⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-08 更新
Gaussian Masked Autoencoders
Authors:Jathushan Rajasegaran, Xinlei Chen, Rulilong Li, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Jitendra Malik, Shiry Ginosar
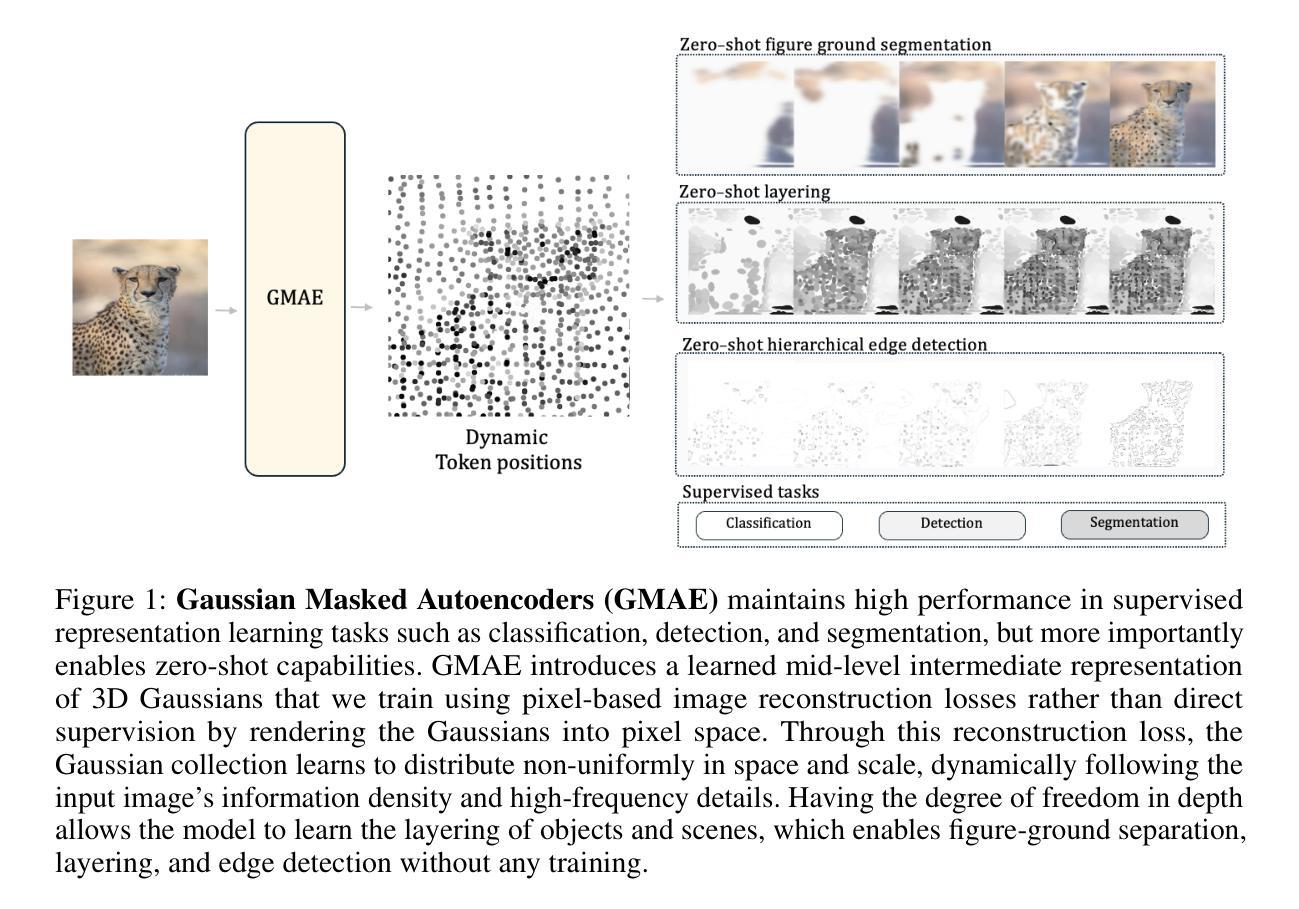
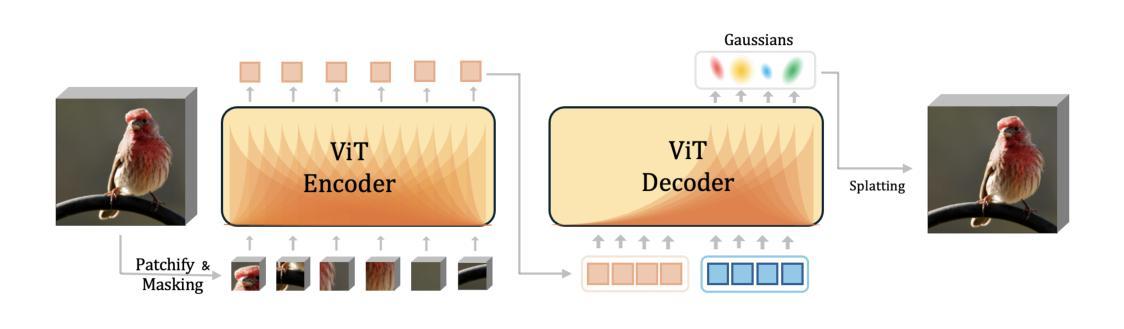
This paper explores Masked Autoencoders (MAE) with Gaussian Splatting. While reconstructive self-supervised learning frameworks such as MAE learns good semantic abstractions, it is not trained for explicit spatial awareness. Our approach, named Gaussian Masked Autoencoder, or GMAE, aims to learn semantic abstractions and spatial understanding jointly. Like MAE, it reconstructs the image end-to-end in the pixel space, but beyond MAE, it also introduces an intermediate, 3D Gaussian-based representation and renders images via splatting. We show that GMAE can enable various zero-shot learning capabilities of spatial understanding (e.g., figure-ground segmentation, image layering, edge detection, etc.) while preserving the high-level semantics of self-supervised representation quality from MAE. To our knowledge, we are the first to employ Gaussian primitives in an image representation learning framework beyond optimization-based single-scene reconstructions. We believe GMAE will inspire further research in this direction and contribute to developing next-generation techniques for modeling high-fidelity visual data. More details at https://brjathu.github.io/gmae
本文探讨了带有高斯拼贴技术的Masked Autoencoders(MAE)。虽然像MAE这样的重建自监督学习框架可以学习良好的语义抽象,但它并没有针对明确的空间感知进行训练。我们的方法,名为高斯掩码自编码器(GMAE),旨在联合学习语义抽象和空间理解。与MAE一样,它在像素空间中端到端地重建图像,但超越了MAE,它还引入了一个基于中间过程的3D高斯表示,并通过拼贴技术呈现图像。我们证明了GMAE可以实现在无需训练的情况下理解空间的各种能力(例如,图地分割、图像分层、边缘检测等),同时保留MAE自监督表示质量的高层语义。据我们所知,我们是第一个在图像表示学习框架中采用高斯基本体的方法,超越了基于优化的单场景重建。我们相信GMAE将激发这一方向上的进一步研究,并为开发下一代高保真视觉数据建模技术做出贡献。更多详情请点击:https://brjathu.github.io/gmae。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了结合掩码自编码器(MAE)与高斯拼贴技术的创新方法。研究提出了一种名为高斯掩码自编码器(GMAE)的新框架,旨在联合学习语义抽象和空间理解。GMAE在像素空间进行端到端的图像重建,同时引入基于3D高斯的中级表示和拼贴渲染。研究表明,GMAE能够在零样本学习情况下实现空间理解的各种能力,如图地分割、图像分层、边缘检测等,同时保留MAE自监督表示法的高层次语义。这是首次在图像表示学习框架中使用高斯原始技术,超越了基于优化的单场景重建。
