⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-08 更新
MotionBench: Benchmarking and Improving Fine-grained Video Motion Understanding for Vision Language Models
Authors:Wenyi Hong, Yean Cheng, Zhuoyi Yang, Weihan Wang, Lefan Wang, Xiaotao Gu, Shiyu Huang, Yuxiao Dong, Jie Tang
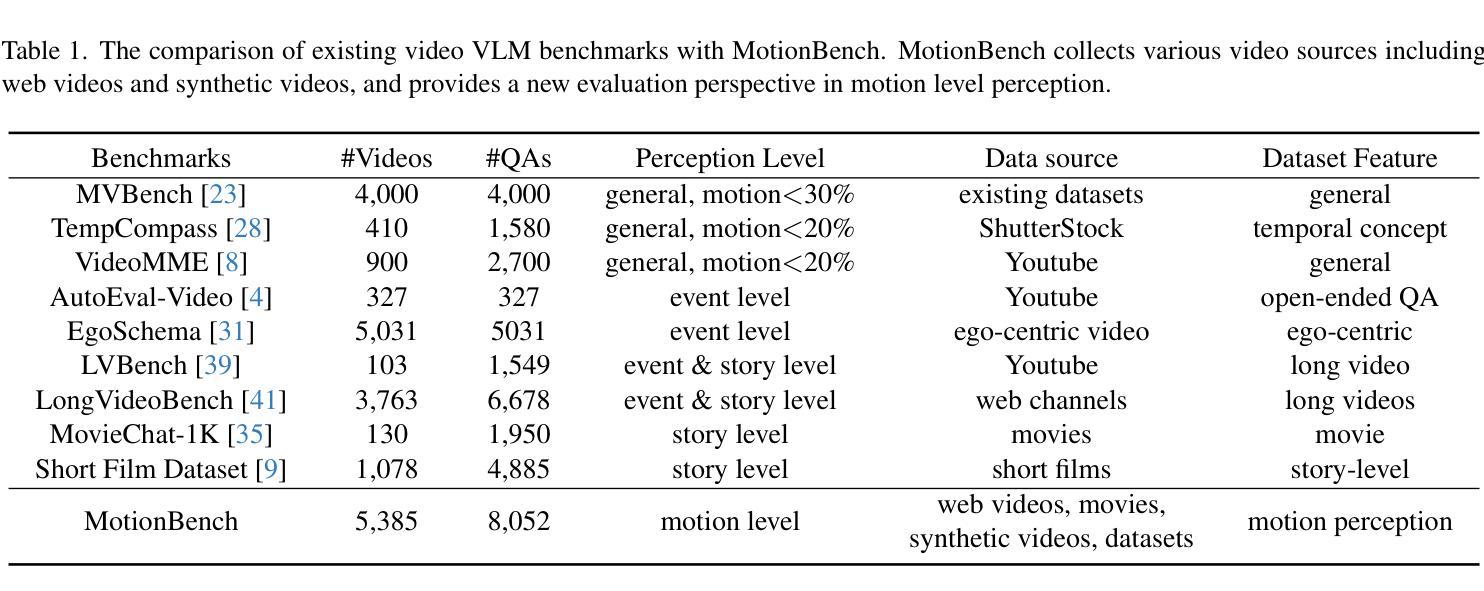
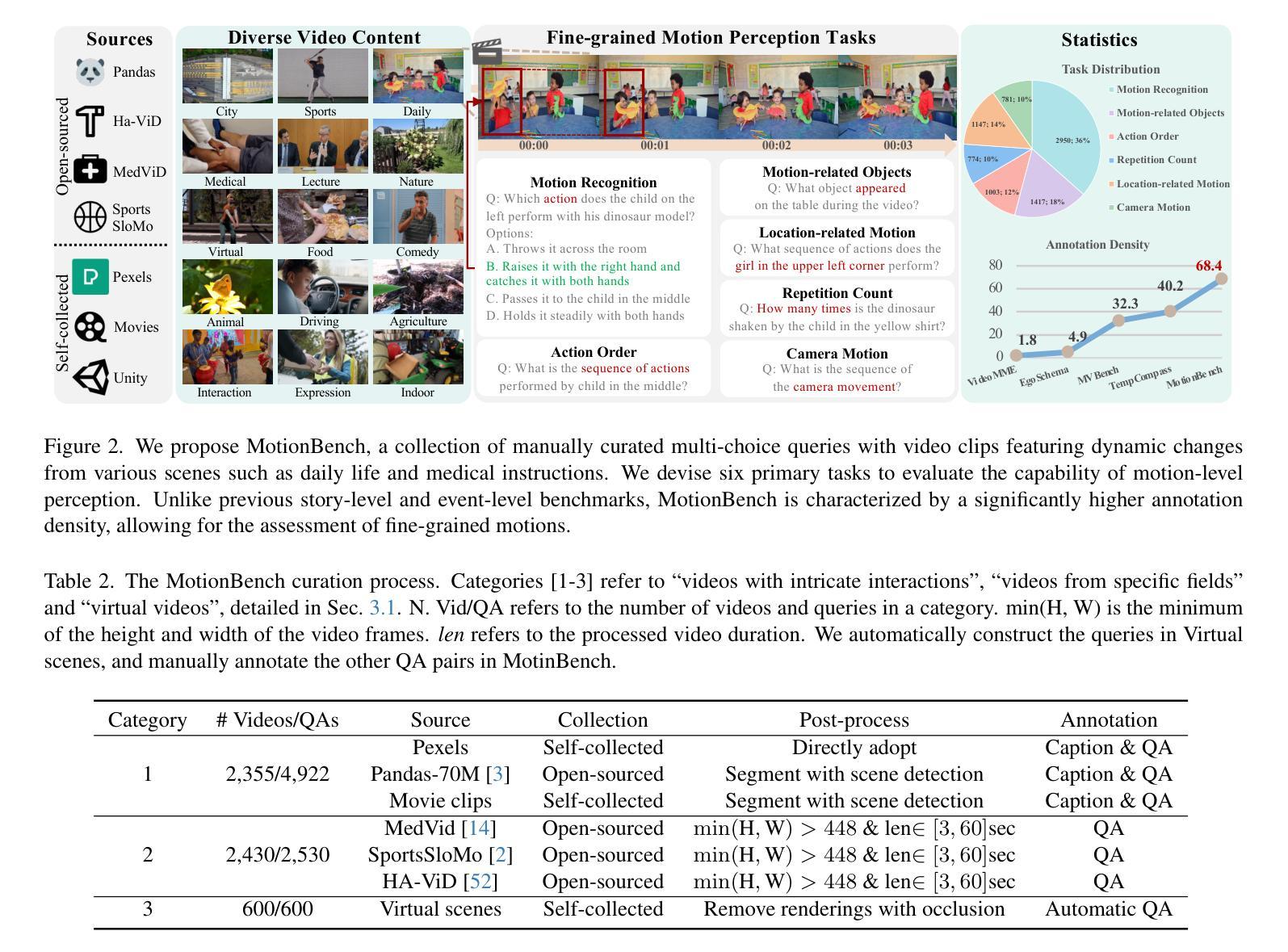
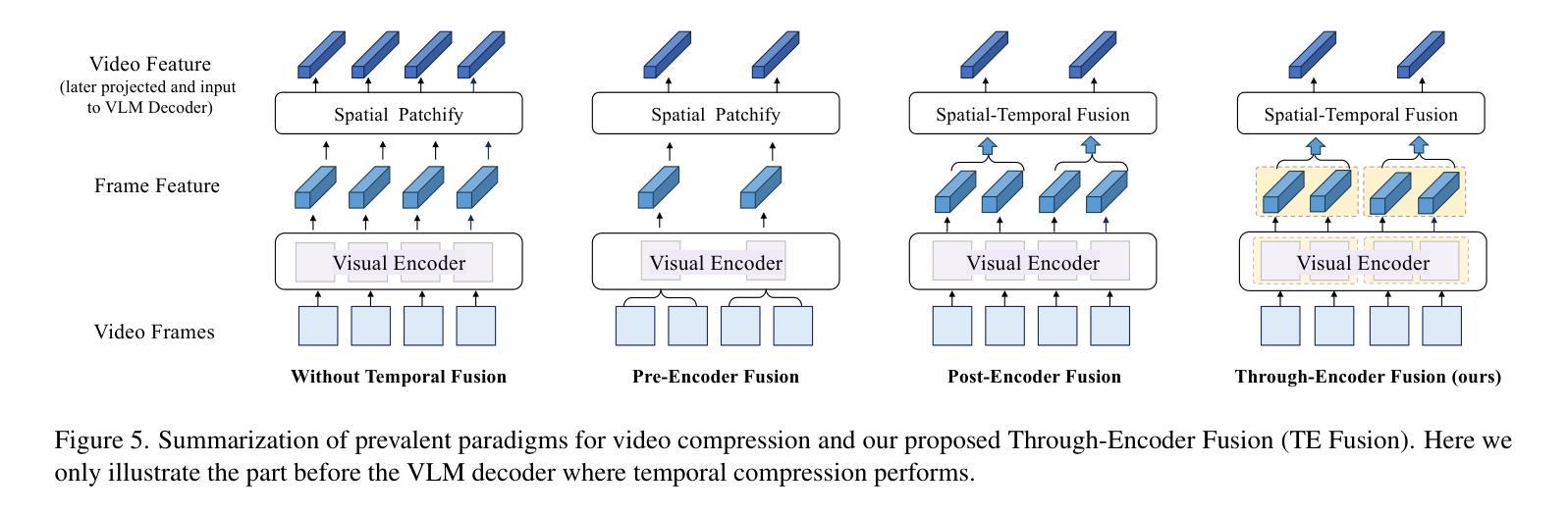
In recent years, vision language models (VLMs) have made significant advancements in video understanding. However, a crucial capability - fine-grained motion comprehension - remains under-explored in current benchmarks. To address this gap, we propose MotionBench, a comprehensive evaluation benchmark designed to assess the fine-grained