⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-08 更新
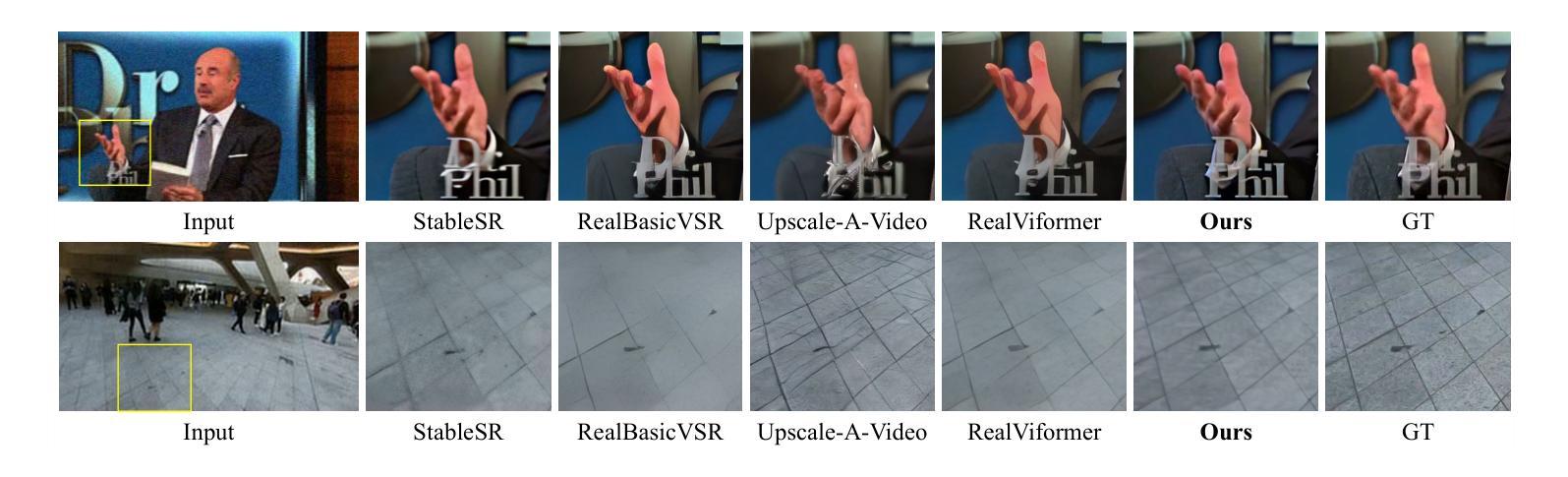
STAR: Spatial-Temporal Augmentation with Text-to-Video Models for Real-World Video Super-Resolution
Authors:Rui Xie, Yinhong Liu, Penghao Zhou, Chen Zhao, Jun Zhou, Kai Zhang, Zhenyu Zhang, Jian Yang, Zhenheng Yang, Ying Tai
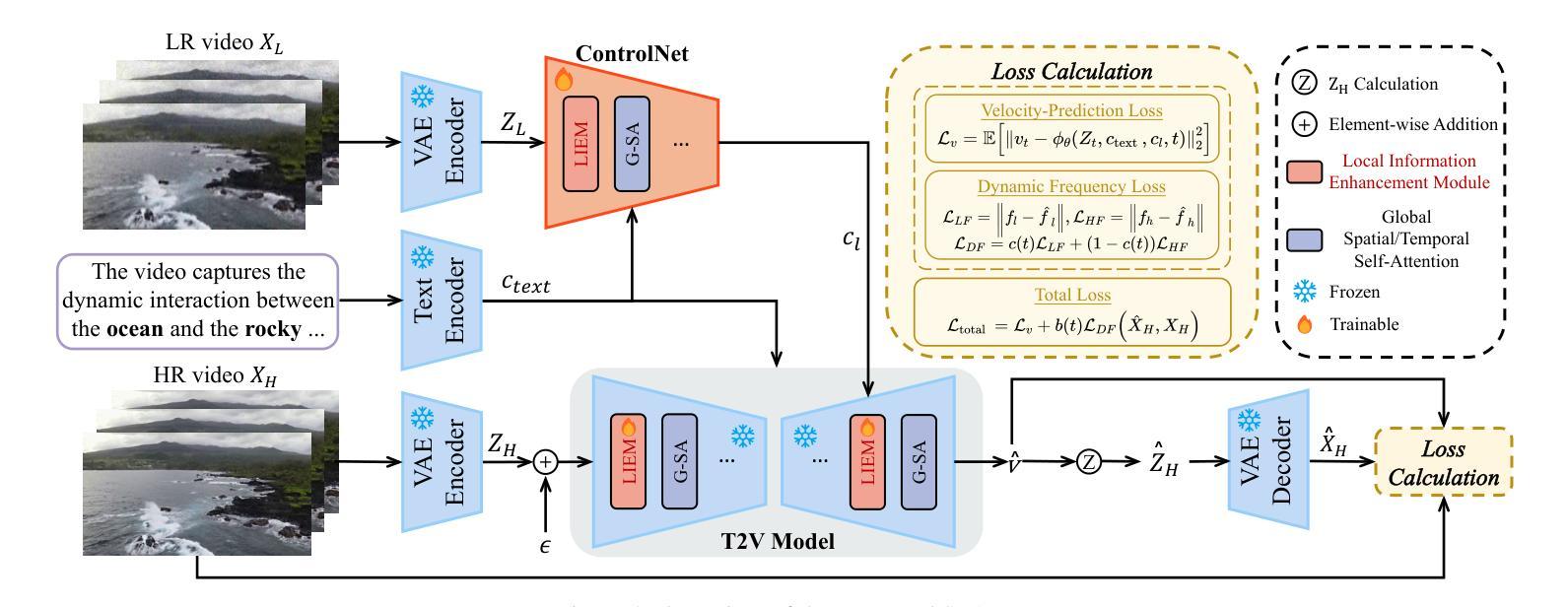
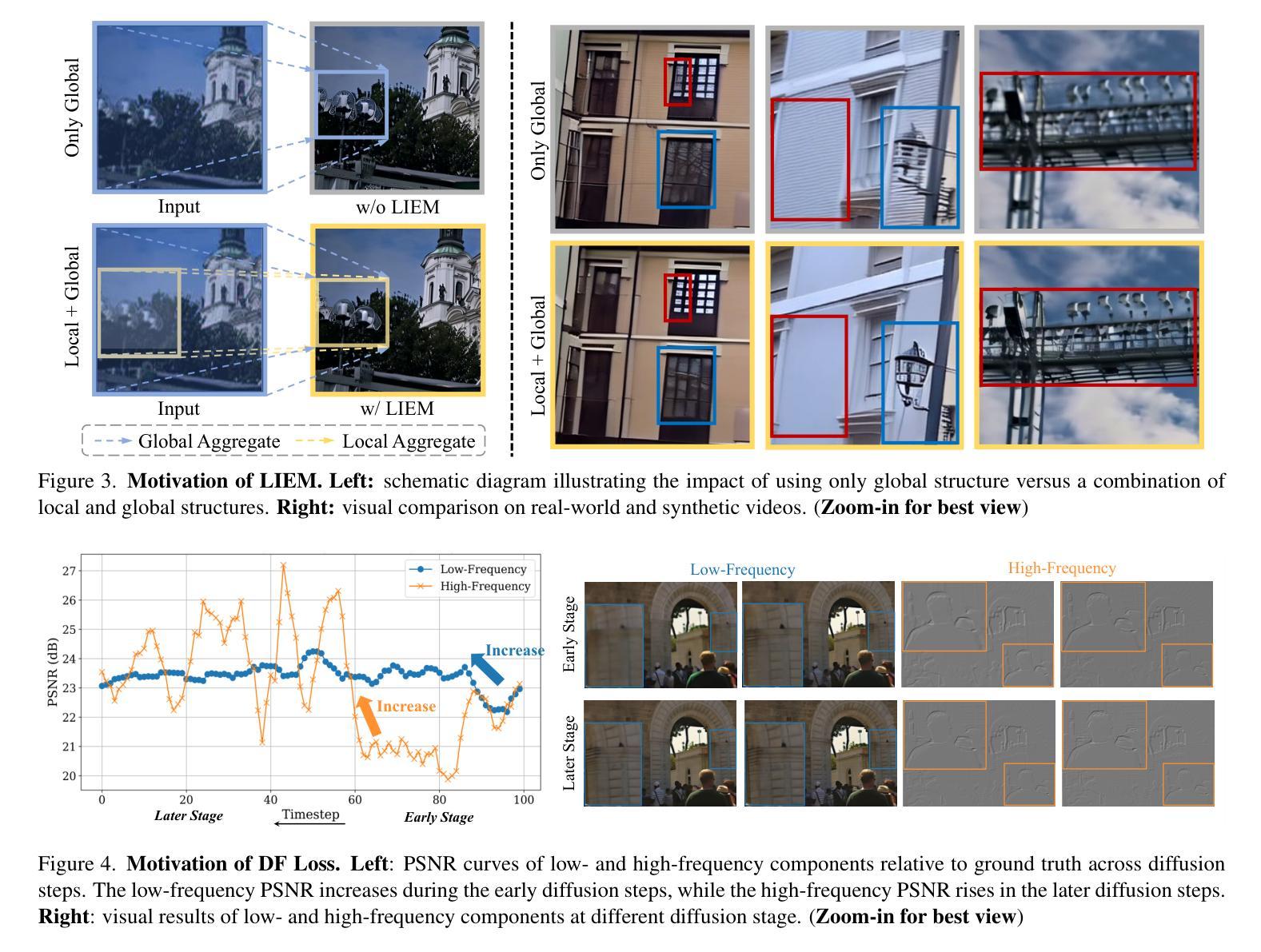
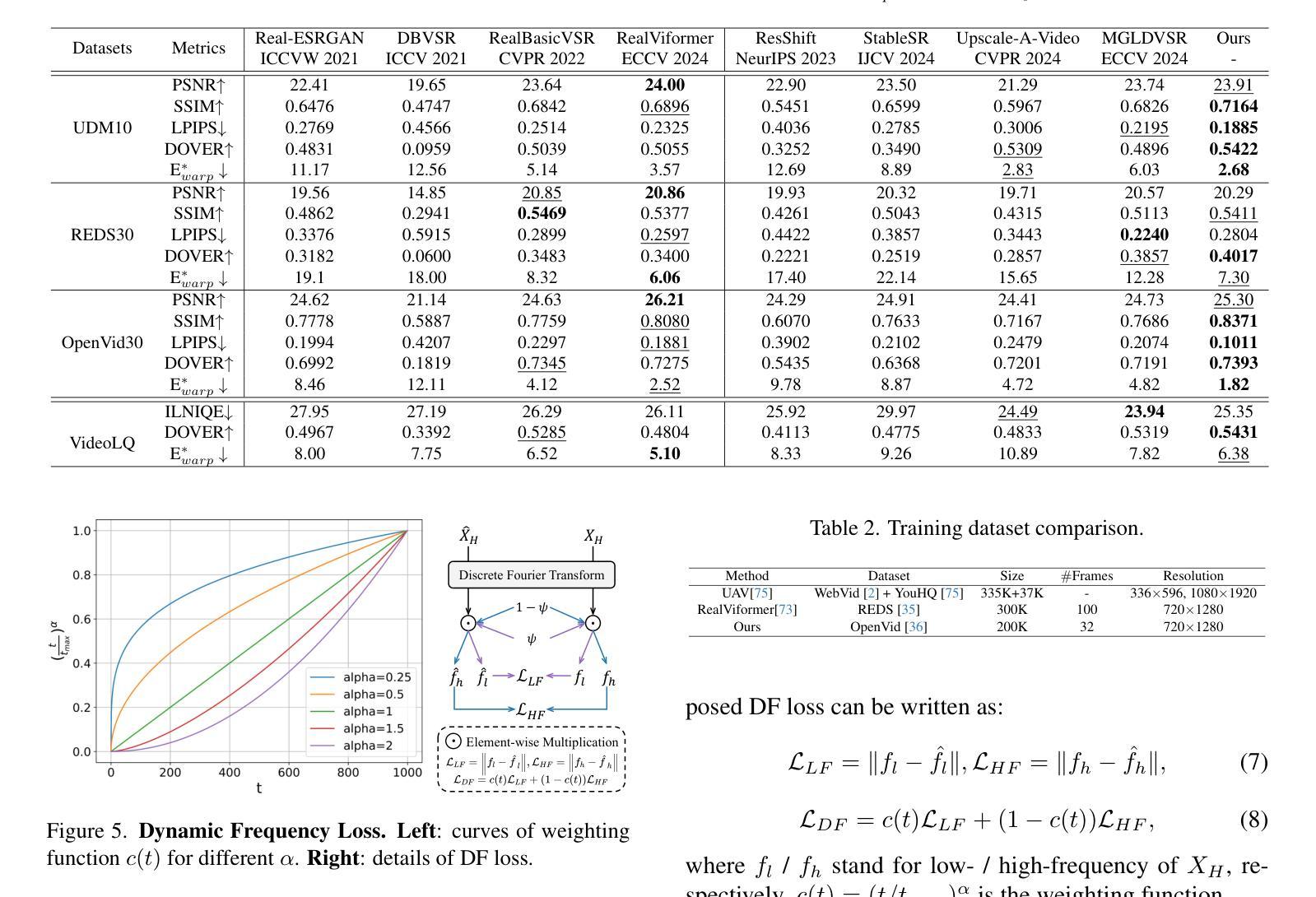
Image diffusion models have been adapted for real-world video super-resolution to tackle over-smoothing issues in GAN-based methods. However, these models struggle to maintain temporal consistency, as they are trained on static images, limiting their ability to capture temporal dynamics effectively. Integrating text-to-video (T2V) models into video super-resolution for improved temporal modeling is straightforward. However, two key challenges remain: artifacts introduced by complex degradations in real-world scenarios, and compromised fidelity due to the strong generative capacity of powerful T2V models (\textit{e.g.}, CogVideoX-5B). To enhance the spatio-temporal quality of restored videos, we introduce\textbf{\name} (\textbf{S}patial-\textbf{T}emporal \textbf{A}ugmentation with T2V models for \textbf{R}eal-world video super-resolution), a novel approach that leverages T2V models for real-world video super-resolution, achieving realistic spatial details and robust temporal consistency. Specifically, we introduce a Local Information Enhancement Module (LIEM) before the global attention block to enrich local details and mitigate degradation artifacts. Moreover, we propose a Dynamic Frequency (DF) Loss to reinforce fidelity, guiding the model to focus on different frequency components across diffusion steps. Extensive experiments demonstrate\textbf{\name}~outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
图像扩散模型已被适应于真实世界视频超分辨率,以解决基于GAN的方法中的过度平滑问题。然而,这些模型在维持时间一致性方面遇到困难,因为它们是在静态图像上训练的,无法有效地捕捉时间动态。将文本到视频(T2V)模型整合到视频超分辨率中以改进时间建模是直接的。然而,还有两个主要挑战:现实世界场景中复杂退化引起的伪影,以及由于强大的T2V模型的生成能力而牺牲的保真度(例如CogVideoX-5B)。为了提高恢复视频的时空质量,我们引入了名为STAR的新方法(利用T2V模型进行真实世界视频超分辨率的时空增强)。具体来说,我们在全局注意力块之前引入了一个局部信息增强模块(LIEM),以丰富局部细节并减轻退化伪影。此外,我们提出了一种动态频率(DF)损失来加强保真度,引导模型在不同的扩散步骤中关注不同的频率分量。大量实验表明,STAR在合成和真实世界数据集上都优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对图像扩散模型在视频超分辨率中遇到的过度平滑问题,本文提出了一种结合文本到视频(T2V)模型的新方法,旨在提高现实世界的视频超分辨率的时空质量。通过引入局部信息增强模块(LIEM)和动态频率(DF)损失,该方法能够在保持时间一致性的同时,实现真实的空间细节和稳健的保真度。实验表明,该方法在合成和真实数据集上均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 图像扩散模型被用于现实世界的视频超分辨率以提高性能并解决过度平滑问题。
- 结合文本到视频(T2V)模型以改善视频超分辨率中的时间建模。
- 面临两个主要挑战:现实场景中复杂退化引入的伪影以及强大T2V模型妥协的保真度。
- 引入了一种新方法——STAR(时空增强与T2V模型结合用于现实世界的视频超分辨率),实现了真实的空间细节和稳健的时间一致性。
- 在STAR方法中,引入了局部信息增强模块(LIEM)来丰富局部细节并减轻退化伪影。
- 提出了动态频率(DF)损失以增强保真度,引导模型在扩散步骤中关注不同的频率成分。
点此查看论文截图


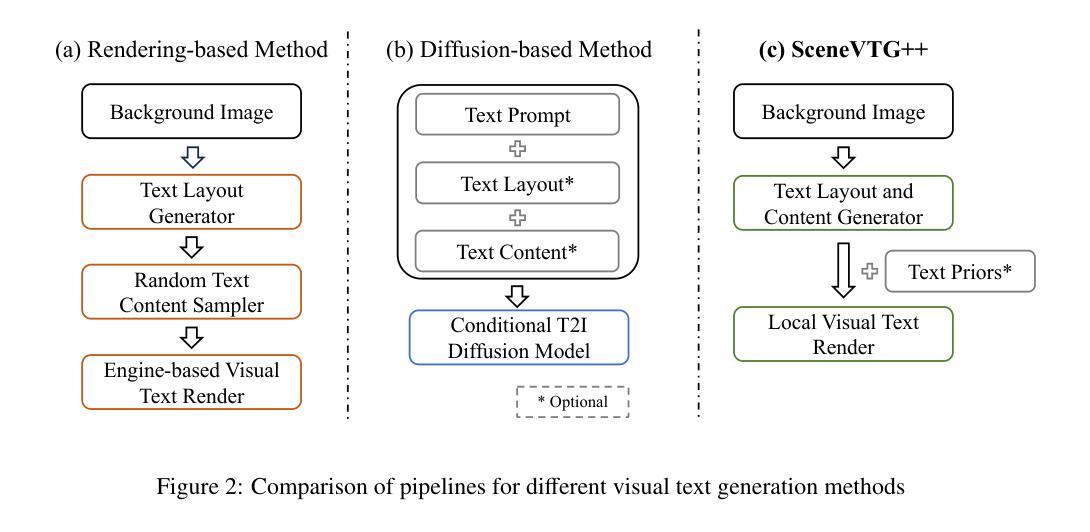
SceneVTG++: Controllable Multilingual Visual Text Generation in the Wild
Authors:Jiawei Liu, Yuanzhi Zhu, Feiyu Gao, Zhibo Yang, Peng Wang, Junyang Lin, Xinggang Wang, Wenyu Liu
Generating visual text in natural scene images is a challenging task with many unsolved problems. Different from generating text on artificially designed images (such as posters, covers, cartoons, etc.), the text in natural scene images needs to meet the following four key criteria: (1) Fidelity: the generated text should appear as realistic as a photograph and be completely accurate, with no errors in any of the strokes. (2) Reasonability: the text should be generated on reasonable carrier areas (such as boards, signs, walls, etc.), and the generated text content should also be relevant to the scene. (3) Utility: the generated text can facilitate to the training of natural scene OCR (Optical Character Recognition) tasks. (4) Controllability: The attribute of the text (such as font and color) should be controllable as needed.In this paper, we propose a two stage method, SceneVTG++, which simultaneously satisfies the four aspects mentioned above. SceneVTG++ consists of a Text Layout and Content Generator (TLCG) and a Controllable Local Text Diffusion (CLTD). The former utilizes the world knowledge of multi modal large language models to find reasonable text areas and recommend text content according to the nature scene background images, while the latter generates controllable multilingual text based on the diffusion model. Through extensive experiments, we respectively verified the effectiveness of TLCG and CLTD, and demonstrated the state-of-the-art text generation performance of SceneVTG++. In addition, the generated images have superior utility in OCR tasks like text detection and text recognition. Codes and datasets will be available.
生成自然场景图像中的视觉文本是一项具有许多未解决问题挑战性的任务。与在人工设计的图像(如海报、封面、漫画等)上生成文本不同,自然场景图像中的文本需要满足以下四个关键标准:(1)保真度:生成的文本应看起来尽可能逼真,并且完全准确,没有任何笔触错误。(2)合理性:文本应生成在合理的载体区域(如板报、标志、墙壁等),并且生成的文本内容也应与场景相关。(3)实用性:生成的文本有助于自然场景OCR(光学字符识别)任务的训练。(4)可控性:文本属性(如字体和颜色)应根据需要可控。在本文中,我们提出了一种两阶段方法SceneVTG++,同时满足上述四个方面。SceneVTG++包括文本布局和内容生成器(TLCG)和可控局部文本扩散(CLTD)。前者利用多模态大型语言模型的世界知识,根据自然场景背景图像找到合理的文本区域,并推荐文本内容;后者基于扩散模型生成可控的多语言文本。通过大量实验,我们分别验证了TLCG和CLTD的有效性,并展示了SceneVTG++的先进文本生成性能。此外,生成的图像在OCR任务(如文本检测和识别)中具有出色的实用性。代码和数据集将可用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种两阶段方法SceneVTG++,用于生成自然场景图像中的视觉文本,同时满足真实性、合理性、实用性和可控性四个关键标准。该方法包括文本布局和内容生成器(TLCG)和可控局部文本扩散(CLTD)。TLCG利用多模态大型语言模型的世界知识,根据自然场景背景图像找到合理的文本区域并推荐文本内容。CLTD则基于扩散模型生成可控的多语言文本。实验证明TLCG和CLTD的有效性,并展示了SceneVTG++在文本生成方面的先进性,同时生成的图像在OCR任务中具有出色的实用性。
关键见解
- 生成自然场景图像中的视觉文本是一项具有挑战性的任务,需要满足真实性、合理性、实用性和可控性四个关键标准。
- SceneVTG++是一种两阶段方法,包括文本布局和内容生成器(TLCG)和可控局部文本扩散(CLTD)。
- TLCG利用多模态大型语言模型的世界知识,根据自然场景背景图像生成合理的文本布局和内容。
- CLTD基于扩散模型生成可控的多语言文本,满足场景文本生成的需求。
- 实验证明TLCG和CLTD的有效性,SceneVTG++在文本生成方面表现出先进性。
- 生成的图像在OCR任务中具有出色的实用性,如文本检测和文本识别。
点此查看论文截图


