⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-08 更新
Phase-contrast imaging of a dense atomic cloud
Authors:M. Frometa Fernandez, P. G. Santos Dias, P. H. Nantes Magnani, M. do Amaral Martins, M. Hugbart, A. Cipris, Ph. W. Courteille, R. Celistrino Teixeira
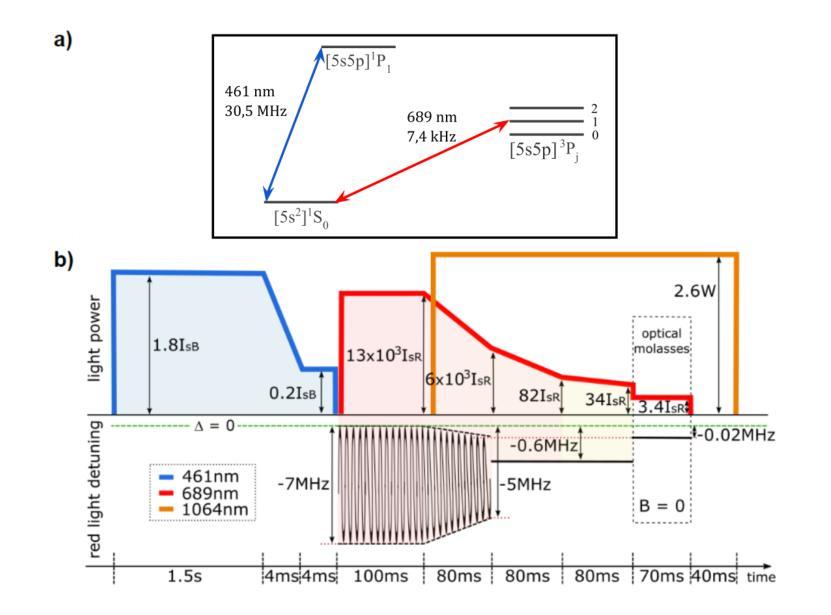
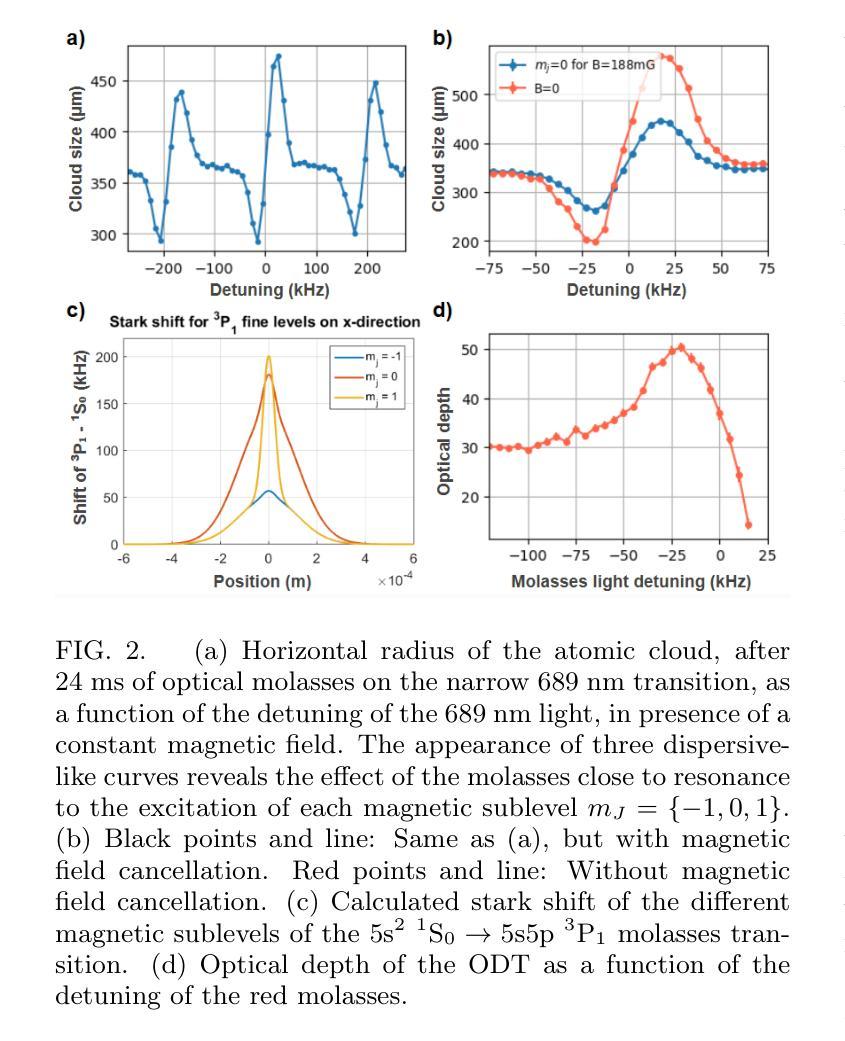
We present the experimental production and characterization of a dense cold atomic cloud of (^{88}\text{Sr}) atoms, optimized for the future studies of light transport in highly dense regimes. Using narrow-line molasses on the 689 nm transition, combined with a far off-resonant optical dipole trap, we achieve spatial densities as high as (7.9 \times 10^{13} , \text{atoms/cm}^3) and optical depths up to 64. This approach stands out from previous methods by integrating narrow-line molasses with an optical dipole trap, enabling high-density samples without relying on evaporative cooling. Unlike traditional absorption imaging, which becomes inaccurate in such dense regimes, we demonstrate that phase-contrast imaging (PCI) can reliably reconstruct the in-situ density profile even for highly spatially and optically dense samples. The use of a spatial light modulator instead of a fixed