motion comprehension of video understanding models. MotionBench evaluates models’ motion-level perception through six primary categories of motion-oriented question types and includes data collected from diverse sources, ensuring a broad representation of real-world video content. Experimental results reveal that existing VLMs perform poorly in understanding fine-grained motions. To enhance VLM’s ability to perceive fine-grained motion within a limited sequence length of LLM, we conduct extensive experiments reviewing VLM architectures optimized for video feature compression and propose a novel and efficient Through-Encoder (TE) Fusion method. Experiments show that higher frame rate inputs and TE Fusion yield improvements in motion understanding, yet there is still substantial room for enhancement. Our benchmark aims to guide and motivate the development of more capable video understanding models, emphasizing the importance of fine-grained motion comprehension. Project page: https://motion-bench.github.io .
近年来,视觉语言模型(VLMs)在视频理解方面取得了重大进展。然而,当前基准测试中仍然存在一个关键能力尚未得到充分的探索和研究,那就是精细动作理解。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了MotionBench基准测试平台,这是一个旨在评估视频理解模型的精细动作理解能力的综合评估基准测试平台。MotionBench通过六个主要的运动导向问题类型评估模型的精细动作感知能力,并包括从不同来源收集的数据,确保能够广泛代表真实世界的视频内容。实验结果表明,现有的视觉语言模型在理解精细动作方面表现不佳。为了增强大型语言模型在有限序列长度内对精细动作的感知能力,我们对优化视频特征压缩的VLM架构进行了广泛的实验审查,并提出了一种新颖高效的通过编码器(TE)融合方法。实验表明,较高的帧速率输入和TE融合可以改善运动理解,但仍存在很大的提升空间。我们的基准测试旨在指导和激励更具能力的视频理解模型的发展,强调精细动作理解的重要性。项目页面:https://motion-bench.github.io 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages
Summary
本文介绍了视觉语言模型(VLMs)在视频理解领域的最新进展,并指出精细动作理解是当前评估基准测试中的一项重要但尚未充分探索的能力。为此,提出了MotionBench评估基准,旨在评估视频理解模型的精细动作理解能力。该基准测试包括六个主要类别的以运动为导向的问题类型,并通过从各种来源收集的数据确保对现实世界视频内容的广泛代表性。实验结果表明,现有的VLMs在理解精细动作方面表现不佳。为提高VLM在有限序列长度内的精细动作感知能力,对针对视频特征压缩优化的VLM架构进行了广泛实验审查,并提出了新的高效Through-Encoder(TE)融合方法。实验显示,高帧率输入和TE融合能提高运动理解能力,但仍有很大的提升空间。该基准测试的旨在推动更有能力的视频理解模型的发展,强调精细动作理解的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在视频理解领域取得显著进展,但精细动作理解仍是未被充分探索的重要能力。
- 提出MotionBench评估基准,旨在评估视频理解模型在精细动作理解方面的能力,包括六个主要类别的运动导向问题类型。
- 现有VLMs在理解精细动作方面表现不佳。
- 通过广泛实验审查,提出针对视频特征压缩优化的VLM架构。
- 提出新的高效Through-Encoder(TE)融合方法以提高VLM的精细动作感知能力。
- 实验显示高帧率输入和TE融合能提高运动理解能力。
点此查看论文截图


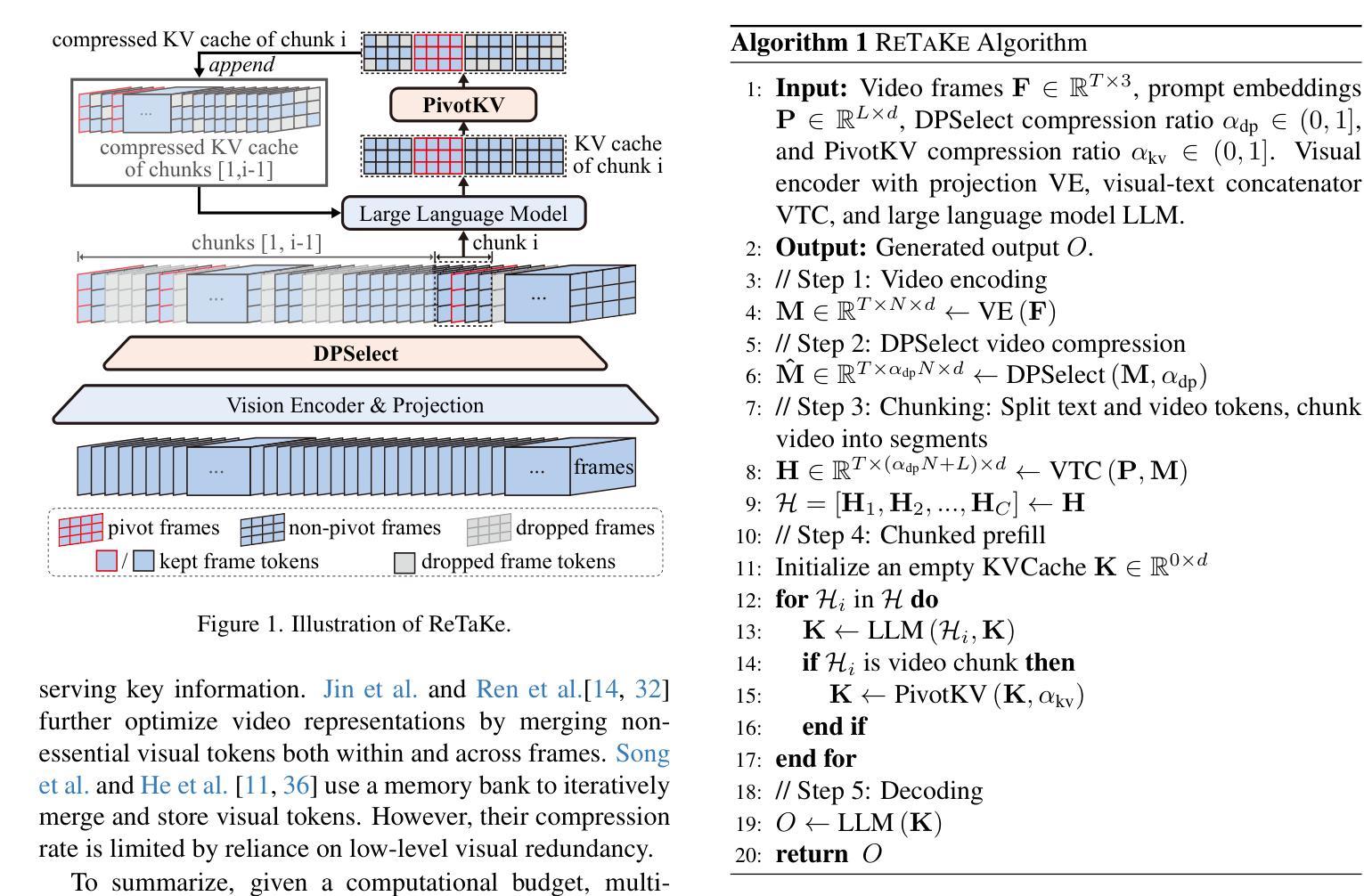
