⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-09 更新
MC-VTON: Minimal Control Virtual Try-On Diffusion Transformer
Authors:Junsheng Luan, Guangyuan Li, Lei Zhao, Wei Xing
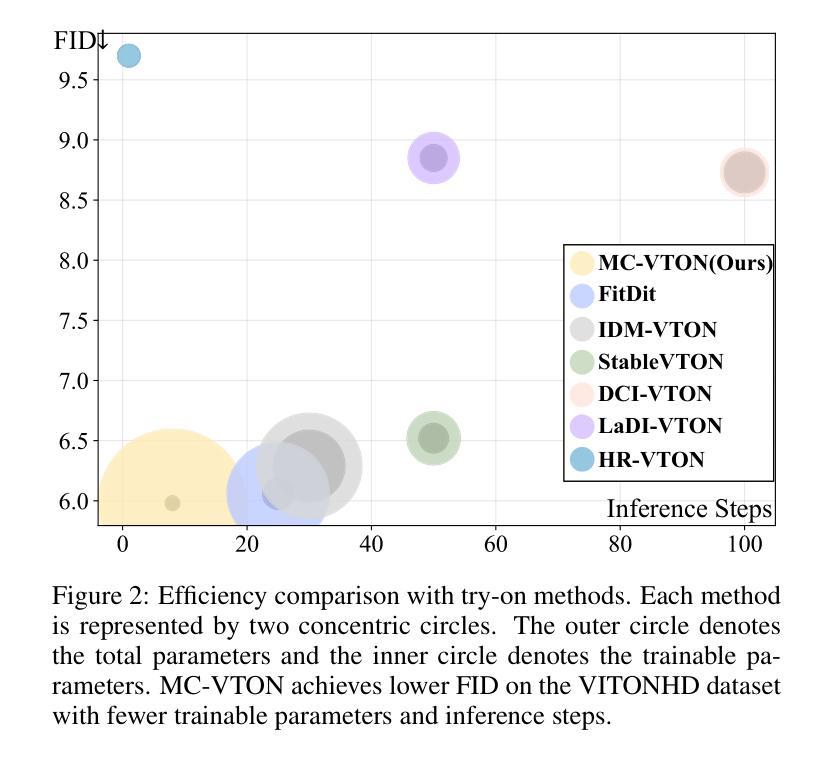
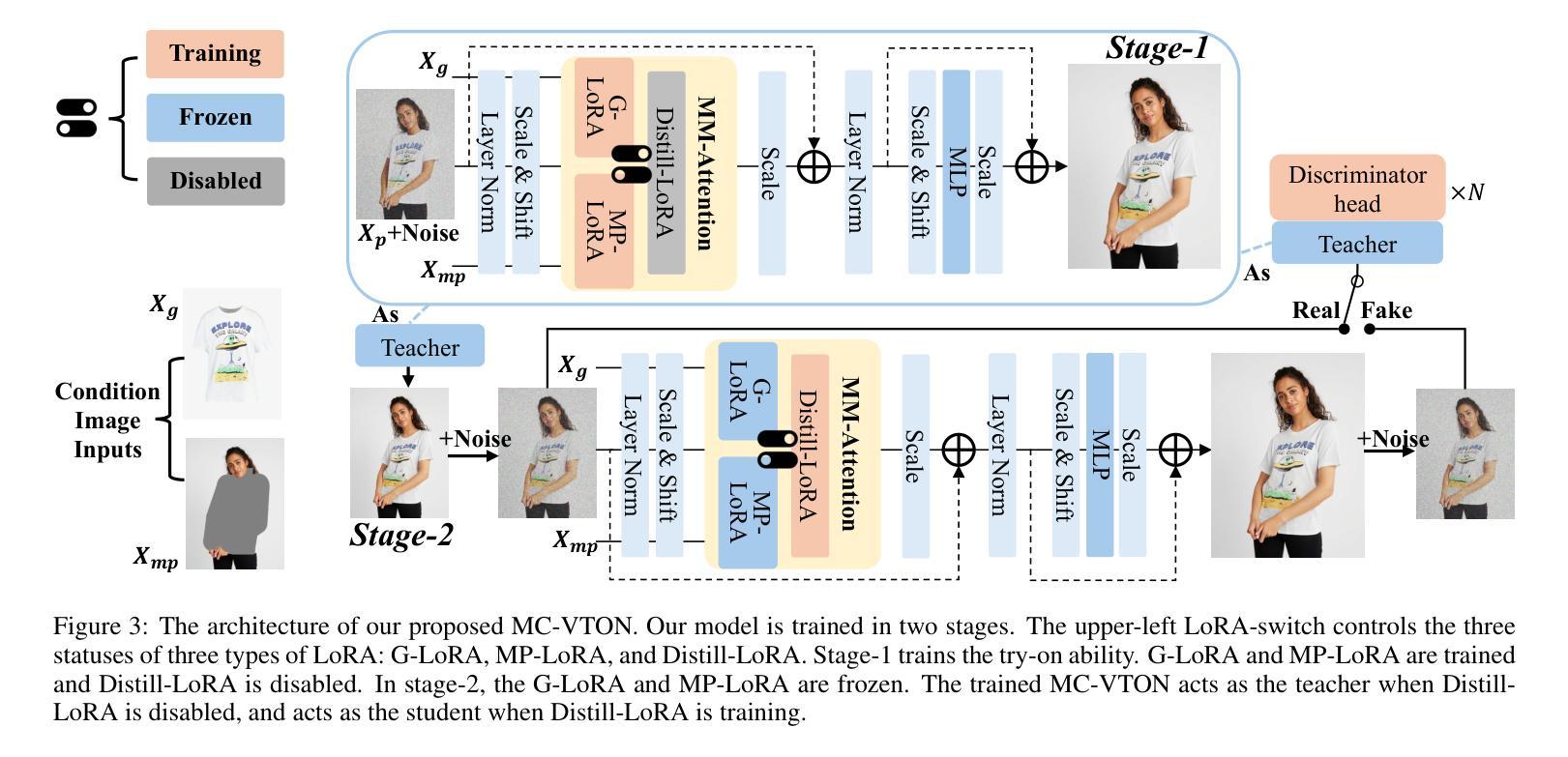
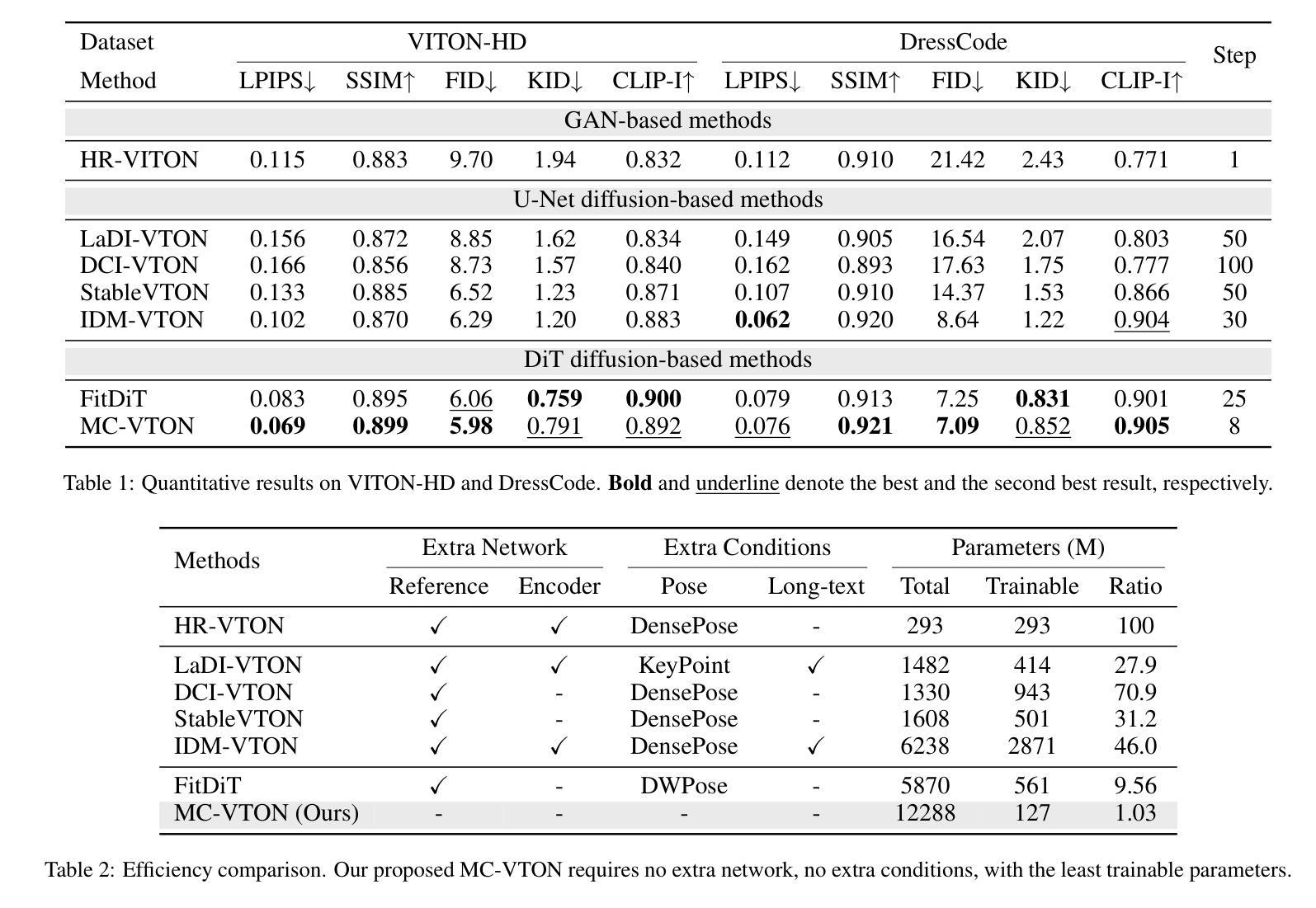
Virtual try-on methods based on diffusion models achieve realistic try-on effects. They use an extra reference network or an additional image encoder to process multiple conditional image inputs, which results in high training costs. Besides, they require more than 25 inference steps, bringing a long inference time. In this work, with the development of diffusion transformer (DiT), we rethink the necessity of reference network or image encoder, then propose MC-VTON, enabling DiT to integrate minimal conditional try-on inputs by utilizing its intrinsic backbone. Compared to existing methods, the superiority of MC-VTON is demonstrated in four aspects: (1)Superior detail fidelity. Our DiT-based MC-VTON exhibits superior fidelity in preserving fine-grained details. (2)Simplified network and inputs. We remove any extra reference network or image encoder. We also remove unnecessary conditions like the long prompt, pose estimation, human parsing, and depth map. We require only the masked person image and the garment image. (3)Parameter-efficient training. To process the try-on task, we fine-tune the FLUX.1-dev with only 39.7M additional parameters 0.33% of the backbone parameters). (4)Less inference steps. We apply distillation diffusion on MC-VTON and only need 8 steps to generate a realistic try-on image, with only 86.8M additional parameters (0.72% of the backbone parameters). Experiments show that MC-VTON achieves superior qualitative and quantitative results with fewer condition inputs, fewer inference steps, and fewer trainable parameters than baseline methods.