phase plate in the PCI setup provides enhanced flexibility and control of imaging parameters, making this imaging technique robust against imaging artifacts and adaptable to varying experimental conditions. Moreover, we derive theoretical conditions for reliable PCI operation in dense regimes and validate these experimentally, showing excellent agreement with time-of-flight measurements even at the highest densities. Our results establish a robust method for producing and characterizing dense atomic clouds.
我们展示了一个密集且温度低的^{88}\text{Sr}原子云的实验产生和特性研究,优化了未来在密集状态下的光传输研究。通过在689 nm跃迁上利用窄线激光束,结合远非共振光学偶极阱,我们实现了高达(7.9 \times 10^{13} , \text{原子/cm}^3)的空间密度和高达64的光学深度。这种方法通过将窄线激光束与光学偶极阱相结合,使得在不依赖蒸发冷却的情况下实现高密度样品成为可能,这与之前的方法有所不同。在传统的吸收成像中,由于在这种密集状态下的误差会变得非常大,因此我们证明了相位对比成像(PCI)即使在高度空间和光学密集的样品中也能可靠地重建原位密度分布。在PCI设置中,使用空间光调制器替代固定的相位板,为成像参数提供了更高的灵活性和控制性,使这种成像技术对各种成像伪影具有鲁棒性,并能适应不同的实验条件。此外,我们推导了在密集状态下可靠PCI操作的理论条件,并通过实验验证,即使在最高的密度下,这些理论也与飞行时间测量结果非常吻合。我们的结果建立了一种生产并表征密集原子云的有效方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 7 figures
Summary
该研究成功利用窄线光减速技术与光学偶极阱相结合,创建了密度极高的冷原子云,适用于未来密集环境下光传输的研究。利用相位对比成像技术,成功重建了高密度原子云的原位密度分布,并通过实验验证了其在高密度环境下的可靠性。此外,该研究还提高了成像参数的灵活性和控制性,为不同实验条件下高密度原子云的研究提供了可靠方法。
Key Takeaways
- 利用窄线光减速技术与光学偶极阱结合,实现了高密度冷原子云的制备。
