⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-08 更新
Revisiting Communication Efficiency in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning from the Dimensional Analysis Perspective
Authors:Chuxiong Sun, Peng He, Rui Wang, Changwen Zheng
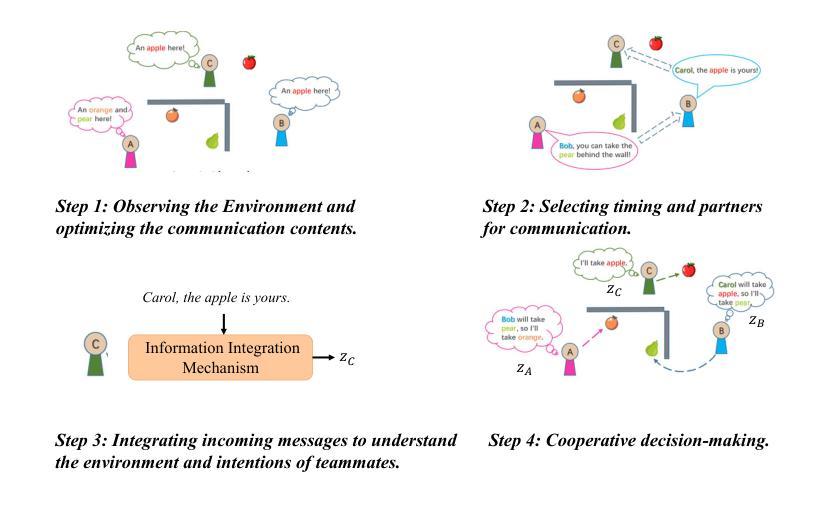
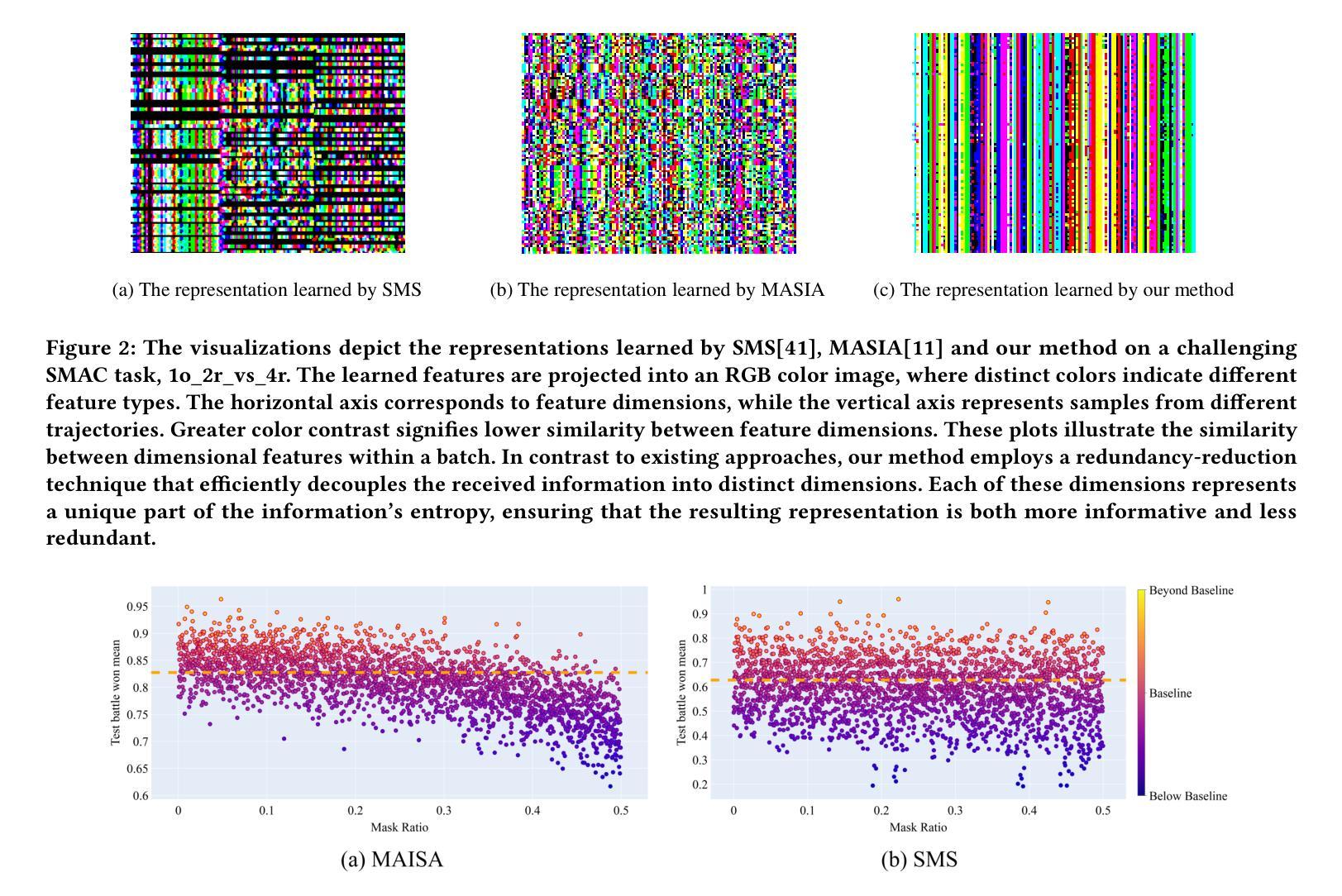
In this work, we introduce a novel perspective, i.e., dimensional analysis, to address the challenge of communication efficiency in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL). Our findings reveal that simply optimizing the content and timing of communication at sending end is insufficient to fully resolve communication efficiency issues. Even after applying optimized and gated messages, dimensional redundancy and confounders still persist in the integrated message embeddings at receiving end, which negatively impact communication quality and decision-making. To address these challenges, we propose Dimensional Rational Multi-Agent Communication (DRMAC), designed to mitigate both dimensional redundancy and confounders in MARL. DRMAC incorporates a redundancy-reduction regularization term to encourage the decoupling of information across dimensions within the learned representations of integrated messages. Additionally, we introduce a dimensional mask that dynamically adjusts gradient weights during training to eliminate the influence of decision-irrelevant dimensions. We evaluate DRMAC across a diverse set of multi-agent tasks, demonstrating its superior performance over existing state-of-the-art methods in complex scenarios. Furthermore, the plug-and-play nature of DRMAC’s key modules highlights its generalizable performance, serving as a valuable complement rather than a replacement for existing multi-agent communication strategies.
在这项工作中,我们引入了一个新的视角,即维度分析,来解决多智能体强化学习(MARL)中的通信效率挑战。我们的研究发现,仅仅优化发送端的通信内容和时机并不能完全解决通信效率问题。即使在应用了优化和门控消息后,接收端的集成消息嵌入中仍然存在维度冗余和混淆因素,这会对通信质量和决策产生负面影响。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了维度理性多智能体通信(DRMAC),旨在减轻MARL中的维度冗余和混淆因素。DRMAC采用了一种减少冗余的正则化项,以鼓励在集成消息的所学表示中,各维度信息的解耦。此外,我们还引入了一个维度掩码,该掩码在训练过程中动态调整梯度权重,以消除决策无关维度的影响。我们在多种多智能体任务中评估了DRMAC的性能,结果表明其在复杂场景中的性能优于现有最先进的方法。此外,DRMAC关键模块的即插即用特性凸显了其通用性能,可作为现有多智能体通信策略的有价值补充,而非替代品。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文引入维度分析的新视角,解决多智能体强化学习(MARL)中的通信效率挑战。研究发现,仅优化发送端的通信内容和时机不足以解决通信效率问题。即使在应用优化和门控消息后,接收端的消息嵌入中仍存在维度冗余和混淆因素,这会对通信质量和决策产生负面影响。为此,提出维度理性多智能体通信(DRMAC)方法,旨在减少MARL中的维度冗余和混淆因素。DRMAC通过引入冗余减少正则化项和鼓励集成消息学习表示中的维度间信息解耦来解决维度冗余问题。此外,还引入了动态调整训练时梯度权重的维度掩码,以消除决策无关维度的影响。在多个多智能体任务上的评估表明,DRMAC在复杂场景中的性能优于现有先进技术方法。而且,DRMAC的关键模块的即插即用特性突显了其通用性能,可作为现有多智能体通信策略的有价值补充,而非替代品。