Key Takeaways
- Masked Autoencoders (MAE) 结合 Gaussian Splatting 技术创新提出 Gaussian Masked Autoencoder (GMAE) 框架。
- GMAE 旨在联合学习语义抽象和空间理解。
- GMAE 在像素空间进行端到端的图像重建。
- GMAE 引入了一个基于3D高斯的中级表示。
- GMAE 通过拼贴渲染图像。
- GMAE 能够实现零样本学习的空间理解能力,如图地分割、图像分层、边缘检测等。
点此查看论文截图


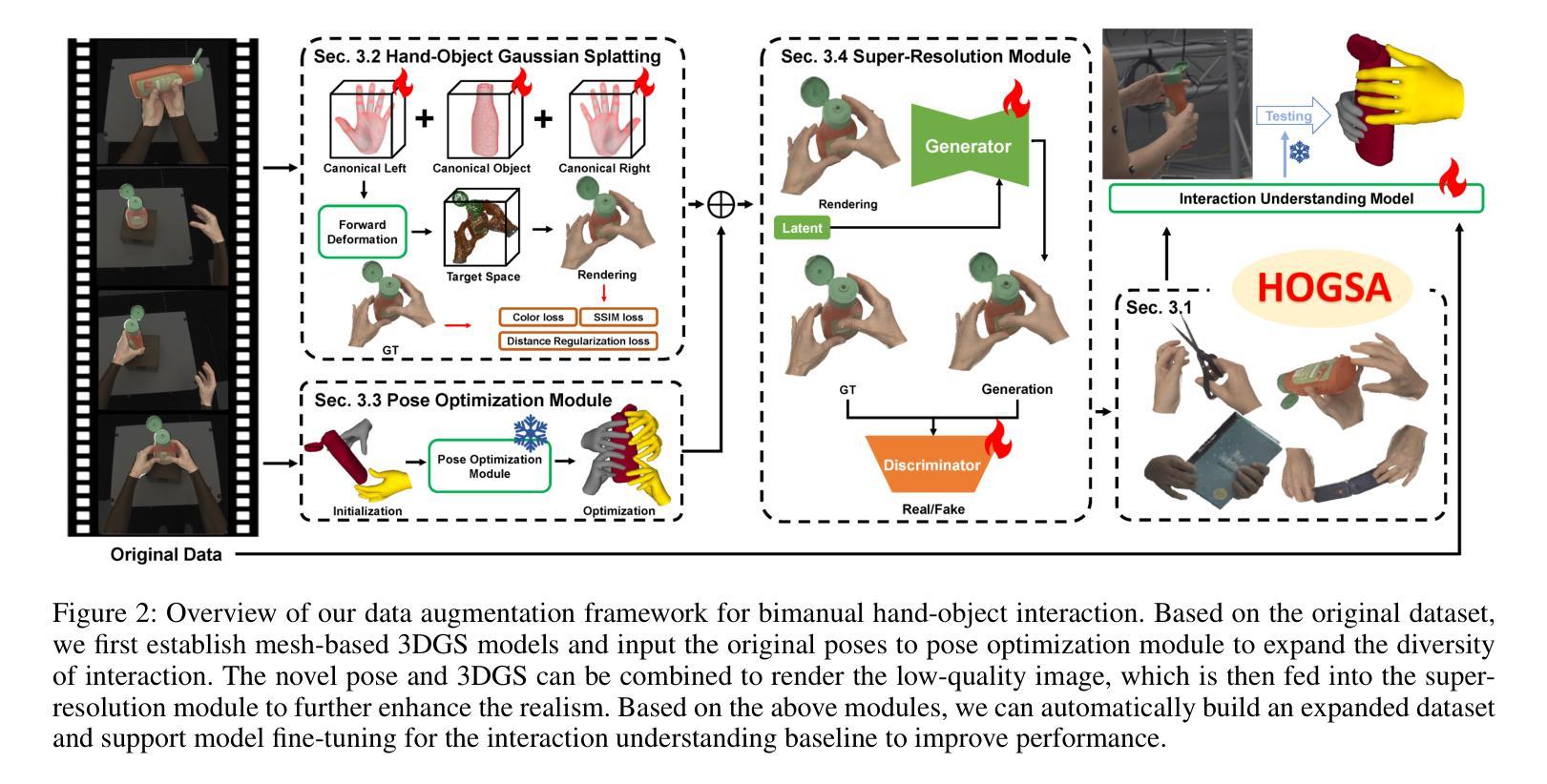
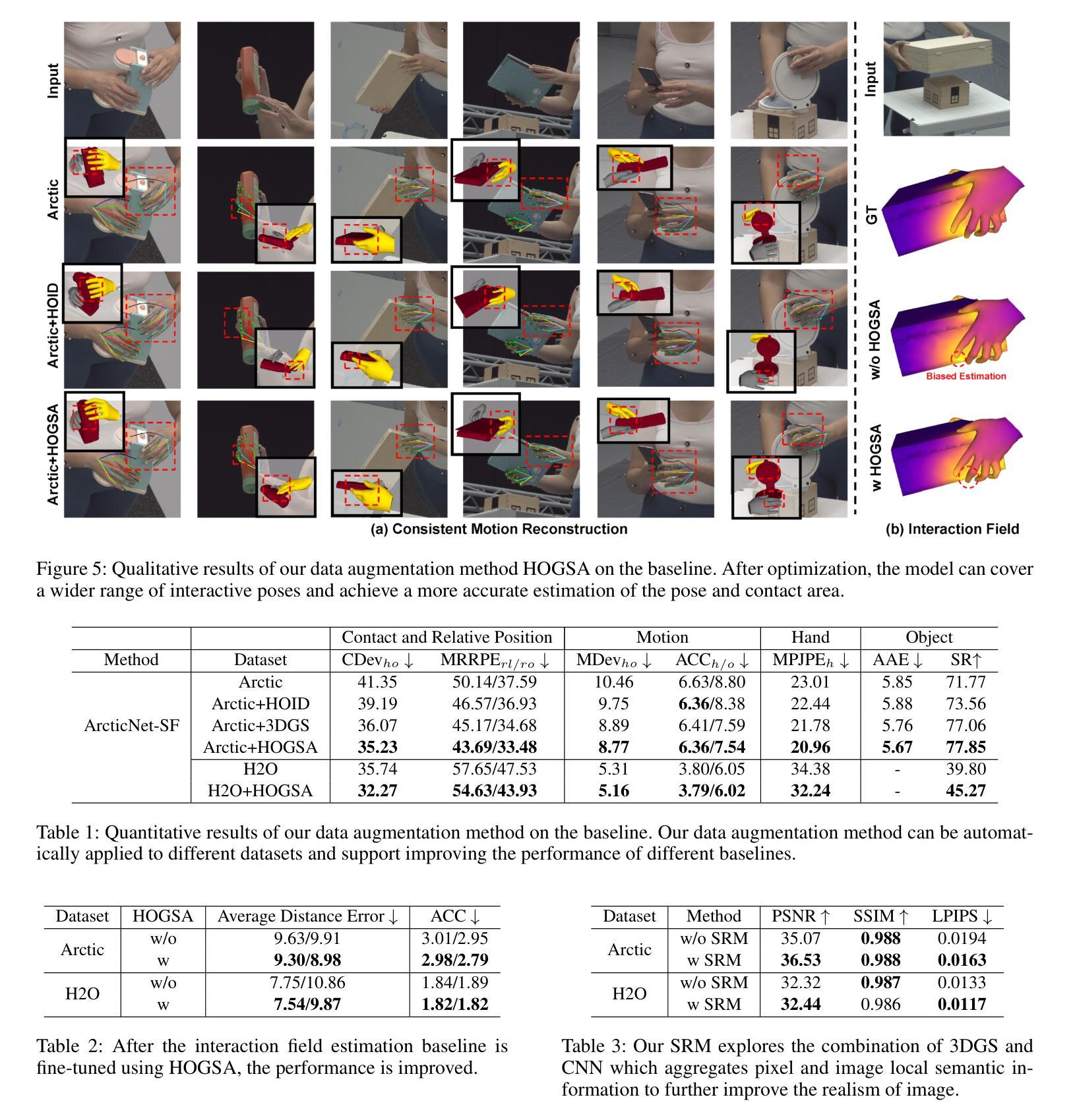
HOGSA: Bimanual Hand-Object Interaction Understanding with 3D Gaussian Splatting Based Data Augmentation
Authors:Wentian Qu, Jiahe Li, Jian Cheng, Jian Shi, Chenyu Meng, Cuixia Ma, Hongan Wang, Xiaoming Deng, Yinda Zhang
Understanding of bimanual hand-object interaction plays an important role in robotics and virtual reality. However, due to significant occlusions between hands and object as well as the high degree-of-freedom motions, it is challenging to collect and annotate a high-quality, large-scale dataset, which prevents further improvement of bimanual hand-object interaction-related baselines. In this work, we propose a new 3D Gaussian Splatting based data augmentation framework for bimanual hand-object interaction, which is capable of augmenting existing dataset to large-scale photorealistic data with various hand-object pose and viewpoints. First, we use mesh-based 3DGS to model objects and hands, and to deal with the rendering blur problem due to multi-resolution input images used, we design a super-resolution module. Second, we extend the single hand grasping pose optimization module for the bimanual hand object to generate various poses of bimanual hand-object interaction, which can significantly expand the pose distribution of the dataset. Third, we conduct an analysis for the impact of different aspects of the proposed data augmentation on the understanding of the bimanual hand-object interaction. We perform our data augmentation on two benchmarks, H2O and Arctic, and verify that our method can improve the performance of the baselines.