- 原子云的空间密度高达(7.9 \times 10^{13} , \text{atoms/cm}^3),光学深度达到64。
- 相位对比成像技术(PCI)在密集环境下能可靠重建原子云的原位密度分布。
- 与传统吸收成像相比,PCI技术在高密度样本中表现出更高的可靠性。
- 使用空间光调制器增强了PCI设置的灵活性和成像参数的控制性。
- 研究人员推导出了可靠PCI操作的理论条件,并通过实验验证了其与飞行时间测量的高度一致性。
- 该研究为创建和表征高密度原子云提供了稳健的方法。
点此查看论文截图

GLFC: Unified Global-Local Feature and Contrast Learning with Mamba-Enhanced UNet for Synthetic CT Generation from CBCT
Authors:Xianhao Zhou, Jianghao Wu, Huangxuan Zhao, Lei Chen, Shaoting Zhang, Guotai Wang, Guotai Wang
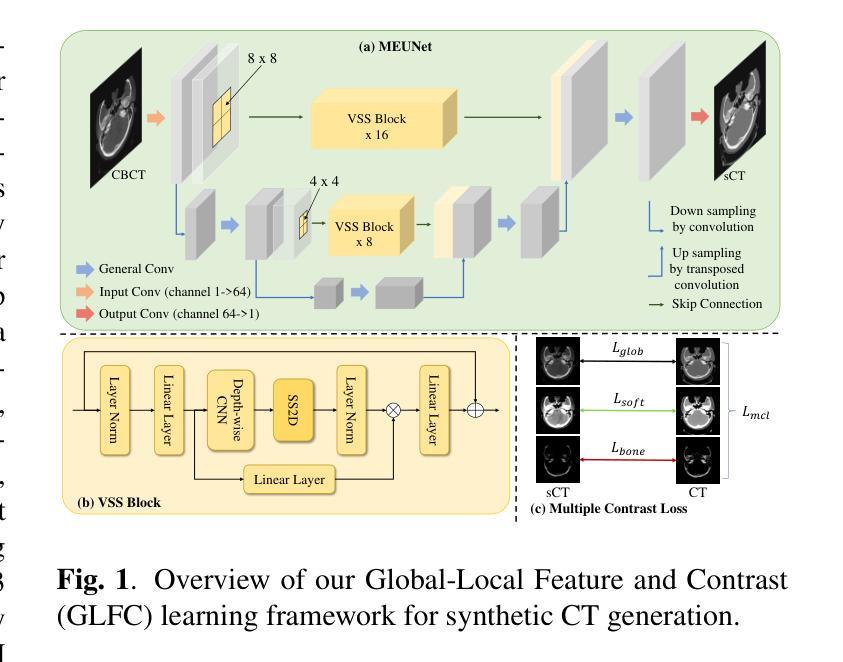
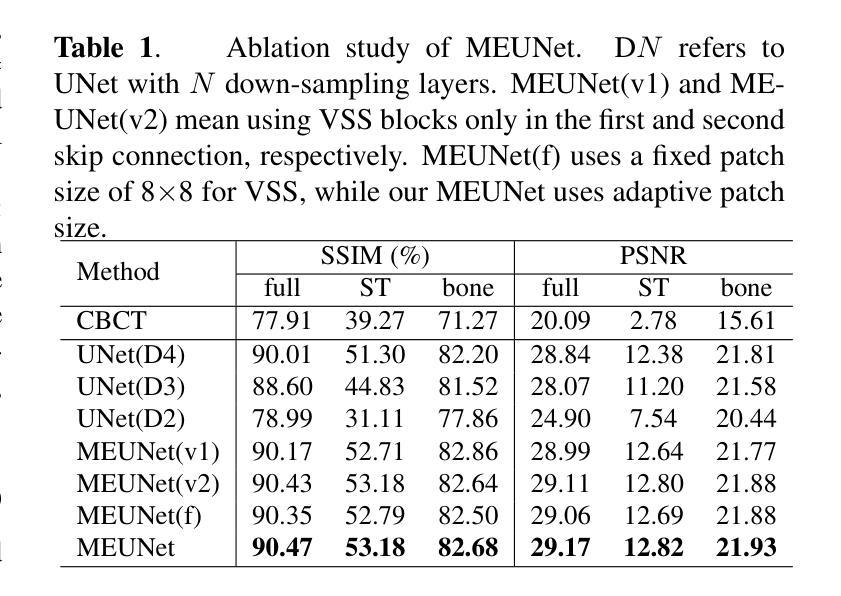
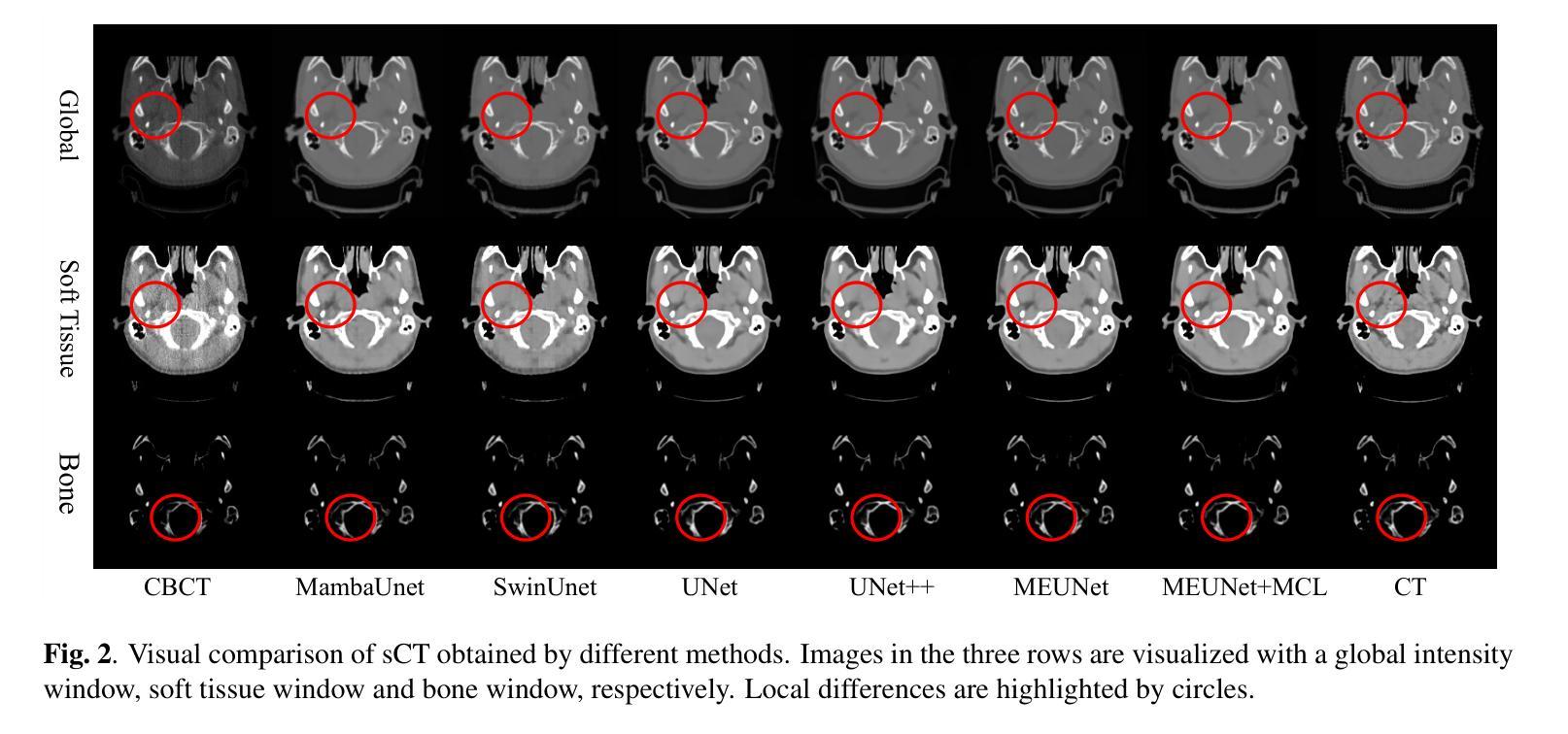
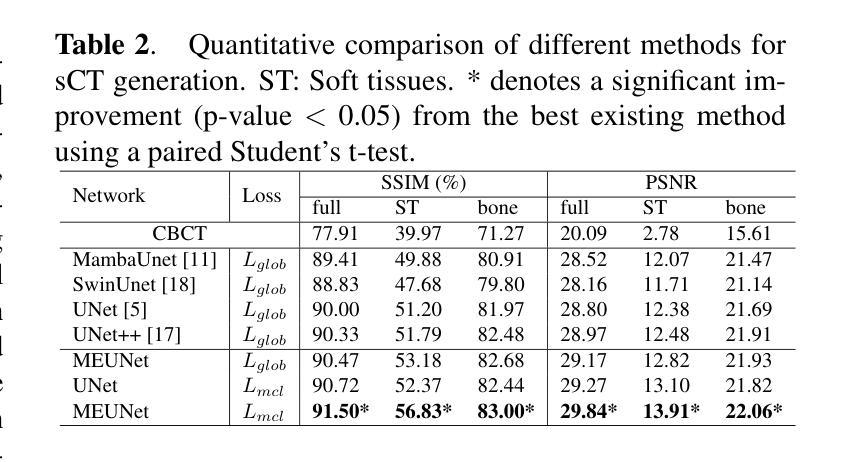
Generating synthetic Computed Tomography (CT) images from Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is desirable for improving the image quality of CBCT. Existing synthetic CT (sCT) generation methods using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Transformers often face difficulties in effectively capturing both global and local features and contrasts for high-quality sCT generation. In this work, we propose a Global-Local Feature and Contrast learning (GLFC) framework for sCT generation. First, a Mamba-Enhanced UNet (MEUNet) is introduced by integrating Mamba blocks into the