⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-09 更新
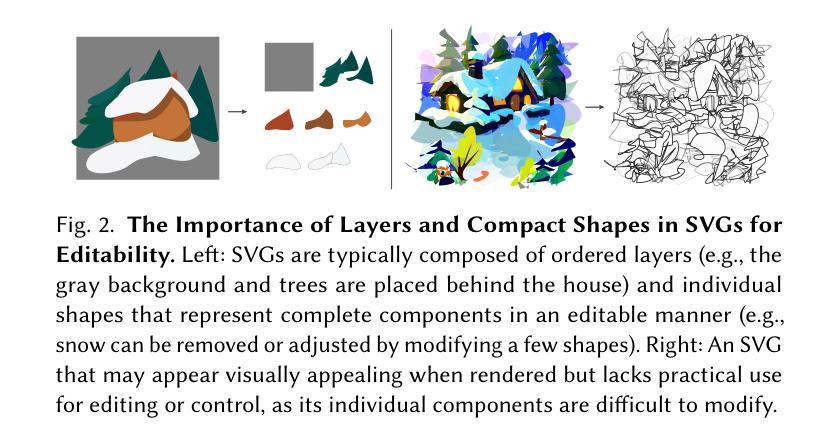
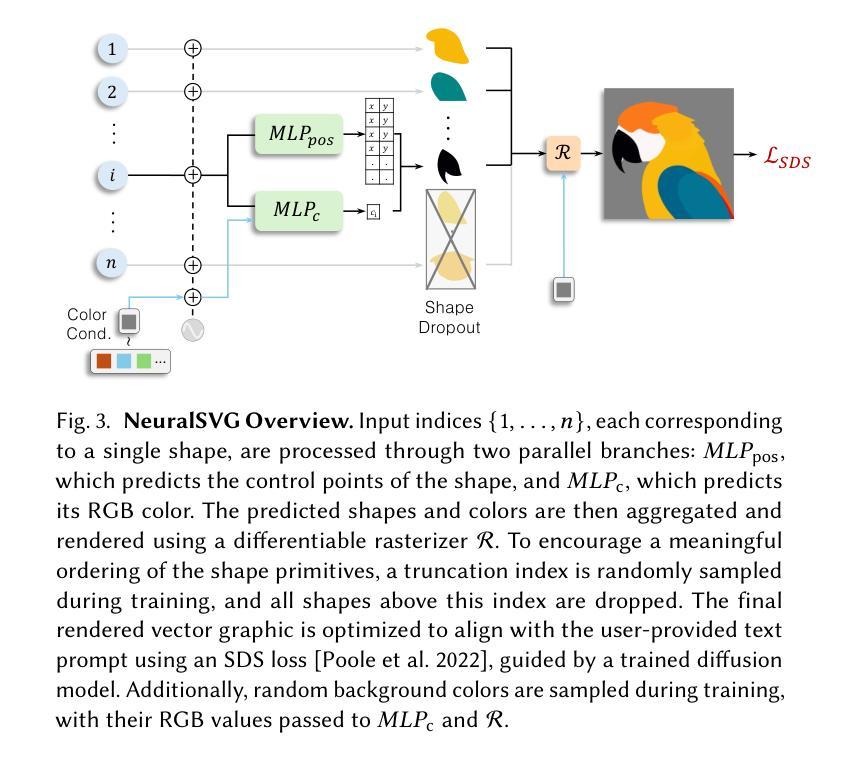
NeuralSVG: An Implicit Representation for Text-to-Vector Generation
Authors:Sagi Polaczek, Yuval Alaluf, Elad Richardson, Yael Vinker, Daniel Cohen-Or
Vector graphics are essential in design, providing artists with a versatile medium for creating resolution-independent and highly editable visual content. Recent advancements in vision-language and diffusion models have fueled interest in text-to-vector graphics generation. However, existing approaches often suffer from over-parameterized outputs or treat the layered structure - a core feature of vector graphics - as a secondary goal, diminishing their practical use. Recognizing the importance of layered SVG representations, we propose NeuralSVG, an implicit neural representation for generating vector graphics from text prompts. Inspired by Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs), NeuralSVG encodes the entire scene into the weights of a small MLP network, optimized using Score Distillation Sampling (SDS). To encourage a layered structure in the generated SVG, we introduce a dropout-based regularization technique that strengthens the standalone meaning of each shape. We additionally demonstrate that utilizing a neural representation provides an added benefit of inference-time control, enabling users to dynamically adapt the generated SVG based on user-provided inputs, all with a single learned representation. Through extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations, we demonstrate that NeuralSVG outperforms existing methods in generating structured and flexible SVG.
