⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-09 更新
AuxDepthNet: Real-Time Monocular 3D Object Detection with Depth-Sensitive Features
Authors:Ruochen Zhang, Hyeung-Sik Choi, Dongwook Jung, Phan Huy Nam Anh, Sang-Ki Jeong, Zihao Zhu
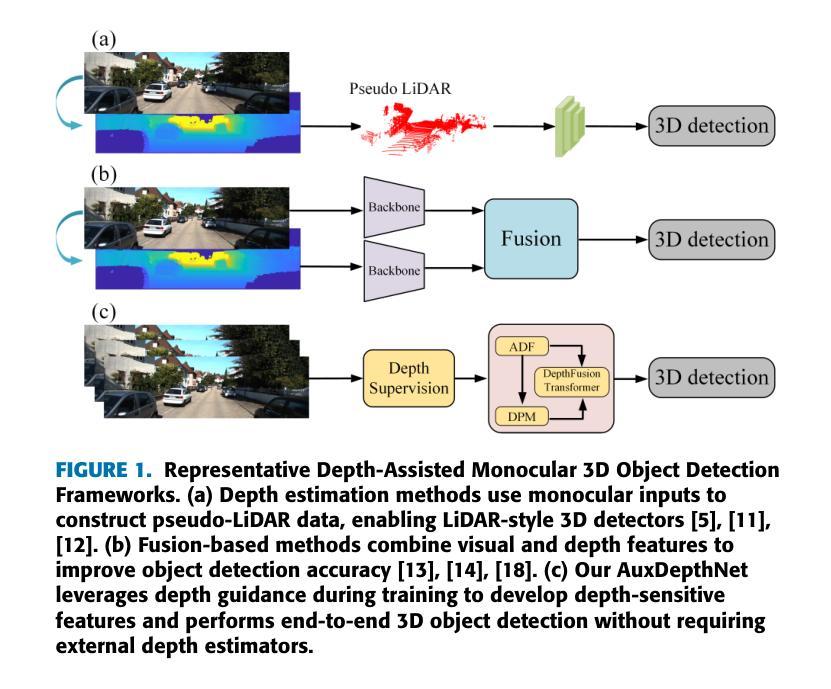
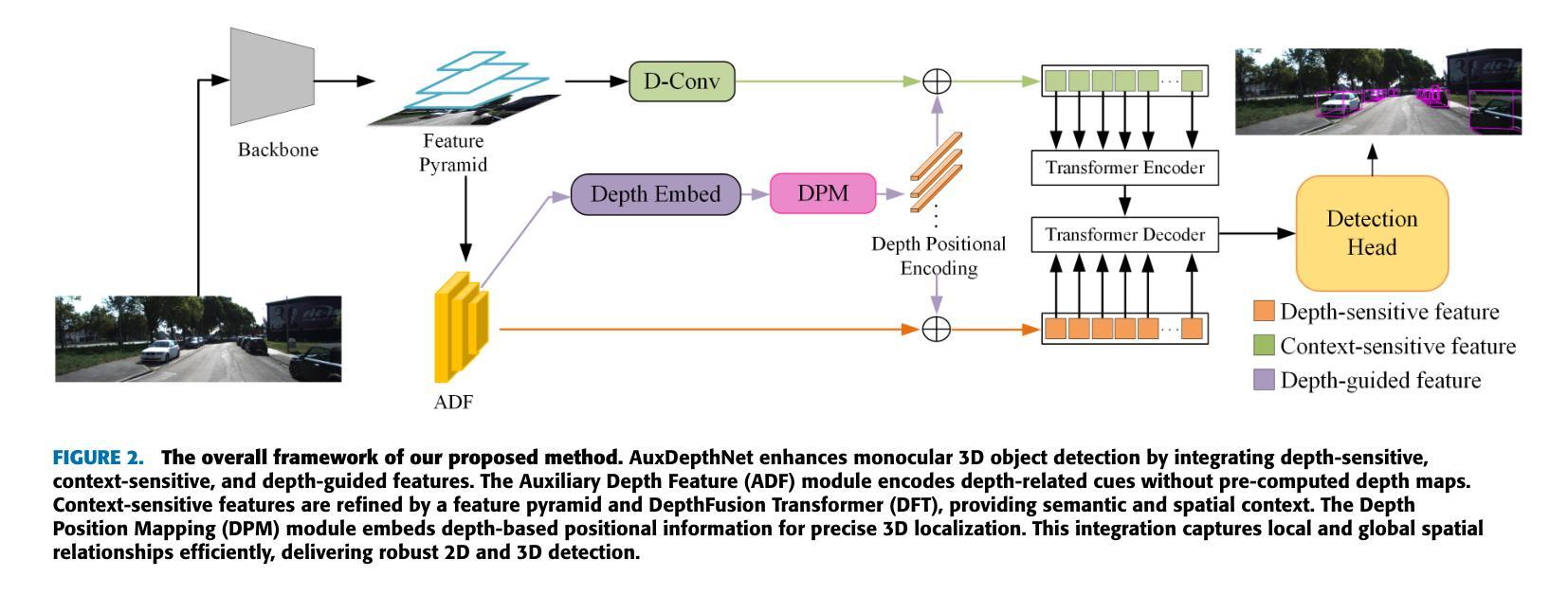
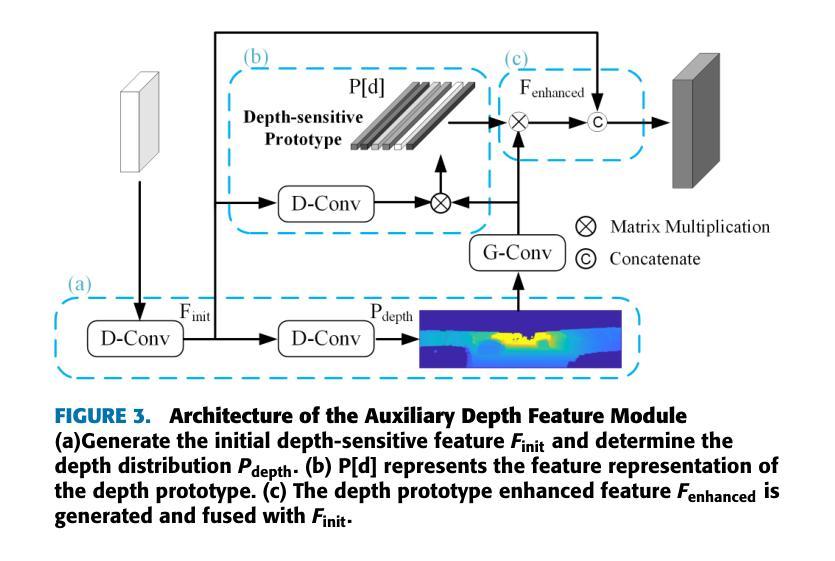
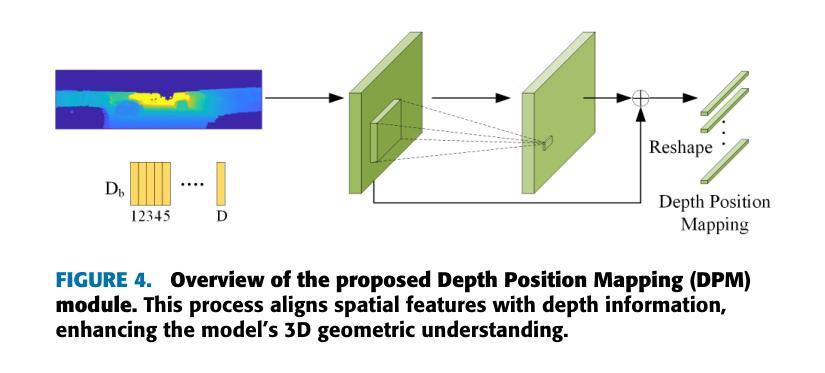
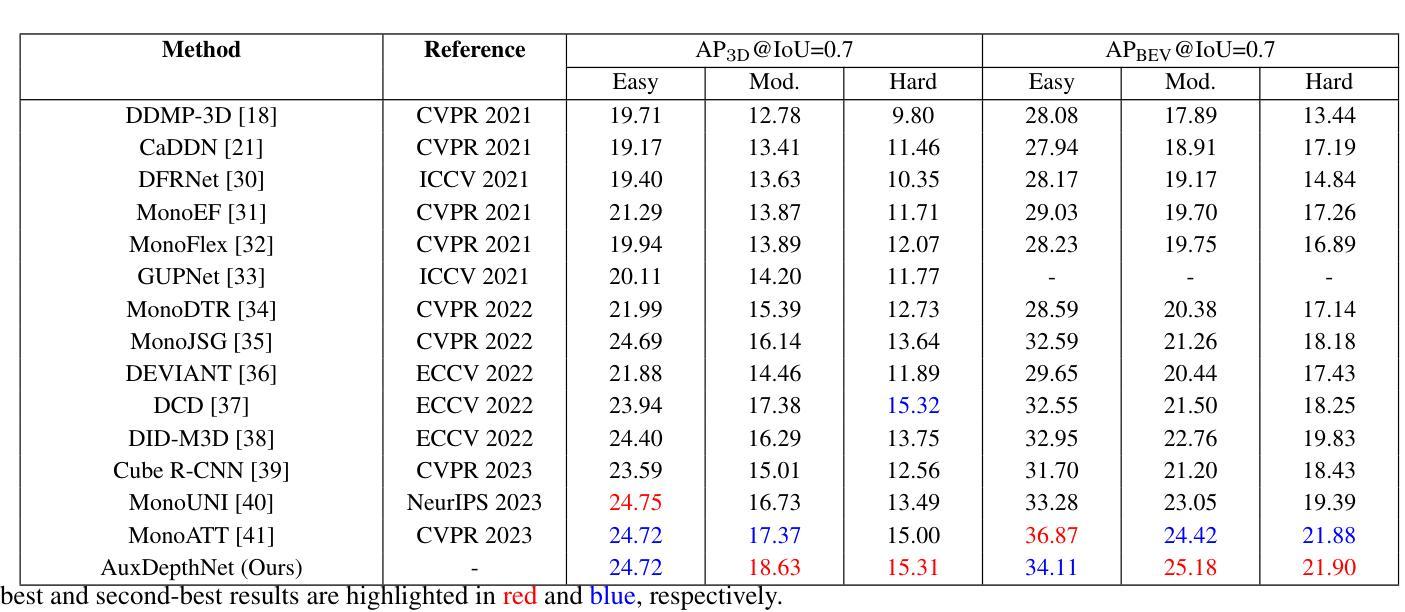
Monocular 3D object detection is a challenging task in autonomous systems due to the lack of explicit depth information in single-view images. Existing methods often depend on external depth estimators or expensive sensors, which increase computational complexity and hinder real-time performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose AuxDepthNet, an efficient framework for real-time monocular 3D object detection that eliminates the reliance on external depth maps or pre-trained depth models. AuxDepthNet introduces two key components: the Auxiliary Depth Feature (ADF) module, which implicitly learns depth-sensitive features to improve spatial reasoning and computational efficiency, and the Depth Position Mapping (DPM) module, which embeds depth positional information directly into the detection process to enable accurate object localization and 3D bounding box regression. Leveraging the DepthFusion Transformer architecture, AuxDepthNet globally integrates visual and depth-sensitive features through depth-guided interactions, ensuring robust and efficient detection. Extensive experiments on the KITTI dataset show that AuxDepthNet achieves state-of-the-art performance, with $\text{AP}{3D}$ scores of 24.72% (Easy), 18.63% (Moderate), and 15.31% (Hard), and $\text{AP}{\text{BEV}}$ scores of 34.11% (Easy), 25.18% (Moderate), and 21.90% (Hard) at an IoU threshold of 0.7.
