⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-09 更新
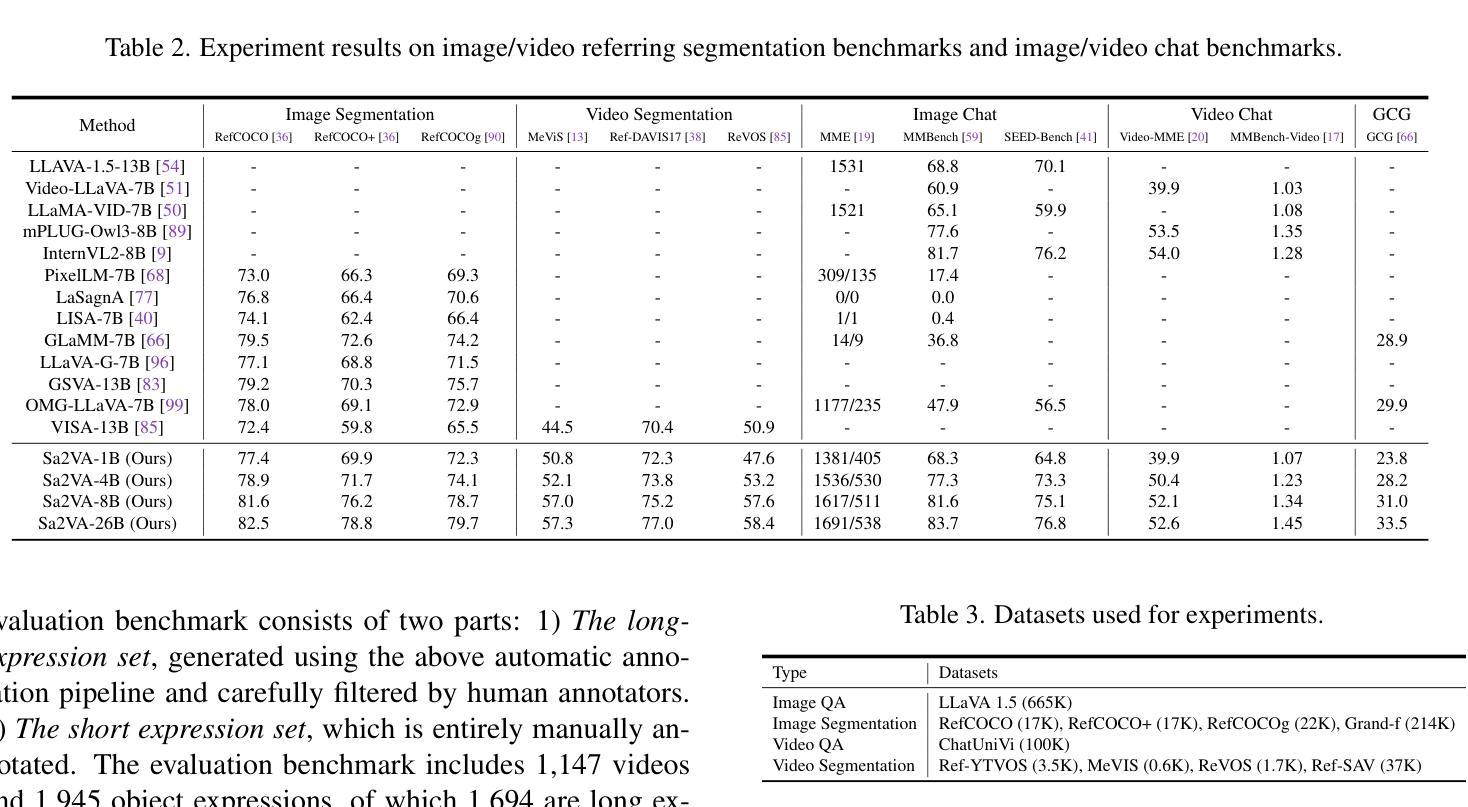
LM-Net: A Light-weight and Multi-scale Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhenkun Lu, Chaoyin She, Wei Wang, Qinghua Huang
Current medical image segmentation approaches have limitations in deeply exploring multi-scale information and effectively combining local detail textures with global contextual semantic information. This results in over-segmentation, under-segmentation, and blurred segmentation boundaries. To tackle these challenges, we explore multi-scale feature representations from different perspectives, proposing a novel, lightweight, and multi-scale architecture (LM-Net) that integrates advantages of both Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) to enhance segmentation accuracy. LM-Net employs a lightweight multi-branch module to capture multi-scale features at the same level. Furthermore, we introduce two modules to concurrently capture local detail textures and global semantics with multi-scale features at different levels: the Local Feature Transformer (LFT) and Global Feature Transformer (GFT). The LFT integrates local window self-attention to capture local detail textures, while the GFT leverages global self-attention to capture global contextual semantics. By combining these modules, our model achieves complementarity between local and global representations, alleviating the problem of blurred segmentation boundaries in medical image segmentation. To evaluate the feasibility of LM-Net, extensive experiments have been conducted on three publicly available datasets with different modalities. Our proposed model achieves state-of-the-art results, surpassing previous methods, while only requiring 4.66G FLOPs and 5.4M parameters. These state-of-the-art results on three datasets with different modalities demonstrate the effectiveness and adaptability of our proposed LM-Net for various medical image segmentation tasks.
当前医学图像分割方法在多尺度信息深度挖掘、局部细节纹理与全局上下文语义信息有效结合方面存在局限性,这会导致过分割、欠分割和分割边界模糊的问题。为了应对这些挑战,我们从不同角度探索多尺度特征表示,提出了一种新颖、轻量级、多尺度的架构(LM-Net),该架构结合了卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉变压器(ViTs)的优点,以提高分割精度。LM-Net采用轻量级的多分支模块,在同一级别捕捉多尺度特征。此外,我们引入了两个模块,分别在各级捕捉多尺度特征的局部细节纹理和全局语义:局部特征转换器(LFT)和全局特征转换器(GFT)。LFT通过局部窗口自注意力机制捕捉局部细节纹理,而GFT利用全局自注意力机制捕捉全局上下文语义。通过结合这些模块,我们的模型实现了局部和全局表示之间的互补性,缓解了医学图像分割中分割边界模糊的问题。为了评估LM-Net的可行性,我们在三个公开的不同模态数据集上进行了大量实验。我们提出的模型达到了最先进的成果,超越了之前的方法,同时仅需要4.66G FLOPs和5.4M的参数。这三个不同模态数据集上的卓越成果,证明了我们提出的LM-Net在各种医学图像分割任务中的有效性和适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的轻量级多尺度架构(LM-Net),结合了卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViTs)的优点,以提高医学图像分割的准确性。LM-Net通过采用轻量级的多分支模块来捕捉同一级别的多尺度特征,并引入局部特征转换器(LFT)和全局特征转换器(GFT)模块,以在不同级别上同时捕捉局部细节纹理和全局语义。通过结合这些模块,实现了局部和全局表示之间的互补,缓解了医学图像分割中边界模糊的问题。在三个公开数据集上进行的大量实验表明,所提出的模型达到了最新水平,超过了以前的方法,只需4.66G FLOPs和5.4M参数。