Key Takeaways
- 引入维度分析来解决多智能体强化学习中的通信效率问题。
- 单纯优化发送端的通信内容和时机不足以解决通信效率挑战。
- 接收端的消息嵌入中存在维度冗余和混淆因素。
- DRMAC方法旨在减少维度冗余并消除混淆因素。
- DRMAC通过冗余减少正则化项和维度解耦来解决维度冗余问题。
- 引入维度掩码来动态调整训练时的梯度权重,以消除决策无关维度的影响。
- 在多个多智能体任务上的评估显示DRMAC性能优越,且其模块具有通用性。
点此查看论文截图

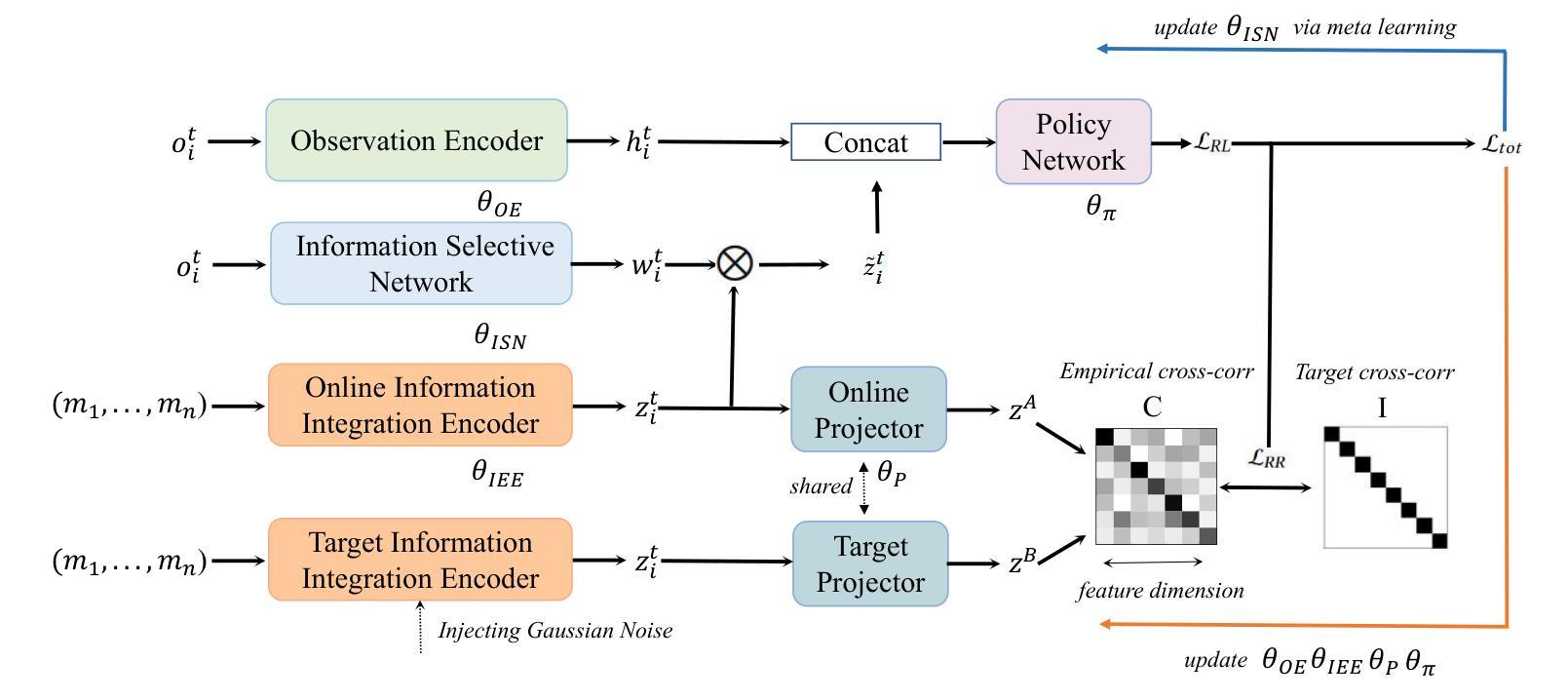

GCP: Guarded Collaborative Perception with Spatial-Temporal Aware Malicious Agent Detection
Authors:Yihang Tao, Senkang Hu, Yue Hu, Haonan An, Hangcheng Cao, Yuguang Fang
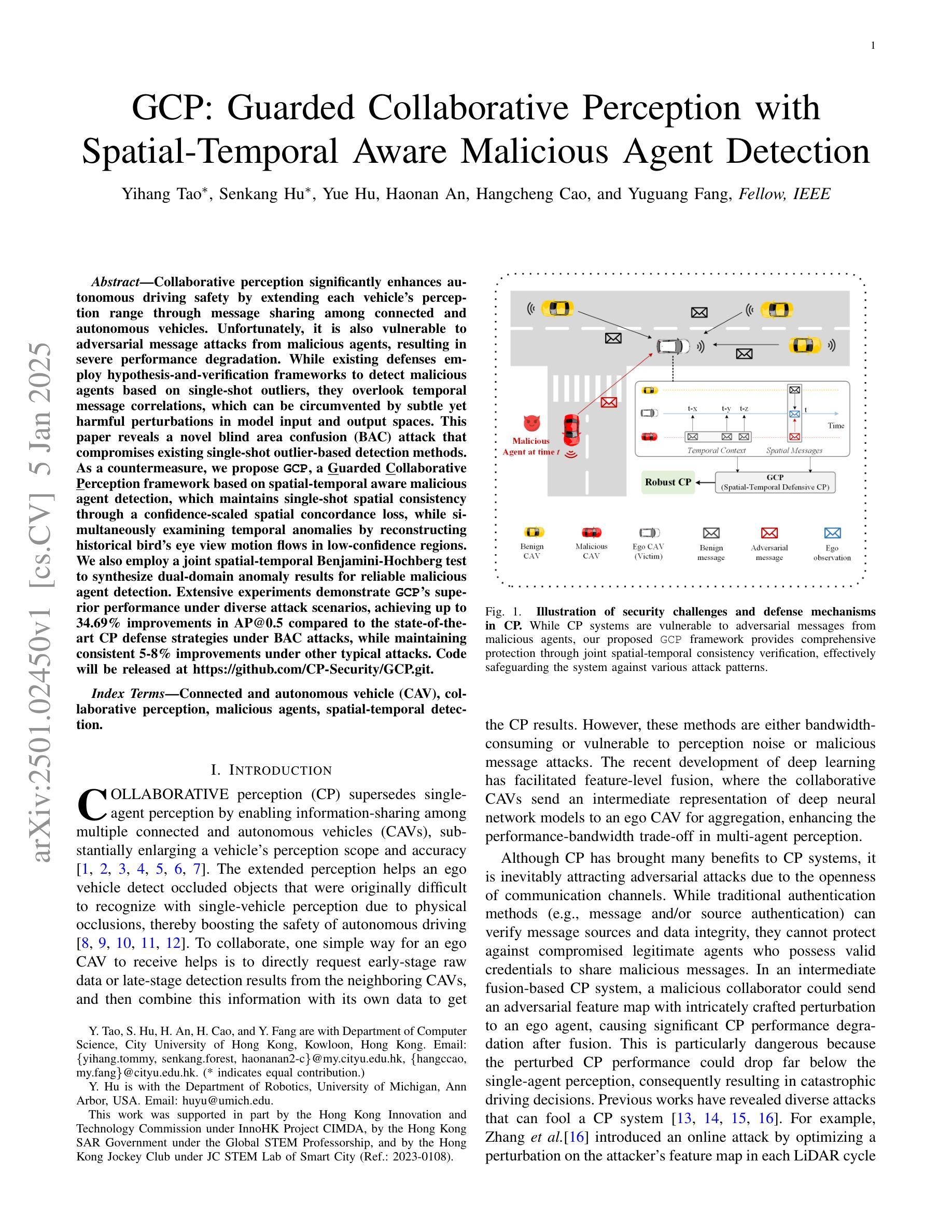
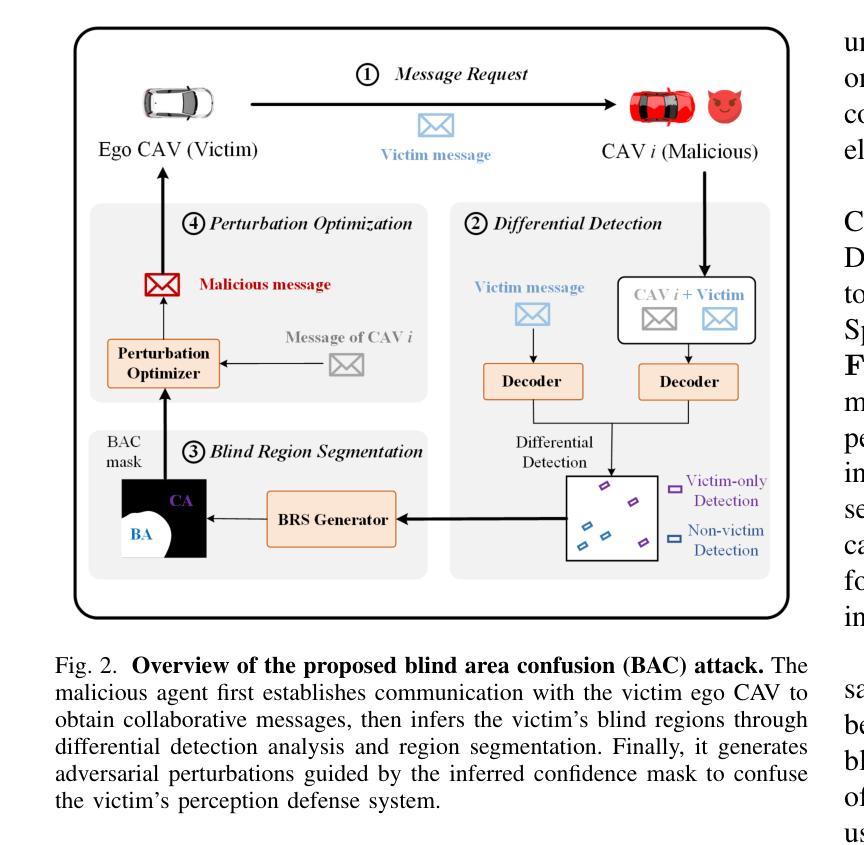
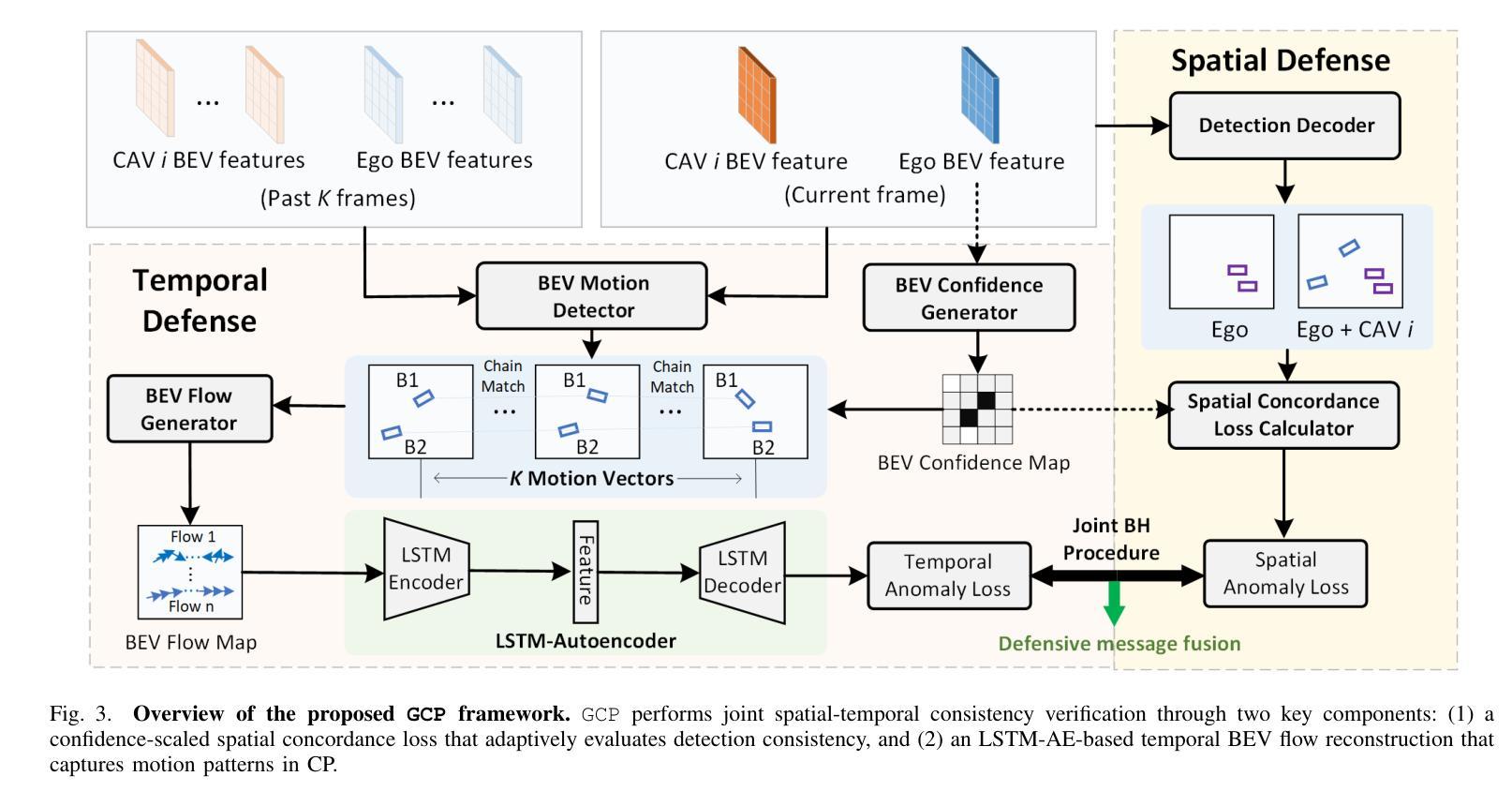
Collaborative perception significantly enhances autonomous driving safety by extending each vehicle’s perception range through message sharing among connected and autonomous vehicles. Unfortunately, it is also vulnerable to adversarial message attacks from malicious agents, resulting in severe performance degradation. While existing defenses employ hypothesis-and-verification frameworks to detect malicious agents based on single-shot outliers, they overlook temporal message correlations, which can be circumvented by subtle yet harmful perturbations in model input and output spaces. This paper reveals a novel blind area confusion (BAC) attack that compromises existing single-shot outlier-based detection methods. As a countermeasure, we propose GCP, a Guarded Collaborative Perception framework based on spatial-temporal aware malicious agent detection, which maintains single-shot spatial consistency through a confidence-scaled spatial concordance loss, while simultaneously examining temporal anomalies by reconstructing historical bird’s eye view motion flows in low-confidence regions. We also employ a joint spatial-temporal Benjamini-Hochberg test to synthesize dual-domain anomaly results for reliable malicious agent detection. Extensive experiments demonstrate GCP’s superior performance under diverse attack scenarios, achieving up to 34.69% improvements in AP@0.5 compared to the state-of-the-art CP defense strategies under BAC attacks, while maintaining consistent 5-8% improvements under other typical attacks. Code will be released at https://github.com/CP-Security/GCP.git.