skip connections of a high-resolution UNet for effective global and local feature learning. Second, we propose a Multiple Contrast Loss (MCL) that calculates synthetic loss at different intensity windows to improve quality for both soft tissues and bone regions. Experiments on the SynthRAD2023 dataset demonstrate that GLFC improved the SSIM of sCT from 77.91% to 91.50% compared with the original CBCT, and significantly outperformed several existing methods for sCT generation. The code is available at https://github.com/intelland/GLFC
从锥束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)生成合成计算机断层扫描(CT)图像是改善CBCT图像质量的理想选择。现有使用卷积神经网络(CNN)和Transformer的合成CT(sCT)生成方法,在有效捕获全局和局部特征以及对比度以生成高质量sCT时常常面临困难。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于sCT生成的全球-局部特征和对比度学习(GLFC)框架。首先,通过在高分辨率UNet的跳过连接中集成Mamba块,引入了Mamba增强UNet(MEUNet),以实现有效的全局和局部特征学习。其次,我们提出了一种多对比度损失(MCL),它在不同的强度窗口计算合成损失,以提高软组织和骨区域的图像质量。在SynthRAD2023数据集上的实验表明,与原始CBCT相比,GLFC将sCT的SSIM从77.91%提高到91.50%,并且在sCT生成方面显著优于几种现有方法。代码可在https://github.com/intelland/GLFC找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ISBI2025
Summary