矢量图形在设计领域中具有重要地位,为艺术家提供了一种多功能的媒介,用于创建分辨率独立且高度可编辑的视觉内容。最近,视觉语言与扩散模型的进步激发了文本到矢量图形生成的兴趣。然而,现有方法常常面临过度参数化的输出问题,或将矢量图形的核心特征——分层结构作为次要目标,从而降低了其实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://sagipolaczek.github.io/NeuralSVG/
Summary
神经网络矢量图形生成技术基于NeRF理念,利用矢量图形(SVG)的分层结构特点,提出一种从文本提示生成矢量图形的隐式神经网络表示方法NeuralSVG。通过引入基于dropout的正则化技术,强化每个形状的独立意义,并展示其优于现有方法的生成效果。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络矢量图形生成技术结合了文本提示与矢量图形生成,利用最新视觉语言模型和扩散模型技术。
- 现有方法在处理矢量图形生成时存在过度参数化或忽视分层结构的问题。
- NeuralSVG采用隐式神经表示技术,借鉴NeRF理念,从文本提示生成矢量图形。
- NeuralSVG通过引入基于dropout的正则化技术,鼓励生成矢量图形的分层结构。
- NeuralSVG提供了推理时间控制,可根据用户输入动态调整生成的SVG。
- 定量和定性评估显示,NeuralSVG在生成结构化、灵活的SVG方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图



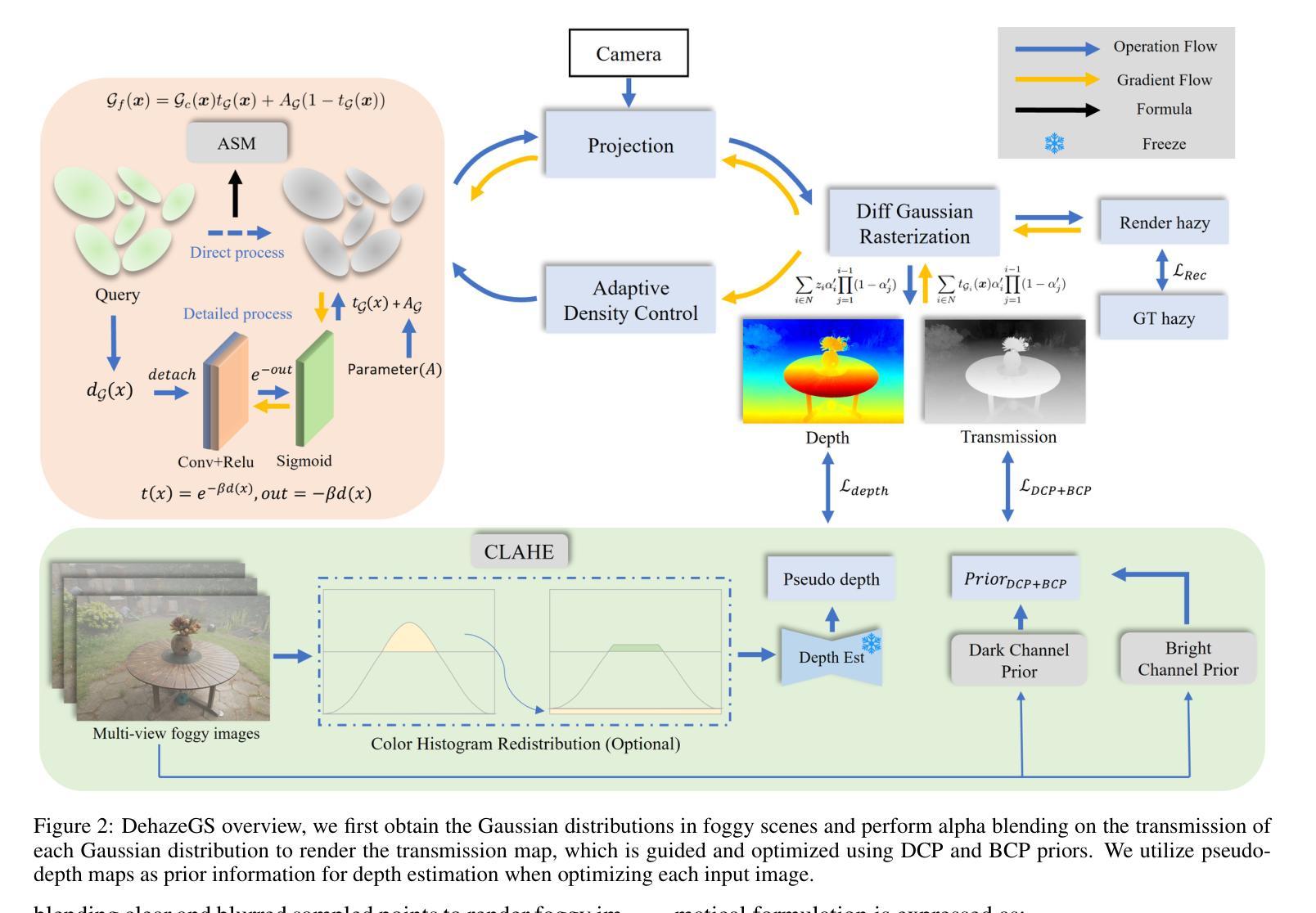
DehazeGS: Seeing Through Fog with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jinze Yu, Yiqun Wang, Zhengda Lu, Jianwei Guo, Yong Li, Hongxing Qin, Xiaopeng Zhang
Current novel view synthesis tasks primarily rely on high-quality and clear images. However, in foggy scenes, scattering and attenuation can significantly degrade the reconstruction and rendering quality. Although NeRF-based dehazing reconstruction algorithms have been developed, their use of deep fully connected neural networks and per-ray sampling strategies leads to high computational costs. Moreover, NeRF’s implicit representation struggles to recover fine details from hazy scenes. In contrast, recent advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting achieve high-quality 3D scene reconstruction by explicitly modeling