⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-10 更新
EditAR: Unified Conditional Generation with Autoregressive Models
Authors:Jiteng Mu, Nuno Vasconcelos, Xiaolong Wang
Recent progress in controllable image generation and editing is largely driven by diffusion-based methods. Although diffusion models perform exceptionally well in specific tasks with tailored designs, establishing a unified model is still challenging. In contrast, autoregressive models inherently feature a unified tokenized representation, which simplifies the creation of a single foundational model for various tasks. In this work, we propose EditAR, a single unified autoregressive framework for a variety of conditional image generation tasks, e.g., image editing, depth-to-image, edge-to-image, segmentation-to-image. The model takes both images and instructions as inputs, and predicts the edited images tokens in a vanilla next-token paradigm. To enhance the text-to-image alignment, we further propose to distill the knowledge from foundation models into the autoregressive modeling process. We evaluate its effectiveness across diverse tasks on established benchmarks, showing competitive performance to various state-of-the-art task-specific methods. Project page: https://jitengmu.github.io/EditAR/
近期可控图像生成和编辑的进展在很大程度上得益于基于扩散的方法。尽管扩散模型在特定任务上表现优异,但建立统一模型仍然具有挑战性。相比之下,自回归模型天生具有统一的令牌化表示,这简化了各种任务单一基础模型的创建。在这项工作中,我们提出了EditAR,这是一个统一的自回归框架,可用于各种条件图像生成任务,例如图像编辑、深度图像、边缘图像、分段图像等。该模型同时接受图像和指令作为输入,并在标准的下一个令牌范式中预测编辑后的图像令牌。为了提高文本到图像的对应性,我们进一步提出将基础模型的知识蒸馏到自回归建模过程中。我们在既定的基准测试上对各项任务进行了有效性评估,显示出与各种最新任务特定方法相竞争的性能。项目页面:https://jitengmu.github.io/EditAR/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://jitengmu.github.io/EditAR/
Summary
基于可控图像生成和编辑的最新进展,研究者提出了一种名为EditAR的统一自回归框架,该框架可用于多种条件图像生成任务,如图像编辑、深度图像生成、边缘图像生成和分割图像生成等。该模型以图像和指令作为输入,采用标准的下一个令牌模式预测编辑后的图像令牌。为提高文本到图像的匹配度,研究还提议在自回归建模过程中从基础模型中提炼知识。在多个任务上的评估结果表明,该框架的性能与各种最先进的任务特定方法相当。
Key Takeaways
- EditAR是一个统一的自回归框架,可用于多种条件图像生成任务。
- 该框架接受图像和指令作为输入,预测编辑后的图像令牌。
- EditAR采用标准的下一个令牌预测范式,简化了图像生成过程。
- 为提高文本到图像的匹配度,研究提议在自回归建模过程中从基础模型中提炼知识。
- 该框架在多个任务上的性能评估显示,其性能与最先进的任务特定方法相当。
- EditAR框架具有潜力成为图像生成领域的一种通用解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


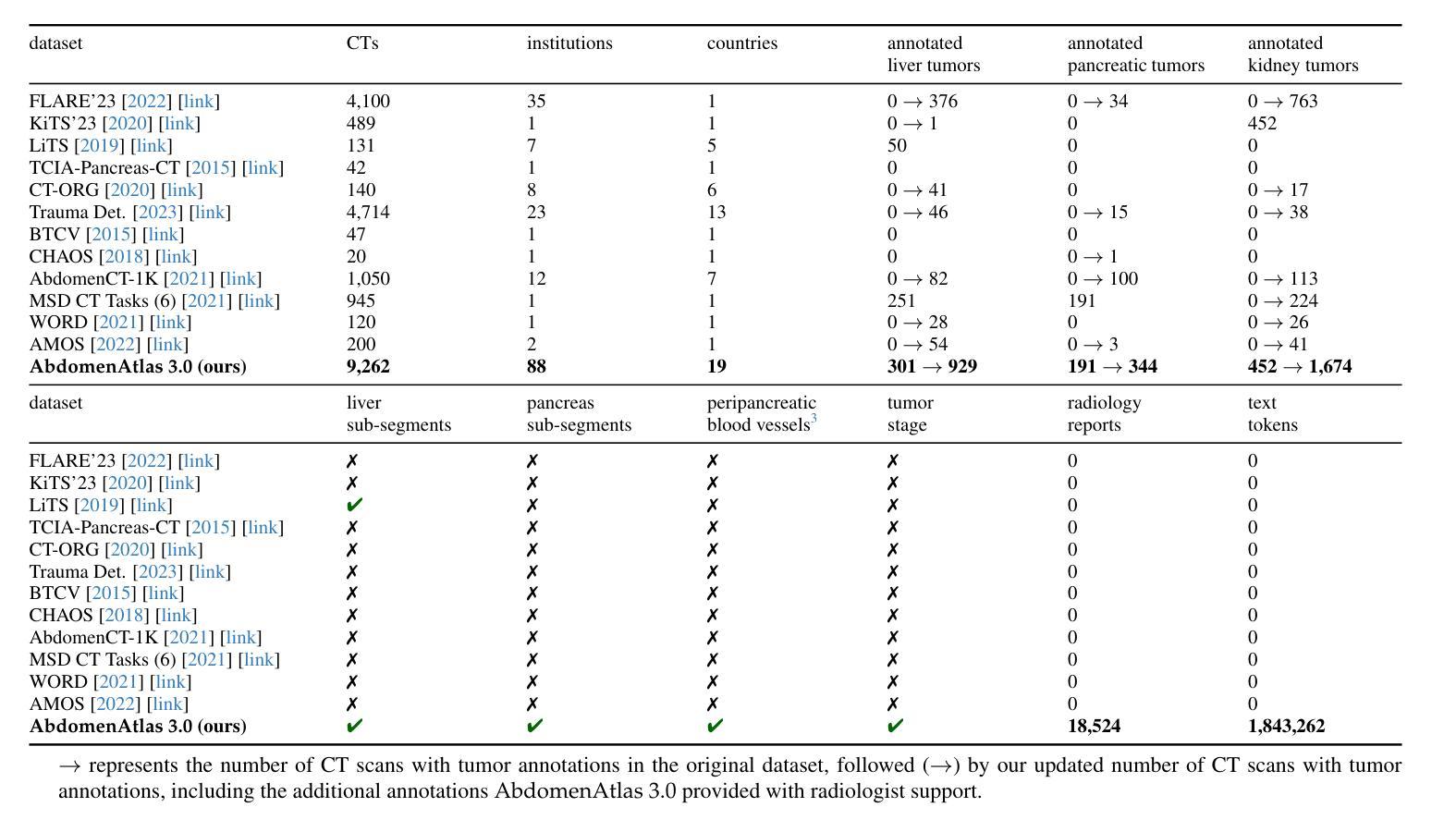
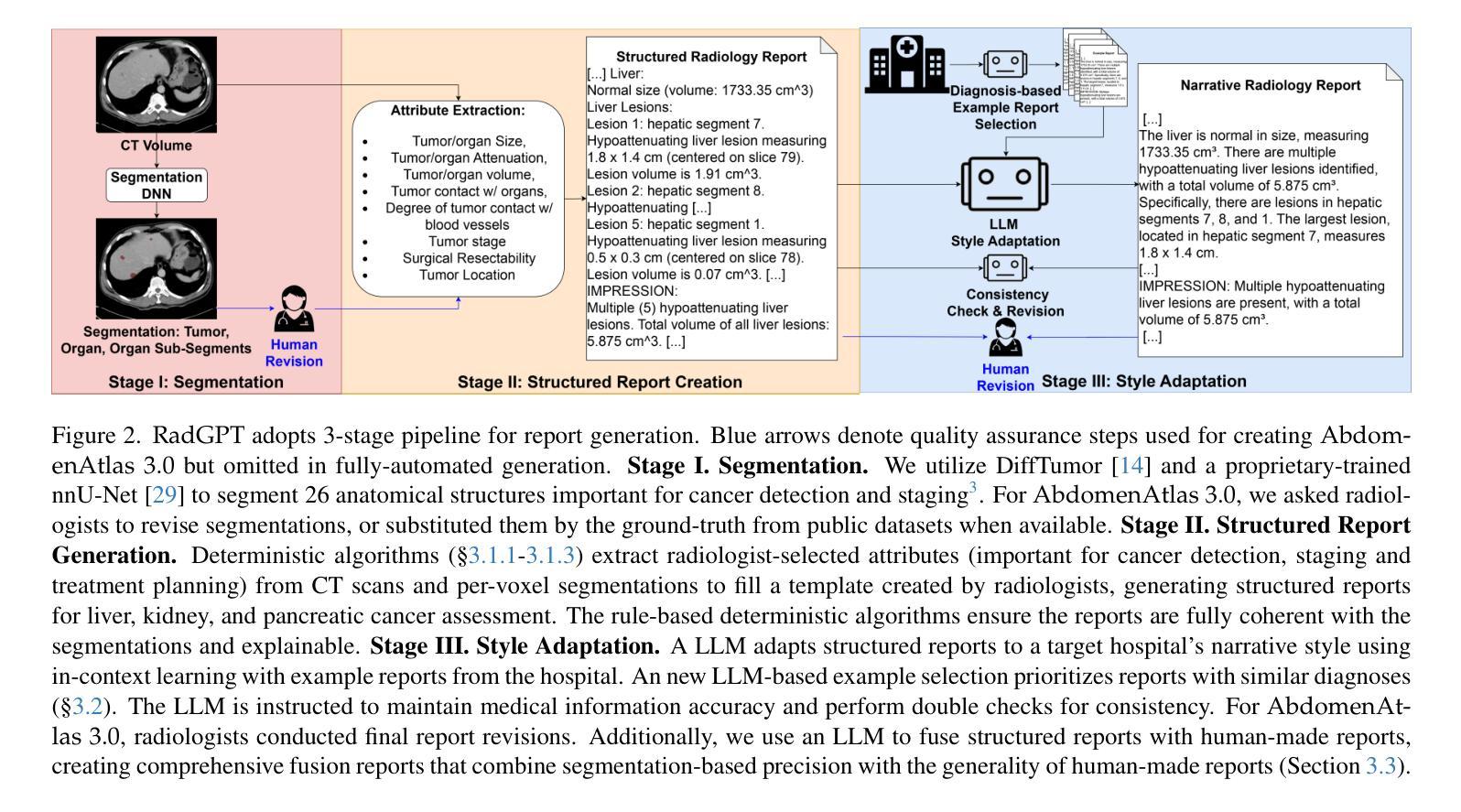
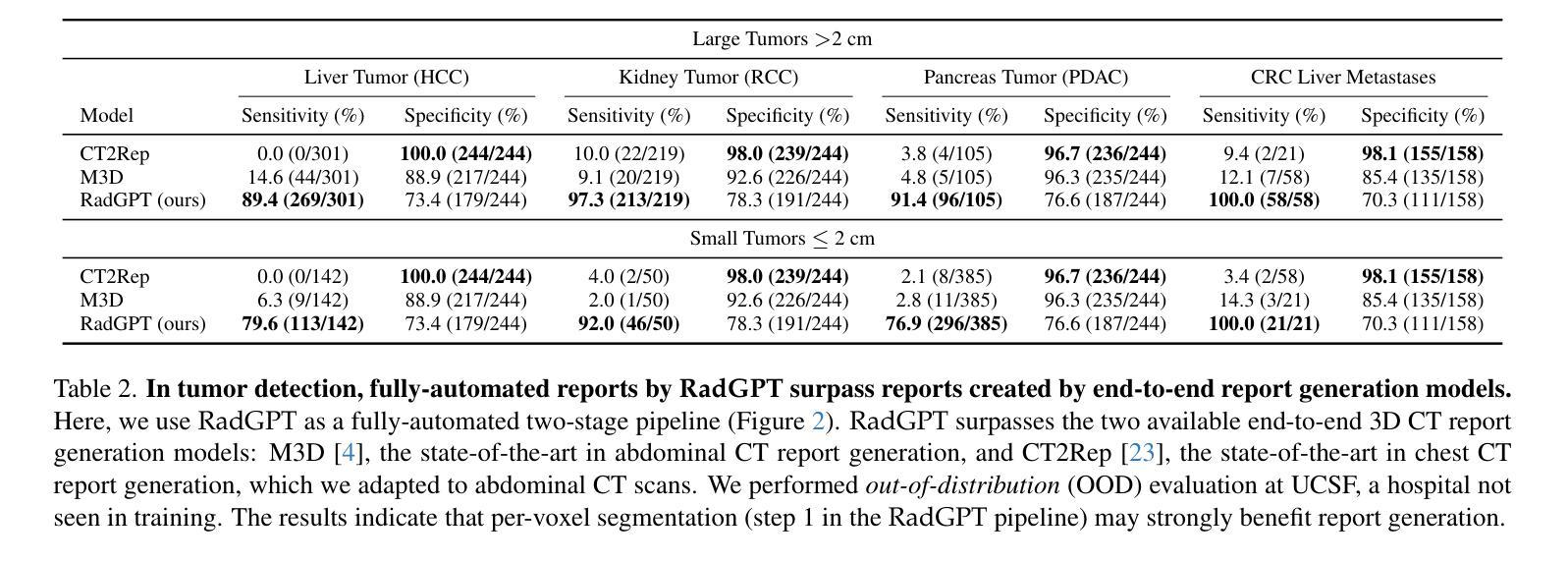
RadGPT: Constructing 3D Image-Text Tumor Datasets
Authors:Pedro R. A. S. Bassi, Mehmet Can Yavuz, Kang Wang, Xiaoxi Chen, Wenxuan Li, Sergio Decherchi, Andrea Cavalli, Yang Yang, Alan Yuille, Zongwei Zhou
