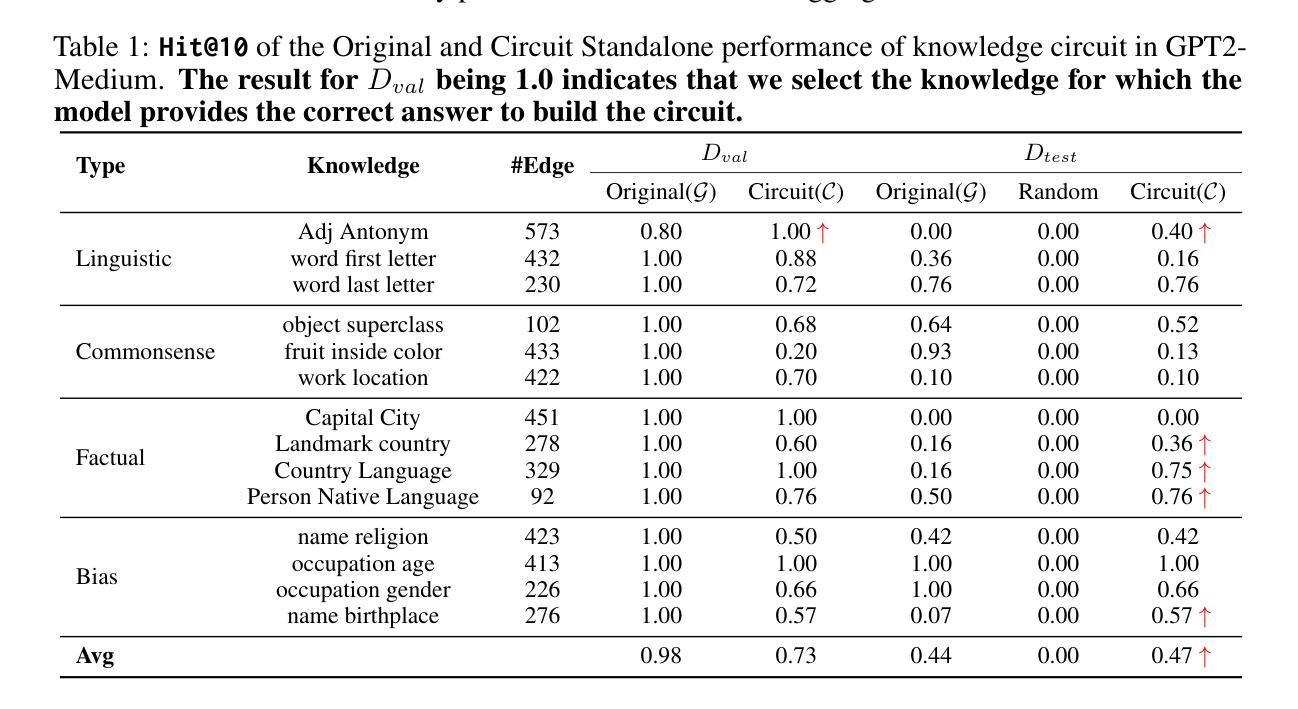
Knowledge Circuits in Pretrained Transformers
Authors:Yunzhi Yao, Ningyu Zhang, Zekun Xi, Mengru Wang, Ziwen Xu, Shumin Deng, Huajun Chen
The remarkable capabilities of modern large language models are rooted in their vast repositories of knowledge encoded within their parameters, enabling them to perceive the world and engage in reasoning. The inner workings of how these models store knowledge have long been a subject of intense interest and investigation among researchers. To date, most studies have concentrated on isolated components within these models, such as the Multilayer Perceptrons and attention head. In this paper, we delve into the computation graph of the language model to uncover the knowledge circuits that are instrumental in articulating specific knowledge. The experiments, conducted with GPT2 and TinyLLAMA, have allowed us to observe how certain information heads, relation heads, and Multilayer Perceptrons collaboratively encode knowledge within the model. Moreover, we evaluate the impact of current knowledge editing techniques on these knowledge circuits, providing deeper insights into the functioning and constraints of these editing methodologies. Finally, we utilize knowledge circuits to analyze and interpret language model behaviors such as hallucinations and in-context learning. We believe the knowledge circuits hold potential for advancing our understanding of Transformers and guiding the improved design of knowledge editing. Code and data are available in https://github.com/zjunlp/KnowledgeCircuits.