Key Takeaways
- 当前医学图像分割方法在探索多尺度信息和结合局部细节纹理与全局语义信息方面存在局限。
- 提出的LM-Net架构结合了CNNs和ViTs的优点,旨在提高医学图像分割的准确性。
- LM-Net采用轻量级的多分支模块来捕捉同一级别的多尺度特征。
- 引入LFT和GFT模块来同时捕捉局部细节纹理和全局语义。
- LFT通过局部窗口自注意力机制捕捉局部细节纹理。
- GFT利用全局自注意力机制捕捉全局上下文语义。
点此查看论文截图

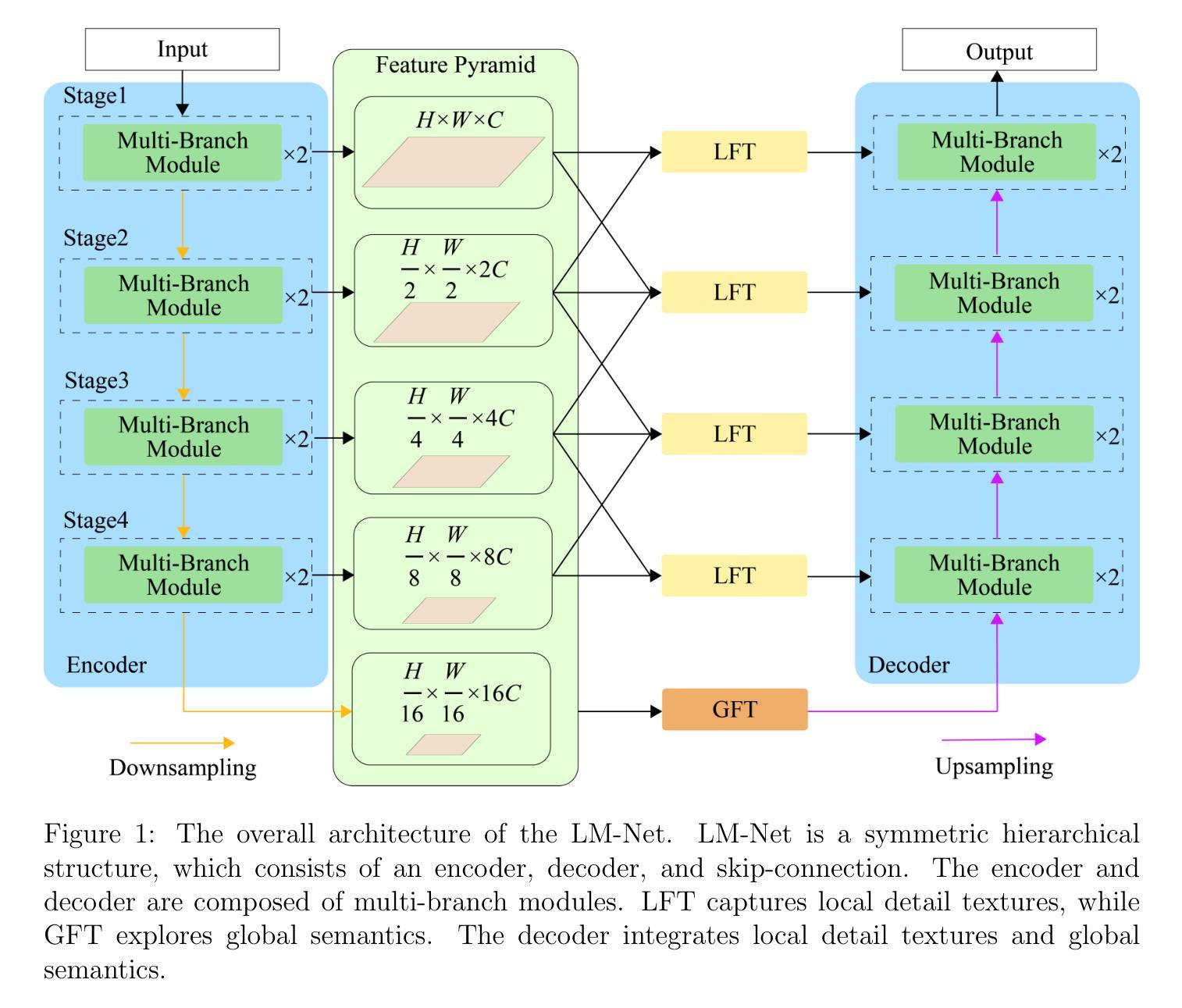
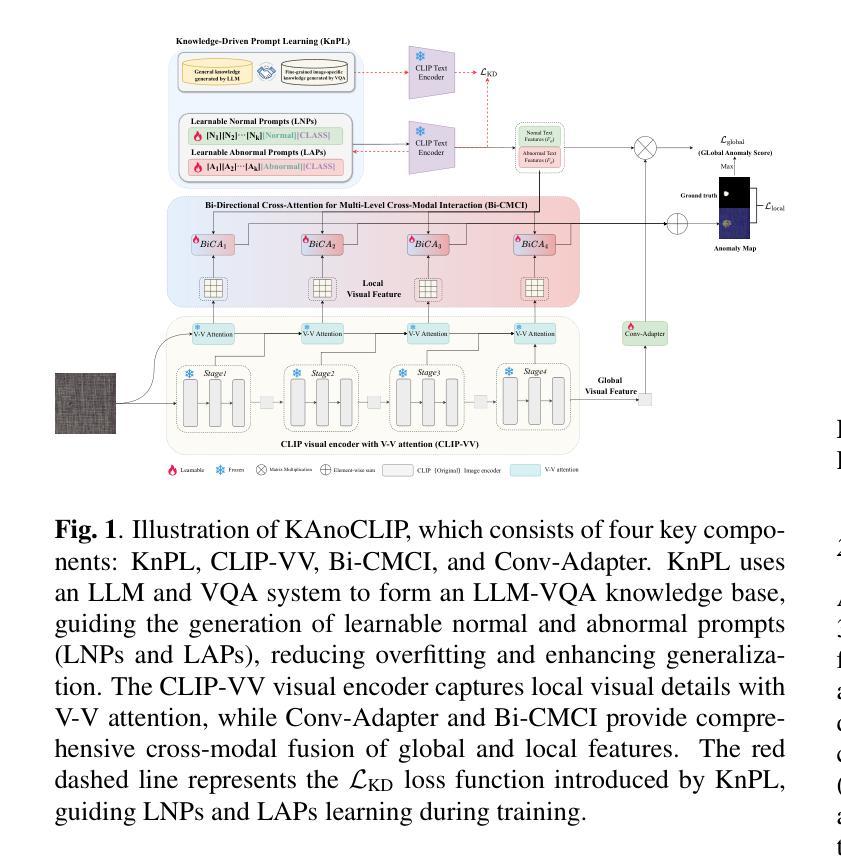
KAnoCLIP: Zero-Shot Anomaly Detection through Knowledge-Driven Prompt Learning and Enhanced Cross-Modal Integration
Authors:Chengyuan Li, Suyang Zhou, Jieping Kong, Lei Qi, Hui Xue
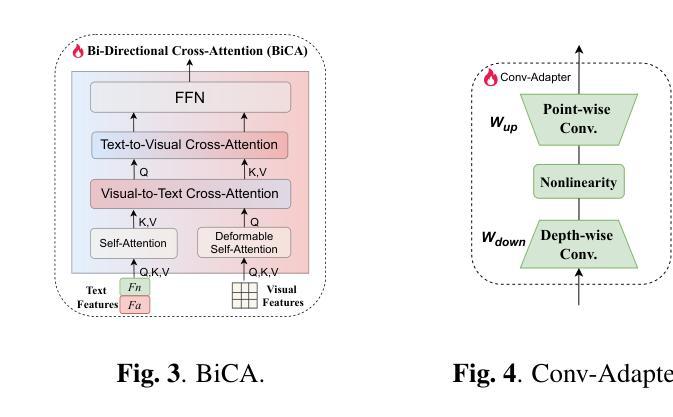
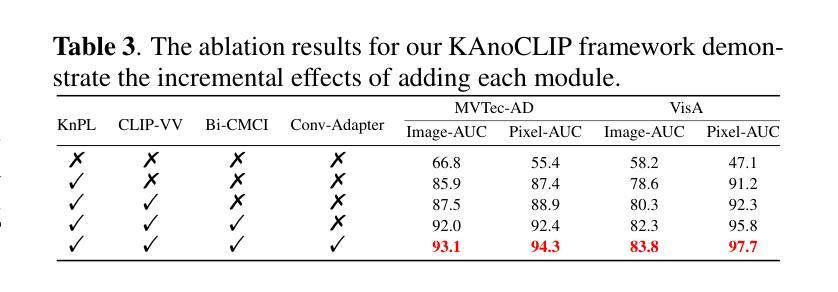
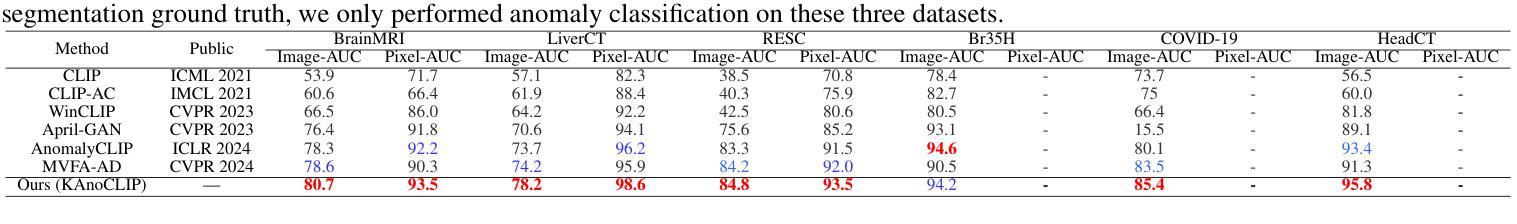
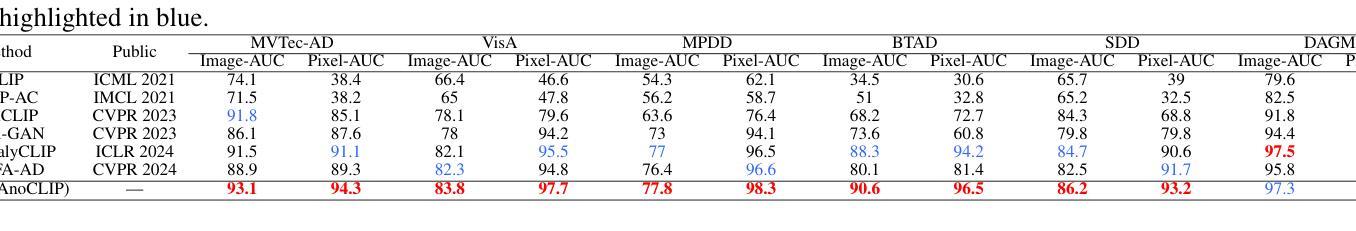
Zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) identifies anomalies without needing training samples from the target dataset, essential for scenarios with privacy concerns or limited data. Vision-language models like CLIP show potential in ZSAD but have limitations: relying on manually crafted fixed textual descriptions or anomaly prompts is time-consuming and prone to semantic ambiguity, and CLIP struggles with pixel-level anomaly segmentation, focusing more on global semantics than local details. To address these limitations, We introduce KAnoCLIP, a novel ZSAD framework that leverages vision-language models. KAnoCLIP combines general knowledge from a Large Language Model (GPT-3.5) and fine-grained, image-specific knowledge from a Visual Question Answering system (Llama3) via Knowledge-Driven Prompt Learning (KnPL). KnPL uses a knowledge-driven (KD) loss function to create learnable anomaly prompts, removing the need for fixed text prompts and enhancing generalization. KAnoCLIP includes the CLIP visual encoder with V-V attention (CLIP-VV), Bi-Directional Cross-Attention for Multi-Level Cross-Modal Interaction (Bi-CMCI), and Conv-Adapter. These components preserve local visual semantics, improve local cross-modal fusion, and align global visual features with textual information, enhancing pixel-level anomaly detection. KAnoCLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance in ZSAD across 12 industrial and medical datasets, demonstrating superior generalization compared to existing methods.