基于扩散模型的虚拟试穿方法实现了逼真的试穿效果。它们使用额外的参考网络或图像编码器来处理多个条件图像输入,这导致了较高的训练成本。此外,它们需要超过25步推理,导致推理时间较长。在这项工作中,随着扩散变压器(DiT)的发展,我们重新思考了参考网络或图像编码器的必要性,然后提出了MC-VTON,使DiT能够通过其内在骨干整合最少的条件试穿输入。与现有方法相比,MC-VTON在四个方面表现出优越性:(1)出色的细节保真度。我们基于DiT的MC-VTON在保持细节方面表现出卓越的保真度。(2)简化的网络和输入。我们移除了任何额外的参考网络或图像编码器。我们还移除了不必要的条件,如长提示、姿势估计、人类解析和深度图。我们只需要遮挡的人物图像和服装图像。(3)高效的参数训练。为了处理试穿任务,我们只使用额外的参数为FLUX微调版开发轻量级训练流程即可完成整个模型的训练过程。(目前我们训练的是使用Flux架构的一个变种版本。)在微调FLUX的基础上只使用39.7M的参数进行训练,仅占总参数的0.33%。(该比例表示额外的参数相对于基础模型的规模很小。)此处的统计数据主要用于解释我们提出方法的参数效率。(在将来发布的版本中将更新详细数值。)只需使用少量的额外参数,我们可以显著增强性能并快速部署新的试用产品。用大量的公共数据进行优化甚至能达到一个不依赖任何特定模型架构的模型训练效果。(4)减少推理步骤。我们对MC-VTON应用蒸馏扩散,只需要8步即可生成逼真的试穿图像,只需要额外的参数86.8M(占骨干参数的0.72%)。实验表明,与基准方法相比,MC-VTON在条件输入较少、推理步骤较少和可训练参数较少的情况下实现了定性和定量结果的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于扩散模型的虚拟试穿方法能实现逼真的试穿效果。它们使用额外的参考网络或图像编码器来处理多个条件图像输入,导致训练成本较高。此外,它们需要超过25步的推理时间,导致推理时间较长。本研究通过发展扩散变压器(DiT),重新思考参考网络或图像编码器的必要性,然后提出MC-VTON,使DiT能够通过其内在骨干集成最少的条件试穿输入。相较于现有方法,MC-VTON在四个方面表现出卓越性:(1)卓越的细节保真度。(2)简化的网络和输入。(3)参数高效的训练。(4)较少的推理步骤。实验表明,MC-VTON在条件输入、推理步骤和可训练参数较少的情况下,较基线方法取得优越的质量和数量结果。
关键见解
- 基于扩散模型的虚拟试穿方法能实现高保真的试穿效果。
- 现有方法使用参考网络或图像编码器处理多条件图像输入,导致高训练成本。
- MC-VTON通过去除额外网络和不必要的条件输入(如长提示、姿势估计、人类解析和深度图),简化了流程和所需数据。
- MC-VTON仅需要遮罩的人物图像和服装图像作为输入。
- MC-VTON通过微调参数进行训练,仅需添加少量参数即可处理试穿任务。
- 通过蒸馏扩散,MC-VTON仅需要少量推理步骤即可生成逼真的试穿图像。
- 实验表明MC-VTON在条件输入、推理步骤和参数方面较基线方法有优越性。
点此查看论文截图


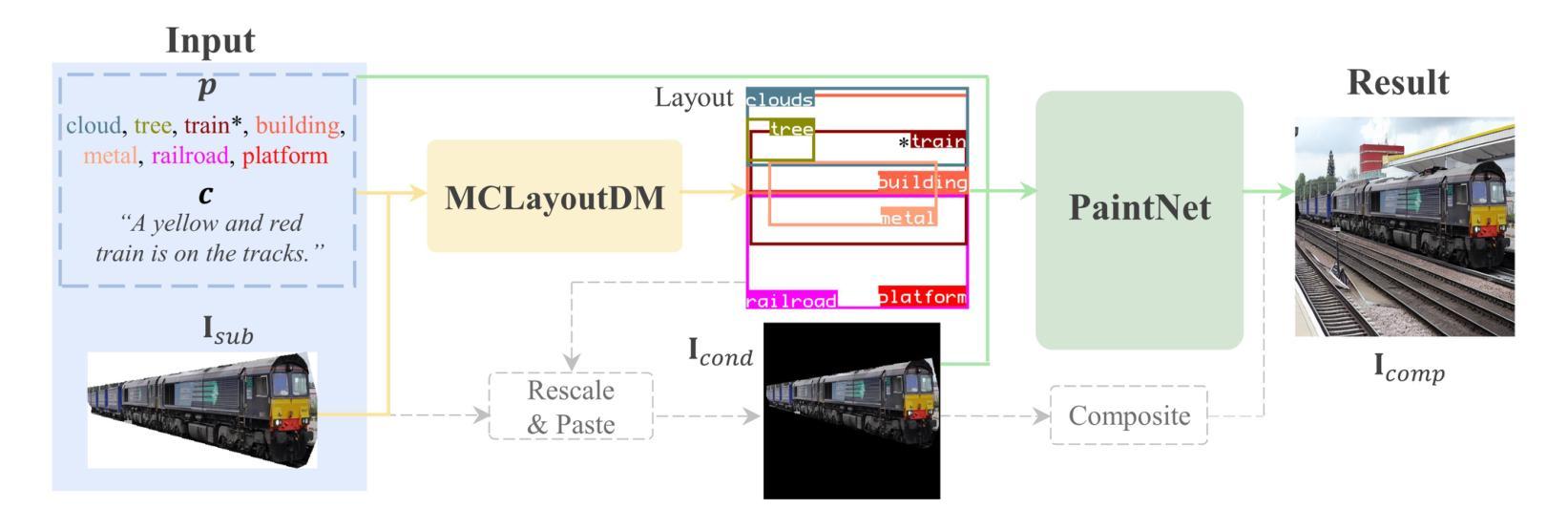
SceneBooth: Diffusion-based Framework for Subject-preserved Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Shang Chai, Zihang Lin, Min Zhou, Xubin Li, Liansheng Zhuang, Houqiang Li
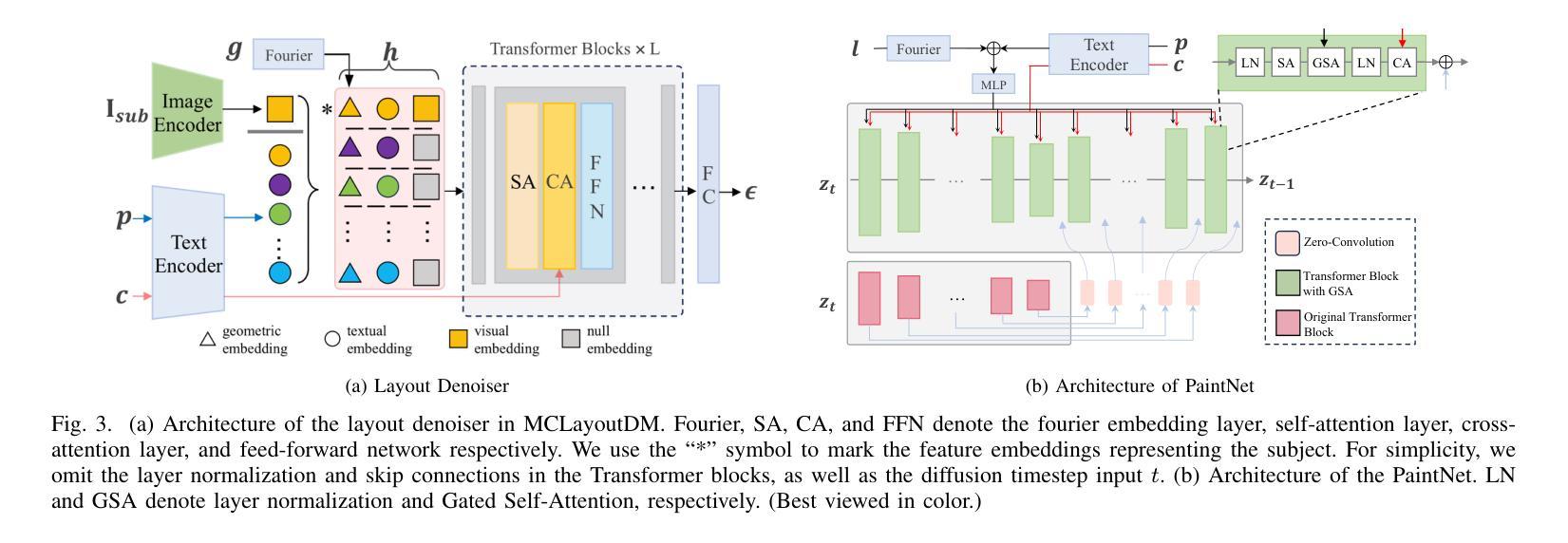
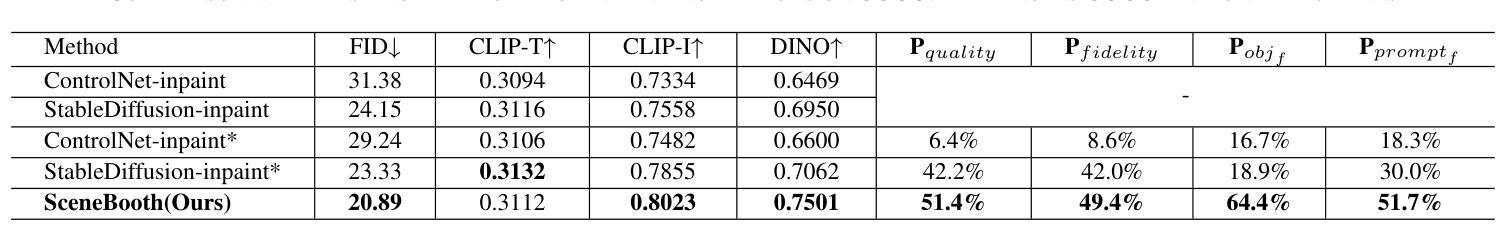
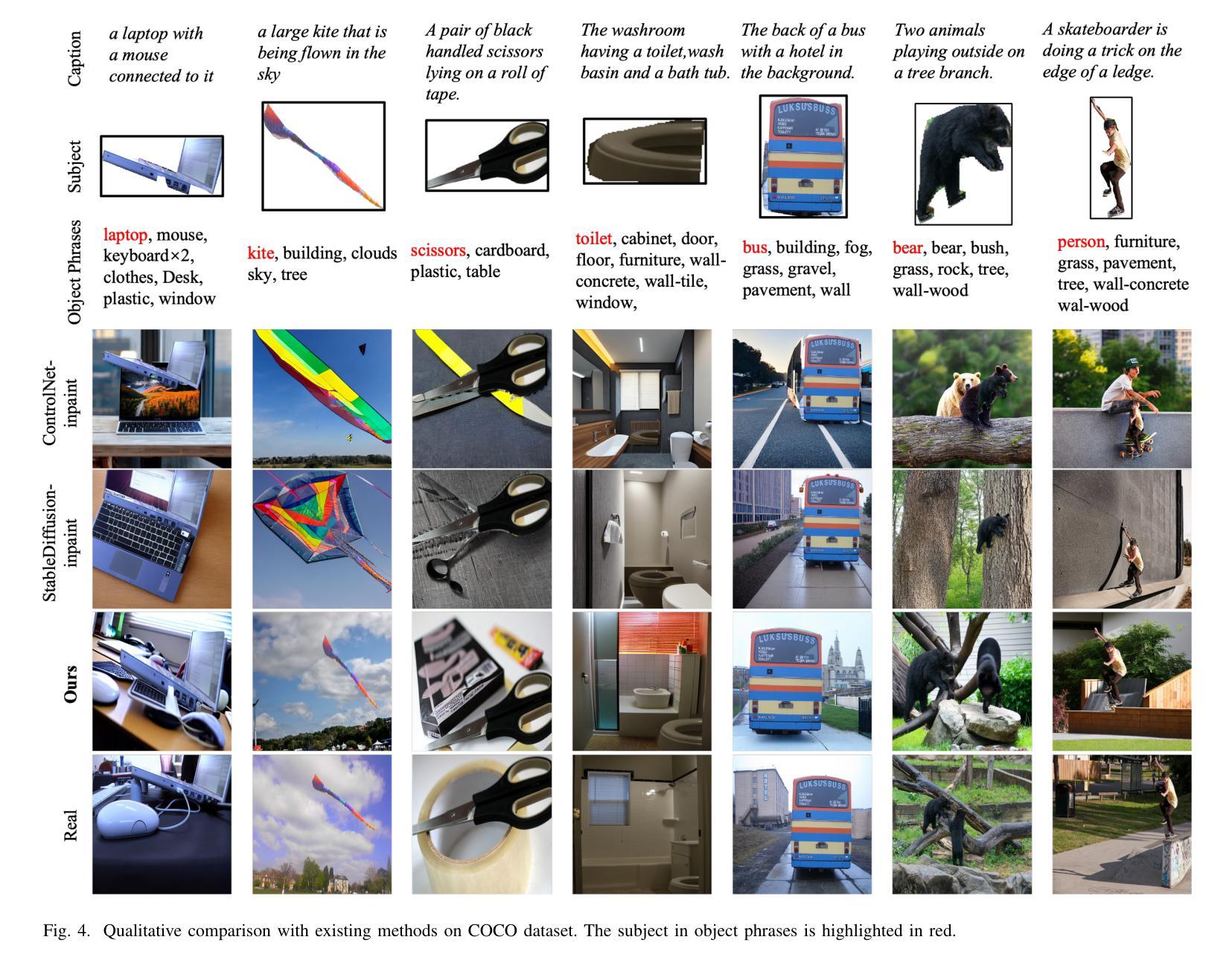
Due to the demand for personalizing image generation, subject-driven text-to-image generation method, which creates novel renditions of an input subject based on text prompts, has received growing research interest. Existing methods often learn subject representation and incorporate it into the prompt embedding to guide image generation, but they struggle with preserving subject fidelity. To solve this issue, this paper approaches a novel framework named SceneBooth for subject-preserved text-to-image generation, which consumes inputs of a subject image, object phrases and text prompts. Instead of learning the subject representation and generating a subject, our SceneBooth fixes the given subject image and generates its background image guided by the text prompts. To this end, our SceneBooth introduces two key components, i.e., a multimodal layout generation module and a background painting module. The former determines the position and scale of the subject by generating appropriate scene layouts that align with text captions, object phrases, and subject visual information. The latter integrates two adapters (ControlNet and Gated Self-Attention) into the latent diffusion model to generate a background that harmonizes with the subject guided by scene layouts and text descriptions. In this manner, our SceneBooth ensures accurate preservation of the subject’s appearance in the output. Quantitative and qualitative experimental results demonstrate that SceneBooth significantly outperforms baseline methods in terms of subject preservation, image harmonization and overall quality.