协同感知通过连通自动驾驶车辆之间的信息分享,扩展了每辆车的感知范围,从而显著提高了自动驾驶的安全性。然而,它也容易受到来自恶意代理的对立消息攻击,导致性能严重下降。现有的防御策略采用假设和验证框架,基于单次离群值检测恶意代理,但它们忽略了消息的时空相关性,这种相关性可能被模型输入和输出空间中的微妙但有害的扰动所规避。本文揭示了一种新的盲区混淆(BAC)攻击,该攻击破坏了现有的基于单次离群值的检测方法。作为应对措施,我们提出了基于时空感知恶意代理检测的GCP(守卫协同感知)框架。该框架通过置信度缩放的空间一致性损失保持单次空间一致性,同时通过重建低置信度区域的历史俯视图运动流来检查时间异常。我们还采用联合时空Benjamini-Hochberg测试,合成双域异常结果,以实现可靠的恶意代理检测。大量实验表明,在多种攻击场景下,GCP的性能优于其他防御策略。与最新CP防御策略相比,GCP在BAC攻击下的AP@0.5提高了34.69%,在其他典型攻击下也保持了5-8%的持续改进。代码将在https://github.com/CP-Security/GCP.git上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages
Summary
协作感知可通过对联网自主车辆之间的消息共享来扩展每辆车的感知范围,从而提升自动驾驶的安全性。然而,它也容易受到恶意代理的对抗性消息攻击,导致性能严重下降。现有防御策略存在盲点混淆攻击等漏洞,本文提出一种基于时空感知恶意代理检测的守卫协作感知框架GCP,通过置信度缩放的空间协和损失来保持单次空间一致性,并通过重建低置信区域的历史鸟瞰运动流来检查临时异常。此外,还采用联合时空Benjamini-Hochberg测试来合成双域异常结果,实现可靠的恶意代理检测。
Key Takeaways
- 协作感知通过车辆间的消息共享增强了自动驾驶的安全性。
- 现有防御策略容易受到对抗性消息攻击的影响,存在盲点混淆攻击等漏洞。
- GCP框架通过空间协和损失和临时异常检测来提高防御能力。
- GCP采用联合时空Benjamini-Hochberg测试来合成双域异常结果,实现可靠的恶意代理检测。
点此查看论文截图

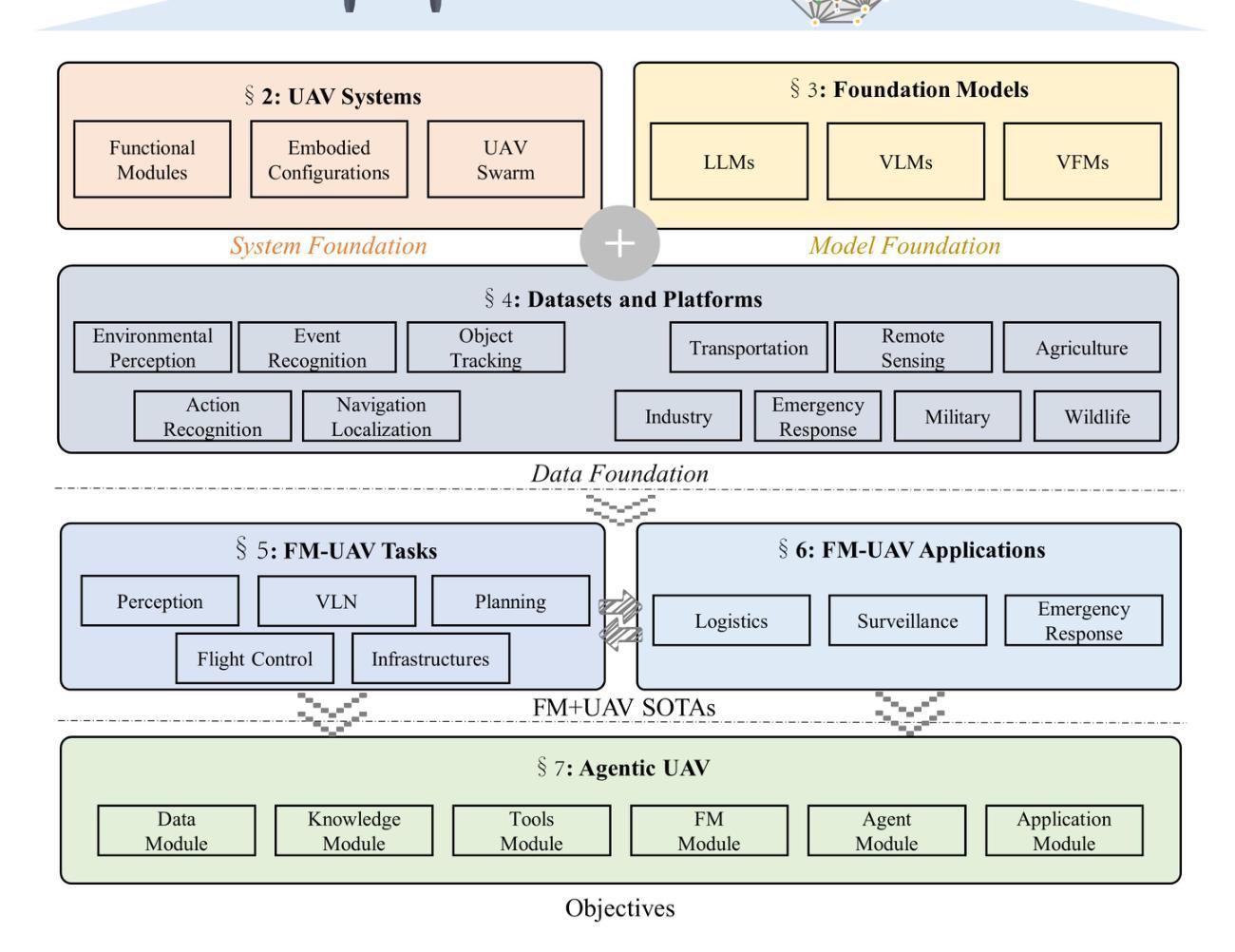
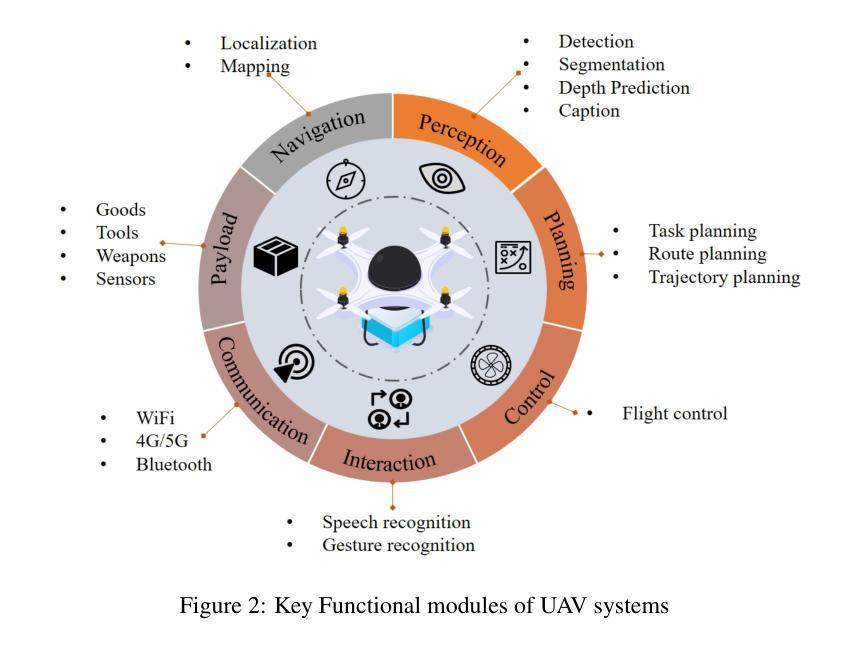
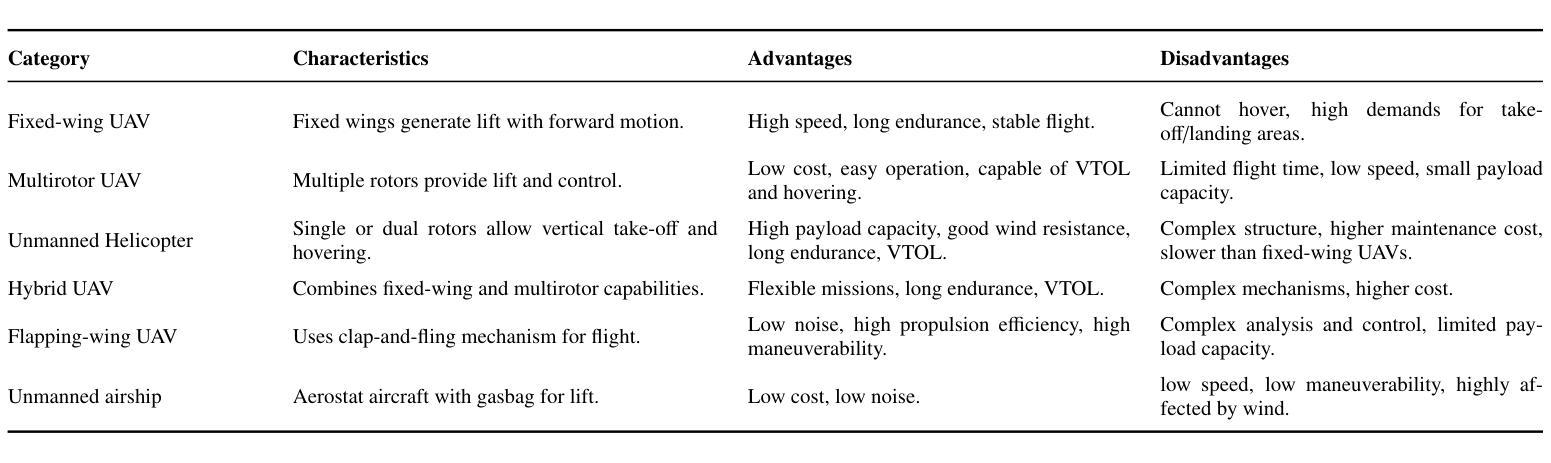
UAVs Meet LLMs: Overviews and Perspectives Toward Agentic Low-Altitude Mobility
Authors:Yonglin Tian, Fei Lin, Yiduo Li, Tengchao Zhang, Qiyao Zhang, Xuan Fu, Jun Huang, Xingyuan Dai, Yutong Wang, Chunwei Tian, Bai Li, Yisheng Lv, Levente Kovács, Fei-Yue Wang
Low-altitude mobility, exemplified by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), has introduced transformative advancements across various domains, like transportation, logistics, and agriculture. Leveraging flexible perspectives and rapid maneuverability, UAVs extend traditional systems’ perception and action capabilities, garnering widespread attention from academia and industry. However, current UAV operations primarily depend on human control, with only limited autonomy in simple scenarios, and lack the intelligence and adaptability needed for more complex environments and tasks. The emergence of large language models (LLMs) demonstrates remarkable problem-solving and generalization capabilities, offering a promising pathway for advancing UAV intelligence. This paper explores the integration of LLMs and UAVs, beginning with an overview of UAV systems’ fundamental components and functionalities, followed by an overview of the state-of-the-art in LLM technology. Subsequently, it systematically highlights the multimodal data resources available for UAVs, which provide critical support for training and evaluation. Furthermore, it categorizes and analyzes key tasks and application scenarios where UAVs and LLMs converge. Finally, a reference roadmap towards agentic UAVs is proposed, aiming to enable UAVs to achieve agentic intelligence through autonomous perception, memory, reasoning, and tool utilization. Related resources are available at https://github.com/Hub-Tian/UAVs_Meet_LLMs.