零样本异常检测(ZSAD)能够在无需目标数据集训练样本的情况下识别异常值,对于存在隐私担忧或数据有限的情况至关重要。视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在ZSAD中显示出潜力,但也存在局限性:依赖手动制作的固定文本描述或异常提示既耗时又容易产生语义歧义,CLIP在像素级异常分割方面存在困难,更侧重于全局语义而非局部细节。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了KAnoCLIP,这是一个利用视觉语言模型的新型ZSAD框架。KAnoCLIP结合了大型语言模型(GPT-3.5)的通用知识和视觉问答系统(Llama3)的精细图像特定知识,通过知识驱动提示学习(KnPL)进行结合。KnPL使用知识驱动(KD)损失函数来创建可学习的异常提示,从而无需固定文本提示并增强泛化能力。KAnoCLIP包括CLIP视觉编码器与V-V注意力(CLIP-VV)、用于多级跨模态交互的双向跨注意力(Bi-CMCI)和Conv-Adapter。这些组件保留了局部视觉语义,改善了局部跨模态融合,并将全局视觉特征与文本信息对齐,提高了像素级异常检测能力。KAnoCLIP在12个工业和医疗数据集上实现了ZSAD的卓越性能,与现有方法相比表现出优越的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
基于零样本异常检测(ZSAD)技术,KAnCLIP框架结合了大型语言模型(GPT-3.5)和视觉问答系统(Llama3)的知识,通过知识驱动提示学习(KnPL)解决了CLIP模型在异常检测中的局限性。该框架增强了模型的泛化能力,并实现了在多个工业医疗数据集上的像素级异常检测,达到了现有方法的先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- ZSAD技术能够在无需目标数据集训练样本的情况下识别异常。
- CLIP等视觉语言模型在ZSAD中有潜力但存在局限性,如依赖手动构建的文本描述和语义模糊问题。
- KAnoCLIP框架结合大型语言模型和视觉问答系统的知识来解决CLIP模型的局限性。
- KAnoCLIP通过知识驱动提示学习(KnPL)创建可学习的异常提示,无需固定的文本提示。
- KAnoCLIP包括CLIP视觉编码器、双向跨模态交互机制等组件,增强了局部视觉语义和跨模态融合。
- KAnoCLIP实现了在多个工业医疗数据集上的像素级异常检测,并达到了先进性能。
点此查看论文截图

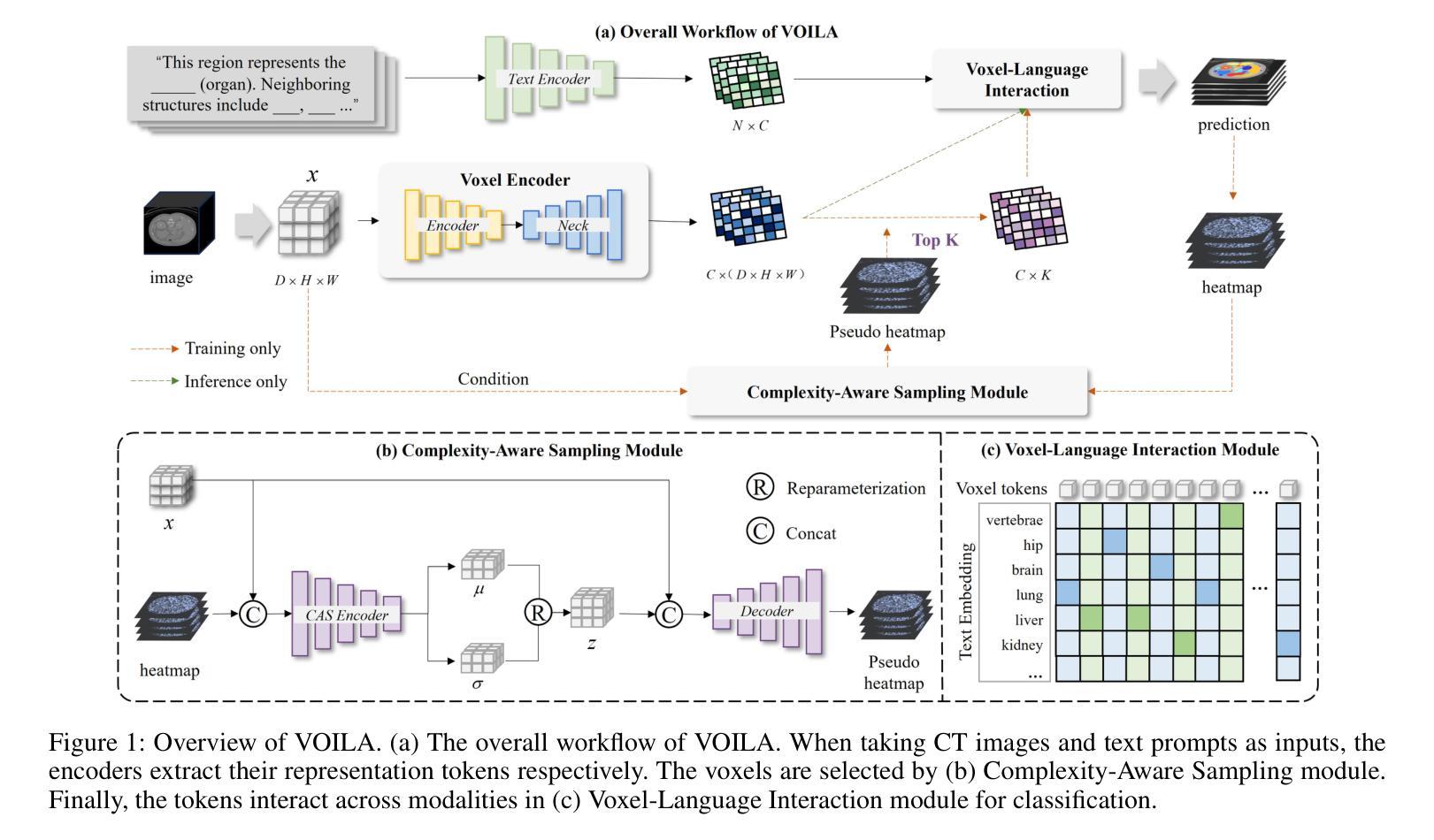
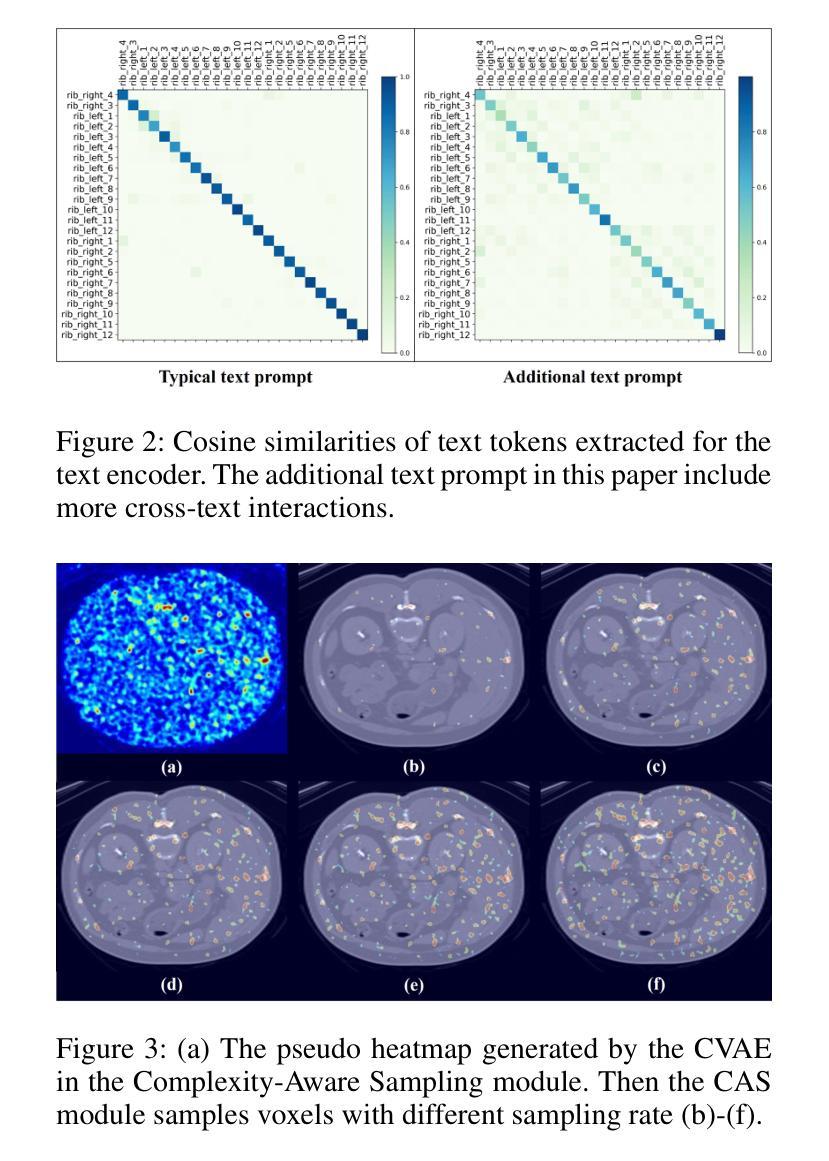
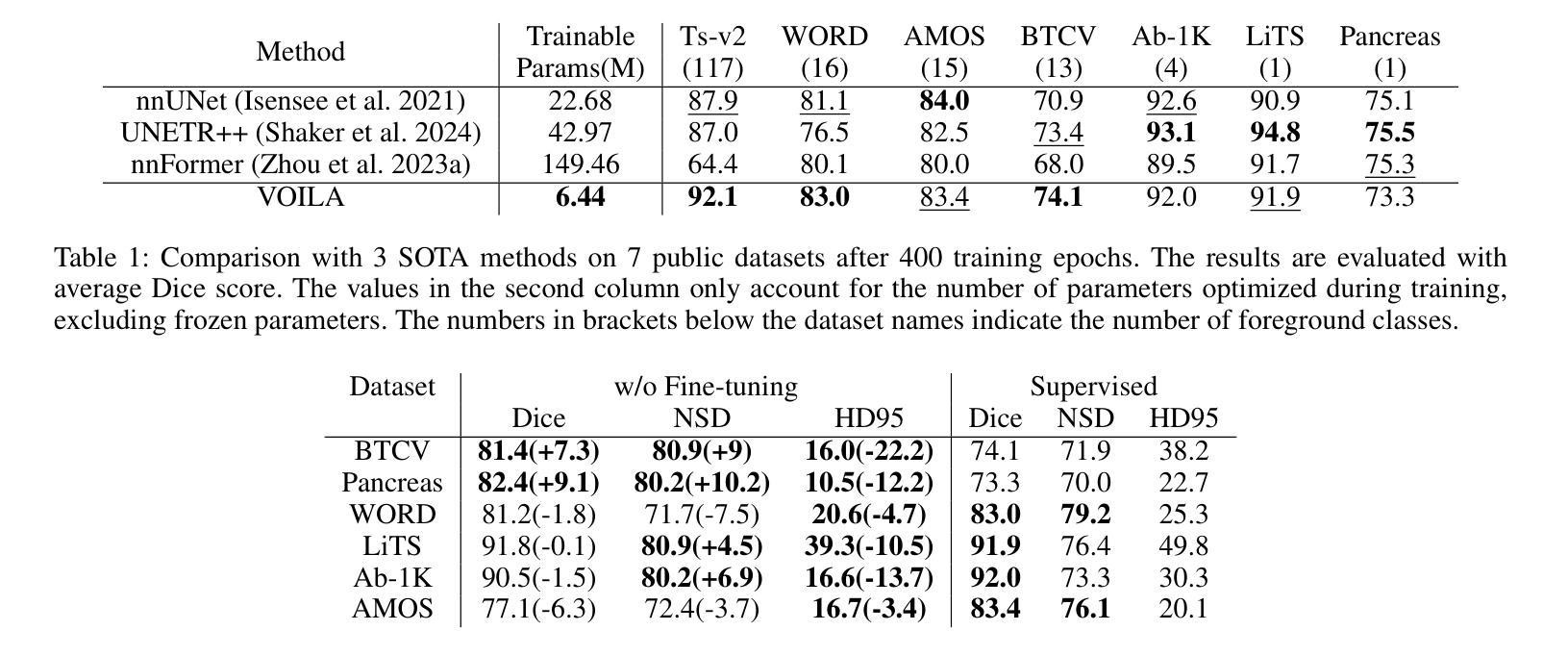
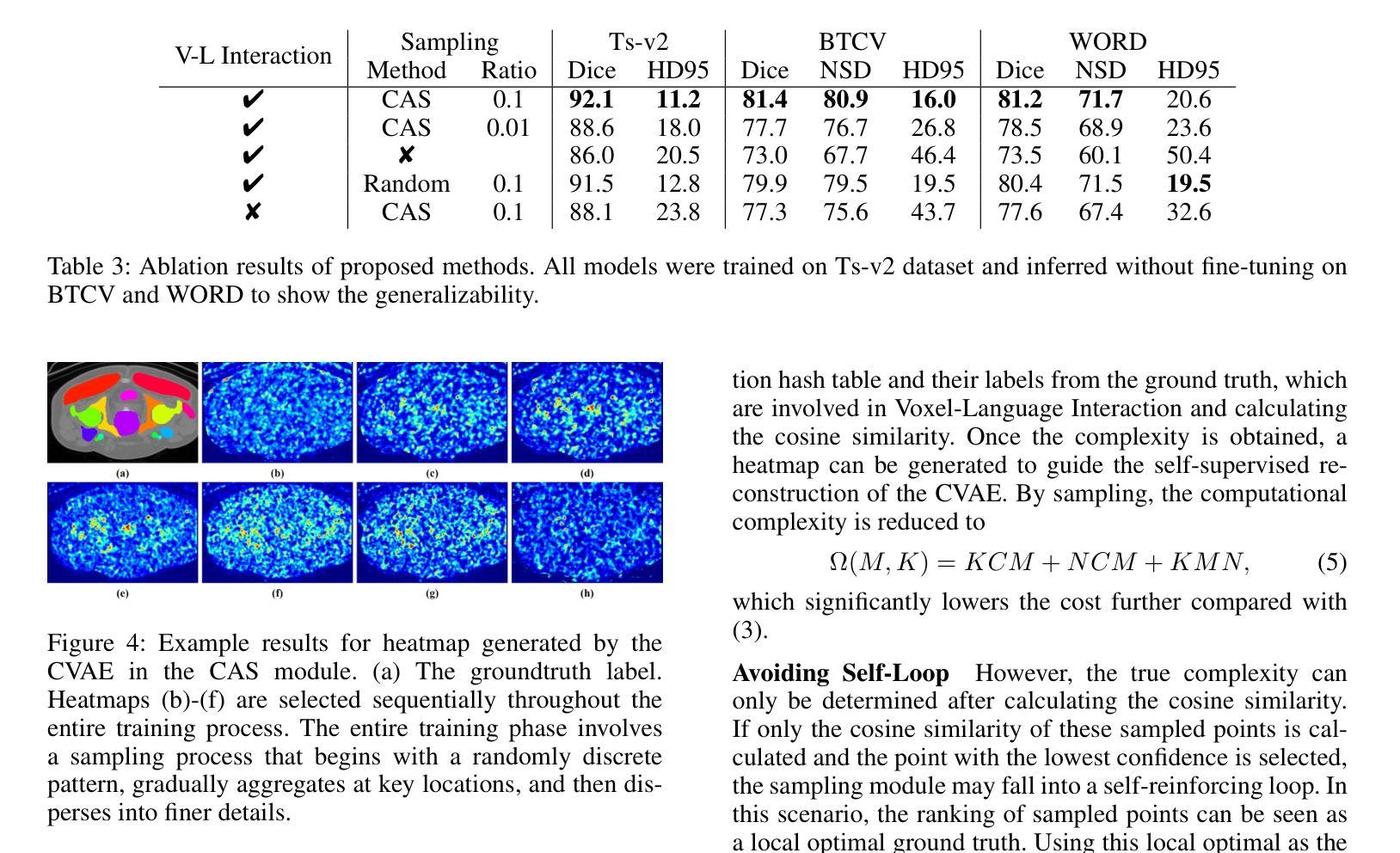
VOILA: Complexity-Aware Universal Segmentation of CT images by Voxel Interacting with Language
Authors:Zishuo Wan, Yu Gao, Wanyuan Pang, Dawei Ding