由于个性化图像生成的需求,以主题为驱动的文本到图像生成方法越来越受到研究关注。该方法根据文本提示创建输入主题的新版本。现有方法通常学习主题表示并将其融入提示嵌入来引导图像生成,但它们难以保持主题保真度。为了解决这一问题,本文提出了一种名为SceneBooth的新型框架,用于主题保留的文本到图像生成。SceneBooth接受主题图像、对象短语和文本提示作为输入。我们的SceneBooth不是学习主题表示并生成主题,而是固定给定的主题图像,并由文本提示引导生成其背景图像。为此,SceneBooth引入了两个关键组件,即多模式布局生成模块和背景绘画模块。前者通过生成与文本描述、对象短语和主题视觉信息对齐的场景布局来确定主题的位置和比例。后者将ControlNet和Gated Self-Attention两个适配器集成到潜在扩散模型中,根据场景布局和文本描述生成与主题协调的背景。通过这种方式,SceneBooth确保输出中主题的外观得到准确保留。定量和定性的实验结果表明,SceneBooth在主题保留、图像和谐度和整体质量方面显著优于基线方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了针对个性化图像生成需求的主体驱动文本到图像生成方法。现有方法往往学习主体表示并将其融入提示嵌入以指导图像生成,但难以保持主体保真度。本文提出了一种名为SceneBooth的新框架,它通过输入主体图像、对象短语和文本提示来解决这一问题。SceneBooth固定给定主体图像,并受文本提示引导生成背景图像。它引入了两个关键组件:多模态布局生成模块和背景绘画模块。前者通过生成与文本描述、对象短语和主题视觉信息对齐的场景布局来确定主体的位置和比例。后者将两个适配器(ControlNet和门控自注意力)集成到潜在扩散模型中,以根据场景布局和文本描述生成与主体协调的背景。SceneBooth确保了输出中主体外观的准确保留。实验结果表明,SceneBooth在主体保留、图像和谐度和整体质量方面显著优于基准方法。
Key Takeaways
- 文本描述了主体驱动文本到图像生成方法的研究现状和发展趋势。
- 现有方法在保留主体保真度方面存在挑战。
- SceneBooth框架通过固定主体图像并生成背景图像来解决这个问题。
- SceneBooth引入了多模态布局生成模块和背景绘画模块两个关键组件。
- 多模态布局生成模块通过生成场景布局来确定主体的位置和比例。
- 背景绘画模块集成适配器来生成与主体协调的背景。
点此查看论文截图
License Plate Images Generation with Diffusion Models
Authors:Mariia Shpir, Nadiya Shvai, Amir Nakib
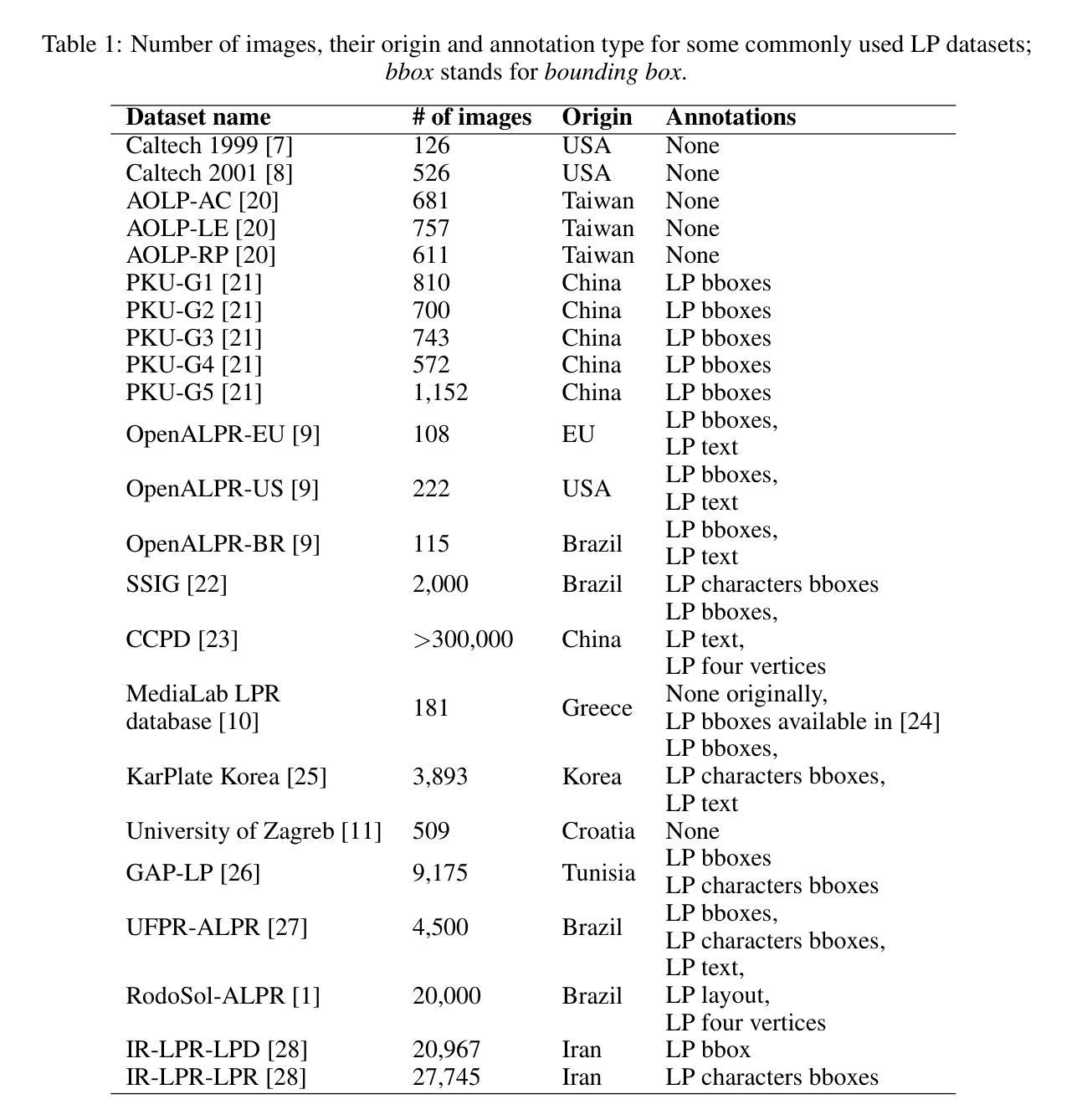
Despite the evident practical importance of license plate recognition (LPR), corresponding research is limited by the volume of publicly available datasets due to privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). To address this challenge, synthetic data generation has emerged as a promising approach. In this paper, we propose to synthesize realistic license plates (LPs) using diffusion models, inspired by recent advances in image and video generation. In our experiments a diffusion model was successfully trained on a Ukrainian LP dataset, and 1000 synthetic images were generated for detailed analysis. Through manual classification and annotation of the generated images, we performed a thorough study of the model output, such as success rate, character distributions, and type of failures. Our contributions include experimental validation of the efficacy of diffusion models for LP synthesis, along with insights into the characteristics of the generated data. Furthermore, we have prepared a synthetic dataset consisting of 10,000 LP images, publicly available at https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.13342102. Conducted experiments empirically confirm the usefulness of synthetic data for the LPR task. Despite the initial performance gap between the model trained with real and synthetic data, the expansion of the training data set with pseudolabeled synthetic data leads to an improvement in LPR accuracy by 3% compared to baseline.