对双手手物交互的理解在机器人和虚拟现实领域扮演着重要角色。然而,由于手部与物体之间的遮挡以及高自由度运动,收集并标注高质量的大规模数据集具有挑战性,这阻碍了双手手物交互基准的进一步改进。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的基于3D高斯涂绘的双手手物交互数据增强框架,该框架能够增强现有数据集,生成大规模照片级真实感数据,具有各种手物姿态和视角。首先,我们使用网格化的3DGS对物体和手部进行建模,为了解决由于使用多分辨率输入图像导致的渲染模糊问题,我们设计了一个超分辨率模块。其次,我们对单手抓取姿态优化模块进行了扩展,以处理双手手物交互,生成各种双手手物交互姿态,这可以显著扩展数据集的动作姿态分布。第三,我们分析了所提出数据增强的不同方面对理解双手手物交互的影响。我们在H2O和北极两个基准测试集上进行了数据增强,并验证了我们的方法可以改进基线性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
基于三维高斯喷绘的数据增强框架,用于理解双手与物体的交互,解决了收集与标注高质量大规模数据集的问题,能够扩充现有数据集为大规模逼真的数据,具有多种手-物体姿态和视角。通过网格建模与超分辨率模块解决渲染模糊问题,扩展单手抓取姿态优化模块以适应双手手物交互,生成多种姿态。在H2O和Arctic两个基准数据集上进行数据增强分析,验证了该方法能提高基线性能。
Key Takeaways
- 双手与物体交互在机器人和虚拟现实领域具有重要作用,但数据集收集与标注存在挑战。
- 提出基于三维高斯喷绘的数据增强框架,用于解决双手与物体交互的大规模数据集问题。
- 使用网格建模进行物体与手的建模,设计超分辨率模块解决多分辨率图像渲染模糊问题。
- 扩展单手抓取姿态优化模块,生成多种双手与物体的交互姿态。
- 在两个基准数据集上进行数据增强分析,验证了方法的有效性。
- 数据增强框架能够提高双手与物体交互相关基线的性能。
点此查看论文截图



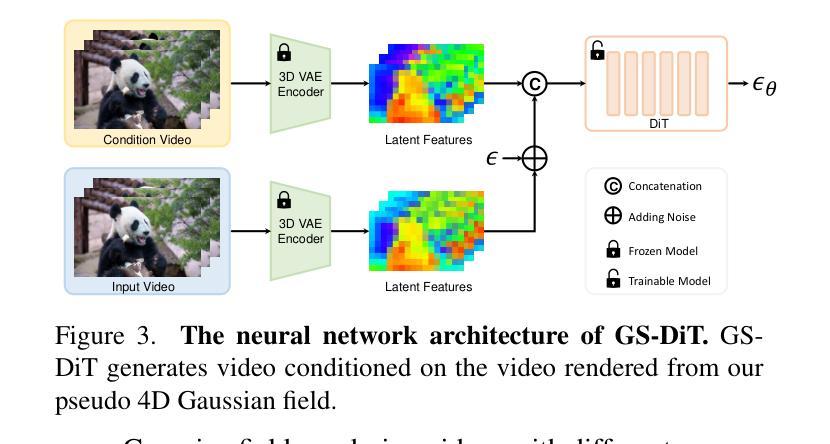
GS-DiT: Advancing Video Generation with Pseudo 4D Gaussian Fields through Efficient Dense 3D Point Tracking
Authors:Weikang Bian, Zhaoyang Huang, Xiaoyu Shi, Yijin Li, Fu-Yun Wang, Hongsheng Li
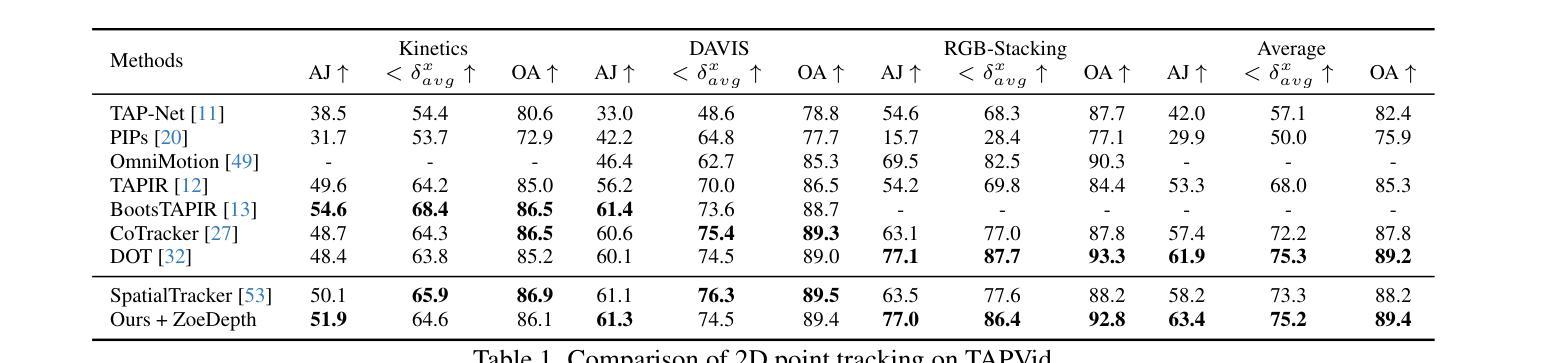
4D video control is essential in video generation as it enables the use of sophisticated lens techniques, such as multi-camera shooting and dolly zoom, which are currently unsupported by existing methods. Training a video Diffusion Transformer (DiT) directly to control 4D content requires expensive multi-view videos. Inspired by Monocular Dynamic novel View Synthesis (MDVS) that optimizes a 4D representation and renders videos according to different 4D elements, such as camera pose and object motion editing, we bring pseudo 4D Gaussian fields to video generation. Specifically, we propose a novel framework that constructs a pseudo 4D Gaussian field with dense 3D point tracking and renders the Gaussian field for all video frames. Then we finetune a pretrained DiT to generate videos following the guidance of the rendered video, dubbed as GS-DiT. To boost the training of the GS-DiT, we also propose an efficient Dense 3D Point Tracking (D3D-PT) method for the pseudo 4D Gaussian field construction. Our D3D-PT outperforms SpatialTracker, the state-of-the-art sparse 3D point tracking method, in accuracy and accelerates the inference speed by two orders of magnitude. During the inference stage, GS-DiT can generate videos with the same dynamic content while adhering to different camera parameters, addressing a significant limitation of current video generation models. GS-DiT demonstrates strong generalization capabilities and extends the 4D controllability of Gaussian splatting to video generation beyond just camera poses. It supports advanced cinematic effects through the manipulation of the Gaussian field and camera intrinsics, making it a powerful tool for creative video production. Demos are available at https://wkbian.github.io/Projects/GS-DiT/.
