⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-08 更新
Rate-My-LoRA: Efficient and Adaptive Federated Model Tuning for Cardiac MRI Segmentation
Authors:Xiaoxiao He, Haizhou Shi, Ligong Han, Chaowei Tan, Bo Liu, Zihao Xu, Meng Ye, Leon Axel, Kang Li, Dimitris Metaxas
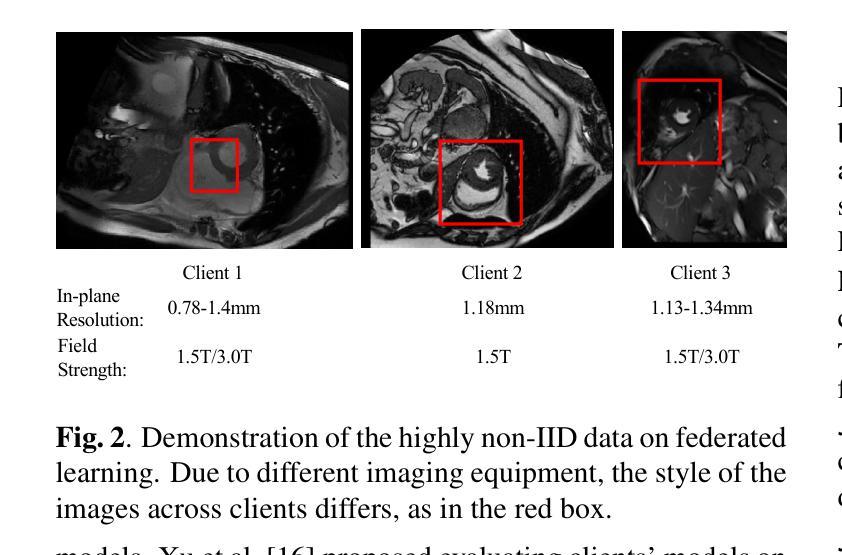
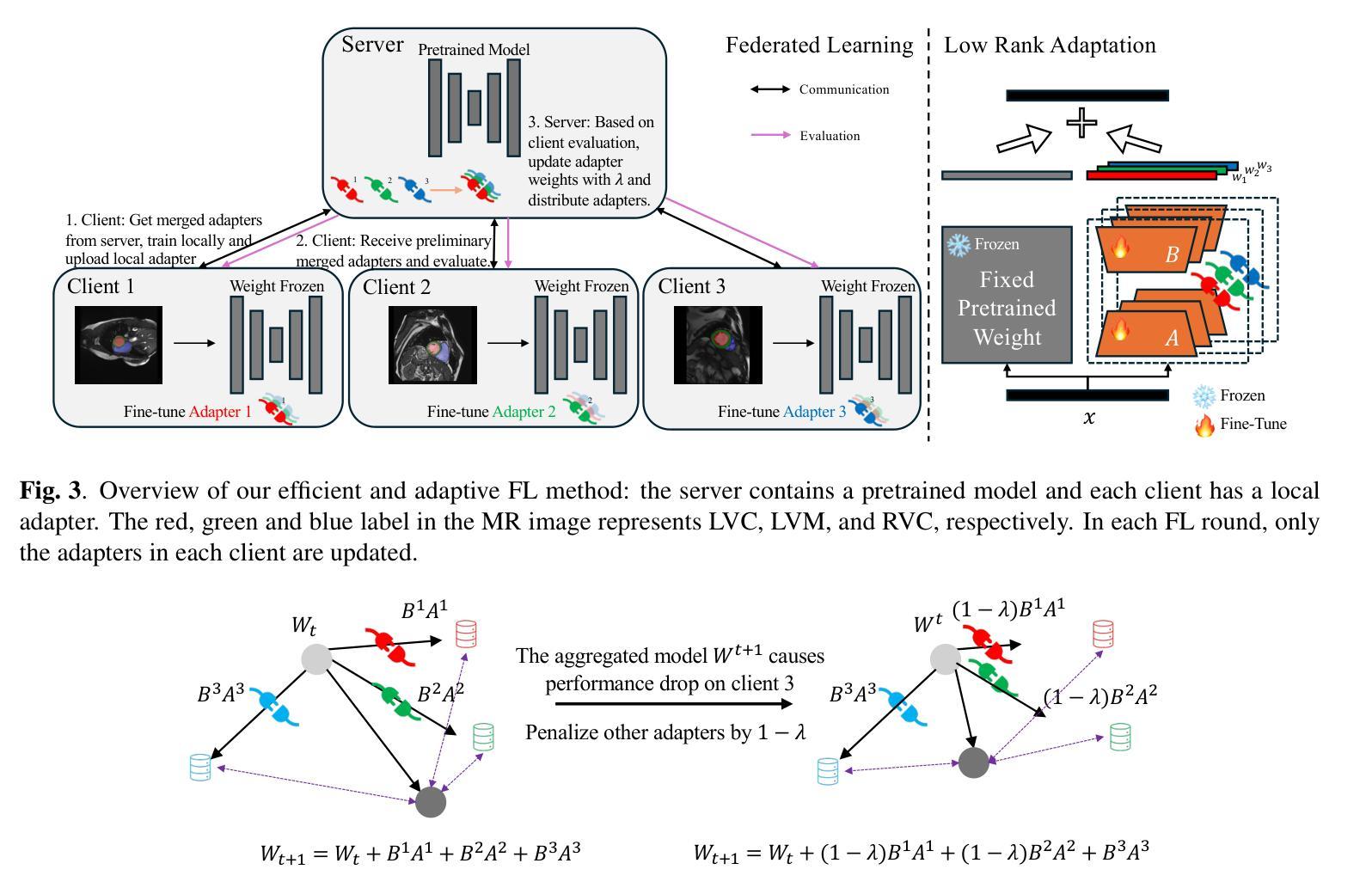
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) and cardiac dyssynchrony are major public health problems in the United States. Precise cardiac image segmentation is crucial for extracting quantitative measures that help categorize cardiac dyssynchrony. However, achieving high accuracy often depends on centralizing large datasets from different hospitals, which can be challenging due to privacy concerns. To solve this problem, Federated Learning (FL) is proposed to enable decentralized model training on such data without exchanging sensitive information. However, bandwidth limitations and data heterogeneity remain as significant challenges in conventional FL algorithms. In this paper, we propose a novel efficient and adaptive federate learning method for cardiac segmentation that improves model performance while reducing the bandwidth requirement. Our method leverages the low-rank adaptation (LoRA) to regularize model weight update and reduce communication overhead. We also propose a \mymethod{} aggregation technique to address data heterogeneity among clients. This technique adaptively penalizes the aggregated weights from different clients by comparing the validation accuracy in each client, allowing better generalization performance and fast local adaptation. In-client and cross-client evaluations on public cardiac MR datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method over other LoRA-based federate learning approaches.
心血管疾病(CVD)和心脏失同步是美国主要的公共卫生问题。精确的心脏图像分割对于提取定量指标,帮助分类心脏失同步至关重要。然而,实现高精确度通常取决于从不同医院集中大量数据集,这可能会因隐私担忧而具有挑战性。为了解决这一问题,提出了联邦学习(FL),能够在不交换敏感信息的情况下,对这类数据进行分散式模型训练。然而,带宽限制和数据异质性仍是传统联邦学习算法中的重大挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型高效自适应联邦学习方法,用于心脏分割,在降低带宽要求的同时提高模型性能。我们的方法利用低秩适应(LoRA)来规范模型权重更新并减少通信开销。我们还提出了一种名为【我的方法】的聚合技术来解决客户端之间的数据异质性。该技术通过比较每个客户端的验证精度来自适应地惩罚来自不同客户端的聚合权重,从而实现更好的泛化性能和快速本地适应。在公共心脏MR数据集上的客户端和跨客户端评估表明,我们的方法优于其他基于LoRA的联邦学习方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ISBI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种新型的高效自适应联邦学习方法,用于心脏图像分割,在不需要交换敏感信息的前提下,解决分散数据集中心脏疾病的模型训练问题。该方法利用低秩适应(LoRA)技术来优化模型权重更新并减少通信开销,并提出一种名为\mymethod{}的聚合技术来解决客户间数据异质性问题。在公共心脏MR数据集上的内部和外部评估显示,该方法优于其他基于LoRA的联邦学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- 心血管疾病和心脏失同步是美国主要的公共卫生问题,精确的心脏图像分割对于提取量化指标以分类心脏失同步至关重要。
- 联邦学习(FL)是解决分散数据集中心脏疾病模型训练的有效方法,无需交换敏感信息。
- 带宽限制和数据异质性是联邦学习中存在的挑战。
- 提出一种新型高效自适应联邦学习方法用于心脏分割,利用低秩适应(LoRA)技术优化模型权重更新并减少通信开销。
- 提出一种名为\mymethod{}的聚合技术来解决客户间数据异质性问题,实现更好的泛化性能和快速本地适应。
- 在公共心脏MR数据集上的评估显示,该方法优于其他基于LoRA的联邦学习方法。
点此查看论文截图

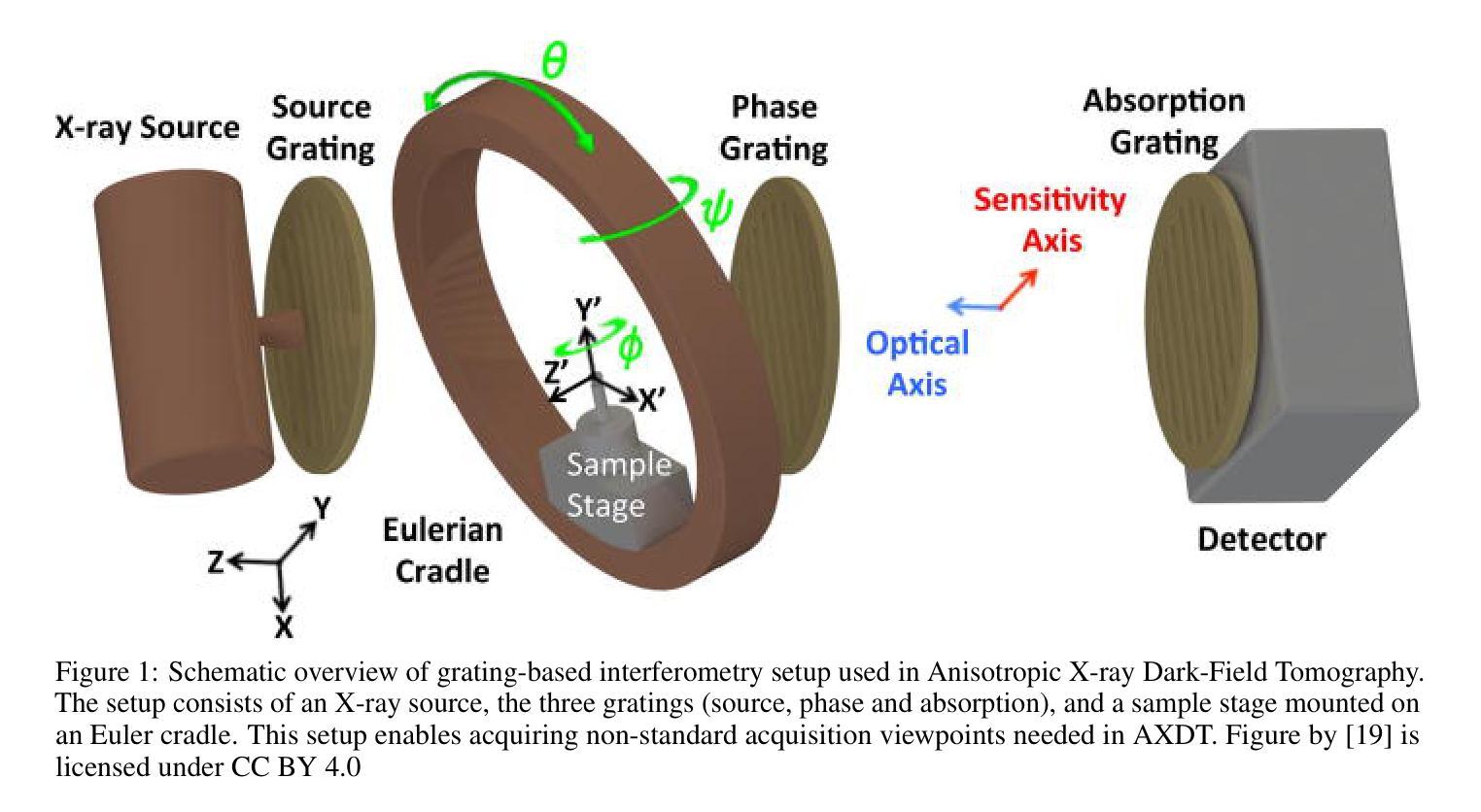
Statistical Reconstruction For Anisotropic X-ray Dark-Field Tomography
Authors:David Frank, Cederik Höfs, Tobias Lasser
Anisotropic X-ray Dark-Field Tomography (AXDT) is a novel imaging technology that enables the extraction of fiber structures on the micrometer scale, far smaller than standard X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) setups. Directional and structural information is relevant in medical diagnostics and material testing. Compared to existing solutions, AXDT could prove a viable alternative. Reconstruction methods in AXDT have so far been driven by practicality. Improved methods could make AXDT more accessible. We contribute numerically stable implementations and validation of advanced statistical reconstruction methods that incorporate the statistical noise behavior of the imaging system. We further provide a new statistical reconstruction formulation that retains the advanced noise assumptions of the imaging setup while being efficient and easy to optimize. Finally, we provide a detailed analysis of the optimization behavior for all models regarding AXDT. Our experiments show that statistical reconstruction outperforms the previously used model, and particularly the noise performance is superior. While the previously proposed statistical method is effective, it is computationally expensive, and our newly proposed formulation proves highly efficient with identical performance. Our theoretical analysis opens the possibility to new and more advanced reconstruction algorithms, which in turn enable future research in AXDT.
基于放射学的暗场层析成像术(AXDT)是一种新兴成像技术,能在微米尺度上提取纤维结构,远小于标准放射线计算机断层扫描(CT)装置。方向性和结构信息在医学诊断和材料测试中具有重要意义。与现有解决方案相比,AXDT可能成为可行替代方案。迄今为止,AXDT的重建方法一直受到实用性的驱动。改进的方法可以使AXDT更加易于获取。我们为先进的统计重建方法提供了数值稳定的实现和验证,这些方法结合了成像系统的统计噪声行为。我们还提供了一种新的统计重建公式,它在保留成像装置的高级噪声假设的同时,还具有高效且易于优化的特点。最后,我们对所有关于AXDT的模型优化行为进行了详细分析。实验表明,统计重建方法优于以前使用的模型,特别是在噪声性能方面表现更优越。虽然之前提出的统计方法有效,但其计算成本较高,而我们新提出的公式在性能相同的情况下具有高效率。我们的理论分析为新的更先进的重建算法打开了可能性,这将为AXDT的未来研究提供可能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
AXDT(各向异性X射线暗场层析成像技术)是一种新兴成像技术,能够在微米尺度上提取纤维结构,远小于标准X射线计算机断层扫描(CT)设备。该技术对于医学诊断和材料测试中的方向和结构信息至关重要。与现有解决方案相比,AXDT可能是一种可行的替代方案。本文介绍了AXDT的重建方法,这些方法以实用性为导向,但改进的方法可以使AXDT更加普及。本文提供了数值稳定的实现和对结合了成像系统噪声行为的先进统计重建方法的验证。此外,我们提供了一种新的统计重建公式,在保留成像设置的先进噪声假设的同时,具有高效性和易于优化的特点。最后,我们对所有关于AXDT的模型的优化行为进行了详细分析。实验表明,统计重建优于以前使用的方法,尤其是噪声性能更为优越。虽然之前提出的统计方法有效,但计算量大,我们新提出的公式效率高且性能相同。我们的理论分析可能为新的和更先进的重建算法打开可能性,这反过来又为AXDT的未来研究提供了机会。
Key Takeaways
- AXDT是一种新兴成像技术,可提取微米尺度的纤维结构信息。
- AXDT技术对于医学诊断和材料测试具有重要价值。
- 与现有成像技术相比,AXDT具备替代潜力。
- 本文提供了先进的统计重建方法和数值稳定的实现验证。
- 新提出的统计重建公式既高效又易于优化,同时考虑了成像系统的噪声行为。
- 统计重建方法显著优于之前使用的方法,特别是在噪声性能方面。
点此查看论文截图

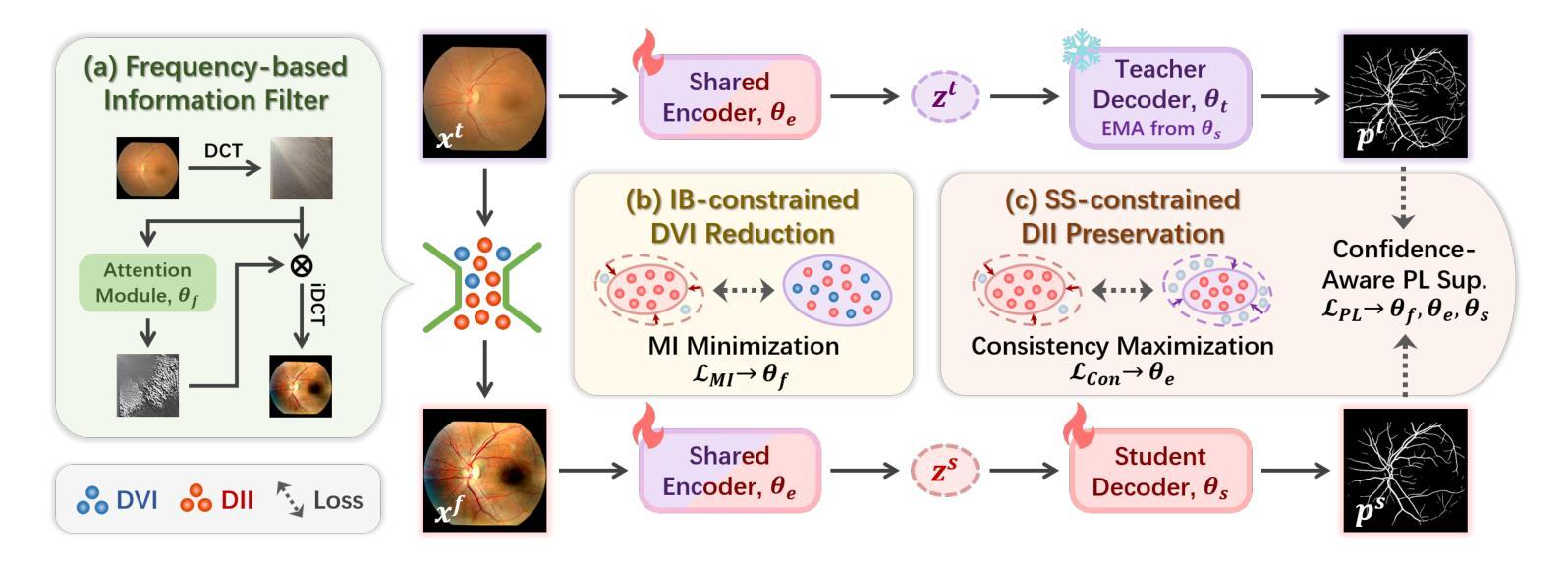
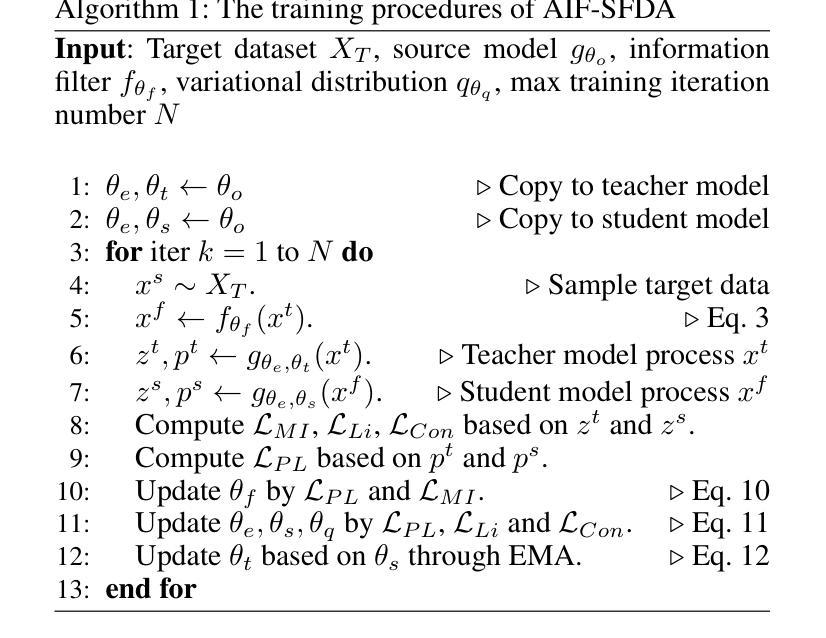
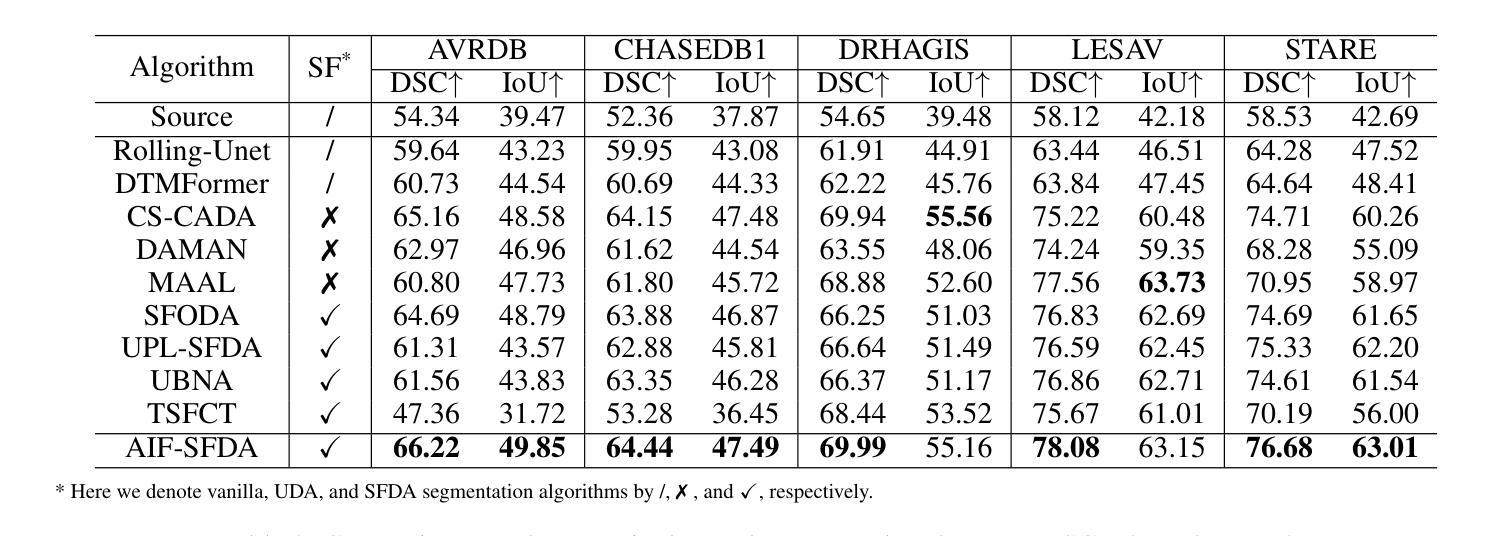
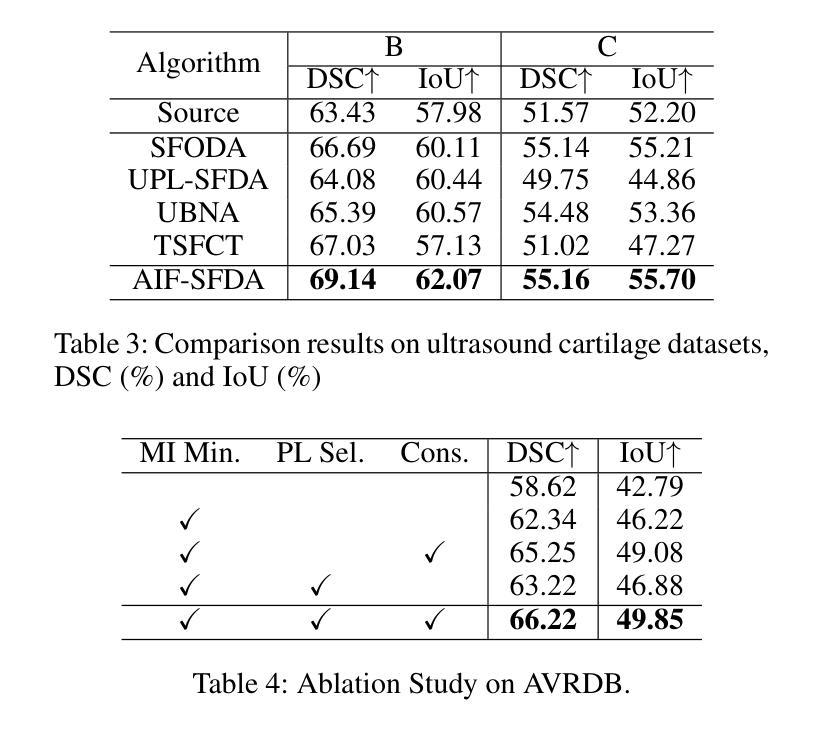
AIF-SFDA: Autonomous Information Filter-driven Source-Free Domain Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Haojin Li, Heng Li, Jianyu Chen, Rihan Zhong, Ke Niu, Huazhu Fu, Jiang Liu
Decoupling domain-variant information (DVI) from domain-invariant information (DII) serves as a prominent strategy for mitigating domain shifts in the practical implementation of deep learning algorithms. However, in medical settings, concerns surrounding data collection and privacy often restrict access to both training and test data, hindering the empirical decoupling of information by existing methods. To tackle this issue, we propose an Autonomous Information Filter-driven Source-free Domain Adaptation (AIF-SFDA) algorithm, which leverages a frequency-based learnable information filter to autonomously decouple DVI and DII. Information Bottleneck (IB) and Self-supervision (SS) are incorporated to optimize the learnable frequency filter. The IB governs the information flow within the filter to diminish redundant DVI, while SS preserves DII in alignment with the specific task and image modality. Thus, the autonomous information filter can overcome domain shifts relying solely on target data. A series of experiments covering various medical image modalities and segmentation tasks were conducted to demonstrate the benefits of AIF-SFDA through comparisons with leading algorithms and ablation studies. The code is available at https://github.com/JingHuaMan/AIF-SFDA.
将领域变体信息(DVI)从领域不变信息(DII)中解耦,是缓解深度学习算法实际应用中领域偏移问题的突出策略。然而,在医疗环境中,关于数据收集和隐私的担忧常常限制了对训练和测试数据的访问,阻碍了现有方法进行信息的实证解耦。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于自主信息滤波器的无源域自适应(AIF-SFDA)算法,该算法利用基于频率的可学习信息滤波器来自主解耦DVI和DII。信息瓶颈(IB)和自我监督(SS)被用来优化可学习的频率滤波器。IB控制滤波器内的信息流,以减少冗余的DVI,而SS则保留与特定任务和图像模态相符的DII。因此,自主信息滤波器可以仅依赖目标数据克服领域偏移问题。进行了一系列实验,涵盖多种医学图像模态和分割任务,通过与其他领先算法的比较和消融研究,证明了AIF-SFDA的优势。代码可在https://github.com/JingHuaMan/AIF-SFDA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages total (7 pages main text, 2 pages references), 6 figures, accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
医学领域在深度学习中存在领域偏移问题,为此现有方法尝试将领域变量信息(DVI)与领域不变信息(DII)分离。然而,在医疗环境中,数据收集和隐私担忧限制了训练和测试数据的访问,阻碍了现有方法的实证分离效果。我们提出了一种基于自主信息过滤器的无源域适应(AIF-SFDA)算法,利用基于频率的可学习信息过滤器自主分离DVI和DII。结合信息瓶颈(IB)和自我监督(SS)优化该过滤器。实验证明,该算法能有效应对不同医学图像模态和分割任务的领域偏移问题,与领先算法相比具有优势。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 领域偏移在医学深度学习中是一个挑战。
- 现有方法试图分离领域变量信息(DVI)和领域不变信息(DII)。
- 在医疗环境中,数据收集和隐私限制对实施这些方法构成挑战。
- 提出的AIF-SFDA算法使用自主信息过滤器来分离DVI和DII。
- 信息瓶颈(IB)和自我监督(SS)用于优化该过滤器的性能。
- AIF-SFDA算法通过一系列实验证明其在不同医学图像模态和分割任务中的优势。
- 该算法的代码已公开发布。
点此查看论文截图