以无人机(UAVs)为代表的低空机动性为运输、物流和农业等各个领域带来了革命性的进步。无人机凭借其灵活的视角和快速机动能力,扩展了传统系统的感知和行动能力,引起了学术界和工业界的广泛关注。然而,目前的无人机操作主要依赖于人为控制,仅在简单场景中具有有限的自主性,缺乏应对复杂环境和任务的智能和适应性。大型语言模型(LLMs)的出现表现出了显著的问题解决和泛化能力,为提升无人机的智能提供了充满希望的途径。本文探讨了LLMs与无人机的集成,首先概述了无人机系统的基础组件和功能,然后介绍了LLM技术的最新研究状态。之后,它系统地强调了无人机可用的多模态数据资源,这些数据资源为训练和评估提供了关键支持。此外,还对无人机和LLMs交汇的关键任务和应用场景进行了分类和分析。最后,提出了实现自主无人机参考路线图,旨在通过自主感知、记忆、推理和工具利用实现无人机的智能化。相关资源可在https://github.com/Hub-Tian/UAVs_Meet_LLMs中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
无人机在低空机动领域的应用,为交通运输、物流、农业等带来了革命性的变革。利用灵活的视角和快速机动性,无人机扩展了传统系统的感知和行动能力,引起了学术界和工业界的广泛关注。然而,当前无人机操作主要依赖人为控制,复杂环境和任务下的智能化和适应性不足。大型语言模型(LLMs)的出现展现出强大的问题解决和泛化能力,为提升无人机智能提供了希望。本文探讨了LLMs与无人机的融合,概述了无人机系统的基础组件和功能以及LLM技术的最新进展,并重点介绍了无人机训练评估所需的多模态数据资源。此外,本文还介绍了无人机与LLMs融合的关键任务和应用场景,并提出了实现自主感知、记忆、推理和工具利用的智能无人机的参考路线图。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机在低空机动领域的应用已经为多个领域带来了变革性的进展。
- 无人机通过与传统系统的感知和行动能力相结合,吸引了学术界和工业界的广泛关注。
- 当前无人机操作主要依赖人为控制,缺乏在复杂环境和任务下的智能化和适应性。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)展现出强大的问题解决和泛化能力,为提升无人机智能提供了潜力。
- 论文探讨了LLMs与无人机的融合,包括无人机系统的基础组件和功能以及LLM技术的概述。
- 多模态数据资源对无人机的训练评估至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

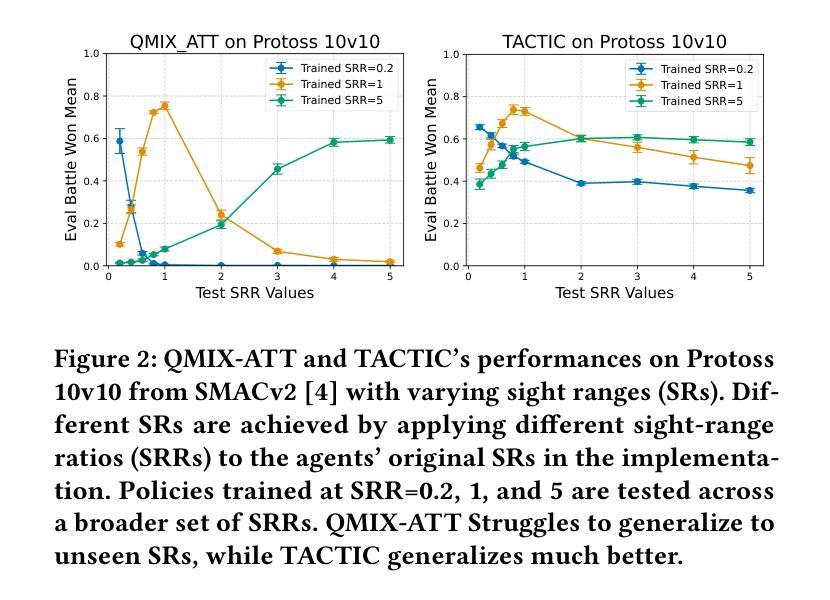
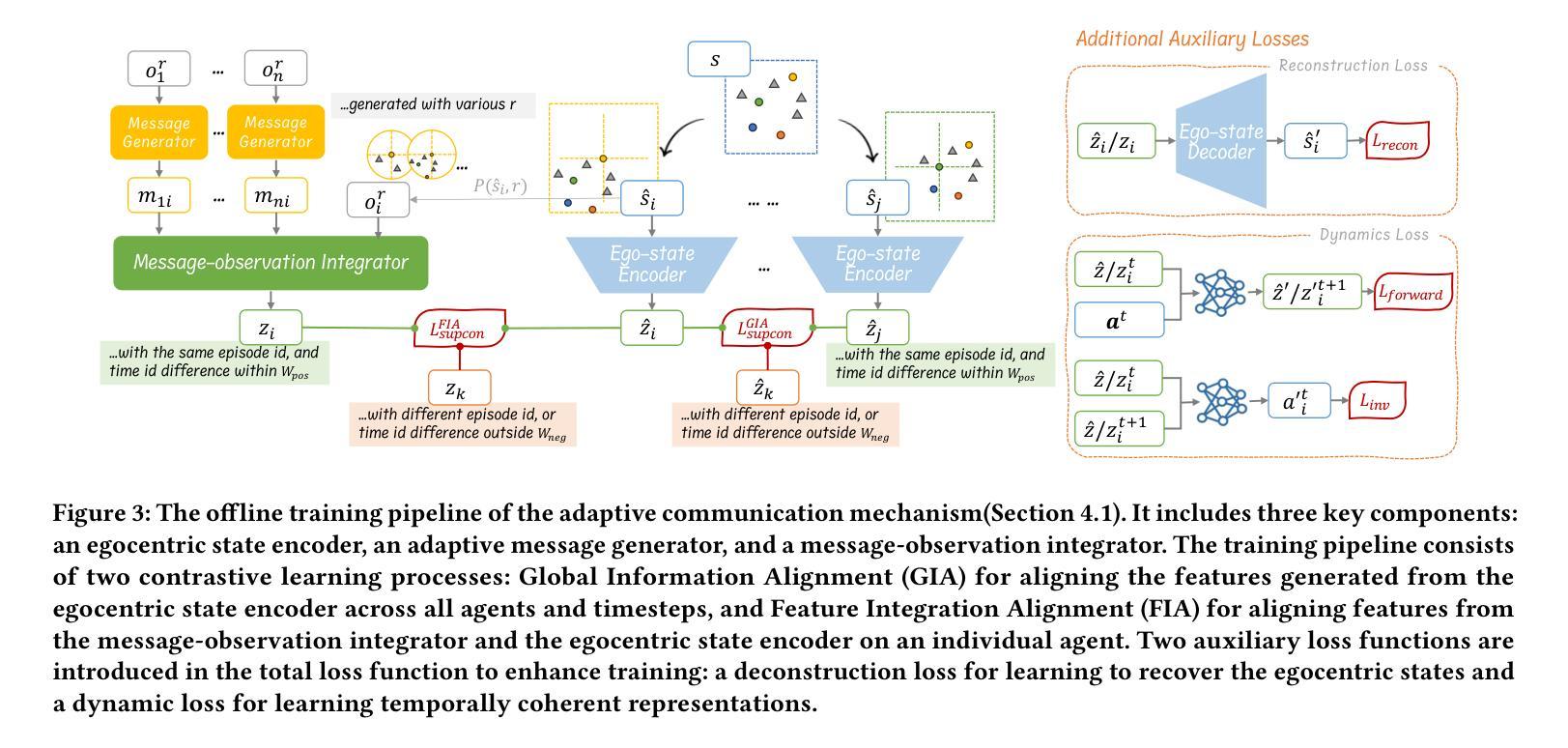
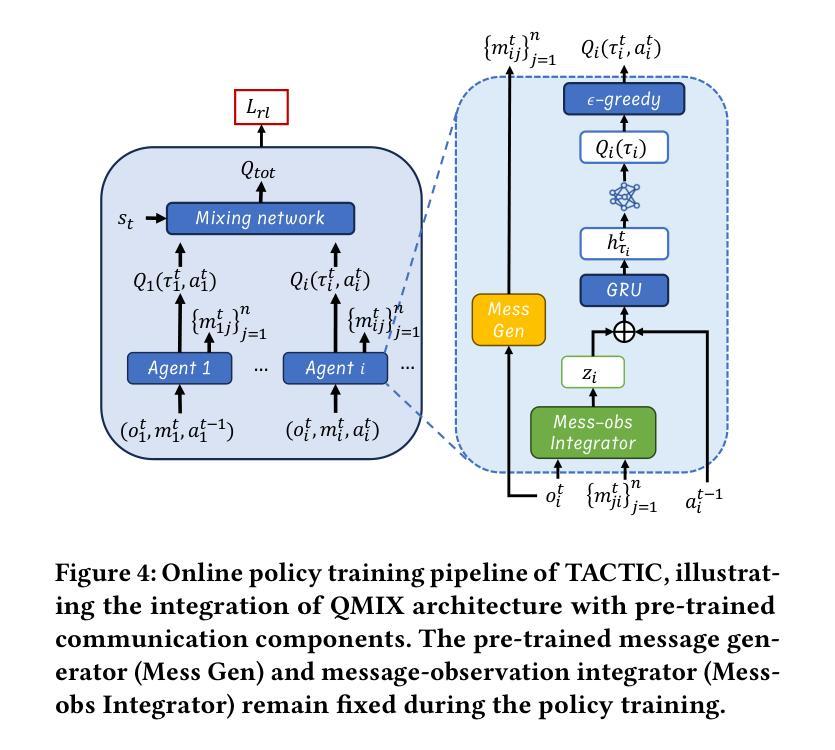
TACTIC: Task-Agnostic Contrastive pre-Training for Inter-Agent Communication
Authors:Peihong Yu, Manav Mishra, Syed Zaidi, Pratap Tokekar
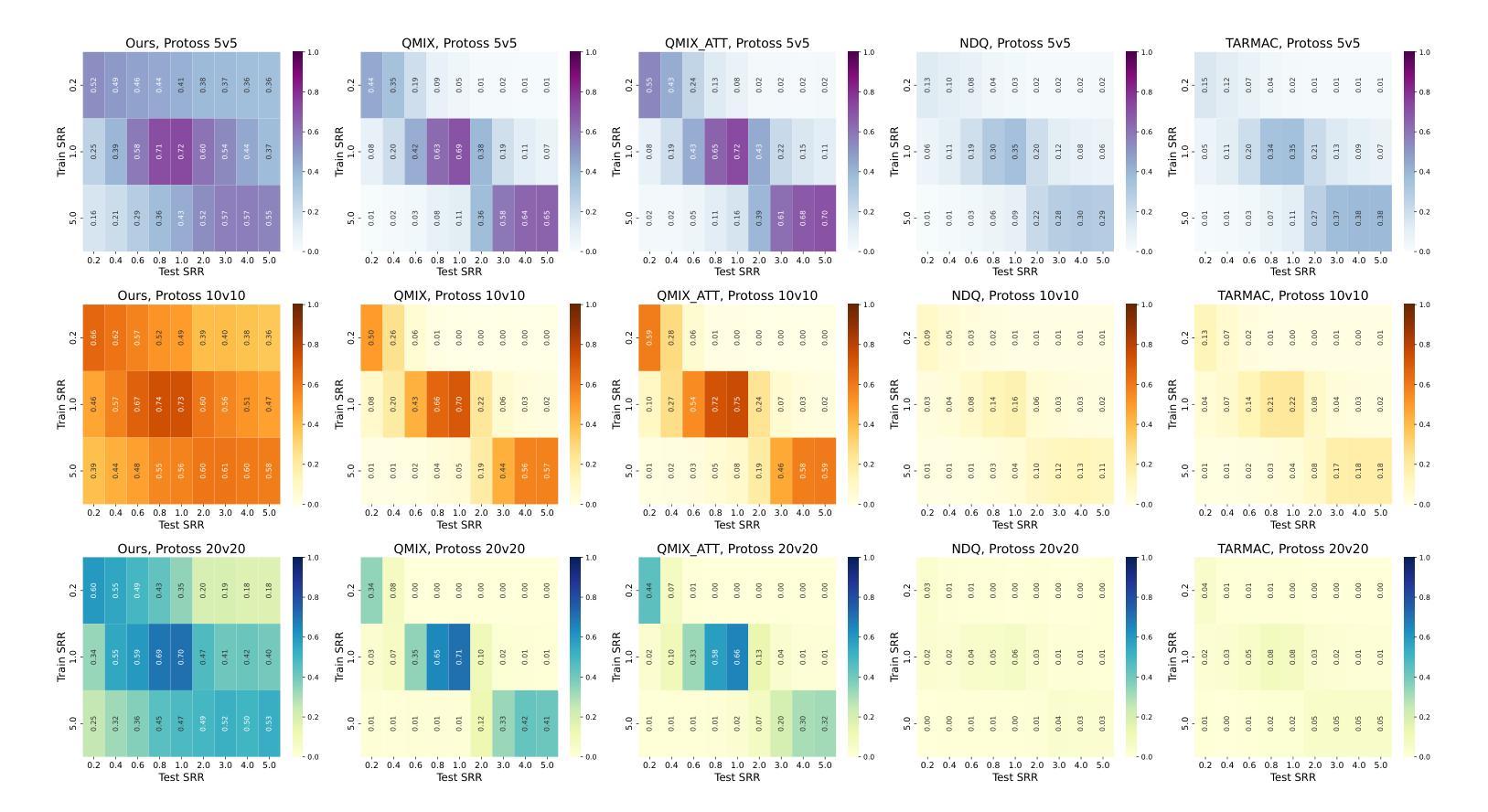
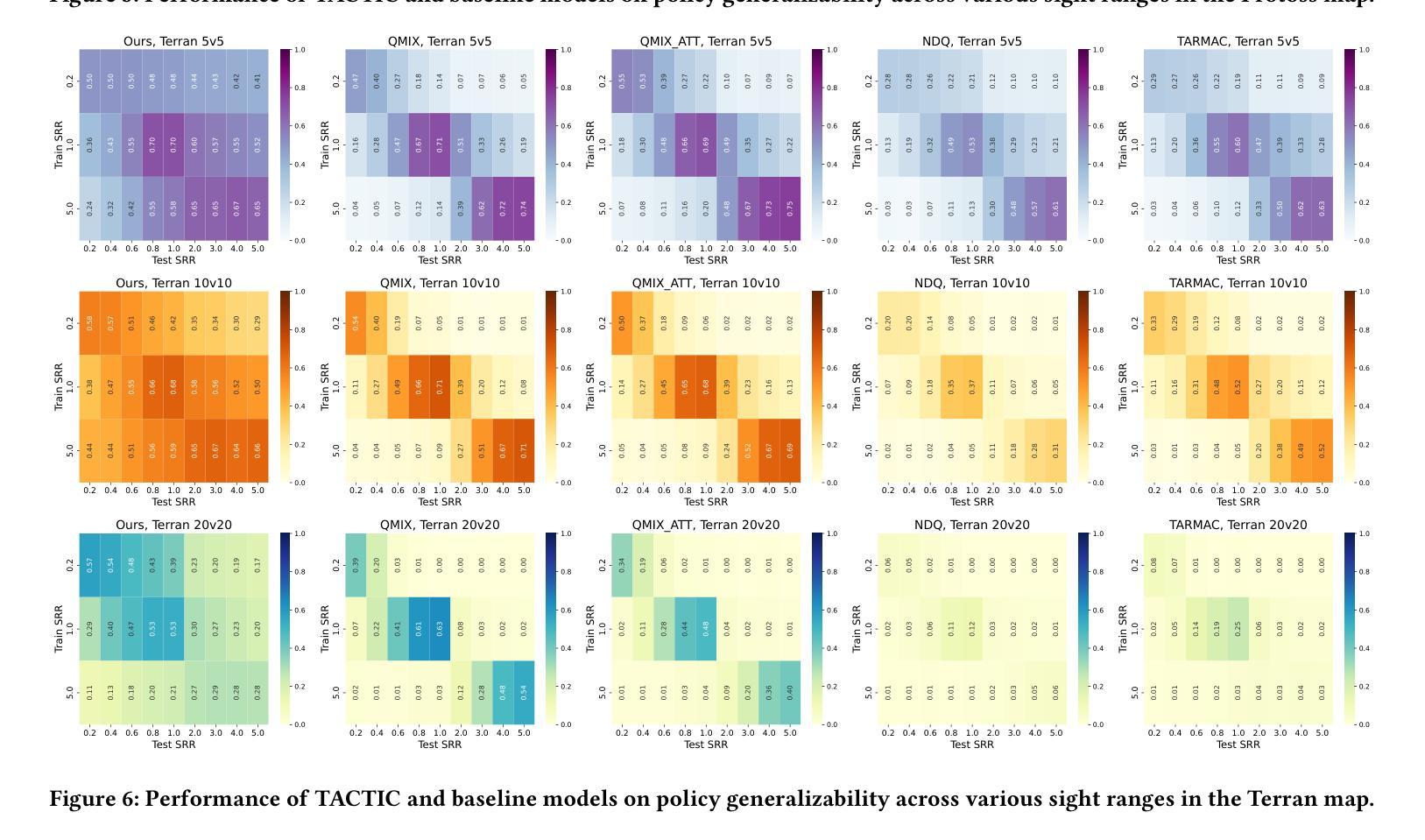
The “sight range dilemma” in cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) presents a significant challenge: limited observability hinders team coordination, while extensive sight ranges lead to distracted attention and reduced performance. While communication can potentially address this issue, existing methods often struggle to generalize across different sight ranges, limiting their effectiveness. We propose TACTIC, Task-Agnostic Contrastive pre-Training strategy Inter-Agent Communication. TACTIC is an adaptive communication mechanism that enhances agent coordination even when the sight range during execution is vastly different from that during training. The communication mechanism encodes messages and integrates them with local observations, generating representations grounded in the global state using contrastive learning. By learning to generate and interpret messages that capture important information about the whole environment, TACTIC enables agents to effectively “see” more through communication, regardless of their sight ranges. We comprehensively evaluate TACTIC on the SMACv2 benchmark across various scenarios with broad sight ranges. The results demonstrate that TACTIC consistently outperforms traditional state-of-the-art MARL techniques with and without communication, in terms of generalizing to sight ranges different from those seen in training, particularly in cases of extremely limited or extensive observability.