point clouds into 3D Gaussians. In this paper, we propose leveraging the explicit Gaussian representation to explain the foggy image formation process through a physically accurate forward rendering process. We introduce DehazeGS, a method capable of decomposing and rendering a fog-free background from participating media using only muti-view foggy images as input. We model the transmission within each Gaussian distribution to simulate the formation of fog. During this process, we jointly learn the atmospheric light and scattering coefficient while optimizing the Gaussian representation of the hazy scene. In the inference stage, we eliminate the effects of scattering and attenuation on the Gaussians and directly project them onto a 2D plane to obtain a clear view. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world foggy datasets demonstrate that DehazeGS achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of both rendering quality and computational efficiency.
当前的新型视图合成任务主要依赖于高质量、清晰的图像。然而,在雾天场景中,散射和衰减会严重降低重建和渲染质量。尽管已经开发了基于NeRF的去雾重建算法,但它们使用深度全连接神经网络和按射线采样策略,导致计算成本较高。此外,NeRF的隐式表示很难从雾天场景中恢复细节。相比之下,最近3D高斯喷射技术的进展通过显式地模拟点云到3D高斯来实现高质量的三维场景重建。在本文中,我们提出利用显式高斯表示法,通过一个物理准确的正向渲染过程来解释雾天图像的形成过程。我们引入了DehazeGS方法,该方法能够从参与介质中分解并渲染无雾背景,仅使用多视角雾天图像作为输入。我们模拟每个高斯分布内的传输来模拟雾的形成。在此过程中,我们联合学习大气光和散射系数,同时优化雾天场景的高斯表示。在推理阶段,我们消除了散射和衰减对高斯的影响,并将其直接投影到二维平面上以获得清晰视图。在合成和真实世界的雾天数据集上的实验表明,DehazeGS在渲染质量和计算效率方面都达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages,4 figures
摘要
在雾天场景中的图像合成任务中,NeRF模型因计算成本高昂和对细节恢复的局限性而面临挑战。本研究结合物理准确的前向渲染过程,利用明确的高斯表示方法来解决雾天场景重建问题。提出了名为DehazeGS的方法,仅需使用多视角的雾天图像作为输入,便能分解并渲染出无雾的背景。通过模拟雾的形成过程,对高斯分布内的传输进行建模,同时学习大气光和散射系数,优化雾天场景的高斯表示。在推断阶段,消除高斯分布的散射和衰减影响,直接投影至二维平面以获取清晰的视图。实验证明,DehazeGS在渲染质量和计算效率上均达到领先水平。