Inverse receptive field attention for naturalistic image reconstruction from the brain
Authors:Lynn Le, Thirza Dado, Katja Seeliger, Paolo Papale, Antonio Lozano, Pieter Roelfsema, Yağmur Güçlütürk, Marcel van Gerven, Umut Güçlü
Visual perception in the brain largely depends on the organization of neuronal receptive fields. Although extensive research has delineated the coding principles of receptive fields, most studies have been constrained by their foundational assumptions. Moreover, while machine learning has successfully been used to reconstruct images from brain data, this approach faces significant challenges, including inherent feature biases in the model and the complexities of brain structure and function. In this study, we introduce an inverse receptive field attention (IRFA) model, designed to reconstruct naturalistic images from neurophysiological data in an end-to-end fashion. This approach aims to elucidate the tuning properties and representational transformations within the visual cortex. The IRFA model incorporates an attention mechanism that determines the inverse receptive field for each pixel, weighting neuronal responses across the visual field and feature spaces. This method allows for an examination of the dynamics of neuronal representations across stimuli in both spatial and feature dimensions. Our results show highly accurate reconstructions of naturalistic data, independent of pre-trained models. Notably, IRF models trained on macaque V1, V4, and IT regions yield remarkably consistent spatial receptive fields across different stimuli, while the features to which neuronal representations are selective exhibit significant variation. Additionally, we propose a data-driven method to explore representational clustering within various visual areas, further providing testable hypotheses.
大脑中的视觉感知在很大程度上依赖于神经元感受野的组织。尽管已经有很多研究阐述了感受野的编码原则,但大多数研究都受到了其基础假设的限制。此外,虽然机器学习已成功用于从脑数据中重建图像,但这种方法面临着重大挑战,包括模型中的固有特征偏见和脑结构和功能的复杂性。在研究中,我们引入了一种逆向感受野注意力(IRFA)模型,旨在以端到端的方式从神经生理数据中重建自然图像。这种方法旨在阐明视觉皮层内的调节属性和代表性转化。IRFA模型采用了一种注意力机制,用于确定每个像素的逆向感受野,对视觉场和特征空间中的神经元响应进行加权。这种方法可以研究刺激在空间和特征维度上神经元表示的动力学。我们的结果表明,无论是否使用预训练模型,都能高度准确地重建自然数据。值得注意的是,在猕猴V1、V4和IT区域训练的IRF模型在不同刺激下产生非常一致的空间感受野,而神经元表示所选择的特征则表现出显著的变化。此外,我们还提出了一种数据驱动的方法来探索各种视觉区域内的代表性聚类,为进一步提供可测试假设提供了依据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为逆感受野注意力(IRFA)的模型,该模型旨在以端到端的方式从神经生理数据中重建自然图像,以阐明视觉皮层的调节特性和表征转换。IRFA模型引入注意力机制,确定每个像素的逆感受野,对视觉场和特征空间的神经元反应进行加权。该方法能够研究神经元表征在刺激、空间和特征维度上的动态变化。
Key Takeaways
- 神经元感受野的组织对大脑中的视觉感知至关重要。
- 现有的研究在理解感受野编码原则方面已取得进展,但仍受到基础假设的限制。
- 机器学习已成功用于从脑数据中重建图像,但面临模型固有特征偏见和大脑结构功能复杂性等挑战。
- 提出的逆感受野注意力(IRFA)模型旨在以端到端的方式从神经生理数据中重建自然图像。
- IRFA模型通过注意力机制确定每个像素的逆感受野,考虑视觉场和特征空间的神经元反应。
- IRFA模型能够在空间和特征维度上研究神经元表征的动态变化。
点此查看论文截图

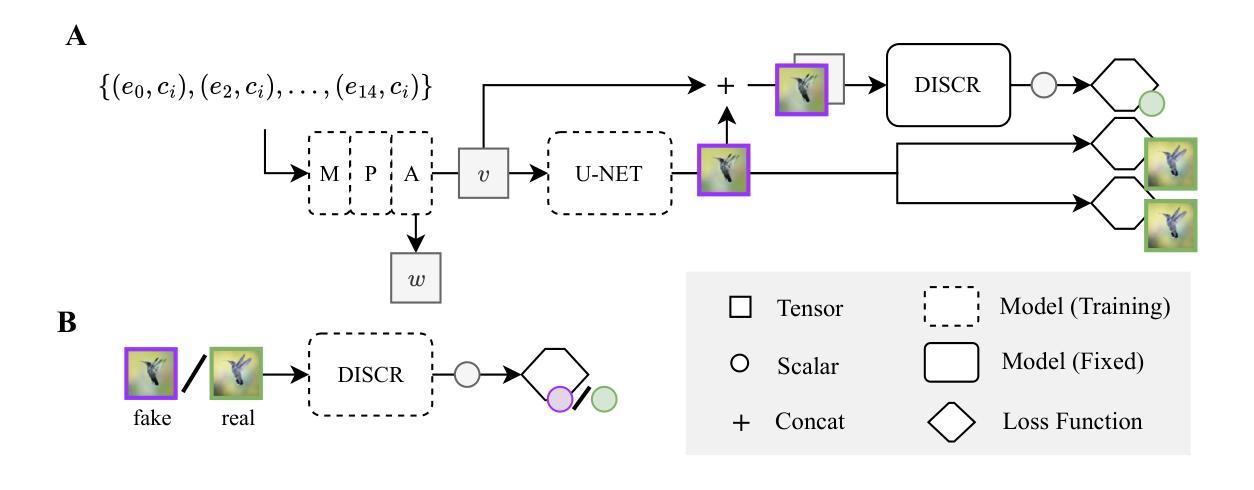
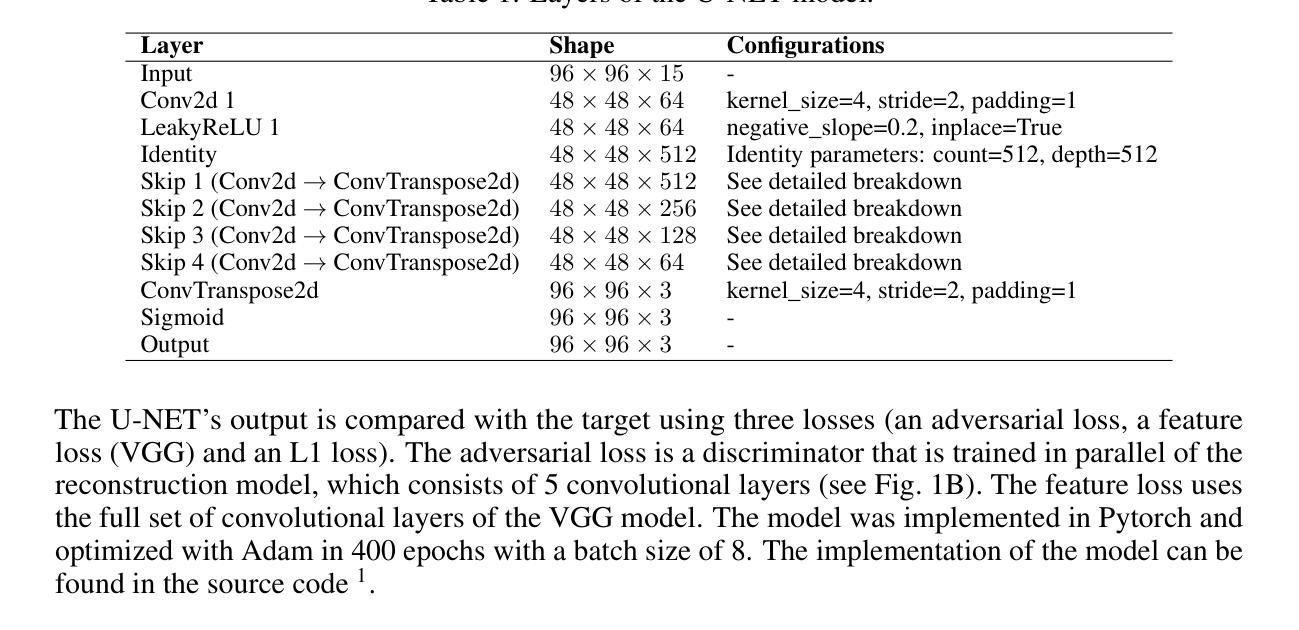
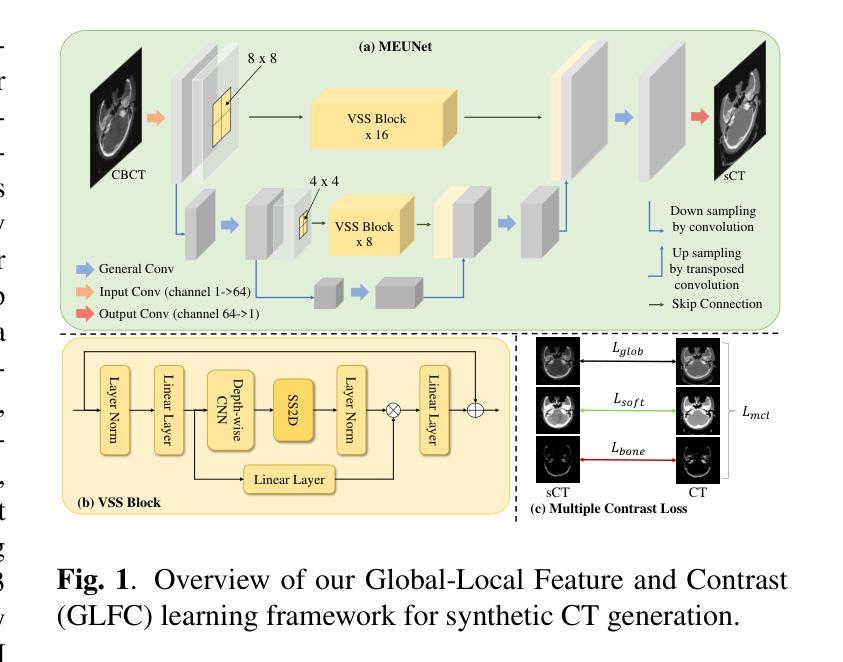
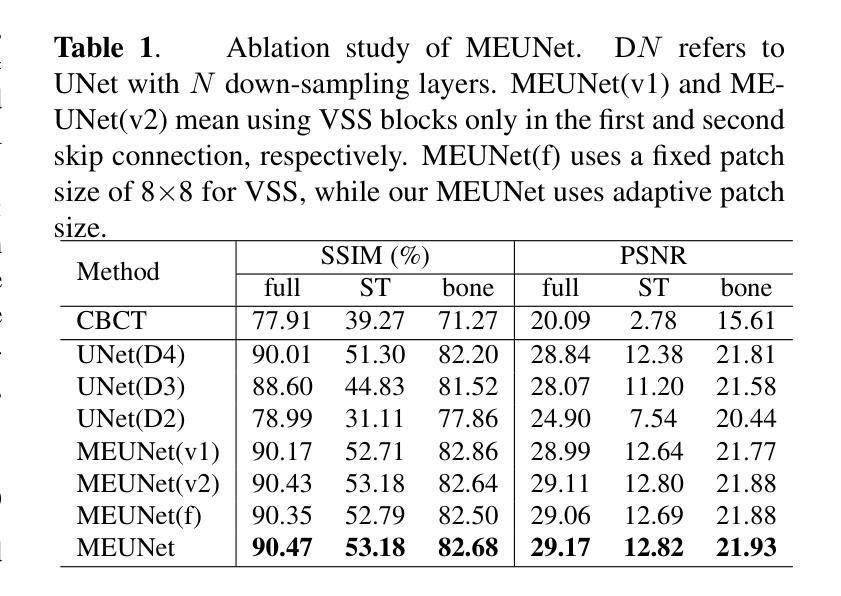
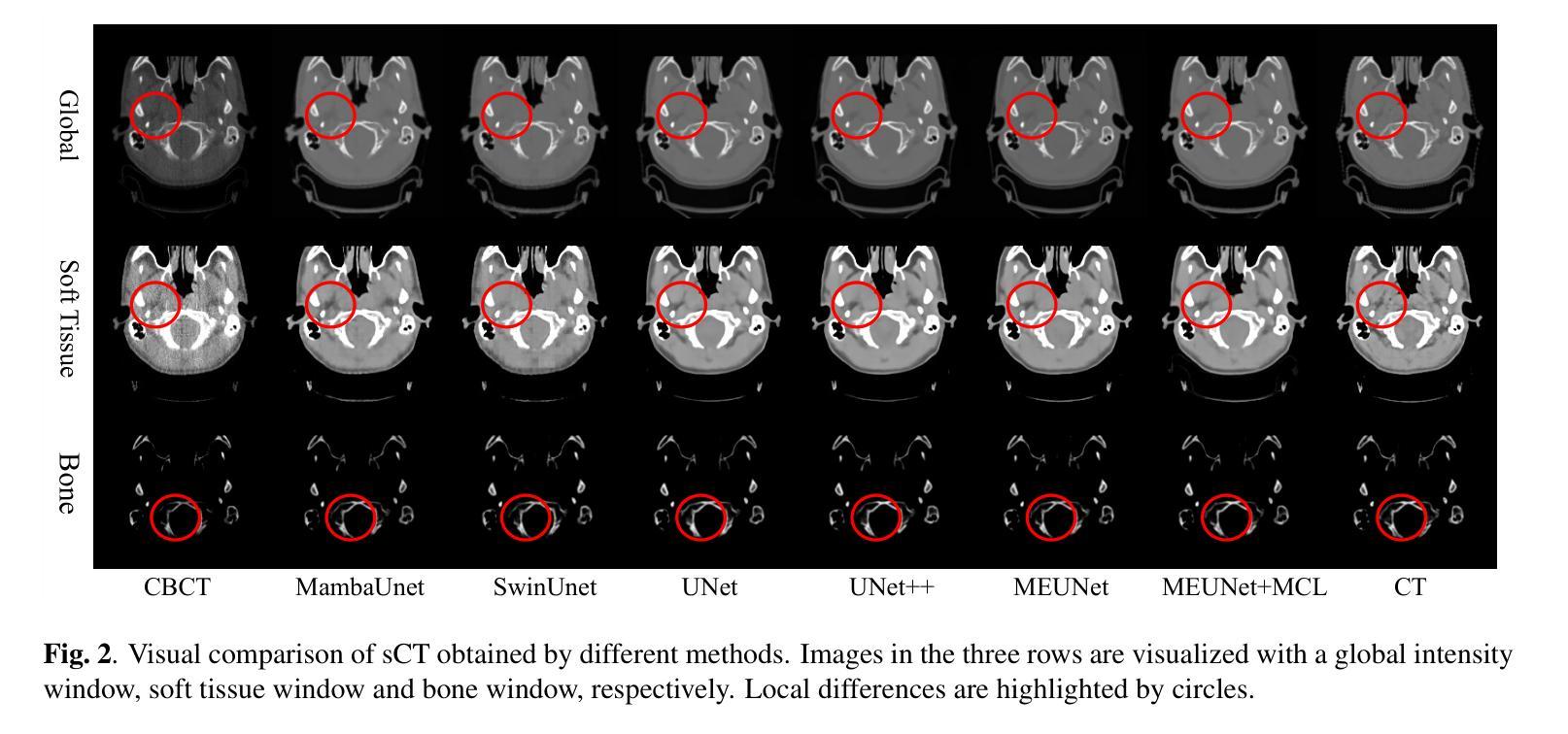
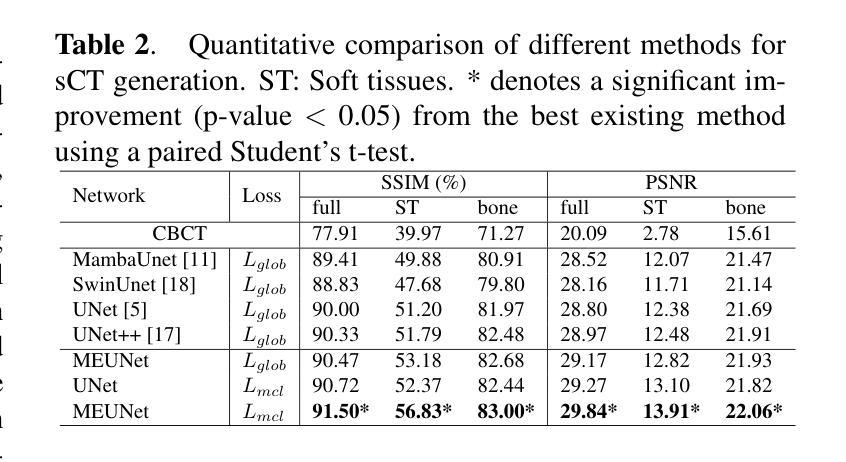
GLFC: Unified Global-Local Feature and Contrast Learning with Mamba-Enhanced UNet for Synthetic CT Generation from CBCT
Authors:Xianhao Zhou, Jianghao Wu, Huangxuan Zhao, Lei Chen, Shaoting Zhang, Guotai Wang, Guotai Wang
Generating synthetic Computed Tomography (CT) images from Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is desirable for improving the image quality of CBCT. Existing synthetic CT (sCT) generation methods using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Transformers often face difficulties in effectively capturing both global and local features and contrasts for high-quality sCT generation. In this work, we propose a Global-Local Feature and Contrast learning (GLFC) framework for sCT generation. First, a Mamba-Enhanced UNet (MEUNet) is introduced by integrating Mamba blocks into the skip connections of a high-resolution UNet for effective global and local feature learning. Second, we propose a Multiple Contrast Loss (MCL) that calculates synthetic loss at different intensity windows to improve quality for both soft tissues and bone regions. Experiments on the SynthRAD2023 dataset demonstrate that GLFC improved the SSIM of sCT from 77.91% to 91.50% compared with the original CBCT, and significantly outperformed several existing methods for sCT generation. The code is available at https://github.com/intelland/GLFC
从锥束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)生成合成计算机断层扫描(CT)图像是提高CBCT图像质量的理想选择。现有的使用卷积神经网络(CNN)和Transformer的合成CT(sCT)生成方法通常难以有效地捕获全局和局部特征以及对比度,以实现高质量的sCT生成。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于sCT生成的Global-Local特征和对比度学习(GLFC)框架。首先,通过在高分辨率UNet的跳过连接中集成Mamba块,引入了Mamba增强UNet(MEUNet),以实现有效的全局和局部特征学习。其次,我们提出了一种多重对比度损失(MCL),该损失在不同的强度窗口上计算合成损失,以提高软组织和骨区域的图像质量。在SynthRAD2023数据集上的实验表明,与原始CBCT相比,GLFC将sCT的SSIM从77.91%提高到91.50%,并且在sCT生成方面显著优于几种现有方法。代码可在https://github.com/intelland/GLFC找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ISBI2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于全球本地特征与对比度学习(GLFC)的医学图像合成方法。通过使用集成Mamba块的增强UNet(MEUNet)模型以及多重对比度损失(MCL),实现了在合成CT图像中对全局和局部特征的捕捉以及对不同组织对比度的优化。实验结果表明,GLFC方法显著提高了合成CT图像的质量,与原始CBCT相比,SSIM指数从77.91%提高到91.50%,并优于其他几种现有的合成CT生成方法。代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于全球本地特征与对比度学习(GLFC)的医学图像合成框架。
- 使用集成Mamba块的增强UNet(MEUNet)模型进行全局和局部特征学习。
- 通过多重对比度损失(MCL)优化了图像的质量,特别是软组织和骨骼区域的对比度。
- 实验结果展示了GLFC方法在合成CT图像生成方面的优越性,显著提高了SSIM指数。
- 该方法相较于其他现有方法表现更优。
- 公开了相关代码以便进一步研究和应用。
点此查看论文截图

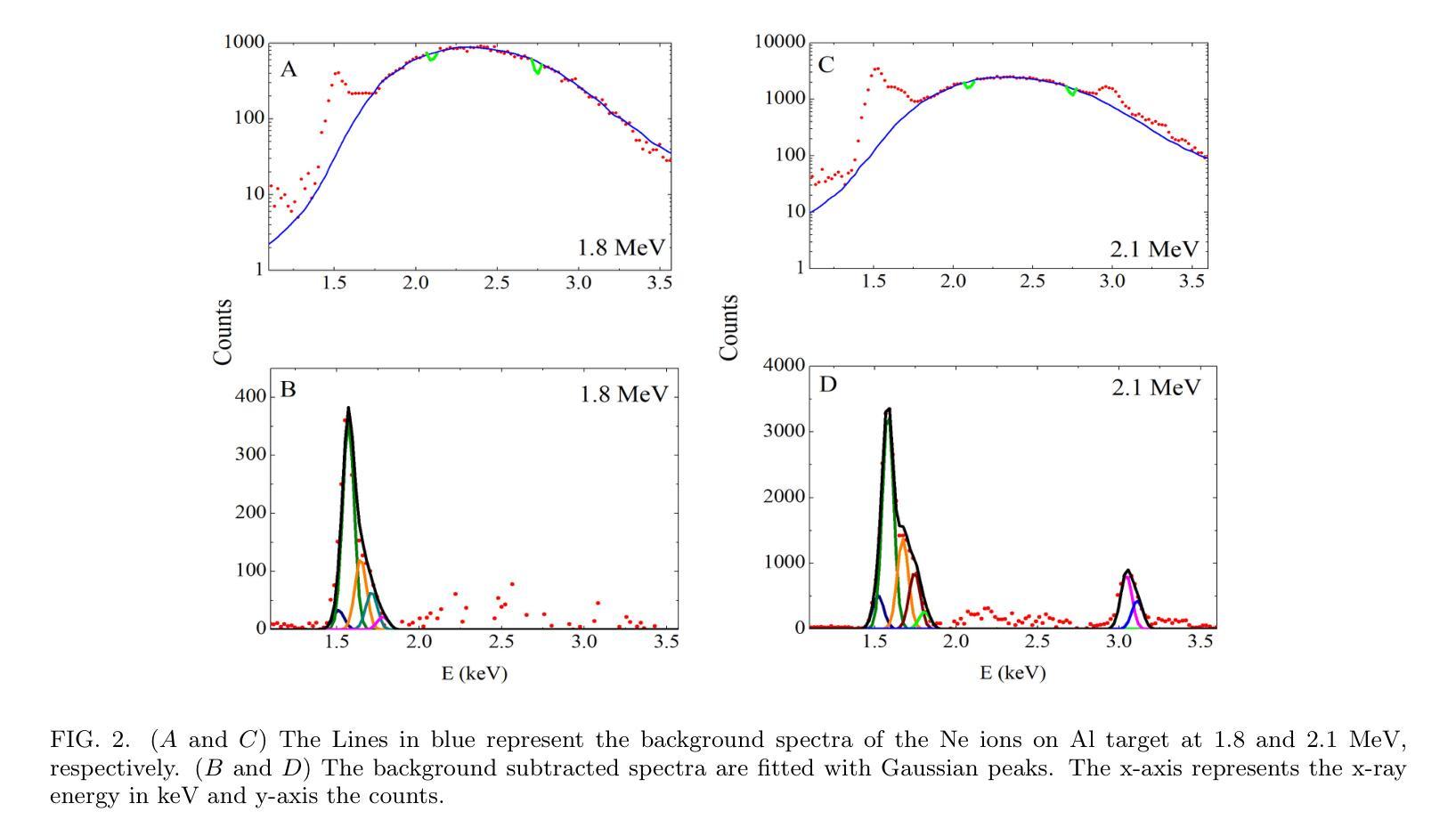
Two-electron one-photon process in collision of 1.8-2.1 MeV neon on aluminum
Authors:Shashank Singh, Narendra Kumar, Soumya Chatterjee, Deepak Swami, Alok Kumar Singh Jha, Mumtaz Oswal, K. P. Singh, T. Nandi
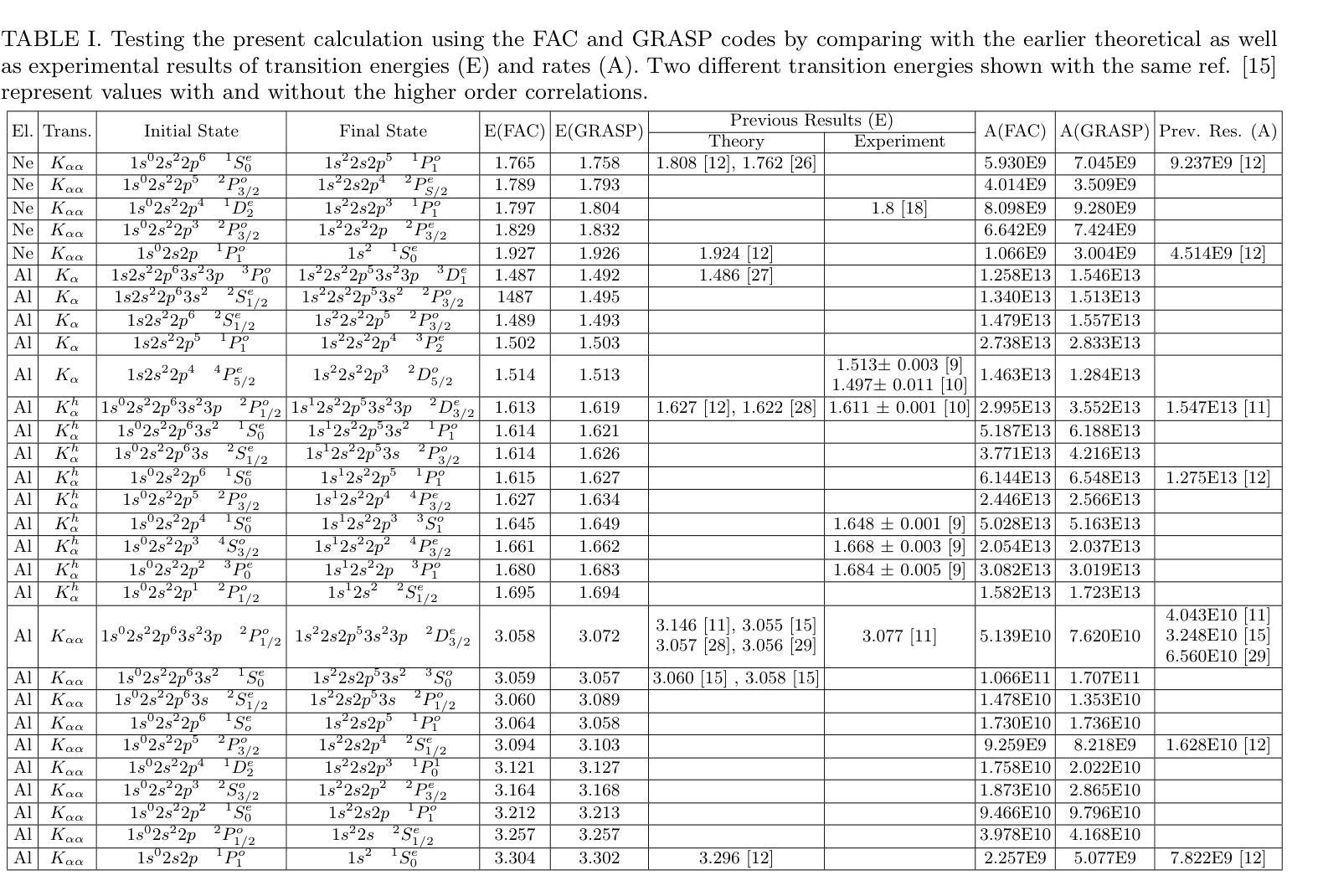
X-ray emissions due to the two-electron one-photon (TEOP) process in the neon projectile and aluminum target have been successfully observed for the beam energy window of 1.8-2.1 MeV. Experimental TEOP transition energies have been compared with theoretical predictions of flexible atomic structure code (FAC) and General-purpose Relativistic Atomic Structure (GRASP) package. Present results have been verified with reported theoretical and experimental values. Transition rates of the TEOP transitions have also been studied using the said codes. The observed lines have been assigned when the measured transition energies are in good agreement with the theoretical values. Such assignments have further been validated with the good agreements between the experimental and theoretical transition rates. Note that only the TEOP lines in projectile ions are seen with 1.8 MeV energy. In contrast, the TEOP lines in target ions are also observed well with 2.1 MeV energy. Thus, this study sheds useful light on the excitation mechanism of the TEOP processes in the low energy regimes.
在能量窗口为1.8-2.1MeV的束流中,成功观察到由于氖射弹和铝靶中的两电子单光子(TEOP)过程产生的X射线发射。实验中的TEOP跃迁能量与灵活原子结构代码(FAC)和通用相对论原子结构(GRASP)软件包的理论预测进行了比较。目前的结果已经与报告的理论值和实验值进行了验证。还使用上述代码研究了TEOP跃迁的跃迁率。当测量的跃迁能量与理论值一致时,已观察到这些谱线。这种分配已通过实验和理论跃迁率之间的良好协议进一步得到验证。值得注意的是,只有1.8MeV能量下的射弹离子才会出现TEOP线。相比之下,目标离子在2.1MeV能量下的TEOP线也被很好地观察到。因此,这项研究对于了解低能状态下的TEOP过程的激发机制具有积极意义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 2 figures, 3 tables. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2201.02566
Summary
该项目成功观察到电子数量为两个,光子为一个(TEOP过程)在氖原子项目和铝靶中的X射线辐射现象。实验涉及的束能窗口为1.8-2.1MeV。实验中的TEOP跃迁能量与柔性原子结构代码(FAC)和通用相对论原子结构(GRASP)软件包的理论预测值进行了比较验证。此外,还研究了TEOP跃迁的跃迁速率。当观察到的谱线与理论值一致时,已被成功分配。同时证实其正确性,发现实验的跃迁速率与理论值相符。值得注意的是,在能量为1.8MeV时,仅在项目离子中观察到TEOP线;而在能量为2.1MeV时,目标离子中也观察到TEOP线。此研究有助于理解低能态下的TEOP过程的激发机制。
Key Takeaways
以下是本次实验的主要发现和要点总结:
- X射线辐射现象成功观察到电子数量为两个、光子为一个(TEOP过程)在氖原子项目和铝靶中的反应。
- 实验涉及的束能窗口为特定的能量范围,即1.8-2.1MeV之间。这是对特定的能段进行观察的主要能量区间,证明此次观测有效性在这个范围之内给出了直接的线索,对该机制的进一步研究有重要意义。
- 实验中的TEOP跃迁能量与FAC和GRASP软件包的理论预测值进行了比较验证,证明了实验结果的有效性及理论的准确性。实验值与理论预测的一致是后续研究的良好依据和基础。这对更深入了解电子跃迁机制有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图



