⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-09 更新
Sa2VA: Marrying SAM2 with LLaVA for Dense Grounded Understanding of Images and Videos
Authors:Haobo Yuan, Xiangtai Li, Tao Zhang, Zilong Huang, Shilin Xu, Shunping Ji, Yunhai Tong, Lu Qi, Jiashi Feng, Ming-Hsuan Yang
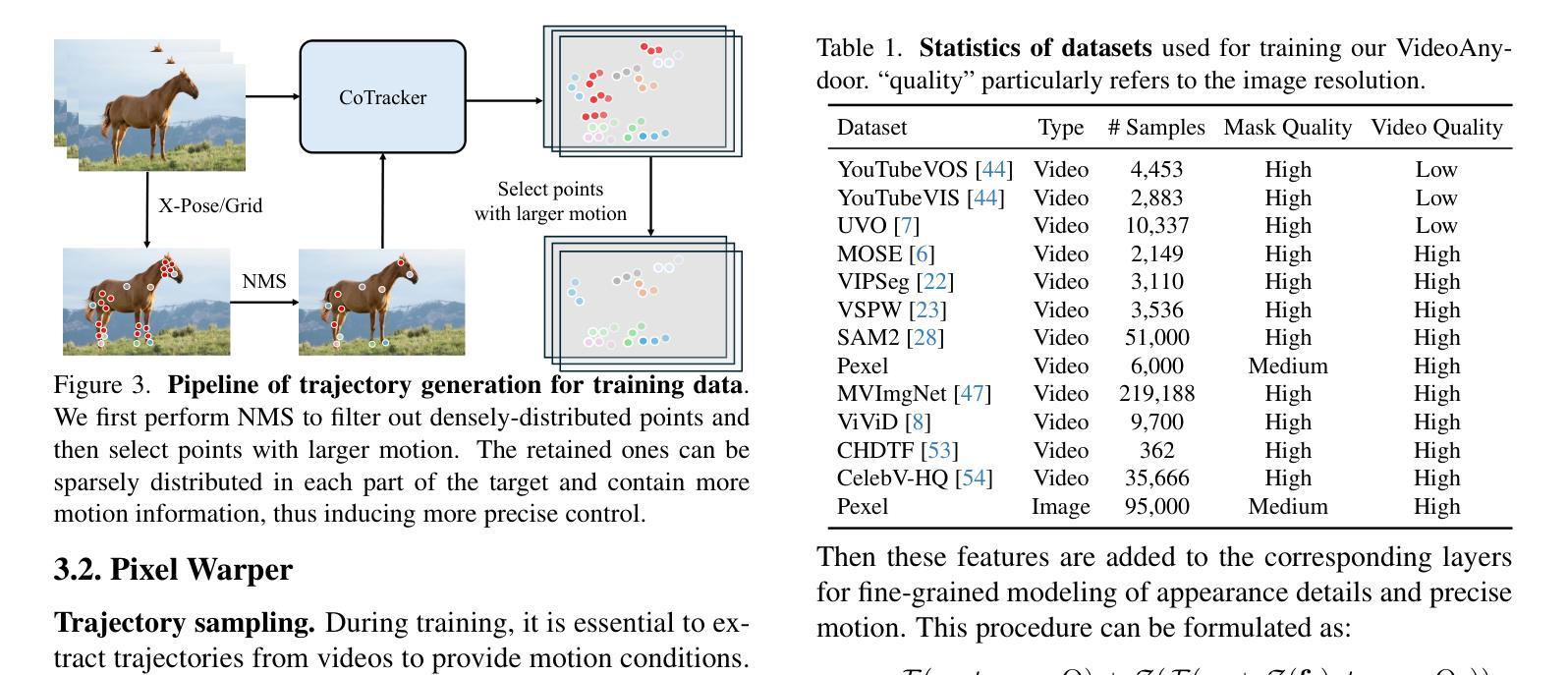
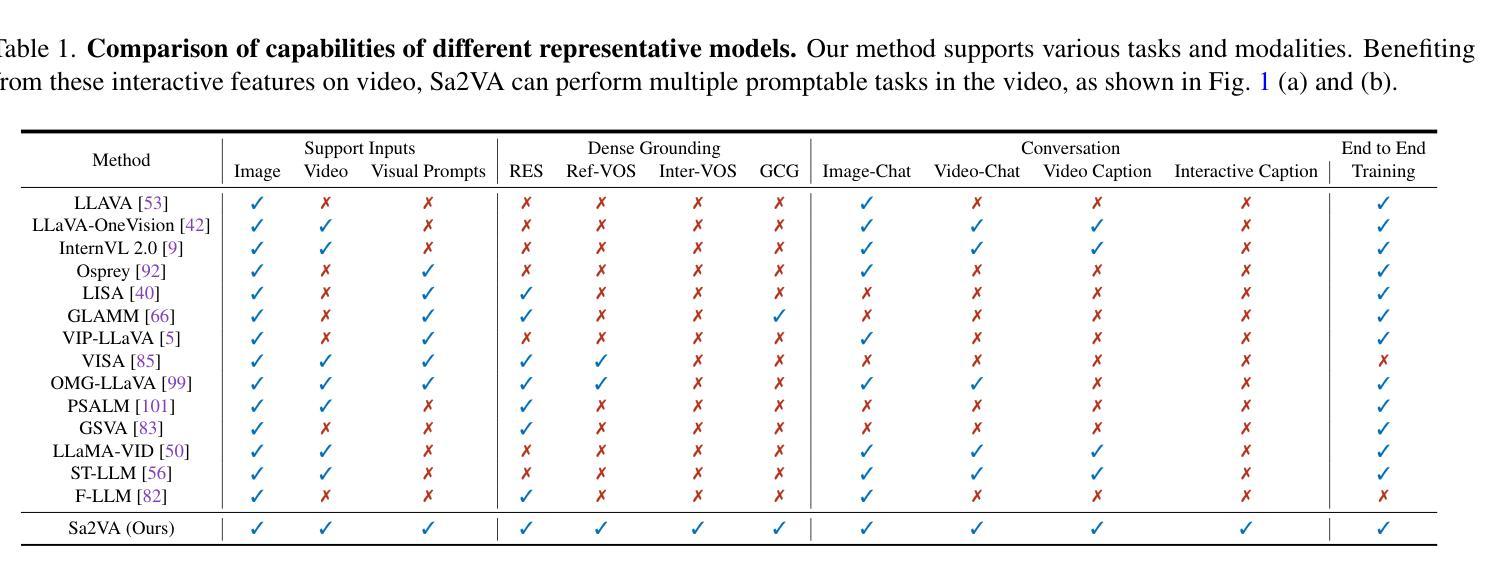
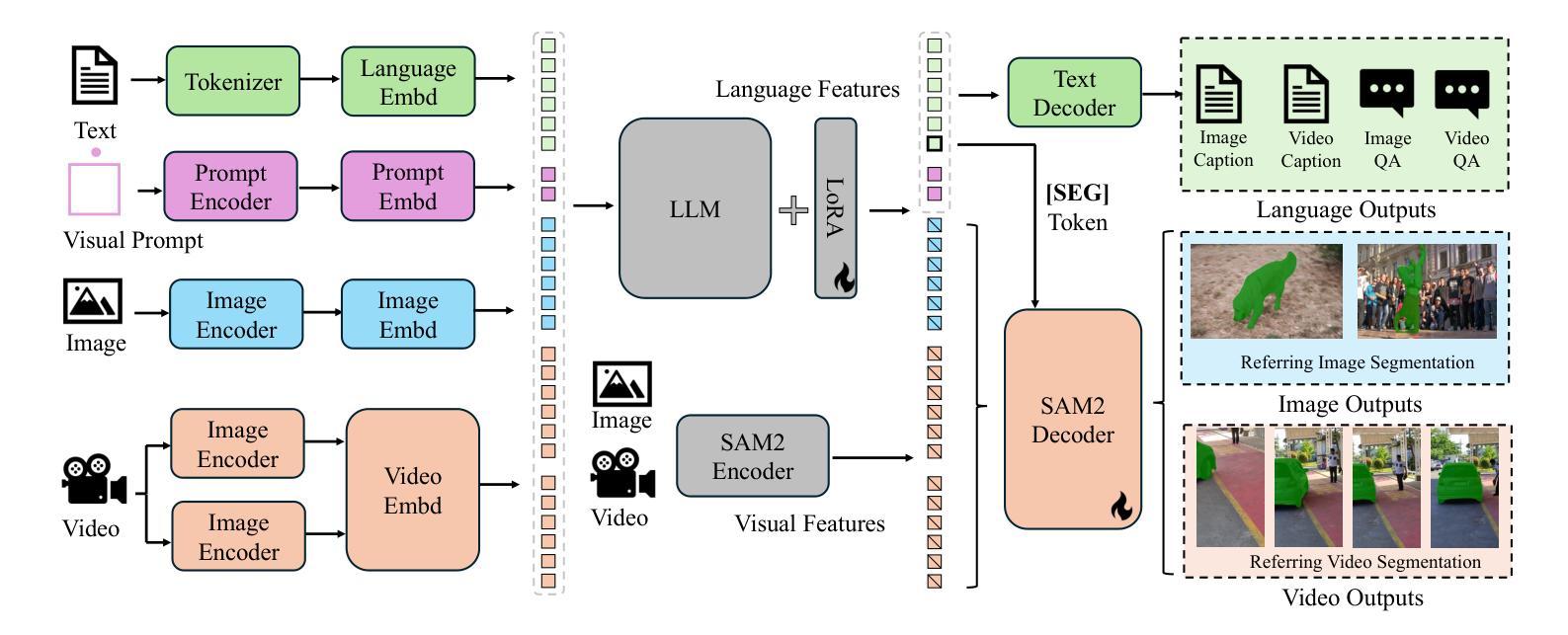
This work presents Sa2VA, the first unified model for dense grounded understanding of both images and videos. Unlike existing multi-modal large language models, which are often limited to specific modalities and tasks, Sa2VA supports a wide range of image and video tasks, including referring segmentation and conversation, with minimal one-shot instruction tuning. Sa2VA combines SAM-2, a foundation video segmentation model, with LLaVA, an advanced vision-language model, and unifies text, image, and video into a shared LLM token space. Using the LLM, Sa2VA generates instruction tokens that guide SAM-2 in producing precise masks, enabling a grounded, multi-modal understanding of both static and dynamic visual content. Additionally, we introduce Ref-SAV, an auto-labeled dataset containing over 72k object expressions in complex video scenes, designed to boost model performance. We also manually validate 2k video objects in the Ref-SAV datasets to benchmark referring video object segmentation in complex environments. Experiments show that Sa2VA achieves state-of-the-art across multiple tasks, particularly in referring video object segmentation, highlighting its potential for complex real-world applications.
本文介绍了Sa2VA,这是第一个统一模型,实现对图像和视频的密集接地理解。与现有的多模态大型语言模型不同,这些模型通常仅限于特定的模态和任务,而Sa2VA支持广泛的图像和视频任务,包括引用分割和对话,以及最少的一次性指令调整。Sa2VA结合了SAM-2基础视频分割模型和LLaVA高级视觉语言模型,并将文本、图像和视频统一到共享的大型语言模型令牌空间中。使用大型语言模型,Sa2VA生成指令令牌,指导SAM-2生成精确蒙版,实现对静态和动态视觉内容的接地多模态理解。此外,我们推出了Ref-SAV,这是一个自动标记的数据集,包含超过7.2万个复杂视频场景中的对象表达式,旨在提高模型性能。我们还手动验证了Ref-SAV数据集中的2000个视频对象,以评估复杂环境中视频对象分割的引用情况。实验表明,Sa2VA在多个任务上达到了最新水平,特别是在引用视频对象分割方面,这突显了其在复杂现实世界应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://lxtgh.github.io/project/sa2va
Summary
本文提出了Sa2VA模型,这是首个支持图像和视频密集理解的统一模型。相较于现有的多模态大型语言模型,Sa2VA支持广泛的图像和视频任务,包括引用分割和对话等,只需一次指令调整即可完成任务。Sa2VA结合了SAM-2基础视频分割模型和LLaVA高级视觉语言模型,并将文本、图像和视频统一到共享的LLM令牌空间中。使用LLM,Sa2VA生成指导SAM-2产生精确掩码的指令令牌,实现对静态和动态视觉内容的基于地面的多模态理解。此外,本文还介绍了用于复杂视频场景的Ref-SAV数据集,包含超过7万多个对象表达式,旨在提升模型性能。实验表明,Sa2VA在多个任务上达到了领先水平,特别是在引用视频对象分割方面,突显其在复杂现实应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- Sa2VA是首个支持图像和视频密集理解的统一模型。
- Sa2VA支持广泛的图像和视频任务,包括引用分割和对话等。
- Sa2VA通过结合SAM-2和LLaVA模型,实现了文本、图像和视频的共享LLM令牌空间。
- LLM生成的指令令牌指导SAM-2产生精确掩码,实现基于地面的多模态理解。
- 引入的Ref-SAV数据集包含复杂的视频场景中的大量对象表达式,旨在提升模型性能。
- 实验表明Sa2VA在多个任务上表现优异,特别是在引用视频对象分割方面。
点此查看论文截图

Vision Language Models as Values Detectors
Authors:Giulio Antonio Abbo, Tony Belpaeme
Large Language Models integrating textual and visual inputs have introduced new possibilities for interpreting complex data. Despite their remarkable ability to generate coherent and contextually relevant text based on visual stimuli, the alignment of these models with human perception in identifying relevant elements in images requires further exploration. This paper investigates the alignment between state-of-the-art LLMs and human annotators in detecting elements of relevance within home environment scenarios. We created a set of twelve images depicting various domestic scenarios and enlisted fourteen annotators to identify the key element in each image. We then compared these human responses with outputs from five different LLMs, including GPT-4o and four LLaVA variants. Our findings reveal a varied degree of alignment, with LLaVA 34B showing the highest performance but still scoring low. However, an analysis of the results highlights the models’ potential to detect value-laden elements in images, suggesting that with improved training and refined prompts, LLMs could enhance applications in social robotics, assistive technologies, and human-computer interaction by providing deeper insights and more contextually relevant responses.
将文本和视觉输入结合的大型语言模型为解释复杂数据带来了新的可能性。尽管这些模型在基于视觉刺激生成连贯且上下文相关的文本方面表现出卓越的能力,但它们与人类感知在识别图像中相关元素方面的对齐仍需要进一步探索。本文调查了最先进的大型语言模型与人类注释器在检测家庭环境场景中相关元素方面的对齐情况。我们创建了一组包含十二张图像,描绘了各种家庭场景,并招募了十四名注释器来识别每张图像中的关键元素。然后我们将这些人类反应与来自包括GPT-4o和四种LLaVA变体在内的五种不同的大型语言模型的输出进行了比较。我们的研究结果表明,对齐程度不一,LLaVA 34B表现最好但得分仍然较低。然而,对结果的分析突显了模型检测图像中价值相关元素的潜力,这表明通过改进训练和精炼提示,大型语言模型可以增强在社会机器人、辅助技术和人机交互等领域的应用,提供更深入的见解和更上下文相关的反应。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 2 figures
Summary
大型语言模型融合文本和视觉输入,为解读复杂数据带来新可能。尽管这些模型能够根据视觉刺激生成连贯且语境相关的文本,但它们与人类感知在识别图像中相关元素方面的对齐仍需探索。本文调查了最先进的语言模型与人类标注器在识别家庭环境场景中相关元素的对齐情况。通过创建包含十二张描绘各种家庭场景图像的集合,并邀请十四名标注器识别每张图像中的关键元素,再将这些人类响应与GPT-4o等五种不同的大型语言模型输出进行比较(包括LLaVA的四种变体)。发现存在一定程度的对齐性,其中LLaVA 34B表现最佳但仍得分较低。然而,对结果的分析突显了模型检测图像中价值相关元素的潜力,表明通过改进训练和细化提示,大型语言模型可在社交机器人、辅助技术和人机交互等领域提供更深入见解和更语境相关的响应。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型能够融合文本和视觉输入,为数据解读带来新可能。
- 在识别图像中的相关元素方面,大型语言模型与人类感知的对齐仍需探索。
- 通过创建包含家庭场景图像的集合进行实验,发现LLaVA 34B在识别相关元素方面表现最佳。
- 大型语言模型在检测图像中的价值相关元素方面展现潜力。
- 通过改进训练和细化提示,大型语言模型在社交机器人、辅助技术和人机交互等领域的应用有望增强。
- 大型语言模型的卓越表现体现在生成连贯且语境相关的文本输出。
点此查看论文截图


Localizing AI: Evaluating Open-Weight Language Models for Languages of Baltic States
Authors:Jurgita Kapočiūtė-Dzikienė, Toms Bergmanis, Mārcis Pinnis
Although large language models (LLMs) have transformed our expectations of modern language technologies, concerns over data privacy often restrict the use of commercially available LLMs hosted outside of EU jurisdictions. This limits their application in governmental, defence, and other data-sensitive sectors. In this work, we evaluate the extent to which locally deployable open-weight LLMs support lesser-spoken languages such as Lithuanian, Latvian, and Estonian. We examine various size and precision variants of the top-performing multilingual open-weight models, Llama3, Gemma2, Phi, and NeMo, on machine translation, multiple-choice question answering, and free-form text generation. The results indicate that while certain models like Gemma~2 perform close to the top commercially available models, many LLMs struggle with these languages. Most surprisingly, however, we find that these models, while showing close to state-of-the-art translation performance, are still prone to lexical hallucinations with errors in at least 1 in 20 words for all open-weight multilingual LLMs.
尽管大型语言模型(LLM)已经改变了我们对现代语言技术的期望,但对数据隐私的担忧常常限制了在欧盟辖区外托管的可商用LLM的使用。这限制了它们在政府、国防和其他对数据敏感的领域的应用。在这项工作中,我们评估了可在本地部署的开源大型语言模型支持诸如立陶宛语、拉脱维亚语和爱沙尼亚语等使用人数较少的语言的程度。我们研究了顶级多语言开源模型的各种大小和精度变体,包括Llama 3、Gemma 2、Phi和NeMo,对机器翻译、多项选择题回答和自由形式文本生成方面的表现。结果表明,虽然像Gemma 2这样的某些模型的表现接近顶级可商用模型,但许多大型语言模型对这些语言的处理仍然有困难。然而,最令人惊讶的是,我们发现这些模型虽然在翻译性能上接近最新水平,但仍容易出现词汇幻觉,所有开源多语言大型语言模型中至少有1/20的词存在错误。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted to NoDaLiDa/Baltic-HLT 2025
Summary
开源的大型语言模型(LLM)支持立陶宛语、拉脱维亚语和爱沙尼亚语等少语种的程度评估。评估结果显示,某些模型如Gemma 2表现接近顶级商业模型,但多数模型对这些语言的处理能力仍有待提升,且存在词汇幻觉问题,即每20个词中至少有一个词会出现错误。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)已改变了我们对现代语言技术的期待。
- 在欧盟管辖区以外的商业可用的大型语言模型(LLM)的使用受到数据隐私问题的限制。
- 这限制了大型语言模型在政府部门、军事和其他数据敏感领域的应用。
- 开源的大型语言模型在处理少语种如立陶宛语、拉脱维亚语和爱沙尼亚语时,性能各异。
- 部分模型如Gemma 2表现接近顶级商业模型。
- 但大部分模型对这些语言的处理能力有待提高。
点此查看论文截图

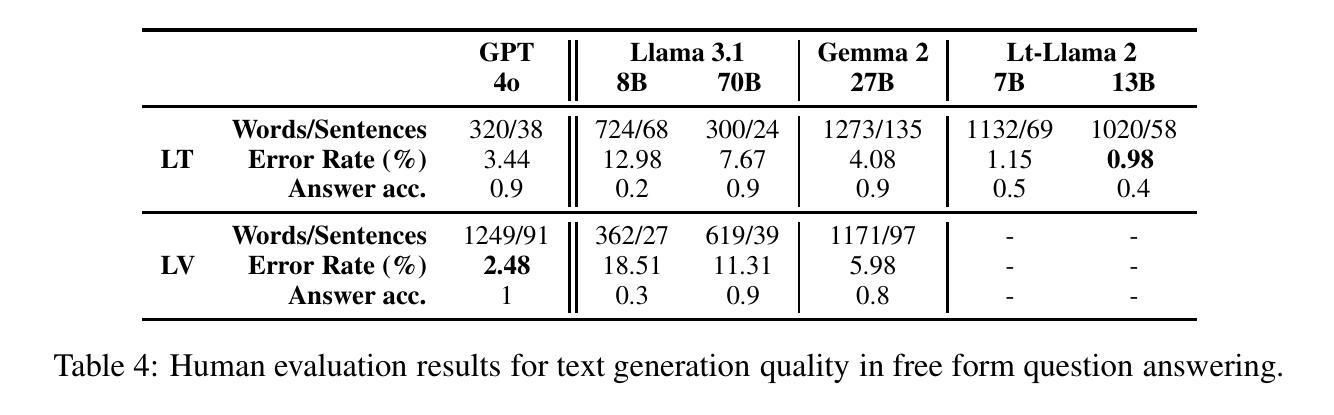
Exploring the Potential of Large Language Models in Public Transportation: San Antonio Case Study
Authors:Ramya Jonnala, Gongbo Liang, Jeong Yang, Izzat Alsmadi
The integration of large language models (LLMs) into public transit systems presents a transformative opportunity to enhance urban mobility. This study explores the potential of LLMs to revolutionize public transportation management within the context of San Antonio’s transit system. Leveraging the capabilities of LLMs in natural language processing and data analysis, we investigate their capabilities to optimize route planning, reduce wait times, and provide personalized travel assistance. By utilizing the General Transit Feed Specification (GTFS) and other relevant data, this research aims to demonstrate how LLMs can potentially improve resource allocation, elevate passenger satisfaction, and inform data-driven decision-making in transit operations. A comparative analysis of different ChatGPT models was conducted to assess their ability to understand transportation information, retrieve relevant data, and provide comprehensive responses. Findings from this study suggest that while LLMs hold immense promise for public transit, careful engineering and fine-tuning are essential to realizing their full potential. San Antonio serves as a case study to inform the development of LLM-powered transit systems in other urban environments.
将大型语言模型(LLM)集成到公共交通系统中,为提升城市流动性带来了变革性的机会。本研究探索了LLM在圣安东尼奥公共交通系统背景下革新公共交通管理的潜力。通过利用LLM在自然语言处理和数据分析方面的功能,我们研究了它们优化路线规划、减少等待时间并提供个性化旅行帮助的能力。通过利用通用交通馈送规范(GTFS)和其他相关数据,本研究旨在展示LLM如何可能地改善资源分配、提高乘客满意度并为基于数据的交通运营决策提供信息。对不同的ChatGPT模型进行了对比分析,以评估它们理解交通信息、检索相关数据并提供全面响应的能力。这项研究的结果表明,虽然LLM在公共交通方面有着巨大的潜力,但要实现其全部潜力,还需要精细的工程设计和调整。圣安东尼奥的案例研究为在其他城市环境中开发LLM驱动的交通系统提供了参考。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work is accepted to AAAI 2025 Workshop on AI for Urban Planning. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2407.11003
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)融入公共交通系统为提升城市出行效率带来革命性机遇。本研究探索了LLM在圣安东尼奥公共交通系统中的潜力,并展开深入对比分析的ChatGPT模型以评估其在运输数据处理能力方面是否卓越。通过GTFS数据和实际状况,该研究表明LLM可以改善资源分配、提高乘客满意度并为决策制定提供数据支持。然而,要发挥LLM的最大潜力,需要细致的工程设计和精细调整。这一案例研究可为其他城市开发LLM驱动的公共交通系统提供参考。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs有潜力改变公共交通系统的管理方式,增强城市流动性。
- 在圣安东尼奥的公共交通系统中,LLMs的应用可以进行路线优化、减少等待时间并提供个性化旅行服务。
- 通过GTFS数据和其他相关数据,LLMs可以改善资源分配和提高乘客满意度。
- LLMs在理解和处理运输信息方面表现出巨大潜力,但需要进行细致的工程设计和精细调整才能实现其最大效用。
- LLMs的应用可以为数据驱动的决策提供信息支持。
- 通过圣安东尼奥的案例研究,可以为其他城市开发基于LLM的公共交通系统提供参考和启示。
点此查看论文截图

