⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-08 更新
Noise-Robust Target-Speaker Voice Activity Detection Through Self-Supervised Pretraining
Authors:Holger Severin Bovbjerg, Jan Østergaard, Jesper Jensen, Zheng-Hua Tan
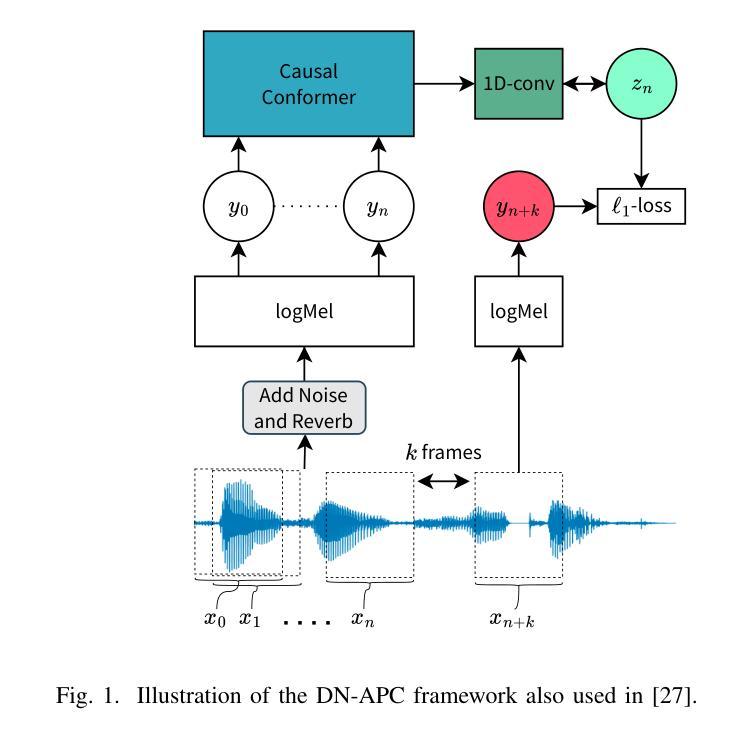
Target-Speaker Voice Activity Detection (TS-VAD) is the task of detecting the presence of speech from a known target-speaker in an audio frame. Recently, deep neural network-based models have shown good performance in this task. However, training these models requires extensive labelled data, which is costly and time-consuming to obtain, particularly if generalization to unseen environments is crucial. To mitigate this, we propose a causal, Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) pretraining framework, called Denoising Autoregressive Predictive Coding (DN-APC), to enhance TS-VAD performance in noisy conditions. We also explore various speaker conditioning methods and evaluate their performance under different noisy conditions. Our experiments show that DN-APC improves performance in noisy conditions, with a general improvement of approx. 2% in both seen and unseen noise. Additionally, we find that FiLM conditioning provides the best overall performance. Representation analysis via tSNE plots reveals robust initial representations of speech and non-speech from pretraining. This underscores the effectiveness of SSL pretraining in improving the robustness and performance of TS-VAD models in noisy environments.
目标说话人语音活动检测(TS-VAD)的任务是在音频帧中检测已知目标说话人的语音是否存在。最近,基于深度神经网络的模型在此任务中表现出良好的性能。然而,训练这些模型需要大量的标注数据,获取这些数据成本高昂且耗时,特别是在推广到未见过的环境至关重要时。为了缓解这一问题,我们提出了一种名为去噪自回归预测编码(DN-APC)的因果自监督学习(SSL)预训练框架,以提高TS-VAD在嘈杂条件下的性能。我们还探索了各种说话人调节方法,并评估了它们在不同的嘈杂条件下的性能。我们的实验表明,DN-APC在嘈杂条件下提高了性能,在可见和不可见噪声条件下总体提高了约2%。此外,我们发现Film调节提供了最佳的整体性能。通过t-SNE图进行的表示分析揭示了预训练中对语音和非语音的稳健初始表示。这突出了SSL预训练在提高TS-VAD模型在嘈杂环境中的稳健性和性能方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing for possible publication. 12 pages, 4 figures, 5 tables
Summary
目标说话人语音活动检测(TS-VAD)任务旨在从音频帧中检测已知目标说话人的语音。深度神经网络模型在该任务中表现出良好的性能,但其训练需要大量标注数据,获取成本高且耗时。为改善在噪声环境下的TS-VAD性能,本文提出了一种名为去噪自回归预测编码(DN-APC)的自监督学习预训练框架。同时,本文探索了多种说话人调节方法,并在不同噪声条件下评估其性能。实验表明,DN-APC在噪声环境下提高了性能,且在可见和不可见噪声下总体提高了约2%。此外,发现FiLM调节提供最佳的整体性能。通过t-SNE图进行表征分析显示,预训练对语音和非语音的初步表征稳健,突显了自监督学习预训练在提升TS-VAD模型在噪声环境中的稳健性和性能方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 目标说话人语音活动检测(TS-VAD)是识别音频帧中已知目标说话人语音的任务。
- 深度神经网络模型在TS-VAD中表现良好,但训练需要大量标注数据。
- 提出了一种自监督学习预训练框架——去噪自回归预测编码(DN-APC),以提高模型在噪声环境下的性能。
- DN-APC在可见和不可见噪声下总体提高了约2%的性能。
- FiLM调节方法提供最佳的整体性能。
- 表征分析显示预训练对语音和非语音的初步表征稳健。
点此查看论文截图

Samba-asr state-of-the-art speech recognition leveraging structured state-space models
Authors:Syed Abdul Gaffar Shakhadri, Kruthika KR, Kartik Basavaraj Angadi
We propose Samba ASR, the first state-of-the-art Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) model leveraging the novel Mamba architecture as both encoder and decoder, built on the foundation of state-space models (SSMs). Unlike transformer-based ASR models, which rely on self-attention mechanisms to capture dependencies, Samba ASR effectively models both local and global temporal dependencies using efficient state-space dynamics, achieving remarkable performance gains. By addressing the limitations of transformers, such as quadratic scaling with input length and difficulty in handling long-range dependencies, Samba ASR achieves superior accuracy and efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate that Samba ASR surpasses existing open-source transformer-based ASR models across various standard benchmarks, establishing it as the new state of the art in ASR. Extensive evaluations on benchmark datasets show significant