⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-08 更新
RW-Net: Enhancing Few-Shot Point Cloud Classification with a Wavelet Transform Projection-based Network
Authors:Haosheng Zhang, Hao Huang
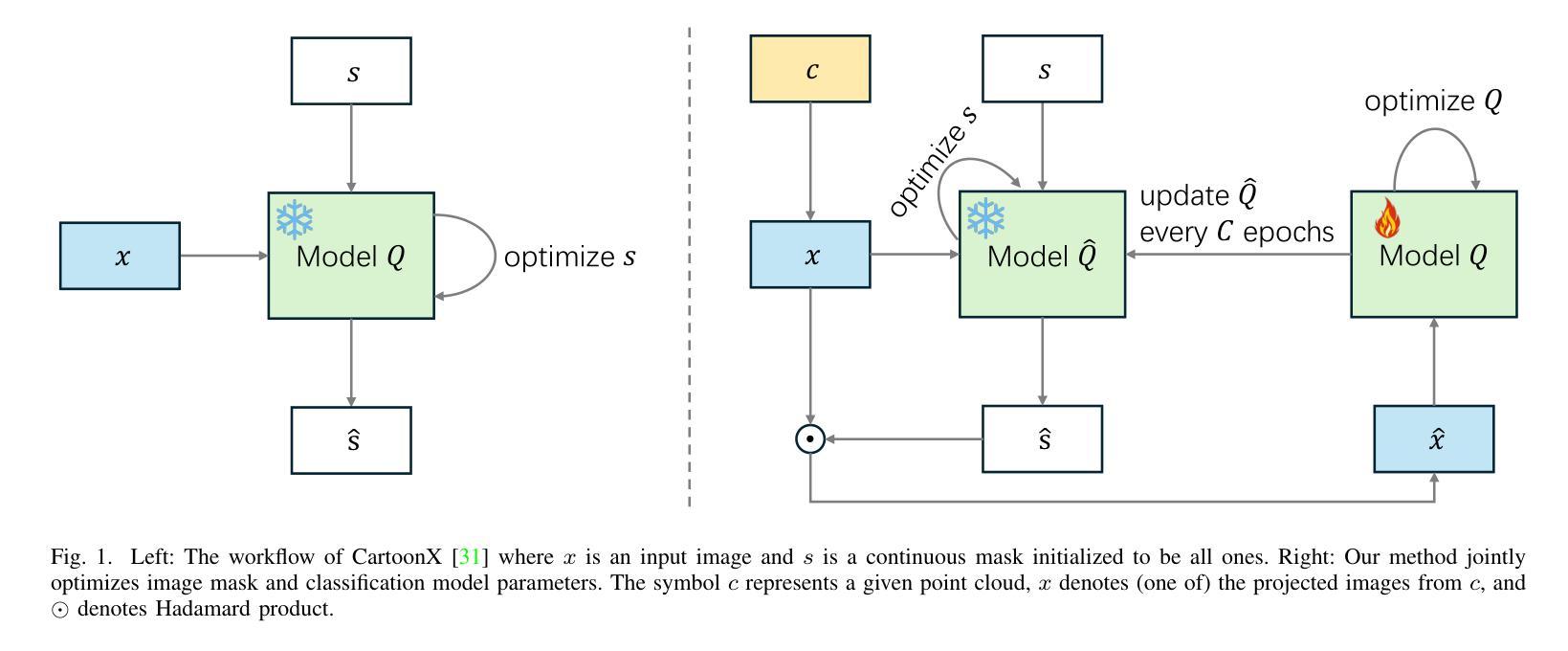
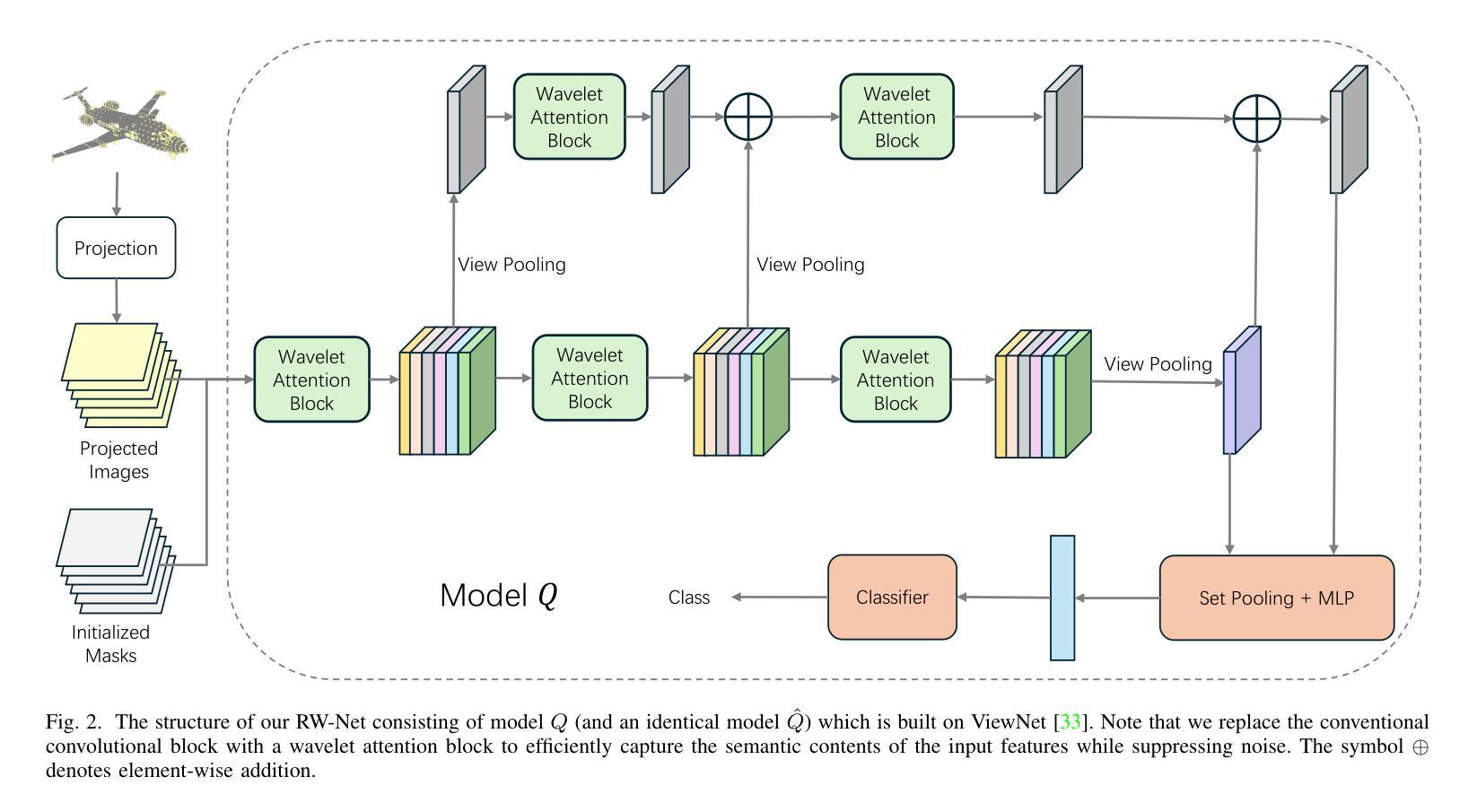
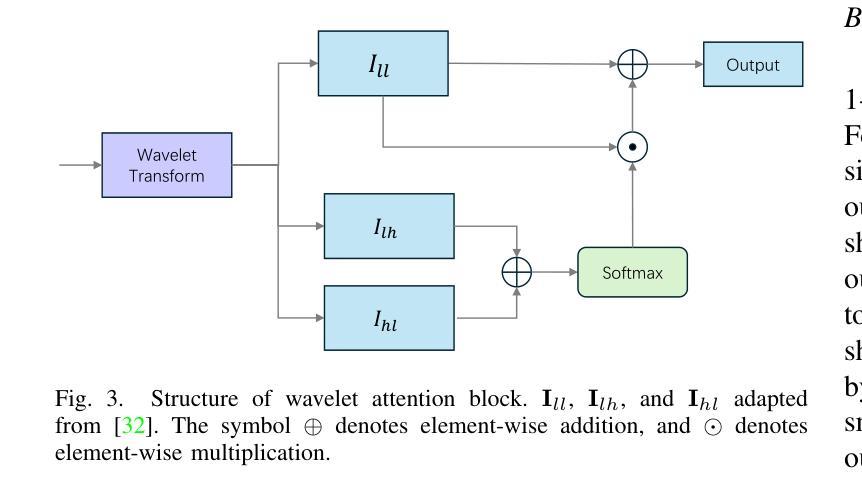
In the domain of 3D object classification, a fundamental challenge lies in addressing the scarcity of labeled data, which limits the applicability of traditional data-intensive learning paradigms. This challenge is particularly pronounced in few-shot learning scenarios, where the objective is to achieve robust generalization from minimal annotated samples. To overcome these limitations, it is crucial to identify and leverage the most salient and discriminative features of 3D objects, thereby enhancing learning efficiency and reducing dependency on large-scale labeled datasets. This work introduces RW-Net, a novel framework designed to address the challenges above by integrating Rate-Distortion Explanation (RDE) and wavelet transform into a state-of-the-art projection-based 3D object classification architecture. The proposed method capitalizes on RDE to extract critical features by identifying and preserving the most informative data components while reducing redundancy. This process ensures the retention of essential information for effective decision-making, optimizing the model’s ability to learn from limited data. Complementing RDE, incorporating the wavelet transform further enhances the framework’s capability to generalize in low-data regimes. By emphasizing low-frequency components of the input data, the wavelet transform captures fundamental geometric and structural attributes of 3D objects. These attributes are instrumental in mitigating overfitting and improving the robustness of the learned representations across diverse tasks and domains. To validate the effectiveness of our RW-Net, we conduct extensive experiments on three datasets: ModelNet40, ModelNet40-C, and ScanObjectNN for few-shot 3D object classification. The results demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance and exhibits superior generalization and robustness in few-shot learning scenarios.
在3D对象分类领域,一个基本挑战在于解决标记数据稀缺的问题,这限制了传统数据密集型学习模式的应用。这种挑战在少量样本学习场景中尤为突出,该场景的目标是从极少的标注样本中实现稳健的泛化。为了克服这些限制,识别和利用3D对象的最突出和最具区分性的特征至关重要,从而提高了学习效率,并减少对大规模标注数据集的依赖。本研究引入了RW-Net,这是一个新型框架,通过整合速率失真解释(RDE)和小波变换,融入基于投影的先进3D对象分类架构,以解决上述挑战。所提出的方法利用RDE通过识别并保留最有信息的数据成分来提取关键特征,同时减少冗余。这一过程确保了保留用于有效决策的必要信息,优化模型从有限数据中学习的能力.
