⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-08 更新
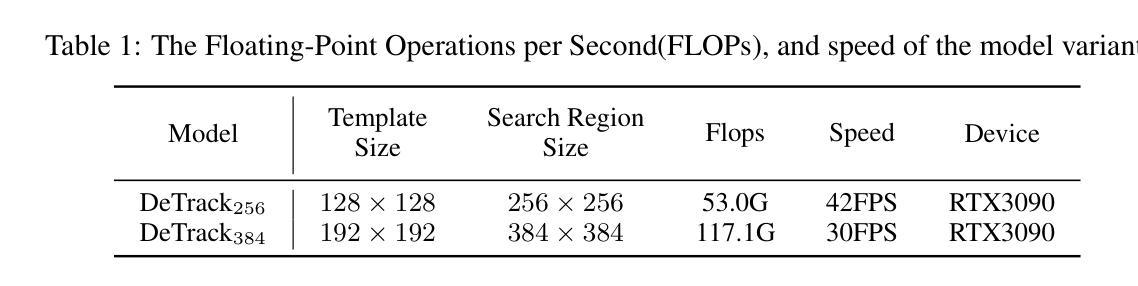
DeTrack: In-model Latent Denoising Learning for Visual Object Tracking
Authors:Xinyu Zhou, Jinglun Li, Lingyi Hong, Kaixun Jiang, Pinxue Guo, Weifeng Ge, Wenqiang Zhang
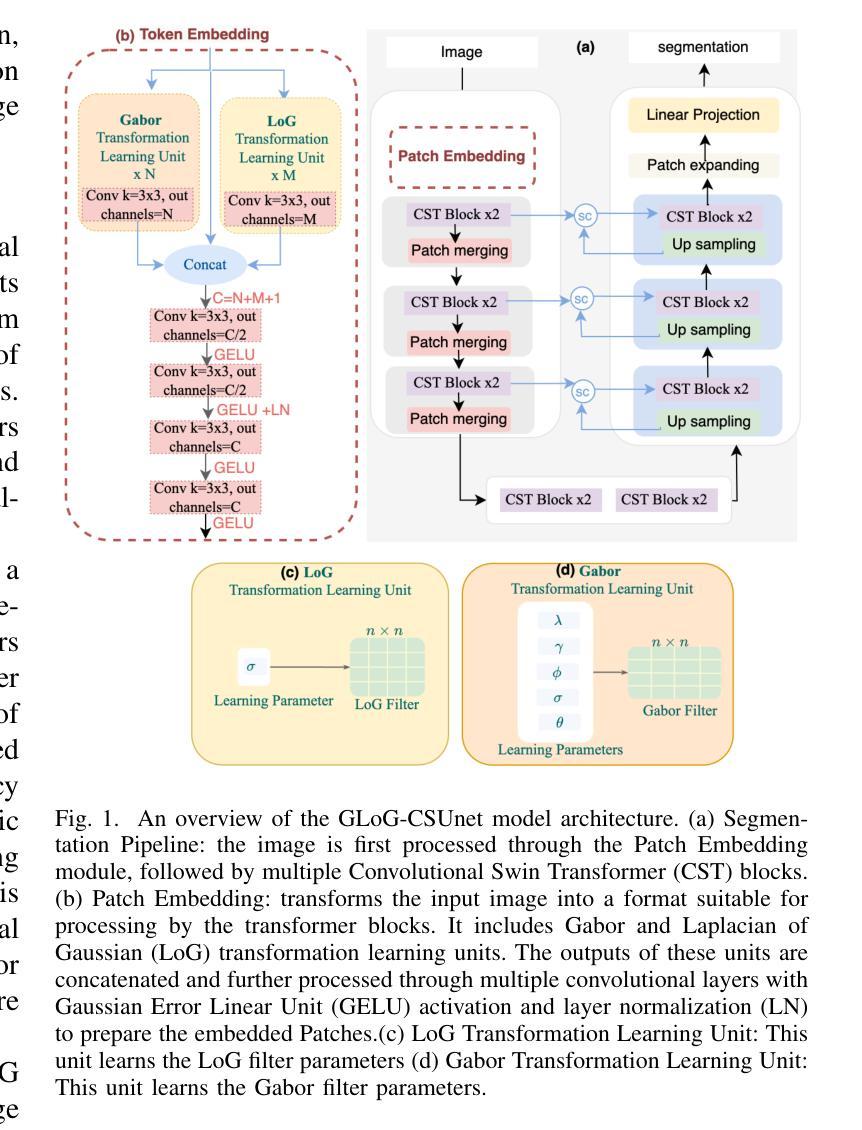
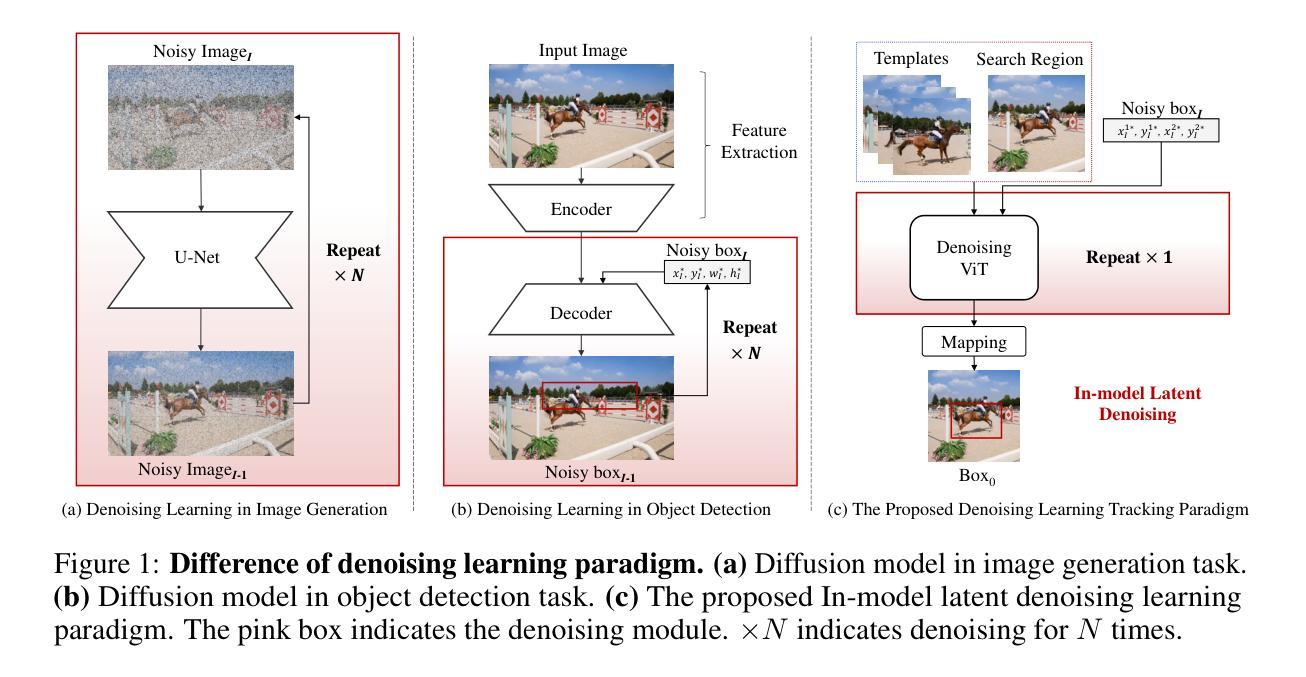
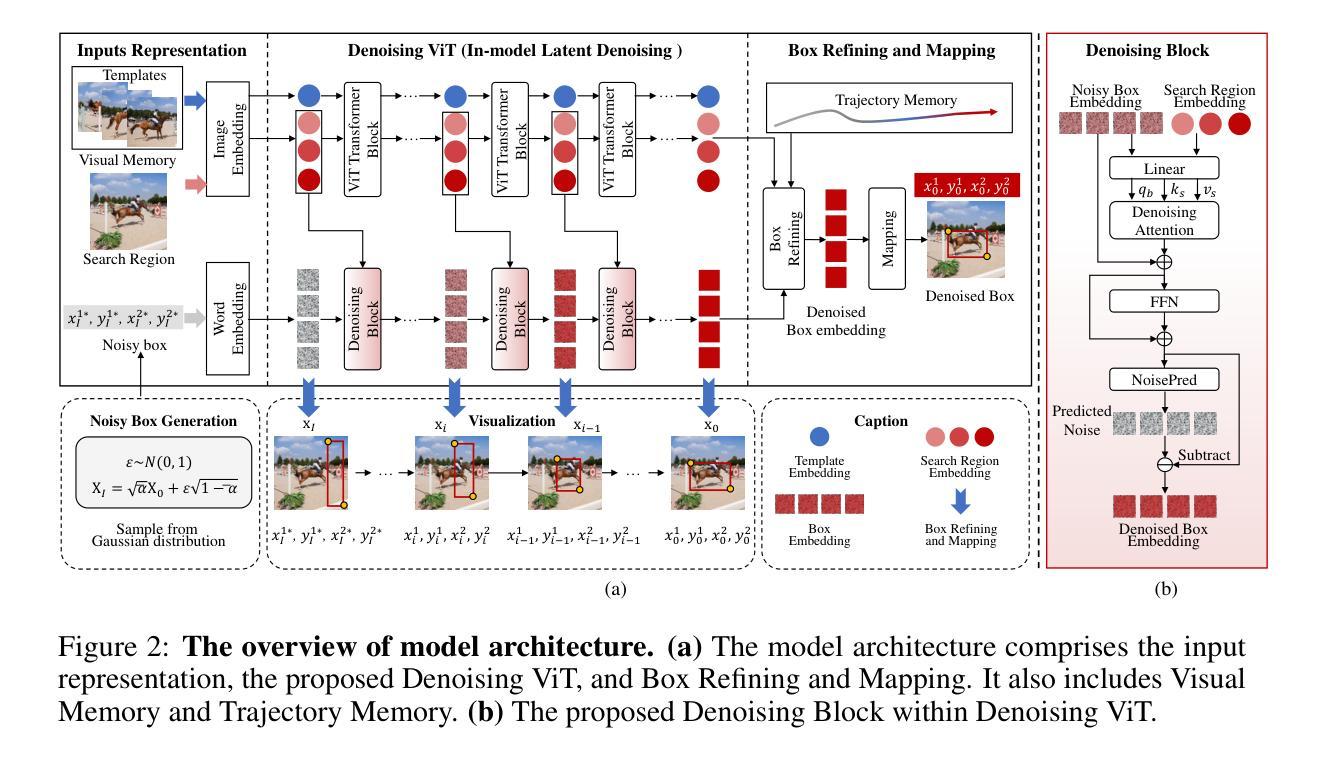
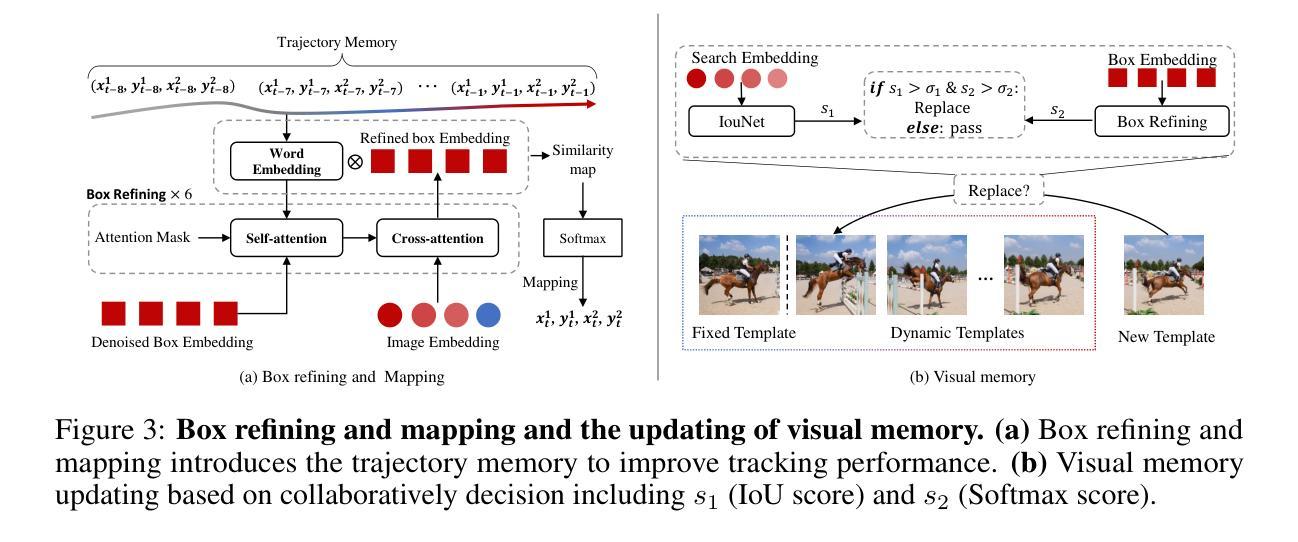
Previous visual object tracking methods employ image-feature regression models or coordinate autoregression models for bounding box prediction. Image-feature regression methods heavily depend on matching results and do not utilize positional prior, while the autoregressive approach can only be trained using bounding boxes available in the training set, potentially resulting in suboptimal performance during testing with unseen data. Inspired by the diffusion model, denoising learning enhances the model’s robustness to unseen data. Therefore, We introduce noise to bounding boxes, generating noisy boxes for training, thus enhancing model robustness on testing data. We propose a new paradigm to formulate the visual object tracking problem as a denoising learning process. However, tracking algorithms are usually asked to run in real-time, directly applying the diffusion model to object tracking