⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-08 更新
GLoG-CSUnet: Enhancing Vision Transformers with Adaptable Radiomic Features for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Niloufar Eghbali, Hassan Bagher-Ebadian, Tuka Alhanai, Mohammad M. Ghassemi
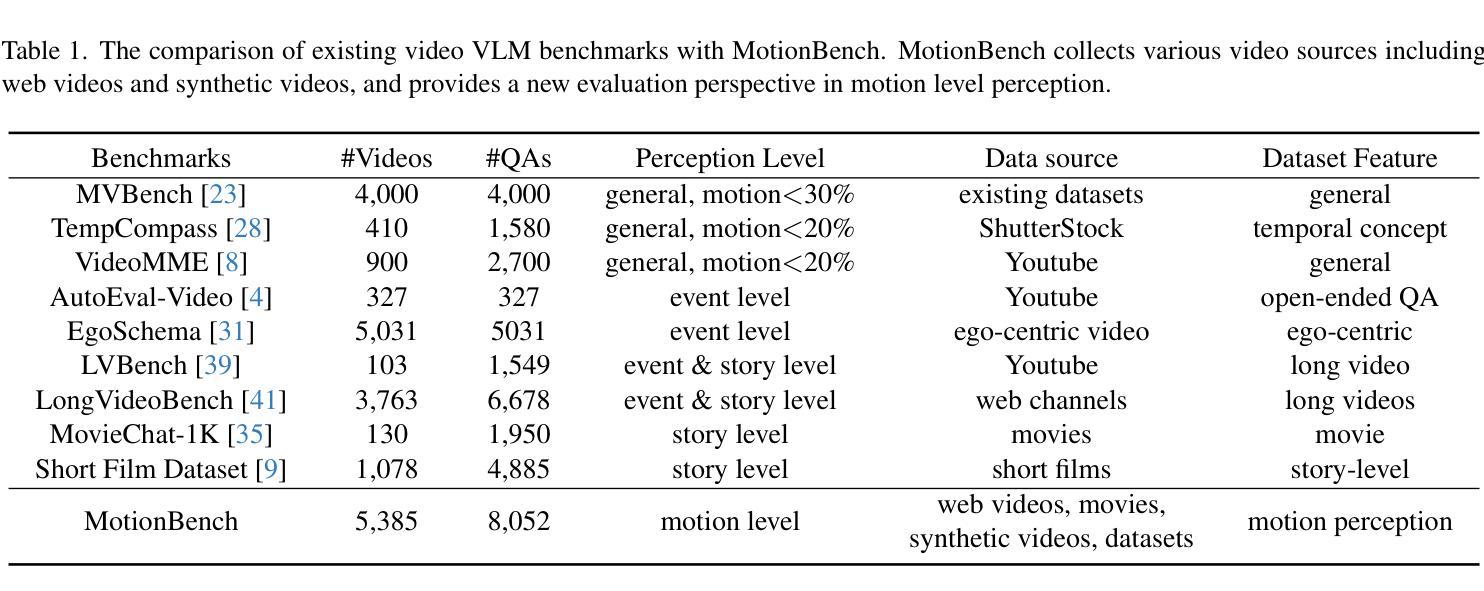
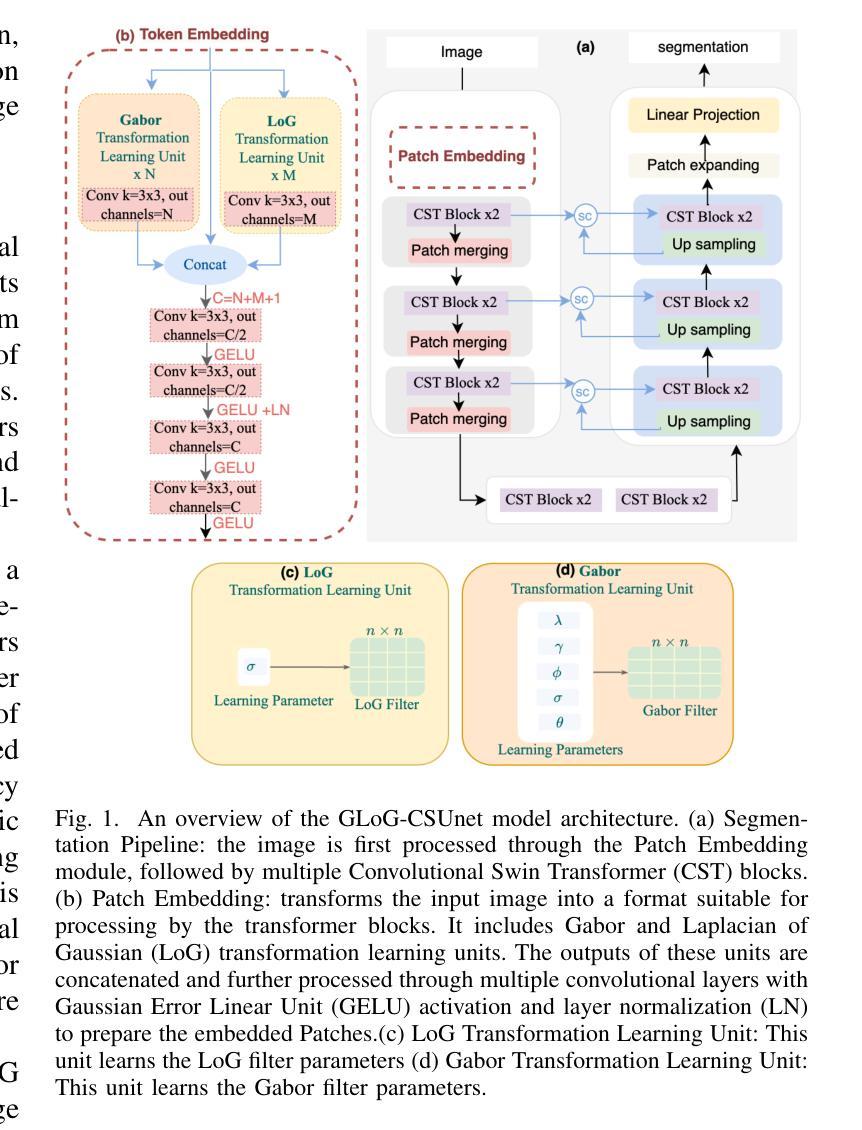
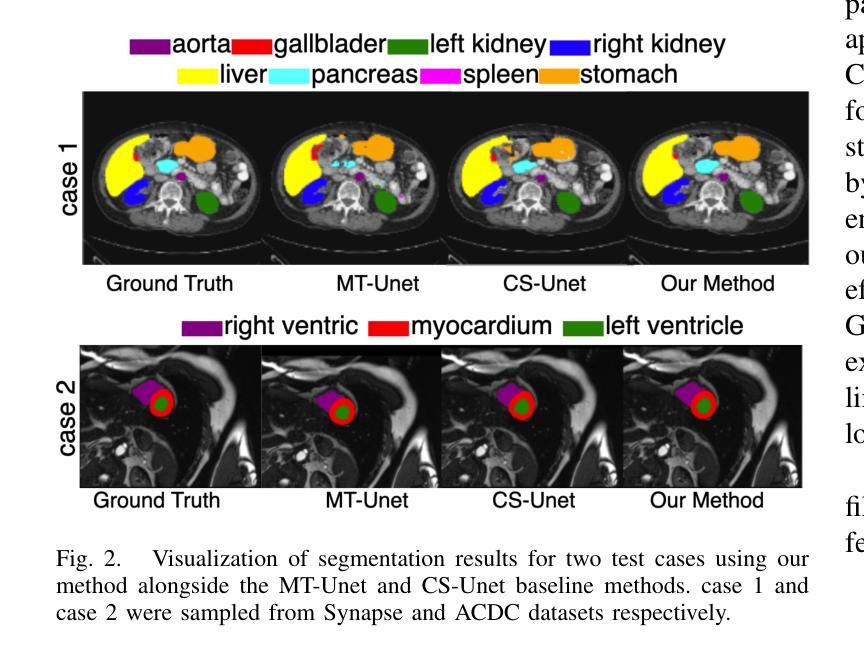
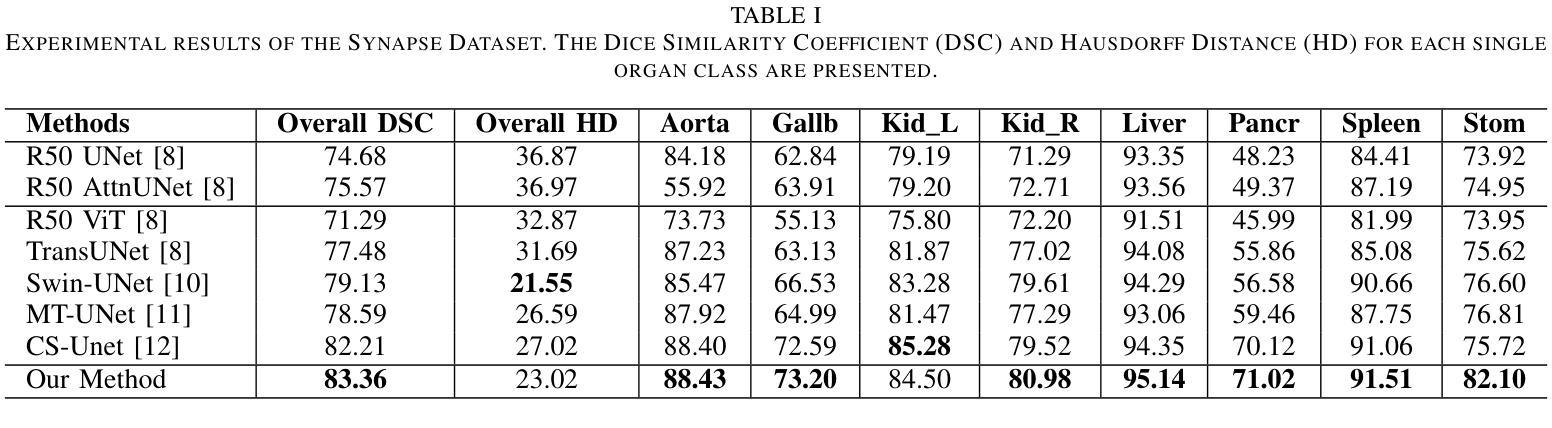
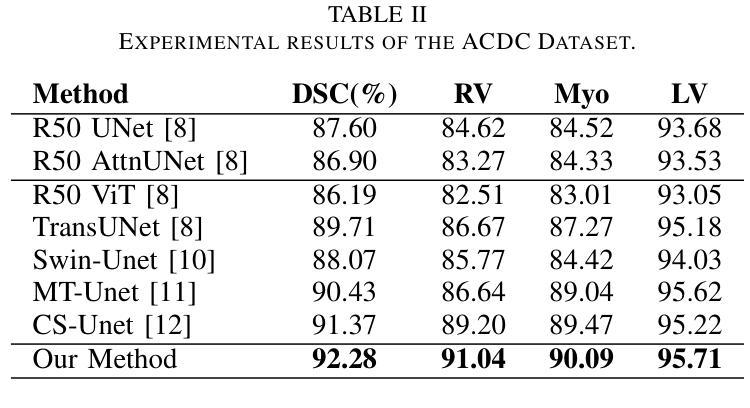
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown promise in medical image semantic segmentation (MISS) by capturing long-range correlations. However, ViTs often struggle to model local spatial information effectively, which is essential for accurately segmenting fine anatomical details, particularly when applied to small datasets without extensive pre-training. We introduce Gabor and Laplacian of Gaussian Convolutional Swin Network (GLoG-CSUnet), a novel architecture enhancing Transformer-based models by incorporating learnable radiomic features. This approach integrates dynamically adaptive Gabor and Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filters to capture texture, edge, and boundary information, enhancing the feature representation processed by the Transformer model. Our method uniquely combines the long-range dependency modeling of Transformers with the texture analysis capabilities of Gabor and LoG features. Evaluated on the Synapse multi-organ and ACDC cardiac segmentation datasets, GLoG-CSUnet demonstrates significant improvements over state-of-the-art models, achieving a 1.14% increase in Dice score for Synapse and 0.99% for ACDC, with minimal computational overhead (only 15 and 30 additional parameters, respectively). GLoG-CSUnet’s flexible design allows integration with various base models, offering a promising approach for incorporating radiomics-inspired feature extraction in Transformer architectures for medical image analysis. The code implementation is available on GitHub at: https://github.com/HAAIL/GLoG-CSUnet.
视觉Transformer(ViT)通过捕捉长程相关性在医学图像语义分割(MISS)方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,ViT往往难以有效地建模局部空间信息,这对于准确分割精细的解剖细节至关重要,尤其是当应用于没有广泛预训练的小数据集时。我们引入了Gabor和Laplacian of Gaussian Convolutional Swin网络(GLoG-CSUnet),这是一种新型架构,通过融入可学习的放射学特征来增强基于Transformer的模型。该方法结合了动态自适应的Gabor和Laplacian of Gaussian(LoG)滤波器,以捕捉纹理、边缘和边界信息,增强Transformer模型处理的特征表示。我们的方法独特地结合了Transformer的长程依赖建模与Gabor和LoG特征的纹理分析能力。在Synapse多器官和ACDC心脏分割数据集上进行评估,GLoG-CSUnet相较于最新模型展现了显著改进,Synapse的Dice得分增加了1.14%,ACDC增加了0.99%,同时计算开销极小(仅分别增加了15和30个额外参数)。GLoG-CSUnet的灵活设计允许与各种基础模型集成,为在Transformer架构中融入放射学启发特征提取提供了有前景的方法,适用于医学图像分析。代码实现可在GitHub上找到:https://github.com/HAAIL/GLoG-CSUnet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ViTs在医学图像语义分割(MISS)中显示出捕捉长程关联性的潜力,但在处理精细解剖细节分割时,往往难以有效地建模局部空间信息。为解决这一问题,本文提出一种名为GLoG-CSUnet的新型架构,它结合了可学习的放射学特征和基于Transformer的模型,通过动态适应的Gabor和LoG滤波器捕捉纹理、边缘和边界信息,增强了特征表示。在Synapse多器官和ACDC心脏分割数据集上的评估表明,GLoG-CSUnet较先进模型有显著改善,Dice得分分别提高1.14%和0.99%,且计算开销较小。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs)已用于医学图像语义分割,但存在对局部空间信息建模不足的问题。
- GLoG-CSUnet架构结合了Transformer模型和放射学特征,旨在解决上述问题。
- GLoG-CSUnet通过动态适应的Gabor和LoG滤波器增强特征表示,捕捉纹理、边缘和边界信息。
- 在Synapse和ACDC数据集上,GLoG-CSUnet较其他模型有显著改善。
- GLoG-CSUnet设计灵活,可与其他基础模型集成。
- GLoG-CSUnet方法有望为医学图像分析中结合放射学特征提取的Transformer架构提供有前途的解决策略。
点此查看论文截图

