⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-09 更新
LM-Net: A Light-weight and Multi-scale Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhenkun Lu, Chaoyin She, Wei Wang, Qinghua Huang
Current medical image segmentation approaches have limitations in deeply exploring multi-scale information and effectively combining local detail textures with global contextual semantic information. This results in over-segmentation, under-segmentation, and blurred segmentation boundaries. To tackle these challenges, we explore multi-scale feature representations from different perspectives, proposing a novel, lightweight, and multi-scale architecture (LM-Net) that integrates advantages of both Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) to enhance segmentation accuracy. LM-Net employs a lightweight multi-branch module to capture multi-scale features at the same level. Furthermore, we introduce two modules to concurrently capture local detail textures and global semantics with multi-scale features at different levels: the Local Feature Transformer (LFT) and Global Feature Transformer (GFT). The LFT integrates local window self-attention to capture local detail textures, while the GFT leverages global self-attention to capture global contextual semantics. By combining these modules, our model achieves complementarity between local and global representations, alleviating the problem of blurred segmentation boundaries in medical image segmentation. To evaluate the feasibility of LM-Net, extensive experiments have been conducted on three publicly available datasets with different modalities. Our proposed model achieves state-of-the-art results, surpassing previous methods, while only requiring 4.66G FLOPs and 5.4M parameters. These state-of-the-art results on three datasets with different modalities demonstrate the effectiveness and adaptability of our proposed LM-Net for various medical image segmentation tasks.
当前医学图像分割方法在多尺度信息深度探索以及局部细节纹理与全局上下文语义信息有效结合方面存在局限性,这导致了过分割、欠分割和分割边界模糊的问题。为了应对这些挑战,我们从不同的角度探索多尺度特征表示,提出了一种新颖、轻量级、多尺度的架构(LM-Net),它结合了卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViTs)的优点,以提高分割精度。LM-Net采用轻量级的多分支模块,在同一层次上捕捉多尺度特征。此外,我们引入了两个模块,即局部特征转换器(LFT)和全局特征转换器(GFT),以在不同层次上同时捕捉局部细节纹理和全局语义以及多尺度特征。LFT通过局部窗口自注意力捕捉局部细节纹理,而GFT利用全局自注意力来捕捉全局上下文语义。通过结合这些模块,我们的模型实现了局部和全局表示之间的互补性,缓解了医学图像分割中模糊分割边界的问题。为了评估LM-Net的可行性,我们在三个不同模态的公开数据集上进行了大量实验。所提出的模型取得了最新结果,超越了之前的方法,仅需4.66G FLOPs和5.4M参数。在三个不同模态数据集上的这些最新结果证明了我们的提出的LM-Net在各种医学图像分割任务中的有效性和适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对当前医学图像分割方法在多尺度信息探索及局部细节纹理与全局上下文语义信息结合方面的不足,提出一种新型轻量级多尺度架构(LM-Net),结合卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViTs)的优点,提高分割准确性。通过采用多分支模块和局部特征转换器(LFT)与全局特征转换器(GFT),实现局部与全局表示的互补,缓解医学图像分割中的边界模糊问题。在三个公开数据集上进行实验验证,所提模型参数少、计算量小,达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 当前医学图像分割方法存在多尺度信息探索不足及局部细节纹理与全局上下文语义信息结合不有效的问题。
- 提出一种新型轻量级多尺度架构(LM-Net),结合CNN和ViT的优点。
- 采用多分支模块捕捉同一层次的多尺度特征。
- 引入LFT和GFT模块,分别在不同的层次上同时捕捉局部细节纹理和全局语义信息。
- LFT模块通过局部窗口自注意力机制捕捉局部细节纹理。
- GFT模块利用全局自注意力机制捕捉全局上下文语义。
点此查看论文截图

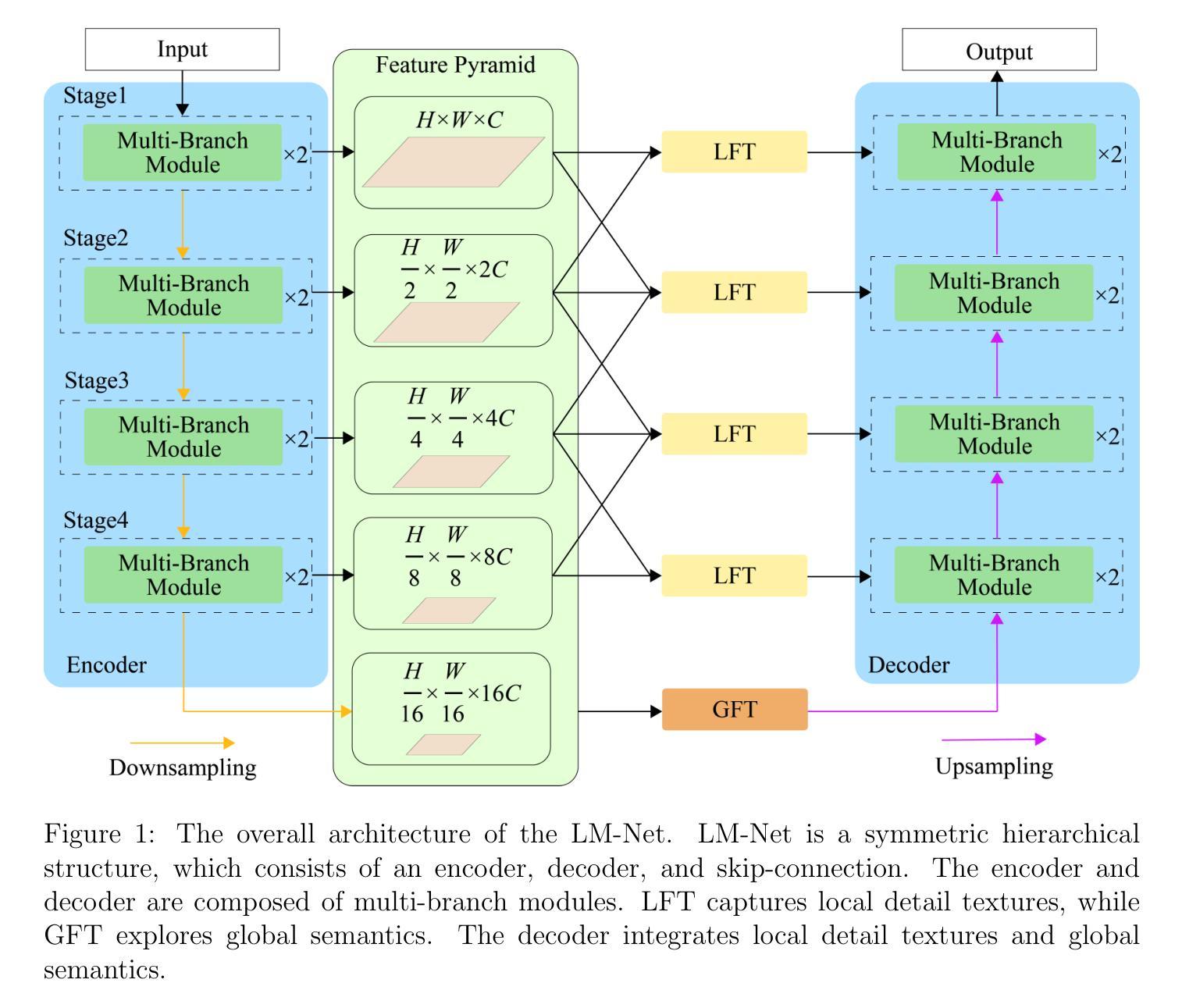
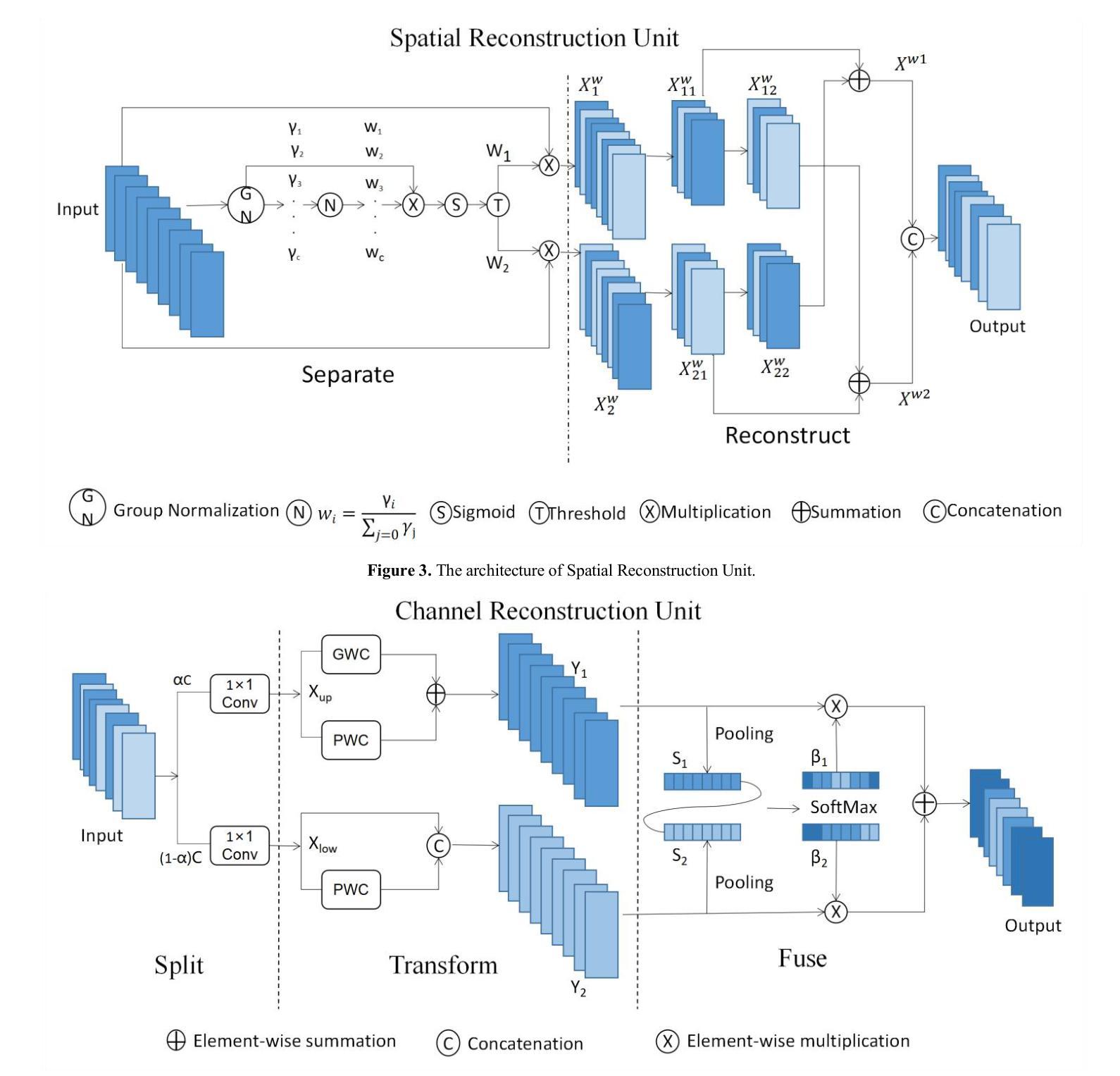
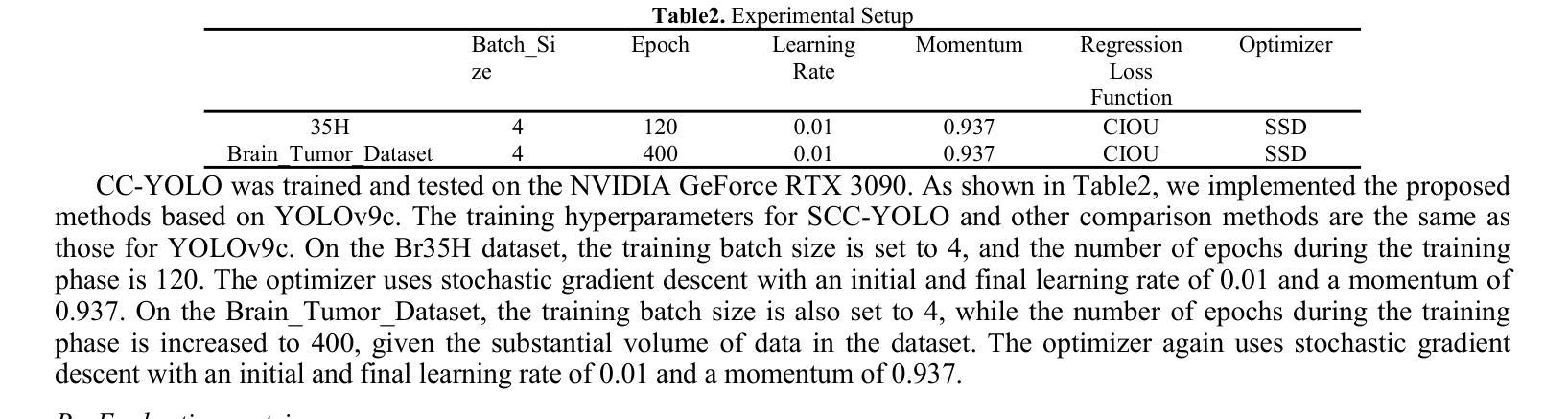
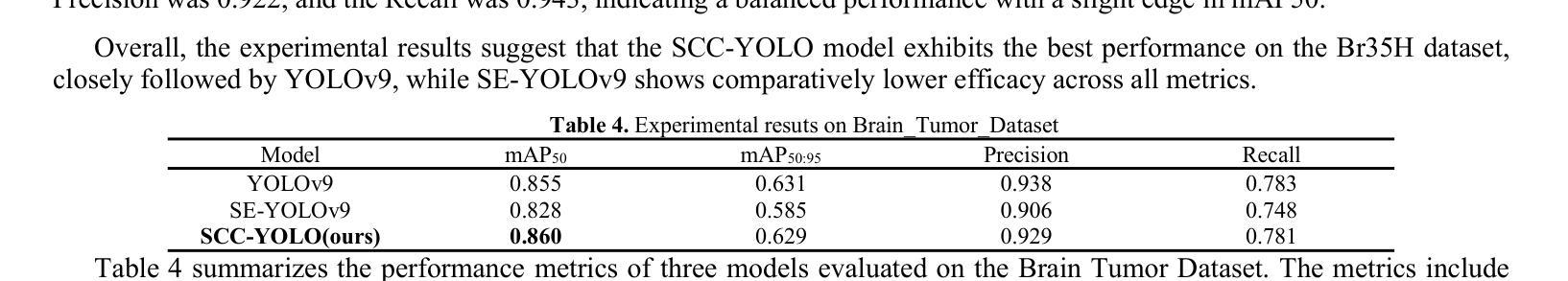
SCC-YOLO: An Improved Object Detector for Assisting in Brain Tumor Diagnosis
Authors:Runci Bai
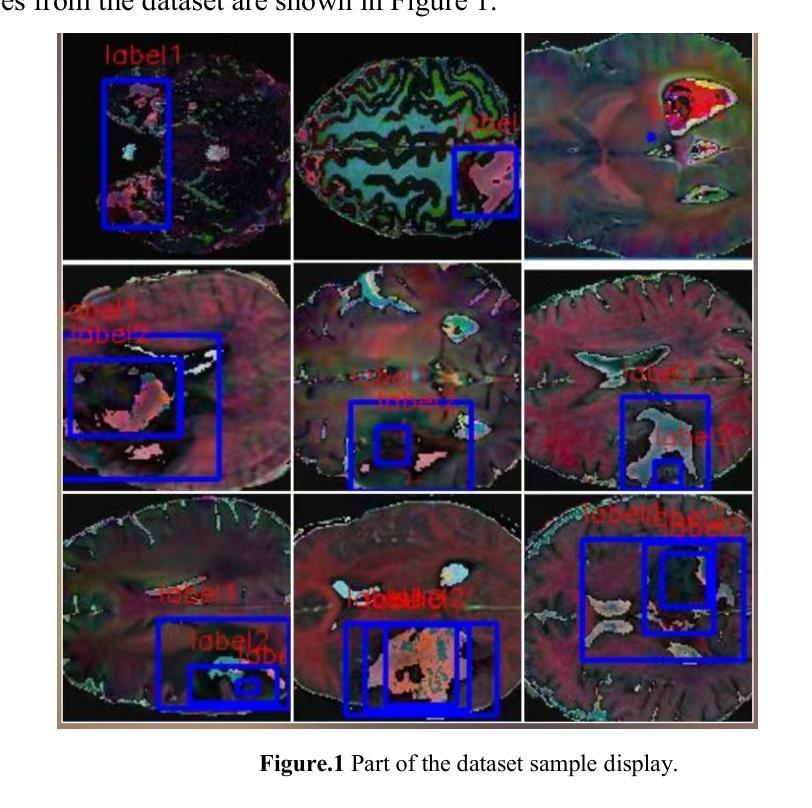
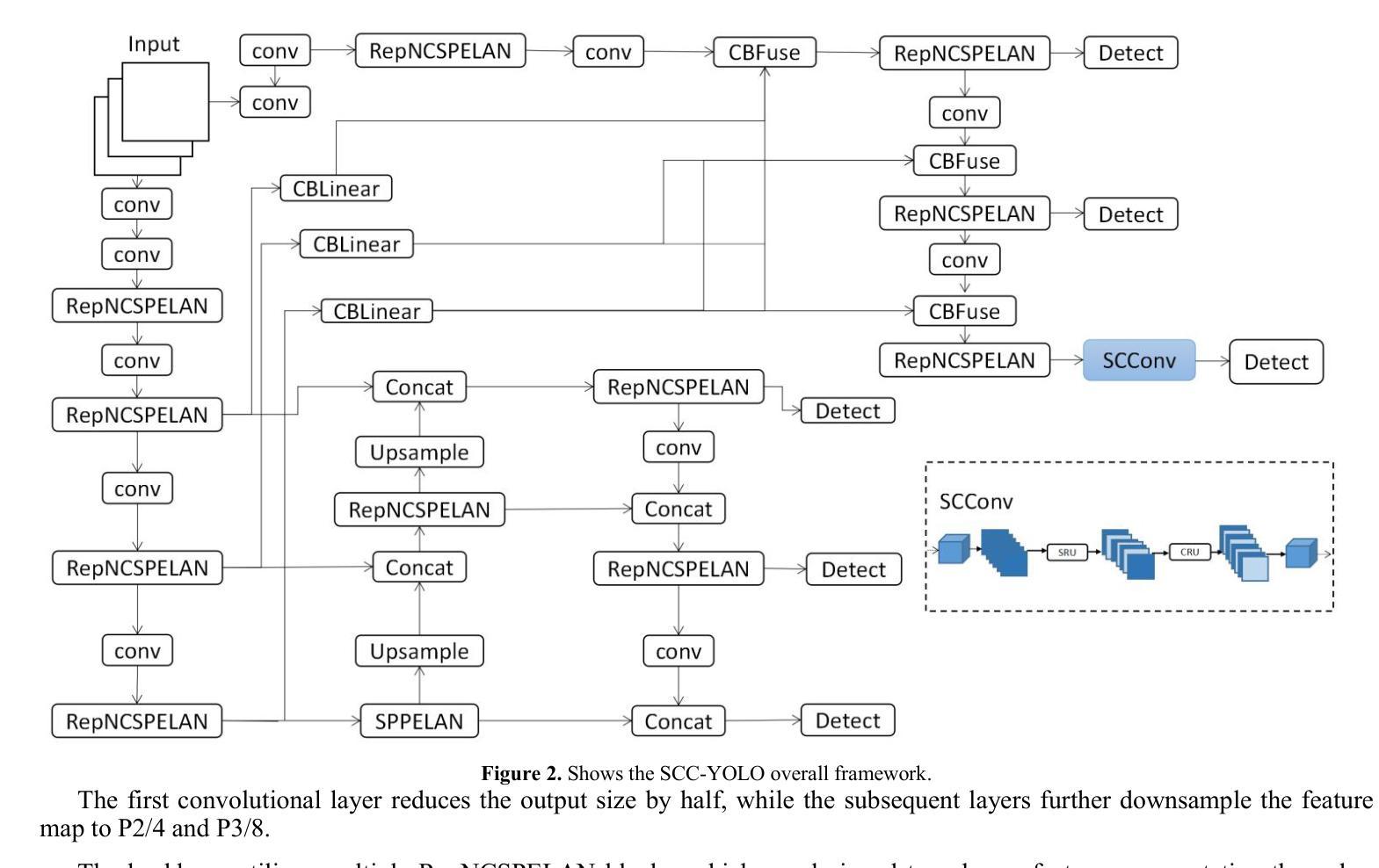
Brain tumors can result in neurological dysfunction, alterations in cognitive and psychological states, increased intracranial pressure, and the occurrence of seizures, thereby presenting a substantial risk to human life and health. The You Only Look Once(YOLO) series models have demonstrated superior accuracy in object detection for medical imaging. In this paper, we develop a novel SCC-YOLO architecture by integrating the SCConv attention mechanism into YOLOv9. The SCConv module reconstructs an efficient convolutional module by reducing spatial and channel redundancy among features, thereby enhancing the learning of image features. We investigate the impact of intergrating different attention mechanisms with the YOLOv9 model on brain tumor image detection using both the Br35H dataset and our self-made dataset(Brain_Tumor_Dataset). Experimental results show that on the Br35H dataset, SCC-YOLO achieved a 0.3% improvement in mAp50 compared to YOLOv9, while on our self-made dataset, SCC-YOLO exhibited a 0.5% improvement over YOLOv9. SCC-YOLO has reached state-of-the-art performance in brain tumor detection. Source code is available at : https://jihulab.com/healthcare-information-studio/SCC-YOLO/-/tree/master
脑肿瘤可能导致神经功能障碍、认知和心理状态改变、颅内压升高以及癫痫发作,从而对人类生命和健康构成重大风险。You Only Look Once(YOLO)系列模型在医学图像的目标检测中表现出了卓越的准确性。在本文中,我们通过将SCConv注意力机制融入YOLOv9,开发了一种新型的SCC-YOLO架构。SCConv模块通过减少特征之间的空间冗余和通道冗余,从而重新构建了一个高效的卷积模块,增强了图像特征的学习。我们使用Br35H数据集和我们自制的Brain_Tumor_Dataset数据集,研究了将不同注意力机制与YOLOv9模型集成对脑肿瘤图像检测的影响。实验结果表明,在Br35H数据集上,SCC-YOLO相较于YOLOv9在mAp50上提高了0.3%;而在我们自制的数据集上,SCC-YOLO相较于YOLOv9提高了0.5%。SCC-YOLO在脑肿瘤检测方面已经达到了业界顶尖的性能。源代码可访问:https://jihulab.com/healthcare-information-studio/SCC-YOLO/-/tree/master。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文开发了一种新型的SCC-YOLO架构,通过将SCConv注意力机制融入YOLOv9模型,提升了脑部肿瘤图像的识别能力。通过在不同数据集上的实验,显示出该模型在脑部肿瘤检测方面的优异性能,达到了业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- SCC-YOLO模型结合了SCConv注意力机制,增强了脑部肿瘤图像的识别精度。
- SCConv模块能有效减少特征的空间和通道冗余,提升图像特征的学习效率。
- 在Br35H数据集上,SCC-YOLO相较于YOLOv9模型提高了0.3%的mAp50指标。
- 在自制数据集Brain_Tumor_Dataset上,SCC-YOLO相较于YOLOv9模型提高了0.5%的识别性能。
- SCC-YOLO模型在脑部肿瘤检测方面达到了业界领先水平。
- 该模型的源代码已公开发布在https://jihulab.com/healthcare-information-studio/SCC-YOLO/-/tree/master。
点此查看论文截图