would severely impair tracking speed. Therefore, we decompose the denoising learning process into every denoising block within a model, not by running the model multiple times, and thus we summarize the proposed paradigm as an in-model latent denoising learning process. Specifically, we propose a denoising Vision Transformer (ViT), which is composed of multiple denoising blocks. In the denoising block, template and search embeddings are projected into every denoising block as conditions. A denoising block is responsible for removing the noise in a predicted bounding box, and multiple stacked denoising blocks cooperate to accomplish the whole denoising process. Subsequently, we utilize image features and trajectory information to refine the denoised bounding box. Besides, we also utilize trajectory memory and visual memory to improve tracking stability. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving competitive performance on several challenging datasets.
之前的视觉对象跟踪方法采用图像特征回归模型或坐标自回归模型进行边界框预测。图像特征回归方法严重依赖于匹配结果,并不利用位置先验,而自回归方法仅可使用训练集中的边界框进行训练,在测试未见数据时可能表现不佳。受扩散模型的启发,去噪学习提高了模型对未见数据的稳健性。因此,我们向边界框引入噪声,生成用于训练的噪声框,从而提高模型在测试数据上的稳健性。我们提出了一种新的范式,将视觉对象跟踪问题表述为一个去噪学习过程。然而,跟踪算法通常需要在实时环境中运行,直接将扩散模型应用于对象跟踪会严重影响跟踪速度。因此,我们将去噪学习过程分解为一个模型内的每个去噪块,而不是通过多次运行模型来实现,因此我们将所提出的范式概括为模型内潜在去噪学习过程。具体来说,我们提出了一种去噪视觉转换器(ViT),它由多个去噪块组成。