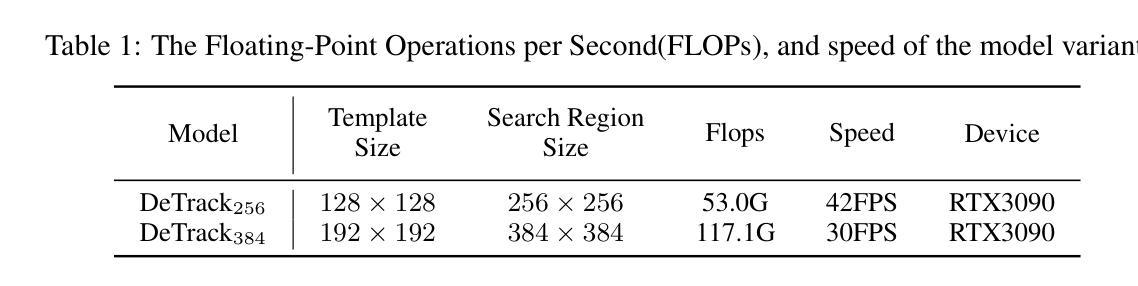
DeTrack: In-model Latent Denoising Learning for Visual Object Tracking
Authors:Xinyu Zhou, Jinglun Li, Lingyi Hong, Kaixun Jiang, Pinxue Guo, Weifeng Ge, Wenqiang Zhang
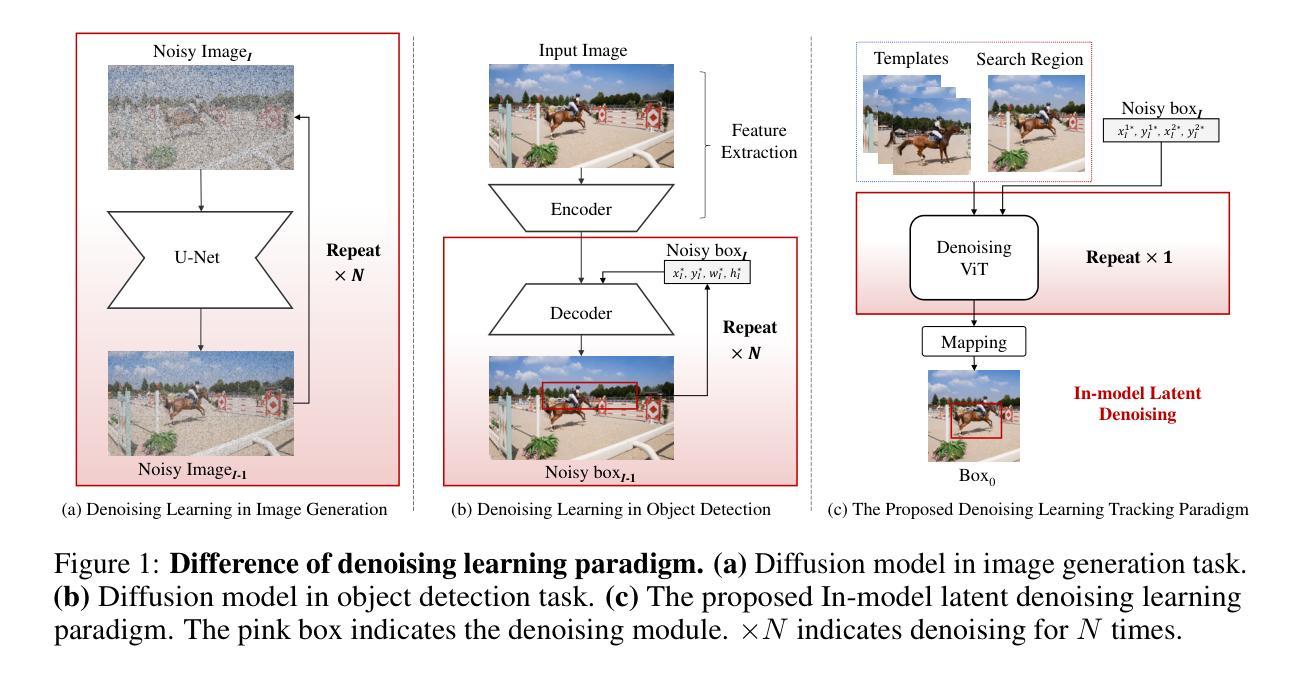
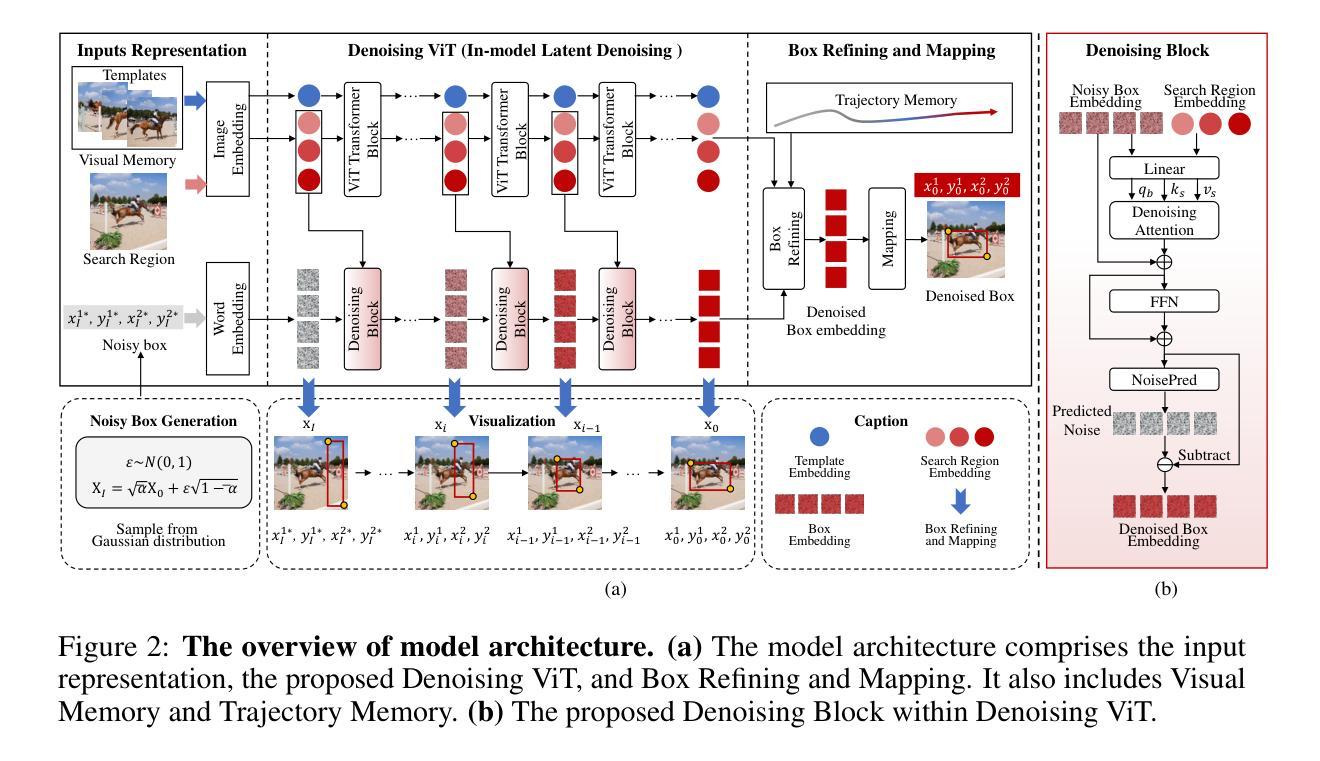
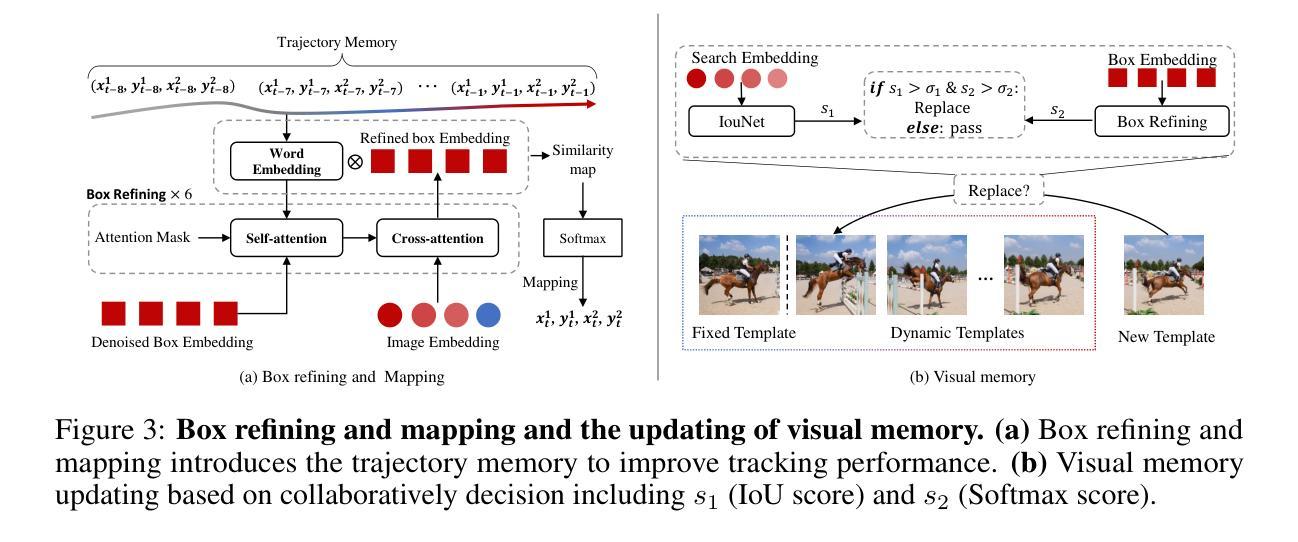
Previous visual object tracking methods employ image-feature regression models or coordinate autoregression models for bounding box prediction. Image-feature regression methods heavily depend on matching results and do not utilize positional prior, while the autoregressive approach can only be trained using bounding boxes available in the training set, potentially resulting in suboptimal performance during testing with unseen data. Inspired by the diffusion model, denoising learning enhances the model’s robustness to unseen data. Therefore, We introduce noise to bounding boxes, generating noisy boxes for training, thus enhancing model robustness on testing data. We propose a new paradigm to formulate the visual object tracking problem as a denoising learning process. However, tracking algorithms are usually asked to run in real-time, directly applying the diffusion model to object tracking would severely impair tracking speed. Therefore, we decompose the denoising learning process into every denoising block within a model, not by running the model multiple times, and thus we summarize the proposed paradigm as an in-model latent denoising learning process. Specifically, we propose a denoising Vision Transformer (ViT), which is composed of multiple denoising blocks. In the denoising block, template and search embeddings are projected into every denoising block as conditions. A denoising block is responsible for removing the noise in a predicted bounding box, and multiple stacked denoising blocks cooperate to accomplish the whole denoising process. Subsequently, we utilize image features and trajectory information to refine the denoised bounding box. Besides, we also utilize trajectory memory and visual memory to improve tracking stability. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving competitive performance on several challenging datasets.