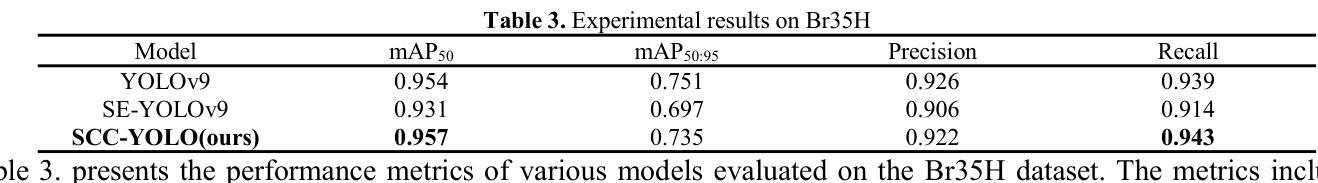
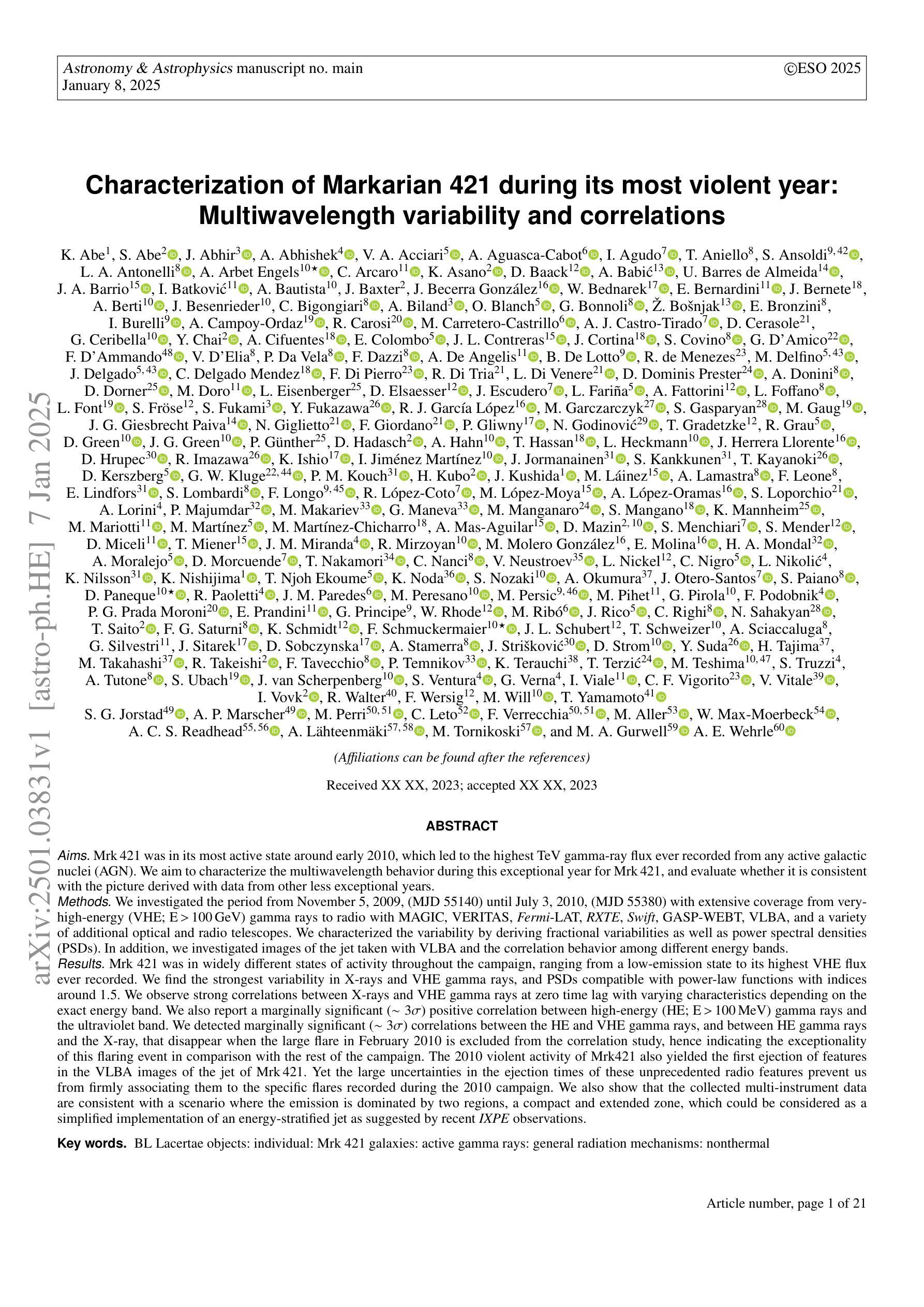
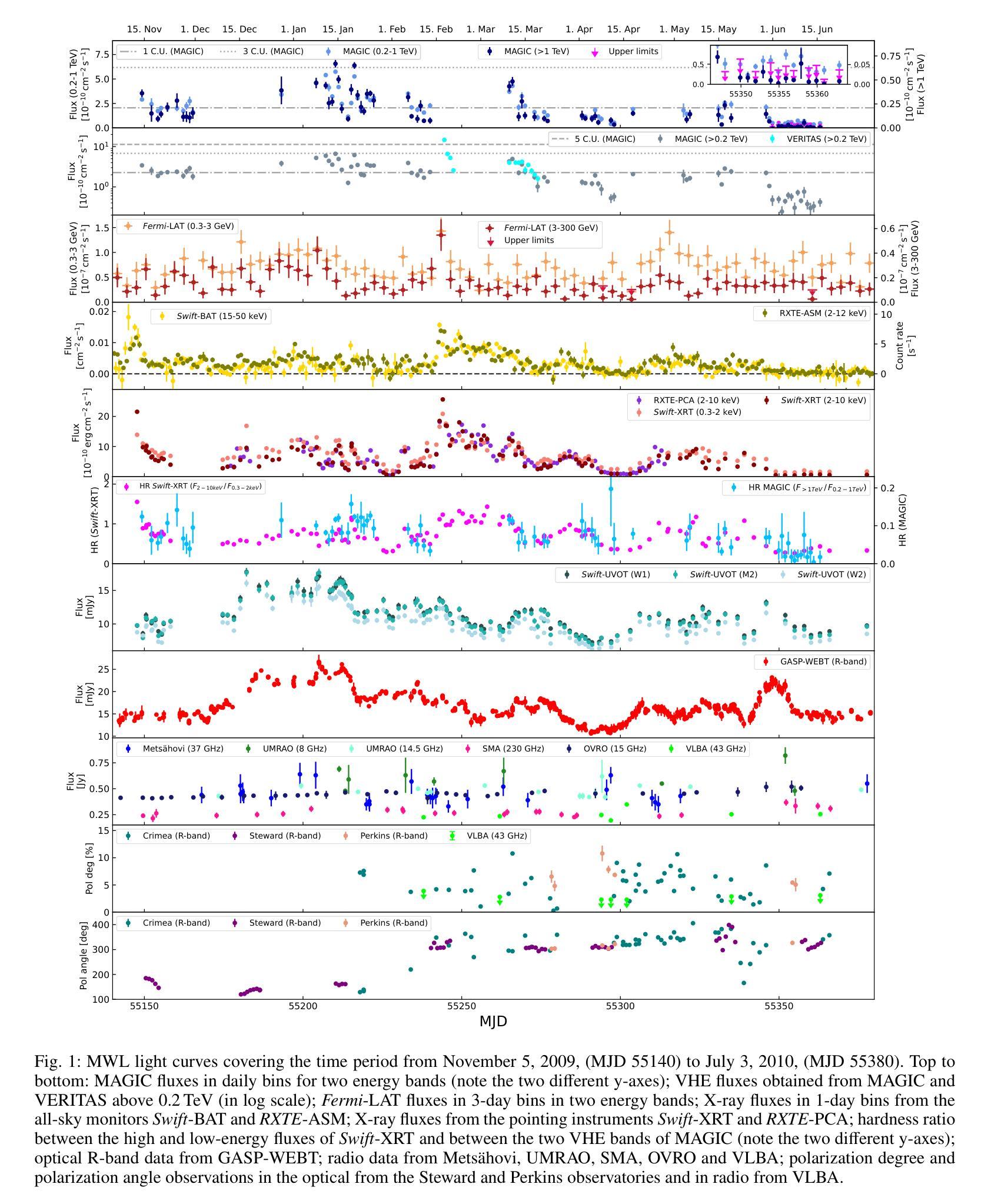
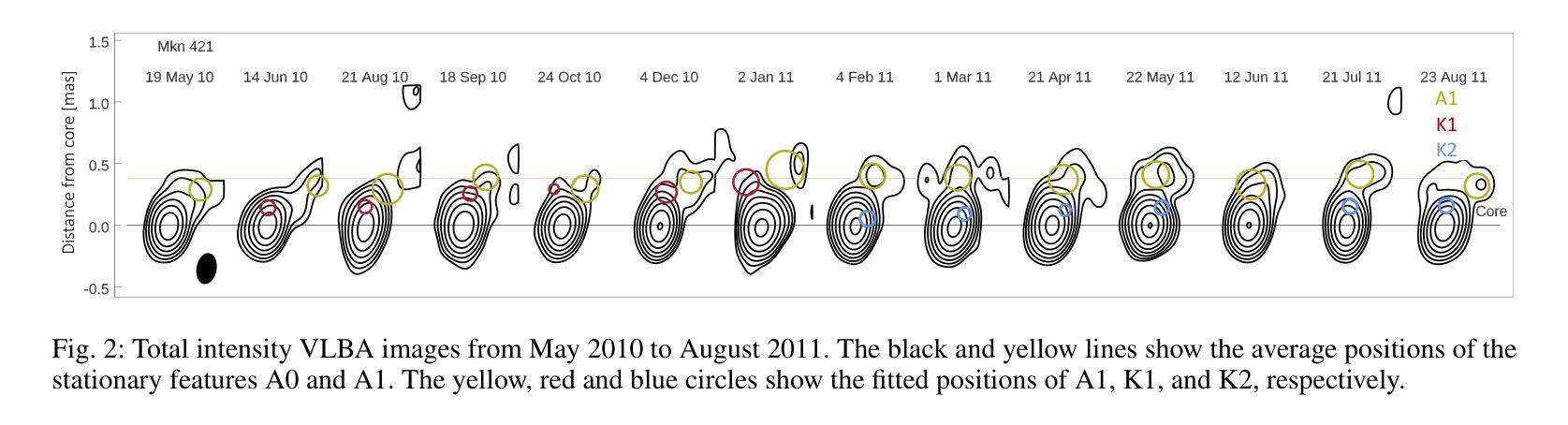
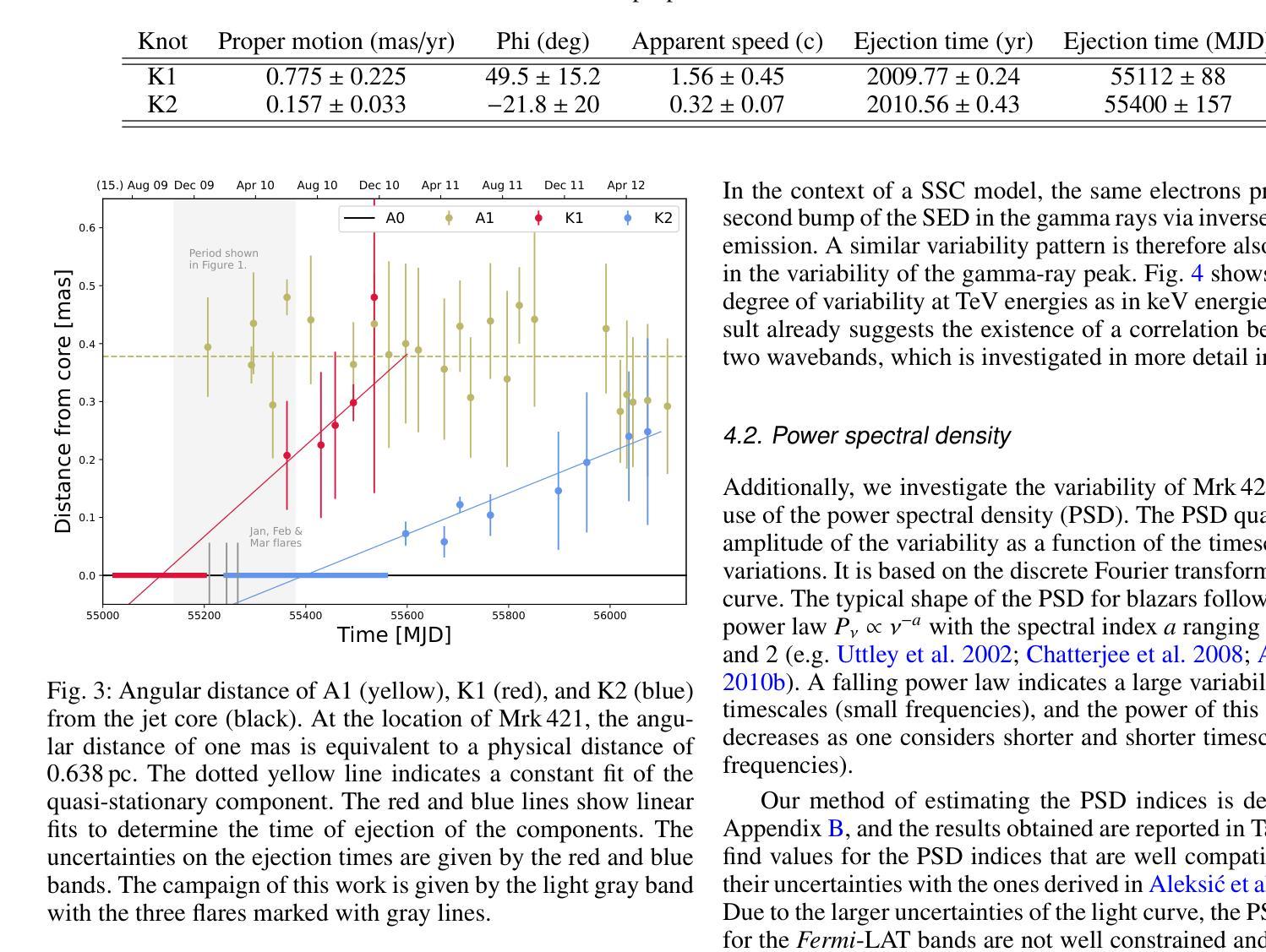
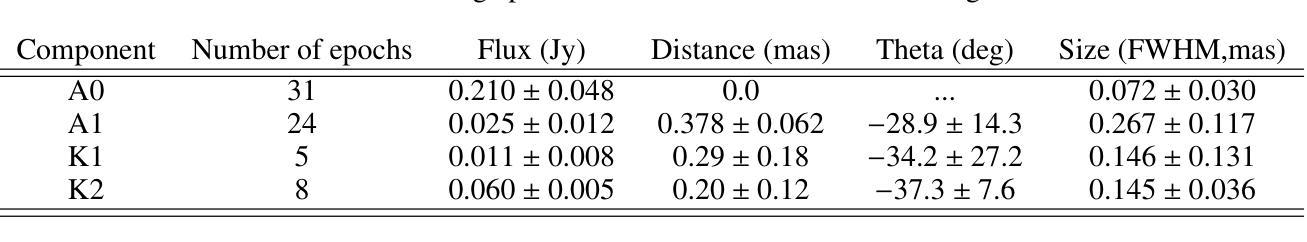
Characterization of Markarian 421 during its most violent year: Multiwavelength variability and correlations
Authors:K. Abe, S. Abe, J. Abhir, A. Abhishek, V. A. Acciari, A. Aguasca-Cabot, I. Agudo, T. Aniello, S. Ansoldi, L. A. Antonelli, A. Arbet Engels, C. Arcaro, K. Asano, D. Baack, A. Babić, U. Barres de Almeida, J. A. Barrio, I. Batković, A. Bautista, J. Baxter, J. Becerra González, W. Bednarek, E. Bernardini, J. Bernete, A. Berti, J. Besenrieder, C. Bigongiari, A. Biland, O. Blanch, G. Bonnoli, Ž. Bošnjak, E. Bronzini, I. Burelli, A. Campoy-Ordaz, R. Carosi, M. Carretero-Castrillo, A. J. Castro-Tirado, D. Cerasole, G. Ceribella, Y. Chai, A. Cifuentes, E. Colombo, J. L. Contreras, J. Cortina, S. Covino, G. D’Amico, F. D’Ammando, V. D’Elia, P. Da Vela, F. Dazzi, A. De Angelis, B. De Lotto, R. de Menezes, M. Delfino, J. Delgado, C. Delgado Mendez, F. Di Pierro, R. Di Tria, L. Di Venere, D. Dominis Prester, A. Donini, D. Dorner, M. Doro, L. Eisenberger, D. Elsaesser, J. Escudero, L. Fariña, A. Fattorini, L. Foffano, L. Font, S. Fröse, S. Fukami, Y. Fukazawa, R. J. García López, M. Garczarczyk, S. Gasparyan, M. Gaug, J. G. Giesbrecht Paiva, N. Giglietto, F. Giordano, P. Gliwny, N. Godinović, T. Gradetzke, R. Grau, D. Green, J. G. Green, P. Günther, D. Hadasch, A. Hahn, T. Hassan, L. Heckmann, J. Herrera Llorente, D. Hrupec, R. Imazawa, K. Ishio, I. Jiménez Martínez, J. Jormanainen, S. Kankkunen, T. Kayanoki, D. Kerszberg, G. W. Kluge, P. M. Kouch, H. Kubo, J. Kushida, M. Láinez, A. Lamastra, F. Leone, E. Lindfors, S. Lombardi, F. Longo, R. López-Coto, M. López-Moya, A. López-Oramas, S. Loporchio, A. Lorini, P. Majumdar, M. Makariev, G. Maneva, M. Manganaro, S. Mangano, K. Mannheim, M. Mariotti, M. Martínez, M. Martínez-Chicharro, A. Mas-Aguilar, D. Mazin, S. Menchiari, S. Mender, D. Miceli, T. Miener, J. M. Miranda, R. Mirzoyan, M. Molero González, E. Molina, H. A. Mondal, A. Moralejo, D. Morcuende, T. Nakamori, C. Nanci, V. Neustroev, L. Nickel, C. Nigro, L. Nikolić, K. Nilsson, K. Nishijima, T. Njoh Ekoume, K. Noda, S. Nozaki, A. Okumura, J. Otero-Santos, S. Paiano, D. Paneque, R. Paoletti, J. M. Paredes, M. Peresano, M. Persic, M. Pihet, G. Pirola, F. Podobnik, P. G. Prada Moroni, E. Prandini, G. Principe, W. Rhode, M. Ribó, J. Rico, C. Righi, N. Sahakyan, T. Saito, F. G. Saturni, K. Schmidt, F. Schmuckermaier, J. L. Schubert, T. Schweizer, A. Sciaccaluga, G. Silvestri, J. Sitarek, D. Sobczynska, A. Stamerra, J. Strišković, D. Strom, Y. Suda, H. Tajima, M. Takahashi, R. Takeishi, F. Tavecchio, P. Temnikov, K. Terauchi, T. Terzić, M. Teshima, S. Truzzi, A. Tutone, S. Ubach, J. van Scherpenberg, S. Ventura, G. Verna, I. Viale, C. F. Vigorito, V. Vitale, I. Vovk, R. Walter, F. Wersig, M. Will, T. Yamamoto, S. G. Jorstad, A. P. Marscher, M. Perri, C. Leto, F. Verrecchia, M. Aller, W. Max-Moerbeck, A. C. S. Readhead, A. Lähteenmäki, M. Tornikoski, M. A. Gurwell, A. E. Wehrle
Mrk 421 was in its most active state around early 2010, which led to the highest TeV gamma-ray flux ever recorded from any active galactic nuclei. We aim to characterize the multiwavelength behavior during this exceptional year for Mrk 421, and evaluate whether it is consistent with the picture derived with data from other less exceptional years. We investigated the period from November 5, 2009, (MJD 55140) until July 3, 2010, (MJD 55380) with extensive coverage from very-high-energy (VHE; E$,>,$100$,$GeV) gamma rays to radio with MAGIC, VERITAS, Fermi-LAT, RXTE, Swift, GASP-WEBT, VLBA, and a variety of additional optical and radio telescopes. We investigated the variability and correlation behavior among different energy bands in great detail. We find the strongest variability in X-rays and VHE gamma rays, and PSDs compatible with power-law functions. We observe strong correlations between X-rays and VHE gamma rays. We also report a marginally significant positive correlation between high-energy (HE; E$,>,$100$,$MeV) gamma rays and the ultraviolet band. We detected marginally significant correlations between the HE and VHE gamma rays, and between HE gamma rays and the X-ray, that disappear when the large flare in February 2010 is excluded from the correlation study. The activity of Mrk 421 also yielded the first ejection of features in the VLBA images of the jet of Mrk 421. Yet the large uncertainties in the ejection times of these radio features prevent us from firmly associating them to the specific flares recorded during the campaign. We also show that the collected multi-instrument data are consistent with a scenario where the emission is dominated by two regions, a compact and extended zone, which could be considered as a simplified implementation of an energy-stratified jet as suggested by recent IXPE observations.
Mrk 421在大约2010年初时处于最活跃状态,产生了迄今为止记录到的来自任何活动星系核的最高TeV伽马射线流量。我们的目标是针对Mrk 421在这不同寻常的一年中的多波长行为进行研究,并评估其是否与其他不那么特殊的年份的数据得出的图像一致。我们研究了从2009年11月5日(MJD 55140)至2010年7月3日(MJD 55380)期间的时期,借助MAGIC、VERITAS、Fermi-LAT、RXTE、Swift、GASP-WEBT、VLBA以及各种其他光学和射电望远镜从极高能(VHE;E>100 GeV)伽马射线到射电波段的广泛覆盖。我们详细研究了不同波段之间的变化和相关行为。我们发现X射线和VHE伽马射线的变化最为强烈,功率谱密度与幂律函数相符。我们观察到X射线和VHE伽马射线之间存在强烈的相关性。我们还报告了在高能(HE;E>100 MeV)伽马射线和紫外波段之间出现边缘显著的正相关。我们还发现了高能伽马射线和甚高能伽马射线之间以及高能伽马射线和X射线之间边缘显著的关联性,这些关联在排除了发生在2010年2月的特大爆发之后消失。Mrk 421的活动还产生了Mrk 421喷射流VLBA图像中的特征首次喷射。然而,这些射电特征喷射时间的巨大不确定性使我们无法将它们与活动期间的特定爆发明确地联系起来。我们还表明,收集的多仪器数据与一种发射情景相一致,该情景由两个区域主导,即紧凑区域和扩展区域,这可以被视为由最近的IXPE观测所提示的能量分层喷射的简化实现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in Astronomy & Astrophysics. Corresponding authors: Felix Schmuckermaier, David Paneque, Axel Arbet Engels
Summary
Mrk 421在大约早期活跃的TeV伽马射线流量时段表现出其最活跃状态。研究者对该时段进行了多波长行为特征分析,发现其在X射线和甚高能伽马射线上的变化最为显著,并观察到这些波段间的强相关性。此外,Mrk 421的活动还产生了首次的喷流特征喷射现象,但无法确定其与特定耀斑之间的直接联系。综合多仪器数据表明,其发射主要由两个区域主导,一个紧凑区域和一个扩展区域,符合简化的能量分层喷射情景。
Key Takeaways
- Mrk 421在大约早期活跃状态期间表现出最高的TeV伽马射线流量记录。
- 多波长行为分析揭示了该时段内强烈的X射线和甚高能伽马射线变化。
- X射线和甚高能伽马射线之间存在强相关性。
- 高能伽马射线与紫外波段之间存在边缘显著正相关。
- 排除大型耀斑后,高能伽马射线与甚高能伽马射线及高能伽马射线与X射线的相关性边缘显著,但并不显著。
- Mrk 421的活动产生了首次的喷流特征喷射现象,但无法确定其与特定耀斑的直接关联。
点此查看论文截图
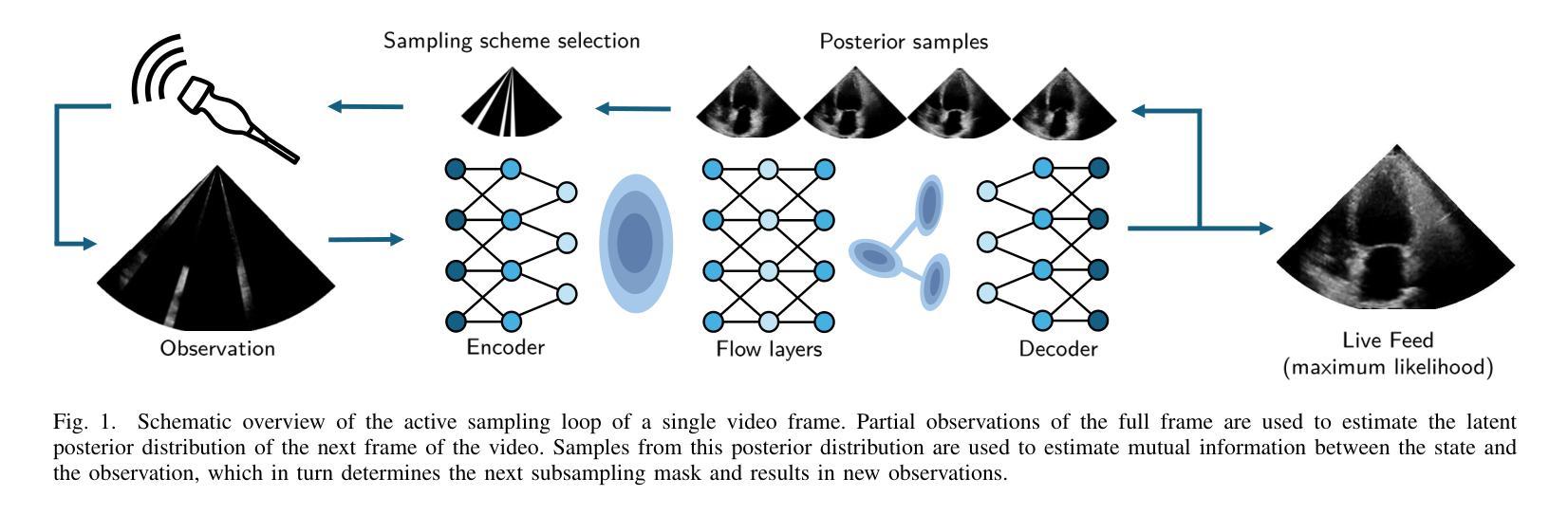
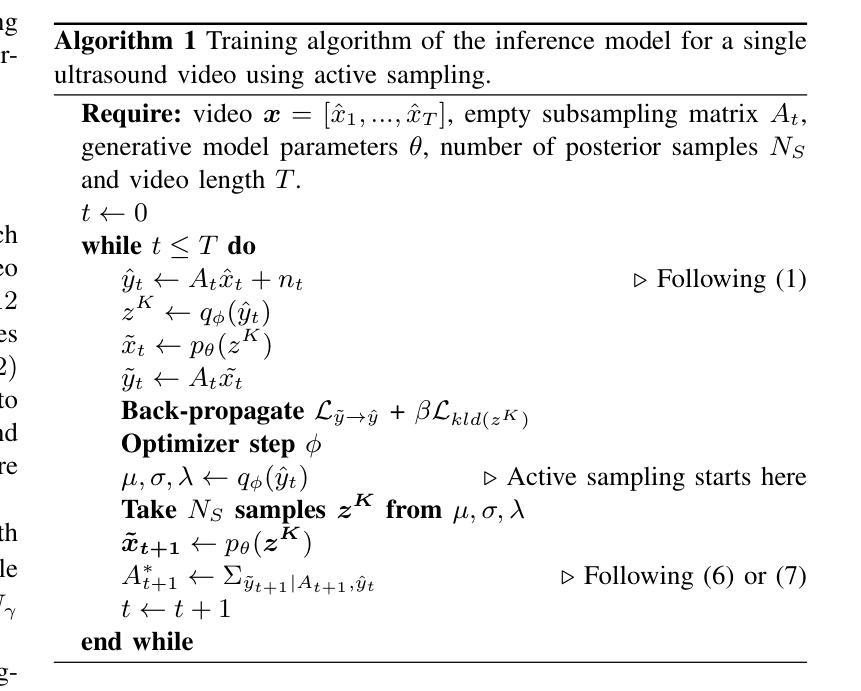
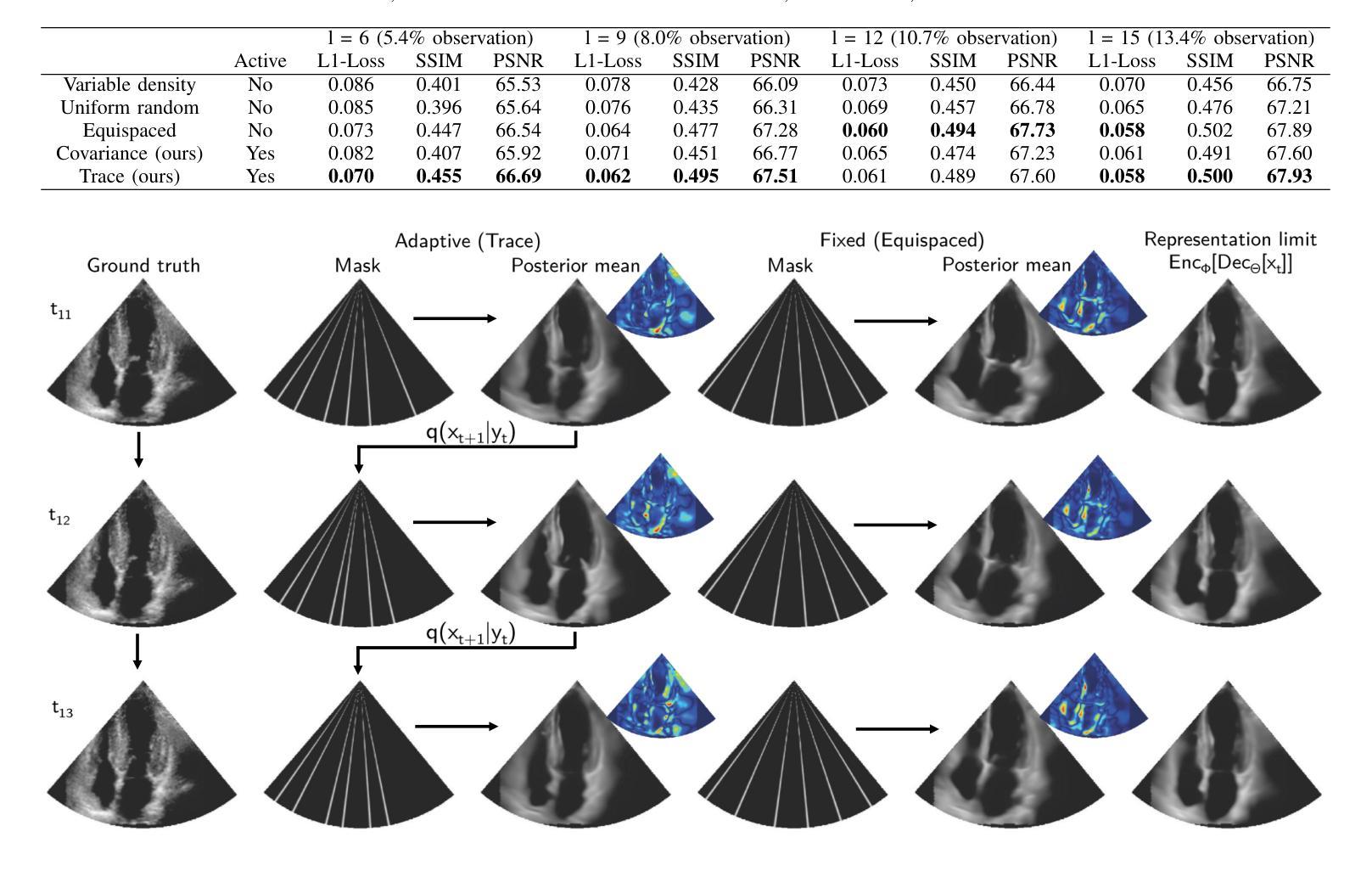
Deep Sylvester Posterior Inference for Adaptive Compressed Sensing in Ultrasound Imaging
Authors:Simon W. Penninga, Hans van Gorp, Ruud J. G. van Sloun
Ultrasound images are commonly formed by sequential acquisition of beam-steered scan-lines. Minimizing the number of required scan-lines can significantly enhance frame rate, field of view, energy efficiency, and data transfer speeds. Existing approaches typically use static subsampling schemes in combination with sparsity-based or, more recently, deep-learning-based recovery. In this work, we introduce an adaptive subsampling method that maximizes intrinsic information gain in-situ, employing a Sylvester Normalizing Flow encoder to infer an approximate Bayesian posterior under partial observation in real-time. Using the Bayesian posterior and a deep generative model for future observations, we determine the subsampling scheme that maximizes the mutual information between the subsampled observations, and the next frame of the video. We evaluate our approach using the EchoNet cardiac ultrasound video dataset and demonstrate that our active sampling method outperforms competitive baselines, including uniform and variable-density random sampling, as well as equidistantly spaced scan-lines, improving mean absolute reconstruction error by 15%. Moreover, posterior inference and the sampling scheme generation are performed in just 0.015 seconds (66Hz), making it fast enough for real-time 2D ultrasound imaging applications.
超声波图像通常是通过连续获取波束转向扫描线形成的。减少所需的扫描线数量可以显著提高帧率、视野、能效和数据传输速度。现有方法通常使用静态子采样方案,结合基于稀疏性或最近兴起的基于深度学习的恢复方法。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种自适应子采样方法,该方法最大限度地提高了现场内在信息增益,采用Sylvester正规化流编码器实时推断部分观测下的近似贝叶斯后验概率。利用贝叶斯后验概率和用于未来观测的深层生成模型,我们确定了使子采样观测与视频的下一帧之间的互信息最大化的子采样方案。我们使用EchoNet心脏超声视频数据集评估了我们的方法,并证明我们的主动采样方法在均匀和可变密度随机采样以及等距间隔扫描线等竞争基线之上表现出优势,平均绝对重建误差提高了15%。此外,后验推断和采样方案生成仅需0.015秒(66Hz),足以用于实时2D超声成像应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本描述了一种基于超声波图像自适应子采样方法的提出,通过实时推理推断近似的贝叶斯后验分布并利用深度生成模型预测未来观测值,最大化子采样观测与下一帧视频之间的互信息。该方法在EchoNet心脏超声视频数据集上表现优越,相比于其他基线采样策略提升了图像重建精度并优化了运行速度,为后续实时二维超声成像应用提供了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 超声波图像通常通过连续获取光束扫描线形成。
- 减少所需扫描线的数量可以显著提高帧率、视野、能量效率和数据传输速度。
- 当前方法通常采用静态子采样方案结合稀疏性或深度学习恢复技术。
- 本文提出了一种自适应子采样方法,该方法最大化内在信息增益,并采用Sylvester Normalizing Flow编码器实时推断部分观测的近似贝叶斯后验分布。
- 利用贝叶斯后验分布和深度生成模型预测未来观测值,确定能最大化子采样观测与下一帧之间的互信息的子采样方案。
点此查看论文截图