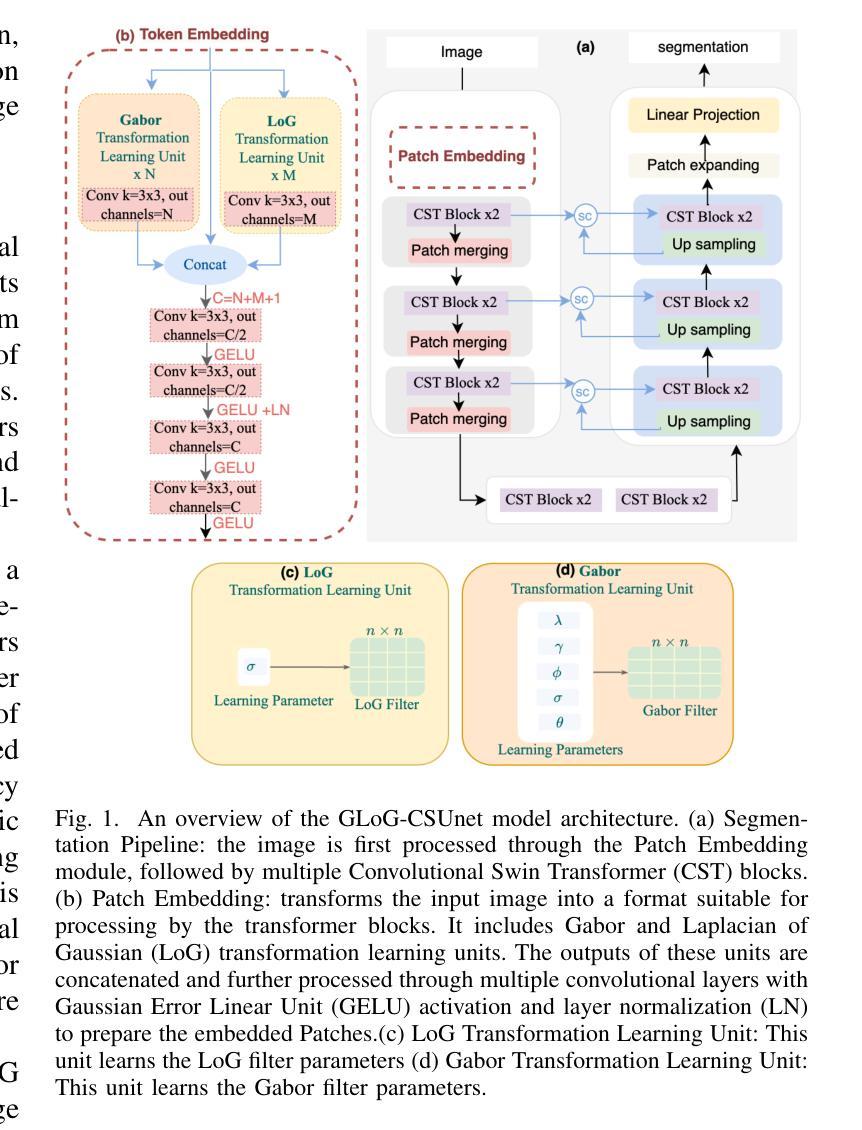
ReTaKe: Reducing Temporal and Knowledge Redundancy for Long Video Understanding
Authors:Xiao Wang, Qingyi Si, Jianlong Wu, Shiyu Zhu, Li Cao, Liqiang Nie
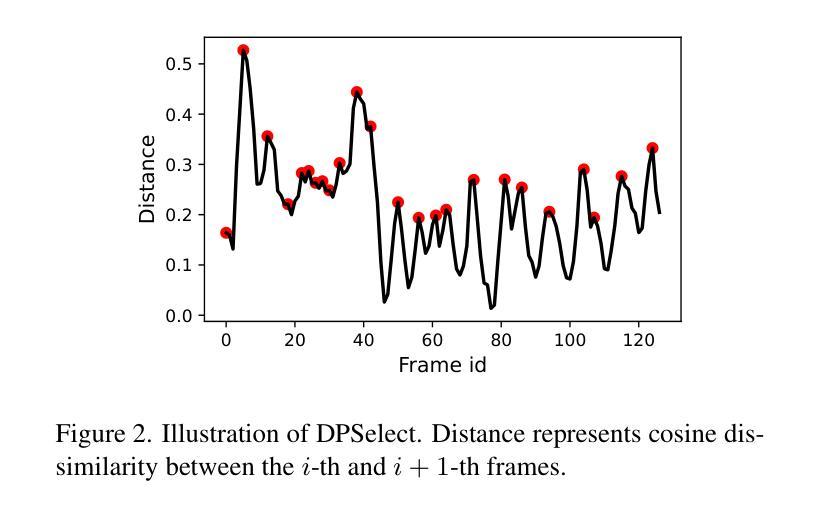
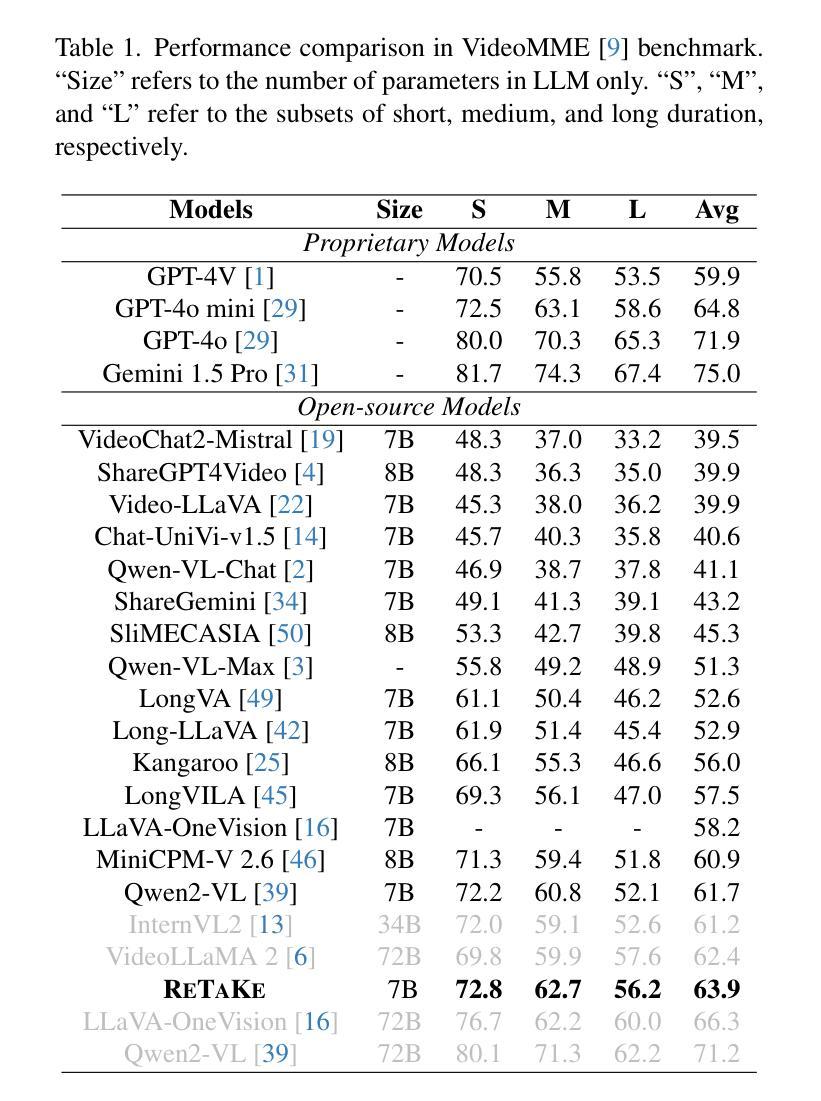
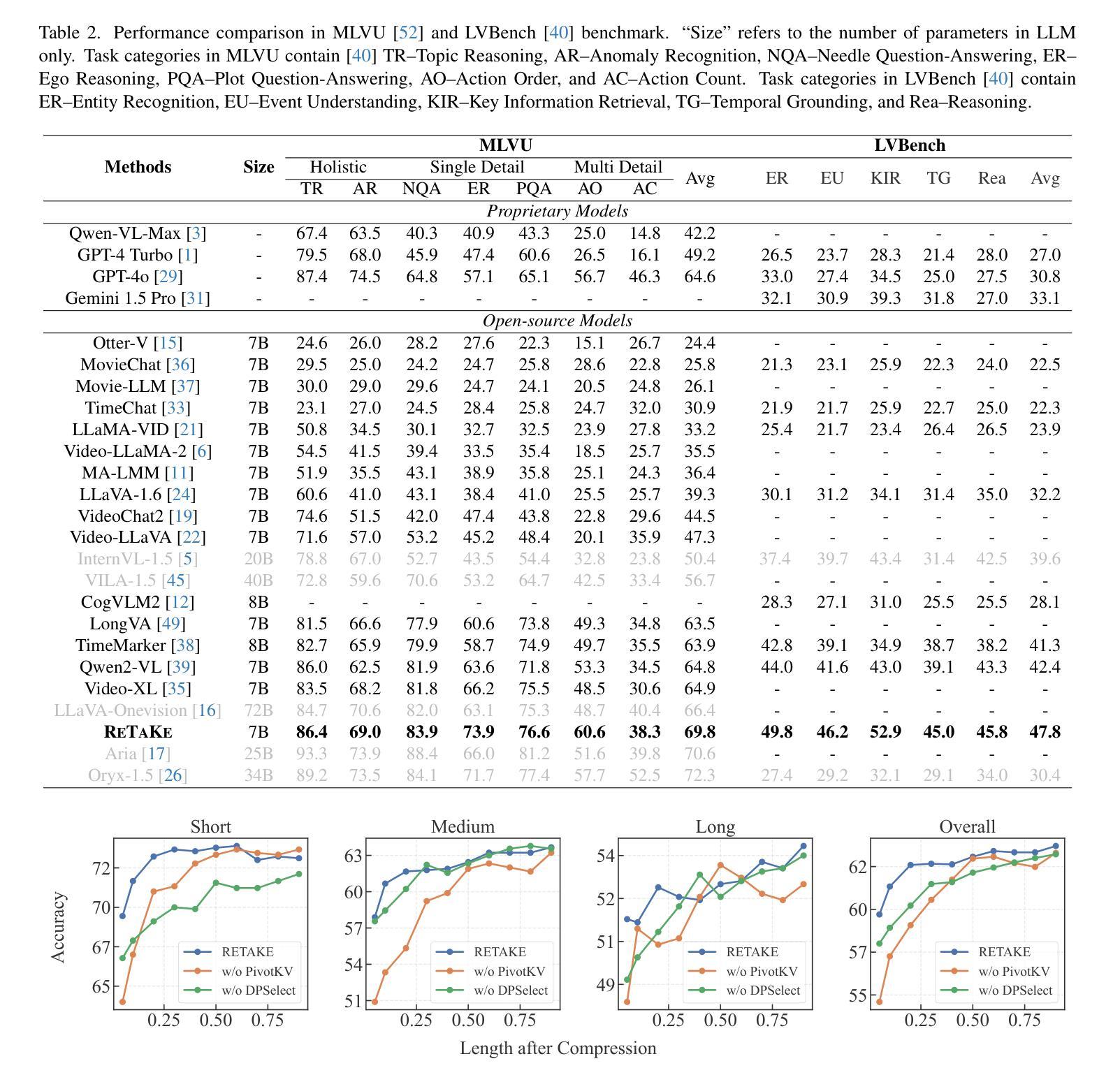
Video Large Language Models (VideoLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in video understanding. However, existing VideoLLMs often inherit the limitations of their backbone LLMs in handling long sequences, leading to challenges for long video understanding. Common solutions either simply uniformly sample videos’ frames or compress visual tokens, which focus primarily on low-level temporal visual