在视频生成中,四维视频控制非常重要,因为它能够使用复杂的多镜头技术,如多相机拍摄和滑轨缩放等当前方法尚不支持的技术。直接训练视频扩散转换器(DiT)以控制四维内容需要昂贵的多视角视频。受单眼动态新颖视图合成(MDVS)的启发,该技术优化了四维表示并根据不同的四维元素(如相机姿态和对象运动编辑)呈现视频,我们将伪四维高斯场引入视频生成。具体来说,我们提出了一个构建伪四维高斯场的新框架,该框架具有密集的三维点跟踪功能,并为所有视频帧呈现高斯场。然后,我们对预训练的DiT进行了微调,以根据呈现的视频的引导生成视频,被称为GS-DiT。为了增强GS-DiT的训练,我们还提出了高效的密集三维点跟踪(D3D-PT)方法用于构建伪四维高斯场。我们的D3D-PT在精度上超越了最新稀疏三维点跟踪方法SpatialTracker,并将推理速度提高了两个数量级。在推理阶段,GS-DiT能够生成具有相同动态内容但符合不同相机参数的视频,解决了当前视频生成模型的一个重要限制。GS-DiT表现出强大的泛化能力,并将高斯展开的四维可控性扩展到不仅仅是相机姿态的视频生成。它通过操纵高斯场和相机内在参数支持高级电影效果,成为创意视频制作的强大工具。演示视频可在[https://wkbian.github.io/Projects/GS-DiT/]查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://wkbian.github.io/Projects/GS-DiT/
摘要
视频生成中引入伪四维高斯场实现视频控制的进阶。通过构建伪四维高斯场,结合密集的三维点追踪和渲染技术,对视频内容进行精准控制。并提出了一种有效的密集三维点跟踪方法,用于构建伪四维高斯场。所提方法能够生成动态内容一致但适应不同相机参数的视频,展现了强大的泛化能力和四维控制能力的扩展。
关键见解
- 介绍了四维视频控制在视频生成中的重要性及其面临的挑战。
- 通过引入伪四维高斯场结合密集的三维点追踪技术来实现更精细的视频控制。
- 提出了一种新的框架来渲染所有视频帧的伪四维高斯场。
- 利用预训练的扩散变压器(DiT)根据渲染的视频进行微调,生成视频,称为GS-DiT。
- 开发了一种高效密集三维点跟踪(D3D-PT)方法来加速伪四维高斯场的构建,该方法超越了当前先进的稀疏三维点跟踪方法的空间追踪(SpatialTracker)的准确性和推理速度。
- GS-DiT在推理阶段可以生成动态内容一致但适应不同相机参数的视频,展示了强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


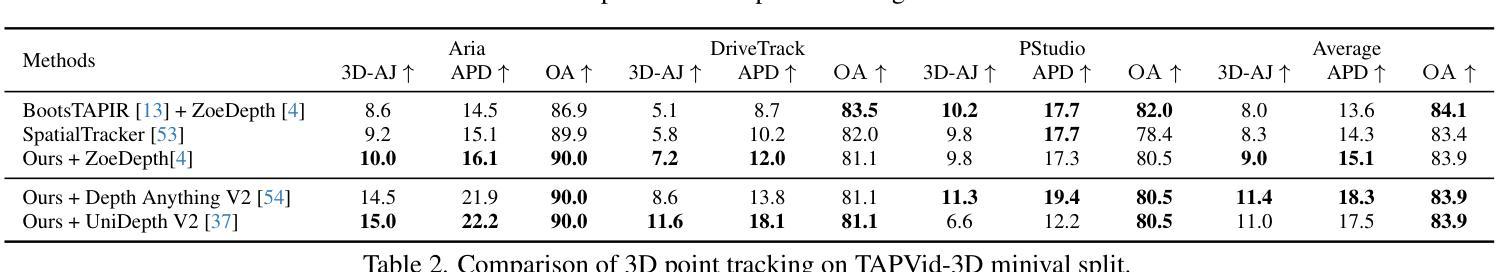
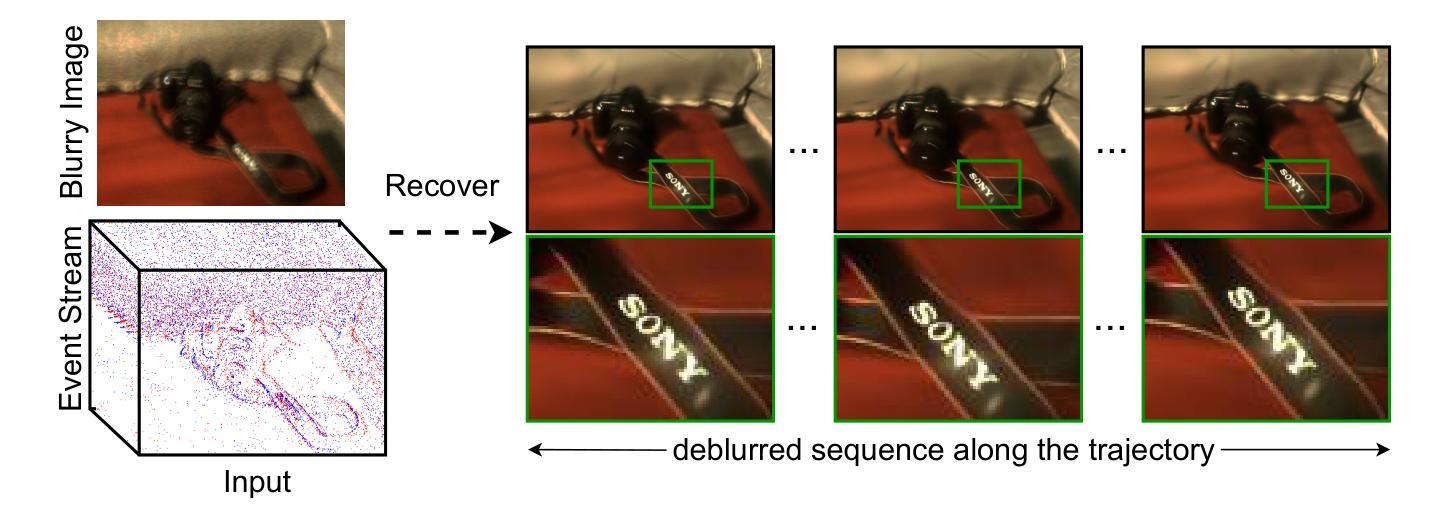
BeSplat: Gaussian Splatting from a Single Blurry Image and Event Stream
Authors:Gopi Raju Matta, Reddypalli Trisha, Kaushik Mitra
Novel view synthesis has been greatly enhanced by the development of radiance field methods. The introduction of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has effectively addressed key challenges, such as long training times and slow rendering speeds, typically associated with Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), while maintaining high-quality reconstructions. In this work (BeSplat), we demonstrate the recovery of sharp radiance field (Gaussian splats) from a single motion-blurred image and its corresponding event stream. Our method jointly learns the scene representation via Gaussian Splatting and recovers the camera motion through Bezier SE(3) formulation effectively, minimizing discrepancies between synthesized and real-world measurements of both blurry image and corresponding event stream. We evaluate our approach on both synthetic and real datasets, showcasing its ability to render view-consistent, sharp images from the learned radiance field and the estimated camera trajectory. To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first work to address this highly challenging ill-posed problem in a Gaussian Splatting framework with the effective incorporation of temporal information captured using the event stream.