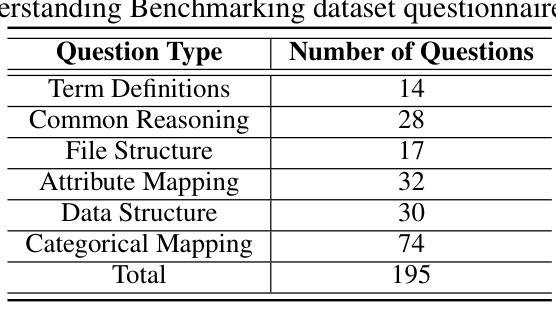
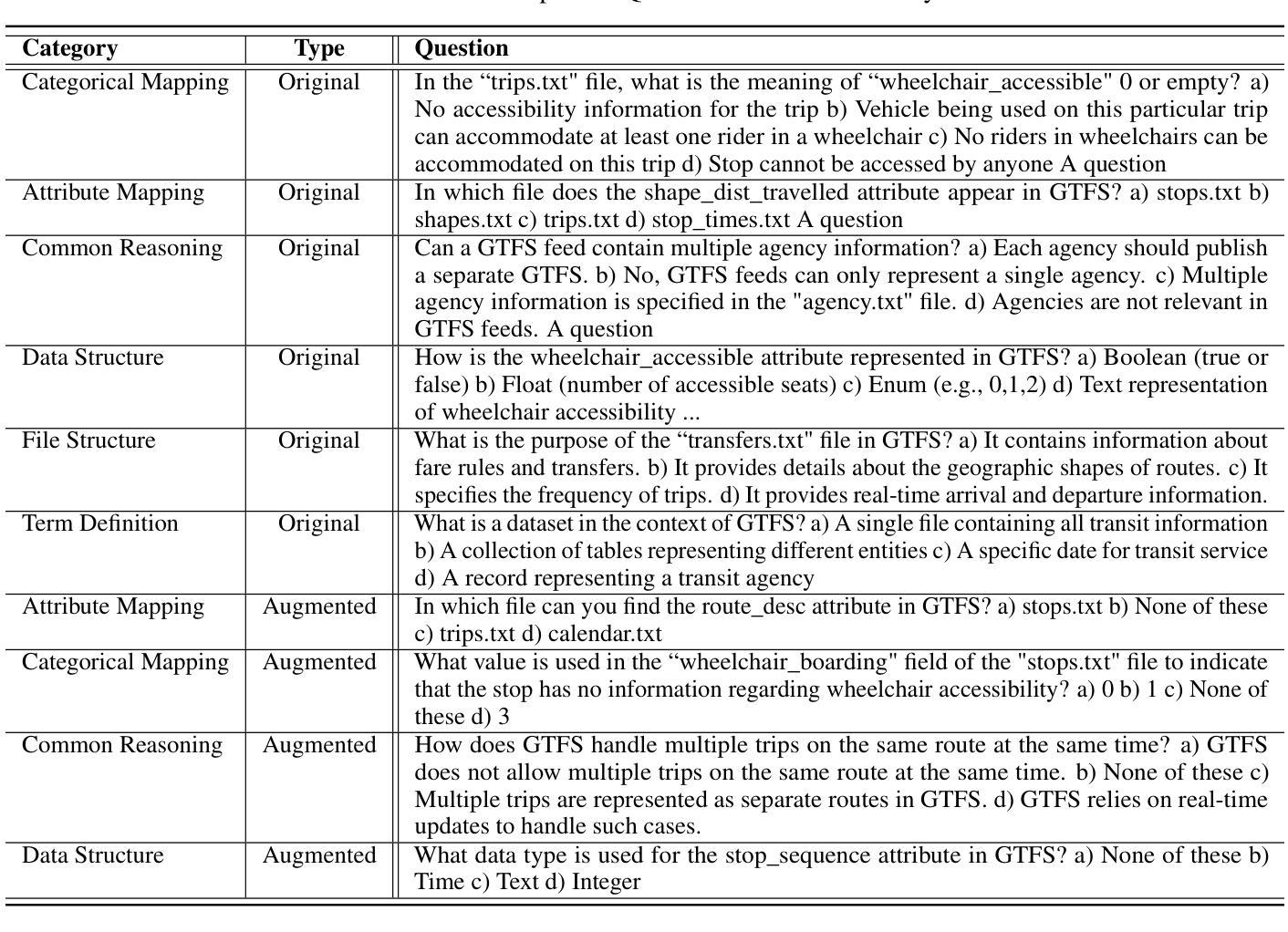
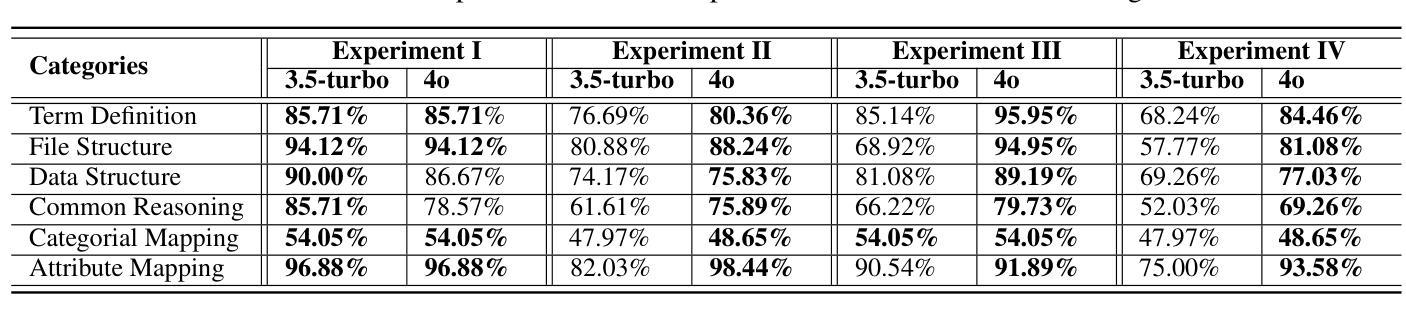
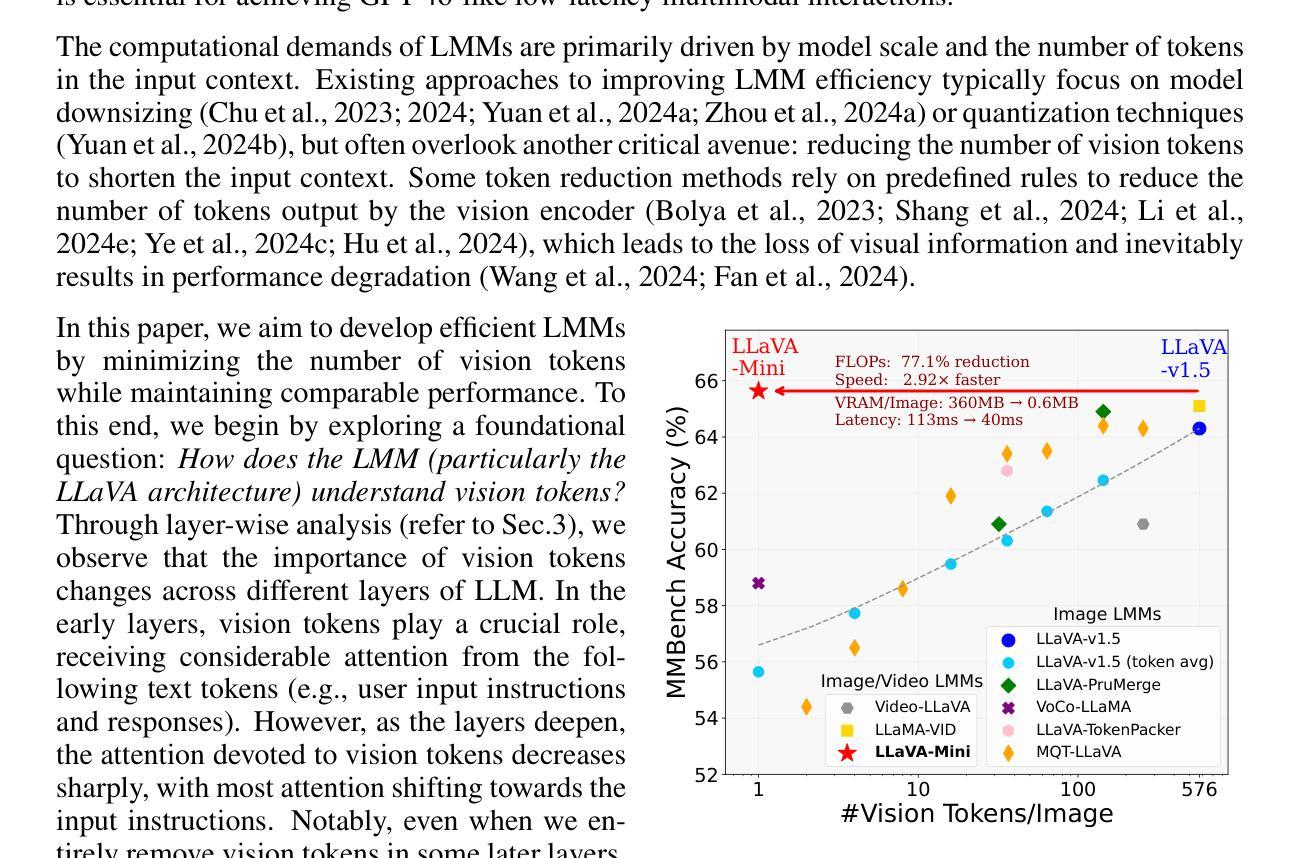
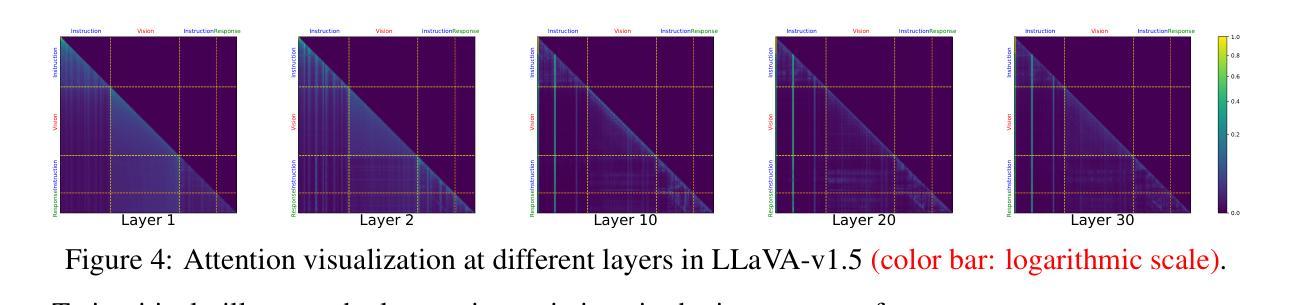
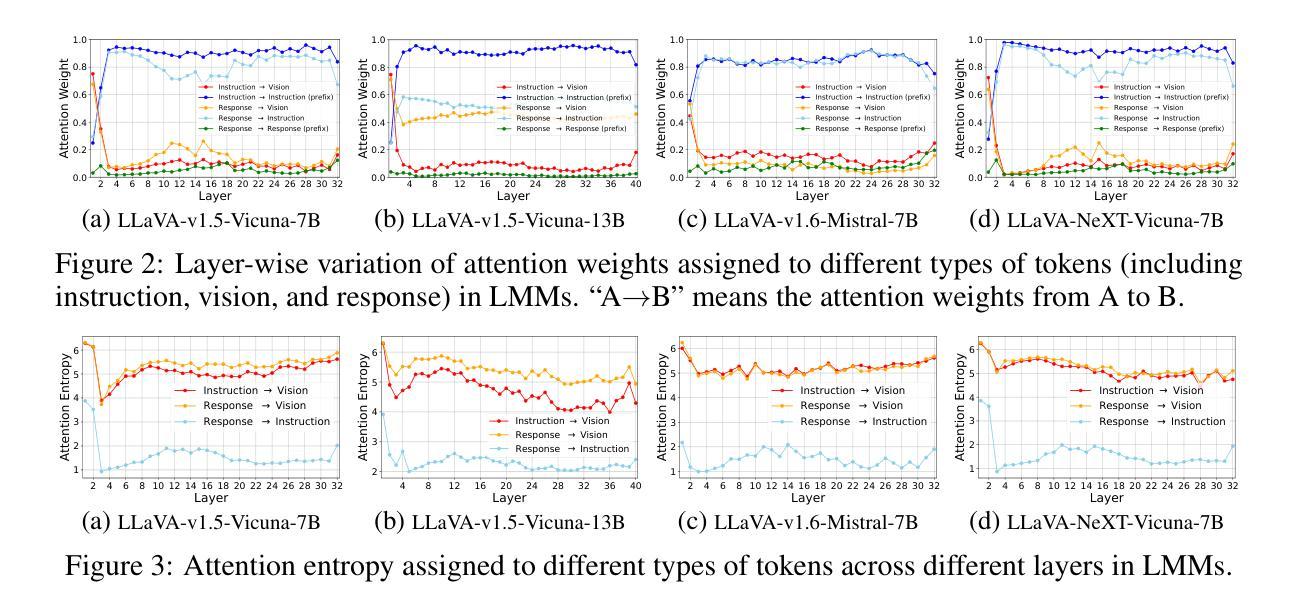
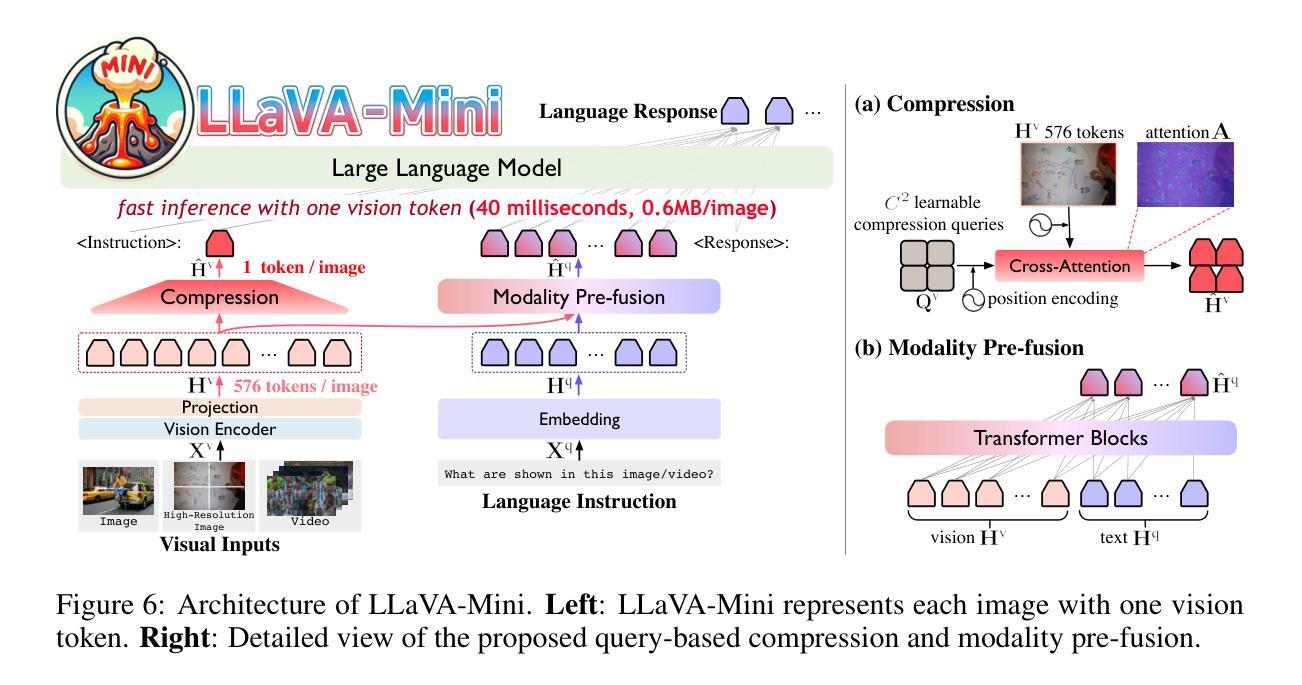
LLaVA-Mini: Efficient Image and Video Large Multimodal Models with One Vision Token
Authors:Shaolei Zhang, Qingkai Fang, Zhe Yang, Yang Feng
The advent of real-time large multimodal models (LMMs) like GPT-4o has sparked considerable interest in efficient LMMs. LMM frameworks typically encode visual inputs into vision tokens (continuous representations) and integrate them and textual instructions into the context of large language models (LLMs), where large-scale parameters and numerous context tokens (predominantly vision tokens) result in substantial computational overhead. Previous efforts towards efficient LMMs always focus on replacing the LLM backbone with smaller models, while neglecting the crucial issue of token quantity. In this paper, we introduce LLaVA-Mini, an efficient LMM with minimal vision tokens. To achieve a high compression ratio of vision tokens while preserving visual information, we first analyze how LMMs understand vision tokens and find that most vision tokens only play a crucial role in the early layers of LLM backbone, where they mainly fuse visual information into text tokens. Building on this finding, LLaVA-Mini introduces modality pre-fusion to fuse visual information into text tokens in advance, thereby facilitating the extreme compression of vision tokens fed to LLM backbone into one token. LLaVA-Mini is a unified large multimodal model that can support the understanding of images, high-resolution images, and videos in an efficient manner. Experiments across 11 image-based and 7 video-based benchmarks demonstrate that LLaVA-Mini outperforms LLaVA-v1.5 with just 1 vision token instead of 576. Efficiency analyses reveal that LLaVA-Mini can reduce FLOPs by 77%, deliver low-latency responses within 40 milliseconds, and process over 10,000 frames of video on the GPU hardware with 24GB of memory.
实时大型多模态模型(LMM)如GPT-4o的出现,引发了人们对高效LMM的极大兴趣。LMM框架通常将视觉输入编码为视觉令牌(连续表示),并将它们和文本指令集成到大型语言模型(LLM)的上下文中。大规模的参数和众多的上下文令牌(主要是视觉令牌)导致了巨大的计算开销。先前对高效LMM的努力总是集中在用较小的模型替换LLM主干,而忽视了令牌数量这一关键问题。在本文中,我们介绍了LLaVA-Mini,这是一种具有最少视觉令牌的高效LMM。为了实现高压缩比的视觉令牌同时保留视觉信息,我们首先分析LMM如何理解视觉令牌,并发现大多数视觉令牌仅在LLM主干的早期层中发挥关键作用,它们主要是将视觉信息融合到文本令牌中。基于这一发现,LLaVA-Mini引入了模态预融合,预先将视觉信息融合到文本令牌中,从而便于将LLM主干所接收的视觉令牌压缩到一个令牌内。LLaVA-Mini是一个统一的大型多模态模型,可以以高效的方式支持图像、高分辨率图像和视频的理解。在11个基于图像和7个基于视频的基准测试上的实验表明,LLaVA-Mini的性能优于使用576个视觉令牌而非仅使用1个令牌的LLaVA-v1.5。效率分析显示,LLaVA-Mini可以减少77%的浮点运算次数(FLOPs),在40毫秒内实现低延迟响应,并在具有24GB内存的GPU硬件上处理超过1万个视频帧。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/ictnlp/LLaVA-Mini; Model: https://huggingface.co/ICTNLP/llava-mini-llama-3.1-8b
Summary
本文介绍了LLaVA-Mini这一高效的多模态模型。它通过预先融合视觉信息,将视觉令牌(tokens)压缩到一个令牌中,并简化了大型语言模型(LLM)的计算量。实验结果证明了LLaVA-Mini相较于先前的模型有更高效的性能,并且在图像和视频任务中表现优秀。其在处理视频任务时具备高度优化的能力,在GPU硬件上实现快速响应和大量处理能力。LLaVA-Mini能在提供有效结果的同时大大减少计算资源和时间的消耗。它不仅减少浮点运算量达77%,并且支持在24GB内存环境下处理超过一万帧的视频数据,并且提供快速的响应时间(低于40毫秒)。总的来说,LLaVA-Mini是一个高效、快速的多模态模型。
Key Takeaways
以下是本文的关键见解要点:
LLaVA-Mini是一种高效的实时多模态模型,引入预融合策略以减少计算量和令牌数量。它能够简化大型语言模型的运算复杂度,大幅提高模型的执行效率。此模型使得复杂的图像理解和视频理解任务变得更为高效。
LLaVA-Mini通过预先融合视觉信息到文本令牌中,大幅减少了对视觉令牌的需求。大多数视觉令牌仅在大型语言模型的早期层次中发挥关键作用,此发现成为设计LLaVA-Mini的基础原理。该模型能够用一个令牌替代传统的数百个视觉令牌,极大提升了效率。
实验结果显示,LLaVA-Mini在图像和视频的多个基准测试中表现出卓越的性能,尤其是在图像处理的速度和效率上相较于其他版本有着显著提升。它通过简洁的计算量和时间消耗展现了显著的性能提升。即使在复杂任务如处理高清晰度图像和视频时也能维持高效表现。
点此查看论文截图

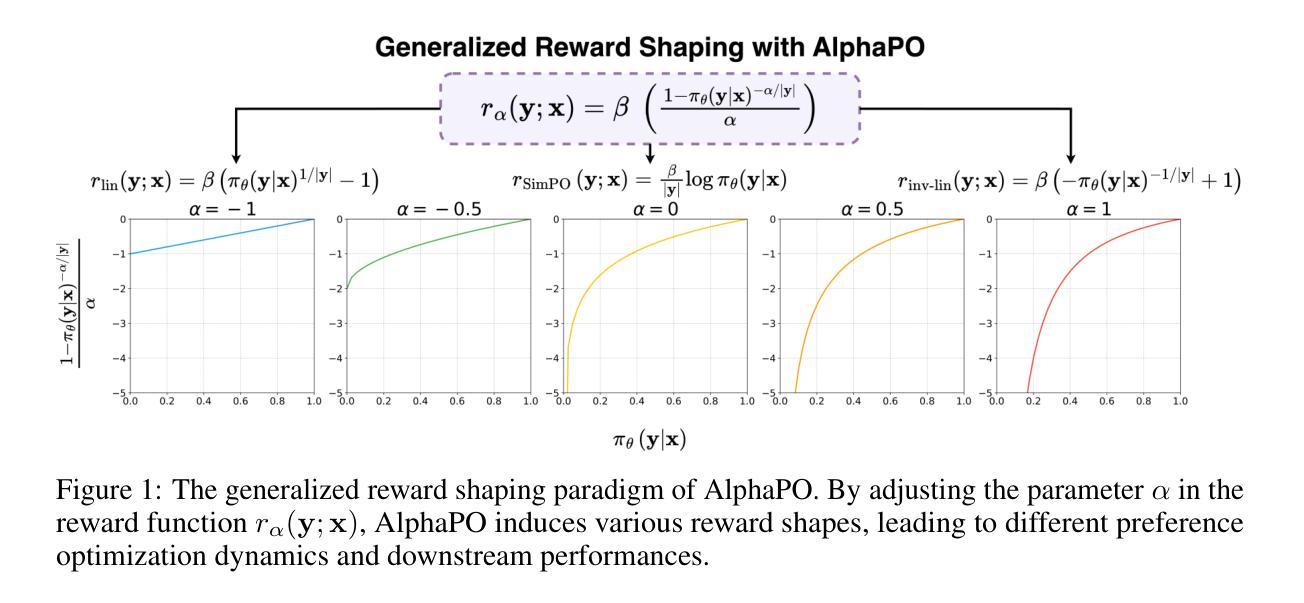
AlphaPO – Reward shape matters for LLM alignment
Authors:Aman Gupta, Shao Tang, Qingquan Song, Sirou Zhu, Jiwoo Hong, Ankan Saha, Viral Gupta, Noah Lee, Eunki Kim, Jason Zhu, Natesh Pillai, S. Sathiya Keerthi
Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) and its variants have made huge strides toward the effective alignment of large language models (LLMs) to follow instructions and reflect human values. More recently, Direct Alignment Algorithms (DAAs) have emerged in which the reward modeling stage of RLHF is skipped by characterizing the reward directly as a function of the policy being learned. Examples include Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and Simple Preference Optimization (SimPO). These methods often suffer from likelihood displacement, a phenomenon by which the probabilities of preferred responses are often reduced undesirably. In this paper, we argue that, for DAAs the reward (function) shape matters. We introduce AlphaPO, a new DAA method that leverages an $\alpha$-parameter to help change the shape of the reward function beyond the standard log reward. AlphaPO helps maintain fine-grained control over likelihood displacement and over-optimization. Compared to SimPO, one of the best performing DAAs, AlphaPO leads to about 7% to 10% relative improvement in alignment performance for the instruct versions of Mistral-7B and Llama3-8B. The analysis and results presented highlight the importance of the reward shape, and how one can systematically change it to affect training dynamics, as well as improve alignment performance.
强化学习结合人类反馈(RLHF)及其变体在使大型语言模型(LLM)有效对齐以遵循指令和反映人类价值观方面取得了巨大进步。最近,直接对齐算法(DAA)应运而生,其中省略了RLHF的奖励建模阶段,通过将奖励直接表征为正在学习的策略的函数来实现。例如,包括直接偏好优化(DPO)和简单偏好优化(SimPO)。这些方法常常遭受可能性位移(likelihood displacement)的问题,这是一种现象,由此产生的优选响应的概率往往被不必要地降低。在本文中,我们主张对于DAAs来说,奖励(函数)的形状很重要。我们引入了AlphaPO,这是一种新的DAA方法,它利用一个α参数来帮助改变超出标准对数奖励的奖励函数的形状。AlphaPO有助于对可能性位移和过度优化进行精细控制。与表现最佳的DAA之一SimPO相比,AlphaPO在对Mistral-7B和Llama3-8B的指令版本的对齐性能上带来了约7%到10%的相对改进。所呈现的分析和结果突出了奖励形状的重要性,以及如何系统地改变它来影响训练动态并提高对齐性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint. Work in progress
Summary
强化学习与人类反馈(RLHF)及其变体在实现大型语言模型(LLM)的有效对齐以遵循指令和反映人类价值观方面取得了巨大进展。最近,直接对齐算法(DAA)的出现跳过了RLHF的奖励建模阶段,直接将奖励表征为正在学习的策略的函数。然而,这些方法常常受到几率位移现象的影响,使得首选响应的概率不恰当地降低。本文提出AlphaPO,一种新型DAA方法,通过利用α参数改变奖励函数的形状,帮助精细控制几率位移和过度优化。相较于表现最佳的DAA之一SimPO,AlphaPO在对齐性能上相对提升了约7%到10%。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习与人类反馈(RLHF)在大型语言模型(LLM)对齐方面取得显著进展。
- 直接对齐算法(DAA)跳过奖励建模阶段,直接表征奖励为正在学习的策略的函数。
- DAA方法常面临几率位移问题,即首选响应的概率降低。
- AlphaPO是一种新型DAA方法,通过利用α参数改变奖励函数形状来解决上述问题。
- AlphaPO相较于SimPO在对齐性能上有相对提升。
- 奖励函数的形状对训练动态和对齐性能有重要影响。
点此查看论文截图