尽管车牌识别(LPR)在实际应用中具有重要意义,但由于《通用数据保护条例》(GDPR)等隐私法规的限制,相关研究受到公开可用数据集数量的限制。为了应对这一挑战,合成数据生成作为一种有前景的方法而出现。在本文中,我们提出利用扩散模型合成逼真的车牌(LPs),这一想法受到图像和视频生成方面最新进展的启发。我们在乌克兰车牌数据集上成功训练了扩散模型,并生成了1000张合成图像进行详细分析。通过对生成图像的手动分类和注释,我们对模型输出进行了深入研究,如成功率、字符分布和失败类型。我们的贡献包括扩散模型在车牌合成中的有效性实验验证,以及关于生成数据特性的见解。此外,我们还准备了一个包含10000张车牌图像的合成数据集,可在https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.13342102上公开获取。进行的实验经验性证实了合成数据对于车牌识别任务的有用性。尽管用真实和合成数据训练的模型之间存在初步性能差距,但通过用伪标签合成数据扩展训练数据集,与基线相比,车牌识别准确率提高了3%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
车牌识别(LPR)的研究受限于公开可用数据集的数量,由于隐私法规如通用数据保护条例(GDPR)的制约。为应对这一挑战,本文提出利用扩散模型生成真实车牌的合成数据。实验证明,扩散模型在乌克兰车牌数据集上的训练成功,生成了1000张合成图像。通过手动分类和标注生成的图像,对模型输出进行了深入研究。本文的贡献包括扩散模型在车牌合成中的有效性实验验证,以及生成数据的特性洞察。此外,我们公开提供了一个包含10,000张车牌合成图像的数据集。实验证实,合成数据对于车牌识别任务非常有用。
Key Takeaways
- 隐私法规限制了车牌识别(LPR)研究可用的公开数据集。
- 合成数据生成是解决这一挑战的有前途的方法。
- 扩散模型被成功训练用于生成乌克兰车牌的合成图像。
- 手动分类和标注生成的图像,对模型输出进行了深入研究。
- 实验验证了扩散模型在车牌合成中的有效性。
- 合成数据对于车牌识别任务非常有用,公开了一个包含大量车牌合成图像的数据集。
点此查看论文截图


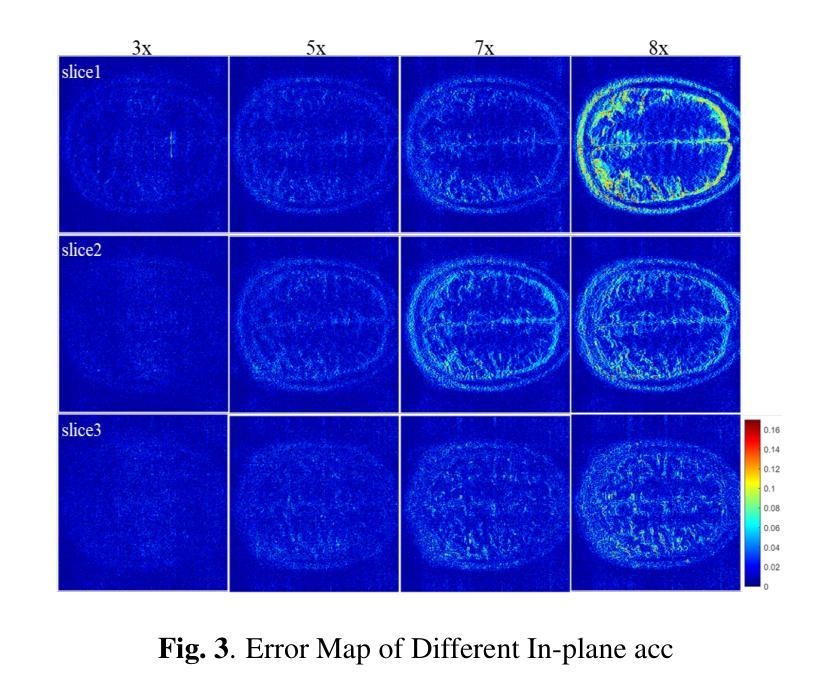
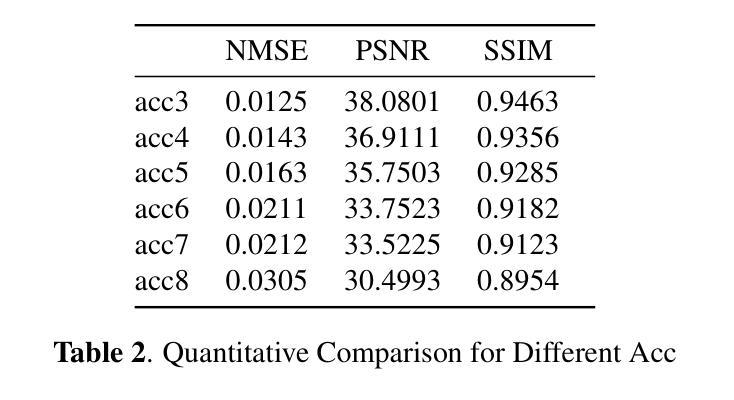
K-space Diffusion Model Based MR Reconstruction Method for Simultaneous Multislice Imaging
Authors:Ting Zhao, Zhuoxu Cui, Congcong Liu, Xingyang Wu, Yihang Zhou, Dong Liang, Haifeng Wang
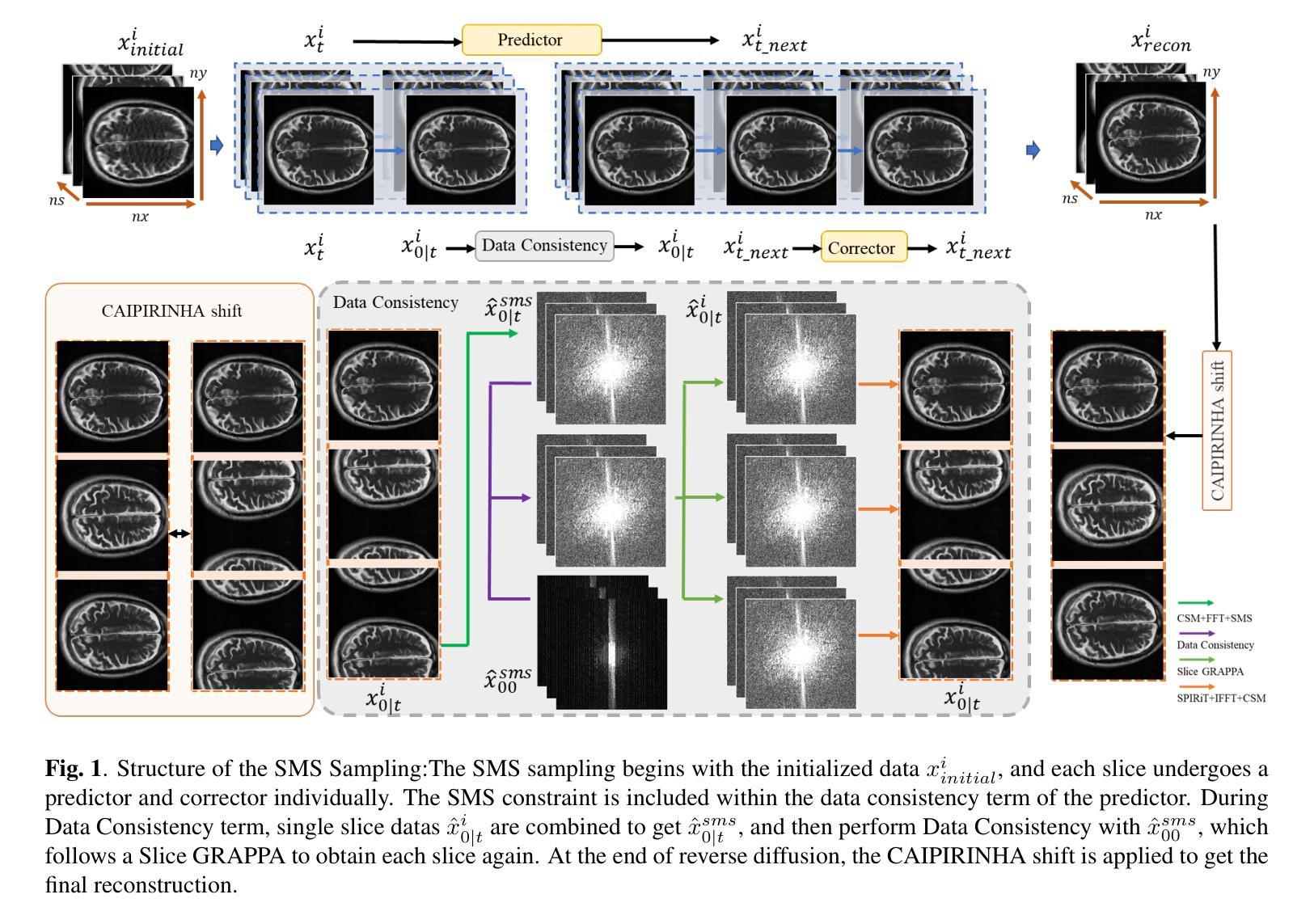
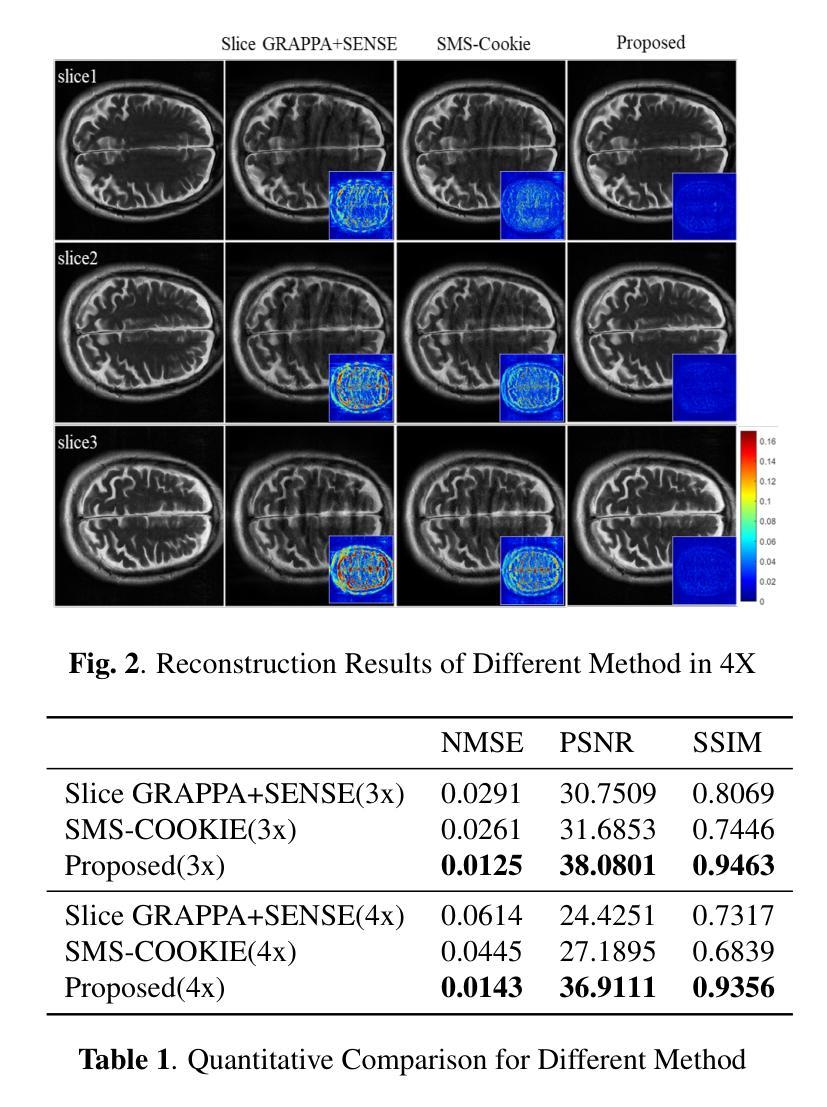
Simultaneous Multi-Slice(SMS) is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique which excites several slices concurrently using multiband radiofrequency pulses to reduce scanning time. However, due to its variable data structure and difficulty in acquisition, it is challenging to integrate SMS data as training data into deep learning frameworks.This study proposed a novel k-space diffusion model of SMS reconstruction that does not utilize SMS data for training. Instead, it incorporates Slice GRAPPA during the sampling process to reconstruct SMS data from different acquisition modes.Our results demonstrated that this method outperforms traditional SMS reconstruction methods and can achieve higher acceleration factors without in-plane aliasing.