在去噪块中,模板和搜索嵌入被投影到每个去噪块作为条件。去噪块负责去除预测边界框中的噪声,多个堆叠的去噪块合作完成整个去噪过程。然后,我们利用图像特征和轨迹信息来优化去噪后的边界框。此外,我们还利用轨迹记忆和视觉记忆来提高跟踪的稳定性。实验结果验证了我们的方法的有效性,在几个具有挑战性的数据集上实现了具有竞争力的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文提出一种基于去噪学习的新范式来解决视觉对象跟踪问题。通过引入噪声到边界框训练,提高模型对未见数据的鲁棒性。将跟踪问题形式化为一个去噪学习过程,并引入去噪视觉转换器(ViT)。每个去噪块负责去除预测边界框中的噪声,多个去噪块合作完成整个去噪过程。同时利用图像特征和轨迹信息优化去噪后的边界框,并利用轨迹记忆和视觉记忆提高跟踪稳定性。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉对象跟踪中,提出了将跟踪问题视为去噪学习的新范式。
- 通过向边界框训练中引入噪声,提高了模型对未见数据的鲁棒性。
- 引入了去噪视觉转换器(ViT),其中每个去噪块负责去除预测边界框中的噪声。
- 多个去噪块合作完成整个去噪过程,优化了对目标对象的跟踪性能。
- 利用图像特征和轨迹信息优化去噪后的边界框,提高了跟踪的准确性。
- 通过引入轨迹记忆和视觉记忆机制,增强了跟踪的稳定性。
点此查看论文截图

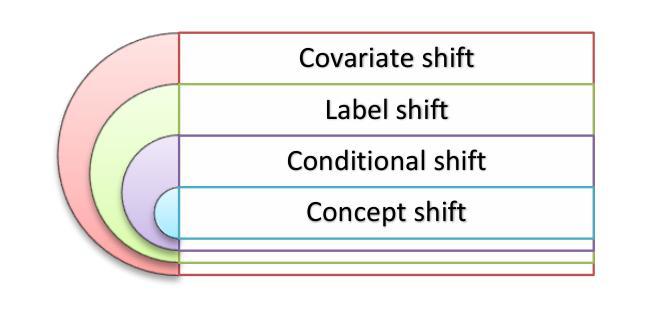
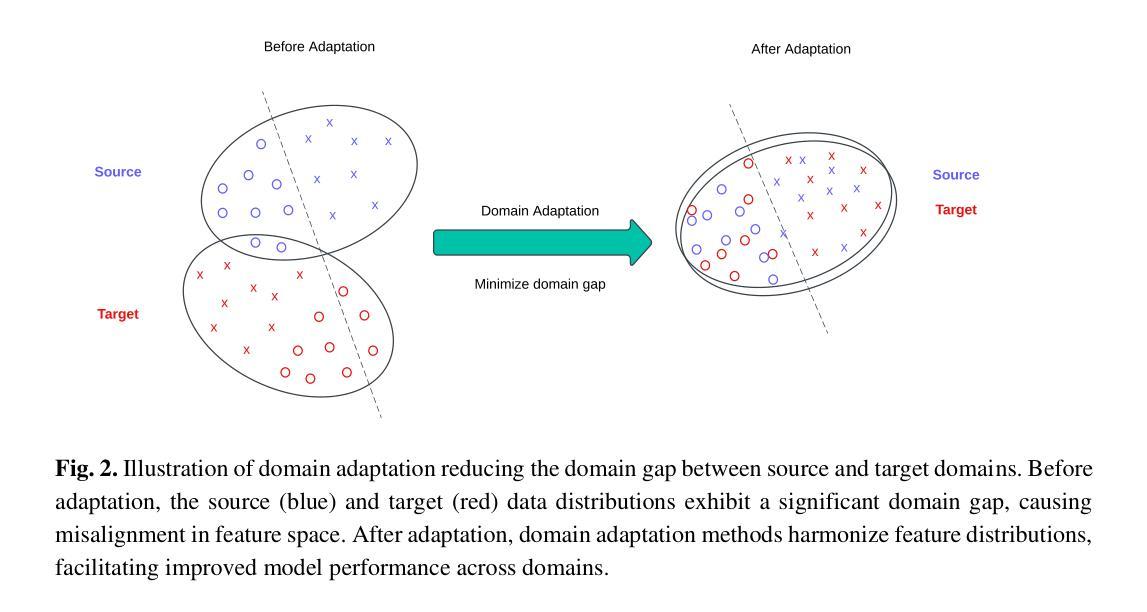
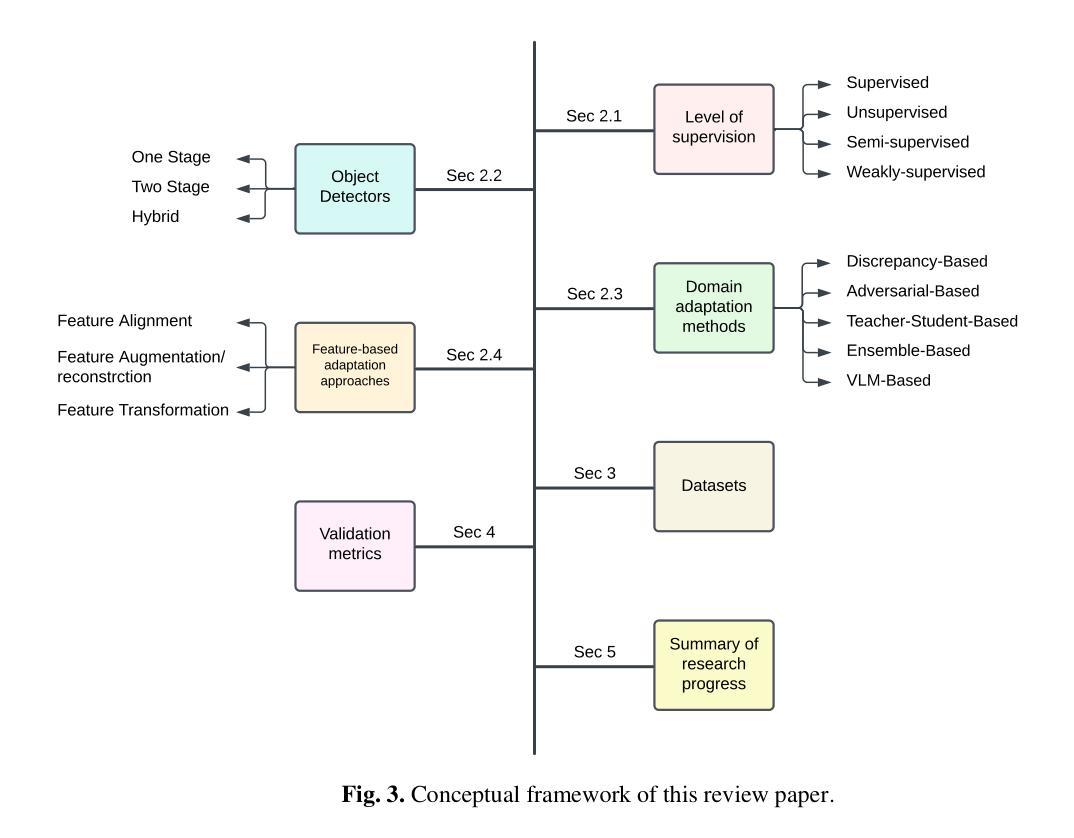
Feature Based Methods in Domain Adaptation for Object Detection: A Review Paper
Authors:Helia Mohamadi, Mohammad Ali Keyvanrad, Mohammad Reza Mohammadi
Domain adaptation, a pivotal branch of transfer learning, aims to enhance the performance of machine learning models when deployed in target domains with distinct data distributions. This is particularly critical for object detection tasks, where domain shifts (caused by factors such as lighting conditions, viewing angles, and environmental variations) can lead to significant performance degradation. This review delves into advanced methodologies for domain adaptation, including adversarial learning, discrepancy-based, multi-domain, teacher-student, ensemble, and Vision Language Models techniques, emphasizing their efficacy in reducing domain gaps and enhancing model robustness. Feature-based methods have emerged as powerful tools for addressing these challenges by harmonizing feature representations across domains. These techniques, such as Feature Alignment, Feature Augmentation/Reconstruction, and Feature Transformation, are employed alongside or as integral parts of other domain adaptation strategies to minimize domain gaps and improve model performance. Special attention is given to strategies that minimize the reliance on extensive labeled data and using unlabeled data, particularly in scenarios involving synthetic-to-real domain shifts. Applications in fields such as autonomous driving and medical imaging are explored, showcasing the potential of these methods to ensure reliable object detection in diverse and complex settings. By providing a thorough analysis of state-of-the-art techniques, challenges, and future directions, this work offers a valuable reference for researchers striving to develop resilient and adaptable object detection frameworks, advancing the seamless deployment of artificial intelligence in dynamic environments.
