⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-07 更新
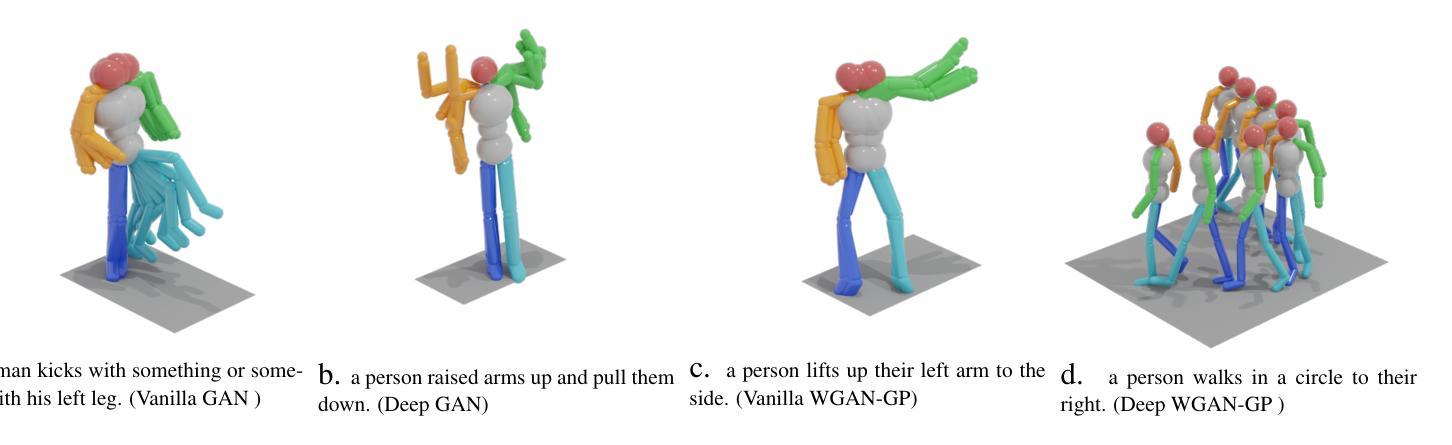
LS-GAN: Human Motion Synthesis with Latent-space GANs
Authors:Avinash Amballa, Gayathri Akkinapalli, Vinitra Muralikrishnan
Human motion synthesis conditioned on textual input has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential applications in various domains such as gaming, film production, and virtual reality. Conditioned Motion synthesis takes a text input and outputs a 3D motion corresponding to the text. While previous works have explored motion synthesis using raw motion data and latent space representations with diffusion models, these approaches often suffer from high training and inference times. In this paper, we introduce a novel framework that utilizes Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) in the latent space to enable faster training and inference while achieving results comparable to those of the state-of-the-art diffusion methods. We perform experiments on the HumanML3D, HumanAct12 benchmarks and demonstrate that a remarkably simple GAN in the latent space achieves a FID of 0.482 with more than 91% in FLOPs reduction compared to latent diffusion model. Our work opens up new possibilities for efficient and high-quality motion synthesis using latent space GANs.