随着辐射场方法的发展,新型视图合成技术得到了极大的增强。3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的引入有效地解决了与神经辐射场(NeRF)通常相关的主要挑战,例如训练时间长和渲染速度慢,同时保持了高质量的重构。在这项工作(BeSplat)中,我们展示了从单个运动模糊图像及其相应的事件流中恢复锐利的辐射场(高斯拼贴)的方法。我们的方法通过高斯拼贴联合学习场景表示,并通过贝塞尔SE(3)公式有效地恢复相机运动,从而最小化合成和真实世界测量之间模糊图像和相应事件流的差异。我们在合成数据集和真实数据集上评估了我们的方法,展示了其从学习的辐射场和估计的相机轨迹呈现一致视图、清晰图像的能力。据我们所知,我们的工作是在高斯拼贴框架中解决这个高度挑战的不适定问题的首批工作之一,有效地结合了通过事件流捕获的时间信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at EVGEN2025, WACV-25 Workshop
总结
新型视图合成因辐射场方法的发展而得到极大增强。3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的引入有效解决了与神经辐射场(NeRF)相关的一些关键挑战,如训练时间长和渲染速度慢,同时保持了高质量的重建。在这项工作(BeSplat)中,我们展示了从单个运动模糊图像及其相应的事件流中恢复尖锐辐射场(高斯拼贴)的能力。我们的方法通过高斯拼贴场景表示和通过贝塞尔SE(3)公式有效恢复相机运动进行联合学习,从而最小化合成和真实世界测量之间的偏差,这些测量既包括模糊的图像,也包括相应的事件流。我们在合成数据集和真实数据集上评估了我们的方法,展示了从学习的辐射场和估计的相机轨迹中渲染出一致、清晰图像的能力。据我们所知,我们的工作是在高斯拼贴框架中解决这一极具挑战性的不适定问题的首批工作之一,并有效结合了使用事件流捕获的临时信息。
要点
- 3DGS解决了NeRF相关的训练时间长和渲染速度慢的关键挑战。
- BeSplat方法能够从运动模糊图像中恢复尖锐的辐射场。
- BeSplat通过联合学习场景表示和相机运动恢复,实现了高清晰度的图像渲染。
- 该方法最小化了合成图像与真实世界测量之间的偏差。
- 评估结果显示,BeSplat能够在合成和真实数据集上有效渲染一致的清晰图像。
- BeSplat是首个在Gaussian Splatting框架内解决具有挑战性的不适定问题的研究之一。
点此查看论文截图

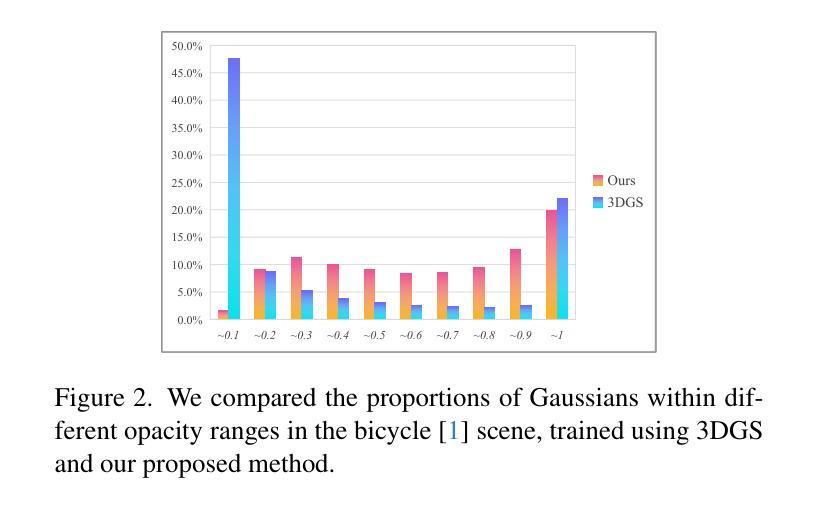
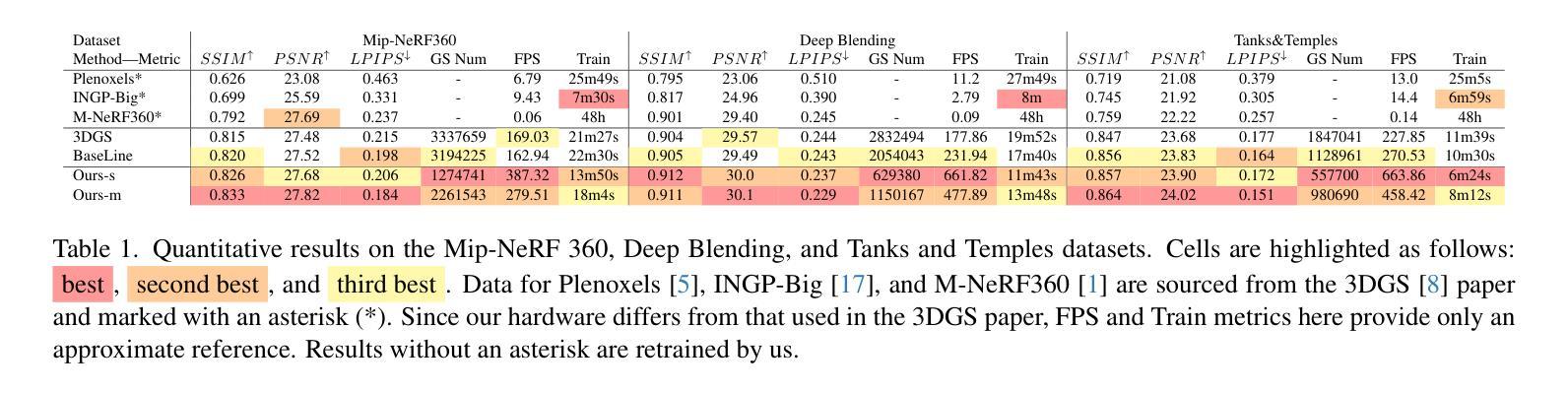
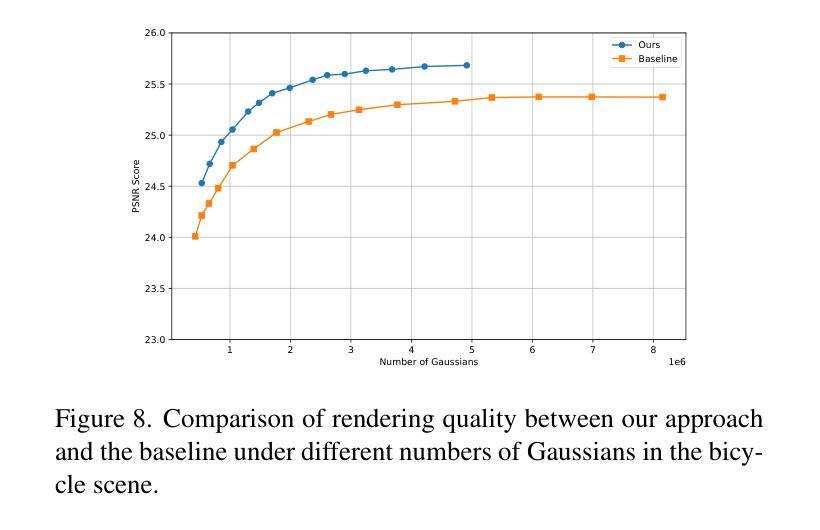
Efficient Density Control for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Xiaobin Deng, Changyu Diao, Min Li, Ruohan Yu, Duanqing Xu