先前视觉目标跟踪方法采用图像特征回归模型或坐标自回归模型进行边界框预测。图像特征回归方法严重依赖于匹配结果,并不利用位置先验信息,而自回归方法只能使用训练集中可用的边界框进行训练,这可能在对未见数据进行测试时导致性能不佳。受扩散模型的启发,去噪学习提高了模型对未见数据的稳健性。因此,我们对边界框引入噪声,生成用于训练的带噪声的边界框,从而提高模型在测试数据上的稳健性。我们提出了一种新的范式,将视觉目标跟踪问题表述为一个去噪学习过程。然而,通常要求跟踪算法实时运行,直接将扩散模型应用于目标跟踪会严重影响跟踪速度。因此,我们将去噪学习过程分解为模型内的每个去噪块,而不是多次运行模型,因此我们将所提出的范式概括为模型内部潜在去噪学习过程。具体来说,我们提出了一种去噪视觉转换器(ViT),它由多个去噪块组成。在去噪块中,模板和搜索嵌入被投影到每个去噪块中作为条件。去噪块负责去除预测边界框中的噪声,多个堆叠的去噪块协同完成整个去噪过程。随后,我们利用图像特征和轨迹信息来修正去噪后的边界框。此外,我们还利用轨迹记忆和视觉记忆来提高跟踪稳定性。实验结果验证了我们的方法的有效性,在几个具有挑战性的数据集上实现了具有竞争力的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文提出了一种新的视觉对象跟踪方法,该方法将问题转化为去噪学习过程,并引入了去噪Vision Transformer(ViT)。该方法通过向边界框添加噪声进行训练,以增强模型对未见数据的鲁棒性,并将去噪过程分解为模型内的多个去噪块。此外,还利用图像特征和轨迹信息来优化去噪后的边界框,并利用轨迹记忆和视觉记忆提高跟踪稳定性。实验结果表明,该方法在多个挑战数据集上取得了具有竞争力的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了去噪学习以增强模型对未见数据的鲁棒性,将视觉对象跟踪问题转化为去噪学习过程。
- 提出了去噪Vision Transformer(ViT),通过多个去噪块完成去噪过程。
- 通过向边界框添加噪声进行训练,以提高模型性能。
- 利用图像特征和轨迹信息优化去噪后的边界框。
- 采用了轨迹记忆和视觉记忆来提高跟踪稳定性。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在多个挑战数据集上取得了具有竞争力的性能。
点此查看论文截图

FedRSClip: Federated Learning for Remote Sensing Scene Classification Using Vision-Language Models
Authors:Hui Lin, Chao Zhang, Danfeng Hong, Kexin Dong, Congcong Wen
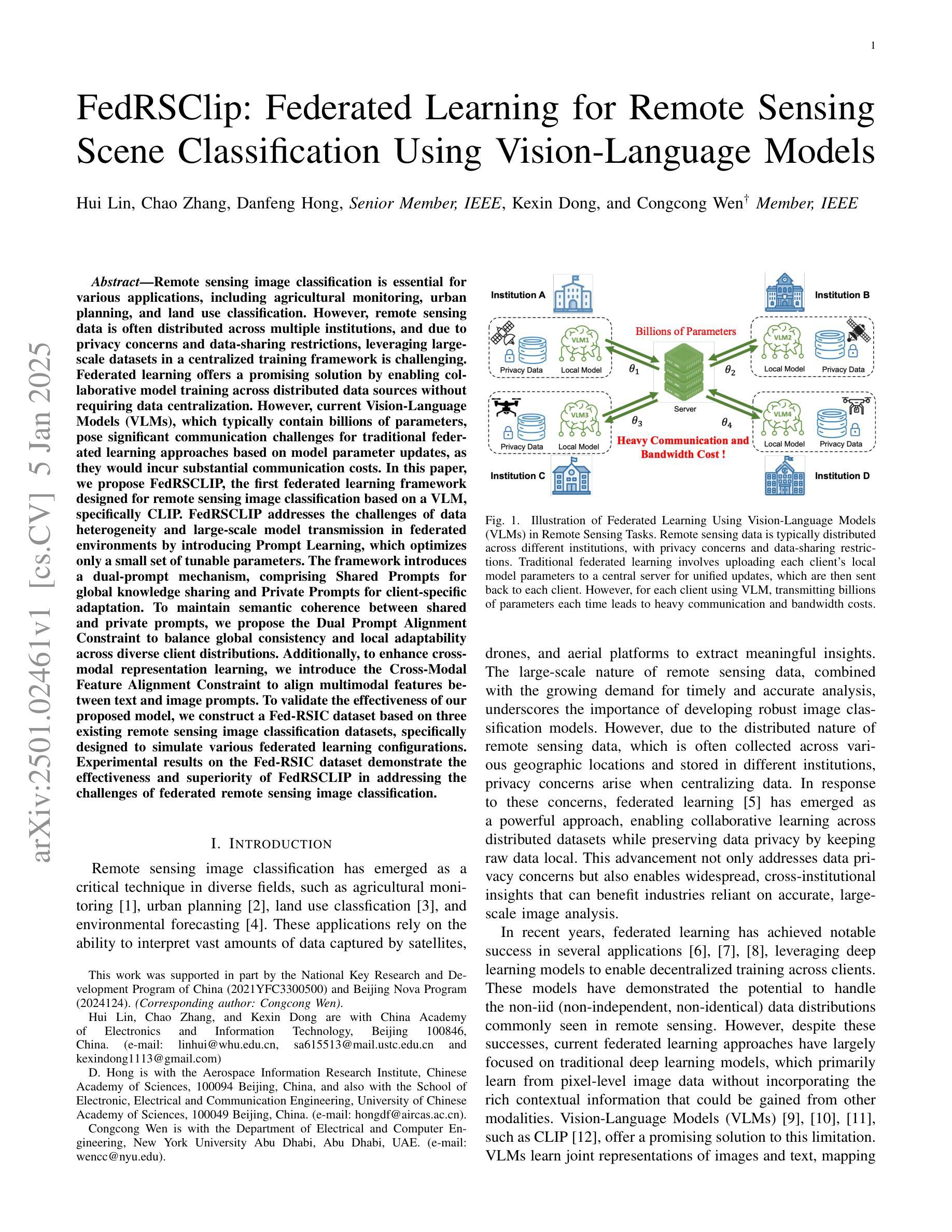
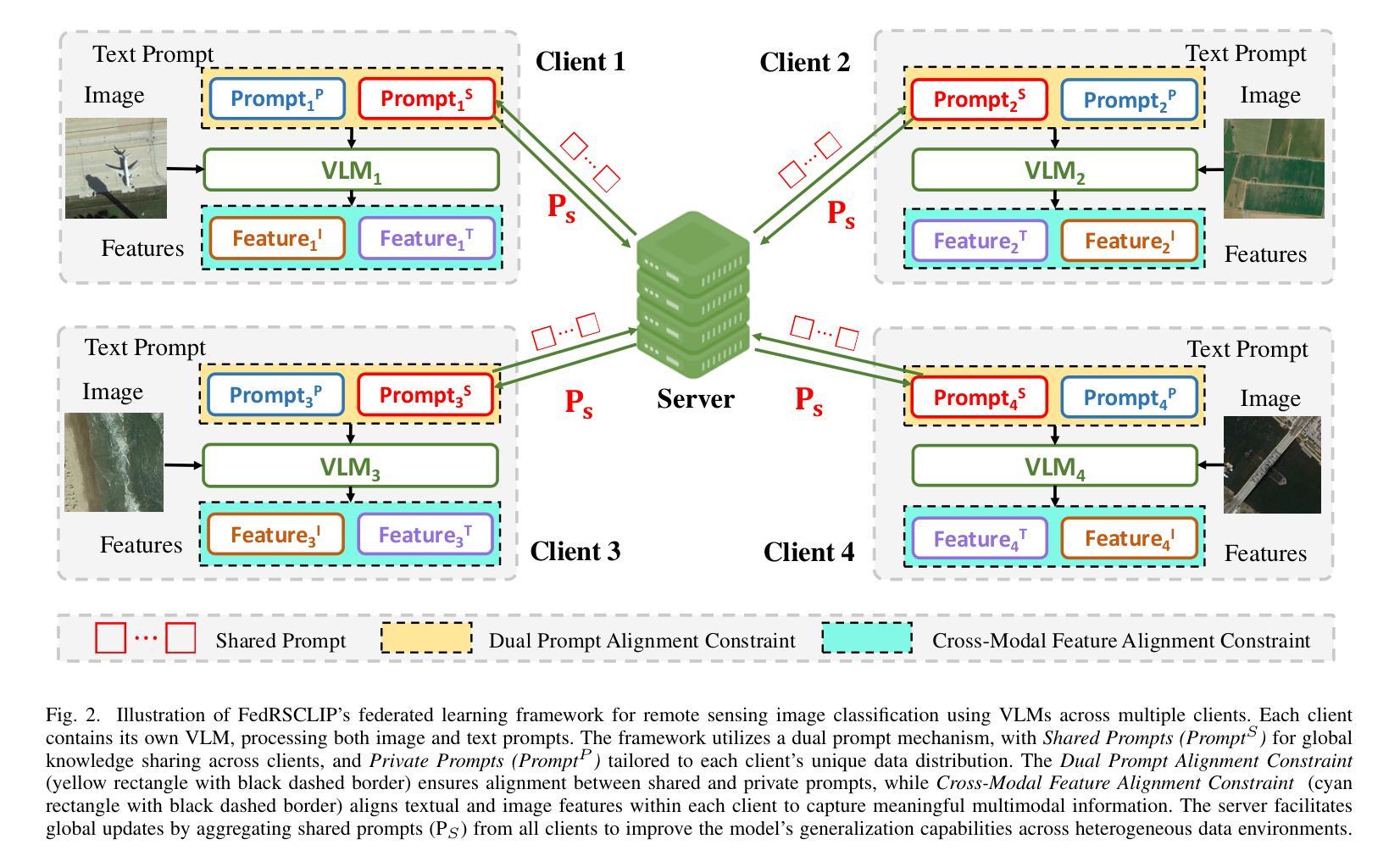
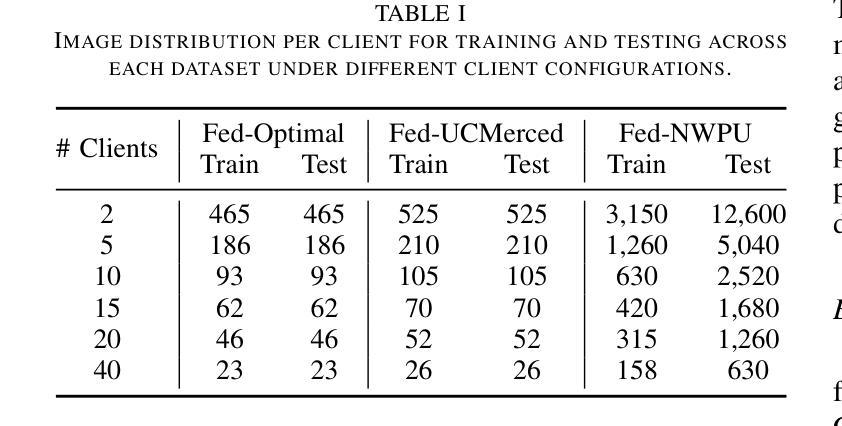