With over 85 million CT scans performed annually in the United States, creating tumor-related reports is a challenging and time-consuming task for radiologists. To address this need, we present RadGPT, an Anatomy-Aware Vision-Language AI Agent for generating detailed reports from CT scans. RadGPT first segments tumors, including benign cysts and malignant tumors, and their surrounding anatomical structures, then transforms this information into both structured reports and narrative reports. These reports provide tumor size, shape, location, attenuation, volume, and interactions with surrounding blood vessels and organs. Extensive evaluation on unseen hospitals shows that RadGPT can produce accurate reports, with high sensitivity/specificity for small tumor (<2 cm) detection: 80/73% for liver tumors, 92/78% for kidney tumors, and 77/77% for pancreatic tumors. For large tumors, sensitivity ranges from 89% to 97%. The results significantly surpass the state-of-the-art in abdominal CT report generation. RadGPT generated reports for 17 public datasets. Through radiologist review and refinement, we have ensured the reports’ accuracy, and created the first publicly available image-text 3D medical dataset, comprising over 1.8 million text tokens and 2.7 million images from 9,262 CT scans, including 2,947 tumor scans/reports of 8,562 tumor instances. Our reports can: (1) localize tumors in eight liver sub-segments and three pancreatic sub-segments annotated per-voxel; (2) determine pancreatic tumor stage (T1-T4) in 260 reports; and (3) present individual analyses of multiple tumors–rare in human-made reports. Importantly, 948 of the reports are for early-stage tumors.
在美国,每年有超过85百万次的CT扫描,对于放射科医生来说,创建与肿瘤相关的报告是一项具有挑战性和耗时的工作。为了应对这一需求,我们推出了RadGPT,这是一种用于从CT扫描生成详细报告的解剖学感知视觉语言人工智能代理。RadGPT首先分割肿瘤(包括良性囊肿和恶性肿瘤)及其周围的解剖结构,然后将这些信息转化为结构化报告和叙述性报告。这些报告提供了关于肿瘤的大小、形状、位置、衰减、体积以及与周围血管和器官相互作用的信息。在未见过的医院进行的广泛评估表明,RadGPT可以生成准确的报告,对于小于2厘米的肿瘤具有高灵敏度和特异性:肝脏肿瘤的灵敏度和特异性分别为80%和73%,肾脏肿瘤的灵敏度和特异性分别为92%和78%,胰腺肿瘤的灵敏度和特异性均为77%。对于较大的肿瘤,灵敏度范围从89%到97%。结果显著超过了腹部CT报告生成领域的最新水平。RadGPT为17个公共数据集生成了报告。通过放射科医生审查和细化,我们确保了报告的准确性,并创建了首个公开可用的图像文本3D医疗数据集,包含超过180万文本标记和270万图像,来自9262次CT扫描,其中包括2947份肿瘤扫描/报告和涉及肿瘤实例的详细数据。我们的报告能够:(1)在八个肝脏子段和每个体素标注的三个胰腺子段中定位肿瘤;(2)在胰腺癌报告中确定肿瘤分期(T1-T4);(3)对多个肿瘤进行个别分析——这在人类制作的报告中很少见。重要的是,其中涉及早期肿瘤的报告有948份。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一款名为RadGPT的医学图像报告生成AI系统。该系统可自动分析CT扫描结果,对肿瘤及其周围结构进行分割,并生成详细的报告。RadGPT生成的报告能够准确描述肿瘤的大小、形状、位置、密度、体积以及与周围血管和器官的关系。其性能在多个医院的数据集上得到了验证,对小肿瘤的检测准确率较高。此外,RadGPT还构建了首个公开可用的图像文本3D医疗数据集。