近年来,基于文本输入的人类动作合成受到了广泛关注,因其在游戏、电影制作和虚拟现实等领域的潜在应用。条件动作合成接受文本输入并输出与文本对应的3D动作。虽然之前的工作已经探索了使用原始运动数据和扩散模型的潜在空间表示来进行动作合成,但这些方法往往存在训练和推理时间长的问题。在本文中,我们介绍了一个利用潜在空间中的生成对抗网络(GANs)的新框架,以实现更快的训练和推理,同时达到与最先进的扩散方法相当的结果。我们在HumanML3D和HumanAct12基准数据集上进行了实验,证明了一个相对简单的潜在空间GAN实现了与潜在扩散模型相比减少了91%以上的FLOPs,同时实现了0.482的FID。我们的工作开启了使用潜在空间GAN进行高效高质量动作合成的新可能性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages
Summary
文本介绍了一种基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的新框架,用于在潜在空间中进行快速训练和推理,以实现高质量的运动合成。该框架以文本输入为条件生成与文本相应的三维运动输出,主要应用于游戏、电影制作和虚拟现实等领域。实验结果表明,该框架在HumanML3D和HumanAct12基准测试中取得了优异的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 基于文本输入生成三维运动输出的条件运动合成技术受到关注,被应用于多个领域如游戏、电影制作和虚拟现实等。
- 新框架利用生成对抗网络(GANs)在潜在空间进行运动合成,实现了快速训练和推理。
- 与当前先进的扩散方法相比,新框架在性能上取得了相当的结果,并在HumanML3D和HumanAct12基准测试中表现出优异性能。