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 5 figures, 9 tables
Summary
在3D目标分类领域,标记数据的稀缺性是最大的挑战之一,这也限制了传统数据密集型学习模式的适用性。特别是在小样本学习中,目标是从极少量的标注样本中实现稳健的泛化。为了克服这些限制,需要识别并利用最显著和有鉴别力的三维物体的特征,以提高学习效率并减少对大规模标记数据集集的依赖。本研究介绍了RW-Net,这是一种新颖的框架,它通过整合率失真解释(RDE)和小波变换来解决上述挑战。所提出的利用RDE提取关键特征的方法确保了有效决策所需的必要信息的保留,优化了模型从有限数据中学习的能力。为了验证RW-Net的有效性,在ModelNet40、ModelNet40-C和ScanObjectNN三个数据集上进行了大量实验。结果表明,该方法实现了最先进的性能,在小样本学习场景中表现出卓越的泛化和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 在处理稀缺的标注数据时,传统的数据密集型学习模式面临挑战。特别是在小样本学习中,实现稳健泛化的难度更大。
- 提出了一种新的框架RW-Net来解决上述问题,结合了率失真解释(RDE)和小波变换技术。
- RDE技术用于提取关键特征,识别并保留最具有信息量的数据组件,同时减少冗余信息。这确保了有效决策所需的必要信息的保留。
- 小波变换增强了框架在低数据环境下的泛化能力。它通过强调输入数据的低频成分来捕捉三维物体的基本几何和结构属性。这些属性有助于减轻过拟合问题并提高在不同任务和领域中的模型稳健性。
点此查看论文截图


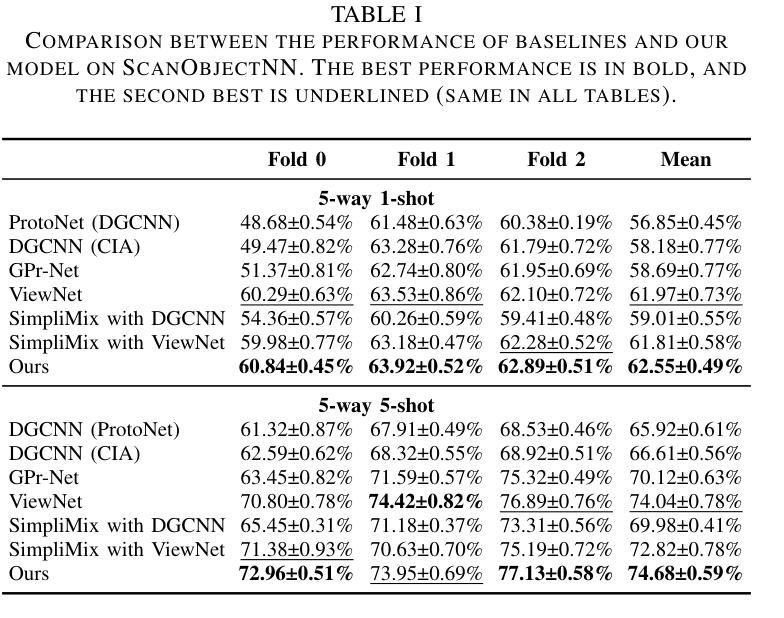
Semantic Captioning: Benchmark Dataset and Graph-Aware Few-Shot In-Context Learning for SQL2Text
Authors:Ali Al-Lawati, Jason Lucas, Prasenjit Mitra
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in various NLP tasks, including semantic parsing, which trans lates natural language into formal code representations. However, the reverse process, translating code into natural language, termed semantic captioning, has received less attention. This task is becoming increasingly important as LLMs are integrated into platforms for code generation, security analysis, and educational purposes. In this paper, we focus on the captioning of SQL query (SQL2Text) to address the critical need for understanding and explaining SQL queries in an era where LLM-generated code poses potential security risks. We repurpose Text2SQL datasets for SQL2Text by introducing an iterative ICL prompt using GPT-4o to generate multiple additional utterances, which enhances the robustness of the datasets for the reverse task. We conduct our experiments using in-context learning (ICL) based on different sample selection methods, emphasizing smaller, more computationally efficient LLMs. Our findings demonstrate that leveraging the inherent graph properties of SQL for ICL sample selection significantly outperforms random selection by up to 39% on BLEU score and provides better results than alternative methods. Dataset and codes are published: \url{https://github.com/aliwister/ast-icl}.