Key Takeaways
- RadGPT是一个解剖学感知的视觉语言AI代理,能够从CT扫描中生成详细的报告。
- RadGPT可以自动分割肿瘤及其周围结构,包括良性囊肿和恶性肿瘤。
- 生成的报告包含肿瘤的多种详细信息,如大小、形状、位置、密度、体积以及与周围血管和器官的关系。
- RadGPT在多个医院的数据集上表现良好,对小肿瘤的检测准确率较高。
- RadGPT生成的报告能够定位肝脏和胰腺的子分段,确定胰腺肿瘤的阶段,并提供多个肿瘤的个人分析。
- 构建了首个公开可用的图像文本3D医疗数据集,包含超过180万个文本标记和超过270万张图像。
点此查看论文截图

MedCoDi-M: A Multi-Prompt Foundation Model for Multimodal Medical Data Generation
Authors:Daniele Molino, Francesco Di Feola, Eliodoro Faiella, Deborah Fazzini, Domiziana Santucci, Linlin Shen, Valerio Guarrasi, Paolo Soda
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing medical practice, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and healthcare delivery. However, its adaptation in medical settings still faces significant challenges, related to data availability and privacy constraints. Synthetic data has emerged as a promising solution to mitigate these issues, addressing data scarcity while preserving privacy. Recently, Latent Diffusion Models have emerged as a powerful tool for generating high-quality synthetic data. Meanwhile, the integration of different modalities has gained interest, emphasizing the need of models capable of handle multimodal medical data.Existing approaches struggle to integrate complementary information and lack the ability to generate modalities simultaneously. To address this challenge, we present MedCoDi-M, a 6.77-billion-parameter model, designed for multimodal medical data generation, that, following Foundation Model paradigm, exploits contrastive learning and large quantity of data to build a shared latent space which capture the relationships between different data modalities. Further, we introduce the Multi-Prompt training technique, which significantly boosts MedCoDi-M’s generation under different settings. We extensively validate MedCoDi-M: first we benchmark it against five competitors on the MIMIC-CXR dataset, a state-of-the-art dataset for Chest X-ray and radiological report generation. Secondly, we perform a Visual Turing Test with expert radiologists to assess the realism and clinical relevance of the generated data, ensuring alignment with real-world scenarios. Finally, we assess the utility of MedCoDi-M in addressing key challenges in the medical field, such as anonymization, data scarcity and imbalance learning. The results are promising, demonstrating the applicability of MedCoDi-M in medical contexts. Project page is at https://cosbidev.github.io/MedCoDi-M/.