关键见解
- 当前视图合成任务在雾天场景中面临挑战,因雾导致的散射和衰减会严重影响重建和渲染质量。
- NeRF模型在处理雾天场景时计算成本高昂,且难以恢复细节。
- 本研究利用明确的高斯表示方法,通过物理准确的前向渲染过程处理雾天图像。
- 提出名为DehazeGS的方法,能从参与介质中分解并渲染出无雾的背景,仅使用多视角的雾天图像作为输入。
- 通过模拟雾的形成过程,对高斯分布内的传输进行建模,同时优化大气光和散射系数的学习。
- 在推断阶段,DehazeGS能消除高斯分布的散射和衰减影响,实现清晰的视图。
点此查看论文截图
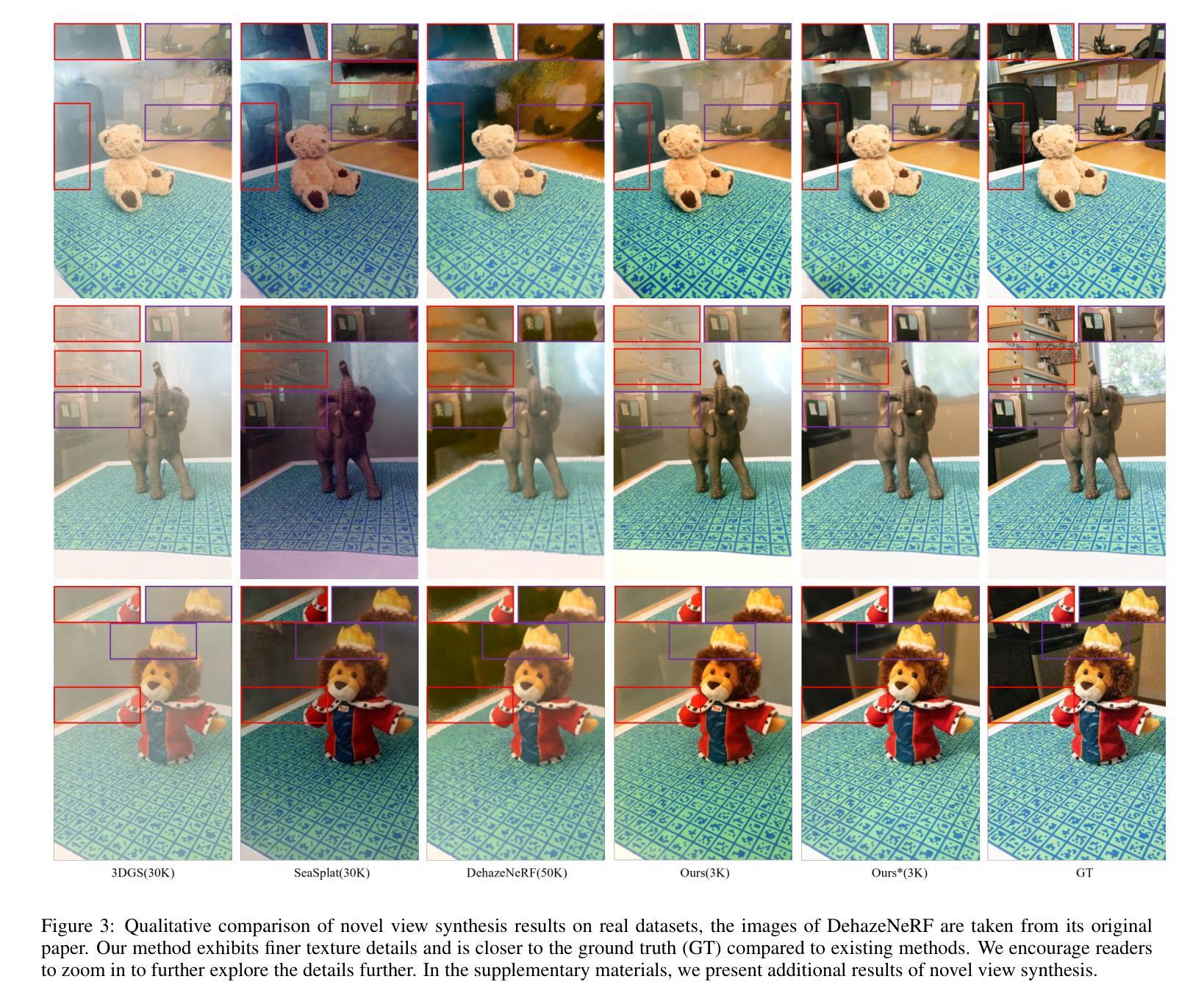


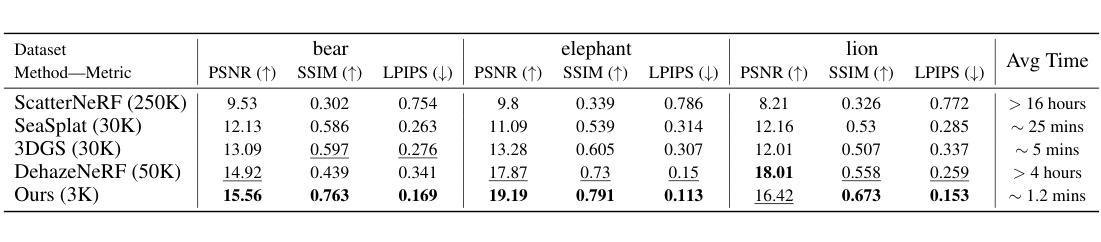
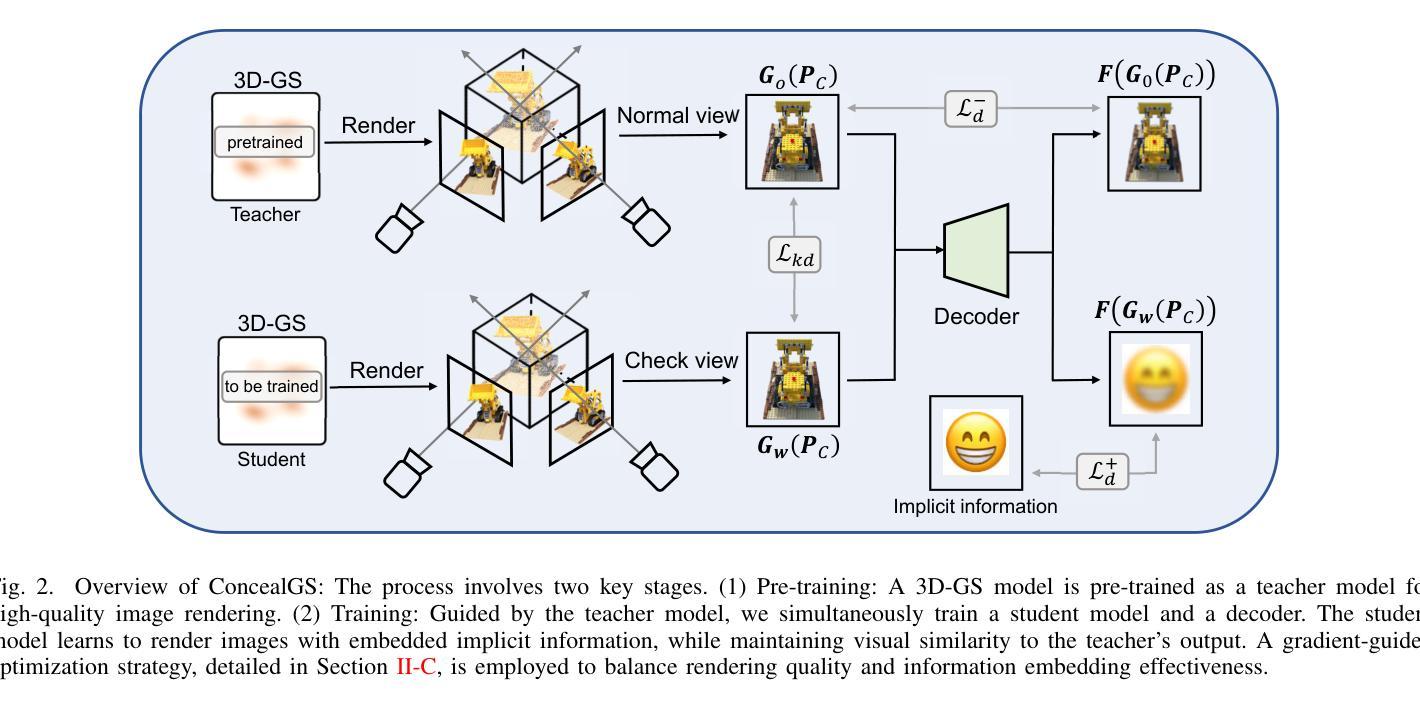
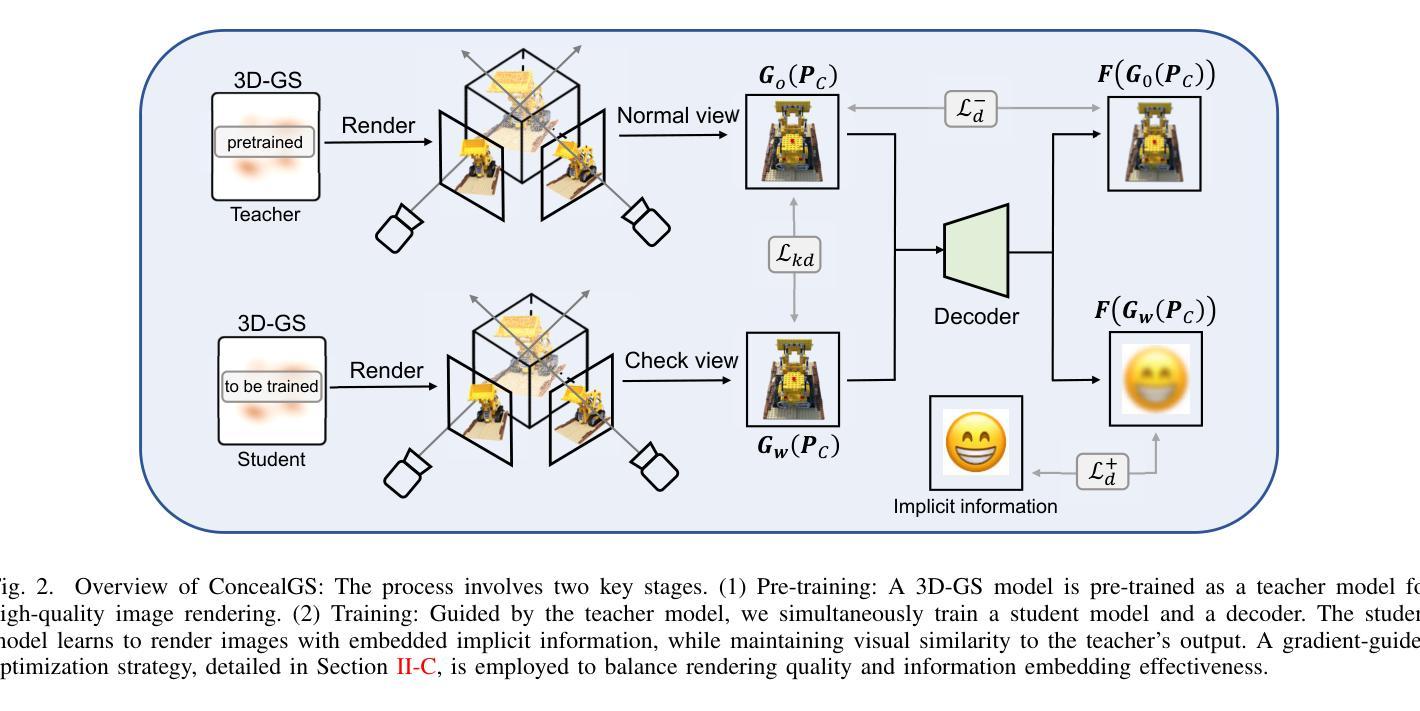
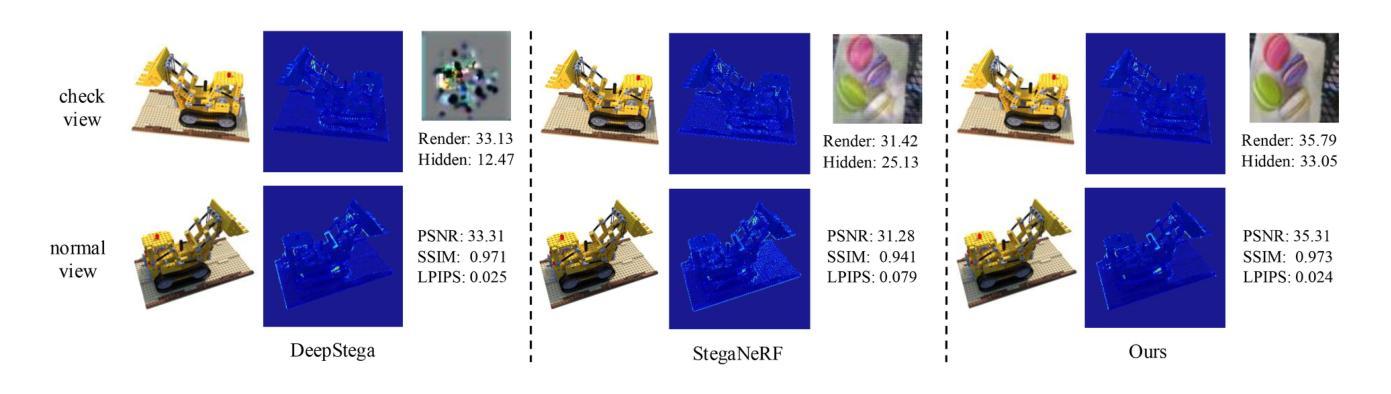
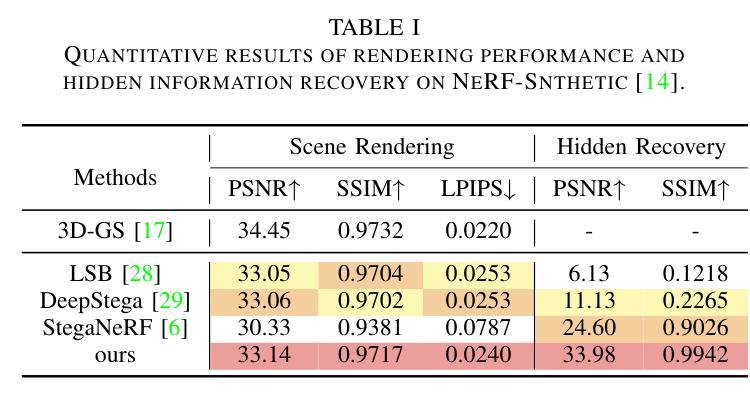
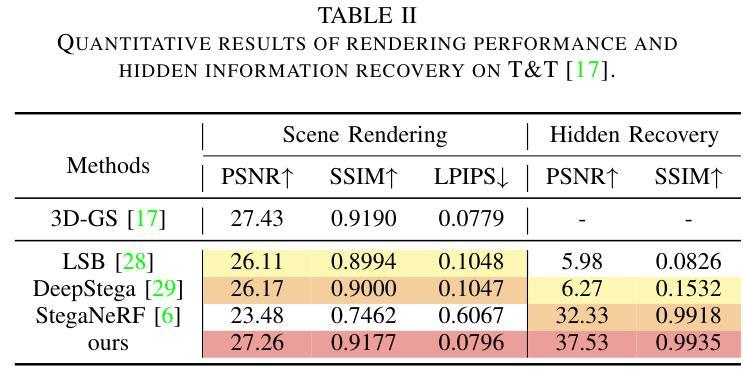
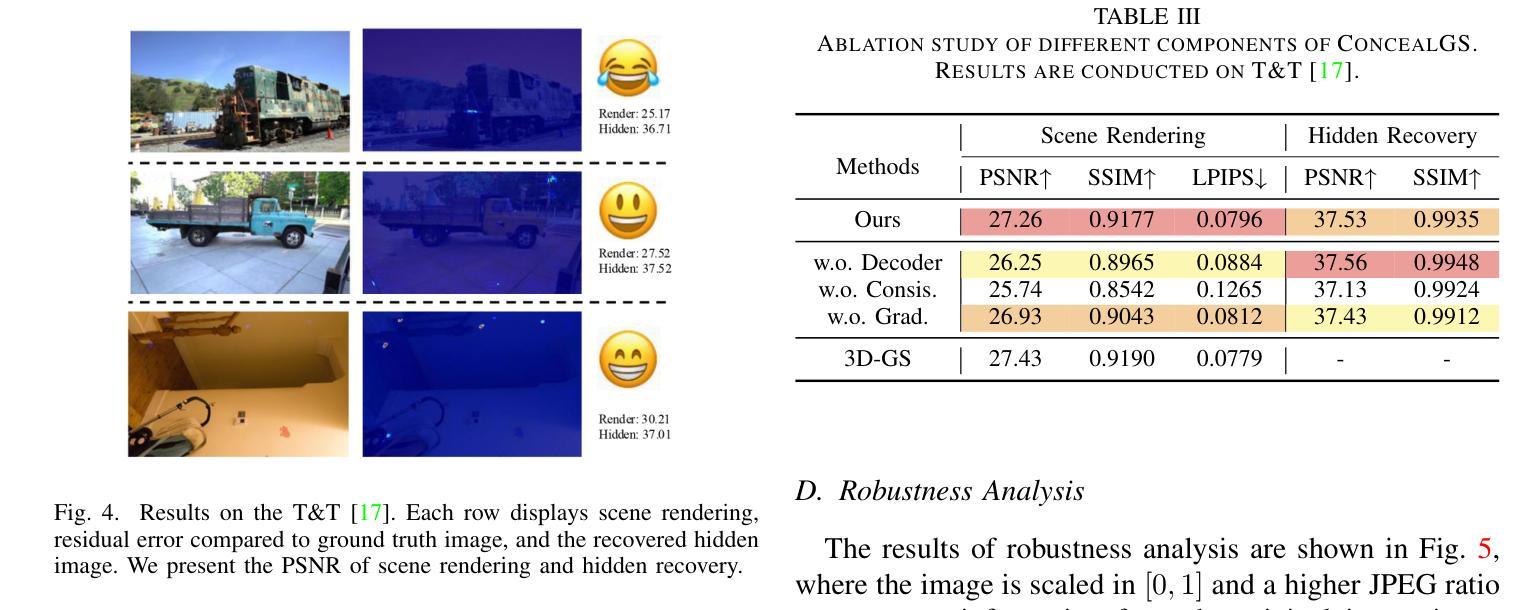
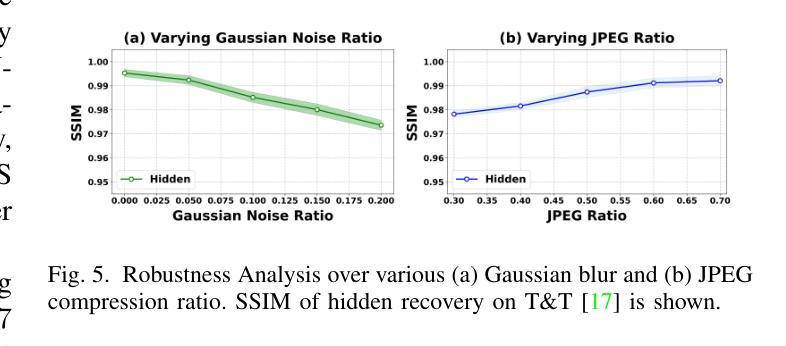
ConcealGS: Concealing Invisible Copyright Information in 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yifeng Yang, Hengyu Liu, Chenxin Li, Yining Sun, Wuyang Li, Yifan Liu, Yiyang Lin, Yixuan Yuan, Nanyang Ye
With the rapid development of 3D reconstruction technology, the widespread distribution of 3D data has become a future trend. While traditional visual data (such as images and videos) and NeRF-based formats already have mature techniques for copyright protection, steganographic techniques for the emerging 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) format have yet to be fully explored. To address this, we propose ConcealGS, an innovative method for embedding implicit information into 3D-GS. By introducing the knowledge distillation and gradient optimization strategy based on 3D-GS, ConcealGS overcomes the limitations of NeRF-based models and enhances the robustness of