improvements in Word Error Rate (WER), with competitive performance even in low-resource scenarios. Furthermore, the computational efficiency and parameter optimization of the Mamba architecture make Samba ASR a scalable and robust solution for diverse ASR tasks. Our contributions include: A new Samba ASR architecture demonstrating the superiority of SSMs over transformer-based models for speech sequence processing. A comprehensive evaluation on public benchmarks showcasing state-of-the-art performance. An analysis of computational efficiency, robustness to noise, and sequence generalization. This work highlights the viability of Mamba SSMs as a transformer-free alternative for efficient and accurate ASR. By leveraging state-space modeling advancements, Samba ASR sets a new benchmark for ASR performance and future research.
我们提出了Samba ASR,这是首个利用新型Mamba架构作为编码器和解码器的先进自动语音识别(ASR)模型,该模型基于状态空间模型(SSMs)构建。不同于基于变压器的ASR模型,它依赖于自注意力机制来捕捉依赖关系,Samba ASR通过使用高效的状态空间动力学有效地对局部和全局时间依赖关系进行建模,实现了显著的性能提升。通过解决变压器模型的局限性,如输入长度的二次扩展和处理长距离依赖关系的困难,Samba ASR在准确性和效率上达到了卓越的水平。
实验结果证明,Samba ASR在各种标准基准测试上超越了现有的开源基于变压器的ASR模型,成为ASR领域的新技术标杆。在基准数据集上的广泛评估显示,其在单词错误率(WER)上有显著改善,即使在资源匮乏的场景中也具有竞争力。此外,Mamba架构的计算效率和参数优化使得Samba ASR成为各种ASR任务的可扩展和稳健解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于状态空间模型(SSMs)的新颖Mamba架构,提出了一款领先的自动语音识别(ASR)模型——Samba ASR。该模型在编码器和解码器中都使用Mamba架构,有效捕捉语音序列的局部和全局时间依赖性,实现了显著的性能提升。与依赖自注意力机制的基于变压器的ASR模型相比,Samba ASR通过解决二次扩展输入长度和难以处理长距离依赖性问题等缺点,实现了更高的准确性和效率。Samba ASR在多种标准基准测试中均超过了现有的开源基于变压器的ASR模型,且在低资源场景中也有出色的表现。同时,Mamba架构的计算效率和参数优化使得Samba ASR成为多样ASR任务的可扩展和稳健解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- Samba ASR是基于状态空间模型(SSMs)的Mamba架构的自动语音识别(ASR)模型。
- 与基于变压器的ASR模型相比,Samba ASR更有效地捕捉语音序列的局部和全局时间依赖性。
- Samba ASR解决了基于变压器模型的缺点,如二次扩展输入长度和长距离依赖性问题处理困难等。
- Samba ASR在多种标准基准测试中表现优异,超过了现有的开源基于变压器的ASR模型。
- Samba ASR在低资源场景中也有出色的表现,且具备良好的计算效率和参数优化。
- 深入研究分析了Samba ASR的可行性,验证了它作为无变压器替代方案的高效性和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Long Speech Sequence Modelling for Time-Domain Depression Level Estimation
Authors:Shuanglin Li, Zhijie Xie, Syed Mohsen Naqvi
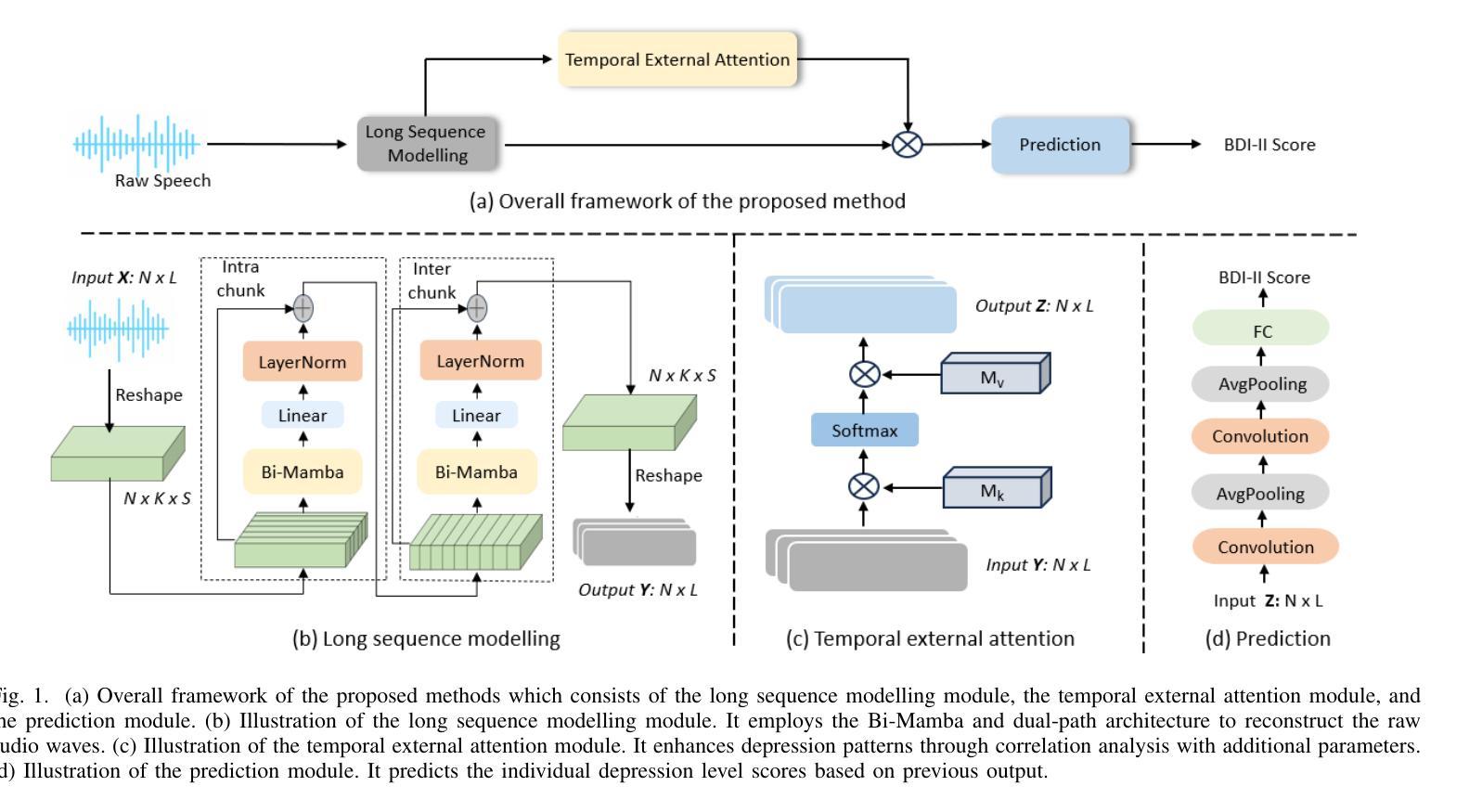
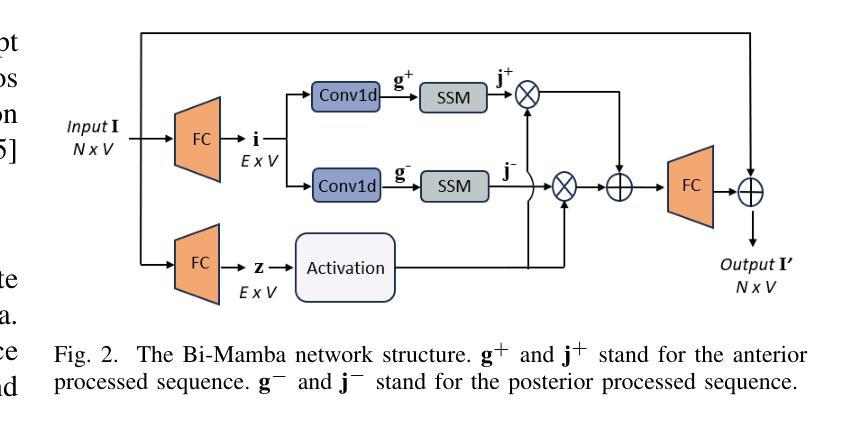
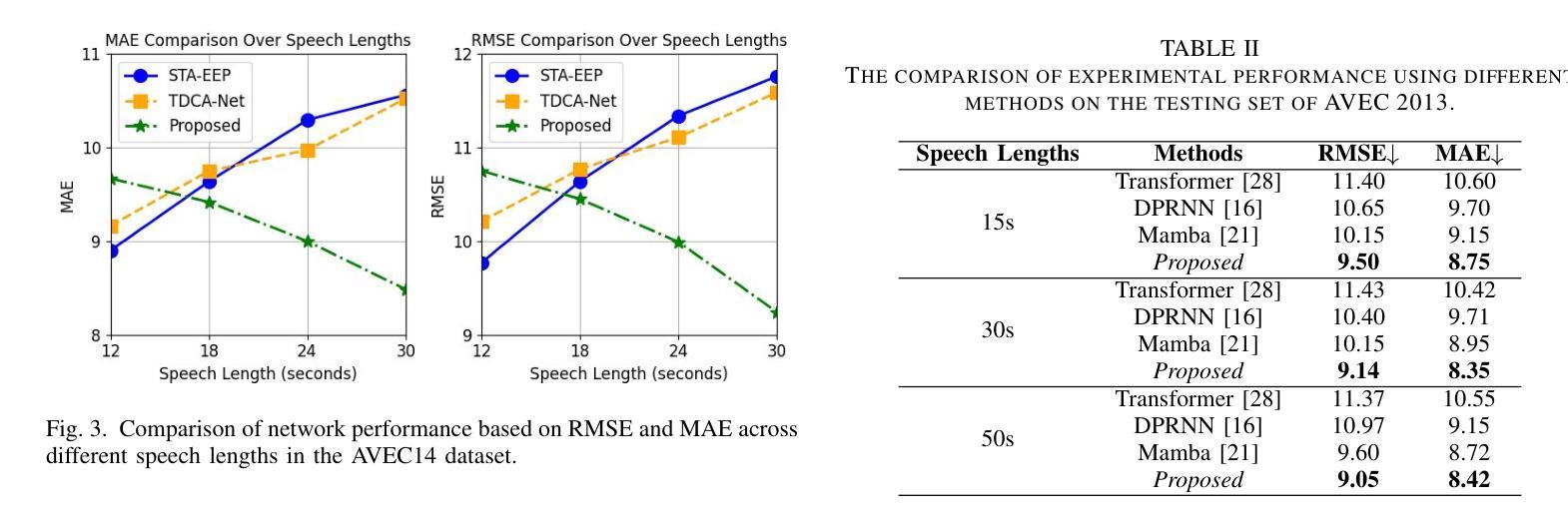
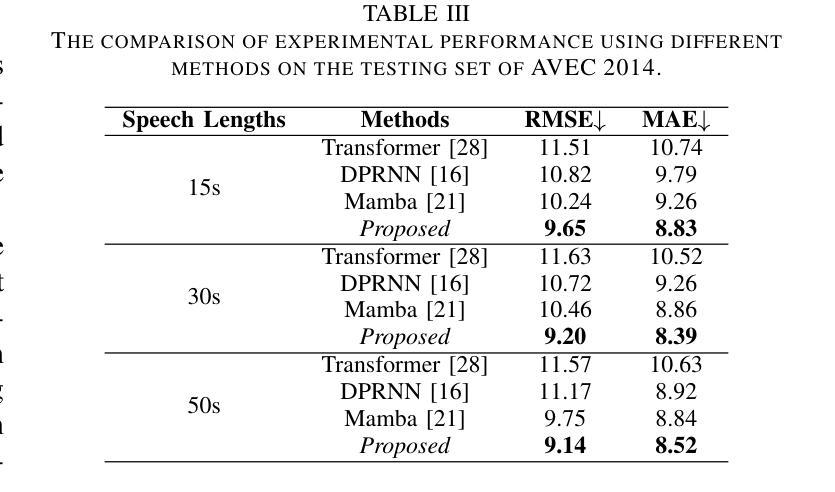
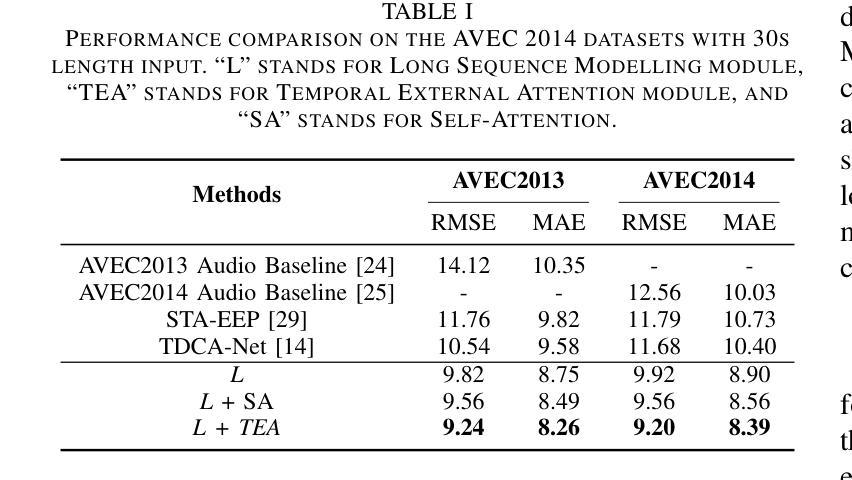
Depression significantly affects emotions, thoughts, and daily activities. Recent research indicates that speech signals contain vital cues about depression, sparking interest in audio-based deep-learning methods for estimating its severity. However, most methods rely on time-frequency representations of speech which have recently been criticized for their limitations due to the loss of information when performing time-frequency projections, e.g. Fourier transform, and Mel-scale transformation. Furthermore, segmenting real-world speech into brief intervals risks losing critical interconnections between recordings. Additionally, such an approach may not adequately reflect real-world scenarios, as individuals with depression often pause and slow down in their conversations and interactions. Building on these observations, we present an efficient method for depression level estimation using long speech signals in the time domain. The proposed method leverages a state space model coupled with the dual-path structure-based long sequence modelling module and temporal external attention module to reconstruct and enhance the detection of depression-related cues hidden in the raw audio waveforms. Experimental results on the AVEC2013 and AVEC2014 datasets show promising results in capturing consequential long-sequence depression cues and demonstrate outstanding performance over the state-of-the-art.