该文提出了一种基于全球局部特征和对比度学习(GLFC)框架的合成计算机断层扫描(sCT)生成方法。通过引入Mamba增强UNet(MEUNet)和多重对比度损失(MCL),该方法能够更有效地捕捉全局和局部特征,并改善软组织和骨区域的图像质量。在SynthRAD2023数据集上的实验表明,GLFC方法将sCT的SSIM指数从77.91%提高到91.50%,并显著优于其他sCT生成方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的合成计算机断层扫描(sCT)生成方法,旨在提高锥束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)的图像质量。
- 引入了Mamba增强UNet(MEUNet),通过集成Mamba块到高分辨率UNet的跳过连接,实现全局和局部特征的有效学习。
- 提出了多重对比度损失(MCL),在不同的强度窗口计算合成损失,以改善软组织和骨区域的图像质量。
- 在SynthRAD2023数据集上的实验表明,GLFC方法显著提高了sCT的SSIM指数。
- GLFC方法相较于其他sCT生成方法表现出优越性。
- 该研究的代码已公开可用,方便后续研究使用。
- 该方法对于改善CBCT图像质量,尤其是在医学诊断和治疗中具有潜在的应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

Enhancing Contrastive Learning for Retinal Imaging via Adjusted Augmentation Scales
Authors:Zijie Cheng, Boxuan Li, André Altmann, Pearse A Keane, Yukun Zhou
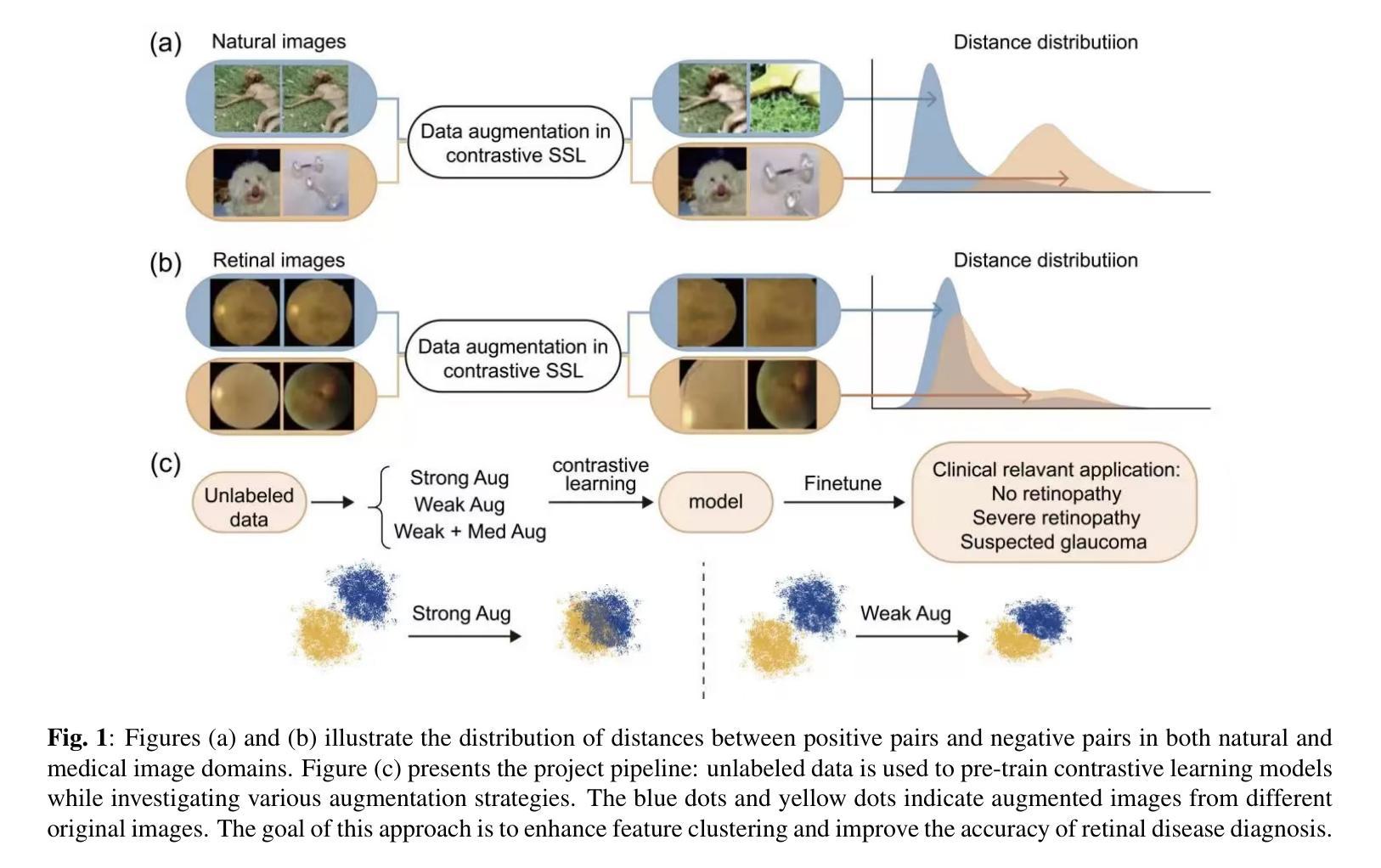
Contrastive learning, a prominent approach within self-supervised learning, has demonstrated significant effectiveness in developing generalizable models for various applications involving natural images. However, recent research indicates that these successes do not necessarily extend to the medical imaging domain. In this paper, we investigate the reasons for this suboptimal performance and hypothesize that the dense distribution of medical images poses challenges to the pretext tasks in contrastive learning, particularly in constructing