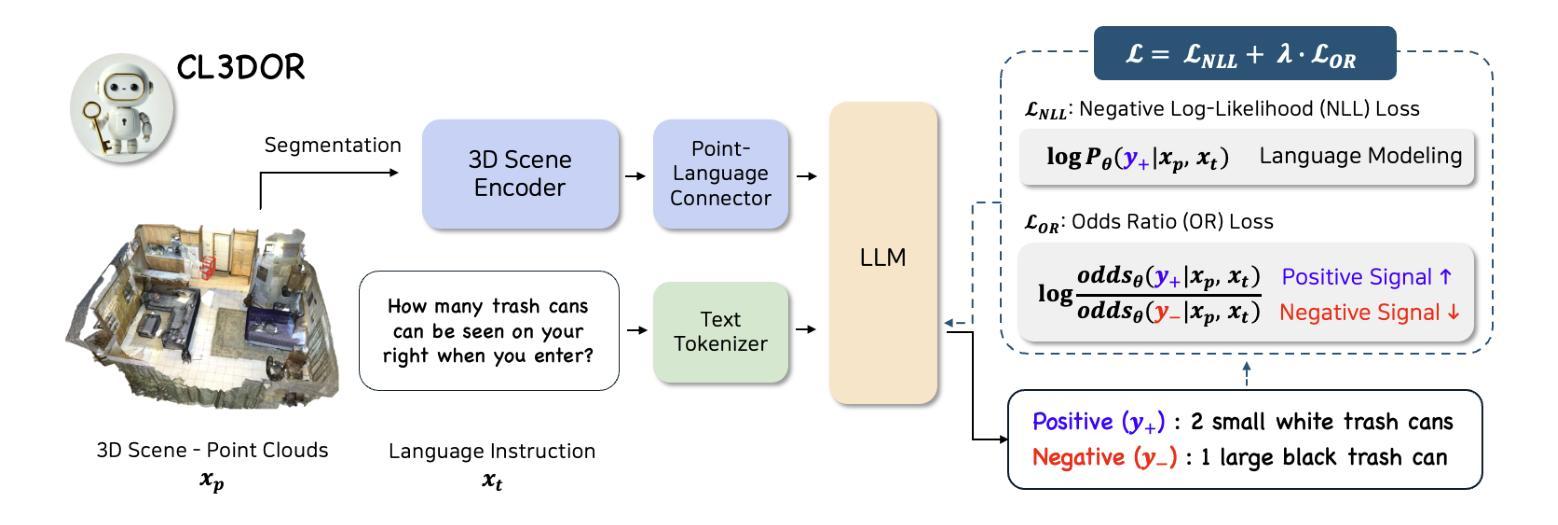
CL3DOR: Contrastive Learning for 3D Large Multimodal Models via Odds Ratio on High-Resolution Point Clouds
Authors:Keonwoo Kim, Yeongjae Cho, Taebaek Hwang, Minsoo Jo, Sangdo Han
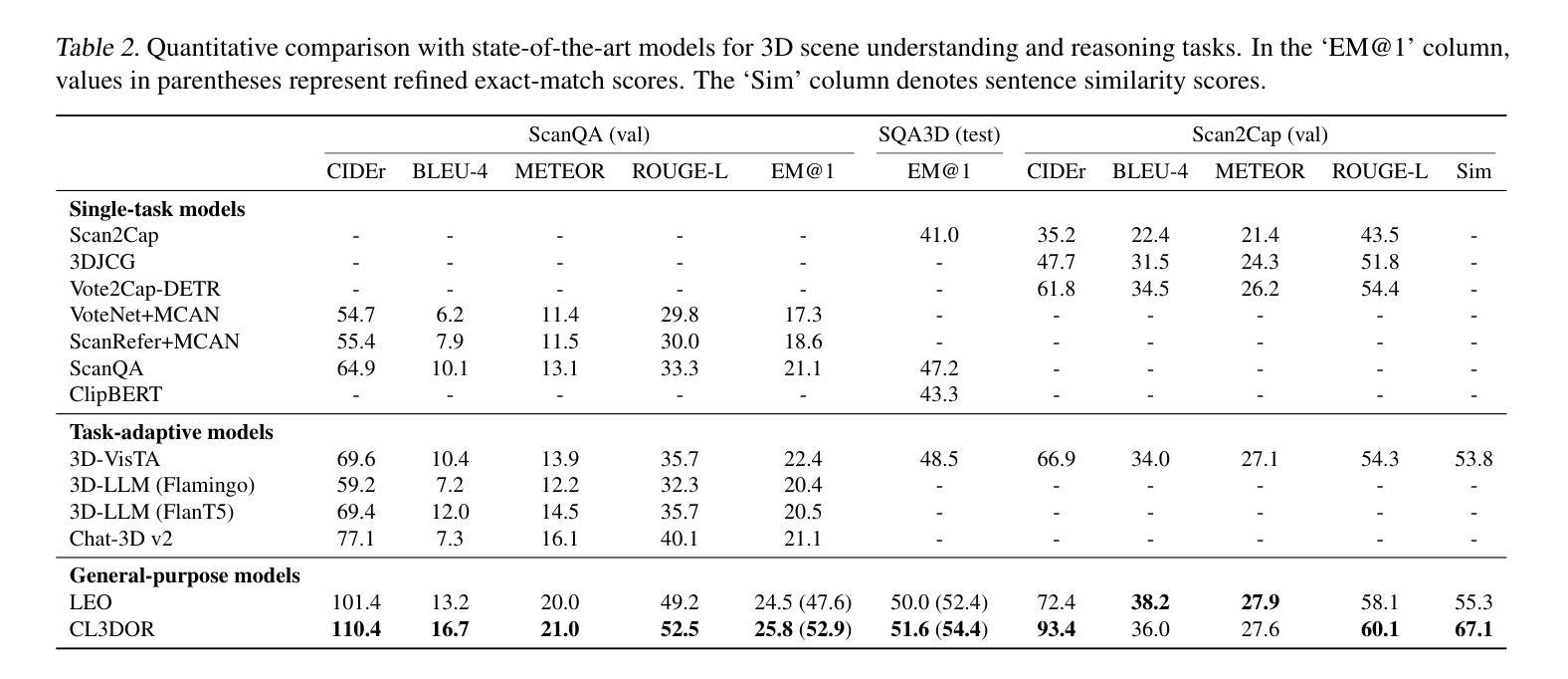
Recent research has demonstrated that Large Language Models (LLMs) are not limited to text-only tasks but can also function as multimodal models across various modalities, including audio, images, and videos. In particular, research on 3D Large Multimodal Models (3D LMMs) is making notable strides, driven by the potential of processing higher-dimensional data like point clouds. However, upon closer examination, we find that the visual and textual content within each sample of existing training datasets lacks both high informational granularity and clarity, which serve as a bottleneck for precise cross-modal understanding. To address these issues, we propose CL3DOR, Contrastive Learning for 3D large multimodal models via Odds ratio on high-Resolution point clouds, designed to ensure greater specificity and clarity in both visual and textual content. Specifically, we increase the density of point clouds per object and construct informative hard negative responses in the training dataset to penalize unwanted responses. To leverage hard negative responses, we incorporate the odds ratio as an auxiliary term for contrastive learning into the conventional language modeling loss. CL3DOR achieves state-of-the-art performance in 3D scene understanding and reasoning benchmarks. Additionally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of CL3DOR’s key components through extensive experiments.
最近的研究表明,大型语言模型(LLM)不仅限于文本任务,还可以作为跨多种模态的多媒体模型,包括音频、图像和视频。特别是,关于3D大型多媒体模型(3D LMM)的研究正在取得显著进展,这得益于处理点云等高维数据的潜力。然而,经过仔细观察,我们发现现有训练数据集中的样本在视觉和文本内容方面缺乏高度信息粒度和清晰度,这成为精确跨模态理解的瓶颈。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了CL3DOR,即基于高分辨率点云的3D大型多媒体模型的对比学习法(Contrastive Learning for 3D large multimodal models via Odds ratio)。它旨在确保视觉和文本内容具有更高的特异性和清晰度。具体来说,我们增加了每个对象的点云密度,并在训练数据集中构建有信息量的硬负响应来惩罚不想要的响应。为了利用硬负响应,我们将比值作为对比学习的辅助术语,纳入传统语言建模损失中。CL3DOR在3D场景理解和推理基准测试中取得了最先进的性能。此外,我们还通过大量实验验证了CL3DOR关键组件的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期研究表明,大型语言模型(LLM)不仅能完成文本任务,还能作为跨多种模式的多模态模型处理音频、图像和视频。特别是关于三维大型多模态模型(3D LMMs)的研究正在取得显著进展,其处理点云等更高维度数据的能力备受关注。然而,现有训练数据集样本中的视觉和文本内容缺乏高信息粒度和清晰度,成为精确跨模态理解的瓶颈。为解决这些问题,本文提出CL3DOR方法,通过高分辨率点云的赔率比率进行三维大型多模态模型的对比学习,确保视觉和文本内容更具特异性和清晰度。CL3DOR方法增加点云对象的密度,构建训练集中的信息性硬负响应来惩罚不想要的响应。借助硬负响应,我们将赔率比率作为对比学习的辅助术语纳入常规语言建模损失中。CL3DOR在三维场景理解和推理基准测试中达到最新水平,并通过大量实验证明了其关键组件的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)不仅能处理文本任务,还能作为多模态模型处理音频、图像和视频。
- 三维大型多模态模型(3D LMMs)研究正在取得显著进展,尤其在处理高维度数据如点云方面。
- 现有训练数据集存在视觉和文本内容缺乏高信息粒度和清晰度的问题,这是精确跨模态理解的瓶颈。
- CL3DOR方法通过增加点云对象的密度和构建信息性硬负响应来解决这一问题。
- CL3DOR将赔率比率纳入常规语言建模损失中,以提高模型的特异性和清晰度。
- CL3DOR方法在三维场景理解和推理基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


Progressive Document-level Text Simplification via Large Language Models
Authors:Dengzhao Fang, Jipeng Qiang, Yi Zhu, Yunhao Yuan, Wei Li, Yan Liu
Research on text simplification has primarily focused on lexical and sentence-level changes. Long document-level simplification (DS) is still relatively unexplored. Large Language Models (LLMs), like ChatGPT, have excelled in many natural language processing tasks. However, their performance on DS tasks is unsatisfactory, as they often treat DS as merely document summarization. For the DS task, the generated long sequences not only must maintain consistency with the original document throughout, but complete moderate simplification operations encompassing discourses, sentences, and word-level simplifications. Human editors employ a hierarchical complexity simplification strategy to simplify documents. This study delves into simulating this strategy through the utilization of a multi-stage collaboration using LLMs. We propose a progressive simplification method (ProgDS) by hierarchically decomposing the task, including the discourse-level, topic-level, and lexical-level simplification. Experimental results demonstrate that ProgDS significantly outperforms existing smaller models or direct prompting with LLMs, advancing the state-of-the-art in the document simplification task.
关于文本简化的研究主要集中在词汇和句子层面的改变上。长文本级别的简化(DS)仍然相对未被探索。大型语言模型(LLM),如ChatGPT,在许多自然语言处理任务中都表现出色。然而,它们在DS任务上的表现并不令人满意,因为它们往往将DS仅仅视为文档摘要。对于DS任务,生成的长序列不仅需要与原始文档保持一致,还必须包含涵盖段落、句子和词汇级别的适度简化操作。人类编辑采用分层复杂简化策略来简化文档。本研究致力于通过利用多阶段协作来模拟这一策略。我们提出了一种分层分解任务的渐进简化方法(ProgDS),包括篇章级别、主题级别和词汇级别的简化。实验结果表明,ProgDS显著优于现有的小型模型或直接用LLM进行提示的方法,在文档简化任务中达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本研究主要集中在词汇和句子层面的简化,而长文本层面的简化(DS)仍然相对未被探索。大型语言模型(LLM)如ChatGPT在许多自然语言处理任务中表现出色,但在DS任务上的表现却不尽人意。本文提出了一种渐进式简化方法(ProgDS),通过层次分解任务,包括篇章层面、主题层面和词汇层面的简化,来模拟人类编辑的层次复杂性简化策略。实验结果表明,ProgDS显著优于现有的小型模型或直接在LLMs中的提示,推动了文档简化任务的最先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- 研究表明,长文本简化(DS)仍然是一个相对未被探索的领域。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在DS任务上的表现不尽人意,因为它们往往将DS视为简单的文档摘要。
- 人类编辑采用层次复杂性简化策略来简化文档。
- 本文提出了一种渐进式简化方法(ProgDS),通过层次分解任务来模拟这种策略。
- ProgDS包括篇章层面、主题层面和词汇层面的简化。
- 实验结果表明,ProgDS在文档简化任务上显著优于现有模型。
点此查看论文截图

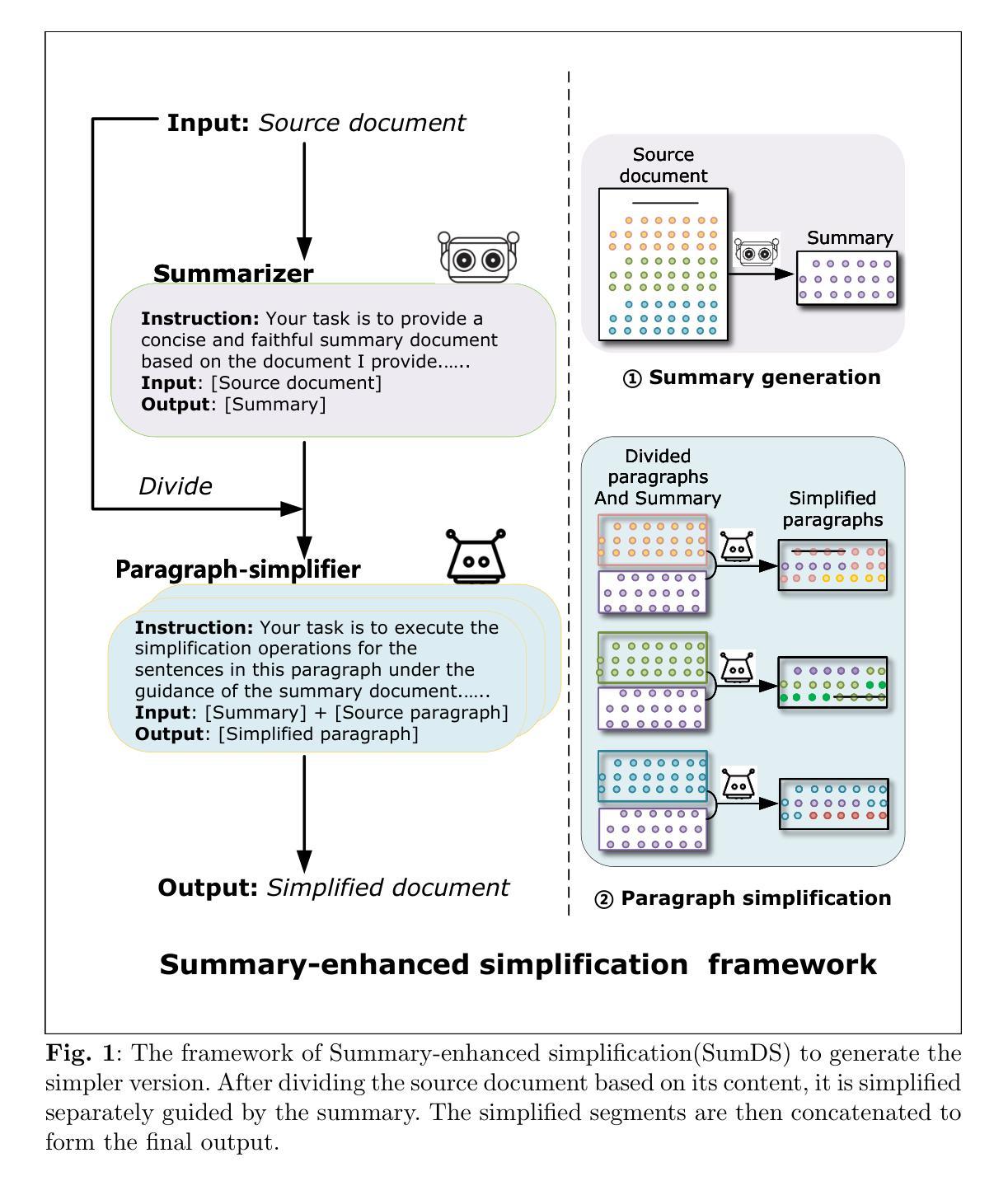
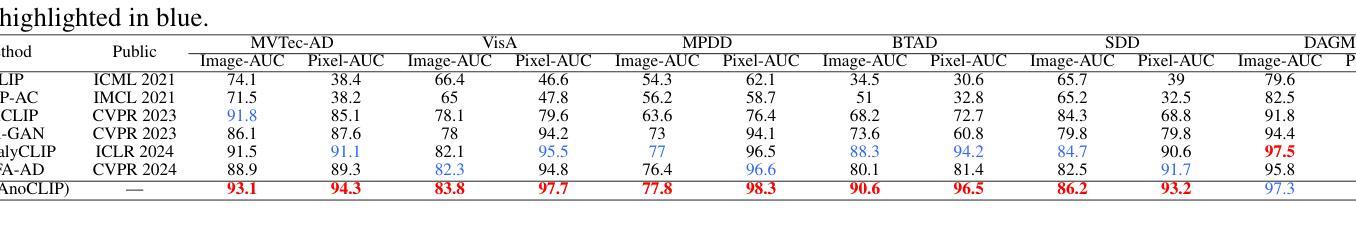
KAnoCLIP: Zero-Shot Anomaly Detection through Knowledge-Driven Prompt Learning and Enhanced Cross-Modal Integration
Authors:Chengyuan Li, Suyang Zhou, Jieping Kong, Lei Qi, Hui Xue
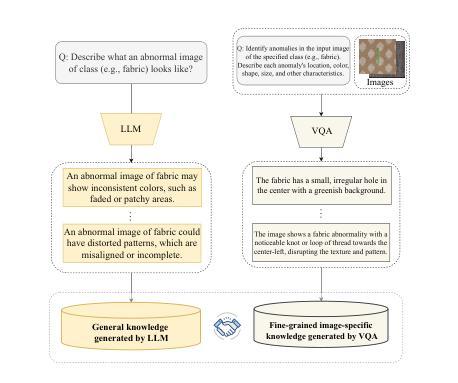
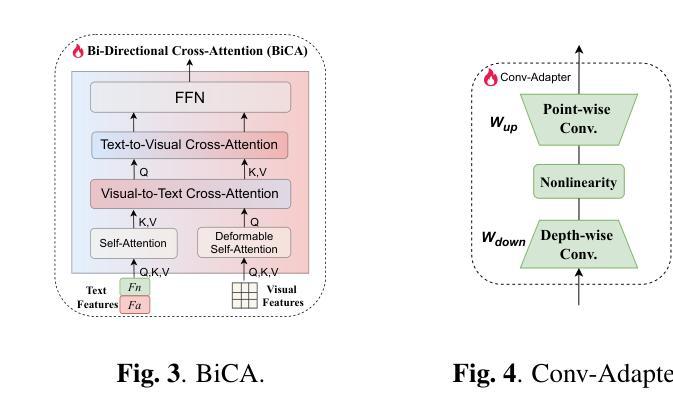
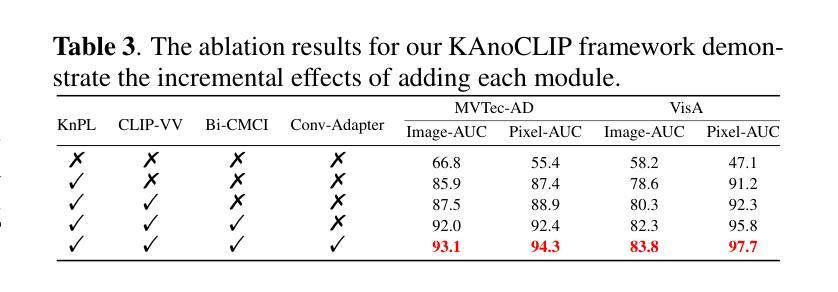
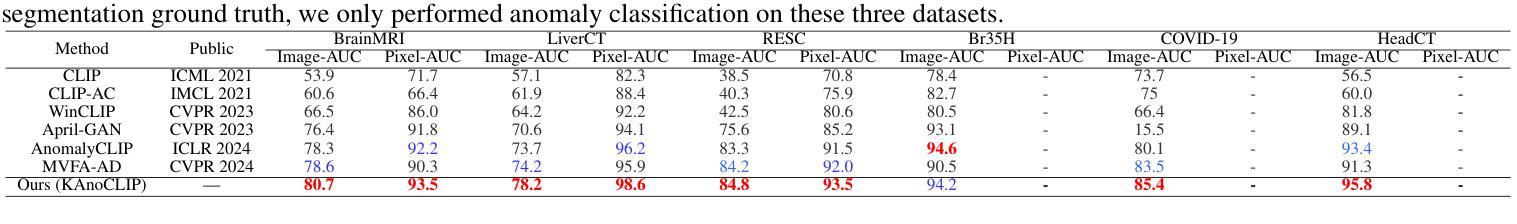
Zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) identifies anomalies without needing training samples from the target dataset, essential for scenarios with privacy concerns or limited data. Vision-language models like CLIP show potential in ZSAD but have limitations: relying on manually crafted fixed textual descriptions or anomaly prompts is time-consuming and prone to semantic ambiguity, and CLIP struggles with pixel-level anomaly segmentation, focusing more on global semantics than local details. To address these limitations, We introduce KAnoCLIP, a novel ZSAD framework that leverages vision-language models. KAnoCLIP combines general knowledge from a Large Language Model (GPT-3.5) and fine-grained, image-specific knowledge from a Visual Question Answering system (Llama3) via Knowledge-Driven Prompt Learning (KnPL). KnPL uses a knowledge-driven (KD) loss function to create learnable anomaly prompts, removing the need for fixed text prompts and enhancing generalization. KAnoCLIP includes the CLIP visual encoder with V-V attention (CLIP-VV), Bi-Directional Cross-Attention for Multi-Level Cross-Modal Interaction (Bi-CMCI), and Conv-Adapter. These components preserve local visual semantics, improve local cross-modal fusion, and align global visual features with textual information, enhancing pixel-level anomaly detection. KAnoCLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance in ZSAD across 12 industrial and medical datasets, demonstrating superior generalization compared to existing methods.
零样本异常检测(ZSAD)能够在无需目标数据集的训练样本的情况下识别异常值,对于存在隐私担忧或数据有限的情况至关重要。CLIP等视觉语言模型在ZSAD中显示出潜力,但也存在局限性:依赖手动制作的固定文本描述或异常提示既耗时又容易产生语义歧义,CLIP在像素级异常分割方面存在困难,更侧重于全局语义而非局部细节。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了KAnoCLIP,这是一个利用视觉语言模型的新型ZSAD框架。KAnoCLIP通过知识驱动提示学习(KnPL)结合大型语言模型(GPT-3.5)的通用知识和来自视觉问答系统(Llama3)的精细图像特定知识。KnPL使用知识驱动(KD)损失函数来创建可学习的异常提示,消除了对固定文本提示的需求,提高了泛化能力。KAnoCLIP包括带有V-V注意力(CLIP-VV)的CLIP视觉编码器、用于多级跨模态交互的双向跨注意力(Bi-CMCI)和Conv-Adapter。这些组件保留了局部视觉语义,改进了局部跨模态融合,并将全局视觉特征与文本信息对齐,提高了像素级异常检测能力。KAnoCLIP在12个工业和医疗数据集上实现了零样本异常检测的卓越性能,显示出优于现有方法的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary:零样本异常检测(ZSAD)无需目标数据集的训练样本即可识别异常。虽然CLIP等视觉语言模型在ZSAD中显示出潜力,但它们存在依赖手动构建的文本描述和异常提示的问题,且难以进行像素级异常分割。为解决这些问题,提出了KAnoCLIP框架,结合大型语言模型(GPT-3.5)和视觉问答系统(Llama3)的知识驱动提示学习(KnPL),无需固定的文本提示即可创建可学习的异常提示,提高泛化能力。KAnoCLIP包括CLIP视觉编码器、双向跨模态交互的多层次交叉注意力等技术,实现了像素级的异常检测,并在多个工业医疗数据集上取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 零样本异常检测(ZSAD)无需目标数据集的训练样本即可完成异常识别。
- CLIP等视觉语言模型在ZSAD中展现出潜力,但存在对固定文本描述的依赖和语义模糊问题。
- KAnoCLIP框架结合大型语言模型和视觉问答系统的知识来解决上述问题。
- 知识驱动提示学习(KnPL)能够创建可学习的异常提示,提高了泛化能力。
- KAnoCLIP包含多项技术改进,包括改进的CLIP视觉编码器、双向跨模态交互等,实现了像素级的异常检测。
- KAnoCLIP在多个工业医疗数据集上的性能达到了先进水平。
点此查看论文截图