人工智能正在推动医疗实践的变革,提高诊断和医疗保健服务的准确性。然而,其在医疗环境中的应用仍面临与数据可用性和隐私约束相关的重大挑战。合成数据作为解决这些问题的有前途的解决方案而出现,它解决了数据稀缺的问题,同时保护了隐私。最近,潜在扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Models)作为一种生成高质量合成数据的强大工具而崭露头角。同时,不同模式的融合引起了人们的兴趣,强调了模型需要处理多模式医疗数据的能力。现有方法难以整合补充信息,并且缺乏同时生成模式的能力。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了MedCoDi-M,这是一个用于多模式医疗数据生成的6.77亿参数模型。它遵循基础模型范式,利用对比学习和大量数据来构建共享潜在空间,该空间可以捕获不同数据模式之间的关系。此外,我们引入了多提示训练技术,这显著提高了MedCoDi-M在不同设置下的生成能力。我们对MedCoDi-M进行了广泛验证:首先,我们在MIMIC-CXR数据集上与五种竞争对手进行基准测试,这是一个用于胸部X光片和放射学报告生成的先进数据集。其次,我们与专家放射科医生一起进行视觉图灵测试,以评估生成数据的真实性和临床相关性,确保其与真实场景的一致性。最后,我们评估了MedCoDi-M在解决医学领域的关键挑战(如匿名化、数据稀缺和不平衡学习)方面的实用性。结果令人鼓舞,证明了MedCoDi-M在医疗环境中的适用性。项目页面为:https://cosbidev.github.io/MedCoDi-M/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能正在革命性地改变医疗实践,提高诊断准确性和医疗服务水平。然而,其在医疗环境中的应用仍面临数据可用性和隐私约束等挑战。合成数据作为解决这些问题的有前途的解决方案,能够在解决数据稀缺问题的同时保护隐私。最近,潜在扩散模型已成为生成高质量合成数据的有力工具。针对多模态医疗数据的需求,我们提出了MedCoDi-M,这是一个用于多模态医疗数据生成的6.77亿参数模型,它采用基础模型范式,利用对比学习和大量数据构建共享潜在空间,捕捉不同数据模态之间的关系。此外,还引入了多提示训练技术,显著提高了MedCoDi-M在不同设置下的生成能力。经过广泛验证,MedCoDi-M在MIMIC-CXR数据集上与五种竞争对手进行了基准测试,表现优异。同时进行了视觉图灵测试,以评估生成数据的真实性和临床相关性。最后,我们评估了MedCoDi-M在医疗领域的关键挑战中的实用性,如匿名化、数据稀缺和不平衡学习。结果显示,MedCoDi-M在医疗环境中具有广泛的应用前景。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在医疗实践中具有提高诊断准确性和医疗服务水平的潜力。
- 数据可用性和隐私约束是人工智能在医疗环境中应用的主要挑战。
- 合成数据作为解决数据稀缺和隐私保护问题的一种有前途的方案。
- 潜在扩散模型是生成高质量合成数据的有效工具。
- MedCoDi-M是一个用于多模态医疗数据生成的模型,具有6.77亿参数。
- MedCoDi-M利用对比学习和大量数据构建共享潜在空间,以处理不同数据模态之间的关系。
点此查看论文截图

Rethinking High-speed Image Reconstruction Framework with Spike Camera
Authors:Kang Chen, Yajing Zheng, Tiejun Huang, Zhaofei Yu
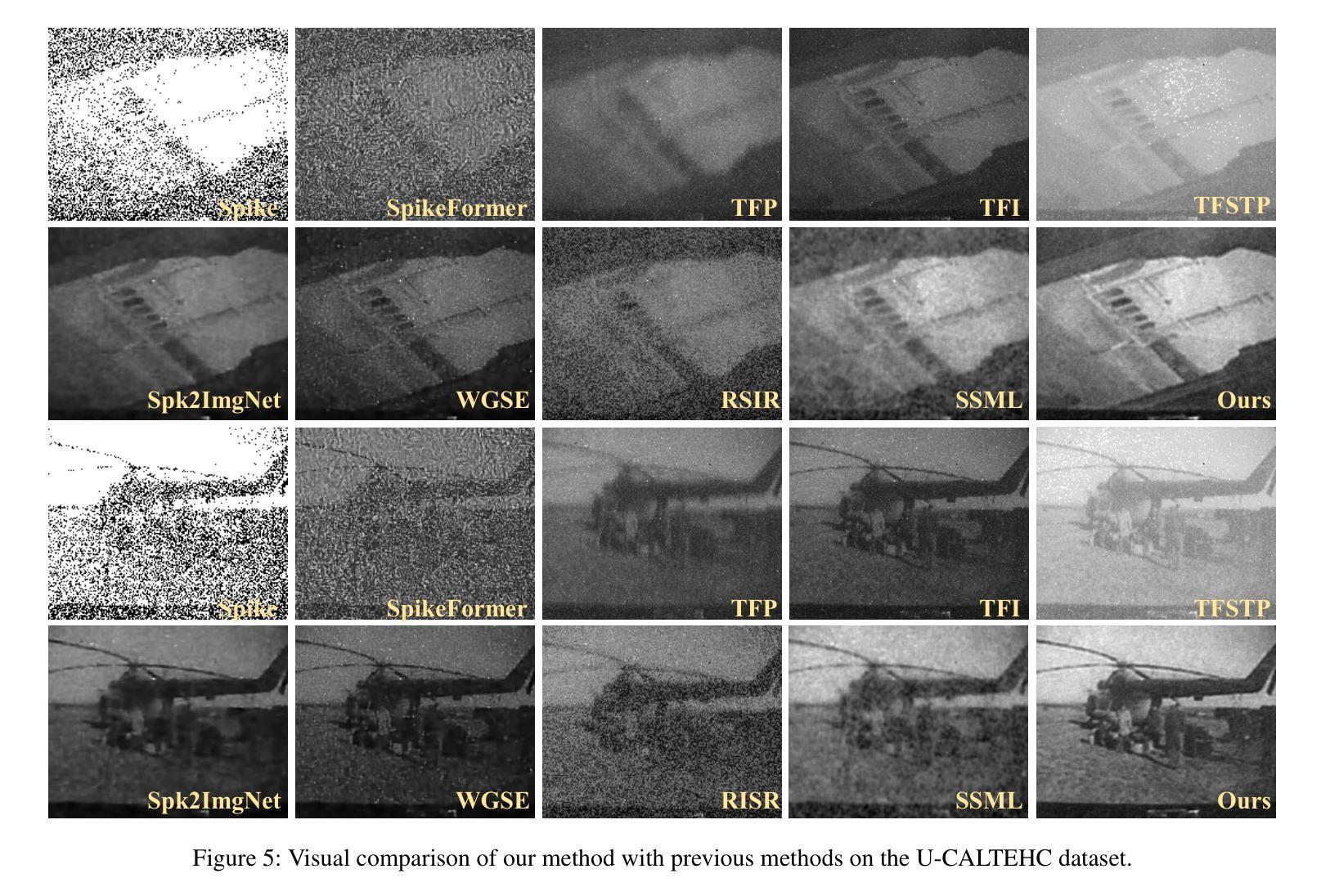