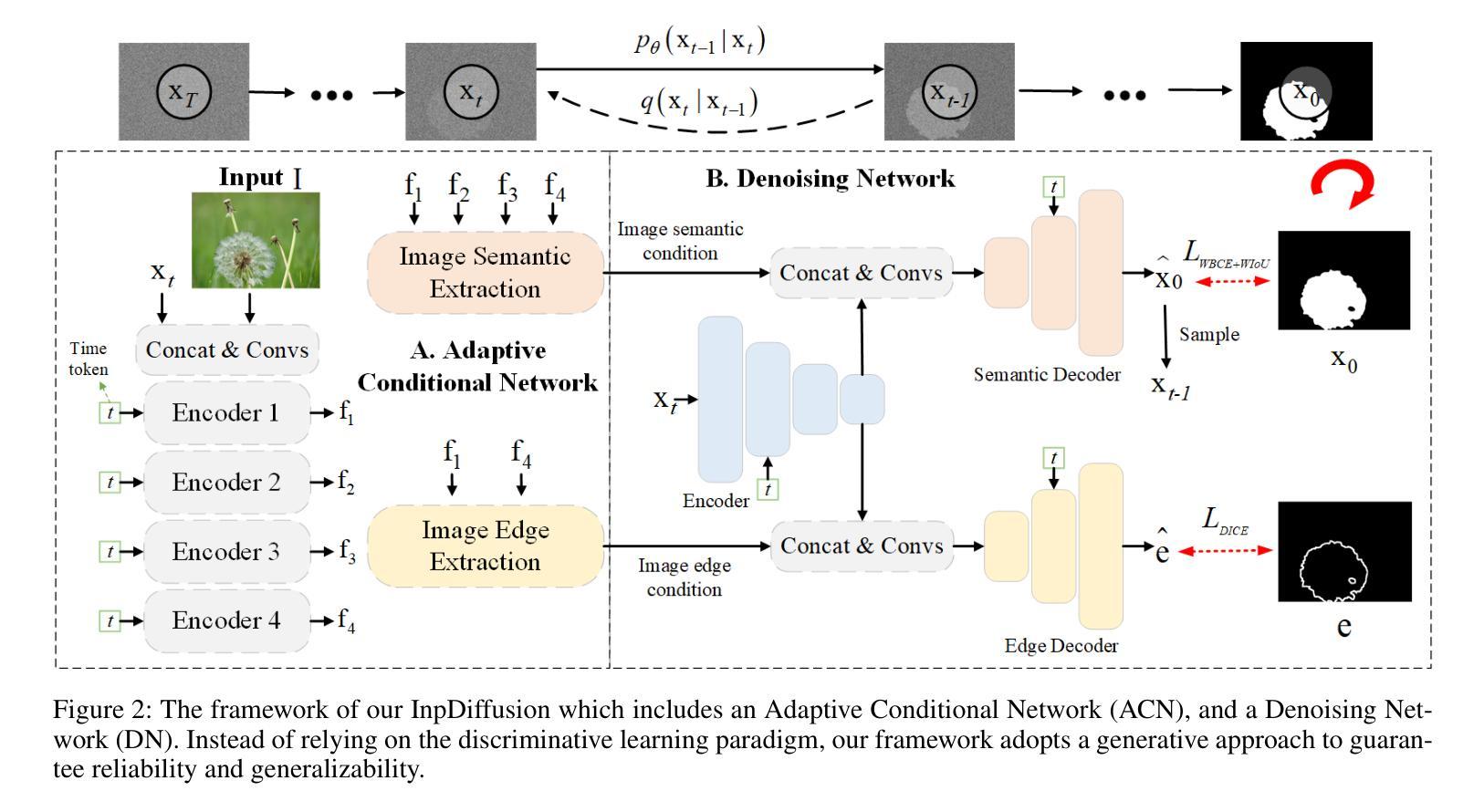
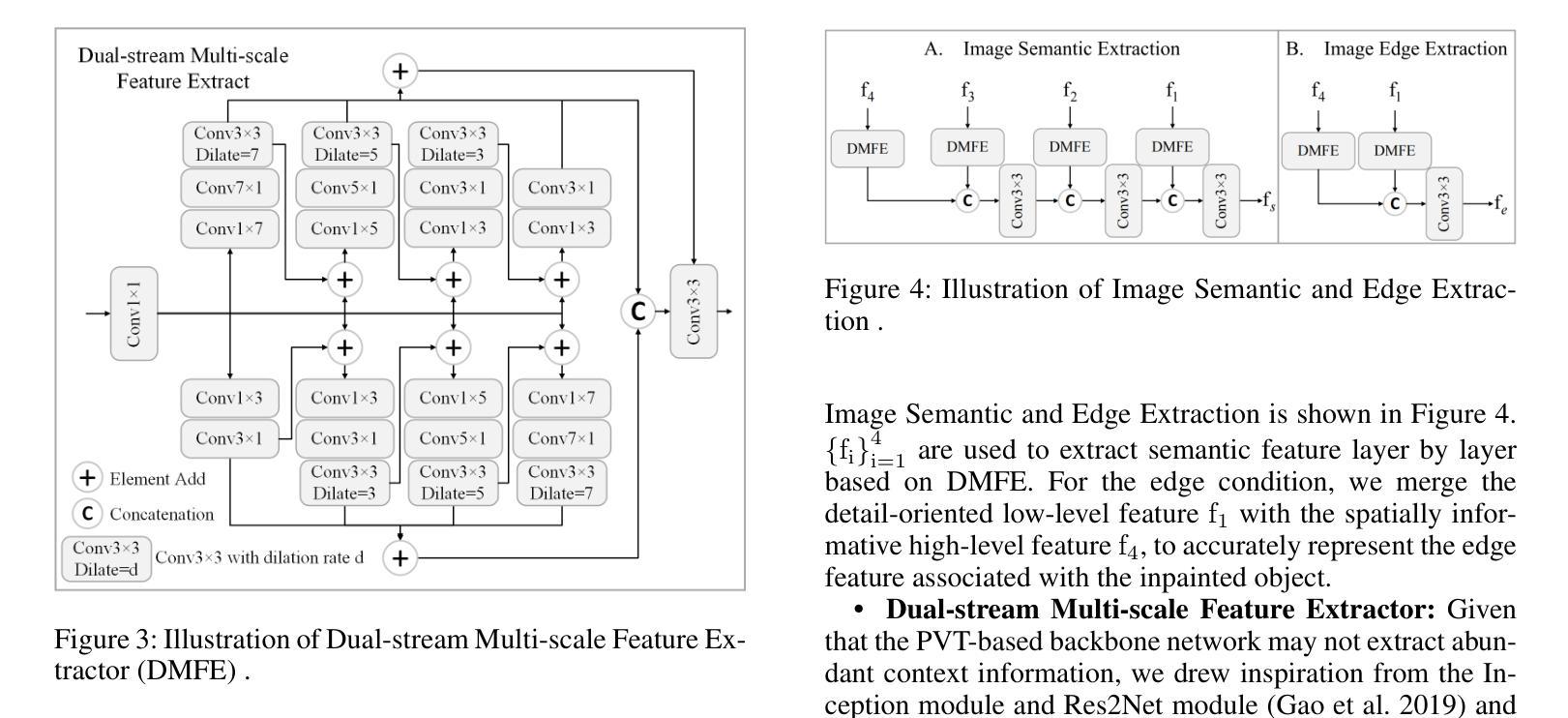
InpDiffusion: Image Inpainting Localization via Conditional Diffusion Models
Authors:Kai Wang, Shaozhang Niu, Qixian Hao, Jiwei Zhang
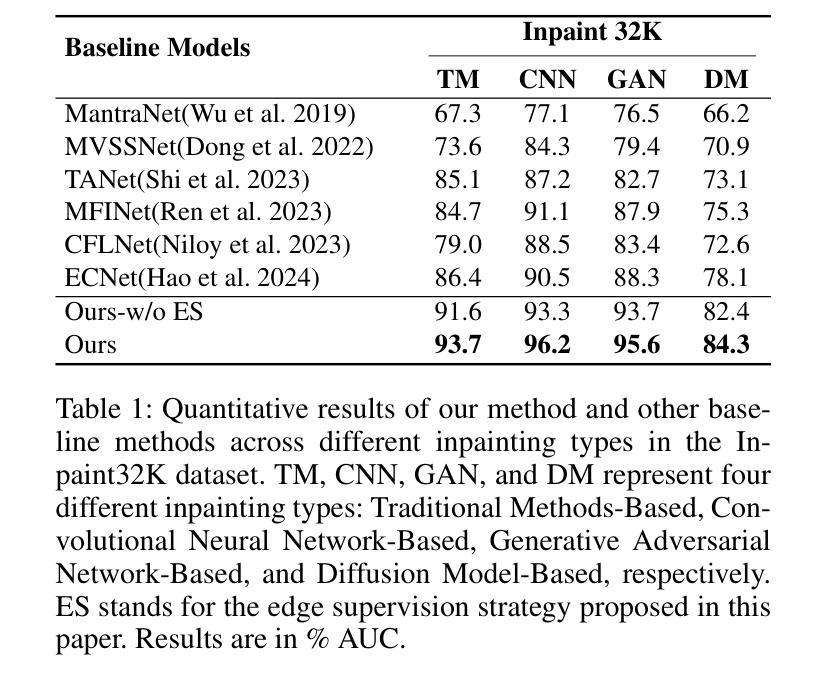
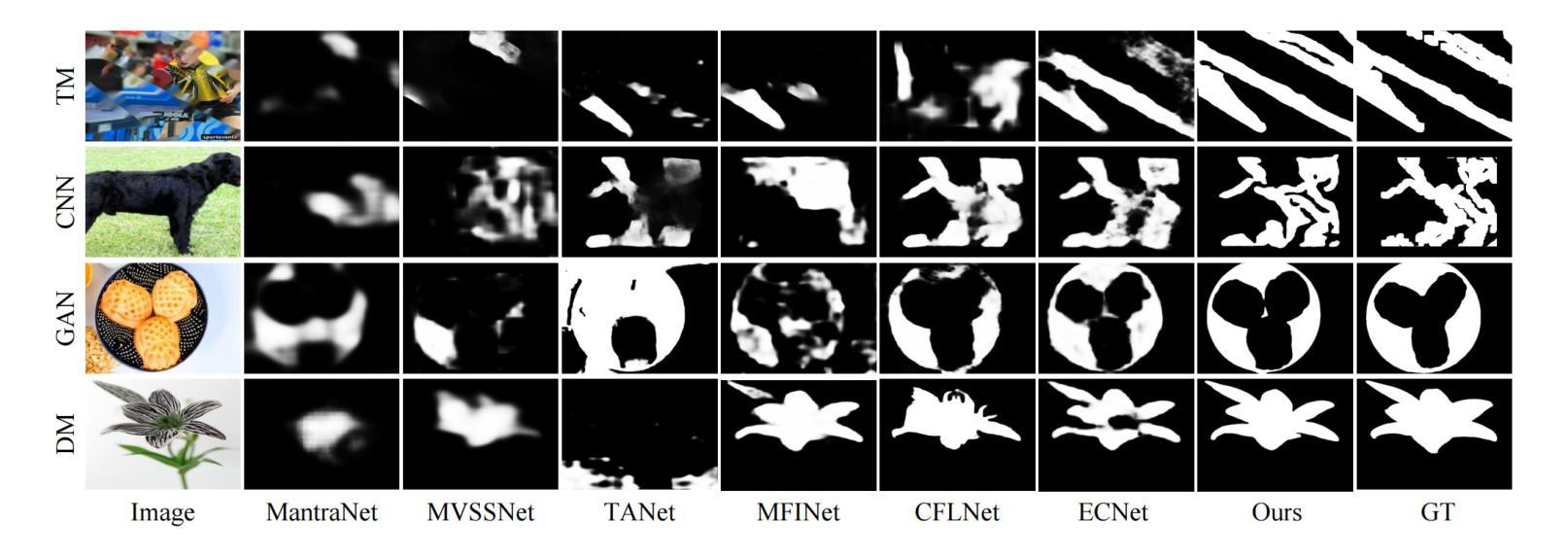
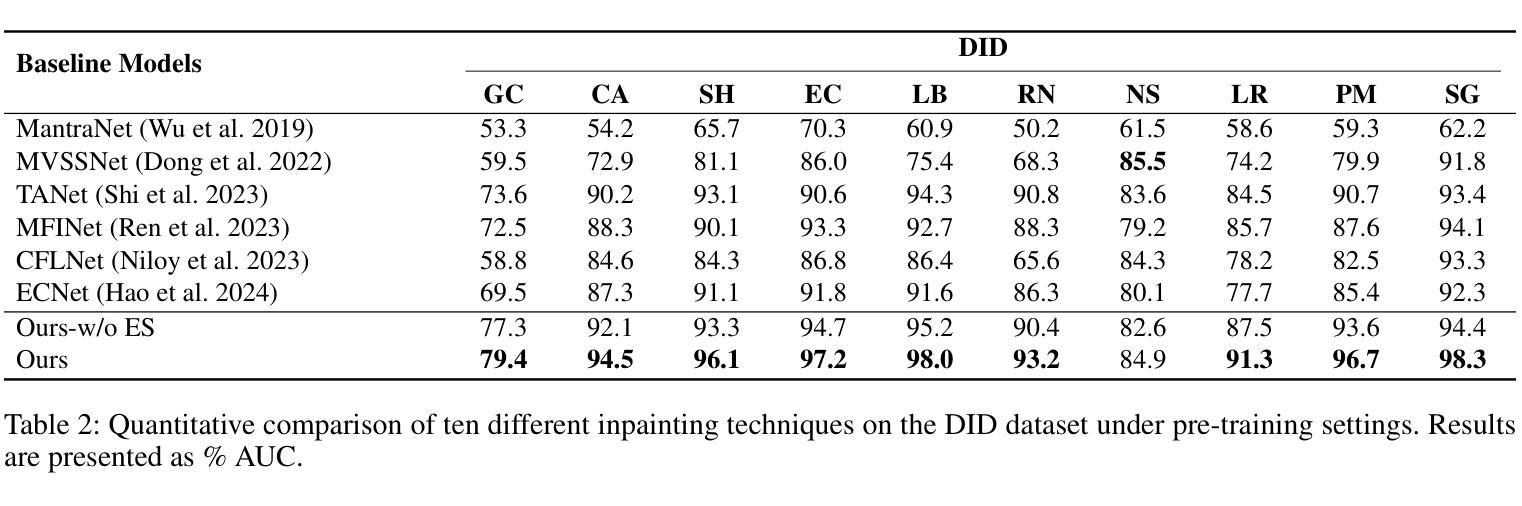
As artificial intelligence advances rapidly, particularly with the advent of GANs and diffusion models, the accuracy of Image Inpainting Localization (IIL) has become increasingly challenging. Current IIL methods face two main challenges: a tendency towards overconfidence, leading to incorrect predictions; and difficulty in detecting subtle tampering boundaries in inpainted images. In response, we propose a new paradigm that treats IIL as a conditional mask generation task utilizing diffusion models. Our method, InpDiffusion, utilizes the denoising process enhanced by the integration of image semantic conditions to progressively refine predictions. During denoising, we employ edge conditions and introduce a novel edge supervision strategy to enhance the model’s perception of edge details in inpainted objects. Balancing the diffusion model’s stochastic sampling with edge supervision of tampered image regions mitigates the risk of incorrect predictions from overconfidence and prevents the loss of subtle boundaries that can result from overly stochastic processes. Furthermore, we propose an innovative Dual-stream Multi-scale Feature Extractor (DMFE) for extracting multi-scale features, enhancing feature representation by considering both semantic and edge conditions of the inpainted images. Extensive experiments across challenging datasets demonstrate that the InpDiffusion significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in IIL tasks, while also showcasing excellent generalization capabilities and robustness.
随着人工智能的快速发展,尤其是生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的兴起,图像修复定位(IIL)的准确性越来越受到挑战。当前的IIL方法面临两大挑战:一是过于自信,导致预测错误;二是难以检测修复图像中细微的篡改边界。针对这些问题,我们提出了一种新的方法,将IIL视为利用扩散模型的条件遮罩生成任务。我们的方法InpDiffusion利用结合图像语义条件增强的去噪过程来逐步优化预测。在去噪过程中,我们采用边缘条件并引入了一种新型边缘监督策略,以增强模型对修复物体边缘细节的认知。平衡扩散模型的随机采样与篡改图像区域的边缘监督,降低了因过于自信而导致错误预测的风险,并防止了因过于随机的过程而丢失细微的边界。此外,我们还提出了一种创新性的双流多尺度特征提取器(DMFE),用于提取多尺度特征,通过考虑修复图像的语义和边缘条件来增强特征表示。在具有挑战性的数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,InpDiffusion在IIL任务上显著优于现有最先进的方法,同时显示出卓越泛化能力和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着人工智能的快速发展,尤其是生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的出现,图像修复定位(IIL)的准确性越来越具有挑战性。针对当前IIL方法面临的主要挑战,包括过度自信导致预测错误和难以检测修复图像中的微妙篡改边界,我们提出了一种新的基于扩散模型的IIL方法——InpDiffusion。该方法将IIL视为条件遮罩生成任务,利用图像语义条件增强的去噪过程逐步优化预测。通过引入边缘条件和一种新的边缘监督策略,平衡扩散模型的随机采样和篡改图像区域的边缘监督,减少过度自信导致的预测错误,防止过于随机的过程导致的微妙边界损失。此外,我们还提出了一种创新的双流多尺度特征提取器(DMFE),用于提取多尺度特征,通过考虑修复图像的语义和边缘条件,增强特征表示。实验表明,InpDiffusion在IIL任务上显著优于现有的一流方法,同时显示出优秀的泛化能力和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能的进步,尤其是GANs和扩散模型的发展,使得图像修复定位(IIL)的准确性面临挑战。
- 当前IIL方法存在两个主要挑战:过度自信导致预测错误和难以检测修复图像中的微妙篡改边界。
- InpDiffusion方法将IIL视为条件遮罩生成任务,利用扩散模型进行处理。
- InpDiffusion利用图像语义条件增强的去噪过程逐步优化预测。
- 通过引入边缘条件和边缘监督策略,提高了模型对修复物体边缘细节的感知。
- 双流多尺度特征提取器(DMFE)用于提取多尺度特征,增强特征表示。
点此查看论文截图