同时多切片(Simultaneous Multi-Slice,简称SMS)是一种磁共振成像(MRI)技术,它通过多频带射频脉冲同时激发多个切片,以缩短扫描时间。然而,由于它的数据结构多变且采集困难,将SMS数据作为训练数据集成到深度学习框架中是一项挑战。本研究提出了一种新型的k空间扩散模型SMS重建方法,该方法不使用SMS数据进行训练。相反,它在采样过程中采用了Slice GRAPPA,从不同采集模式重建SMS数据。我们的结果表明,该方法优于传统SMS重建方法,可在不出现平面混叠的情况下实现更高的加速因子。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 3 figures
Summary
该文本介绍了一种名为Simultaneous Multi-Slice(SMS)的磁共振成像技术及其在深度学习框架中的应用挑战。该研究提出了一种新的k空间扩散模型进行SMS重建,其不依赖SMS数据进行训练,而是在采样过程中采用Slice GRAPPA技术从不同采集模式重建SMS数据。此方法表现优于传统SMS重建方法,能在不产生平面混叠的情况下实现更高的加速因子。
Key Takeaways
- Simultaneous Multi-Slice(SMS)是一种磁共振成像技术,通过多频带射频脉冲同时激发多个切片,以缩短扫描时间。
- SMS数据由于其数据结构变化和采集难度,难以整合到深度学习框架中进行训练。
- 研究提出了一种新的k空间扩散模型进行SMS重建,该模型不依赖SMS数据进行训练。
- 新的模型通过采用Slice GRAPPA技术在采样过程中进行重建,能够从不同采集模式重建SMS数据。
- 该方法表现优于传统SMS重建方法。
- 新的模型能在不产生平面混叠的情况下实现更高的加速因子。
点此查看论文截图

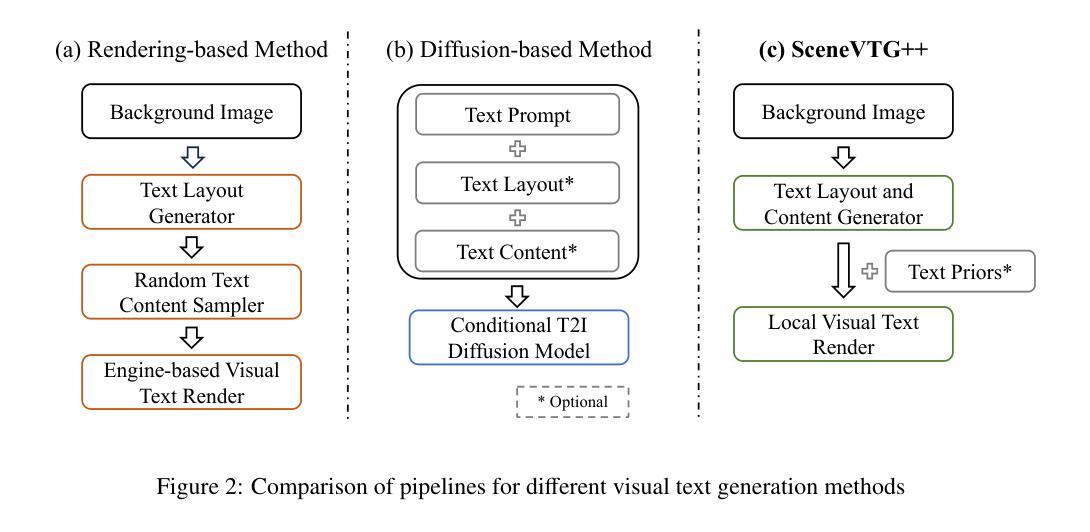
SceneVTG++: Controllable Multilingual Visual Text Generation in the Wild
Authors:Jiawei Liu, Yuanzhi Zhu, Feiyu Gao, Zhibo Yang, Peng Wang, Junyang Lin, Xinggang Wang, Wenyu Liu
Generating visual text in natural scene images is a challenging task with many unsolved problems. Different from generating text on artificially designed images (such as posters, covers, cartoons, etc.), the text in natural scene images needs to meet the following four key criteria: (1) Fidelity: the generated text should appear as realistic as a photograph and be completely accurate, with no errors in any of the strokes. (2) Reasonability: the text should be generated on reasonable carrier areas (such as boards, signs, walls, etc.), and the generated text content should also be relevant to the scene. (3) Utility: the generated text can facilitate to the training of natural scene OCR (Optical Character Recognition) tasks. (4) Controllability: The attribute of the text (such as font and color) should be controllable as needed. In this paper, we propose a two stage method, SceneVTG++, which simultaneously satisfies the four aspects mentioned above. SceneVTG++ consists of a Text Layout and Content Generator (TLCG) and a Controllable Local Text Diffusion (CLTD). The former utilizes the world knowledge of multi modal large language models to find reasonable text areas and recommend text content according to the nature scene background images, while the latter generates controllable multilingual text based on the diffusion model. Through extensive experiments, we respectively verified the effectiveness of TLCG and CLTD, and demonstrated the state-of-the-art text generation performance of SceneVTG++. In addition, the generated images have superior utility in OCR tasks like text detection and text recognition. Codes and datasets will be available.
生成自然场景图像中的文本是一项具有许多未解决问题且具有挑战性的任务。与在人工设计的图像(如海报、封面、漫画等)上生成文本不同,自然场景图像中的文本需要满足以下四个关键标准:(1)保真度:生成的文本应看起来尽可能逼真,并且完全准确,没有任何笔画错误。(2)合理性:文本应在合理的载体区域(如板报、标志、墙壁等)上生成,并且生成的文本内容应与场景相关。(3)实用性:生成的文本有助于自然场景OCR(光学字符识别)任务的训练。(4)可控性:文本的属性(如字体和颜色)应根据需要可控。在本文中,我们提出了一种两阶段方法SceneVTG++,它同时满足上述四个方面。SceneVTG++包括文本布局和内容生成器(TLCG)和可控局部文本扩散(CLTD)。前者利用多模态大型语言模型的世界知识,根据自然场景背景图像找到合理的文本区域并推荐文本内容,后者基于扩散模型生成可控的多语言文本。通过大量实验,我们分别验证了TLCG和CLTD的有效性,并展示了SceneVTG++的先进文本生成性能。此外,生成的图像在OCR任务(如文本检测和文本识别)中具有出色的实用性。代码和数据集将可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种两阶段方法SceneVTG++用于生成自然场景图像中的视觉文本,满足真实性、合理性、实用性和可控性四个关键标准。该方法包括文本布局和内容生成器(TLCG)和可控局部文本扩散(CLTD)。TLCG利用多模态大型语言模型的世界知识来寻找合理的文本区域并根据自然场景背景图像推荐文本内容。CLTD则基于扩散模型生成可控的多语言文本。实验证明TLCG和CLTD的有效性,并展示了SceneVTG++在文本生成方面的卓越性能,生成的图像在OCR任务中具有出色的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 自然场景图像中的文本生成具有挑战性,需满足真实性、合理性、实用性和可控性四个关键标准。
- SceneVTG++是一种两阶段方法,包括文本布局和内容生成器(TLCG)和可控局部文本扩散(CLTD)。
- TLCG利用多模态大型语言模型的世界知识寻找合理的文本区域并推荐相关文本内容。
- CLTD基于扩散模型生成可控的多语言文本。
- 实验证明TLCG和CLTD的有效性,SceneVTG++在文本生成方面表现出卓越性能。
- 生成的图像在OCR任务中具有出色的实用性。
点此查看论文截图


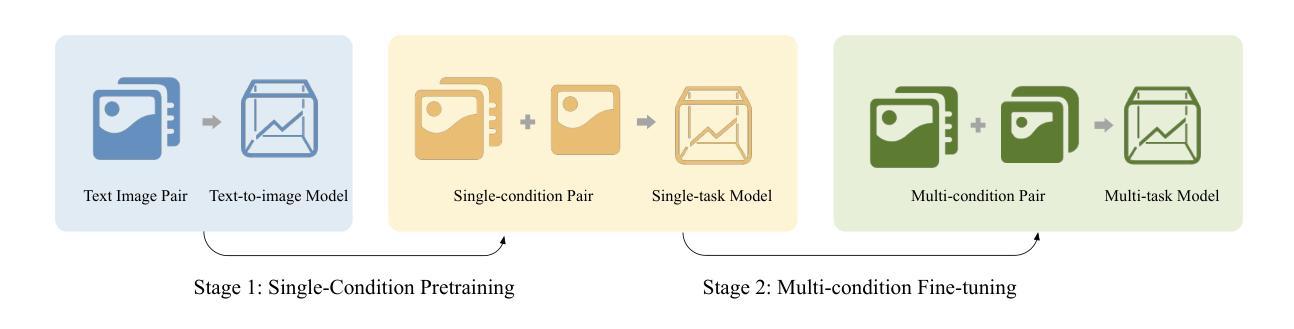
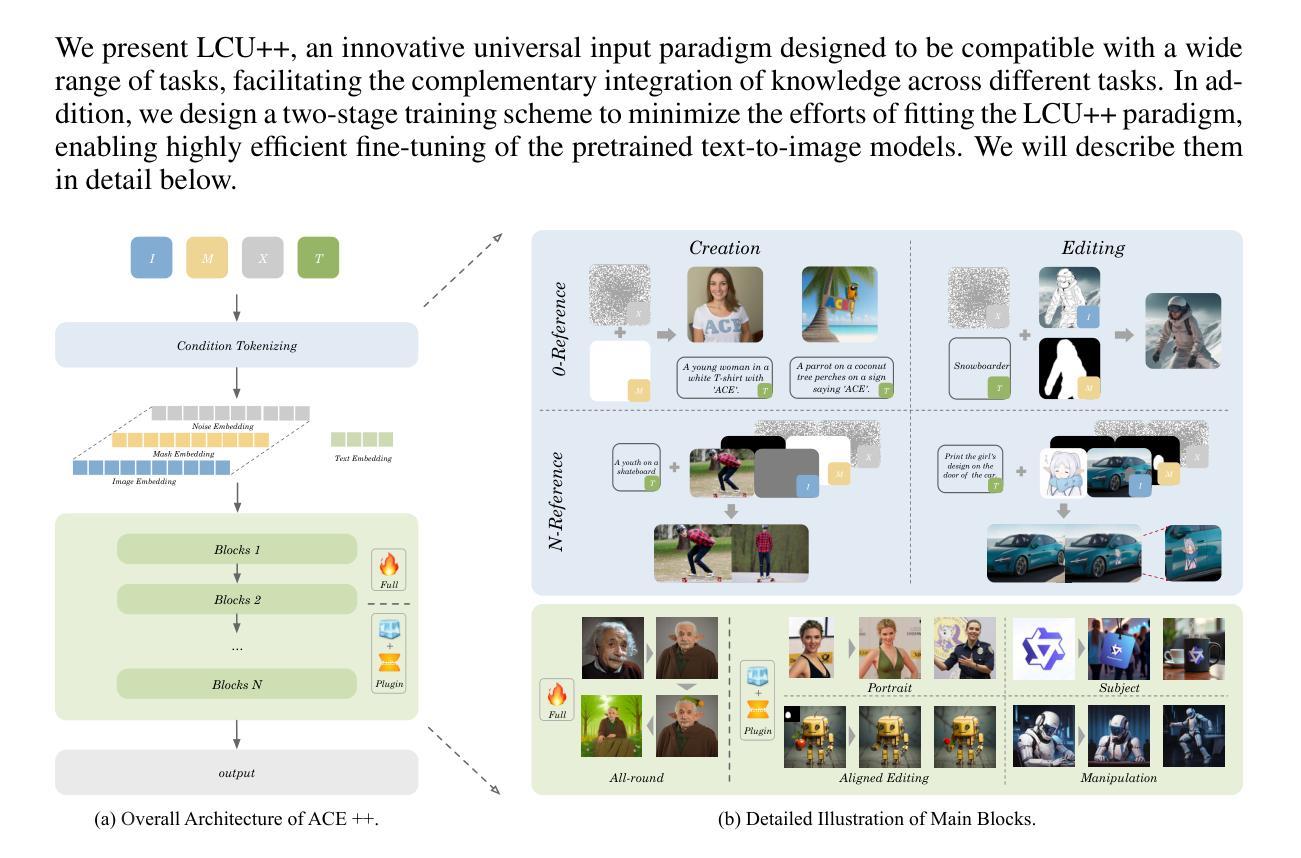
ACE++: Instruction-Based Image Creation and Editing via Context-Aware Content Filling
Authors:Chaojie Mao, Jingfeng Zhang, Yulin Pan, Zeyinzi Jiang, Zhen Han, Yu Liu, Jingren Zhou
We report ACE++, an instruction-based diffusion framework that tackles various image generation and editing tasks. Inspired by the input format for the inpainting task proposed by FLUX.1-Fill-dev, we improve the Long-context Condition Unit (LCU) introduced in ACE and extend this input paradigm to any editing and generation tasks. To take full advantage of image generative priors, we develop a two-stage training scheme to minimize the efforts of finetuning powerful text-to-image diffusion models like FLUX.1-dev. In the first stage, we pre-train the model using task data with the 0-ref tasks from the text-to-image model. There are many models in the community based on the post-training of text-to-image foundational models that meet this training paradigm of the first stage. For example, FLUX.1-Fill-dev deals primarily with painting tasks and can be used as an initialization to accelerate the training process. In the second stage, we finetune the above model to support the general instructions using all tasks defined in ACE. To promote the widespread application of ACE++ in different scenarios, we provide a comprehensive set of models that cover both full finetuning and lightweight finetuning, while considering general applicability and applicability in vertical scenarios. The qualitative analysis showcases the superiority of ACE++ in terms of generating image quality and prompt following ability. Code and models will be available on the project page: https://ali-vilab. github.io/ACE_plus_page/.