现代大型语言模型的卓越能力根植于其参数中编码的庞大知识库,使它们能够感知世界并参与推理。这些模型如何存储知识的内部工作机制长期以来一直是研究人员关注的热点和调查对象。迄今为止,大多数研究都集中在这些模型的孤立组件上,如多层感知器和注意力头。在本文中,我们深入语言模型的计算图,以揭示对于表达特定知识至关重要的知识回路。我们与GPT2和TinyLLAMA进行的实验使我们能够观察到某些信息头、关系头和多层感知器如何在模型中协同编码知识。此外,我们还评估了当前知识编辑技术对这些知识回路的影响,为这些编辑方法的运作和局限性提供了更深入的了解。最后,我们利用知识回路分析和解释语言模型的行为,如幻觉和上下文学习。我们相信知识回路在推动我们对Transformer的理解以及指导知识编辑的改进设计方面具有潜力。代码和数据可在https://github.com/zjunlp/KnowledgeCircuits找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024, 26 pages
Summary
现代大型语言模型的强大能力源于其参数中编码的丰富知识库,能够感知世界并进行推理。本文深入探究了语言模型的计算图,揭示了表达特定知识的关键知识回路。通过GPT2和TinyLLAMA的实验,我们观察到信息头、关系头和多层感知器等如何协同在模型中编码知识。此外,本文还评估了当前知识编辑技术对知识回路的影响,为这些编辑方法的运作和局限性提供了深刻见解。最后,我们利用知识回路分析和解释语言模型的行为,如幻觉和上下文学习。知识回路有助于我们更好地理解Transformer并引导知识编辑的改进设计。
Key Takeaways
- 现代大型语言模型的强大能力源于其参数中编码的丰富知识库。
- 语言模型的知识回路对于表达特定知识至关重要。
- 信息头、关系头和多层感知器等协同在模型中编码知识。
- 当前知识编辑技术对知识回路有影响。
- 知识回路可用于分析和解释语言模型的行为,如幻觉和上下文学习。
- 知识回路研究有助于更好地理解Transformer。
点此查看论文截图


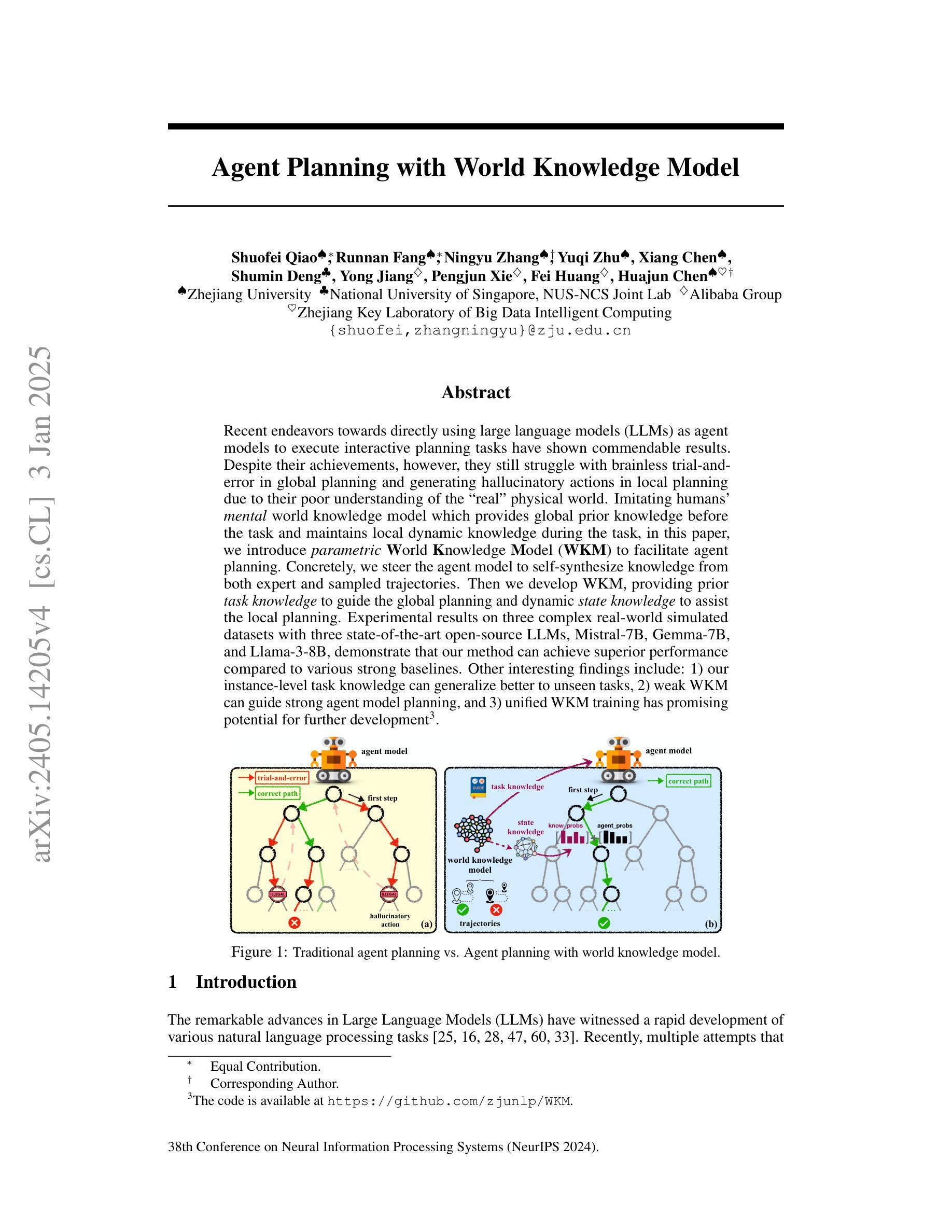
Agent Planning with World Knowledge Model
Authors:Shuofei Qiao, Runnan Fang, Ningyu Zhang, Yuqi Zhu, Xiang Chen, Shumin Deng, Yong Jiang, Pengjun Xie, Fei Huang, Huajun Chen
Recent endeavors towards directly using large language models (LLMs) as agent models to execute interactive planning tasks have shown commendable results. Despite their achievements, however, they still struggle with brainless trial-and-error in global planning and generating hallucinatory actions in local planning due to their poor understanding of the ``real’’ physical world. Imitating humans’ mental world knowledge model which provides global prior knowledge before the task and maintains local dynamic knowledge during the task, in this paper, we introduce parametric World Knowledge Model (WKM) to facilitate agent planning. Concretely, we steer the agent model to self-synthesize knowledge from both expert and sampled trajectories. Then we develop WKM, providing prior task knowledge to guide the global planning and dynamic state knowledge to assist the local planning. Experimental results on three complex real-world simulated datasets with three state-of-the-art open-source LLMs, Mistral-7B, Gemma-7B, and Llama-3-8B, demonstrate that our method can achieve superior performance compared to various strong baselines. Besides, we analyze to illustrate that our WKM can effectively alleviate the blind trial-and-error and hallucinatory action issues, providing strong support for the agent’s understanding of the world. Other interesting findings include: 1) our instance-level task knowledge can generalize better to unseen tasks, 2) weak WKM can guide strong agent model planning, and 3) unified WKM training has promising potential for further development. The code is available at https://github.com/zjunlp/WKM.