Face-MakeUp: Multimodal Facial Prompts for Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Dawei Dai, Mingming Jia, Yinxiu Zhou, Hang Xing, Chenghang Li
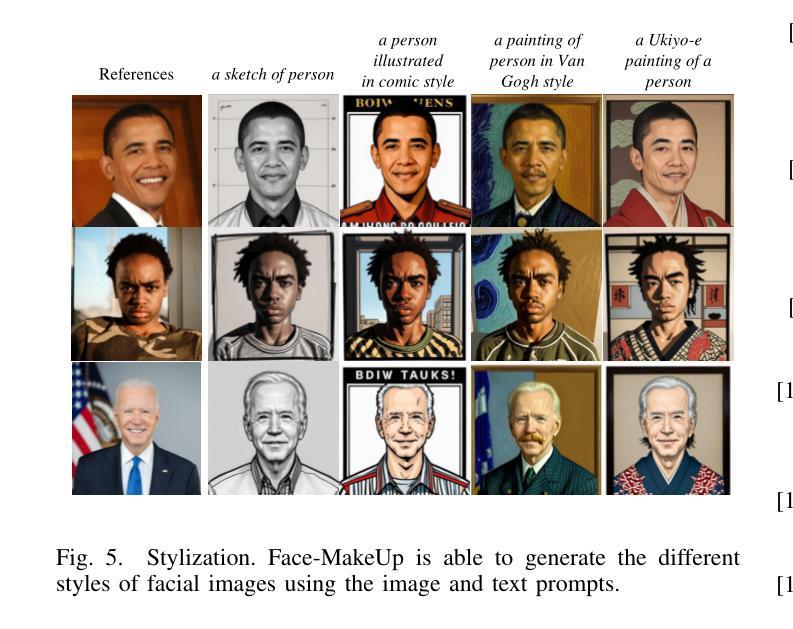
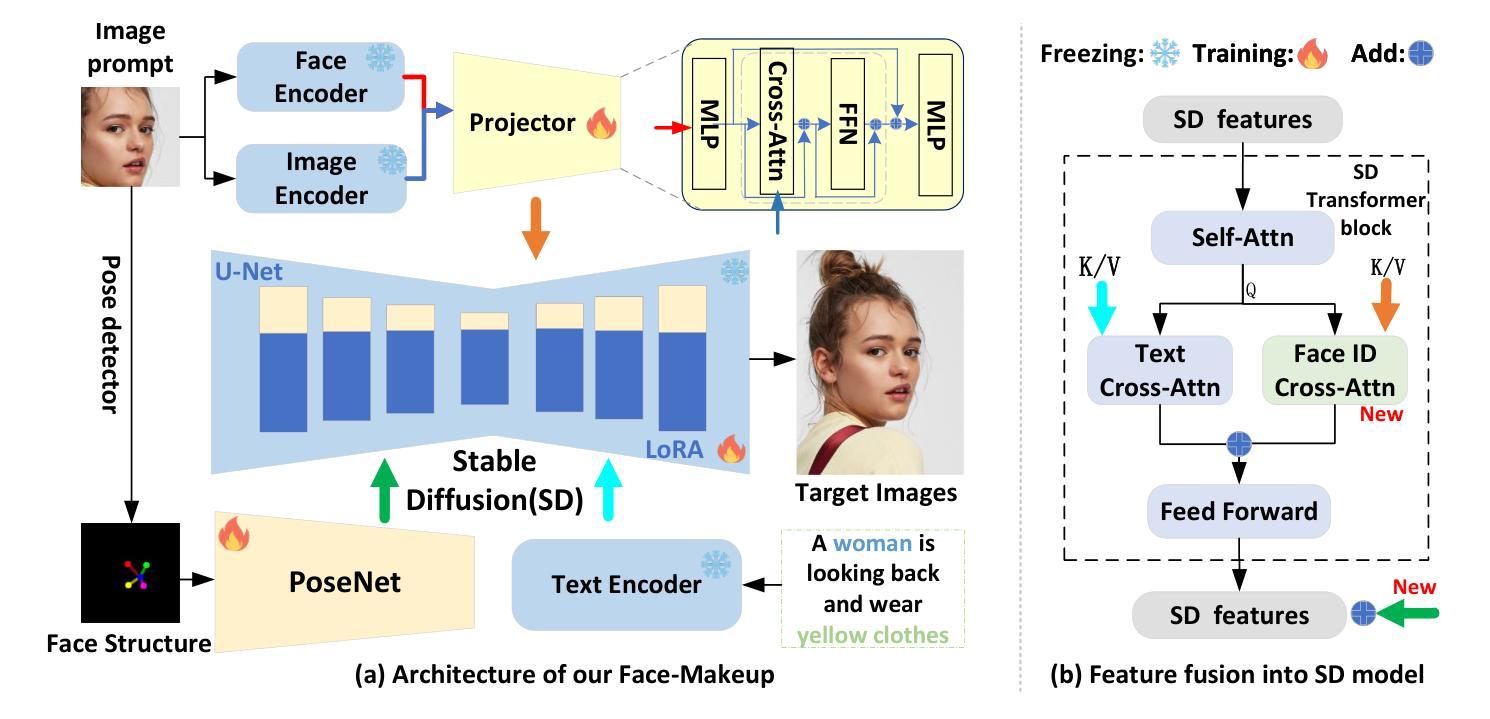
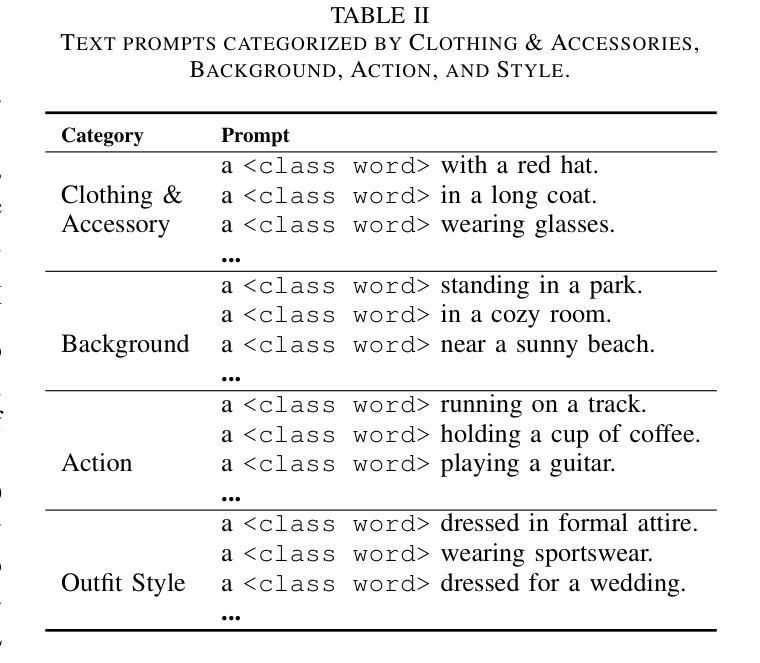
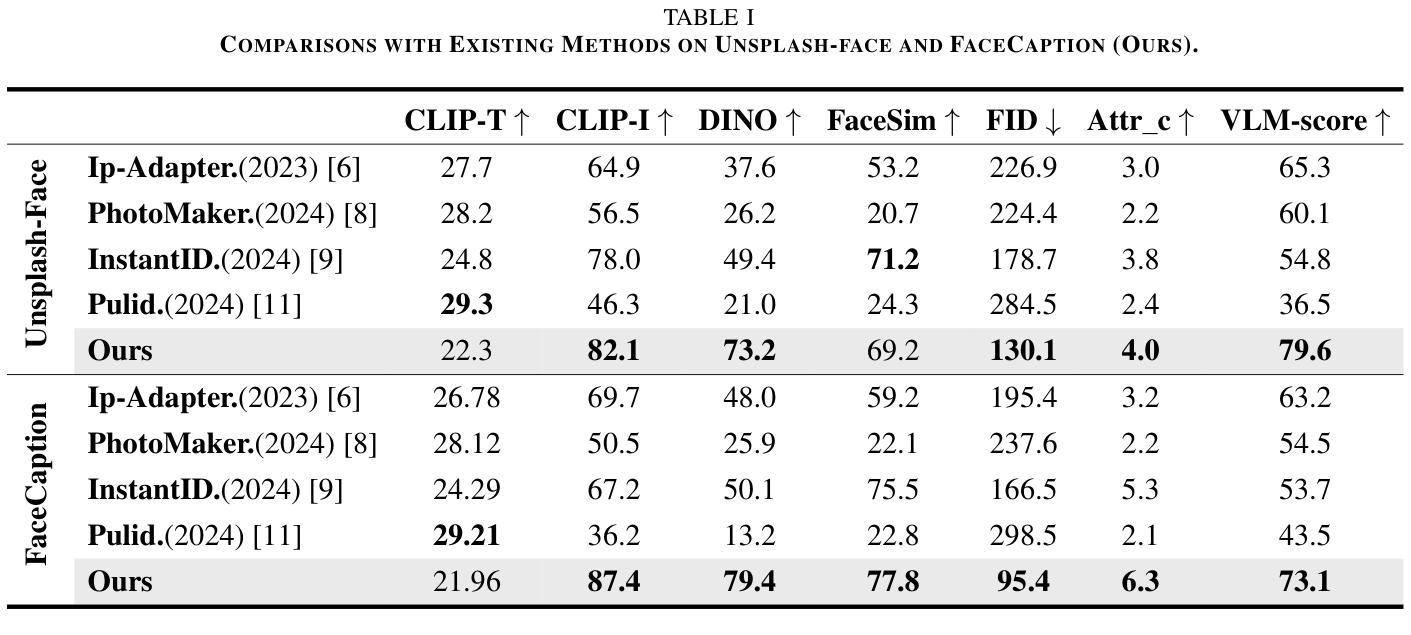
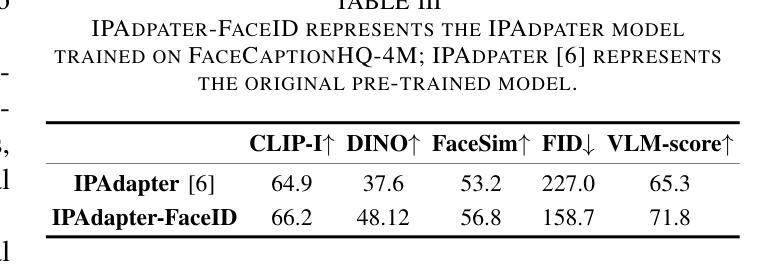
Facial images have extensive practical applications. Although the current large-scale text-image diffusion models exhibit strong generation capabilities, it is challenging to generate the desired facial images using only text prompt. Image prompts are a logical choice. However, current methods of this type generally focus on general domain. In this paper, we aim to optimize image makeup techniques to generate the desired facial images. Specifically, (1) we built a dataset of 4 million high-quality face image-text pairs (FaceCaptionHQ-4M) based on LAION-Face to train our Face-MakeUp model; (2) to maintain consistency with the reference facial image, we extract/learn multi-scale content features and pose features for the facial image, integrating these into the diffusion model to enhance the preservation of facial identity features for diffusion models. Validation on two face-related test datasets demonstrates that our Face-MakeUp can achieve the best comprehensive performance.All codes are available at:https://github.com/ddw2AIGROUP2CQUPT/Face-MakeUp
面部图像具有广泛的应用。虽然现有的大规模文本-图像扩散模型表现出强大的生成能力,但仅使用文本提示生成所需的面部图像是一个挑战。图像提示是一种合理的选择。然而,目前的方法通常集中在一般领域。本文旨在优化化妆技术来生成所需的面部图像。具体来说,(1)我们基于LAION-Face构建了包含4百万个高质量面部图像文本对的数据集FaceCaptionHQ-4M,用于训练我们的Face-MakeUp模型;(2)为了保持与参考面部图像的一致性,我们提取/学习面部图像的多尺度内容特征和姿态特征,将这些特征集成到扩散模型中,以提高扩散模型对面部身份特征的保留能力。在两个与面部相关的测试数据集上的验证表明,我们的Face-MakeUp可以达到最佳的综合性能。所有代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/ddw2AIGROUP2CQUPT/Face-MakeUp。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了针对面部图像生成优化的研究。文中构建了大规模的面部图像文本对数据集FaceCaptionHQ-4M,并基于此训练了Face-MakeUp模型。模型在集成扩散模型时,提取多尺度内容和姿势特征以保持与参考面部图像的一致性,增强了面部特征的保护能力。在两项面部测试数据集上的验证表明,Face-MakeUp取得了最佳的综合性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文本主要关注面部图像的生成优化问题。
- 构建了一个大规模的面部图像文本对数据集FaceCaptionHQ-4M用于训练模型。
- Face-MakeUp模型通过提取多尺度内容和姿势特征来保持与参考面部图像的一致性。
- 该模型在集成扩散模型时增强了面部特征的保护能力。
- Face-MakeUp模型在两项面部测试数据集上实现了最佳的综合性能。
- 提供的链接中包含模型的代码资源供下载和学习。
点此查看论文截图



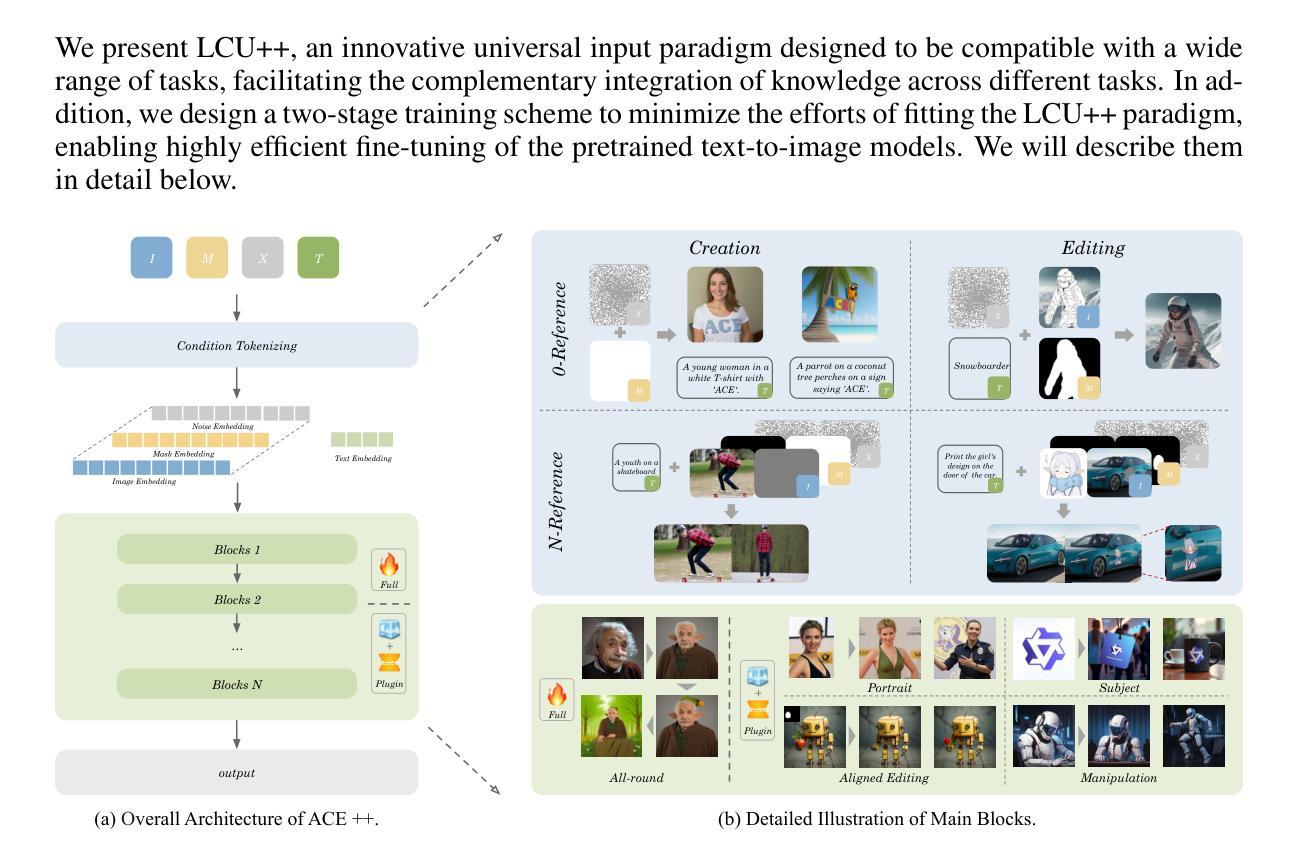
ACE++: Instruction-Based Image Creation and Editing via Context-Aware Content Filling
Authors:Chaojie Mao, Jingfeng Zhang, Yulin Pan, Zeyinzi Jiang, Zhen Han, Yu Liu, Jingren Zhou
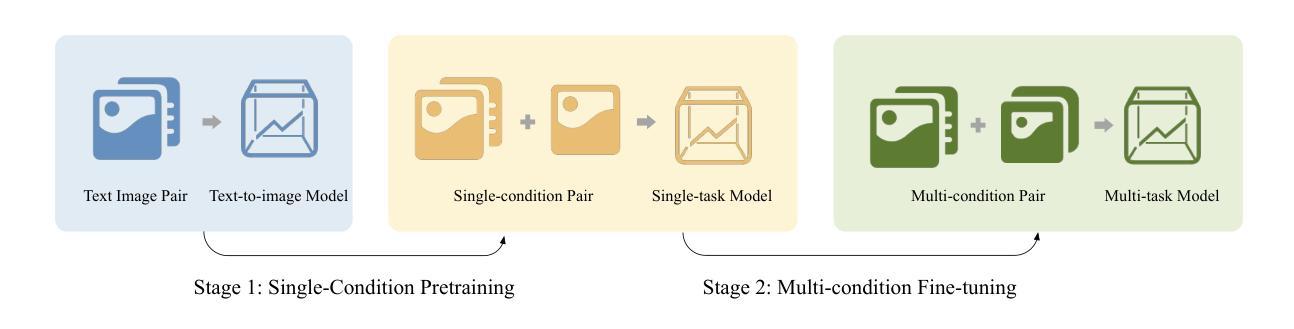
We report ACE++, an instruction-based diffusion framework that tackles various image generation and editing tasks. Inspired by the input format for the inpainting task proposed by FLUX.1-Fill-dev, we improve the Long-context Condition Unit (LCU) introduced in ACE and extend this input paradigm to any editing and generation tasks. To take full advantage of image generative priors, we develop a two-stage training scheme to minimize the efforts of finetuning powerful text-to-image diffusion models like FLUX.1-dev. In the first stage, we pre-train the model using task data with the 0-ref tasks from the text-to-image model. There are many models in the community based on the post-training of text-to-image foundational models that meet this training paradigm of the first stage. For example, FLUX.1-Fill-dev deals primarily with painting tasks and can be used as an initialization to accelerate the training process. In the second stage, we finetune the above model to support the general instructions using all tasks defined in ACE. To promote the widespread application of ACE++ in different scenarios, we provide a comprehensive set of models that cover both full finetuning and lightweight finetuning, while considering general applicability and applicability in vertical scenarios. The qualitative analysis showcases the superiority of ACE++ in terms of generating image quality and prompt following ability.
我们报告了ACE++,这是一个基于指令的扩散框架,用于处理各种图像生成和编辑任务。我们受到FLUX.1-Fill-dev提出的填充任务输入格式的启发,改进了ACE中的长上下文条件单元(LCU),并将这一输入范式扩展到任何编辑和生成任务。为了充分利用图像生成的先验知识,我们开发了一种两阶段训练方案,以最小化调整强大文本到图像扩散模型(如FLUX.1-dev)的努力。在第一阶段,我们使用文本到图像模型的0-ref任务数据对模型进行预训练。社区中有许多基于文本到图像基础模型的后续训练模型,符合第一阶段的这种训练范式。例如,FLUX.1-Fill-dev主要处理绘画任务,并可以用作初始化来加速训练过程。在第二阶段,我们对上述模型进行微调,以使用ACE中定义的所有任务来支持一般指令。为了促进ACE++在不同场景中的广泛应用,我们提供了一套全面的模型,涵盖全量微调和轻量级微调,同时考虑通用性和垂直场景适用性。定性分析展示了ACE++在生成图像质量和遵循提示方面的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
报告了ACE++,一个基于指令的扩散框架,用于处理各种图像生成和编辑任务。受FLUX.1-Fill-dev对补全任务输入格式的启发,改进了ACE中的长上下文条件单元(LCU),并将此输入范式扩展到任何编辑和生成任务。为了充分利用图像生成先验知识,开发了一个两阶段训练方案,以最小化微调强大文本到图像扩散模型(如FLUX.1-dev)的努力。首先使用文本到图像模型的0-ref任务进行模型预训练,然后进行模型微调以支持通用指令集。此外,提供了涵盖全量微调与轻量级微调的综合模型集,考虑了通用应用和垂直场景的应用。ACE++在生成图像质量和遵循提示方面表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- ACE++是一个基于指令的扩散框架,用于处理图像生成和编辑任务。
- 改进了ACE中的长上下文条件单元(LCU),并扩展了输入范式以支持多种任务。
- 开发了一个两阶段训练方案,以利用图像生成先验知识并简化微调过程。
- 预训练阶段使用文本到图像模型的0-ref任务数据。
- FLUX.1-Fill-dev等模型符合第一阶段训练模式,可用于加速训练过程。
- 提供涵盖全量微调与轻量级微调的模型集以适应不同应用场景的需求。
点此查看论文截图

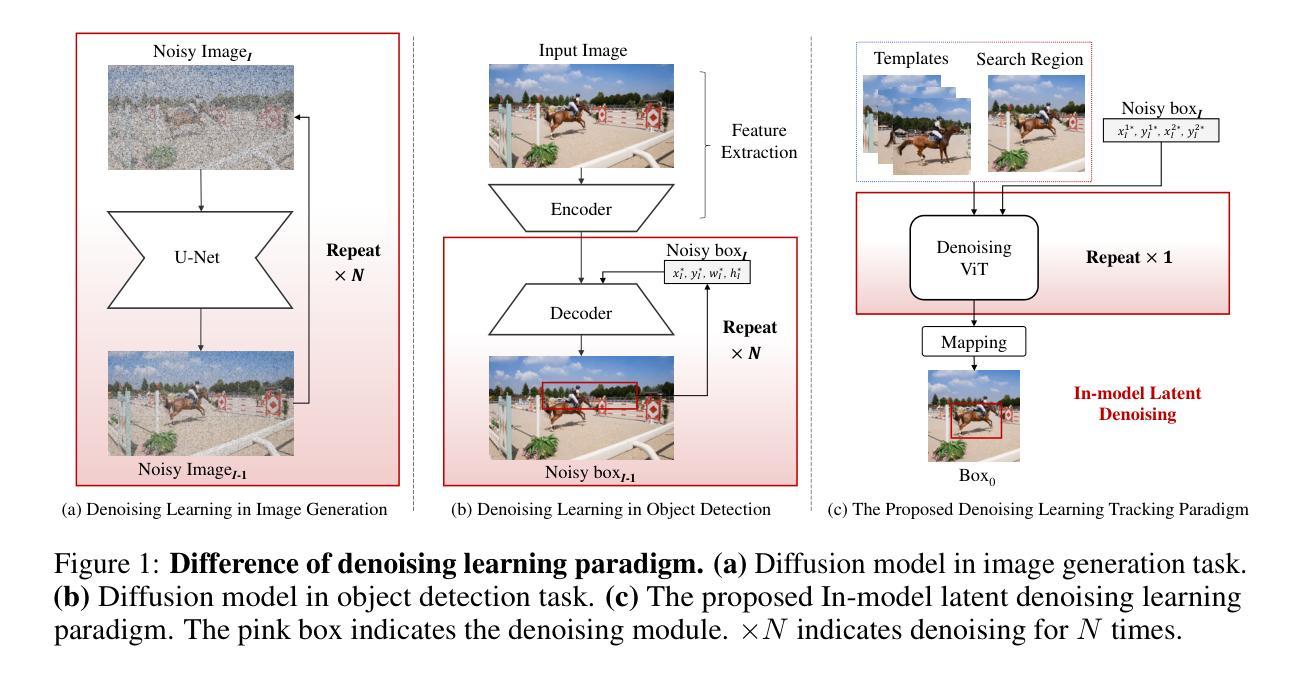
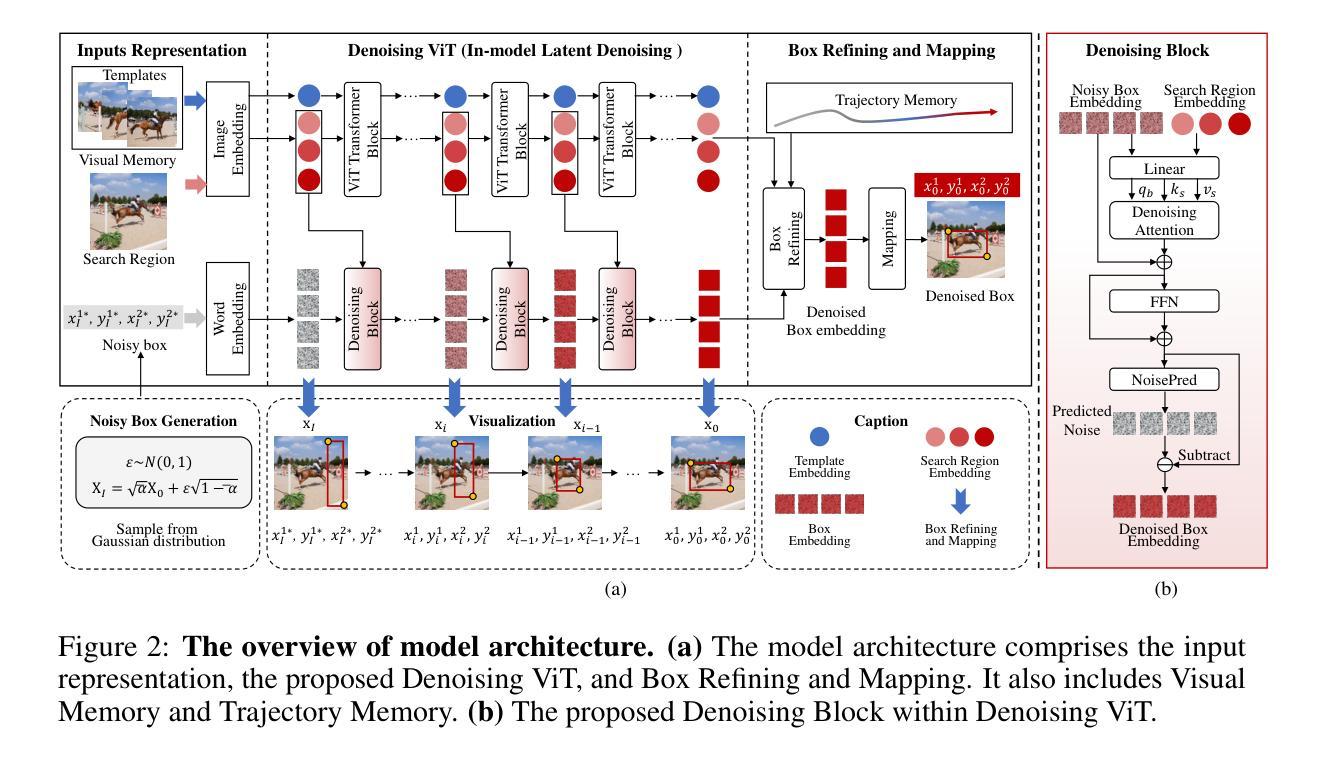
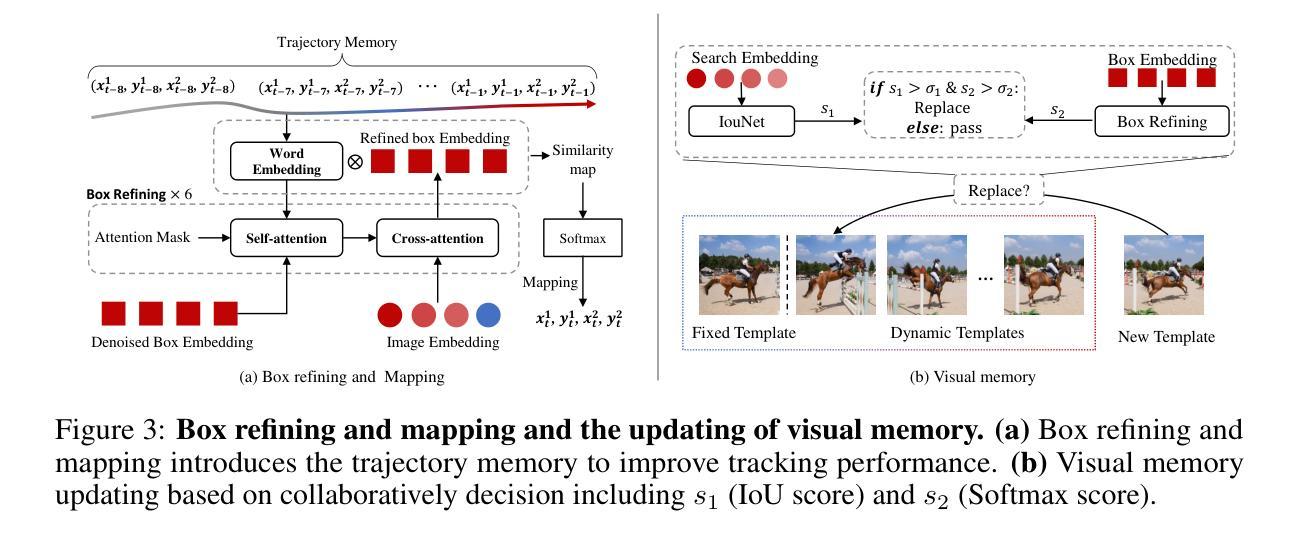
DeTrack: In-model Latent Denoising Learning for Visual Object Tracking
Authors:Xinyu Zhou, Jinglun Li, Lingyi Hong, Kaixun Jiang, Pinxue Guo, Weifeng Ge, Wenqiang Zhang
Previous visual object tracking methods employ image-feature regression models or coordinate autoregression models for bounding box prediction. Image-feature regression methods heavily depend on matching results and do not utilize positional prior, while the autoregressive approach can only be trained using bounding boxes available in the training set, potentially resulting in suboptimal performance during testing with unseen data. Inspired by the diffusion model, denoising learning enhances the model’s robustness to unseen data. Therefore, We introduce noise to bounding boxes, generating noisy boxes for training, thus enhancing model robustness on testing data. We propose a new paradigm to formulate the visual object tracking problem as a denoising learning process. However, tracking algorithms are usually asked to run in real-time, directly applying the diffusion model to object tracking would severely impair tracking speed. Therefore, we decompose the denoising learning process into every denoising block within a model, not by running the model multiple times, and thus we summarize the proposed paradigm as an in-model latent denoising learning process. Specifically, we propose a denoising Vision Transformer (ViT), which is composed of multiple denoising blocks. In the denoising block, template and search embeddings are projected into every denoising block as conditions. A denoising block is responsible for removing the noise in a predicted bounding box, and multiple stacked denoising blocks cooperate to accomplish the whole denoising process. Subsequently, we utilize image features and trajectory information to refine the denoised bounding box. Besides, we also utilize trajectory memory and visual memory to improve tracking stability. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving competitive performance on several challenging datasets.
先前视觉对象跟踪方法采用图像特征回归模型或坐标自回归模型进行边界框预测。图像特征回归方法严重依赖于匹配结果,并不利用位置先验,而自回归方法只能使用训练集中可用的边界框进行训练,在测试未见数据时可能表现不佳。受扩散模型的启发,去噪学习提高了模型对未见数据的鲁棒性。因此,我们向边界框引入噪声,生成用于训练的噪声框,从而提高模型在测试数据上的鲁棒性。我们提出了一种新的范式,将视觉对象跟踪问题表述为一个去噪学习过程。然而,通常要求跟踪算法实时运行,直接将扩散模型应用于对象跟踪会严重损害跟踪速度。因此,我们将去噪学习过程分解为模型内的每个去噪块,而不是多次运行模型,因此我们将所提出的方法概括为模型内的潜在去噪学习过程。具体来说,我们提出了一种去噪视觉转换器(ViT),它由多个去噪块组成。在去噪块中,模板和搜索嵌入被投射到每个去噪块作为条件。去噪块负责去除预测边界框中的噪声,多个堆叠的去噪块协同完成整个去噪过程。然后,我们利用图像特征和轨迹信息来优化去噪后的边界框。此外,我们还利用轨迹记忆和视觉记忆来提高跟踪的稳定性。实验结果验证了我们的方法的有效性,在几个具有挑战性的数据集上实现了具有竞争力的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文提出了一个新的视觉物体跟踪方法,采用扩散模型中的去噪学习来提升模型性能。为提高模型鲁棒性,引入噪声到边界框训练中,并将物体跟踪问题转化为去噪学习过程。为提高跟踪速度,将去噪学习过程分解为模型内的各个去噪块,而非多次运行模型。提出一种去噪视觉转换器(ViT),包含多个去噪块,利用图像特征和轨迹信息优化去噪边界框,同时使用轨迹记忆和视觉记忆提高跟踪稳定性。实验结果表明该方法有效,在多个挑战数据集上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 引入扩散模型的去噪学习提升视觉物体跟踪模型的性能。
- 通过在训练中引入噪声提高模型对未见数据的鲁棒性。
- 将视觉物体跟踪问题转化为去噪学习过程。
- 为提高跟踪速度,将去噪学习过程分解为模型内的各个去噪块。
- 提出一种去噪视觉转换器(ViT),包含多个去噪块。
- 利用图像特征和轨迹信息优化去噪边界框。
点此查看论文截图