我们报告了ACE++,这是一个基于指令的扩散框架,用于处理各种图像生成和编辑任务。我们受到FLUX.1-Fill-dev提出的补全任务输入格式的启发,改进了ACE中的长上下文条件单元(LCU),并将这一输入范式扩展到任何编辑和生成任务。为了充分利用图像生成的先验知识,我们开发了两阶段训练方案,以最小化调整强大文本到图像扩散模型(如FLUX.1-dev)的努力。在第一阶段,我们使用文本到图像模型的0-ref任务对模型进行预训练。社区中有许多基于文本到图像基础模型的后续训练模型,符合第一阶段的训练范式。例如,FLUX.1-Fill-dev主要处理绘画任务,并可作为初始化来加速训练过程。在第二阶段,我们对上述模型进行微调,以使用ACE中定义的所有任务来支持一般指令。为了促进ACE++在不同场景中的广泛应用,我们提供了一套全面的模型,包括完全微调和轻量级微调,同时考虑通用性和垂直场景的应用性。定性分析展示了ACE++在生成图像质量和遵循提示方面的优越性。代码和模型将在项目页面上进行公开:https://ali-vilab.github.io/ACE_plus_page/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ACE++是一个基于指令的扩散框架,用于处理各种图像生成和编辑任务。它改进了ACE中的长上下文条件单元(LCU),并扩展到任何编辑和生成任务。该框架采用两阶段训练方案,以充分利用图像生成先验知识,最小化对强大文本到图像扩散模型进行微调的努力。首先,使用文本到图像模型的0-ref任务进行模型预训练。然后,通过ACE定义的所有任务对模型进行微调,以支持一般指令。ACE++提供全面的模型,涵盖全量微调与轻量化微调,兼顾通用性和垂直场景应用。其生成的图像质量和遵循提示的能力均表现卓越。
Key Takeaways
- ACE++是一个基于指令的扩散框架,用于处理图像生成和编辑任务。
- 它改进并扩展了ACE中的LCU,以适应更多任务。
- ACE++采用两阶段训练方案,先预训练模型,再对模型进行微调以支持一般指令。
- 框架利用图像生成先验知识,最小化对强大文本到图像扩散模型的微调努力。
- ACE++提供全面的模型,满足不同需求和场景。
- ACE++在图像质量和遵循提示方面的表现卓越。
- 框架的代码和模型将在项目页面上进行共享。
点此查看论文截图

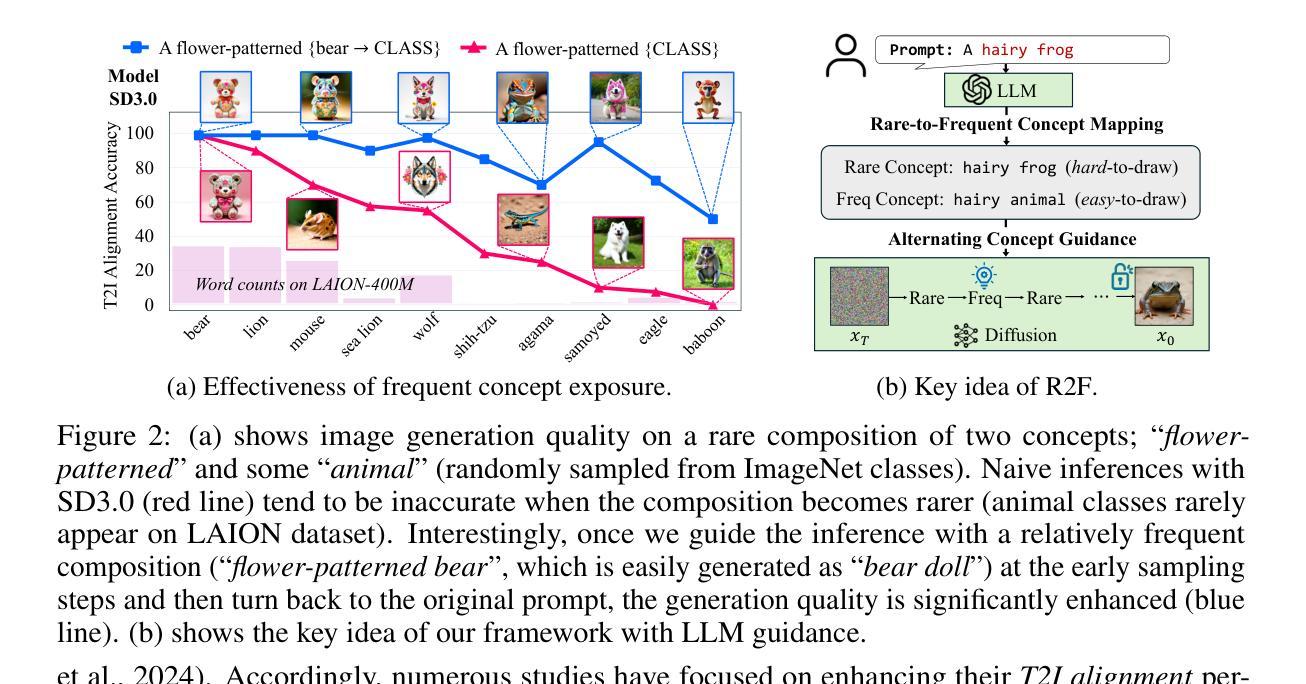
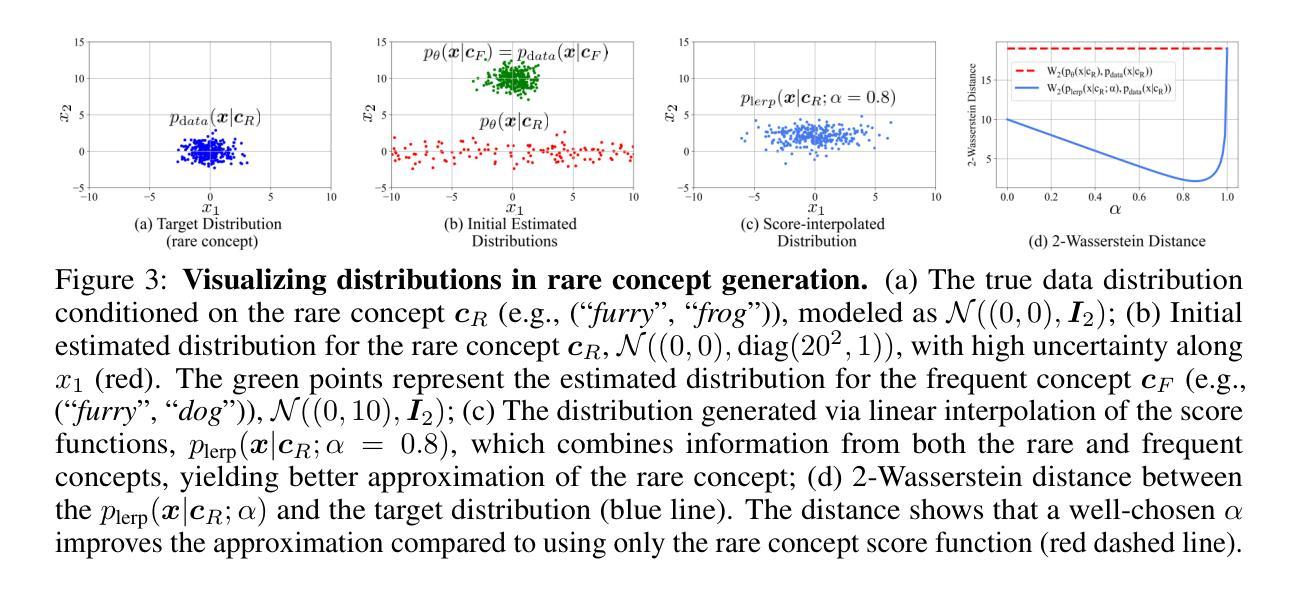
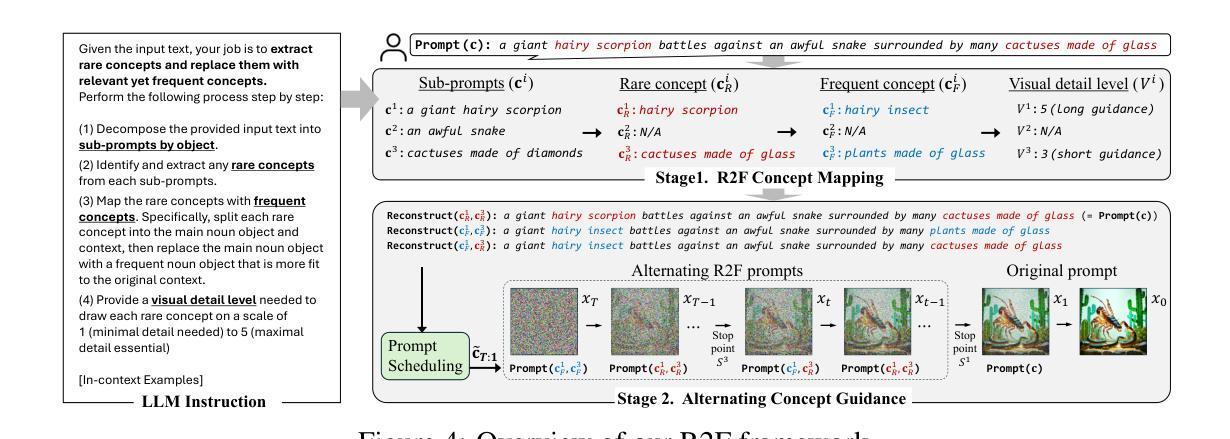
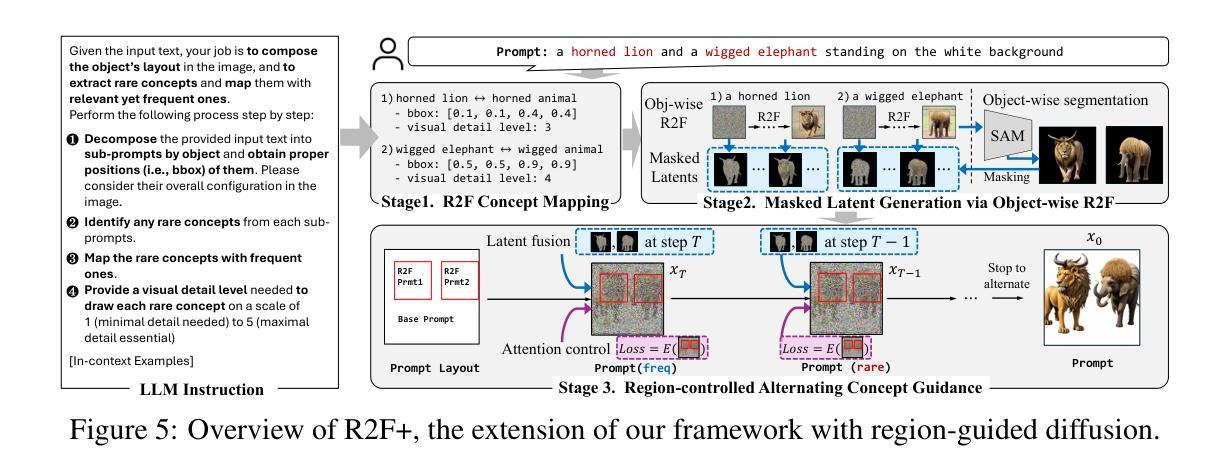
Rare-to-Frequent: Unlocking Compositional Generation Power of Diffusion Models on Rare Concepts with LLM Guidance
Authors:Dongmin Park, Sebin Kim, Taehong Moon, Minkyu Kim, Kangwook Lee, Jaewoong Cho
State-of-the-art text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models often struggle to generate rare compositions of concepts, e.g., objects with unusual attributes. In this paper, we show that the compositional generation power of diffusion models on such rare concepts can be significantly enhanced by the Large Language Model (LLM) guidance. We start with empirical and theoretical analysis, demonstrating that exposing frequent concepts relevant to the target rare concepts during the diffusion sampling process yields more accurate concept composition. Based on this, we propose a training-free approach, R2F, that plans and executes the overall rare-to-frequent concept guidance throughout the diffusion inference by leveraging the abundant semantic knowledge in LLMs. Our framework is flexible across any pre-trained diffusion models and LLMs, and can be seamlessly integrated with the region-guided diffusion approaches. Extensive experiments on three datasets, including our newly proposed benchmark, RareBench, containing various prompts with rare compositions of concepts, R2F significantly surpasses existing models including SD3.0 and FLUX by up to 28.1%p in T2I alignment. Code is available at https://github.com/krafton-ai/Rare-to-Frequent.