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种自然语言处理任务中表现出了显著的性能,包括将自然语言转换为正式代码表示的语义解析。然而,将代码转换为自然语言的逆向过程,即语义描述,受到的关注度较少。随着LLM被集成到代码生成、安全分析和教育目的的平台中,这项任务变得越来越重要。在本文中,我们关注SQL查询的标注(SQL2Text),以解决在LLM生成的代码存在潜在安全风险的时代,理解和解释SQL查询的迫切需求。我们通过对GPT-4o引入迭代ICL提示来重新利用Text2SQL数据集进行SQL2Text任务,生成多个附加话语,这增强了数据集在逆向任务中的稳健性。我们的实验使用基于不同样本选择方法进行的上下文内学习(ICL),侧重于更小、更计算高效的LLM。研究结果表明,利用SQL的固有图形属性进行ICL样本选择显著优于随机选择,BLEU得分提高了高达39%,并且比其他方法提供了更好的结果。数据集和代码已发布:\url{https://github.com/aliwister/ast-icl}。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to COLING’25
Summary
本文探讨了大语言模型在语义捕捉领域的应用,特别是在将代码转化为自然语言的任务中的重要性。针对SQL查询的语义捕捉(SQL2Text)问题,文章使用GPT-4o进行迭代ICL提示来生成额外的描述语句,增强数据集对反向任务的稳健性。实验采用基于不同样本选择方法的上下文学习(ICL),并强调更小、更高效的LLM的优势。利用SQL的内在图形属性进行ICL样本选择显著优于随机选择,BLEU得分提高了高达39%。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型(LLMs)在语义捕捉,特别是代码到自然语言的转化任务中扮演重要角色。
- SQL查询的语义捕捉(SQL2Text)对于理解LLM生成的SQL查询至关重要,尤其在存在潜在安全风险的环境下。
- 使用GPT-4o进行迭代ICL提示,通过生成额外的描述语句来增强数据集。
- 采用基于不同样本选择方法的上下文学习(ICL)进行实验。
- 利用SQL的内在图形属性进行ICL样本选择显著提高性能,BLEU得分提升高达39%。
- 与随机选择和其它方法相比,利用SQL内在图形属性的ICL样本选择表现出更好的结果。
点此查看论文截图

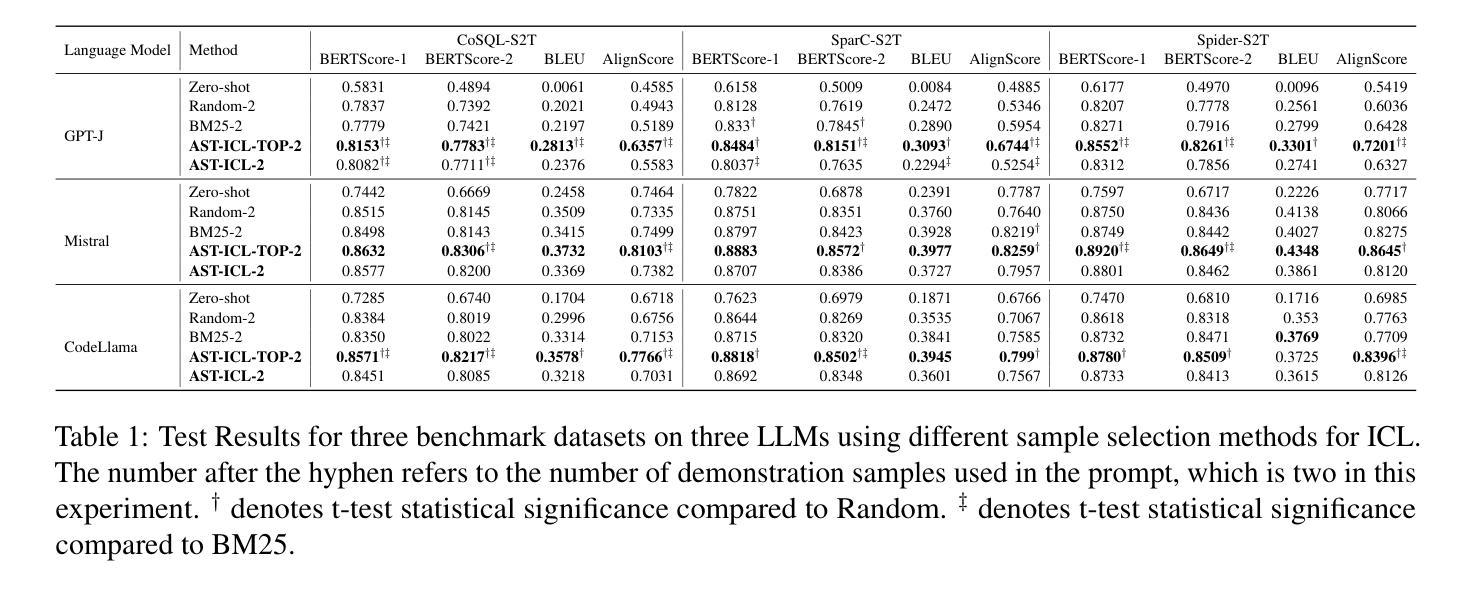
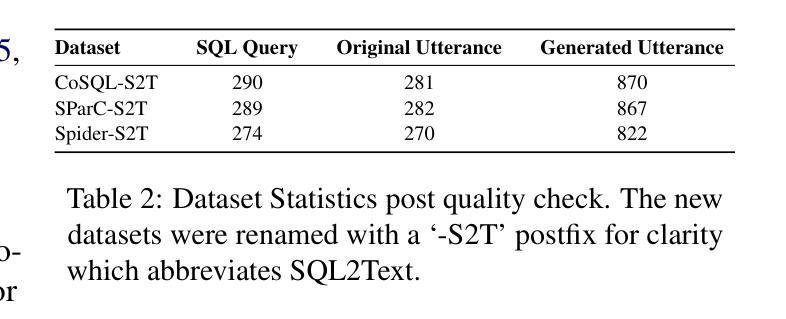
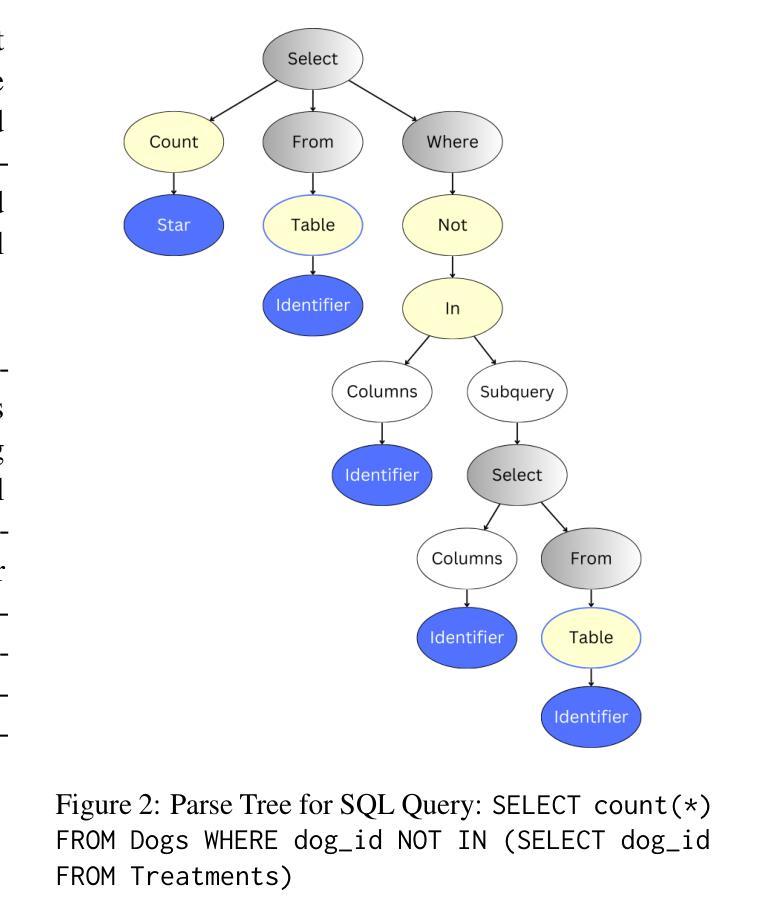
Graph-based Retrieval Augmented Generation for Dynamic Few-shot Text Classification
Authors:Yubo Wang, Haoyang Li, Fei Teng, Lei Chen
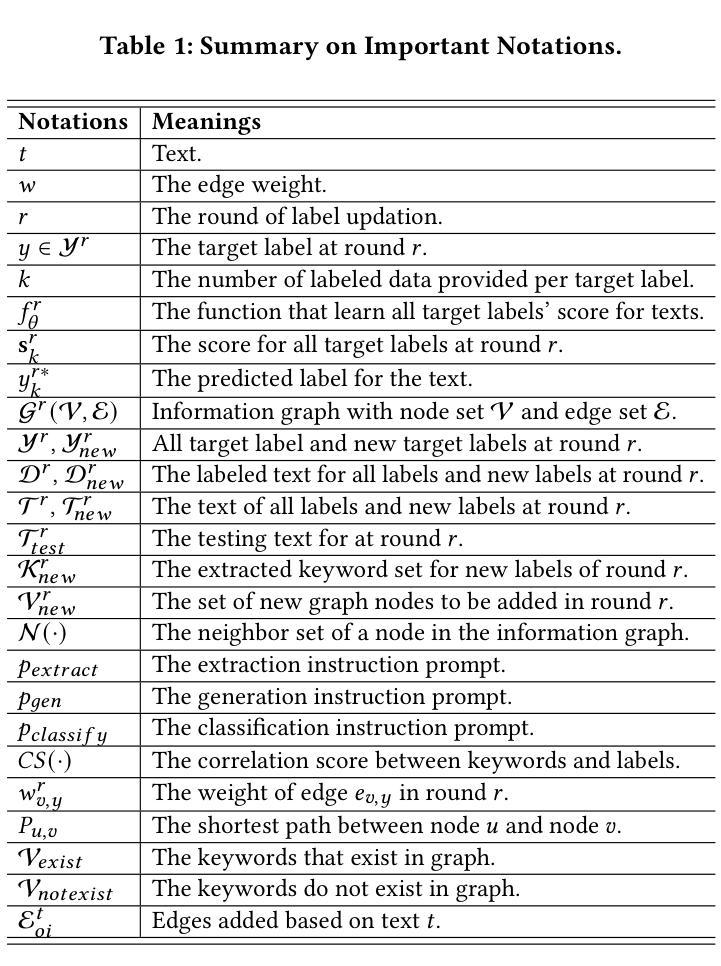
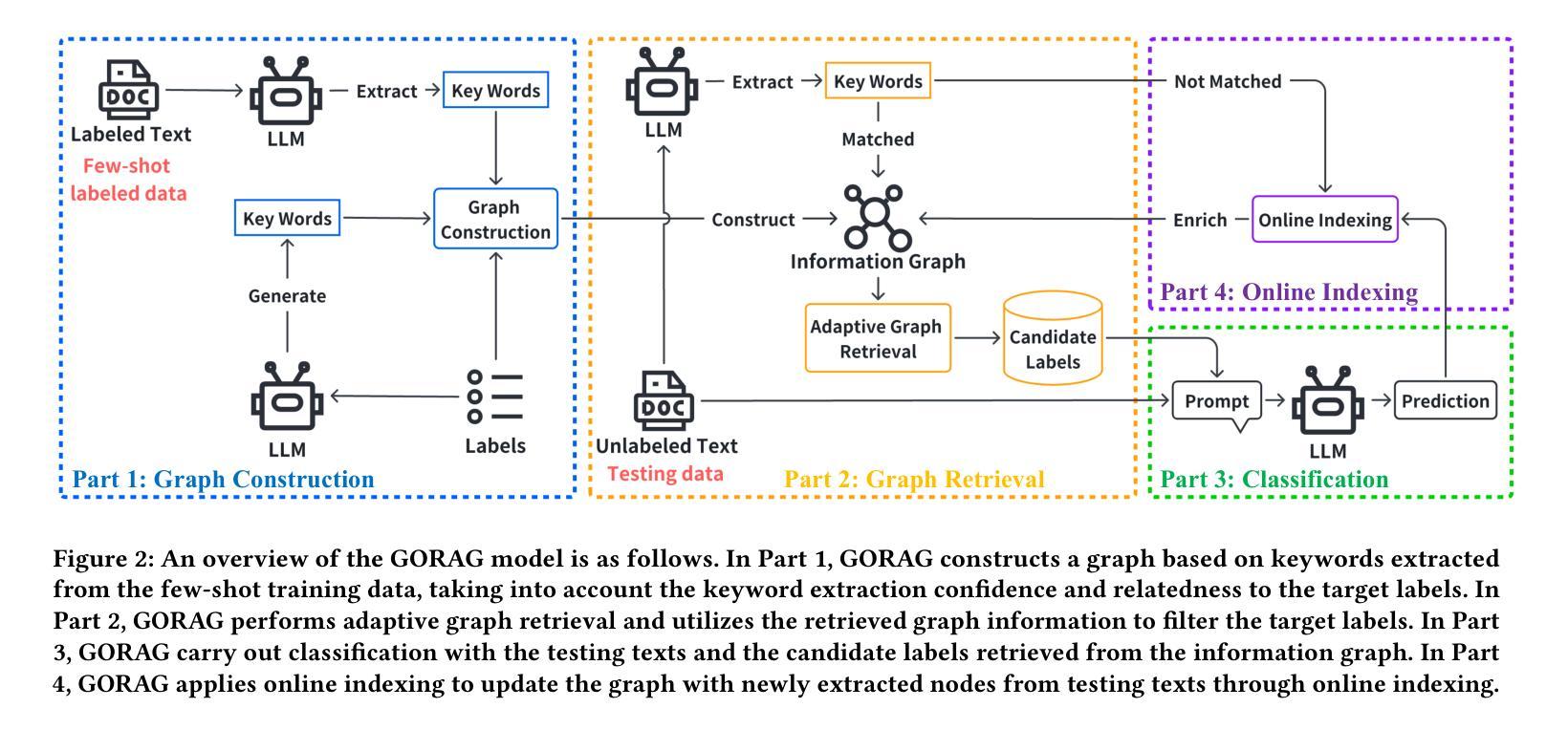
Text classification is a fundamental task in natural language processing, pivotal to various applications such as query optimization, data integration, and schema matching. While neural network-based models, such as CNN and BERT, have demonstrated remarkable performance in text classification, their effectiveness heavily relies on abundant labeled training data. This dependency makes these models less effective in dynamic few-shot text classification, where labeled data is scarce, and target labels frequently evolve based on application needs. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have shown promise due to their extensive pretraining and contextual understanding. Current approaches provide LLMs with text inputs, candidate labels, and additional side information (e.g., descriptions) to predict text labels. However, their effectiveness is hindered by the increased input size and the noise introduced through side information processing. To address these limitations, we propose a graph-based online retrieval-augmented generation framework, namely GORAG, for dynamic few-shot text classification. GORAG constructs and maintains an adaptive information graph by extracting side information across all target texts, rather than treating each input independently. It employs a weighted edge mechanism to prioritize the importance and reliability of extracted information and dynamically retrieves relevant context using a minimum-cost spanning tree tailored for each text input. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that GORAG outperforms existing approaches by providing more comprehensive and accurate contextual information.