领域自适应是迁移学习中的一个重要分支,旨在提高机器学习模型在目标领域(具有不同数据分布)中的性能。这对于目标检测任务尤为重要,因为领域变化(由光照条件、观察角度和环境变化等因素引起)可能导致性能显著下降。本文深入探讨了领域自适应的高级方法,包括对抗性学习、基于差异的方法、多领域、师徒制、集成和视觉语言模型技术,重点介绍了它们在减少领域差距和提高模型稳健性方面的有效性。基于特征的方法已成为解决这些挑战的有力工具,通过协调不同领域的特征表示来发挥作用。这些方法,如特征对齐、特征增强/重建和特征变换等,与其他领域自适应策略一起使用或作为其不可或缺的一部分,以尽量减少领域差距并提高模型性能。特别注意的是尽量减少对大量标记数据的依赖,并在使用无标记数据的情况下,特别是在涉及从合成到现实的领域转变的场景中。在自动驾驶和医学影像等领域的应用展示了这些方法在多样化和复杂环境中确保可靠目标检测的潜力。通过对最新技术、挑战和未来方向的深入分析,这项工作为研究人员开发具有弹性和适应性的目标检测框架提供了有价值的参考,推动了人工智能在动态环境中的无缝部署。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 48 pages, 13 figures, It will be submitted to the Artificial Intelligence Review journal
Summary:
本文综述了领域自适应(Domain Adaptation)在对象检测任务中的重要性,深入探讨了先进的领域自适应方法,如对抗性学习、差异化方法、多领域、教师-学生、集成和视觉语言模型技术。文章强调这些方法在缩小领域差距、提高模型稳健性方面的有效性,并特别关注特征基方法在处理领域自适应挑战中的作用。文章还介绍了这些方法在自动驾驶和医疗成像等领域的应用,展示了它们在确保可靠对象检测方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- 领域自适应是迁移学习的重要分支,旨在提高机器学习模型在目标领域的性能,特别是在对象检测任务中。
- 领域差异可能导致模型性能显著下降。
- 先进的领域自适应方法包括对抗性学习、差异化方法、多领域、教师-学生、集成和视觉语言模型技术。
- 特征基方法是处理领域自适应挑战的有力工具,通过协调不同领域的特征表示来缩小领域差距。
- 这些方法特别关注如何减少大量标注数据的依赖,利用无标签数据,特别是在从合成到现实的领域转移场景中。
- 在自动驾驶和医疗成像等领域的应用展示了这些方法的潜力,确保在多样化和复杂环境中进行可靠的物体检测。
点此查看论文截图

UDA4Inst: Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Instance Segmentation
Authors:Yachan Guo, Yi Xiao, Danna Xue, Jose Luis Gomez Zurita, Antonio M. Lopez
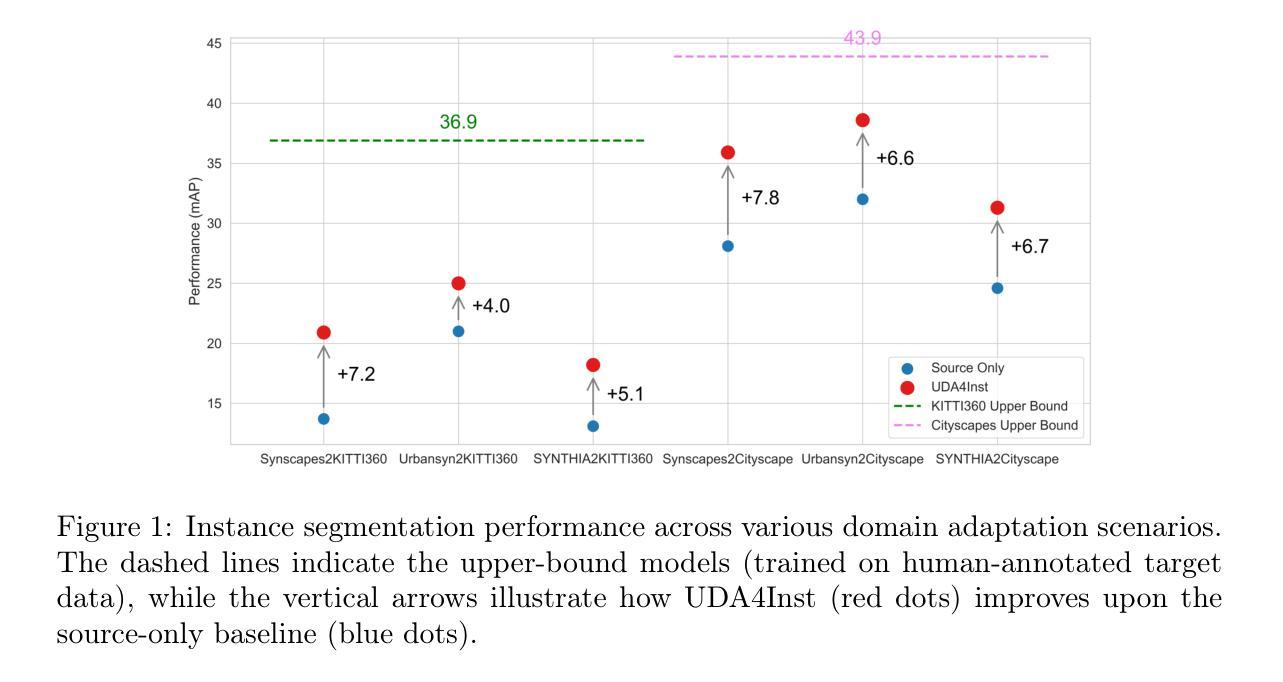
Instance segmentation is crucial for autonomous driving but is hindered by the lack of annotated real-world data due to expensive labeling costs. Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) offers a solution by transferring knowledge from labeled synthetic data to unlabeled real-world data. While UDA methods for synthetic to real-world domains (synth-to-real) show remarkable performance in tasks such as semantic segmentation and object