单目3D目标检测是自主系统中一项具有挑战性的任务,由于缺乏单视图图像中的明确深度信息。现有方法通常依赖于外部深度估计器或昂贵的传感器,这增加了计算复杂性并阻碍了实时性能。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了AuxDepthNet,这是一个用于实时单目3D目标检测的高效框架,它消除了对外部深度图或预训练深度模型的依赖。AuxDepthNet引入了两个关键组件:辅助深度特征(ADF)模块,它隐式地学习深度敏感特征以提高空间推理和计算效率;以及深度位置映射(DPM)模块,它将深度位置信息直接嵌入到检测过程中,以实现准确的目标定位和3D边界框回归。借助DepthFusion Transformer架构,AuxDepthNet通过深度引导交互全局整合视觉和深度敏感特征,确保稳健高效的检测。在KITTI数据集上的广泛实验表明,AuxDepthNet达到了最先进的性能,在IoU阈值为0.7的情况下,其$\text{AP}{3D}$得分分别为Easy模式下的24.72%、Moderate模式下的18.63%以及Hard模式下的15.31%,而$\text{AP}{\text{BEV}}$得分分别为Easy模式下的34.11%、Moderate模式下的25.18%以及Hard模式下的21.90%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
该文针对单目摄像头下的三维目标检测提出了一种高效的实时检测框架AuxDepthNet,无需依赖外部深度图或预训练的深度模型。通过引入辅助深度特征模块和深度位置映射模块,实现了深度敏感特征的隐式学习和深度位置信息的直接嵌入检测过程,从而提高了空间推理和计算效率,实现了准确的目标定位和三维边界框回归。实验结果表明,在KITTI数据集上,AuxDepthNet达到了先进水平。
Key Takeaways:
- 单目摄像头下的三维目标检测是自主系统中的一个挑战任务,缺乏明确的深度信息是其主要难点。