当前先进的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成罕见概念组合方面经常遇到困难,例如具有不寻常属性的物体。在本文中,我们展示了大语言模型(LLM)指导可以显著增强扩散模型在这种罕见概念上的组合生成能力。我们首先进行实证和理论分析,证明在扩散采样过程中暴露与目标罕见概念相关的频繁概念可以产生更精确的概念组合。基于此,我们提出了一种无需训练的方法R2F,它利用LLM中的丰富语义知识,通过扩散推理,规划和执行从罕见到频繁的整体概念指导。我们的框架灵活适用于任何预训练的扩散模型和语言大模型,并能无缝集成到区域引导的扩散方法中。在包括我们新提出的基准测试集RareBench在内的三个数据集上进行的大量实验表明,R2F在各种包含罕见概念组合的提示下,显著超越了SD3.0和FLUX模型,文本到图像的匹配度提高了高达28.1%。代码可在https://github.com/krafton-ai/Rare-to-Frequent找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成罕见概念组合时面临挑战。本文展示通过大型语言模型(LLM)指导,可以显著提高扩散模型在罕见概念上的组合生成能力。通过实证和理论分析,本文发现扩散采样过程中暴露与目标罕见概念相关的频繁概念,可以更准确地进行概念组合。基于此,本文提出了一种无需训练的方法R2F,利用LLM中的丰富语义知识,通过扩散推断,实现罕见到频繁的概念指导。该方法灵活适用于任何预训练的扩散模型和LLM,并可无缝集成到区域引导扩散方法中。在包括新提出的基准测试集RareBench在内的三个数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,R2F在T2I对齐方面显著超越了现有模型,包括SD3.0和FLUX,提高了高达28.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成罕见概念组合时存在挑战。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)指导有助于提高扩散模型在罕见概念上的组合生成能力。
- 在扩散采样过程中暴露与目标罕见概念相关的频繁概念,能更准确地进行概念组合。
- 提出了一种无需训练的方法R2F,通过利用LLM的丰富语义知识,实现罕见到频繁的概念指导。
- R2F方法灵活适用于各种预训练的扩散模型和LLM,并可集成到区域引导扩散方法中。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,R2F在T2I对齐方面显著优于现有模型。
- R2F方法的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

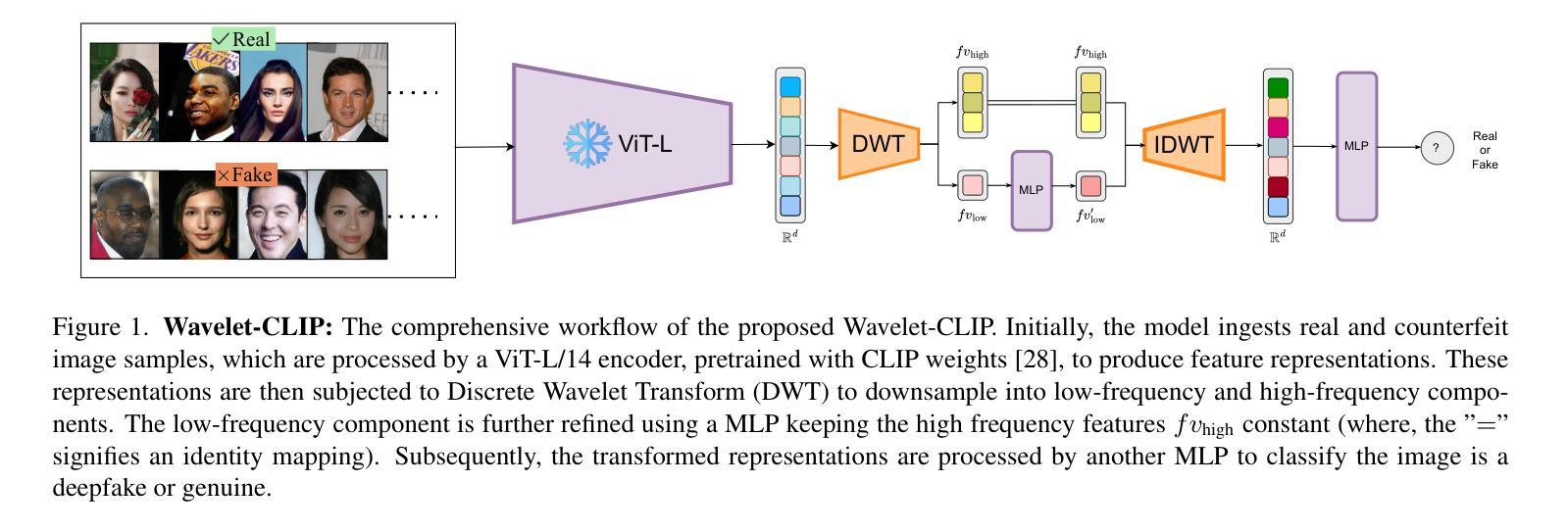
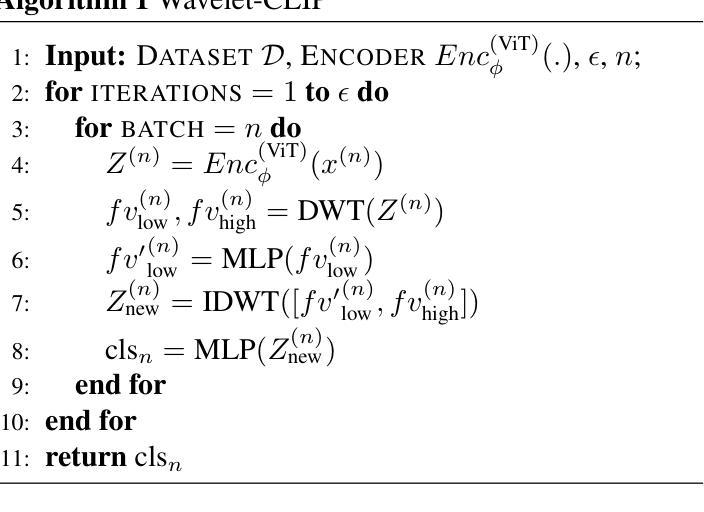
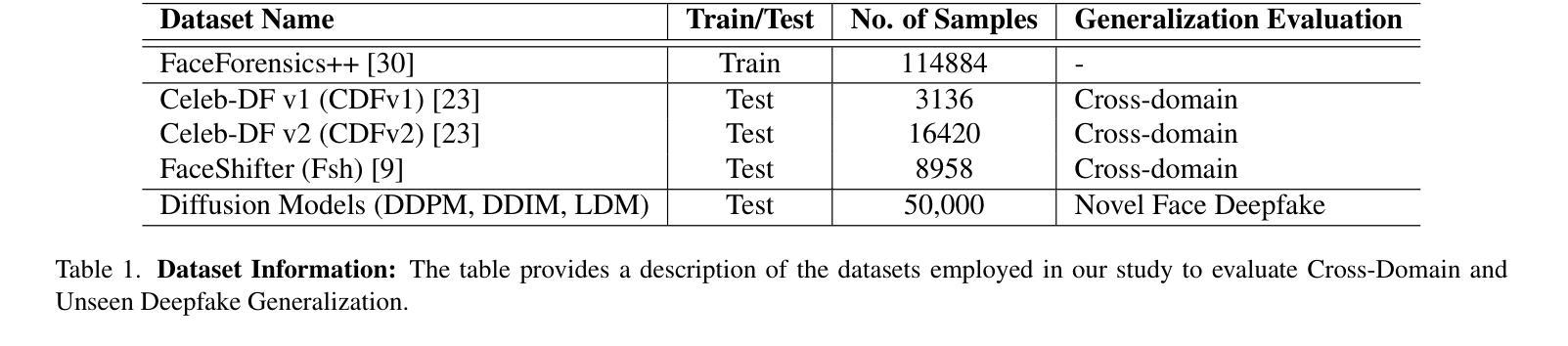
Wavelet-Driven Generalizable Framework for Deepfake Face Forgery Detection
Authors:Lalith Bharadwaj Baru, Rohit Boddeda, Shilhora Akshay Patel, Sai Mohan Gajapaka
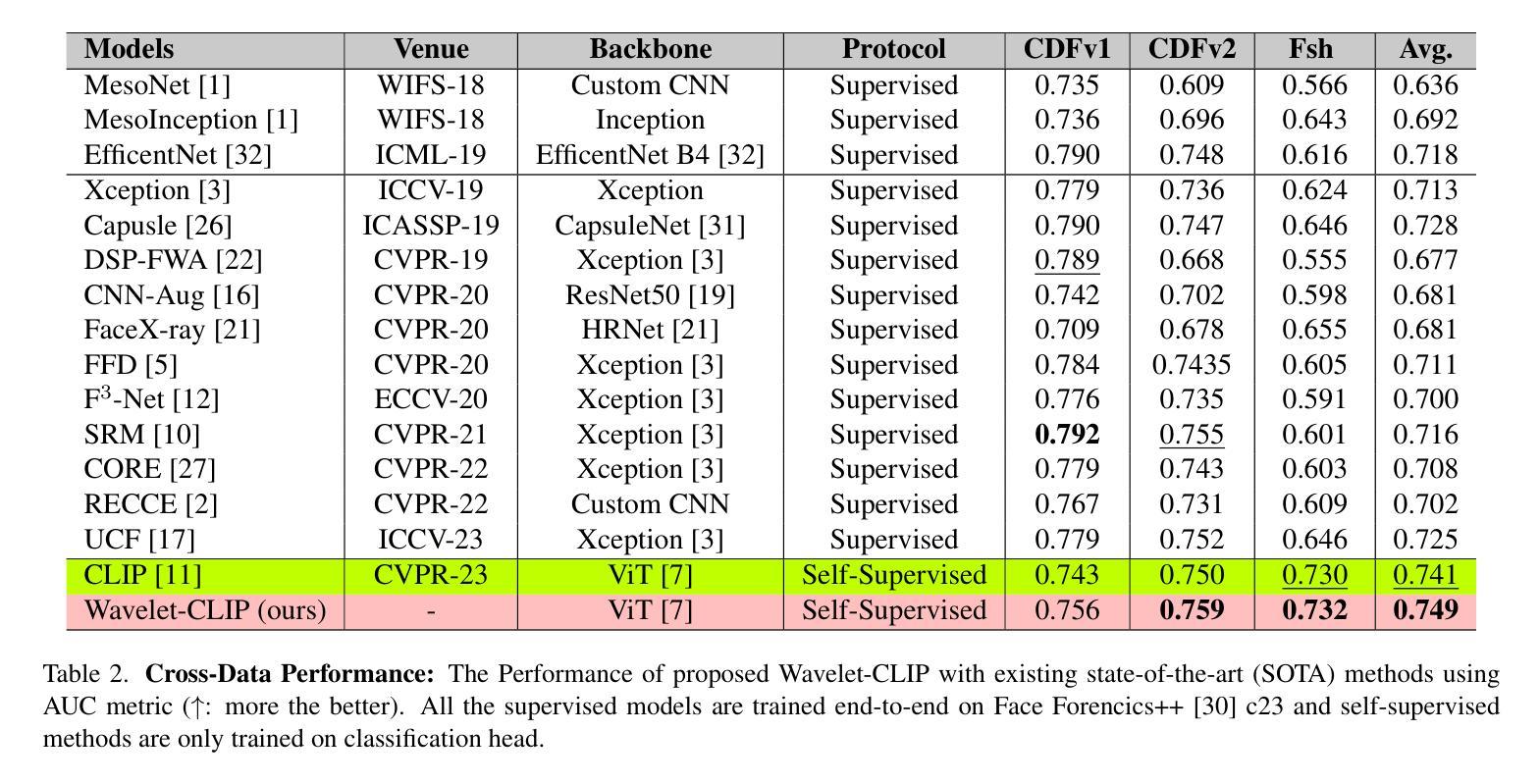
The evolution of digital image manipulation, particularly with the advancement of deep generative models, significantly challenges existing deepfake detection methods, especially when the origin of the deepfake is obscure. To tackle the increasing complexity of these forgeries, we propose \textbf{Wavelet-CLIP}, a deepfake detection framework that integrates wavelet transforms with features derived from the ViT-L/14 architecture, pre-trained in the CLIP fashion. Wavelet-CLIP utilizes Wavelet Transforms to deeply analyze both spatial and frequency features from images, thus enhancing the model’s capability to detect sophisticated deepfakes. To verify the effectiveness of our approach, we conducted extensive evaluations against existing state-of-the-art methods for cross-dataset generalization and detection of unseen images generated by standard diffusion models. Our method showcases outstanding performance, achieving an average AUC of 0.749 for cross-data generalization and 0.893 for robustness against unseen deepfakes, outperforming all compared methods. The code can be reproduced from the repo: \url{https://github.com/lalithbharadwajbaru/Wavelet-CLIP}
数字图像操作的演变,尤其是随着深度生成模型的进步,对现有深度伪造检测方法的挑战日益显著,尤其是在深度伪造的来源不明确的情况下。为了应对这些伪造品日益复杂的特性,我们提出了Wavelet-CLIP,这是一个深度伪造检测框架,它将小波变换与从ViT-L/14架构中派生的特征相结合,以CLIP方式进行预训练。Wavelet-CLIP利用小波变换深入分析图像的空间和频率特征,从而增强模型检测复杂深度伪造的能力。为了验证我们方法的有效性,我们对现有的最先进方法进行了广泛的评估,以实现对跨数据集生成的未见图像进行泛化和检测。我们的方法表现出卓越的性能,在跨数据泛化方面平均AUC达到0.749,在对抗未见深度伪造时达到0.893的AUC,优于所有比较的方法。代码可从仓库重现:https://github.com/lalithbharadwajbaru/Wavelet-CLIP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 Pages, 2 Figures, 3 Tables
Summary