Satisfactory progress has been achieved recently in universal segmentation of CT images. Following the success of vision-language methods, there is a growing trend towards utilizing text prompts and contrastive learning to develop universal segmentation models. However, there exists a significant imbalance in information density between 3D images and text prompts. Moreover, the standard fully connected layer segmentation approach faces significant challenges in handling multiple classes and exhibits poor generalizability. To address these challenges, we propose the VOxel Interacting with LAnguage method (VOILA) for universal CT image segmentation. Initially, we align voxels and language into a shared representation space and classify voxels on the basis of cosine similarity. Subsequently, we develop the Voxel-Language Interaction framework to mitigate the impact of class imbalance caused by foreground-background discrepancies and variations in target volumes. Furthermore, a Complexity-Aware Sampling method is proposed to focus on region hard to segment, achieved by generating pseudo-heatmaps from a trainable Gaussian mixture distribution. Our results indicate the proposed VOILA is capable to achieve improved performance with reduced parameters and computational cost during training. Furthermore, it demonstrates significant generalizability across diverse datasets without additional fine-tuning.
近期在CT图像的通用分割方面取得了令人满意的进展。随着视觉语言方法的成功,利用文本提示和对比学习来开发通用分割模型的趋势日益增强。然而,3D图像和文本提示之间存在信息密度的不平衡。此外,标准的全连接层分割方法在处理多个类别时面临巨大挑战,且其泛化能力较差。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了用于通用CT图像分割的VOxel与LAnguage交互方法(VOILA)。首先,我们将体素和语言对齐到共享表示空间,并根据余弦相似性对体素进行分类。随后,我们开发了Voxel-Language交互框架,以减轻由前景背景差异和目标体积变化引起的类别不平衡的影响。此外,还提出了一种复杂度感知采样方法,通过从可训练的高斯混合分布生成伪热图来关注难以分割的区域。我们的结果表明,所提出的VOILA能够在减少参数和训练过程中的计算成本的同时,实现性能的提升。此外,它在多种数据集上表现出显著的泛化能力,无需额外的微调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