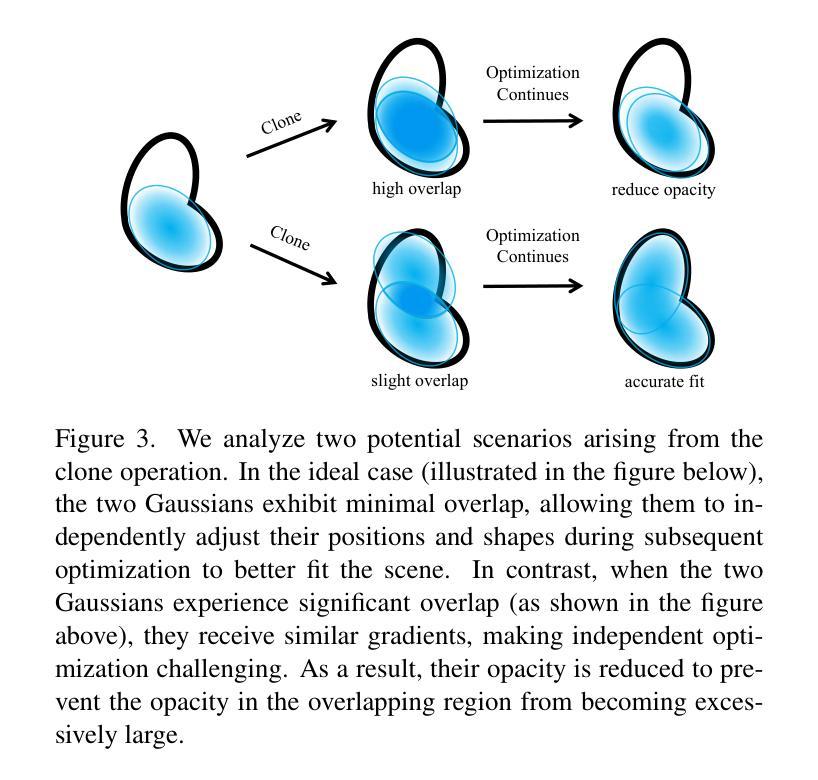
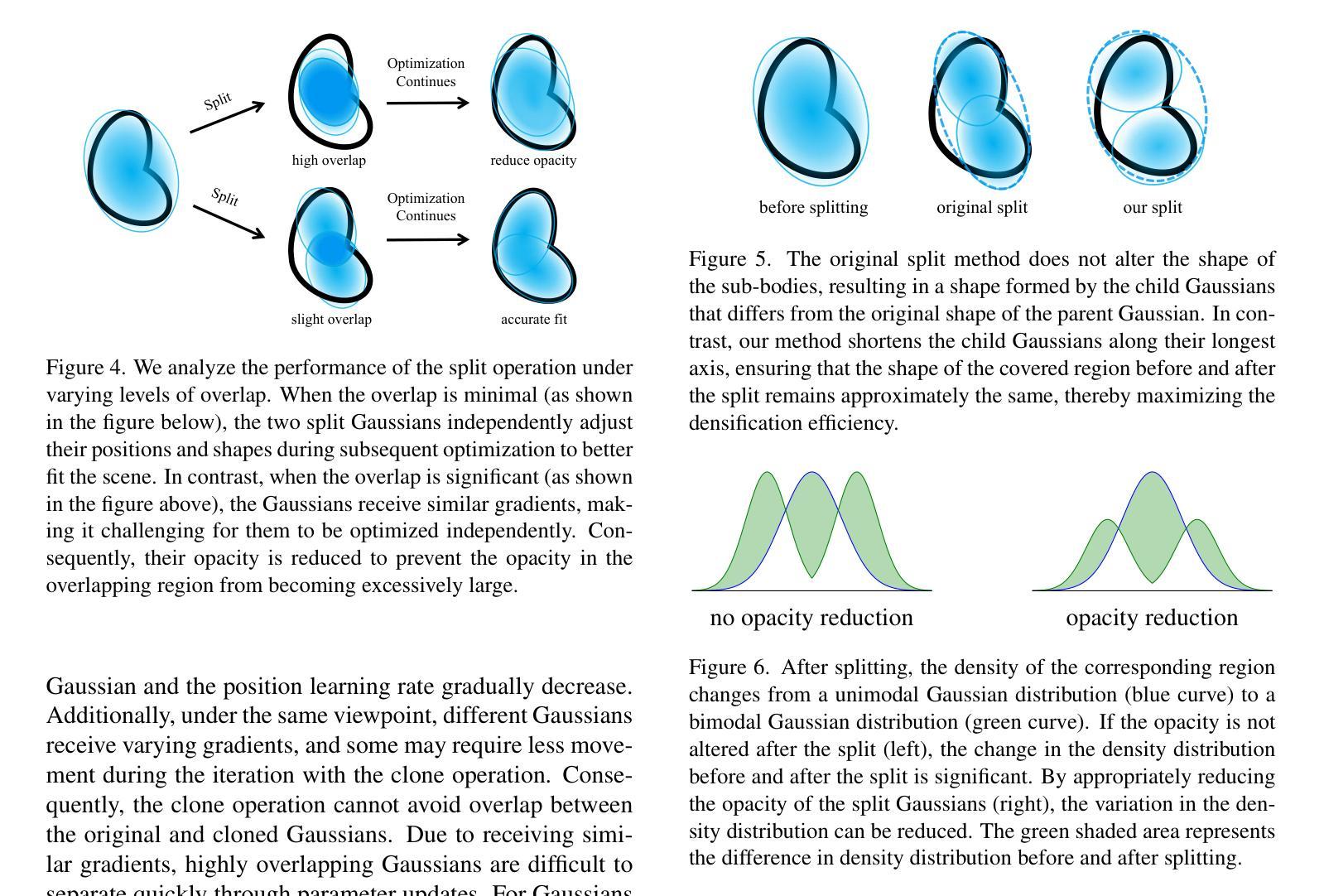
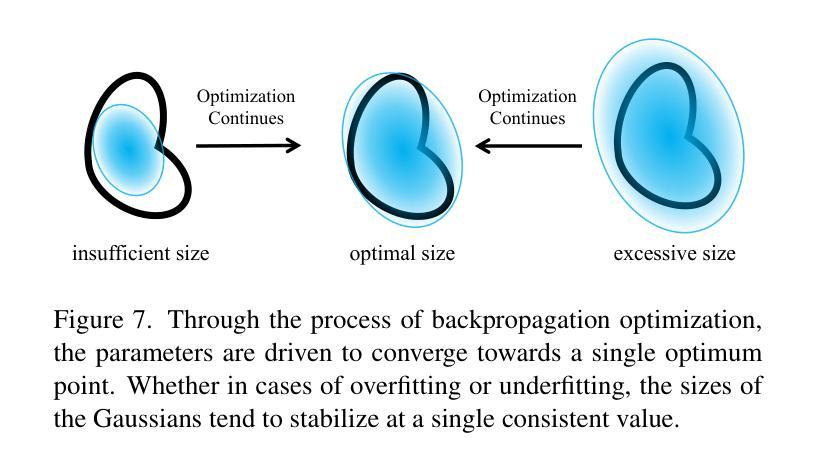
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) excels in novel view synthesis, balancing advanced rendering quality with real-time performance. However, in trained scenes, a large number of Gaussians with low opacity significantly increase rendering costs. This issue arises due to flaws in the split and clone operations during the densification process, which lead to extensive Gaussian overlap and subsequent opacity reduction. To enhance the efficiency of Gaussian utilization, we improve the adaptive density control of 3DGS. First, we introduce a more efficient long-axis split operation to replace the original clone and split, which mitigates Gaussian overlap and improves densification efficiency.Second, we propose a simple adaptive pruning technique to reduce the number of low-opacity Gaussians. Finally, by dynamically lowering the splitting threshold and applying importance weighting, the efficiency of Gaussian utilization is further improved. We evaluate our proposed method on various challenging real-world datasets. Experimental results show that our Efficient Density Control (EDC) can enhance both the rendering speed and quality. Code is available at https://github.com/XiaoBin2001/EDC.