redundancy, overlooking high-level knowledge redundancy. This limits the achievable compression rate with minimal loss. To this end. we introduce a training-free method, $\textbf{ReTaKe}$, containing two novel modules DPSelect and PivotKV, to jointly model and reduce both temporal visual redundancy and knowledge redundancy for long video understanding. Specifically, DPSelect identifies keyframes with local maximum peak distance based on their visual features, which are closely aligned with human video perception. PivotKV employs the obtained keyframes as pivots and conducts KV-Cache compression for the non-pivot tokens with low attention scores, which are derived from the learned prior knowledge of LLMs. Experiments on benchmarks VideoMME, MLVU, and LVBench, show that ReTaKe can support 4x longer video sequences with minimal performance loss (<1%) and outperform all similar-size VideoLLMs with 3%-5%, even surpassing or on par with much larger ones. Our code is available at https://github.com/SCZwangxiao/video-ReTaKe
视频大语言模型(VideoLLMs)在视频理解方面取得了显著的进步。然而,现有的VideoLLMs通常继承了其主干LLMs在处理长序列时的局限性,这给长视频理解带来了挑战。常见的解决方案要么简单地均匀采样视频的帧,要么压缩视觉令牌,这些解决方案主要关注低级别的时序视觉冗余,而忽略了高级别的知识冗余。这限制了可达到的压缩率,同时损失很小。为此,我们介绍了一种无需训练的方法ReTaKe,包含两个新颖模块DPSelect和PivotKV,以联合建模和减少时序视觉冗余和知识冗余,用于长视频理解。具体来说,DPSelect基于其视觉特征识别具有局部最大峰值距离的关键帧,这些关键帧与人类视频感知紧密相关。PivotKV将获得的关键帧作为支点,并使用KV-Cache压缩低注意力分数的非支点令牌,这些令牌来源于LLMs学习的先验知识。在VideoMME、MLVU和LVBench等基准测试上的实验表明,ReTaKe可以在性能损失极小(<1%)的情况下支持4倍更长的视频序列,并且超越所有类似规模的VideoLLMs达3%-5%,甚至超过或可与更大的模型相媲美。