文本分类是自然语言处理中的一项基本任务,在查询优化、数据集成和模式匹配等应用中发挥着关键作用。尽管基于神经网络(如CNN和BERT)的模型在文本分类方面表现出卓越的性能,但它们的有效性严重依赖于丰富的标记训练数据。这种依赖性使得这些模型在动态少样本文本分类中的效果较差,其中标记数据稀缺,目标标签经常根据应用需求而演变。最近,由于大型语言模型的广泛预训练和上下文理解,它们显示出巨大的潜力。当前的方法为大型语言模型提供文本输入、候选标签和额外的侧面信息(例如描述)来预测文本标签。然而,其有效性受到输入大小增加和通过侧面信息处理引入的噪声的阻碍。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了一种基于图的在线检索增强生成框架,名为GORAG,用于动态少样本文本分类。GORAG通过提取所有目标文本的侧面信息来构建和维护自适应信息图,而不是独立处理每个输入。它采用加权边机制来优先考虑提取信息的重要性和可靠性,并使用针对每个文本输入量身定制的最低成本生成树动态检索相关上下文。经验评估表明,GORAG通过提供更全面和准确的上文信息,在现有方法的基础上实现了性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了基于图的在线检索增强生成框架(GORAG)在动态少样本文本分类中的应用。针对神经网络模型在少样本情况下的不足,GORAG通过构建和维护一个自适应信息图,提取目标文本的所有侧信息,采用加权边机制,为每篇文本输入定制最小成本生成树,实现动态检索相关上下文,从而提高文本分类的准确性和全面性。
Key Takeaways
- 文本分类是自然语言处理中的基础任务,对于查询优化、数据集成和模式匹配等多种应用至关重要。
- 神经网络模型(如CNN和BERT)在文本分类中表现出卓越性能,但它们在少样本情况下效果较差。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在预训练和上下文理解方面具有潜力。
- 当前LLM方法面临输入大小增加和侧信息处理引入的噪声问题。
- GORAG框架通过构建自适应信息图解决上述问题,提取目标文本的所有侧信息并进行管理。
- GORAG采用加权边机制,优先处理重要且可靠的信息。
点此查看论文截图

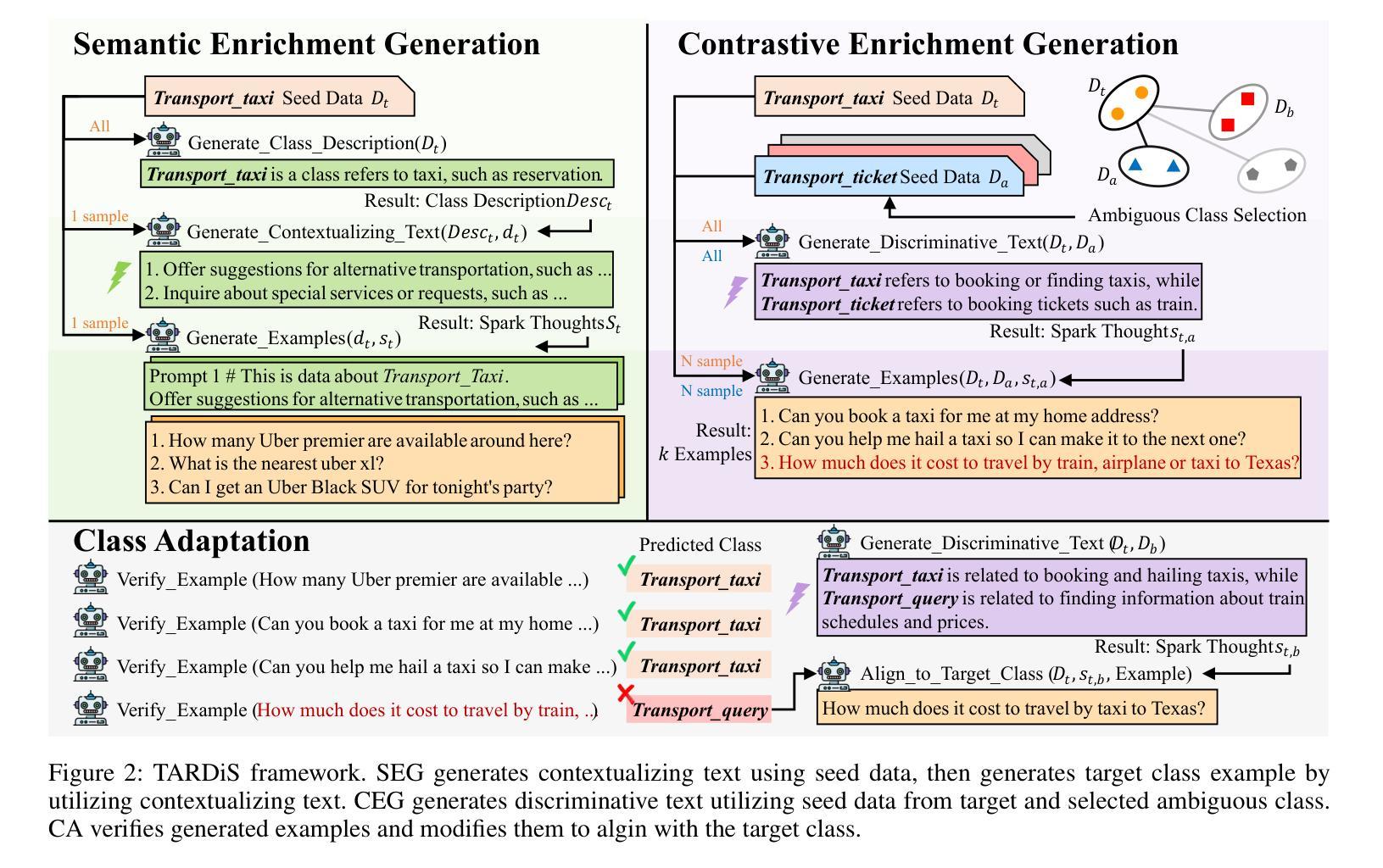
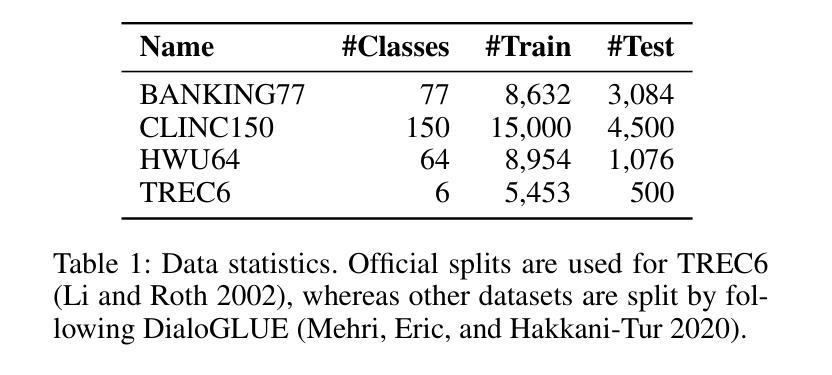
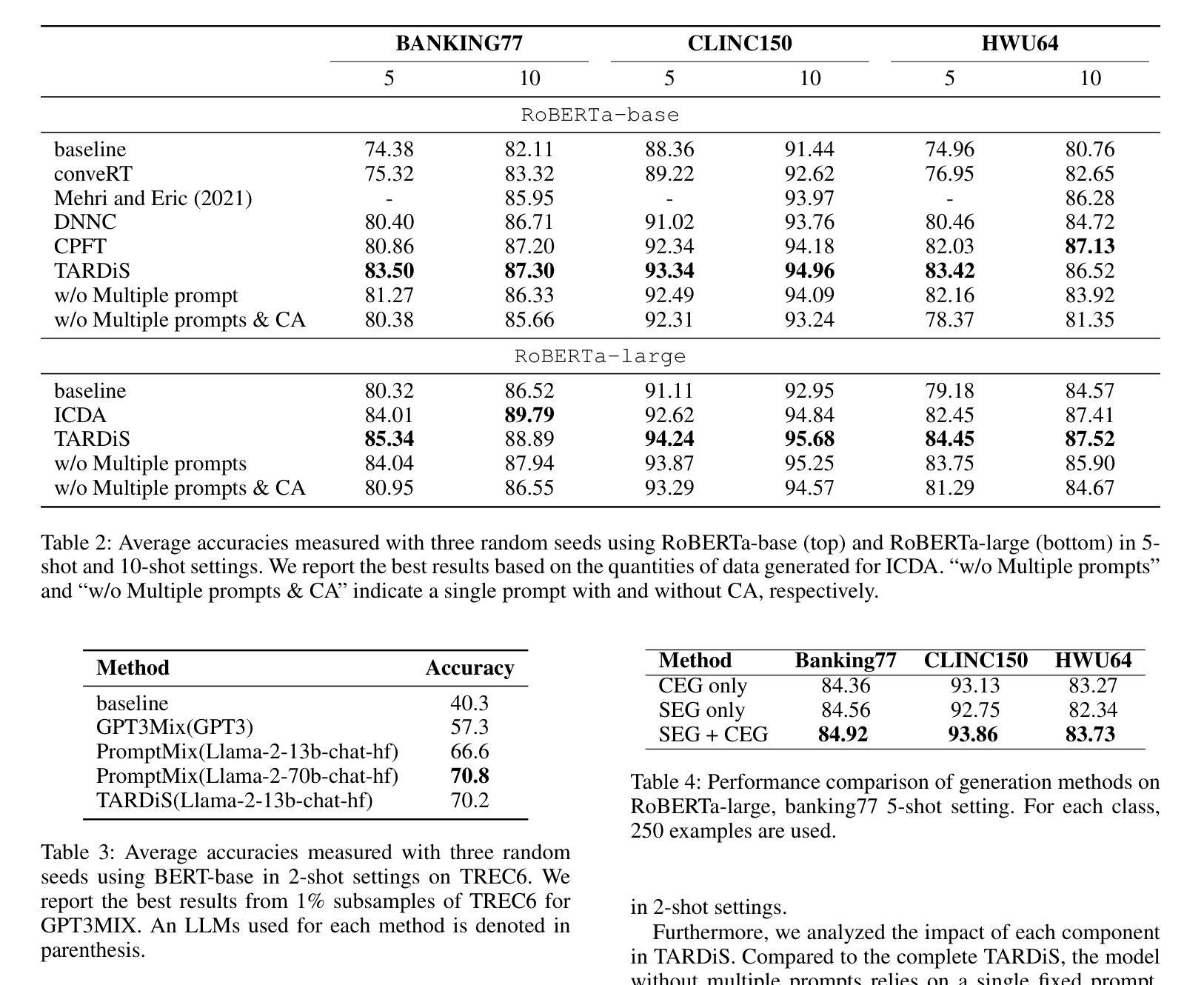
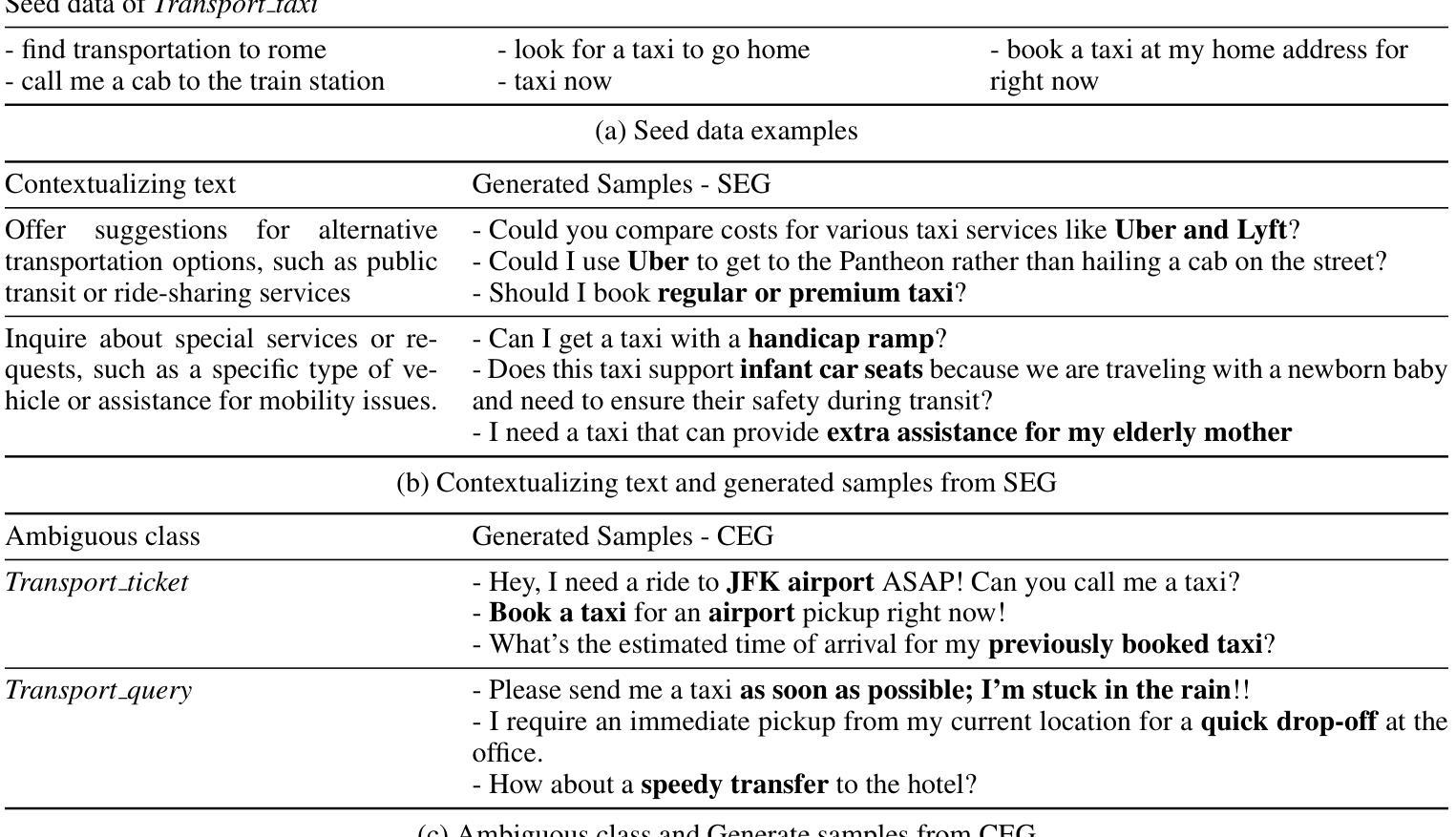
TARDiS : Text Augmentation for Refining Diversity and Separability
Authors:Kyungmin Kim, SangHun Im, GiBaeg Kim, Heung-Seon Oh
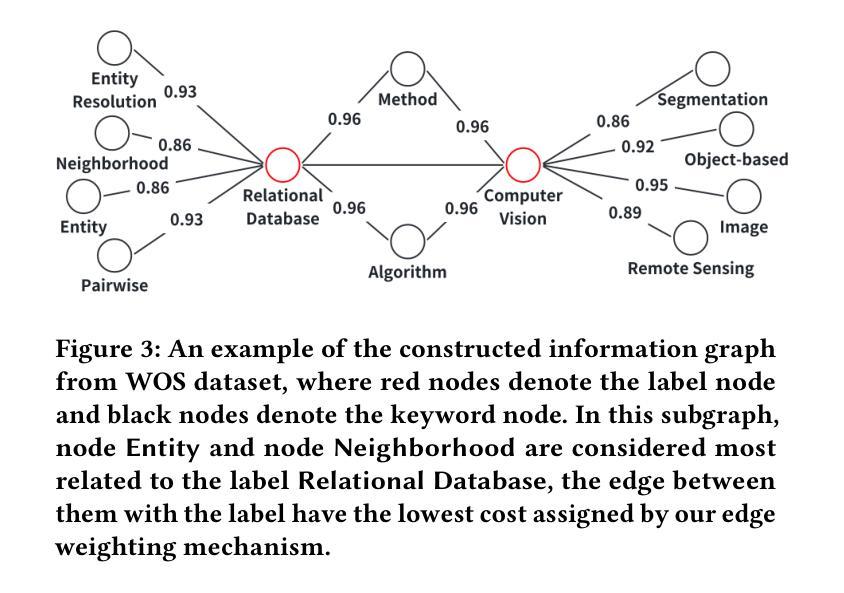
Text augmentation (TA) is a critical technique for text classification, especially in few-shot settings. This paper introduces a novel LLM-based TA method, TARDiS, to address challenges inherent in the generation and alignment stages of two-stage TA methods. For the generation stage, we propose two generation processes, SEG and CEG, incorporating multiple class-specific prompts to enhance diversity and separability. For the alignment stage, we introduce a class adaptation (CA) method to ensure that generated examples align with their target classes through verification and modification. Experimental results demonstrate TARDiS’s effectiveness, outperforming state-of-the-art LLM-based TA methods in various few-shot text classification tasks. An in-depth analysis confirms the detailed behaviors at each stage.