基于计算机视觉和文本信息融合的方法在CT图像通用分割上取得了显著进展。针对现有方法在处理多类别时面临的挑战以及信息密度不平衡问题,本文提出了VOxel与语言交互(VOILA)方法。该方法通过将体素与语言对齐到共享表示空间进行分类,开发Voxel-Language交互框架来减少由前景背景差异引起的类别不平衡影响,并提出了复杂度感知采样方法来关注难以分割的区域。实验表明,VOILA方法能在减少参数和计算成本的同时提高性能,并在不同数据集上表现出显著的可推广性。
Key Takeaways
- 计算机视觉和文本信息融合方法在CT图像通用分割上取得进展。
- 存在信息密度不平衡和多种类别处理挑战的问题。
- 提出了VOxel与语言交互(VOILA)方法来解决这些问题。
- VOILA通过对齐体素和语言到共享表示空间进行分类,并开发Voxel-Language交互框架来解决类别不平衡问题。
- 复杂度感知采样方法用于关注难以分割的区域。
- 实验结果显示,VOILA能提高性能,减少训练参数和计算成本。
点此查看论文截图

Vim-F: Visual State Space Model Benefiting from Learning in the Frequency Domain
Authors:Juntao Zhang, Shaogeng Liu, Kun Bian, You Zhou, Pei Zhang, Wenbo An, Jun Zhou, Kun Shao
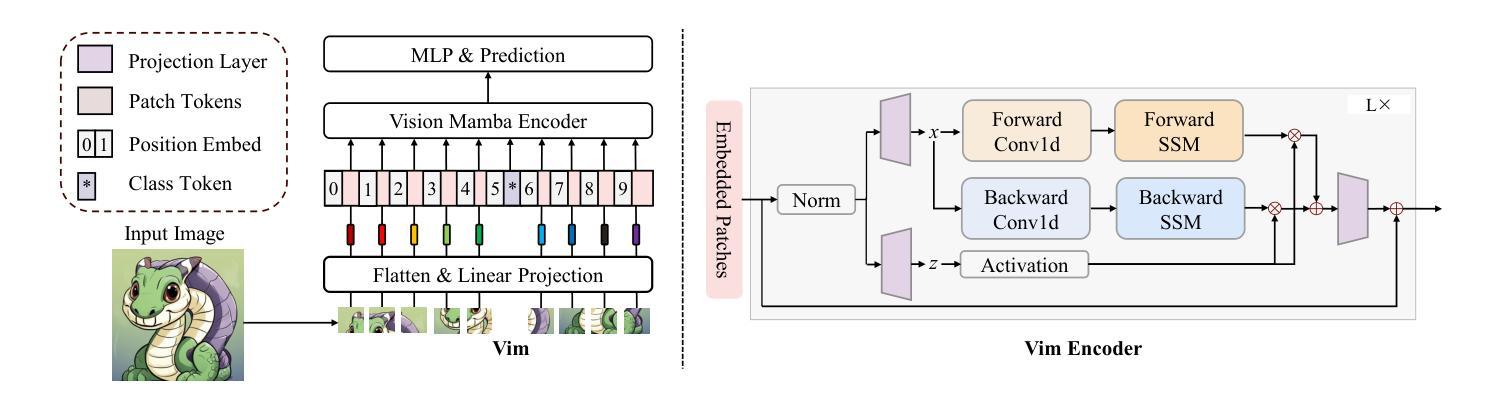
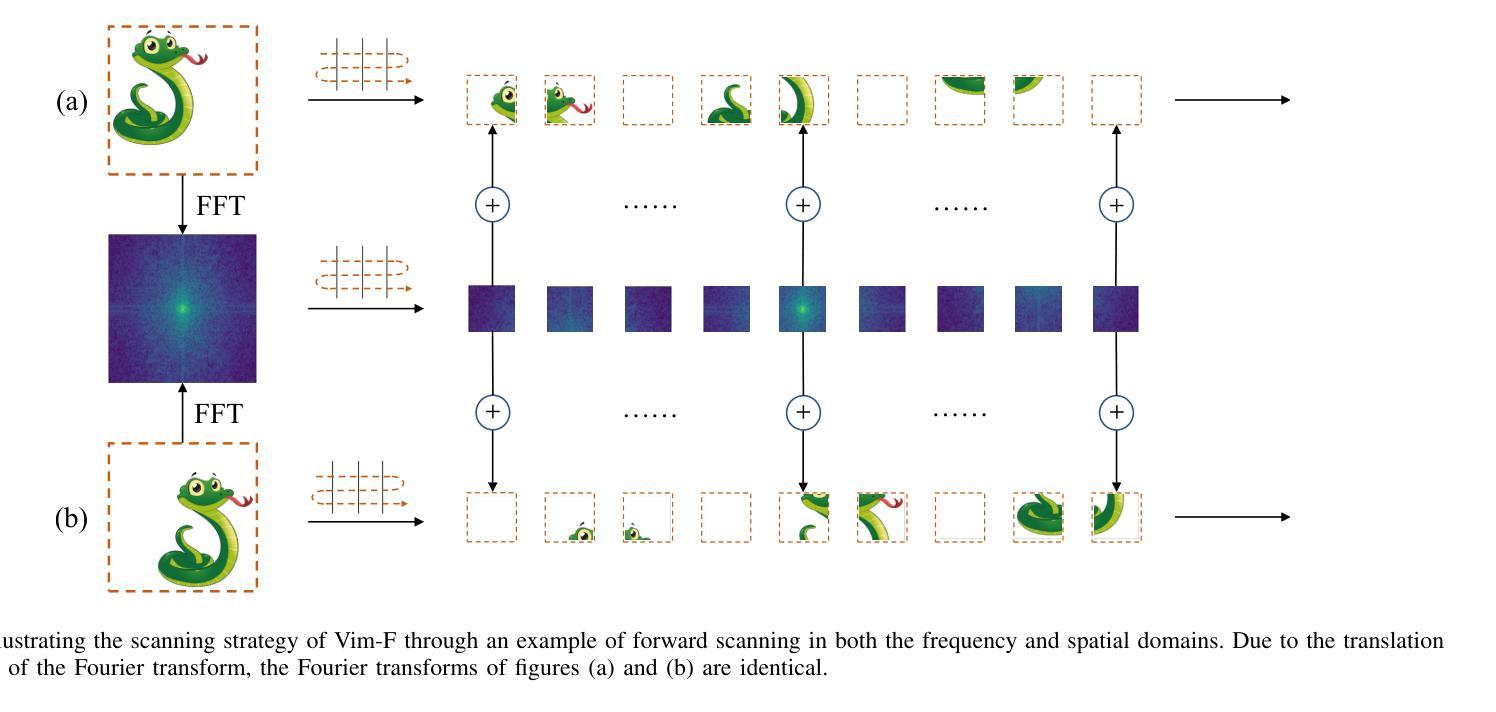
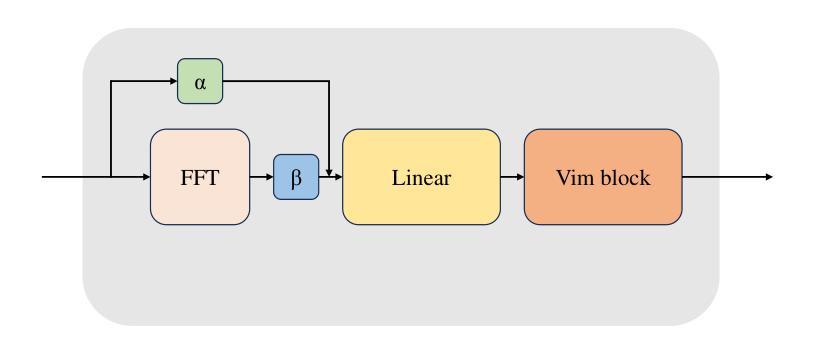
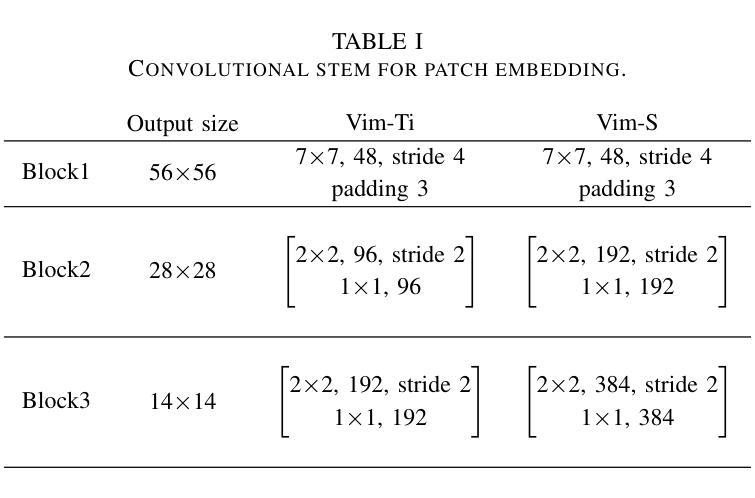
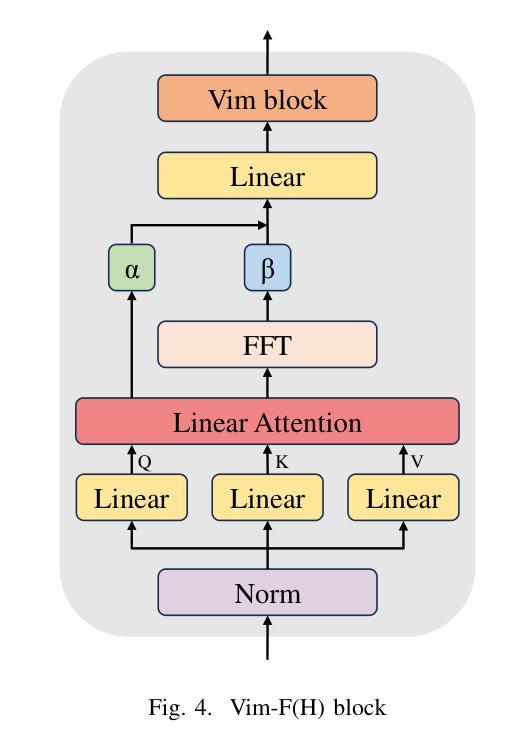
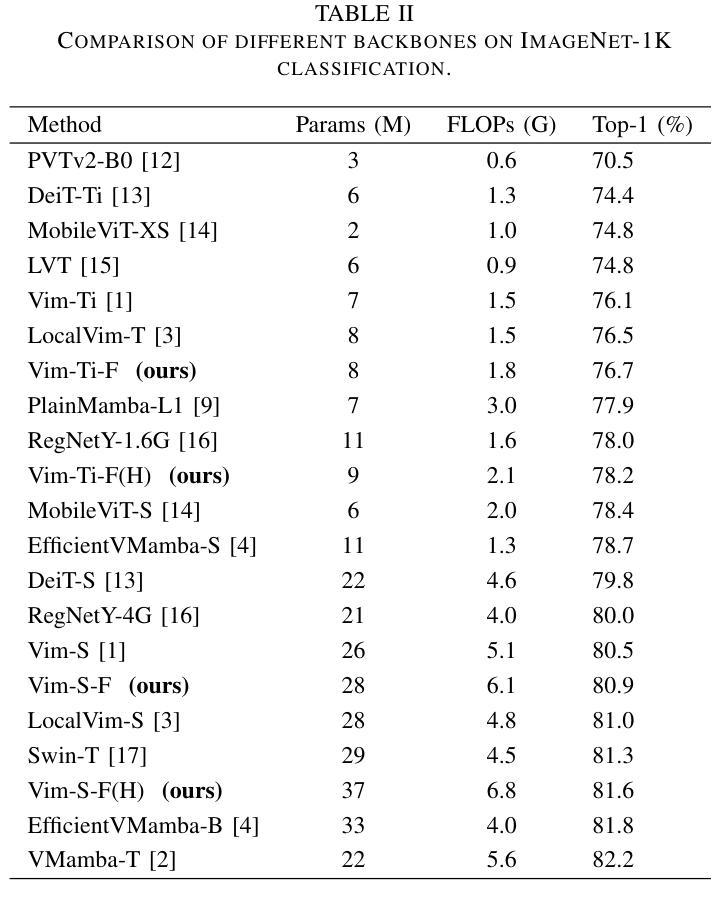
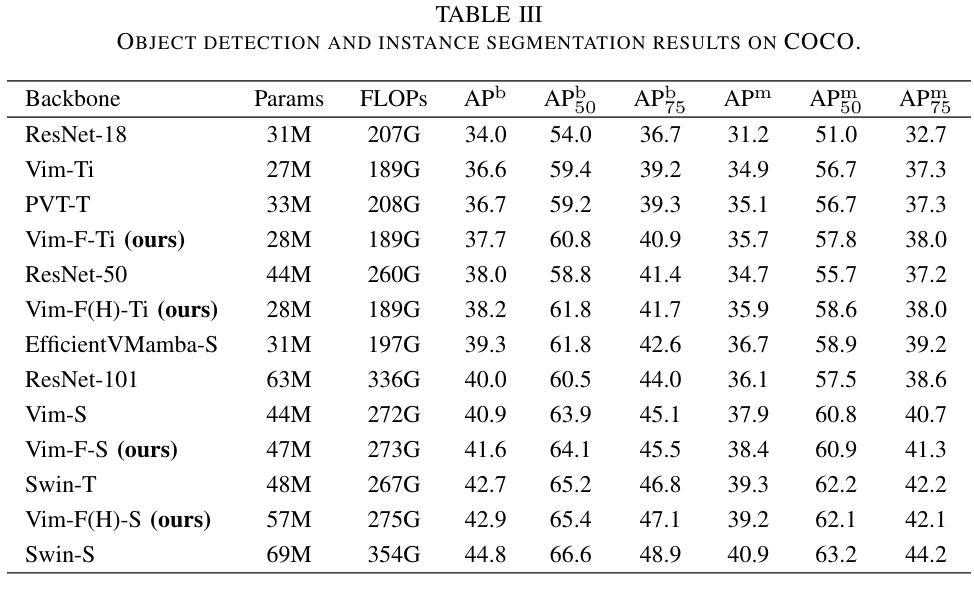
In recent years, State Space Models (SSMs) with efficient hardware-aware designs, known as the Mamba deep learning models, have made significant progress in modeling long sequences such as language understanding. Therefore, building efficient and general-purpose visual backbones based on SSMs is a promising direction. Compared to traditional convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs), the performance of Vision Mamba (ViM) methods is not yet fully competitive. To enable SSMs to process image data, ViMs typically flatten 2D images into 1D sequences, inevitably ignoring some 2D local dependencies, thereby