- 当前方法通常依赖于外部深度估计器或昂贵的传感器,增加了计算复杂性并影响了实时性能。
- AuxDepthNet框架被提出用于解决这一问题,无需依赖外部深度图或预训练深度模型。
- AuxDepthNet包含两个关键组件:辅助深度特征模块和深度位置映射模块。
- 辅助深度特征模块通过隐式学习深度敏感特征来提高空间推理和计算效率。
- 深度位置映射模块通过将深度位置信息直接嵌入检测过程中,实现了准确的目标定位和三维边界框回归。
点此查看论文截图

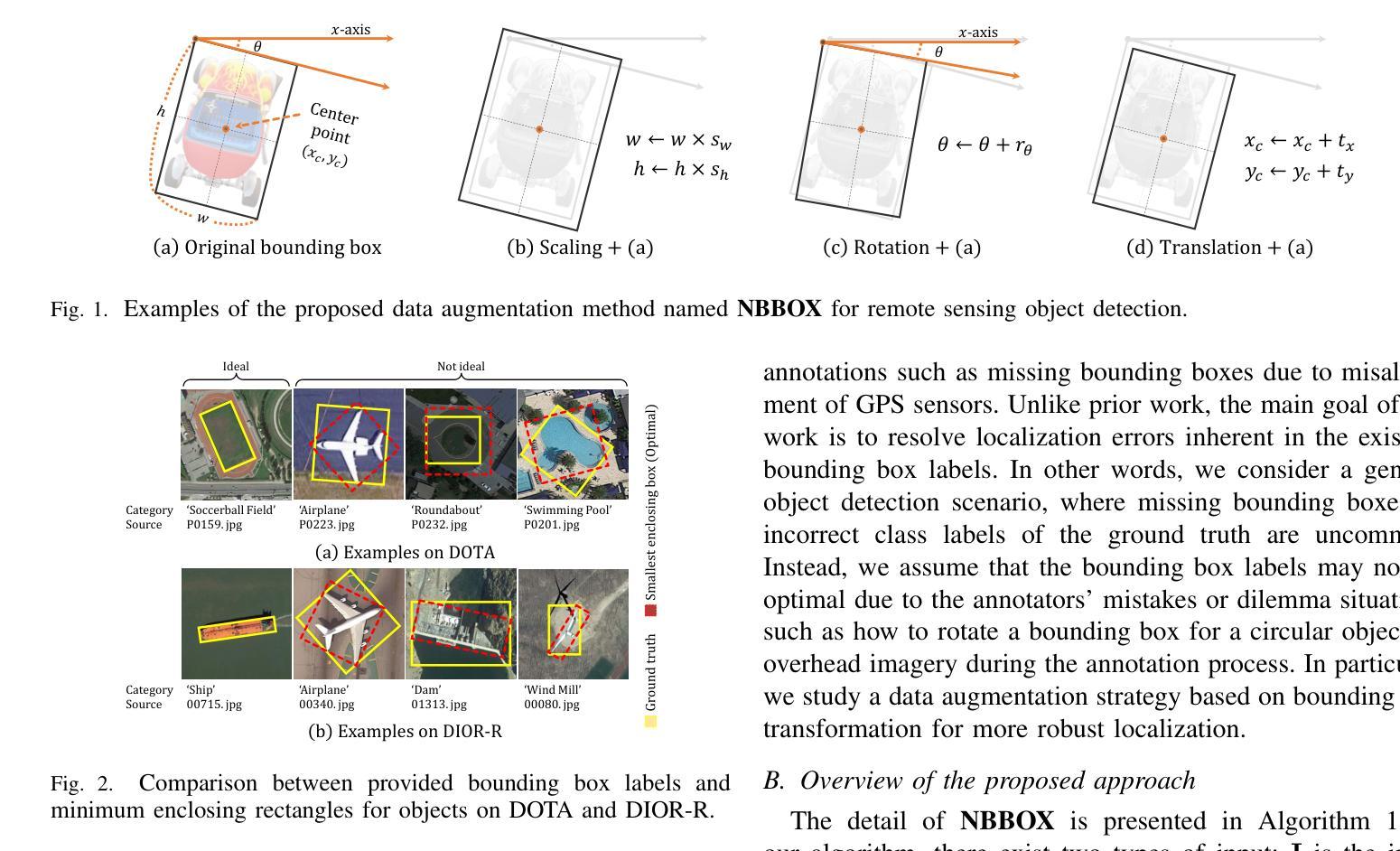
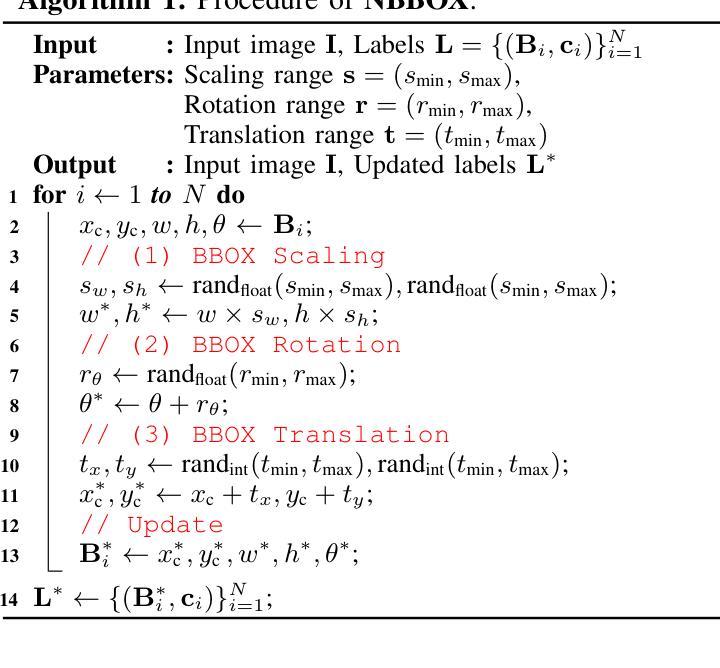
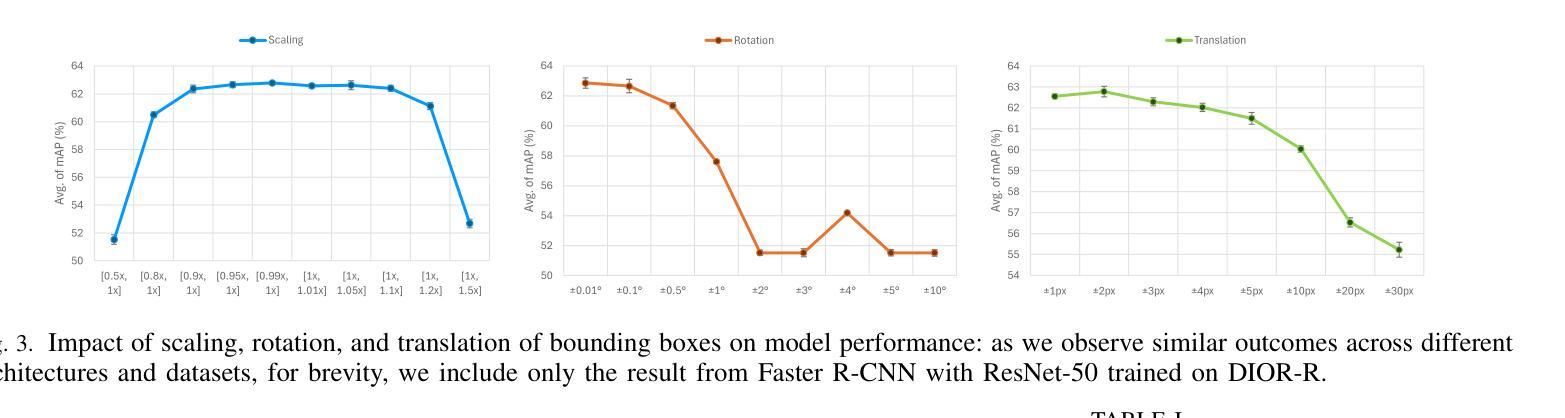
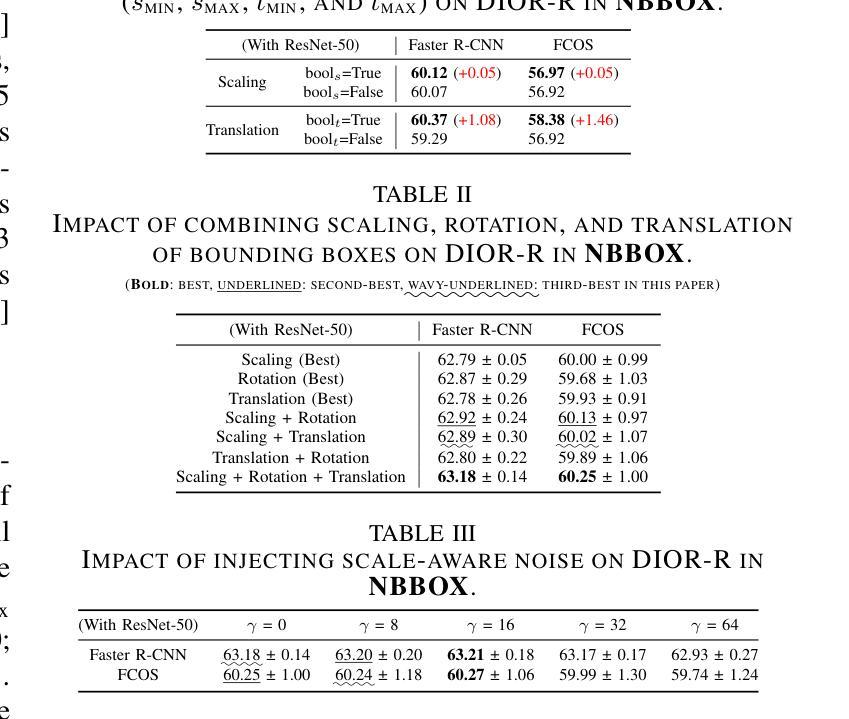
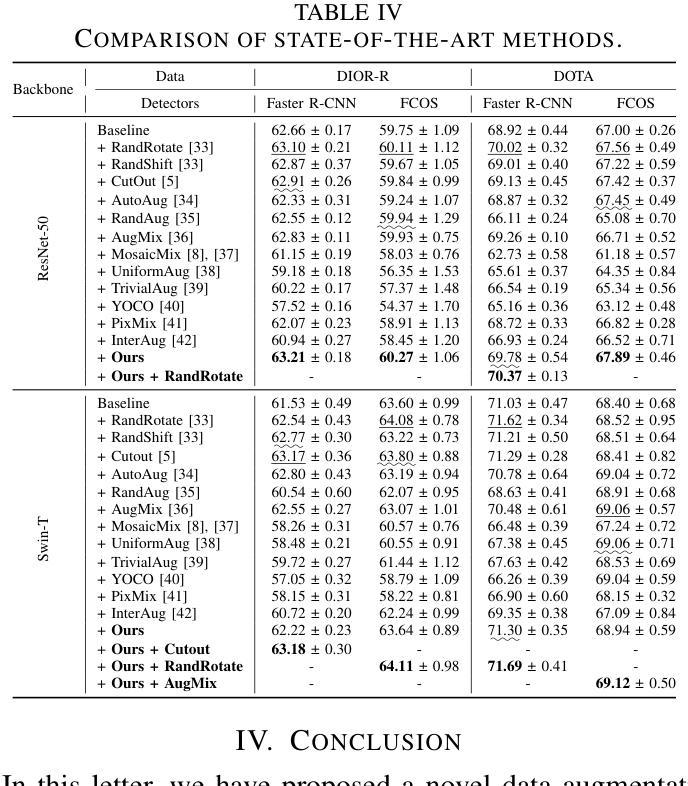
NBBOX: Noisy Bounding Box Improves Remote Sensing Object Detection
Authors:Yechan Kim, SooYeon Kim, Moongu Jeon
Data augmentation has shown significant advancements in computer vision to improve model performance over the years, particularly in scenarios with limited and insufficient data. Currently, most studies focus on adjusting the image or its features to expand the size, quality, and variety of samples during training in various tasks including object detection. However, we argue that it is necessary to investigate bounding box transformations as a data augmentation technique rather than image-level transformations, especially in aerial imagery due to potentially inconsistent bounding box annotations. Hence, this letter presents a thorough investigation of bounding box transformation in terms of scaling, rotation, and translation for remote sensing object detection. We call this augmentation strategy NBBOX (Noise Injection into Bounding Box). We conduct extensive experiments on DOTA and DIOR-R, both well-known datasets that include a variety of rotated generic objects in aerial images. Experimental results show that our approach significantly improves remote sensing object detection without whistles and bells and it is more time-efficient than other state-of-the-art augmentation strategies.