文本增强(TA)是文本分类中的一项关键技术,尤其在少量样本的情况下尤为重要。本文介绍了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的新型TA方法TARDiS,以解决两阶段TA方法在生成和对齐阶段所面临的固有挑战。在生成阶段,我们提出了两种生成过程,即SEG和CEG,它们通过融入多个特定类别的提示来增强多样性和可分性。在对齐阶段,我们引入了一种类适应(CA)方法,以确保生成的例子通过验证和修改与其目标类别对齐。实验结果表明TARDiS的有效性,在各种少量文本分类任务中优于最先进的大型语言模型TA方法。深入分析证实了每一阶段的详细行为。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
文本扩充(TA)在文本分类中尤为关键,特别是在小样本场景中。本文提出了一种新型的大型语言模型基础TA方法TARDiS,旨在解决两阶段TA方法中的生成和校准阶段所面临的挑战。在生成阶段,我们提出了两种生成过程SEG和CEG,融入多种类别特定提示以强化多样性和可分离性。在校准阶段,我们引入类别适应(CA)方法确保生成示例与目标类别对齐,通过验证与修改来实现。实验结果证明TARDiS的有效性,在各种小样本文本分类任务中优于现有大型语言模型基础的TA方法。
Key Takeaways
- TARDiS是一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的文本扩充(TA)方法,旨在改进小样本文本分类。
- TARDiS解决了传统两阶段文本扩充方法中的生成和校准阶段的挑战。
- 在生成阶段,TARDiS使用SEG和CEG两种生成过程,通过融入类别特定提示来提高多样性和可分离性。
- 在校准阶段,TARDiS通过类别适应(CA)方法确保生成的示例与目标类别对齐。
- 实验证明TARDiS在各种小样本文本分类任务中的性能优于现有方法。
- TARDiS方法包含多个阶段,每个阶段都有详细的操作分析。
点此查看论文截图

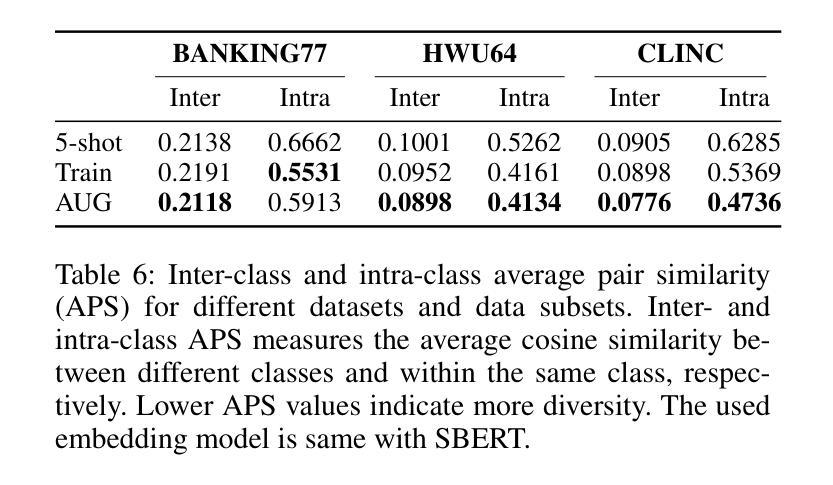
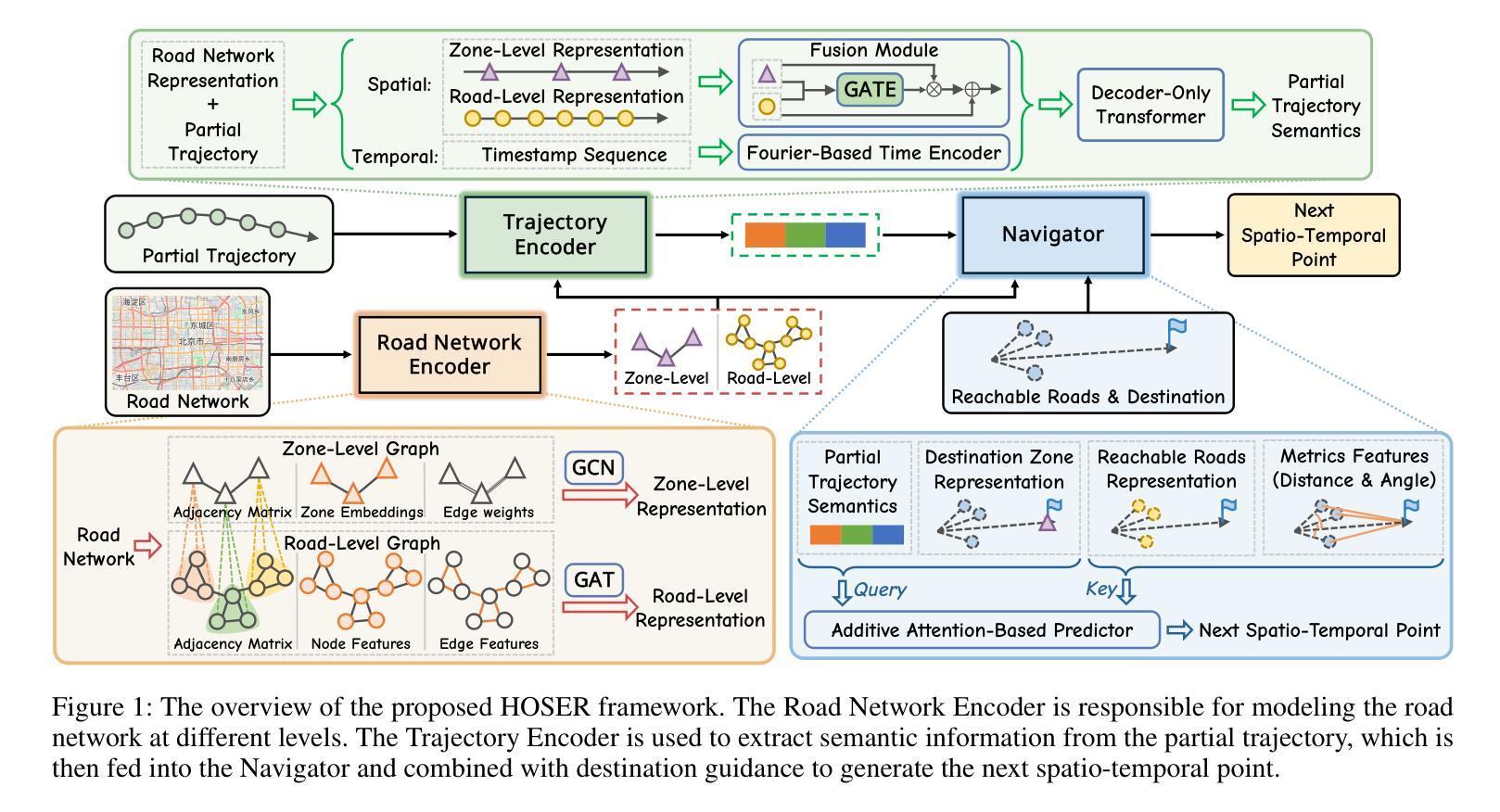
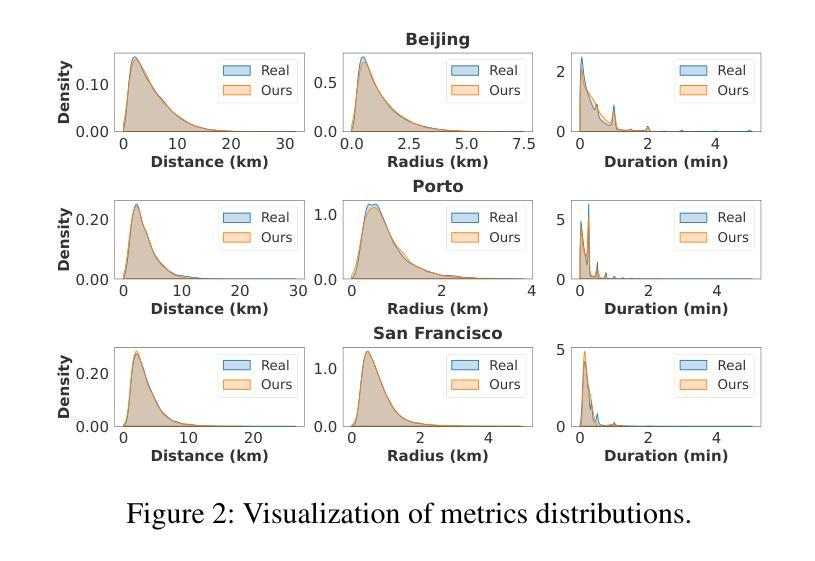
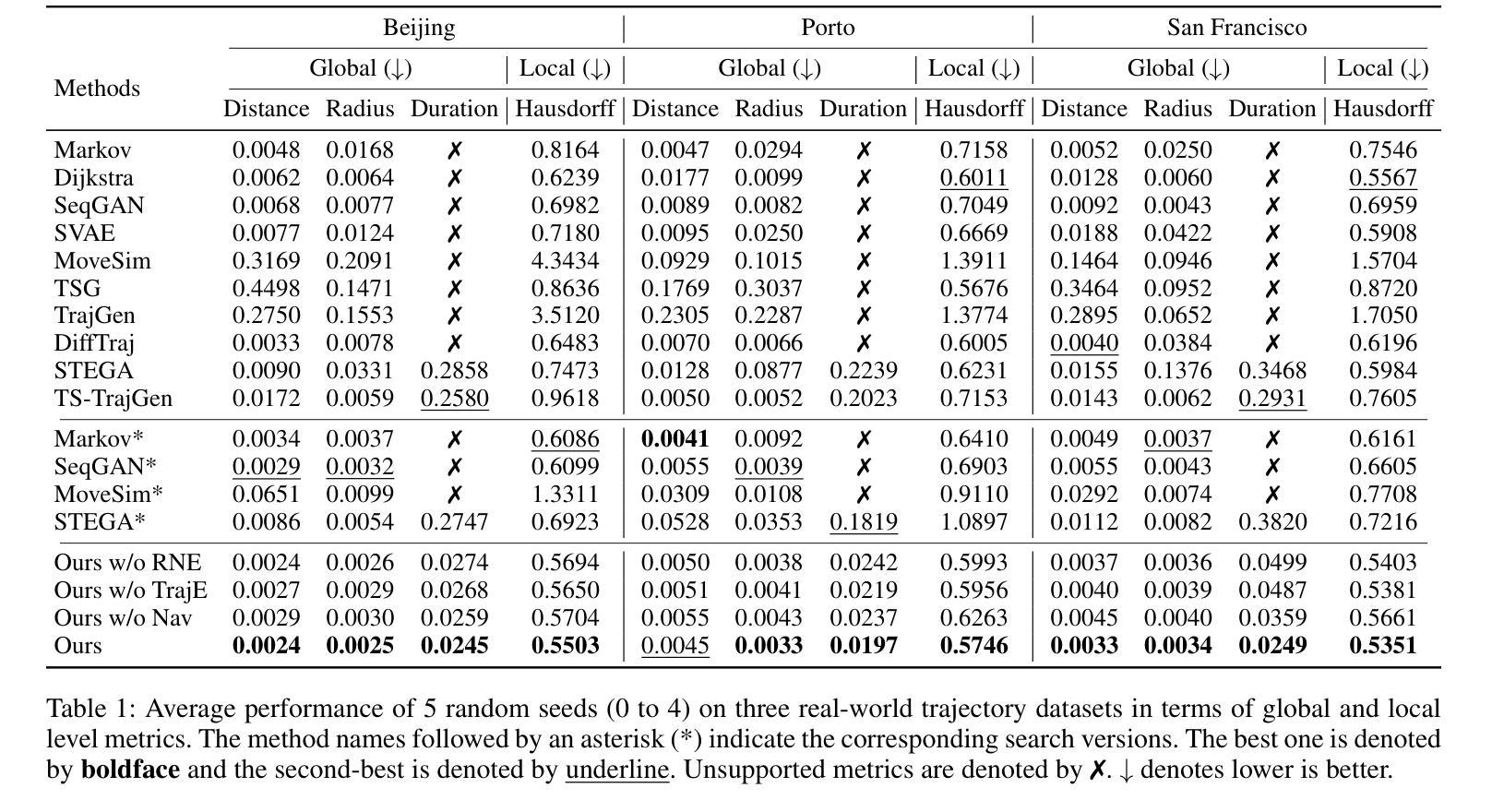
Holistic Semantic Representation for Navigational Trajectory Generation
Authors:Ji Cao, Tongya Zheng, Qinghong Guo, Yu Wang, Junshu Dai, Shunyu Liu, Jie Yang, Jie Song, Mingli Song
Trajectory generation has garnered significant attention from researchers in the field of spatio-temporal analysis, as it can generate substantial synthesized human mobility trajectories that enhance user privacy and alleviate data scarcity. However, existing trajectory generation methods often focus on improving trajectory generation quality from a singular perspective, lacking a comprehensive semantic understanding across various scales. Consequently, we are inspired to develop a HOlistic SEmantic Representation (HOSER) framework for navigational trajectory generation. Given an origin-and-destination (OD) pair and the starting time point of a latent trajectory, we first propose a Road Network Encoder to expand the receptive field of road- and zone-level semantics. Second, we design a Multi-Granularity Trajectory Encoder to integrate the spatio-temporal semantics of the generated trajectory at both the point and trajectory levels. Finally, we employ a Destination-Oriented Navigator to seamlessly integrate destination-oriented guidance. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that HOSER outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by a significant margin. Moreover, the model’s performance in few-shot learning and zero-shot learning scenarios further verifies the effectiveness of our holistic semantic representation.