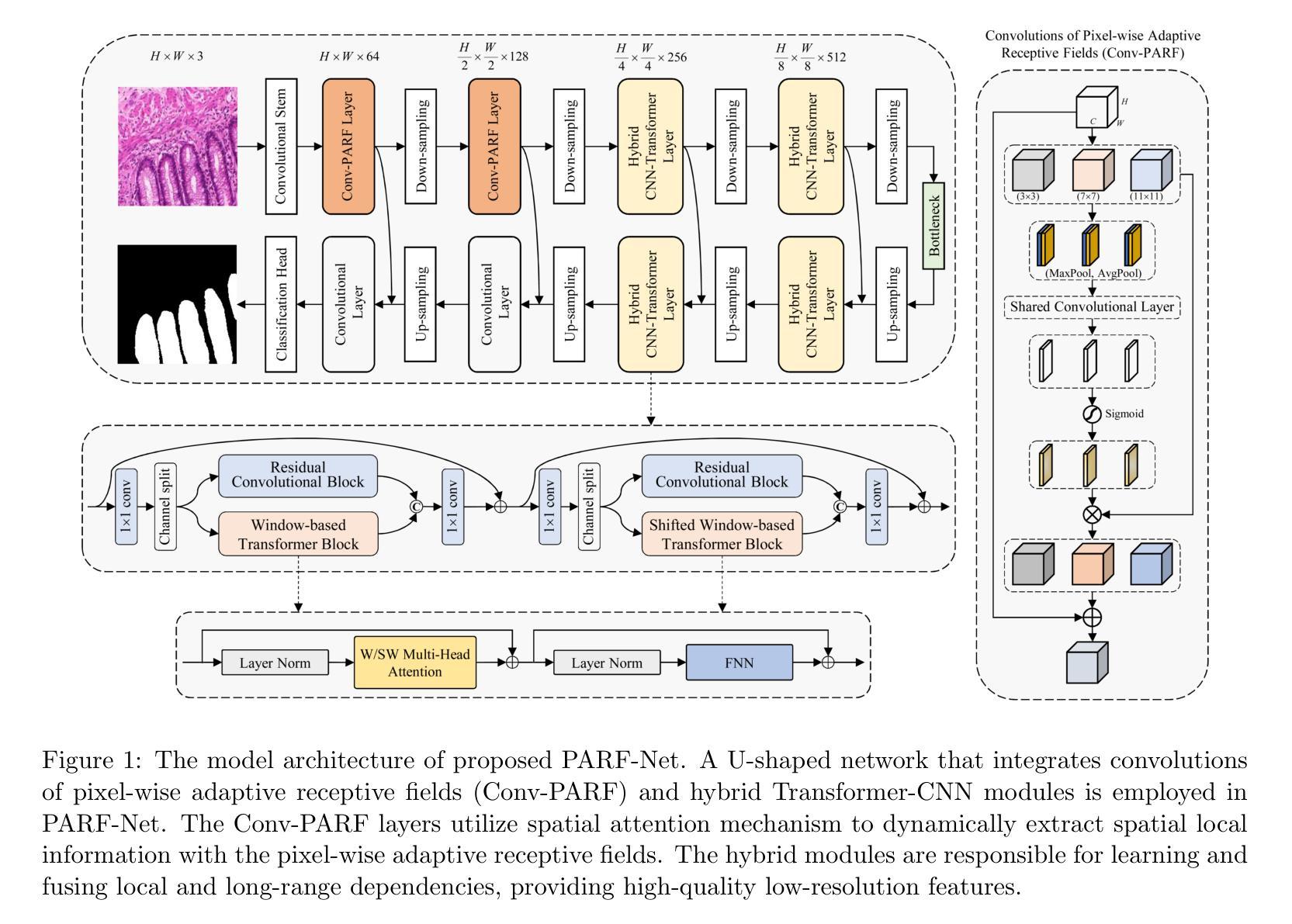
PARF-Net: integrating pixel-wise adaptive receptive fields into hybrid Transformer-CNN network for medical image segmentation
Authors:Xu Ma, Mengsheng Chen, Junhui Zhang, Lijuan Song, Fang Du, Zhenhua Yu
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) excel in local feature extraction while Transformers are superior in processing global semantic information. By leveraging the strengths of both, hybrid Transformer-CNN networks have become the major architectures in medical image segmentation tasks. However, existing hybrid methods still suffer deficient learning of local semantic features due to the fixed receptive fields of convolutions, and also fall short in effectively integrating local and long-range dependencies. To address these issues, we develop a new method PARF-Net to integrate convolutions of Pixel-wise Adaptive Receptive Fields (Conv-PARF) into hybrid Network for medical image segmentation. The Conv-PARF is introduced to cope with inter-pixel semantic differences and dynamically adjust convolutional receptive fields for each pixel, thus providing distinguishable features to disentangle the lesions with varying shapes and scales from the background. The features derived from the Conv-PARF layers are further processed using hybrid Transformer-CNN blocks under a lightweight manner, to effectively capture local and long-range dependencies, thus boosting the segmentation performance. By assessing PARF-Net on four widely used medical image datasets including MoNuSeg, GlaS, DSB2018 and multi-organ Synapse, we showcase the advantages of our method over the state-of-the-arts. For instance, PARF-Net achieves 84.27% mean Dice on the Synapse dataset, surpassing existing methods by a large margin.
卷积神经网络(CNNs)在局部特征提取方面表现出色,而Transformer在处理全局语义信息方面更擅长。通过结合两者的优势,混合Transformer-CNN网络已成为医学图像分割任务中的主要架构。然而,现有的混合方法仍然存在一些缺陷,由于卷积的固定感受野,其对局部语义特征的学习不足,并且在有效整合局部和长距离依赖方面也存在不足。为了解决这些问题,我们开发了一种新的方法PARF-Net,它将像素级自适应感受野(Conv-PARF)的卷积融入到混合网络中进行医学图像分割。Conv-PARF的引入是为了应对像素间语义差异,并动态调整每个像素的卷积感受野,从而为不同形状和尺度的病变提供可识别的特征,将其与背景分离。从Conv-PARF层派生的特征进一步使用混合Transformer-CNN块以轻便的方式进行处理,以有效地捕获局部和长距离依赖关系,从而提高分割性能。通过在四个广泛使用的医学图像数据集MoNuSeg、GlaS、DSB2018和多器官Synapse上评估PARF-Net,我们展示了我们的方法相较于最新技术所具有的优势。例如,在Synapse数据集上,PARF-Net的平均Dice系数为84.27%,大大超越了现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
卷积神经网络(CNN)擅长局部特征提取,而Transformer在处理全局语义信息方面表现出卓越性能。通过结合两者的优势,混合Transformer-CNN网络已成为医学图像分割任务中的主要架构。然而,现有的混合方法仍然因为卷积的固定感受野而存在着对局部语义特征学习不足的问题,并且在整合局部和长距离依赖方面也存在不足。为解决这些问题,我们开发了一种新的方法PARF-Net,将像素级自适应感受野(Conv-PARF)的卷积融入医学图像分割的混合网络。Conv-PARF被引入以处理像素间的语义差异,并动态调整每个像素的卷积感受野,从而提供可区分特征来区分不同形状和尺度的病变与背景。从Conv-PARF层派生的特征进一步使用混合Transformer-CNN块以轻便的方式处理,以有效地捕获局部和长距离依赖关系,从而提高分割性能。在四个广泛使用的医学图像数据集上评估PARF-Net,包括MoNuSeg、GlaS、DSB2018和多器官Synapse数据集,展示了我们的方法相较于最新技术的优势。例如,在Synapse数据集上,PARF-Net的平均Dice系数为84.27%,大大超过了现有方法。
关键见解
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)和Transformer在医学图像分割中各有优势,CNN擅长局部特征提取,而Transformer擅长处理全局语义信息。
- 现有混合方法存在对局部语义特征学习不足以及整合局部和长距离依赖关系不足的问题。
- 新方法PARF-Net通过引入像素级自适应感受野(Conv-PARF)的卷积来解决这些问题。
- Conv-PARF能够处理像素间的语义差异,并动态调整卷积感受野,以提供可区分特征。
- PARF-Net使用混合Transformer-CNN块以轻便方式处理特征,有效捕获局部和长距离依赖关系。
- PARF-Net在多个医学图像数据集上进行了评估,并展示了相较于最新技术的显著优势。
点此查看论文截图

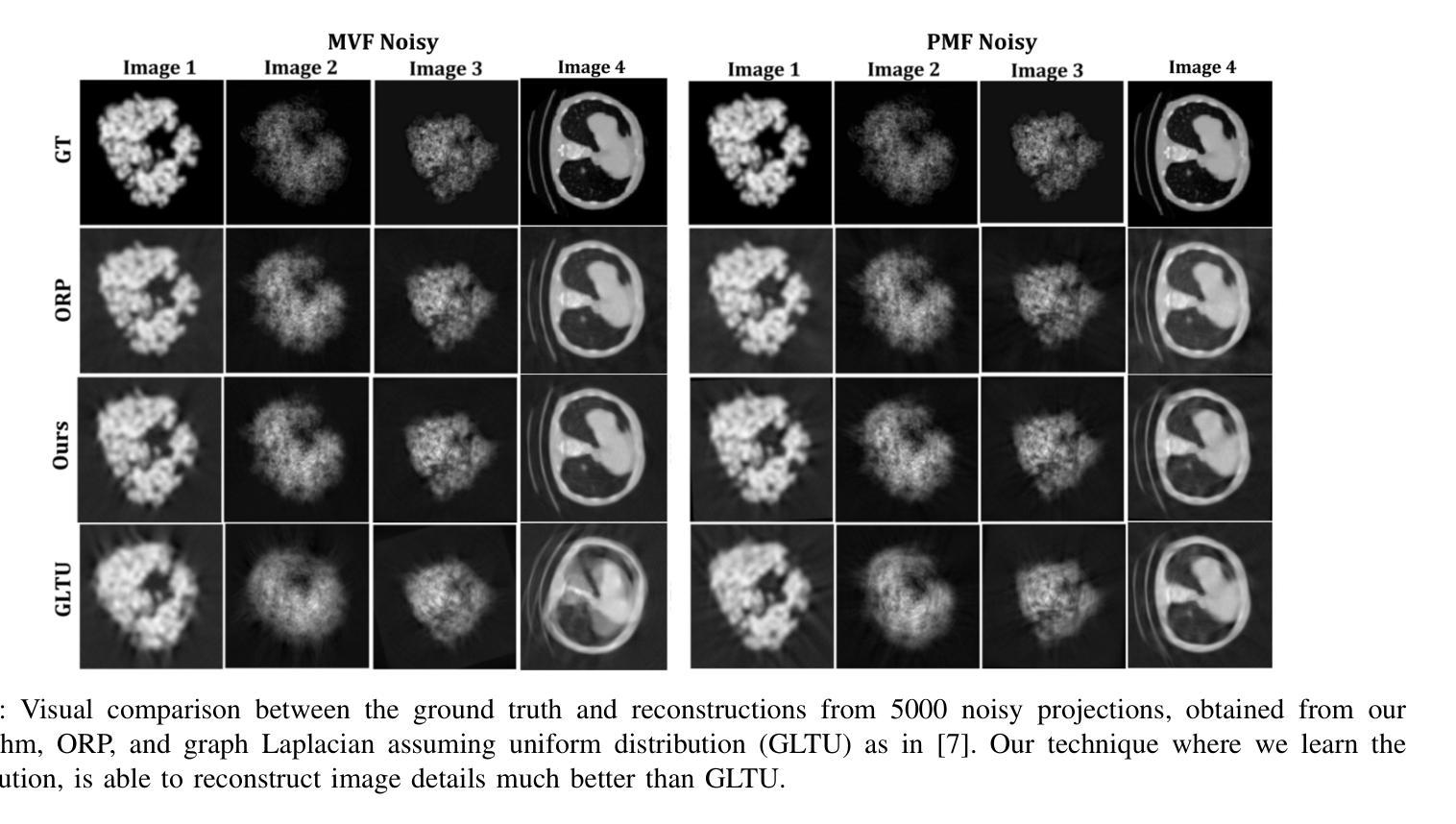
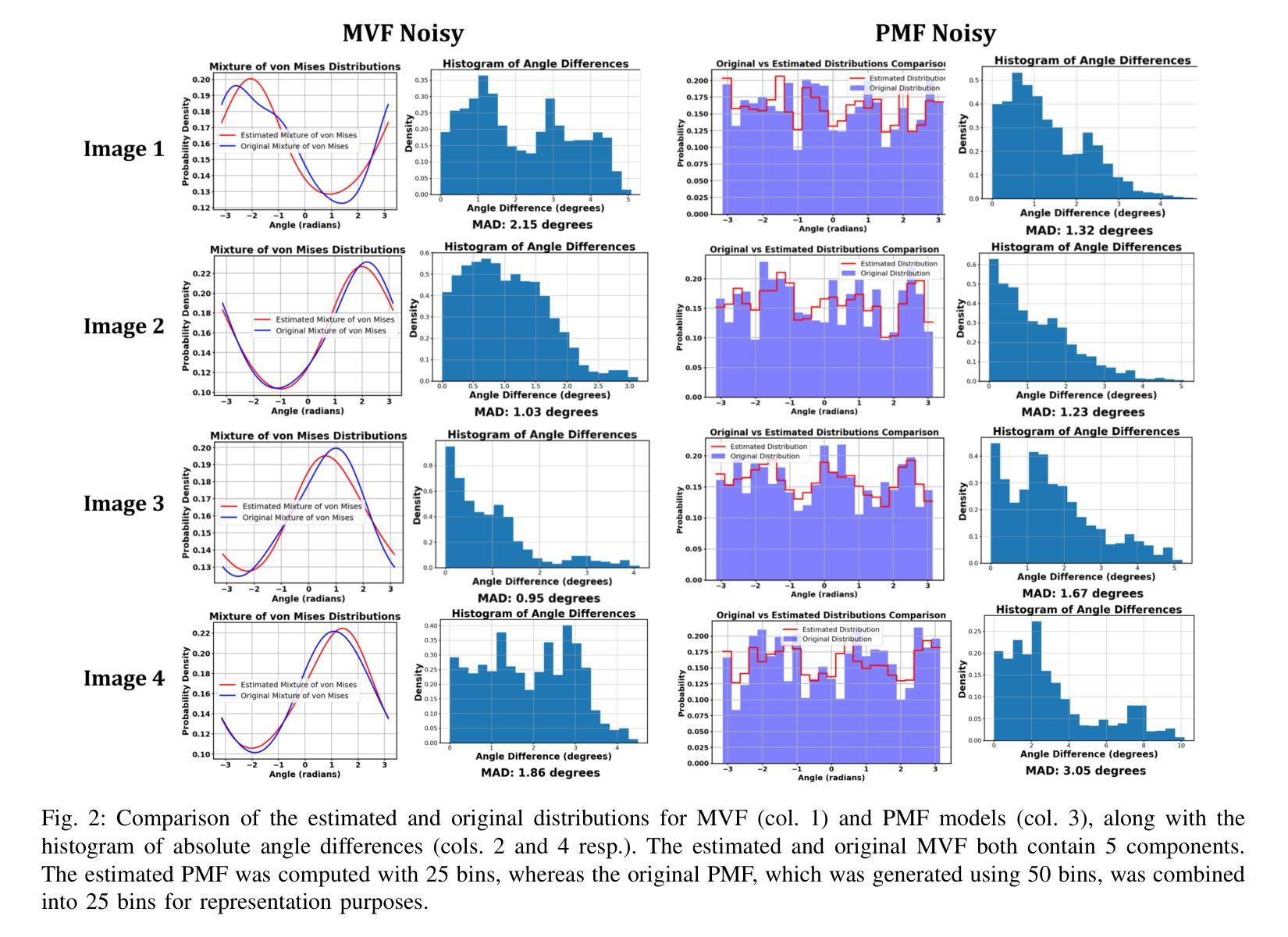
Two-Dimensional Unknown View Tomography from Unknown Angle Distributions
Authors:Kaishva Chintan Shah, Karthik S. Gurumoorthy, Ajit Rajwade
This study presents a technique for 2D tomography under unknown viewing angles when the distribution of the viewing angles is also unknown. Unknown view tomography (UVT) is a problem encountered in cryo-electron microscopy and in the geometric calibration of CT systems. There exists a moderate-sized literature on the 2D UVT problem, but most existing 2D UVT algorithms assume knowledge of the angle distribution which is not available usually. Our proposed methodology formulates the problem as an optimization task based on cross-validation error, to estimate the angle distribution jointly with the underlying 2D structure in an alternating fashion. We explore the algorithm’s capabilities for the case of two probability distribution models: a semi-parametric mixture of von Mises densities and a probability mass function model. We evaluate our algorithm’s performance under noisy projections using a PCA-based denoising technique and Graph Laplacian Tomography (GLT) driven by order statistics of the estimated distribution, to ensure near-perfect ordering, and compare our algorithm to intuitive baselines.
本研究介绍了一种在未知视角和视角分布未知的情况下进行二维层析成像的技术。未知视角层析成像(UVT)是冷冻电子显微镜和计算机断层扫描系统几何校准中遇到的问题。关于二维UVT问题的文献数量适中,但大多数现有的二维UVT算法都假设已知角度分布,这在现实中通常无法获得。我们提出的方法将问题表述为一个基于交叉验证误差的优化任务,以交替方式估计角度分布和潜在的二维结构。我们探索了两种概率分布模型下该算法的能力:半参数的冯米塞斯密度混合模型和概率质量函数模型。我们使用基于主成分分析的去噪技术和由估计分布的排序统计驱动的图形拉普拉斯层析成像(GLT),确保近乎完美的排序,在噪声投影下评估我们的算法性能,并将其与直观基线进行比较。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP) 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种解决二维未知视角层析成像技术的方法,当视角分布未知时尤为适用。该技术主要应用于冷冻电子显微镜和计算机断层扫描系统的几何校准等领域。尽管关于二维未知视角层析成像问题的研究已有一定规模,但大多数现有算法都假设已知角度分布,这在现实中通常无法获得。本研究将问题建模为基于交叉验证误差的优化任务,旨在交替估计角度分布和潜在的二维结构。研究探讨了两种概率分布模型下的算法能力:半参数混合冯米塞斯密度和概率质量函数模型。通过主成分分析去噪技术和基于分布估计顺序统计的图拉普拉斯层析成像技术评估算法性能,并将其与直观基线进行比较。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种解决二维未知视角层析成像(UVT)的新技术。
- UVT问题是冷冻电子显微镜和CT系统几何校准中的常见问题。
- 现有大多数UVT算法假设已知角度分布,但这在现实中通常无法获得。
- 本研究将UVT问题建模为优化任务,旨在估计角度分布和潜在二维结构。
- 研究涉及两种概率分布模型:半参数混合冯米塞斯密度和概率质量函数模型。
- 通过PCA去噪技术和图拉普拉斯层析成像技术评估算法性能。
点此查看论文截图