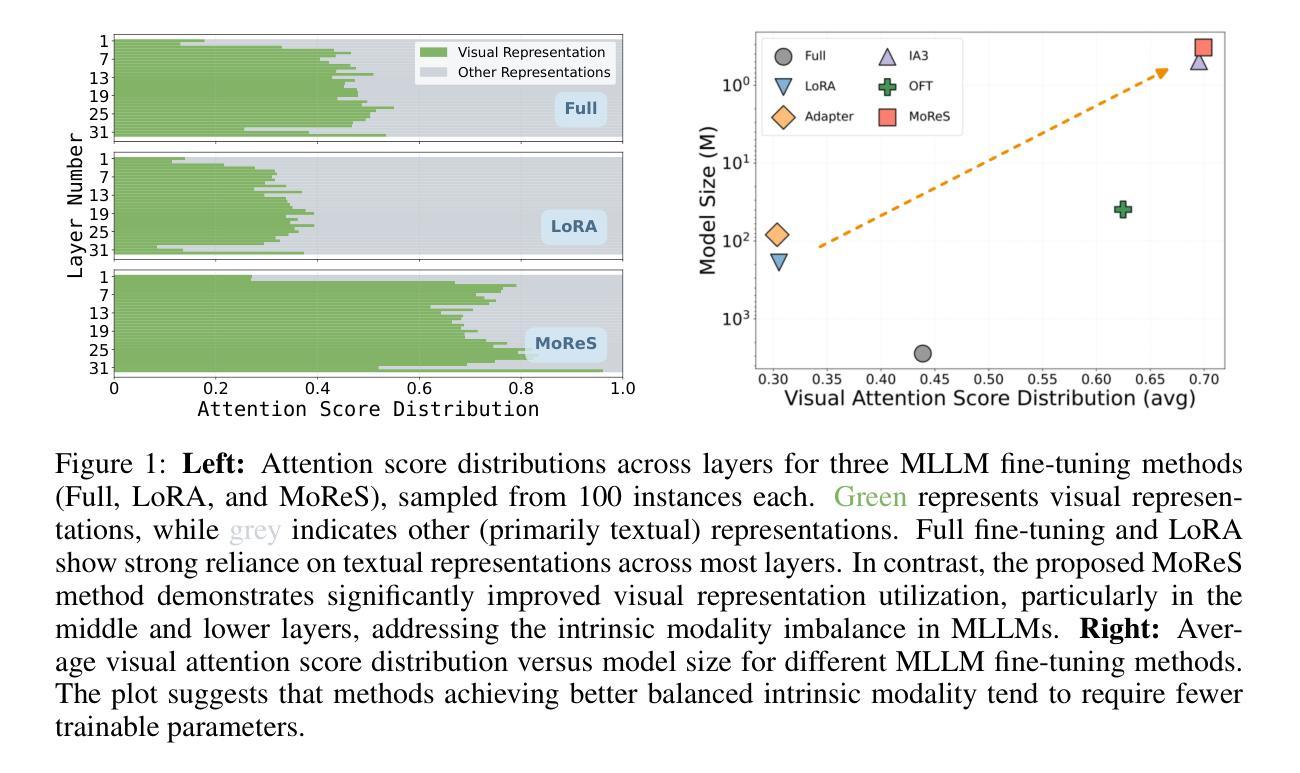
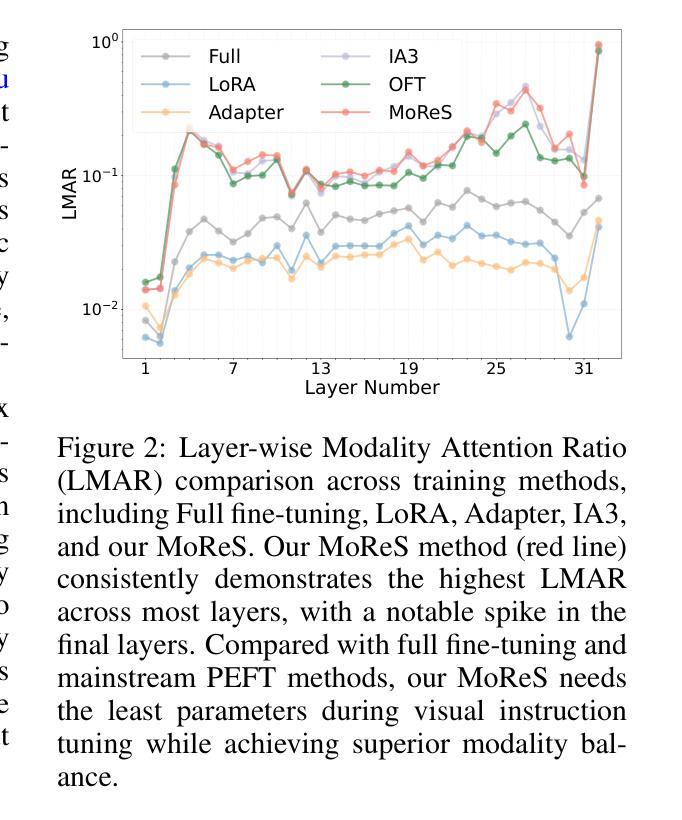
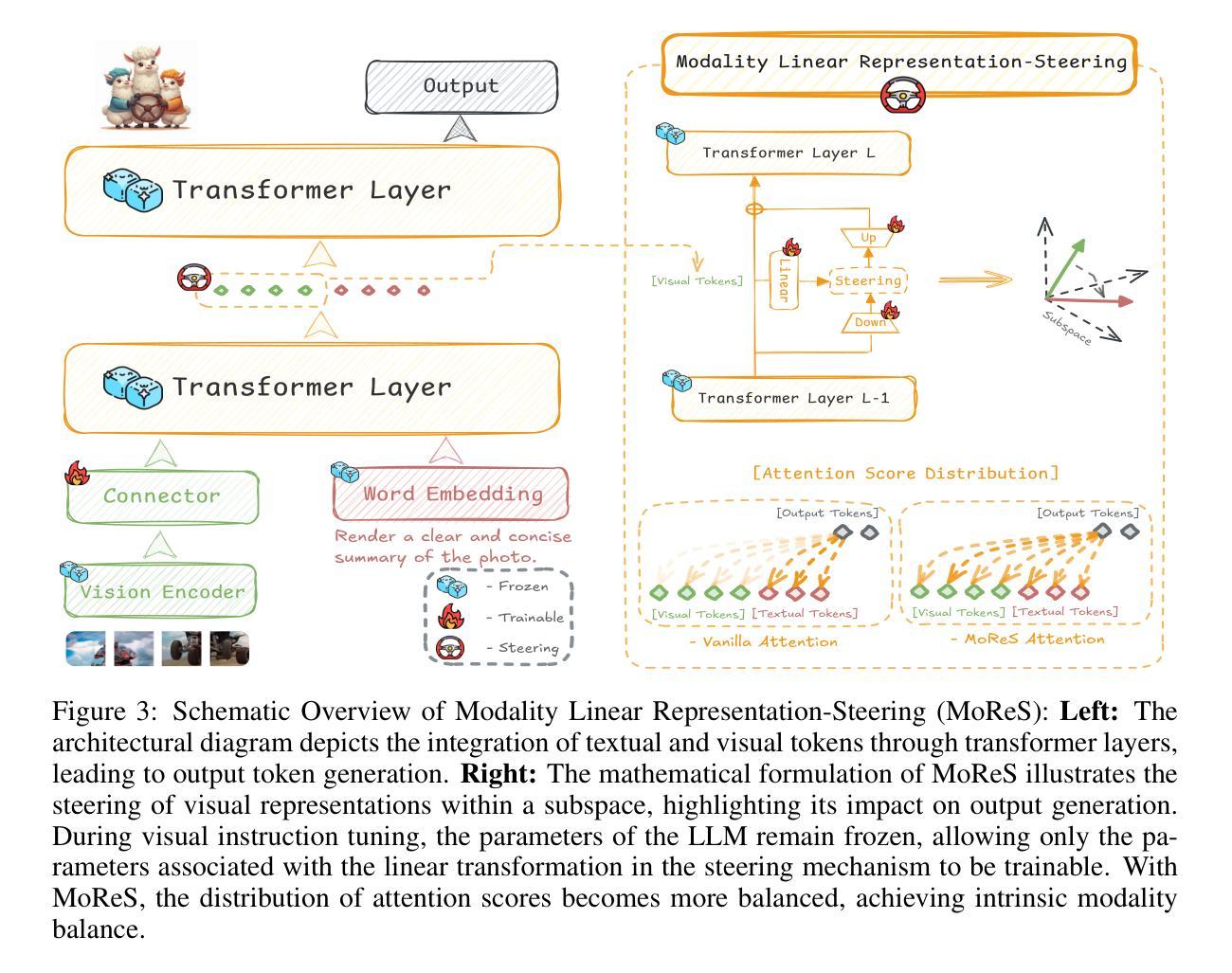
LLaVA Steering: Visual Instruction Tuning with 500x Fewer Parameters through Modality Linear Representation-Steering
Authors:Jinhe Bi, Yujun Wang, Haokun Chen, Xun Xiao, Artur Hecker, Volker Tresp, Yunpu Ma
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly advanced visual tasks by integrating visual representations into large language models (LLMs). The textual modality, inherited from LLMs, equips MLLMs with abilities like instruction following and in-context learning. In contrast, the visual modality enhances performance in downstream tasks by leveraging rich semantic content, spatial information, and grounding capabilities. These intrinsic modalities work synergistically across various visual tasks. Our research initially reveals a persistent imbalance between these modalities, with text often dominating output generation during visual instruction tuning. This imbalance occurs when using both full fine-tuning and parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods. We then found that re-balancing these modalities can significantly reduce the number of trainable parameters required, inspiring a direction for further optimizing visual instruction tuning. We introduce Modality Linear Representation-Steering (MoReS) to achieve the goal. MoReS effectively re-balances the intrinsic modalities throughout the model, where the key idea is to steer visual representations through linear transformations in the visual subspace across each model layer. To validate our solution, we composed LLaVA Steering, a suite of models integrated with the proposed MoReS method. Evaluation results show that the composed LLaVA Steering models require, on average, 500 times fewer trainable parameters than LoRA needs while still achieving comparable performance across three visual benchmarks and eight visual question-answering tasks. Last, we present the LLaVA Steering Factory, an in-house developed platform that enables researchers to quickly customize various MLLMs with component-based architecture for seamlessly integrating state-of-the-art models, and evaluate their intrinsic modality imbalance.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)通过将视觉表示集成到大型语言模型(LLMs)中,显著地推进了视觉任务的发展。文本模态继承自LLMs,使MLLMs具备指令遵循和上下文学习等功能。相比之下,视觉模态通过利用丰富的语义内容、空间信息和定位能力,提高了下游任务的性能。这些内在模态在不同的视觉任务中协同工作。我们的研究最初揭示了这些模态之间持久的失衡,文本通常在视觉指令调整过程中主导输出生成。这种不平衡在使用全微调(Full Fine-tuning)和参数高效微调(PEFT)方法时都会发生。随后,我们发现重新平衡这些模态可以大大减少所需的训练参数数量,为进一步优化视觉指令调整提供了方向。我们引入模态线性表示转向(MoReS)来实现这一目标。MoReS有效地在整个模型中重新平衡了内在模态,其关键思想是通过每个模型层的视觉子空间的线性转换来引导视觉表示。为了验证我们的解决方案,我们开发了LLaVA转向套件,这是一套集成了所提出的MoReS方法的模型。评估结果表明,LLaVA转向套件组成的模型平均需要比LoRA少500倍的训练参数,同时在三个视觉基准测试和八个视觉问答任务中仍能保持相当的性能。最后,我们推出了LLaVA转向工厂——一个内部开发的平台,使研究人员能够迅速定制各种MLLMs,通过组件式架构无缝集成最新模型,并评估其内在模态失衡情况。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在集成视觉表征到大型语言模型(LLMs)后对视觉任务的显著改进。文本模态赋予MLLMs指令遵循和上下文学习的能力,而视觉模态则通过丰富的语义内容、空间信息和接地能力增强下游任务性能。研究发现,在视觉指令微调中存在文本和视觉模态之间的持久不平衡,文本通常主导输出生成。通过重新平衡这些模态,可以减少所需的训练参数数量。为此,引入了模态线性表示转向(MoReS)方法,该方法通过线性变换引导视觉表示,有效平衡了内在模态。评估结果显示,使用MoReS的LLaVA转向模型在减少大量训练参数的同时,在三个视觉基准测试和八个视觉问答任务上取得了相当的性能。还介绍了LLaVA转向工厂,这是一个组件化架构的平台,使研究人员能够快速地定制各种MLLMs,无缝集成最新模型并评估其内在模态不平衡性。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs通过集成视觉表征显著改进了视觉任务性能。
- MLLMs具备文本和视觉两种模态,分别赋予不同的能力。
- 在视觉指令微调中,存在文本和视觉模态之间的不平衡。
- 重新平衡文本和视觉模态可以减少所需的训练参数数量。
- 引入MoReS方法,通过线性变换引导视觉表示,有效平衡内在模态。
- LLaVA转向模型使用MoReS方法,在减少大量训练参数的同时取得了良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

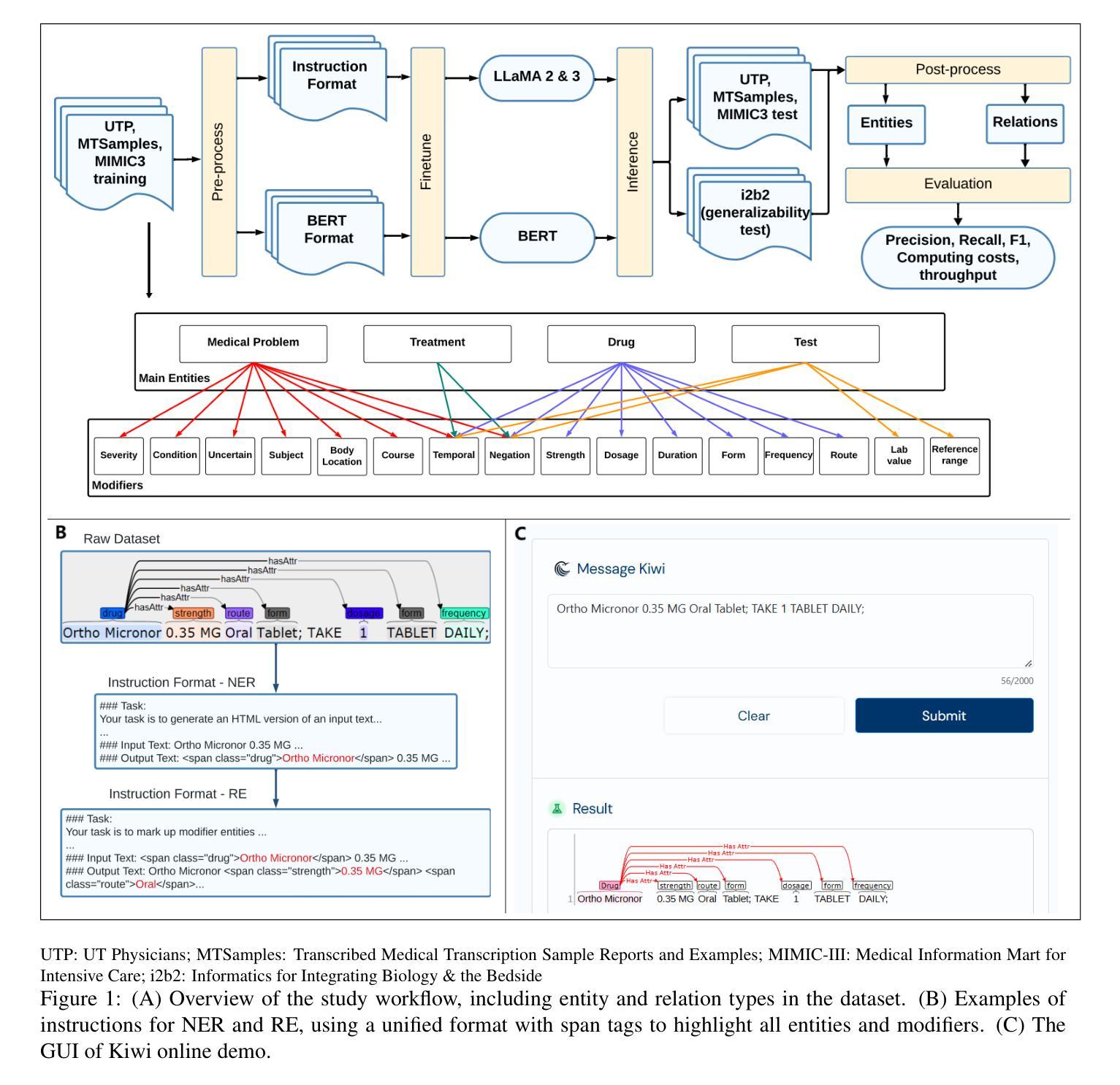
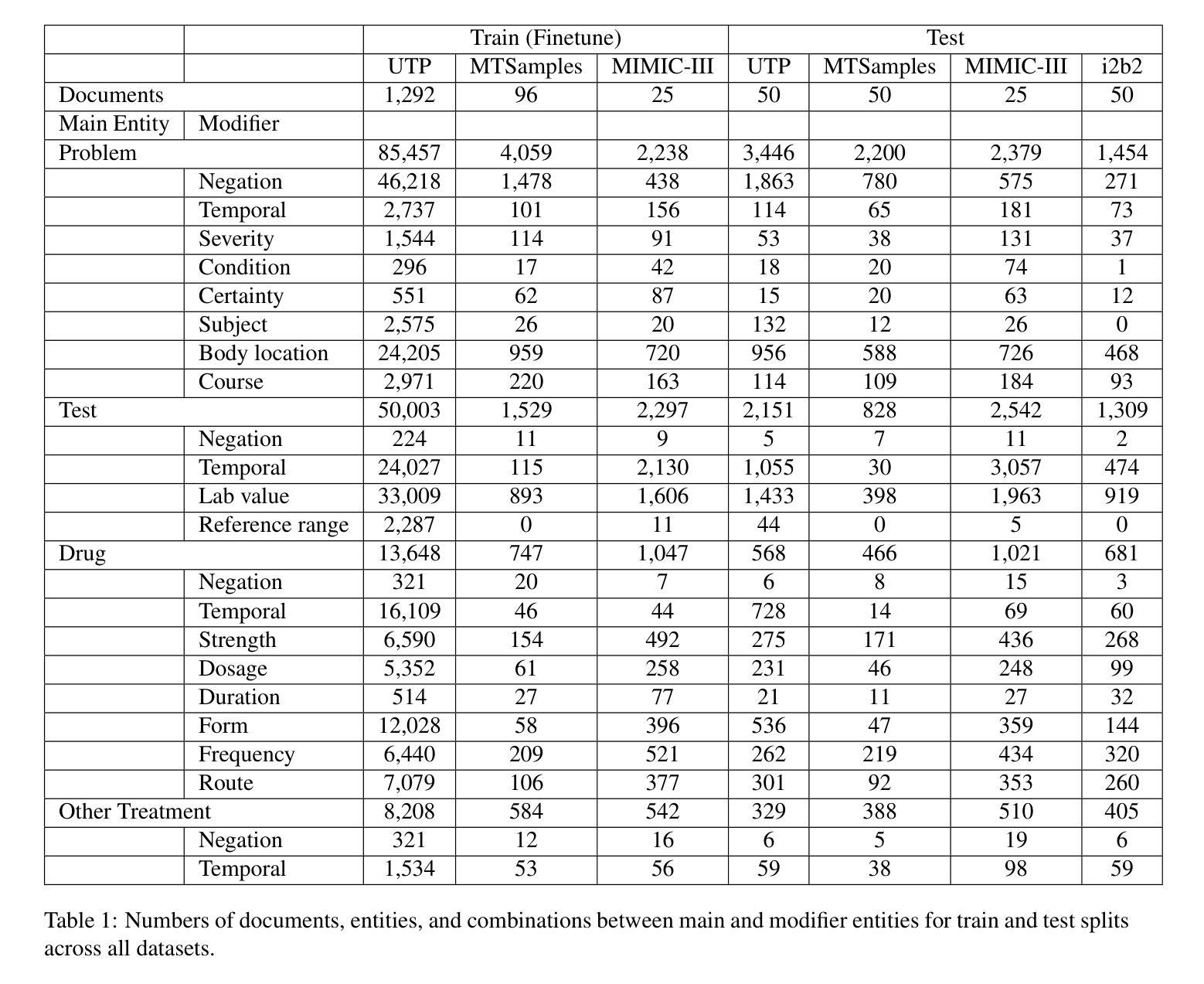
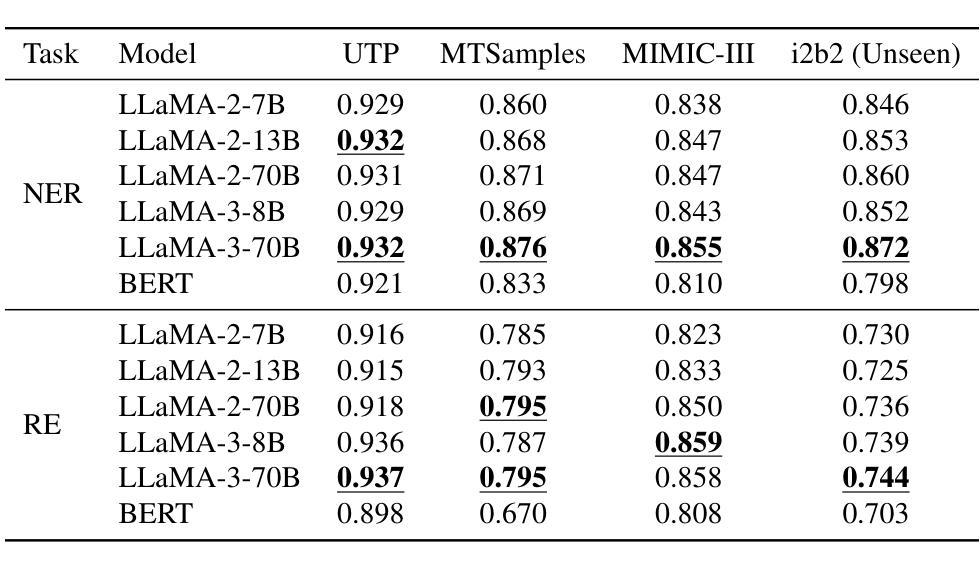
Information Extraction from Clinical Notes: Are We Ready to Switch to Large Language Models?
Authors:Yan Hu, Xu Zuo, Yujia Zhou, Xueqing Peng, Jimin Huang, Vipina K. Keloth, Vincent J. Zhang, Ruey-Ling Weng, Qingyu Chen, Xiaoqian Jiang, Kirk E. Roberts, Hua Xu
Backgrounds: Information extraction (IE) is critical in clinical natural language processing (NLP). While large language models (LLMs) excel on generative tasks, their performance on extractive tasks remains debated. Methods: We investigated Named Entity Recognition (NER) and Relation Extraction (RE) using 1,588 clinical notes from four sources (UT Physicians, MTSamples, MIMIC-III, and i2b2). We developed an annotated corpus covering 4 clinical entities and 16 modifiers, and compared instruction-tuned LLaMA-2 and LLaMA-3 against BERT in terms of performance, generalizability, computational resources, and throughput to BERT. Results: LLaMA models outperformed BERT across datasets. With sufficient training data, LLaMA showed modest improvements (1% on NER, 1.5-3.7% on RE); improvements were larger with limited training data. On unseen i2b2 data, LLaMA-3-70B outperformed BERT by 7% (F1) on NER and 4% on RE. However, LLaMA models required more computing resources and ran up to 28 times slower. We implemented “Kiwi,” a clinical IE package featuring both models, available at https://kiwi.clinicalnlp.org/. Conclusion: This study is among the first to develop and evaluate a comprehensive clinical IE system using open-source LLMs. Results indicate that LLaMA models outperform BERT for clinical NER and RE but with higher computational costs and lower throughputs. These findings highlight that choosing between LLMs and traditional deep learning methods for clinical IE applications should remain task-specific, taking into account both performance metrics and practical considerations such as available computing resources and the intended use case scenarios.
背景:信息提取(IE)在临床自然语言处理(NLP)中至关重要。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在生成任务方面表现出色,但它们在提取任务上的表现仍存在争议。
方法:我们研究了命名实体识别(NER)和关系提取(RE),使用了来自四个来源的1588份临床笔记(UT Physicians、MTSample、MIMIC-III和i2b2)。我们开发了一个涵盖4个临床实体和16个修饰词的注释语料库,并比较了针对指令调整的LLaMA-2和LLaMA-3与BERT在性能、通用性、计算资源和吞吐量方面的表现。
结果:LLaMA模型在多个数据集上的表现均优于BERT。在充足的训练数据下,LLaMA的改进幅度较小(NER上提高1%,RE上提高1.5-3.7%);而在有限训练数据下,改进幅度较大。在未见过的i2b2数据集上,LLaMA-3-70B在NER上的F1分数高出BERT 7%,RE上高出4%。然而,LLaMA模型需要更多的计算资源,运行速度最慢时高达BERT的28倍。我们开发了名为“Kiwi”的临床信息提取软件包,它同时包含这两种模型,可在https://kiwi.clinicalnlp.org/获取。
结论:本研究是首批使用开源LLM进行临床信息提取系统的开发和评估之一。结果表明,LLaMA模型在临床NER和RE方面的表现优于BERT,但计算成本更高,吞吐量更低。这些发现表明,在选择用于临床信息提取应用的LLM和传统的深度学习方法时,应考虑到性能和实际因素,如可用的计算资源以及预期的使用场景。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLMs)在临床信息提取(IE)任务上的表现。研究通过对比LLMs模型(LLaMA-2和LLaMA-3)与传统BERT模型,在命名实体识别(NER)和关系抽取(RE)任务上进行性能、泛化能力、计算资源和处理速度的评估。结果显示,LLaMA模型在跨数据集上表现优于BERT,特别是在有限训练数据情况下改进更大。然而,LLaMA模型需要更多的计算资源并且运行速度较慢。研究还推出了一款融合两种模型的临床IE工具“Kiwi”。总之,本研究是首批利用开源LLMs开发并评估临床IE系统的研究之一,发现LLaMA模型在临床NER和RE任务上优于BERT,但计算成本更高。实际应用中需根据任务特点、性能指标、计算资源等因素选择模型。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在临床信息提取(IE)中的表现被研究。
- 对比了LLaMA-2和LLaMA-3与BERT在命名实体识别(NER)和关系抽取(RE)任务上的性能。
- LLaMA模型在多个数据集上表现优于BERT,尤其在有限训练数据情况下改进更大。
- LLaMA模型需要更多的计算资源且运行速度较慢。
- 研究推出了一款融合两种模型的临床IE工具“Kiwi”。
- 本研究是首批利用开源LLMs进行临床IE研究的其中之一。
- 结果表明,在选择临床IE应用的模型时,需综合考虑任务特点、性能指标、计算资源等因素。
点此查看论文截图

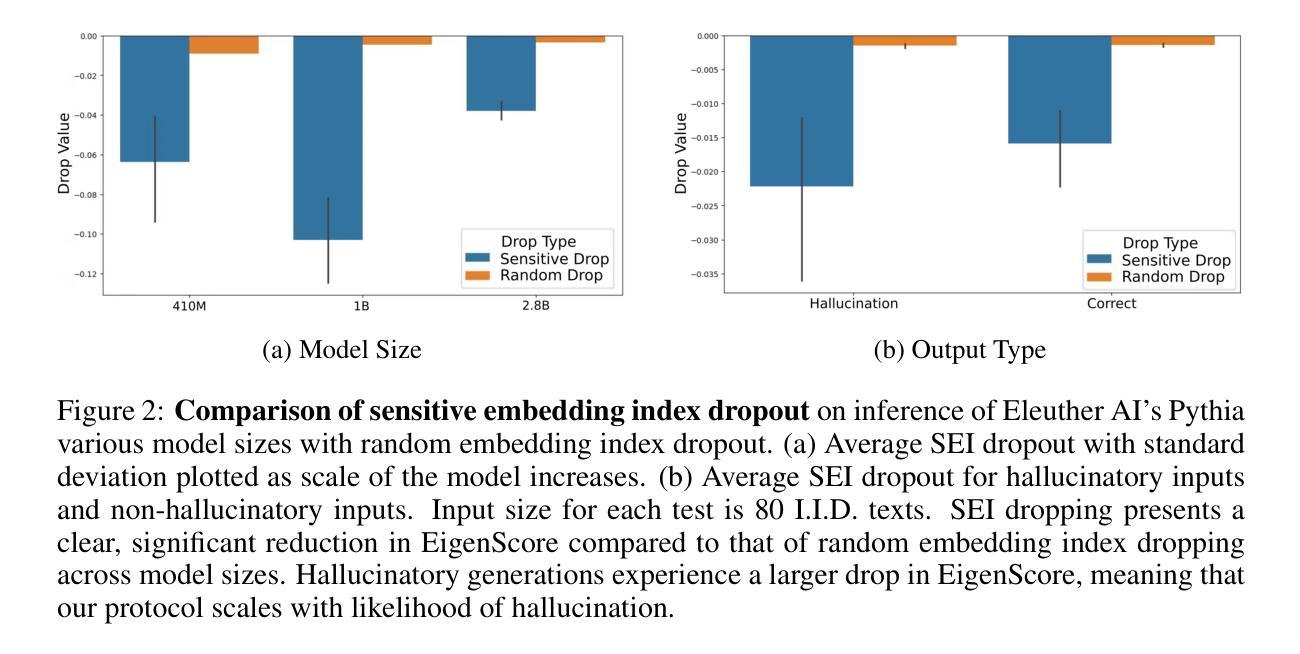
Hallucination Detox: Sensitivity Dropout (SenD) for Large Language Model Training
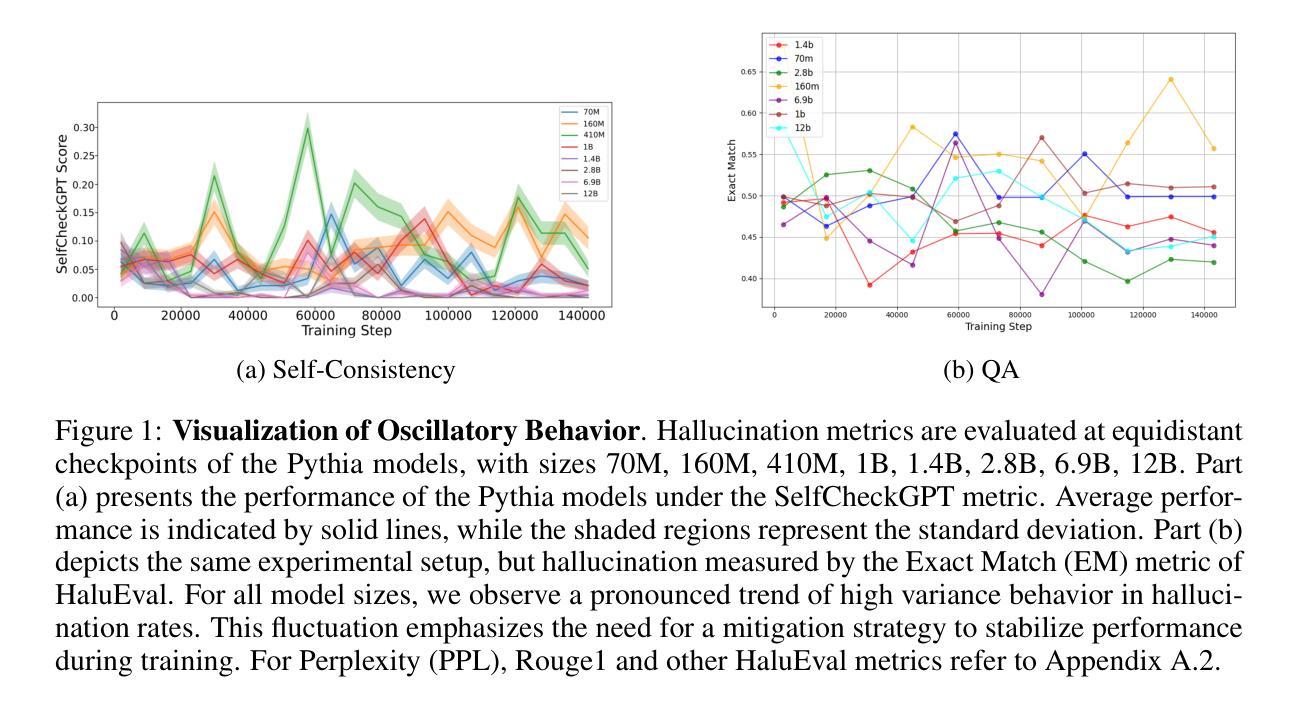
Authors:Shahrad Mohammadzadeh, Juan David Guerra, Marco Bonizzato, Reihaneh Rabbany, Golnoosh Farnadi
As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed across various industries, concerns regarding their reliability, particularly due to hallucinations - outputs that are factually inaccurate or irrelevant to user input - have grown. Our research investigates the relationship between the training process and the emergence of hallucinations to address a key gap in existing research that focuses primarily on post hoc detection and mitigation strategies. Using models from the Pythia suite (70M - 12B parameters) and several hallucination detection metrics, we analyze hallucination trends throughout training and explore LLM internal dynamics. We introduce Sensitivity Dropout (SenD), a novel training protocol designed to mitigate hallucinations by reducing variance during training. SenD achieves this by deterministically dropping embedding indices with significant variability, referred to as Sensitive Embedding Indices. In addition, we develop an unsupervised hallucination detection metric, Efficient EigenScore (EES), which approximates the traditional EigenScore at 2x speed. This efficient metric is integrated into our protocol, allowing SenD to be both computationally scalable and effective at reducing hallucinations. Our empirical evaluation demonstrates that our approach improves LLM reliability at test time by up to 40% compared to normal training while also providing an efficient method to improve factual accuracy when adapting LLMs to Wikipedia, Medical, and LegalBench domains.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在各行业的部署日益增多,关于其可靠性的担忧,特别是因幻觉输出(即事实上不准确或与用户输入不相关的输出)而产生的担忧也在增长。我们的研究旨在调查训练过程与幻觉出现之间的关系,以填补现有研究主要关注事后检测和缓解策略的不足。我们使用Pythia套件(从7千万至十亿参数)的模型和几种幻觉检测指标,分析训练过程中的幻觉趋势,并探索LLM的内部动态。我们引入了敏感性丢弃(SenD),这是一种新型训练协议,旨在通过减少训练过程中的方差来缓解幻觉。SenD通过确定性地丢弃具有重大可变性的嵌入索引来实现这一点,这些索引被称为敏感嵌入索引。此外,我们开发了一种高效的幻觉检测指标——高效特征得分(EES),该指标以两倍的速度近似传统特征得分。此高效的指标已集成到我们的协议中,使得SenD在计算上既可扩展,又能有效地减少幻觉。我们的经验评估表明,与正常训练相比,我们的方法在提高测试时LLM的可靠性方面提高了高达百分之四十,同时提供了一种在适应LLM到Wikipedia、医学和法律判例等域时提高事实准确性的高效方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 15 figures, under review at ICLR, accepted to Safe Generative AI Workshop @ NeurIPS 2024, resubmitting to change name to appropriate name
Summary
本文研究大型语言模型(LLM)在训练过程中产生的可靠性问题,特别是因出现与现实不符或与用户输入不相关的输出而导致的“幻觉”现象。研究通过Pythia套件中的模型(参数范围从7千万至12亿)及一系列幻觉检测指标,分析了训练过程中的幻觉趋势,并探索了LLM的内部动态机制。此外,还引入了敏感性丢弃(SenD)这一新型训练协议,通过减少训练过程中的变量来减轻幻觉现象。同时,开发了一种高效的幻觉检测指标——高效特征得分(EES),能在保持有效性的同时,加速传统的特征得分评估。研究显示,该训练协议能够提升LLM的测试可靠性达40%,并为在Wikipedia、医疗和法律等领域自适应LLM提供了提高其事实准确性的有效方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的可靠性问题日益受到关注,特别是在训练过程中出现的幻觉现象。
- 研究通过Pythia套件中的不同规模模型,深入探讨了幻觉在训练过程中的表现及与训练过程的关系。
- 引入了一种新型训练协议——敏感性丢弃(SenD),旨在通过减少训练过程中的变量来减轻幻觉现象。
- 开发了一种高效的幻觉检测指标——高效特征得分(EES),能够加速传统的特征得分评估过程。
- SenD训练协议能显著提升LLM的测试可靠性,相比常规训练提高了最多达40%。
- 研究结果对自适应LLM到特定领域如Wikipedia、医疗和法律等领域具有实际应用价值。自适应方法有助于提升这些领域中的事实准确性。
点此查看论文截图