抑郁症显著影响情绪、思维和日常活动。最新研究表明,语音信号包含关于抑郁症的重要线索,这引发了人们对基于音频的深度学习方法在估计其严重程度方面的兴趣。然而,大多数方法依赖于语音的时间-频率表示,由于在进行时间-频率投影(例如傅立叶变换和梅尔尺度变换)时存在信息丢失而受到批评,这些时间频率表示存在局限性。此外,将现实世界中的语音分割成简短的间隔区间可能丢失关键录音之间的连接。再者,由于抑郁症患者通常在对话和互动中会停顿并放慢速度,这种方法可能无法充分反映现实场景。基于这些观察,我们提出了一种在时域内使用长语音信号进行抑郁程度估计的有效方法。该方法利用状态空间模型与基于双路径结构的长期序列建模模块和临时外部注意力模块相结合,重建并提高对隐藏在原始音频波形中的抑郁相关线索的检测。在AVEC2013和AVEC2014数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在捕捉重要的长期抑郁线索方面表现出良好的潜力,并在最新的技术研究中展现出卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
抑郁症严重影响情绪、思维及日常活动。最新研究表明,语音信号中包含关于抑郁症的重要线索,引发音频深度学习方法估算其严重性的兴趣。但多数方法依赖于语音的时间频率表示,此法因投影过程中的信息丢失而受到批评。为克服这些限制,我们提出了一种在时域使用长语音信号进行抑郁症水平估计的有效方法。该方法结合状态空间模型、双路径结构的长序列建模模块和临时外部注意力模块,重建并增强原始音频波形中隐藏的抑郁症相关线索的检测。在AVEC2013和AVEC2014数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在捕捉长期抑郁症线索方面表现出良好效果,并在最新技术上展现了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 抑郁症对情绪、思维和日常活动产生显著影响。
- 语音信号包含关于抑郁症的重要线索,引发音频深度学习方法的兴趣。
- 当前方法主要依赖于语音的时间频率表示,但此法存在信息丢失的批评。
- 提出一种在时域使用长语音信号的有效方法,以克服上述限制。
- 所提出的方法结合状态空间模型、双路径结构建模和临时外部注意力模块。
- 方法在捕捉长期抑郁症线索方面表现良好。
点此查看论文截图

Adapting Whisper for Code-Switching through Encoding Refining and Language-Aware Decoding
Authors:Jiahui Zhao, Hao Shi, Chenrui Cui, Tianrui Wang, Hexin Liu, Zhaoheng Ni, Lingxuan Ye, Longbiao Wang
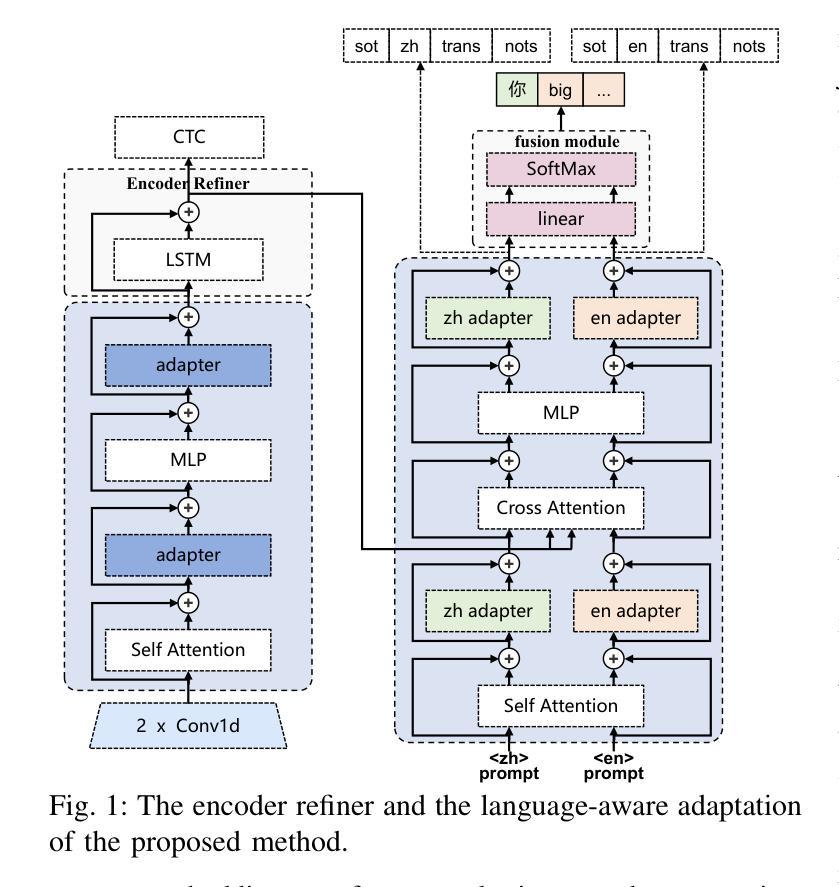
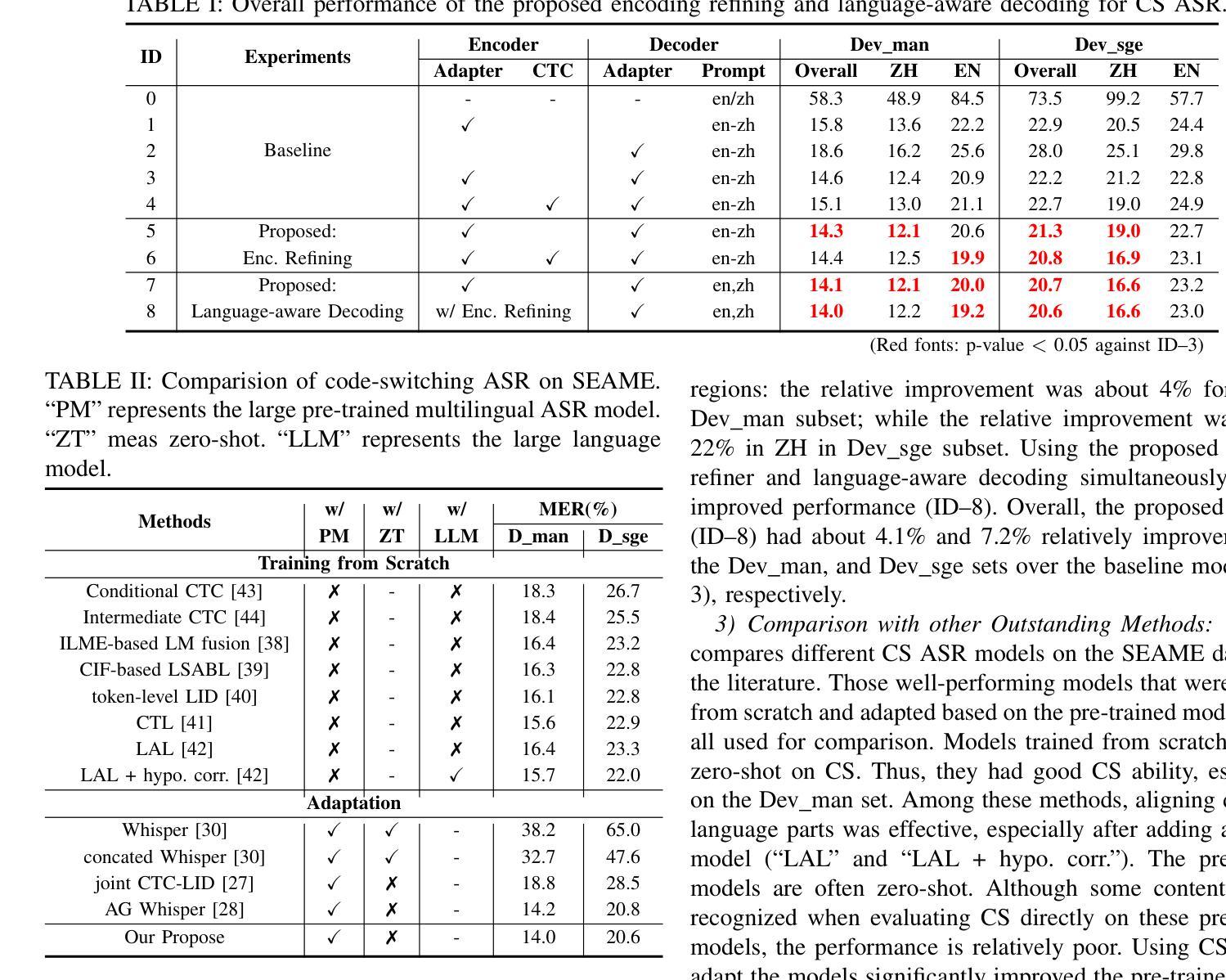
Code-switching (CS) automatic speech recognition (ASR) faces challenges due to the language confusion resulting from accents, auditory similarity, and seamless language switches. Adaptation on the pre-trained multi-lingual model has shown promising performance for CS-ASR. In this paper, we adapt Whisper, which is a large-scale multilingual pre-trained speech recognition model, to CS from both encoder and decoder parts. First, we propose an encoder refiner to enhance the encoder’s capacity of intra-sentence swithching. Second, we propose using two sets of language-aware adapters with different language prompt embeddings to achieve language-specific decoding information in each decoder layer. Then, a fusion module is added to fuse the language-aware decoding. The experimental results using the SEAME dataset show that, compared with the baseline model, the proposed approach achieves a relative MER reduction of 4.1% and 7.2% on the dev_man and dev_sge test sets, respectively, surpassing state-of-the-art methods. Through experiments, we found that the proposed method significantly improves the performance on non-native language in CS speech, indicating that our approach enables Whisper to better distinguish between the two languages.