COph100: A comprehensive fundus image registration dataset from infants constituting the “RIDIRP” database
Authors:Yan Hu, Mingdao Gong, Zhongxi Qiu, Jiabao Liu, Hongli Shen, Mingzhen Yuan, Xiaoqing Zhang, Heng Li, Hai Lu, Jiang Liu
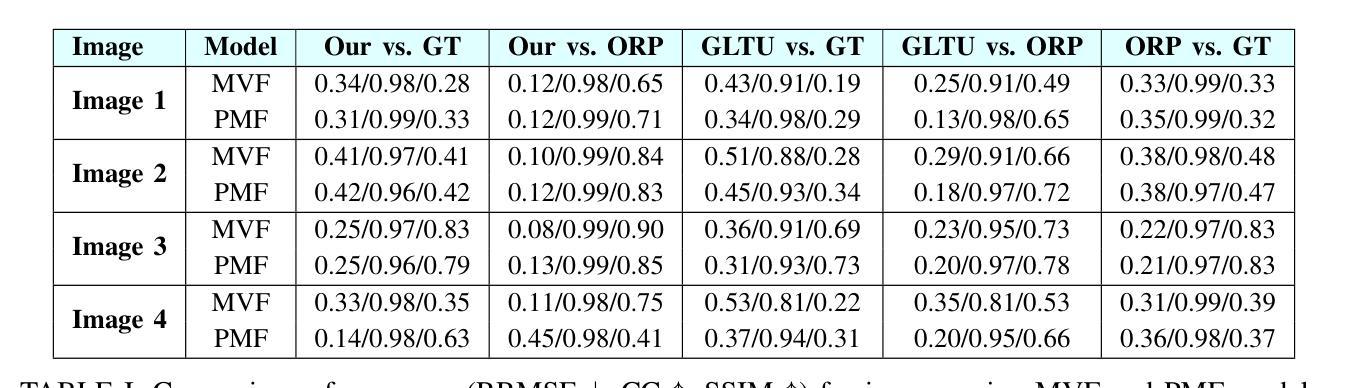
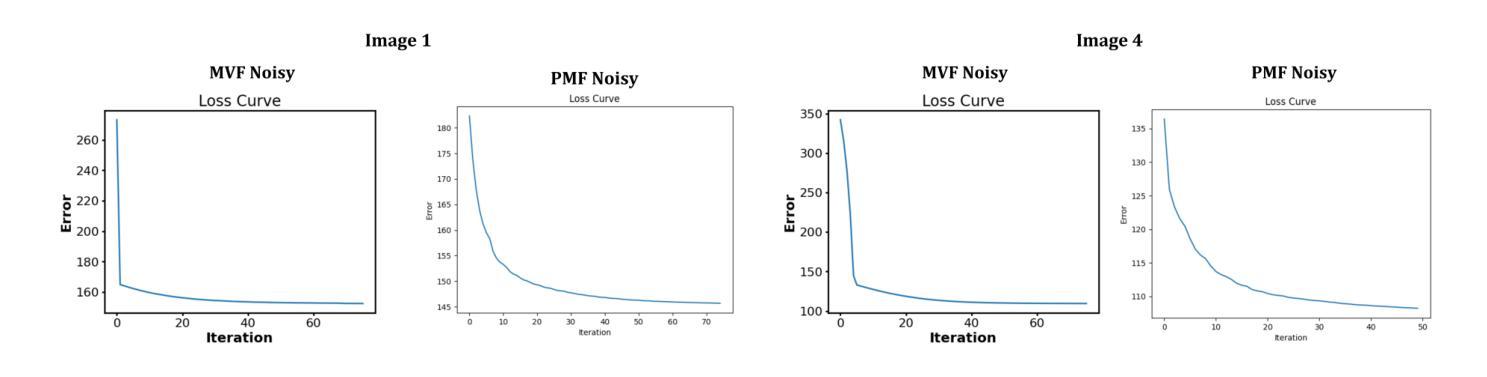
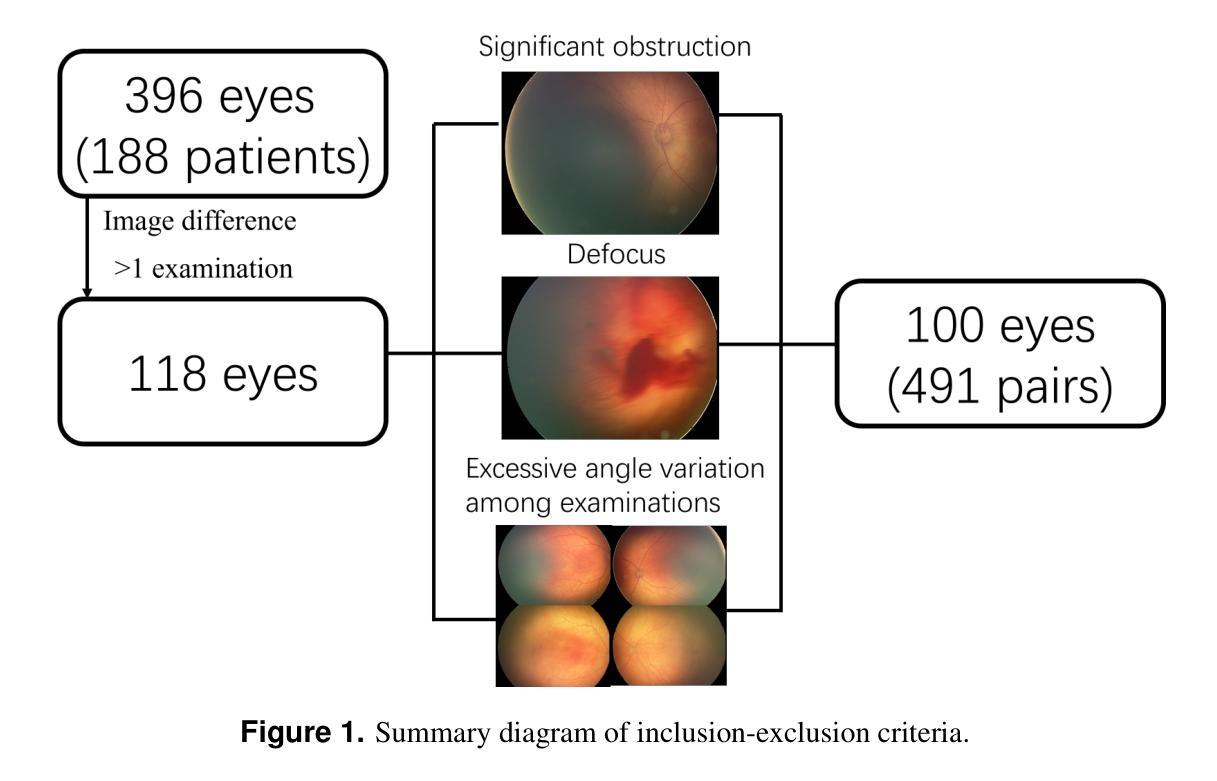
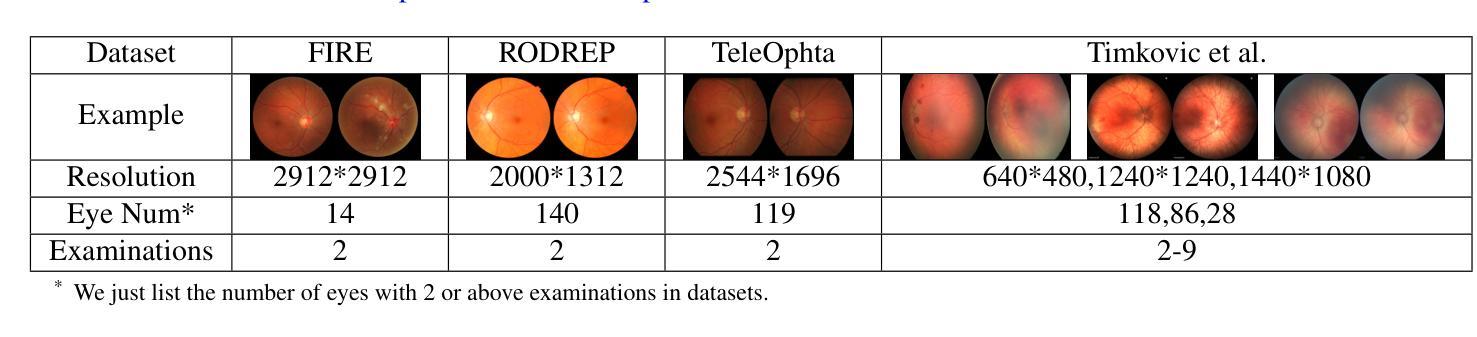
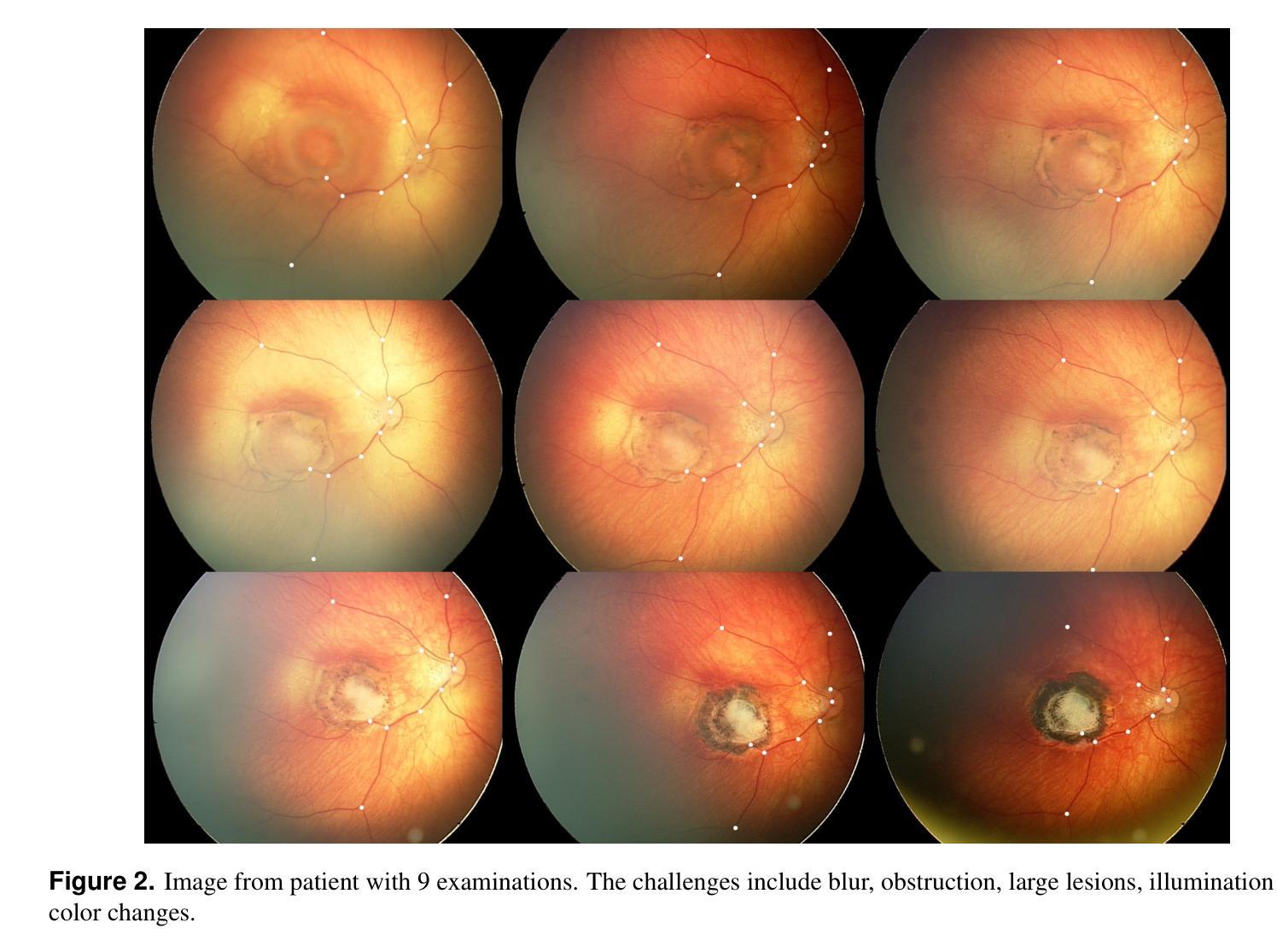
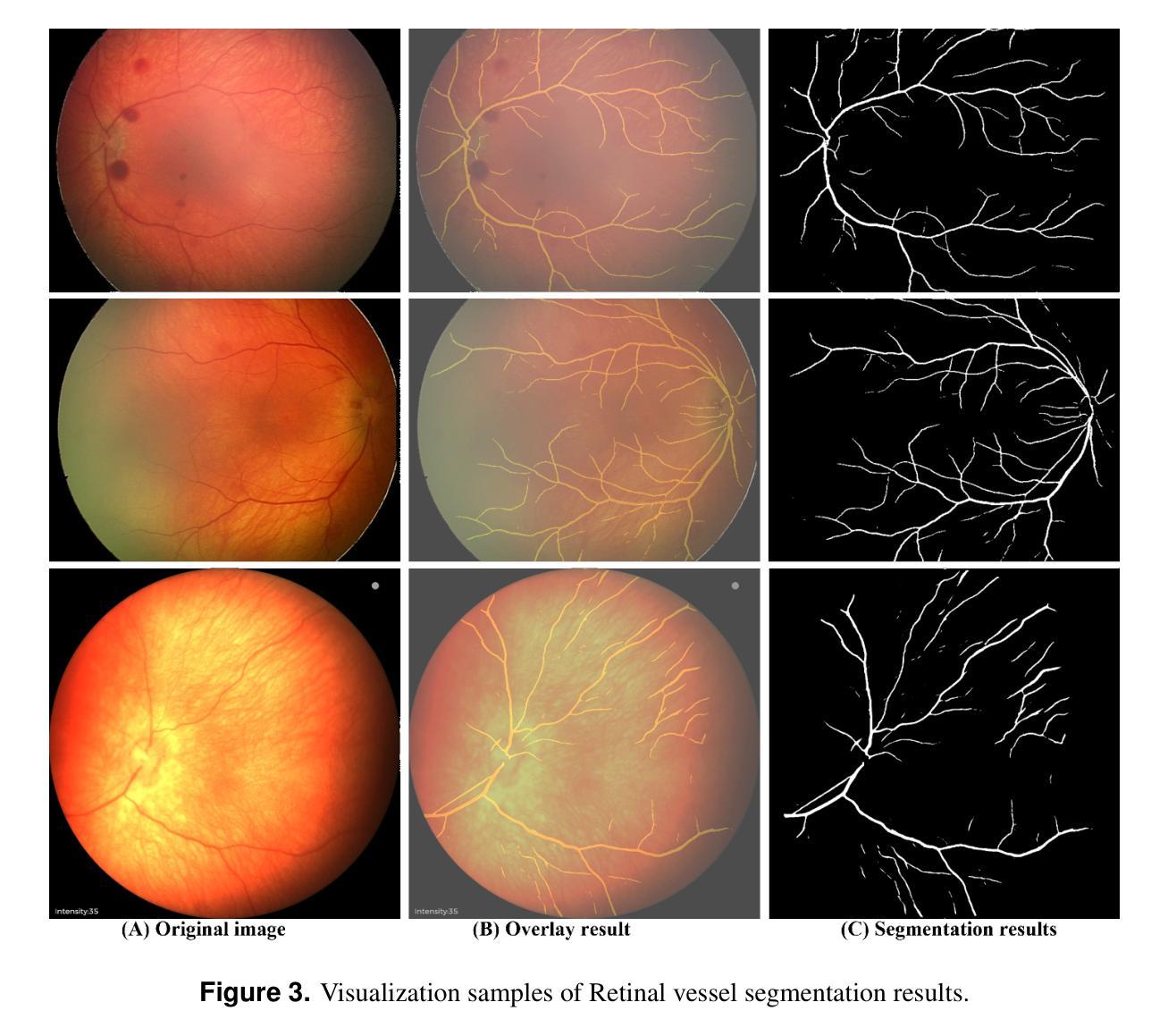
Retinal image registration is vital for diagnostic therapeutic applications within the field of ophthalmology. Existing public datasets, focusing on adult retinal pathologies with high-quality images, have limited number of image pairs and neglect clinical challenges. To address this gap, we introduce COph100, a novel and challenging dataset known as the Comprehensive Ophthalmology Retinal Image Registration dataset for infants with a wide range of image quality issues constituting the public “RIDIRP” database. COph100 consists of 100 eyes, each with 2 to 9 examination sessions, amounting to a total of 491 image pairs carefully selected from the publicly available dataset. We manually labeled the corresponding ground truth image points and provided automatic vessel segmentation masks for each image. We have assessed COph100 in terms of image quality and registration outcomes using state-of-the-art algorithms. This resource enables a robust comparison of retinal registration methodologies and aids in the analysis of disease progression in infants, thereby deepening our understanding of pediatric ophthalmic conditions.
视网膜图像配准对于眼科领域的诊断和治疗应用至关重要。现有的公共数据集主要关注具有高质量图像的成人视网膜病理,图像对数量有限,并忽略了临床挑战。为了弥补这一空白,我们介绍了COph100,这是一个新型且具有挑战性的数据集,名为“综合眼科视网膜图像配准数据集”,专门针对婴幼儿,涵盖广泛的图像质量问题,构成公共“RIDIRP”数据库。COph100包含100只眼睛,每只眼睛有2至9次检查会话,总共从公开可用的数据集中精心挑选了491张图像对。我们手动标记了相应的真实图像点,并为每张图像提供了自动血管分割掩膜。我们采用最先进的算法对COph100的图像质量和配准结果进行了评估。这一资源能够稳健地比较视网膜配准方法,有助于分析婴幼儿疾病进展,从而加深对儿科眼科状况的理解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文介绍了视网膜图像配准在眼科诊断和治疗方法中的重要性。现有的公共数据集主要关注成人视网膜病理的高品质图像,但图像对数量有限,忽视了临床挑战。为解决这一问题,本文引入了COph100数据集,这是一个全面的眼科视网膜图像配准数据集,专门针对婴幼儿,并涵盖了广泛的图像质量问题,构成公共“RIDIRP”数据库。COph100由来自公开数据集的491个图像对组成,这些图像对是从100只眼睛、每只眼睛有2至9次检查会话中精心挑选出来的。本文手动标记了相应的地面真实图像点,并为每张图像提供了自动血管分割掩膜。已经使用最先进的算法评估了COph100的图像质量和配准结果。此资源能够可靠地比较视网膜配准方法,并有助于分析婴儿的疾病进展,从而加深对儿科眼科状况的理解。
Key Takeaways
- 视网膜图像配准在眼科诊断和治疗中非常重要。
- 现有公共数据集主要关注成人视网膜病理的高品质图像,但对婴幼儿的临床挑战重视不足。
- COph100数据集的介绍,该数据集是专门针对婴幼儿的眼科视网膜图像配准数据集。
- COph100包含来自公开数据库的491个图像对,涵盖了广泛的图像质量问题。
- 手动标记了对应的地面真实图像点,并为每个图像提供了自动血管分割掩膜。
- 使用最先进的算法评估了COph100的图像质量和配准效果。
点此查看论文截图
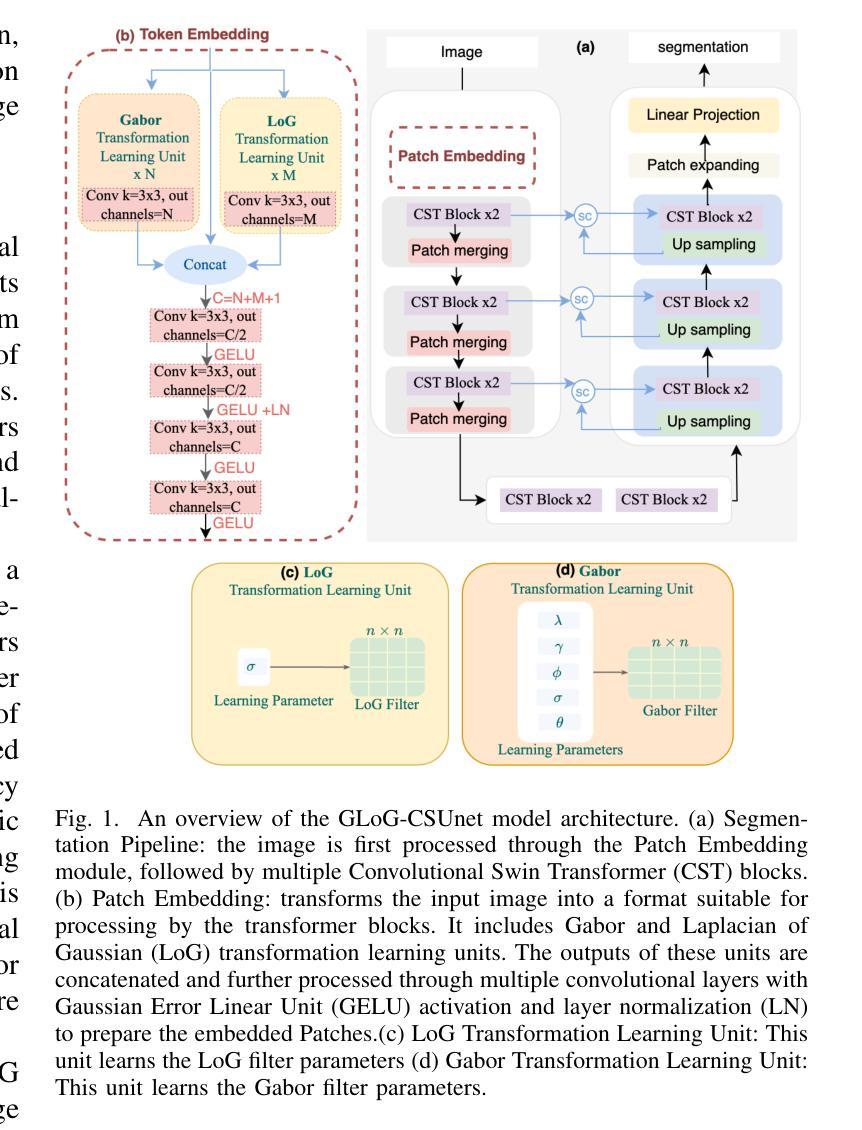
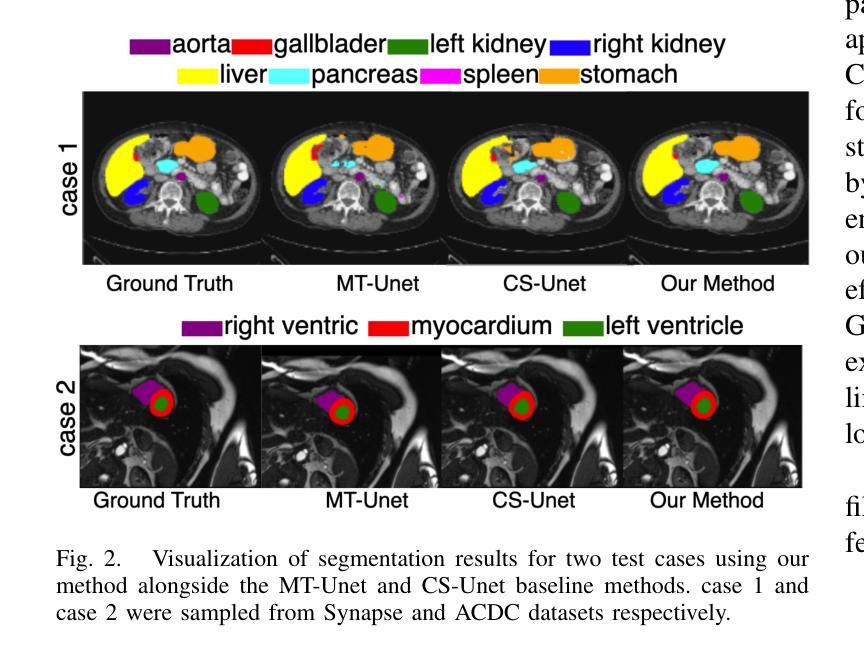
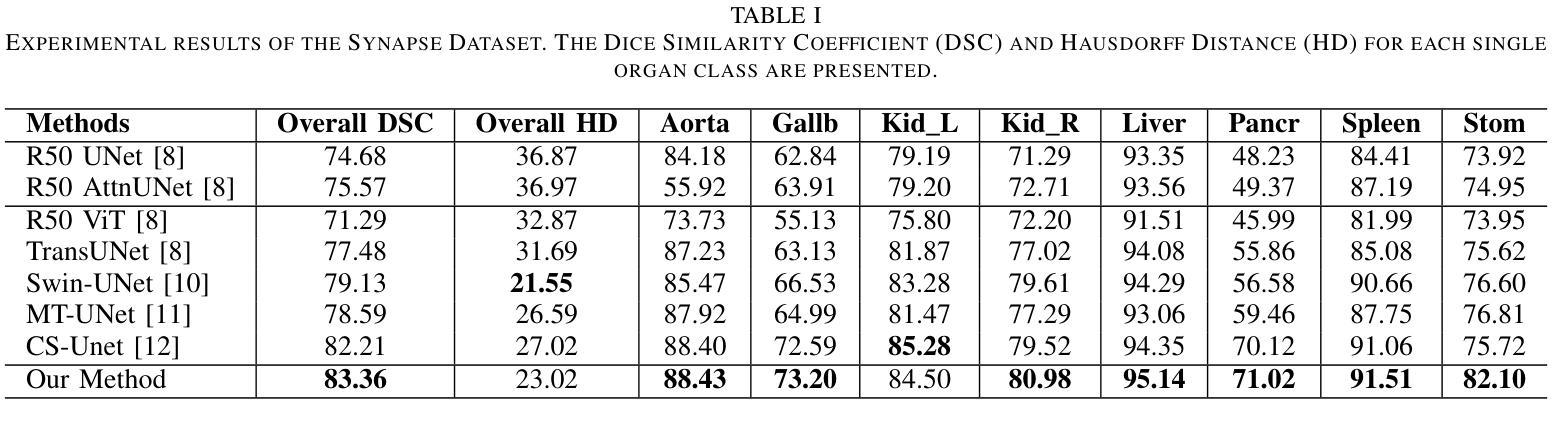
GLoG-CSUnet: Enhancing Vision Transformers with Adaptable Radiomic Features for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Niloufar Eghbali, Hassan Bagher-Ebadian, Tuka Alhanai, Mohammad M. Ghassemi
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown promise in medical image semantic segmentation (MISS) by capturing long-range correlations. However, ViTs often struggle to model local spatial information effectively, which is essential for accurately segmenting fine anatomical details, particularly when applied to small datasets without extensive pre-training. We introduce Gabor and Laplacian of Gaussian Convolutional Swin Network (GLoG-CSUnet), a novel architecture enhancing Transformer-based models by incorporating learnable radiomic features. This approach integrates dynamically adaptive Gabor and Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filters to capture texture, edge, and boundary information, enhancing the feature representation processed by the Transformer model. Our method uniquely combines the long-range dependency modeling of Transformers with the texture analysis capabilities of Gabor and LoG features. Evaluated on the Synapse multi-organ and ACDC cardiac segmentation datasets, GLoG-CSUnet demonstrates significant improvements over state-of-the-art models, achieving a 1.14% increase in Dice score for Synapse and 0.99% for ACDC, with minimal computational overhead (only 15 and 30 additional parameters, respectively). GLoG-CSUnet’s flexible design allows integration with various base models, offering a promising approach for incorporating radiomics-inspired feature extraction in Transformer architectures for medical image analysis. The code implementation is available on GitHub at: https://github.com/HAAIL/GLoG-CSUnet.
视觉Transformer(ViTs)通过捕捉长程关联在医学图像语义分割(MISS)方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,ViTs在建模局部空间信息方面往往表现不佳,这对于准确分割精细的解剖细节至关重要,尤其是在未进行广泛预训练的情况下应用于小规模数据集时。我们引入了Gabor和Laplacian of Gaussian卷积Swin网络(GLoG-CSUnet),这是一种新型架构,通过融入可学习的放射学特征来增强基于Transformer的模型。这种方法结合了动态自适应的Gabor和Laplacian of Gaussian(LoG)滤波器,以捕捉纹理、边缘和边界信息,增强Transformer模型处理的特征表示。我们的方法独特地结合了Transformer的长程依赖建模和Gabor与LoG特征的纹理分析能力。在Synapse多器官和ACDC心脏分割数据集上进行评估,GLoG-CSUnet在最新模型上实现了显著改进,Synapse的Dice得分增加了1.14%,ACDC增加了0.99%,同时计算开销极小(仅增加了15个和30个额外参数)。GLoG-CSUnet的灵活设计可融入各种基础模型,为在Transformer架构中融入放射学启发特征提取提供了有前景的方法,适用于医学图像分析。代码实现可在GitHub上找到:https://github.com/HAAIL/GLoG-CSUnet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学图像语义分割(MISS),本文提出一种融合Gabor和Laplacian of Gaussian卷积神经网络的新型架构GLoG-CSUnet。它通过集成可学习的放射学特征,提高了基于Transformer的模型性能。该架构结合了Transformer的长程依赖性建模与Gabor和LoG滤波器的纹理分析功能,可在Synapse多器官和ACDC心脏分割数据集上实现显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 在医学图像语义分割中展现潜力,但难以有效建模局部空间信息。
- GLoG-CSUnet新型架构通过结合可学习的放射学特征,提高了Transformer模型的性能。
- GLoG-CSUnet融合了Transformer的长程依赖性建模与Gabor和LoG滤波器的纹理分析功能。
- 在Synapse多器官和ACDC心脏分割数据集上,GLoG-CSUnet较现有模型有显著改善,Dice得分分别提高1.14%和0.99%。
- GLoG-CSUnet设计灵活,可集成于各种基础模型,为医学图像分析中融入放射学特征提取的Transformer架构提供了有前景的方法。
点此查看论文截图