3D高斯混合技术(3DGS)在新视角合成方面表现出色,在实时性能与高级渲染质量之间达到了平衡。然而,在已训练的场景中,大量的低不透明度的高斯增加了渲染成本。这一问题是由于在密集化过程中的分裂和克隆操作中的缺陷所导致的,导致了大量高斯重叠以及随后的不透明度降低。为了提高高斯利用的效率,我们改进了3DGS的自适应密度控制。首先,我们引入了一种更高效的长轴分裂操作来替代原始的克隆和分裂,这减轻了高斯重叠现象并提高了密集化效率。其次,我们提出了一种简单的自适应修剪技术来减少低不透明度的高斯数量。最后,通过动态降低分裂阈值并应用重要性加权,进一步提高了高斯利用的效率。我们在各种具有挑战性的真实世界数据集上评估了我们提出的方法。实验结果表明,我们的高效密度控制(EDC)可以同时提高渲染速度和质量。代码可通过https://github.com/XiaoBin2001/EDC获取。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
3DGS在新型视图合成方面表现出色,可在实时性能和高品质渲染之间取得平衡。但在已训练场景中,大量的低透明度高斯增加了渲染成本。为了解决这一问题,本文介绍了高斯的有效密度控制策略,采用更有效的长轴分裂操作替代原有的克隆和分裂,减少了高斯重叠并提高了密度效率。此外,本文还提出了一种简单的自适应修剪技术来减少低透明度的高斯数量。通过动态降低分裂阈值并应用重要性加权,进一步提高了高斯利用的效率。在具有挑战性的真实数据集上的实验结果表明,本文提出的EDC方法可以提高渲染速度和品质。
关键见解
- 3DGS在视图合成方面表现出卓越性能,实现了高质量渲染与实时性能的平衡。
- 在已训练场景中,存在大量低透明度的高斯导致渲染成本增加。
- 引入更有效的长轴分裂操作,减少高斯重叠并提高密度效率。
- 提出自适应修剪技术来减少低透明度的高斯数量。
- 通过动态调整分裂阈值和重要性加权,进一步优化高斯利用的效率。
- 在多个真实数据集上的实验结果表明,EDC方法能提高渲染速度和品质。
点此查看论文截图

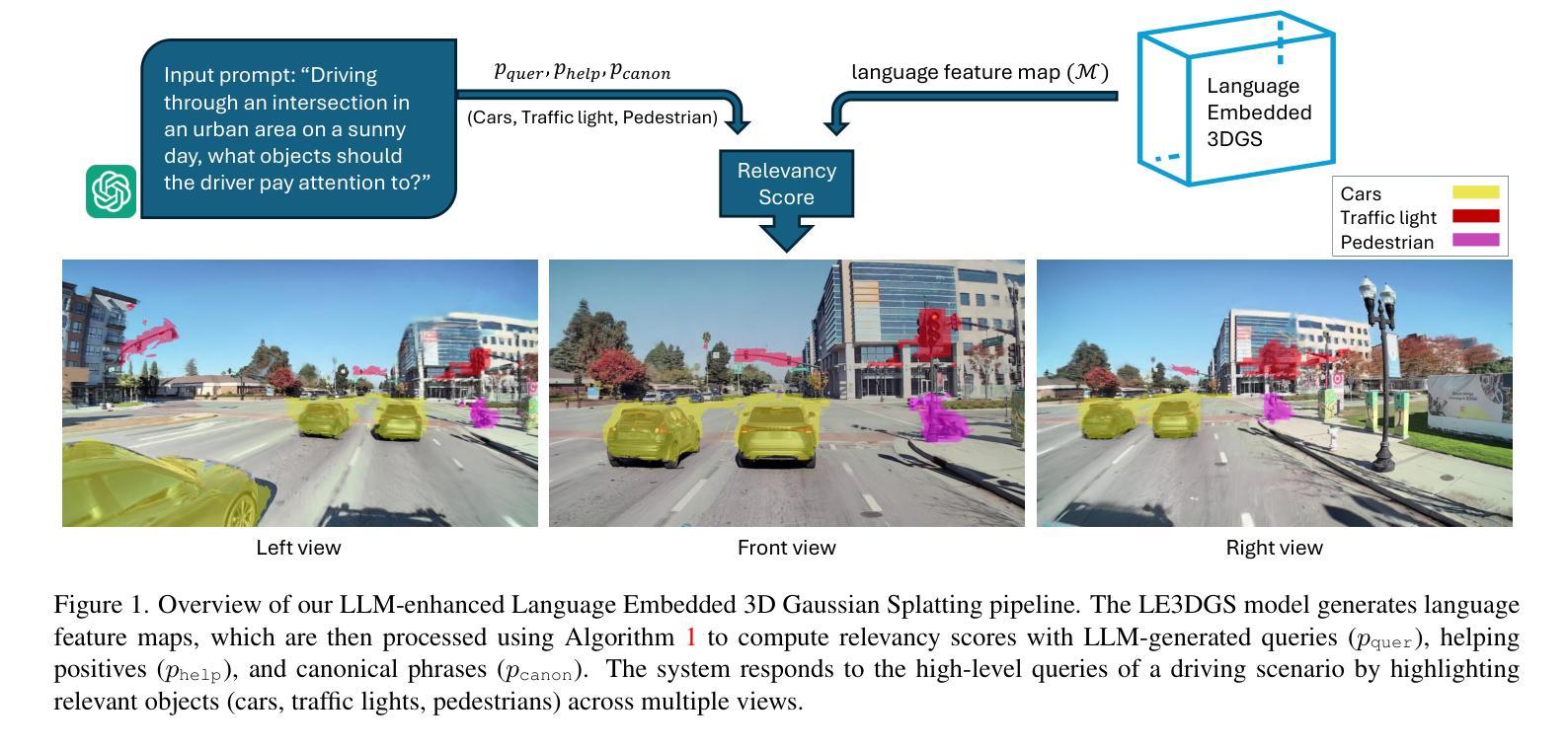
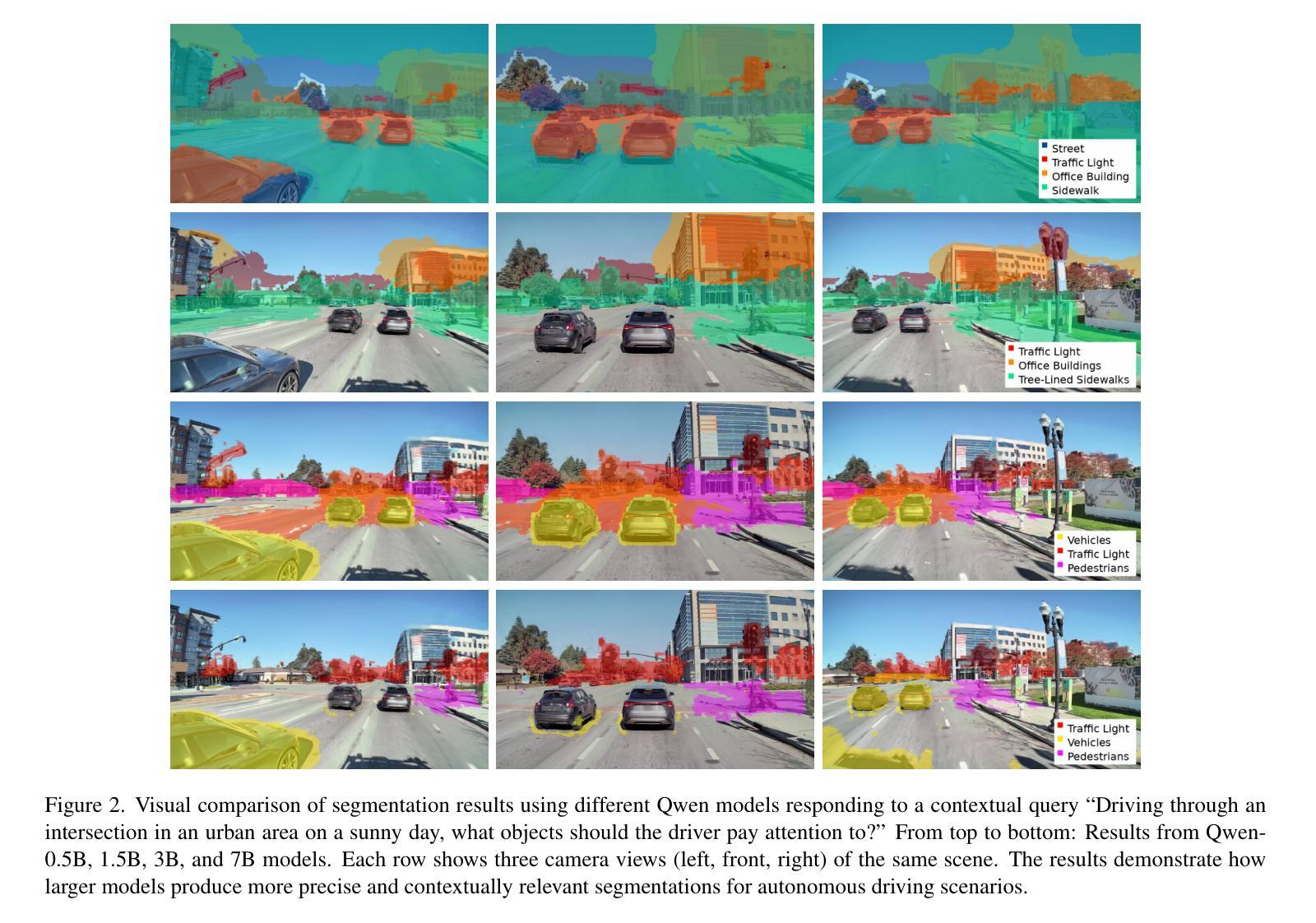
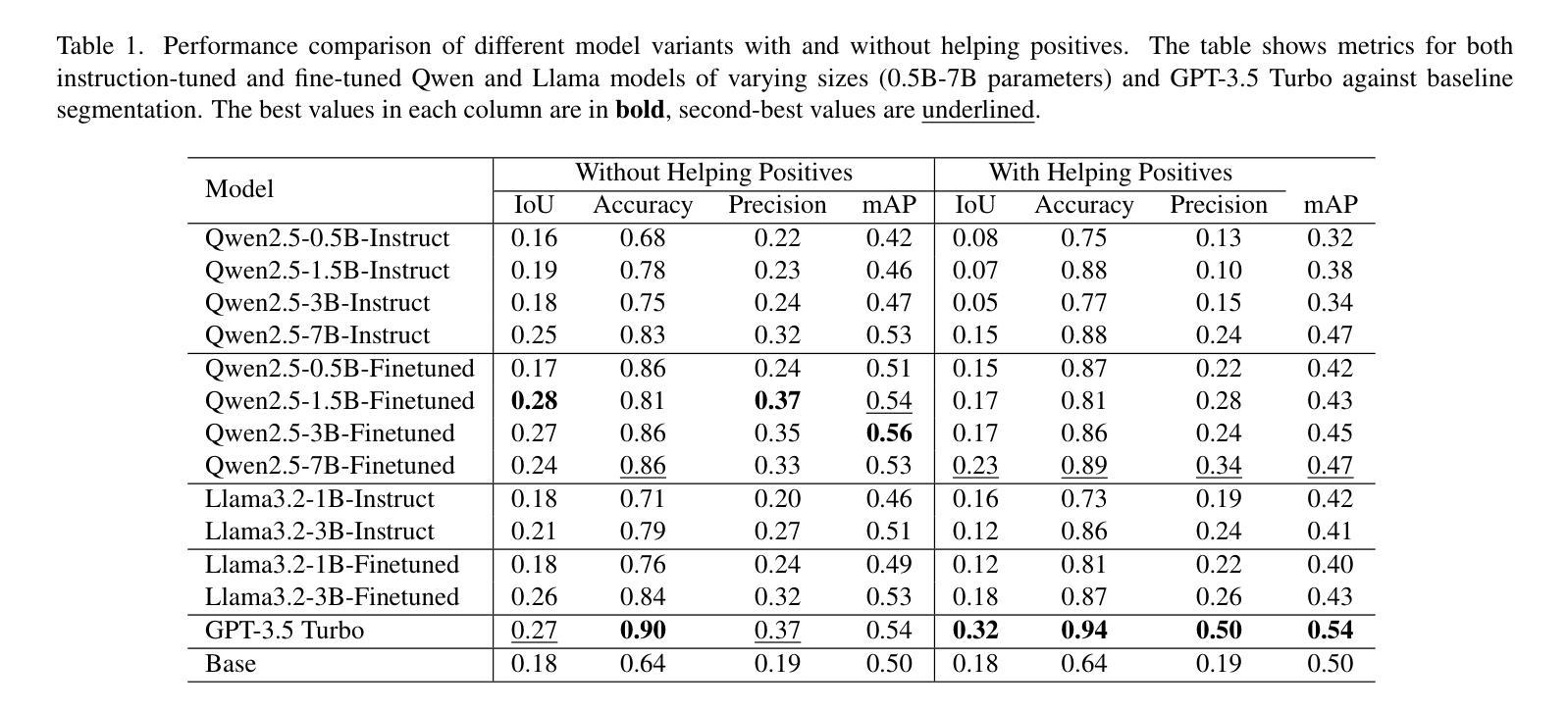
Query3D: LLM-Powered Open-Vocabulary Scene Segmentation with Language Embedded 3D Gaussian
Authors:Amirhosein Chahe, Lifeng Zhou
This paper introduces a novel method for open-vocabulary 3D scene querying in autonomous driving by combining Language Embedded 3D Gaussians with Large Language Models (LLMs). We propose utilizing LLMs to generate both contextually canonical phrases and helping positive words for enhanced segmentation and scene interpretation. Our method leverages GPT-3.5 Turbo as an expert model to create a high-quality text dataset, which we then use to fine-tune smaller, more efficient LLMs for on-device deployment. Our comprehensive evaluation on the WayveScenes101 