implicit information and the quality of 3D reconstruction. We evaluate ConcealGS in various potential application scenarios, and experimental results have demonstrated that ConcealGS not only successfully recovers implicit information but also has almost no impact on rendering quality, providing a new approach for embedding invisible and recoverable information into 3D models in the future.
随着三维重建技术的快速发展,三维数据的广泛应用已成为未来的趋势。虽然传统的视觉数据(如图像和视频)和基于NeRF的格式已经拥有成熟的版权保护技术,但针对新兴的三维高斯平铺(3D-GS)格式的秘密编码技术尚未得到充分探索。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了ConcealGS,这是一种将隐含信息嵌入到3D-GS中的创新方法。通过引入基于3D-GS的知识蒸馏和梯度优化策略,ConcealGS克服了基于NeRF模型的局限性,提高了隐含信息的稳健性和三维重建的质量。我们在各种潜在的应用场景中评估了ConcealGS的性能,实验结果表明,ConcealGS不仅成功地恢复了隐含信息,而且对渲染质量几乎没有影响,为未来在三维模型中嵌入可恢复和不可见信息提供了新的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于三维重建技术的快速发展,新兴的三维高斯喷射(3D-GS)格式的隐写技术尚未得到充分探索。为解决这一问题,我们提出了ConcealGS方法,通过引入基于3D-GS的知识蒸馏和梯度优化策略,该方法克服了NeRF模型的局限性,提高了嵌入信息的鲁棒性和三维重建质量。实验结果表明,ConcealGS不仅能成功恢复嵌入信息,而且对渲染质量几乎没有影响,为未来在三维模型中嵌入可恢复的无痕信息提供了新的途径。
Key Takeaways
- 3D重建技术的发展促进了三维数据的广泛应用。
- 传统视觉数据和NeRF格式的版权保护技术已经成熟,但新兴的三维高斯喷射(3D-GS)格式的隐写技术尚未得到充分探索。
- ConcealGS方法通过引入知识蒸馏和梯度优化策略,成功克服了NeRF模型的局限性。
- ConcealGS提高了嵌入信息的鲁棒性和三维重建质量。
- 实验结果表明,ConcealGS可以成功恢复嵌入的信息且对渲染质量几乎没有影响。
- ConcealGS为在三维模型中嵌入可恢复的无痕信息提供了新的途径。
点此查看论文截图

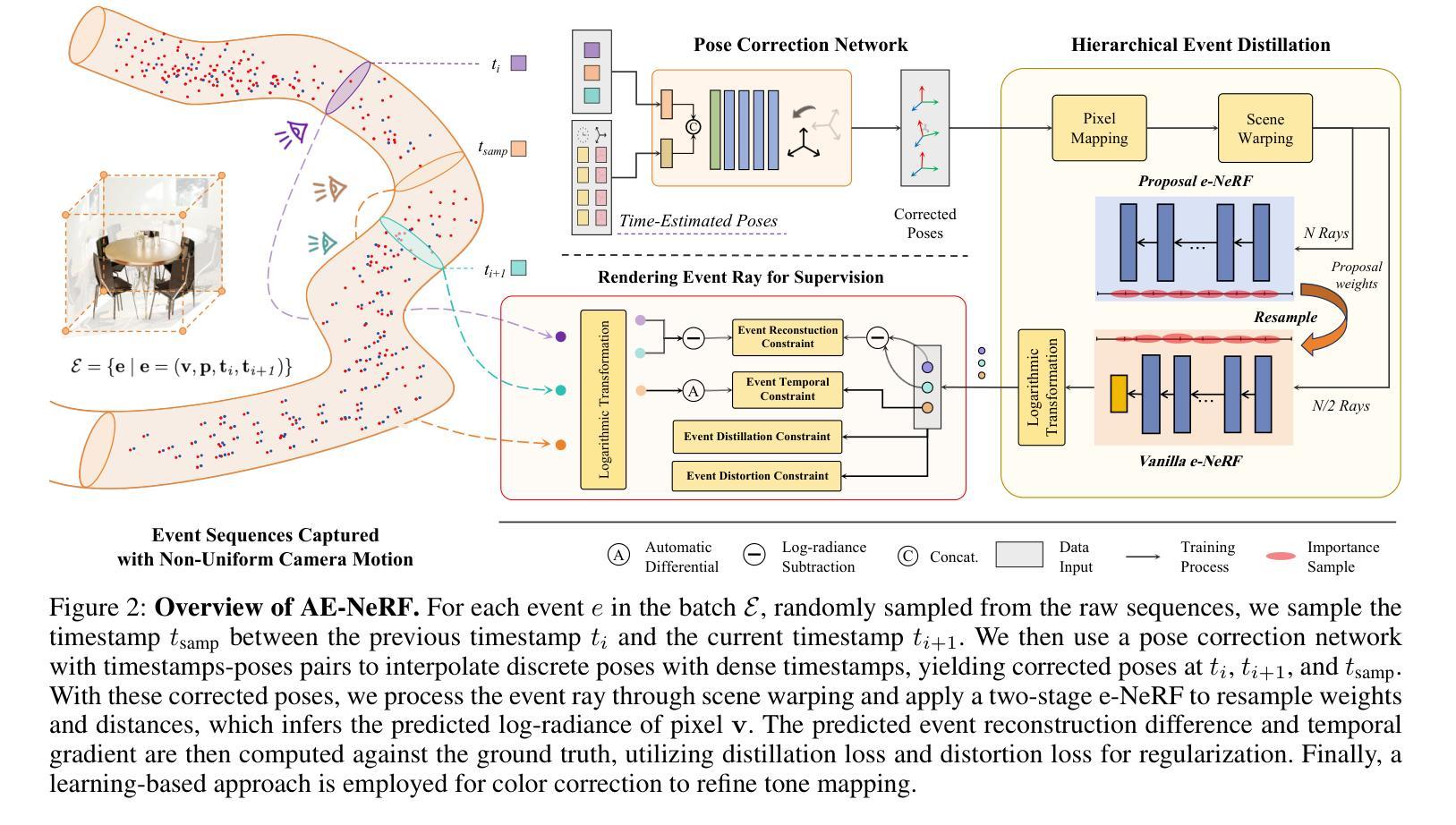
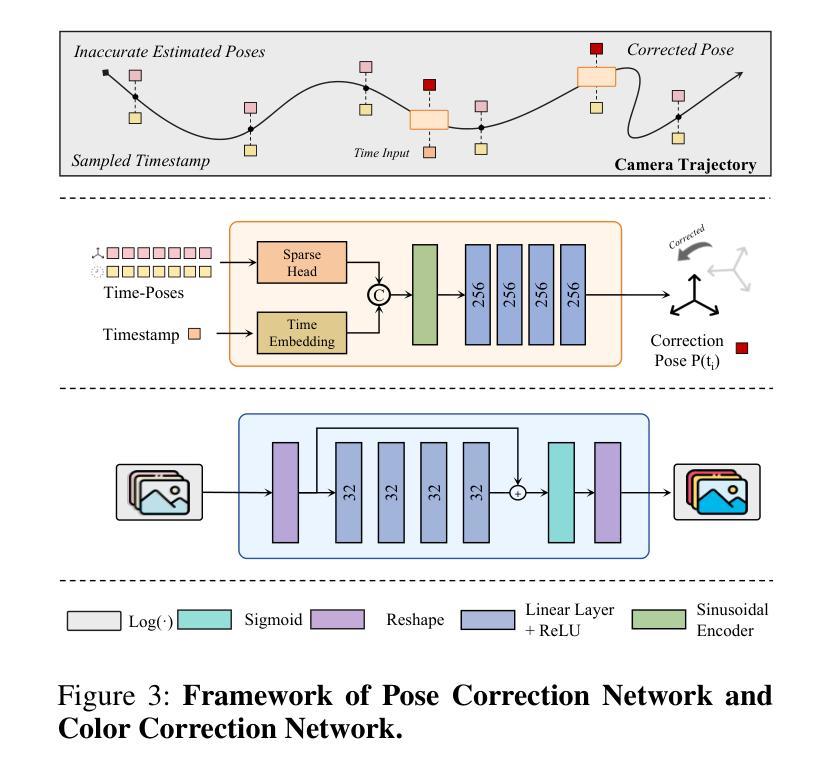
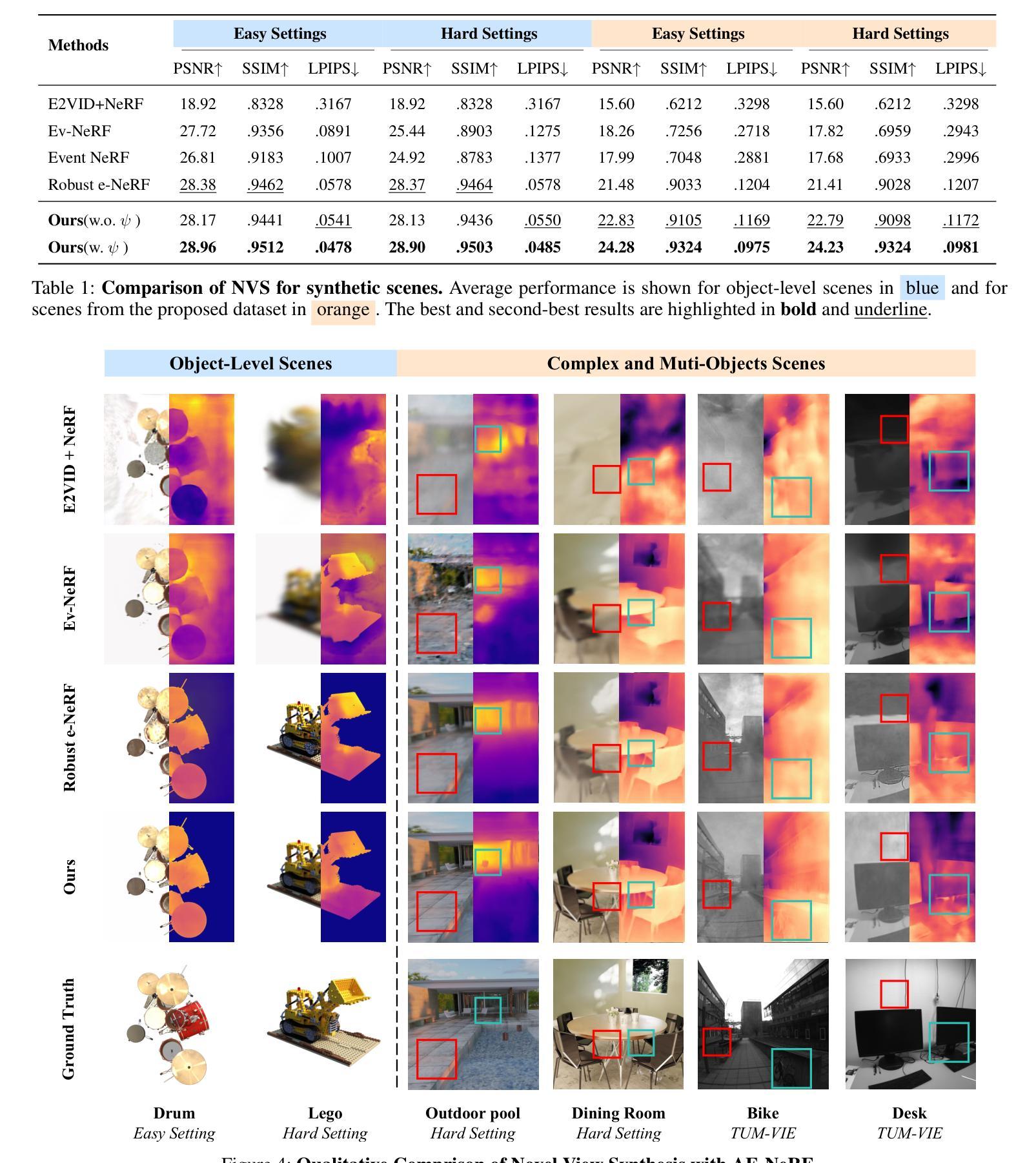
AE-NeRF: Augmenting Event-Based Neural Radiance Fields for Non-ideal Conditions and Larger Scene
Authors:Chaoran Feng, Wangbo Yu, Xinhua Cheng, Zhenyu Tang, Junwu Zhang, Li Yuan, Yonghong Tian