detection, very few have been proposed for instance segmentation in vision-based autonomous driving. Moreover, existing methods rely on suboptimal baselines, which severely limits performance. We introduce \textbf{UDA4Inst}, a powerful framework for synth-to-real UDA in instance segmentation. Our framework enhances instance segmentation through \textit{Semantic Category Training} and \textit{Bidirectional Mixing Training}. With the Semantic Category Training method, semantically related classes are grouped and trained separately, enabling the generation of higher-quality pseudo-labels and improved segmentation performance. We further propose a bidirectional cross-domain data mixing strategy that combines instance-wise and patch-wise mixing techniques to effectively utilize data from both source and target domains, producing realistic composite images that improve the model’s generalization performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods. Our approach establishes a new state-of-the-art on the SYNTHIA->Cityscapes benchmark with mAP 31.3. Notably, we are the first to report results on multiple novel synth-to-real instance segmentation datasets, using UrbanSyn and Synscapes as source domains while Cityscapes and KITTI360 serve as target domains. Our code will be released soon.
实例分割对于自动驾驶至关重要,但由于昂贵的标注成本,缺乏标注的真实世界数据阻碍了其发展。无监督域自适应(UDA)通过将从标记的合成数据转移到未标记的真实世界数据来提供解决方案。虽然用于合成到真实世界域的UDA方法(合成到现实)在语义分割和对象检测等任务中表现出卓越的性能,但针对基于视觉的自动驾驶中的实例分割提出的方法却很少。此外,现有方法依赖于次优基线,这严重限制了性能。我们介绍了UDA4Inst,这是一个强大的合成到现实的实例分割UDA框架。我们的框架通过语义类别训练和双向混合训练增强了实例分割。语义类别训练方法将语义相关的类别分组并分别训练,能够生成更高质量的伪标签并提高分割性能。我们进一步提出了一种双向跨域数据混合策略,该策略结合了实例级和补丁级的混合技术,以有效利用源域和目标域的数据,生成逼真的合成图像,提高模型的泛化性能。大量实验证明了我们的方法的有效性。我们的方法在SYNTHIA->Cityscapes基准测试上建立了新的最先进的水平,mAP为31.3。值得注意的是,我们是首批在多个新的合成到现实实例分割数据集上报告结果的团队,使用UrbanSyn和Synscapes作为源域,而Cityscapes和KITTI360作为目标域。