⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-09 更新
Diverse Rare Sample Generation with Pretrained GANs
Authors:Subeen Lee, Jiyeon Han, Soyeon Kim, Jaesik Choi
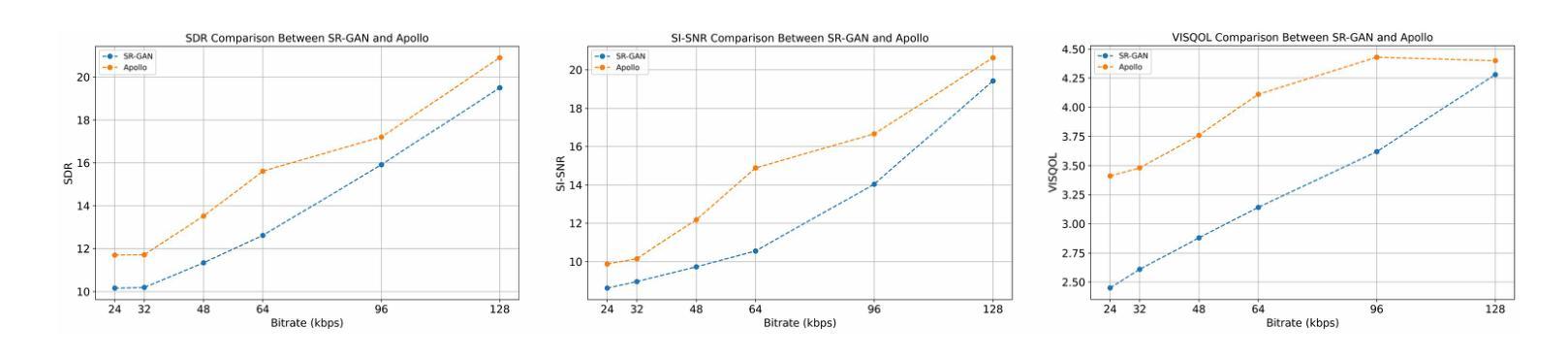
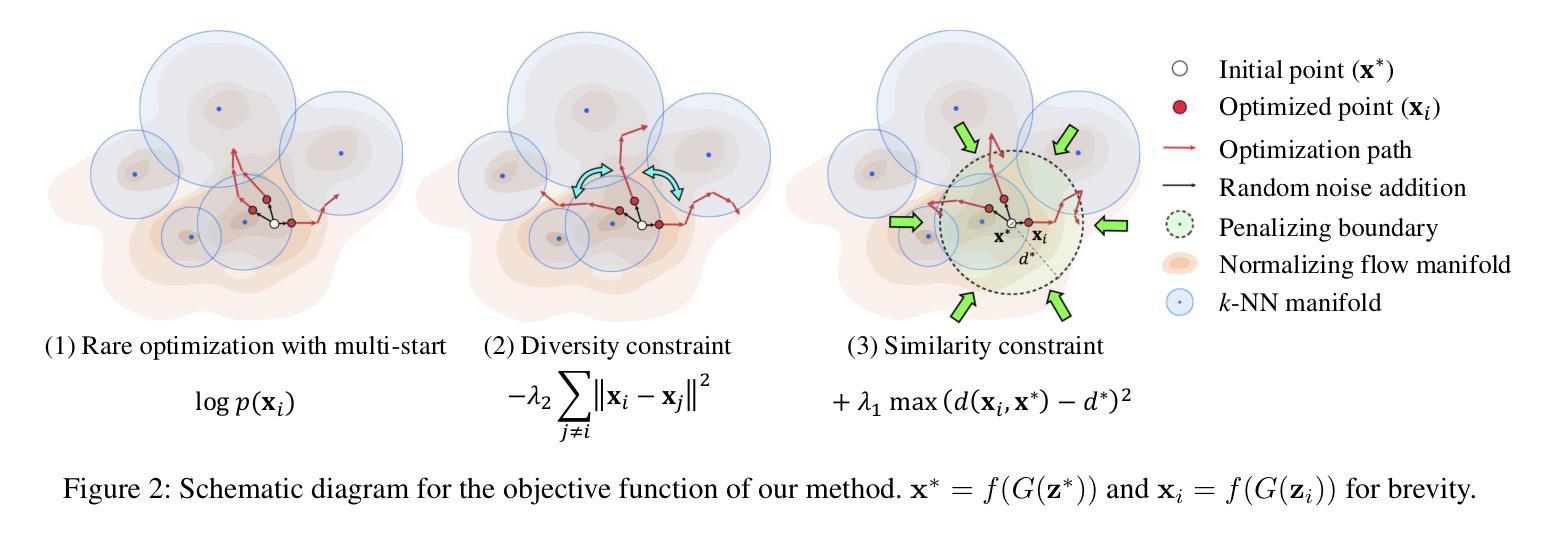
Deep generative models are proficient in generating realistic data but struggle with producing rare samples in low density regions due to their scarcity of training datasets and the mode collapse problem. While recent methods aim to improve the fidelity of generated samples, they often reduce diversity and coverage by ignoring rare and novel samples. This study proposes a novel approach for generating diverse rare samples from high-resolution image datasets with pretrained GANs. Our method employs gradient-based optimization of latent vectors within a multi-objective framework and utilizes normalizing flows for density estimation on the feature space. This enables the generation of diverse rare images, with controllable parameters for rarity, diversity, and similarity to a reference image. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach both qualitatively and quantitatively across various datasets and GANs without retraining or fine-tuning the pretrained GANs.