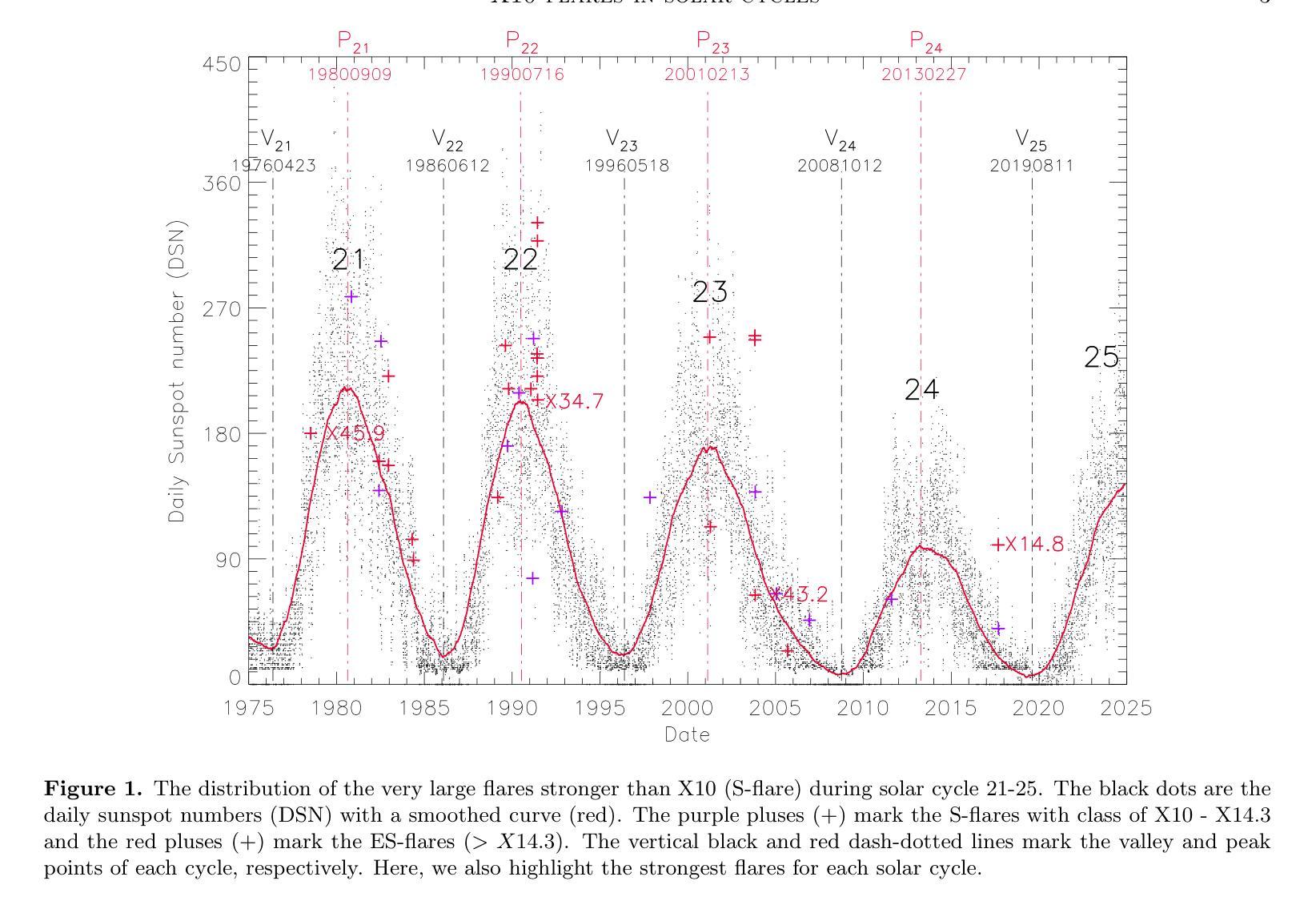
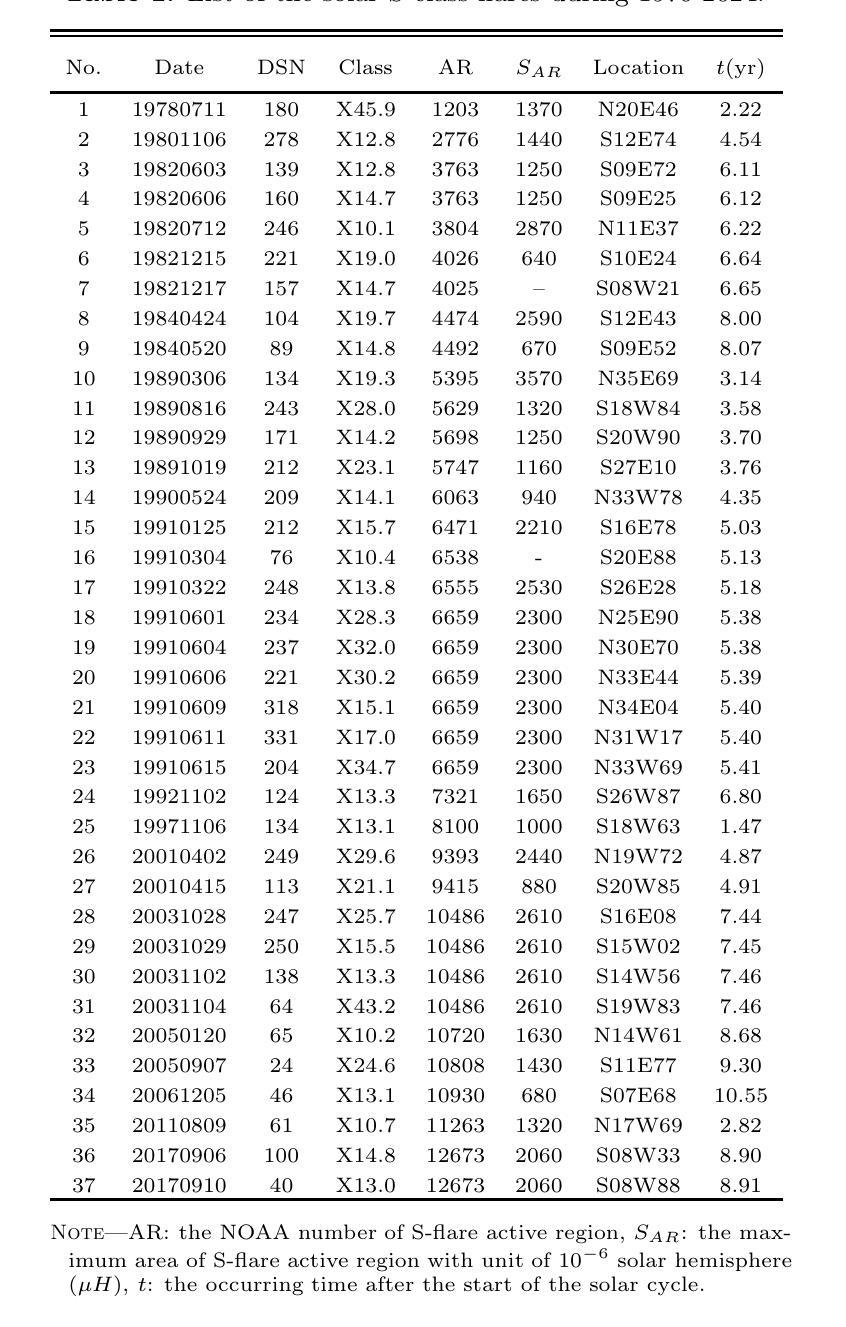
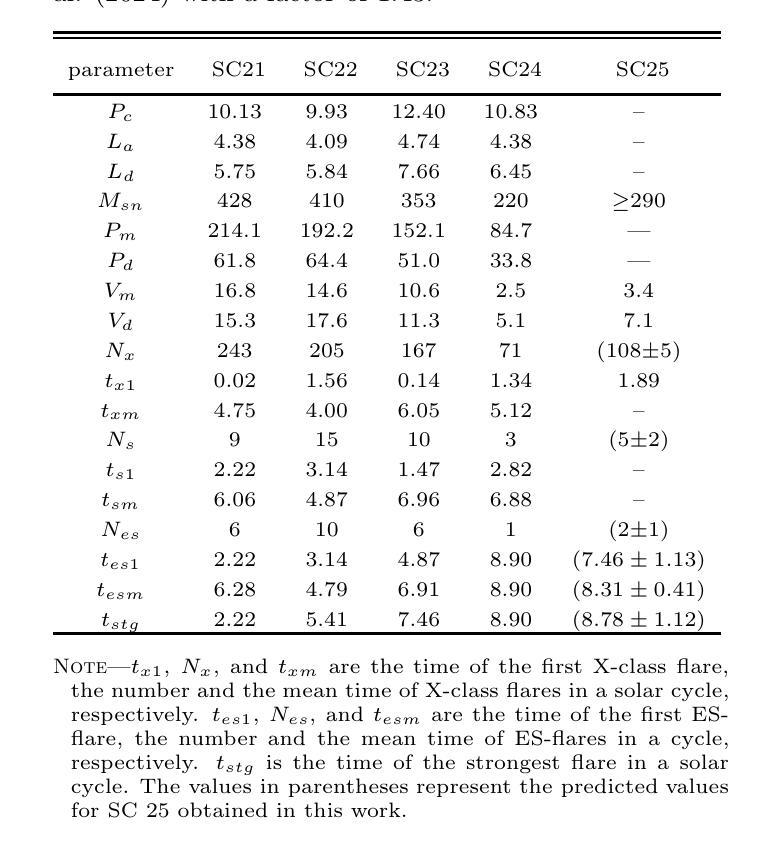
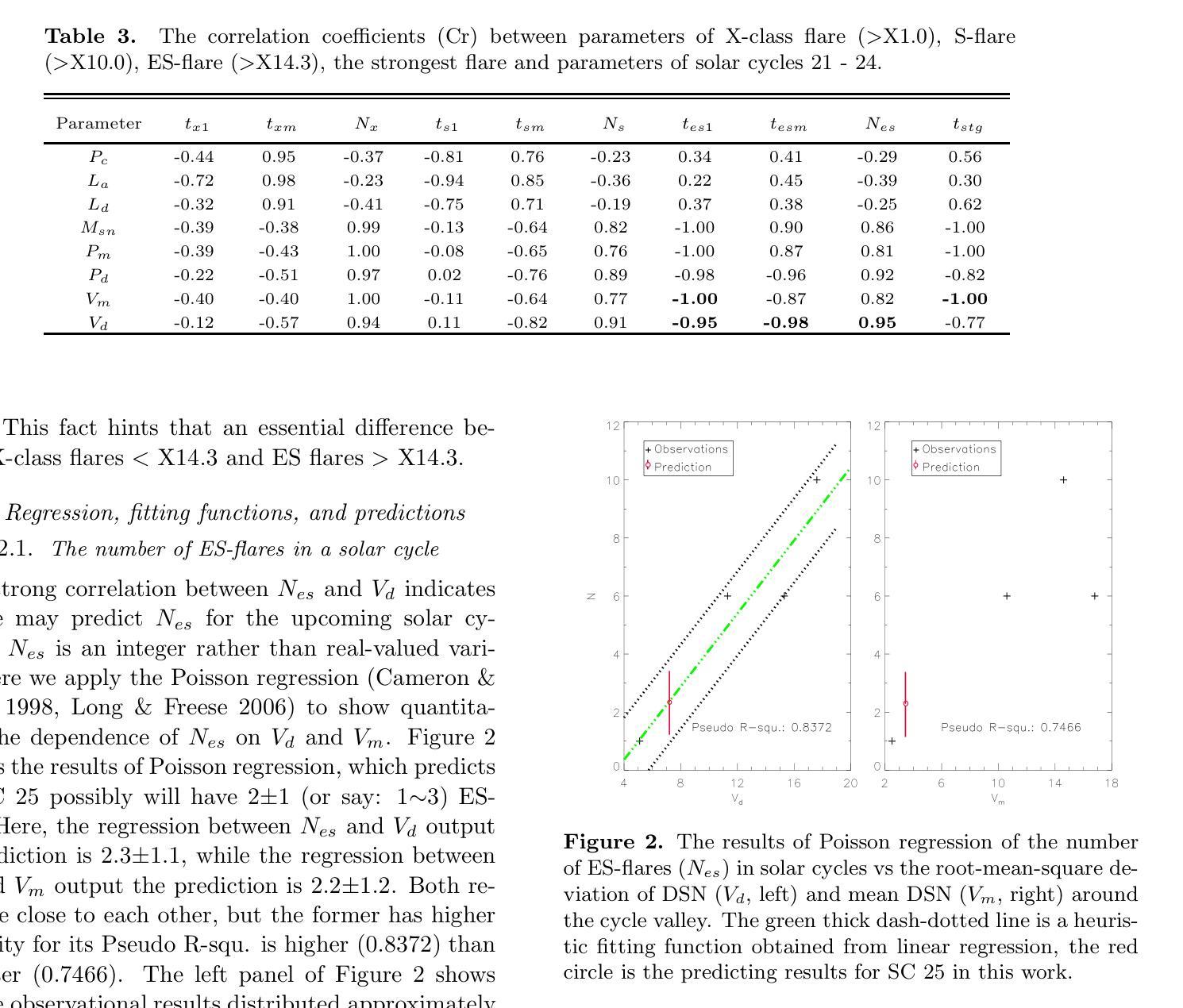
The occurrence of powerful flares stronger than X10 class in Solar Cycles
Authors:Baolin Tan, Yin Zhang, Jing Huang, Kaifan Ji
Solar flares stronger than X10 (S-flares, >X10) are the highest class flares which significantly impact on the Sun’s evolution and space weather. Based on observations of Geostationary Orbiting Environmental Satellites (GOES) at soft X-ray (SXR) wavelength and the daily sunspot numbers (DSNs) since 1975, we obtained some interesting and heuristic conclusions: (1) Both S-flares and the more powerful extremely strong flares (ES-flares, >X14.3) mostly occur in the late phases of solar cycles and low-latitude regions on the solar disk; (2) Similar to X-class flares, the occurrence of S-flares in each solar cycle is somewhat random, but the occurrence of ES-flares seems to be dominated by the mean DSN (Vm) and its root-mean-square deviation during the valley phase (Vd) before the cycle: the ES-flare number is strongly correlated with Vd, and the occurrence time of the first ES-flare is anti-correlated with Vd and Vm. These facts indicate that the higher the Vm and Vd, the stronger the solar cycle, the more the ES-flares and the earlier they occurred. We proposed that the Sun may have a low-latitude active zone (LAZ), and most ES-flares are generated from the interaction between LAZ and the newly emerging active regions. The correlations and the linear regression functions may provide an useful method to predict the occurrence of ES-flares in an upcoming solar cycle, which derives that solar cycle 25 will have about 2 ES-flares after the spring of 2027.
太阳耀斑中强度超过X10(S级耀斑,>X10)的耀斑是对太阳演化和太空天气产生重大影响的最高级别耀斑。基于对地球静止轨道环境卫星(GOES)在软X射线(SXR)波长下的观测以及自1975年以来的每日太阳黑子数(DSN),我们得到了一些有趣且具有启发性的结论:(1)S级耀斑和更强大的极端强耀斑(ES级耀斑,>X14.3)大多发生在太阳周期后期和太阳圆盘低纬度区域;(2)与X级耀斑类似,S级耀斑在每个太阳周期中的发生有些随机,但ES级耀斑的发生似乎受到周期前低谷阶段的平均DSN(Vm)及其均方根偏差(Vd)的主导:ES级耀斑数与Vd强烈相关,而首个ES级耀斑的发生时间与Vd和Vm呈负相关。这些事实表明,Vm和Vd越高,太阳周期越强,ES级耀斑越多且发生时间越早。我们提出,太阳可能有一个低纬度活跃区(LAZ),大多数ES级耀斑产生于LAZ与新兴活跃区域的相互作用。相关性和线性回归函数可能提供了一种预测即将来临的太阳周期内ES级耀斑发生的方法,由此推断,太阳周期25将在2027年春季后有大约2次ES级耀斑。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 4 figures, 3 tables, accepted by ApJ Letters
Summary
太阳耀斑中强度超过X10的耀斑(S-flares)对太阳演化和太空天气产生重要影响。通过观测地球同步轨道环境卫星(GOES)的软X射线(SXR)波长和自1975年以来的日面暗斑数(DSNs),发现S-flares和更强大的极端强耀斑(ES-flares)大多出现在太阳周期后期和低纬度区域;ES-flares的发生与低谷期的平均日面暗斑数(Vm)和均方根偏差(Vd)密切相关。提出太阳可能存在一个低纬度活动区(LAZ),多数ES-flares源于LAZ与新生活动区的相互作用。这些发现有助于预测未来太阳周期中ES-flares的发生,预测太阳周期25将在2027年春季后发生约2次ES-flares。
Key Takeaways
- S-flares和ES-flares主要出现在太阳周期后期和低纬度区域。
- ES-flares的发生与Vm和Vd密切相关,其中与Vd的关联尤为强烈。
- 第一场ES-flare的发生时间与Vm和Vd呈负相关。
- 太阳可能存在一个低纬度活动区(LAZ)。
- LAZ与新生活动区的相互作用是产生多数ES-flares的原因。
- 发现了预测未来太阳周期中ES-flares发生的方法和指标。
点此查看论文截图

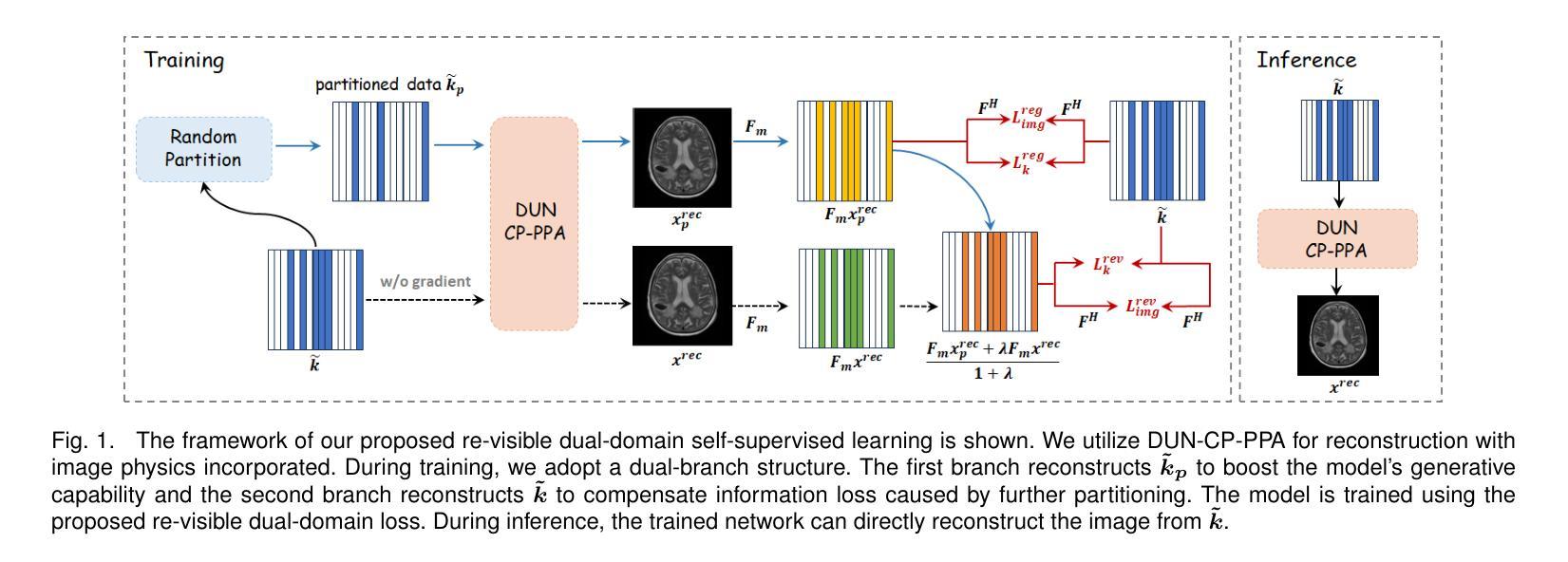
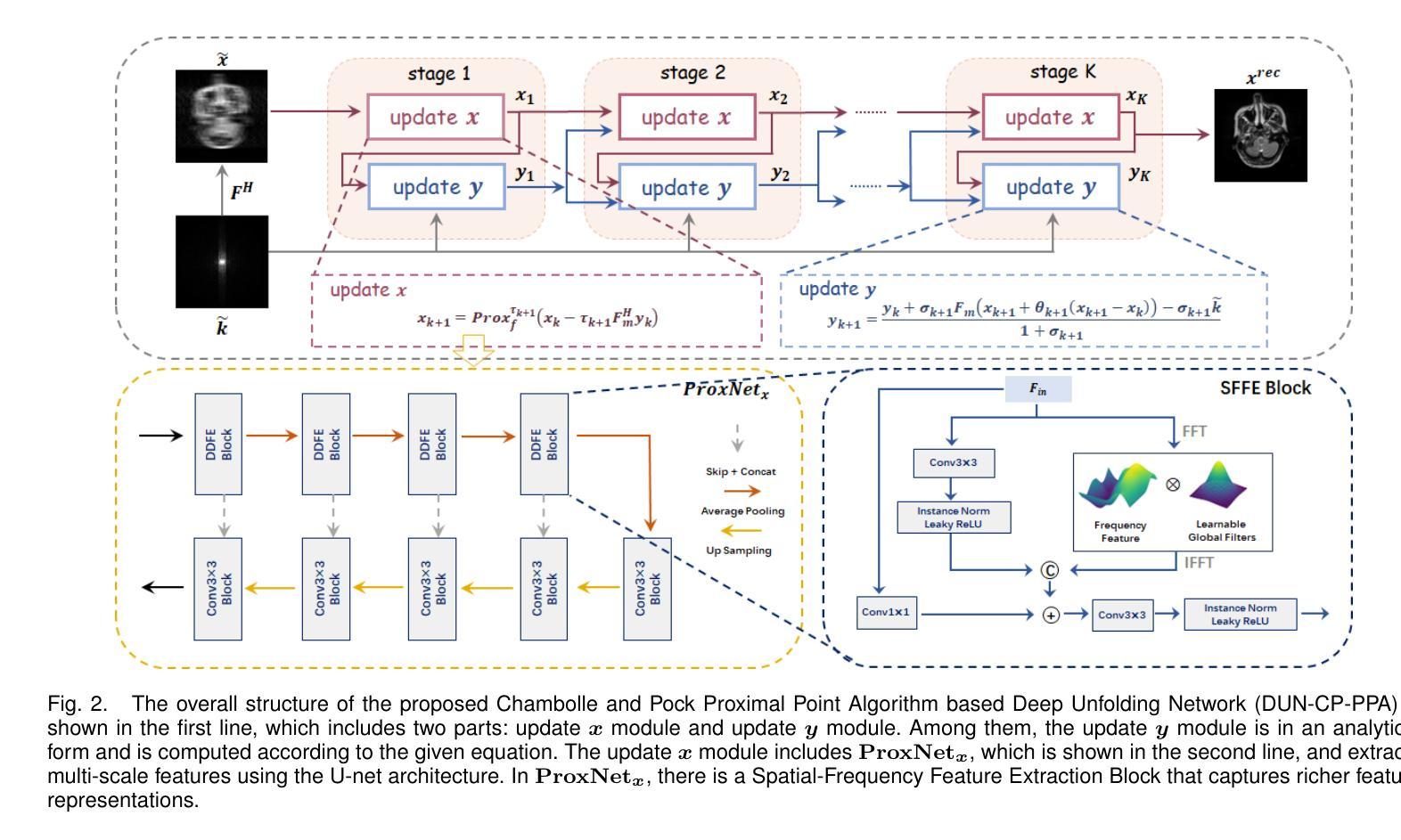
Re-Visible Dual-Domain Self-Supervised Deep Unfolding Network for MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Hao Zhang, Qi Wang, Jian Sun, Zhijie Wen, Jun Shi, Shihui Ying
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is widely used in clinical practice, but suffered from prolonged acquisition time. Although deep learning methods have been proposed to accelerate acquisition and demonstrate promising performance, they rely on high-quality fully-sampled datasets for training in a supervised manner. However, such datasets are time-consuming and expensive-to-collect, which constrains their broader applications. On the other hand, self-supervised methods offer an alternative by enabling learning from under-sampled data alone, but most existing methods rely on further partitioned under-sampled k-space data as model’s input for training, resulting in a loss of valuable information. Additionally, their models have not fully incorporated image priors, leading to degraded reconstruction performance. In this paper, we propose a novel re-visible dual-domain self-supervised deep unfolding network to address these issues when only under-sampled datasets are available. Specifically, by incorporating re-visible dual-domain loss, all under-sampled k-space data are utilized during training to mitigate information loss caused by further partitioning. This design enables the model to implicitly adapt to all under-sampled k-space data as input. Additionally, we design a deep unfolding network based on Chambolle and Pock Proximal Point Algorithm (DUN-CP-PPA) to achieve end-to-end reconstruction, incorporating imaging physics and image priors to guide the reconstruction process. By employing a Spatial-Frequency Feature Extraction (SFFE) block to capture global and local feature representation, we enhance the model’s efficiency to learn comprehensive image priors. Experiments conducted on the fastMRI and IXI datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in terms of reconstruction performance.
磁共振成像(MRI)在临床实践中得到广泛应用,但存在采集时间长的问题。虽然已提出深度学习方法来加速采集并展现出有前景的性能,但它们依赖于高质量的全采样数据集进行有监督训练。然而,这种数据集耗时且收集成本高昂,限制了其更广泛的应用。另一方面,自监督方法能够通过仅从欠采样数据中进行学习来提供替代方案,但大多数现有方法依赖于进一步分区的欠采样k-空间数据作为模型训练的输入,导致有价值的信息丢失。此外,它们的模型没有完全融入图像先验知识,导致重建性能下降。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的可视双域自监督深度展开网络,以解决仅有欠采样数据集可用时的问题。具体来说,通过融入可视双域损失,所有欠采样k-空间数据在训练过程中都得到利用,以减轻因进一步分区而造成的信息损失。这种设计使模型能够隐式适应所有欠采样k-空间数据作为输入。此外,我们基于Chambolle和Pock近端点算法(DUN-CP-PPA)设计了一个深度展开网络,以实现端到端的重建,融入成像物理和图像先验知识来指导重建过程。通过采用空间频率特征提取块来捕获全局和局部特征表示,我们提高了模型学习全面图像先验知识的效率。在fastMRI和IXI数据集上进行的实验表明,我们的方法显著优于最新技术的重建性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的可视双重领域的自监督深度展开网络,用于解决仅使用欠采样数据集时的问题。通过引入可视双重领域损失,充分利用欠采样k空间数据,减少因进一步分区而产生的信息损失。结合成像物理和图像先验的端到端重建过程,实现了高效的重建效果。在fastMRI和IXI数据集上的实验表明,该方法在重建性能上显著优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新型的可视双重领域的自监督深度展开网络来优化MRI图像重建过程。
- 通过引入可视双重领域损失,充分利用欠采样数据,减少信息损失。
- 结合成像物理和图像先验,实现端到端的重建过程。
- 采用空间频率特征提取块(SFFE),增强了学习图像先验的效率。
点此查看论文截图
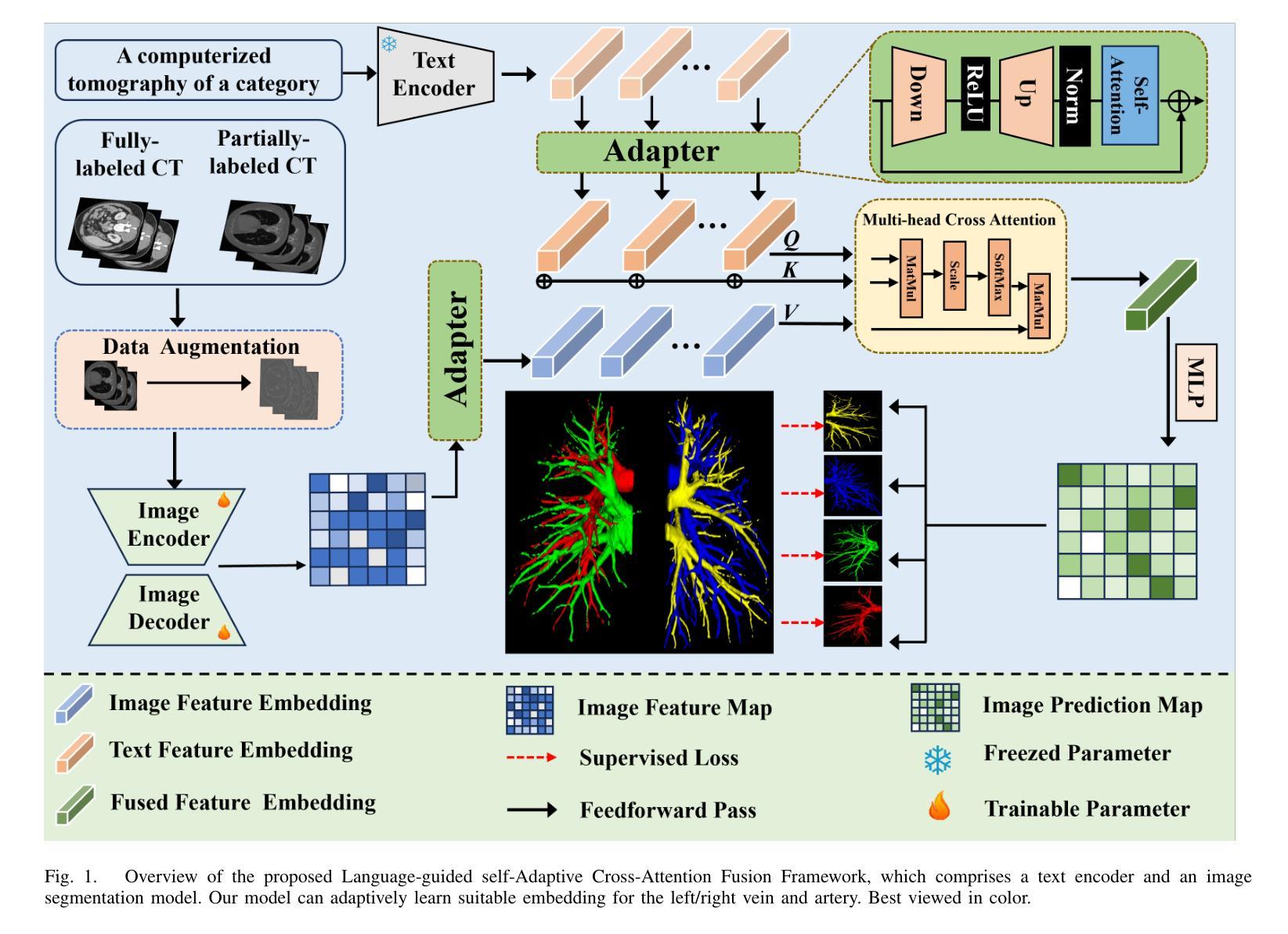
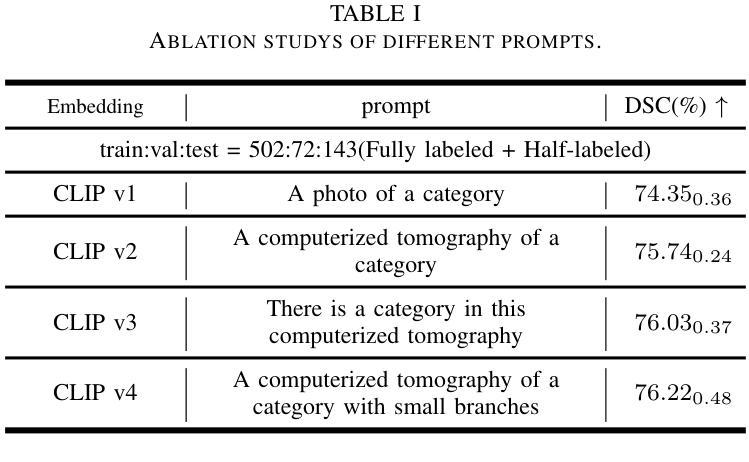
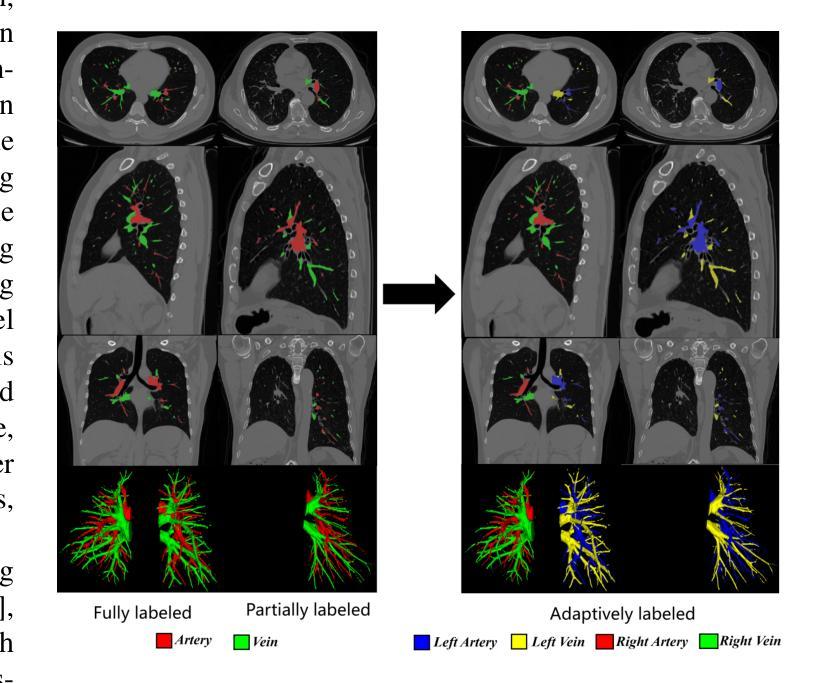
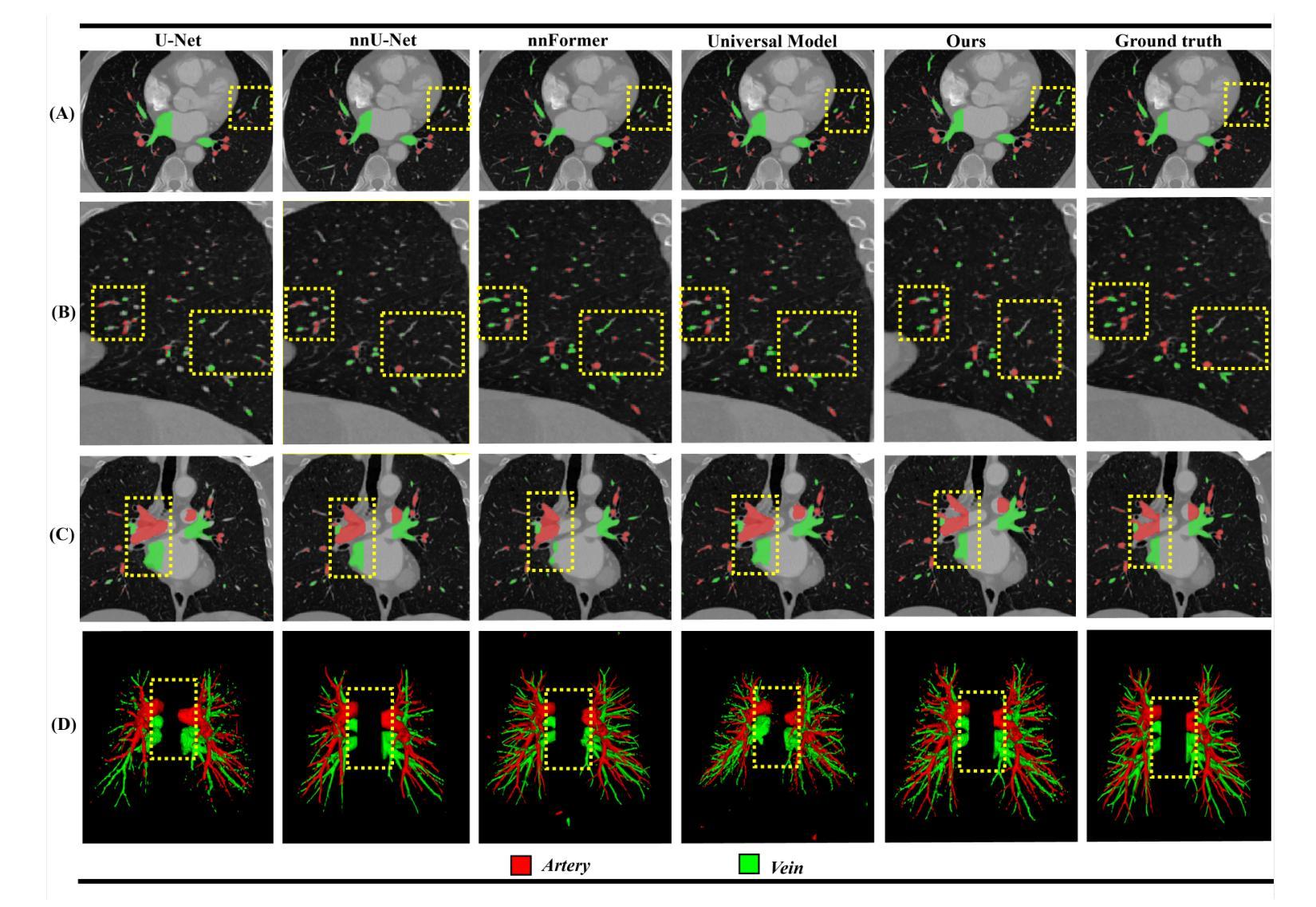
Self-adaptive vision-language model for 3D segmentation of pulmonary artery and vein
Authors:Xiaotong Guo, Deqian Yang, Dan Wang, Haochen Zhao, Yuan Li, Zhilin Sui, Tao Zhou, Lijun Zhang, Yanda Meng
Accurate segmentation of pulmonary structures iscrucial in clinical diagnosis, disease study, and treatment planning. Significant progress has been made in deep learning-based segmentation techniques, but most require much labeled data for training. Consequently, developing precise segmentation methods that demand fewer labeled datasets is paramount in medical image analysis. The emergence of pre-trained vision-language foundation models, such as CLIP, recently opened the door for universal computer vision tasks. Exploiting the generalization ability of these pre-trained foundation models on downstream tasks, such as segmentation, leads to unexpected performance with a relatively small amount of labeled data. However, exploring these models for pulmonary artery-vein segmentation is still limited. This paper proposes a novel framework called Language-guided self-adaptive Cross-Attention Fusion Framework. Our method adopts pre-trained CLIP as a strong feature extractor for generating the segmentation of 3D CT scans, while adaptively aggregating the cross-modality of text and image representations. We propose a s pecially designed adapter module to fine-tune pre-trained CLIP with a self-adaptive learning strategy to effectively fuse the two modalities of embeddings. We extensively validate our method on a local dataset, which is the largest pulmonary artery-vein CT dataset to date and consists of 718 labeled data in total. The experiments show that our method outperformed other state-of-the-art methods by a large margin. Our data and code will be made publicly available upon acceptance.
肺结构的精确分割在临床诊断、疾病研究、和治疗方案制定中至关重要。虽然基于深度学习的分割技术已经取得了重大进展,但大多数技术需要大量的标注数据来进行训练。因此,在医学图像分析中,开发需要较少标注数据集的高精度分割方法至关重要。最近出现的预训练视觉语言基础模型(如CLIP)为通用计算机视觉任务打开了大门。利用这些预训练基础模型在下游任务(如分割)上的泛化能力,可以在相对较少的标注数据上实现意想不到的性能。然而,将这些模型用于肺动脉-静脉分割的研究仍然有限。本文提出了一种名为语言引导的自适应交叉注意力融合框架的新型框架。我们的方法采用预训练的CLIP作为强大的特征提取器,用于生成3D CT扫描的分割,同时自适应地聚合文本和图像表示的跨模态信息。我们提出了一种专门设计的适配器模块,采用自适应学习策略对预训练的CLIP进行微调,以有效地融合两种模态的嵌入。我们在本地数据集上进行了广泛验证,该数据集是目前最大的肺动脉-静脉CT数据集,总共包含718个标注数据。实验表明,我们的方法大大优于其他最先进的方法。我们的数据和代码将在接受后公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages,3 figures
Summary
基于深度学习的医学图像分割技术在临床诊疗、疾病研究和治疗计划中发挥着重要作用,但依赖大量标注数据。预训练视觉语言模型的出现为医学图像分割提供了新的方向,具有少标注数据下良好表现的可能。本文提出一种名为语言引导自适应跨注意力融合框架的新方法,利用预训练CLIP模型作为特征提取器,对三维CT扫描进行分割,并自适应融合文本和图像表示。通过本地数据集验证,该方法大幅优于其他先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割在临床诊疗、疾病研究和治疗计划中至关重要。
- 深度学习在医学图像分割中取得显著进展,但依赖大量标注数据。
- 预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)为医学图像分析提供了新方向。
- 本文提出一种语言引导自适应跨注意力融合框架,利用预训练CLIP模型进行肺动脉血管分割。
- 框架包括自适应地融合文本和图像表示的特殊适配器模块。
- 在本地数据集上的实验表明,该方法显著优于其他先进方法。
点此查看论文截图