代码切换(CS)自动语音识别(ASR)面临着由于口音、听觉相似性和无缝语言切换导致的语言混淆所带来的挑战。预训练的多元语言模型的适配已经显示出对CS-ASR的有前途的性能。在本文中,我们适配了whisper这一大规模的多语种预训练语音识别模型,用于句子内和句子间的代码切换。首先,我们提出了一种编码器优化器,以提高编码器在句子内部切换的能力。其次,我们建议使用两组带有不同语言提示嵌入的语言感知适配器,以实现每个解码器层中的语言特定解码信息。然后,添加一个融合模块来融合语言感知解码。使用SEAME数据集的实验结果表明,与基线模型相比,所提出的方法在dev_man和dev_sge测试集上分别实现了相对误差率(MER)降低4.1%和7.2%,超过了最新方法。通过实验,我们发现该方法在非母语语言的CS语音性能上有了显著提高,这表明我们的方法使whisper能够更好地区分两种语言。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对代码切换(CS)自动语音识别(ASR)中的语言混淆、口音、听觉相似性和无缝语言切换等问题,本文采用预训练的多语言模型进行适应并展现出良好性能。研究团队对大型预训练语音识别模型Whisper进行了适应,从编码器和解码器两个方面进行改进。通过提出编码器精炼器增强了编码器对句子内切换的处理能力,同时使用两组语言感知适配器和不同的语言提示嵌入来实现解码器的语言特异性。添加融合模块以融合语言感知的解码结果。在SEAME数据集上的实验结果表明,与基线模型相比,该方法在dev_man和dev_sge测试集上相对实现了4.1%和7.2%的单词错误率(MER)降低,超越了现有最先进的方法。实验还发现,该方法对非本族语的CS语音表现有明显的提升,证明该方法能更好地区分两种语言。
Key Takeaways
- 代码切换(CS)自动语音识别(ASR)面临多种挑战,包括口音、听觉相似性导致的语言混淆和无缝语言切换问题。
- 预训练的多语言模型适应于CS-ASR显示出良好性能。
- 研究团队通过改进编码器和解码器两部分来增强模型处理CS语音的能力。
- 编码器精炼器增强了编码器处理句子内切换的能力。
- 使用语言感知适配器和不同的语言提示嵌入来实现解码器的语言特异性。
- 融合模块用于融合不同语言的解码结果。
点此查看论文截图

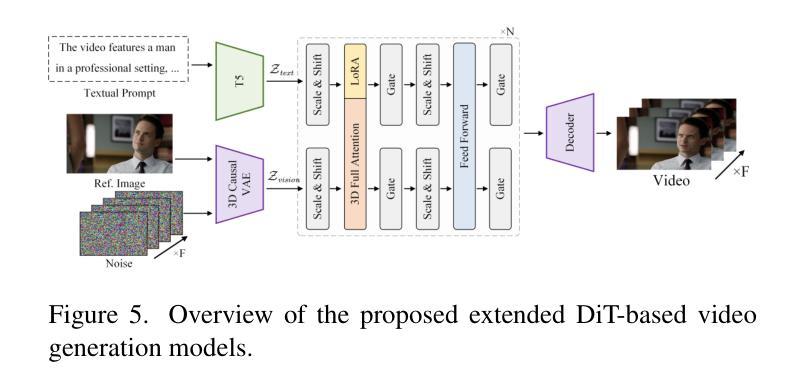
OpenHumanVid: A Large-Scale High-Quality Dataset for Enhancing Human-Centric Video Generation
Authors:Hui Li, Mingwang Xu, Yun Zhan, Shan Mu, Jiaye Li, Kaihui Cheng, Yuxuan Chen, Tan Chen, Mao Ye, Jingdong Wang, Siyu Zhu
Recent advancements in visual generation technologies have markedly increased the scale and availability of video datasets, which are crucial for training effective video generation models. However, a significant lack of high-quality, human-centric video datasets presents a challenge to progress in this field. To bridge this gap, we introduce OpenHumanVid, a large-scale and high-quality human-centric video dataset characterized by precise and detailed captions that encompass both human appearance and motion states, along with supplementary human motion conditions, including skeleton sequences and speech audio. To validate the efficacy of this dataset and the associated training strategies, we propose an extension of existing classical diffusion transformer architectures and conduct further pretraining of our models on the proposed dataset. Our findings yield two critical insights: First, the incorporation of a large-scale, high-quality dataset substantially enhances evaluation metrics for generated human videos while preserving performance in general video generation tasks. Second, the effective alignment of text with human appearance, human motion, and facial motion is essential for producing high-quality video outputs. Based on these insights and corresponding methodologies, the straightforward extended network trained on the proposed dataset demonstrates an obvious improvement in the generation of human-centric videos. Project page https://fudan-generative-vision.github.io/OpenHumanVid