我们的代码将很快发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对自动驾驶中的实例分割问题,由于标注真实世界数据的成本高昂,缺乏标注数据成为一大挑战。无监督域自适应(UDA)通过将从合成数据中学到的知识转移到未标记的真实世界数据上,为解决这一问题提供了解决方案。尽管UDA在语义分割和对象检测任务中表现出色,但在基于视觉的自动驾驶实例分割中的研究仍很少见。此外,现有方法依赖于次优基线,这严重限制了性能。本文介绍了UDA4Inst框架,该框架针对合成到真实世界的实例分割进行无监督域自适应。通过语义类别训练和双向混合训练增强实例分割。语义类别训练将语义相关的类别分组并分别训练,提高了伪标签的质量和分割性能。我们还提出了一种双向跨域数据混合策略,结合了实例级和补丁级混合技术,以有效利用源和目标域的数据,生成逼真的复合图像,提高模型的泛化性能。实验证明了该方法的有效性。该方法在SYNTHIA->Cityscapes基准测试中建立了新的最先进的水平,mAP达到31.3。值得注意的是,我们首次在多个新的合成到真实的实例分割数据集上报告了结果,使用UrbanSyn和Synscapes作为源域,而Cityscapes和KITTI360作为目标域。我们的代码将很快发布。
关键见解
- 实例分割在自动驾驶中至关重要,但由于标注真实世界数据的高成本,缺乏标注数据成为一个挑战。
- 无监督域自适应(UDA)为解决这一问题提供了解决方案,能够通过从合成数据到真实数据的转换来转移知识。
- 当前针对自动驾驶实例分割的UDA研究较少,且现有方法依赖于次优基线。
- 引入的UDA4Inst框架通过语义类别训练和双向混合训练增强了实例分割的性能。
- 语义类别训练能够将语义相关的类别分组并分别训练,从而提高伪标签的质量和分割性能。
- 提出的双向跨域数据混合策略结合了实例级和补丁级混合技术,有效利用源和目标域的数据生成逼真的复合图像。
点此查看论文截图

Polyp-DDPM: Diffusion-Based Semantic Polyp Synthesis for Enhanced Segmentation
Authors:Zolnamar Dorjsembe, Hsing-Kuo Pao, Furen Xiao
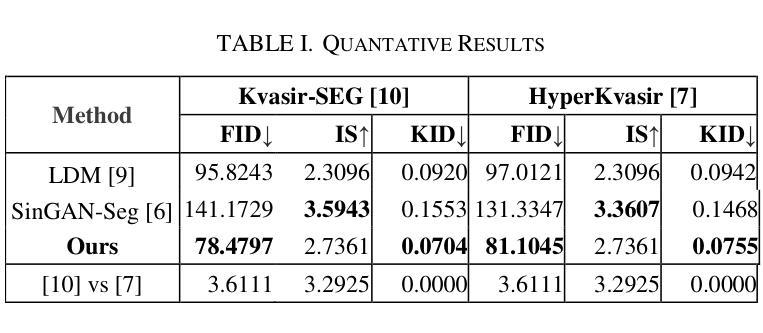
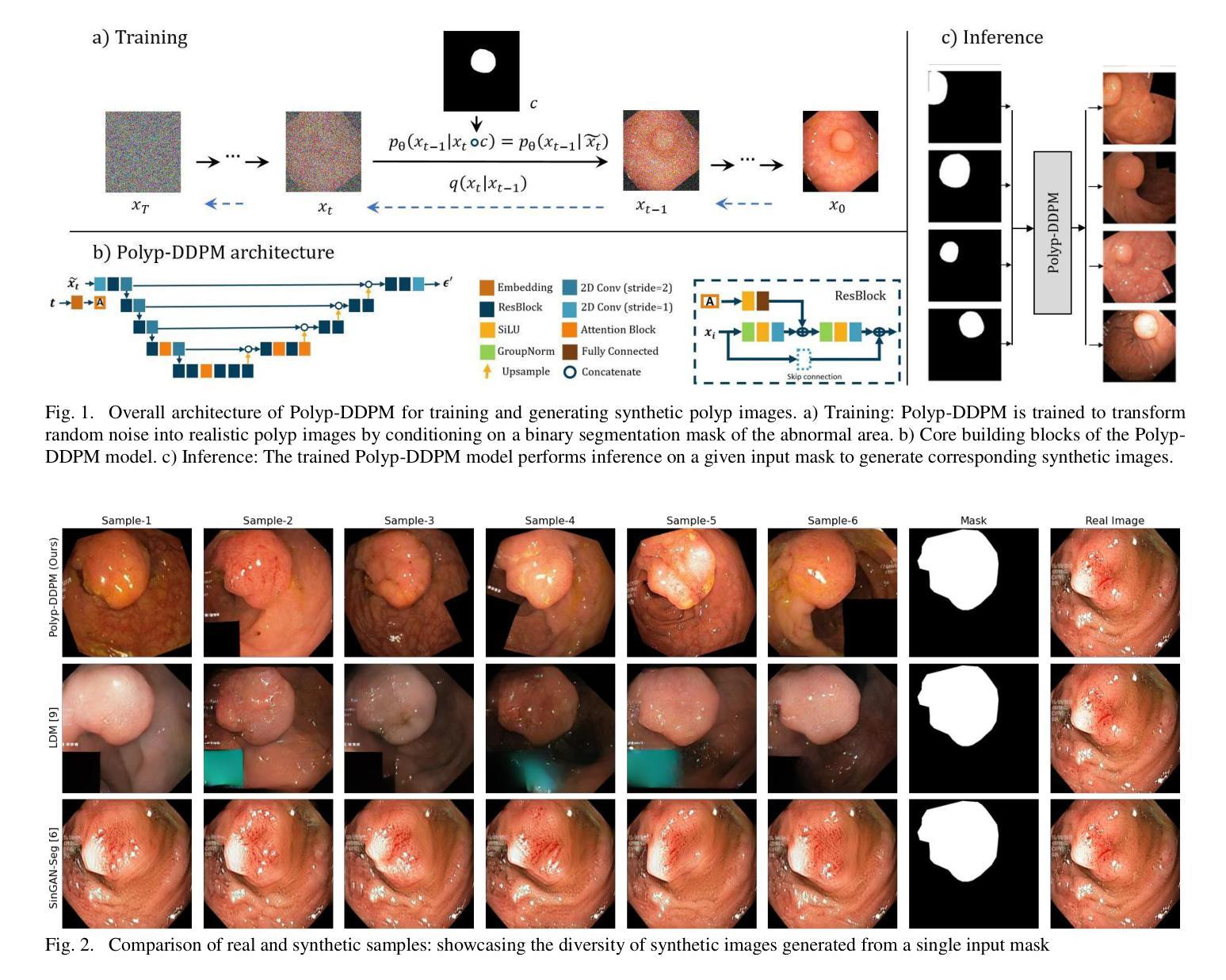
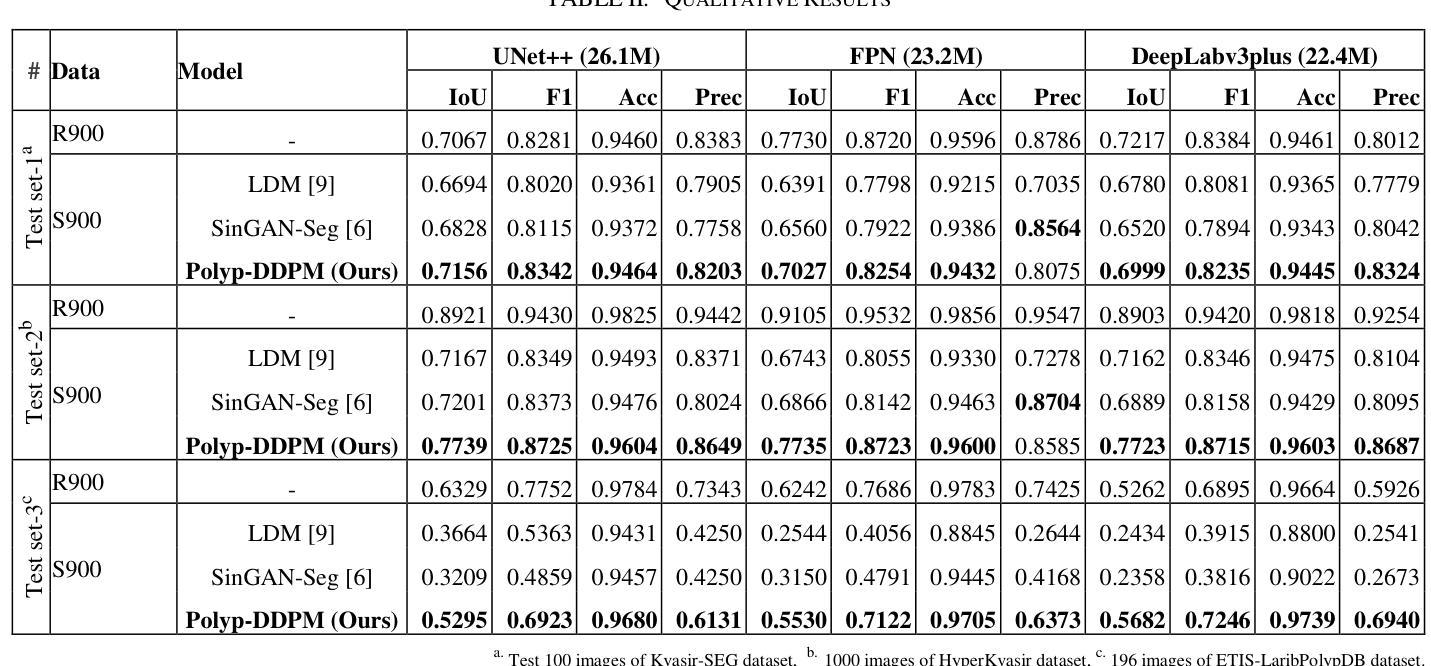
This study introduces Polyp-DDPM, a diffusion-based method for generating realistic images of polyps conditioned on masks, aimed at enhancing the segmentation of gastrointestinal (GI) tract polyps. Our approach addresses the challenges of data limitations, high annotation costs, and privacy concerns associated with medical images. By conditioning the diffusion model on segmentation masks-binary masks that represent abnormal areas-Polyp-DDPM outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of image quality (achieving a Frechet Inception Distance (FID) score of 78.47, compared to scores above 83.79) and segmentation performance (achieving an