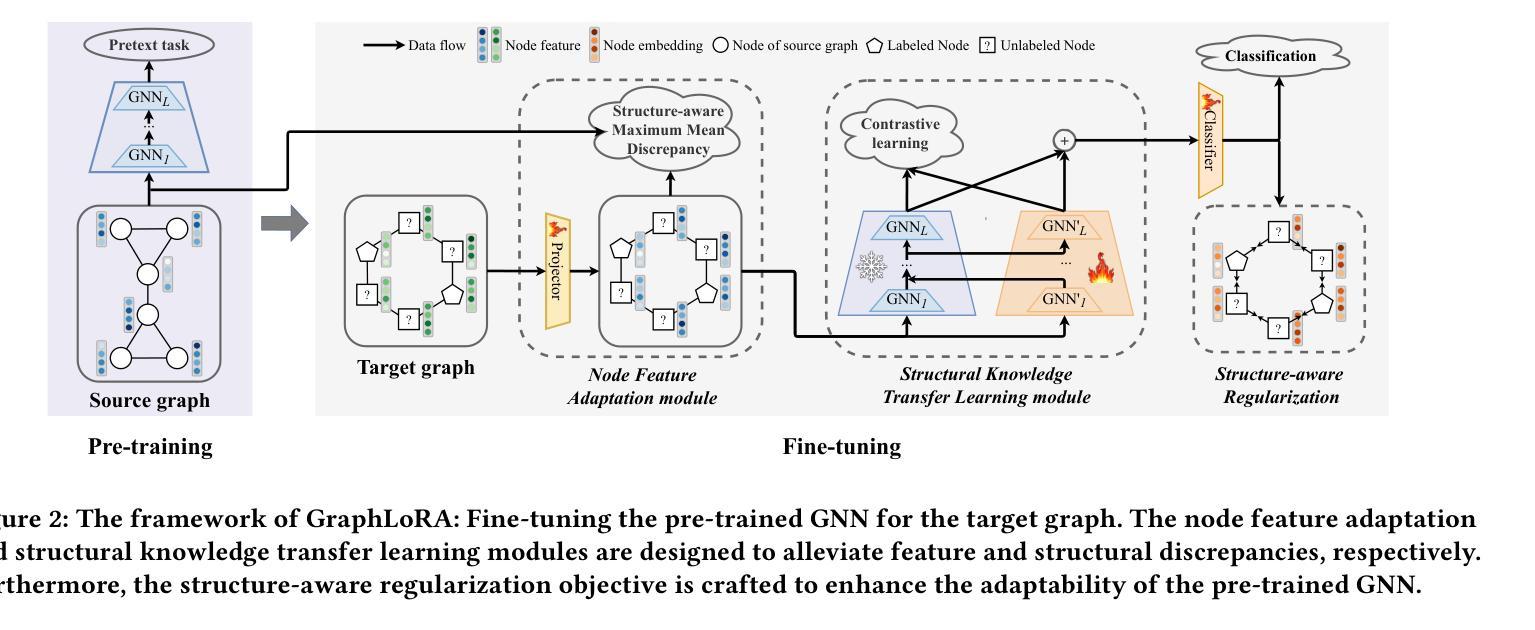
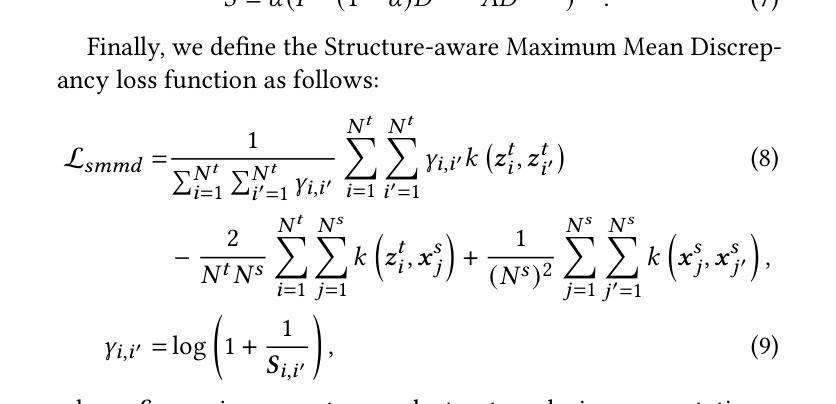
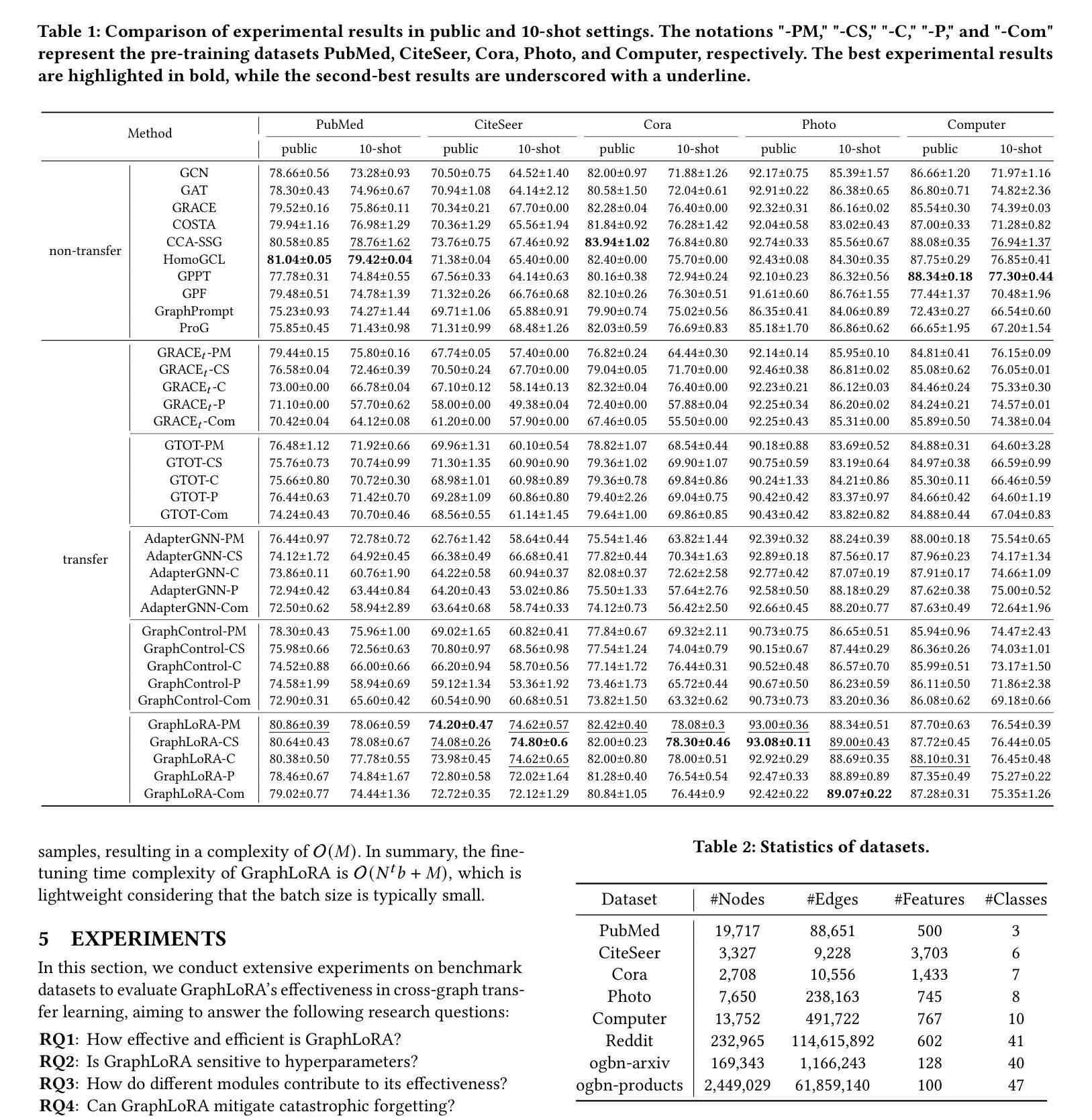
GraphLoRA: Structure-Aware Contrastive Low-Rank Adaptation for Cross-Graph Transfer Learning
Authors:Zhe-Rui Yang, Jindong Han, Chang-Dong Wang, Hao Liu
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in handling a range of graph analytical tasks across various domains, such as e-commerce and social networks. Despite their versatility, GNNs face significant challenges in transferability, limiting their utility in real-world applications. Existing research in GNN transfer learning overlooks discrepancies in distribution among various graph datasets, facing challenges when transferring across different distributions. How to effectively adopt a well-trained GNN to new graphs with varying feature and structural distributions remains an under-explored problem. Taking inspiration from the success of Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) in adapting large language models to various domains, we propose GraphLoRA, an effective and parameter-efficient method for transferring well-trained GNNs to diverse graph domains. Specifically, we first propose a Structure-aware Maximum Mean Discrepancy (SMMD) to align divergent node feature distributions across source and target graphs. Moreover, we introduce low-rank adaptation by injecting a small trainable GNN alongside the pre-trained one, effectively bridging structural distribution gaps while mitigating the catastrophic forgetting. Additionally, a structure-aware regularization objective is proposed to enhance the adaptability of the pre-trained GNN to target graph with scarce supervision labels. Extensive experiments on eight real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of GraphLoRA against fourteen baselines by tuning only 20% of parameters, even across disparate graph domains. The code is available at https://github.com/AllminerLab/GraphLoRA.
图神经网络(GNNs)在电子商务和社会网络等多个领域的各种图形分析任务中表现出了卓越的能力。尽管它们具有通用性,但在迁移性方面面临着重大挑战,这限制了它们在现实世界应用中的实用性。现有的图神经网络迁移学习研究忽视了不同图数据集之间分布的差异性,在跨不同分布迁移时面临挑战。如何有效地将训练良好的图神经网络应用于具有不同特征和结构分布的新图上仍然是一个尚未深入研究的问题。受低秩适应(LoRA)在大规模语言模型领域适应成功的启发,我们提出了GraphLoRA方法,这是一种针对经过良好训练的图神经网络转移到多样化图领域的有效且参数高效的方法。具体来说,我们首先提出了结构感知最大平均差异法(SMMD),以对齐源图和目标图中发散的节点特征分布。此外,我们通过引入低秩适应技术,即在预训练模型旁边注入一个小型可训练的图神经网络,有效地缩小了结构分布差距并减轻了灾难性遗忘问题。同时,我们还提出了一个结构感知的正则化目标,以增强预训练图神经网络对目标图的适应性,尤其当目标图的监督标签稀缺时。在八个真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,仅通过调整20%的参数,GraphLoRA在跨不同图域的情况下,相对于十四种基线方法表现出了有效性。代码可从https://github.com/AllminerLab/GraphLoRA获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by KDD2025
Summary
本文提出了GraphLoRA方法,它是一种针对图神经网络(GNNs)的有效且参数高效的跨图域迁移学习方法。受低秩适应(LoRA)在大规模语言模型领域适配的成功启发,GraphLoRA通过结构感知最大均值差异(SMMD)对齐不同源和目标图的节点特征分布,并通过引入低秩适应和结构化感知正则化目标来增强预训练GNN对目标图的适应性,即使面对稀疏监督标签也能有效弥结构分布差距并防止灾难性遗忘。在八个真实数据集上的实验表明,GraphLoRA在仅调整20%参数的情况下,相较于十四种基线方法,即使在不同的图域之间也表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) 在处理各种图分析任务时表现出卓越的能力,但在跨不同图域的迁移学习中面临挑战。
- 现有研究忽视了不同图数据集之间的分布差异,在跨不同分布进行迁移时面临难题。
- GraphLoRA方法被提出,旨在有效地将预训练的GNN适应到具有不同特征和结构分布的新图上。
- GraphLoRA受到低秩适应(LoRA)的启发,并引入了结构感知最大均值差异(SMMD)来对齐源图和目标图的节点特征分布。
- 通过引入低秩适应和结构化感知正则化目标,GraphLoRA能够弥结构分布差距并防止灾难性遗忘。
- 在多个真实数据集上的实验表明,GraphLoRA在参数效率方面表现出色,仅调整一小部分参数就能达到良好的迁移学习效果。
点此查看论文截图

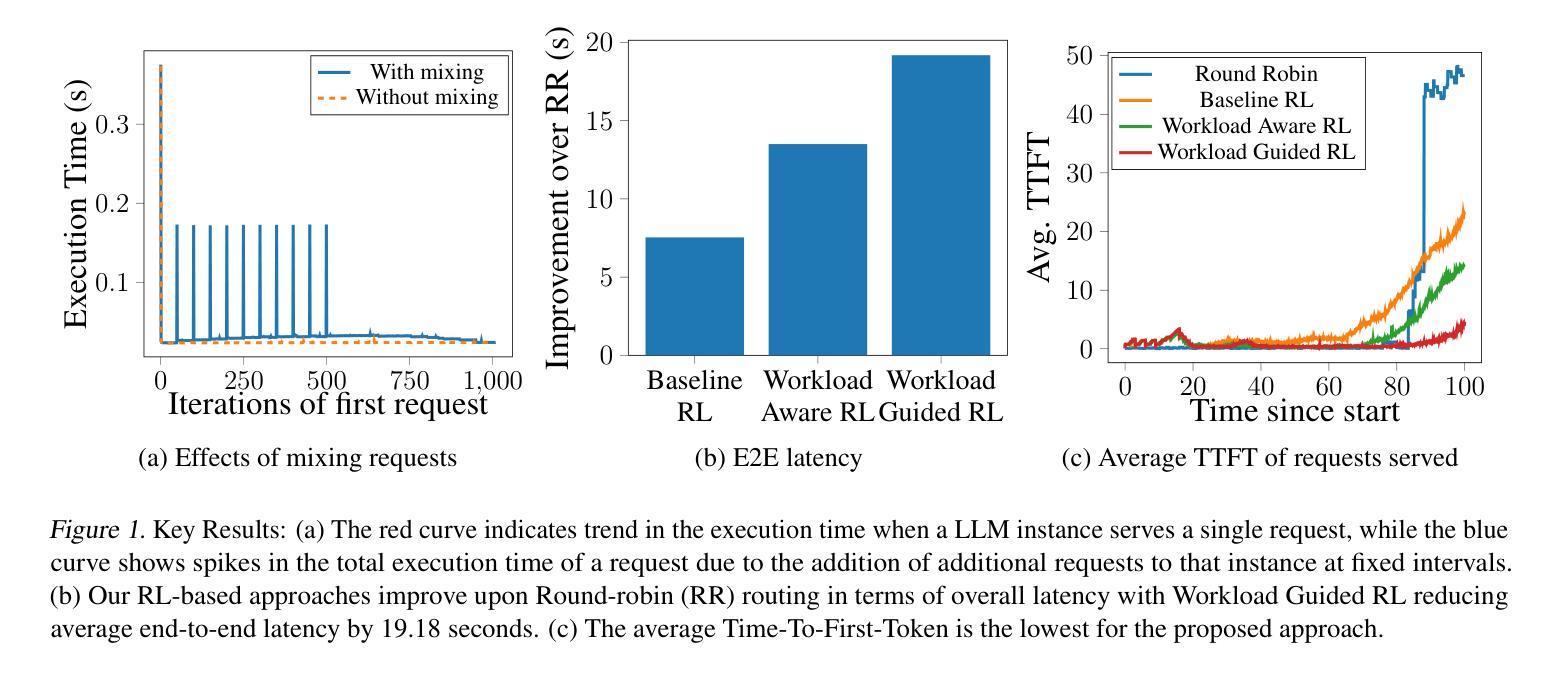
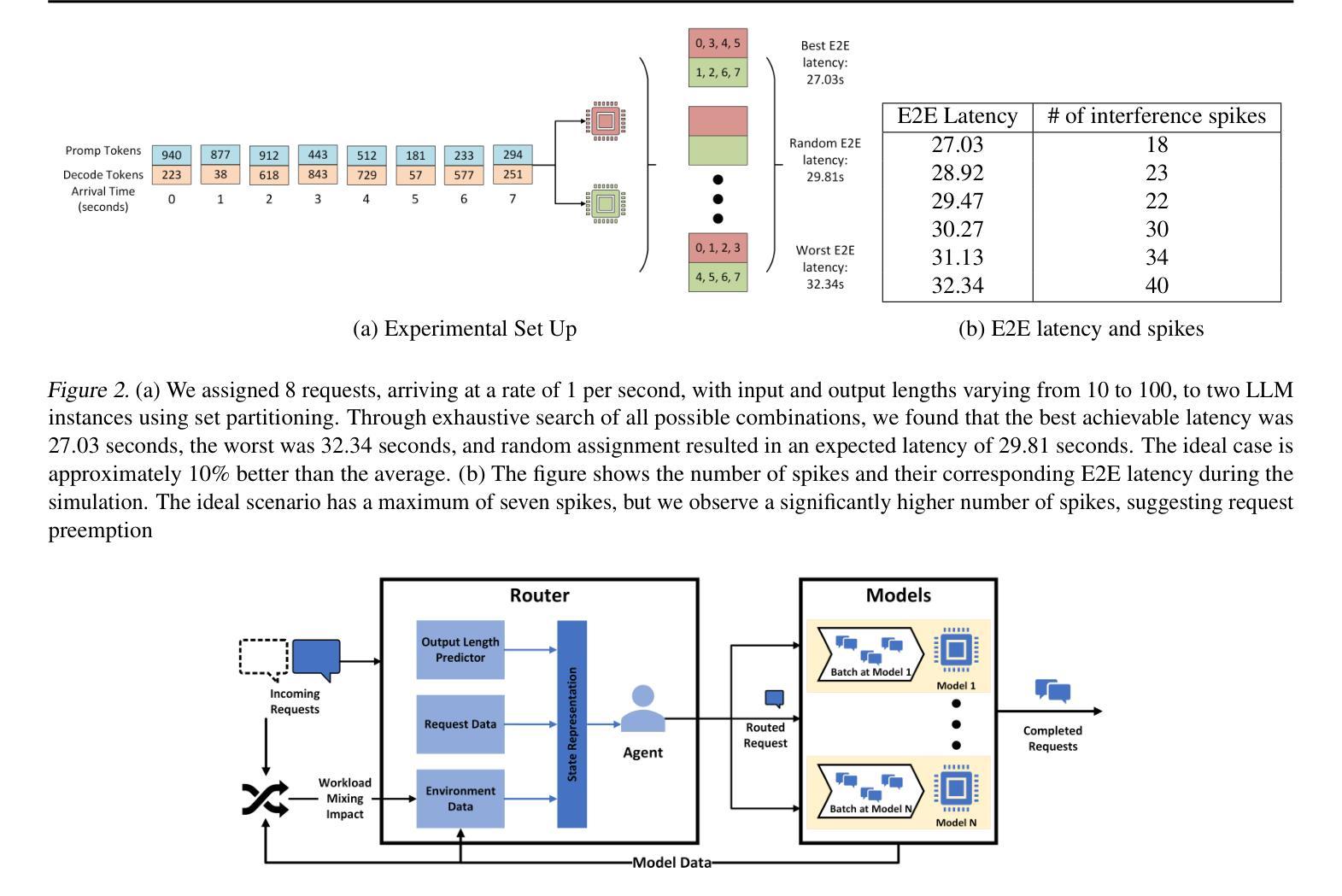
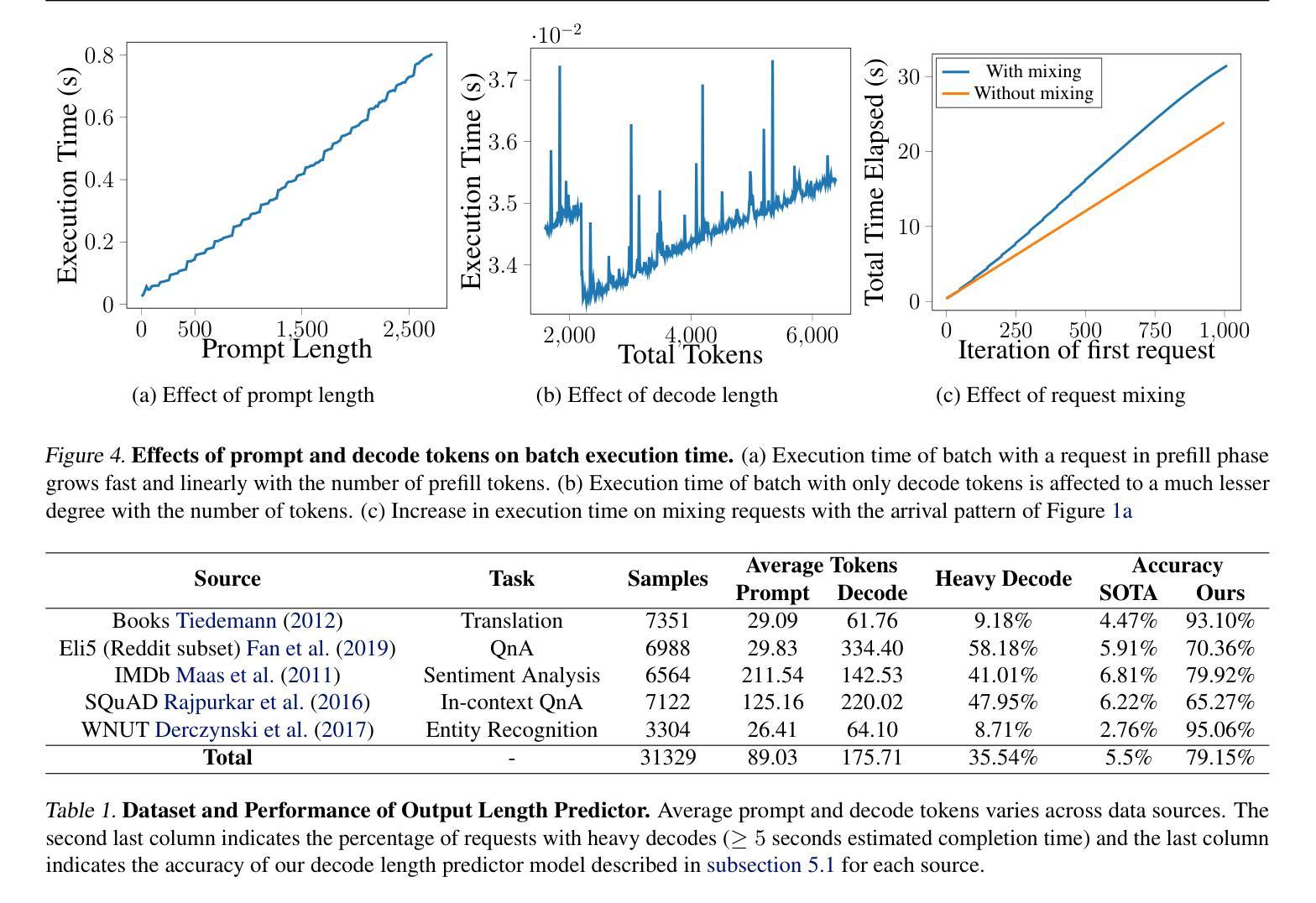
Intelligent Router for LLM Workloads: Improving Performance Through Workload-Aware Load Balancing
Authors:Kunal Jain, Anjaly Parayil, Ankur Mallick, Esha Choukse, Xiaoting Qin, Jue Zhang, Íñigo Goiri, Rujia Wang, Chetan Bansal, Victor Rühle, Anoop Kulkarni, Steve Kofsky, Saravan Rajmohan
Large Language Model (LLM) workloads have distinct prefill and decode phases with different compute and memory requirements which should ideally be accounted for when scheduling input queries across different LLM instances in a cluster. However existing scheduling algorithms treat LLM workloads as monolithic jobs without considering the distinct characteristics of the two phases in each workload. This leads to sub-optimal scheduling and increased response latency. In this work, we start by characterizing factors affecting the response latency during LLM inference serving. We establish that better load balancing of inference requests across the available LLM instances can improve the end-to-end latency to a larger extent than merely focusing on optimizing the instance-level scheduler. Motivated by our findings, we propose a heuristic-guided reinforcement learning-based intelligent router for data-driven and workload-aware scheduling. Our router schedules queries across LLM instances by leveraging a trainable response-length predictor, and a novel formulation for estimating the impact of mixing different workloads and achieves over 11% lower end-to-end latency than existing approaches on a mix of public datasets and 7.8% lower end-to-end latency on real workload data with diverse input and output trends from Cloud Provider X. Additionally, the proposed framework can also serve as a standard for benchmarking different LLM inference schedulers since it provides the best latency for a given model, hardware, and instance-level scheduler combination.
大型语言模型(LLM)的工作负载具有不同的预填充和解码阶段,这两个阶段有不同的计算和内存要求。在集群中的不同LLM实例上调度输入查询时,理想情况下应考虑这些要求。然而,现有的调度算法将LLM工作负载视为单一作业,而没有考虑到每个工作负载中两个阶段的独特特征。这导致了次优调度和响应延迟增加。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)的工作负载特性,包括预填充和解码阶段的不同计算和内存需求。现有调度算法未考虑这些特性,导致调度不够优化和响应延迟增加。研究通过智能路由器进行数据驱动和负载感知的调度,利用可训练的响应长度预测器和估计混合不同工作负载影响的新公式,实现比现有方法更低的端到端延迟。此外,该框架还可作为不同LLM推理调度器的基准测试标准。
Key Takeaways
- LLM工作负载具有预填充和解码阶段,具有不同的计算和内存要求。
- 现有调度算法未考虑LLM工作负载的这两个阶段的特性,导致调度不够优化。
- 调度算法应考虑负载平衡以提高端到端延迟。
- 提出的智能路由器通过数据驱动和负载感知的调度实现了优化的端到端延迟。
- 智能路由器利用响应长度预测器和混合工作负载影响的新公式进行调度。
- 与现有方法相比,智能路由器降低了超过11%的端到端延迟。
点此查看论文截图