dataset demonstrates that LLM-guided segmentation significantly outperforms traditional approaches based on predefined canonical phrases. Notably, our fine-tuned smaller models achieve performance comparable to larger expert models while maintaining faster inference times. Through ablation studies, we discover that the effectiveness of helping positive words correlates with model scale, with larger models better equipped to leverage additional semantic information. This work represents a significant advancement towards more efficient, context-aware autonomous driving systems, effectively bridging 3D scene representation with high-level semantic querying while maintaining practical deployment considerations.
本文介绍了一种结合语言嵌入3D高斯分布与大型语言模型(LLM)进行开放词汇3D场景查询的新型方法。我们提出利用LLM生成上下文规范短语和帮助积极词汇,以提高分割和场景解释能力。我们的方法利用GPT-3.5 Turbo作为专家模型来创建高质量文本数据集,然后我们使用这些数据集对更小、更高效的在设备部署LLM进行微调。我们在WayveScenes101数据集上的全面评估表明,LLM引导的分割显著优于基于预定义规范短语的传统方法。值得注意的是,我们微调的小型模型的性能与大型专家模型相当,同时保持更快的推理时间。通过消融研究,我们发现帮助积极词汇的有效性与模型规模有关,较大的模型能够更好地利用额外的语义信息。这项工作标志着向更高效、更具备上下文意识的自动驾驶系统的重要进步,有效地将3D场景表示与高级语义查询相结合,同时考虑实际部署需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种结合语言嵌入3D高斯与大型语言模型(LLMs)的开放词汇3D场景查询新方法,应用于自动驾驶领域。文章建议使用LLMs生成上下文规范短语和辅助积极词汇,以提高场景分割和解读能力。该方法利用GPT-3.5 Turbo作为专家模型创建高质量文本数据集,进而微调更小、更高效的LLMs,用于设备端部署。在WayveScenes101数据集上的综合评估显示,LLM引导的分割显著优于基于预定义规范短语的传统方法。微调后的小型模型在保持较快推理时间的同时,实现了与大型专家模型相当的性能。通过消融研究,发现辅助积极词汇的有效性与模型规模有关,大型模型更能利用额外的语义信息。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种结合语言嵌入3D高斯与大型语言模型(LLMs)的开放词汇3D场景查询新方法。
- 利用LLMs生成上下文规范短语和辅助积极词汇,提升场景分割和解读。
- 使用GPT-3.5 Turbo作为专家模型创建文本数据集,并微调小型LLMs用于实际部署。
- 在WayveScenes101数据集上,LLM引导分割表现优于传统方法。
- 消融研究显示辅助积极词汇的有效性受模型规模影响。
- 这种方法实现了更高效、上下文感知的自动驾驶系统。
点此查看论文截图