positive and negative pairs. We explore model performance under different augmentation strategies and compare the results to those achieved with strong augmentations. Our study includes six publicly available datasets covering multiple clinically relevant tasks. We further assess the model’s generalizability through external evaluations. The model pre-trained with weak augmentation outperforms those with strong augmentation, improving AUROC from 0.838 to 0.848 and AUPR from 0.523 to 0.597 on MESSIDOR2, and showing similar enhancements across other datasets. Our findings suggest that optimizing the scale of augmentation is critical for enhancing the efficacy of contrastive learning in medical imaging.
对比学习是自监督学习中的突出方法,在自然图像相关的各种应用中已经显示出其在构建通用模型方面的显著有效性。然而,最近的研究表明,这些成功并不必然推广到医学成像领域。在本文中,我们调查了性能不佳的原因,并假设医学图像的密集分布给对比学习中的预文本任务带来了挑战,特别是在构建正负面样本对时。我们探索了不同增强策略下的模型性能,并将结果与强增强所达到的结果进行了比较。我们的研究包括六个公开数据集,涵盖多个临床相关任务。我们还通过外部评估对模型的泛化性进行了评估。用弱增强进行预训练的模型优于用强增强进行预训练的模型,在MESSIDOR2数据集上,AUROC从0.838提高到0.848,AUPR从0.523提高到0.597,在其他数据集上也表现出类似的改进。我们的研究结果表明,优化增强的规模对于提高医学成像中对比学习的效果至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