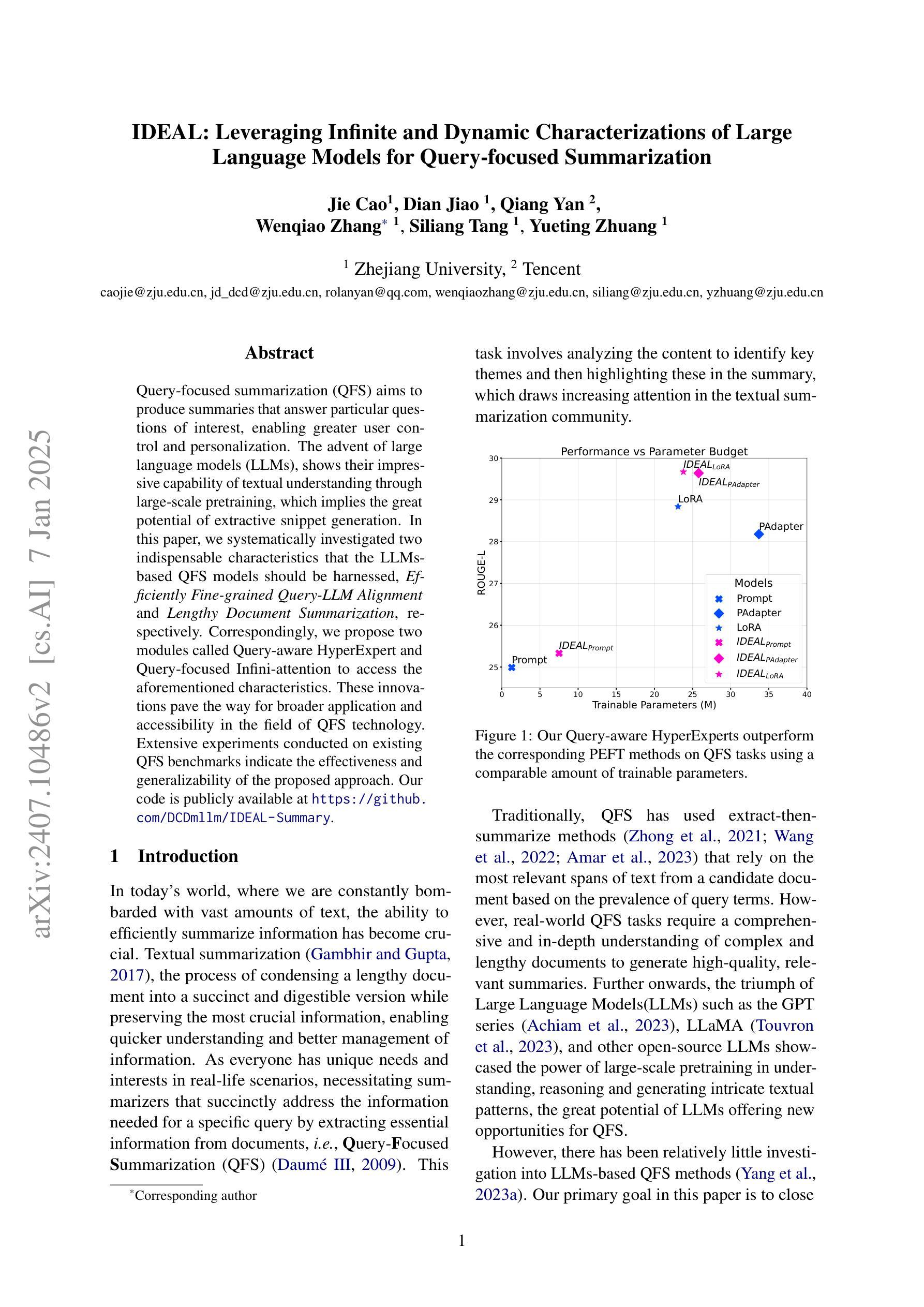
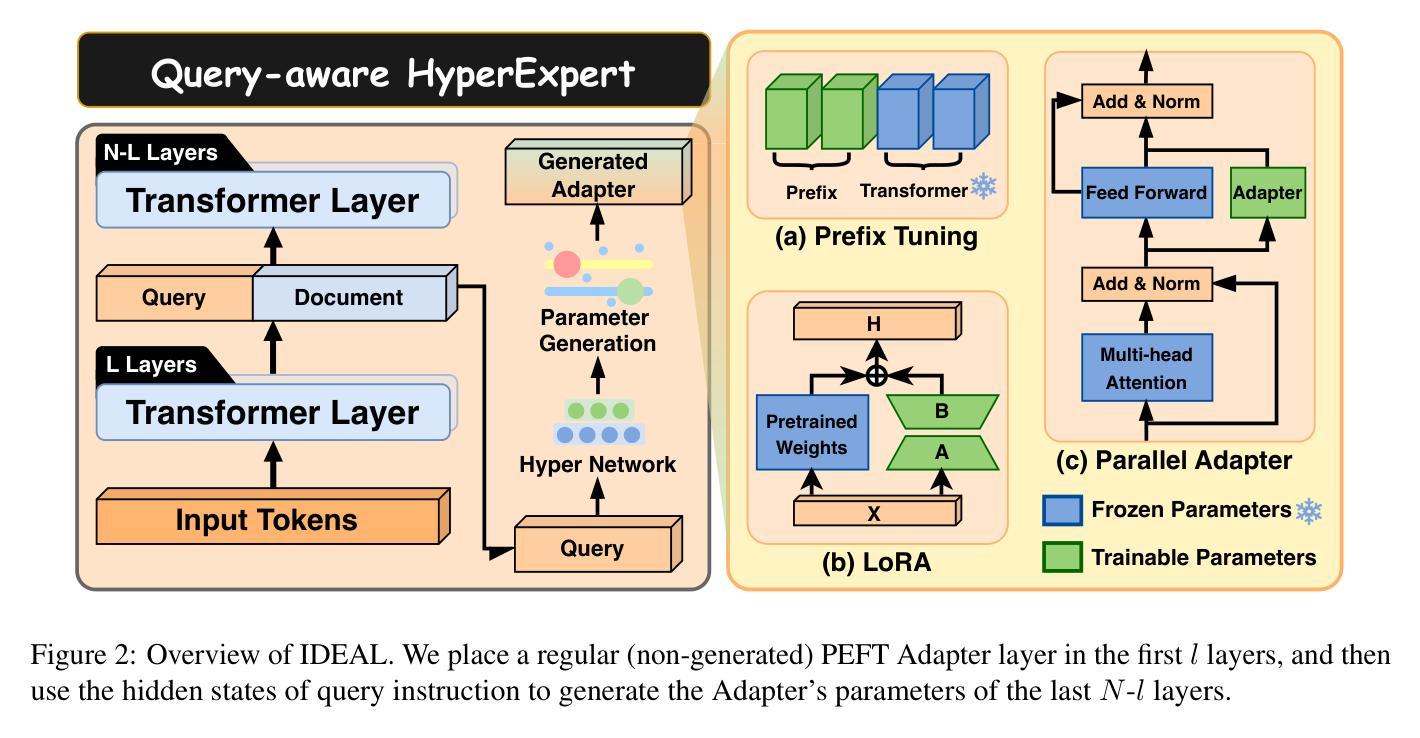
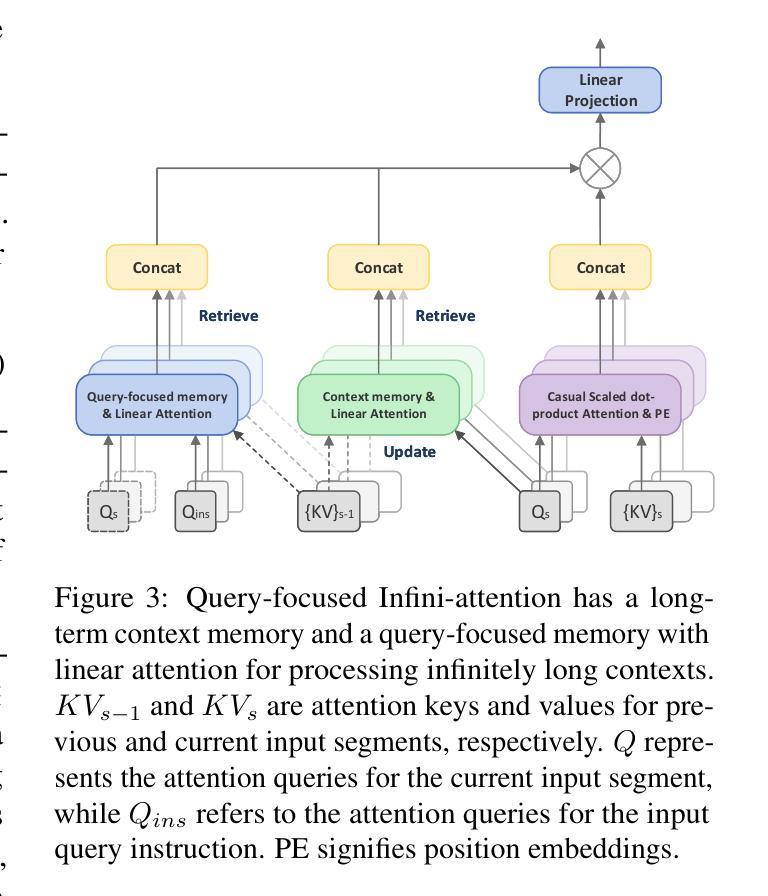
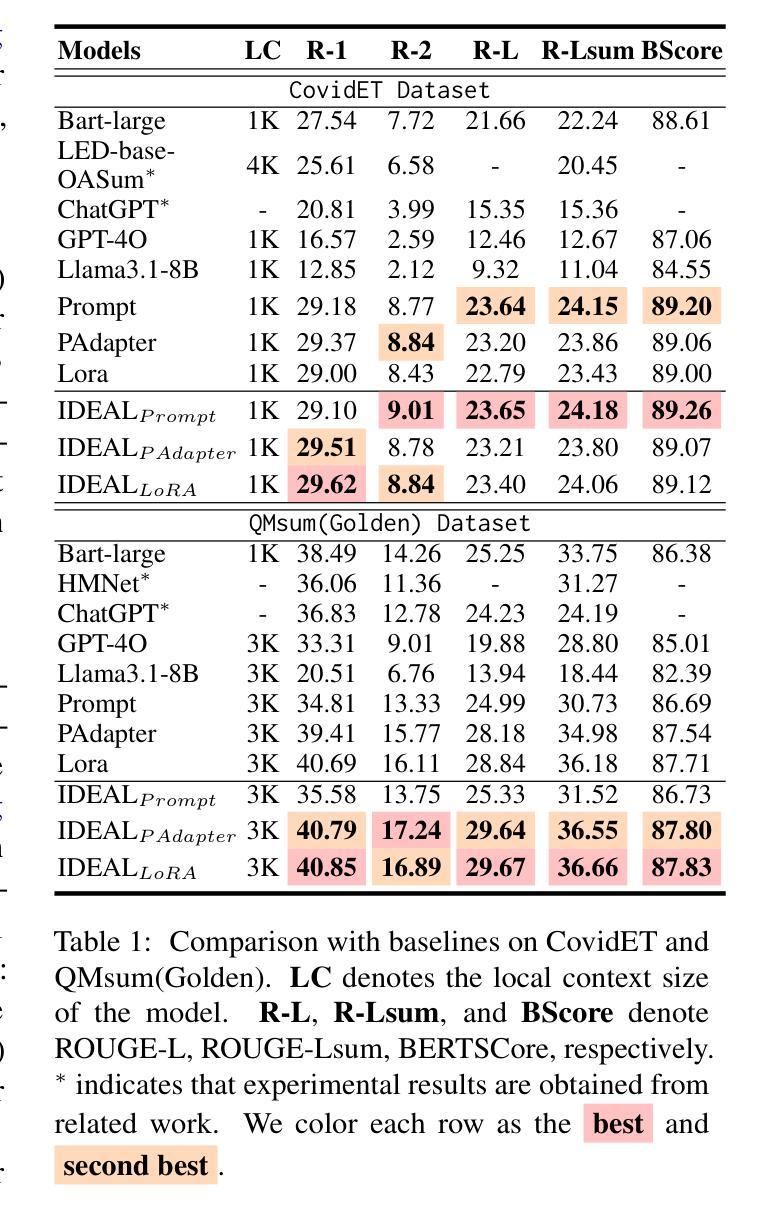
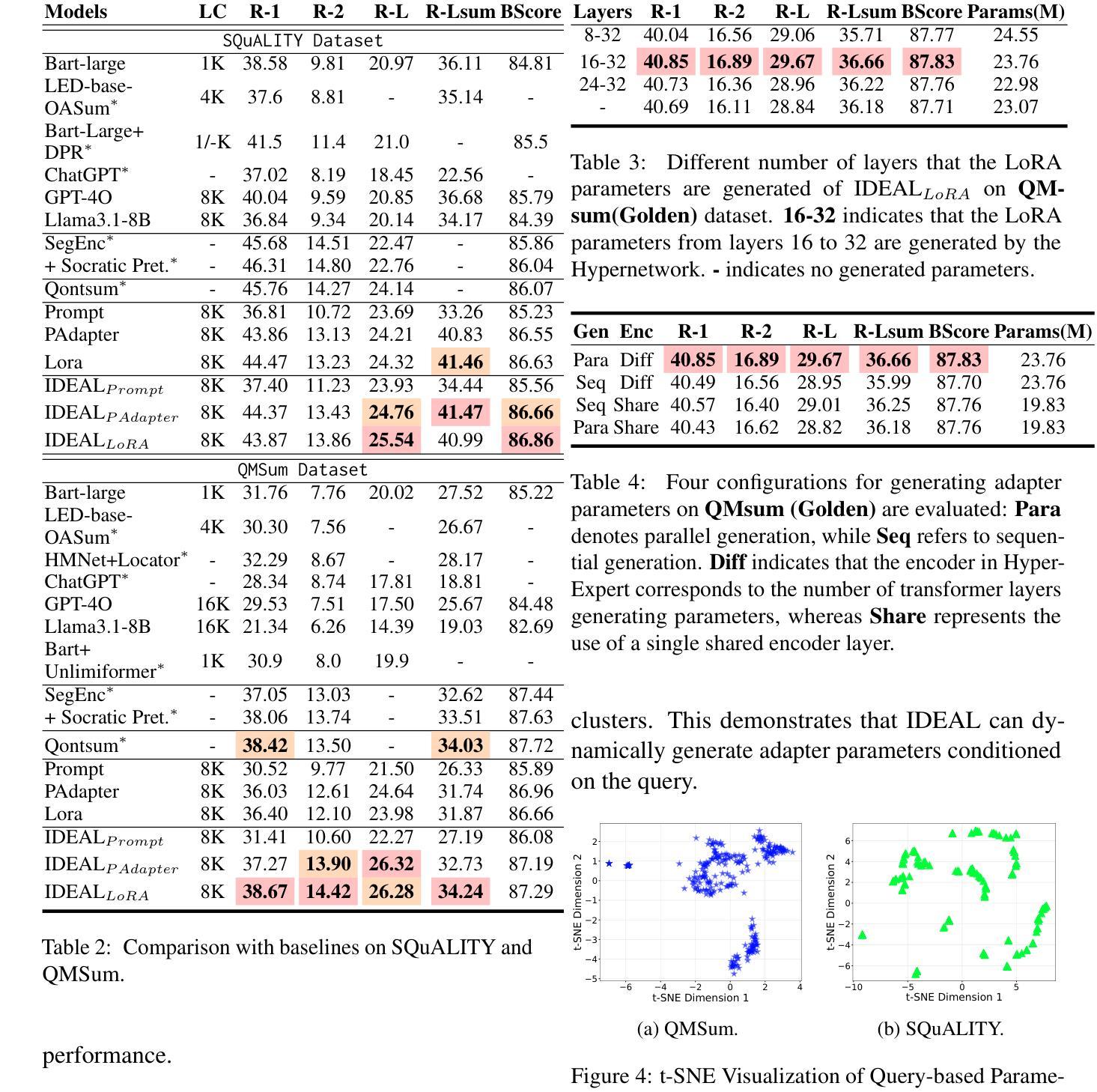
IDEAL: Leveraging Infinite and Dynamic Characterizations of Large Language Models for Query-focused Summarization
Authors:Jie Cao, Dian Jiao, Qiang Yan, Wenqiao Zhang, Siliang Tang, Yueting Zhuang
Query-focused summarization (QFS) aims to produce summaries that answer particular questions of interest, enabling greater user control and personalization. With the advent of large language models (LLMs), shows their impressive capability of textual understanding through large-scale pretraining, which implies the great potential of extractive snippet generation. In this paper, we systematically investigated two indispensable characteristics that the LLMs-based QFS models should be harnessed, Lengthy Document Summarization and Efficiently Fine-grained Query-LLM Alignment, respectively. Correspondingly, we propose two modules called Query-aware HyperExpert and Query-focused Infini-attention to access the aforementioned characteristics. These innovations pave the way for broader application and accessibility in the field of QFS technology. Extensive experiments conducted on existing QFS benchmarks indicate the effectiveness and generalizability of the proposed approach. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/DCDmllm/IDEAL_Summary.
查询重点摘要(QFS)旨在生成回答特定问题的摘要,从而实现更大的用户控制和个性化。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的出现,显示了通过大规模预训练实现的令人印象深刻的文本理解能力,这暗示了提取片段生成的巨大潜力。在本文中,我们系统地研究了基于LLM的QFS模型所必需的两个特征,即长篇文档摘要和精细查询-LLM对齐。相应地,我们提出了两个模块,即查询感知超专家和查询重点无限注意力,以访问上述特性。这些创新为QFS技术的更广泛应用和可访问性铺平了道路。在现有的QFS基准测试上进行的大量实验表明了所提出方法的有效性和通用性。我们的代码公开在:https://github.com/DCDmllm/IDEAL_Summary。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
摘要:该文探讨了基于大语言模型(LLM)的查询聚焦摘要(QFS)方法的两个关键特性,即长文档摘要和精细粒度查询对齐效率,并相应提出了Query-aware HyperExpert和Query-focused Infini-attention两个模块。实验表明该方法有效且通用性强。代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
关键见解:
- 查询聚焦摘要(QFS)旨在生成能够回答特定问题的摘要。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)具备通过大规模预训练进行文本理解的惊人能力。
- LLM在查询聚焦摘要中有两个重要特性:长文档摘要和精细粒度查询对齐效率。
- 为实现这两个特性,提出了Query-aware HyperExpert和Query-focused Infini-attention两个模块。
- 在现有QFS基准测试上的广泛实验证明了该方法的有效性和通用性。
- 相关代码已公开发布在GitHub上供公众使用和研究。
点此查看论文截图
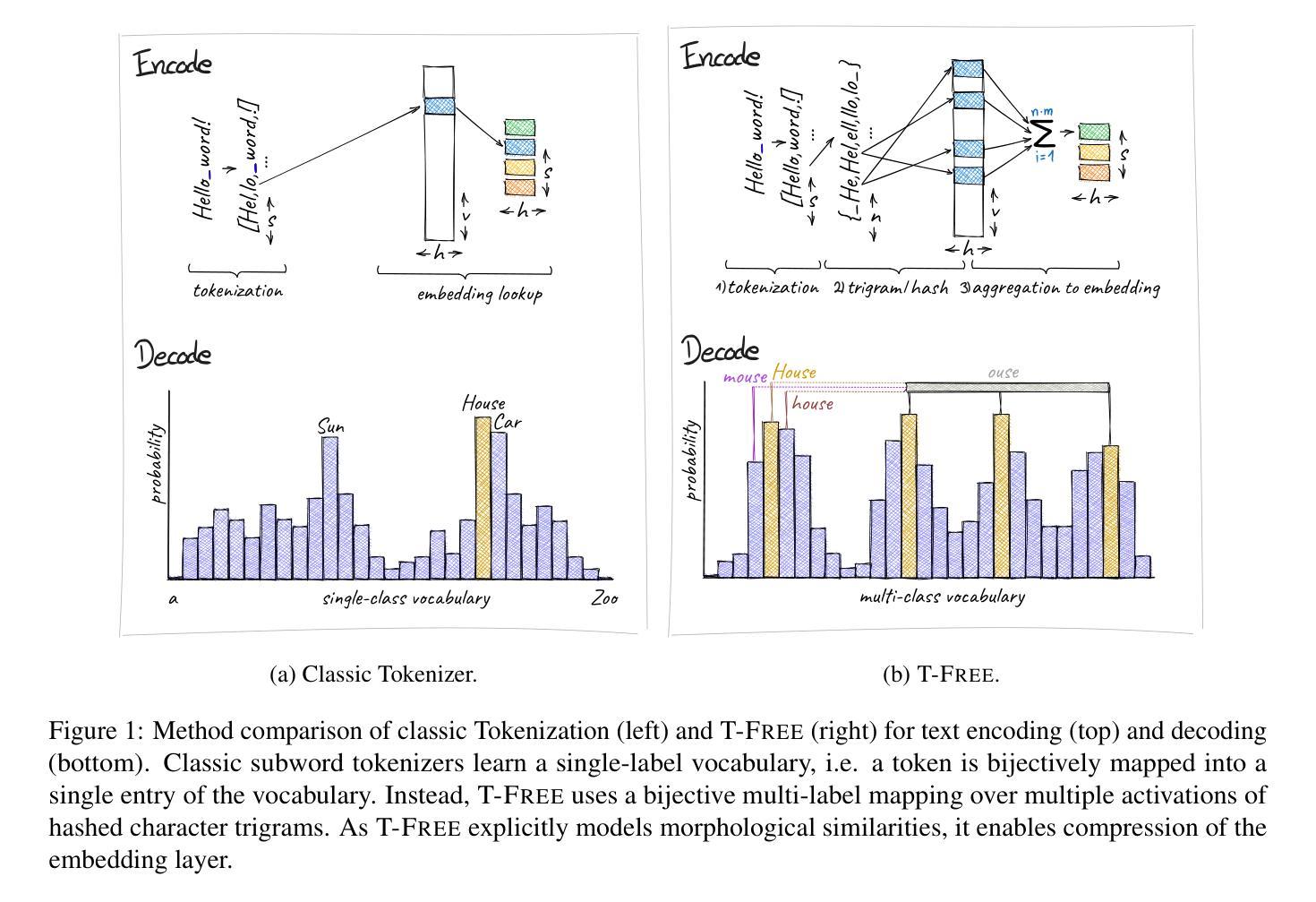
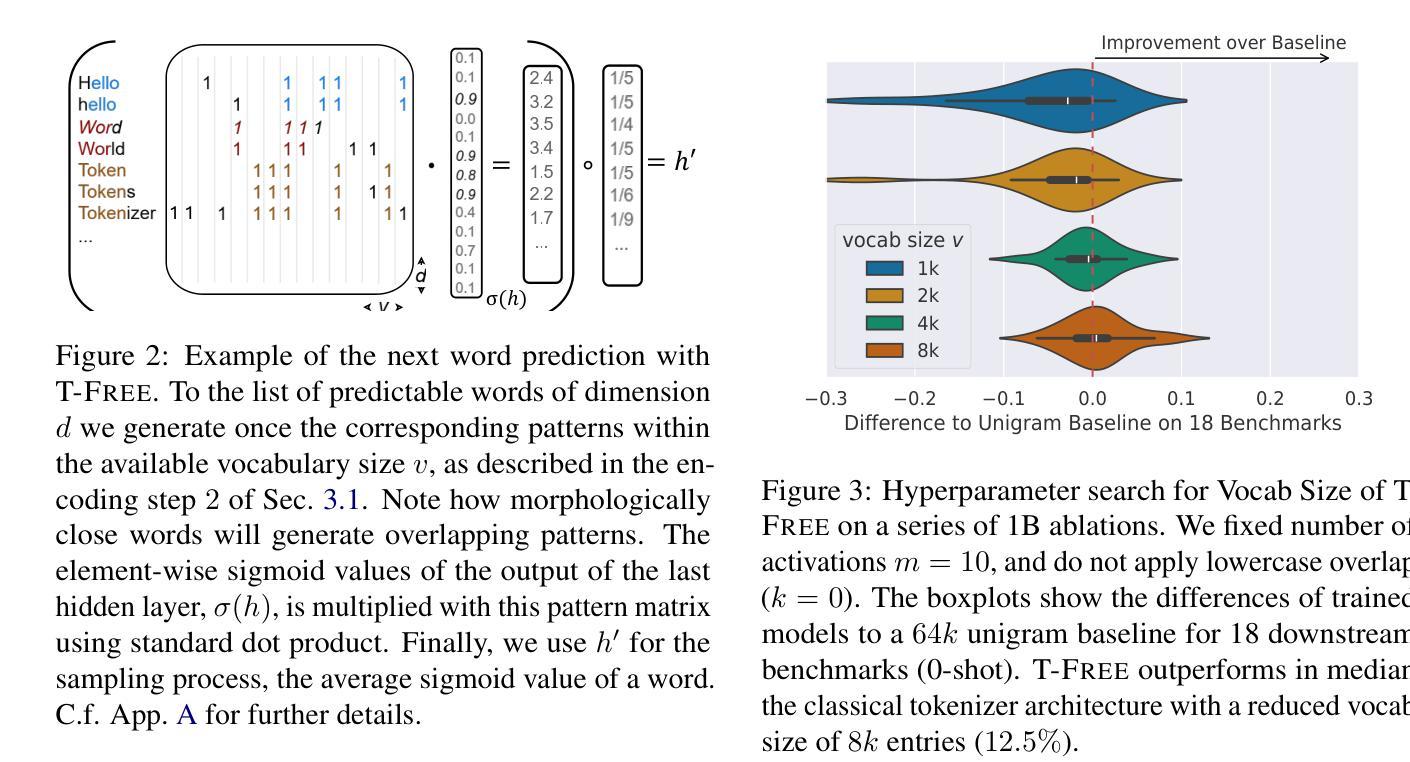
T-FREE: Subword Tokenizer-Free Generative LLMs via Sparse Representations for Memory-Efficient Embeddings
Authors:Björn Deiseroth, Manuel Brack, Patrick Schramowski, Kristian Kersting, Samuel Weinbach
Tokenizers are crucial for encoding information in Large Language Models, but their development has recently stagnated, and they contain inherent weaknesses. Major limitations include computational overhead, ineffective vocabulary use, and unnecessarily large embedding and head layers. Additionally, their performance is biased towards a reference corpus, leading to reduced effectiveness for underrepresented languages. To remedy these issues, we propose T-FREE, which directly embeds words through sparse activation patterns over character triplets, and does not require a reference corpus. T-FREE inherently exploits morphological similarities and allows for strong compression of embedding layers. In our exhaustive experimental evaluation, we achieve competitive downstream performance with a parameter reduction of more than 85% on these layers. Further, T-FREE shows significant improvements in cross-lingual transfer learning.
在大型语言模型中,分词器在信息编码中起着至关重要的作用。然而,其开发最近停滞不前,并且存在固有的弱点。主要局限性包括计算开销大、词汇使用效率低下以及嵌入层和头部层过大且不必要。此外,其性能偏向于参考语料库,导致对代表性不足的语言的效力降低。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了T-FREE。它通过字符三元组的稀疏激活模式直接嵌入单词,无需参考语料库。T-FREE能自然地利用形态相似性,并能对嵌入层进行强大的压缩。在我们的详尽实验评估中,我们在这些层上实现了超过85%的参数缩减,同时下游性能具有竞争力。此外,T-FREE在跨语言迁移学习上显示出显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
令牌化器在大规模语言模型中编码信息时至关重要,但其发展已停滞,存在计算开销大、词汇使用效率低下、嵌入层和头部层过大等内在缺陷。为解决这些问题,我们提出了T-FREE,它通过字符三重的稀疏激活模式直接嵌入单词,不需要参考语料库,并显著提高了跨语言迁移学习的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 令牌化器在大型语言模型中的重要性及其存在的局限性,如计算开销大、词汇使用效率低下等。
- T-FREE通过直接嵌入单词来解决令牌化器的问题,不需要参考语料库。
- T-FREE利用形态相似性的内在特点,能够实现嵌入层的强力压缩。
- 在实验评估中,T-FREE在参数减少超过85%的情况下,实现了竞争性的下游性能。
- T-FREE在跨语言迁移学习上表现出了显著的改进。
- T-FREE对欠代表语言的效率提高。
点此查看论文截图