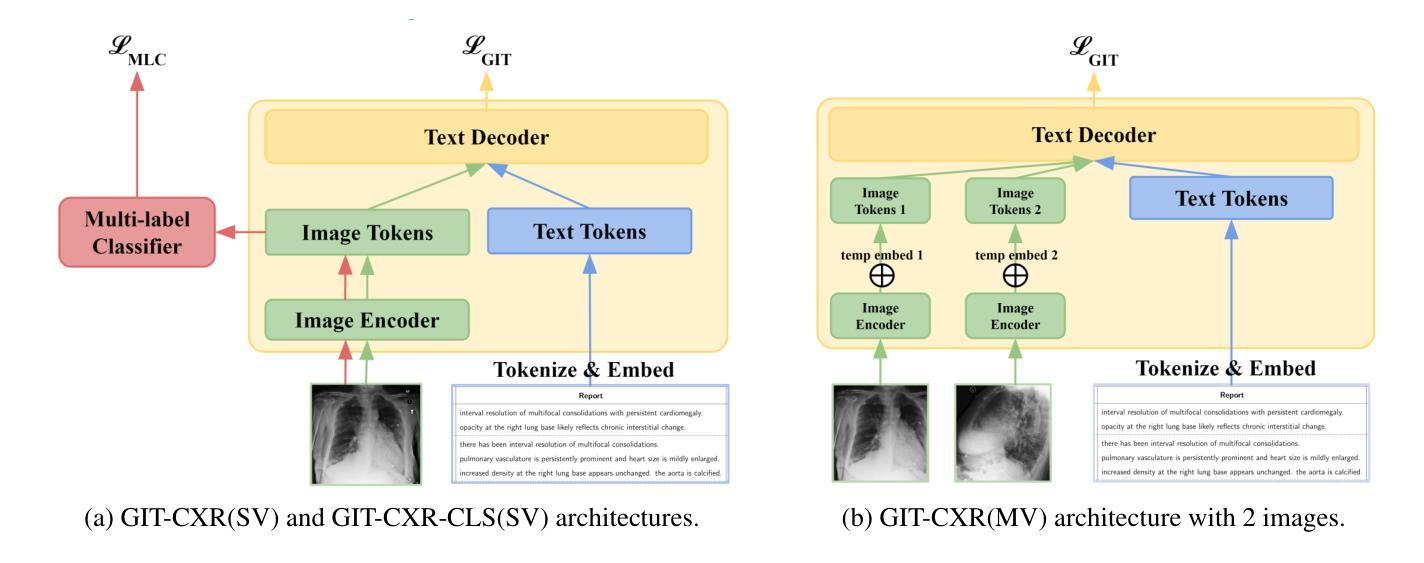
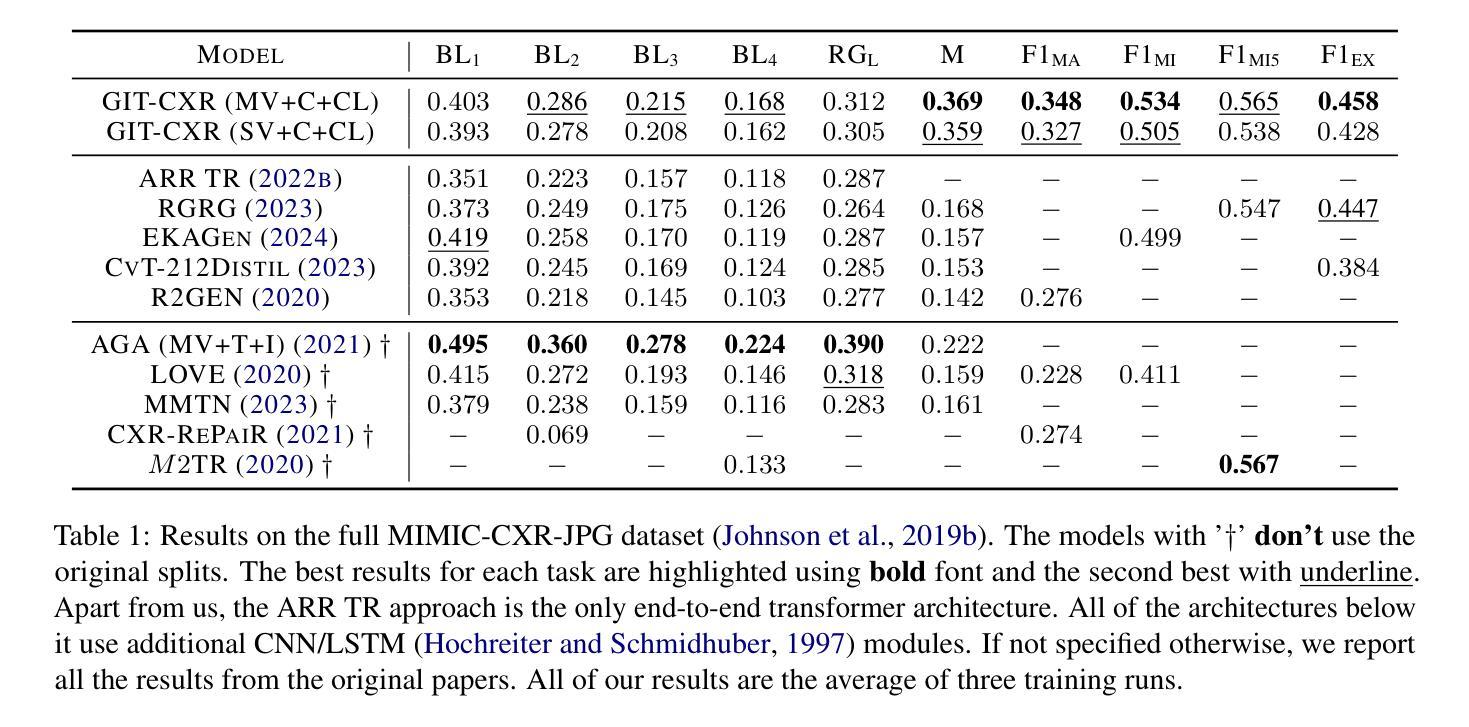
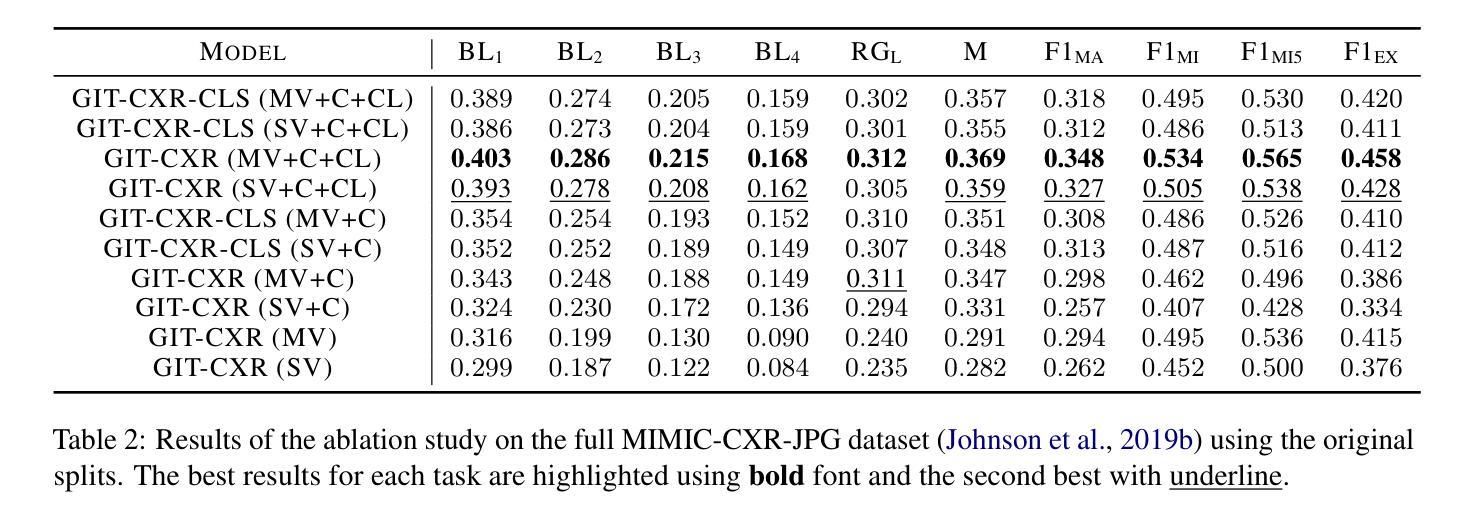
GIT-CXR: End-to-End Transformer for Chest X-Ray Report Generation
Authors:Iustin Sîrbu, Iulia-Renata Sîrbu, Jasmina Bogojeska, Traian Rebedea
Medical imaging is crucial for diagnosing, monitoring, and treating medical conditions. The medical reports of radiology images are the primary medium through which medical professionals attest their findings, but their writing is time consuming and requires specialized clinical expertise. The automated generation of radiography reports has thus the potential to improve and standardize patient care and significantly reduce clinicians workload. Through our work, we have designed and evaluated an end-to-end transformer-based method to generate accurate and factually complete radiology reports for X-ray images. Additionally, we are the first to introduce curriculum learning for end-to-end transformers in medical imaging and demonstrate its impact in obtaining improved performance. The experiments have been conducted using the MIMIC-CXR-JPG database, the largest available chest X-ray dataset. The results obtained are comparable with the current state-of-the-art on the natural language generation (NLG) metrics BLEU and ROUGE-L, while setting new state-of-the-art results on F1 examples-averaged, F1-macro and F1-micro metrics for clinical accuracy and on the METEOR metric widely used for NLG.
医学成像对于疾病的诊断、监测和治疗至关重要。放射影像报告的医学报告是医学专业人士证明其发现的主要媒介,但其写作耗时且需要专业的临床经验。因此,放射报告的自动生成具有改善和标准化患者护理以及显著减少临床医生工作量的潜力。通过我们的工作,我们设计并评估了一种基于端到端转换器的方法,为X射线图像生成准确且事实完整的放射报告。此外,我们是首次在医学成像端到端转换器中引入课程学习,并展示了其在获得改进性能方面的作用。实验使用的是最大的可用胸部X射线数据集MIMIC-CXR-JPG数据库。所获得的结果与自然语言生成(NLG)指标BLEU和ROUGE-L的当前最新水平相当,同时在F1示例平均值、F1宏和F1微观度量指标的临床准确性和广泛应用于NLG的METEOR指标上取得了最新成果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学影像学对于疾病的诊断、监测和治疗至关重要。医学专家主要通过放射影像学报告的医学影像来验证他们的发现,但手写报告耗时且需要专业临床经验。因此,自动生成放射学报告具有改善和标准化患者护理以及大幅减轻临床医生工作量的潜力。本研究设计并评估了一种基于端到端转换器的方法,用于生成针对X光图像的准确且事实完整的放射学报告。此外,本研究首次引入医学成像端到端转换器的课程学习,并展示了其对提高性能的影响。实验采用最大的可用胸部X光数据集MIMIC-CXR-JPG数据库进行,结果与自然语言生成(NLG)的最新技术相比具有竞争力,并在临床准确性的F1示例平均、F1宏观和F1微观指标以及广泛使用的NLG度量指标METEOR上取得了最新技术成果。
Key Takeaways
- 医学影像学在疾病诊断、监测和治疗中起关键作用。
- 医学专家通过放射影像学报告验证他们的发现,但报告编写耗时且需要专业经验。
- 自动生成放射学报告能够改善和标准化患者护理,并大幅减轻临床医生的工作量。
- 研究者设计了一种基于端到端转换器的方法,用于生成针对X光图像的准确且事实完整的放射学报告。
- 本研究首次在医学成像中引入课程学习,以提高端到端转换器的性能。
- 实验采用MIMIC-CXR-JPG数据库进行,结果与自然语言生成(NLG)的最新技术相比具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图


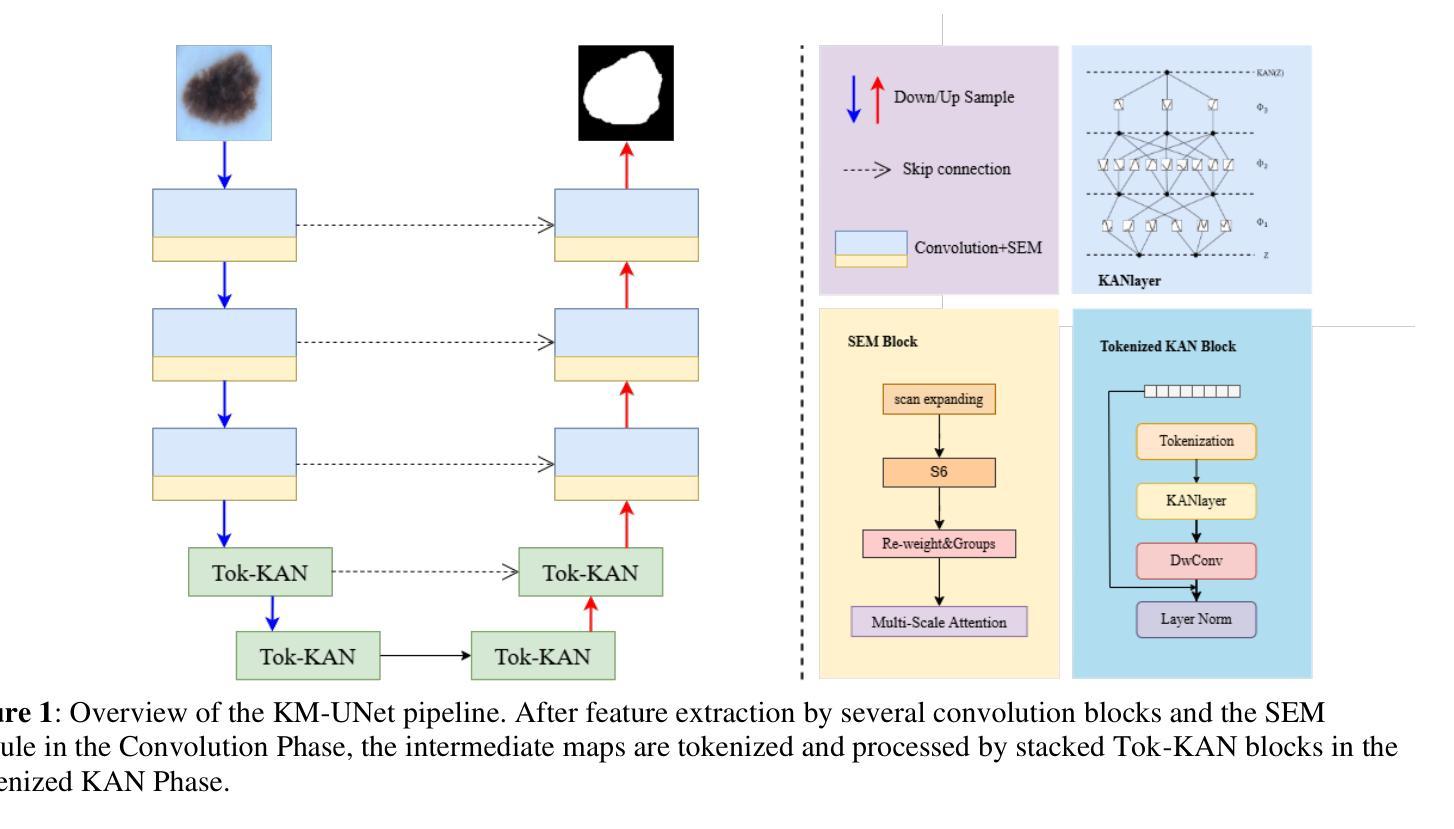
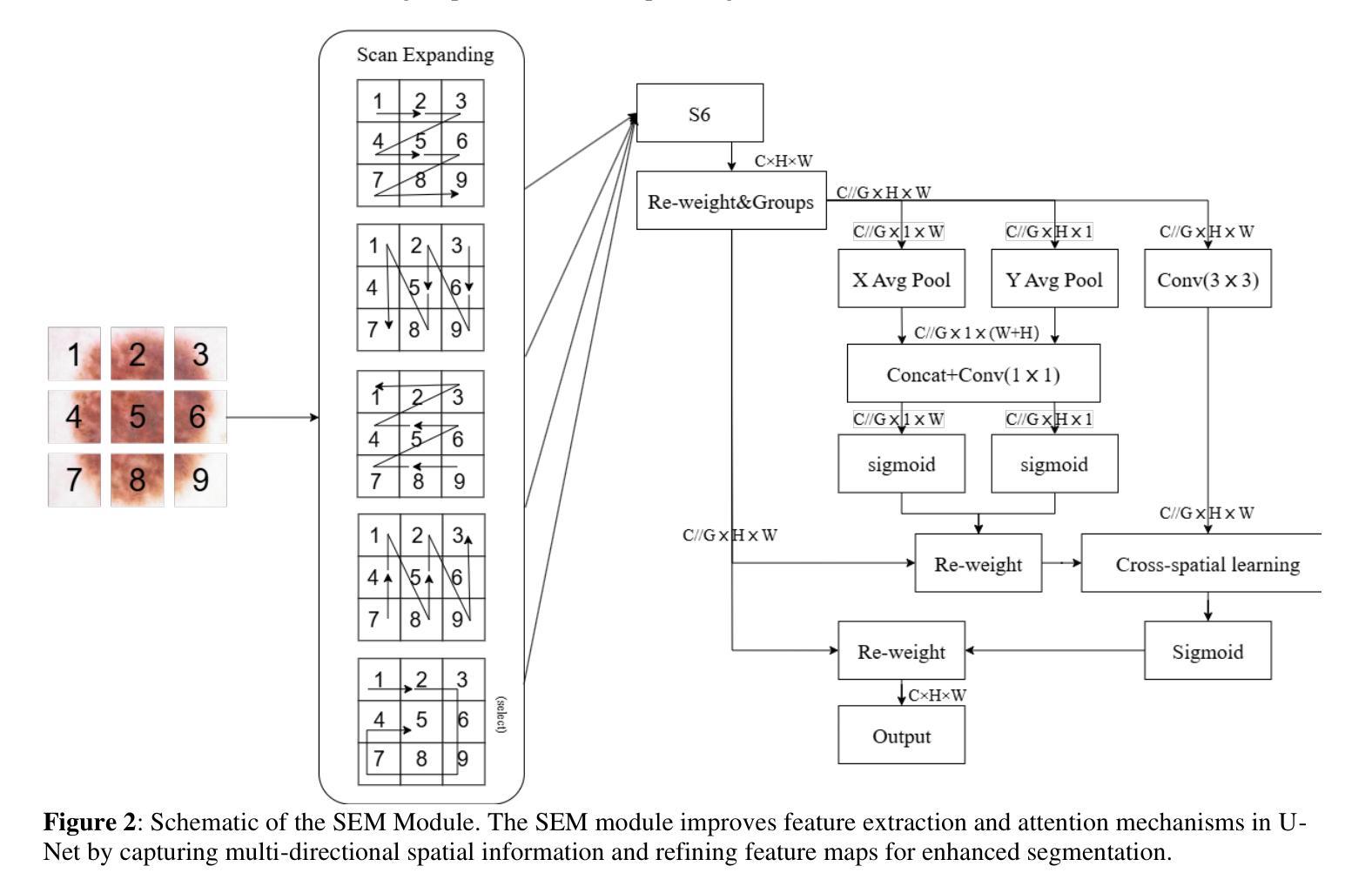
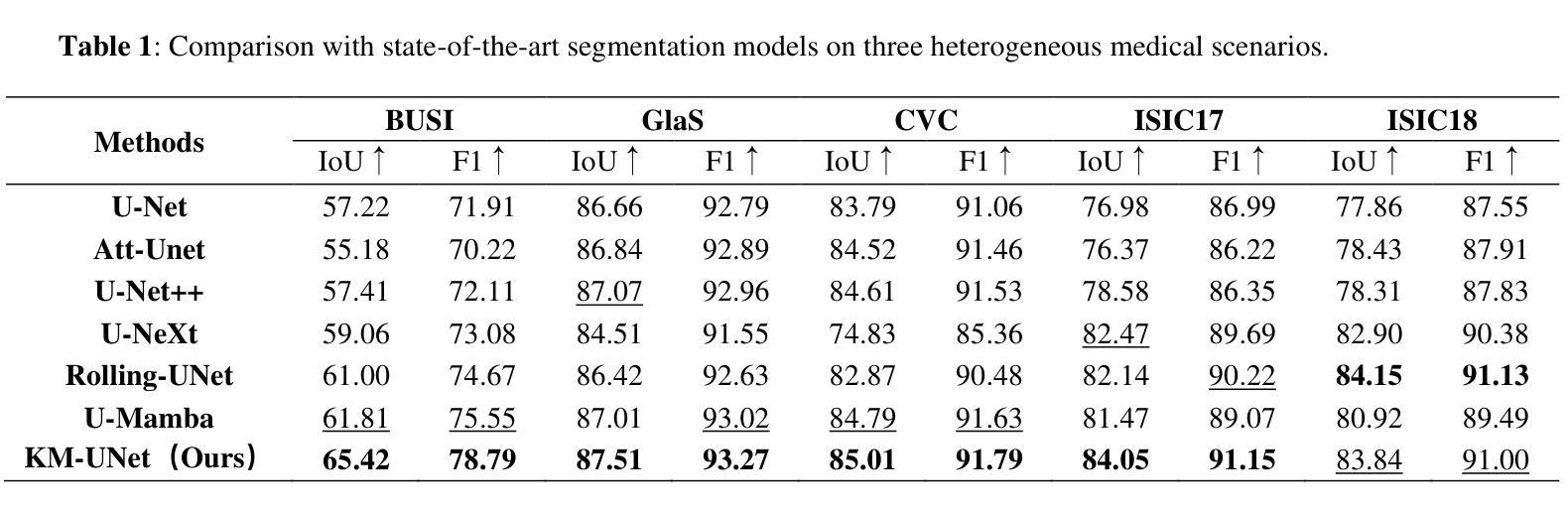
KM-UNet KAN Mamba UNet for medical image segmentation
Authors:Yibo Zhang
Medical image segmentation is a critical task in medical imaging analysis. Traditional CNN-based methods struggle with modeling long-range dependencies, while Transformer-based models, despite their success, suffer from quadratic computational complexity. To address these limitations, we propose KM-UNet, a novel U-shaped network architecture that combines the strengths of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) and state-space models (SSMs). KM-UNet leverages the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem for efficient feature representation and SSMs for scalable long-range modeling, achieving a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency. We evaluate KM-UNet on five benchmark datasets: ISIC17, ISIC18, CVC, BUSI, and GLAS. Experimental results demonstrate that KM-UNet achieves competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art methods in medical image segmentation tasks. To the best of our knowledge, KM-UNet is the first medical image segmentation framework integrating KANs and SSMs. This work provides a valuable baseline and new insights for the development of more efficient and interpretable medical image segmentation systems. The code is open source at https://github.com/2760613195/KM_UNet Keywords:KAN,Manba, state-space models,UNet, Medical image segmentation, Deep learning
医学图像分割是医学影像分析中的一项关键任务。传统的基于CNN的方法在建模长距离依赖关系时遇到困难,而基于Transformer的模型虽然取得了成功,但存在计算复杂度为二次方的问题。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了KM-UNet,这是一种新型U型网络架构,结合了Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)和状态空间模型(SSMs)的优点。KM-UNet利用Kolmogorov-Arnold表示定理进行高效的特征表示,并利用SSM进行可扩展的长距离建模,在准确性和计算效率之间取得了平衡。我们在五个基准数据集上评估了KM-UNet:ISIC17、ISIC18、CVC、BUSI和GLAS。实验结果表明,KM-UNet在医学图像分割任务上的性能与最先进的方法相比具有竞争力。据我们所知,KM-UNet是第一个将KANs和SSMs整合到医学图像分割框架中的。这项工作为开发更高效和可解释的医学图像分割系统提供了有价值的基准和新的见解。代码已开源在https://github.com/2760613195/KM_UNet。关键词:KAN,Manba,状态空间模型,UNet,医学图像分割,深度学习。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学图像分割任务,提出KM-UNet模型,融合Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)与状态空间模型(SSMs),在效率和精度之间取得平衡,且是首个结合两者在医学图像分割中的应用框架。通过多项基准测试证明性能优越性,对医学图像分割研究有重要意义。相关代码已开源共享。
Key Takeaways
- 传统CNN方法在医学图像分割中的局限性在于难以建模长距离依赖关系。
- Transformer模型虽然成功,但计算复杂度为二次方。
- 提出KM-UNet模型,结合Kolmogorov-Arnold网络和状态空间模型的优点。
- KM-UNet利用Kolmogorov-Arnold表示定理进行高效特征表示和SSM进行可扩展的长距离建模。
- 在五个基准数据集上的实验结果表明KM-UNet在医学图像分割任务中具有竞争力。
- KM-UNet是首个结合KANs和SSMs的医学图像分割框架。
点此查看论文截图