weakening the model’s ability to interpret spatial relationships from a global perspective. We use Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to obtain the spectrum of the feature map and add it to the original feature map, enabling ViM to model a unified visual representation in both frequency and spatial domains. The introduction of frequency domain information enables ViM to have a global receptive field during scanning. We propose a novel model called Vim-F, which employs pure Mamba encoders and scans in both the frequency and spatial domains. Moreover, we question the necessity of position embedding in ViM and remove it accordingly in Vim-F, which helps to fully utilize the efficient long-sequence modeling capability of ViM. Finally, we redesign a patch embedding for Vim-F, leveraging a convolutional stem to capture more local correlations, further improving the performance of Vim-F. Code is available at: \url{https://github.com/yws-wxs/Vim-F}.
近年来,具有高效硬件感知设计的状态空间模型(SSMs),被称为Mamba深度学习模型,在建模长序列(如语言理解)方面取得了显著进展。因此,基于SSMs构建高效且通用的视觉主干是一个充满希望的方向。与传统的卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViTs)相比,视觉Mamba(ViM)方法的性能尚未达到完全竞争水平。为了使SSM能够处理图像数据,ViM通常将2D图像压平为1D序列,这不可避免地会忽略一些2D局部依赖性,从而削弱了模型从全局角度解释空间关系的能力。我们使用快速傅里叶变换(FFT)获得特征图的频谱并将其添加到原始特征图,使ViM能够在频率和空间域中建立统一的视觉表示。引入频域信息使ViM在扫描过程中具有全局感受野。我们提出了一种新型模型Vim-F,它采用纯Mamba编码器并在频率和空间域中进行扫描。此外,我们对ViM中位置嵌入的必要性提出了质疑,并在Vim-F中相应地将其移除,这有助于充分利用ViM对长序列建模的高效能力。最后,我们为Vim-F重新设计了补丁嵌入,利用卷积主干来捕获更多的局部相关性,进一步提高了Vim-F的性能。代码可用在:\url{https://github.com/yws-wxs/Vim-F}。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期,基于状态空间模型(SSMs)的高效硬件感知设计深度学习模型(称为Mamba模型)在序列建模方面取得了显著进展,尤其在语言理解方面。