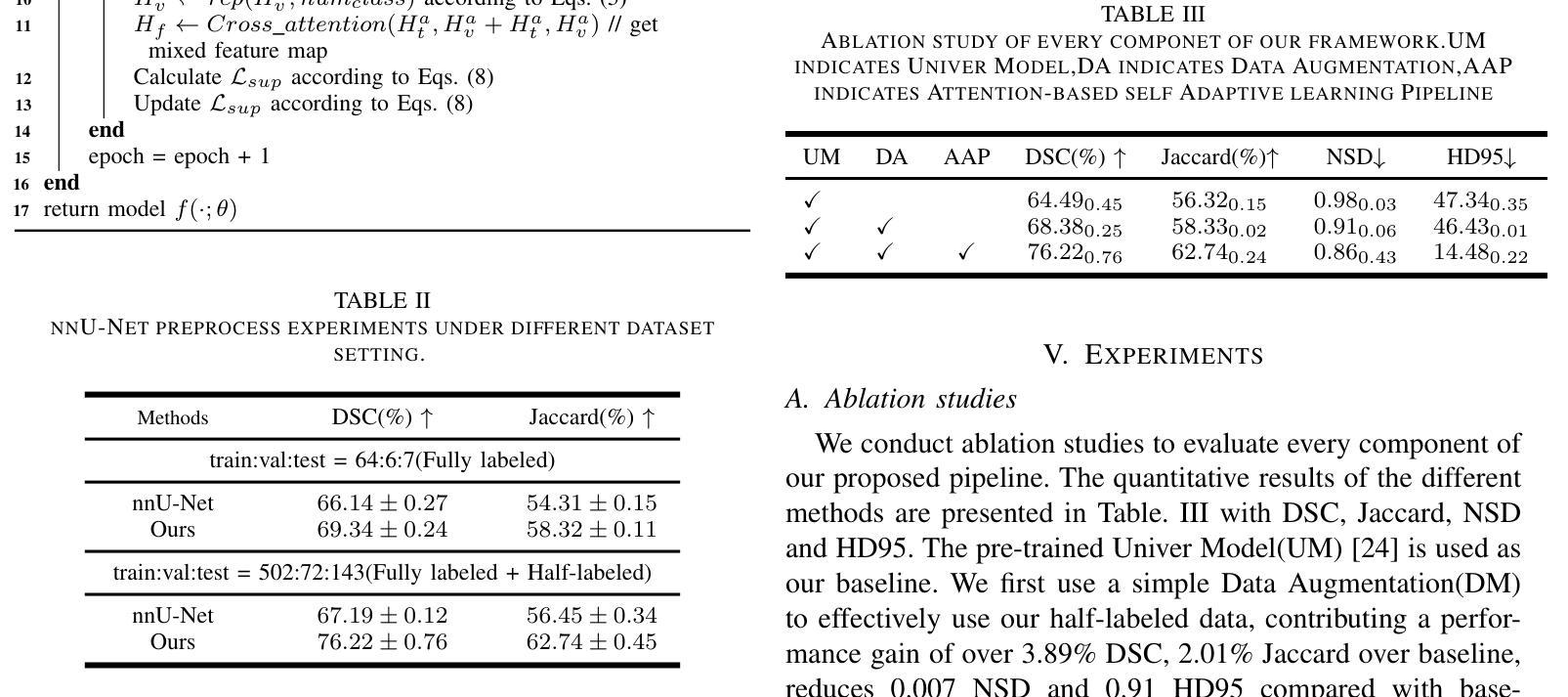
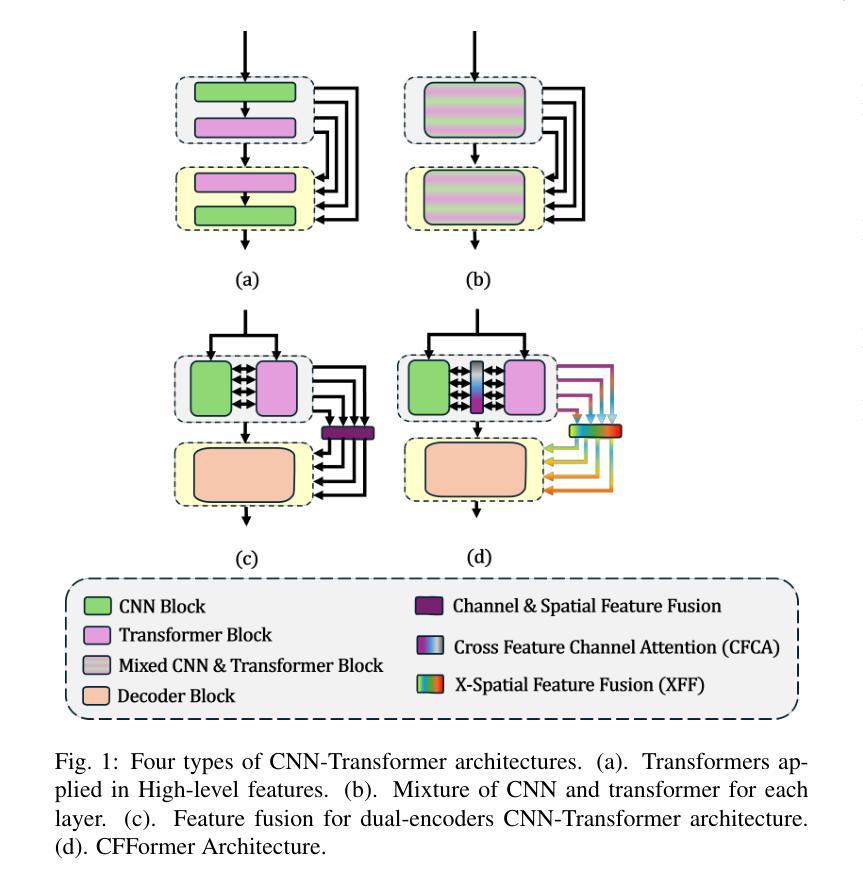
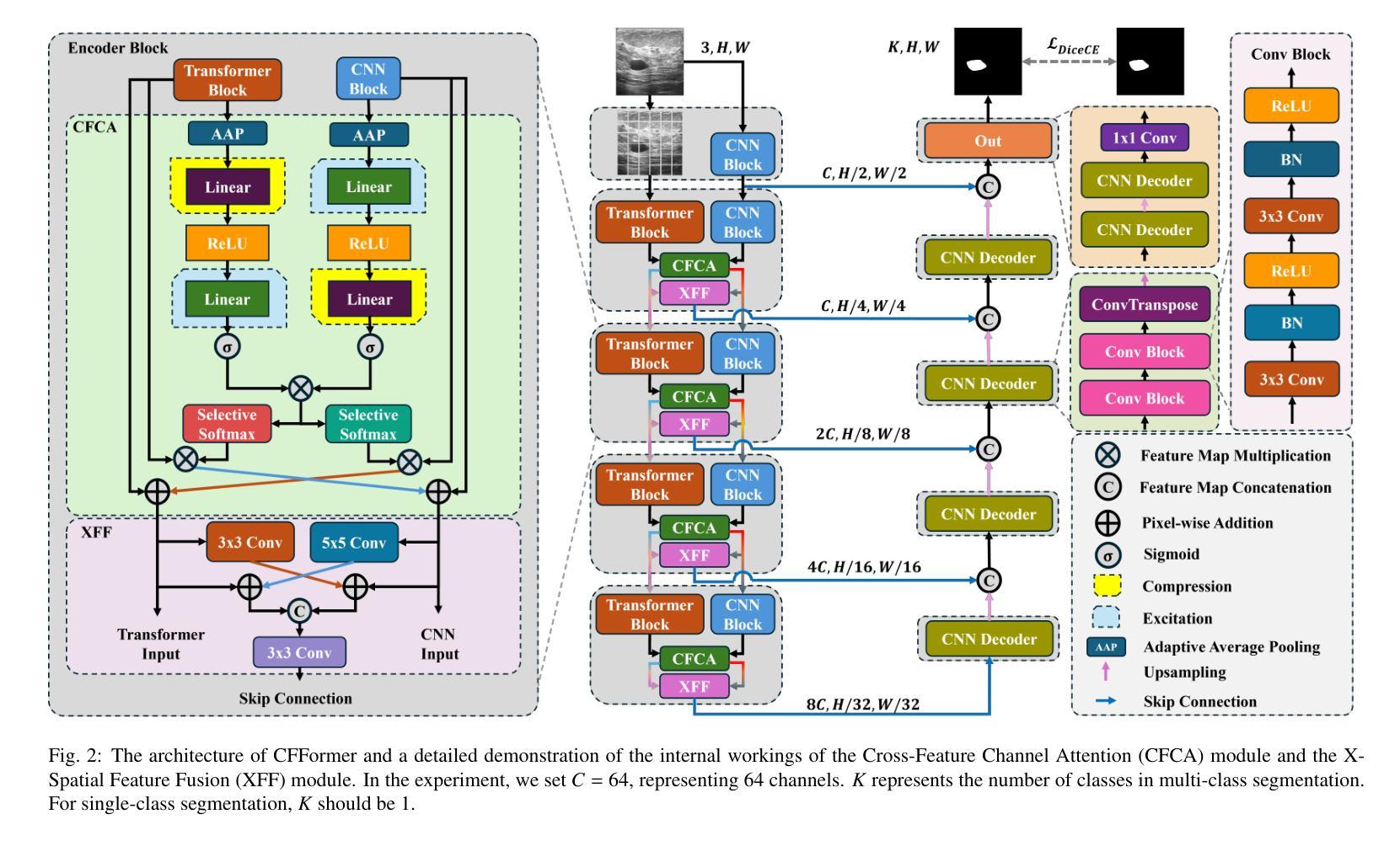
CFFormer: Cross CNN-Transformer Channel Attention and Spatial Feature Fusion for Improved Segmentation of Low Quality Medical Images
Authors:Jiaxuan Li, Qing Xu, Xiangjian He, Ziyu Liu, Daokun Zhang, Ruili Wang, Rong Qu, Guoping Qiu
Hybrid CNN-Transformer models are designed to combine the advantages of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformers to efficiently model both local information and long-range dependencies. However, most research tends to focus on integrating the spatial features of CNNs and Transformers, while overlooking the critical importance of channel features. This is particularly significant for model performance in low-quality medical image segmentation. Effective channel feature extraction can significantly enhance the model’s ability to capture contextual information and improve its representation capabilities. To address this issue, we propose a hybrid CNN-Transformer model, CFFormer, and introduce two modules: the Cross Feature Channel Attention (CFCA) module and the X-Spatial Feature Fusion (XFF) module. The model incorporates dual encoders, with the CNN encoder focusing on capturing local features and the Transformer encoder modeling global features. The CFCA module filters and facilitates interactions between the channel features from the two encoders, while the XFF module effectively reduces the significant semantic information differences in spatial features, enabling a smooth and cohesive spatial feature fusion. We evaluate our model across eight datasets covering five modalities to test its generalization capability. Experimental results demonstrate that our model outperforms current state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, with particularly superior performance on datasets characterized by blurry boundaries and low contrast.
混合CNN-Transformer模型旨在结合卷积神经网络(CNN)和Transformer的优势,以有效地对局部信息和长距离依赖关系进行建模。然而,大多数研究倾向于关注CNN和Transformer的空间特征的融合,而忽略了通道特征的关键重要性。这对于低质量医学图像分割的模型性能尤为重要。有效的通道特征提取可以显著增强模型捕获上下文信息的能力,提高其表示能力。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种混合CNN-Transformer模型CFFormer,并引入了两个模块:跨特征通道注意力(CFCA)模块和X空间特征融合(XFF)模块。该模型采用双编码器结构,CNN编码器专注于捕获局部特征,而Transformer编码器则对全局特征进行建模。CFCA模块过滤并促进两个编码器之间通道特征的交互,而XFF模块有效地减少了空间特征中的重大语义信息差异,实现了平滑和连贯的空间特征融合。我们在八个数据集上进行了评估,涵盖了五种模态,以测试模型的泛化能力。实验结果表明,我们的模型优于当前最先进的模型(SOTA),特别是在边界模糊、对比度低的数据集上表现更为优越。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The article consists of 15 pages, including 10 figures and 7 tables. The code will be made open-source once the article is accepted by the journal
Summary
本文提出一种混合CNN-Transformer模型,名为CFFormer,用于处理医学图像分割问题。该模型通过引入Cross Feature Channel Attention(CFCA)模块和X-Spatial Feature Fusion(XFF)模块,实现了对CNN和Transformer双重编码器的有效结合,能够同时捕捉局部特征和全局特征,并通过交互增强通道特征提取,提高模型捕捉上下文信息的能力和对低质量医学图像的表示能力。实验结果表明,该模型在模糊边界和低对比度数据集上表现尤为出色,优于当前先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 混合CNN-Transformer模型结合了CNN和Transformer的优点,能同时建模局部信息和长距离依赖关系。
- 现有研究多关注空间特征的整合,忽视了通道特征的重要性,特别是在低质量医学图像分割中。
- 提出的CFFormer模型通过引入CFCA和XFF模块解决了这个问题。
- CFCA模块促进CNN和Transformer编码器之间的通道特征交互。
- XFF模块有效减少空间特征的语义信息差异,实现平滑一致的空间特征融合。
- 模型在多个数据集上的实验结果表明其良好的通用性和卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

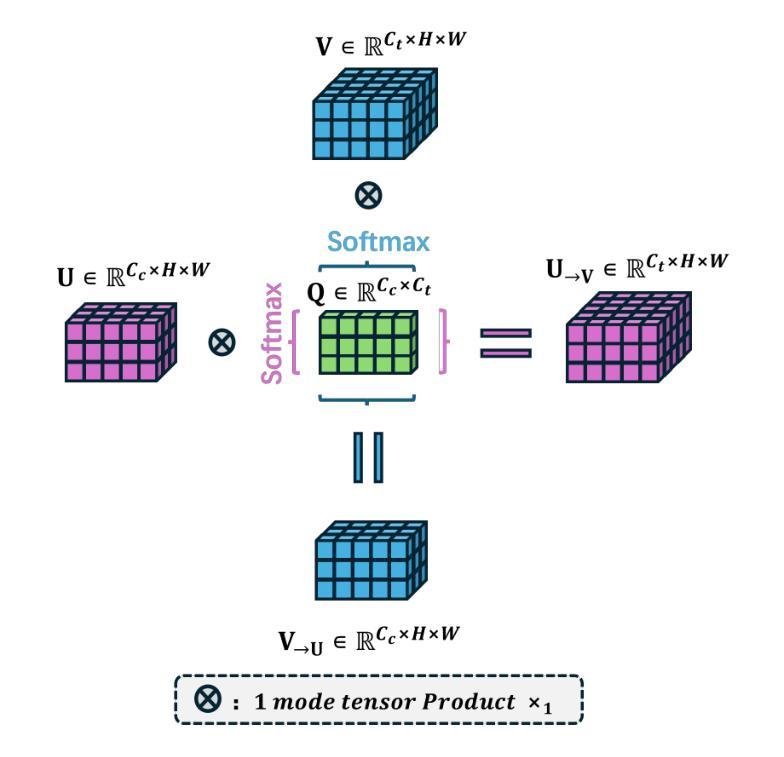
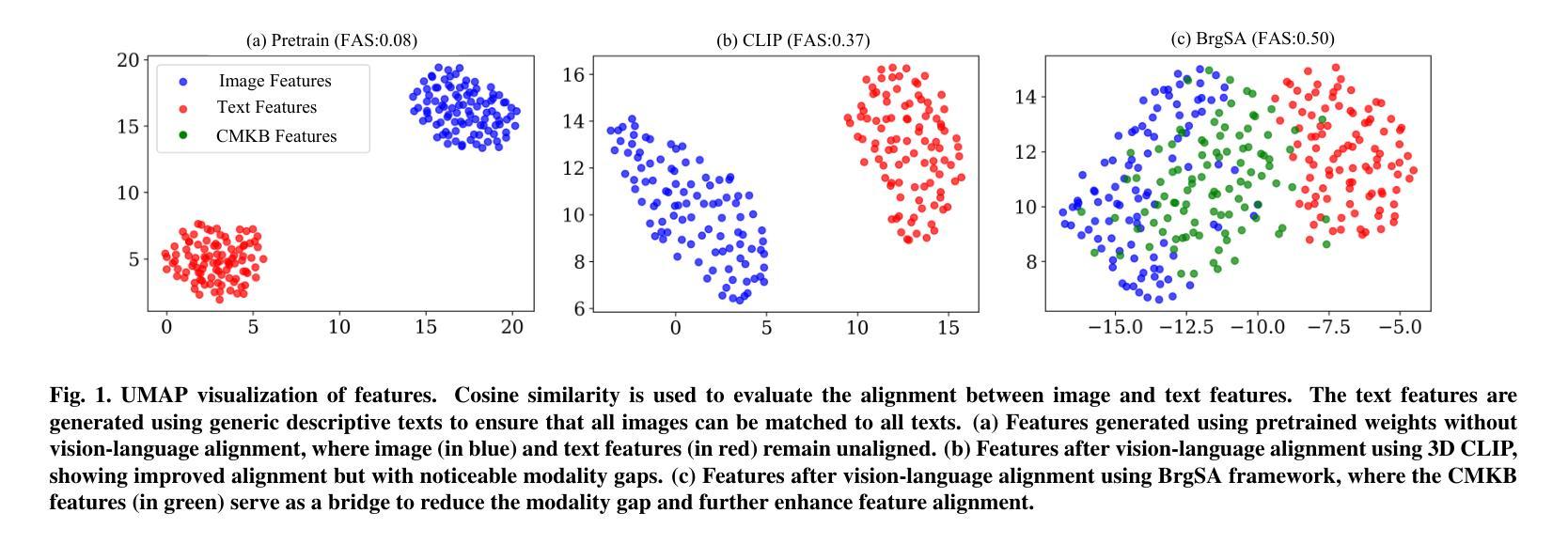
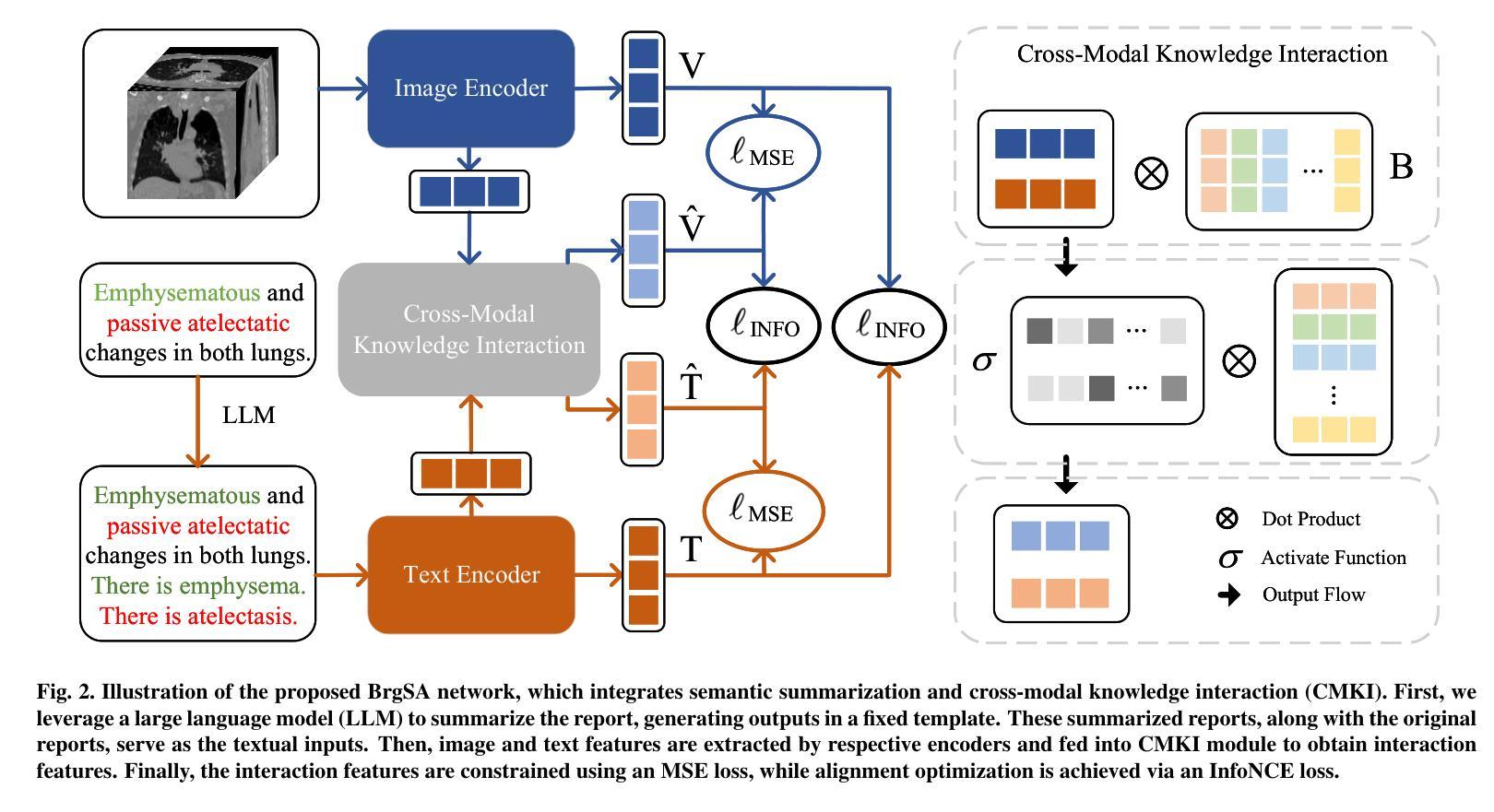
Bridged Semantic Alignment for Zero-shot 3D Medical Image Diagnosis
Authors:Haoran Lai, Zihang Jiang, Qingsong Yao, Rongsheng Wang, Zhiyang He, Xiaodong Tao, Wei Wei, Weifu Lv, S. Kevin Zhou
3D medical images such as Computed tomography (CT) are widely used in clinical practice, offering a great potential for automatic diagnosis. Supervised learning-based approaches have achieved significant progress but rely heavily on extensive manual annotations, limited by the availability of training data and the diversity of abnormality types. Vision-language alignment (VLA) offers a promising alternative by enabling zero-shot learning without additional annotations. However, we empirically discover that the visual and textural embeddings after alignment endeavors from existing VLA methods form two well-separated clusters, presenting a wide gap to be bridged. To bridge this gap, we propose a Bridged Semantic Alignment (BrgSA) framework. First, we utilize a large language model to perform semantic summarization of reports, extracting high-level semantic information. Second, we design a Cross-Modal Knowledge Interaction (CMKI) module that leverages a cross-modal knowledge bank as a semantic bridge, facilitating interaction between the two modalities, narrowing the gap, and improving their alignment. To comprehensively evaluate our method, we construct a benchmark dataset that includes 15 underrepresented abnormalities as well as utilize two existing benchmark datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that BrgSA achieves state-of-the-art performances on both public benchmark datasets and our custom-labeled dataset, with significant improvements in zero-shot diagnosis of underrepresented abnormalities.
三维医学图像,如计算机断层扫描(CT),在临床实践中得到广泛应用,为自动诊断提供了巨大的潜力。基于监督学习的方法取得了显著的进步,但严重依赖于大量的手动标注,受限于训练数据的可用性和异常类型的多样性。视觉语言对齐(VLA)提供了一种有前途的替代方案,能够实现无需额外标注的零样本学习。然而,我们通过实证研究发现,现有VLA方法对齐后的视觉和纹理嵌入形成两个分离良好的聚类,存在一个较大的差距需要弥合。为了弥合这个差距,我们提出了一个名为Bridged Semantic Alignment(BrgSA)的框架。首先,我们利用大型语言模型对报告进行语义摘要,提取高级语义信息。其次,我们设计了一个跨模态知识交互(CMKI)模块,该模块利用跨模态知识库作为语义桥梁,促进两种模态之间的交互,缩小差距,提高对齐效果。为了全面评估我们的方法,我们构建了一个包含15种代表性较差的异常的基准数据集,并使用了两个现有的基准数据集。实验结果表明,BrgSA在公共基准数据集和我们自定义标记的数据集上都实现了最先进的性能,在代表性较差异常的零样本诊断方面取得了显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像如CT在临床实践中应用广泛,自动诊断潜力巨大。基于监督学习的方法取得了显著进展,但受限于训练数据的可用性和异常类型的多样性。视觉语言对齐(VLA)为实现零样本学习提供了有前途的替代方案。然而,我们发现现有的VLA方法在视觉和纹理嵌入对齐后形成两个分离明显的集群,存在较大差距。为此,我们提出了Bridged Semantic Alignment(BrgSA)框架。首先利用大型语言模型对报告进行语义摘要,提取高级语义信息。其次,设计了一种跨模态知识交互(CMKI)模块,利用跨模态知识库作为语义桥梁,促进两种模态的互动,缩小差距并改进对齐。我们的方法在基准数据集上的表现达到了业界领先水平,且在代表性不足的异常疾病的零样本诊断中取得了显著的提升。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像如CT在临床实践中对自动诊断有巨大潜力。
- 基于监督学习的方法在医学图像诊断中受限于训练数据的可用性和异常类型的多样性。
- 视觉语言对齐(VLA)为医学图像自动诊断提供了零样本学习的可能性。
- 现有的VLA方法在视觉和纹理嵌入对齐后存在明显的差距。
- 我们提出了Bridged Semantic Alignment(BrgSA)框架来缩小这一差距。
- BrgSA框架包括利用大型语言模型进行语义摘要和跨模态知识交互模块。
点此查看论文截图