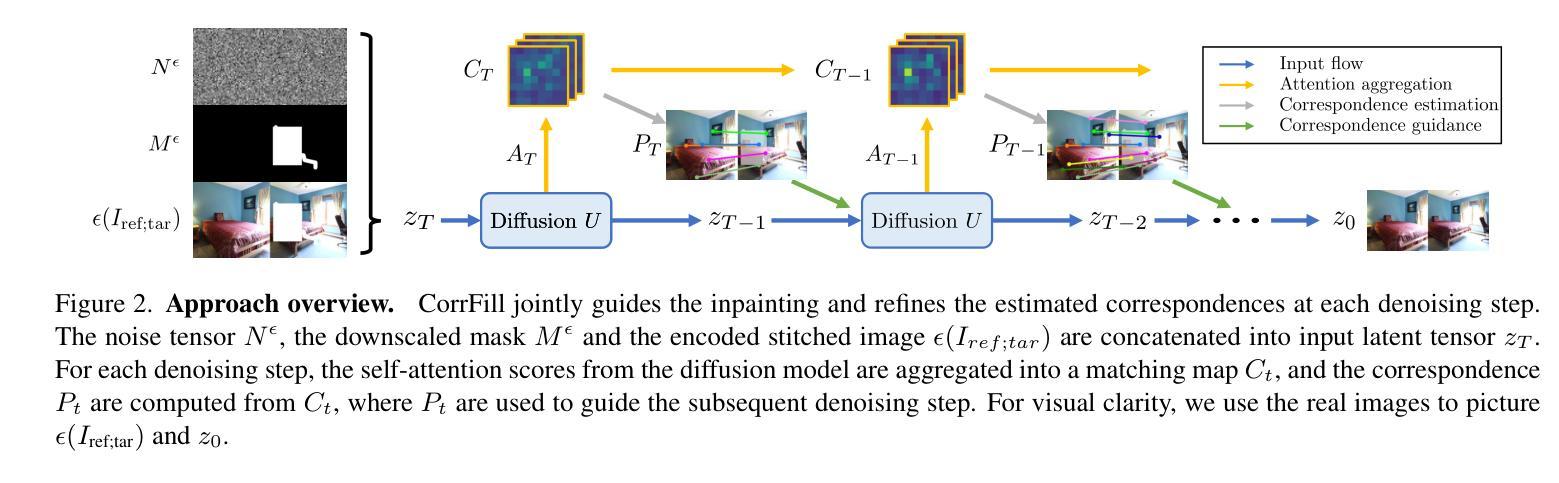
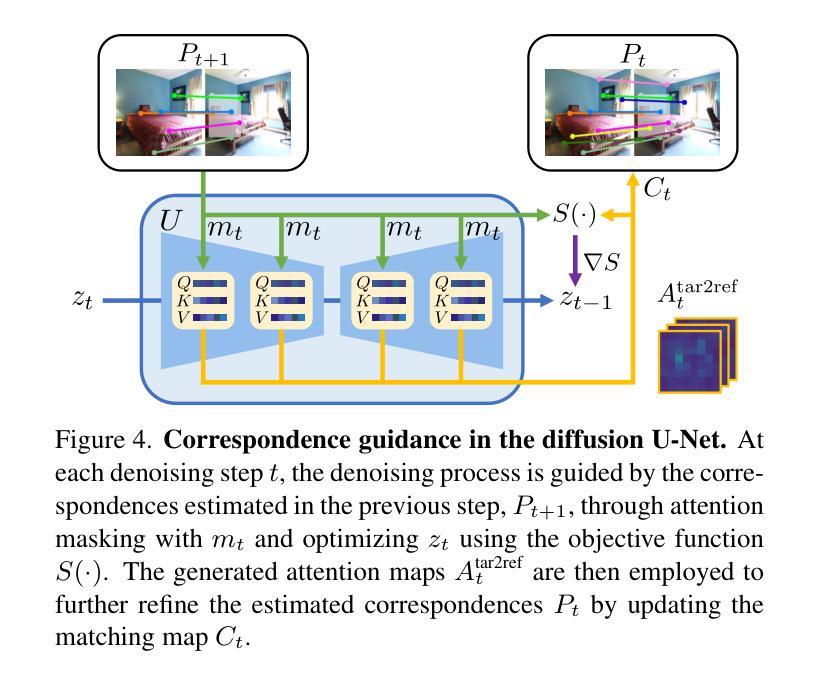
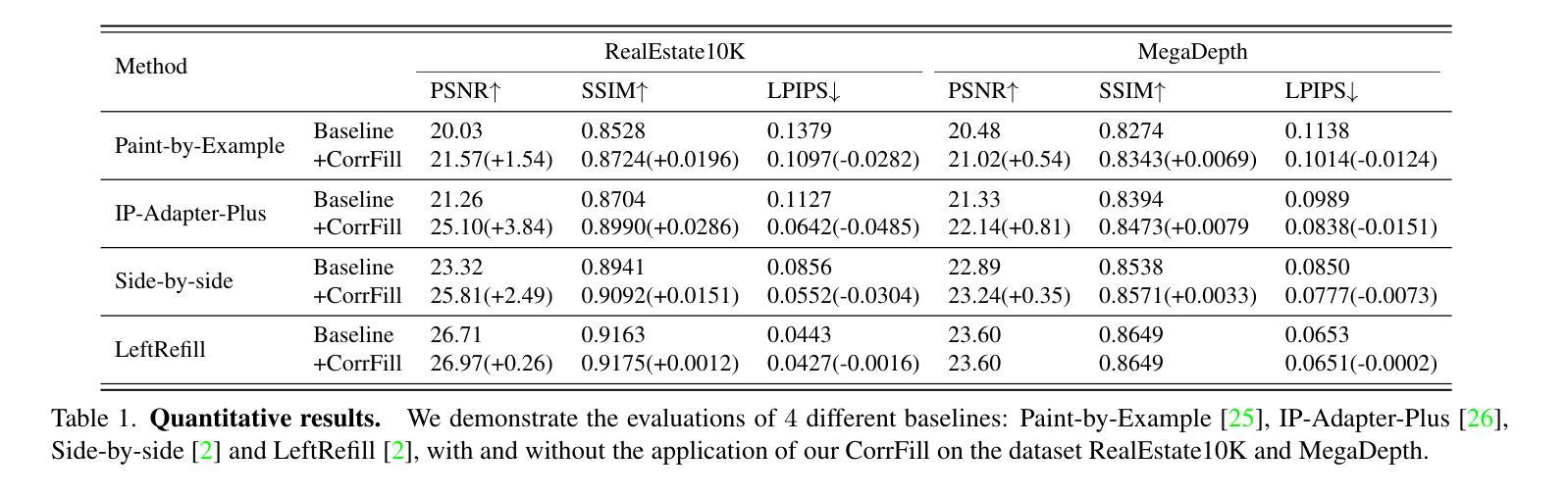
CorrFill: Enhancing Faithfulness in Reference-based Inpainting with Correspondence Guidance in Diffusion Models
Authors:Kuan-Hung Liu, Cheng-Kun Yang, Min-Hung Chen, Yu-Lun Liu, Yen-Yu Lin
In the task of reference-based image inpainting, an additional reference image is provided to restore a damaged target image to its original state. The advancement of diffusion models, particularly Stable Diffusion, allows for simple formulations in this task. However, existing diffusion-based methods often lack explicit constraints on the correlation between the reference and damaged images, resulting in lower faithfulness to the reference images in the inpainting results. In this work, we propose CorrFill, a training-free module designed to enhance the awareness of geometric correlations between the reference and target images. This enhancement is achieved by guiding the inpainting process with correspondence constraints estimated during inpainting, utilizing attention masking in self-attention layers and an objective function to update the input tensor according to the constraints. Experimental results demonstrate that CorrFill significantly enhances the performance of multiple baseline diffusion-based methods, including state-of-the-art approaches, by emphasizing faithfulness to the reference images.
在基于参考的图像修复任务中,提供额外的参考图像以将损坏的目标图像恢复到其原始状态。扩散模型的进步,特别是Stable Diffusion,为此任务提供了简单的公式。然而,现有的基于扩散的方法在参考图像和受损图像之间的相关性上往往缺乏明确的约束,导致修复结果对参考图像的忠实度较低。在这项工作中,我们提出了CorrFill,这是一个无需训练的设计模块,旨在增强参考图像和目标图像之间几何关系的意识。这种增强是通过在修复过程中使用在修复过程中估计的对应约束来实现的,利用自注意力层中的注意力掩码和客观函数来根据约束更新输入张量。实验结果表明,CorrFill通过强调对参考图像的忠实度,显著提高了多种基线扩散方法的性能,包括最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WACV 2025. Project page: https://corrfill.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了基于参考图像的修复任务中,利用扩散模型尤其是Stable Diffusion的进步简化了任务。然而现有扩散方法缺乏参考图像与受损图像间关联的显式约束,导致修复结果对参考图像的忠实度较低。本研究提出一种无需训练的模块CorrFill,通过估计修复过程中的对应约束来增强两者之间的几何关联,利用自注意力层的注意力掩码和客观函数来更新输入张量以适应这些约束。实验结果显示,CorrFill能显著提高多种基线扩散方法的性能,包括最先进的方法,重点提高结果对参考图像的忠实度。
Key Takeaways
- 参考图像修复任务中引入了扩散模型,特别是Stable Diffusion,简化了任务流程。
- 现有扩散方法缺乏对参考与受损图像间关联的显式约束。
- CorrFill是一种无需训练的模块,旨在增强参考图像和目标图像之间的几何关联。
- CorrFill通过估计修复过程中的对应约束来指导修复过程。
- 利用自注意力层的注意力掩码实现CorrFill的增强功能。
- 通过客观函数更新输入张量以适应对应约束。
点此查看论文截图


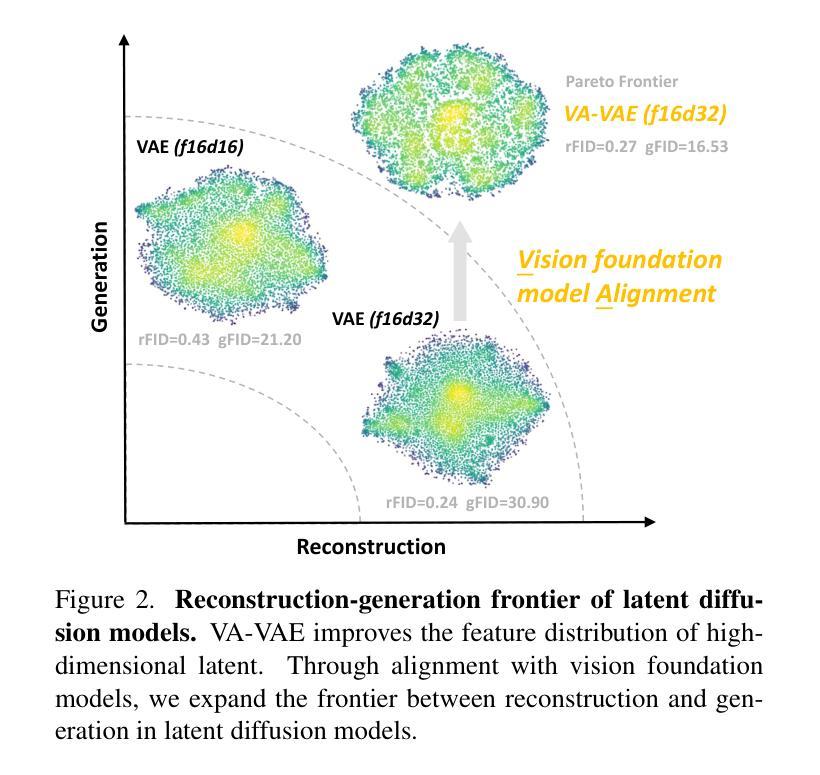
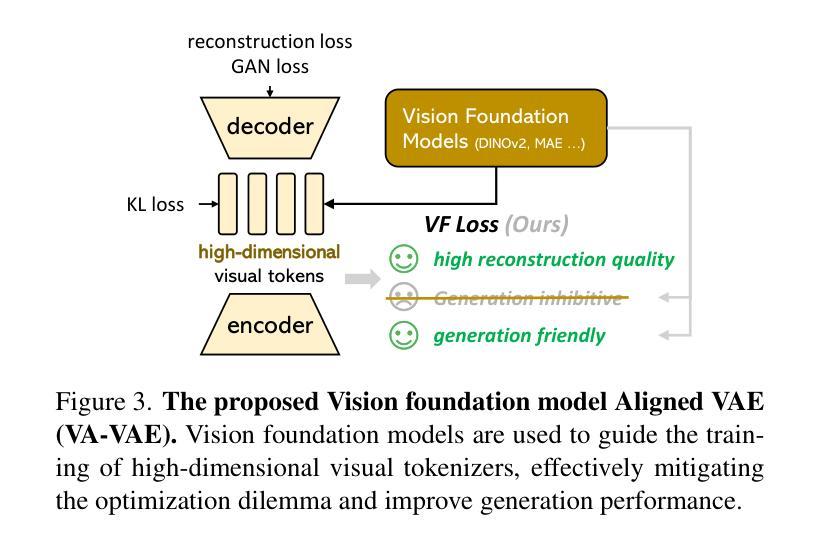
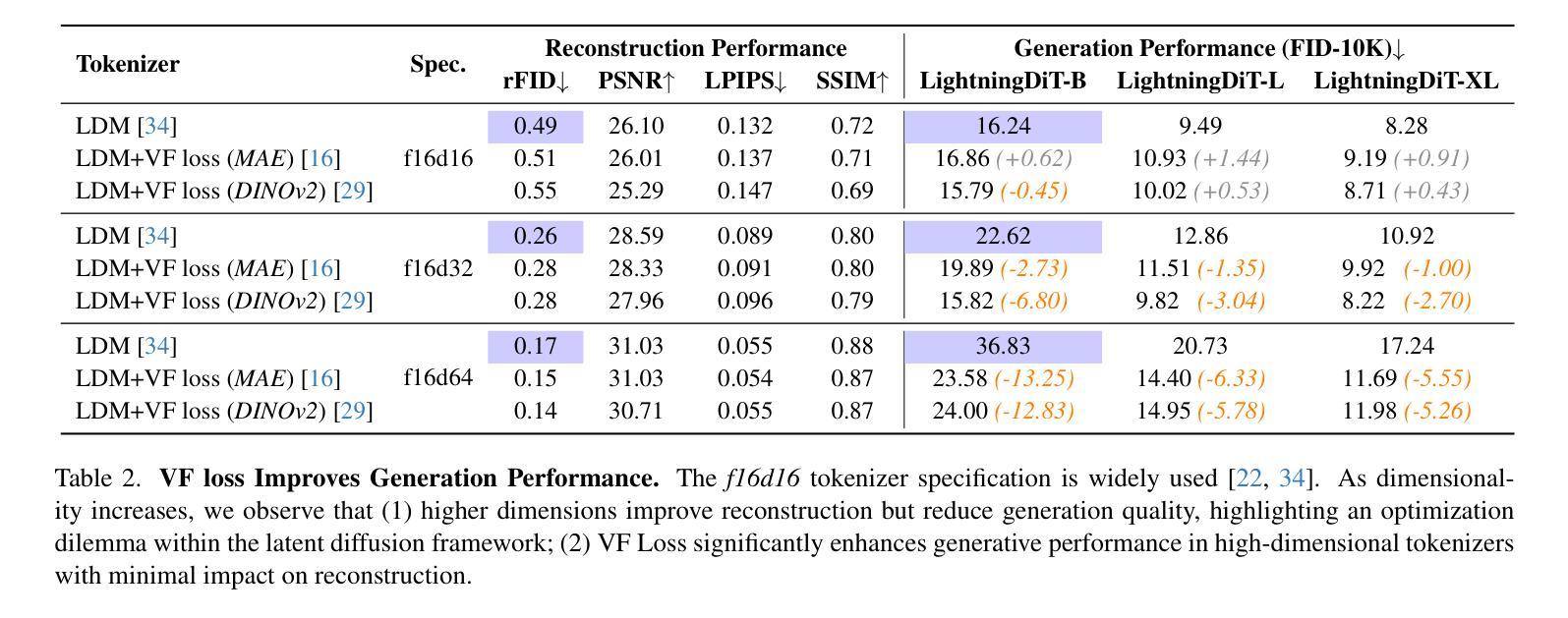
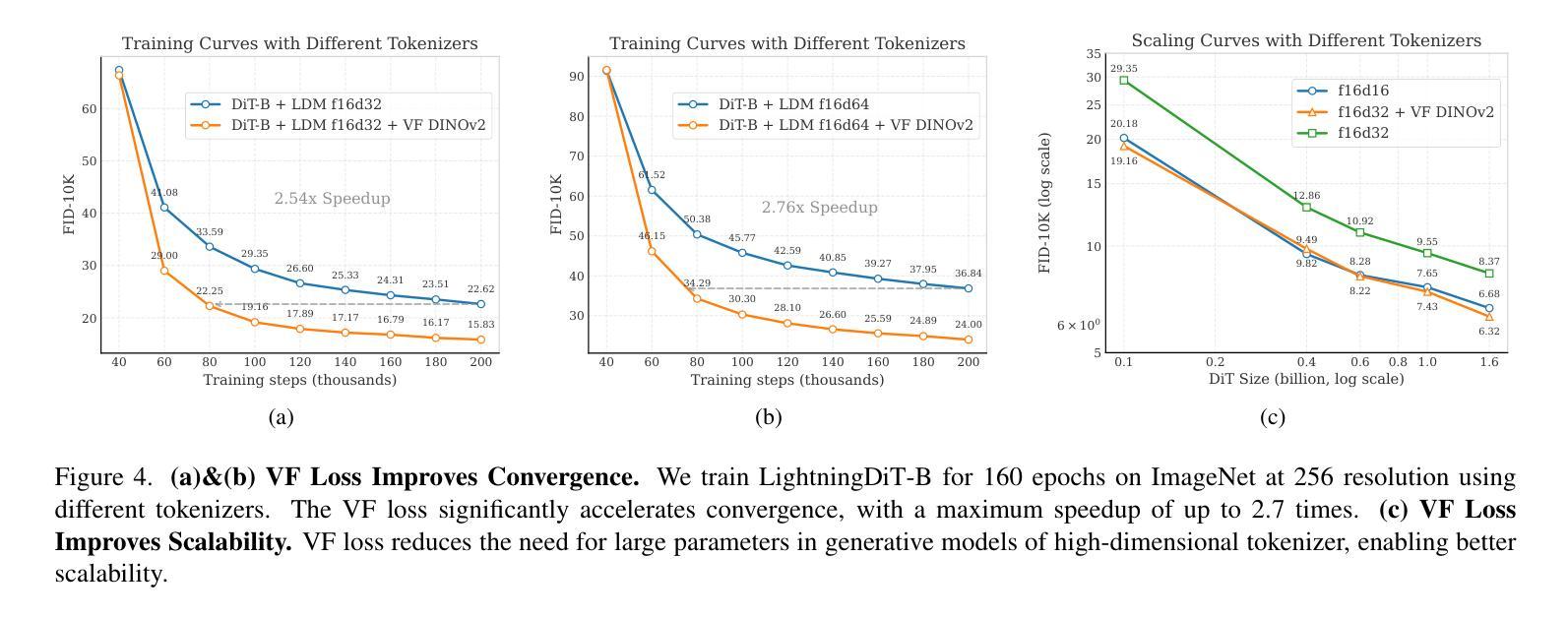
Reconstruction vs. Generation: Taming Optimization Dilemma in Latent Diffusion Models
Authors:Jingfeng Yao, Xinggang Wang
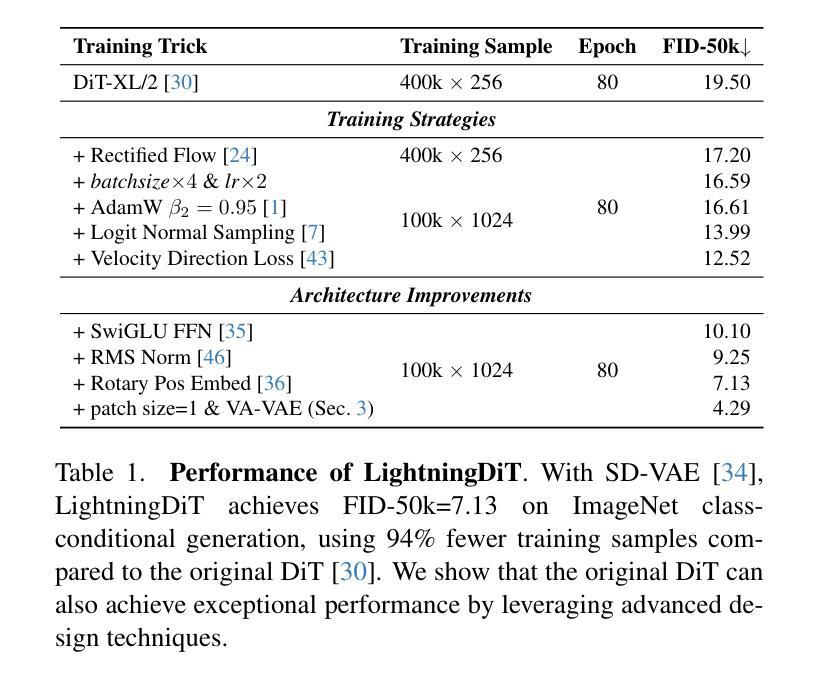
Latent diffusion models with Transformer architectures excel at generating high-fidelity images. However, recent studies reveal an optimization dilemma in this two-stage design: while increasing the per-token feature dimension in visual tokenizers improves reconstruction quality, it requires substantially larger diffusion models and more training iterations to achieve comparable generation performance. Consequently, existing systems often settle for sub-optimal solutions, either producing visual artifacts due to information loss within tokenizers or failing to converge fully due to expensive computation costs. We argue that this dilemma stems from the inherent difficulty in learning unconstrained high-dimensional latent spaces. To address this, we propose aligning the latent space with pre-trained vision foundation models when training the visual tokenizers. Our proposed VA-VAE (Vision foundation model Aligned Variational AutoEncoder) significantly expands the reconstruction-generation frontier of latent diffusion models, enabling faster convergence of Diffusion Transformers (DiT) in high-dimensional latent spaces. To exploit the full potential of VA-VAE, we build an enhanced DiT baseline with improved training strategies and architecture designs, termed LightningDiT. The integrated system achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on ImageNet 256x256 generation with an FID score of 1.35 while demonstrating remarkable training efficiency by reaching an FID score of 2.11 in just 64 epochs–representing an over 21 times convergence speedup compared to the original DiT. Models and codes are available at: https://github.com/hustvl/LightningDiT.
基于Transformer架构的潜在扩散模型在生成高保真图像方面表现出色。然而,最近的研究揭示了这种两阶段设计中的优化困境:虽然增加视觉标记器中的每令牌特征维度提高了重建质量,但要实现相当的生成性能,需要大量的扩散模型以及更多的训练迭代次数。因此,现有系统通常选择次优解决方案,要么由于标记器中的信息丢失而产生视觉伪影,要么由于计算成本高昂而无法完全收敛。我们认为,这种困境源于学习无约束的高维潜在空间的固有难度。针对这一问题,我们提出在训练视觉标记器时,将其潜在空间与预训练的视觉基础模型进行对齐。我们提出的VA-VAE(视觉基础模型对齐变分自编码器)显著扩展了潜在扩散模型的重建-生成边界,使扩散Transformer(DiT)在高维潜在空间中更快收敛。为了充分发挥VA-VAE的潜力,我们采用改进的训练策略和架构设计,建立了一个增强的DiT基线,称为LightningDiT。集成系统在ImageNet 256x256生成任务上实现了最新性能,FID得分为1.35,同时显示出显著的训练效率,仅在64个周期内就达到了2.11的FID得分,与原始DiT相比,实现了超过21倍的收敛速度提升。模型和代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/hustvl/LightningDiT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Models and codes are available at: https://github.com/hustvl/LightningDiT
Summary
本文介绍了基于Transformer架构的潜在扩散模型在高保真图像生成方面的优势。研究揭示了该模型的两阶段设计中的优化困境:提高视觉标记器中的每令牌特征维度可提高重建质量,但需要更大的扩散模型和更多的训练迭代来达到相当的生成性能。为此,提出了与预训练视觉基础模型对齐训练视觉标记器的方法,并推出了VA-VAE(与视觉基础模型对齐的变分自动编码器)。这显著扩展了潜在扩散模型的重建-生成边界,使扩散Transformer(DiT)在高维潜在空间中更快收敛。配合增强的DiT基线(LightningDiT),在ImageNet 256x256生成方面达到最新性能,FID得分为1.35,并在仅64个周期内达到2.11的FID得分,实现了超过21倍的收敛速度提升。
Key Takeaways
- 潜在扩散模型可生成高保真图像,但存在优化困境:提高视觉标记器中的每令牌特征维度会提高重建质量,但增加扩散模型大小和训练迭代次数。
- 现有解决方案常产生视觉伪影或计算成本高昂,无法完全收敛。
- 问题的根源在于学习无约束的高维潜在空间的内在困难。
- 提出VA-VAE(与视觉基础模型对齐的变分自动编码器)来解决此问题,显著扩展了潜在扩散模型的重建-生成边界。
- VA-VAE配合增强DiT(LightningDiT)实现快速收敛,在ImageNet 256x256生成方面达到最新性能。
- LightningDiT在ImageNet上实现了FID 1.35的优异成绩,并在仅64个周期内达到FID 2.11,相比原始DiT有显著的训练效率提升。
点此查看论文截图