- 新框架具有显著减少计算浮点数运算量(FLOPs)的能力,达到了超过91%的减少。
- 新框架的出现为高效高质量的运动合成提供了新的可能性。
- GANs在潜在空间的应用在运动合成任务中表现出了显著的优势。
点此查看论文截图

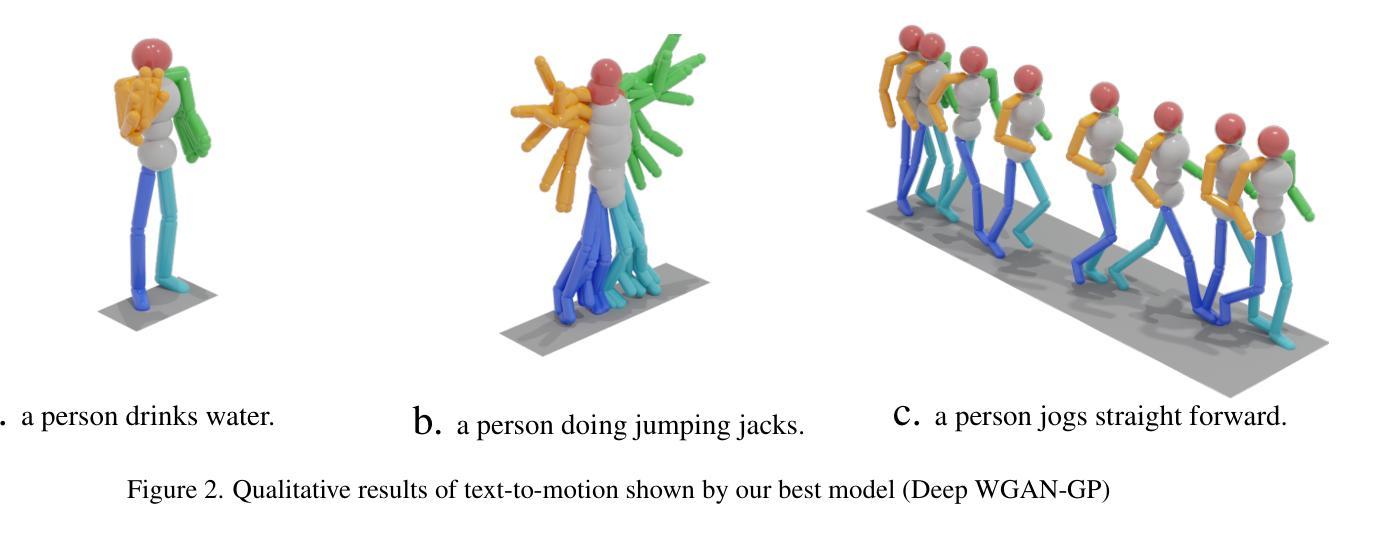
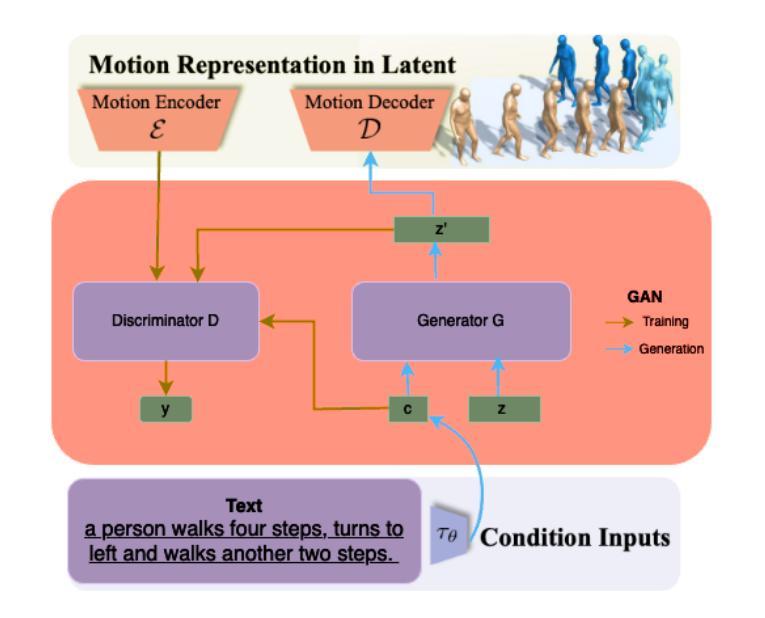
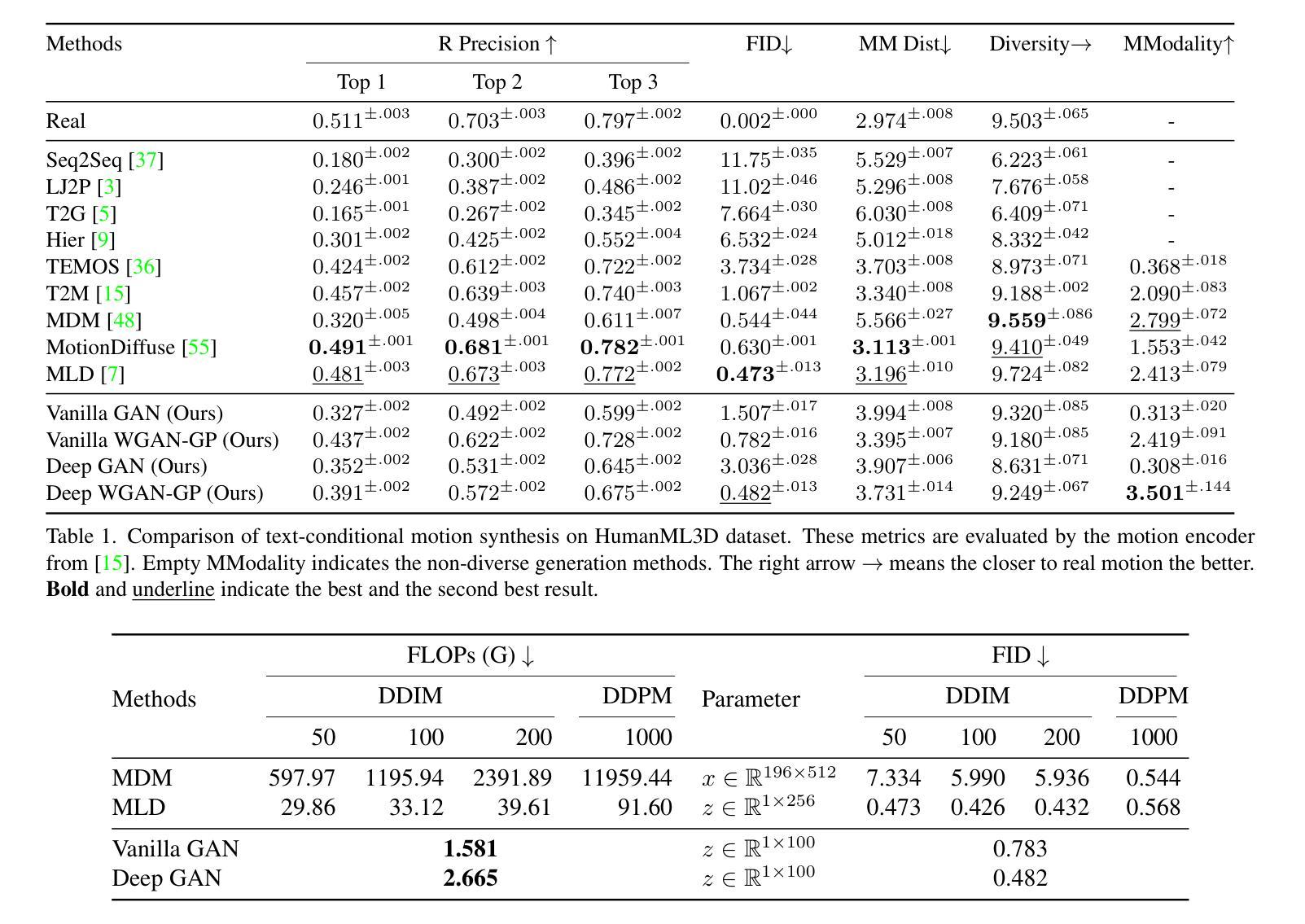
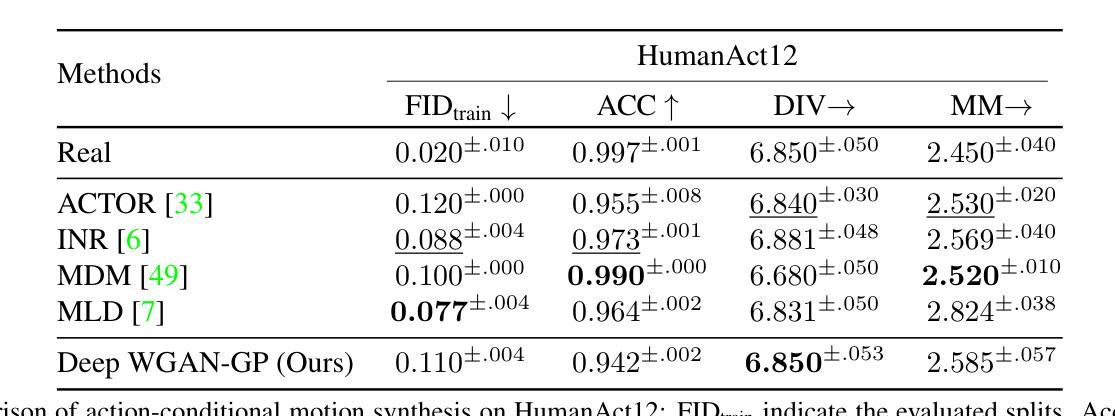
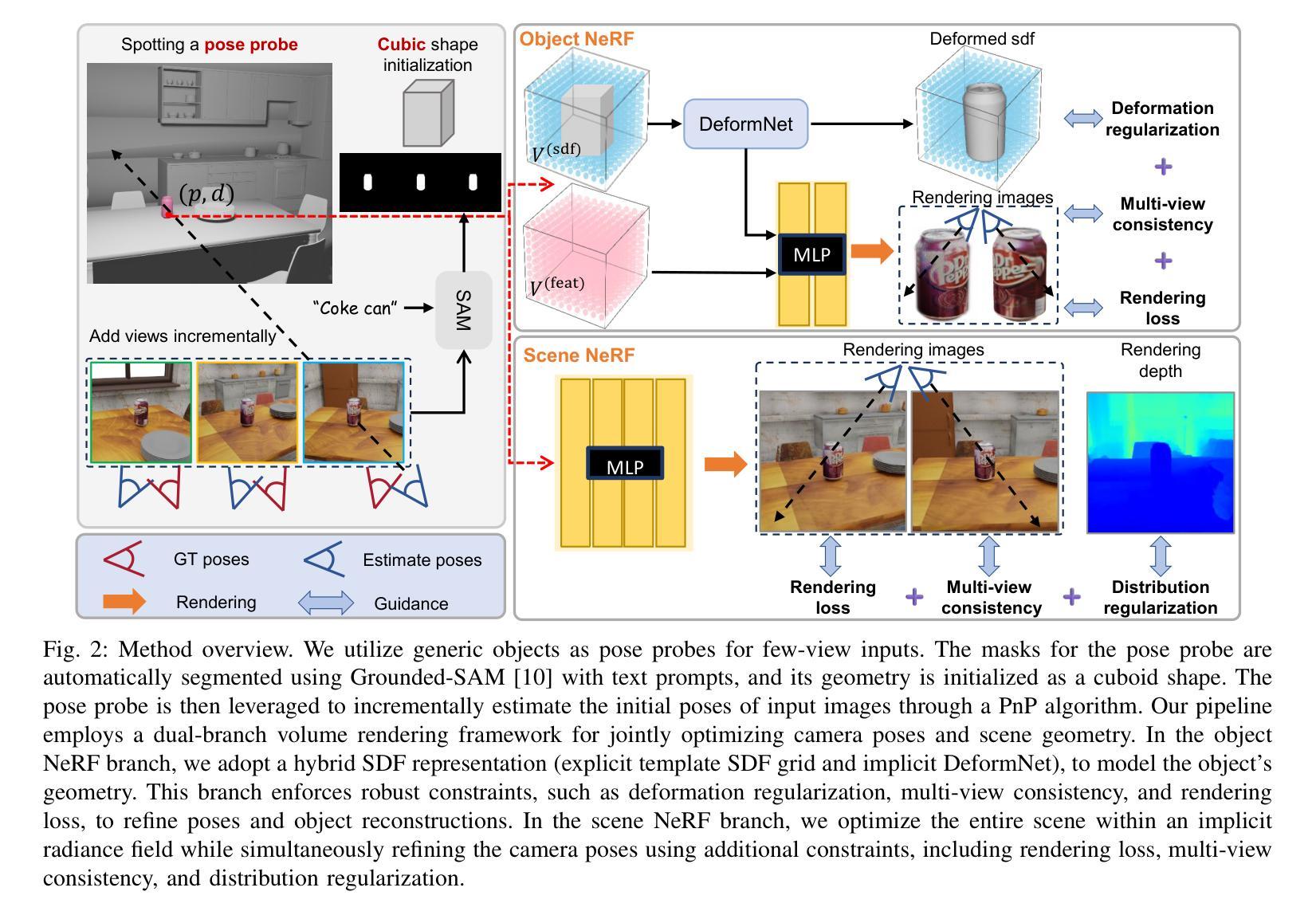
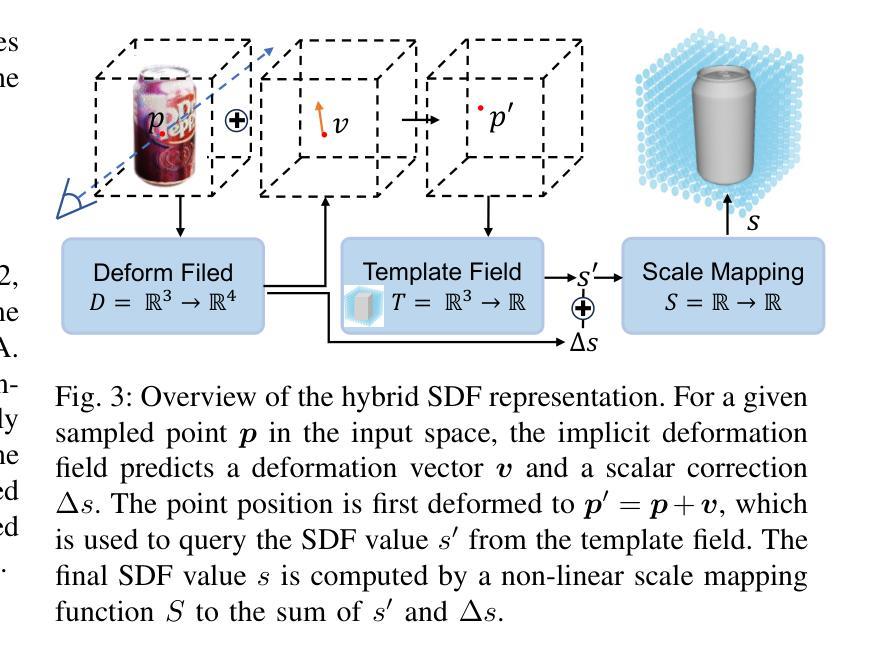
Generic Objects as Pose Probes for Few-shot View Synthesis
Authors:Zhirui Gao, Renjiao Yi, Chenyang Zhu, Ke Zhuang, Wei Chen, Kai Xu
Radiance fields including NeRFs and 3D Gaussians demonstrate great potential in high-fidelity rendering and scene reconstruction, while they require a substantial number of posed images as inputs. COLMAP is frequently employed for preprocessing to estimate poses, while it necessitates a large number of feature matches to operate