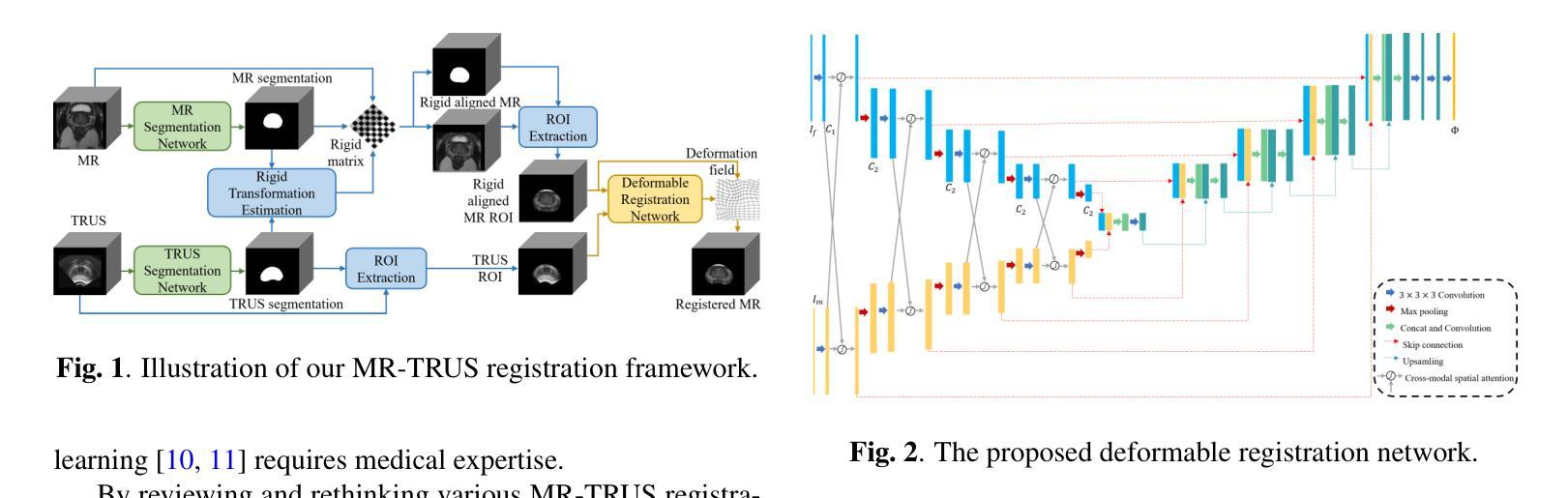
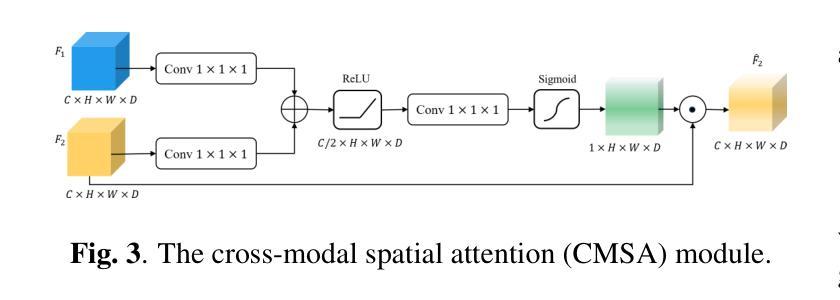
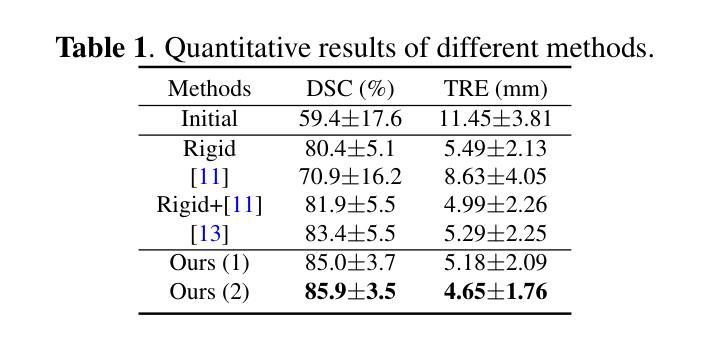
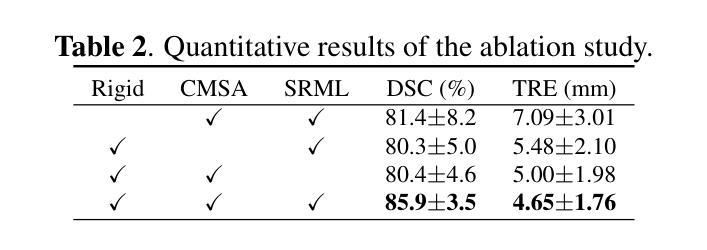
Salient Region Matching for Fully Automated MR-TRUS Registration
Authors:Zetian Feng, Dong Ni, Yi Wang
Prostate cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality in men. The registration of magnetic resonance (MR) and transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) can provide guidance for the targeted biopsy of prostate cancer. In this study, we propose a salient region matching framework for fully automated MR-TRUS registration. The framework consists of prostate segmentation, rigid alignment and deformable registration. Prostate segmentation is performed using two segmentation networks on MR and TRUS respectively, and the predicted salient regions are used for the rigid alignment. The rigidly-aligned MR and TRUS images serve as initialization for the deformable registration. The deformable registration network has a dual-stream encoder with cross-modal spatial attention modules to facilitate multi-modality feature learning, and a salient region matching loss to consider both structure and intensity similarity within the prostate region. Experiments on a public MR-TRUS dataset demonstrate that our method achieves satisfactory registration results, outperforming several cutting-edge methods. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/mock1ngbrd/salient-region-matching.
前列腺癌是男性癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一。磁共振(MR)和经直肠超声(TRUS)的注册可以为前列腺癌的靶向活检提供指导。在本研究中,我们提出了一种用于全自动MR-TRUS注册的显著区域匹配框架。该框架包括前列腺分段、刚性对齐和可变形注册。前列腺分段分别在MR和TRUS上采用两个分段网络进行,预测的显著区域用于刚性对齐。刚性对齐的MR和TRUS图像为可变形注册提供初始化。可变形注册网络具有双流编码器,配备跨模态空间注意力模块,以促进多模态特征学习,并考虑前列腺区域内结构和强度的相似性,采用显著区域匹配损失。在公共MR-TRUS数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法取得了令人满意的注册结果,优于几种前沿方法。代码公开在https://github.com/mock1ngbrd/salient-region-matching。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于显著区域匹配的MR-TRUS自动化注册框架,用于前列腺癌的靶向活检。该框架包括前列腺分割、刚性对齐和可变形注册。通过MR和TRUS上的两个分割网络进行前列腺分割,预测显著区域用于刚性对齐。刚性对齐的MR和TRUS图像为可变形注册提供初始化。可变形注册网络具有带有跨模态空间注意力模块的双重流编码器,以促进多模态特征学习,并考虑前列腺区域内的结构和强度相似性。在公共MR-TRUS数据集上的实验表明,该方法取得了令人满意的注册结果,优于一些前沿方法。
Key Takeaways
- 前列腺癌是男性癌症死亡的主要原因之一,MR-TRUS注册对于靶向活检具有重要意义。
- 提出了一种基于显著区域匹配的自动化MR-TRUS注册框架。
- 框架包括前列腺分割、刚性对齐和可变形注册三个主要步骤。
- 使用两个分割网络在MR和TRUS上进行前列腺分割,预测显著区域用于刚性对齐。
- 刚性对齐的MR和TRUS图像为可变形注册提供初始化。
- 可变形注册网络具有双重流编码器和跨模态空间注意力模块,以促进多模态特征学习。
点此查看论文截图


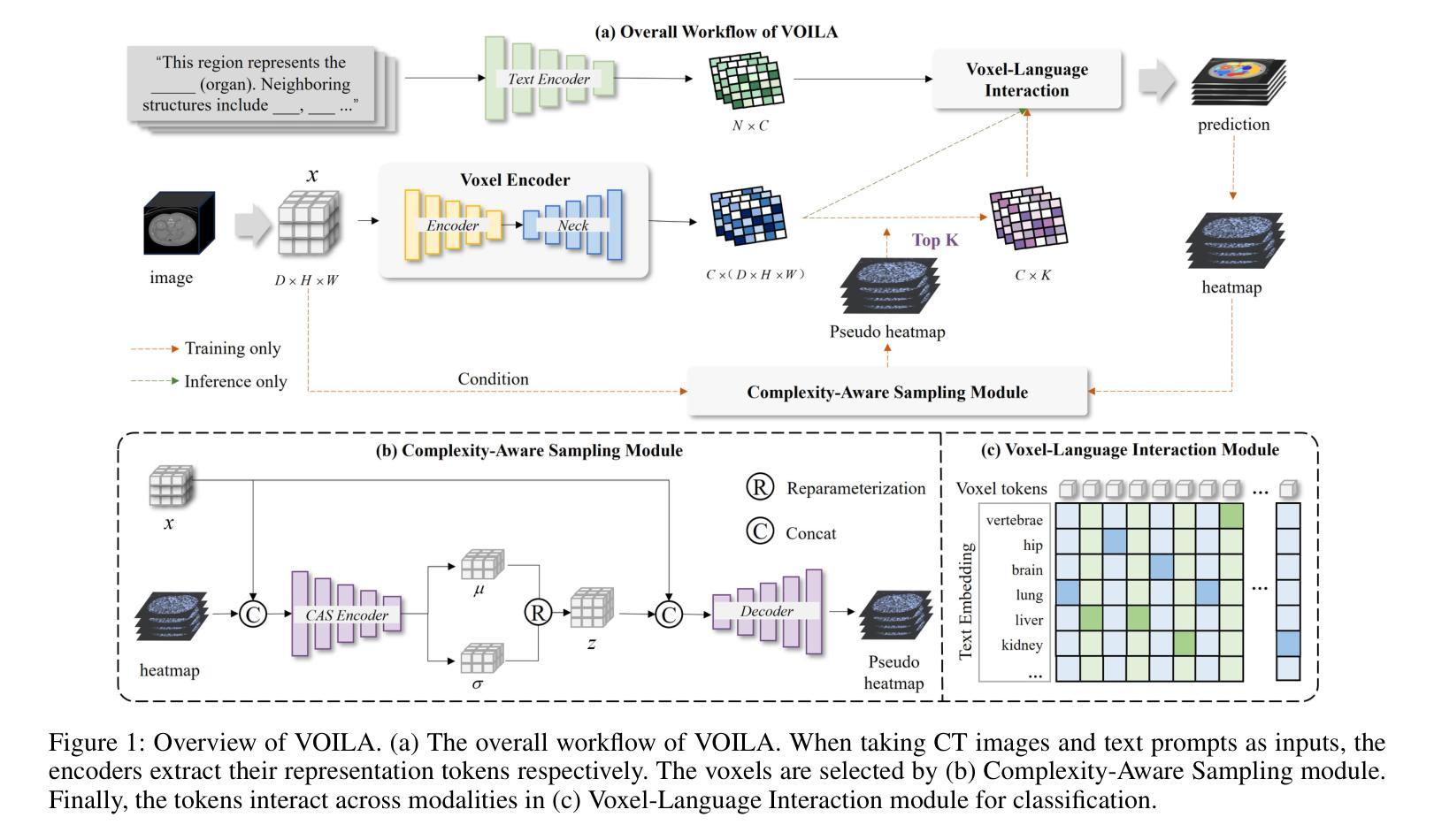
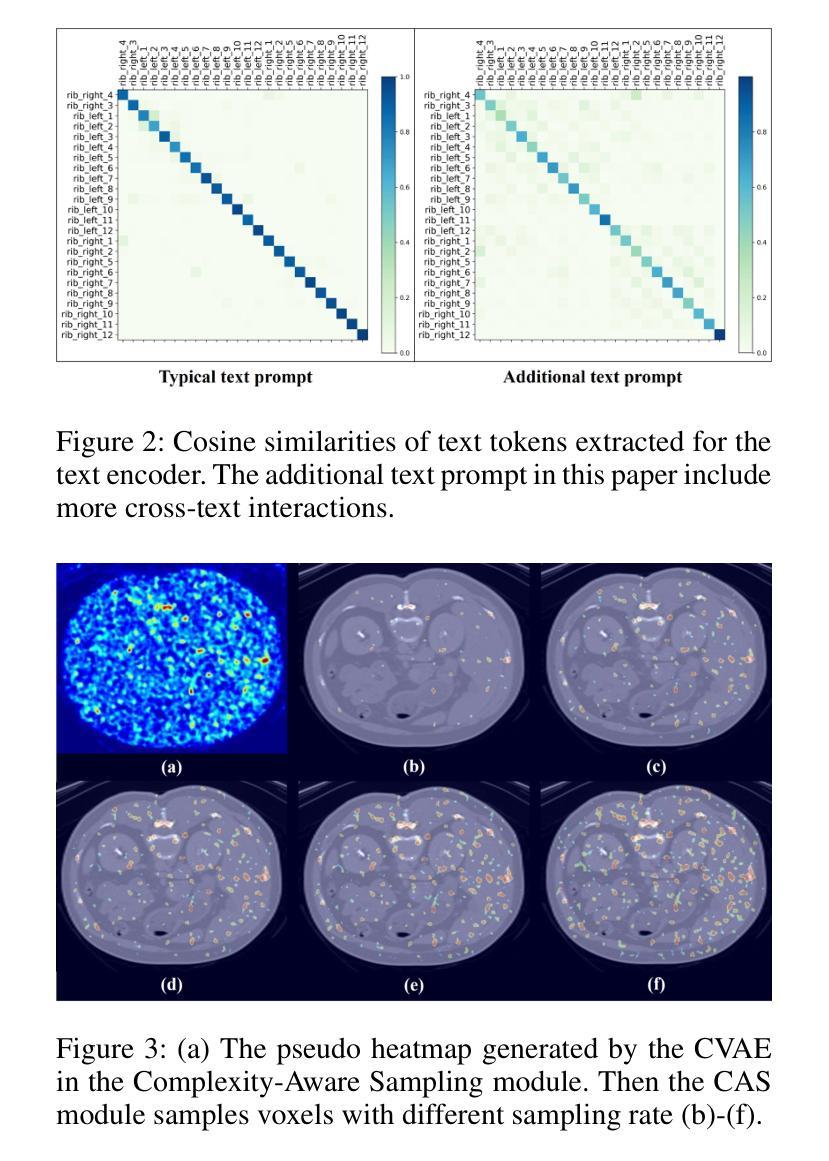
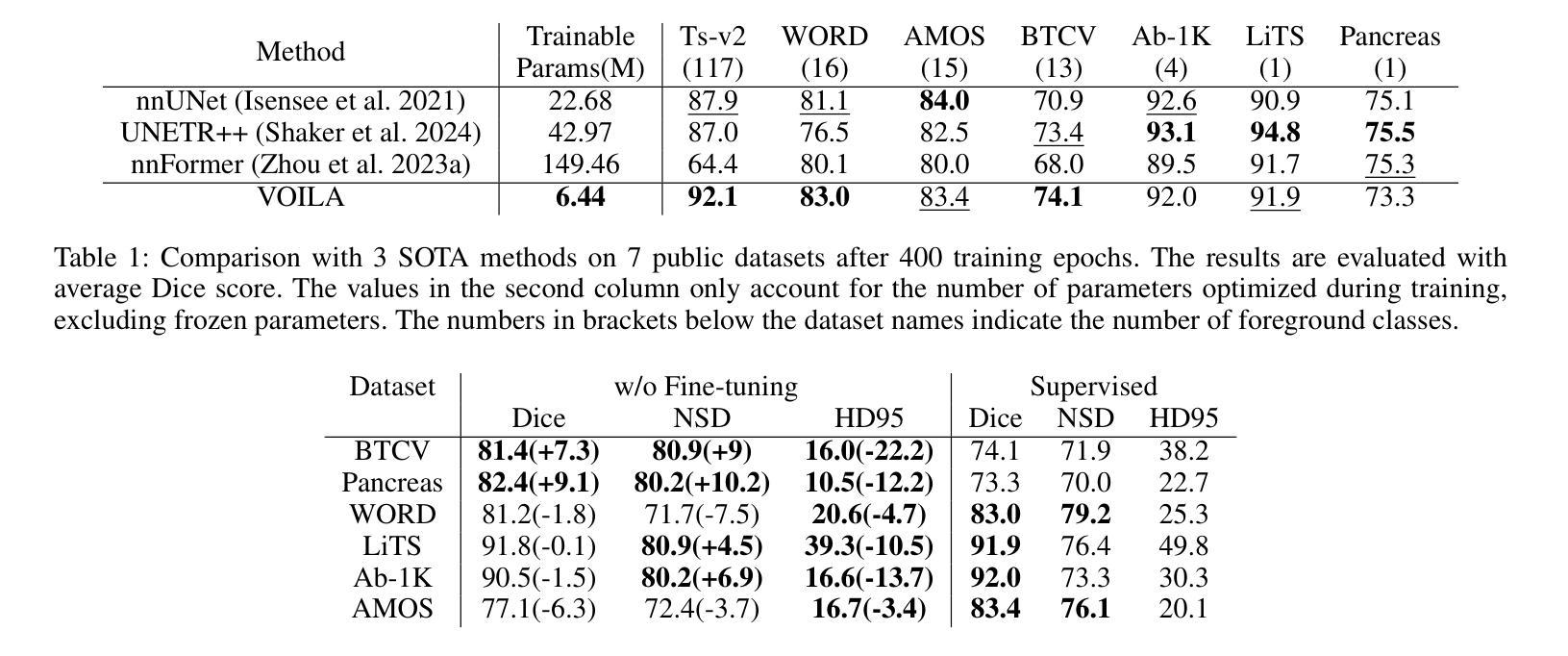
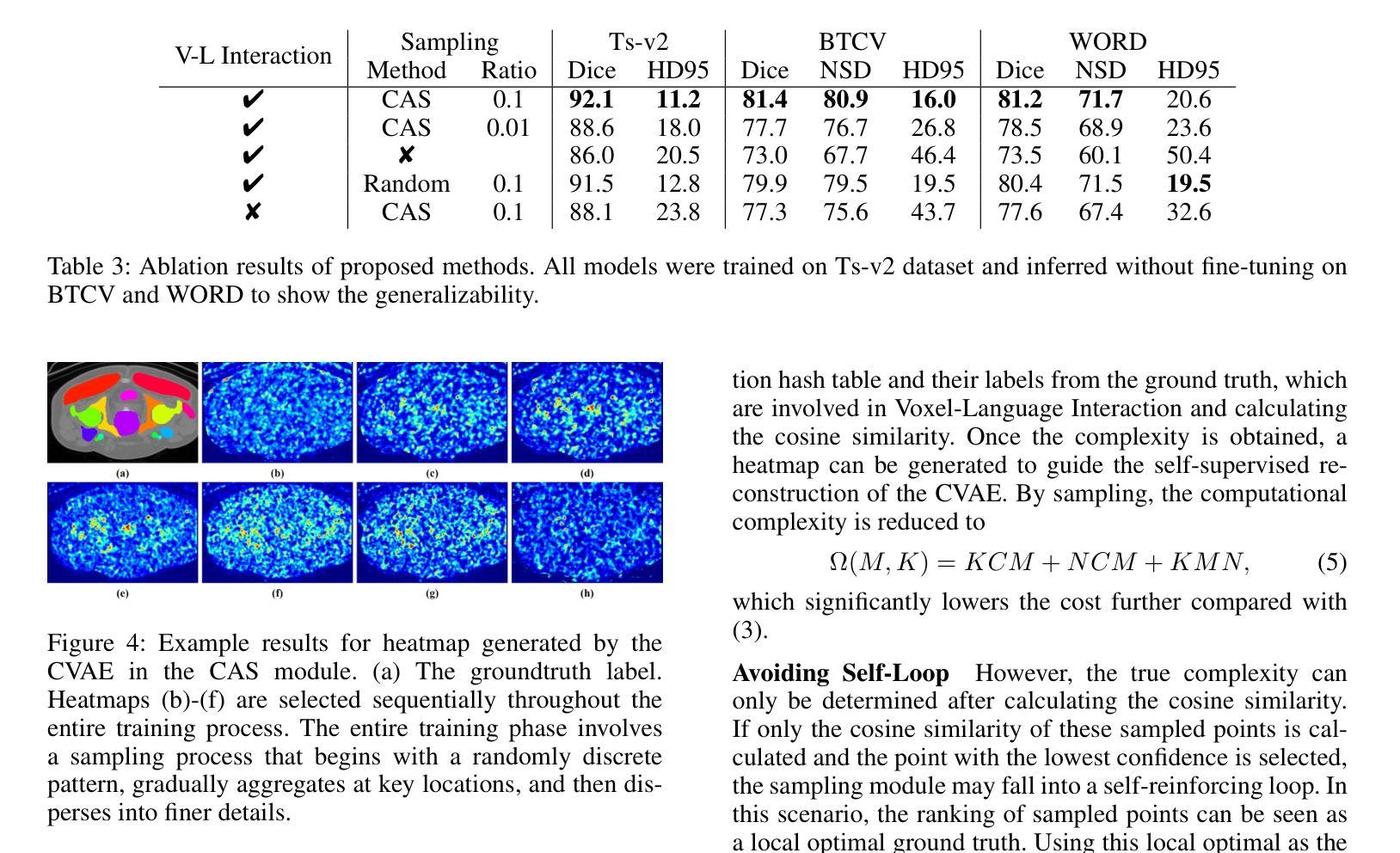
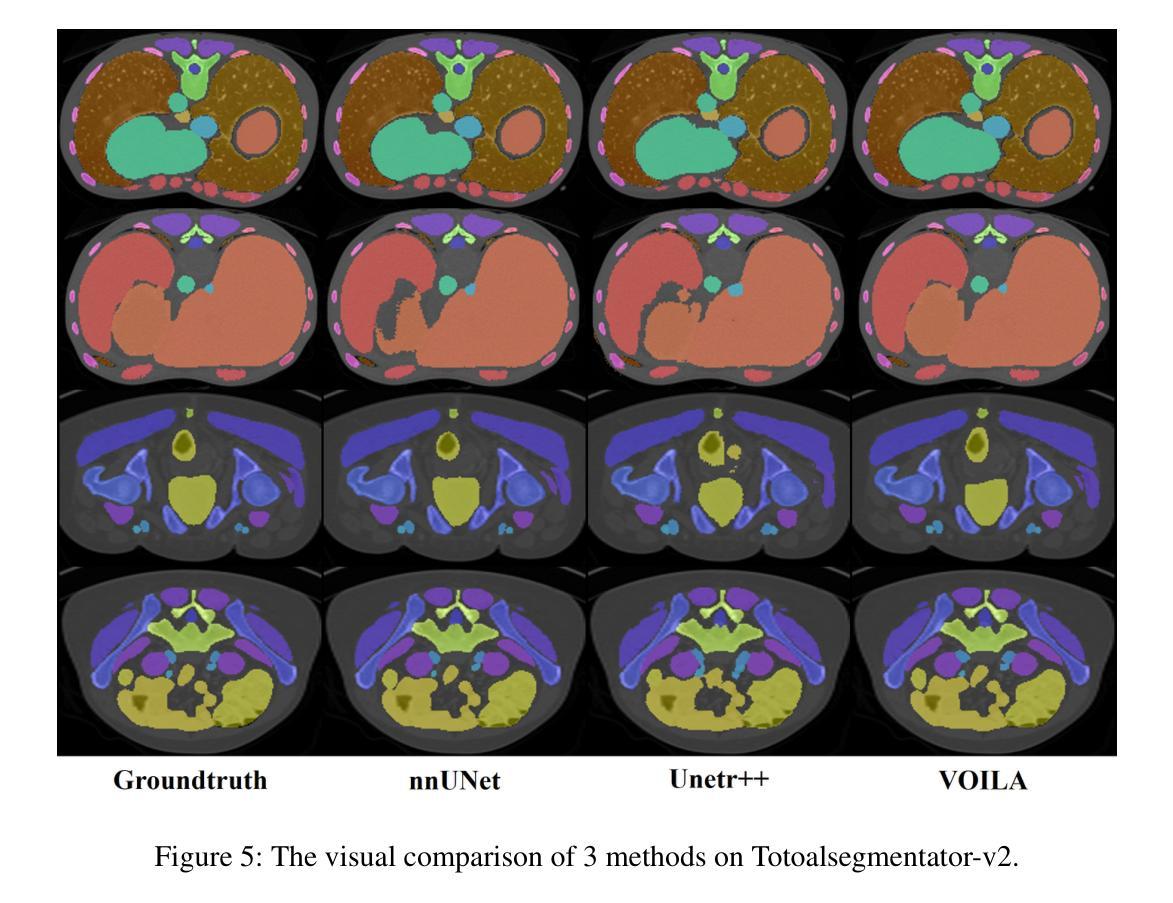
VOILA: Complexity-Aware Universal Segmentation of CT images by Voxel Interacting with Language
Authors:Zishuo Wan, Yu Gao, Wanyuan Pang, Dawei Ding
Satisfactory progress has been achieved recently in universal segmentation of CT images. Following the success of vision-language methods, there is a growing trend towards utilizing text prompts and contrastive learning to develop universal segmentation models. However, there exists a significant imbalance in information density between 3D images and text prompts. Moreover, the standard fully connected layer segmentation approach faces significant challenges in handling multiple classes and exhibits poor generalizability. To address these challenges, we propose the VOxel Interacting with LAnguage method (VOILA) for universal CT image segmentation. Initially, we align voxels and language into a shared representation space and classify voxels on the basis of cosine similarity. Subsequently, we develop the Voxel-Language Interaction framework to mitigate the impact of class imbalance caused by foreground-background discrepancies and variations in target volumes. Furthermore, a Complexity-Aware Sampling method is proposed to focus on region hard to segment, achieved by generating pseudo-heatmaps from a trainable Gaussian mixture distribution. Our results indicate the proposed VOILA is capable to achieve improved performance with reduced parameters and computational cost during training. Furthermore, it demonstrates significant generalizability across diverse datasets without additional fine-tuning.
近期计算机断层扫描(CT)图像通用分割取得了令人满意的进展。随着视觉语言方法的成功,利用文本提示和对比学习开发通用分割模型的趋势日益明显。然而,3D图像和文本提示之间存在信息密度的不平衡现象。此外,标准全连接层分割方法在处理多类别时面临巨大挑战,其泛化能力较差。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了VOxel与LAnguage交互方法(VOILA)用于通用CT图像分割。首先,我们将体素和语言对齐到一个共享表示空间,并根据余弦相似性对体素进行分类。随后,我们开发了体素语言交互框架,以减轻由前景背景差异和目标体积变化引起的类别不平衡的影响。此外,还提出了一种复杂度感知采样方法,通过生成来自可训练高斯混合分布的伪热图来重点关注难以分割的区域。我们的结果表明,所提出的VOILA方法能够在减少参数和训练过程中计算成本的同时,实现性能提升。此外,它在不同的数据集上表现出显著的一般性,无需额外的微调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
近期CT图像通用分割取得显著进展,趋势是结合视觉和语言方法,利用文本提示和对比学习开发通用分割模型。但存在图像与文本提示信息密度不平衡问题,且全连接层分割方法在处理多类别时面临挑战,通用性较差。为此,我们提出VOxel与语言交互(VOILA)方法,通过共享表示空间分类体素、建立体素语言交互框架、使用复杂度感知采样等方法解决挑战。实验结果显示,VOILA能提高性能、减少参数和计算成本,并在不同数据集上表现出良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 近期CT图像通用分割进展显著,结合视觉和语言方法成为趋势。
- 文本提示和对比学习在开发通用分割模型中的应用逐渐增多。
- 存在图像与文本提示信息密度不平衡的问题。
- 全连接层分割方法处理多类别时面临挑战,通用性较差。
- VOILA方法通过共享表示空间分类体素,建立体素与语言的交互框架来解决这些问题。
- VOILA采用复杂度感知采样,关注难以分割的区域。
- VOILA能提高性能,减少训练参数和计算成本,具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