在合作多智能体强化学习(MARL)中,“视野范围困境”构成了一大挑战:有限的观察性阻碍了团队协调,而广阔的视野范围则导致注意力分散和性能下降。虽然通信可能潜在解决此问题,但现有方法往往难以在不同视野范围之间进行泛化,从而限制了其有效性。我们提出TACTIC,即任务无关对比预训练策略-跨智能体通信。TACTIC是一种自适应通信机制,即使在执行过程中的视野范围与训练过程中的视野范围大不相同,也能增强智能体的协调。该通信机制对消息进行编码,并与局部观察结果相结合,使用对比学习生成基于全局状态的表示。通过学习生成和解释捕捉整个环境重要信息的消息,TACTIC能够通过通信有效地“看到”更多内容,而无论其视野范围如何。我们在具有广泛视野范围的SMACv2基准测试上全面评估了TACTIC在各种场景下的表现。结果表明,TACTIC在泛化到与训练过程中不同的视野范围方面,尤其是在观察性极端有限或广阔的情况下,持续优于有通信和无通信的传统最先进的MARL技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAMAS 2025
Summary
在合作型多智能体强化学习(MARL)中,“视野范围困境”是一个重大挑战:有限的观察能力阻碍了团队协作,而视野范围过大则会导致注意力分散和性能下降。尽管沟通可以解决这一问题,但现有方法往往难以在不同视野范围内进行推广,限制了其有效性。本文提出一种自适应的通信机制TACTIC,即使在执行时的视野范围与训练时的视野范围大相径庭的情况下,也能提高智能体的协作能力。该通信机制通过对比学习将消息编码并与局部观察相结合,生成基于全局状态的表示。通过学习与解读能够捕捉整个环境重要信息的消息,TACTIC能够让智能体通过沟通“看到”更多,无论其视野范围如何。我们在SMACv2基准测试上对TACTIC进行了全面的评估,在各种视野范围广泛的场景下进行了测试。结果表明,TACTIC在训练和测试时面对不同视野范围的泛化能力上,始终优于传统先进MARL技术,特别是在观察能力极其有限或过于广泛的情况下。
Key Takeaways
- “视野范围困境”在合作型多智能体强化学习中是一个挑战,因为它影响了团队协作和性能。
- 现有通信方法难以在不同视野范围内推广其有效性。
- TACTIC是一种自适应通信机制,旨在提高智能体在不同视野范围下的协作能力。
- TACTIC利用对比学习将消息编码并与局部观察结合,生成基于全局状态的表示。
- TACTIC让智能体通过沟通“看到”更多,无论其视野如何。
- TACTIC在多种视野范围的场景下表现优异,泛化能力强。
点此查看论文截图

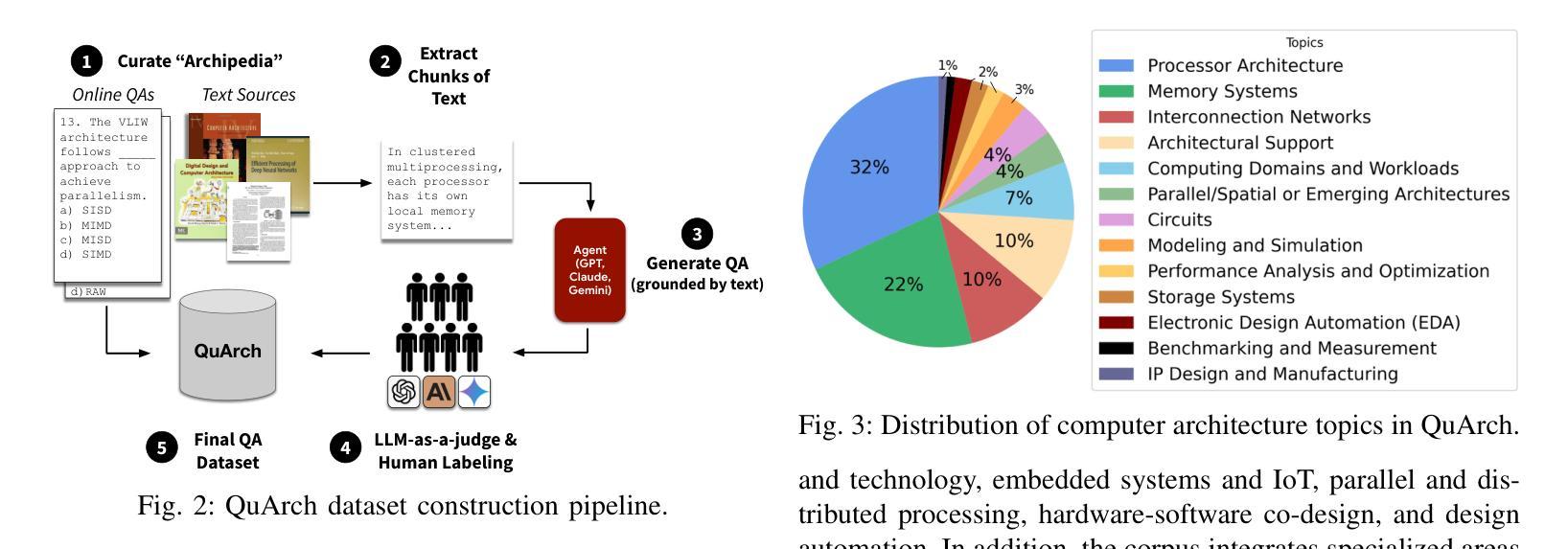
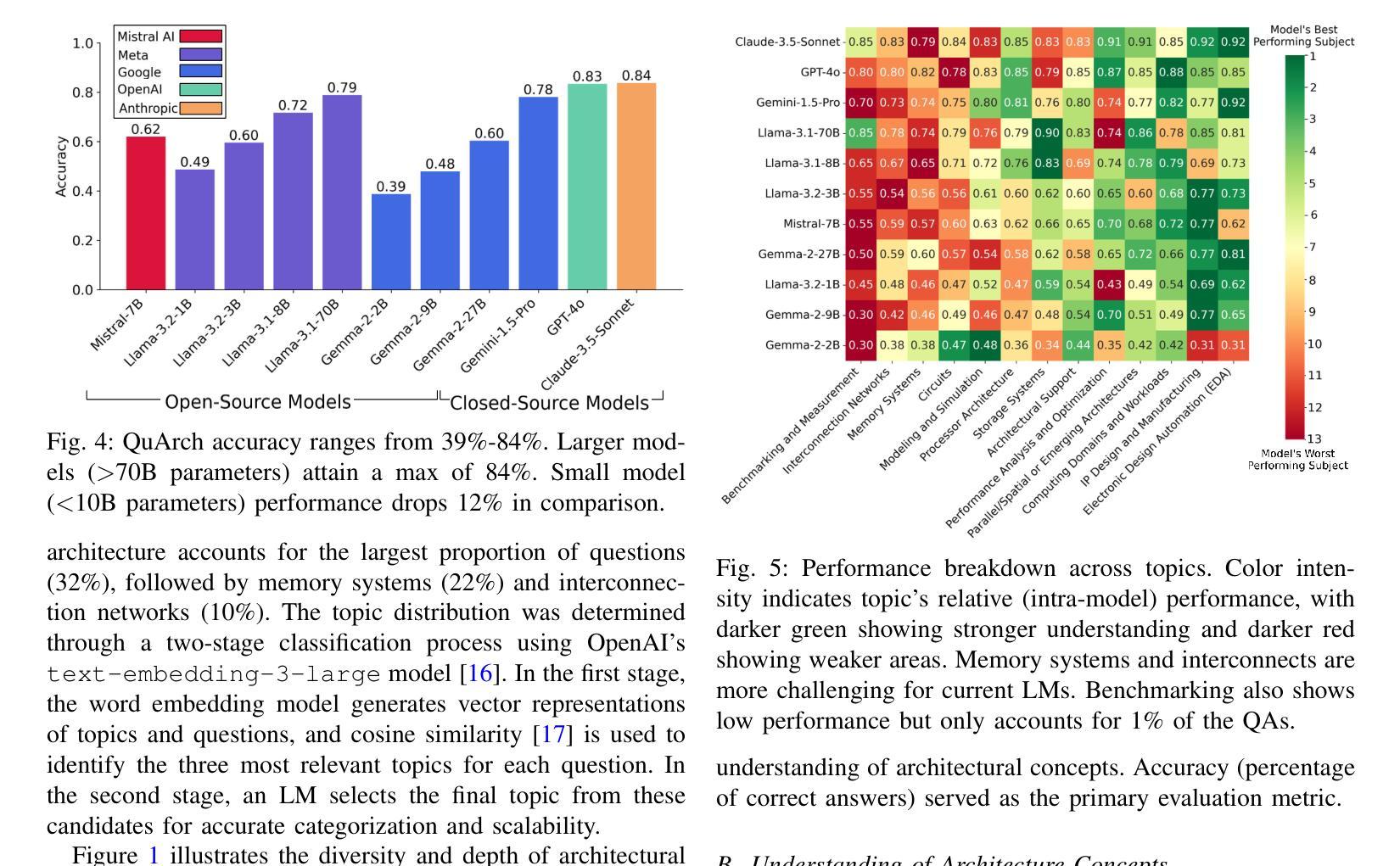
QuArch: A Question-Answering Dataset for AI Agents in Computer Architecture
Authors:Shvetank Prakash, Andrew Cheng, Jason Yik, Arya Tschand, Radhika Ghosal, Ikechukwu Uchendu, Jessica Quaye, Jeffrey Ma, Shreyas Grampurohit, Sofia Giannuzzi, Arnav Balyan, Fin Amin, Aadya Pipersenia, Yash Choudhary, Ankita Nayak, Amir Yazdanbakhsh, Vijay Janapa Reddi
We introduce QuArch, a dataset of 1500 human-validated question-answer pairs designed to evaluate and enhance language models’ understanding of computer architecture. The dataset covers areas including processor design, memory systems, and performance optimization. Our analysis highlights a significant performance gap: the best closed-source model achieves 84% accuracy, while the top small open-source model reaches 72%. We observe notable struggles in memory systems, interconnection networks, and benchmarking. Fine-tuning with QuArch improves small model accuracy by up to 8%, establishing a foundation for advancing AI-driven computer architecture research. The dataset and leaderboard are at https://harvard-edge.github.io/QuArch/.