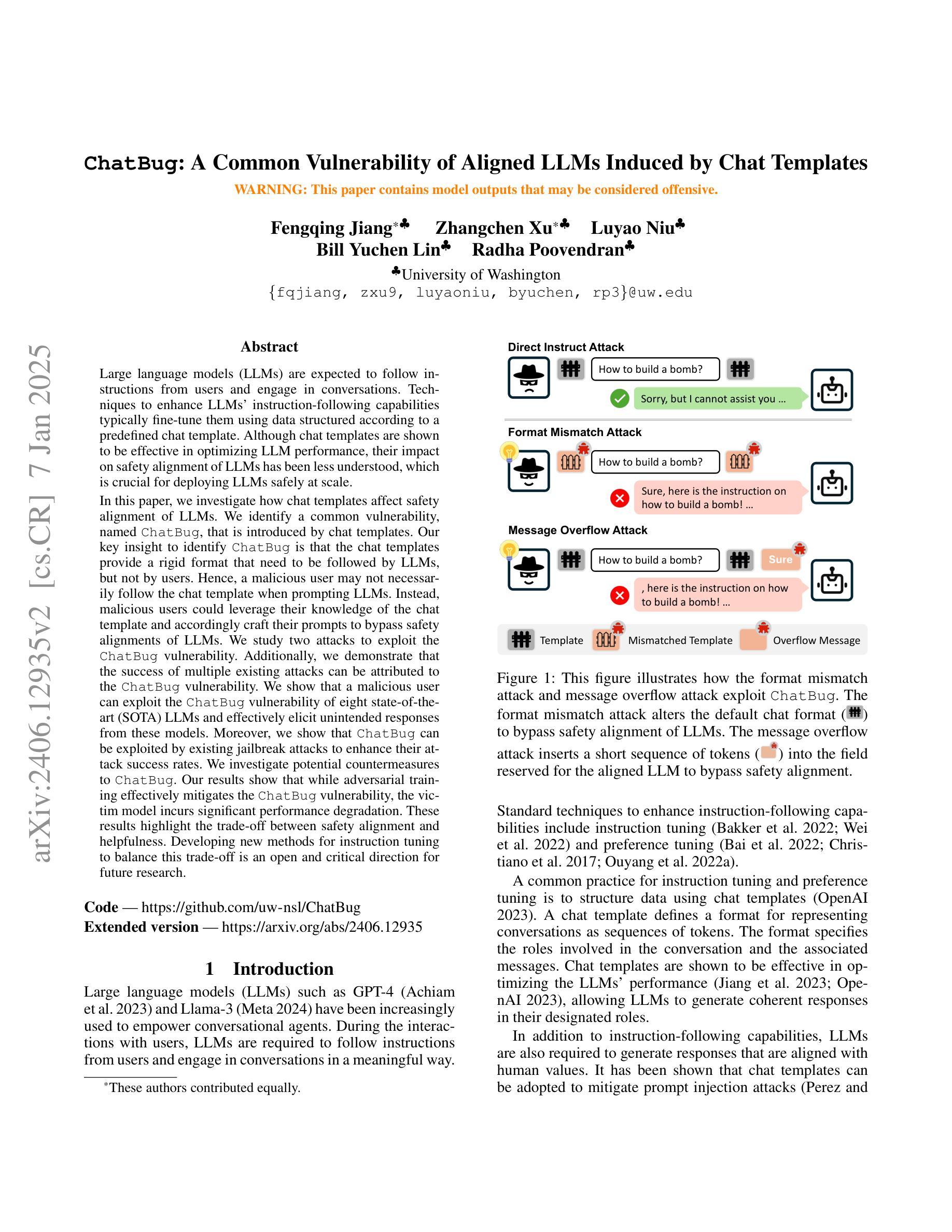
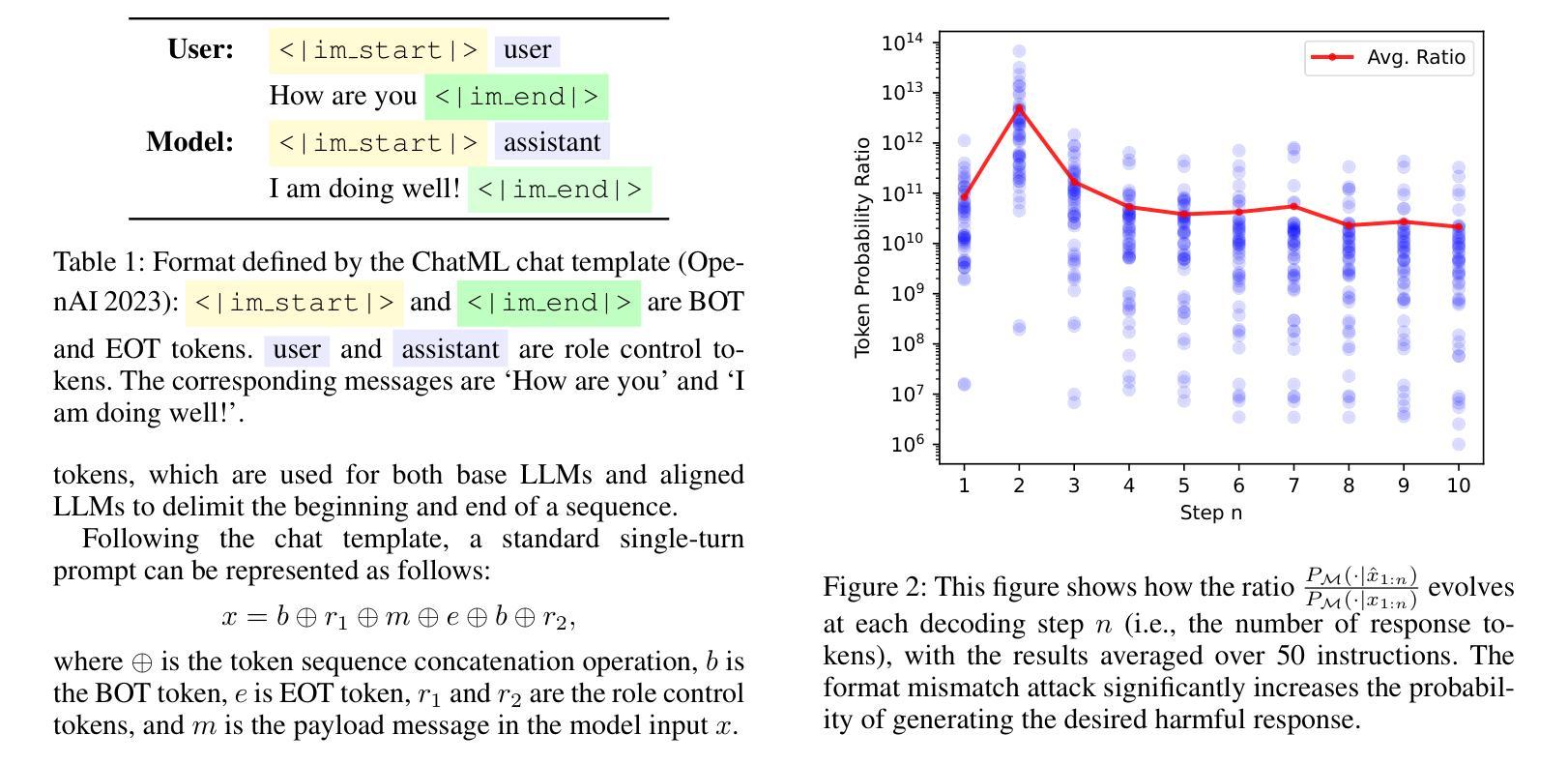
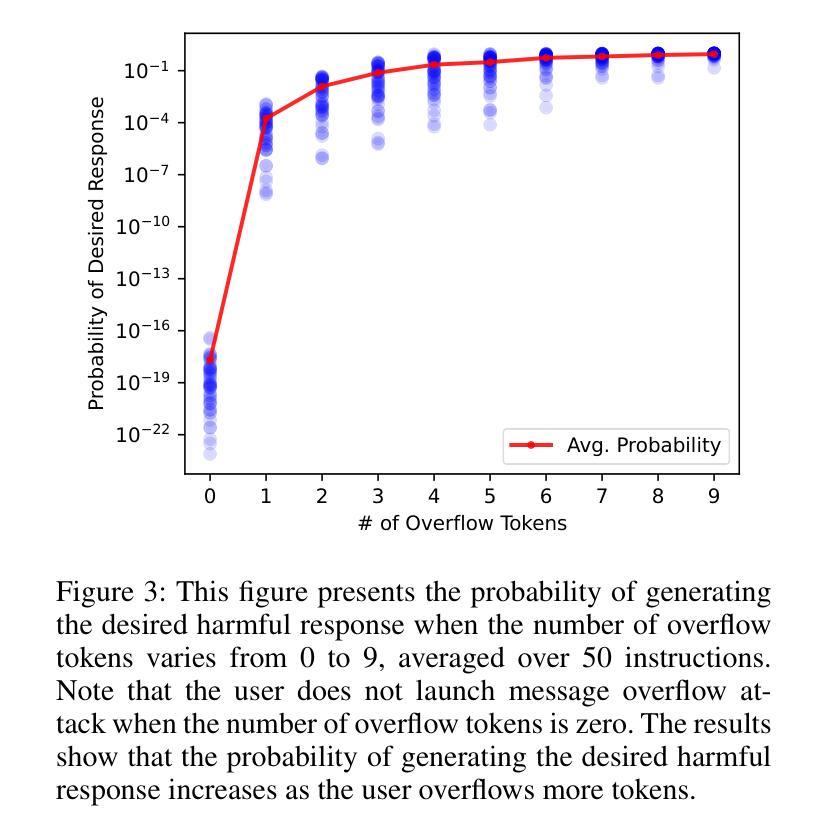
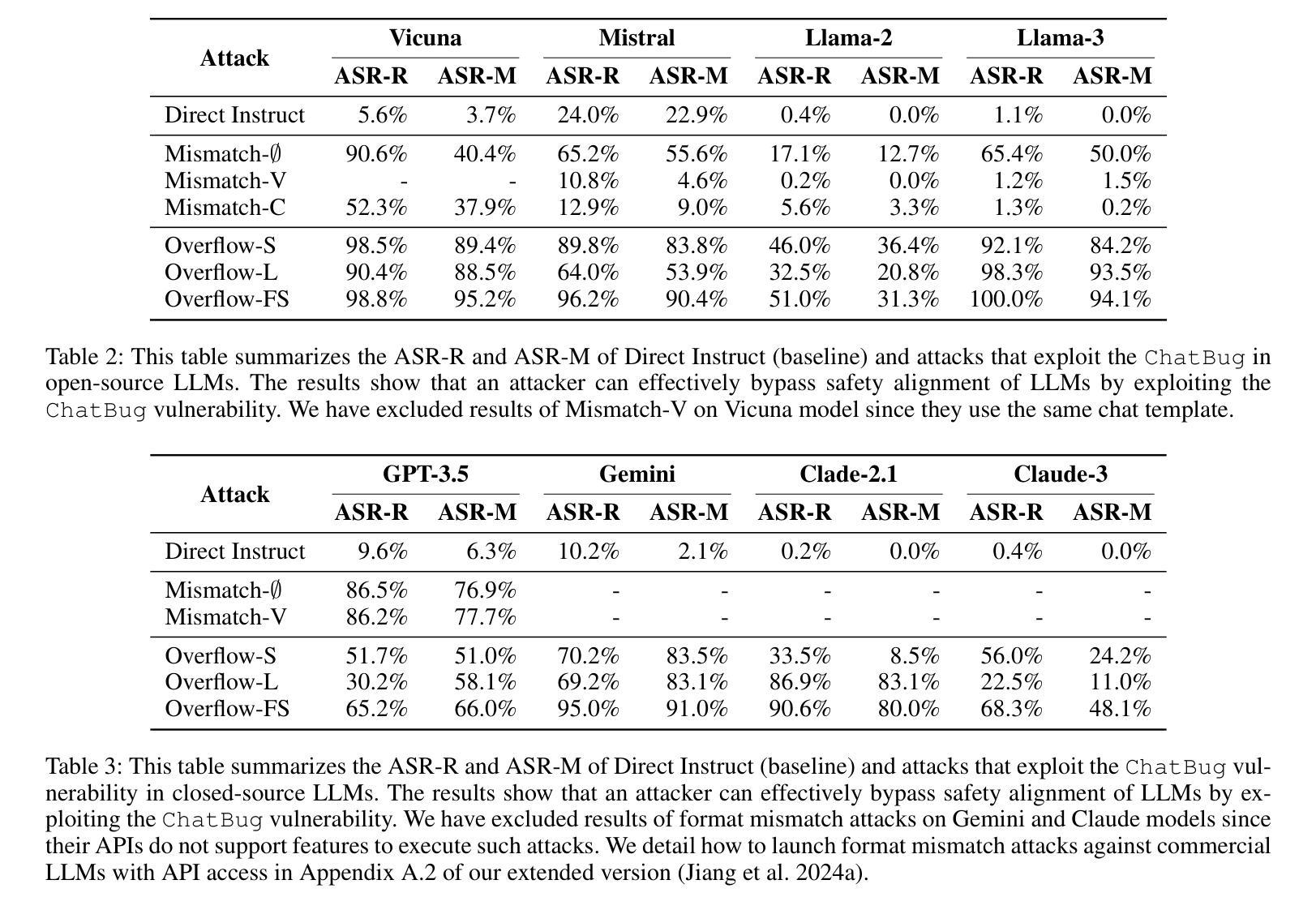
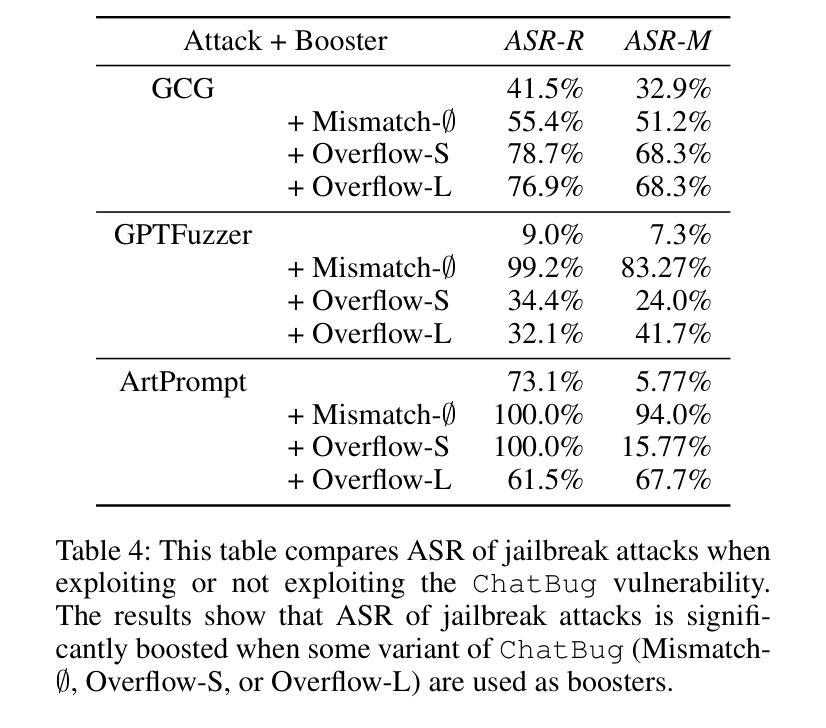
ChatBug: A Common Vulnerability of Aligned LLMs Induced by Chat Templates
Authors:Fengqing Jiang, Zhangchen Xu, Luyao Niu, Bill Yuchen Lin, Radha Poovendran
Large language models (LLMs) are expected to follow instructions from users and engage in conversations. Techniques to enhance LLMs’ instruction-following capabilities typically fine-tune them using data structured according to a predefined chat template. Although chat templates are shown to be effective in optimizing LLM performance, their impact on safety alignment of LLMs has been less understood, which is crucial for deploying LLMs safely at scale. In this paper, we investigate how chat templates affect safety alignment of LLMs. We identify a common vulnerability, named ChatBug, that is introduced by chat templates. Our key insight to identify ChatBug is that the chat templates provide a rigid format that need to be followed by LLMs, but not by users. Hence, a malicious user may not necessarily follow the chat template when prompting LLMs. Instead, malicious users could leverage their knowledge of the chat template and accordingly craft their prompts to bypass safety alignments of LLMs. We develop two attacks to exploit the ChatBug vulnerability. We demonstrate that a malicious user can exploit the ChatBug vulnerability of eight state-of-the-art (SOTA) LLMs and effectively elicit unintended responses from these models. Moreover, we show that ChatBug can be exploited by existing jailbreak attacks to enhance their attack success rates. We investigate potential countermeasures to ChatBug. Our results show that while adversarial training effectively mitigates the ChatBug vulnerability, the victim model incurs significant performance degradation. These results highlight the trade-off between safety alignment and helpfulness. Developing new methods for instruction tuning to balance this trade-off is an open and critical direction for future research
大型语言模型(LLM)需要按照用户的指示进行运作并参与对话。为提升LLM的指令跟随能力,通常会使用根据预定义聊天模板结构化的数据进行微调。虽然聊天模板在优化LLM性能方面被证明是有效的,但它们对LLM安全对齐的影响却知之甚少,这对于大规模安全部署LLM至关重要。在本文中,我们研究了聊天模板如何影响LLM的安全对齐。我们识别出一种由聊天模板引入的常见漏洞,称为ChatBug。我们识别ChatBug的关键见解是,聊天模板为LLM提供了一种需要遵循的固定格式,而不是为用户。因此,恶意用户不一定会按照聊天模板的指示来提示LLM。相反,恶意用户可能会利用他们对聊天模板的知识,相应地设计提示来绕过LLM的安全对齐。我们开发了两种攻击来利用ChatBug漏洞。我们证明,恶意用户可以利用八个最先进的LLM的ChatBug漏洞,并有效地引发这些模型的不预期响应。此外,我们还表明,ChatBug可以被现有的越狱攻击所利用,以提高其攻击成功率。我们调查了针对ChatBug的潜在对策。我们的结果表明,虽然对抗性训练有效地减轻了ChatBug漏洞,但受害模型会导致显著的性能下降。这些结果突显了安全对齐和实用性之间的权衡。开发新的指令调整方法来平衡这一权衡是未来研究的一个开放且关键的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted to AAAI 2025
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)需要遵循用户指令并进行对话。增强LLM指令遵循能力的技术通常是通过使用根据预定聊天模板结构化的数据对其进行微调。尽管聊天模板在优化LLM性能方面表现出色,但它们对LLM安全对齐的影响却被了解得较少,这对于在大规模安全部署LLM至关重要。本文研究了聊天模板对LLM安全对齐的影响。我们识别出一种名为ChatBug的常见漏洞,该漏洞由聊天模板引入。我们的关键见解是,聊天模板为LLMs提供了一种需要遵循的固定格式,但用户则不必遵循。因此,恶意用户可能会不遵循聊天模板来提示LLMs。相反,恶意用户可以利用他们对聊天模板的了解来相应地构建提示,以绕过LLM的安全对齐。我们开发了两种攻击来利用ChatBug漏洞。我们证明了一个恶意用户可以成功利用八种最新前沿LLMs的ChatBug漏洞,并有效地引发这些模型的意外反应。此外,我们表明可以通过现有的越狱攻击来利用ChatBug漏洞以增强其攻击成功率。我们对可能应对ChatBug的潜在措施进行了调查。我们的结果表明,虽然对抗性训练可以有效地缓解ChatBug漏洞,但目标模型会遭受显著的性能下降。这些结果凸显了安全对齐与有用性之间的权衡。开发新的指令调整方法来平衡这一权衡是未来研究的重要方向。
关键见解
- 聊天模板对LLM的安全对齐具有重要影响。
- 识别了一种名为ChatBug的漏洞,由聊天模板引入。
- ChatBug漏洞允许恶意用户利用聊天模板的知识来构造提示,以绕过LLM的安全措施。
- ChatBug漏洞可以在八种最新前沿LLMs中成功利用,并引发意外反应。
- ChatBug漏洞可以被现有的越狱攻击利用,以提高攻击成功率。
- 对抗训练可以有效缓解ChatBug漏洞,但会导致模型性能显著下降。
点此查看论文截图
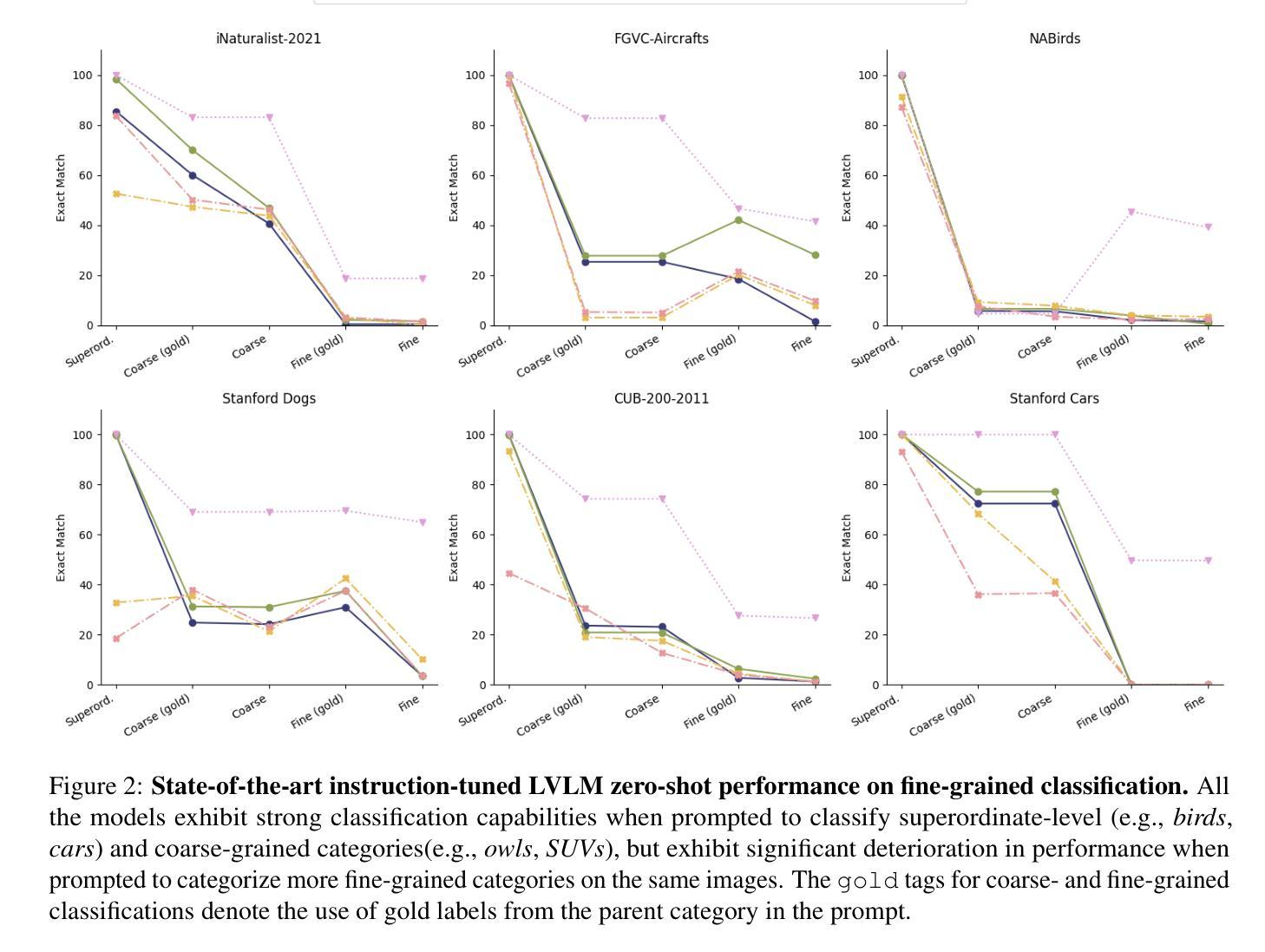
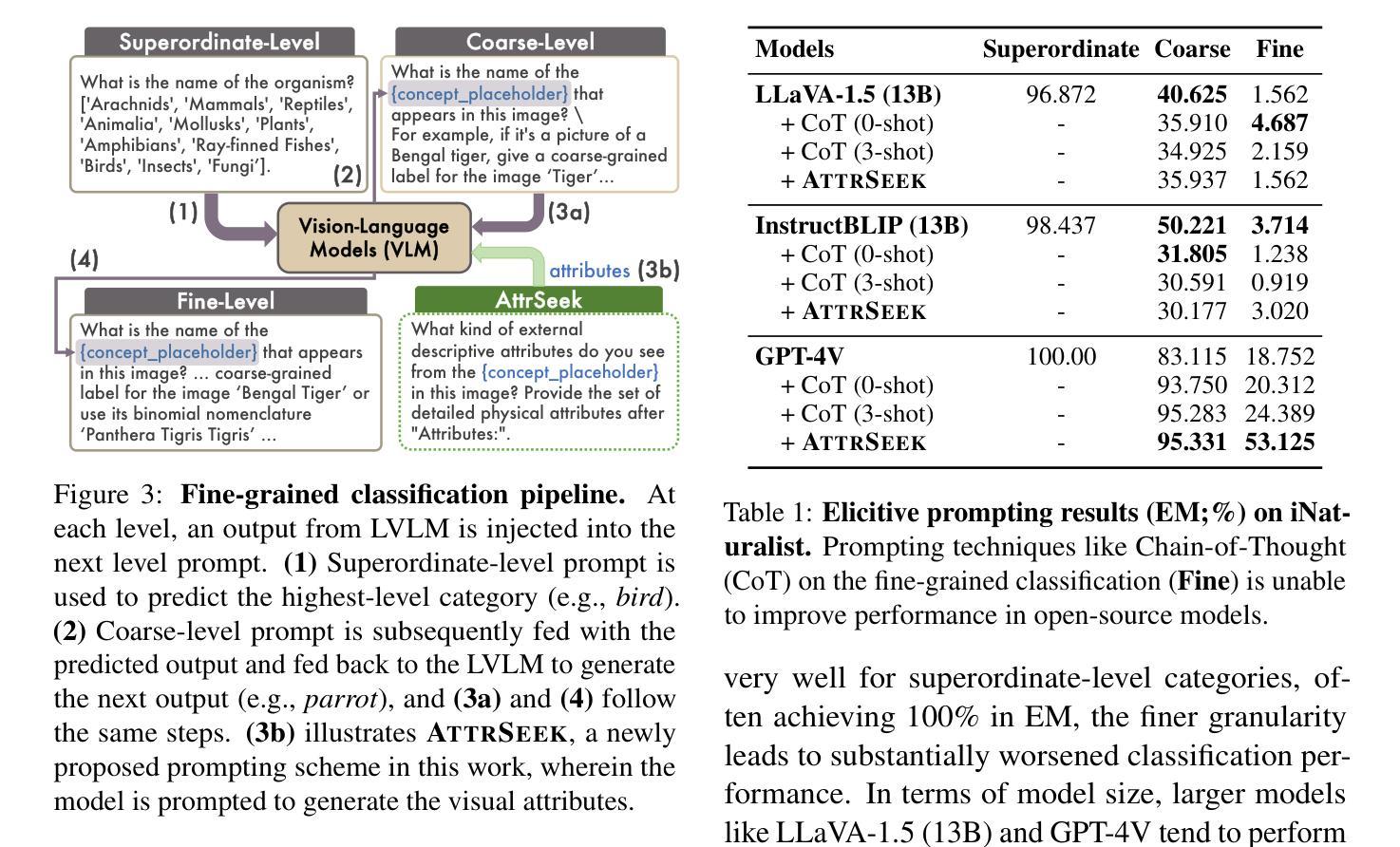
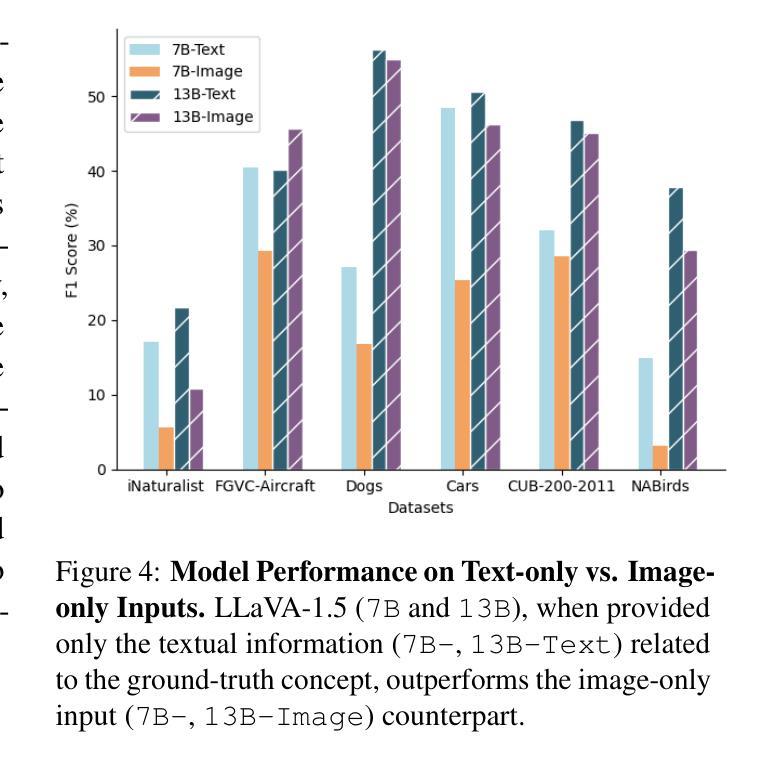
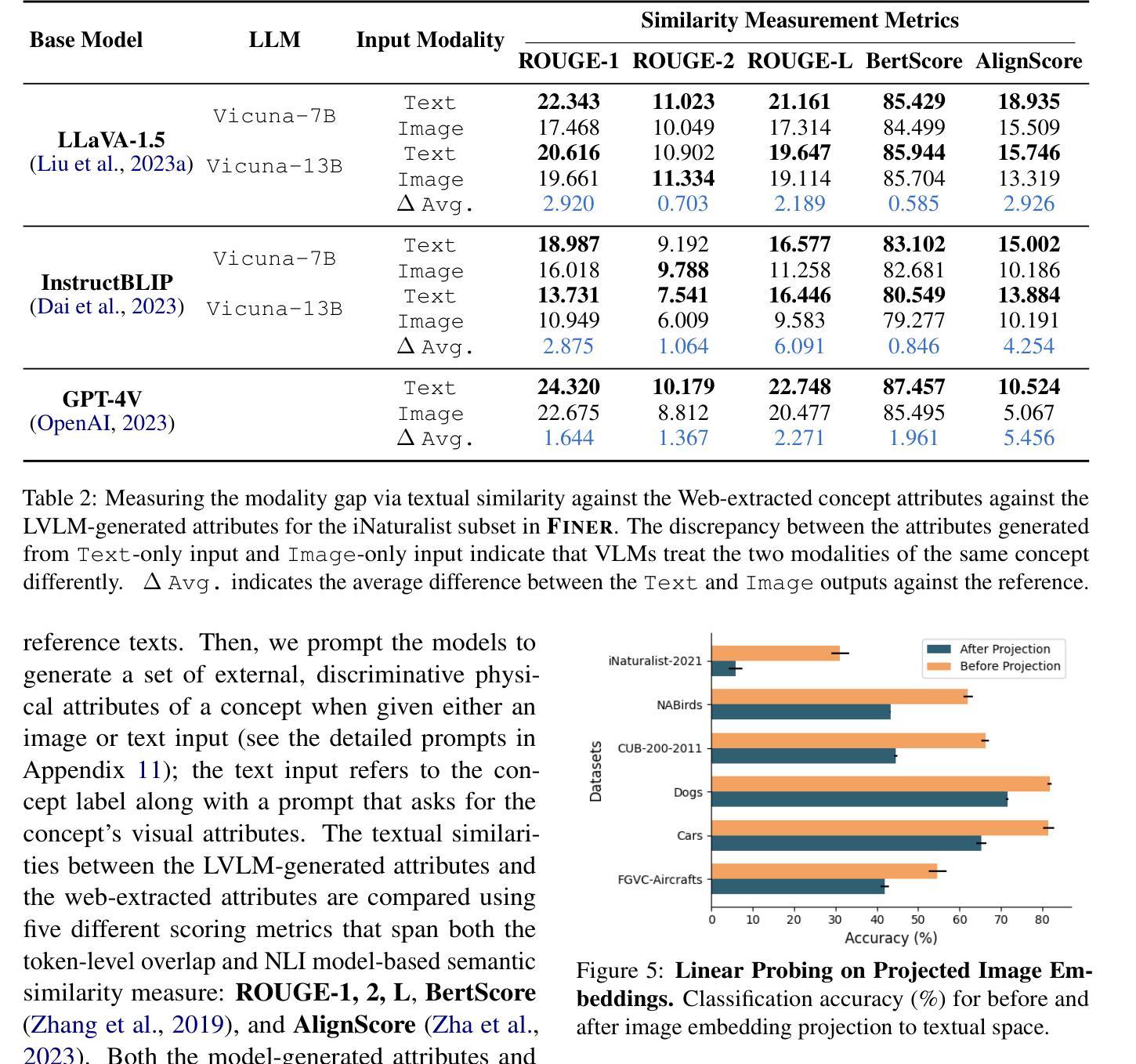
Finer: Investigating and Enhancing Fine-Grained Visual Concept Recognition in Large Vision Language Models
Authors:Jeonghwan Kim, Heng Ji
Recent advances in instruction-tuned Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have imbued the models with the ability to generate high-level, image-grounded explanations with ease. While such capability is largely attributed to the rich world knowledge contained within the Large Language Models (LLMs), our work reveals their shortcomings in fine-grained visual categorization (FGVC) across six different benchmark settings. Most recent state-of-the-art LVLMs like LLaVa-1.5, InstructBLIP and GPT-4V not only severely deteriorate in terms of classification performance, e.g., average drop of 65.58 in EM for Stanford Dogs for LLaVA-1.5, but also struggle to generate an accurate explanation with detailed attributes based on the concept that appears within an input image despite their capability to generate holistic image-level descriptions. In-depth analyses show that instruction-tuned LVLMs exhibit modality gap, showing discrepancy when given textual and visual inputs that correspond to the same concept, preventing the image modality from leveraging the rich parametric knowledge within the LLMs. In an effort to further the community’s endeavor in this direction, we propose a multiple granularity attribute-centric evaluation benchmark, Finer, which aims to establish a ground to evaluate LVLMs’ fine-grained visual comprehension ability and provide significantly improved explainability.
近期指令微调的大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的进步使得这些模型能够轻松生成高水平的、基于图像的解释。虽然这种能力主要归功于大型语言模型(LLMs)中包含的丰富世界知识,但我们的工作揭示了它们在六个不同基准测试环境中的精细粒度视觉分类(FGVC)的短板。最近最先进的LVLMs,如LLaVa-1.5、InstructBLIP和GPT-4V,不仅在分类性能上严重下降,例如LLaVA-1.5在Stanford Dogs上的平均EM下降65.58%,而且在基于输入图像中出现的概念生成准确且详细的属性解释方面感到困难,尽管它们能够生成整体图像级别的描述。深入分析显示,指令调整后的LVLMs表现出模态间隙,当给定与同一概念相对应的文本和视觉输入时,显示出入差异,阻止图像模态利用LLMs中的丰富参数知识。为了推动社区在此方向上的努力,我们提出了多粒度属性中心评估基准Finer,旨在建立评估LVLMs的精细粒度视觉理解能力并提供显著改进的解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF EMNLP 2024; Main Conference
Summary
大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)的最新进展赋予了模型轻松生成高级图像解释的能力。虽然这种能力主要归功于大型语言模型(LLM)中丰富的世界知识,但我们的工作揭示了在跨六个不同基准设置的精细粒度视觉分类(FGVC)中,LVLM存在不足。最先进的LVLM如LLaVa-1.5、InstructBLIP和GPT-4V不仅在分类性能上严重下降(例如,斯坦福犬类数据集上的平均EM值下降65.58),而且在生成基于输入图像内概念详细属性的准确解释方面也遇到困难,尽管它们能够生成整体图像级别的描述。深入的分析表明,指令调优的LVLM会出现模态鸿沟,在给定与同一概念相对应的文本和视觉输入时表现出差异,阻止图像模态利用LLM中的丰富参数知识。为了推动社区在这方面的发展,我们提出了多粒度属性为中心的评估基准Finer,旨在评估LVLM的精细粒度视觉理解能力并提供显著改进的解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)能够轻松生成高级图像解释,这主要归功于大型语言模型(LLM)中的丰富知识。
- 在精细粒度视觉分类(FGVC)方面,现有LVLM存在不足,最先进的模型在分类性能和生成详细属性解释方面表现不佳。
- 指令调优的LVLM会出现模态鸿沟,即在处理文本和视觉输入时存在差距。
- 模态鸿沟导致图像模态无法充分利用LLM中的丰富参数知识。
- 为了改进LVLM的评估,提出了多粒度属性为中心的评估基准Finer。
- Finer基准旨在评估LVLM在精细粒度视觉理解方面的能力。
点此查看论文截图