对比学习是自监督学习中的一种重要方法,在自然图像应用领域已展现出显著效果。然而,在医学成像领域,其表现并不理想。本文探究了其原因,并假设医学图像的密集分布给对比学习的预设任务带来了挑战,特别是在构建正负样本对时。通过探索不同增强策略下的模型性能并与强增强结果进行比较,研究发现预训练使用弱增强的模型表现较好。在MESSIDOR2数据集上,弱增强模型的AUROC从0.838提高到0.848,AUPR从0.523提高到0.597。其他数据集也显示出类似提升。这表明优化增强的规模对于提高医学成像中对比学习的效果至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 对比学习在自然图像领域表现良好,但在医学成像领域表现不佳。
- 医学图像的密集分布给对比学习的预设任务带来了挑战。
- 预训练使用弱增强的模型在医学成像领域表现较好。
- 在不同数据集上,弱增强模型的性能有所提升。
- 优化增强的规模能增强对比学习在医学成像中的效果。
- 模型在AUROC和AUPR指标上有所提升。
点此查看论文截图


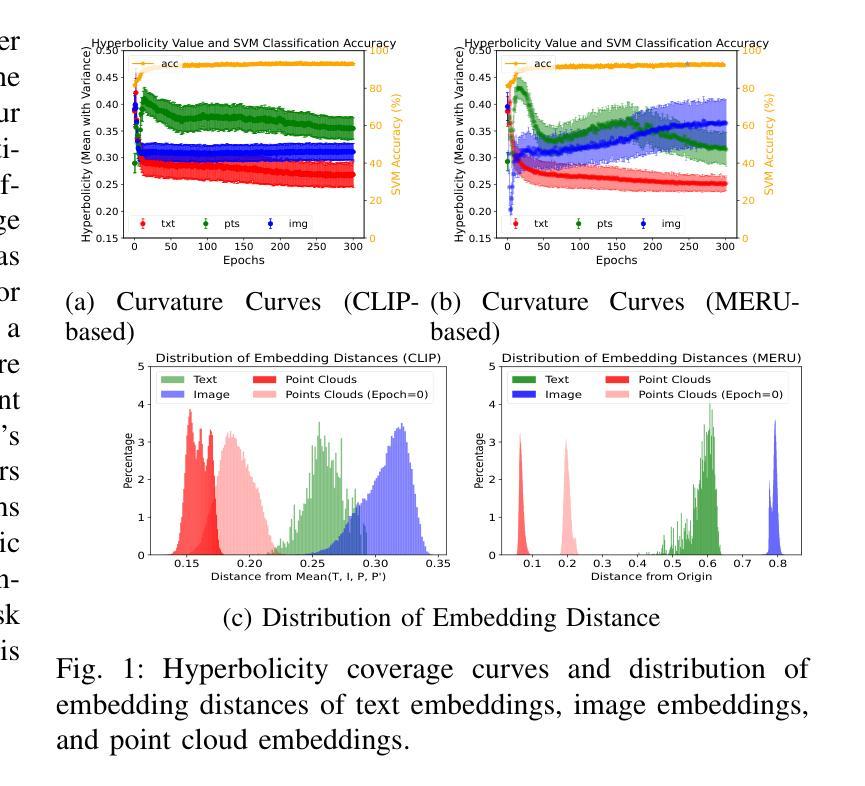
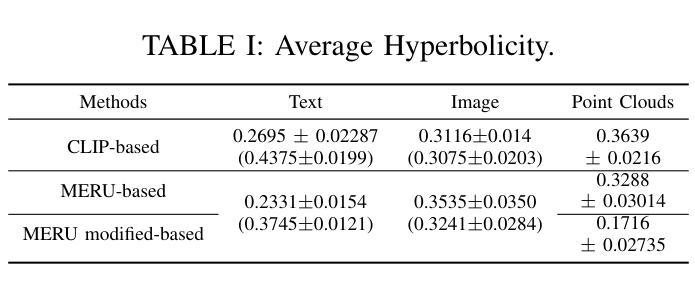
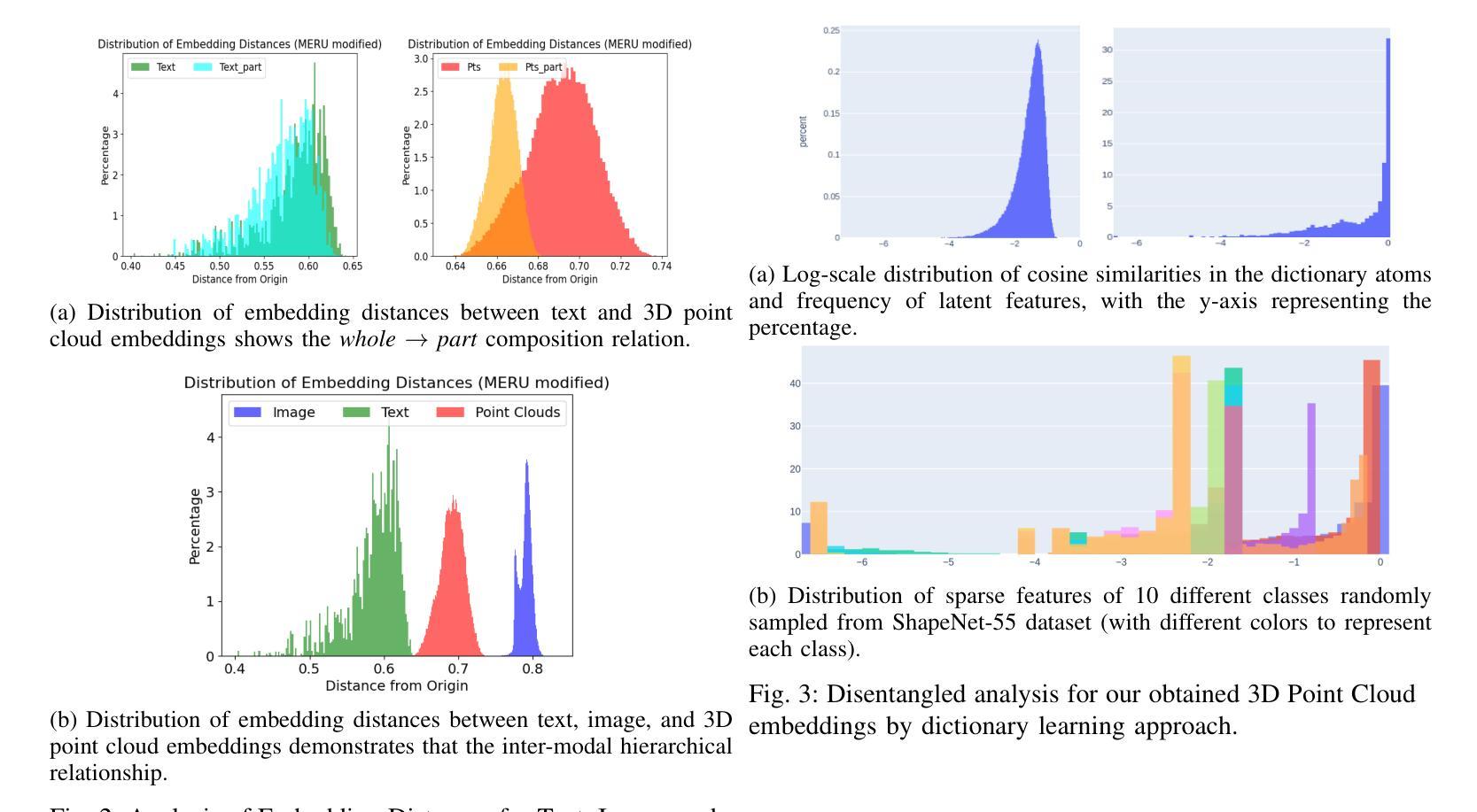
Hyperbolic Contrastive Learning for Hierarchical 3D Point Cloud Embedding
Authors:Yingjie Liu, Pengyu Zhang, Ziyao He, Mingsong Chen, Xuan Tang, Xian Wei
Hyperbolic spaces allow for more efficient modeling of complex, hierarchical structures, which is particularly beneficial in tasks involving multi-modal data. Although hyperbolic geometries have been proven effective for language-image pre-training, their capabilities to unify language, image, and 3D Point Cloud modalities are under-explored. We extend the 3D Point Cloud modality in hyperbolic multi-modal contrastive pre-training. Additionally, we explore the entailment, modality gap, and alignment regularizers for learning hierarchical 3D embeddings and facilitating the transfer of knowledge from