Compared to frame-based methods, computational neuromorphic imaging using event cameras offers significant advantages, such as minimal motion blur, enhanced temporal resolution, and high dynamic range. The multi-view consistency of Neural Radiance Fields combined with the unique benefits of event cameras, has spurred recent research into reconstructing NeRF from data captured by moving event cameras. While showing impressive performance, existing methods rely on ideal conditions with the availability of uniform and high-quality event sequences and accurate camera poses, and mainly focus on the object level reconstruction, thus limiting their practical applications. In this work, we propose AE-NeRF to address the challenges of learning event-based NeRF from non-ideal conditions, including non-uniform event sequences, noisy poses, and various scales of scenes. Our method exploits the density of event streams and jointly learn a pose correction module with an event-based NeRF (e-NeRF) framework for robust 3D reconstruction from inaccurate camera poses. To generalize to larger scenes, we propose hierarchical event distillation with a proposal e-NeRF network and a vanilla e-NeRF network to resample and refine the reconstruction process. We further propose an event reconstruction loss and a temporal loss to improve the view consistency of the reconstructed scene. We established a comprehensive benchmark that includes large-scale scenes to simulate practical non-ideal conditions, incorporating both synthetic and challenging real-world event datasets. The experimental results show that our method achieves a new state-of-the-art in event-based 3D reconstruction.