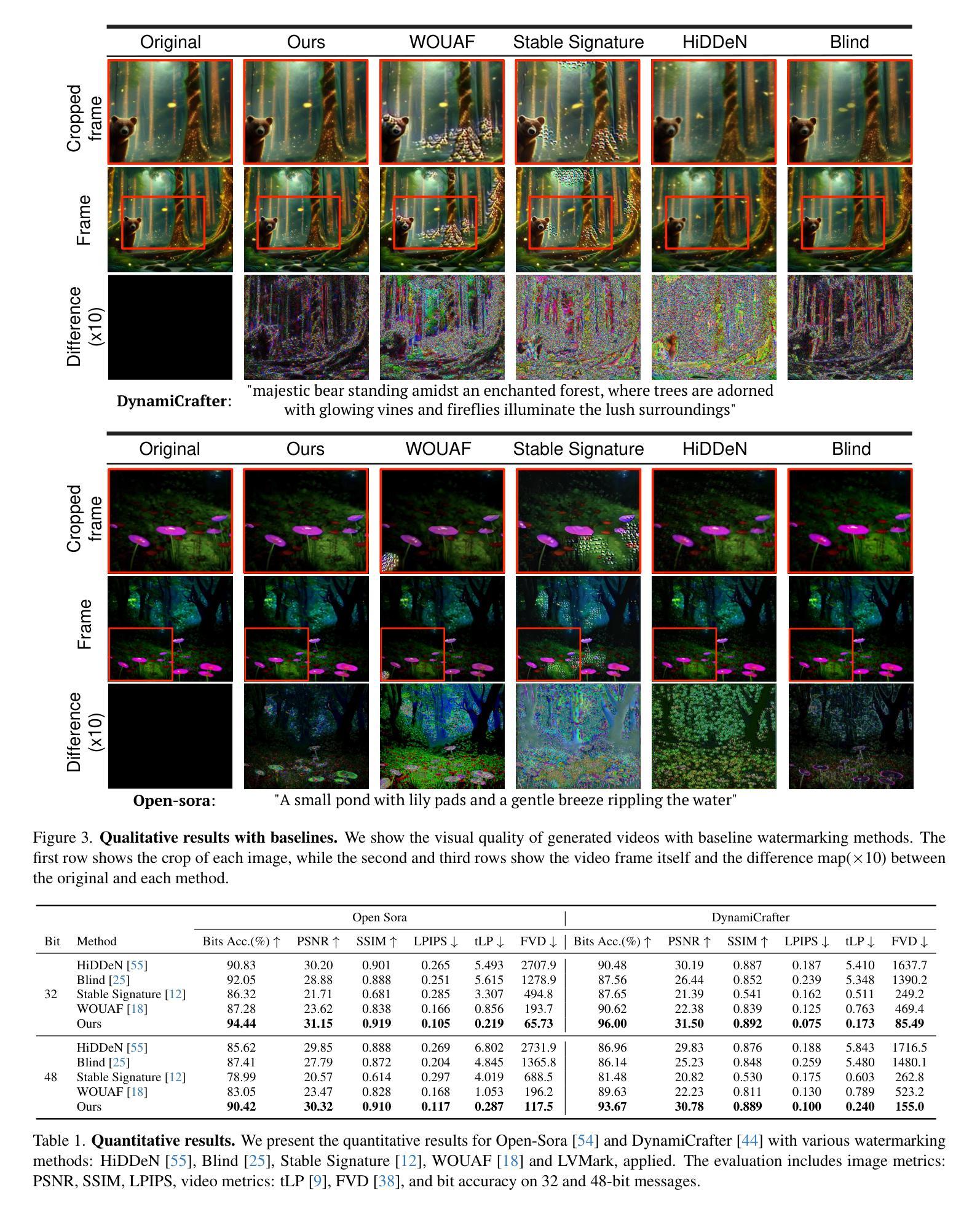
LVMark: Robust Watermark for latent video diffusion models
Authors:MinHyuk Jang, Youngdong Jang, JaeHyeok Lee, Kodai Kawamura, Feng Yang, Sangpil Kim
Rapid advancements in generative models have made it possible to create hyper-realistic videos. As their applicability increases, their unauthorized use has raised significant concerns, leading to the growing demand for techniques to protect the ownership of the generative model itself. While existing watermarking methods effectively embed watermarks into image-generative models, they fail to account for temporal information, resulting in poor performance when applied to video-generative models. To address this issue, we introduce a novel watermarking method called LVMark, which embeds watermarks into video diffusion models. A key component of LVMark is a selective weight modulation strategy that efficiently embeds watermark messages into the video diffusion model while preserving the quality of the generated videos. To accurately decode messages in the presence of malicious attacks, we design a watermark decoder that leverages spatio-temporal information in the 3D wavelet domain through a cross-attention module. To the best of our knowledge, our approach is the first to highlight the potential of video-generative model watermarking as a valuable tool for enhancing the effectiveness of ownership protection in video-generative models.
生成模型的快速发展使得创建超现实视频成为可能。随着其适用性的增强,未经授权的广泛使用引发了重大担忧,因此对保护生成模型本身所有权的技术需求不断增长。虽然现有的水印方法能够有效地将水印嵌入图像生成模型中,但它们无法考虑时间信息,当应用于视频生成模型时,表现不佳。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型水印方法——LVMark,该方法将水印嵌入视频扩散模型中。LVMark的关键组成部分是选择性权重调制策略,该策略能够高效地将水印信息嵌入视频扩散模型中,同时保持生成视频的质量。为了准确解码恶意攻击中的信息,我们设计了一种水印解码器,它利用三维小波域中的时空信息,通过交叉注意模块实现。据我们所知,我们的方法是第一个强调视频生成模型水印在增强视频生成模型所有权保护方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代生成模型技术迅速崛起,能够在视频领域生成超逼真的内容。随着其应用的广泛,未经授权的使用引发了人们对保护生成模型所有权的强烈需求。现有的水印方法虽然能嵌入图像生成模型中,但无法处理视频中的时间信息,因此在视频生成模型中的应用表现不佳。为解决这一问题,我们推出了一种名为LVMark的新型水印方法,它能选择性地嵌入视频扩散模型中。该方法的关键在于选择性权重调制策略,能够在保证视频质量的同时高效嵌入水印信息。同时,我们还设计了一种水印解码器,通过利用三维小波域中的时空信息以及交叉注意力模块,来抵御恶意攻击并准确解码信息。我们的方法开辟了视频生成模型水印技术的新可能,提高了保护视频生成模型所有权的效率。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型技术迅速发展,带来高度逼真的视频内容创作能力。
- 未经授权的生成模型使用引发所有权保护需求。
- 现有水印方法无法有效处理视频中的时间信息。
- LVMark方法通过选择性权重调制策略嵌入水印信息。
- LVMark能够保护视频生成模型的所有权。
- 设计的水印解码器利用时空信息及交叉注意力模块应对恶意攻击。
点此查看论文截图


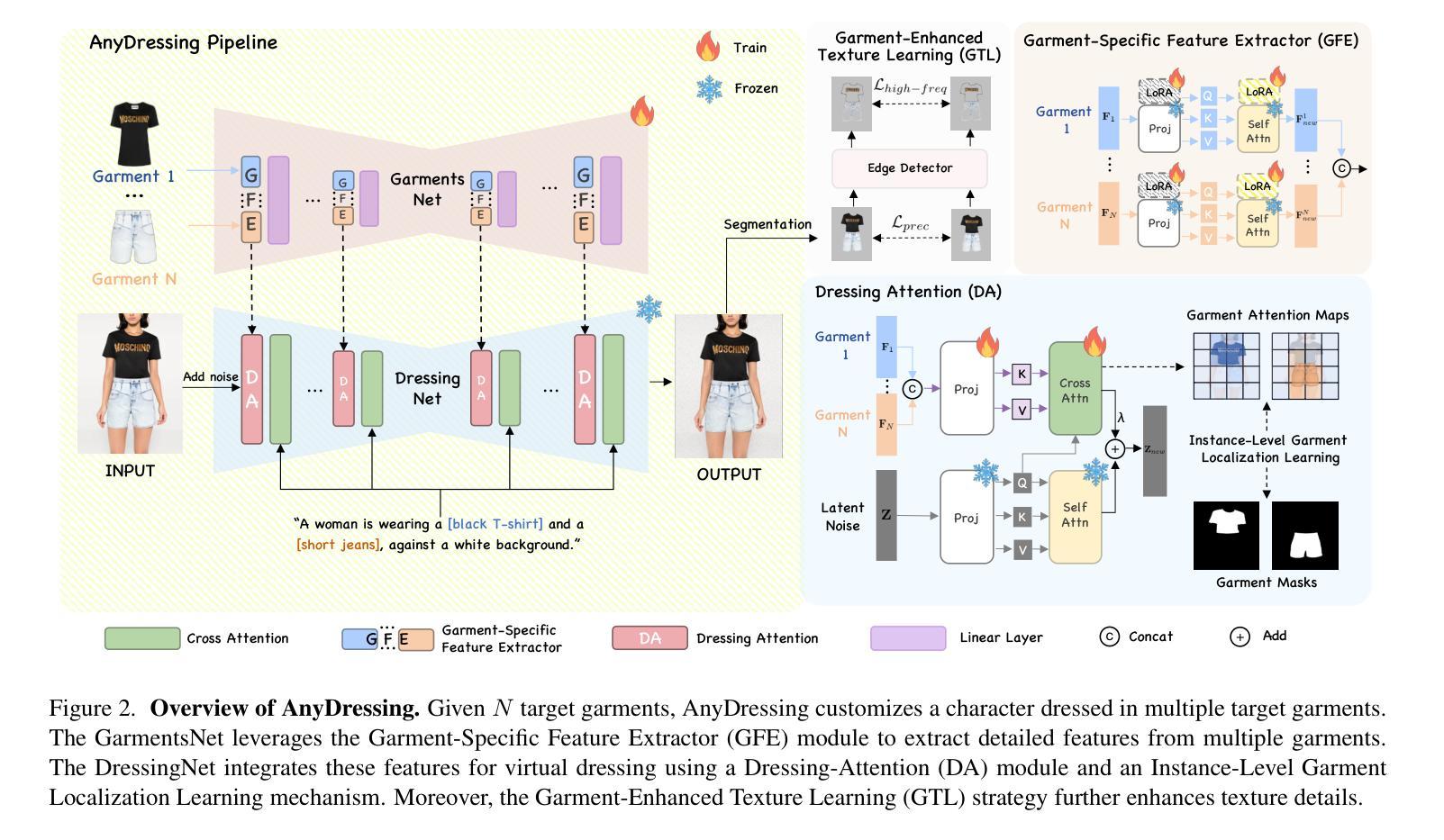
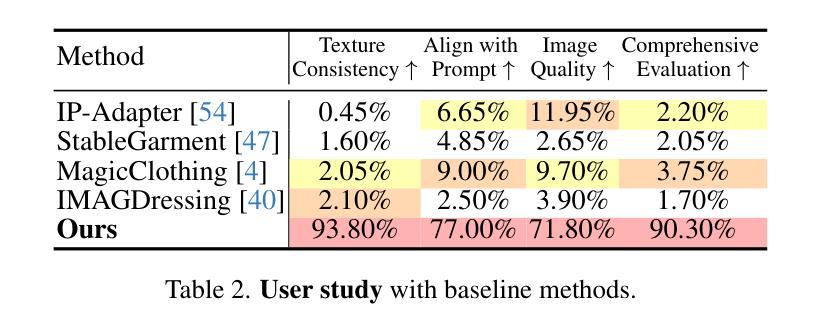
AnyDressing: Customizable Multi-Garment Virtual Dressing via Latent Diffusion Models
Authors:Xinghui Li, Qichao Sun, Pengze Zhang, Fulong Ye, Zhichao Liao, Wanquan Feng, Songtao Zhao, Qian He
Recent advances in garment-centric image generation from text and image prompts based on diffusion models are impressive. However, existing methods lack support for various combinations of attire, and struggle to preserve the garment details while maintaining faithfulness to the text prompts, limiting their performance across diverse scenarios. In this paper, we focus on a new task, i.e., Multi-Garment Virtual Dressing, and we propose a novel AnyDressing method for customizing characters conditioned on any combination of garments and any personalized text prompts. AnyDressing comprises two primary networks named GarmentsNet and DressingNet, which are respectively dedicated to extracting detailed clothing features and generating customized images. Specifically, we propose an efficient and scalable module called Garment-Specific Feature Extractor in GarmentsNet to individually encode garment textures in parallel. This design prevents garment confusion while ensuring network efficiency. Meanwhile, we design an adaptive Dressing-Attention mechanism and a novel Instance-Level Garment Localization Learning strategy in DressingNet to accurately inject multi-garment features into their corresponding regions. This approach efficiently integrates multi-garment texture cues into generated images and further enhances text-image consistency. Additionally, we introduce a Garment-Enhanced Texture Learning strategy to improve the fine-grained texture details of garments. Thanks to our well-craft design, AnyDressing can serve as a plug-in module to easily integrate with any community control extensions for diffusion models, improving the diversity and controllability of synthesized images. Extensive experiments show that AnyDressing achieves state-of-the-art results.
基于扩散模型的文本和图像提示的服装中心图像生成方面的最新进展令人印象深刻。然而,现有方法不支持多种服装组合,并且在保持对文本提示的忠实度的同时,难以保留服装细节,这在多种场景中限制了它们的性能。在本文中,我们专注于一个新的任务,即多服装虚拟换装,并提出了一种新的AnyDressing方法,用于根据任何服装组合和任何个性化文本提示进行角色定制。AnyDressing主要包括两个网络,即GarmentsNet和DressingNet,它们分别专注于提取详细的服装特征和生成定制图像。具体来说,我们在GarmentsNet中提出了一个高效且可扩展的模块,称为服装特定特征提取器,以并行方式单独编码服装纹理。这种设计可以防止服装混淆,同时确保网络效率。同时,我们在DressingNet中设计了一种自适应的着装注意力机制和一种新颖的实例级服装定位学习策略,以准确地将多服装特征注入其相应区域。这种方法有效地将多服装纹理线索融入生成的图像中,并进一步增强了文本-图像的一致性。此外,我们还引入了一种服装增强纹理学习策略,以提高服装的细粒度纹理细节。由于我们精心设计,AnyDressing可以作为一个插件模块轻松集成到任何扩散模型的社区控制扩展中,提高合成图像的多样性和可控性。大量实验表明,AnyDressing达到了最先进的成果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://crayon-shinchan.github.io/AnyDressing/
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散模型的衣物导向图像生成技术的新进展。针对现有方法缺乏对不同衣物组合的支持以及在保持衣物细节和忠实于文本提示方面的挑战,提出了一种新的方法AnyDressing。AnyDressing包含两个主要网络:GarmentsNet和DressingNet,分别用于提取衣物详细特征和生成定制图像。通过采用高效的Garment-Specific Feature Extractor和创新的Dressing-Attention机制等技术,AnyDressing能够在生成图像中准确融入多衣物纹理,并提升文本与图像的契合度。此外,AnyDressing还可作为插件模块轻松集成到任何扩散模型的社区控制扩展中,提高了生成图像的多样性和可控性。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了基于扩散模型的衣物导向图像生成的新进展。
- 现有方法在面对不同衣物组合及保持衣物细节和文本提示忠实度方面存在挑战。
- AnyDressing方法包含GarmentsNet和DressingNet两个主要网络,分别用于提取衣物特征和生成定制图像。
- AnyDressing采用了高效的Garment-Specific Feature Extractor来并行编码衣物纹理,防止衣物混淆并保证网络效率。
- 创新的Dressing-Attention机制和Instance-Level Garment Localization Learning策略用于准确将多衣物特征注入对应区域,并提升文本与图像的契合度。
- 引入Garment-Enhanced Texture Learning策略,以提高衣物的精细纹理细节。
- AnyDressing可作为插件模块集成到扩散模型中,提高了生成图像的多样性和可控性。
点此查看论文截图