数据增强在计算机视觉领域已经取得了显著进展,多年来在提高模型性能,特别是在数据有限和不足的场景下,发挥了重要作用。目前,大多数研究都集中在调整图像或其特征上,以扩大样本的大小、质量和多样性,用于各种任务,包括目标检测。然而,我们认为有必要研究边界框变换作为一种数据增强技术,而不是图像级别的变换,特别是在航空图像中,因为边界框注释可能存在潜在的不一致性。因此,本文全面研究了边界框变换在缩放、旋转和平移方面的遥感目标检测。我们将这种增强策略称为NBBOX(噪声注入边界框)。我们在DOTA和DIOR-R这两个包含航空图像中各种旋转通用对象的数据集上进行了大量实验。实验结果表明,我们的方法在不需要繁琐操作的情况下,显著提高了遥感目标检测的精度,并且相较于其他先进的增强策略更加省时高效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters
Summary
数据增强在计算机视觉领域已经取得了显著进展,特别是在数据有限和不足的情况下提高模型性能。当前研究主要集中在调整图像或其特征以扩大样本规模、质量和多样性,用于各种任务,包括目标检测。本文主张研究边界框转换作为数据增强技术,特别是在航空图像中,因为边界框注释可能存在不一致。因此,本文全面研究了边界框转换(缩放、旋转和翻译)在遥感目标检测中的应用。我们称这种增强策略为NBBOX(噪声注入边界框)。在包含航空图像中旋转通用对象的数据集DOTA和DIOR-R上进行的实验表明,该方法显著提高遥感目标检测性能,且比其他先进的数据增强策略更省时高效。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强技术在计算机视觉领域持续进步,特别是在有限数据下提升模型性能。
- 当前研究主要集中在图像级别的数据增强,而本文强调边界框转换的重要性。
- 边界框转换包括缩放、旋转和翻译,对于航空图像中的遥感目标检测至关重要。
- 提出的数据增强策略NBBOX通过注入噪声到边界框内,提高了遥感目标检测的准确性。
- 在知名数据集DOTA和DIOR-R上的实验证实NBBOX策略的有效性。
- NBBOX方法比其他先进的数据增强策略更省时高效。
点此查看论文截图


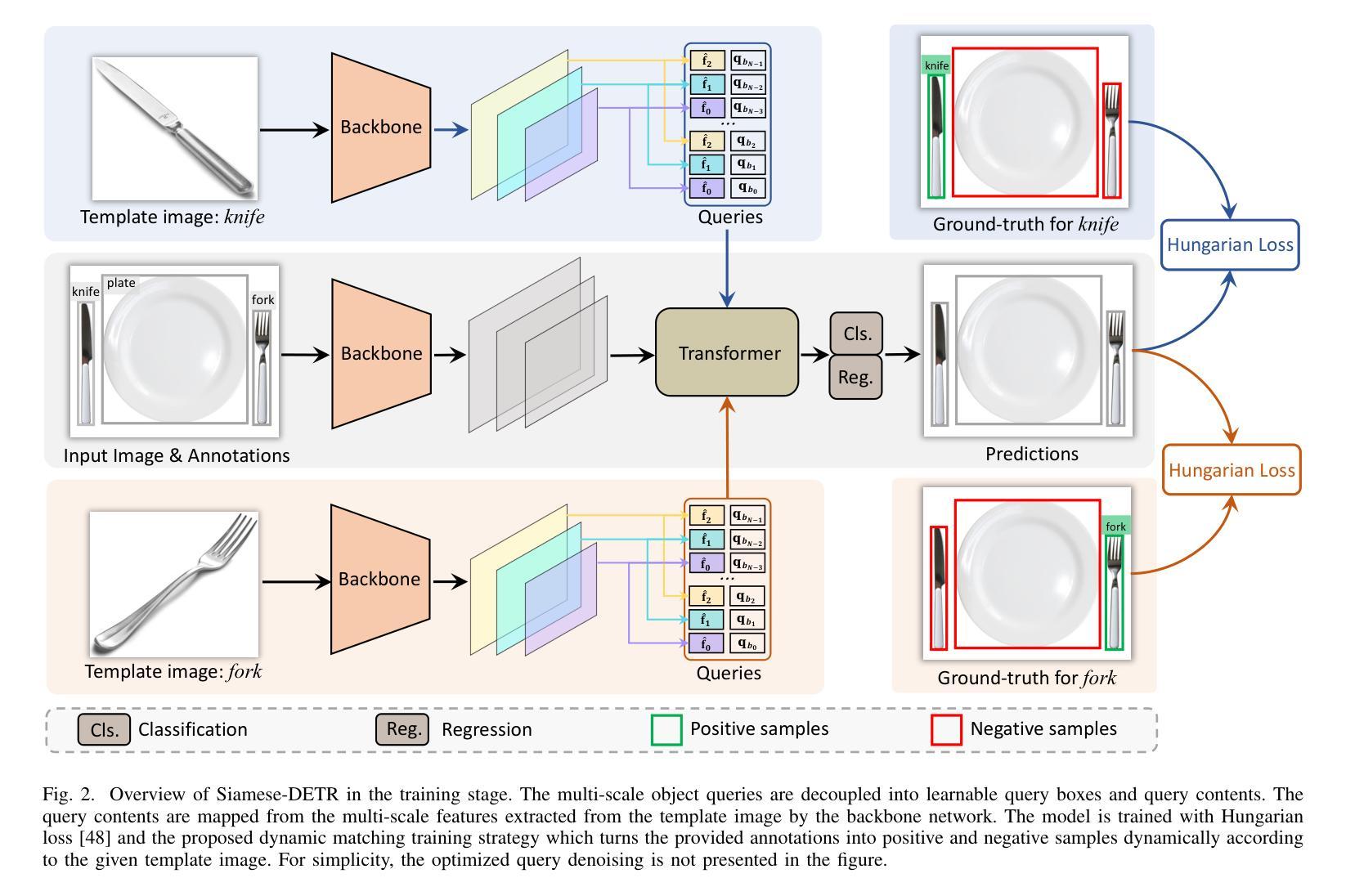
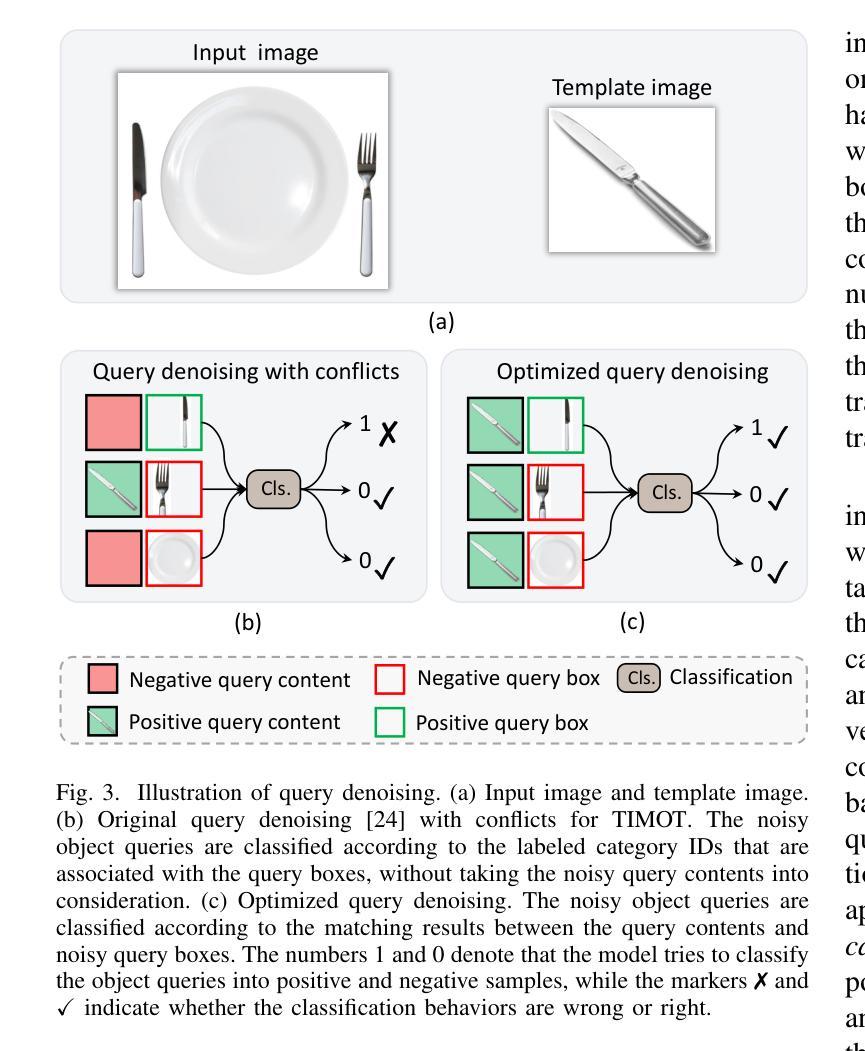
Siamese-DETR for Generic Multi-Object Tracking
Authors:Qiankun Liu, Yichen Li, Yuqi Jiang, Ying Fu
The ability to detect and track the dynamic objects in different scenes is fundamental to real-world applications, e.g., autonomous driving and robot navigation. However, traditional Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) is limited to tracking objects belonging to the pre-defined closed-set categories. Recently, Open-Vocabulary MOT (OVMOT) and Generic MOT (GMOT) are proposed to track interested objects beyond pre-defined categories with the given text prompt and template image. However, the expensive well pre-trained (vision-)language model and fine-grained category annotations are required to train OVMOT models. In this paper, we focus on GMOT and propose a simple but effective method, Siamese-DETR, for GMOT. Only the commonly used detection datasets (e.g., COCO) are required for training. Different from existing GMOT methods, which train a Single Object Tracking (SOT) based detector to detect interested objects and then apply a data association based MOT tracker to get the trajectories, we leverage the inherent object queries in DETR variants. Specifically: 1) The multi-scale object queries are designed based on the given template image, which are effective for detecting different scales of objects with the same category as the template image; 2) A dynamic matching training strategy is introduced to train Siamese-DETR on commonly used detection datasets, which takes full advantage of provided annotations; 3) The online tracking pipeline is simplified through a tracking-by-query manner by incorporating the tracked boxes in previous frame as additional query boxes. The complex data association is replaced with the much simpler Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Extensive experimental results show that Siamese-DETR surpasses existing MOT methods on GMOT-40 dataset by a large margin. Codes are avaliable at \url{https://github.com/yumu-173/Siamese-DETR}.