与传统基于帧的方法相比,使用事件相机进行计算的神经形态成像具有显著优势,例如最小的运动模糊、增强的时间分辨率和高动态范围。神经辐射场的多视角一致性结合了事件相机的独特优势,激发了最近关于从移动事件相机捕获的数据重建神经辐射场的研究。尽管现有方法表现出了令人印象深刻的效果,但它们依赖于理想条件,需要均匀和高质量的事件序列以及准确的相机姿态,并且主要关注对象级别的重建,从而限制了其实际应用。在本研究中,我们提出AE-NeRF来解决从非理想条件中学习基于事件NeRF所面临的挑战,包括非均匀事件序列、噪声姿态和各种场景尺度。我们的方法利用事件流的密度,并与基于事件的NeRF(e-NeRF)框架联合学习姿态校正模块,以进行稳健的3D重建。为了适用于更大的场景,我们提出了层次化事件蒸馏方法,包括一个提案e-NeRF网络和一个普通e-NeRF网络,以重新采样和细化重建过程。我们还提出了事件重建损失和时间损失来提高重建场景视图的一致性。我们建立了一个全面的基准测试,包括大规模场景来模拟实际非理想条件,同时纳入合成和具有挑战性的真实世界事件数据集。实验结果表明,我们的方法在基于事件的3D重建中达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
事件相机在计算机视觉领域的应用日益受到关注,尤其是与神经网络辐射场(NeRF)结合时。然而,现有方法受限于理想条件,如均匀高质量的事件序列和精确的相机姿态。本文提出AE-NeRF方法,解决了在非理想条件下的基于事件学习的NeRF挑战,包括非均匀事件序列、噪声姿态和各种场景尺度。通过联合学习姿态校正模块和基于事件NeRF框架,实现了从不准确相机姿态的稳健三维重建。同时提出层次事件蒸馏法以提高重建质量并推广至更大场景。实验结果显示,该方法在基于事件的3D重建方面达到新的水平。
Key Takeaways
- 事件相机相较于帧基方法在计算机视觉中具有显著优势,包括减少运动模糊、提高时间分辨率和高动态范围。
- Neural Radiance Fields(NeRF)的多视角一致性结合事件相机的独特优势,激发了对从移动事件相机数据中重建NeRF的研究。
- 现有方法受限于理想条件,如均匀事件序列和精确相机姿态,主要关注对象级别的重建,限制了实际应用。
- AE-NeRF方法解决了在非理想条件下的基于事件学习的NeRF挑战,包括非均匀事件序列、噪声姿态和不同场景尺度。
- AE-NeRF通过联合学习姿态校正模块和基于事件NeRF框架,实现了稳健的三维重建,即使在不准确的相机姿态下。
- 层次事件蒸馏法用于提高重建质量并推广至更大场景。
点此查看论文截图

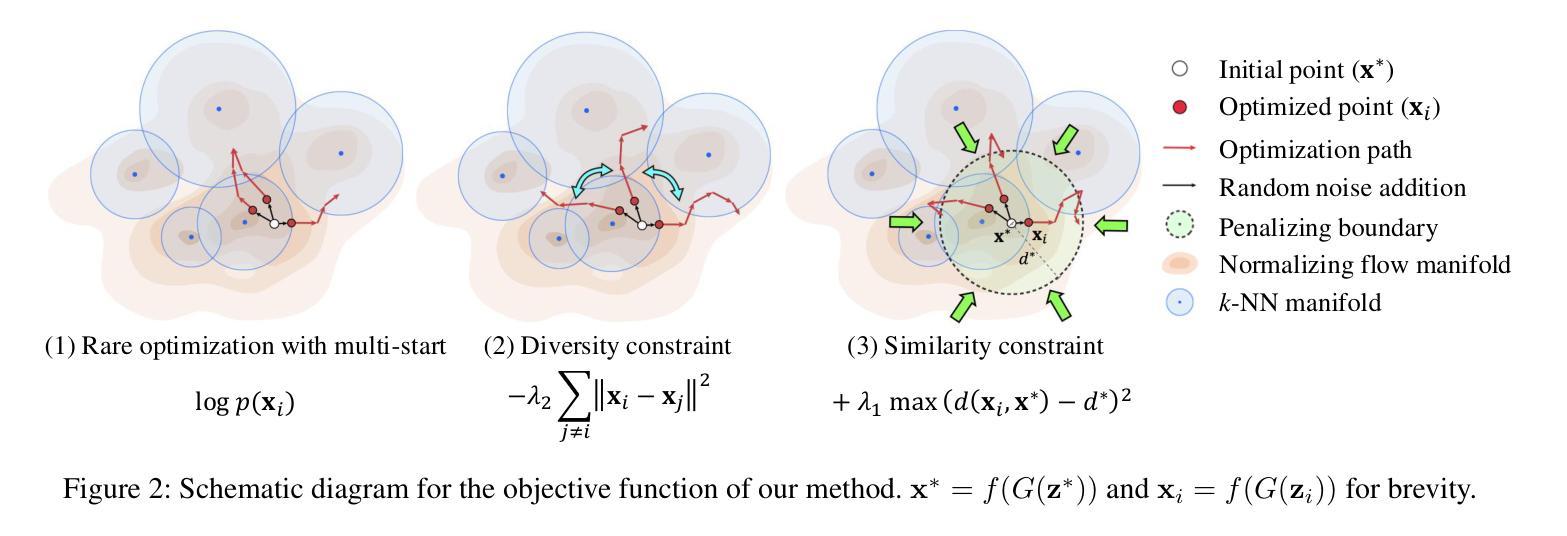
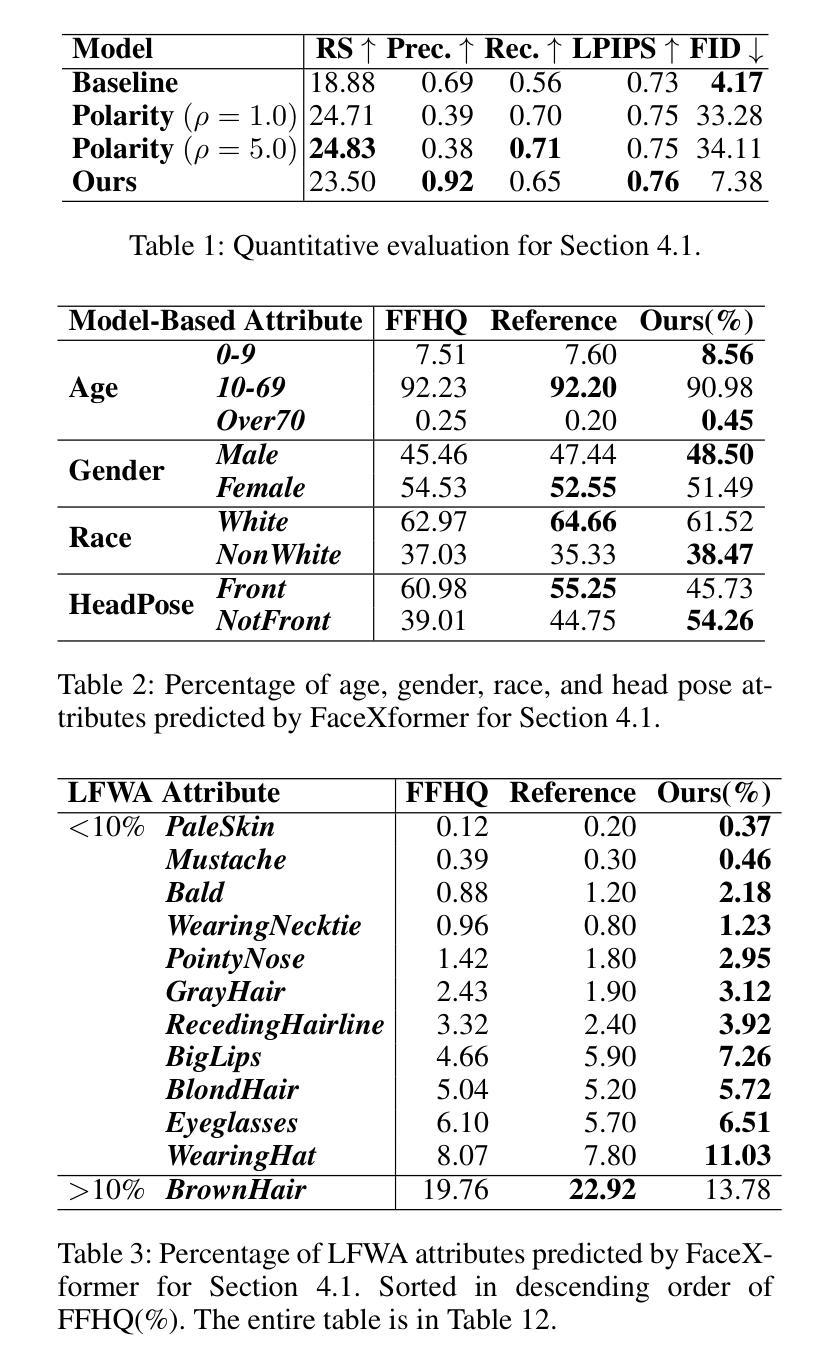
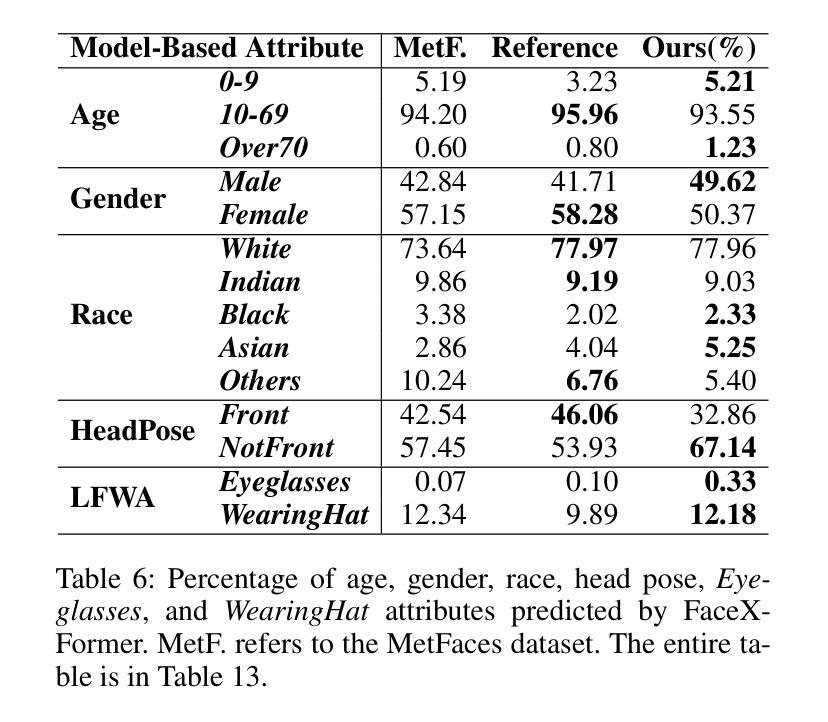
Diverse Rare Sample Generation with Pretrained GANs
Authors:Subeen Lee, Jiyeon Han, Soyeon Kim, Jaesik Choi