近期,直接使用大型语言模型(LLM)作为代理模型来执行交互式规划任务的研究取得了值得赞扬的成果。尽管取得了成就,然而,它们在全局规划方面仍面临着盲目的试错问题,在局部规划方面由于缺乏对“真实”物理世界的理解,会产生幻觉行为。
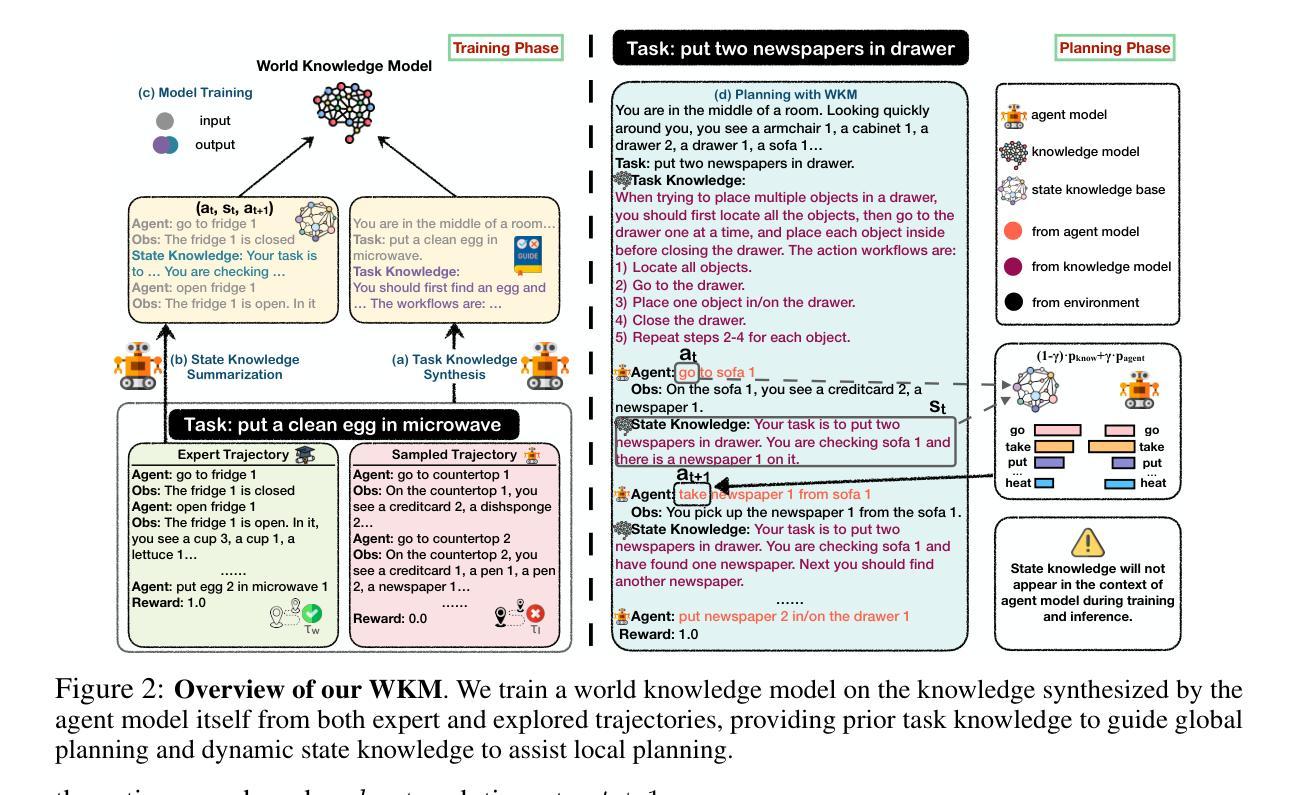
本文中,我们引入参数化世界知识模型(WKM),以辅助代理规划,模仿人类在执行任务前提供全局先验知识,并在任务过程中保持局部动态知识。具体来说,我们引导代理模型从专家轨迹和采样轨迹中自行合成知识。然后,我们开发WKM,提供任务先验知识以指导全局规划,并提供动态状态知识以辅助局部规划。
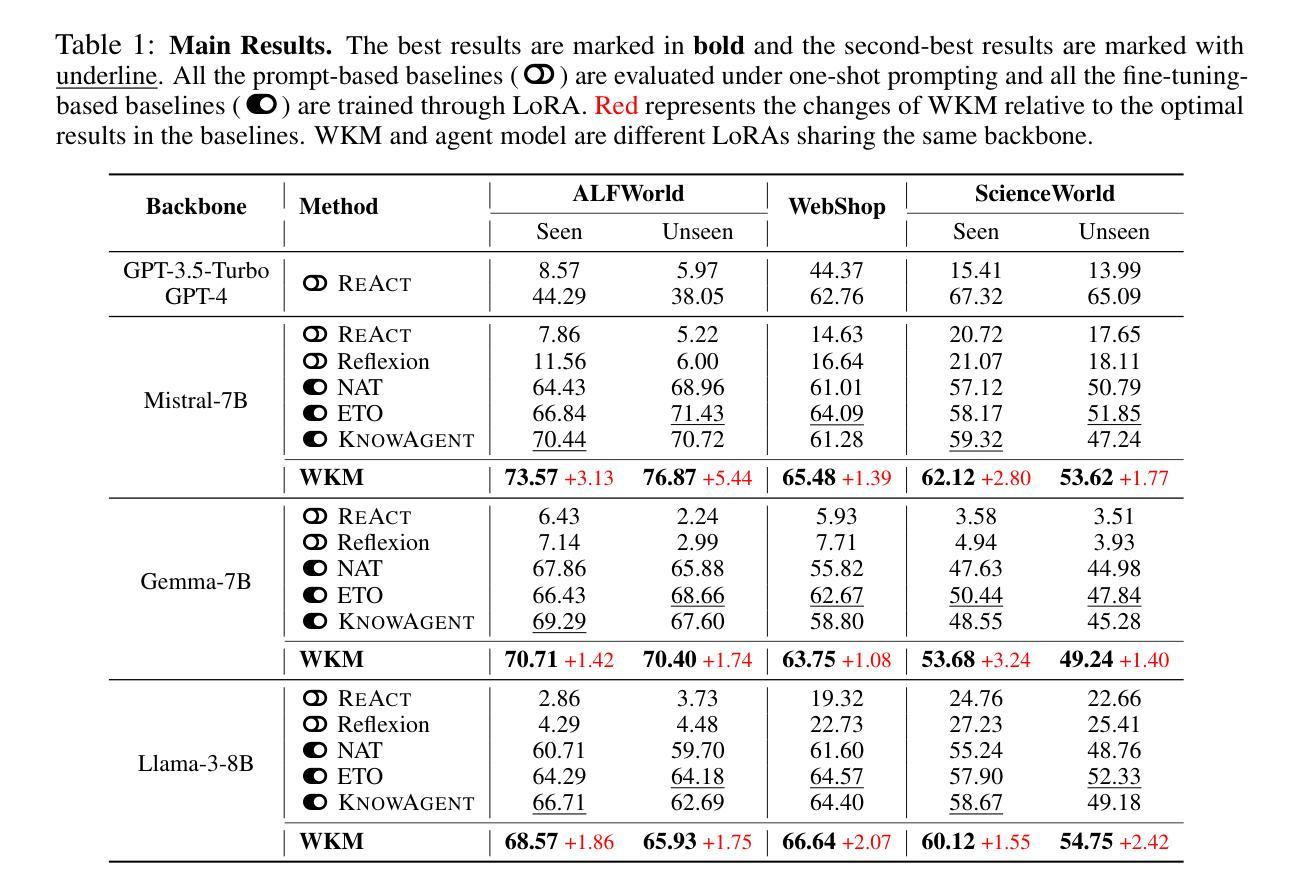
在三个复杂真实世界模拟数据集上,使用三种最新开源LLM(Mistral-7B、Gemma-7B和Llama-3-8B)进行的实验结果表明,我们的方法相比各种强大的基线方法可以实现优越的性能。此外,我们通过分析证明,我们的WKM可以有效地减轻盲目试错和幻觉行为问题,为代理对世界的理解提供强有力的支持。其他有趣的发现包括:1)我们的实例级任务知识可以更好地推广到未见过的任务;2)弱的WKM可以指导强代理模型规划;3)统一的WKM训练具有进一步开发的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024