深度生成模型擅长生成真实数据,但由于训练数据集稀缺和模式崩溃问题,它们在生成低密度区域的稀有样本时遇到困难。虽然最近的方法旨在提高生成样本的保真度,但它们往往通过忽略稀有和新颖的样本来减少多样性和覆盖范围。本研究提出了一种利用预训练GAN从高分辨率图像数据集生成多样稀有样本的新方法。我们的方法在多目标框架内对潜在向量进行基于梯度的优化,并利用归一化流对特征空间进行密度估计。这能够生成各种罕见的图像,具有可控的参数,可针对稀有性、多样性和与参考图像的相似性进行调整。我们通过各种数据集和GAN定性和定量地证明了我们的方法的有效性,并且无需对预训练的GAN进行再训练或微调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种利用预训练的GAN生成多样化稀有样本的新方法,适用于高分辨率图像数据集。该方法基于梯度优化潜在向量,在多目标框架内进行,并利用归一化流进行特征空间的密度估计。此方法能够生成多样化的稀有图像,并且具有可控的参数,包括稀有度、多样性和与参考图像的相似性。此方法无需重新训练或微调预训练的GAN,在各种数据集上均表现出有效性和实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练的GAN在生成稀有样本时面临挑战,缺乏训练数据集和模式崩溃问题限制了其生成能力。
- 本研究提出了一种利用梯度优化潜在向量和多目标框架内的方法,旨在解决生成稀有样本的问题。
- 归一化流被用于特征空间的密度估计,这有助于提高生成图像的多样性和质量。
- 该方法允许通过可控参数调整生成图像的稀有度、多样性和与参考图像的相似性。
- 该方法无需重新训练或微调预训练的GAN,具有广泛的应用性和实用性。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在多种数据集和GAN模型上均表现出有效性。
点此查看论文截图




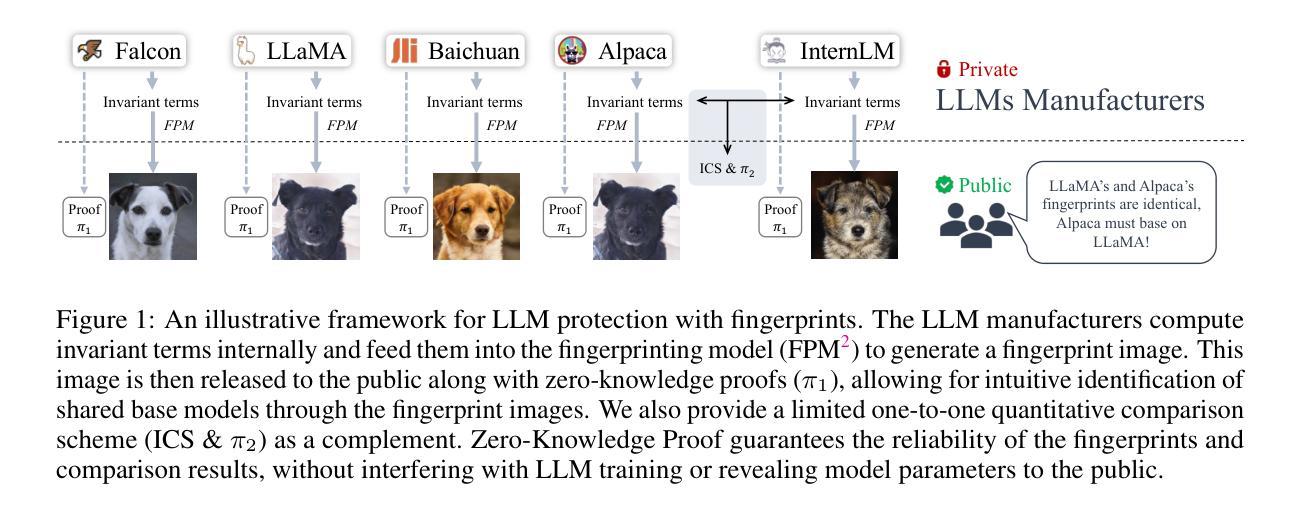
HuRef: HUman-REadable Fingerprint for Large Language Models
Authors:Boyi Zeng, Lizheng Wang, Yuncong Hu, Yi Xu, Chenghu Zhou, Xinbing Wang, Yu Yu, Zhouhan Lin
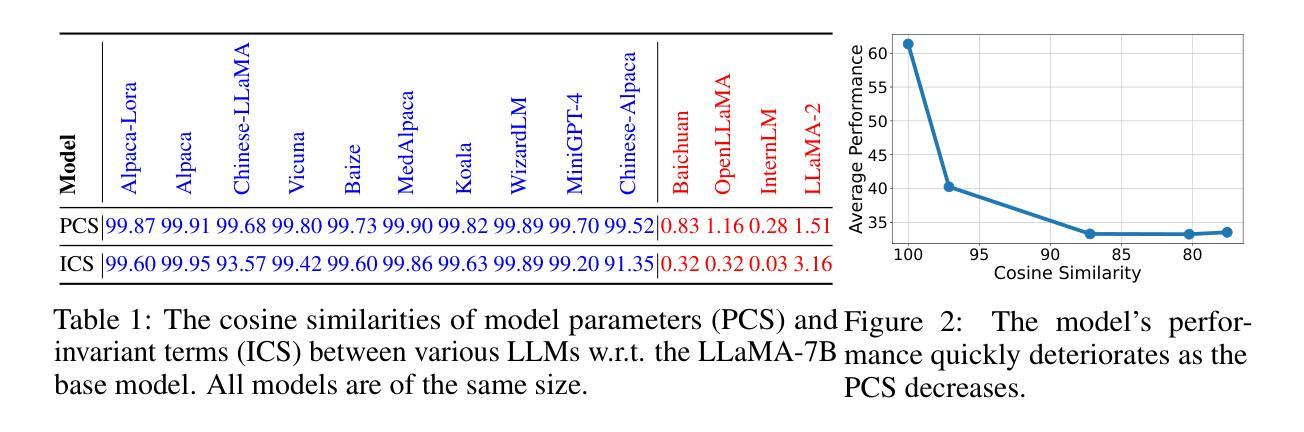
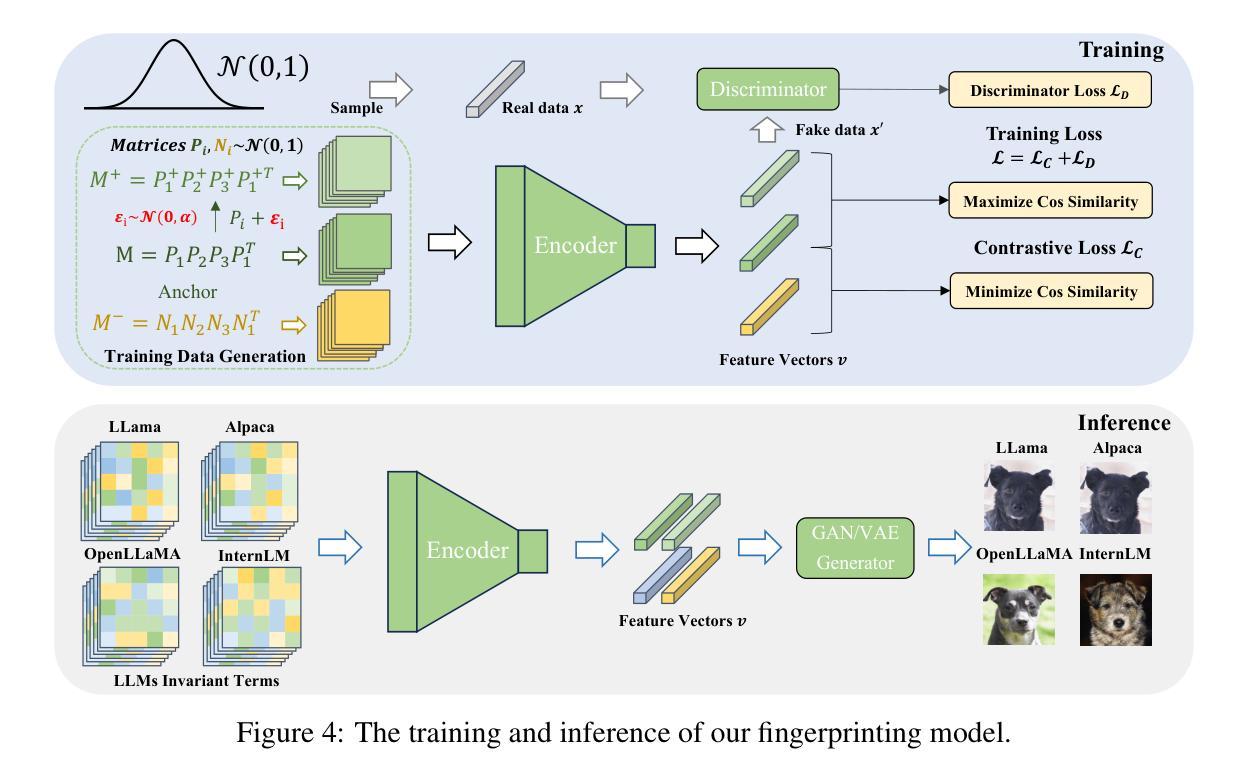
Protecting the copyright of large language models (LLMs) has become crucial due to their resource-intensive training and accompanying carefully designed licenses. However, identifying the original base model of an LLM is challenging due to potential parameter