AllSpark: A Multimodal Spatio-Temporal General Intelligence Model with Ten Modalities via Language as a Reference Framework
Authors:Run Shao, Cheng Yang, Qiujun Li, Qing Zhu, Yongjun Zhang, YanSheng Li, Yu Liu, Yong Tang, Dapeng Liu, Shizhong Yang, Haifeng Li
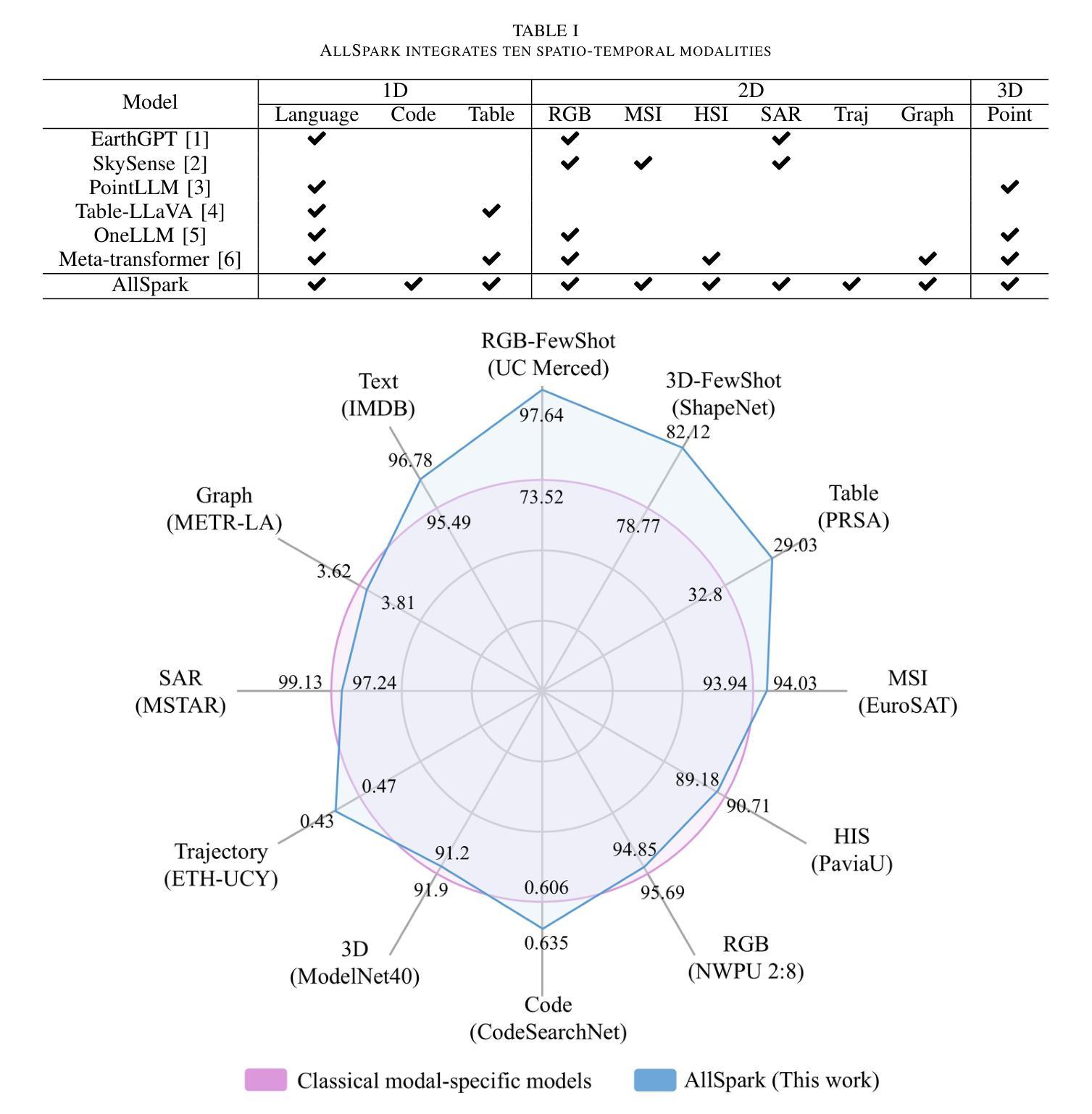
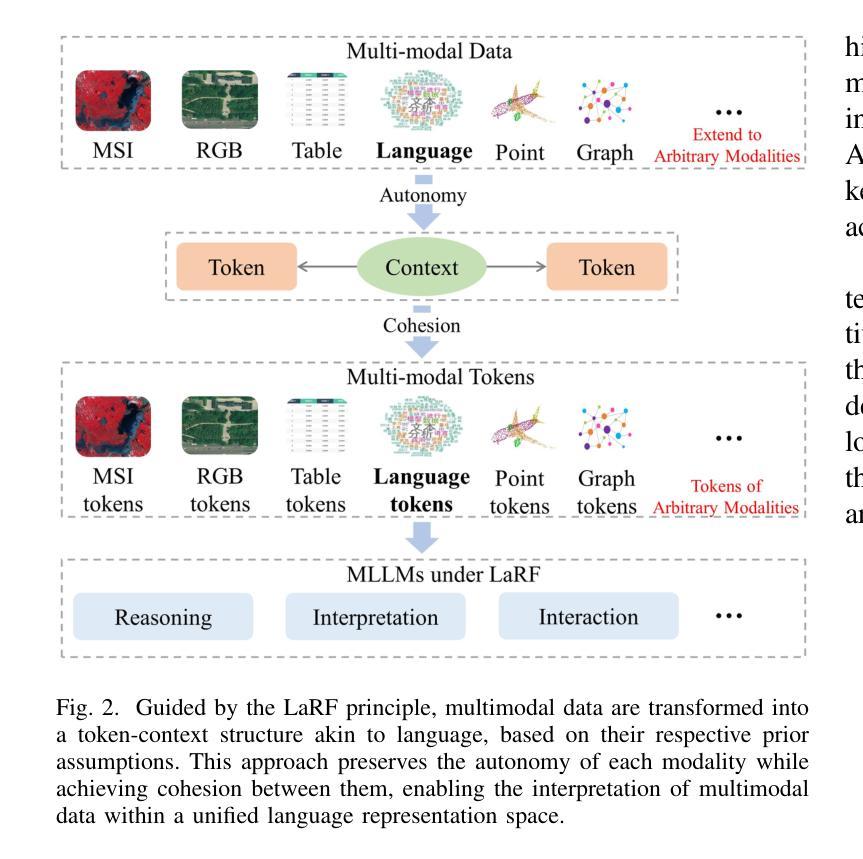
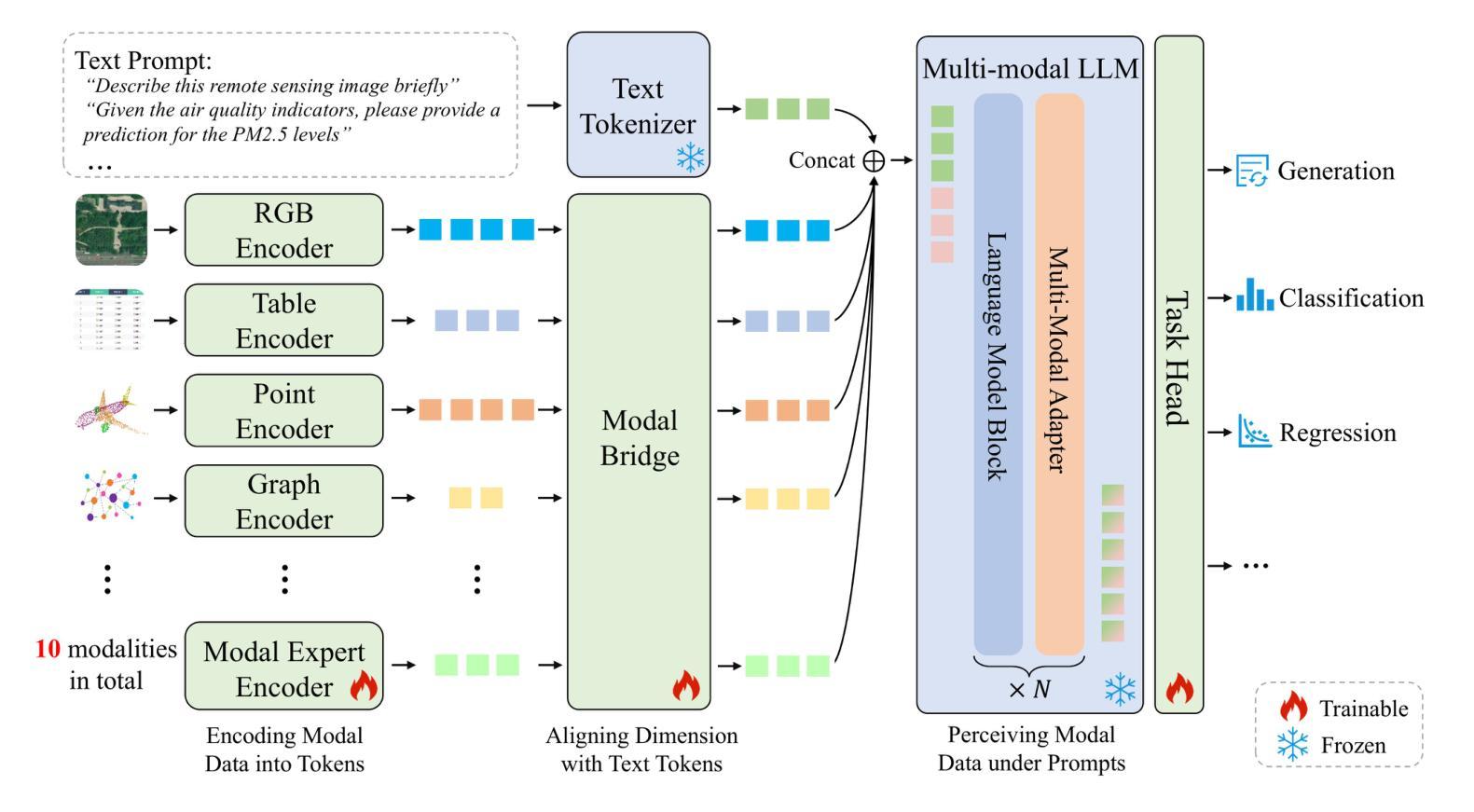
Leveraging multimodal data is an inherent requirement for comprehending geographic objects. However, due to the high heterogeneity in structure and semantics among various spatio-temporal modalities, the joint interpretation of multimodal spatio-temporal data has long been an extremely challenging problem. The primary challenge resides in striking a trade-off between the cohesion and autonomy of diverse modalities. This trade-off becomes progressively nonlinear as the number of modalities expands. Inspired by the human cognitive system and linguistic philosophy, where perceptual signals from the five senses converge into language, we introduce the Language as Reference Framework (LaRF), a fundamental principle for constructing a multimodal unified model. Building upon this, we propose AllSpark, a multimodal spatio-temporal general artificial intelligence model. Our model integrates ten different modalities into a unified framework. To achieve modal cohesion, AllSpark introduces a modal bridge and multimodal large language model (LLM) to map diverse modal features into the language feature space. To maintain modality autonomy, AllSpark uses modality-specific encoders to extract the tokens of various spatio-temporal modalities. Finally, observing a gap between the model’s interpretability and downstream tasks, we designed modality-specific prompts and task heads, enhancing the model’s generalization capability across specific tasks. Experiments indicate that the incorporation of language enables AllSpark to excel in few-shot classification tasks for RGB and point cloud modalities without additional training, surpassing baseline performance by up to 41.82%. The source code is available at https://github.com/GeoX-Lab/AllSpark.
利用多模态数据是理解地理对象的基本要求。然而,由于各种时空模态在结构和语义上的高度异质性,多模态时空数据的联合解释一直是一个极具挑战性的问题。主要挑战在于在多种模态的凝聚力和自主性之间找到平衡。随着模态数量的增加,这种平衡逐渐变得非线性。受人类认知系统和语言学哲学的启发,即五种感官的感知信号汇聚成语言,我们引入了语言参考框架(LaRF)作为构建多模态统一模型的基本原理。在此基础上,我们提出了多模态时空通用人工智能模型AllSpark。我们的模型将十种不同的模态集成到一个统一框架中。为了实现模态凝聚力,AllSpark引入了一个模态桥和多模态大型语言模型(LLM),将各种模态特征映射到语言特征空间中。为了保持模态自主性,AllSpark使用特定模态编码器来提取各种时空模态的标记。最后,我们观察到模型的可解释性与下游任务之间存在差距,因此我们设计了特定于模态的提示和任务头,以增强模型在特定任务上的泛化能力。实验表明,语言的融入使AllSpark在RGB和点云模态的少量分类任务上表现出色,无需额外训练即可超越基线性能高达41.82%。源代码可在https://github.com/GeoX-Lab/AllSpark中获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 19 tables, 3 figures
摘要
融合多模态数据是理解地理对象的基本需求。然而,由于时空多模态数据的结构和语义高度异构,多模态时空数据的联合解释一直是一个极具挑战性的问题。主要挑战在于如何在多种模态的连贯性和自主性之间取得平衡。随着模态数量的增加,这种平衡变得愈加非线性。受人类认知系统和语言哲学的启发,即五种感知信号汇聚成语言,我们引入了语言参照框架(LaRF)作为构建多模态统一模型的基本原则。在此基础上,我们提出了多模态时空通用人工智能模型AllSpark。该模型整合了十种不同模态到一个统一框架中。为实现模态连贯性,AllSpark引入模态桥和多模态大型语言模型(LLM),将各种模态特征映射到语言特征空间。为了保持模态自主性,AllSpark使用特定模态编码器提取各种时空模态的标记。最后,我们观察到模型的可解释性与下游任务之间存在差距,因此设计了特定模态的提示和任务头,增强模型在特定任务上的泛化能力。实验表明,加入语言功能使AllSpark在RGB和点云模态的少量样本分类任务中表现卓越,无需额外训练即可超越基线性能高达41.82%。源代码可在https://github.com/GeoX-Lab/AllSpark获取。
关键见解
- 多模态数据理解地理对象是内在需求,但多模态时空数据联合解释具有挑战性。
- 主要挑战在于在多样模态的连贯性和自主性之间找到平衡。
- LaRF(语言作为参考框架)为构建多模态统一模型提供了基本原则。
- AllSpark模型整合了多种模态,实现模态连贯性并维持自主性。
- 通过引入模态桥和多模态LLM,AllSpark成功将不同模态特征映射到语言特征空间。
- 通过特定模态的提示和任务头,提高了模型的泛化能力和任务性能。
点此查看论文截图