摘要
本文介绍了参数化世界知识模型(WKM)在促进基于大语言模型(LLM)的代理规划方面的应用。通过结合专家轨迹和采样轨迹,WKM为代理模型提供任务先验知识,以指导全局规划,并提供动态状态知识以辅助局部规划。实验结果表明,该方法在三个复杂现实世界的模拟数据集上,使用三种最新的开源LLM,相较于各种强大的基线方法,取得了卓越的性能。此外,WKM能有效缓解盲目试错和幻觉动作问题,为代理对世界的理解提供了强有力的支持。研究还发现,实例级任务知识可以更好泛化到未见过的任务,弱WKM可以指导强代理模型规划,统一WKM训练具有进一步开发的潜力。
关键见解
- 介绍大语言模型(LLM)在交互式规划任务中的直接应用已取得显著成果。
- LLM仍面临全球规划中的无脑试错和局部规划中的幻觉动作问题。
- 提出参数化世界知识模型(WKM)以促进代理规划。
- WKM能结合专家轨迹和采样轨迹,为代理模型提供先验任务知识和动态状态知识。
- 实验证明WKM在复杂现实世界的模拟数据集上表现优越。
- WKM能有效缓解盲目试错和幻觉动作问题,增强代理对世界的理解。
- 研究发现实例级任务知识泛化性好,弱WKM可指导强代理模型规划,统一WKM训练具有发展潜力。
点此查看论文截图