轨迹生成已引起时空分析领域研究人员的广泛关注,因为它可以生成大量合成的人类移动轨迹,增强用户隐私并缓解数据稀缺问题。然而,现有的轨迹生成方法往往从单一角度改进轨迹生成质量,缺乏跨不同尺度的全面语义理解。因此,我们受到启发,开发出用于导航轨迹生成的HOlistic SEmantic Representation(HOSER)框架。给定起点和终点对以及潜在轨迹的起始时间点,我们首先提出一种道路网络编码器,以扩大道路和区域级别的语义感受野。其次,我们设计了一种多粒度轨迹编码器,以整合生成轨迹的点和轨迹级别的时空语义。最后,我们采用目标导向导航器,无缝集成以目的地为导向的导航。在三个真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,HOSER显著优于最新基线。此外,该模型在少样本学习和零样本学习场景中的性能进一步验证了我们的整体语义表示的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
轨迹生成受到时空分析领域研究者的关注,因为它能生成大量合成的人类移动轨迹,增强用户隐私并缓解数据稀缺问题。然而,现有轨迹生成方法往往从单一角度改进轨迹生成质量,缺乏跨不同尺度的全面语义理解。因此,我们提出一种整体的语义表示(HOSER)框架来进行导航轨迹生成。给定起点和终点对以及潜在轨迹的起始时间点,我们首先提出道路网络编码器来扩展道路和区域级别的语义感受野。其次,我们设计了一种多粒度轨迹编码器,以整合生成轨迹的点和轨迹级别的时空语义。最后,我们采用面向目的地的导航器无缝集成目的地导向的导航。在三个真实世界数据集上的广泛实验表明,HOSER显著优于最新基线。此外,该模型在少样本学习和零样本学习场景中的表现进一步验证了其全面的语义表示的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 轨迹生成是时空分析领域的重要研究方向,能生成合成的人类移动轨迹,增强用户隐私并缓解数据稀缺问题。
- 现有轨迹生成方法主要关注提高轨迹生成质量,但缺乏跨不同尺度的全面语义理解。
- HOSER框架包含三个主要部分:道路网络编码器、多粒度轨迹编码器和面向目的地的导航器。
- 道路网络编码器扩大道路和区域级别的语义感受野。
- 多粒度轨迹编码器整合生成轨迹的点和轨迹级别的时空语义。
- 面向目的地的导航器无缝集成目的地导向的导航。
点此查看论文截图

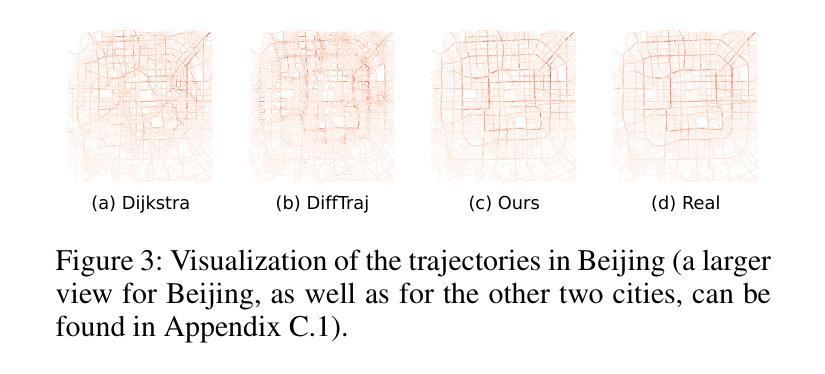
Noise-Tolerant Hybrid Prototypical Learning with Noisy Web Data
Authors:Chao Liang, Linchao Zhu, Zongxin Yang, Wei Chen, Yi Yang
We focus on the challenging problem of learning an unbiased classifier from a large number of potentially relevant but noisily labeled web images given only a few clean labeled images. This problem is particularly practical because it reduces the expensive annotation costs by utilizing freely accessible web images with noisy labels. Typically, prototypes are representative images or features used to classify or identify other images. However, in the few clean and many noisy scenarios, the class prototype can be severely biased due to the presence of irrelevant noisy images. The resulting prototypes are less compact and discriminative, as previous methods do not take into account the diverse range of images in the noisy web image collections. On the other hand, the relation modeling between noisy and clean images is not learned for the class prototype generation in an end-to-end manner, which results in a suboptimal class prototype. In this article, we introduce a similarity maximization loss named SimNoiPro. Our SimNoiPro first generates noise-tolerant hybrid prototypes composed of clean and noise-tolerant prototypes and then pulls them closer to each other. Our approach considers the diversity of noisy images by explicit division and overcomes the optimization discrepancy issue. This enables better relation modeling between clean and noisy images and helps extract judicious information from the noisy image set. The evaluation results on two extended few-shot classification benchmarks confirm that our SimNoiPro outperforms prior methods in measuring image relations and cleaning noisy data.
我们关注从大量可能相关但带有噪声标签的网络图像中学习无偏见分类器的问题,仅使用少量干净标记的图像。这个问题特别实用,因为它通过利用带有噪声标签的可自由访问的网络图像来降低了昂贵的标注成本。然而,通常原型是用于分类或识别其他图像的代表图像或特征。但在少数清洁和大量噪声场景中,由于存在不相关的噪声图像,类原型可能会受到严重偏见。由此产生的原型不够紧凑和鉴别力不强,因为以前的方法没有考虑到噪声网络图像集合中图像的多样性范围。另一方面,类原型的生成并没有以端到端的方式学习噪声图像和干净图像之间的关系建模,这导致了次优的类原型。在本文中,我们引入了一种名为SimNoiPro的相似性最大化损失。我们的SimNoiPro首先生成由清洁和噪声容忍原型组成的噪声容忍混合原型,然后将它们彼此拉近。我们的方法通过显式划分考虑了噪声图像的多样性,并克服了优化差异问题。这能够实现对清洁和噪声图像之间关系的更好建模,并有助于从噪声图像集中提取明智的信息。在两个扩展的小样本分类基准上的评估结果证实,我们的SimNoiPro在衡量图像关系和清理噪声数据方面优于先前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TOMM 2024
Summary
本文关注从大量潜在相关但带有噪声标签的网络图像中学习无偏见分类器的问题,其中只有少数干净标签的图像。通过引入SimNoiPro相似性最大化损失,生成噪声容忍的混合原型,并将它们彼此拉近,以更好地模拟清洁和噪声图像之间的关系,并从噪声图像集中提取明智的信息。评价结果显示,SimNoiPro在衡量图像关系和清理噪声数据方面优于先前的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 本文关注从大量网络图像中学习无偏见分类器的问题,这些图像带有噪声标签,但仅有少数干净标签的图像。
- 引入SimNoiPro相似性最大化损失,用于处理噪声容忍和原型生成。
- 生成噪声容忍的混合原型,由干净和噪声容忍的原型组成。
- 将生成的原型彼此拉近,以更好地模拟清洁和噪声图像之间的关系。
- 方法考虑了噪声图像的多样性,并通过明确划分来克服优化差异问题。
- 能从噪声图像集中提取明智的信息。
点此查看论文截图

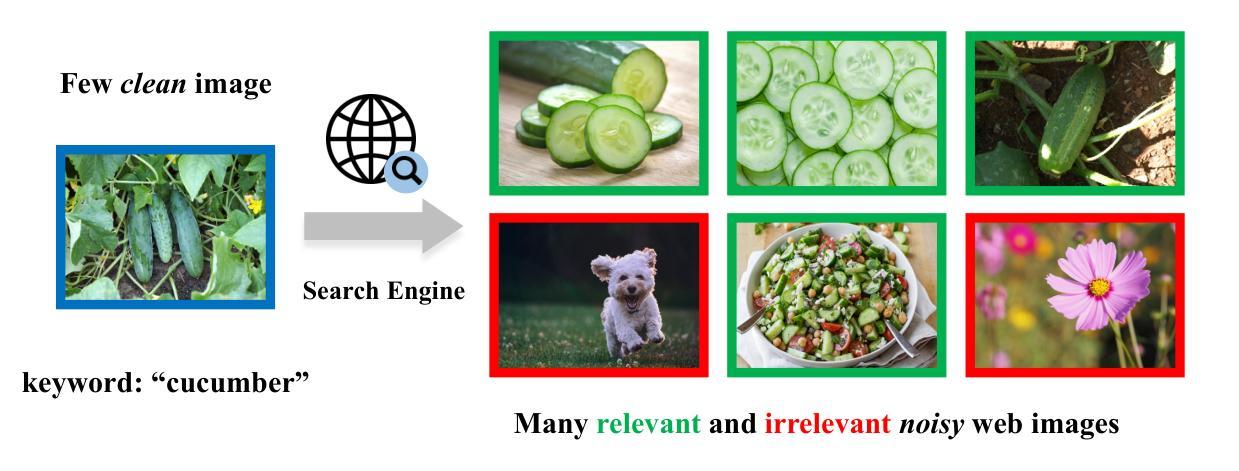
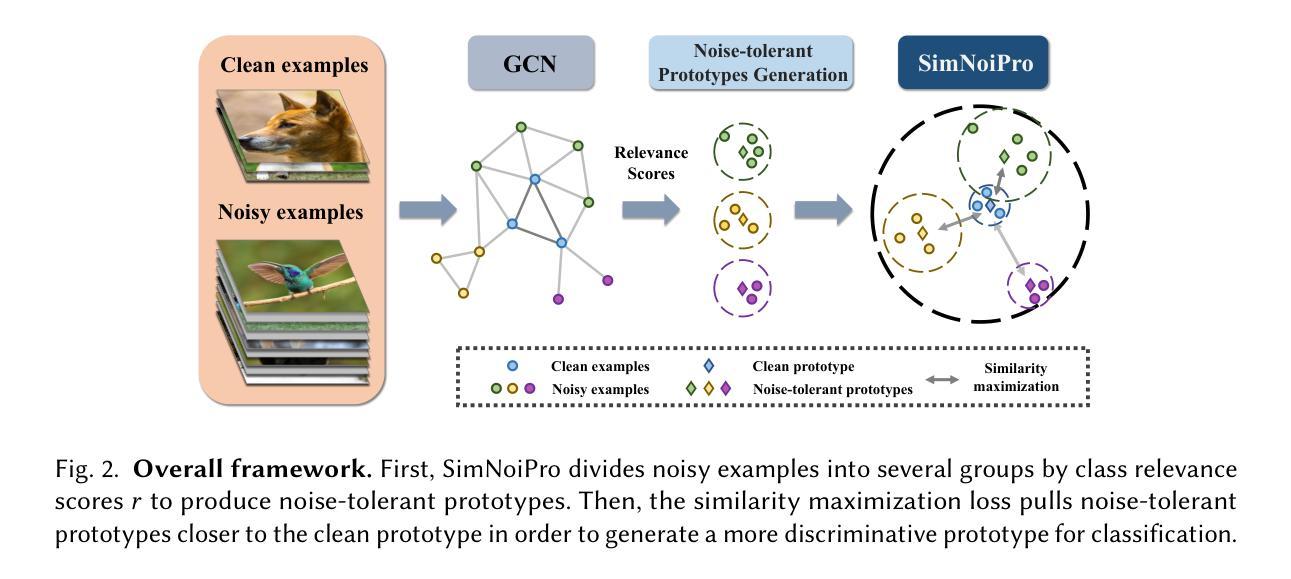
Generalization-Enhanced Few-Shot Object Detection in Remote Sensing
Authors:Hui Lin, Nan Li, Pengjuan Yao, Kexin Dong, Yuhan Guo, Danfeng Hong, Ying Zhang, Congcong Wen
Remote sensing object detection is particularly challenging due to the high resolution, multi-scale features, and diverse ground object characteristics inherent in satellite and UAV imagery. These challenges necessitate more advanced approaches for effective object detection in such environments. While deep learning methods have achieved remarkable success in remote sensing object detection, they typically rely on large amounts of labeled data. Acquiring sufficient labeled data, particularly for novel or rare objects, is both challenging and time-consuming in remote sensing scenarios, limiting the generalization capabilities of existing models. To address these challenges, few-shot learning (FSL) has emerged as a promising approach, aiming to enable models to learn new classes from limited labeled examples. Building on this concept, few-shot object detection (FSOD) specifically targets object detection challenges in data-limited conditions. However, the generalization capability of FSOD models, particularly in remote sensing, is often constrained by the complex and diverse characteristics of the objects present in such environments. In this paper, we propose the Generalization-Enhanced Few-Shot Object Detection (GE-FSOD) model to improve the generalization capability in remote sensing FSOD tasks. Our model introduces three key innovations: the Cross-Level Fusion Pyramid Attention Network (CFPAN) for enhanced multi-scale feature representation, the Multi-Stage Refinement Region Proposal Network (MRRPN) for more accurate region proposals, and the Generalized Classification Loss (GCL) for improved classification performance in few-shot scenarios. Extensive experiments on the DIOR and NWPU VHR-10 datasets show that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance for few-shot object detection in remote sensing.