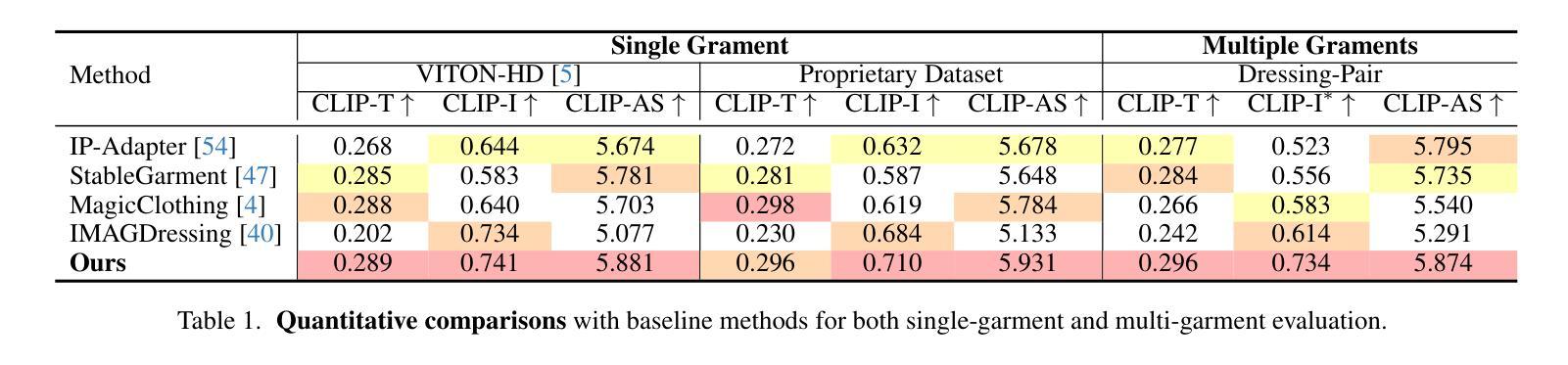
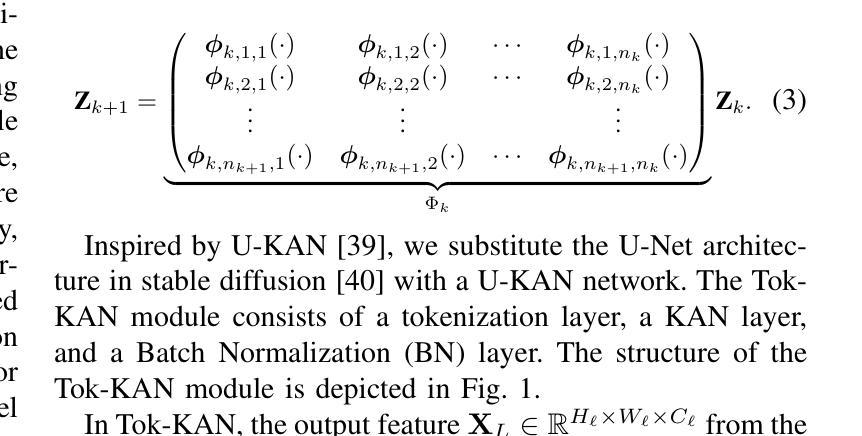
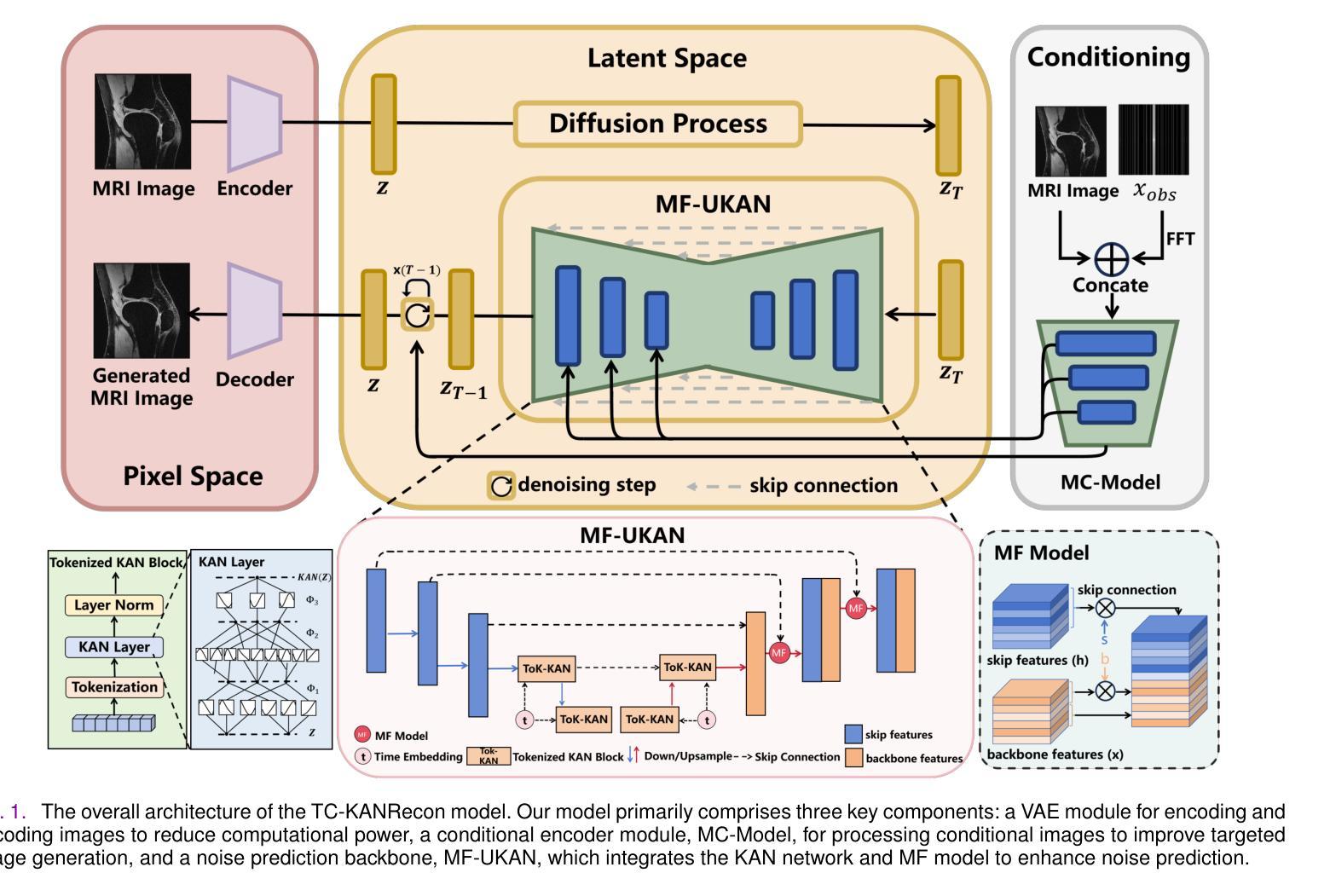
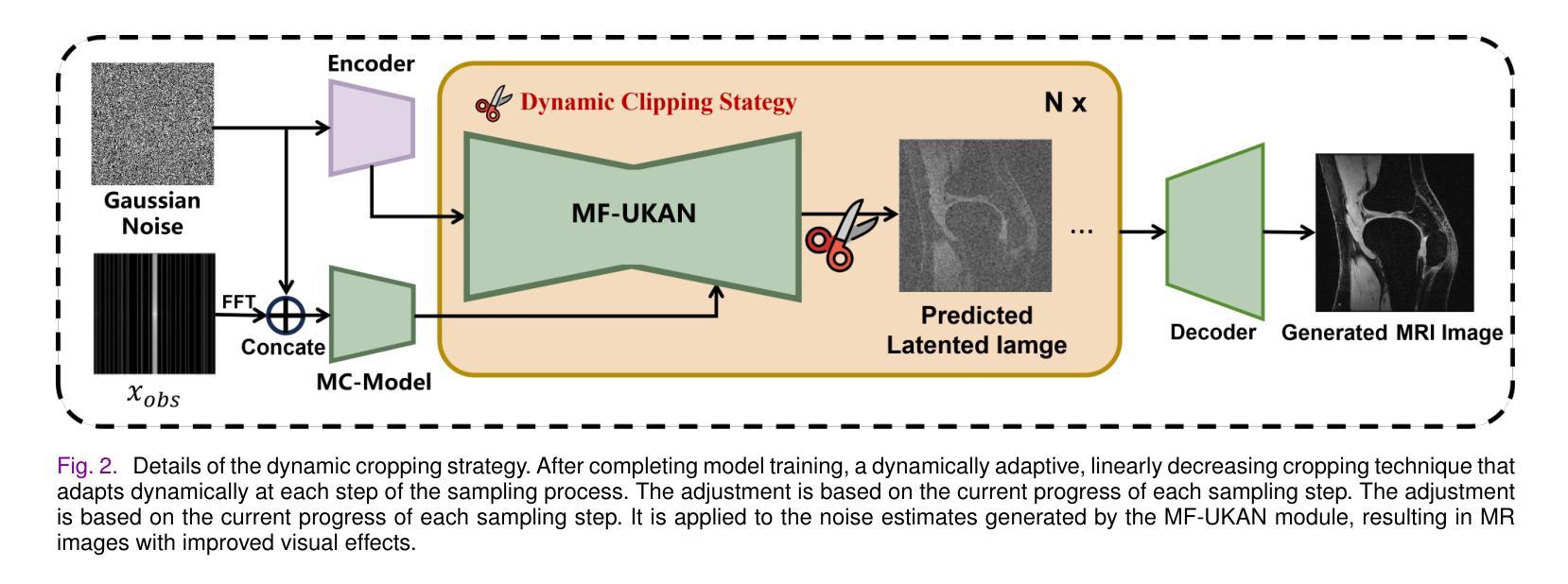
TC-KANRecon: High-Quality and Accelerated MRI Reconstruction via Adaptive KAN Mechanisms and Intelligent Feature Scaling
Authors:Ruiquan Ge, Xiao Yu, Yifei Chen, Guanyu Zhou, Fan Jia, Shenghao Zhu, Junhao Jia, Chenyan Zhang, Yifei Sun, Dong Zeng, Changmiao Wang, Qiegen Liu, Shanzhou Niu
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has become essential in clinical diagnosis due to its high resolution and multiple contrast mechanisms. However, the relatively long acquisition time limits its broader application. To address this issue, this study presents an innovative conditional guided diffusion model, named as TC-KANRecon, which incorporates the Multi-Free U-KAN (MF-UKAN) module and a dynamic clipping strategy. TC-KANRecon model aims to accelerate the MRI reconstruction process through deep learning methods while maintaining the quality of the reconstructed images. The MF-UKAN module can effectively balance the tradeoff between image denoising and structure preservation. Specifically, it presents the multi-head attention mechanisms and scalar modulation factors, which significantly enhances the model’s robustness and structure preservation capabilities in complex noise environments. Moreover, the dynamic clipping strategy in TC-KANRecon adjusts the cropping interval according to the sampling steps, thereby mitigating image detail loss typicalching the visual features of the images. Furthermore, the MC-Model incorporates full-sampling k-space information, realizing efficient fusion of conditional information, enhancing the model’s ability to process complex data, and improving the realism and detail richness of reconstructed images. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms other MRI reconstruction methods in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. Notably, TC-KANRecon method exhibits excellent reconstruction results when processing high-noise, low-sampling-rate MRI data. Our source code is available at https://github.com/lcbkmm/TC-KANRecon.
磁共振成像(MRI)因其高分辨率和多种对比机制在临床诊断中变得至关重要。然而,相对较长的采集时间限制了其更广泛的应用。为解决这一问题,本研究提出了一种创新的有条件引导扩散模型,名为TC-KANRecon。它结合了多自由度U-KAN(MF-UKAN)模块和动态裁剪策略。TC-KANRecon模型旨在通过深度学习方法加速MRI重建过程,同时保持重建图像的质量。MF-UKAN模块可以有效地平衡图像去噪和结构保持之间的权衡。具体来说,它引入了多头注意机制和标量调制因子,这显著增强了模型在复杂噪声环境中的稳健性和结构保持能力。此外,TC-KANRecon中的动态裁剪策略根据采样步骤调整裁剪间隔,从而减轻图像细节损失,保留图像视觉特征。此外,MC模型结合了全采样k空间信息,实现了条件信息的有效融合,提高了模型处理复杂数据的能力,提高了重建图像的逼真度和细节丰富度。实验结果表明,所提出的方法在定性和定量评估方面都优于其他MRI重建方法。值得注意的是,TC-KANRecon方法在处理高噪声、低采样率的MRI数据时表现出优异的重建效果。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/lcbkmm/TC-KANRecon上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures
Summary
该研究提出了一种名为TC-KANRecon的条件引导扩散模型,用于加速MRI重建过程。该模型结合了Multi-Free U-KAN模块和动态裁剪策略,旨在通过深度学习方法提高MRI图像重建的速度和质量。TC-KANRecon在复杂噪声环境中具有出色的鲁棒性和结构保持能力,并能有效平衡图像去噪和结构保持之间的权衡。此外,该模型的动态裁剪策略可根据采样步骤调整裁剪间隔,减少图像细节损失。实验结果表明,该方法在定性和定量评估上都优于其他MRI重建方法,尤其适用于处理高噪声、低采样率的MRI数据。
Key Takeaways
- TC-KANRecon是一种基于深度学习的条件引导扩散模型,旨在加速MRI图像重建过程。
- 该模型结合了Multi-Free U-KAN模块,具有出色的鲁棒性和结构保持能力,能在复杂噪声环境中有效平衡图像去噪和结构保持之间的权衡。
- TC-KANRecon采用动态裁剪策略,可根据采样步骤调整裁剪间隔,减少图像细节损失。
- 实验结果表明,TC-KANRecon在MRI图像重建方面优于其他方法,特别是在处理高噪声、低采样率的MRI数据时表现优异。
- TC-KANRecon模型实现了全采样k-空间信息的融合,提高了模型处理复杂数据的能力,增强了重建图像的真实感和细节丰富度。
- 模型的源代码已公开发布在指定GitHub仓库,方便研究者和医生等人员获取和使用。
点此查看论文截图

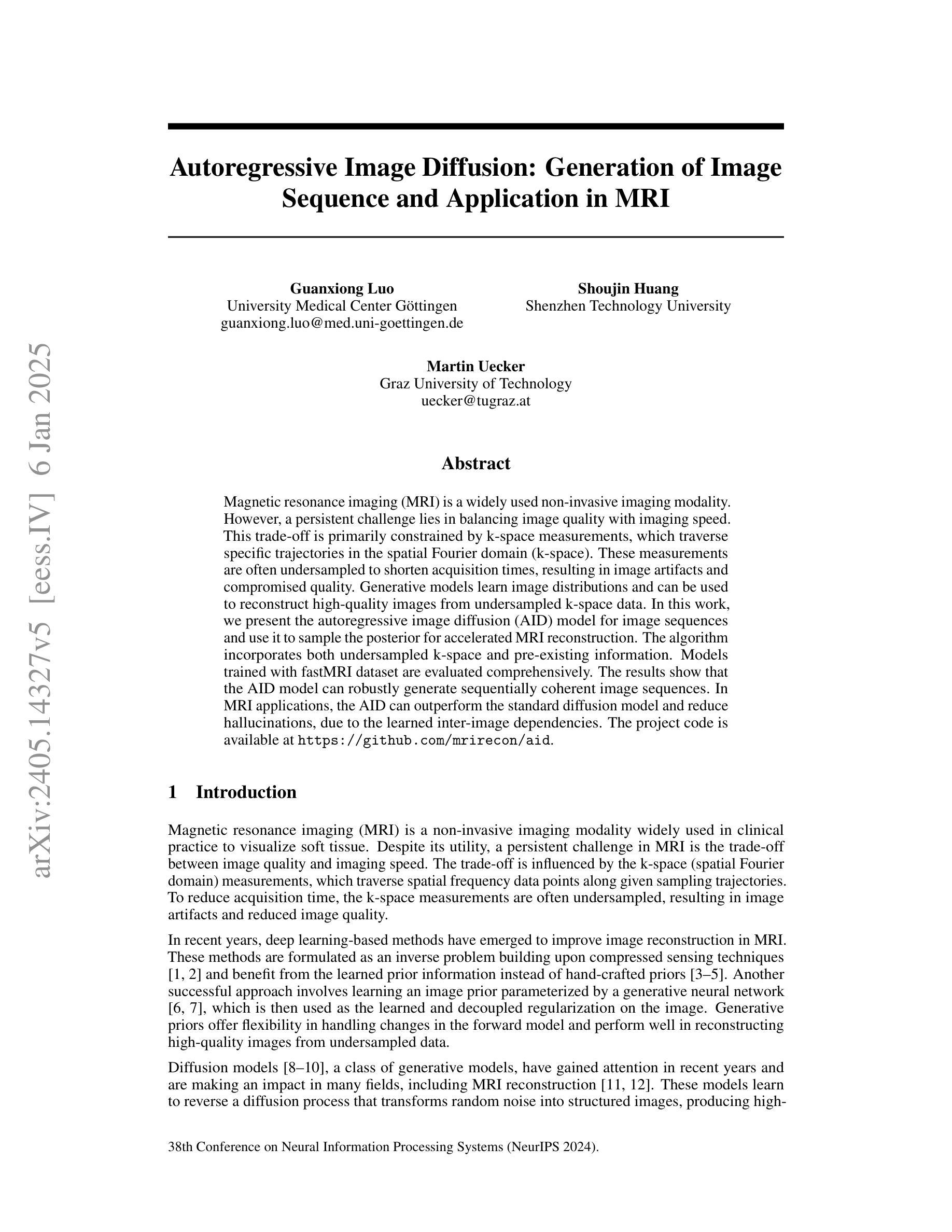
Autoregressive Image Diffusion: Generation of Image Sequence and Application in MRI
Authors:Guanxiong Luo, Shoujin Huang, Martin Uecker
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a widely used non-invasive imaging modality. However, a persistent challenge lies in balancing image quality with imaging speed. This trade-off is primarily constrained by k-space measurements, which traverse specific trajectories in the spatial Fourier domain (k-space). These measurements are often undersampled to shorten acquisition times, resulting in image artifacts and compromised quality. Generative models learn image distributions and can be used to reconstruct high-quality images from undersampled k-space data. In this work, we present the autoregressive image diffusion (AID) model for image sequences and use it to sample the posterior for accelerated MRI reconstruction. The algorithm incorporates both undersampled k-space and pre-existing information. Models trained with fastMRI dataset are evaluated comprehensively. The results show that the AID model can robustly generate sequentially coherent image sequences. In MRI applications, the AID can outperform the standard diffusion model and reduce hallucinations, due to the learned inter-image dependencies. The project code is available at https://github.com/mrirecon/aid.
磁共振成像(MRI)是一种广泛使用的非侵入性成像方式。然而,持续面临的挑战在于平衡图像质量与成像速度。这种权衡主要受到k空间测量的限制,这些测量在空间傅里叶域(k空间)沿特定轨迹行进。为了减少采集时间,这些测量往往进行欠采样,导致图像出现伪影和质量下降。生成模型学习图像分布,可用于从欠采样的k空间数据中重建高质量图像。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于图像序列的自回归图像扩散(AID)模型,并将其用于采样后加速MRI重建。该算法结合了欠采样的k空间和现有信息。用fastMRI数据集训练的模型进行了全面的评估。结果表明,AID模型能够稳健地生成连续的图像序列。在MRI应用中,由于学习到的图像间依赖性,AID可以优于标准扩散模型并减少幻觉。项目代码可在https://github.com/mrirecon/aid获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在磁共振成像(MRI)中面临的挑战,即在图像质量与成像速度之间的平衡。文章提出使用生成模型来解决这一问题,特别是介绍了一种名为autoregressive image diffusion(AID)的模型。该模型能够学习图像分布,从欠采样的k-space数据中重建高质量图像。研究结果表明,AID模型能够稳健地生成连续的图像序列,并在MRI应用中表现出优于标准扩散模型的性能,减少了幻觉现象。
Key Takeaways
- 磁共振成像(MRI)在图像质量与成像速度之间存在权衡挑战。
- k-space测量在MRI中起到关键作用,但其欠采样会导致图像伪影和质量下降。
- 生成模型如autoregressive image diffusion(AID)能够从欠采样的k-space数据中重建高质量图像。
- AID模型能够学习图像序列的分布,并生成连续的图像序列。
- 在MRI应用中,AID模型表现出优于标准扩散模型的性能。
- AID模型通过利用图像间的依赖性,减少了幻觉现象的出现。
点此查看论文截图
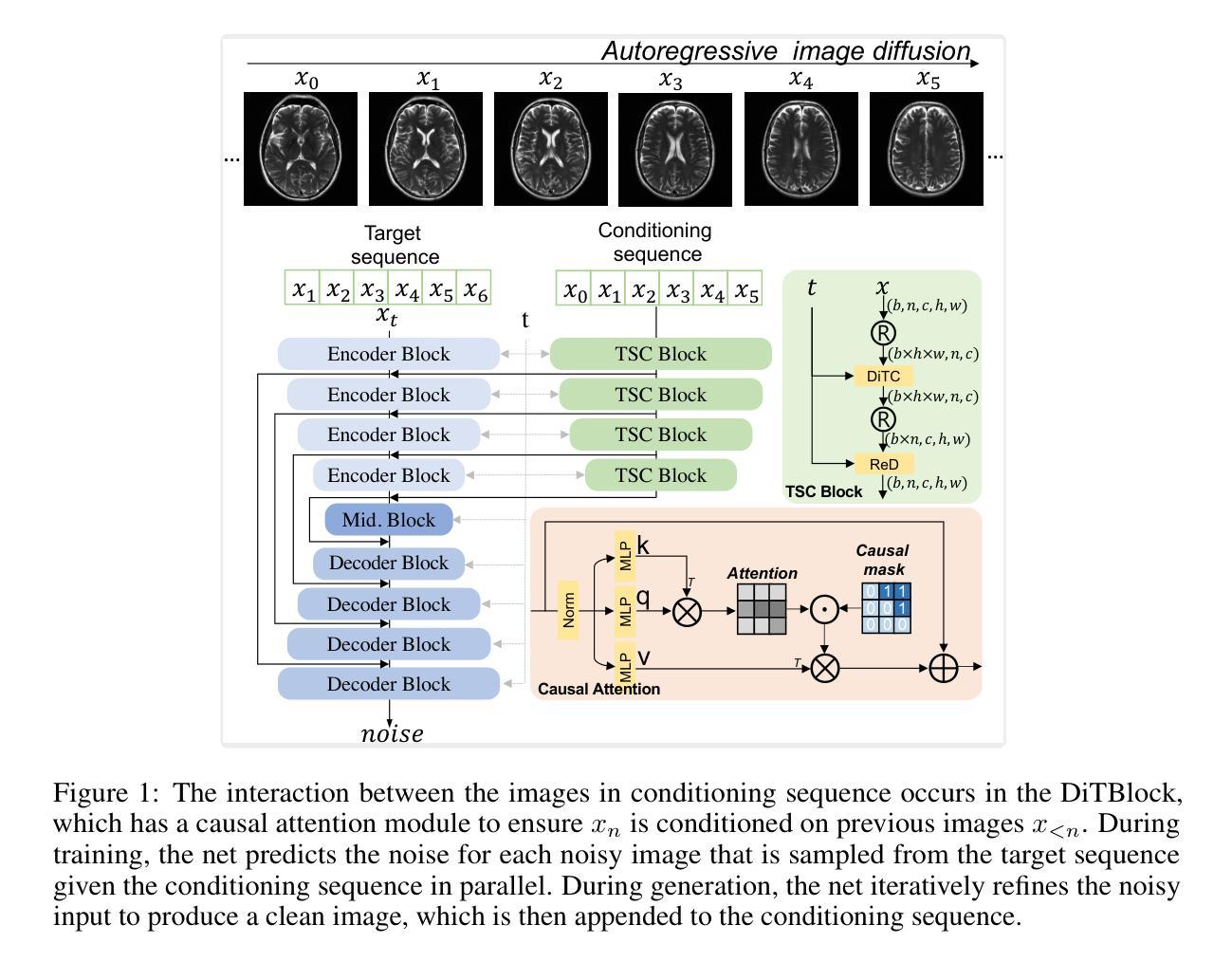