Intersection over Union (IoU) of 0.7156, versus less than 0.6694 for synthetic images from baseline models and 0.7067 for real data). Our method generates a high-quality, diverse synthetic dataset for training, thereby enhancing polyp segmentation models to be comparable with real images and offering greater data augmentation capabilities to improve segmentation models. The source code and pretrained weights for Polyp-DDPM are made publicly available at https://github.com/mobaidoctor/polyp-ddpm.
本研究介绍了Polyp-DDPM,这是一种基于扩散的方法,根据掩膜生成逼真的息肉图像,旨在提高胃肠道(GI)息肉的分割效果。我们的方法解决了与医学图像相关的数据限制、高标注成本和隐私关注方面的挑战。通过将扩散模型应用于表示异常区域的二元掩膜,Polyp-DDPM在图像质量和分割性能方面超越了最先进的方法(在Frechet Inception Distance(FID)方面达到78.47的得分,高于83.79;在Intersection over Union(IoU)方面达到0.7156,而基线模型生成的合成图像得分低于0.6694,真实数据得分为0.7067)。我们的方法生成高质量、多样化的合成数据集用于训练,从而提高息肉分割模型与真实图像的匹配度,并提供更强的数据增强能力,以改善分割模型。Polyp-DDPM的源代码和预训练权重已在https://github.com/mobaidoctor/polyp-ddpm公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This preprint has been accepted for publication in the proceedings of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC 2024). The final published version is available at https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC53108.2024.10782077. The copyright for this work has been transferred to IEEE
Summary
该研究提出一种基于扩散模型的Polyp-DDPM方法,用于根据掩膜生成逼真的息肉图像,旨在提高胃肠道息肉分割的效果。该方法解决了数据限制、高标注成本和医疗图像隐私关注等挑战。通过为扩散模型设定掩膜条件,Polyp-DDPM在图像质量和分割性能上均表现出卓越性能,达到了Frechet Inception Distance(FID)分数为78.47和Intersection over Union(IoU)分数为0.7156的高水平。此外,该方法生成高质量的多样合成数据集用于训练,提高了息肉分割模型性能,可与现实图像相媲美,并提供强大的数据增强能力。
Key Takeaways
- Polyp-DDPM是一种基于扩散模型的图像生成方法,旨在提高胃肠道息肉分割的效果。
- 该方法解决了数据限制、高标注成本和医疗图像隐私关注等挑战。
- 通过设定掩膜条件,Polyp-DDPM在图像质量和分割性能上表现出卓越性能。
- Polyp-DDPM生成的图像质量高、多样性强,可合成用于训练的数据集。
- 该方法提高了息肉分割模型的性能,使其与现实图像相媲美。
- Polyp-DDPM具备强大的数据增强能力,有助于改善分割模型。
点此查看论文截图