我们介绍了QuArch数据集,它包含1500个经过人类验证的问题答案对,旨在评估和增强语言模型对计算机架构的理解。该数据集涵盖处理器设计、内存系统和性能优化等领域。我们的分析突显了一个显著的性能差距:最佳闭源模型的准确率为84%,而顶尖的小型开源模型的准确率仅为72%。我们在内存系统、互联网络和基准测试方面遇到了明显的困难。使用QuArch进行微调可以提高小型模型的准确率,最高可达8%,为推进AI驱动的计算机架构研究奠定了基础。数据集和排行榜可在https://harvard-edge.github.io/QuArch/查看。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
QuArch数据集包含1500个经过人类验证的问题答案对,旨在评估和增强语言模型对计算机架构的理解。该数据集涵盖处理器设计、内存系统和性能优化等领域。分析显示,最佳封闭源模型准确率为84%,而顶尖的小型开源模型准确率为72%,在内存系统、互联网络和基准测试方面存在明显困难。使用QuArch微调可提高小型模型准确率高达8%,为AI驱动的计算机架构研究奠定基础。相关数据集和排行榜可访问https://harvard-edge.github.io/QuArch/。
Key Takeaways
- QuArch数据集包含1500个问题答案对,旨在评估语言模型对计算机架构的理解。
- 数据集覆盖处理器设计、内存系统和性能优化等领域。
- 最佳封闭源模型的准确率为84%,而顶尖小型开源模型的准确率为72%。
- 在内存系统、互联网络和基准测试方面存在性能差距和挑战。
- 使用QuArch微调可以提高小型模型的准确率高达8%。
- QuArch为AI驱动的计算机架构研究提供了基础。
点此查看论文截图

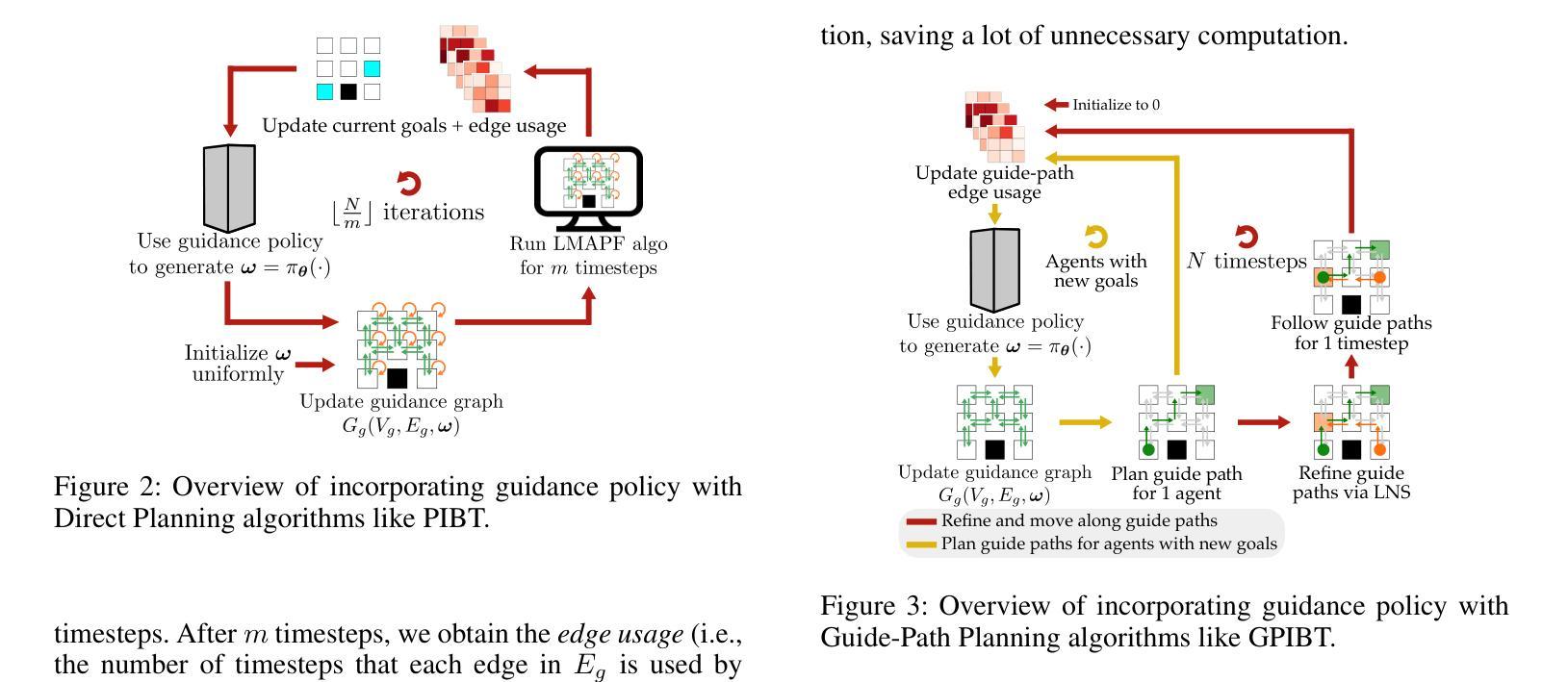
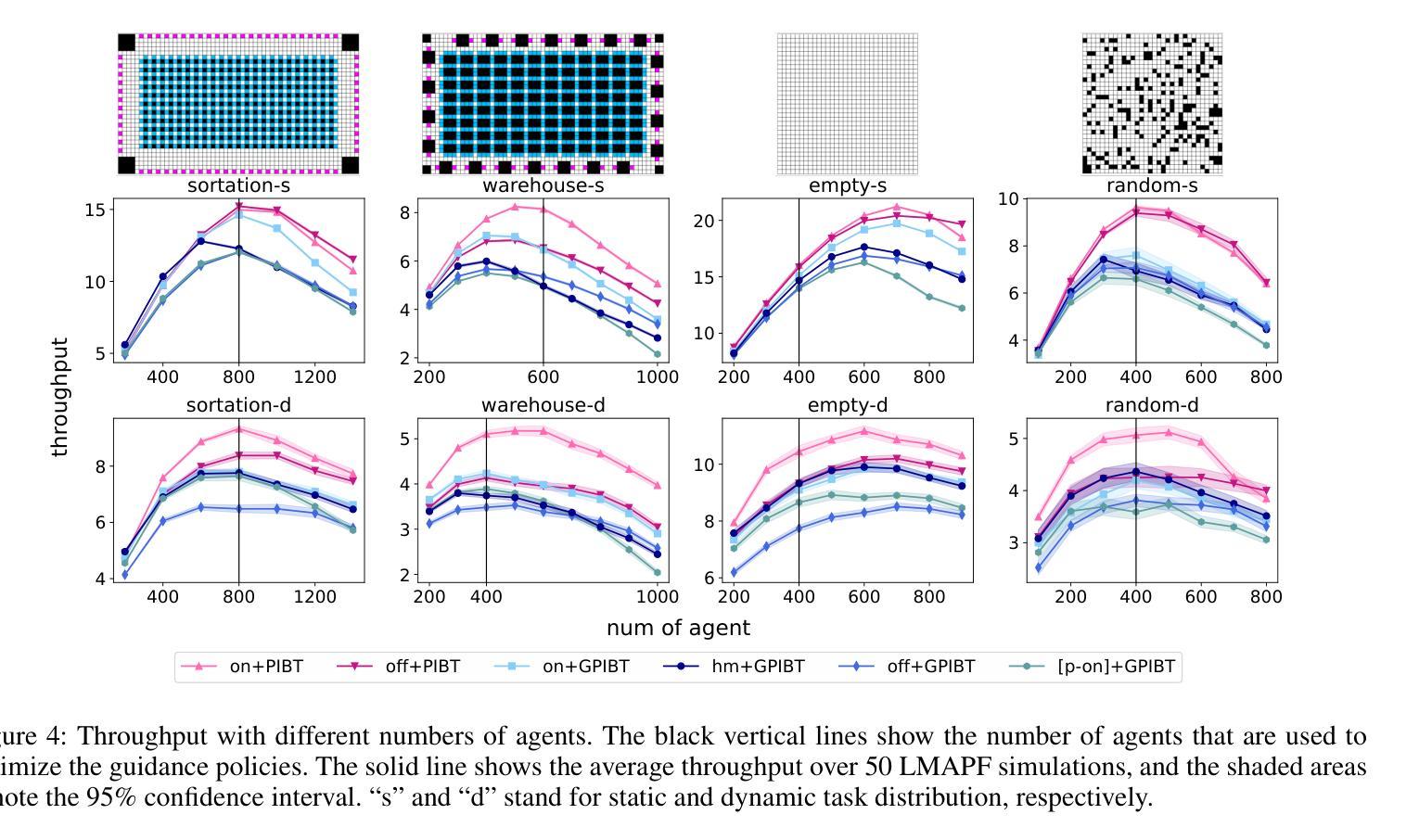
Online Guidance Graph Optimization for Lifelong Multi-Agent Path Finding
Authors:Hongzhi Zang, Yulun Zhang, He Jiang, Zhe Chen, Daniel Harabor, Peter J. Stuckey, Jiaoyang Li
We study the problem of optimizing a guidance policy capable of dynamically guiding the agents for lifelong Multi-Agent Path Finding based on real-time traffic patterns. Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) focuses on moving multiple agents from their starts to goals without collisions. Its lifelong variant, LMAPF, continuously assigns new goals to agents. In this work, we focus on improving the solution quality of PIBT, a state-of-the-art rule-based LMAPF algorithm, by optimizing a policy to generate adaptive guidance. We design two pipelines to incorporate guidance in PIBT in two different ways. We demonstrate the superiority of the optimized policy over both static guidance and human-designed policies. Additionally, we explore scenarios where task distribution changes over time, a challenging yet common situation in real-world applications that is rarely explored in the literature.
我们研究了优化导向策略的问题,该策略能够基于实时交通模式动态地指导代理进行终生多代理路径查找。多代理路径查找(MAPF)专注于在没有碰撞的情况下将多个代理从其起点移动到目标点。其终生变体LMAPF则不断地为代理分配新的目标点。在这项工作中,我们专注于通过优化策略来提高基于规则的LMAPF算法PIBT的解决方案质量,以生成自适应指导。我们设计了两种管道,以两种方式在PIBT中融入指导。我们证明了优化策略在静态指导和人工设计的政策方面的优越性。此外,我们还探索了任务分布随时间变化的情况,这在现实应用中是常见且具挑战性的情况,但在文献中很少被探索。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages for the main text, 2 pages for reference and acknowledgement, 5 pages for appendix. 11 figures in total
Summary
在实时交通模式的基础上,研究优化指导策略,该策略能够动态指导终身多智能体路径寻找问题。多智能体路径寻找(MAPF)侧重于在没有碰撞的情况下,将多个智能体从起点移动到目标点。其终身版本(LMAPF)则持续为智能体分配新的目标点。本研究重点在于优化PIBT这一基于规则的LMAPF算法的解决方案质量,通过优化指导策略以产生适应性指导。本研究设计两种整合指导策略的管道,采用不同的方式将指导策略融入PIBT。展示优化后的策略相较于静态指导策略以及人工制定的策略更具优势。此外,该研究探索任务分布随时间变化的情况,虽然这在现实应用中极具挑战且较为常见,但在文献中却鲜有研究。
Key Takeaways
- 研究内容集中在优化终身多智能体路径寻找(LMAPF)问题的指导策略上。
- LMAPF问题中,智能体需要从起点动态地移动到目标点,且不能发生碰撞。
- 研究重点是优化PIBT这一基于规则的LMAPF算法,通过优化指导策略来提高解决方案的质量。
- 设计了两种将指导策略融入PIBT的管道。
- 优化的指导策略在性能上超越了静态指导和人工制定的策略。
- 研究考虑了任务分布随时间变化的场景,这是一个现实应用中常见的挑战。
点此查看论文截图

AgentForge: A Flexible Low-Code Platform for Reinforcement Learning Agent Design
Authors:Francisco Erivaldo Fernandes Junior, Antti Oulasvirta
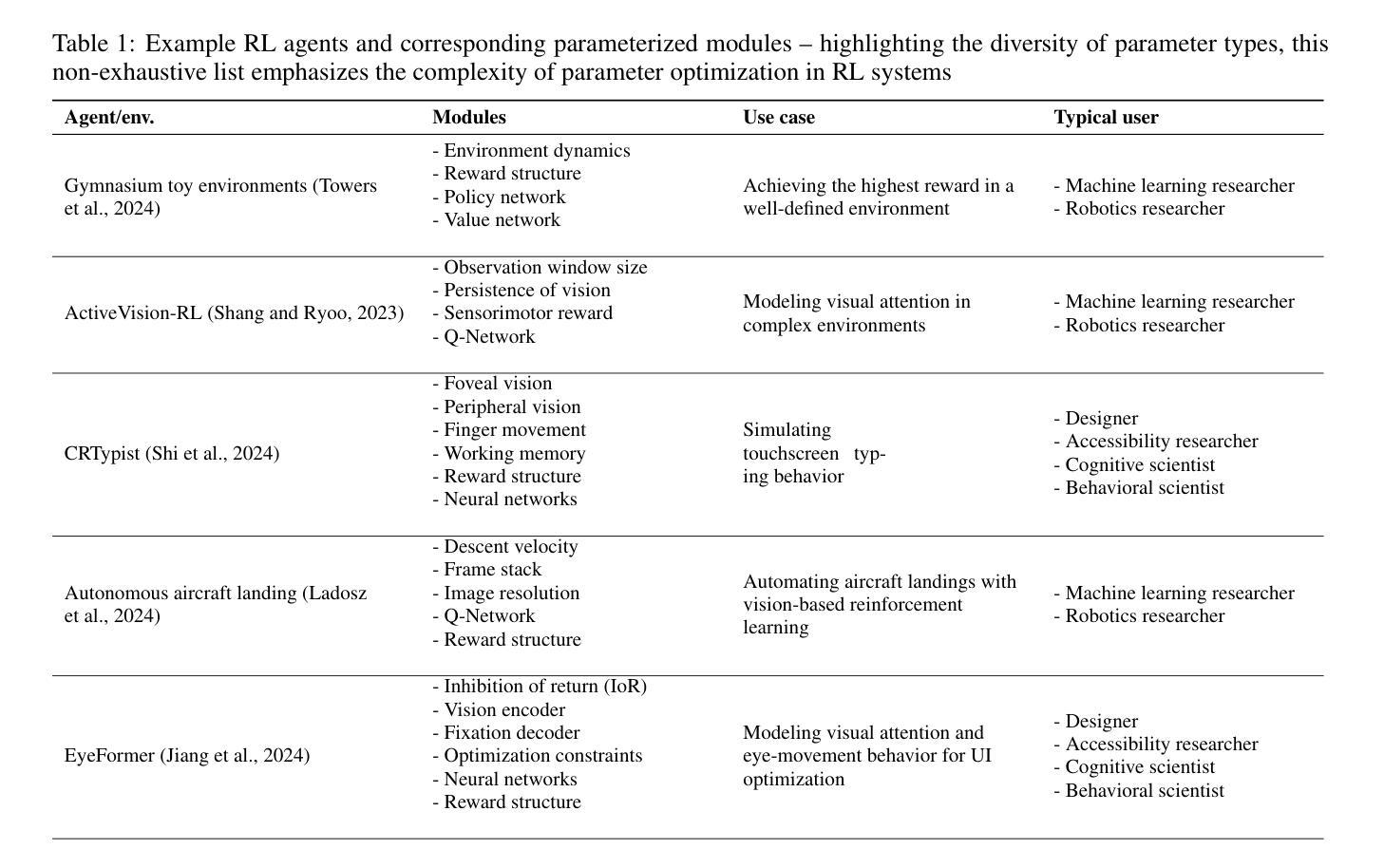
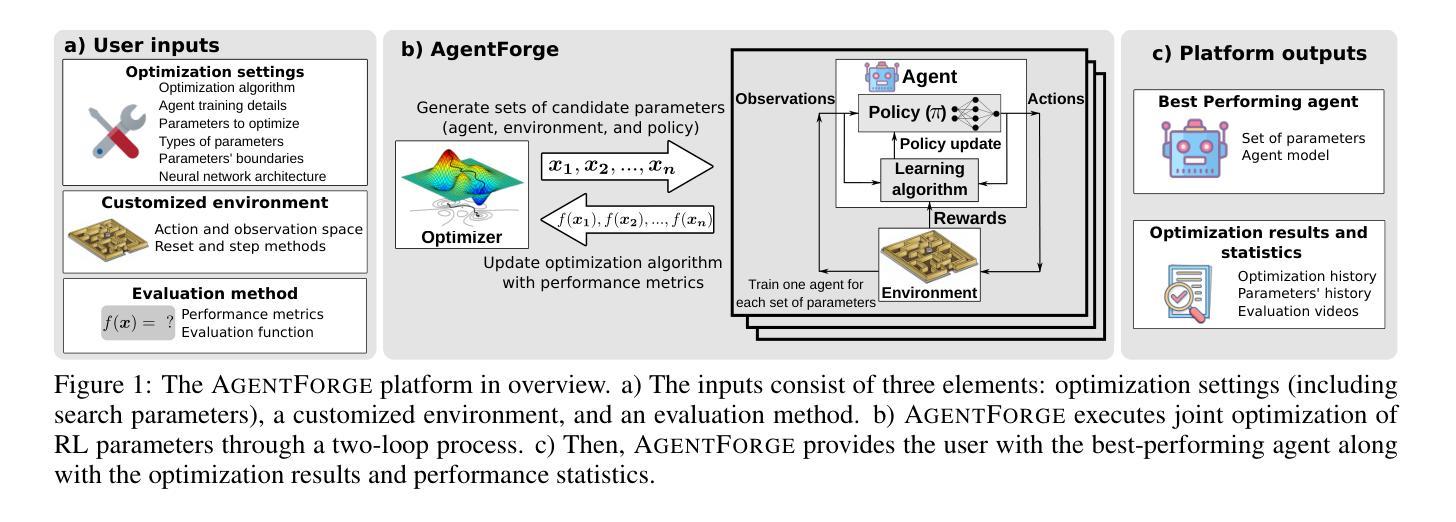
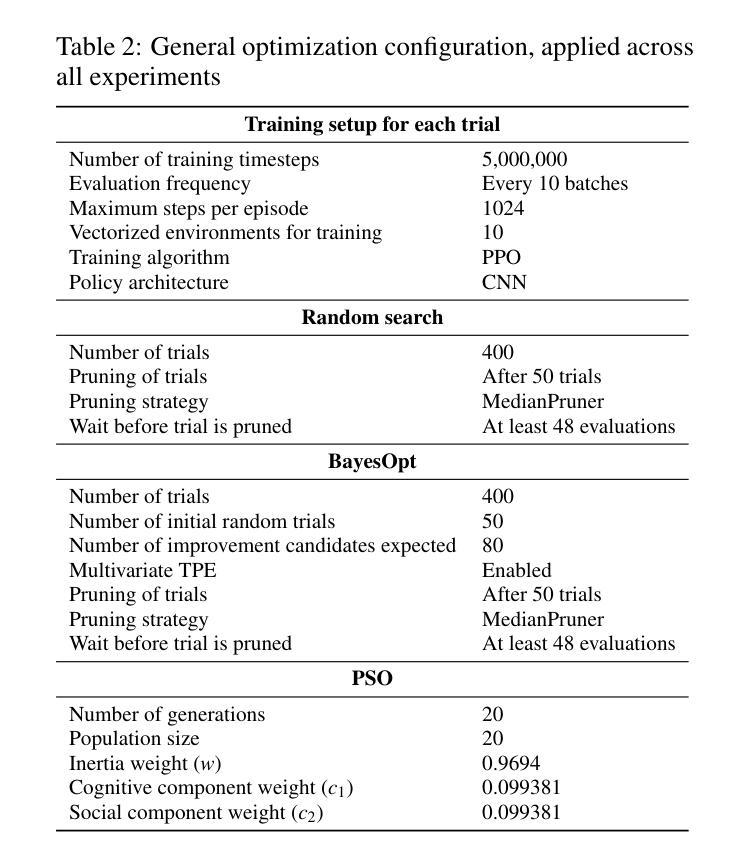
Developing a reinforcement learning (RL) agent often involves identifying values for numerous parameters, covering the policy, reward function, environment, and agent-internal architecture. Since these parameters are interrelated in complex ways, optimizing them is a black-box problem that proves especially challenging for nonexperts. Although existing optimization-as-a-service platforms (e.g., Vizier and Optuna) can handle such problems, they are impractical for RL systems, since the need for manual user mapping of each parameter to distinct components makes the effort cumbersome. It also requires understanding of the optimization process, limiting the systems’ application beyond the machine learning field and restricting access in areas such as cognitive science, which models human decision-making. To tackle these challenges, the paper presents \name, a flexible low-code platform to optimize any parameter set across an RL system. Available at https://github.com/feferna/AgentForge, it allows an optimization problem to be defined in a few lines of code and handed to any of the interfaced optimizers. With AgentForge, the user can optimize the parameters either individually or jointly. The paper presents an evaluation of its performance for a challenging vision-based RL problem.