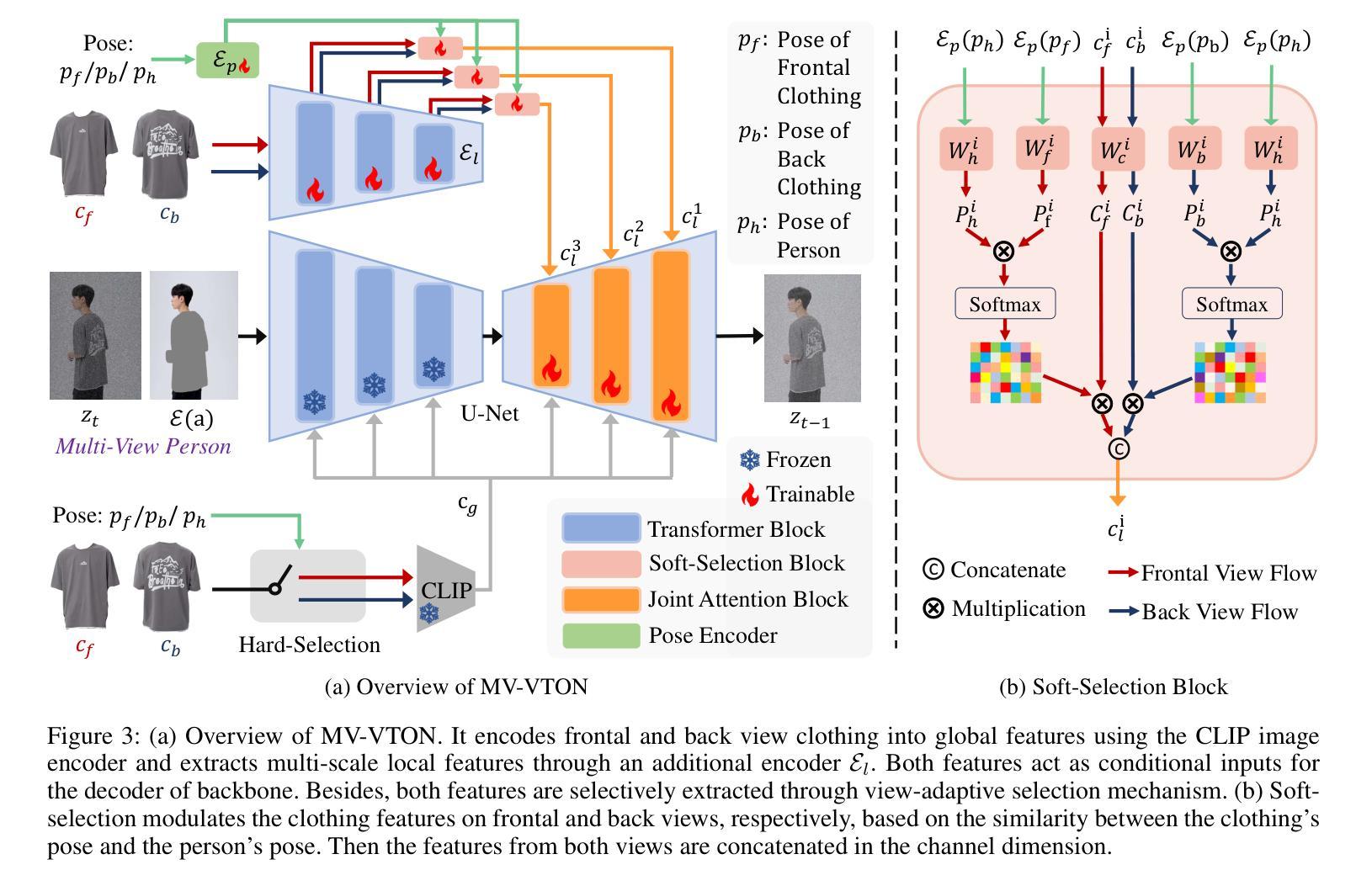
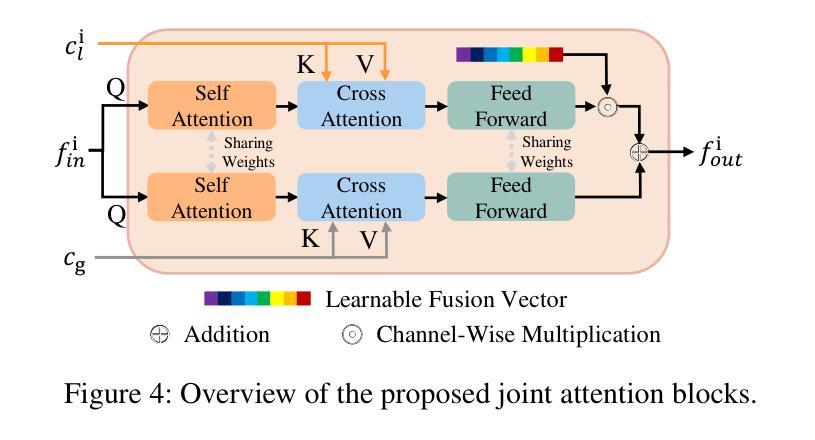
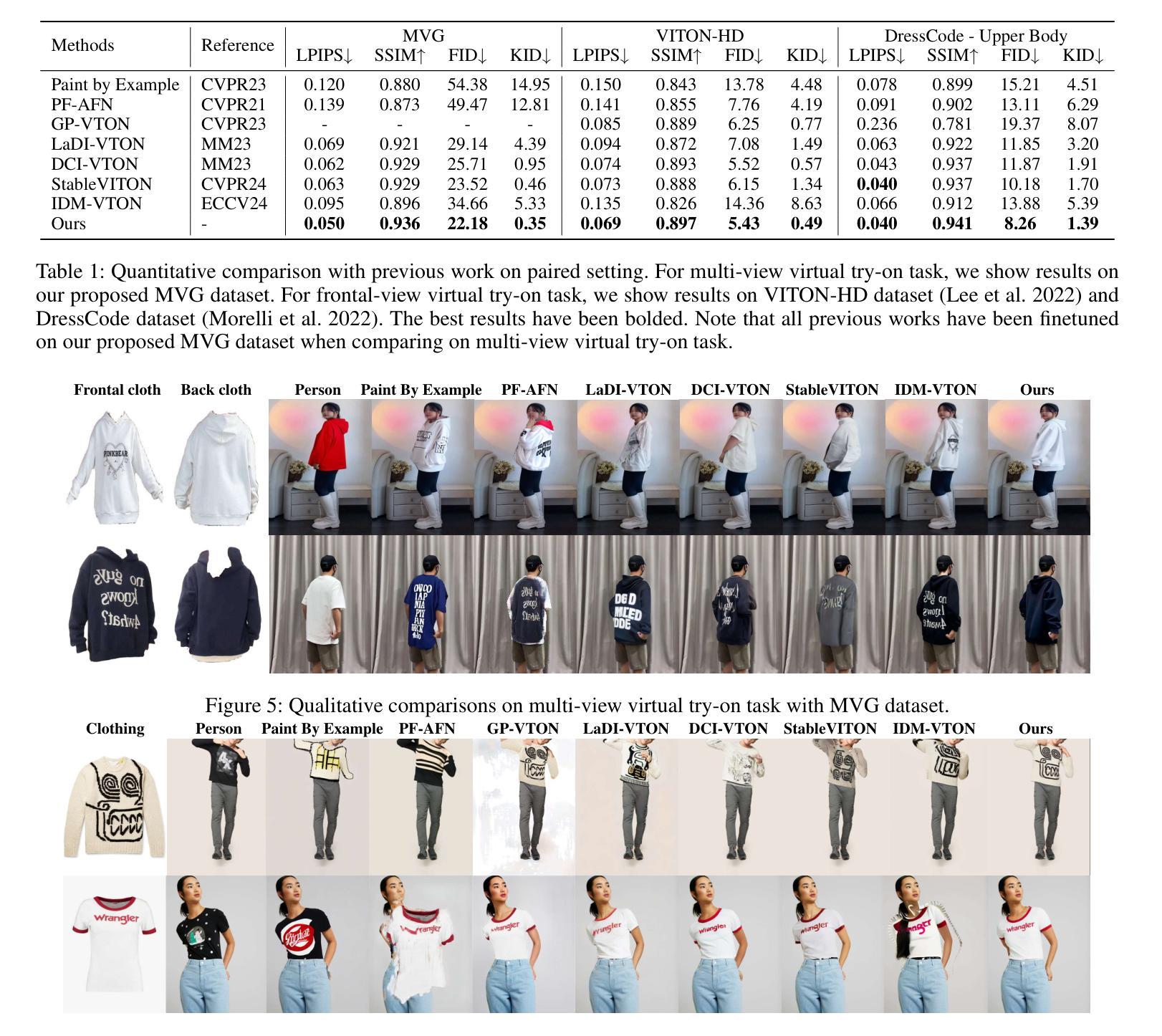
MV-VTON: Multi-View Virtual Try-On with Diffusion Models
Authors:Haoyu Wang, Zhilu Zhang, Donglin Di, Shiliang Zhang, Wangmeng Zuo
The goal of image-based virtual try-on is to generate an image of the target person naturally wearing the given clothing. However, existing methods solely focus on the frontal try-on using the frontal clothing. When the views of the clothing and person are significantly inconsistent, particularly when the person’s view is non-frontal, the results are unsatisfactory. To address this challenge, we introduce Multi-View Virtual Try-ON (MV-VTON), which aims to reconstruct the dressing results from multiple views using the given clothes. Given that single-view clothes provide insufficient information for MV-VTON, we instead employ two images, i.e., the frontal and back views of the clothing, to encompass the complete view as much as possible. Moreover, we adopt diffusion models that have demonstrated superior abilities to perform our MV-VTON. In particular, we propose a view-adaptive selection method where hard-selection and soft-selection are applied to the global and local clothing feature extraction, respectively. This ensures that the clothing features are roughly fit to the person’s view. Subsequently, we suggest joint attention blocks to align and fuse clothing features with person features. Additionally, we collect a MV-VTON dataset MVG, in which each person has multiple photos with diverse views and poses. Experiments show that the proposed method not only achieves state-of-the-art results on MV-VTON task using our MVG dataset, but also has superiority on frontal-view virtual try-on task using VITON-HD and DressCode datasets.
基于图像的虚拟试穿的目标是生成目标人物自然穿着给定服装的图像。然而,现有方法仅专注于使用正面服装进行正面试穿。当服装和人物的视角存在显著差异,特别是人物视角非正面时,结果往往不尽人意。为了解决这一挑战,我们引入了多视角虚拟试穿(MV-VTON),旨在利用给定的服装从多个视角重建着装效果。鉴于单视角衣物为MV-VTON提供的信息不足,我们转而使用两张图像,即服装的正面和背面视图,以尽可能涵盖完整的视图。此外,我们采用了扩散模型,该模型在MV-VTON任务中表现出了卓越的能力。特别是,我们提出了一种视适应选择方法,其中硬选择和软选择分别应用于全局和局部服装特征提取,以确保服装特征大致适应人物的视角。随后,我们建议使用联合注意力块来对齐和融合服装特征与人物特征。此外,我们收集了一个MV-VTON数据集MVG,其中每个人物都有多张具有不同视角和姿态的照片。实验表明,所提出的方法不仅在我们自己的MVG数据集上实现了最先进的MV-VTON任务结果,而且在VITON-HD和DressCode数据集上的正面虚拟试穿任务中也具有优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept by AAAI 2025. Project url: https://hywang2002.github.io/MV-VTON/
Summary
本文介绍了多视角虚拟试穿(MV-VTON)技术,该技术旨在通过给定的衣物从多个视角重建着装效果。为解决单一视角衣物信息不足的问题,采用前视和后视两张衣物图像来尽可能全面地覆盖视角。采用扩散模型执行MV-VTON任务,并提出一种视图自适应选择方法,对全局和局部衣物特征进行硬选择和软选择。此外,建议采用联合注意力块对齐和融合衣物特征与人像特征。最后收集MVG数据集用于实验验证,结果显示该方法在MV-VTON任务上表现优秀。
Key Takeaways
- MV-VTON技术旨在通过给定的衣物从多个视角重建着装效果,解决视角不一致导致的不满意结果问题。
- 采用前视和后视两张衣物图像来更全面覆盖视角,解决单一视角衣物信息不足的问题。
- 采用扩散模型执行MV-VTON任务,表现出卓越的能力。
- 提出一种视图自适应选择方法,对全局和局部衣物特征进行硬选择和软选择,确保衣物特征与人像视角相适应。
- 采用联合注意力块来对齐和融合衣物特征与人像特征。
- 收集MVG数据集用于实验验证。
点此查看论文截图


SRAGAN: Saliency Regularized and Attended Generative Adversarial Network for Chinese Ink-wash Painting Generation
Authors:Xiang Gao, Yuqi Zhang
Recent style transfer problems are still largely dominated by Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) from the perspective of cross-domain image-to-image (I2I) translation, where the pivotal issue is to learn and transfer target-domain style patterns onto source-domain content images. This paper handles the problem of translating real pictures into traditional Chinese ink-wash paintings, i.e., Chinese ink-wash painting style transfer. Though a wide range of I2I models tackle this problem, a notable challenge is that the content details of the source image could be easily erased or corrupted due to the transfer of ink-wash style elements. To remedy this issue, we propose to incorporate saliency detection into the unpaired I2I framework to regularize image content, where the detected saliency map is utilized from two aspects: (\romannumeral1) we propose saliency IOU (SIOU) loss to explicitly regularize object content structure by enforcing saliency consistency before and after image stylization; (\romannumeral2) we propose saliency adaptive normalization (SANorm) which implicitly enhances object structure integrity of the generated paintings by dynamically injecting image saliency information into the generator to guide stylization process. Besides, we also propose saliency attended discriminator which harnesses image saliency information to focus generative adversarial attention onto the drawn objects, contributing to generating more vivid and delicate brush strokes and ink-wash textures. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate superiority of our approach over related advanced image stylization methods in both GAN and diffusion model paradigms.
近期风格迁移问题仍然主要从跨域图像到图像(I2I)转换的角度由生成对抗网络(GAN)主导,关键在于学习和将目标域的风格模式转移到源域内容图像上。本文处理将真实图片翻译成传统水墨画的问题,即水墨画风格转换。尽管有许多I2I模型处理这个问题,但一个显著的挑战是源图像的内容细节在转移水墨风格元素时容易被抹去或破坏。为了解决这个问题,我们提出将显著性检测融入非配对I2I框架以规范图像内容,从两个方面利用检测到的显著性图:(1)我们提出显著性IOU(SIOU)损失,通过强制显著性一致性在图像风格化之前和之后显式地规范对象内容结构;(2)我们提出显著性自适应归一化(SANorm),通过动态将图像显著性信息注入生成器以指导风格化过程,隐式地增强生成画作的对象结构完整性。此外,我们还提出了显著性关注鉴别器,它利用图像显著性信息将生成对抗性注意力集中在绘制的对象上,有助于生成更生动、更精细的笔触和水墨纹理。大量的定性和定量实验表明,我们的方法在生成对抗网络和扩散模型范式中均优于相关的先进图像风格化方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 34 pages, 15 figures
Summary
本文解决了将真实图片转化为中国传统水墨画的问题,即水墨画风格转换。文章引入了显著性检测来解决在风格转换过程中源图像内容细节容易丢失或损坏的问题。通过结合无配对图像到图像的框架,提出两种策略:一是显著性IOU(SIOU)损失,通过强制风格化前后的显著性一致性来明确规范对象内容结构;二是显著性自适应归一化(SANorm),通过动态注入图像显著性信息来隐式增强生成画作的对象结构完整性。此外,还提出了显著性关注鉴别器,利用图像显著性信息将生成对抗性注意力集中在绘制对象上,有助于生成更生动、细腻的画笔笔触和墨水纹理。实验证明,该方法在GAN和扩散模型范式中均优于其他先进的图像风格化方法。
Key Takeaways
- 文章解决了真实图片转化为水墨画风格的难题,即风格转换问题。
- 针对风格转换过程中源图像内容细节可能丢失的问题,引入了显著性检测。
- 提出了两种策略来结合显著性检测:SIOU损失和SANorm方法。
- SHOU损失通过强制风格化前后的显著性一致性来规范对象内容结构。
- SANorm方法通过动态注入图像显著性信息增强生成画作的对象结构完整性。
- 引入显著性关注鉴别器,将生成对抗性注意力集中在绘制对象上,提高生成画作的质量。
点此查看论文截图



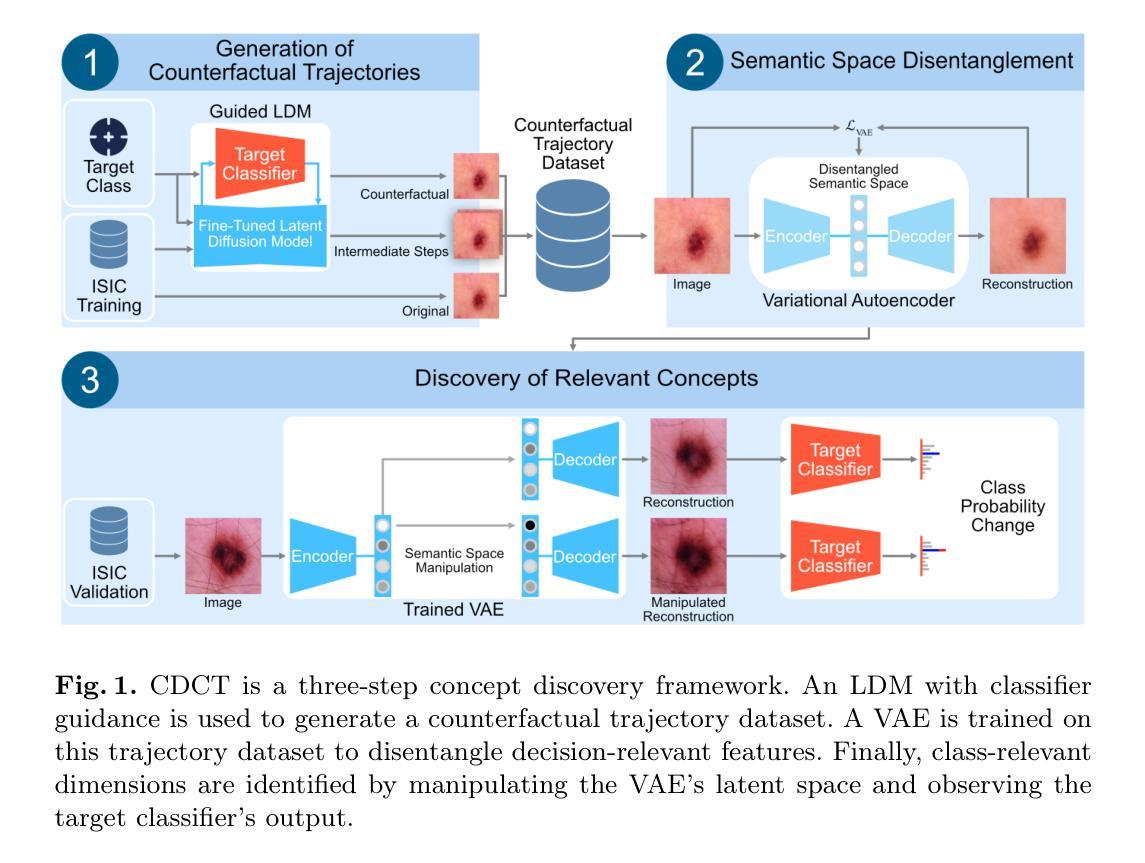
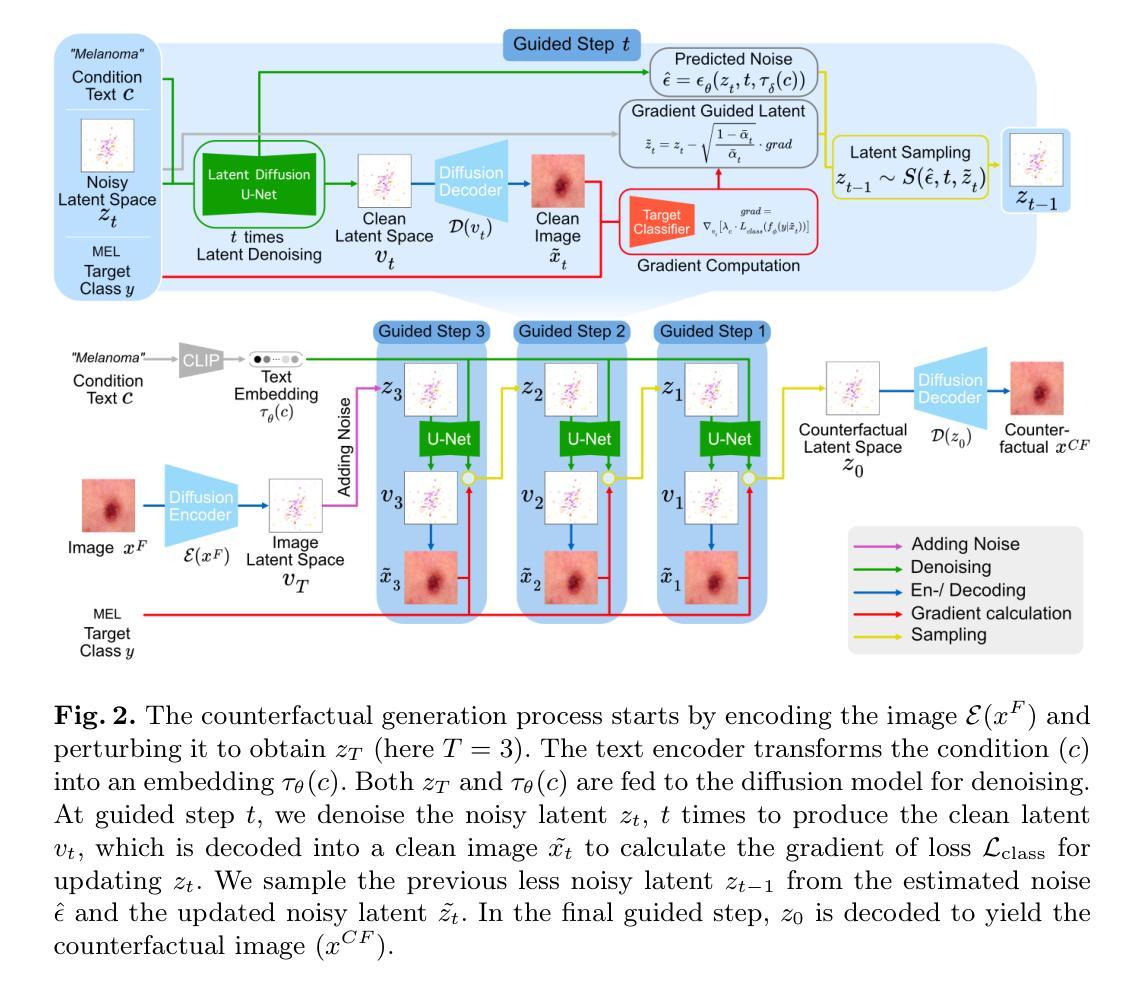
Generating Counterfactual Trajectories with Latent Diffusion Models for Concept Discovery
Authors:Payal Varshney, Adriano Lucieri, Christoph Balada, Andreas Dengel, Sheraz Ahmed
Trustworthiness is a major prerequisite for the safe application of opaque deep learning models in high-stakes domains like medicine. Understanding the decision-making process not only contributes to fostering trust but might also reveal previously unknown decision criteria of complex models that could advance the state of medical research. The discovery of decision-relevant concepts from black box models is a particularly challenging task. This study proposes Concept Discovery through Latent Diffusion-based Counterfactual Trajectories (CDCT), a novel three-step framework for concept discovery leveraging the superior image synthesis capabilities of diffusion models. In the first step, CDCT uses a Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) to generate a counterfactual trajectory dataset. This dataset is used to derive a disentangled representation of classification-relevant concepts using a Variational Autoencoder (VAE). Finally, a search algorithm is applied to identify relevant concepts in the disentangled latent space. The application of CDCT to a classifier trained on the largest public skin lesion dataset revealed not only the presence of several biases but also meaningful biomarkers. Moreover, the counterfactuals generated within CDCT show better FID scores than those produced by a previously established state-of-the-art method, while being 12 times more resource-efficient. Unsupervised concept discovery holds great potential for the application of trustworthy AI and the further development of human knowledge in various domains. CDCT represents a further step in this direction.
在医学等高风险领域,可信性是安全应用不透明的深度学习模型的主要先决条件。理解决策过程不仅有助于建立信任,还可能揭示复杂模型的先前未知决策标准,从而推动医学研究的发展。从黑箱模型中发现与决策相关的概念是一项特别具有挑战性的任务。本研究提出了通过基于潜在扩散的反事实轨迹进行概念发现(CDCT),这是一种利用扩散模型的优越图像合成能力进行概念发现的新型三步框架。首先,CDCT使用潜在扩散模型(LDM)生成反事实轨迹数据集。该数据集用于使用变分自编码器(VAE)派生出与分类相关的概念的脱节表示。最后,应用搜索算法来识别脱节潜在空间中的相关概念。将CDCT应用于在最大的公共皮肤病变数据集上训练的分类器,不仅发现了多种偏见,还发现了有意义的生物标志物。此外,CDCT内产生的反事实事实表现出比先前建立的最先进方法更好的FID分数,同时资源效率提高了12倍。无监督概念发现在可信人工智能的应用和各个领域人类知识的进一步发展方面具有巨大潜力。CDCT是朝着这个方向迈出的一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR) 2024
Summary
本研究提出一种名为CDCT的新概念发现框架,通过利用扩散模型的图像合成能力,对深度学习中决策相关的概念进行发现。CDCT包括三个步骤:生成对抗性轨迹数据集、使用变分自编码器进行概念解耦表示,以及在解耦的潜在空间中进行搜索识别相关概念。应用于皮肤病变数据集分类器的应用显示,CDCT不仅揭示了偏见,还发现了有意义的生物标志物,且比现有方法更高效。这一发现对可信赖人工智能的应用和各个领域的人类知识发展具有巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究强调了在医疗等高风险领域,对深度学习模型的可信度的需求。
- 提出新概念发现框架CDCT,用于揭示深度学习模型的决策标准。
- CDCT利用扩散模型生成对抗性轨迹数据集,以解开分类相关的概念。
- 使用变分自编码器(VAE)进行概念解耦表示。
- 通过搜索算法在解耦的潜在空间中识别相关概念。
- 在皮肤病变数据集上的实验揭示了模型的偏见和有意义的生物标志物。
点此查看论文截图