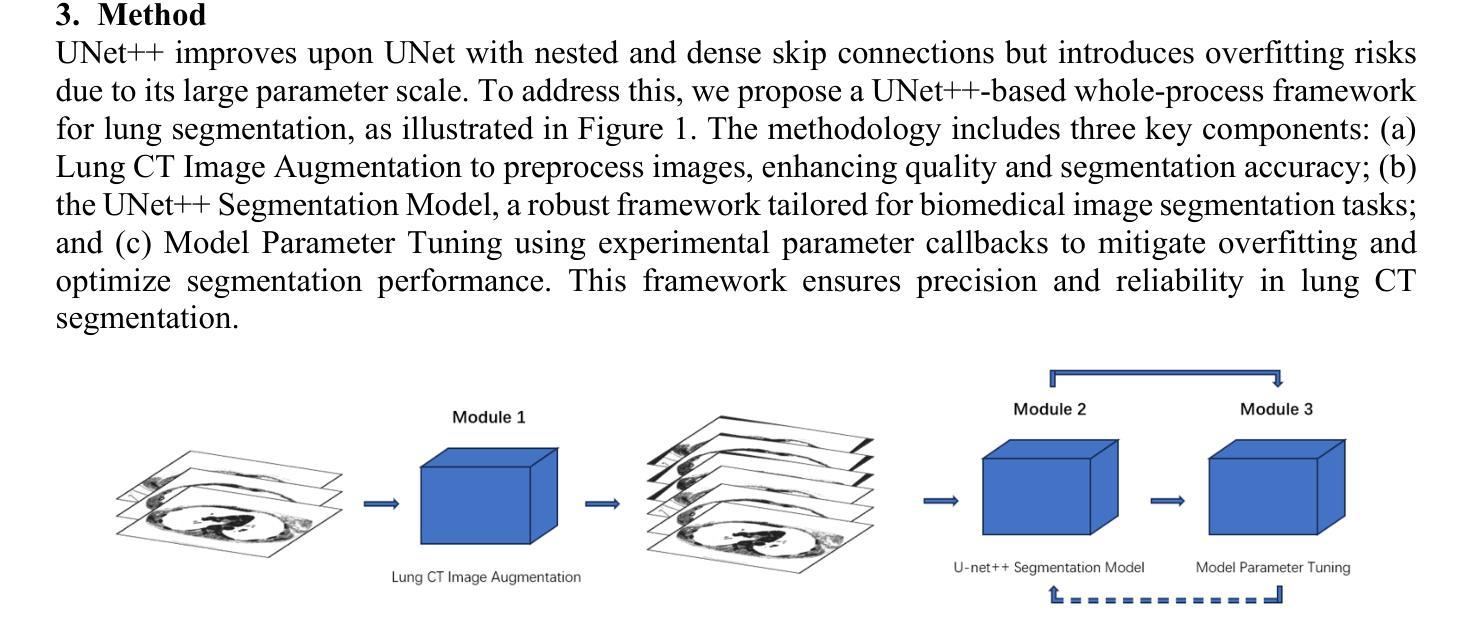
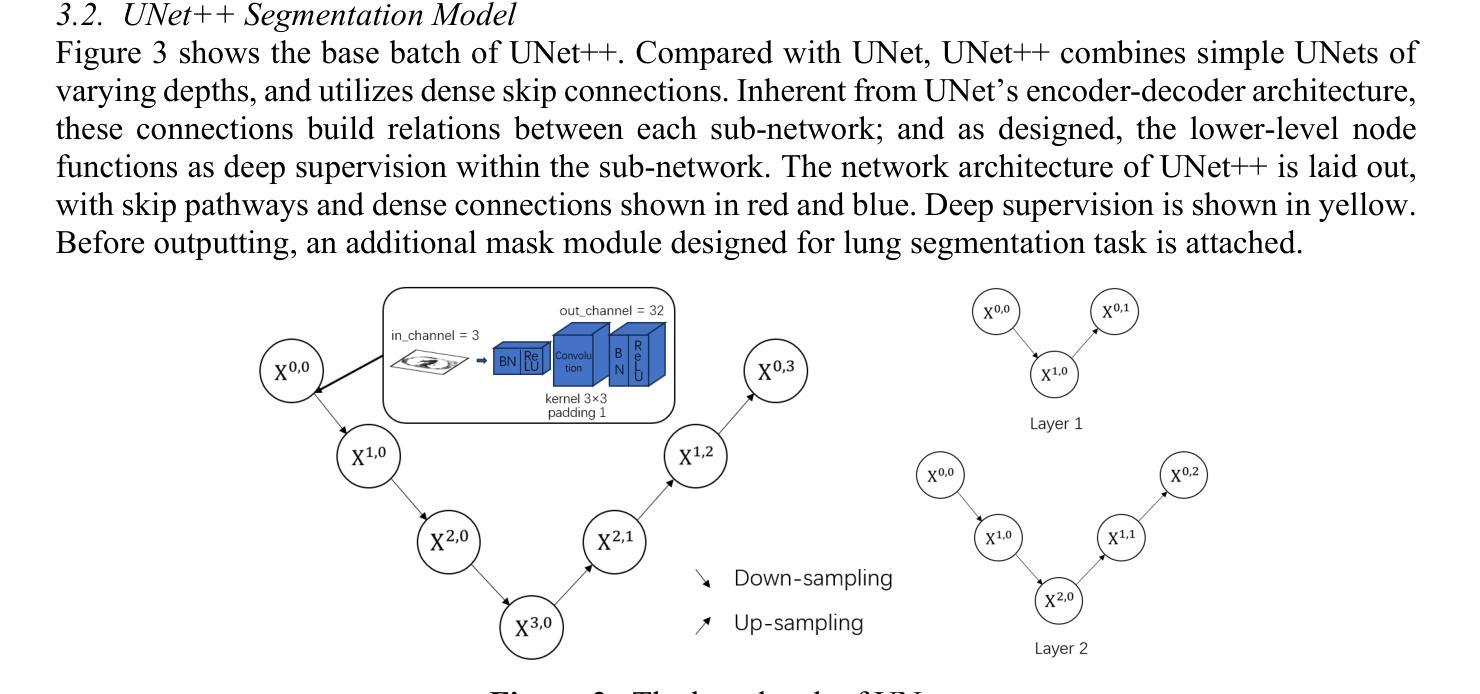
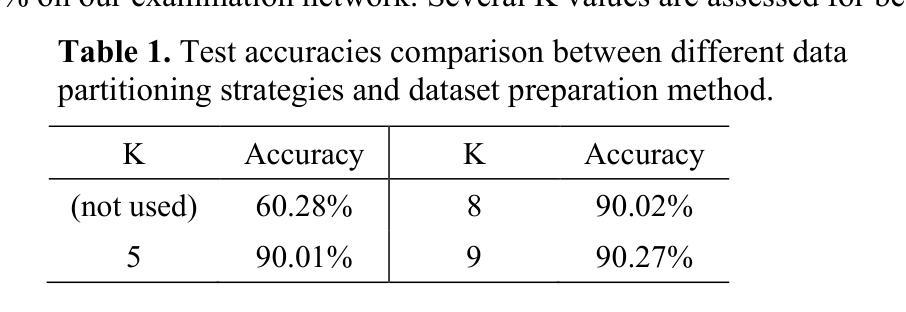
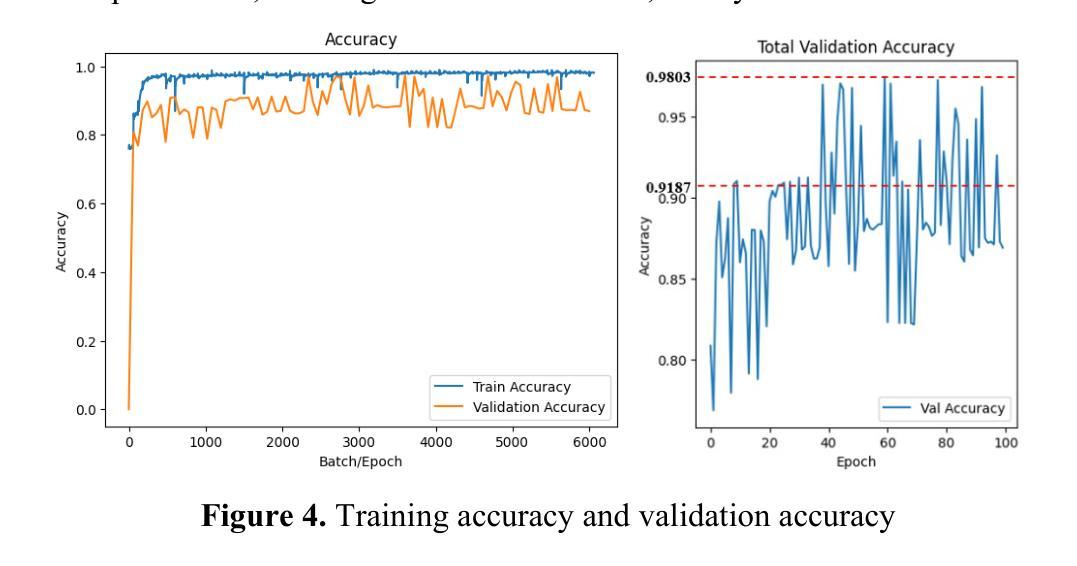
Framework for lung CT image segmentation based on UNet++
Authors:Hao Ziang, Jingsi Zhang, Lixian Li
Recently, the state-of-art models for medical image segmentation is U-Net and their variants. These networks, though succeeding in deriving notable results, ignore the practical problem hanging over the medical segmentation field: overfitting and small dataset. The over-complicated deep neural networks unnecessarily extract meaningless information, and a majority of them are not suitable for lung slice CT image segmentation task. To overcome the two limitations, we proposed a new whole-process network merging advanced UNet++ model. The network comprises three main modules: data augmentation, optimized neural network, parameter fine-tuning. By incorporating diverse methods, the training results demonstrate a significant advantage over similar works, achieving leading accuracy of 98.03% with the lowest overfitting. potential. Our network is remarkable as one of the first to target on lung slice CT images.
最近,医学图像分割领域的最先进的模型为U-Net及其变体。这些网络虽然成功取得了显著的结果,但忽略了医学分割领域存在的实际问题:过拟合和小数据集。过于复杂的深度神经网络会不必要地提取无意义的信息,而且大多数网络都不适用于肺部CT图像分割任务。为了克服这两个局限性,我们提出了一种新的全过程网络,融合了先进的UNet++模型。该网络包含三个主要模块:数据增强、优化神经网络、参数微调。通过结合多种方法,训练结果相较于类似工作展现出显著优势,以最低的过拟合风险实现了高达98.03%的领先准确率。我们的网络作为首批专注于肺部CT图像的网络之一,表现尤为突出。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学图像分割领域存在的过拟合和小数据集问题,提出了一种融合UNet++模型的新全程网络。该网络包含数据增强、优化神经网络和参数微调三个主要模块,通过采用多种方法,在CT肺切片图像分割任务上取得了显著的成果,准确率达到了98.03%,并具有较低过拟合潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 当前先进的医学图像分割模型如U-Net及其变体虽然取得了显著成果,但存在过拟合和小数据集问题。
- 过复杂的深度神经网络可能提取无意义的信息,且多数模型不适用于肺切片CT图像分割任务。
- 针对上述问题,提出了一种新的全程网络,融合了UNet++模型。
- 该网络包含数据增强、优化神经网络和参数微调三个主要模块。
- 通过结合多种方法,该网络在CT肺切片图像分割上取得了显著成果,准确率高达98.03%。
- 该网络具有较低过拟合潜力。
点此查看论文截图


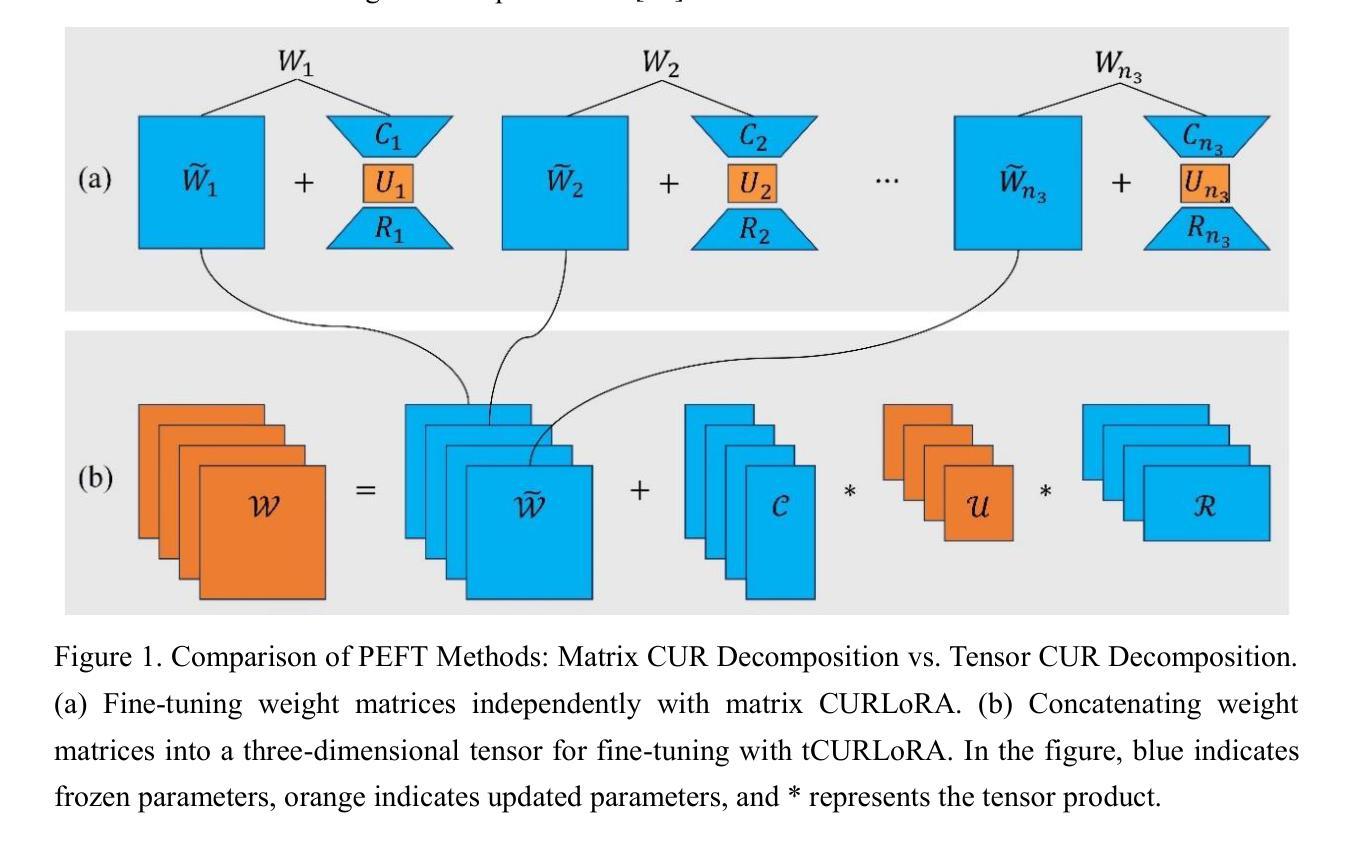
tCURLoRA: Tensor CUR Decomposition Based Low-Rank Parameter Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Guanghua He, Wangang Cheng, Hancan Zhu, Xiaohao Cai, Gaohang Yu
Transfer learning, by leveraging knowledge from pre-trained models, has significantly enhanced the performance of target tasks. However, as deep neural networks scale up, full fine-tuning introduces substantial computational and storage challenges in resource-constrained environments, limiting its widespread adoption. To address this, parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods have been developed to reduce computational complexity and storage requirements by minimizing the number of updated parameters. While matrix decomposition-based PEFT methods, such as LoRA, show promise, they struggle to fully capture the high-dimensional structural characteristics of model weights. In contrast, high-dimensional tensors offer a more natural representation of neural network weights, allowing for a more comprehensive capture of higher-order features and multi-dimensional interactions. In this paper, we propose tCURLoRA, a novel fine-tuning method based on tensor CUR decomposition. By concatenating pre-trained weight matrices into a three-dimensional tensor and applying tensor CUR decomposition, we update only the lower-order tensor components during fine-tuning, effectively reducing computational and storage overhead. Experimental results demonstrate that tCURLoRA outperforms existing PEFT methods in medical image segmentation tasks.
利用预训练模型的知识进行迁移学习已显著提高目标任务的性能。然而,随着深度神经网络规模的扩大,全微调在资源受限环境中引入了巨大的计算和存储挑战,限制了其广泛应用。为解决这一问题,开发了参数高效微调(PEFT)方法,通过最小化更新参数的数量来降低计算复杂性和存储要求。虽然基于矩阵分解的PEFT方法(如LoRA)显示出潜力,但它们难以完全捕获模型权重的高维结构特征。相反,高维张量提供了神经网络权重的更自然表示,能够更全面地捕获高阶特征和多维交互。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于张量CUR分解的新型微调方法tCURLoRA。通过将预训练权重矩阵拼接成三维张量并应用张量CUR分解,我们只在微调过程中更新低阶张量组件,从而有效地降低了计算和存储开销。实验结果表明,在医学图像分割任务中,tCURLoRA优于现有的PEFT方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
通过利用预训练模型的知识,迁移学习已显著提高目标任务的性能。然而,随着深度神经网络规模的扩大,完全微调带来了资源受限环境中计算和存储方面的挑战,限制了其广泛应用。为解决此问题,开发了参数高效微调(PEFT)方法,以减少计算和存储复杂性,并最小化更新的参数数量。尽管基于矩阵分解的PEFT方法(如LoRA)显示出潜力,但它们难以完全捕获模型权重的高维结构特征。相反,高维张量提供更自然的神经网络权重表示,能够更全面地捕获高阶特征和多维交互。本文提出一种基于张量CUR分解的新型微调方法tCURLoRA。通过将预训练权重矩阵连接成三维张量并应用张量CUR分解,我们只在微调期间更新低阶张量组件,有效减少计算和存储开销。实验结果证明tCURLoRA在医学图像分割任务中优于现有PEFT方法。
Key Takeaways
- 迁移学习利用预训练模型知识提升了目标任务的性能。
- 完全微调深度神经网络在资源受限环境中面临计算和存储挑战。
- 参数高效微调(PEFT)方法旨在减少计算和存储复杂性。
- 现有矩阵分解方法如LoRA难以捕获模型权重的全部高维结构特征。
- 高维张量为神经网络权重提供更自然的表示,有助于捕获高阶特征和多维交互。
- tCURLoRA是一种新型微调方法,基于张量CUR分解,旨在更有效地更新模型权重。
点此查看论文截图

Phase Retrieval by Quaternionic Reweighted Amplitude Flow on Image Reconstruction
Authors:Ren Hu, Pan Lian
Quaternionic signal processing provides powerful tools for efficiently managing color signals by preserving the intrinsic correlations among signal dimensions through quaternion algebra. In this paper, we address the quaternionic phase retrieval problem by systematically developing novel algorithms based on an amplitude-based model. Specifically, we propose the Quaternionic Reweighted Amplitude Flow (QRAF) algorithm, which is further enhanced by three of its variants: incremental, accelerated, and adapted QRAF algorithms. In addition, we introduce the Quaternionic Perturbed Amplitude Flow (QPAF) algorithm, which has linear convergence. Extensive numerical experiments on both synthetic data and real images, demonstrate that our proposed methods significantly improve recovery performance and computational efficiency compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
四元信号处理技术提供了强大的工具,能够通过四元代数保留信号维度之间的内在关联来有效地管理彩色信号。在本文中,我们解决了四元相位恢复问题,系统地开发了基于振幅模型的新型算法。具体来说,我们提出了四元重加权振幅流(QRAF)算法,该算法通过其三种变体得到了进一步的增强:增量、加速和自适应QRAF算法。此外,我们还介绍了四元扰动振幅流(QPAF)算法,它具有线性收敛性。对合成数据和真实图像的大量数值实验表明,与最新方法相比,我们提出的方法在恢复性能和计算效率方面都有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像处理中,四元数信号处理通过保留信号维度间的内在关联提供了有效的工具。本文解决四元数相位恢复问题,基于振幅模型系统地开发新型算法。提出四元数重加权振幅流算法及其增量、加速和自适应变体,并引入四元数扰动振幅流算法,具有线性收敛性。数值实验表明,所提方法显著提高了恢复性能和计算效率。
Key Takeaways
- 四元数信号处理能够高效地管理颜色信号,保持信号维度间的内在关联。
- 本文解决四元数相位恢复问题,这是信号处理中的一个关键挑战。
- 提出了基于振幅模型的四元数重加权振幅流算法(QRAF)及其改进版本。
- 引入四元数扰动振幅流(QPAF)算法,具有线性收敛特性。
- 通过大量数值实验验证了所提算法在合成数据和真实图像上的优越性。
- 与现有方法相比,所提算法显著提高恢复性能和计算效率。
点此查看论文截图

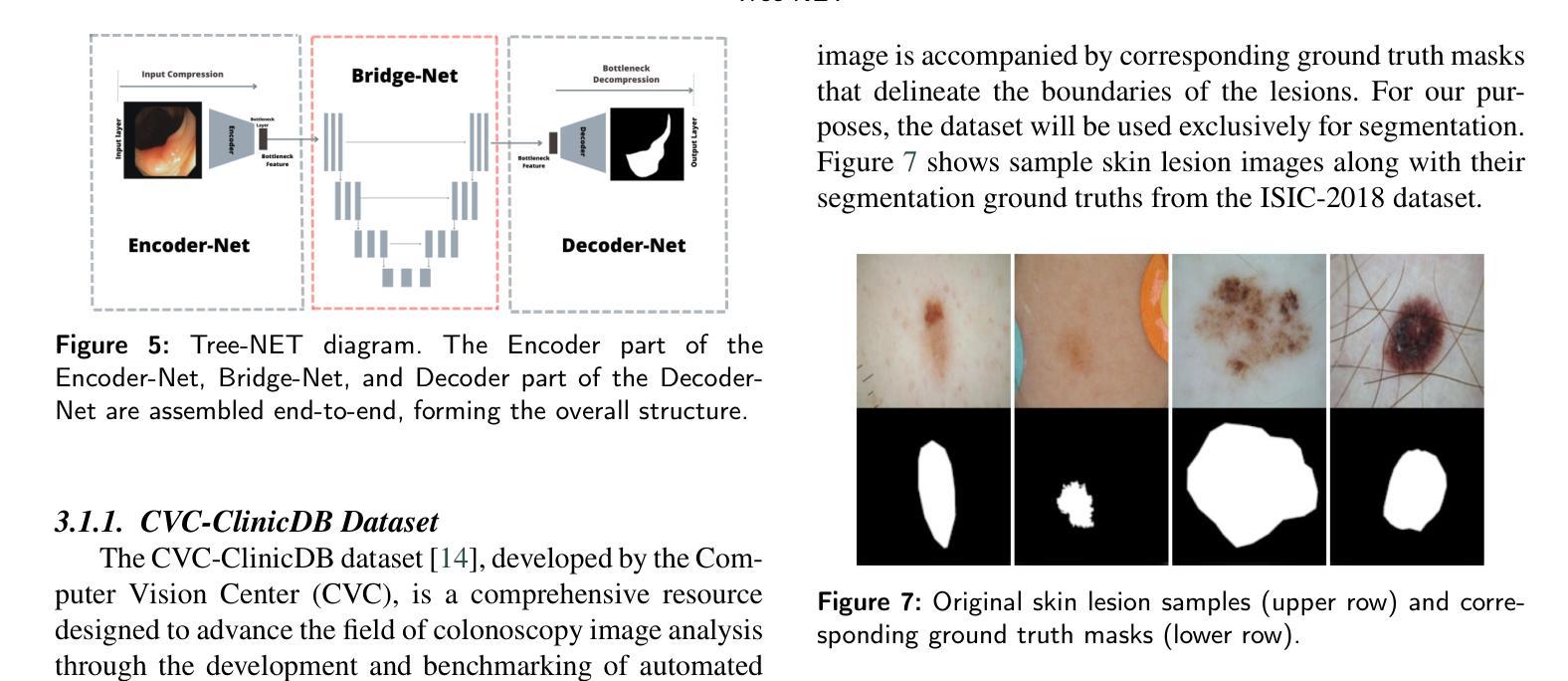
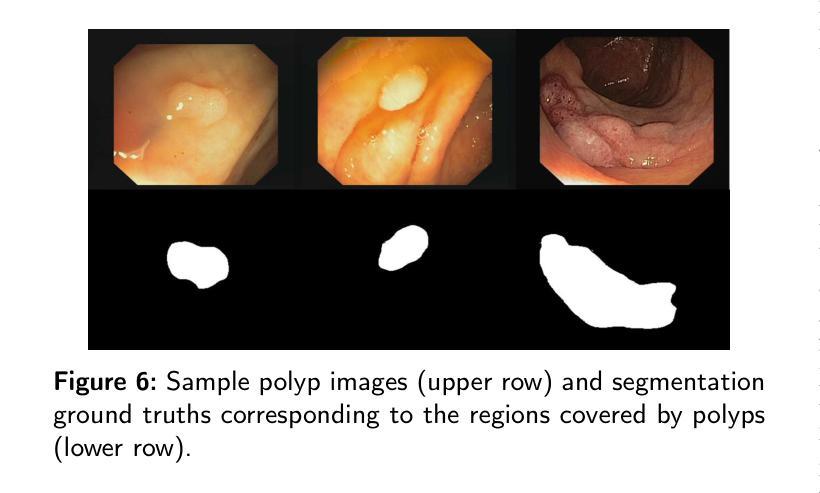
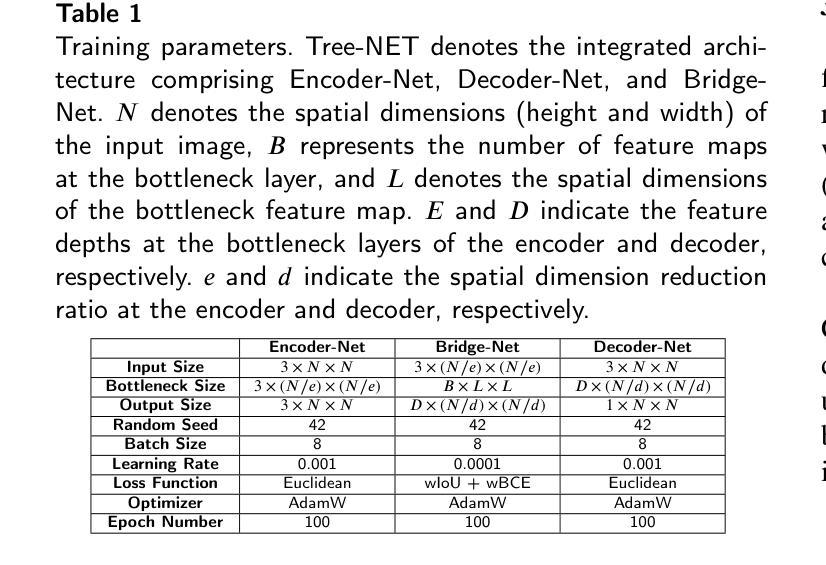
Tree-NET: Enhancing Medical Image Segmentation Through Efficient Low-Level Feature Training
Authors:Orhan Demirci, Bulent Yilmaz
This paper introduces Tree-NET, a novel framework for medical image segmentation that leverages bottleneck feature supervision to enhance both segmentation accuracy and computational efficiency. While previous studies have employed bottleneck feature supervision, their applications have largely been limited to the training phase, offering no computational benefits during training or evaluation. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to propose a framework that incorporates two additional training phases for segmentation models, utilizing bottleneck features at both input and output stages. This approach significantly improves computational performance by reducing input and output dimensions with a negligible addition to parameter count, without compromising accuracy. Tree-NET features a three-layer architecture comprising Encoder-Net and Decoder-Net, which are autoencoders designed to compress input and label data, respectively, and Bridge-Net, a segmentation framework that supervises the bottleneck features. By focusing on dense, compressed representations, Tree-NET enhances operational efficiency and can be seamlessly integrated into existing segmentation models without altering their internal structures or increasing model size. We evaluate Tree-NET on two critical segmentation tasks – skin lesion and polyp segmentation – using various backbone models, including U-NET variants and Polyp-PVT. Experimental results demonstrate that Tree-NET reduces FLOPs by a factor of 4 to 13 and decreases memory usage, while achieving comparable or superior accuracy compared to the original architectures. These findings underscore Tree-NET’s potential as a robust and efficient solution for medical image segmentation.
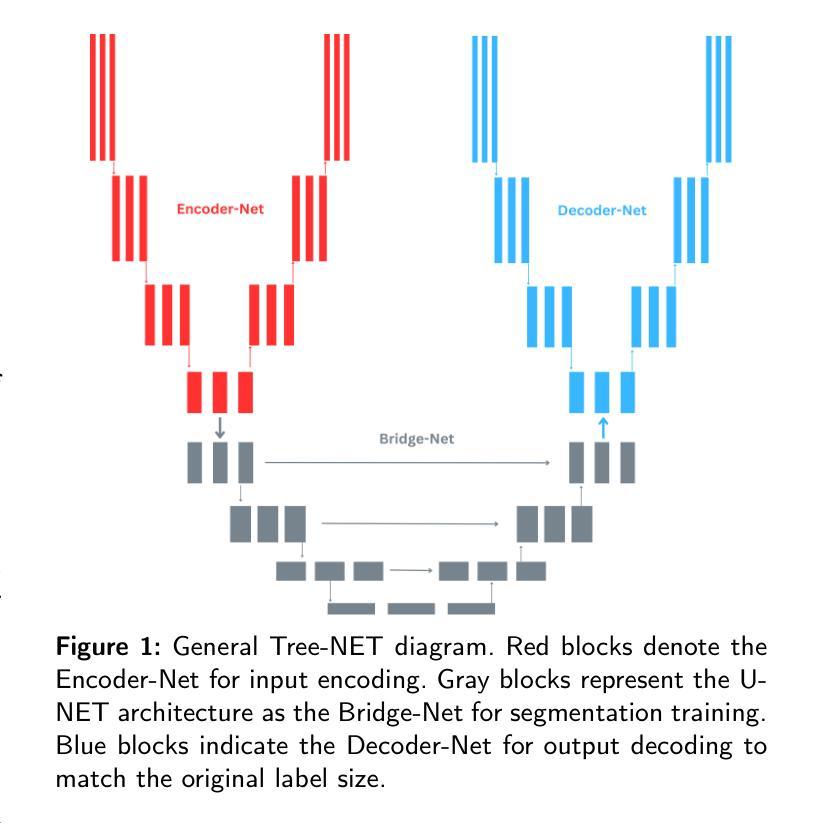
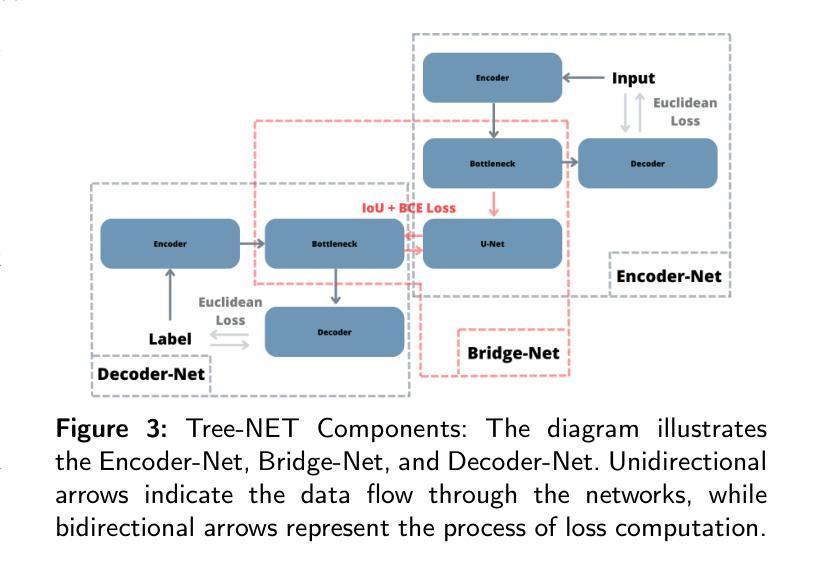
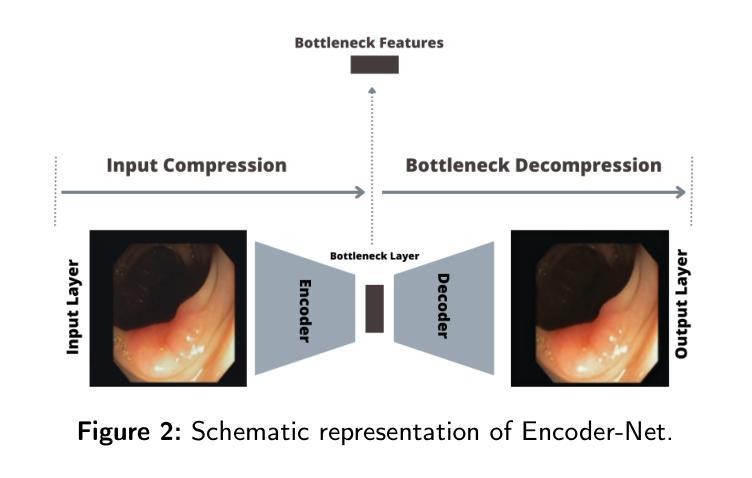
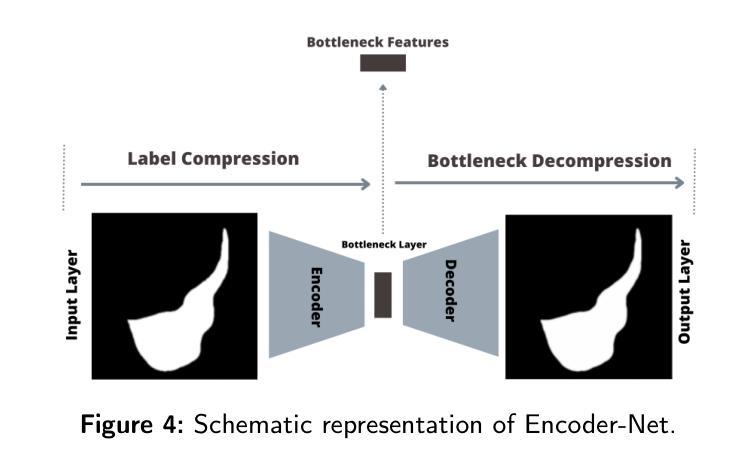
本文介绍了Tree-NET,这是一种新型的医学图像分割框架。它利用瓶颈特征监督来提高分割精度和计算效率。尽管之前的研究已经使用了瓶颈特征监督,但它们的应用大多仅限于训练阶段,在训练和评估过程中并没有提供计算上的优势。据我们所知,本研究首次提出了一种结合两个额外训练阶段的分割模型框架,在输入和输出阶段都利用瓶颈特征。这种方法通过减少输入和输出维度,在参数计数增加微乎其微的情况下,显著提高了计算性能,同时不损害准确性。Tree-NET采用三层架构,包括Encoder-Net和Decoder-Net,它们是分别设计来压缩输入和标签数据的自编码器,以及Bridge-Net,一个监督瓶颈特征的分割框架。通过关注密集、压缩的表示形式,Tree-NET提高了操作效率,可以无缝地集成到现有的分割模型中,而无需改变其内部结构或增加模型大小。我们在两个关键的分割任务——皮肤病变和息肉分割上评估了Tree-NET,使用了各种基础模型,包括U-NET变体和Polyp-PVT。实验结果表明,Tree-NET将FLOPs减少了4到13倍,并减少了内存使用,同时实现了与原始架构相当或更高的准确性。这些发现突出了Tree-NET作为医学图像分割的稳健高效解决方案的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This manuscript is 10 pages long, includes 10 figures and 3 tables, and presents a novel framework for medical image segmentation. It has been submitted to the Medical Image Analysis journal for review
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Tree-NET的新型医学图像分割框架,它利用瓶颈特征监督来提高分割精度和计算效率。Tree-NET采用三层架构,包括用于压缩输入数据的Encoder-Net和用于压缩标签数据的Decoder-Net,以及Bridge-Net分割框架,该框架对瓶颈特征进行监督。它通过关注密集、压缩的表示形式来提高操作效率,并可以无缝地集成到现有的分割模型中,而不改变其内部结构或增加模型大小。在皮肤病变和息肉分割等关键分割任务上的实验结果表明,Tree-NET在达到或超过原始架构准确性的同时,减少了FLOPs和内存使用。
Key Takeaways
- Tree-NET是一个新型的医学图像分割框架,采用瓶颈特征监督来提高分割精度和计算效率。
- 相比之前的研究,Tree-NET首次将瓶颈特征监督应用于输入和输出阶段,显著提高了计算性能。
- Tree-NET具有三层架构,包括Encoder-Net、Decoder-Net和Bridge-Net,分别用于压缩输入数据和标签数据,以及进行分割。
- Tree-NET关注密集、压缩的表示形式,提高了操作效率,可无缝集成到现有分割模型中。
- Tree-NET在皮肤病变和息肉分割等关键任务上的实验结果表明其潜力。
- Tree-NET在减少FLOPs和内存使用方面表现出优势,同时保持或提高准确性。
点此查看论文截图