开发强化学习(RL)代理通常涉及为众多参数设定值,这些参数包括策略、奖励函数、环境和代理内部架构。由于这些参数以复杂的方式相互关联,因此对其进行优化是一个黑箱问题,对非专家来说尤其具有挑战性。尽管现有的优化即服务平台(例如Vizier和Optuna)可以处理此类问题,但它们对于RL系统来说并不实用,因为需要手动将每个参数映射到不同的组件,这使得工作变得繁琐。这还需要了解优化过程,限制了系统在机器学习领域之外的应用,并限制了其在认知科学等领域的访问权限,认知科学模拟人类的决策过程。为了应对这些挑战,论文提出了名为“AgentForge”的灵活低代码平台,用于优化RL系统中的任何参数集。该平台可在https://github.com/feferna/AgentForge上访问,允许在几行代码内定义优化问题并将其传递给任何接口优化器。使用AgentForge,用户可以单独或联合优化参数。论文对其在处理具有挑战性的基于视觉的RL问题上的性能进行了评估。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted at the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025)
Summary
文本介绍了在强化学习(RL)代理开发过程中面临的参数优化问题。针对该问题,存在优化即服务(optimization-as-a-service)的平台,如Vizier和Optuna,但它们对于RL系统来说并不实用。因此,论文提出了名为AgentForge的灵活低代码平台,旨在解决优化RL系统中的参数集的问题。通过该平台,用户可以定义几行代码来解决优化问题并将其传递给接口中的任何优化器。使用AgentForge,用户可以单独或联合优化参数。文本还提供了对解决具有挑战性的基于视觉的RL问题的性能评估。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习(RL)代理开发涉及众多参数的识别与设置,包括策略、奖励功能、环境和代理内部架构等参数之间相互关联,优化它们是一个黑箱问题,对非专家来说尤其具有挑战性。
- 现存的优化即服务平台(如Vizier和Optuna)在处理此类问题时显得不实用,因为需要对每个参数进行手动映射到不同的组件,这既繁琐又要求理解优化过程。
- AgentForge是一个灵活的低代码平台,用于优化RL系统中的任何参数集,旨在解决上述挑战。
- 使用AgentForge平台,用户只需在几行代码中定义优化问题,然后将其传递给接口中的任何优化器。
- AgentForge允许用户单独或联合优化参数,提供了更大的灵活性。
- 文本对AgentForge的性能进行了评估,表明其在解决具有挑战性的基于视觉的RL问题时具有实用性。
点此查看论文截图



LLM-Based Multi-Agent Systems are Scalable Graph Generative Models
Authors:Jiarui Ji, Runlin Lei, Jialing Bi, Zhewei Wei, Xu Chen, Yankai Lin, Xuchen Pan, Yaliang Li, Bolin Ding
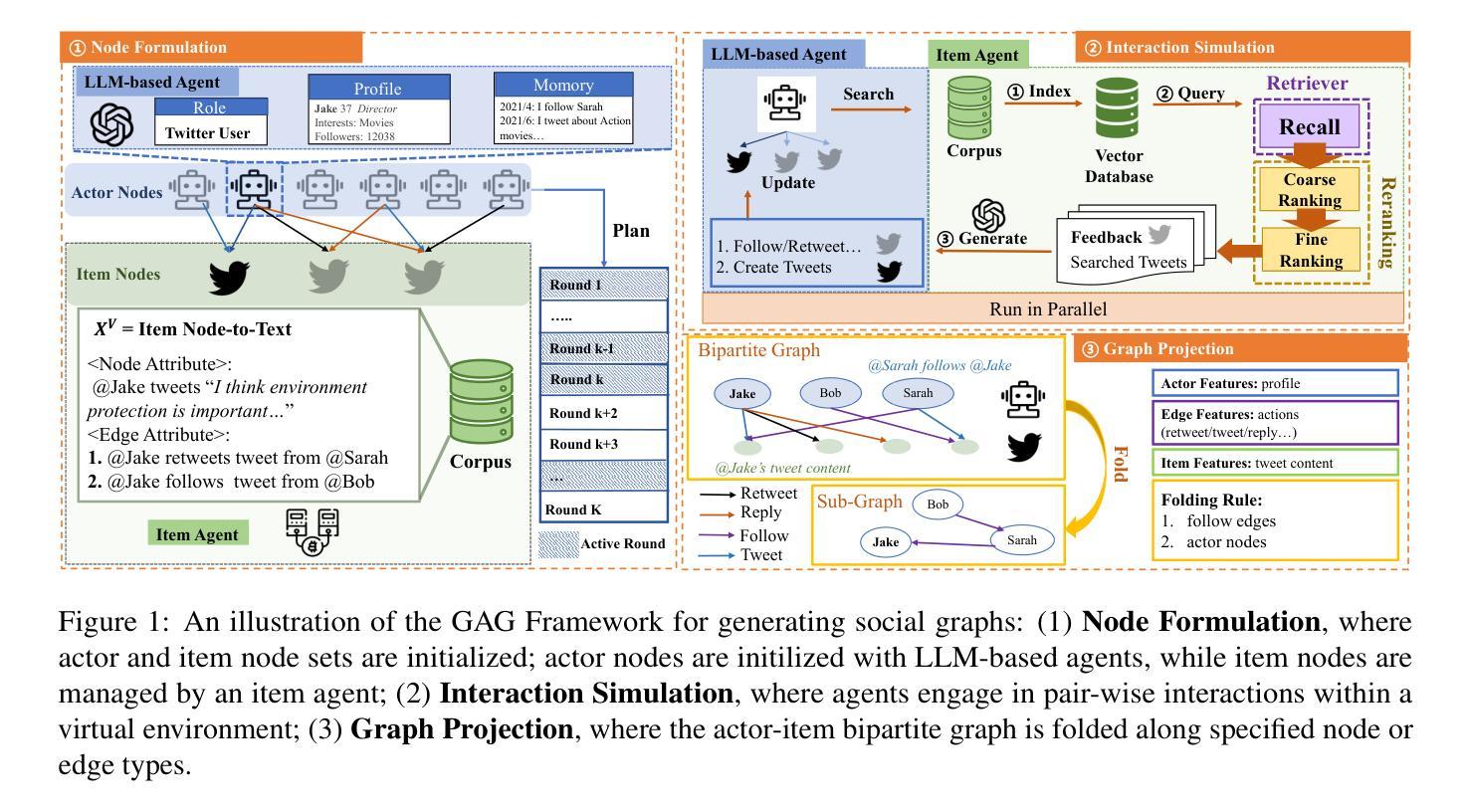
The structural properties of naturally arising social graphs are extensively studied to understand their evolution. Prior approaches for modeling network dynamics typically rely on rule-based models, which lack realism and generalizability, or deep learning-based models, which require large-scale training datasets. Social graphs, as abstract graph representations of entity-wise interactions, present an opportunity to explore network evolution mechanisms through realistic simulations of human-item interactions. Leveraging the pre-trained social consensus knowledge embedded in large language models (LLMs), we present GraphAgent-Generator (GAG), a novel simulation-based framework for dynamic, text-attributed social graph generation. GAG simulates the temporal node and edge generation processes for zero-shot social graph generation. The resulting graphs exhibit adherence to seven key macroscopic network properties, achieving an 11% improvement in microscopic graph structure metrics. Through the node classification benchmarking task, we validate GAG effectively captures the intricate text-structure correlations in graph generation. Furthermore, GAG supports generating graphs with up to nearly 100,000 nodes or 10 million edges through large-scale LLM-based agent simulation with parallel acceleration, achieving a minimum speed-up of 90.4%. The source code is available at https://github.com/Ji-Cather/GraphAgent.