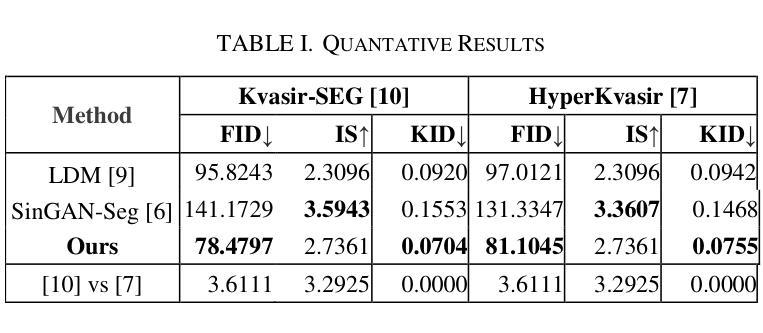
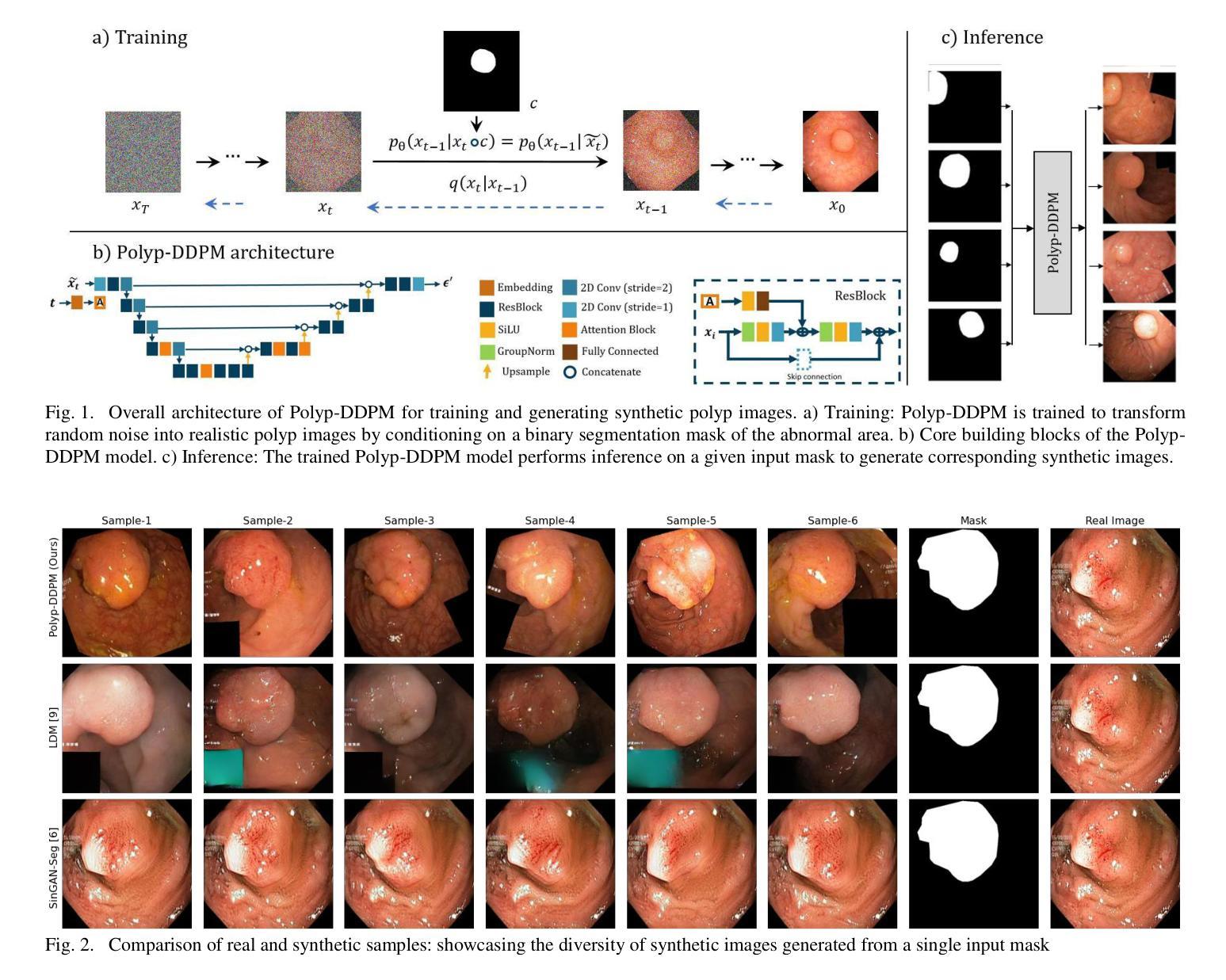
Polyp-DDPM: Diffusion-Based Semantic Polyp Synthesis for Enhanced Segmentation
Authors:Zolnamar Dorjsembe, Hsing-Kuo Pao, Furen Xiao
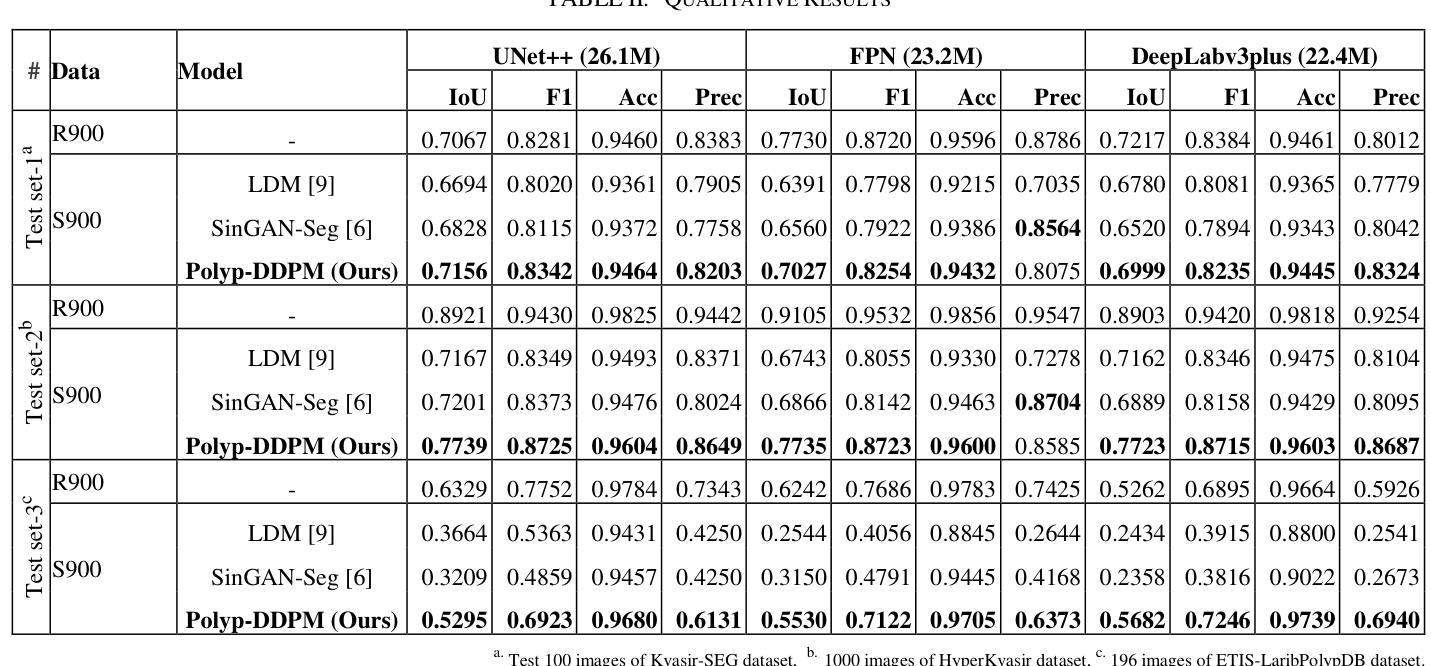
This study introduces Polyp-DDPM, a diffusion-based method for generating realistic images of polyps conditioned on masks, aimed at enhancing the segmentation of gastrointestinal (GI) tract polyps. Our approach addresses the challenges of data limitations, high annotation costs, and privacy concerns associated with medical images. By conditioning the diffusion model on segmentation masks-binary masks that represent abnormal areas-Polyp-DDPM outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of image quality (achieving a Frechet Inception Distance (FID) score of 78.47, compared to scores above 83.79) and segmentation performance (achieving an Intersection over Union (IoU) of 0.7156, versus less than 0.6694 for synthetic images from baseline models and 0.7067 for real data). Our method generates a high-quality, diverse synthetic dataset for training, thereby enhancing polyp segmentation models to be comparable with real images and offering greater data augmentation capabilities to improve segmentation models. The source code and pretrained weights for Polyp-DDPM are made publicly available at https://github.com/mobaidoctor/polyp-ddpm.
本研究介绍了Polyp-DDPM,这是一种基于扩散的方法,用于根据掩膜生成逼真的息肉图像,旨在提高胃肠道(GI)息肉的分割效果。我们的方法解决了与医学图像相关的数据限制、高标注成本和隐私关注等挑战。通过扩散模型采用分割掩膜(代表异常区域的二进制掩膜),Polyp-DDPM在图像质量和分割性能上均优于现有先进技术。在图像质量方面,其弗雷歇因塞特距离(FID)得分为78.47(高于83.79),而在分割性能方面,其交并比(IoU)达到0.7156(基线模型生成的合成图像低于0.6694,真实数据为0.7067)。我们的方法生成高质量、多样化的合成数据集用于训练,从而提高了息肉分割模型的性能,使其与真实图像相当,并提供更大的数据增强能力以改进分割模型。Polyp-DDPM的源代码和预训练权重已在https://github.com/mobaidoctor/polyp-ddpm公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This preprint has been accepted for publication in the proceedings of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC 2024). The final published version is available at https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC53108.2024.10782077. The copyright for this work has been transferred to IEEE
摘要
本研究提出了Polyp-DDPM,这是一种基于扩散的方法,用于根据掩膜生成逼真的息肉图像,旨在提高胃肠道(GI)息肉的分割效果。该方法解决了与医学图像相关的数据限制、高标注成本和隐私关注的挑战。通过扩散模型对分割掩膜的条件化——代表异常区域的二进制掩膜,Polyp-DDPM在图像质量和分割性能上均优于现有先进技术。在图像质量方面,其Frechet Inception Distance(FID)得分为78.47(优于83.79),在分割性能方面,其Intersection over Union(IoU)得分为0.7156(优于基线模型生成的合成图像的0.6694及以下得分和真实数据的0.7067)。该方法生成高质量、多样化的合成数据集,可用于训练,使息肉分割模型可与真实图像相媲美,并提供更大的数据增强能力,以提高分割模型的性能。Polyp-DDPM的源代码和预训练权重已公开提供于https://github.com/mobaidoctor/polyp-ddpm。
要点
- Polyp-DDPM是一种基于扩散的方法,用于根据掩膜生成逼真的息肉图像。
- 该方法旨在解决医学图像中的数据限制、高标注成本和隐私关注的挑战。
- Polyp-DDPM通过条件扩散模型在图像质量和分割性能上均表现出卓越的性能。
- 在图像质量方面,其FID得分优于现有技术。
- 在分割性能方面,其IoU得分也高于基线模型生成的合成图像和真实数据。
- Polyp-DDPM生成的高质量、多样化合成数据集可用于训练,提高息肉分割模型的性能。
- 该研究的源代码和预训练权重已公开提供,方便其他研究者使用。
点此查看论文截图

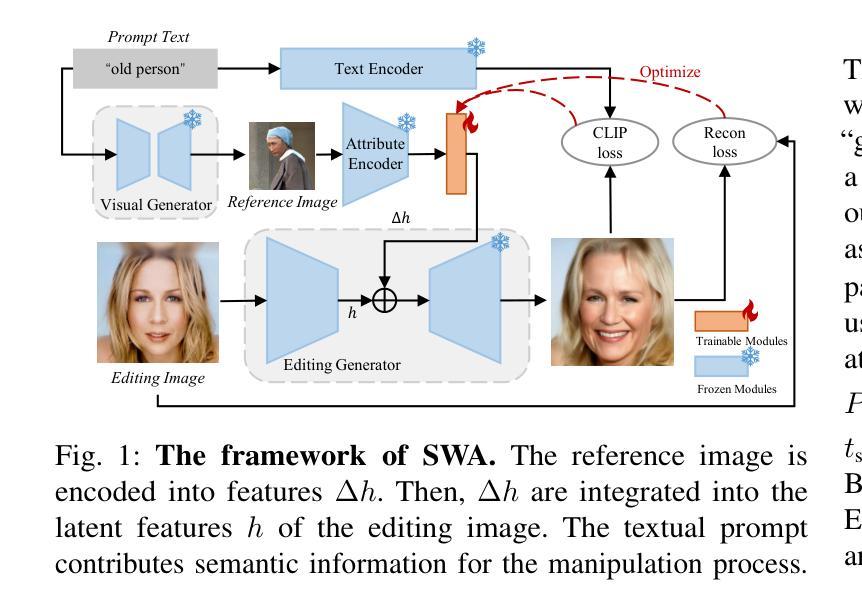
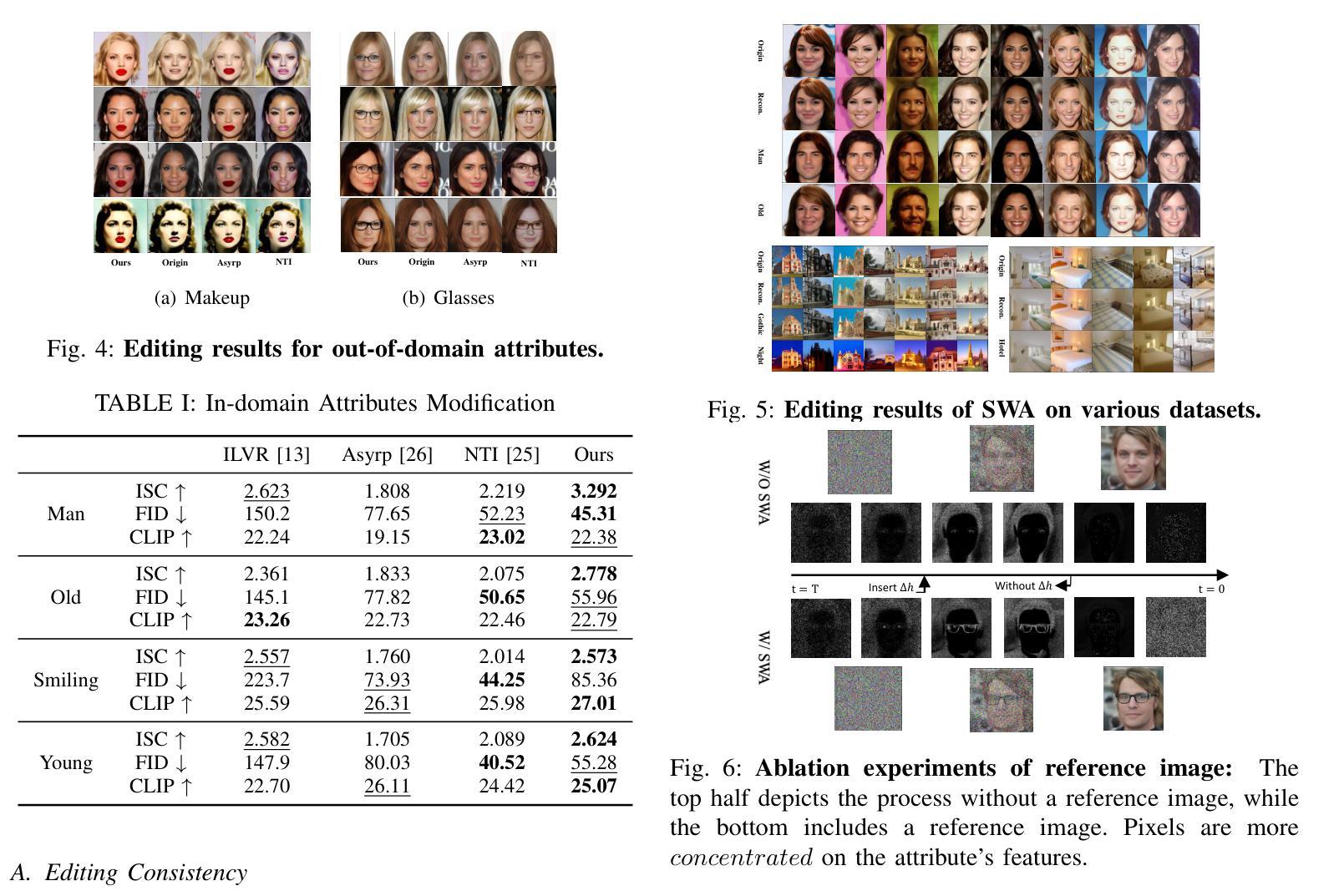
Textual and Visual Prompt Fusion for Image Editing via Step-Wise Alignment
Authors:Zhanbo Feng, Zenan Ling, Xinyu Lu, Ci Gong, Feng Zhou, Wugedele Bao, Jie Li, Fan Yang, Robert C. Qiu
The use of denoising diffusion models is becoming increasingly popular in the field of image editing. However, current approaches often rely on either image-guided methods, which provide a visual reference but lack control over semantic consistency, or text-guided methods, which ensure alignment with the text guidance but compromise visual quality. To resolve this issue, we propose a framework that integrates a fusion of generated visual references and text guidance into the semantic latent space of a \textit{frozen} pre-trained diffusion model. Using only a tiny neural network, our framework provides control over diverse content and attributes, driven intuitively by the text prompt. Compared to state-of-the-art methods, the framework generates images of higher quality while providing realistic editing effects across various benchmark datasets.
去噪扩散模型在图像编辑领域的应用越来越受欢迎。然而,当前的方法通常依赖于图像引导方法,这些方法提供了视觉参考,但缺乏语义一致性的控制,或者文本引导方法,这些方法确保了与文本指导的对齐,但牺牲了视觉质量。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一个框架,它将生成的视觉参考和文本指导融合到一个“冻结”的预训练扩散模型的语义潜在空间中。仅使用一个微小的神经网络,我们的框架就能够控制多样的内容和属性,并由文本提示直观地驱动。与最先进的方法相比,该框架生成的图像质量更高,同时在各种基准数据集上提供逼真的编辑效果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本提出一种融合生成视觉参考和文本指导的框架,解决了当前图像编辑领域中使用的降噪扩散模型所面临的视觉参考缺乏语义一致性和文本指导影响视觉质量的问题。该框架在冻结的预训练扩散模型的语义潜在空间内集成视觉参考和文本指导的融合,仅使用微小的神经网络就能实现对多样化内容和属性的控制,并由文本提示直觉驱动。相较于现有方法,该框架生成的图像质量更高,同时在各种基准数据集上实现逼真的编辑效果。
Key Takeaways
- 当前图像编辑中的降噪扩散模型面临视觉参考缺乏语义一致性和文本指导影响视觉质量的问题。
- 提出的框架融合了生成的视觉参考和文本指导。
- 框架在冻结的预训练扩散模型的语义潜在空间内操作。
- 仅使用微小的神经网络,实现对多样化内容和属性的控制。
- 框架由文本提示直觉驱动。
- 与现有方法相比,该框架生成的图像质量更高。
点此查看论文截图