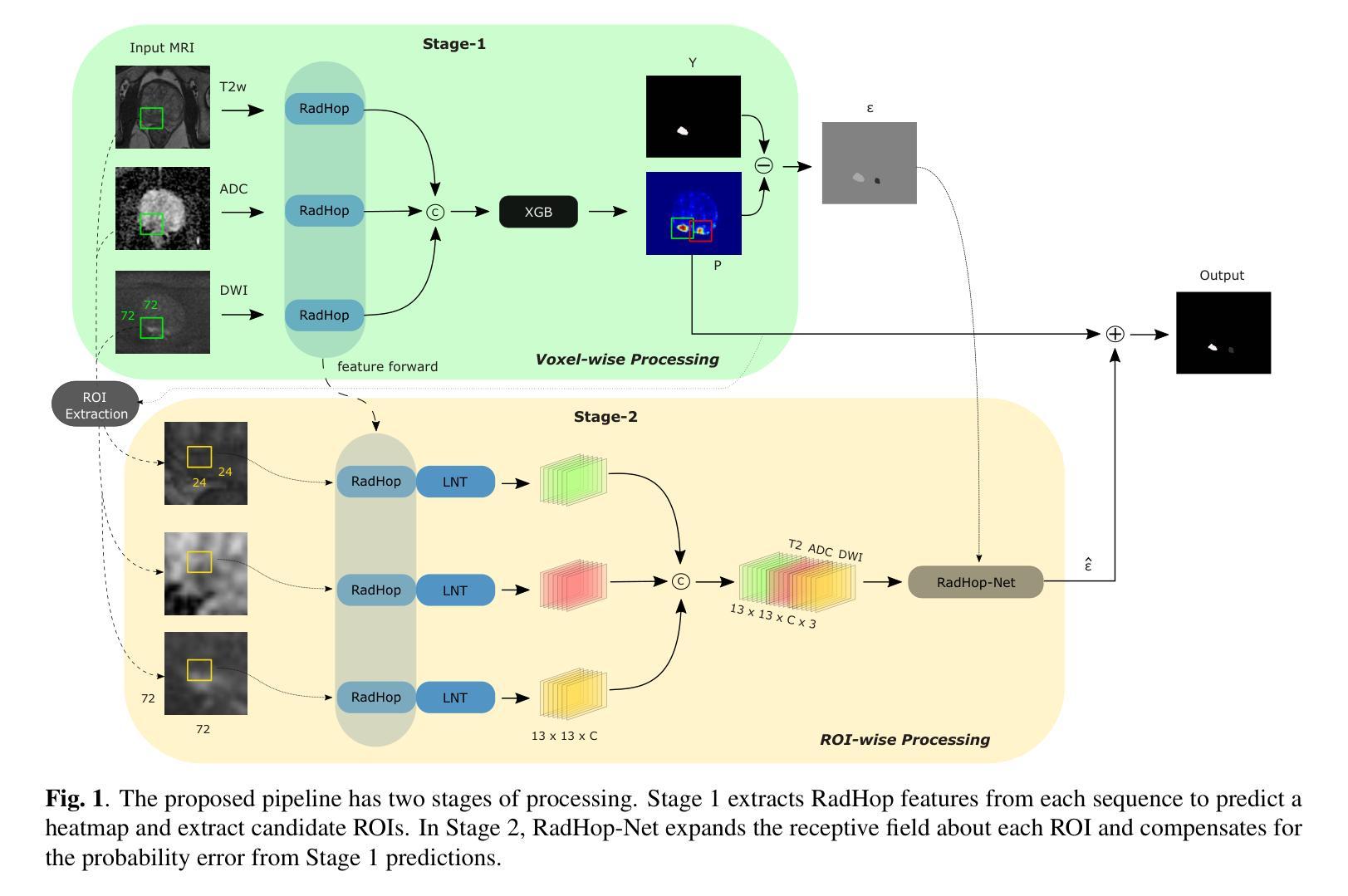
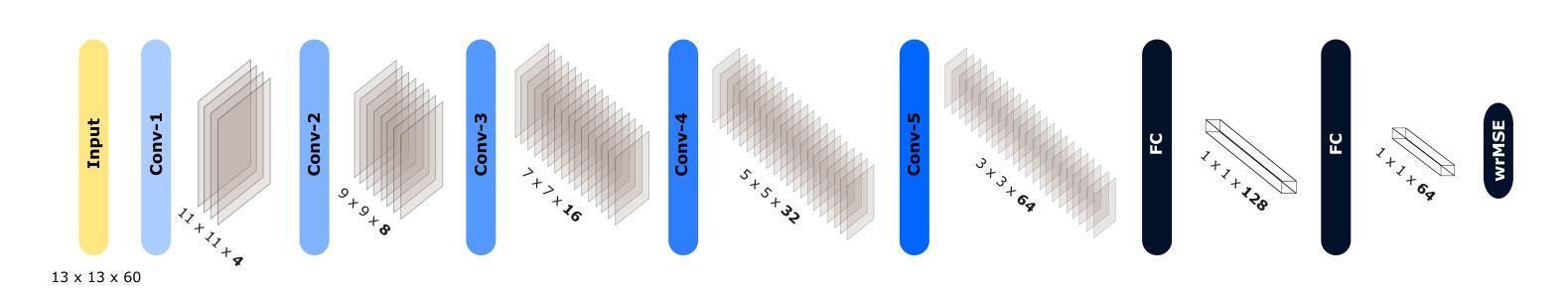
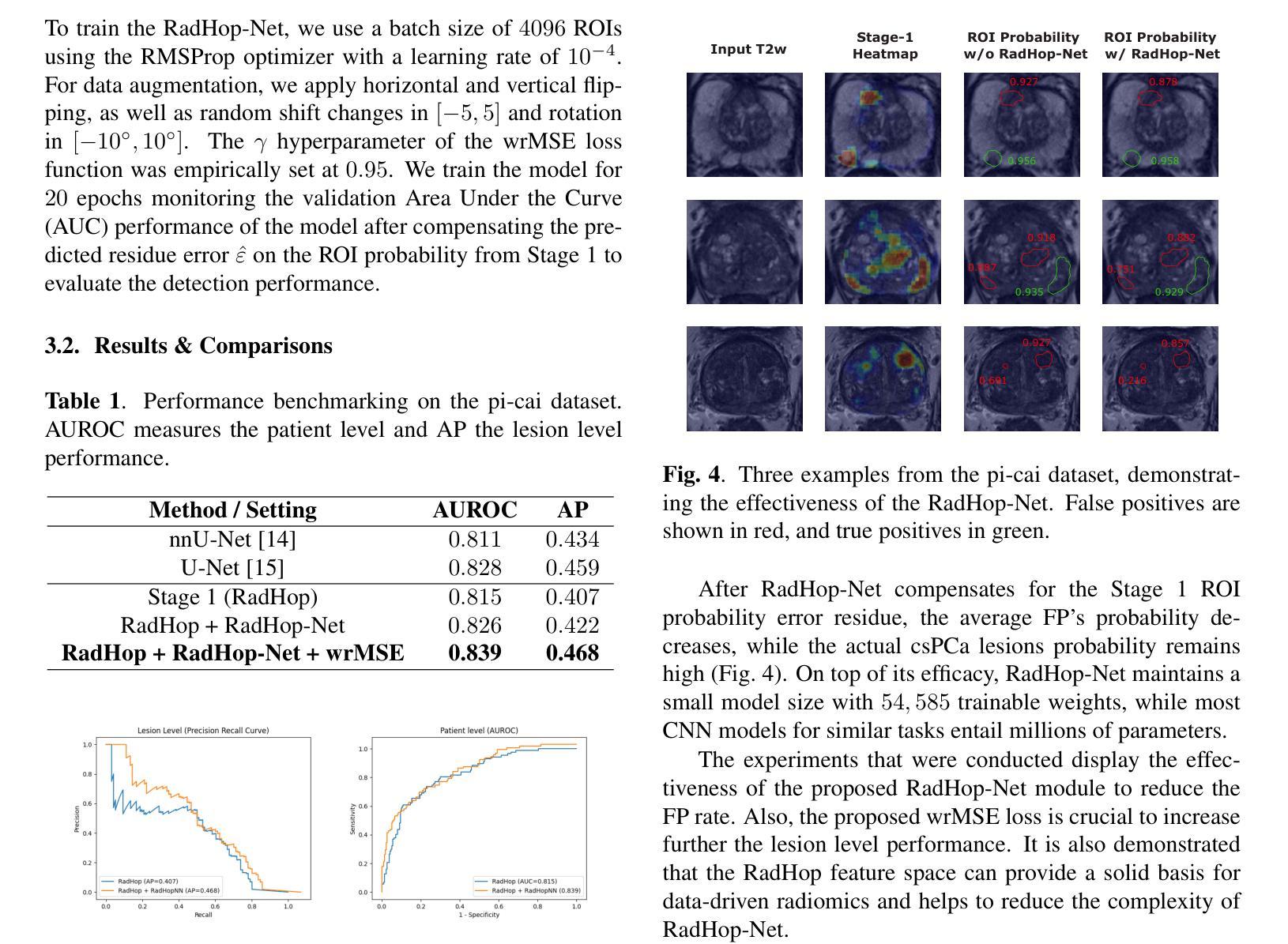
RadHop-Net: A Lightweight Radiomics-to-Error Regression for False Positive Reduction In MRI Prostate Cancer Detection
Authors:Vasileios Magoulianitis, Jiaxin Yang, Catherine A. Alexander, C. -C. Jay Kuo
Clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) is a leading cause of cancer death in men, yet it has a high survival rate if diagnosed early. Bi-parametric MRI (bpMRI) reading has become a prominent screening test for csPCa. However, this process has a high false positive (FP) rate, incurring higher diagnostic costs and patient discomfort. This paper introduces RadHop-Net, a novel and lightweight CNN for FP reduction. The pipeline consists of two stages: Stage 1 employs data driven radiomics to extract candidate ROIs. In contrast, Stage 2 expands the receptive field about each ROI using RadHop-Net to compensate for the predicted error from Stage 1. Moreover, a novel loss function for regression problems is introduced to balance the influence between FPs and true positives (TPs). RadHop-Net is trained in a radiomics-to-error manner, thus decoupling from the common voxel-to-label approach. The proposed Stage 2 improves the average precision (AP) in lesion detection from 0.407 to 0.468 in the publicly available pi-cai dataset, also maintaining a significantly smaller model size than the state-of-the-art.
临床显著前列腺癌(csPCa)是男性癌症死亡的主要原因之一,但早期诊断后的存活率较高。双参数磁共振成像(bpMRI)阅读已成为csPCa的重要筛查测试。然而,这个过程具有较高的假阳性率(FP),导致诊断成本增加和患者不适。本文介绍了RadHop-Net,这是一种新型的轻量级CNN,用于降低FP率。该管道分为两个阶段:第一阶段采用数据驱动放射学方法提取候选ROI。相比之下,第二阶段使用RadHop-Net扩大每个ROI的接收场,以弥补第一阶段预测误差。此外,引入了一种用于回归问题的新型损失函数,以平衡FP和真阳性(TP)之间的相互影响。RadHop-Net以放射学到误差的方式进行训练,从而与常见的体素到标签方法解耦。所提出第二阶段在公开的pi-cai数据集上将病变检测的平均精度(AP)从0.407提高到0.468,并且模型大小也显著小于当前最先进技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 4 figures - Accepted to IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于减少前列腺癌双参数MRI(bpMRI)检测中假阳性率(FP)的新型轻量化卷积神经网络(RadHop-Net)。RadHop-Net包含两个阶段,第一阶段利用数据驱动放射学提取候选感兴趣区域(ROIs),第二阶段使用RadHop-Net扩大每个ROI的感知场以补偿第一阶段的预测误差。此外,该研究还提出了一种适用于回归问题的新型损失函数,以平衡假阳性和真阳性之间的比率。相较于传统的体素到标签方法,RadHop-Net通过放射学到误差的方式进行训练,并在公开数据集pi-cai上实现了较高的平均精度(AP),同时模型体积较小。
Key Takeaways
- RadHop-Net是一种新型的轻量化卷积神经网络,用于减少前列腺癌双参数MRI检测中的假阳性率。
- RadHop-Net包含两个阶段,第一阶段提取候选感兴趣区域,第二阶段扩大感知场以补偿预测误差。
- 研究提出了一种适用于回归问题的新型损失函数,以平衡假阳性和真阳性之间的比率。
- RadHop-Net在公开数据集pi-cai上实现了较高的平均精度,从0.407提高到了0.468。
- RadHop-Net通过放射学到误差的方式进行训练,与传统的体素到标签方法不同。
- 该方法在保证检测性能的同时,模型体积较小。
点此查看论文截图

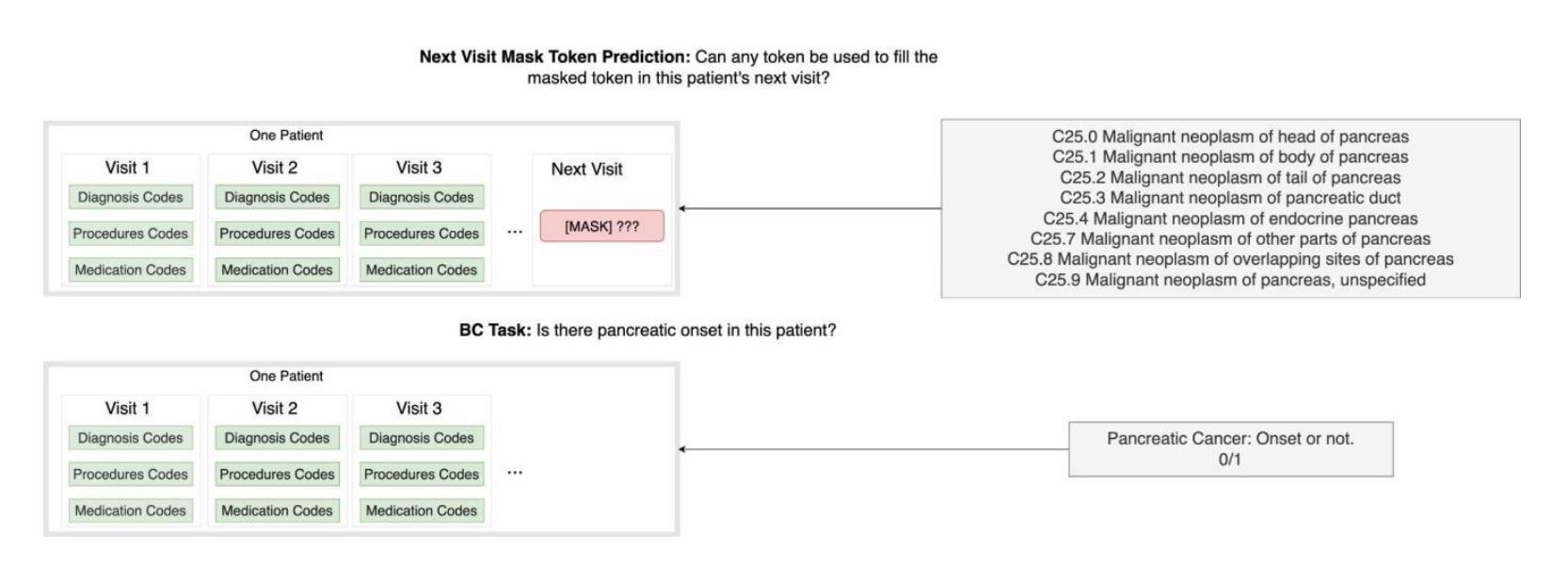
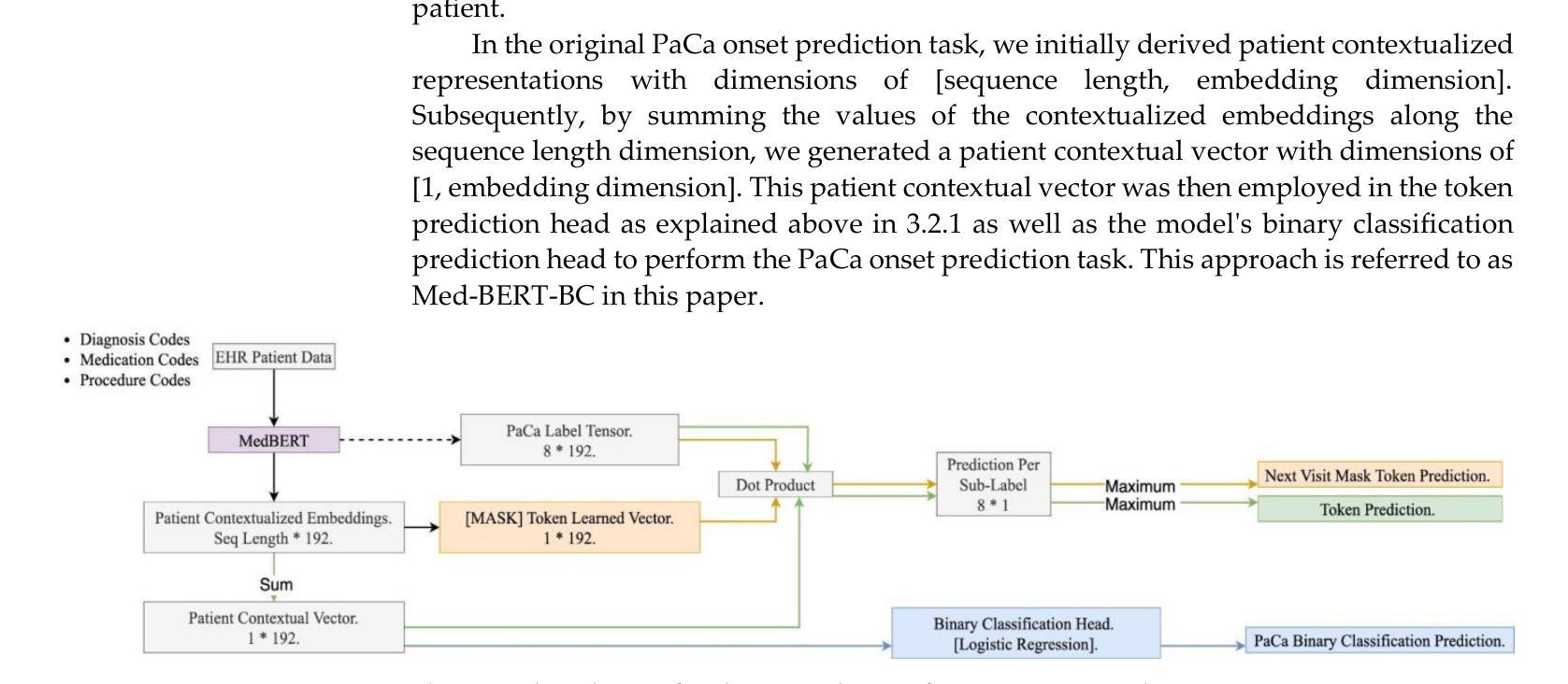
Advancing Pancreatic Cancer Prediction with a Next Visit Token Prediction Head on top of Med-BERT
Authors:Jianping He, Laila Rasmy, Degui Zhi, Cui Tao
Background: Recently, numerous foundation models pretrained on extensive data have demonstrated efficacy in disease prediction using Electronic Health Records (EHRs). However, there remains some unanswered questions on how to best utilize such models especially with very small fine-tuning cohorts. Methods: We utilized Med-BERT, an EHR-specific foundation model, and reformulated the disease binary prediction task into a token prediction task and a next visit mask token prediction task to align with Med-BERT’s pretraining task format in order to improve the accuracy of pancreatic cancer (PaCa) prediction in both few-shot and fully supervised settings. Results: The reformulation of the task into a token prediction task, referred to as Med-BERT-Sum, demonstrates slightly superior performance in both few-shot scenarios and larger data samples. Furthermore, reformulating the prediction task as a Next Visit Mask Token Prediction task (Med-BERT-Mask) significantly outperforms the conventional Binary Classification (BC) prediction task (Med-BERT-BC) by 3% to 7% in few-shot scenarios with data sizes ranging from 10 to 500 samples. These findings highlight that aligning the downstream task with Med-BERT’s pretraining objectives substantially enhances the model’s predictive capabilities, thereby improving its effectiveness in predicting both rare and common diseases. Conclusion: Reformatting disease prediction tasks to align with the pretraining of foundation models enhances prediction accuracy, leading to earlier detection and timely intervention. This approach improves treatment effectiveness, survival rates, and overall patient outcomes for PaCa and potentially other cancers.
背景:最近,许多在大量数据上训练的预训练基础模型在利用电子健康记录(EHRs)进行疾病预测方面显示出其有效性。然而,关于如何最好地利用这些模型(特别是在微调数据集非常小的情况下),仍然存在一些未解决的问题。方法:我们使用了针对EHR的Med-BERT模型,并将疾病二分类预测任务重新制定为令牌预测任务和下次就诊掩码令牌预测任务,以便与Med-BERT的预训练任务格式对齐,从而提高在少样本和完全监督设置下胰腺癌(PaCa)预测的准确性。结果:将任务重新制定为令牌预测任务(称为Med-BERT-Sum)在少样本场景和较大的数据样本中都表现出略微优越的性能。此外,将预测任务重新制定为下次就诊掩码令牌预测任务(Med-BERT-Mask)在数据规模从10到500个样本的少样本场景中,与传统的二分类(BC)预测任务(Med-BERT-BC)相比,其表现提高了3%至7%。这些发现表明,将下游任务与Med-BERT的预训练目标对齐,可以显著提高模型的预测能力,从而提高其在预测罕见和常见疾病方面的有效性。结论:重新格式化疾病预测任务,以与基础模型的预训练对齐,可以提高预测准确性,从而实现早期检测和及时干预。这种方法提高了胰腺癌和其他潜在癌症的治疗效果、存活率和总体患者预后。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
利用Med-BERT这一电子健康记录特定基础模型进行疾病预测任务的重构,包括标记预测任务和后续访问掩码标记预测任务,旨在提高胰腺癌预测的准确性。结果显示,在少量样本和完全监督条件下,任务重构均展现出轻微优势。特别是在任务重构为Next Visit Mask Token Prediction(Med-BERT-Mask)时,其在少量样本场景中相较于传统的Binary Classification(Med-BERT-BC)预测任务有3%-7%的提升。研究结果表明,下游任务与Med-BERT预训练目标的对齐能显著提高模型的预测能力,对罕见疾病和常见疾病的预测均有积极影响。改革疾病预测任务格式能提高预测准确性,从而有助于早期发现并及时干预,对胰腺癌和其他癌症的治疗效果和患者生存率产生积极影响。
关键见解
- 利用Med-BERT进行疾病预测任务的重构是提高准确性的有效方法。
- 通过将预测任务转换为标记预测任务和后续访问掩码标记预测任务,轻微提升了在少量样本和完全监督条件下的性能。
- Next Visit Mask Token Prediction任务(Med-BERT-Mask)在少量样本场景中显著优于传统的Binary Classification预测任务。
- 对齐下游任务与Med-BERT的预训练目标能显著提高模型的预测能力。
- 改革疾病预测任务格式有助于提高预测准确性,对早期发现和及时干预有积极影响。
点此查看论文截图