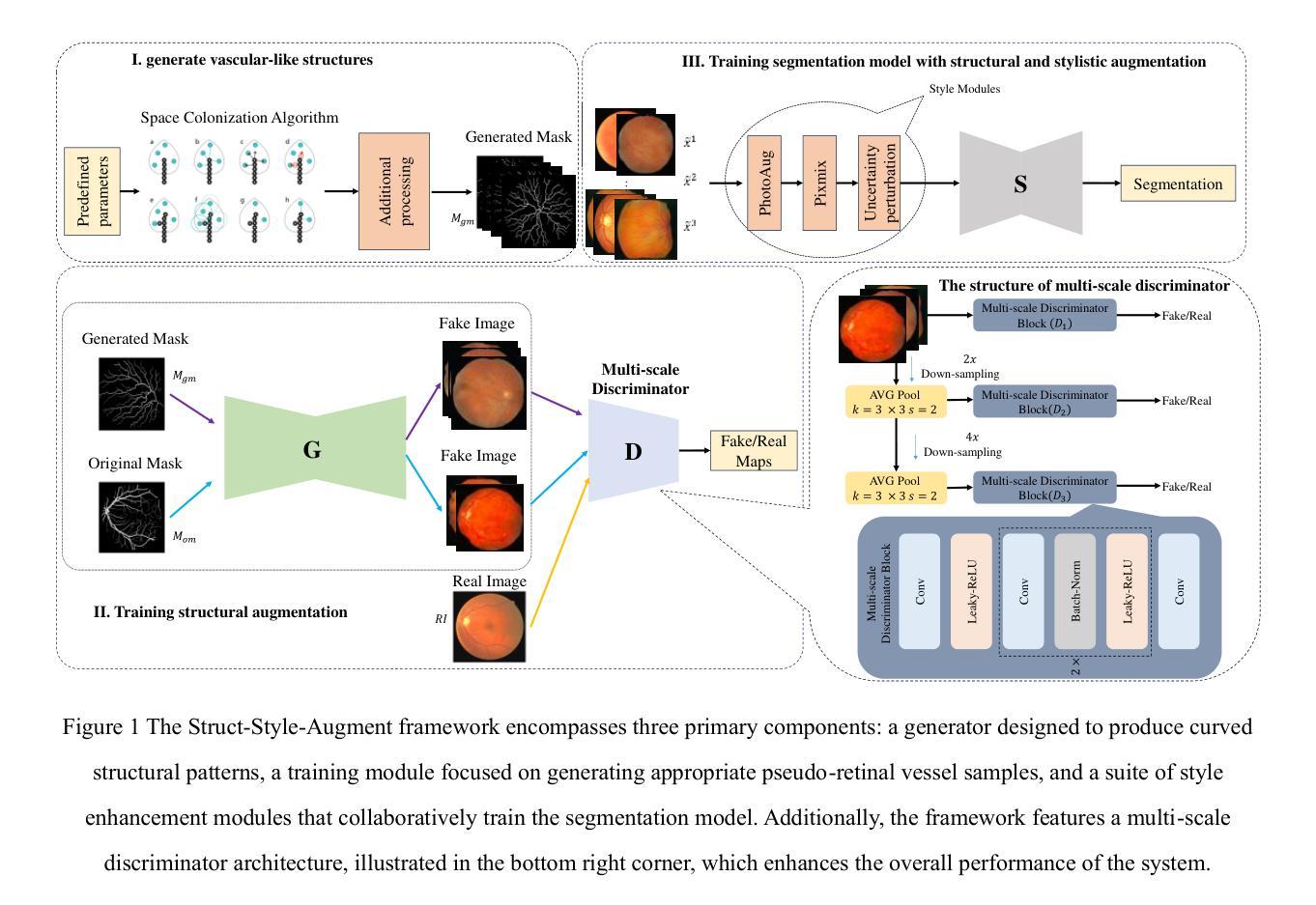
DGSSA: Domain generalization with structural and stylistic augmentation for retinal vessel segmentation
Authors:Bo Liu, Yudong Zhang, Shuihua Wang, Siyue Li, Jin Hong
Retinal vascular morphology is crucial for diagnosing diseases such as diabetes, glaucoma, and hypertension, making accurate segmentation of retinal vessels essential for early intervention. Traditional segmentation methods assume that training and testing data share similar distributions, which can lead to poor performance on unseen domains due to domain shifts caused by variations in imaging devices and patient demographics. This paper presents a novel approach, DGSSA, for retinal vessel image segmentation that enhances model generalization by combining structural and style augmentation strategies. We utilize a space colonization algorithm to generate diverse vascular-like structures that closely mimic actual retinal vessels, which are then used to generate pseudo-retinal images with an improved Pix2Pix model, allowing the segmentation model to learn a broader range of structure distributions. Additionally, we utilize PixMix to implement random photometric augmentations and introduce uncertainty perturbations, thereby enriching stylistic diversity and significantly enhancing the model’s adaptability to varying imaging conditions. Our framework has been rigorously evaluated on four challenging datasets-DRIVE, CHASEDB, HRF, and STARE-demonstrating state-of-the-art performance that surpasses existing methods. This validates the effectiveness of our proposed approach, highlighting its potential for clinical application in automated retinal vessel analysis.
视网膜血管形态对于诊断糖尿病、青光眼和高血压等疾病至关重要,因此,对视网膜血管进行准确分割对于早期干预至关重要。传统的分割方法假设训练和测试数据具有相似的分布,但由于成像设备和患者人口统计信息的差异导致的域偏移,这可能导致在未见过的域上表现不佳。本文提出了一种用于视网膜血管图像分割的新方法DGSSA,通过结合结构和风格增强策略,提高了模型的泛化能力。我们利用空间殖民化算法生成多样化的血管状结构,这些结构紧密模仿实际的视网膜血管,然后用于生成改进的Pix2Pix模型的伪视网膜图像,从而使分割模型能够学习更广泛的结构分布。此外,我们还使用PixMix实现随机光度增强并引入不确定性扰动,从而丰富了风格多样性,并显著提高了模型对不同成像条件的适应性。我们的框架在四个具有挑战性的数据集(DRIVE、CHASEDB、HRF和STARE)上进行了严格评估,表现出了超越现有方法的最新性能,这验证了我们所提出方法的有效性,并突出了其在临床自动视网膜血管分析中的潜在应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出了一种新型的视网膜血管图像分割方法DGSSA,通过结合结构和风格增强策略提高了模型的泛化能力。该方法利用空间殖民算法生成模拟视网膜血管的血管状结构,再通过改进的Pix2Pix模型生成伪视网膜图像。同时,引入PixMix实现随机光度增强和不确定性扰动,从而丰富了风格多样性,显著提高了模型对不同成像条件的适应能力。在四个具有挑战性的数据集上的评估结果表明,该方法性能卓越,超过现有方法,验证了其临床应用于自动化视网膜血管分析的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 视网膜血管形态对于诊断糖尿病、青光眼和高血压等疾病至关重要,因此准确的视网膜血管分割对于早期干预至关重要。
- 传统分割方法假设训练和测试数据具有相似的分布,这可能导致在由于成像设备和患者人口统计学特征变化而引起的未见领域上表现不佳。
- DGSSA方法通过结合结构和风格增强策略,提高了模型在视网膜血管图像分割中的泛化能力。
- 利用空间殖民算法生成模拟视网膜血管的血管状结构,然后使用改进的Pix2Pix模型生成伪视网膜图像。
- 通过PixMix实施随机光度增强和不确定性扰动,以丰富风格多样性和提高模型对不同成像条件的适应能力。
- 在四个具有挑战性的数据集上的评估证明了该方法的有效性,超过了现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

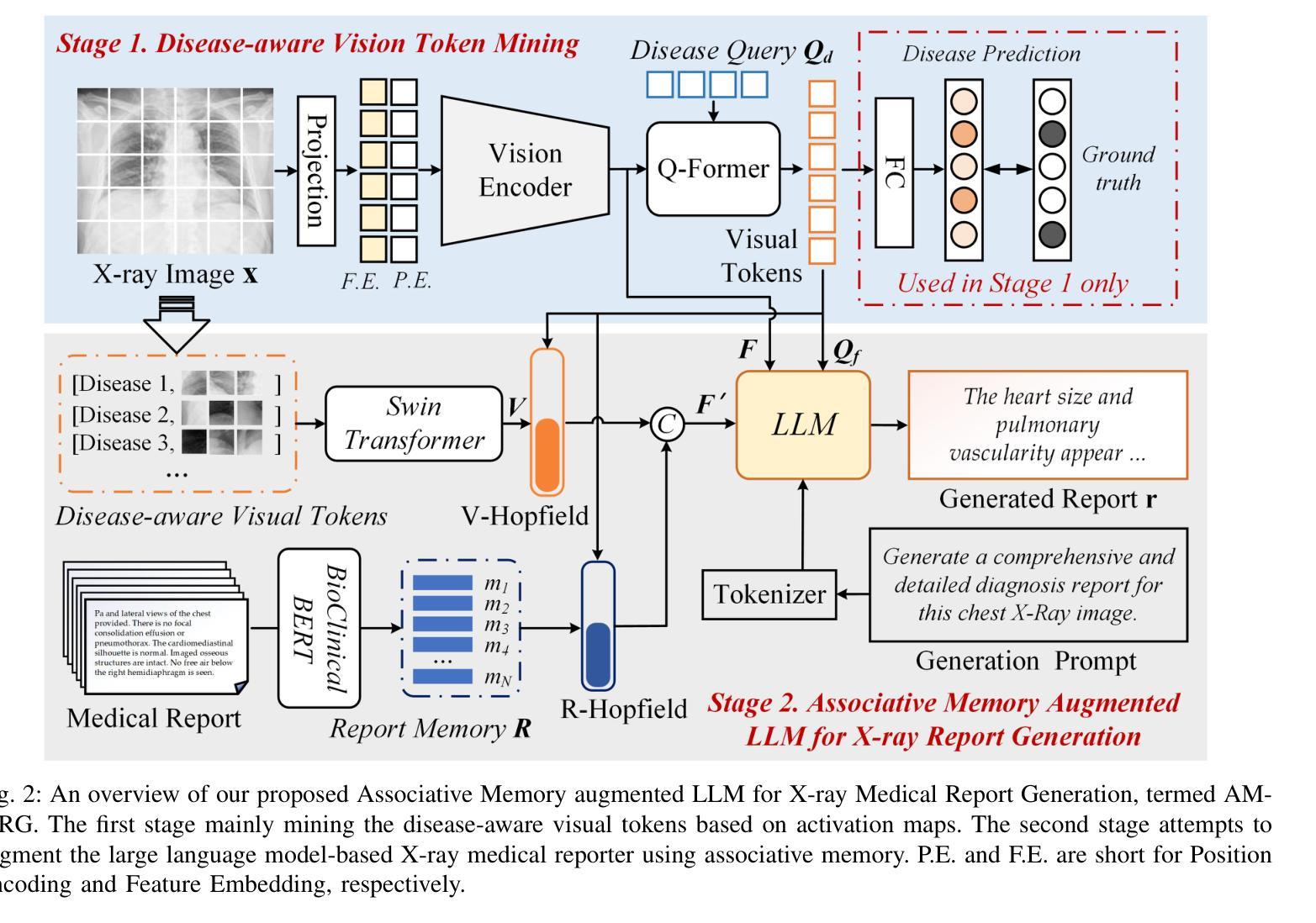
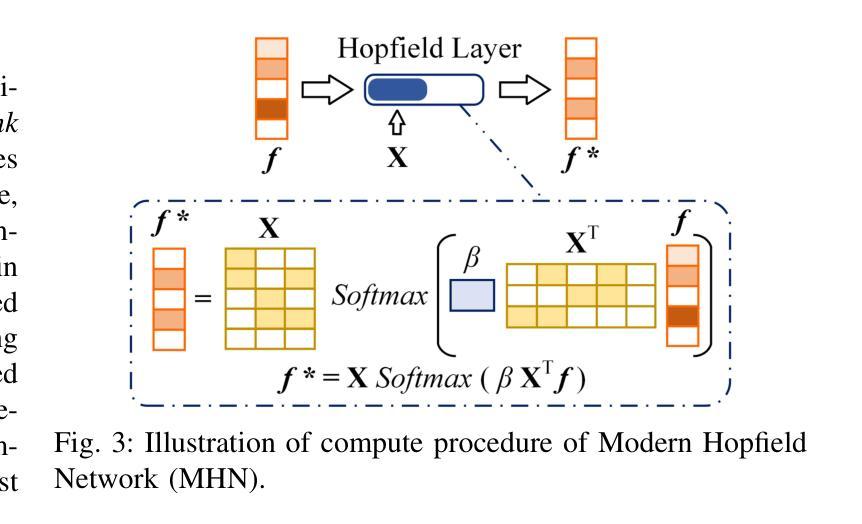
Activating Associative Disease-Aware Vision Token Memory for LLM-Based X-ray Report Generation
Authors:Xiao Wang, Fuling Wang, Haowen Wang, Bo Jiang, Chuanfu Li, Yaowei Wang, Yonghong Tian, Jin Tang
X-ray image based medical report generation achieves significant progress in recent years with the help of the large language model, however, these models have not fully exploited the effective information in visual image regions, resulting in reports that are linguistically sound but insufficient in describing key diseases. In this paper, we propose a novel associative memory-enhanced X-ray report generation model that effectively mimics the process of professional doctors writing medical reports. It considers both the mining of global and local visual information and associates historical report information to better complete the writing of the current report. Specifically, given an X-ray image, we first utilize a classification model along with its activation maps to accomplish the mining of visual regions highly associated with diseases and the learning of disease query tokens. Then, we employ a visual Hopfield network to establish memory associations for disease-related tokens, and a report Hopfield network to retrieve report memory information. This process facilitates the generation of high-quality reports based on a large language model and achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmark datasets, including the IU X-ray, MIMIC-CXR, and Chexpert Plus. The source code of this work is released on \url{https://github.com/Event-AHU/Medical_Image_Analysis}.
基于X光图像的医学报告生成近年来在大型语言模型的帮助下取得了显著进展。然而,这些模型尚未充分利用图像区域中的有效信息,导致生成的报告虽然在语言上通顺,但在描述关键疾病方面却不足。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型关联记忆增强型X光报告生成模型,有效模拟了专业医生撰写医学报告的过程。它兼顾全局和局部视觉信息的挖掘,并关联历史报告信息以更好地完成当前报告的撰写。具体来说,给定一张X光片,我们首先使用分类模型及其激活图来完成与疾病高度相关的视觉区域的挖掘和学习疾病查询令牌。然后,我们采用视觉Hopfield网络建立与疾病相关的令牌的内存关联,并采用报告Hopfield网络来检索报告内存信息。此过程基于大型语言模型生成高质量报告,并在IU X光、MIMIC-CXR和Chexpert Plus等多个基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能。该工作的源代码已发布在https://github.com/Event-AHU/Medical_Image_Analysis上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In Peer Review
Summary
提出了一种新型关联记忆增强的X光报告生成模型,该模型有效模拟专业医生撰写医疗报告的过程,同时挖掘全局和局部视觉信息,并关联历史报告信息,以完成当前报告的撰写。该模型在多个基准数据集上表现卓越,包括IU X-ray、MIMIC-CXR和Chexpert Plus。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种新型的关联记忆增强X光报告生成模型,旨在提高医疗报告的质量。
- 模型结合了全局和局部视觉信息的挖掘。
- 模型通过关联历史报告信息,模拟了专业医生撰写报告的过程。
- 模型在多个基准数据集上进行了测试,包括IU X-ray、MIMIC-CXR和Chexpert Plus,并表现出卓越的性能。
- 模型通过分类模型和激活图来完成与疾病高度相关的视觉区域的挖掘和学习疾病查询令牌。
- 模型采用视觉Hopfield网络为疾病相关令牌建立内存关联,并采用报告Hopfield网络检索报告内存信息。
点此查看论文截图
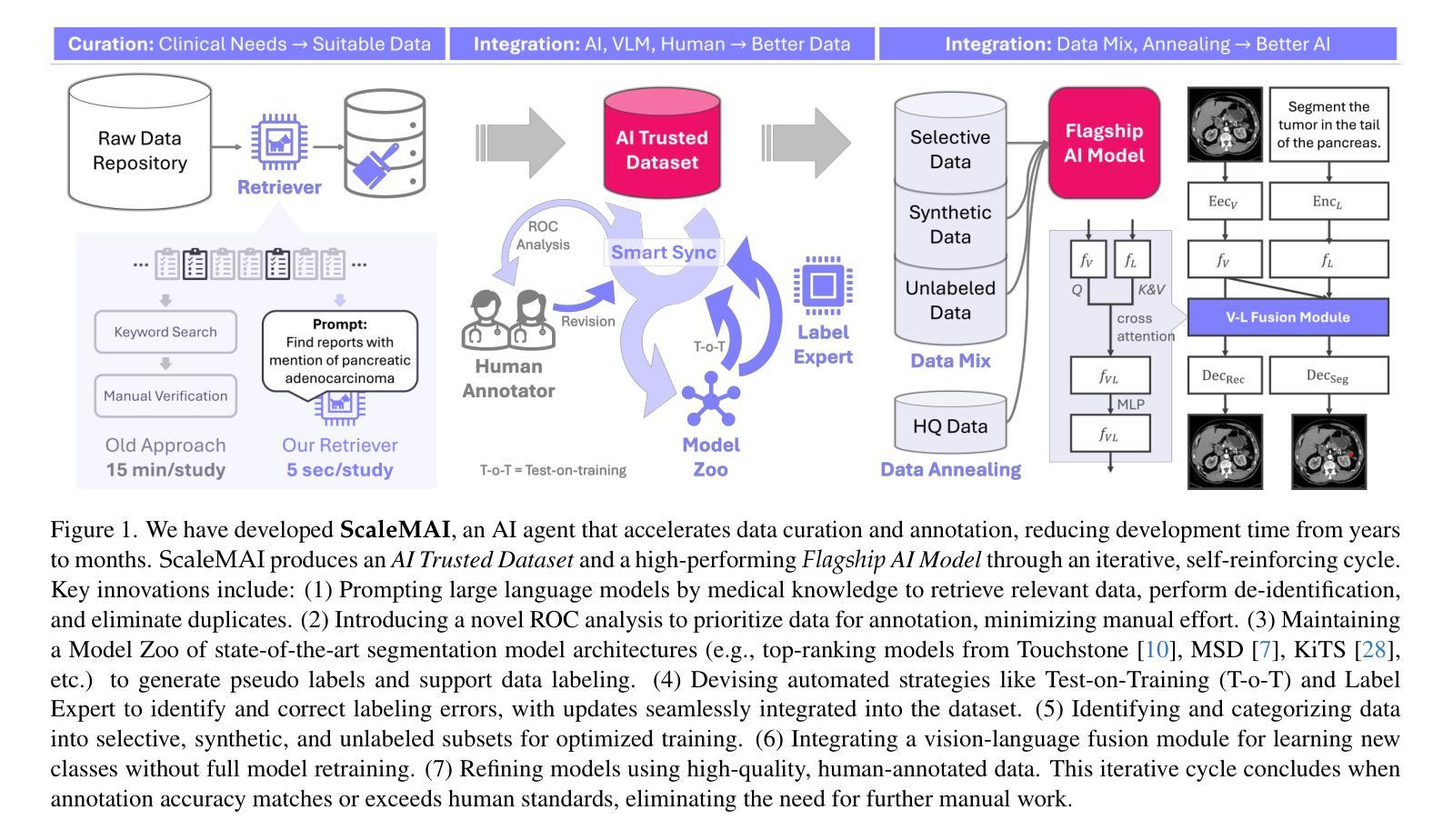
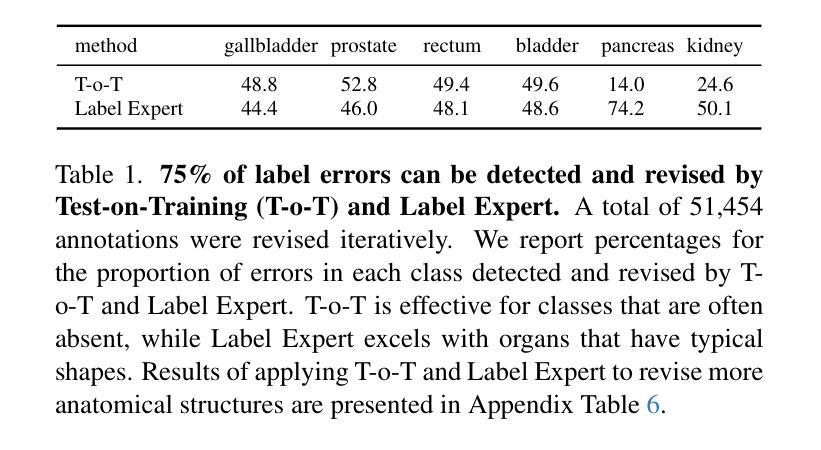
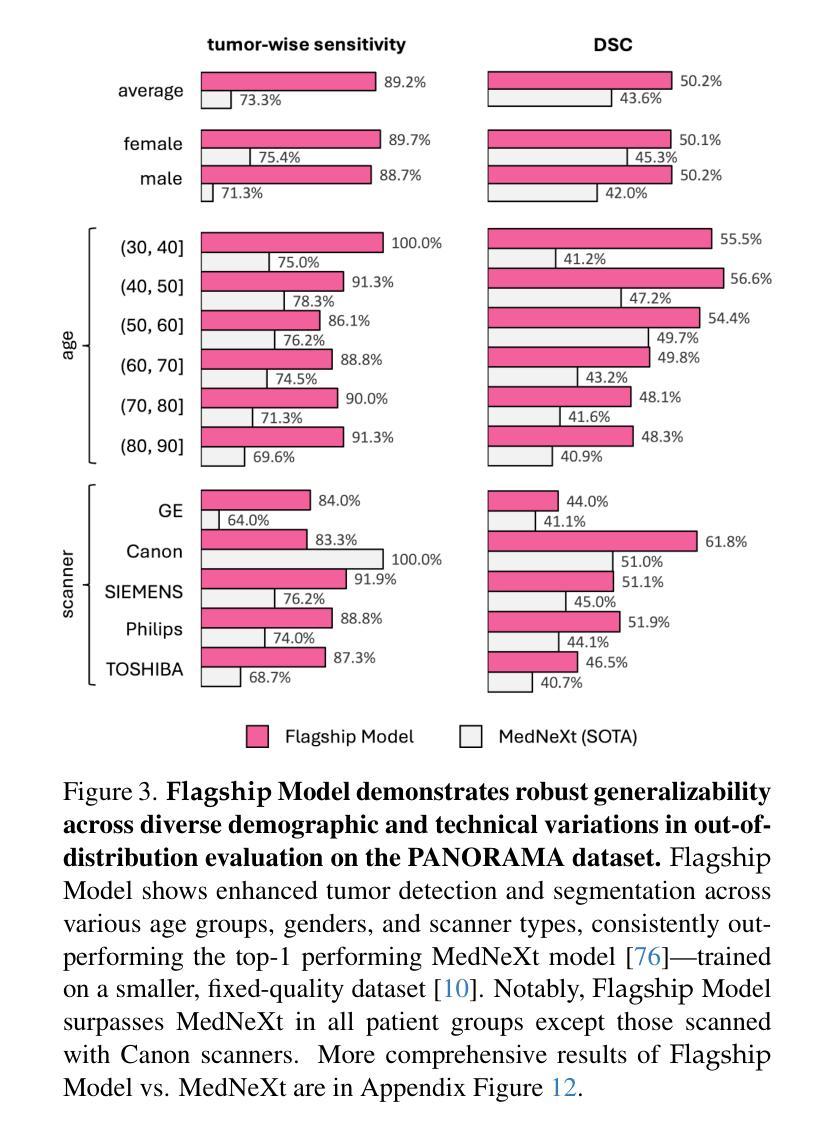
ScaleMAI: Accelerating the Development of Trusted Datasets and AI Models
Authors:Wenxuan Li, Pedro R. A. S. Bassi, Tianyu Lin, Yu-Cheng Chou, Xinze Zhou, Yucheng Tang, Fabian Isensee, Kang Wang, Qi Chen, Xiaowei Xu, Xiaoxi Chen, Lizhou Wu, Qilong Wu, Yannick Kirchhoff, Maximilian Rokuss, Saikat Roy, Yuxuan Zhao, Dexin Yu, Kai Ding, Constantin Ulrich, Klaus Maier-Hein, Yang Yang, Alan L. Yuille, Zongwei Zhou
Building trusted datasets is critical for transparent and responsible Medical AI (MAI) research, but creating even small, high-quality datasets can take years of effort from multidisciplinary teams. This process often delays AI benefits, as human-centric data creation and AI-centric model development are treated as separate, sequential steps. To overcome this, we propose ScaleMAI, an agent of AI-integrated data curation and annotation, allowing data quality and AI performance to improve in a self-reinforcing cycle and reducing development time from years to months. We adopt pancreatic tumor detection as an example. First, ScaleMAI progressively creates a dataset of 25,362 CT scans, including per-voxel annotations for benign/malignant tumors and 24 anatomical structures. Second, through progressive human-in-the-loop iterations, ScaleMAI provides Flagship AI Model that can approach the proficiency of expert annotators (30-year experience) in detecting pancreatic tumors. Flagship Model significantly outperforms models developed from smaller, fixed-quality datasets, with substantial gains in tumor detection (+14%), segmentation (+5%), and classification (72%) on three prestigious benchmarks. In summary, ScaleMAI transforms the speed, scale, and reliability of medical dataset creation, paving the way for a variety of impactful, data-driven applications.
构建可信赖的数据集对于透明和负责任的医疗人工智能(MAI)研究至关重要。但是,即使是小规模的高质量数据集也需要多学科团队数年的努力。这一过程往往延缓了人工智能的优势,因为以人类为中心的数据创建和以人工智能为中心的模型开发被视为独立且连续的几个步骤。为了克服这一问题,我们提出了ScaleMAI,这是一个人工智能集成数据整理和注释的代理,允许数据质量和人工智能性能在一个自我加强的循环中不断提高,并将开发时间从数年缩短到数月。我们以胰腺肿瘤检测为例。首先,ScaleMAI逐步创建一个包含25362次CT扫描的数据集,包括每个体素的良性/恶性肿瘤和24个解剖结构的注释。其次,通过逐步的人类在循环中的迭代,ScaleMAI提供了旗舰人工智能模型,该模型可以接近具有30年经验的专家注释者在检测胰腺肿瘤方面的熟练程度。旗舰模型在三个权威基准测试中表现出显著的肿瘤检测优势(+ 14%),分割(+ 5%)和分类(准确率提高了72%),其性能远优于从小规模固定质量数据集中开发的模型。总而言之,ScaleMAI转变了医疗数据集创建的速度、规模和可靠性,为各种有影响力的数据驱动应用程序铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ScaleMAI通过集成人工智能进行数据整理和标注,提高了医疗数据集的质量与创建速度,实现了从多年到数月的飞跃。以胰腺癌检测为例,ScaleMAI创建的大规模数据集和旗舰AI模型显著提高了肿瘤检测的准确性、分割的精细度和分类的可靠性。这一创新为医疗领域的数据驱动应用开辟了道路。
Key Takeaways
- ScaleMAI是一个集成人工智能的数据整理和标注工具,能显著提高医疗数据集的质量和创建速度。
- 通过ScaleMAI,数据集创建时间从多年缩短到数月。
- 以胰腺癌检测为例,ScaleMAI创建的大规模数据集包含每体素良性/恶性肿瘤和24个解剖结构的注释。
- ScaleMAI提供旗舰AI模型,在胰腺癌检测方面接近拥有30年经验的专家标注者的专业水平。
- 旗舰AI模型在三个重要基准测试中,肿瘤检测准确率提高14%,分割精细度提高5%,分类可靠性达到72%。
- ScaleMAI的引入改变了医疗数据集创建的速度、规模和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图