Spike cameras, as innovative neuromorphic devices, generate continuous spike streams to capture high-speed scenes with lower bandwidth and higher dynamic range than traditional RGB cameras. However, reconstructing high-quality images from the spike input under low-light conditions remains challenging. Conventional learning-based methods often rely on the synthetic dataset as the supervision for training. Still, these approaches falter when dealing with noisy spikes fired under the low-light environment, leading to further performance degradation in the real-world dataset. This phenomenon is primarily due to inadequate noise modelling and the domain gap between synthetic and real datasets, resulting in recovered images with unclear textures, excessive noise, and diminished brightness. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel spike-to-image reconstruction framework SpikeCLIP that goes beyond traditional training paradigms. Leveraging the CLIP model’s powerful capability to align text and images, we incorporate the textual description of the captured scene and unpaired high-quality datasets as the supervision. Our experiments on real-world low-light datasets U-CALTECH and U-CIFAR demonstrate that SpikeCLIP significantly enhances texture details and the luminance balance of recovered images. Furthermore, the reconstructed images are well-aligned with the broader visual features needed for downstream tasks, ensuring more robust and versatile performance in challenging environments.
脉冲相机作为一种创新的神经形态设备,能够产生连续的脉冲流,以低于传统RGB相机的带宽和更高的动态范围来捕捉高速场景。然而,在低光照条件下从脉冲输入重建高质量图像仍然是一个挑战。传统的学习型方法通常依赖于合成数据集作为训练过程中的监督信息。然而,这些方法在处理低光环境下产生的噪声脉冲时常常出现问题,导致在真实世界数据集上的性能进一步下降。这一现象的主要原因是噪声建模不足以及合成数据集和真实数据集之间的领域差距,导致恢复出的图像纹理不清晰、噪声过多以及亮度降低。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了新型的脉冲到图像重建框架SpikeCLIP,它超越了传统的训练模式。我们借助CLIP模型的强大文本和图像对齐能力,将捕获场景的文字描述和未配对的高质量数据集作为监督信息。我们在真实世界的低光数据集U-CALTECH和U-CIFAR上的实验表明,SpikeCLIP显著提高了恢复图像的纹理细节和亮度平衡。此外,重建的图像与下游任务所需的更广泛的视觉特征相吻合,确保在具有挑战性的环境中具有更稳健和多功能性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