针对数字图像操纵的进化,特别是深度生成模型的进步,对现有的深度伪造检测方法提出了重大挑战,特别是在深度伪造来源不明朗的情况下。为解决这些伪造品日益复杂的局面,我们提出了结合小波变换与ViT-L/14架构特征的深度伪造检测框架——Wavelet-CLIP,该框架采用CLIP预训练方式。Wavelet-CLIP利用小波变换深入图像的空间和频率特征分析,从而增强模型检测高级深度伪造的能力。实验证明,我们的方法相较于最新的先进方法,在跨数据集推广和检测标准扩散模型生成的未见图像方面表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 数字图像操纵的进化对现有深度伪造检测方法构成挑战。
- 小波变换用于深入图像的空间和频率特征分析以增强检测能力。
- 提出了一种名为Wavelet-CLIP的深度伪造检测框架,结合了ViT-L/14架构特征和小波变换。
- Wavelet-CLIP采用了CLIP预训练方式。
- Wavelet-CLIP在跨数据集推广和检测未见图像方面表现出卓越性能。
- 与现有先进方法相比,Wavelet-CLIP在检测深度伪造方面表现出更高的性能。
点此查看论文截图

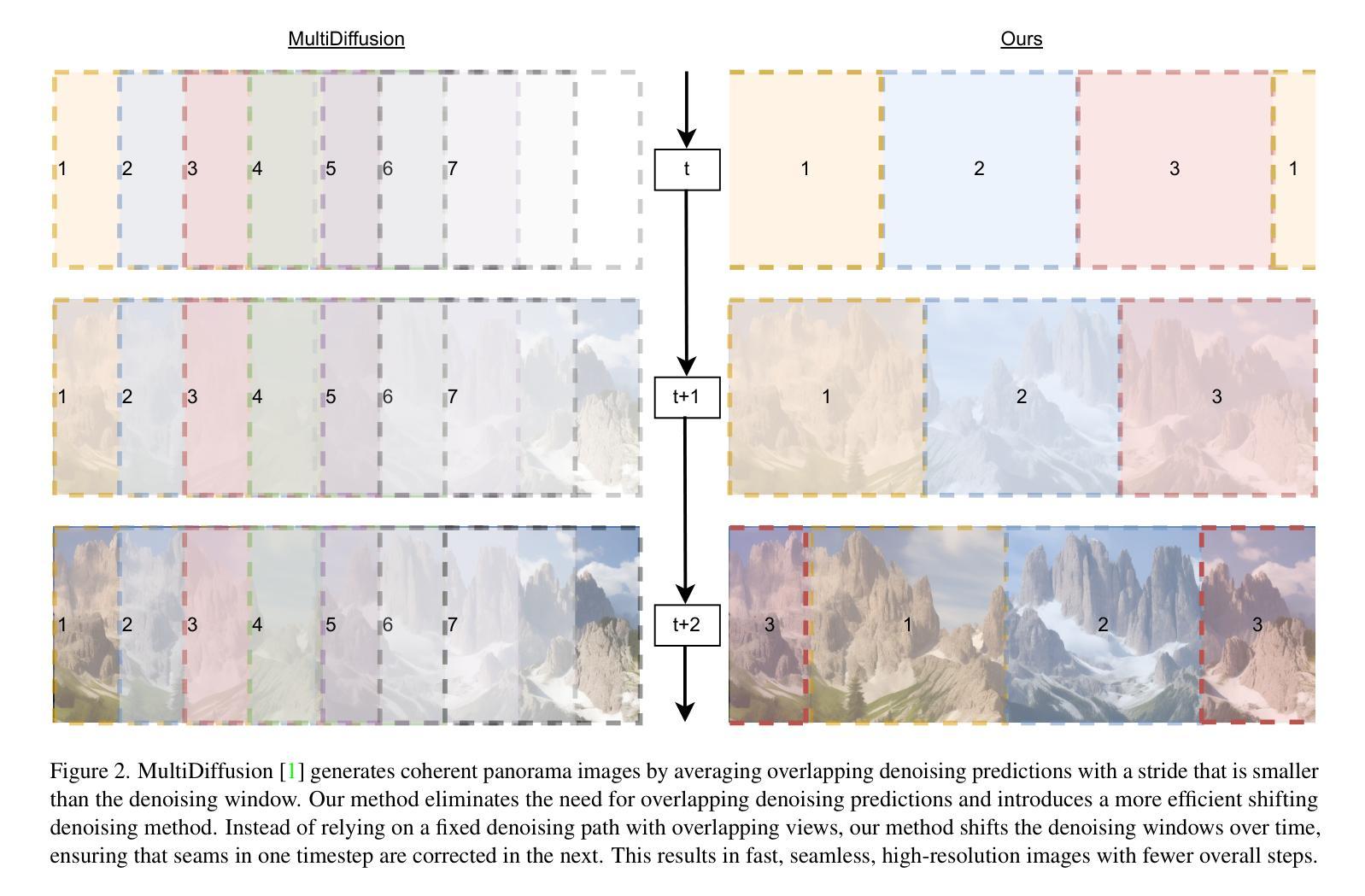
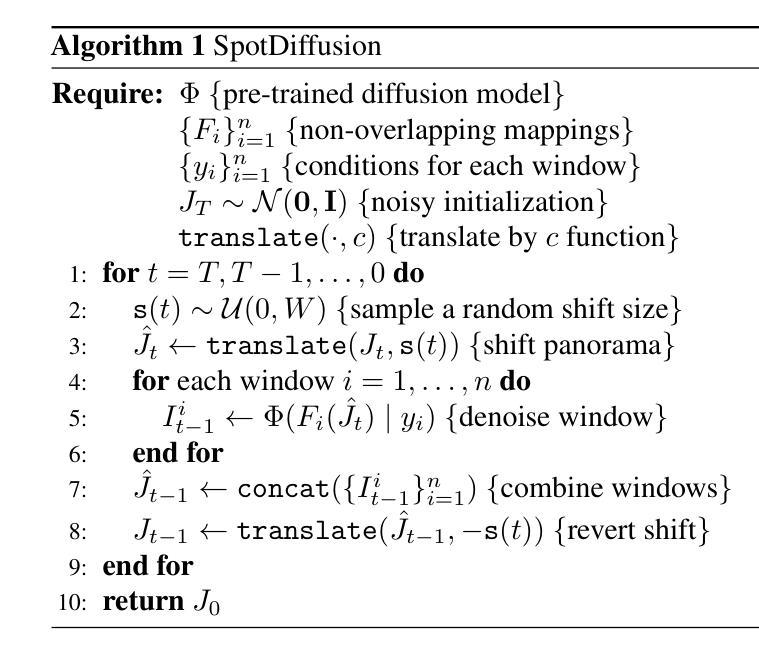
SpotDiffusion: A Fast Approach For Seamless Panorama Generation Over Time
Authors:Stanislav Frolov, Brian B. Moser, Andreas Dengel
Generating high-resolution images with generative models has recently been made widely accessible by leveraging diffusion models pre-trained on large-scale datasets. Various techniques, such as MultiDiffusion and SyncDiffusion, have further pushed image generation beyond training resolutions, i.e., from square images to panorama, by merging multiple overlapping diffusion paths or employing gradient descent to maintain perceptual coherence. However, these methods suffer from significant computational inefficiencies due to generating and averaging numerous predictions, which is required in practice to produce high-quality and seamless images. This work addresses this limitation and presents a novel approach that eliminates the need to generate and average numerous overlapping denoising predictions. Our method shifts non-overlapping denoising windows over time, ensuring that seams in one timestep are corrected in the next. This results in coherent, high-resolution images with fewer overall steps. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach through qualitative and quantitative evaluations, comparing it with MultiDiffusion, SyncDiffusion, and StitchDiffusion. Our method offers several key benefits, including improved computational efficiency and faster inference times while producing comparable or better image quality. Link to code https://github.com/stanifrolov/spotdiffusion
利用在大规模数据集上预训练的扩散模型,生成模型生成高分辨率图像的方法近期已经变得广泛可用。通过各种技术,如MultiDiffusion和SyncDiffusion,图像生成已经超越了训练分辨率,例如从方形图像到全景图像,通过合并多个重叠的扩散路径或采用梯度下降法来维持感知连贯性。然而,这些方法由于需要生成和平均大量预测来产生高质量、无缝图像,因此存在显著的计算效率低下问题。本研究解决了这一限制,提出了一种新方法,消除了生成和平均多个重叠的去噪预测的需要。我们的方法随时间移动非重叠的去噪窗口,确保一个时间步长的接缝在下一个时间步长中得到修正。这导致在更少的总体步骤中产生连贯的高分辨率图像。我们通过定性和定量评估来展示我们方法的有效性,并将其与MultiDiffusion、SyncDiffusion和StitchDiffusion进行比较。我们的方法提供了几个关键优势,包括提高计算效率和更快的推理时间,同时产生相当或更好的图像质量。代码链接 https://github.com/stanifrolov/spotdiffusion
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://spotdiffusion.github.io/
Summary
基于扩散模型预训练的大规模数据集,生成高质量图像已变得广泛可行。近期,通过消除对生成和平均大量重叠降噪预测的需求,一种新方法解决了现有技术如MultiDiffusion和SyncDiffusion的计算效率低下的问题。该方法通过随时间移动非重叠的降噪窗口,确保一个时间步长的接缝在下一个时间步长中得到修正,从而生成连贯的高分辨率图像,总体步骤更少。通过与MultiDiffusion、SyncDiffusion和StitchDiffusion的比较,证明了该方法在计算效率和推理速度方面提供了几个关键优势,同时产生了相当或更好的图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型预训练的大规模数据集使得生成高质量图像变得广泛可行。
- 现有技术如MultiDiffusion和SyncDiffusion虽然能够生成高分辨率图像,但存在计算效率低下的问题。
- 新方法通过消除对生成和平均大量重叠降噪预测的需求,提高了计算效率。
- 该方法通过移动非重叠的降噪窗口,确保图像生成的连贯性,并减少总体步骤。
- 该方法与现有技术相比,具有更高的计算效率和更快的推理速度。
- 新方法生成的图像质量相当或更好。
点此查看论文截图