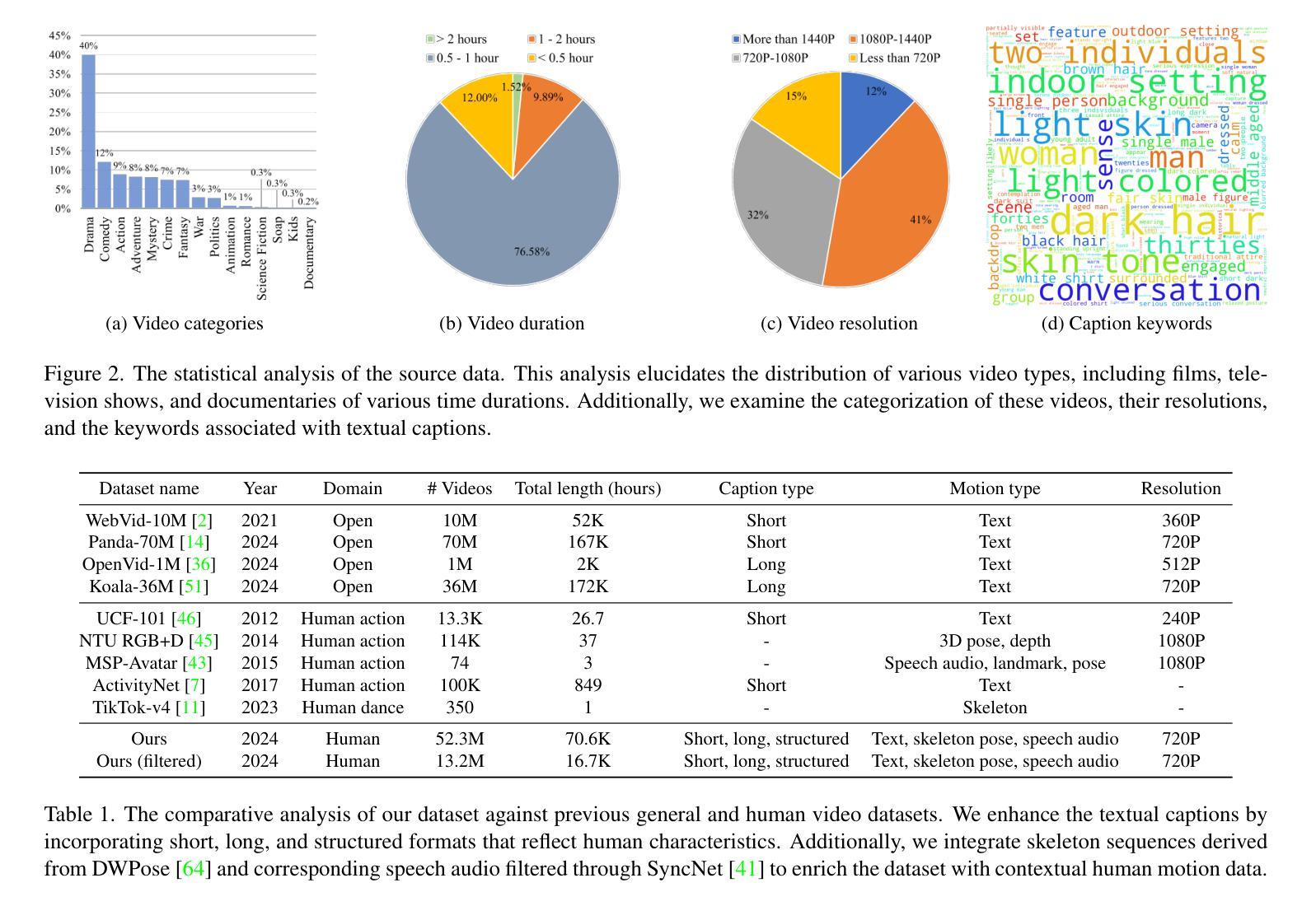
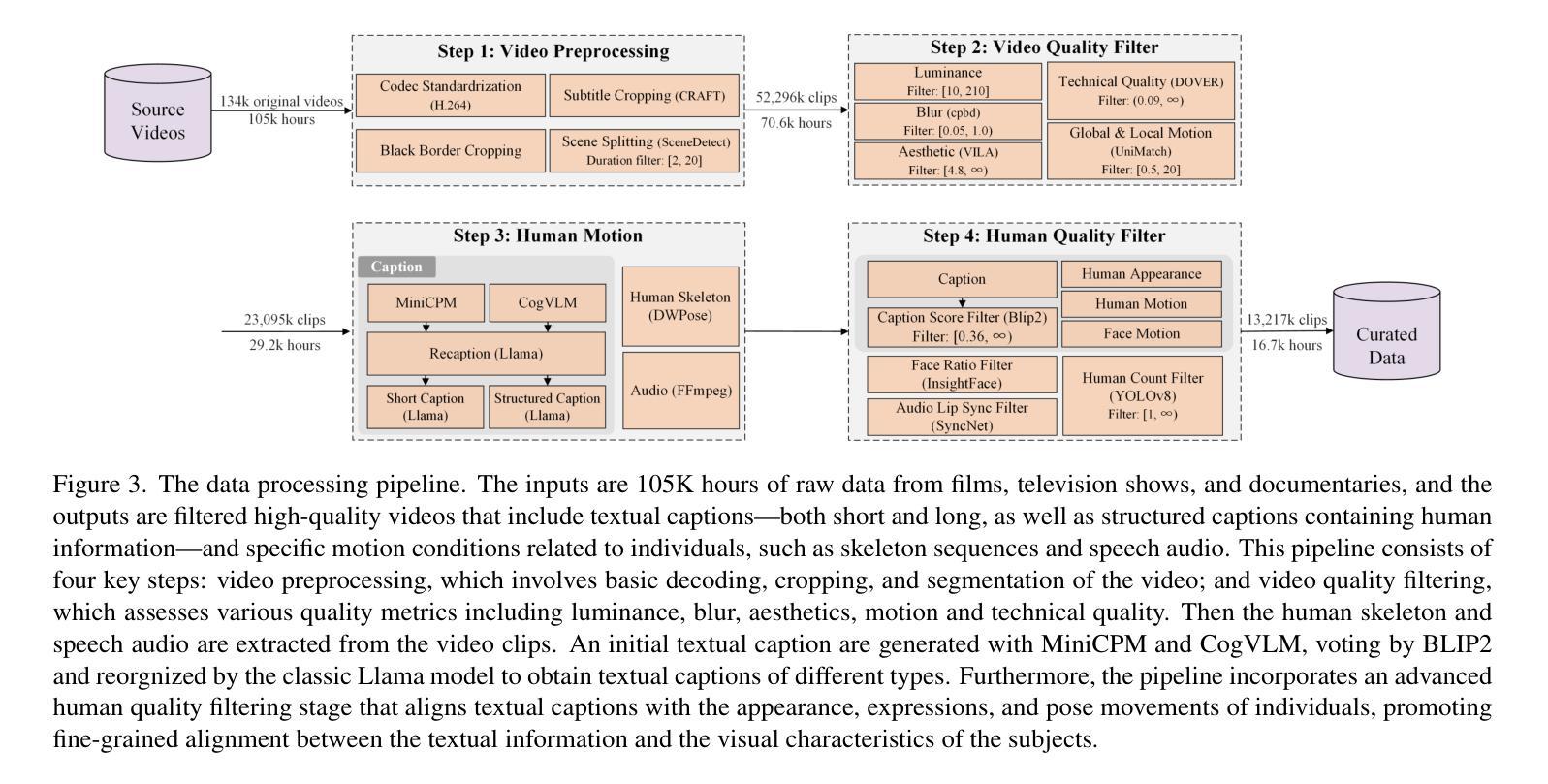
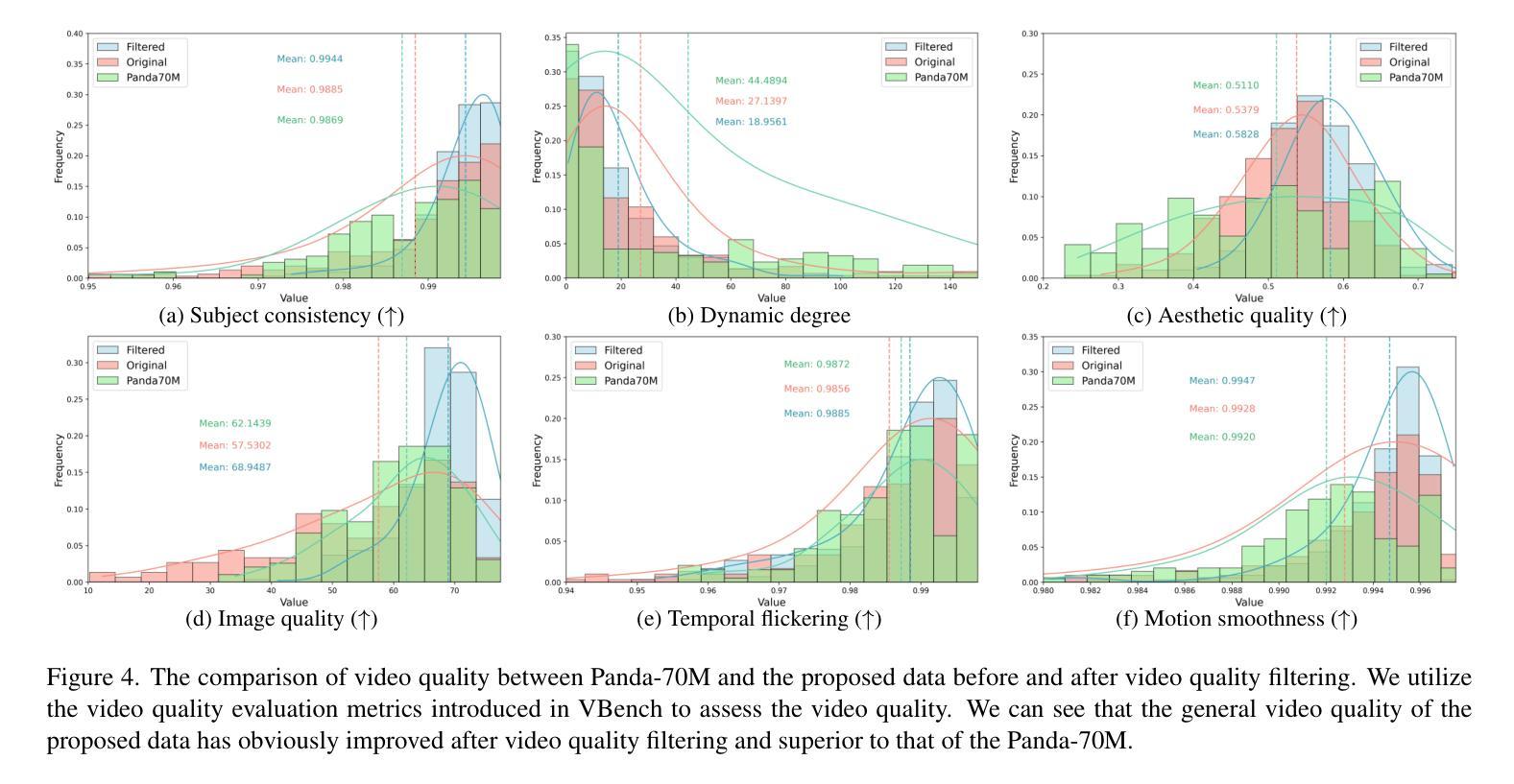
随着视觉生成技术的最新进展,视频数据集的数量和可用性显著增加,这对于训练有效的视频生成模型至关重要。然而,高质量、以人类为中心的视频数据集的匮乏给该领域的进步带来了挑战。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了OpenHumanVid,这是一个大规模、高质量、以人类为中心的视频数据集,其特点是拥有精确详细的字幕,涵盖了人类外观和运动状态,还包括额外的人类运动条件,如骨骼序列和语音音频。为了验证该数据集和相关训练策略的有效性,我们对现有的经典扩散变压器架构进行了扩展,并在所提出的数据集上对我们的模型进行了进一步的预训练。我们的研究发现两个关键见解:首先,使用大规模、高质量的数据集可以显著提高生成的人类视频的评价指标,同时保留了一般视频生成任务中的性能;其次,文本与人类外观、人类运动和面部运动的有效对齐对于生成高质量视频输出至关重要。基于这些见解和相应的方法论,在所提出的数据集上训练的简单扩展网络在人类为中心的视频生成方面显示出明显的改进。项目页面 https://fudan-generative-vision.github.io/OpenHumanVid
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 8 figures, 5 tables
Summary
随着视觉生成技术的进步,视频数据集规模和可用性的显著提升对训练有效的视频生成模型至关重要。然而,缺乏高质量的人类中心视频数据集成为该领域进展的挑战。为此,我们推出了OpenHumanVid,这是一个大规模、高质量的人类中心视频数据集,以精确详细的字幕为特色,涵盖人类外观和运动状态,以及包括骨架序列和语音音频等额外人类运动条件。为了验证该数据集和相关训练策略的有效性,我们对现有的经典扩散变压器架构进行了扩展,并在该数据集上对我们的模型进行了预训练。研究发现,大规模高质量数据集的引入显著提高了生成的人类视频的评价指标,同时保持了通用视频生成任务的性能;文本与人类外观、运动和面部运动的有效对齐对于生成高质量视频输出至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 视频生成技术因视觉生成技术的进展而得到显著提升,对大规模高质量视频数据集的需求增加。
- 缺乏高质量的人类中心视频数据集是当前的挑战。
- OpenHumanVid是一个大规模、高质量的人类中心视频数据集,包含详细字幕、人类外观和运动状态以及额外的人类运动条件。
- 数据集的引入显著提高了生成的人类视频的评价指标。
- 文本与人类外观、运动和面部运动的对齐是生成高质量视频的关键。
- 通过对现有经典扩散变压器架构的扩展和在该数据集上的预训练,模型在生成人类中心视频时表现出明显的改进。
点此查看论文截图



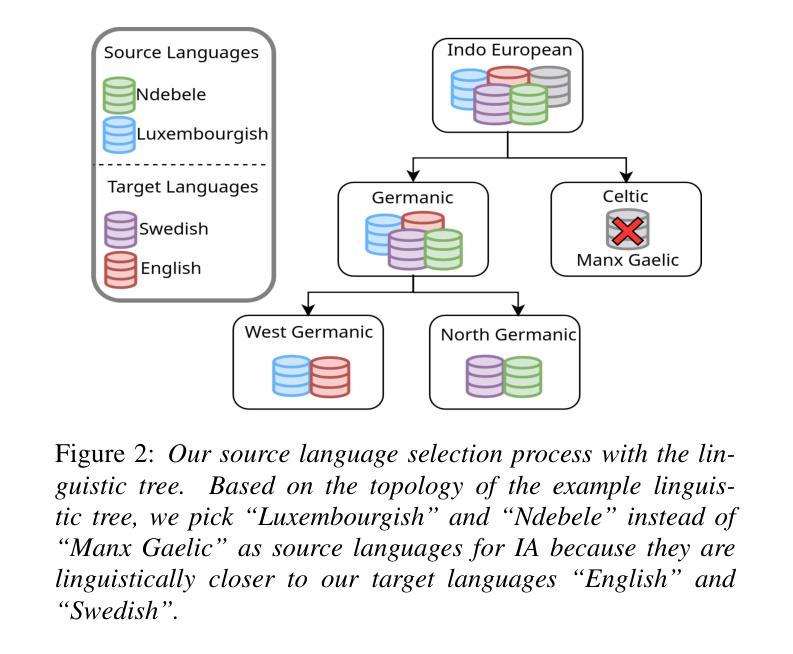
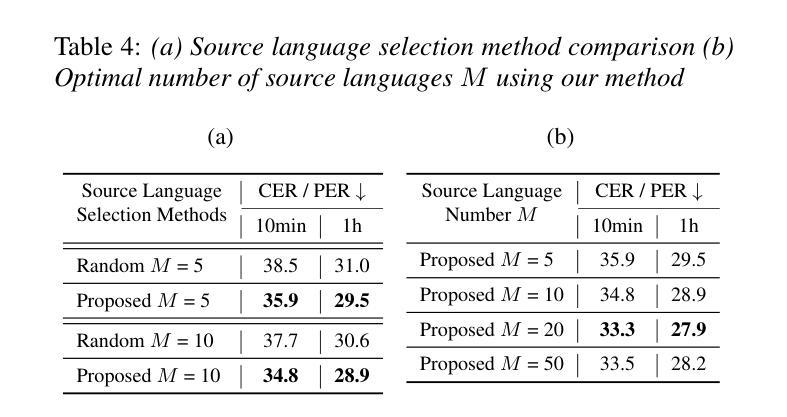
How to Learn a New Language? An Efficient Solution for Self-Supervised Learning Models Unseen Languages Adaption in Low-Resource Scenario
Authors:Shih-Heng Wang, Zih-Ching Chen, Jiatong Shi, Ming-To Chuang, Guan-Ting Lin, Kuan-Po Huang, David Harwath, Shang-Wen Li, Hung-yi Lee
The utilization of speech Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) models achieves impressive performance on Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). However, in low-resource language ASR, they encounter the domain mismatch problem between pre-trained and low-resource languages. Typical solutions like fine-tuning the SSL model suffer from high computation costs while using frozen SSL models as feature extractors comes with poor performance. To handle these issues, we extend a conventional efficient fine-tuning scheme based on the adapter. We add an extra intermediate adaptation to warm up the adapter and downstream model initialization. Remarkably, we update only 1-5% of the total model parameters to achieve the adaptation. Experimental results on the ML-SUPERB dataset show that our solution outperforms conventional efficient fine-tuning. It achieves up to a 28% relative improvement in the Character/Phoneme error rate when adapting to unseen languages.