Remote sensing data is often distributed across multiple institutions, and due to privacy concerns and data-sharing restrictions, leveraging large-scale datasets in a centralized training framework is challenging. Federated learning offers a promising solution by enabling collaborative model training across distributed data sources without requiring data centralization. However, current Vision-Language Models (VLMs), which typically contain billions of parameters, pose significant communication challenges for traditional federated learning approaches based on model parameter updates, as they would incur substantial communication costs. In this paper, we propose FedRSCLIP, the first federated learning framework designed for remote sensing image classification based on a VLM, specifically CLIP. FedRSCLIP addresses the challenges of data heterogeneity and large-scale model transmission in federated environments by introducing Prompt Learning, which optimizes only a small set of tunable parameters. The framework introduces a dual-prompt mechanism, comprising Shared Prompts for global knowledge sharing and Private Prompts for client-specific adaptation. To maintain semantic coherence between shared and private prompts, we propose the Dual Prompt Alignment Constraint to balance global consistency and local adaptability across diverse client distributions. Additionally, to enhance cross-modal representation learning, we introduce the Cross-Modal Feature Alignment Constraint to align multimodal features between text and image prompts. To validate the effectiveness of our proposed model, we construct a Fed-RSIC dataset based on three existing remote sensing image classification datasets, specifically designed to simulate various federated learning configurations. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of FedRSCLIP in remote sensing image classification.
遥感数据通常分布在多个机构之间,由于隐私担忧和数据共享限制,在集中式训练框架中使用大规模数据集是一项挑战。联邦学习提供了一种有前景的解决方案,它能够在分布式数据源上实现协同模型训练,而无需数据集中化。然而,当前的视觉语言模型(VLMs),通常包含数十亿参数,对于基于模型参数更新的传统联邦学习方法来说,它们带来了巨大的通信挑战,因为这将产生大量的通信成本。在本文中,我们提出了针对遥感图像分类的联邦学习框架FedRSCLIP,它是基于VLM特别是CLIP设计的第一个联邦学习框架。FedRSCLIP通过引入提示学习来解决联邦环境中数据异质性和大规模模型传输的挑战,提示学习仅优化一小部分可调参数。该框架引入了一种双提示机制,包括用于全球知识共享的共同提示和用于客户端特定适应的私有提示。为了保持共享提示和私有提示之间的语义连贯性,我们提出了双提示对齐约束来平衡全局一致性和局部适应性在多种客户端分布中的平衡。此外,为了增强跨模态表示学习,我们引入了跨模态特征对齐约束,以对文本和图像提示之间的多模态特征进行对齐。为了验证我们提出的模型的有效性,我们基于三个现有的遥感图像分类数据集构建了Fed-RSIC数据集,专门用于模拟各种联邦学习配置。实验结果表明,FedRSCLIP在遥感图像分类中的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出FedRSCLIP框架,针对遥感图像分类的联邦学习环境下的数据异质性和大规模模型传输挑战,引入基于CLIP的VLM的Prompt学习机制。通过共享提示和私有提示的双重提示机制,实现全局知识共享和客户端特定适应。通过双提示对齐约束保持语义连贯性,并通过跨模态特征对齐约束增强跨模态表示学习。构建Fed-RSIC数据集验证模型有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感数据多机构分布,数据集中训练困难,联邦学习为解决此问题提供解决方案。
- 传统联邦学习在VLM上应用面临沟通挑战,提出FedRSCLIP框架专为遥感图像分类设计。
- FedRSCLIP引入Prompt学习机制,优化小规模可调参数,应对数据异质性和大规模模型传输问题。
- 框架包含共享提示和私有提示的双重提示机制,实现全局和本地适应平衡。
- 通过双提示对齐约束保持语义连贯性。
- 引入跨模态特征对齐约束,增强跨模态表示学习。
点此查看论文截图