遥感目标检测因其固有的高分辨率、多尺度特征和地面目标特性多样性,在卫星和无人机图像中面临巨大挑战。这些挑战要求更先进的方法在这样的环境中进行有效的目标检测。虽然深度学习方法在遥感目标检测中取得了显著的成功,但它们通常依赖于大量的标记数据。在遥感场景中,获取足够的有标签数据,特别是对于新型或稀有目标,既具有挑战性又非常耗时,这限制了现有模型的泛化能力。为了解决这些挑战,小样本学习(FSL)作为一种有前景的方法应运而生,旨在使模型能够从有限的标记示例中学习新的类别。在此基础上,小样本目标检测(FSOD)专门解决数据有限条件下的目标检测挑战。然而,FSOD模型的泛化能力,特别是在遥感领域,往往受到此类环境中对象复杂和多样特性的制约。在本文中,我们提出了通用增强小样本目标检测(GE-FSOD)模型,以提高遥感FSOD任务的泛化能力。我们的模型引入了三个关键创新点:用于增强多尺度特征表示的跨级融合金字塔注意力网络(CFPAN)、用于更精确区域提议的多阶段细化区域提议网络(MRRPN)以及用于改进小样本场景中分类性能的广义分类损失(GCL)。在DIOR和NWPU VHR-10数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的模型在遥感小样本目标检测方面达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了遥感物体检测面临的挑战,如高分辨率、多尺度特征和地面物体特性的多样性。深度学习方法虽然取得了显著的成功,但依赖于大量标记数据。为解决获取足够标记数据的挑战,文中提出了基于泛化能力提升的少镜头目标检测模型(GE-FSOD)。该模型引入了三个关键创新点:跨层次融合金字塔注意力网络(CFPAN)用于增强多尺度特征表示,多阶段细化区域提议网络(MRRPN)用于更准确的区域提议,以及广义分类损失(GCL)用于提高少镜头场景中的分类性能。在DIOR和NWPU VHR-10数据集上的实验表明,该模型在遥感少镜头目标检测方面达到了最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感物体检测面临高分辨率、多尺度特征和地面物体多样性等挑战。
- 深度学习方法在遥感物体检测中取得了显著成功,但依赖大量标记数据。
- 获取足够标记数据在遥感场景中具有挑战性和时间成本。
- 少镜头学习(FSL)旨在从有限标记示例中学习新类别,是解决上述挑战的有前途的方法。
- 本文提出了基于泛化能力提升的少镜头目标检测模型(GE-FSOD)。
- GE-FSOD模型引入了三个关键创新点:CFPAN、MRRPN和GCL。
点此查看论文截图



Advancing Pancreatic Cancer Prediction with a Next Visit Token Prediction Head on top of Med-BERT
Authors:Jianping He, Laila Rasmy, Degui Zhi, Cui Tao
Background: Recently, numerous foundation models pretrained on extensive data have demonstrated efficacy in disease prediction using Electronic Health Records (EHRs). However, there remains some unanswered questions on how to best utilize such models especially with very small fine-tuning cohorts. Methods: We utilized Med-BERT, an EHR-specific foundation model, and reformulated the disease binary prediction task into a token prediction task and a next visit mask token prediction task to align with Med-BERT’s pretraining task format in order to improve the accuracy of pancreatic cancer (PaCa) prediction in both few-shot and fully supervised settings. Results: The reformulation of the task into a token prediction task, referred to as Med-BERT-Sum, demonstrates slightly superior performance in both few-shot scenarios and larger data samples. Furthermore, reformulating the prediction task as a Next Visit Mask Token Prediction task (Med-BERT-Mask) significantly outperforms the conventional Binary Classification (BC) prediction task (Med-BERT-BC) by 3% to 7% in few-shot scenarios with data sizes ranging from 10 to 500 samples. These findings highlight that aligning the downstream task with Med-BERT’s pretraining objectives substantially enhances the model’s predictive capabilities, thereby improving its effectiveness in predicting both rare and common diseases. Conclusion: Reformatting disease prediction tasks to align with the pretraining of foundation models enhances prediction accuracy, leading to earlier detection and timely intervention. This approach improves treatment effectiveness, survival rates, and overall patient outcomes for PaCa and potentially other cancers.
背景:最近,许多在大量数据上进行预训练的基石模型在利用电子健康记录(EHRs)进行疾病预测方面表现出了有效性。然而,关于如何最好在非常小的微调群体中使用这些模型的问题仍未得到解答。方法:我们使用了针对EHR的基石模型Med-BERT,并将疾病二分类预测任务重新制定为标记预测任务和下次就诊掩码标记预测任务,以与Med-BERT的预训练任务格式对齐,以提高胰腺癌(PaCa)在少量镜头和完全监督设置中的预测准确性。结果:将任务重新制定为标记预测任务(称为Med-BERT-Sum)在少量镜头场景和较大的数据样本中都表现出略微优越的性能。此外,将预测任务重新制定为下次就诊掩码标记预测任务(Med-BERT-Mask)比传统的二分类(BC)预测任务(Med-BERT-BC)在样本量从10到500的少量镜头场景中高出3%至7%。这些发现表明,将下游任务与Med-BERT的预训练目标对齐可以显著提高模型的预测能力,从而提高其在预测罕见疾病和常见疾病方面的有效性。结论:重新格式化疾病预测任务,以与基石模型的预训练对齐,可以提高预测准确性,从而实现早期检测和及时干预。这种方法提高了胰腺癌和其他潜在癌症的治疗效率、存活率和整体患者结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了利用Med-BERT这一针对电子健康记录(EHR)的预训练模型进行疾病预测的方法。通过改革任务形式,将疾病二分类预测任务转化为token预测任务和下次就诊mask token预测任务,提高了胰腺癌预测的准确性,特别是在小样数据场景下。实验结果表明,改革后的模型性能在少数样本和大样本下均表现更优,显示了对齐下游任务和预训练任务能提高模型的预测能力,特别是在预测罕见病方面。
Key Takeaways
- 采用Med-BERT模型进行疾病预测具有有效性和潜力。
- 任务形式的改革,如token预测任务和下次就诊mask token预测任务,能提高胰腺癌预测的准确性。
- 在小样数据场景下,改革后的模型表现出更高的性能。
- 对齐下游任务和预训练任务能提高模型的预测能力。
- 该方法可能对预测罕见疾病和常见疾病都有效。
- 改革后的模型有助于提高胰腺癌及其他癌症的治疗效果和患者生存率。
点此查看论文截图




Training-Free Point Cloud Recognition Based on Geometric and Semantic Information Fusion
Authors:Yan Chen, Di Huang, Zhichao Liao, Xi Cheng, Xinghui Li, Lone Zeng
The trend of employing training-free methods for point cloud recognition is becoming increasingly popular due to its significant reduction in computational resources and time costs. However, existing approaches are limited as they typically extract either geometric or semantic features. To address this limitation, we are the first to propose a novel training-free method that integrates both geometric and semantic features. For the geometric branch, we adopt a non-parametric strategy to extract geometric features. In the semantic branch, we leverage a model aligned with text features to obtain semantic features. Additionally, we introduce the GFE module to complement the geometric information of point clouds and the MFF module to improve performance in few-shot settings. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art training-free approaches on mainstream benchmark datasets, including ModelNet and ScanObiectNN.