这是一篇关于神经形态设备Spike摄像头的文章。Spike摄像头通过生成连续脉冲流捕捉高速场景,相较于传统RGB摄像头拥有更低的带宽和更高的动态范围。然而,在低光照条件下从脉冲输入重建高质量图像仍是一大挑战。当前学习法方法依赖于合成数据集进行训练,但在处理低光照环境下产生的噪声脉冲时表现不佳,导致在实际数据集上的性能下降。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种新型的脉冲到图像重建框架SpikeCLIP,它超越了传统训练模式。SpikeCLIP借助CLIP模型的文本与图像对齐能力,将场景文本描述和未配对的高质量数据集作为监督。实验表明,SpikeCLIP在真实世界的低光照数据集U-CALTECH和U-CIFAR上显著提高了图像的纹理细节和亮度平衡。此外,重建的图像与下游任务所需的更广泛的视觉特征对齐,确保在具有挑战性的环境中表现得更稳健和通用。
Key Takeaways
- Spike摄像头是一种新型的神经形态设备,可通过连续脉冲流捕捉高速场景,相较于传统RGB摄像头具有优势。
- 低光照条件下从脉冲输入重建高质量图像是一大挑战。
- 当前学习法方法在处理低光照环境下的噪声脉冲时表现不佳,主要原因是噪声建模不足以及合成和真实数据集之间的域差距。
- SpikeCLIP是一种新型的脉冲到图像重建框架,借助CLIP模型的文本与图像对齐能力来提高图像重建质量。
- SpikeCLIP利用场景文本描述和未配对的高质量数据集作为监督,有效提高了在真实世界的低光照数据集上的图像纹理细节和亮度平衡。
- SpikeCLIP重建的图像与下游任务所需的视觉特征对齐,表现得更稳健和通用。
点此查看论文截图


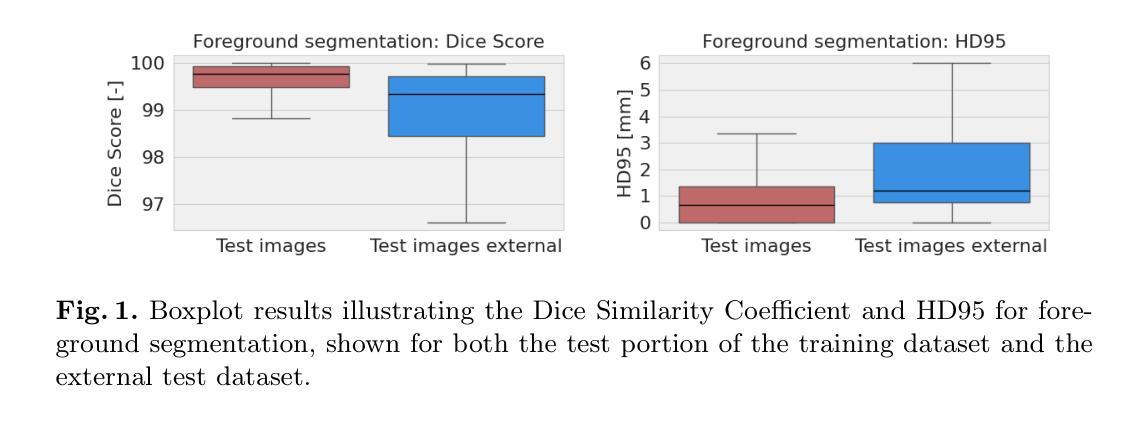
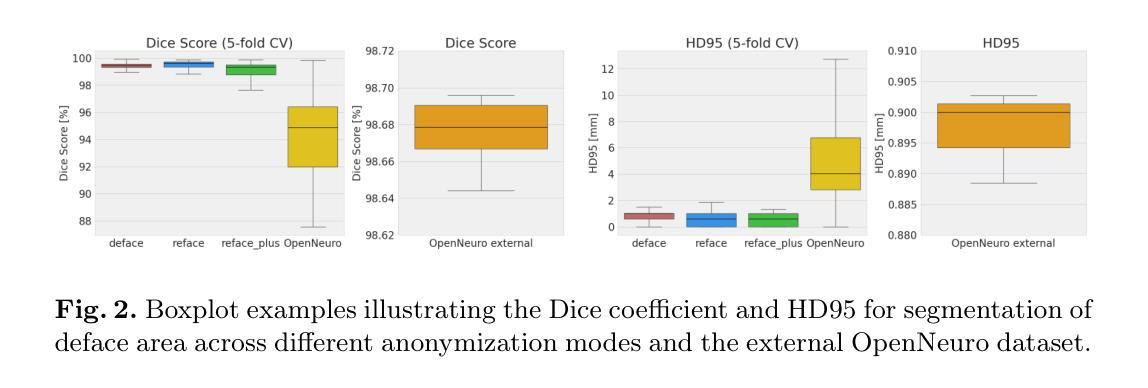
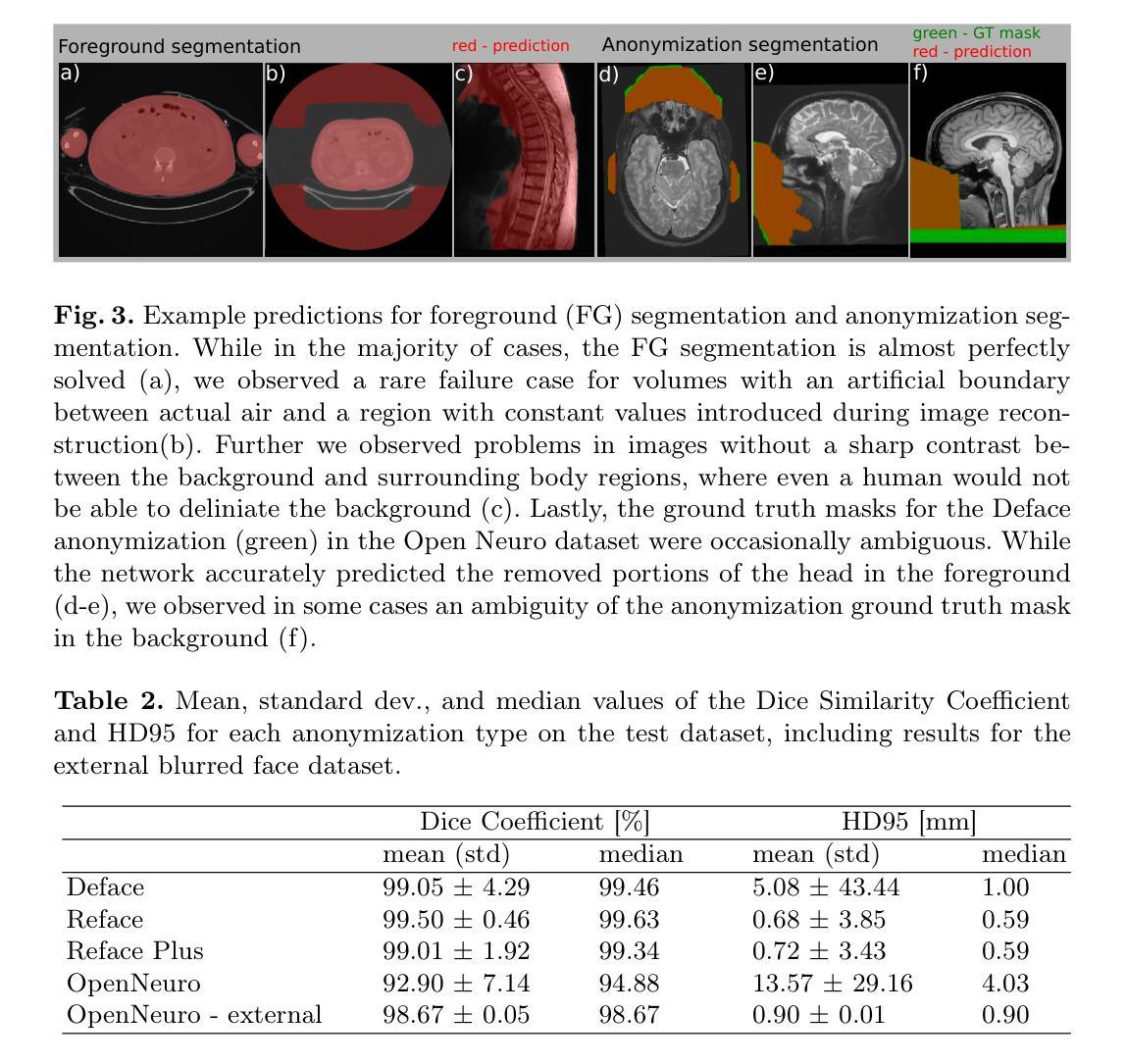
A Unified Framework for Foreground and Anonymization Area Segmentation in CT and MRI Data
Authors:Michal Nohel, Constantin Ulrich, Jonathan Suprijadi, Tassilo Wald, Klaus Maier-Hein
This study presents an open-source toolkit to address critical challenges in preprocessing data for self-supervised learning (SSL) for 3D medical imaging, focusing on data privacy and computational efficiency. The toolkit comprises two main components: a segmentation network that delineates foreground regions to optimize data sampling and thus reduce training time, and a segmentation network that identifies anonymized regions, preventing erroneous supervision in reconstruction-based SSL methods. Experimental results demonstrate high robustness, with mean Dice scores exceeding 98.5 across all anonymization methods and surpassing 99.5 for foreground segmentation tasks, highlighting the efficacy of the toolkit in supporting SSL applications in 3D medical imaging for both CT and MRI images. The weights and code is available at https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/Foreground-and-Anonymization-Area-Segmentation.