检测并跟踪不同场景中的动态对象对于实际应用(例如自动驾驶和机器人导航)至关重要。然而,传统的多对象跟踪(MOT)仅限于跟踪属于预定义封闭集类别中的对象。最近,提出了开放词汇MOT(OVMOT)和通用MOT(GMOT)来跟踪给定文本提示和模板图像中预定义类别以外的感兴趣对象。然而,昂贵的预先训练好的(视觉)语言模型和精细的类别注释是训练OVMOT模型所必需的。在本文中,我们专注于GMOT并提出了一种简单而有效的方法Siamese-DETR。只需要常用的检测数据集(例如COCO)进行训练。与现有的GMOT方法不同,这些方法会训练一个基于单目标跟踪(SOT)的检测器来检测感兴趣的对象,然后应用基于数据关联的MOT跟踪器来获得轨迹,我们利用DETR变体的固有对象查询。具体来说:1)基于给定的模板图像设计多尺度对象查询,对于检测与模板图像同一类别的不同尺度的对象非常有效;2)引入动态匹配训练策略,对常用的检测数据集进行Siamese-DETR的训练,充分利用提供的注释;3)通过融入前一帧的跟踪框作为额外的查询框,以查询方式简化了在线跟踪管道。复杂的数据关联被相对简单的非最大抑制(NMS)所取代。大量的实验结果表明,Siamese-DETR在GMOT-40数据集上的表现大大超过了现有的MOT方法。代码可在https://github.com/yumu-173/Siamese-DETR上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注通用多目标跟踪(GMOT),并提出了一种简单有效的Siamese-DETR方法。该方法无需昂贵的预训练(视觉)语言模型和精细类别的标注,仅使用通用的检测数据集进行训练。通过设计基于模板图像的多尺度目标查询,引入动态匹配训练策略,并简化在线跟踪管道,实现了对感兴趣对象的有效跟踪。在GMOT-40数据集上的实验结果表明,Siamese-DETR大幅度超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 本文关注通用多目标跟踪(GMOT),该领域对于超越预定义类别的感兴趣对象的跟踪具有重要意义。
- 提出的Siamese-DETR方法无需昂贵的预训练(视觉)语言模型和精细类别的标注,降低了训练成本。
- 方法通过设计基于模板图像的多尺度目标查询,增强了目标检测的准确性。
- 引入动态匹配训练策略,充分利用现有检测数据集进行训练。
- 简化了在线跟踪管道,通过查询方式融入前一帧的跟踪框,减少了复杂的数据关联过程。
- 采用非极大值抑制(NMS)替代复杂的数据关联,提高了跟踪效率。
- 在GMOT-40数据集上的实验结果表明,Siamese-DETR性能显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

GUPNet++: Geometry Uncertainty Propagation Network for Monocular 3D Object Detection
Authors:Yan Lu, Xinzhu Ma, Lei Yang, Tianzhu Zhang, Yating Liu, Qi Chu, Tong He, Yonghui Li, Wanli Ouyang
Geometry plays a significant role in monocular 3D object detection. It can be used to estimate object depth by using the perspective projection between object’s physical size and 2D projection in the image plane, which can introduce mathematical priors into deep models. However, this projection process also introduces error amplification, where the error of the estimated height is amplified and reflected into the projected depth. It leads to unreliable depth inferences and also impairs training stability. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel Geometry Uncertainty Propagation Network (GUPNet++) by modeling geometry projection in a probabilistic manner. This ensures depth predictions are well-bounded and associated with a reasonable uncertainty. The significance of introducing such geometric uncertainty is two-fold: (1). It models the uncertainty propagation relationship of the geometry projection during training, improving the stability and efficiency of the end-to-end model learning. (2). It can be derived to a highly reliable confidence to indicate the quality of the 3D detection result, enabling more reliable detection inference. Experiments show that the proposed approach not only obtains (state-of-the-art) SOTA performance in image-based monocular 3D detection but also demonstrates superiority in efficacy with a simplified framework.
几何在单目3D目标检测中扮演着重要角色。它可以通过目标物理尺寸与图像平面上2D投影之间的透视投影来估计目标深度,从而将数学先验知识引入深度模型。然而,这个投影过程也会带来误差放大,估计高度的误差会被放大并反映到投影深度上。这导致了深度推断不可靠,也影响了训练稳定性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新型的几何不确定性传播网络(GUPNet++),以概率方式建模几何投影。这确保了深度预测是明确的,并与合理的不确定性相关联。引入这种几何不确定性的重要性有两方面:(1)它建模了训练过程中几何投影的不确定性传播关系,提高了端到端模型学习的稳定性和效率。(2)它可以推导出一个高度可靠的置信度,以指示3D检测结果的质量,从而实现更可靠的检测推断。实验表明,所提出的方法不仅在基于图像的单目3D检测中达到了(最新技术水平的)顶尖性能,而且在具有简化框架的情况下也显示了其优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 9 figures
Summary
几何在单目3D物体检测中作用显著。利用物体物理尺寸与图像平面上2D投影之间的透视投影估计物体深度,可将数学先验知识引入深度模型。然而,此投影过程会引入误差放大,估计高度误差会被放大并反映到投影深度上,导致深度推断不可靠,并影响训练稳定性。为解决这一问题,我们提出一种新型几何不确定性传播网络(GUPNet++),以概率方式建模几何投影。这确保深度预测被良好界定,并与合理的不确定性相关联。引入这种几何不确定性的重要性有两方面:(1)它模拟了训练过程中几何投影的不确定性传播关系,提高了端到端模型学习的稳定性和效率。(2)它可以推导出高度可靠的置信度,以指示3D检测结果的质量,使检测推断更加可靠。实验表明,该方法不仅在基于图像的单目3D检测中达到(最新)先进水平,而且在具有简化框架的情况下也显示出其高效性。
Key Takeaways
- 几何在单目3D物体检测中非常重要,可以通过透视投影估计物体深度。
- 投影过程会引入误差放大,影响深度推断的可靠性和训练稳定性。
- 提出了一种新的几何不确定性传播网络(GUPNet++),以概率方式处理几何投影。
- 引入几何不确定性的重要性在于提高模型学习的稳定性和效率,并可以指示3D检测结果的质量。
- GUPNet++通过建模几何投影的不确定性传播关系,改进了端到端模型的学习。
- 实验表明,GUPNet++在单目3D检测中表现优异,达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图