自然产生的社会图的结构特性得到了广泛的研究,以了解其演化过程。之前对网络动态建模的方法通常依赖于基于规则的模型,这些模型缺乏现实性和通用性,或者基于深度学习的模型,这些模型则需要大规模的训练数据集。社会图作为实体间互动的抽象图形表示,通过模拟人与物品的互动,为探索网络演化机制提供了机会。我们借助大型语言模型(LLM)中嵌入的社会共识知识,提出了GraphAgent-Generator(GAG)这一基于模拟的动态文本属性社会图生成新框架。GAG模拟节点和边的生成过程,实现了零起步的社会图生成。生成的图符合七个关键的宏观网络属性,在微观图结构指标上提高了11%。通过节点分类基准测试任务,我们验证了GAG在图形生成中有效地捕捉了复杂的文本结构相关性。此外,GAG支持通过基于大型语言模型的代理模拟进行并行加速,生成包含近10万个节点或1000万个边的图,实现至少90.4%的速度提升。源代码可在https://github.com/Ji-Cather/GraphAgent获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型预训练的社会共识知识,提出GraphAgent-Generator(GAG),一种模拟动态文本属性社会图生成的新型框架。该框架模拟节点和边的动态生成过程,生成的社会图符合七大宏观网络属性,提高微观图结构指标的准确性,并能有效捕捉文本与结构的复杂关联。此外,GAG支持大规模LLM代理模拟生成大型图,实现并行加速和高效性能。
Key Takeaways
- GraphAgent-Generator(GAG)利用大型语言模型(LLM)的预训练社会共识知识,用于模拟动态文本属性社会图的生成。
- GAG模拟节点和边的生成过程,实现零起点社会图生成。
- 生成的社会图符合七大宏观网络属性。
- GAG提高了微观图结构指标的准确性,达到11%的改进。
- 通过节点分类基准测试任务验证了GAG有效捕捉了图中复杂的文本与结构关联。
- GAG支持生成包含近10万个节点或1000万个边的大型图。
点此查看论文截图


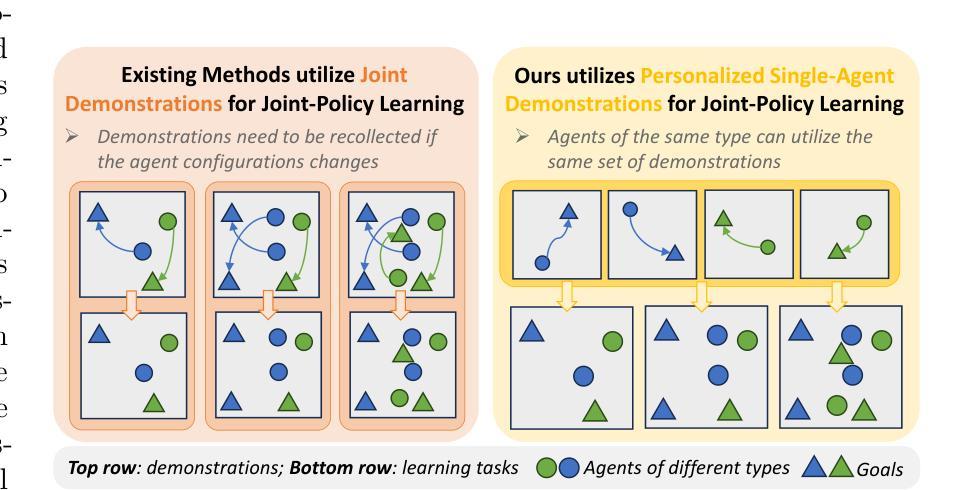
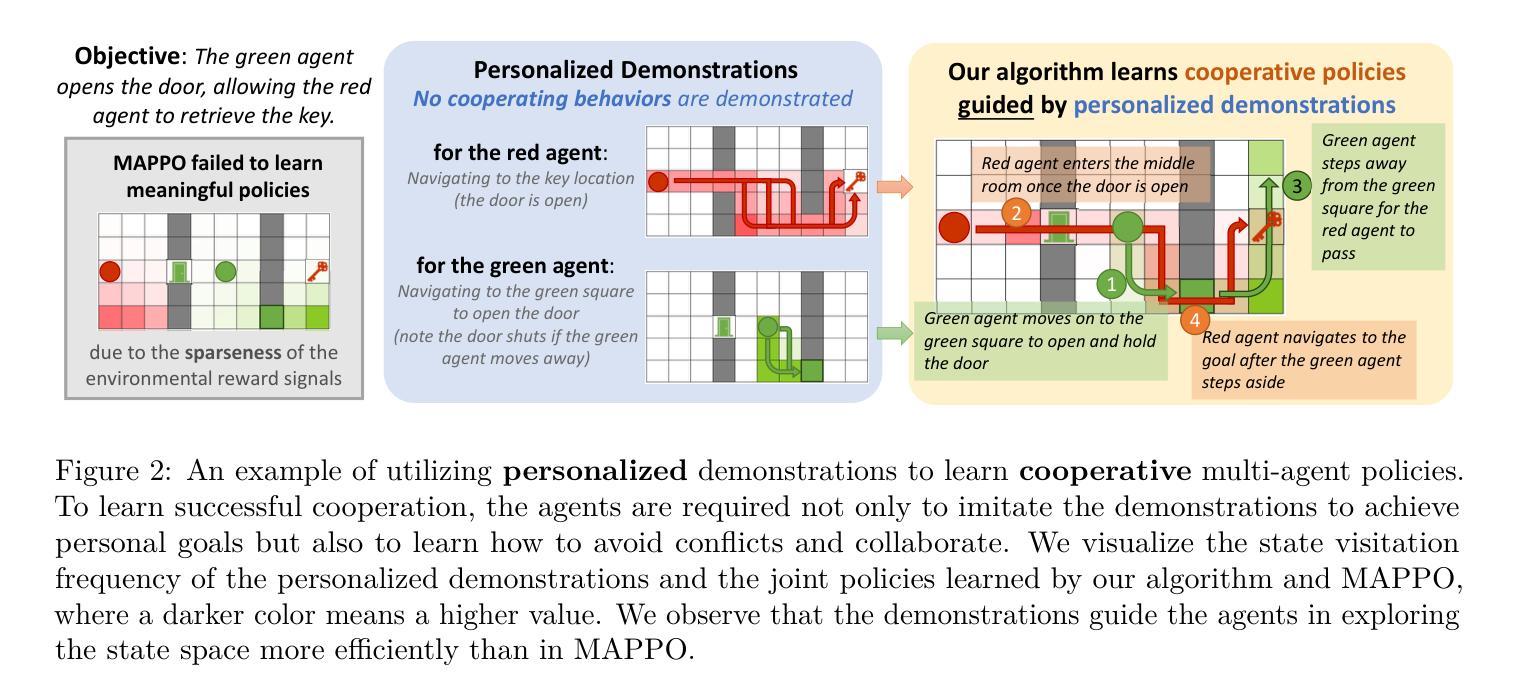
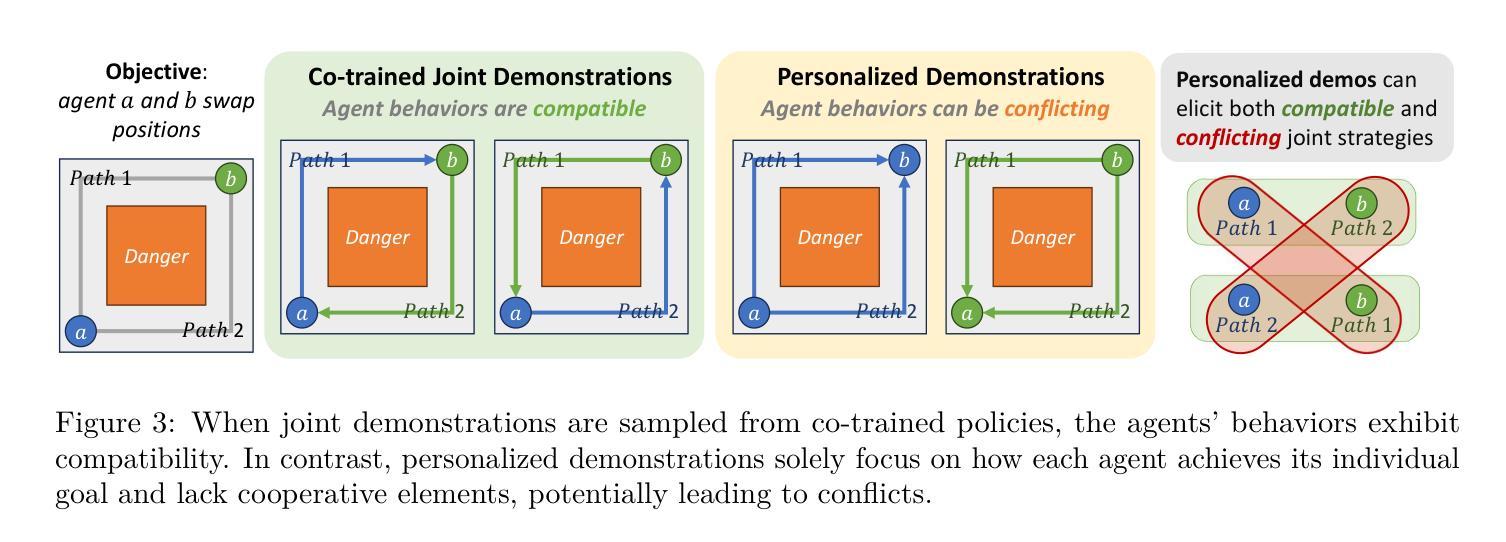
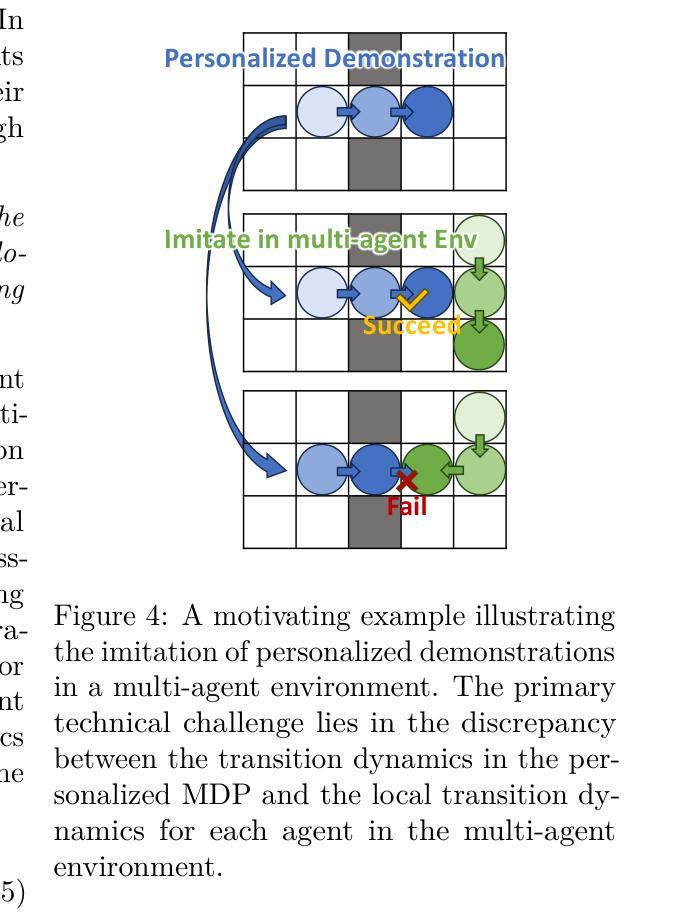
Beyond Joint Demonstrations: Personalized Expert Guidance for Efficient Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Peihong Yu, Manav Mishra, Alec Koppel, Carl Busart, Priya Narayan, Dinesh Manocha, Amrit Bedi, Pratap Tokekar
Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) algorithms face the challenge of efficient exploration due to the exponential increase in the size of the joint state-action space. While demonstration-guided learning has proven beneficial in single-agent settings, its direct applicability to MARL is hindered by the practical difficulty of obtaining joint expert demonstrations. In this work, we introduce a novel concept of personalized expert demonstrations, tailored for each individual agent or, more broadly, each individual type of agent within a heterogeneous team. These demonstrations solely pertain to single-agent behaviors and how each agent can achieve personal goals without encompassing any cooperative elements, thus naively imitating them will not achieve cooperation due to potential conflicts. To this end, we propose an approach that selectively utilizes personalized expert demonstrations as guidance and allows agents to learn to cooperate, namely personalized expert-guided MARL (PegMARL). This algorithm utilizes two discriminators: the first provides incentives based on the alignment of individual agent behavior with demonstrations, and the second regulates incentives based on whether the behaviors lead to the desired outcome. We evaluate PegMARL using personalized demonstrations in both discrete and continuous environments. The experimental results demonstrate that PegMARL outperforms state-of-the-art MARL algorithms in solving coordinated tasks, achieving strong performance even when provided with suboptimal personalized demonstrations. We also showcase PegMARL’s capability of leveraging joint demonstrations in the StarCraft scenario and converging effectively even with demonstrations from non-co-trained policies.
多智能体强化学习(MARL)算法面临由于联合状态-行动空间的规模呈指数增长而导致的有效探索挑战。演示引导学习在单智能体环境中已经证明是有益的,但其直接应用于MARL受到获得联合专家演示的实际困难的阻碍。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个针对每个个体智能体或更广泛地说,针对异质团队中每个类型的智能体的个性化专家演示的新概念。这些演示仅涉及单智能体行为以及每个智能体如何实现个人目标,而不包含任何合作元素,因此仅仅盲目模仿它们不会导致合作,因为可能存在潜在冲突。为此,我们提出了一种有选择地利用个性化专家演示作为指导的方法,并允许智能体学习合作,即个性化专家引导的多智能体强化学习(PegMARL)。该算法使用两个鉴别器:第一个基于个体智能体行为与演示的对齐情况提供激励,第二个则基于行为是否达到期望结果来调节激励。我们在离散和连续环境中使用个性化演示来评估PegMARL。实验结果表明,在解决协调任务方面,PegMARL优于最新的MARL算法,即使在提供次优个性化演示的情况下也能实现强大的性能。我们还展示了PegMARL在星际争霸场景中使用联合演示的能力,并展示了即使在非协同训练策略的指导下也能有效地收敛。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted in Transactions on Machine Learning Research
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对多智能体强化学习(MARL)算法面临的高效探索挑战的解决方案。通过引入个性化专家演示的概念,为每种类型的智能体提供针对其个人的行为演示,以促进学习过程中的探索效率。该算法采用两个鉴别器,一个用于激励个体行为与演示的对齐,另一个用于调节是否能达成预期结果的行为激励。实验结果表明,使用个性化演示的PegMARL在解决协调任务方面优于最新的MARL算法,甚至在提供次优个性化演示时也能取得强大的性能。此外,展示了PegMARL在星际争霸场景中使用联合演示的能力,即使与非协同训练策略相结合,也能有效地收敛。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体强化学习(MARL)面临高效探索的挑战,由于联合状态动作空间的规模呈指数增长。
- 引入个性化专家演示的概念,针对每种类型的智能体提供单独的演示,促进学习过程中的探索效率。
- PegMARL算法使用两个鉴别器:一个激励个体行为与演示对齐,另一个调节是否达成预期结果的行为激励。
- PegMARL在解决协调任务方面优于最新的MARL算法,即使在提供次优个性化演示时也能取得强大的性能。
- PegMARL能够在星际争霸场景中使用联合演示,展示了其灵活性和实用性。
- PegMARL能有效收敛,即使与非协同训练的演示策略相结合也能表现良好。
点此查看论文截图