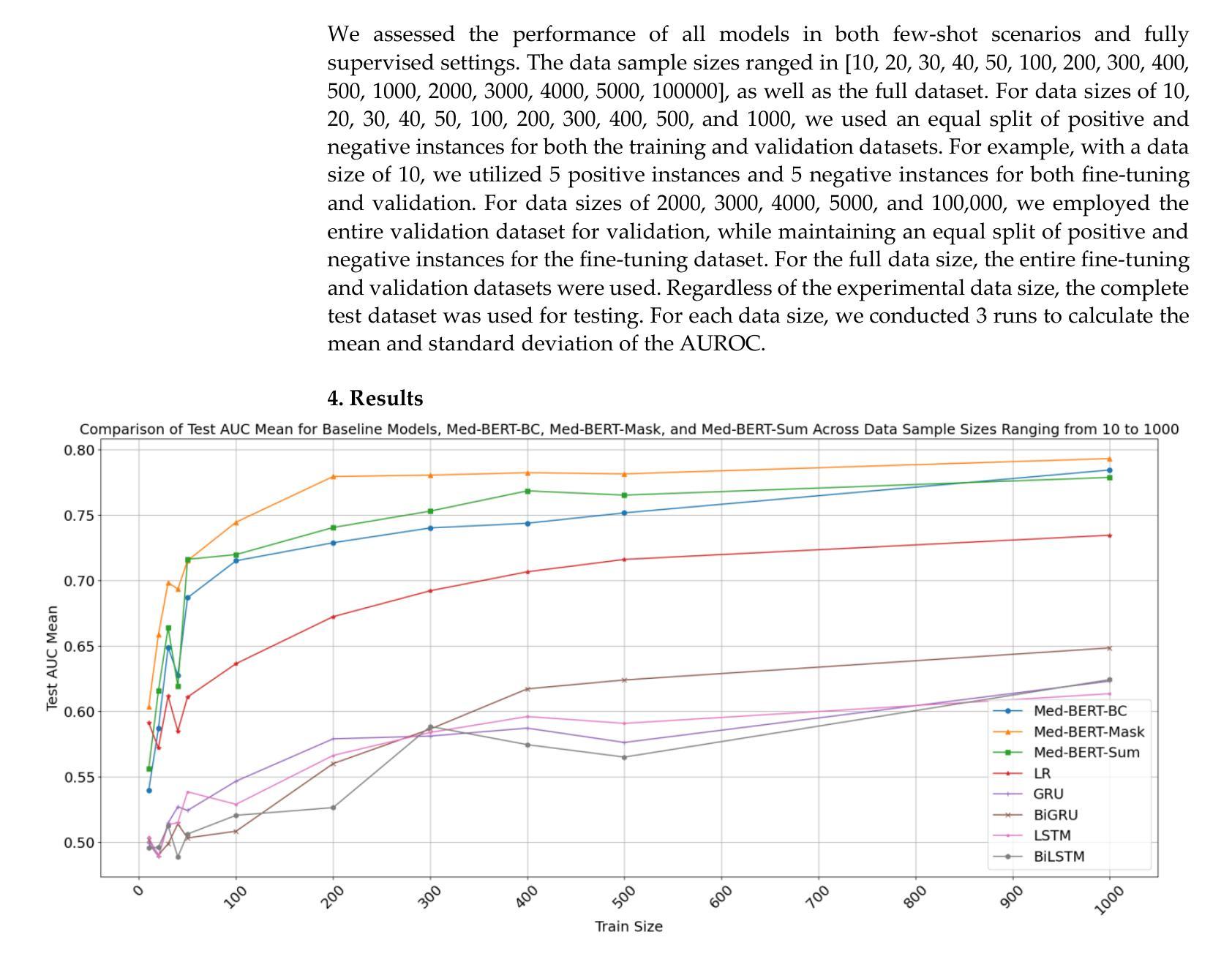
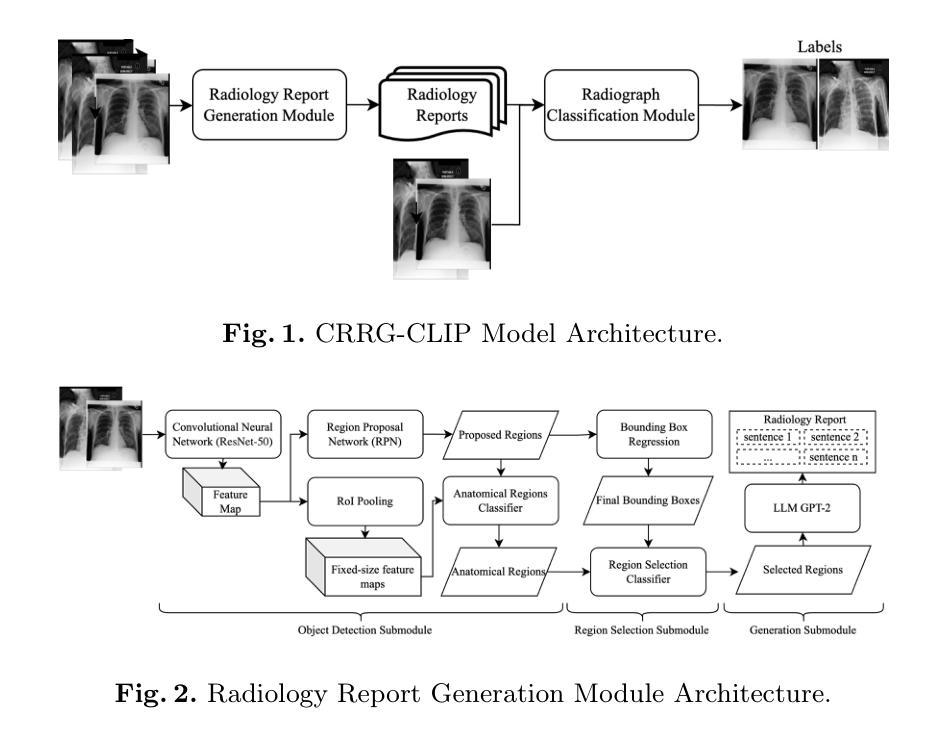
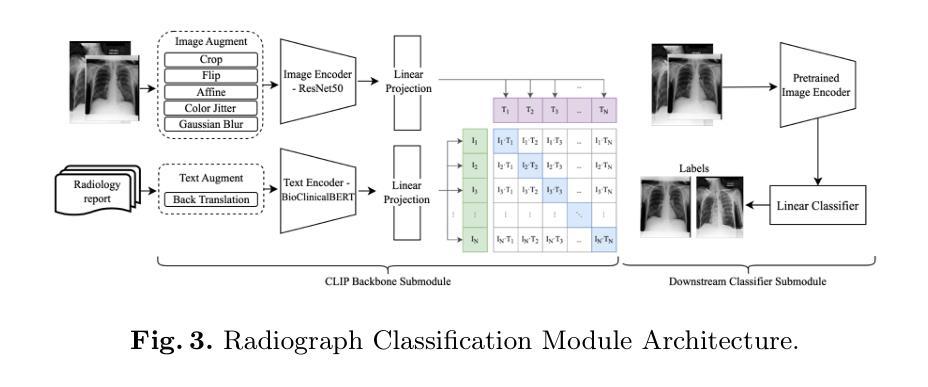
CRRG-CLIP: Automatic Generation of Chest Radiology Reports and Classification of Chest Radiographs
Authors:Jianfei Xu, Thanet Markchom, Huizhi Liang
The complexity of stacked imaging and the massive number of radiographs make writing radiology reports complex and inefficient. Even highly experienced radiologists struggle to maintain accuracy and consistency in interpreting radiographs under prolonged high-intensity work. To address these issues, this work proposes the CRRG-CLIP Model (Chest Radiology Report Generation and Radiograph Classification Model), an end-to-end model for automated report generation and radiograph classification. The model consists of two modules: the radiology report generation module and the radiograph classification module. The generation module uses Faster R-CNN to identify anatomical regions in radiographs, a binary classifier to select key regions, and GPT-2 to generate semantically coherent reports. The classification module uses the unsupervised Contrastive Language Image Pretraining (CLIP) model, addressing the challenges of high-cost labelled datasets and insufficient features. The results show that the generation module performs comparably to high-performance baseline models on BLEU, METEOR, and ROUGE-L metrics, and outperformed the GPT-4o model on BLEU-2, BLEU-3, BLEU-4, and ROUGE-L metrics. The classification module significantly surpasses the state-of-the-art model in AUC and Accuracy. This demonstrates that the proposed model achieves high accuracy, readability, and fluency in report generation, while multimodal contrastive training with unlabelled radiograph-report pairs enhances classification performance.
医学影像的复杂性以及大量的放射影像使得书写放射学报告变得复杂且效率低下。即使在长时间高强度工作下,经验丰富的放射科医生也很难保持解读放射影像的准确性和一致性。为了解决这些问题,本研究提出了CRRG-CLIP模型(胸部放射学报告生成和放射影像分类模型),这是一个用于自动报告生成和放射影像分类的端到端模型。该模型由两个模块组成:放射学报告生成模块和放射影像分类模块。生成模块使用Faster R-CNN识别放射影像中的解剖区域,使用二元分类器选择关键区域,并使用GPT-2生成语义连贯的报告。分类模块使用无监督的对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型,解决了高成本标签数据集和特征不足的挑战。结果表明,在BLEU、METEOR和ROUGE-L指标上,生成模块的性能与高性能基线模型相当,在BLEU-2、BLEU-3、BLEU-4和ROUGE-L指标上优于GPT-4o模型。分类模块在AUC和准确度方面远远超过了最先进模型的性能。这证明所提出的模型在报告生成方面达到了高准确性、可读性和流畅性,使用无标签的放射影像-报告对进行多模式对比训练增强了分类性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要介绍了使用CRRG-CLIP模型解决放射影像学报告生成和放射图像分类问题的复杂性和挑战。该模型包括两个模块:放射学报告生成模块和放射图像分类模块。生成模块使用Faster R-CNN识别放射图像中的解剖区域,使用二元分类器选择关键区域,并使用GPT-2生成语义连贯的报告。分类模块采用无监督对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型,解决了高成本标签数据集和特征不足的问题。实验结果表明,该模型在报告生成方面具有较高的准确性、可读性和流畅性,并在分类性能方面通过多模态对比训练增强了性能。
Key Takeaways
- 放射学报告生成和放射图像分类面临复杂性和效率问题。
- CRRG-CLIP模型包括报告生成和图像分类两个模块。
- 生成模块使用Faster R-CNN识别解剖区域,二元分类器选关键区域,GPT-2生成报告。
- 分类模块采用无监督的CLIP模型,解决高成本标签数据集和特征不足问题。
- 模型在报告生成方面表现出高准确性、可读性和流畅性。
- 多模态对比训练增强了模型的分类性能。
点此查看论文截图

Scale-wise Bidirectional Alignment Network for Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Authors:Kun Li, George Vosselman, Michael Ying Yang
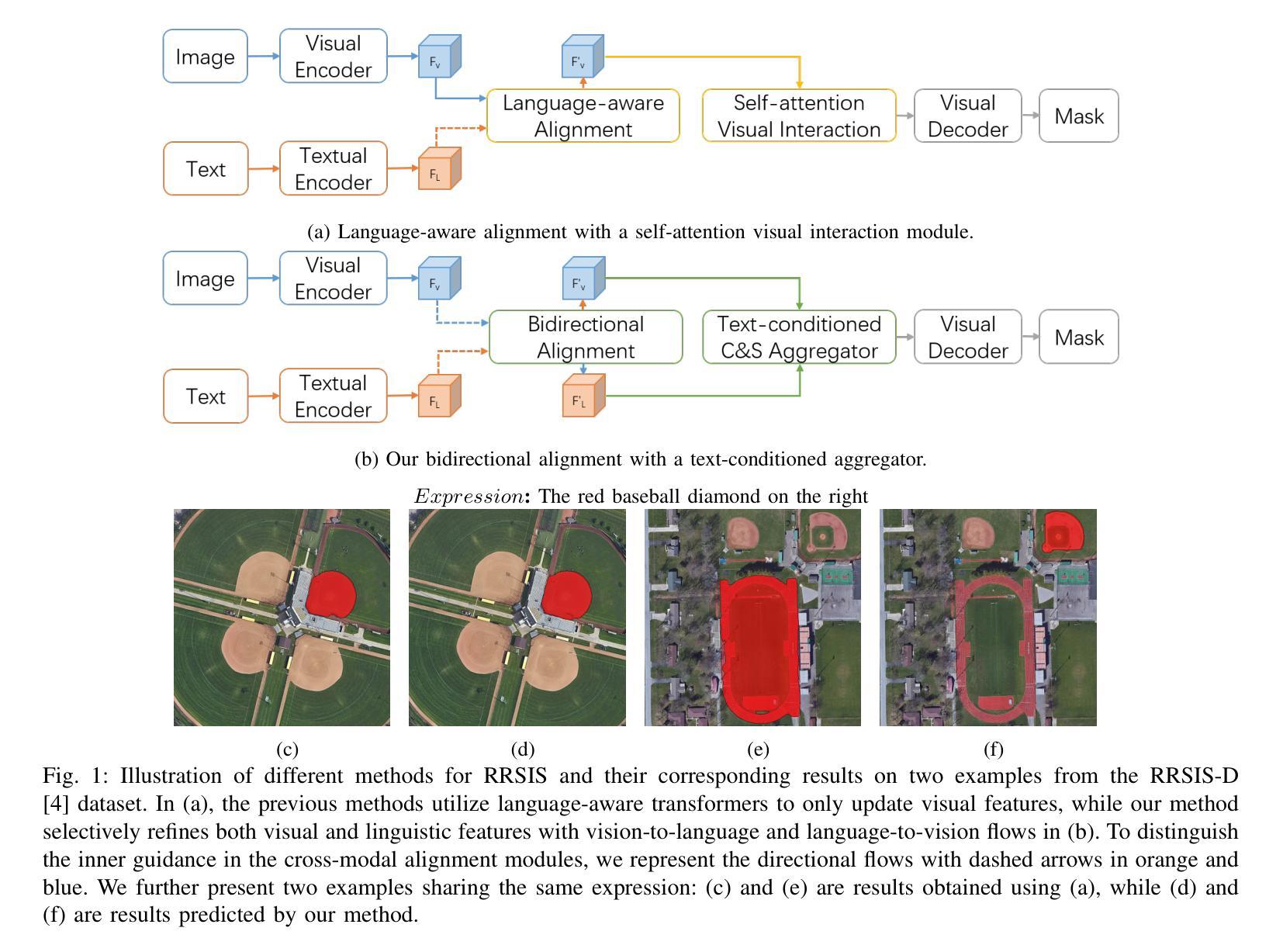
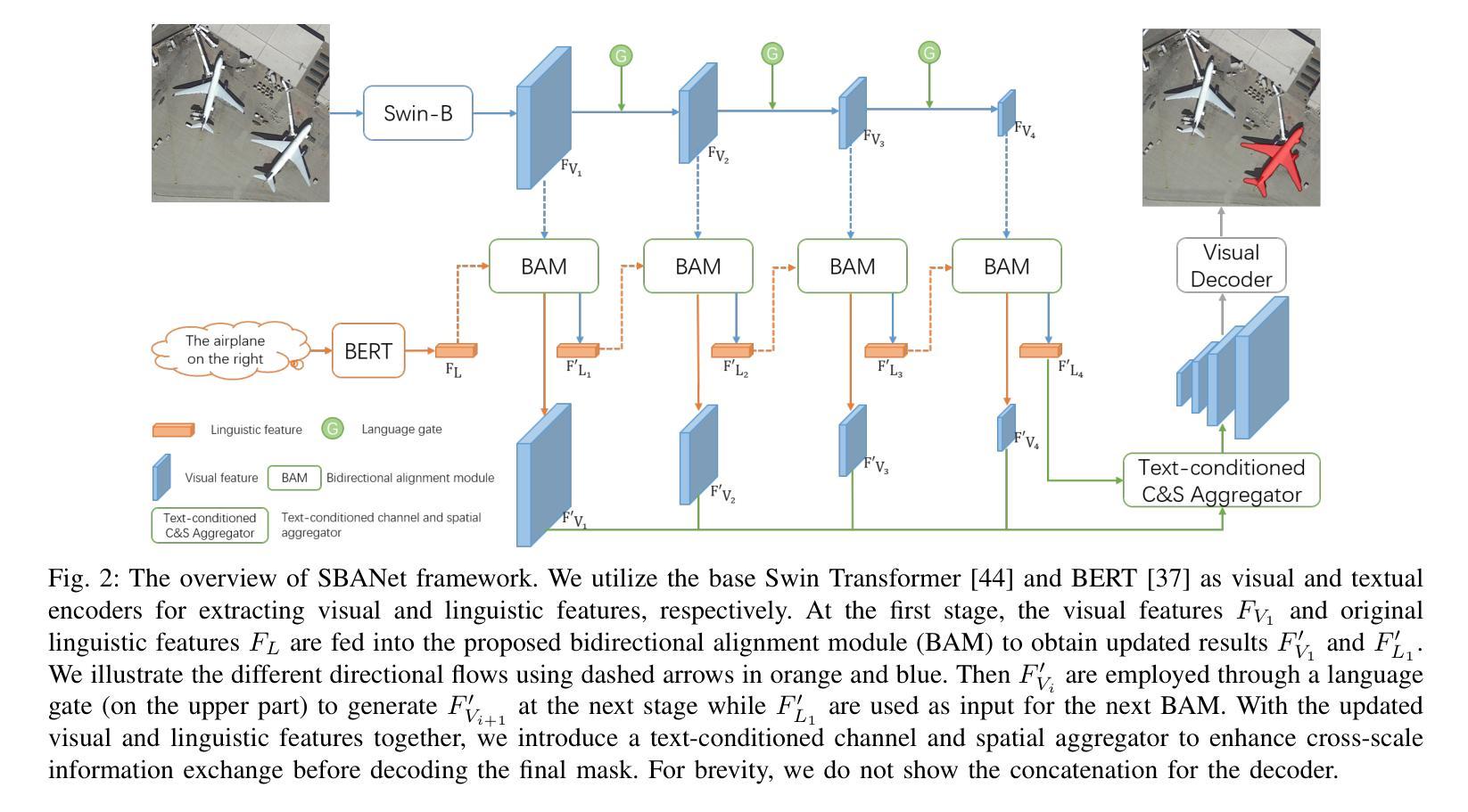
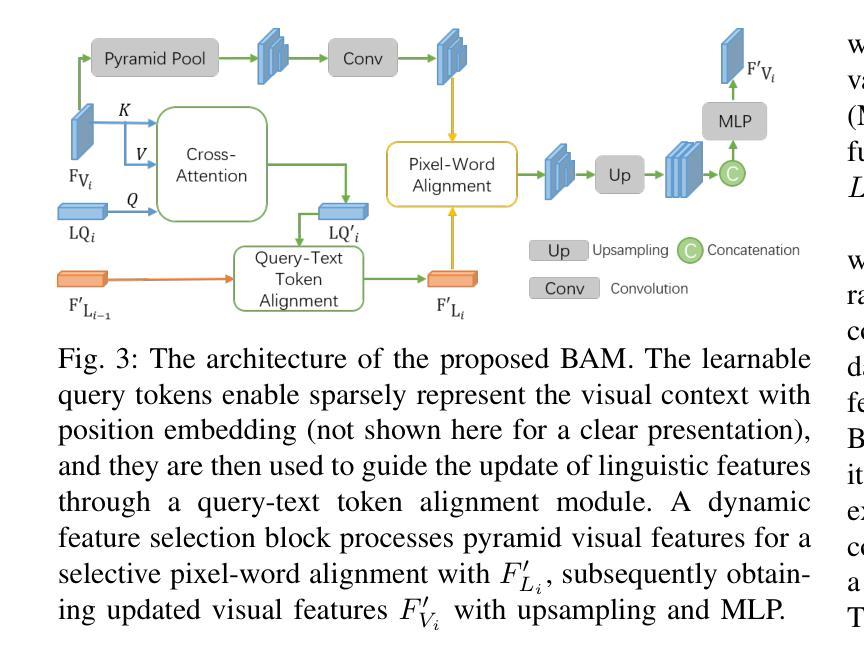
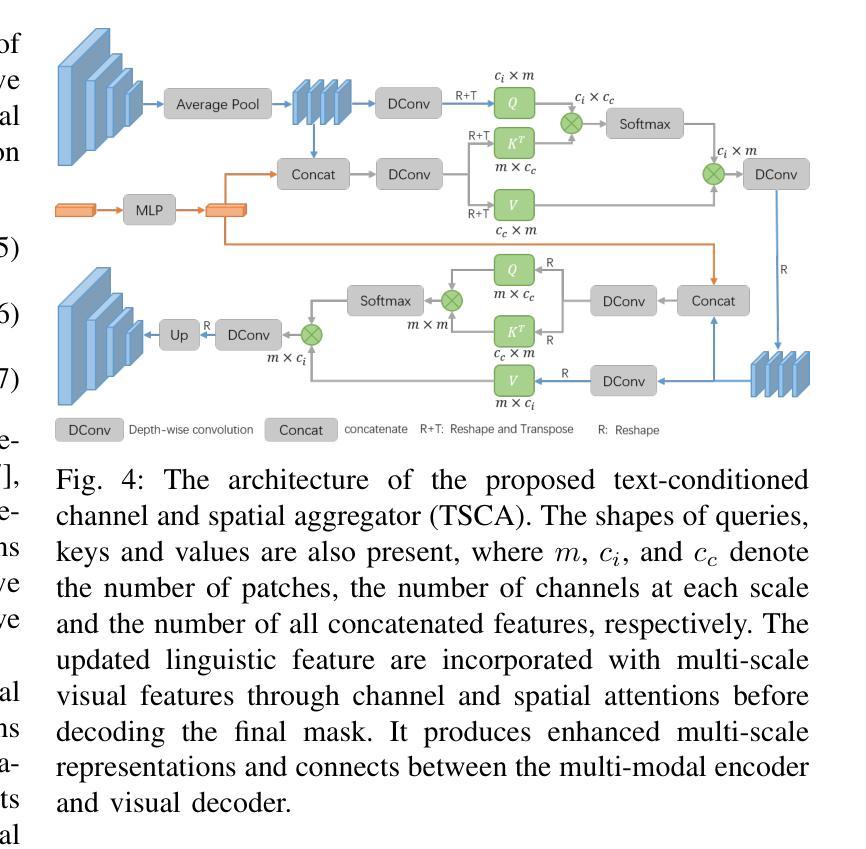
The goal of referring remote sensing image segmentation (RRSIS) is to extract specific pixel-level regions within an aerial image via a natural language expression. Recent advancements, particularly Transformer-based fusion designs, have demonstrated remarkable progress in this domain. However, existing methods primarily focus on refining visual features using language-aware guidance during the cross-modal fusion stage, neglecting the complementary vision-to-language flow. This limitation often leads to irrelevant or suboptimal representations. In addition, the diverse spatial scales of ground objects in aerial images pose significant challenges to the visual perception capabilities of existing models when conditioned on textual inputs. In this paper, we propose an innovative framework called Scale-wise Bidirectional Alignment Network (SBANet) to address these challenges for RRSIS. Specifically, we design a Bidirectional Alignment Module (BAM) with learnable query tokens to selectively and effectively represent visual and linguistic features, emphasizing regions associated with key tokens. BAM is further enhanced with a dynamic feature selection block, designed to provide both macro- and micro-level visual features, preserving global context and local details to facilitate more effective cross-modal interaction. Furthermore, SBANet incorporates a text-conditioned channel and spatial aggregator to bridge the gap between the encoder and decoder, enhancing cross-scale information exchange in complex aerial scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method achieves superior performance in comparison to previous state-of-the-art methods on the RRSIS-D and RefSegRS datasets, both quantitatively and qualitatively. The code will be released after publication.
遥感图像分割(RRSIS)的目标是通过自然语言表达式提取航空图像中特定的像素级区域。最近的进步,特别是基于Transformer的融合设计,已经在这个领域取得了显著的进展。然而,现有方法主要集中在跨模态融合阶段的以语言为中心的指导下对视觉特征的精炼,忽视了互补的视到语言的流程。这一局限性通常会导致无关或次优的表示。此外,航空图像中地面对象多样的空间尺度给现有模型在文本输入条件下的视觉感知能力带来了重大挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为Scale-wise Bidirectional Alignment Network(SBANet)的创新框架,以解决RRSIS的这些挑战。具体来说,我们设计了一个带有可学习查询令牌的双向对齐模块(BAM),以选择性和有效地表示视觉和语言特征,并强调与关键令牌相关的区域。BAM进一步通过一个动态特征选择块增强功能,旨在提供宏观和微观层面的视觉特征,保留全局上下文和局部细节,以促进更有效的跨模态交互。此外,SBANet还采用了文本条件通道和空间聚合器,以缩小编码器和解码器之间的差距,增强复杂航空场景中跨尺度信息的交换。大量实验表明,与RRSIS-D和RefSegRS数据集上的最新方法相比,我们的方法在定量和定性方面均实现了卓越的性能。代码将在发表后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
摘要
遥感图像分割(RRSIS)的目标是通过自然语言表达式提取航空图像中的特定像素级区域。最近的进步,特别是基于Transformer的融合设计,已经在这个领域取得了显著的进步。然而,现有方法主要集中在利用语言感知指导来优化视觉特征,忽视了从视觉到语言的互补流动。这种局限性通常会导致表示不相关或次优。此外,航空图像中地面对象的空间尺度多样性对现有模型的视觉感知能力提出了挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为Scale-wise Bidirectional Alignment Network (SBANet)的创新框架,以解决RRSIS的这些挑战。我们设计了带有可学习查询令牌的双向对齐模块(BAM),以选择和有效地表示视觉和语言特征,并强调与关键令牌相关的区域。BAM进一步通过动态特征选择块得到增强,旨在提供宏观和微观的视觉特征,保留全局上下文和局部细节,以促进更有效的跨模态交互。此外,SBANet结合了文本条件通道和空间聚合器,以缩小编码器和解码器之间的差距,增强复杂航空场景中的跨尺度信息交换。大量实验表明,与RRSIS-D和RefSegRS数据集上的最新方法相比,我们提出的方法在定量和定性方面都实现了卓越的性能。代码将在发表后发布。
要点
- 遥感图像分割(RRSIS)旨在通过自然语言表达式从航空图像中提取特定像素级区域。
- 现有方法主要关注于使用语言感知指导在跨模态融合阶段优化视觉特征,但忽视了从视觉到语言的互补流动。
- 本文提出了一种名为SBANet的创新框架,通过双向对齐模块(BAM)和动态特征选择块来解决这些挑战。
- BAM能够选择和有效地表示视觉和语言特征,并强调与关键令牌相关的区域。
- SBANet结合了文本条件通道和空间聚合器,以增强跨模态交互和跨尺度信息交换。
- 在RRSIS-D和RefSegRS数据集上的实验表明,SBANet在性能上超越了以前的方法。
- 代码将在发表后公开。
点此查看论文截图