因此,基于SSMs构建高效且通用的视觉骨干网是一个有前途的研究方向。尽管与传统的卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉变压器(ViTs)相比,视觉Mamba(ViM)方法的性能尚未达到全面竞争水平,但ViM通过融合频域和空域信息,实现了统一的视觉表征建模。此外,本研究提出了新型模型Vim-F,采用纯Mamba编码器并融合频域和空域扫描,并移除了位置嵌入以增强ViM对长序列的建模能力。Vim-F重新设计了补丁嵌入并引入了卷积干细胞以捕捉更多局部相关性,提高了性能。相关代码已发布在:[https://github.com/yws-wxs/Vim-F]。](https://github.com/yws-wxs/Vim-F%E3%80%82)
Key Takeaways
- 状态空间模型(SSMs)在序列建模方面取得了显著进展,尤其在语言理解领域。
- 将SSMs应用于图像处理是一个有前途的研究方向。
- 相比传统模型,视觉Mamba(ViM)性能尚未达到全面竞争水平。
- ViM通过融合频域和空域信息实现统一视觉表征建模。
- 新型模型Vim-F采用纯Mamba编码器并融合频域和空域扫描。
- Vim-F移除了位置嵌入以增强ViM对长序列的建模能力。
点此查看论文截图

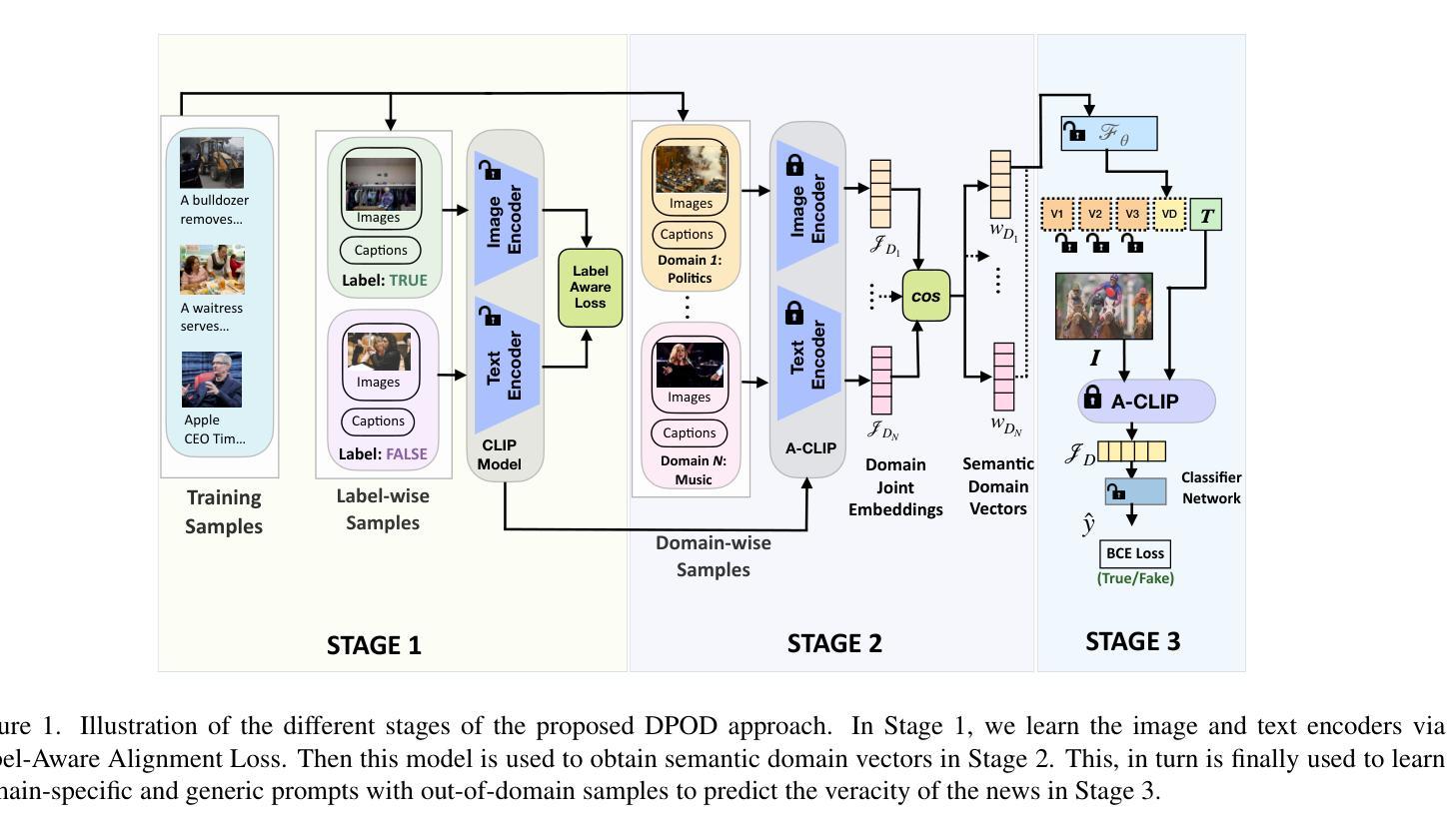
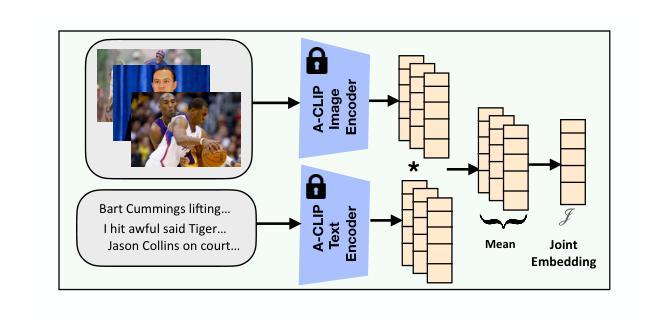
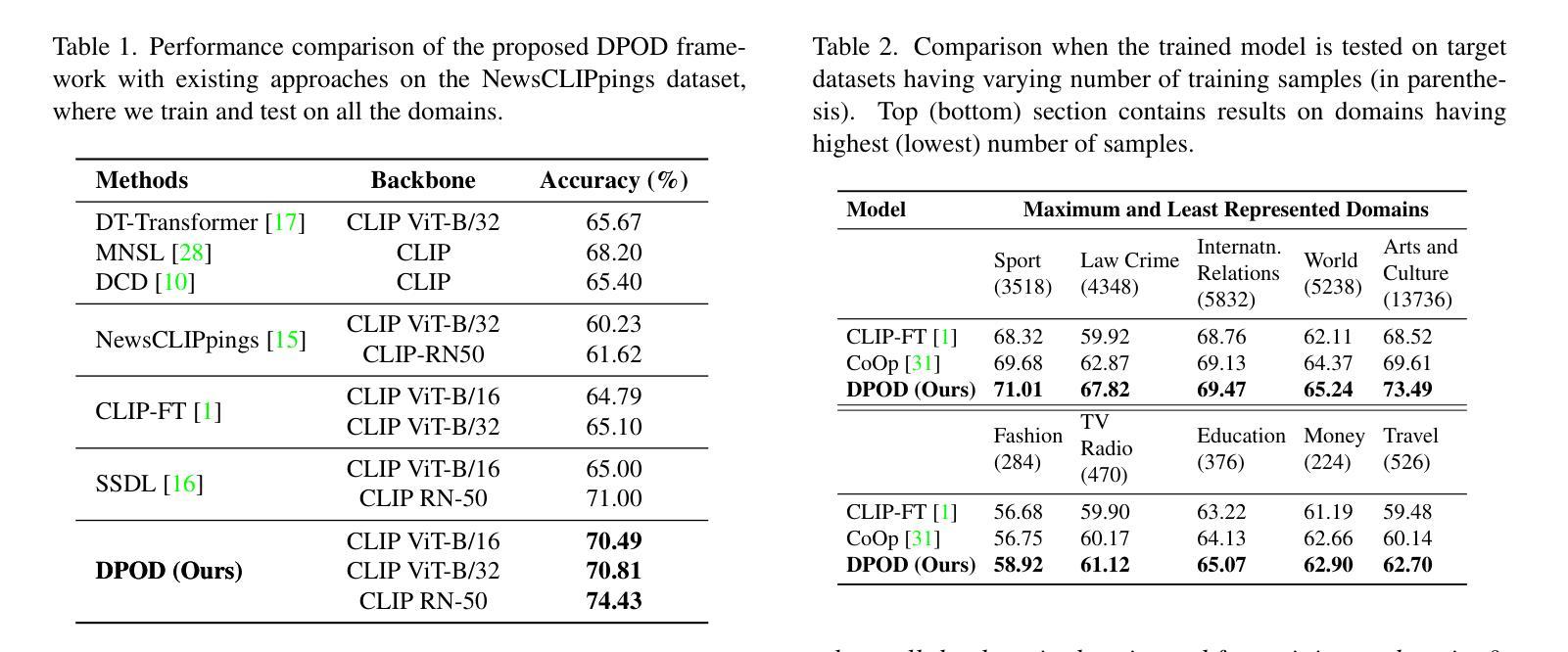
Can Out-of-Domain data help to Learn Domain-Specific Prompts for Multimodal Misinformation Detection?
Authors:Amartya Bhattacharya, Debarshi Brahma, Suraj Nagaje Mahadev, Anmol Asati, Vikas Verma, Soma Biswas
Spread of fake news using out-of-context images and captions has become widespread in this era of information overload. Since fake news can belong to different domains like politics, sports, etc. with their unique characteristics, inference on a test image-caption pair is contingent on how well the model has been trained on similar data. Since training individual models for each domain is not practical, we propose a novel framework termed DPOD (Domain-specific Prompt tuning using Out-of-domain data), which can exploit out-of-domain data during training to improve fake news detection of all desired domains simultaneously. First, to compute generalizable features, we modify the