语音自监督学习(SSL)模型的利用在自动语音识别(ASR)方面取得了令人印象深刻的性能。然而,在低资源语言ASR中,它们遇到了预训练模型与低资源语言之间的域不匹配问题。典型的解决方案,如微调SSL模型,存在计算成本高的问题,而使用冻结的SSL模型作为特征提取器则性能较差。为了解决这些问题,我们基于适配器扩展了一种常规的精细调整方案。我们添加一个额外的中间适应过程来预热适配器和下游模型初始化。值得注意的是,我们只需要更新模型总参数的1-5%就可以实现适配。在ML-SUPERB数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的解决方案优于传统的有效微调方法。在适应未见语言时,它实现了高达28%的相对改进在字符/音素错误率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语音自监督学习(SSL)模型在自动语音识别(ASR)方面表现出卓越性能。但在低资源语言ASR中,它们面临预训练模型与低资源语言之间领域不匹配的问题。常见的解决方案如微调SSL模型计算成本高,而使用冻结的SSL模型作为特征提取器性能较差。为了解决这个问题,我们基于适配器扩展了传统的有效微调方案,并添加了额外的中间适应来预热适配器和下游模型初始化。我们仅更新模型总参数的1-5%即可实现适应。在ML-SUPERB数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的解决方案优于传统的有效微调方法,在适应未见语言时,字符/音素错误率相对提高了高达28%。
Key Takeaways
- 语音自监督学习(SSL)模型在自动语音识别(ASR)中具有卓越性能。
- 在低资源语言ASR中,存在预训练模型与低资源语言之间的领域不匹配问题。
- 传统的SSL模型微调方案计算成本高,而使用冻结模型作为特征提取器效果欠佳。
- 通过基于适配器的扩展方案,实现了高效的模型适应。
- 额外中间适应步骤用于预热适配器和下游模型初始化。
- 仅更新少量模型参数(1-5%)即可实现适应。
- 在ML-SUPERB数据集上的实验表明,新方法在适应未见语言时相对改进了28%的字符/音素错误率。
点此查看论文截图


Modulating State Space Model with SlowFast Framework for Compute-Efficient Ultra Low-Latency Speech Enhancement
Authors:Longbiao Cheng, Ashutosh Pandey, Buye Xu, Tobi Delbruck, Vamsi Krishna Ithapu, Shih-Chii Liu
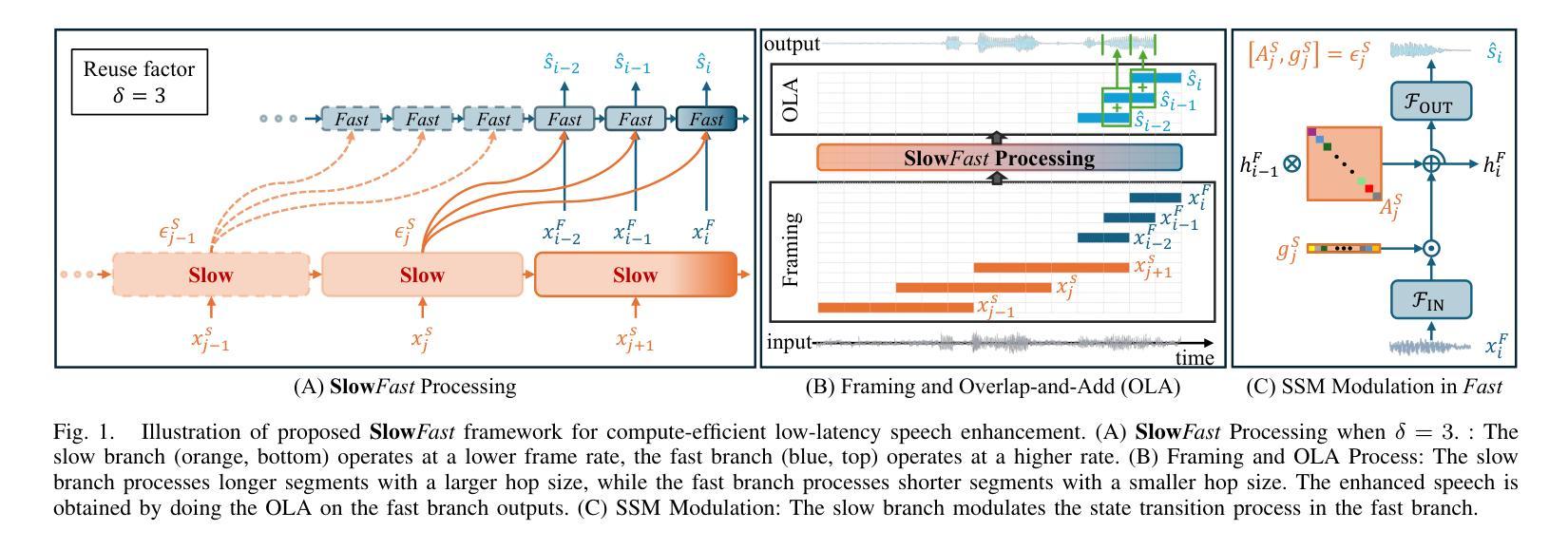
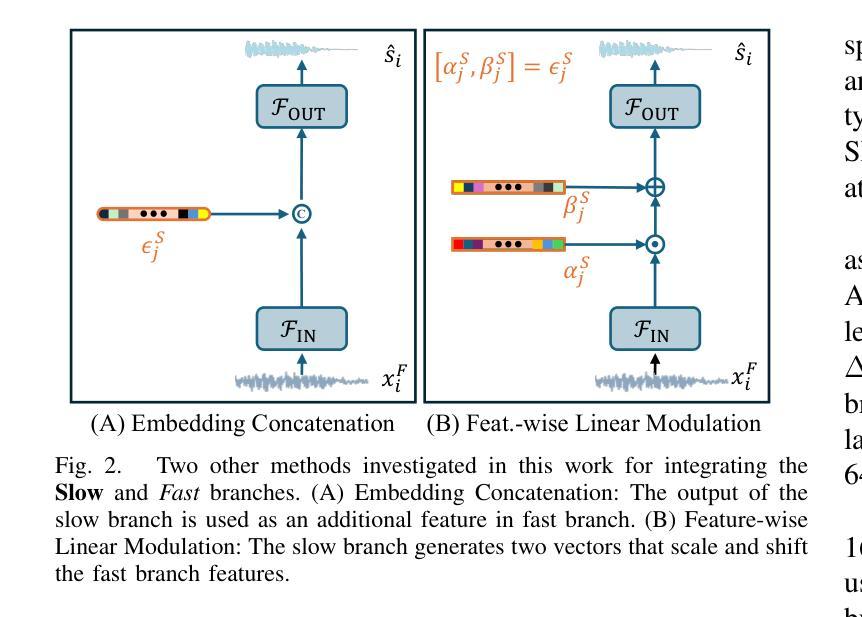
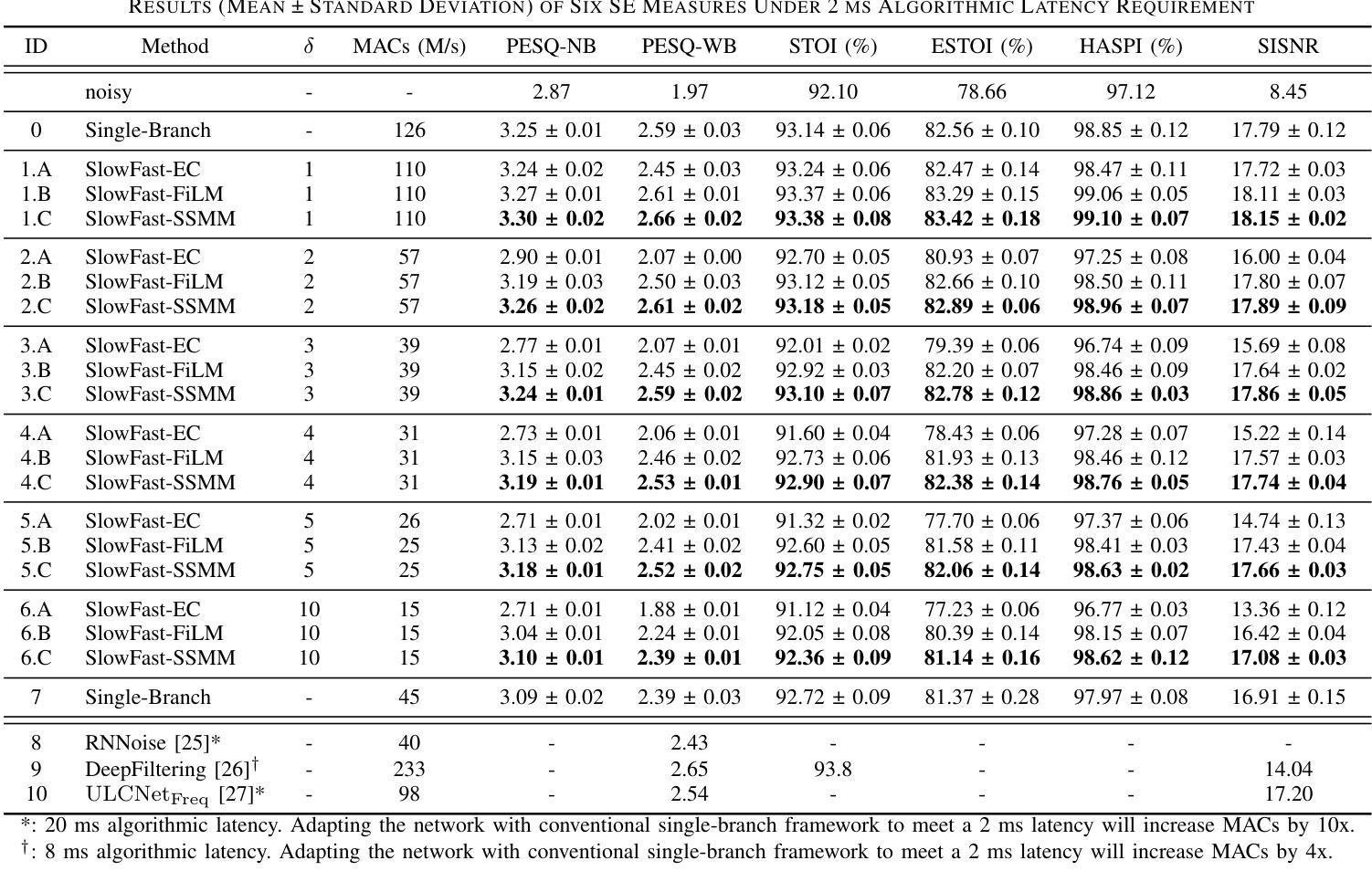
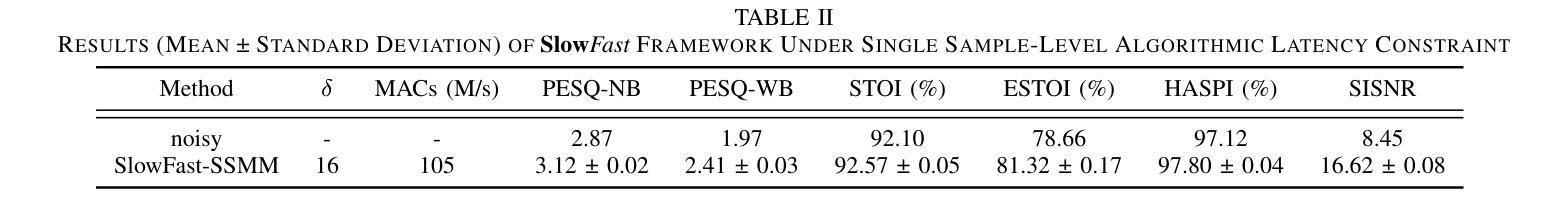
Deep learning-based speech enhancement (SE) methods often face significant computational challenges when needing to meet low-latency requirements because of the increased number of frames to be processed. This paper introduces the SlowFast framework which aims to reduce computation costs specifically when low-latency enhancement is needed. The framework consists of a slow branch that analyzes the acoustic environment at a low frame rate, and a fast branch that performs