Deep generative models are proficient in generating realistic data but struggle with producing rare samples in low density regions due to their scarcity of training datasets and the mode collapse problem. While recent methods aim to improve the fidelity of generated samples, they often reduce diversity and coverage by ignoring rare and novel samples. This study proposes a novel approach for generating diverse rare samples from high-resolution image datasets with pretrained GANs. Our method employs gradient-based optimization of latent vectors within a multi-objective framework and utilizes normalizing flows for density estimation on the feature space. This enables the generation of diverse rare images, with controllable parameters for rarity, diversity, and similarity to a reference image. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach both qualitatively and quantitatively across various datasets and GANs without retraining or fine-tuning the pretrained GANs.
深度生成模型擅长生成真实数据,但由于训练数据集的稀缺性和模式崩溃问题,它们很难在低密度区域生成稀有样本。虽然最近的方法旨在提高生成样本的保真度,但它们往往通过忽略稀有和新颖的样本来降低多样性和覆盖范围。本研究提出了一种利用预训练GAN从高分辨率图像数据集生成多样稀有样本的新方法。我们的方法采用基于梯度的潜在向量优化和多目标框架,并利用归一化流对特征空间进行密度估计。这能够生成多样化的稀有图像,通过可控参数控制稀有性、多样性和与参考图像的相似性。我们在各种数据集和GAN上定性和定量地证明了我们的方法的有效性,而无需对预训练的GAN进行再训练或微调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种利用预训练的GANs从高分辨率图像数据集中生成多样化稀有样本的新方法。该方法基于梯度优化潜在向量和多目标框架,并利用归一化流进行特征空间的密度估计。该方法能够生成多样化的稀有图像,并可通过参数控制稀有性、多样性和与参考图像的相似性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度生成模型在生成现实数据方面表现出色,但在产生低密度区域的稀有样本时遇到困难。
- 现有方法在提高样本逼真度的同时,往往会减少多样性和覆盖范围,忽略了稀有和新颖的样本。
- 本文提出了一种利用预训练的GANs生成多样化稀有样本的新方法。
- 该方法通过梯度优化潜在向量和多目标框架来实现。
- 利用归一化流进行特征空间的密度估计,使生成多样化稀有图像成为可能。
- 该方法可以控制稀有性、多样性和与参考图像的相似性。
点此查看论文截图