本研究提出了一种开源工具包,旨在解决3D医学影像自监督学习(SSL)数据预处理中的关键挑战,重点关注数据隐私和计算效率。该工具包主要包括两个组件:一个分割网络,用于划定前景区域以优化数据采样,从而减少训练时间;另一个分割网络则用于识别匿名区域,防止基于重建的SSL方法中发生错误监督。实验结果表现出高稳健性,所有匿名化方法的平均Dice得分超过98.5%,前景分割任务的得分超过99.5%,突显了该工具包在支持CT和MRI图像的3D医学图像SSL应用方面的有效性。相关权重和代码可通过https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/Foreground-and-Anonymization-Area-Segmentation获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages
Summary
本文介绍了一个开源工具包,该工具包针对三维医学影像自监督学习中数据预处理阶段的重难点问题进行了全面解决,特别聚焦于数据隐私和计算效率两大挑战。该工具包包含两个核心组件,分别用于前景区域分割和匿名区域识别。实验结果显示,该工具包在支持三维医学影像自监督学习方面表现出高鲁棒性,前景分割任务的Dice系数超过99.5%,所有匿名化方法的Dice系数均超过98.5%。有关权重和代码可访问链接 https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/Foreground-and-Anonymization-Area-Segmentation 了解。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究解决三维医学影像自监督学习数据预处理阶段的挑战。
- 工具包包含两个核心组件:前景区域分割网络和匿名区域识别网络。
- 前景区域分割可优化数据采样,缩短训练时间。
- 匿名区域识别可防止重建式自监督学习中的错误监督。
- 实验结果展示出高鲁棒性,前景分割任务的Dice系数超过99.5%。
- 所有匿名化方法的Dice系数均超过98.5%。
点此查看论文截图

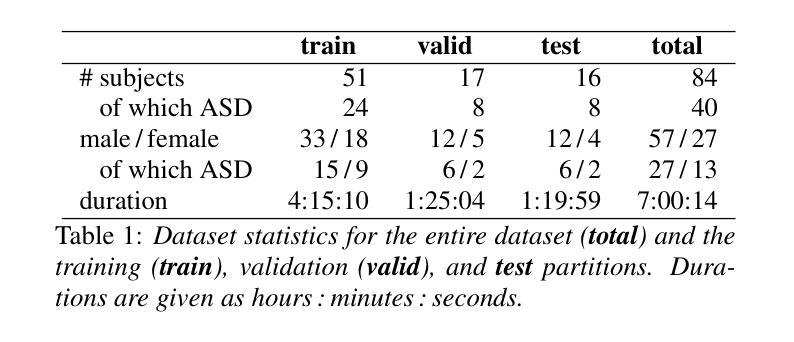
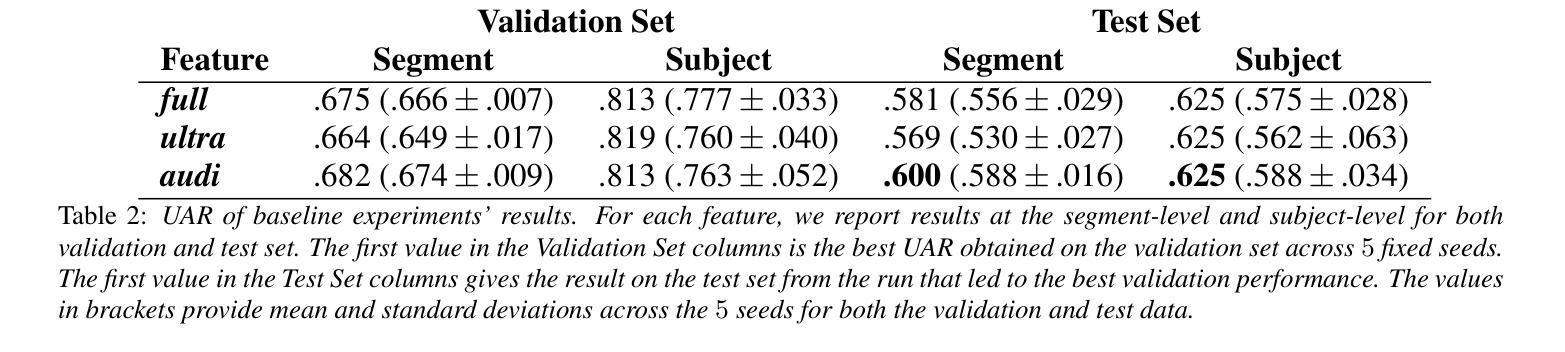
MAD-UV: The 1st INTERSPEECH Mice Autism Detection via Ultrasound Vocalization Challenge
Authors:Zijiang Yang, Meishu Song, Xin Jing, Haojie Zhang, Kun Qian, Bin Hu, Kota Tamada, Toru Takumi, Björn W. Schuller, Yoshiharu Yamamoto
The Mice Autism Detection via Ultrasound Vocalization (MAD-UV) Challenge introduces the first INTERSPEECH challenge focused on detecting autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in mice through their vocalizations. Participants are tasked with developing models to automatically classify mice as either wild-type or ASD models based on recordings with a high sampling rate. Our baseline system employs a simple CNN-based classification using three different spectrogram features. Results demonstrate the