both Text and Image modalities. These regularizers enable the learning of intra-modal hierarchy within each modality and inter-modal hierarchy across text, 2D images, and 3D Point Clouds.Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed training strategy yields an outstanding 3D Point Cloud encoder, and the obtained 3D Point Cloud hierarchical embeddings significantly improve performance on various downstream tasks.
超球面空间允许对复杂、层次结构进行更有效的建模,这在涉及多模态数据的任务中特别有益。尽管超几何结构已被证明在语言图像预训练中是有效的,但它们统一语言、图像和3D点云模式的能力尚未得到充分探索。我们在超几何多模态对比预训练中扩展了3D点云模式。此外,我们探索了蕴涵、模态间隙和对齐正则化器,用于学习层次化的3D嵌入并促进文本和图像两种模式的知识的迁移。这些正则化器能够在每个模态内部学习模态内层次结构和跨文本、二维图像和三维点云的模态间层次结构。实验结果表明,我们提出的训练策略生成了一个出色的三维点云编码器,所获得的三维点云层次嵌入显著提高了各种下游任务性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了超球面空间在建模复杂、层次结构中的优势,特别是在涉及多模态数据任务中的应用。文章介绍了超球面几何在语言和图像预训练中的有效性,并探索了其在统一语言、图像和3D点云模态方面的潜力。文章扩展了超球面多模态对比预训练中的3D点云模态,并探讨了用于学习层次化3D嵌入和推动文本和图像知识迁移的蕴涵、模态差距和对齐正则化技术。这些正则化技术能够在各模态内部学习模态内层次结构和跨文本、二维图像和三维点云的模态间层次结构。实验结果表明,所提出的训练策略得到了出色的三维点云编码器,所获得的三维点云层次嵌入显著提高了各种下游任务性能。
Key Takeaways
- 超球面空间能够更有效地建模复杂、层次结构,对于多模态数据任务特别有益。
- 超球面几何在语言和图像预训练中已被证明是有效的。
- 3D点云模态在超球面多模态对比预训练中得到扩展。
- 蕴涵、模态差距和对齐正则化技术被探索,用于学习层次化的3D嵌入和推动知识在文本和图像之间的迁移。
- 正则化技术有助于学习模态内和模态间的层次结构。
- 实验结果表明,所提出训练策略得到的3D点云编码器表现优异。
点此查看论文截图