effectively, and it struggles with scenes characterized by sparse features, large baselines between images, or a limited number of input images. We aim to tackle few-view NeRF reconstruction using only 3 to 6 unposed scene images. Traditional methods often use calibration boards but they are not common in images. We propose a novel idea of utilizing everyday objects, commonly found in both images and real life, as “pose probes”. The probe object is automatically segmented by SAM, whose shape is initialized from a cube. We apply a dual-branch volume rendering optimization (object NeRF and scene NeRF) to constrain the pose optimization and jointly refine the geometry. Specifically, object poses of two views are first estimated by PnP matching in an SDF representation, which serves as initial poses. PnP matching, requiring only a few features, is suitable for feature-sparse scenes. Additional views are incrementally incorporated to refine poses from preceding views. In experiments, PoseProbe achieves state-of-the-art performance in both pose estimation and novel view synthesis across multiple datasets. We demonstrate its effectiveness, particularly in few-view and large-baseline scenes where COLMAP struggles. In ablations, using different objects in a scene yields comparable performance. Our project page is available at: \href{https://zhirui-gao.github.io/PoseProbe.github.io/}{this https URL}
辐射场,包括NeRF和3D高斯场,在高保真渲染和场景重建方面表现出巨大的潜力,但它们需要大量的姿态图像作为输入。COLMAP常用于预处理以估计姿态,但需要大量的特征匹配才能有效运行,对于特征稀疏、图像间基线大或输入图像数量有限的场景,它处理起来比较吃力。我们的目标是仅使用3到6张未定位的场景图像解决少量视角的NeRF重建问题。传统方法通常使用校准板,但在图像中并不常见。我们提出了一种利用在图像和现实生活中都常见的日常对象作为“姿态探针”的新理念。