Vision-Language Model, CLIP to extract features that helps to align the representations of the images and corresponding captions of both the in-domain and out-of-domain data in a label-aware manner. Further, we propose a domain-specific prompt learning technique which leverages training samples of all the available domains based on the extent they can be useful to the desired domain. Extensive experiments on the large-scale NewsCLIPpings and VERITE benchmarks demonstrate that DPOD achieves state of-the-art performance for this challenging task. Code: https://github.com/scviab/DPOD.
在信息过载的时代,使用脱离上下文的图像和标题传播假新闻已经变得非常普遍。由于假新闻可以涉及政治、体育等不同领域,具有其独特特性,因此对测试图像-标题对的推断取决于模型在类似数据上的训练程度。由于针对每个领域训练单个模型并不实际,因此我们提出了一种新型框架,称为DPOD(使用域外数据进行特定域的提示调整),它可以在训练期间利用域外数据,以同时提高所有目标领域的假新闻检测能力。首先,为了计算可推广的特征,我们修改了视觉语言模型CLIP,以提取有助于以标签感知的方式对齐域内数据和域外数据的图像和相应标题表示的特征。此外,我们提出了一种特定于域的提示学习技术,该技术基于所有可用领域的训练样本在目标领域的效用程度进行利用。在大规模NewsCLIPpings和VERITE基准测试上的广泛实验表明,DPOD在应对这一具有挑战性的任务时取得了最新性能。代码地址:https://github.com/scviab/DPOD 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
信息过载时代,假新闻借助断章取义的图片和标题广泛传播。由于假新闻涉及不同领域,如政治、体育等,各自具备独特特性,因此对测试图像和标题对的推断取决于模型在类似数据上的训练情况。提出一种名为DPOD(基于域外数据的域特定提示调整)的新框架,可在训练期间利用域外数据,同时提高所有所需领域的假新闻检测能力。通过修改视觉语言模型CLIP来计算可推广特征,以标签感知方式对齐各领域内外数据的图像和相应标题表示。此外,提出了一种域特定提示学习技术,该技术基于训练样本对目标域的效用,利用所有可用领域的训练样本。在大规模NewsCLIPpings和VERITE基准测试上的广泛实验表明,DPOD在此具有挑战性的任务上达到了最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 假新闻在信息过载时代通过断章取义的图片和标题广泛传播。
- 假新闻涉及不同领域,如政治、体育等,模型训练需考虑领域特性。
- 训练单独的模型应对每个领域不切实际,需寻求一种通用的解决方案。
- 提出了名为DPOD的新框架,可基于域外数据进行训练,提高假新闻检测能力。
- DPOD框架通过修改CLIP模型计算可推广特征,实现图像和标题表示的对齐。
- DPOD采用了一种域特定提示学习技术,利用不同领域训练样本的效用。
点此查看论文截图