Plant Leaf Disease Detection and Classification Using Deep Learning: A Review and A Proposed System on Bangladesh’s Perspective
Authors:Md. Jalal Uddin Chowdhury, Zumana Islam Mou, Rezwana Afrin, Shafkat Kibria
A very crucial part of Bangladeshi people’s employment, GDP contribution, and mainly livelihood is agriculture. It plays a vital role in decreasing poverty and ensuring food security. Plant diseases are a serious stumbling block in agricultural production in Bangladesh. At times, humans can’t detect the disease from an infected leaf with the naked eye. Using inorganic chemicals or pesticides in plants when it’s too late leads in vain most of the time, deposing all the previous labor. The deep-learning technique of leaf-based image classification, which has shown impressive results, can make the work of recognizing and classifying all diseases trouble-less and more precise. In this paper, we’ve mainly proposed a better model for the detection of leaf diseases. Our proposed paper includes the collection of data on three different kinds of crops: bell peppers, tomatoes, and potatoes. For training and testing the proposed CNN model, the plant leaf disease dataset collected from Kaggle is used, which has 17,430 images. The images are labeled with 14 separate classes of damage. The developed CNN model performs efficiently and could successfully detect and classify the tested diseases. The proposed CNN model may have great potency in crop disease management.
农业在孟加拉国人民的就业、国内生产总值贡献以及主要生计中扮演着非常重要的角色。它对减少贫困和确保粮食安全起着至关重要的作用。植物疾病是孟加拉国农业生产中的一个严重障碍。有时,人类无法用肉眼从受感染的叶片上检测到疾病。在疾病已经严重时才使用无机化学物质或农药通常会导致之前所有的努力付诸东流。基于叶片图像的深度学习分类技术已经取得了令人印象深刻的结果,可以使识别和分类所有疾病的工作更加无忧和精确。在本文中,我们主要提出了一种用于检测叶片疾病的更好模型。我们的论文涵盖了三种不同作物的数据收集:甜椒、番茄和土豆。为了训练和测试所提出的CNN模型,我们使用了从Kaggle收集的包含17430张图像的植物叶片疾病数据集,这些图像被标记为包含有14种不同的损害类别。所开发的CNN模型运行效率高,并能成功检测和分类测试中的疾病。所提出的CNN模型在农作物疾病管理中具有巨大的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习技术在农作物叶片图像分类上的应用对于孟加拉国农业领域具有重要意义,能有效识别与分类植物病害,提高农业生产效率,降低损失。
Key Takeaways
- 农业在孟加拉国人民的就业、GDP贡献以及生计中占据重要地位,对于减少贫困和保障粮食安全至关重要。
- 植物病害是孟加拉国农业生产中的一大障碍。
- 有时人类无法仅凭肉眼从受感染的叶片中检测出病害。
- 深度学习技术在叶片图像分类方面表现出色,能更精确、高效地识别与分类所有病害。
- 本研究提出了一个针对叶片病害检测的改进模型。
- 研究人员使用了三种不同作物的数据:辣椒、番茄和土豆,并使用了来自Kaggle的植物叶片病害数据集,包含17,430张图像,分为14个独立的损伤类别。
点此查看论文截图

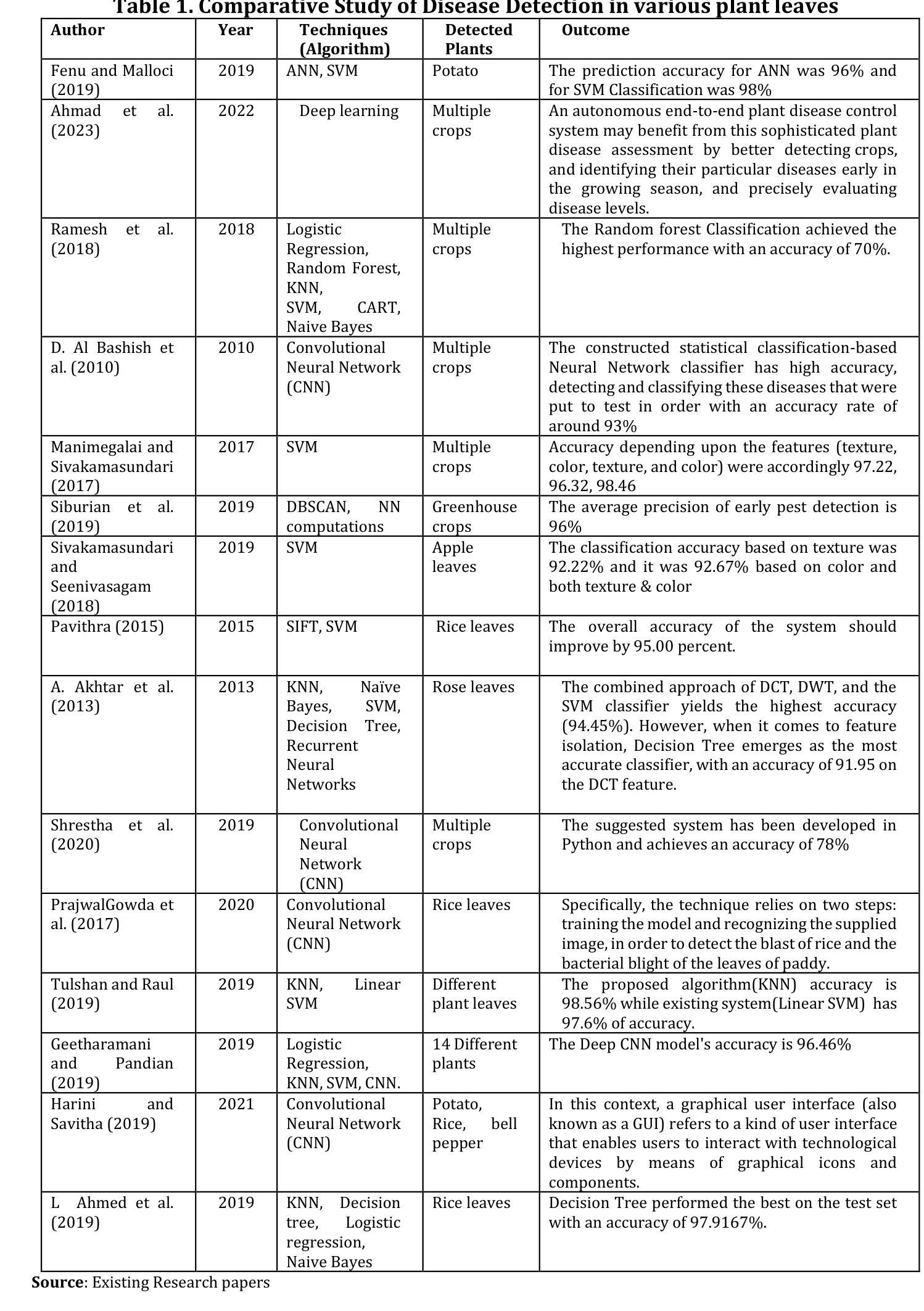
Regulating radiology AI medical devices that evolve in their lifecycle
Authors:Camila González, Moritz Fuchs, Daniel Pinto dos Santos, Philipp Matthies, Manuel Trenz, Maximilian Grüning, Akshay Chaudhari, David B. Larson, Ahmed Othman, Moon Kim, Felix Nensa, Anirban Mukhopadhyay
Over time, the distribution of medical image data drifts due to multiple factors, including shifts in patient demographics, acquisition devices, and disease manifestation. While human radiologists can extrapolate their knowledge to such changes, AI systems cannot. In fact, deep learning models are highly susceptible to even slight variations in image characteristics. Therefore, manufacturers must update their models with new data to ensure that they remain safe and effective. Until recently, conducting such model updates in the USA and European Union meant applying for re-approval. Given the time and monetary costs associated with these processes, updates were infrequent, and obsolete systems continued functioning for too long. During 2024, several developments in the regulatory frameworks of these regions have taken place that promise to streamline the process of rolling out model updates safely: The European Artificial Intelligence Act came into effect last August, and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released the final marketing submission recommendations for a Predetermined Change Control Plan (PCCP) in December. We give an overview of the requirements and objectives of recent regulatory efforts and summarize the building blocks needed for successfully deploying dynamic systems. At the center of these pieces of regulation - and as prerequisites for manufacturers to conduct model updates without re-approval - are the need to describe the data collection and re-training processes and to establish real-world quality monitoring mechanisms.
随着时间的推移,由于患者人口统计学、采集设备和疾病表现的变化等多个因素,医学图像数据的分布会发生变化。虽然人类放射科医生可以推断他们的知识以适应这些变化,但人工智能系统却无法做到。事实上,深度学习模型甚至对图像特征中的轻微变化都高度敏感。因此,制造商必须使用新数据更新他们的模型,以确保它们仍然安全有效。直到最近,在美国和欧盟进行此类模型更新意味着需要重新申请批准。由于这些流程涉及的时间和金钱成本,更新并不频繁,且过时的系统继续运行了太长时间。在2024年期间,这些地区监管框架的若干发展事件有望简化安全推出模型更新的流程:欧洲《人工智能法案》已于去年八月生效,美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)在十二月发布了预定的变更控制计划(PCCP)的最终市场推广建议。我们概述了近期监管工作的要求和目标,并总结了成功部署动态系统所需的构建模块。这些法规的核心——以及制造商进行模型更新而不需重新批准的先决条件——是需要描述数据收集和再训练过程,并建立现实世界的质量监控机制。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着医学图像数据的分布因患者人口变化、采集设备和疾病表现等因素而逐渐漂移,人工智能系统难以适应这种变化。制造商必须更新其模型以确保其安全性和有效性。近期美国和欧盟的法规发展简化了模型更新的流程。这些法规要求描述数据采集和再训练过程,并建立了现实世界的质量监控机制,为制造商进行无需重新审批的模型更新提供了前提。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像数据的分布因多种因素而发生变化,这包括患者人口变化、采集设备和疾病表现等。
- 与人类放射科医生相比,人工智能系统难以适应医学图像数据的这种变化。
- 制造商需要定期更新其模型以确保其安全性和有效性。
- 在美国和欧洲联盟,最近的法规发展简化了模型更新的流程。
- 这些新法规的核心要求包括描述数据采集和再训练过程,以及建立现实世界的质量监控机制。
- 这些法规为制造商进行无需重新审批的模型更新提供了前提。
点此查看论文截图

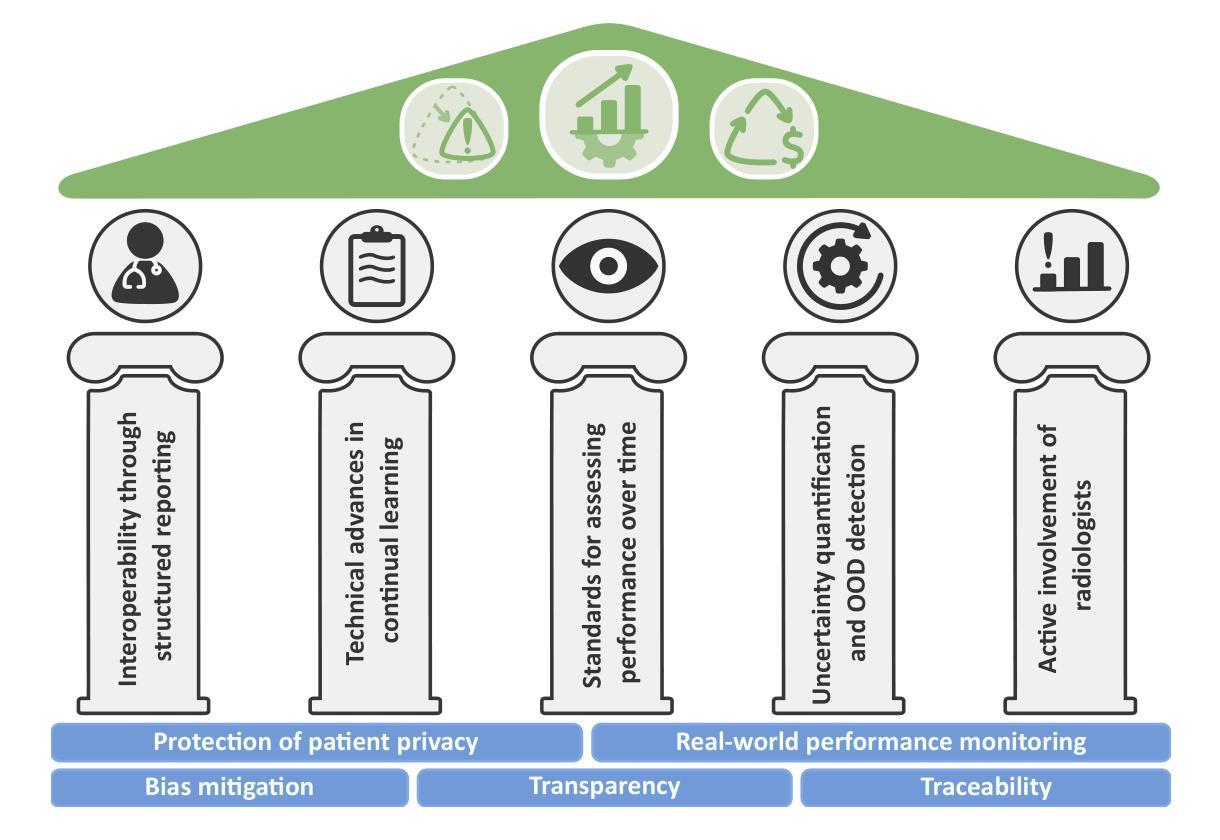
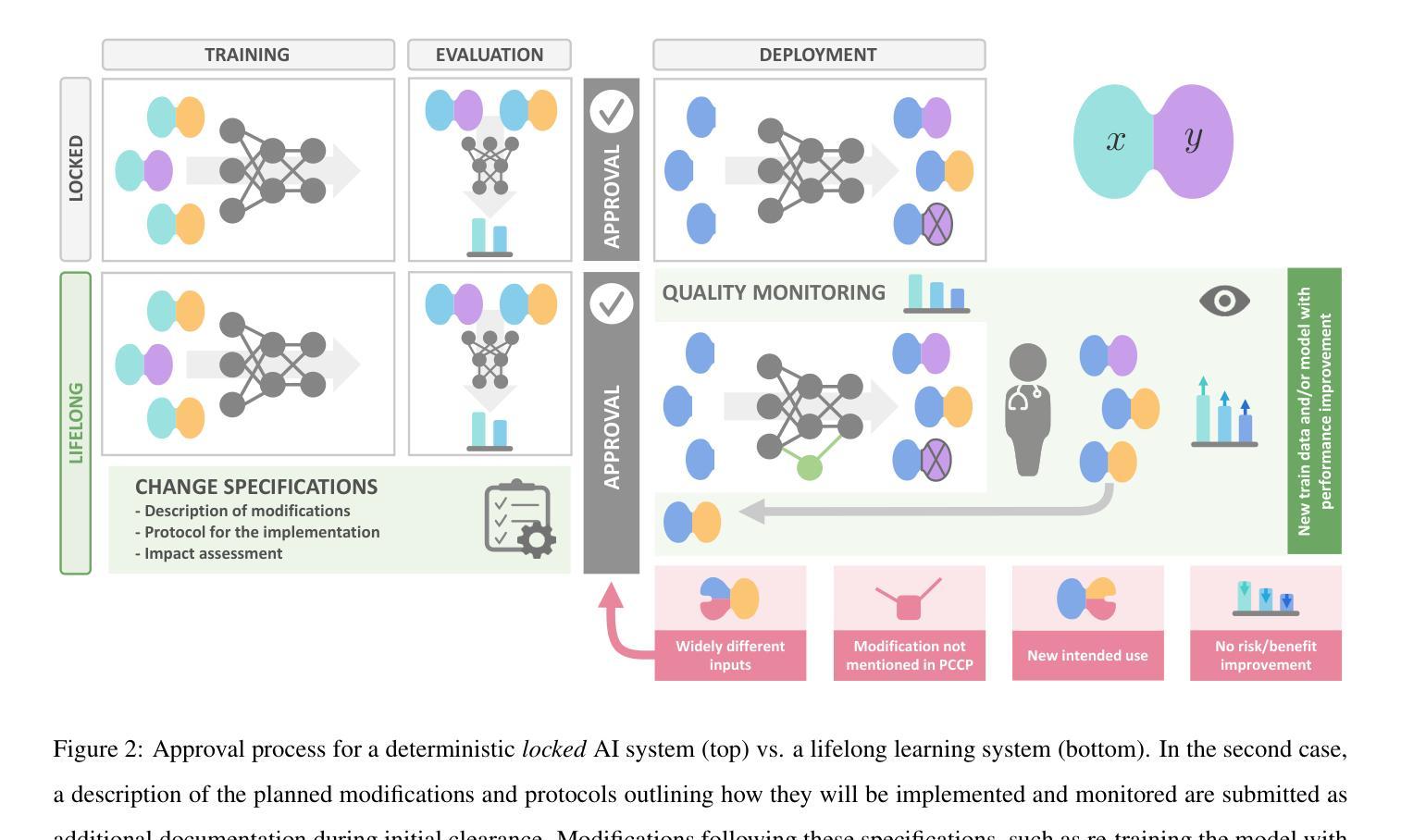
Flemme: A Flexible and Modular Learning Platform for Medical Images
Authors:Guoqing Zhang, Jingyun Yang, Yang Li
As the rapid development of computer vision and the emergence of powerful network backbones and architectures, the application of deep learning in medical imaging has become increasingly significant. Unlike natural images, medical images lack huge volumes of data but feature more modalities, making it difficult to train a general model that has satisfactory performance across various datasets. In practice, practitioners often suffer from manually creating and testing models combining independent backbones and architectures, which is a laborious and time-consuming process. We propose Flemme, a FLExible and Modular learning platform for MEdical images. Our platform separates encoders from the model architectures so that different models can be constructed via various combinations of supported encoders and architectures. We construct encoders using building blocks based on convolution, transformer, and state-space model (SSM) to process both 2D and 3D image patches. A base architecture is implemented following an encoder-decoder style, with several derived architectures for image segmentation, reconstruction, and generation tasks. In addition, we propose a general hierarchical architecture incorporating a pyramid loss to optimize and fuse vertical features. Experiments demonstrate that this simple design leads to an average improvement of 5.60% in Dice score and 7.81% in mean interaction of units (mIoU) for segmentation models, as well as an enhancement of 5.57% in peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and 8.22% in structural similarity (SSIM) for reconstruction models. We further utilize Flemme as an analytical tool to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of various encoders across different tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/wlsdzyzl/flemme.
随着计算机视觉的快速发展以及强大的网络主干和架构的出现,深度学习在医学成像领域的应用变得越来越重要。与自然图像不同,医学图像虽然数据量不大,但具有更多的模态,这使得训练在各种数据集上表现良好的通用模型变得困难。在实践中,实践者经常面临手动创建和测试结合独立主干和架构的模型的问题,这是一个既繁琐又耗时的过程。我们提出了Flemme,这是一个用于医学图像的灵活模块化学习平台。我们的平台将编码器从模型架构中分离出来,以便可以通过支持的编码器和架构的各种组合来构建不同的模型。我们使用基于卷积、变压器和状态空间模型(SSM)的构建块来构建编码器,以处理2D和3D图像补丁。我们采用编码器-解码器风格的基准架构,并为其衍生出用于图像分割、重建和生成任务的几种架构。此外,我们提出了一种通用的层次化架构,该架构结合了金字塔损失来优化和融合垂直特征。实验表明,这种简单的设计导致分割模型的Dice得分平均提高了5.60%,平均单元交互(mIoU)提高了7.81%,重建模型的峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高了5.57%,结构相似性(SSIM)提高了8.22%。我们进一步将Flemme用作分析工具,以评估不同编码器在不同任务中的有效性和效率。代码可在https://github.com/wlsdzyzl/flemme上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures
摘要
医学图像处理领域,提出一种灵活模块化的学习平台Flemme,可构建多种模型。平台将编码器与模型架构分离,利用卷积、变压器和状态空间模型等构建块处理2D和3D图像补丁。实现基础架构后,进行图像分割、重建和生成等任务。采用金字塔损失优化和融合垂直特征,实验证明该设计提高了分割和重建模型的性能。此外,Flemme可作为分析工具评估不同编码器的有效性和效率。
要点
- 计算机视觉的快速发展和强大的网络backbone及架构的出现,深度学习在医学成像中的应用越来越重要。
- 医学图像数据量少、模态多,训练通用模型难度大。
- 实践中,手动创建和测试结合独立backbone和架构的模型是耗时且繁琐的过程。
- 提出Flemme平台,可灵活构建多种模型,将编码器与模型架构分离。
- 利用卷积、变压器和状态空间模型等构建块处理2D和3D图像。
- 实现基础架构并衍生出用于图像分割、重建和生成等任务的模型。
- 采用金字塔损失优化垂直特征融合,实验证明性能提升显著。Flemme还提供分析工具评估编码器效能。
点此查看论文截图

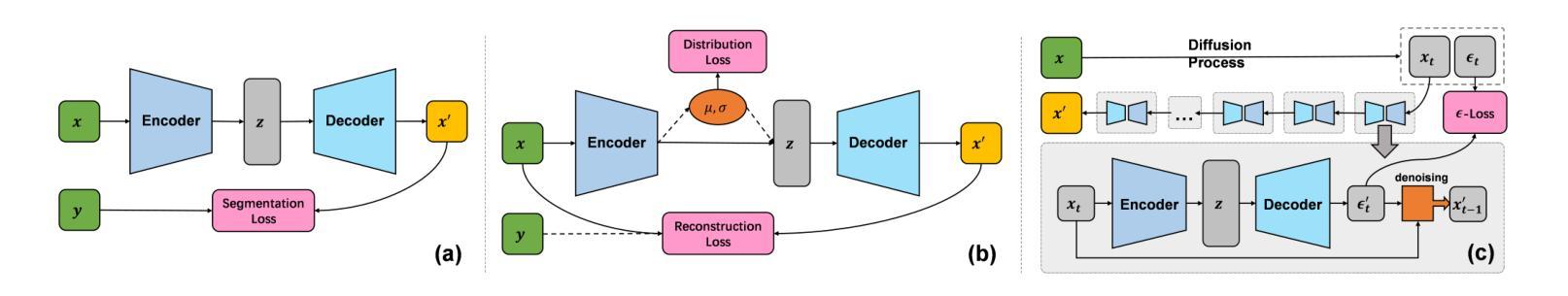
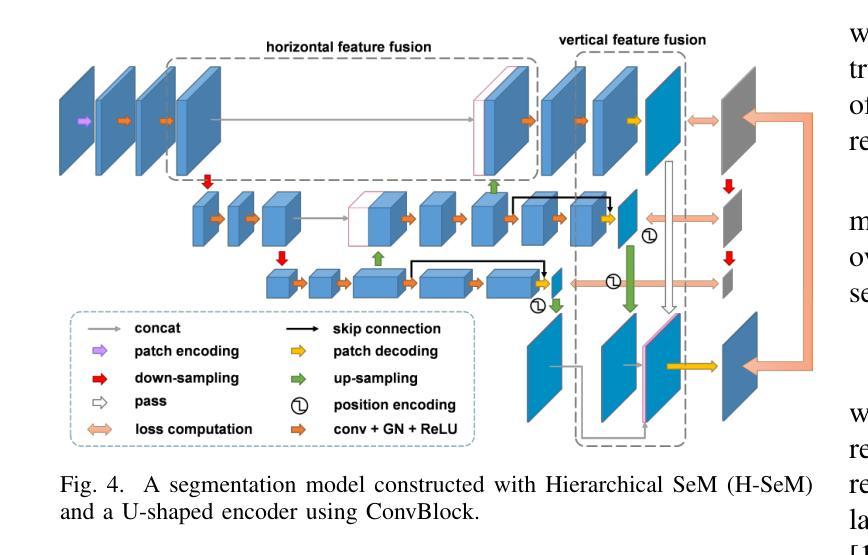
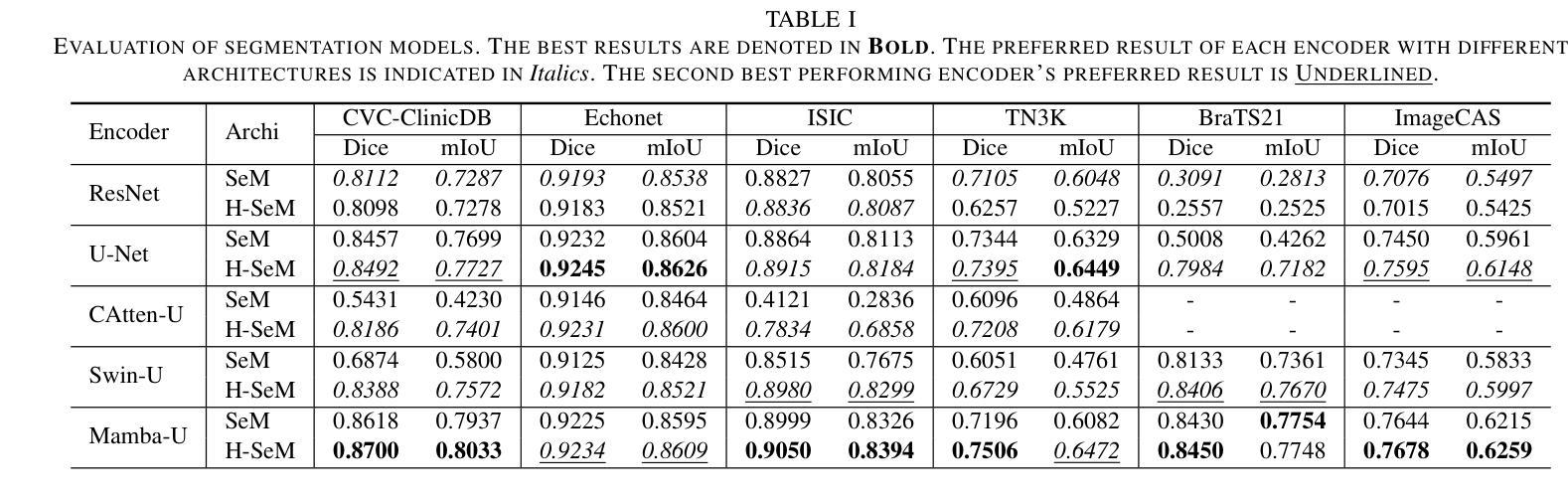
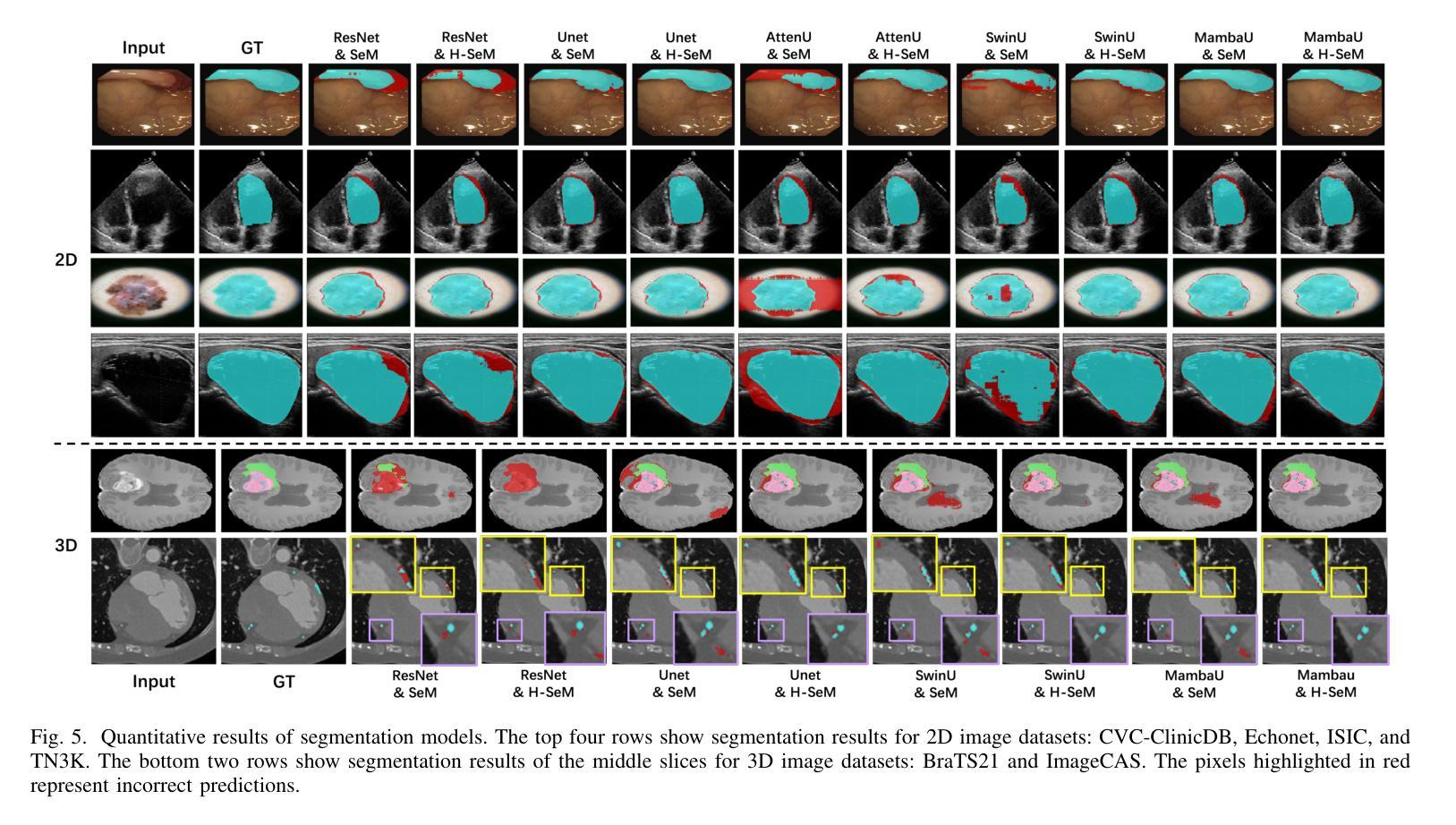
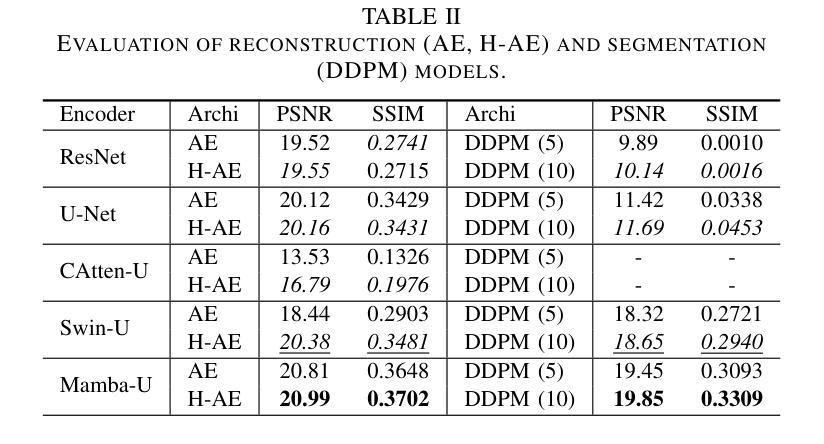
Distillation Learning Guided by Image Reconstruction for One-Shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Feng Zhou, Yanjie Zhou, Longjie Wang, Yun Peng, David E. Carlson, Liyun Tu
Traditional one-shot medical image segmentation (MIS) methods use registration networks to propagate labels from a reference atlas or rely on comprehensive sampling strategies to generate synthetic labeled data for training. However, these methods often struggle with registration errors and low-quality synthetic images, leading to poor performance and generalization. To overcome this, we introduce a novel one-shot MIS framework based on knowledge distillation, which allows the network to directly ‘see’ real images through a distillation process guided by image reconstruction. It focuses on anatomical structures in a single labeled image and a few unlabeled ones. A registration-based data augmentation network creates realistic, labeled samples, while a feature distillation module helps the student network learn segmentation from these samples, guided by the teacher network. During inference, the streamlined student network accurately segments new images. Evaluations on three public datasets (OASIS for T1 brain MRI, BCV for abdomen CT, and VerSe for vertebrae CT) show superior segmentation performance and generalization across different medical image datasets and modalities compared to leading methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/NoviceFodder/OS-MedSeg.
传统的一次性医学图像分割(MIS)方法使用注册网络来从参考图谱传播标签,或者依赖全面的采样策略来生成合成标记数据以进行训练。然而,这些方法经常面临注册错误和低质量合成图像的问题,导致性能不佳和泛化能力差。为了克服这一问题,我们引入了一种基于知识蒸馏的新型一次性MIS框架,该框架允许网络通过由图像重建引导的蒸馏过程直接“查看”真实图像。它专注于单个标记图像和少量未标记图像中的解剖结构。基于注册的数据增强网络创建逼真的标记样本,而特征蒸馏模块帮助学生网络从这些样本中学习分割,由教师网络进行引导。在推理过程中,简化的学生网络能够准确地对新图像进行分割。在三个公共数据集(用于T1脑MRI的OASIS、用于腹部CT的BCV和用于椎体CT的VerSe)上的评估显示,与领先的方法相比,我们的方法在跨不同医学图像数据集和模态的分割性能和泛化能力方面表现出优越性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/NoviceFodder/OS-MedSeg上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于知识蒸馏的新型单镜头医学图像分割框架,该框架解决了传统方法面临的注册误差和低质量合成图像问题。通过图像重建引导蒸馏过程,使网络能够直接“看到”真实图像。该框架侧重于单个标记图像和少量未标记图像中的解剖结构。通过注册数据增强网络创建逼真的标记样本,特征蒸馏模块帮助学生网络从这些样本中学习分割,并在推理阶段准确分割新图像。在三个公共数据集上的评估证明了其在不同医学图像数据集和模态上的优越分割性能和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种基于知识蒸馏的新型单镜头医学图像分割框架,解决了传统方法面临的注册误差问题。
- 通过图像重建过程,使网络能够直接“看到”真实图像,提高了分割性能。
- 框架侧重于单个标记图像和少量未标记图像中的解剖结构。
- 注册数据增强网络创建逼真的标记样本,增强了模型的泛化能力。
- 特征蒸馏模块帮助学生网络从标记样本中学习分割。
- 在三个公共数据集上的评估证明了该框架的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图