SE in the time domain at the needed higher frame rate to match the required latency. Specifically, the fast branch employs a state space model where its state transition process is dynamically modulated by the slow branch. Experiments on a SE task with a 2 ms algorithmic latency requirement using the Voice Bank + Demand dataset show that our approach reduces computation cost by 70% compared to a baseline single-branch network with equivalent parameters, without compromising enhancement performance. Furthermore, by leveraging the SlowFast framework, we implemented a network that achieves an algorithmic latency of just 62.5 {\mu}s (one sample point at 16 kHz sample rate) with a computation cost of 100 M MACs/s, while scoring a PESQ-NB of 3.12 and SISNR of 16.62.
基于深度学习的语音增强(SE)方法在满足低延迟要求时面临着巨大的计算挑战,因为需要处理的帧数增加。本文介绍了SlowFast框架,该框架旨在减少在低延迟增强时所需的计算成本。框架包含一个慢速分支,以低帧率分析声学环境,以及一个快速分支,以所需的高帧率在时域执行SE,以匹配所需的延迟。具体来说,快速分支采用状态空间模型,其状态转换过程受到慢速分支的动态调制。在Voice Bank + Demand数据集上使用具有2毫秒算法延迟要求的语音增强任务实验表明,与具有等效参数的基线单分支网络相比,我们的方法在计算成本方面降低了70%,同时不损害增强性能。此外,通过利用SlowFast框架,我们实现了一个网络,该网络达到了仅62.5μs的算法延迟(在16kHz采样率下的一个样本点),计算成本为每秒1亿次乘累加(MACs),同时获得PESQ-NB得分为3.12和SISNR得分为16.62。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于深度学习的语音增强方法在低延迟要求下所面临的计算挑战,并为此引入了SlowFast框架。该框架包括一个以低帧率分析声学环境的慢分支,以及一个以所需的高帧率进行时域语音增强的快分支。实验表明,相较于基线单分支网络,SlowFast框架在降低计算成本的同时,不妥协增强性能。此外,利用SlowFast框架实现的网络在算法延迟仅为62.5微秒的情况下,计算成本为每秒百万次乘累加(MACs)运算,性能评估指标PESQ-NB和SISNR分别达到了3.12和16.62。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习的语音增强方法在低延迟环境下存在计算挑战。
- SlowFast框架旨在降低低延迟增强时的计算成本。
- SlowFast框架包括一个慢分支用于分析声学环境,一个快分支用于时域增强。
- 快分支采用状态空间模型,其状态转换过程受慢分支动态调制。
- 实验表明,相较于基线网络,SlowFast框架在计算成本降低70%的同时,不妥协增强性能。
- 利用SlowFast框架实现的网络在算法延迟仅为62.5微秒时表现出良好的性能。
- 该网络的计算成本为每秒百万次乘累加(MACs)运算,性能评估指标高。
点此查看论文截图

LlamaPartialSpoof: An LLM-Driven Fake Speech Dataset Simulating Disinformation Generation