采用无训练方法处理点云识别的趋势正越来越受欢迎,因为它能显著减少计算资源和时间成本。然而,现有方法通常仅限于提取几何或语义特征。为了解决这一局限性,我们首次提出了一种新型的无训练方法,该方法融合了几何和语义特征。在几何分支中,我们采用非参数策略来提取几何特征。在语义分支中,我们利用与文本特征对齐的模型来获取语义特征。此外,我们还引入了GFE模块来补充点云的几何信息,并引入了MFF模块来提高小样本场景下的性能。实验结果表明,我们的方法在主流基准数据集(包括ModelNet和ScanObiectNN)上的表现优于现有的最新无训练方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
训练免费的方法在点云识别中越来越受欢迎,因为它能显著减少计算资源和时间成本。一种新型训练免费方法首次被提出,它整合了几何和语义特征,提高了点云识别的性能。采用非参数策略提取几何特征,利用与文本特征对齐的模型获取语义特征。此外,还引入了GFE模块来补充点云的几何信息,MFF模块提升在few-shot场景中的表现。实验结果证明,该方法在主流基准数据集ModelNet和ScanObiectNN上的表现优于现有的先进训练免费方法。
Key Takeaways
- 训练免费方法在点云识别中逐渐普及,主要得益于其减少的计算资源和时间成本。
- 新型训练免费方法首次结合几何和语义特征进行点云识别。
- 采用非参数策略提取几何特征,利用与文本特征对齐的模型获取语义特征。
- GFE模块的引入用于补充点云的几何信息。
- MFF模块旨在提升在数据稀缺场景(few-shot)下的表现。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在主流基准数据集上的表现优于其他训练免费方法。
- 该方法具有潜力为点云识别领域带来革新。
点此查看论文截图




Distillation Learning Guided by Image Reconstruction for One-Shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Feng Zhou, Yanjie Zhou, Longjie Wang, Yun Peng, David E. Carlson, Liyun Tu
Traditional one-shot medical image segmentation (MIS) methods use registration networks to propagate labels from a reference atlas or rely on comprehensive sampling strategies to generate synthetic labeled data for training. However, these methods often struggle with registration errors and low-quality synthetic images, leading to poor performance and generalization. To overcome this, we introduce a novel one-shot MIS framework based on knowledge distillation, which allows the network to directly ‘see’ real images through a distillation process guided by image reconstruction. It focuses on anatomical structures in a single labeled image and a few unlabeled ones. A registration-based data augmentation network creates realistic, labeled samples, while a feature distillation module helps the student network learn segmentation from these samples, guided by the teacher network. During inference, the streamlined student network accurately segments new images. Evaluations on three public datasets (OASIS for T1 brain MRI, BCV for abdomen CT, and VerSe for vertebrae CT) show superior segmentation performance and generalization across different medical image datasets and modalities compared to leading methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/NoviceFodder/OS-MedSeg.
传统的单镜头医学图像分割(MIS)方法使用注册网络来传播来自参考图谱的标签,或者依赖于全面的采样策略来生成合成标记数据进行训练。然而,这些方法常常受到注册错误和低质量合成图像的影响,导致性能不佳和泛化能力差。为了克服这一问题,我们引入了一种基于知识蒸馏的新型单镜头MIS框架,该框架允许网络通过由图像重建引导的蒸馏过程直接“查看”真实图像。它专注于单个标记图像和少量未标记图像中的解剖结构。基于注册的数据增强网络创建逼真的标记样本,而特征蒸馏模块则帮助学生网络从这些样本中学习分割,并受教师网络的指导。在推理过程中,简化的学生网络能够准确地对新图像进行分割。在三个公共数据集(OASIS用于T1脑MRI、BCV用于腹部CT和VerSe用于椎体CT)上的评估显示,与领先的方法相比,我们的方法在医学图像数据集和不同模态的分割性能及泛化能力上具有优势。我们的代码可在https://github.com/NoviceFodder/OS-MedSeg上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于知识蒸馏的新型单次医学图像分割(MIS)框架,解决了传统方法面临的注册误差和低质量合成图像问题。该框架通过图像重建引导蒸馏过程,使网络能够直接“看到”真实图像。它专注于单张标记图像和少量未标记图像中的解剖结构。注册式数据增强网络创建逼真的标记样本,特征蒸馏模块帮助学生网络从这些样本中学习分割,受教师网络的引导。在新图像上的评估表现出卓越的分割性能和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 新型单次医学图像分割框架引入知识蒸馏技术,解决传统方法的注册误差和低质量合成图像问题。
- 框架允许网络通过蒸馏过程直接“看到”真实图像。
- 框架专注于单张标记图像和少量未标记图像中的解剖结构。
- 使用注册式数据增强网络创建逼真的标记样本。
- 特征蒸馏模块帮助学生网络从标记样本中学习分割,受教师网络的引导。
- 在三个公共数据集上的评估显示,该框架的分割性能和泛化能力优于领先方法。
点此查看论文截图




A Survey of Recent Backdoor Attacks and Defenses in Large Language Models
Authors:Shuai Zhao, Meihuizi Jia, Zhongliang Guo, Leilei Gan, Xiaoyu Xu, Xiaobao Wu, Jie Fu, Yichao Feng, Fengjun Pan, Luu Anh Tuan
Large Language Models (LLMs), which bridge the gap between human language understanding and complex problem-solving, achieve state-of-the-art performance on several NLP tasks, particularly in few-shot and zero-shot settings. Despite the demonstrable efficacy of LLMs, due to constraints on computational resources, users have to engage with open-source language models or outsource the entire training process to third-party platforms. However, research has demonstrated that language models are susceptible to potential security vulnerabilities, particularly in backdoor attacks. Backdoor attacks are designed to introduce targeted vulnerabilities into language models by poisoning training samples or model weights, allowing attackers to manipulate model responses through malicious triggers. While existing surveys on backdoor attacks provide a comprehensive overview, they lack an in-depth examination of backdoor attacks specifically targeting LLMs. To bridge this gap and grasp the latest trends in the field, this paper presents a novel perspective on backdoor attacks for LLMs by focusing on fine-tuning methods. Specifically, we systematically classify backdoor attacks into three categories: full-parameter fine-tuning, parameter-efficient fine-tuning, and no fine-tuning Based on insights from a substantial review, we also discuss crucial issues for future research on backdoor attacks, such as further exploring attack algorithms that do not require fine-tuning, or developing more covert attack algorithms.
大型语言模型(LLMs)弥合了人类语言理解与复杂问题求解之间的鸿沟,并在多个自然语言处理任务上达到了最先进的性能,特别是在小样本和零样本设置中。尽管LLM的效用已经得到了证明,但由于计算资源的限制,用户不得不使用开源语言模型或将整个训练过程外包给第三方平台。然而,研究表明,语言模型容易受到潜在的安全漏洞的影响,特别是在后门攻击中。后门攻击旨在通过毒害训练样本或模型权重来引入有针对性的漏洞,从而使攻击者能够通过恶意触发因素来操纵模型响应。虽然关于后门攻击的现有调查提供了全面的概述,但它们缺乏对针对LLM的后门攻击的深入研究。为了弥补这一差距并了解该领域的最新趋势,本文提出了一种关于LLM后门攻击的新视角,重点关注微调方法。具体来说,我们将后门攻击系统地分为三类:全参数微调、参数有效微调和无微调。基于大量的审查结果,我们还讨论了未来研究后门攻击的关键问题,如进一步探索不需要微调的攻击算法,或开发更隐蔽的攻击算法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in TMLR
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在多个自然语言处理任务上实现了卓越的性能,特别是在小样例和零样例设置下。然而,由于计算资源限制,用户需要使用开源语言模型或将整个训练过程外包给第三方平台。此外,语言模型容易遭受安全漏洞攻击,特别是后门攻击。本文重点介绍了针对LLM的后门攻击的新视角,重点介绍了微调方法。我们将后门攻击系统地分为全参数微调、参数有效微调和无微调三类,并基于大量研究讨论了未来研究的关键问题。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在自然语言处理任务上表现卓越,尤其在小样例和零样例设置下。
- 由于计算资源限制,用户需依赖开源语言模型或第三方平台进行训练。
- 语言模型容易受到后门攻击等安全漏洞的影响。
- 后门攻击可以通过对训练样本或模型权重进行毒害,操纵模型响应。
- 现有后门攻击调查缺乏针对LLMs的深入研究。
- 本文对后门攻击针对LLMs进行了分类,包括全参数微调、参数有效微调和无微调三种类型。
点此查看论文截图




RETTA: Retrieval-Enhanced Test-Time Adaptation for Zero-Shot Video Captioning
Authors:Yunchuan Ma, Laiyun Qing, Guorong Li, Yuankai Qi, Amin Beheshti, Quan Z. Sheng, Qingming Huang
Despite the significant progress of fully-supervised video captioning, zero-shot methods remain much less explored. In this paper, we propose a novel zero-shot video captioning framework named Retrieval-Enhanced Test-Time Adaptation (RETTA), which takes advantage of existing pretrained large-scale vision and language models to directly generate captions with test-time adaptation. Specifically, we bridge video and text using four key models: a general video-text retrieval model XCLIP, a general image-text matching model CLIP, a text alignment model AnglE, and a text generation model GPT-2, due to their source-code availability. The main challenge is how to enable the text generation model to be sufficiently aware of the content in a given video so as to generate corresponding captions. To address this problem, we propose using learnable tokens as a communication medium among these four frozen models GPT-2, XCLIP, CLIP, and AnglE. Different from the conventional way that trains these tokens with training data, we propose to learn these tokens with soft targets of the inference data under several carefully crafted loss functions, which enable the tokens to absorb video information catered for GPT-2. This procedure can be efficiently done in just a few iterations (we use 16 iterations in the experiments) and does not require ground truth data. Extensive experimental results on three widely used datasets, MSR-VTT, MSVD, and VATEX, show absolute 5.1%-32.4% improvements in terms of the main metric CIDEr compared to several state-of-the-art zero-shot video captioning methods.
尽管全监督视频描述取得了重大进展,但零样本方法仍然被研究得较少。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的零样本视频描述框架,名为“基于检索的测试时间自适应(RETTA)”,它利用现有的预训练大规模视觉和语言模型,通过测试时间自适应直接生成描述。具体来说,我们使用四个关键模型来连接视频和文本:通用的视频文本检索模型XCLIP,通用的图像文本匹配模型CLIP,文本对齐模型AnglE,以及文本生成模型GPT-2,原因是这些模型有源代码可供使用。主要挑战在于如何让文本生成模型充分意识到给定视频的内容,从而生成相应的描述。为了解决这个问题,我们提出使用可学习的令牌作为这四个冻结模型GPT-2、XCLIP、CLIP和AnglE之间的通信媒介。不同于使用训练数据训练这些令牌的传统方式,我们提出使用精心设计的损失函数下的推理数据的软目标来学习这些令牌,使令牌能够吸收针对GPT-2的视频信息。这个过程只需几次迭代就能高效完成(我们在实验中使用16次迭代),并且不需要真实数据。在三个广泛使用的数据集MSR-VTT、MSVD和VATEX上的大量实验结果表明,与几种最先进的零样本视频描述方法相比,主要指标CIDEr的绝对改进率为5.1%~32.4%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Retrieval-Enhanced Test-Time Adaptation(RETTA)的零样本视频描述框架,利用现有的预训练大规模视觉和语言模型,通过测试时适应技术直接生成视频描述。该框架结合四种模型,包括视频文本检索模型XCLIP、图像文本匹配模型CLIP、文本对齐模型AnglE和文本生成模型GPT-2,通过可学习令牌作为沟通媒介,在几个精心设计的损失函数下,使令牌吸收视频信息并适应GPT-2,以生成相应的视频描述。这一流程在仅几次迭代中即可完成,无需真实数据。在三个广泛应用的数据集上进行了实验验证,与最先进的零样本视频描述方法相比,主要指标CIDEr有显著改善。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种名为RETTA的零样本视频描述框架,结合预训练的大型视觉和语言模型进行视频描述生成。
- 利用四种关键模型:XCLIP、CLIP、AnglE和GPT-2,通过可学习令牌作为媒介进行信息交互。
- 提出了使用软目标在测试时学习令牌的方法,通过精心设计的损失函数使令牌吸收视频信息并适应GPT-2。
- 该流程无需真实数据,可在仅几次迭代中完成。
- 在三个广泛应用的数据集上进行了实验验证,显示出显著的性能改进。
- RETTA框架在零样本视频描述方面具有巨大的潜力,为未来的相关研究提供了新的方向。
点此查看论文截图