我们的代码可在https://github.com/SCZwangxiao/video-ReTaKe找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Update performance in MLVU-dev and LVBench
Summary
视频大型语言模型(VideoLLMs)在视频理解方面取得了显著进展,但在处理长序列视频时面临挑战。现有方法主要关注低级别的时间视觉冗余,而忽视高级别知识冗余。为此,提出了一种无需训练的方法ReTaKe,包括DPSelect和PivotKV两个新模块,以联合建模和减少时间视觉冗余和知识冗余,用于长视频理解。实验表明,ReTaKe可以在性能损失极小的情况下支持4倍长的视频序列,并在基准测试中优于其他类似规模的VideoLLMs,甚至超过或相当于更大的模型。
Key Takeaways
- VideoLLMs在视频理解方面取得显著进展,但在处理长序列视频时存在局限性。
- 现有方法主要关注低级别的时间视觉冗余,而忽视高级别知识冗余。
- 引入了一种无需训练的方法ReTaKe,包括DPSelect和PivotKV两个新模块。
- DPSelect基于视觉特征识别具有局部最大峰值距离的关键帧,与人类视频感知紧密对齐。
- PivotKV使用获得的关键帧作为中心点,并对非中心令牌进行KV-Cache压缩,这些令牌具有较低的注意力分数,源于LLMs学习的先验知识。
- 实验表明,ReTaKe支持4倍长的视频序列,性能损失极小,并在基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图