Authors:Hieu-Thi Luong, Haoyang Li, Lin Zhang, Kong Aik Lee, Eng Siong Chng
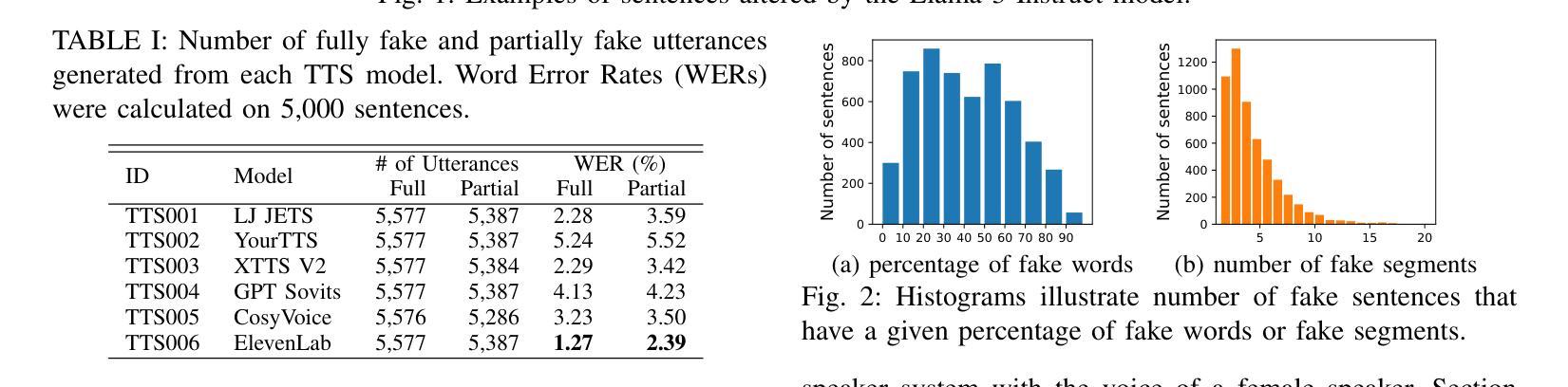
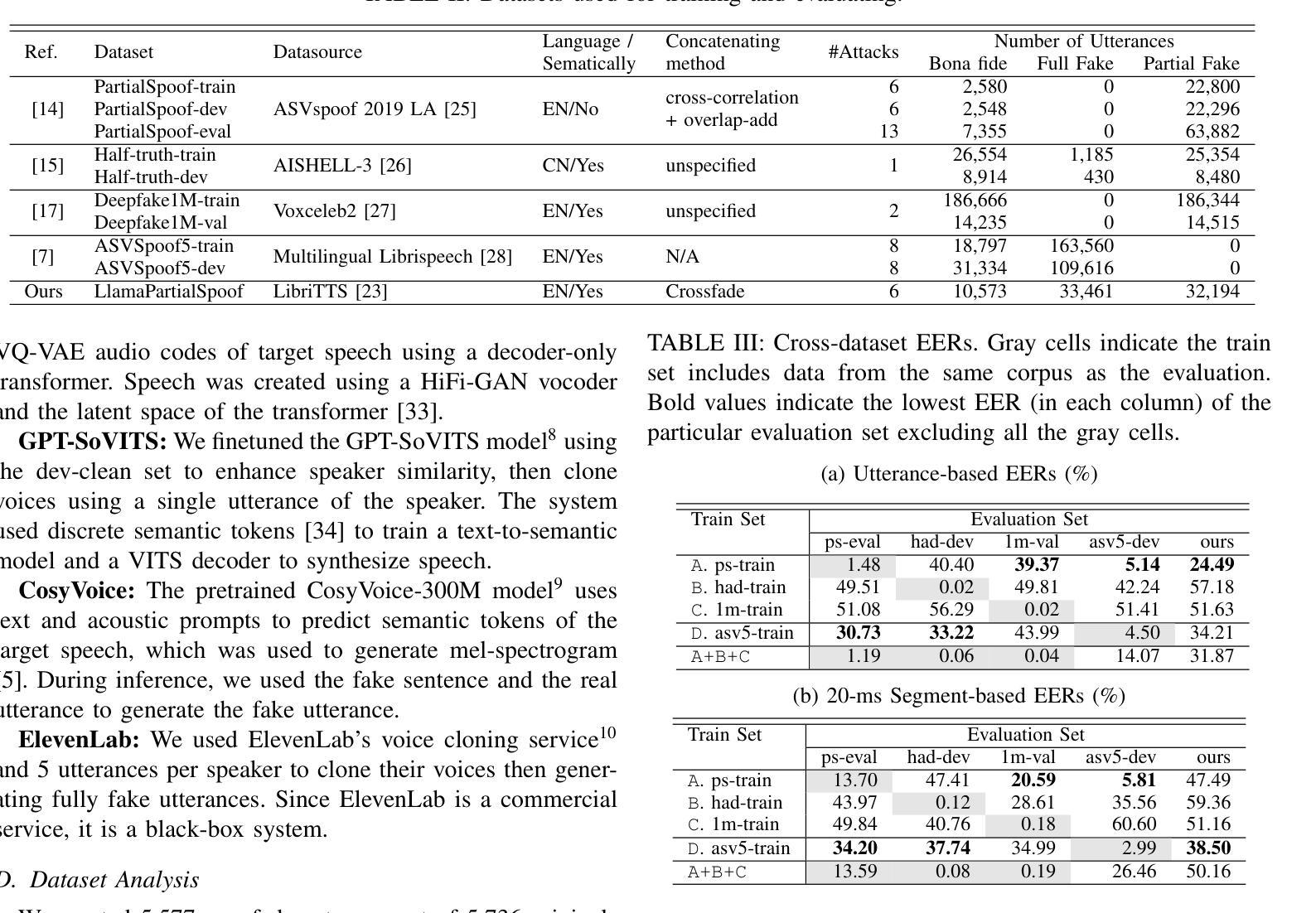
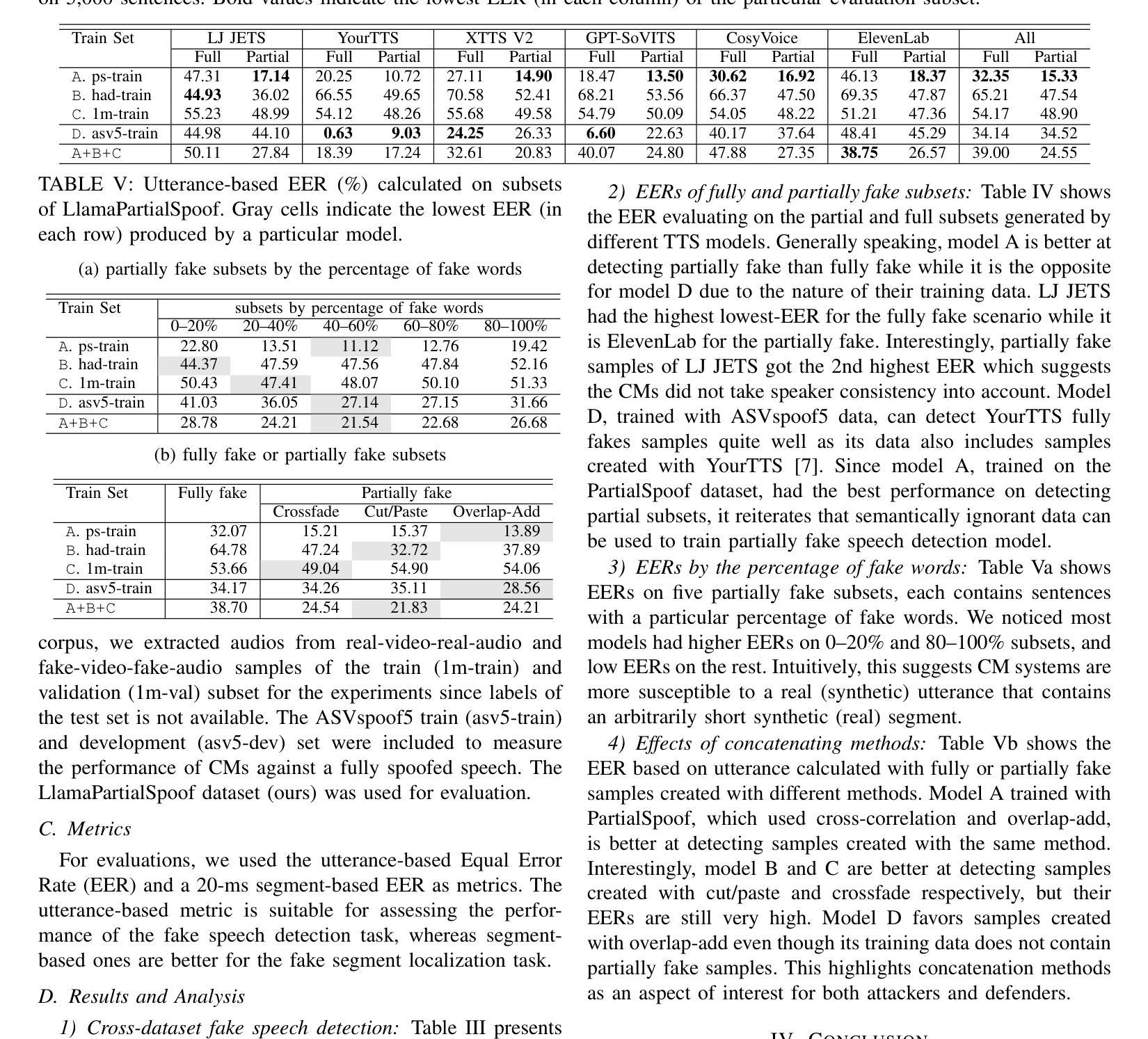
Previous fake speech datasets were constructed from a defender’s perspective to develop countermeasure (CM) systems without considering diverse motivations of attackers. To better align with real-life scenarios, we created LlamaPartialSpoof, a 130-hour dataset that contains both fully and partially fake speech, using a large language model (LLM) and voice cloning technologies to evaluate the robustness of CMs. By examining valuable information for both attackers and defenders, we identify several key vulnerabilities in current CM systems, which can be exploited to enhance attack success rates, including biases toward certain text-to-speech models or concatenation methods. Our experimental results indicate that the current fake speech detection system struggle to generalize to unseen scenarios, achieving a best performance of 24.49% equal error rate.
之前的虚假语音数据集是从防御者的角度构建的,旨在开发对抗措施(CM)系统,而没有考虑到攻击者的不同动机。为了更好地符合现实场景,我们创建了LlamaPartialSpoof数据集,这是一个包含完全和部分虚假语音的130小时数据集,利用大型语言模型(LLM)和语音克隆技术来评估对抗措施的稳健性。通过对攻击者和防御者有价值信息的考察,我们发现了当前对抗措施系统中的几个关键漏洞,这些漏洞可以被利用来提高攻击成功率,包括对某些文本到语音模型的偏见或拼接方法。我们的实验结果表明,当前的虚假语音检测系统很难推广到未见过的场景,最佳性能为达到24.49%的等误码率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文创建了一个名为LlamaPartialSpoof的新假语音数据集,用于评估现有语音反篡改系统的鲁棒性。数据集包括完全和部分假语音,采用大型语言模型和语音克隆技术生成。通过分析攻击者和防御者的有价值信息,发现当前反篡改系统的关键漏洞,这些漏洞可被利用提高攻击成功率。实验结果表明,现有假语音检测系统在新场景下的泛化能力较弱。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了名为LlamaPartialSpoof的新假语音数据集,包含完全和部分假语音。
- 利用大型语言模型和语音克隆技术生成假语音数据。
- 通过对数据集的分析,发现了现有语音反篡改系统的关键漏洞。
- 这些漏洞可被攻击者利用以提高攻击成功率。
- 当前假语音检测系统在新场景下的泛化能力较弱。
- 最佳性能的反假语音系统实现了24.49%的误判率。
点此查看论文截图