探针对象通过SAM自动分割,其形状从立方体初始化。我们采用双分支体积渲染优化(对象NeRF和场景NeRF)来约束姿态优化并共同优化几何结构。具体来说,首先通过PnP匹配在SDF表示中估计两个视角的对象姿态,作为初始姿态。PnP匹配仅需要几个特征,适用于特征稀疏的场景。然后逐步增加其他视图,以从先前的视图优化姿态。在实验中,PoseProbe在多数据集上的姿态估计和新颖视图合成方面达到了最先进的性能。我们证明了其在少量视角和大基线场景中的有效性,这是COLMAP处理起来比较困难的。在实验中,使用场景中不同的对象可以获得相当的性能。我们的项目页面位于:此https URL。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了NeRF和3D高斯辐射场在高保真渲染和场景重建方面的潜力。针对COLMAP在特征稀疏场景、大基线间隔或输入图像数量有限的情况下表现不佳的问题,提出利用常见物体作为“姿态探针”(PoseProbe)进行姿态估计的新方法。通过自动分割、双分支体积渲染优化和姿态优化迭代改进,PoseProbe在多个数据集上实现了姿态估计和新颖视角合成的最佳性能,特别是在少视角和大基线场景中效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF和3D高斯辐射场在高保真渲染和场景重建中有很大潜力。
- COLMAP在特征稀疏、大基线间隔或少量输入图像的场景中表现不佳。
- 提出了利用常见物体作为“姿态探针”(PoseProbe)进行姿态估计的新方法。
- PoseProbe通过自动分割、双分支体积渲染优化和姿态优化迭代改进,实现了姿态估计和新颖视角合成的最佳性能。
- PoseProbe在少视角和大基线场景中的效果特别显著。
- 不同物体的使用在实验中产生了相当的性能。
点此查看论文截图