alterations. In this study, we introduce HuRef, a human-readable fingerprint for LLMs that uniquely identifies the base model without interfering with training or exposing model parameters to the public. We first observe that the vector direction of LLM parameters remains stable after the model has converged during pretraining, with negligible perturbations through subsequent training steps, including continued pretraining, supervised fine-tuning, and RLHF, which makes it a sufficient condition to identify the base model. The necessity is validated by continuing to train an LLM with an extra term to drive away the model parameters’ direction and the model becomes damaged. However, this direction is vulnerable to simple attacks like dimension permutation or matrix rotation, which significantly change it without affecting performance. To address this, leveraging the Transformer structure, we systematically analyze potential attacks and define three invariant terms that identify an LLM’s base model. Due to the potential risk of information leakage, we cannot publish invariant terms directly. Instead, we map them to a Gaussian vector using an encoder, then convert it into a natural image using StyleGAN2, and finally publish the image. In our black-box setting, all fingerprinting steps are internally conducted by the LLMs owners. To ensure the published fingerprints are honestly generated, we introduced Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP). Experimental results across various LLMs demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The code is available at https://github.com/LUMIA-Group/HuRef.
保护大型语言模型(LLM)的版权对于其资源密集型训练和伴随的精心设计的许可证而言变得至关重要。然而,由于潜在参数改动,确定LLM的原始基础模型是有挑战性的。在这项研究中,我们介绍了HuRef,这是一种人类可读的LLM指纹,可以唯一地识别基础模型,而不会干扰训练或向公众暴露模型参数。我们首先观察到,在预训练期间模型收敛后,LLM参数的向量方向保持稳定,随后的训练步骤包括继续预训练、监督微调以及RLHF带来的扰动微乎其微,这使得它成为识别基础模型的充分条件。这一观点通过继续训练LLM并添加额外项来驱离模型参数的方向而得到了验证,而这样的操作会损害模型。然而,这个方向容易受到简单的攻击,如维度置换或矩阵旋转,这些攻击会显著改变方向而不影响性能。为了解决这一问题,我们利用Transformer结构系统地分析了潜在攻击并定义了三个不变术语来识别LLM的基础模型。由于信息泄露的潜在风险,我们无法直接公布这些不变术语。相反,我们使用编码器将其映射到高斯向量,然后使用StyleGAN2将其转换为自然图像,并最终发布图像。在我们的黑箱设置中,所有指纹打印步骤均由LLM所有者内部进行。为了确保发布的指纹是诚实生成的,我们引入了零知识证明(ZKP)。在不同LLM上的实验结果表明了我们的方法的有效性。相关代码可在https://github.com/LUMIA-Group/HuRef找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对大型语言模型(LLM)的新型版权保护方法——HuRef。该方法通过生成人类可读的指纹来唯一识别LLM的基础模型,且不会干扰训练或公开模型参数。研究观察到LLM参数向量方向在预训练收敛后保持稳定,通过利用Transformer结构分析潜在攻击并定义三个不变术语来识别LLM的基础模型。为解决信息泄露风险,采用编码器将指纹映射为高斯向量,再通过StyleGAN2转换为自然图像发表。实验结果显示该方法有效,代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的版权保护至关重要,因其在资源密集型训练过程中涉及到复杂的许可协议。
- HuRef作为一种新型版权保护方法,通过生成人类可读的指纹唯一地识别LLM的基础模型。
- LLM参数向量方向在预训练收敛后的稳定性成为识别基础模型的关键。
- 通过利用Transformer结构,系统分析了潜在攻击并定义了三个不变术语来识别LLM的基础模型。
- 采用编码器和StyleGAN2技术将指纹转换为图像发表,以应对潜在的信息泄露风险。
- 实验结果显示HuRef方法的有效性,并已公开相关代码。
点此查看论文截图