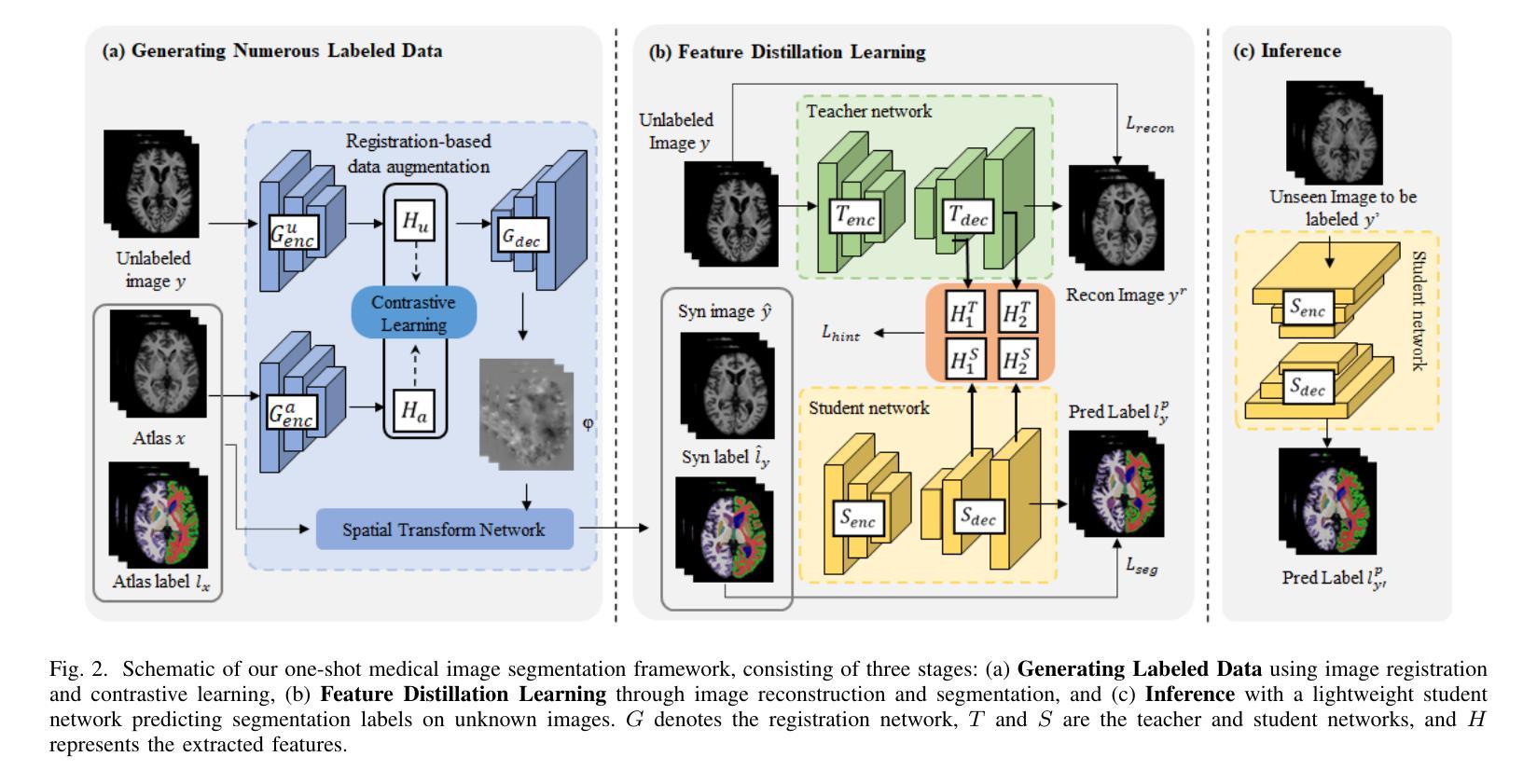
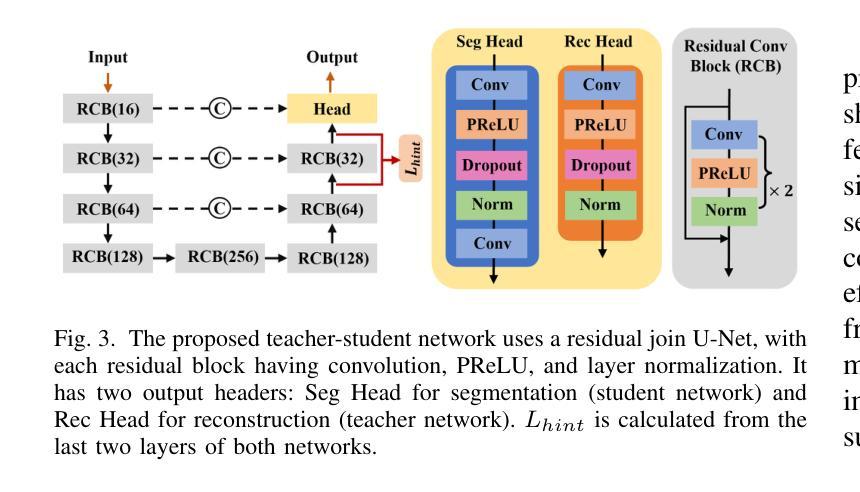
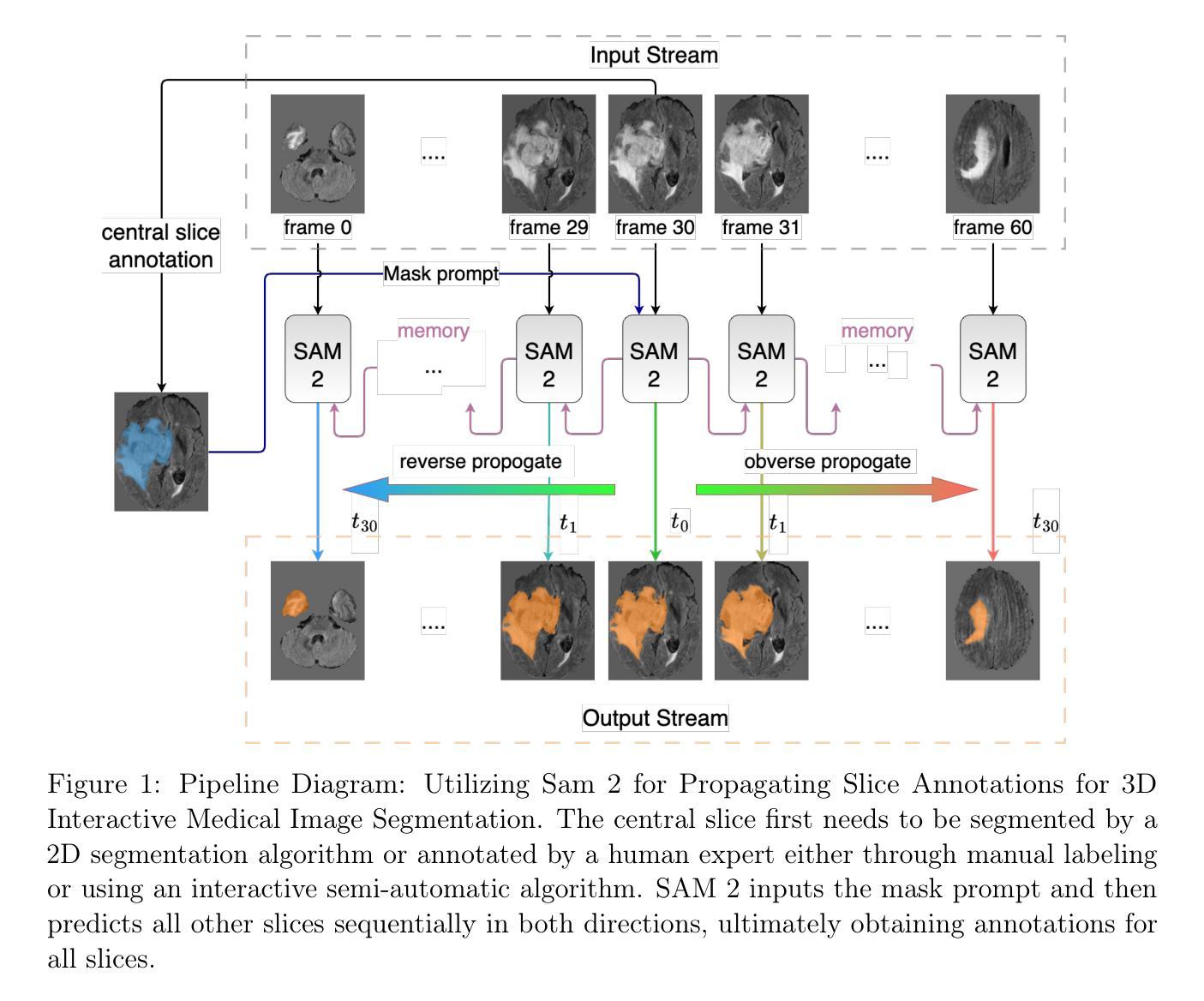
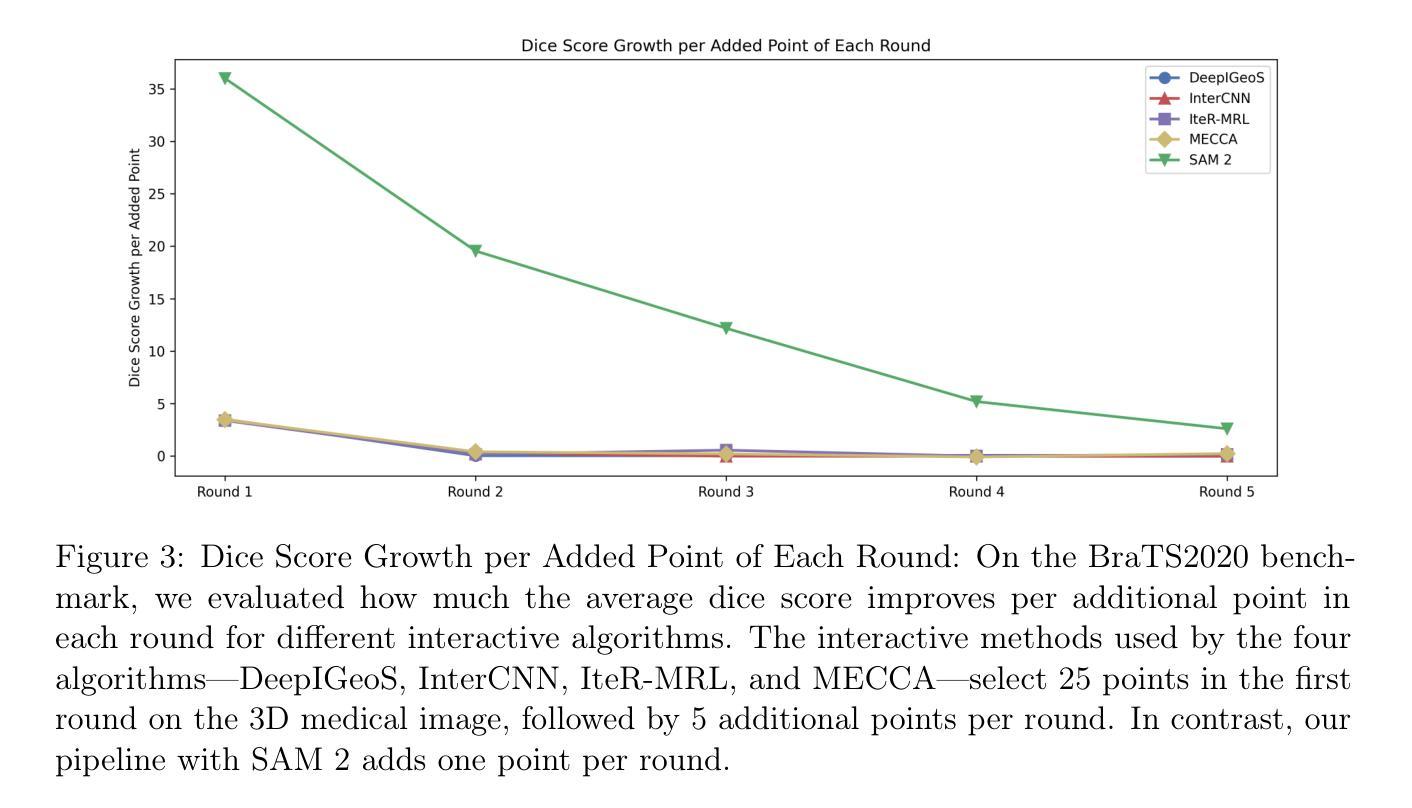
Interactive 3D Medical Image Segmentation with SAM 2
Authors:Chuyun Shen, Wenhao Li, Yuhang Shi, Xiangfeng Wang
Interactive medical image segmentation (IMIS) has shown significant potential in enhancing segmentation accuracy by integrating iterative feedback from medical professionals. However, the limited availability of enough 3D medical data restricts the generalization and robustness of most IMIS methods. The Segment Anything Model (SAM), though effective for 2D images, requires expensive semi-auto slice-by-slice annotations for 3D medical images. In this paper, we explore the zero-shot capabilities of SAM 2, the next-generation Meta SAM model trained on videos, for 3D medical image segmentation. By treating sequential 2D slices of 3D images as video frames, SAM 2 can fully automatically propagate annotations from a single frame to the entire 3D volume. We propose a practical pipeline for using SAM 2 in 3D medical image segmentation and present key findings highlighting its efficiency and potential for further optimization. Concretely, numerical experiments on the BraTS2020 and the medical segmentation decathlon datasets demonstrate that SAM 2 still has a gap with supervised methods but can narrow the gap in specific settings and organ types, significantly reducing the annotation burden on medical professionals. Our code will be open-sourced and available at https://github.com/Chuyun-Shen/SAM_2_Medical_3D.
交互式医学图像分割(IMIS)通过整合医学专家的迭代反馈,在提升分割精度方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,充足3D医学数据的有限可用性限制了大多数IMIS方法的通用性和稳健性。Segment Anything Model(SAM)对于2D图像非常有效,但对于3D医学图像需要昂贵的半自动切片级标注。在本文中,我们探索了基于视频的下一代Meta SAM模型SAM 2在3D医学图像分割中的零样本能力。通过将3D图像的连续2D切片视为视频帧,SAM 2可以完全自动地将单个帧的标注传播到整个3D体积。我们提出了一个使用SAM 2进行3D医学图像分割的实际流程,并介绍了关键发现,突出其效率和进一步优化的潜力。具体地说,在BraTS2020和医学分割十项全能数据集上的数值实验表明,SAM 2与监督方法之间仍存在一定差距,但在特定设置和器官类型中可以缩小差距,显著减少医学专业人士的标注负担。我们的代码将在https://github.com/Chuyun-Shen/SAM_2_Medical_3D开源并提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割的零标注能力研究:Segment Anything Model 2(SAM 2)模型基于视频训练的下一代模型,用于全自动地处理3D医学图像分割的标注问题。该模型可将单帧标注自动传播到整个三维体积,从而显著减少医学专业人士的标注负担。本文提出使用SAM 2进行医学图像分割的实际流程,并通过实验验证其在特定场景和器官类型中的表现潜力。代码已开源。
Key Takeaways
- IMIS通过整合专业人员的反馈提高了分割准确性。
- 3D医学数据的有限可用性限制了大多数IMIS方法的泛化和稳健性。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)对于2D图像有效,但对3D医学图像需要昂贵的半自动切片标注。
- SAM 2模型具备零标注能力,可全自动地从单个帧传播标注到整个三维体积。
- SAM 2在BraTS2020和医学分割十项全能数据集上的实验表现表明其在特定设置和器官类型中有缩小与监督方法差距的潜力。
- SAM 2模型的开源代码可供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图


Restore-RWKV: Efficient and Effective Medical Image Restoration with RWKV
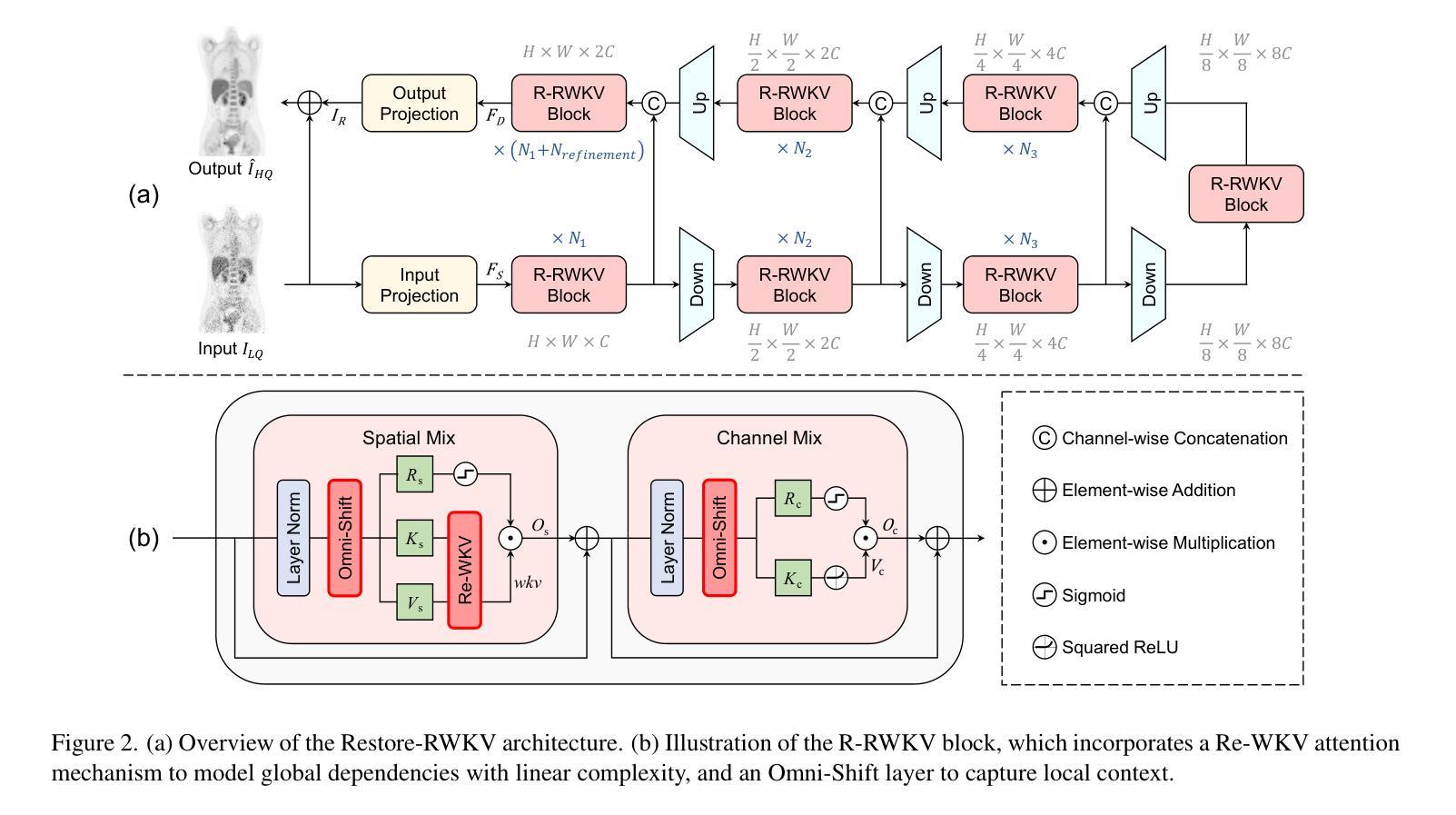
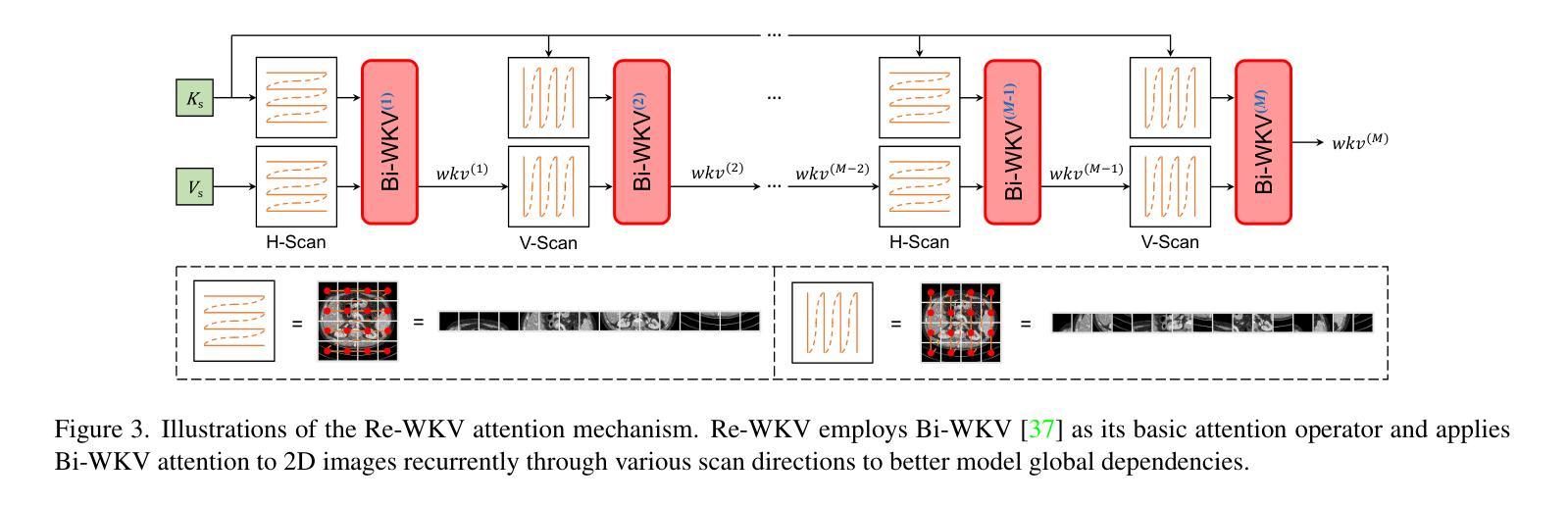
Authors:Zhiwen Yang, Jiayin Li, Hui Zhang, Dan Zhao, Bingzheng Wei, Yan Xu
Transformers have revolutionized medical image restoration, but the quadratic complexity still poses limitations for their application to high-resolution medical images. The recent advent of the Receptance Weighted Key Value (RWKV) model in the natural language processing field has attracted much attention due to its ability to process long sequences efficiently. To leverage its advanced design, we propose Restore-RWKV, the first RWKV-based model for medical image restoration. Since the original RWKV model is designed for 1D sequences, we make two necessary modifications for modeling spatial relations in 2D medical images. First, we present a recurrent WKV (Re-WKV) attention mechanism that captures global dependencies with linear computational complexity. Re-WKV incorporates bidirectional attention as basic for a global receptive field and recurrent attention to effectively model 2D dependencies from various scan directions. Second, we develop an omnidirectional token shift (Omni-Shift) layer that enhances local dependencies by shifting tokens from all directions and across a wide context range. These adaptations make the proposed Restore-RWKV an efficient and effective model for medical image restoration. Even a lightweight variant of Restore-RWKV, with only 1.16 million parameters, achieves comparable or even superior results compared to existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the resulting Restore-RWKV achieves SOTA performance across a range of medical image restoration tasks, including PET image synthesis, CT image denoising, MRI image super-resolution, and all-in-one medical image restoration. Code is available at: https://github.com/Yaziwel/Restore-RWKV.
Transformer已经彻底改变了医学图像修复领域,但是其二次复杂度仍然限制了其在高分辨率医学图像上的应用。自然语言处理领域最近出现的接纳加权键值(Receptance Weighted Key Value,简称RWKV)模型因其高效处理长序列的能力而备受关注。为了利用它的先进设计,我们提出了基于RWKV模型的医学图像修复模型Restore-RWKV。由于原始的RWKV模型是为1D序列设计的,因此我们对建模二维医学图像中的空间关系进行了两项必要的修改。首先,我们提出了一种循环WKV(Re-WKV)注意力机制,它以线性计算复杂度捕获全局依赖关系。Re-WKV将双向注意力作为基本全局感受野和循环注意力,以有效地从各种扫描方向对二维依赖性进行建模。其次,我们开发了一个全方向令牌移位(Omni-Shift)层,它通过从各个方向移动令牌并在广泛的上下文范围内进行操作来增强局部依赖性。这些适应性调整使得提出的Restore-RWKV成为医学图像修复的有效且高效的模型。即使是一个只有116万个参数的Restore-RWKV的轻量级变体,也能达到或超越现有最先进的(SOTA)方法的结果。大量实验表明,恢复后的Restore-RWKV在多种医学图像修复任务中均达到SOTA性能,包括PET图像合成、CT图像去噪、MRI图像超分辨率以及全方位的医学图像修复。相关代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/Yaziwel/Restore-RWKV 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper introduces the first RWKV-based model for image restoration
Summary
本文介绍了针对医学图像恢复的RWKV模型的应用。针对原始RWKV模型设计用于一维序列的问题,本文提出针对二维医学图像的改进版模型Restore-RWKV。此模型采用递归WKV注意力机制和全方位token位移层来处理二维依赖性。结果证明Restore-RWKV在多种医学图像恢复任务上均达到或超越现有最佳水平。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了Transformers在医学图像恢复中的局限性,尤其是二次复杂性对于高分辨率图像的挑战。
- RWKV模型在自然语言处理领域受到关注,由于其处理长序列的效率。
- 提出Restore-RWKV模型,是首个基于RWKV的医学图像恢复模型。
- 为适应二维医学图像的空间关系,对原始RWKV模型进行了两项必要修改:递归WKV注意力机制和全方位token位移层。
- Restore-RWKV模型在多种医学图像恢复任务上表现出卓越性能,包括PET图像合成、CT图像去噪、MRI图像超分辨率等。
- 模型具有高效性,即使是轻量级变体也能达到或超越现有最佳方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图