feasibility of automated ASD detection, with the considered audible-range features achieving the best performance (UAR of 0.600 for segment-level and 0.625 for subject-level classification). This challenge bridges speech technology and biomedical research, offering opportunities to advance our understanding of ASD models through machine learning approaches. The findings suggest promising directions for vocalization analysis and highlight the potential value of audible and ultrasound vocalizations in ASD detection.
通过超声发声(MAD-UV)挑战检测小鼠自闭症介绍了首个INTERSPEECH挑战,该挑战的重点是通过小鼠的鸣叫检测自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)。参赛者的任务是开发模型,根据高采样率录音自动将小鼠分类为野生型或ASD模型。我们的基线系统采用基于简单CNN的分类方法,使用三种不同的频谱特征。结果表明,自动化ASD检测是可行的,所考虑的音频范围特征实现了最佳性能(分段级UAR为0.600,主体级分类为0.625)。该挑战架起了语音技术与生物医学研究之间的桥梁,通过机器学习的方法推进我们对ASD模型的理解。研究结果为发声分析提供了有前景的方向,并突出了可听声和超声波发声在ASD检测中的潜在价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 1 figure and 2 tables. For MAD-UV Challenge 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了利用超声发声(Ultrasound Vocalization)技术检测小鼠自闭症(Autism Spectrum Disorder,ASD)的挑战。挑战要求参与者开发模型,根据高采样率的录音自动将小鼠分类为野生型或ASD模型。基线系统采用基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的简单分类方法,使用三种不同的频谱特征。结果证明了自动化检测ASD的可行性,其中考虑的音频范围特征表现最佳,达到分段级别和用户级别的识别率分别为0.6和0.625。该挑战将语音技术与生物医学研究相结合,为通过机器学习手段了解ASD模型提供了机会,同时揭示了发声分析的潜在方向以及声音和超声在ASD检测中的价值。
Key Takeaways
- MAD-UV挑战聚焦于通过小鼠的发声来检测自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)。
- 挑战要求参与者开发模型,根据高采样率的录音自动分类小鼠。
- 基线系统采用CNN分类方法,并结合三种不同的频谱特征。
- 音频范围特征在自动化ASD检测中表现最佳。
- 该挑战将语音技术与生物医学研究相结合,为理解ASD提供了新的视角。
- 结果揭示了发声分析在ASD检测中的潜在价值。
点此查看论文截图

Continual Self-supervised Learning Considering Medical Domain Knowledge in Chest CT Images
Authors:Ren Tasai, Guang Li, Ren Togo, Minghui Tang, Takaaki Yoshimura, Hiroyuki Sugimori, Kenji Hirata, Takahiro Ogawa, Kohsuke Kudo, Miki Haseyama
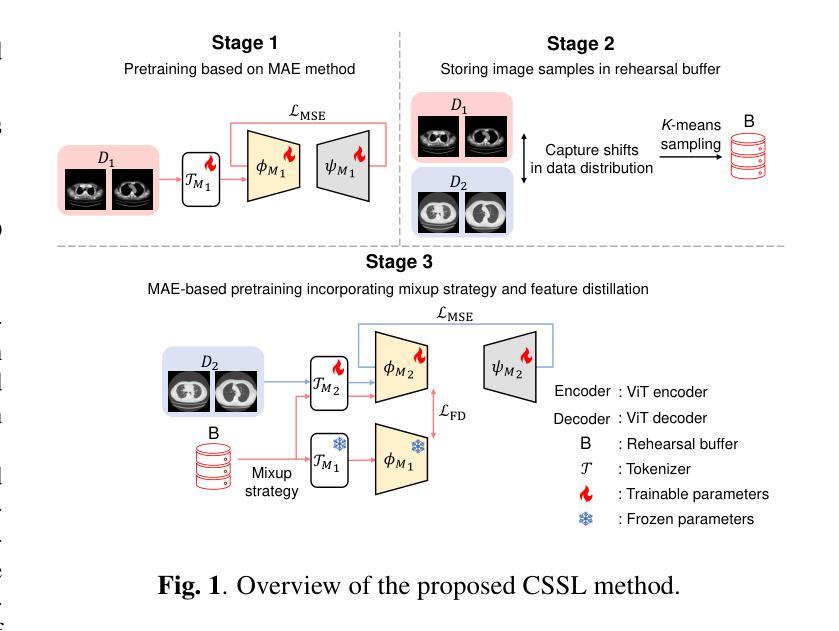
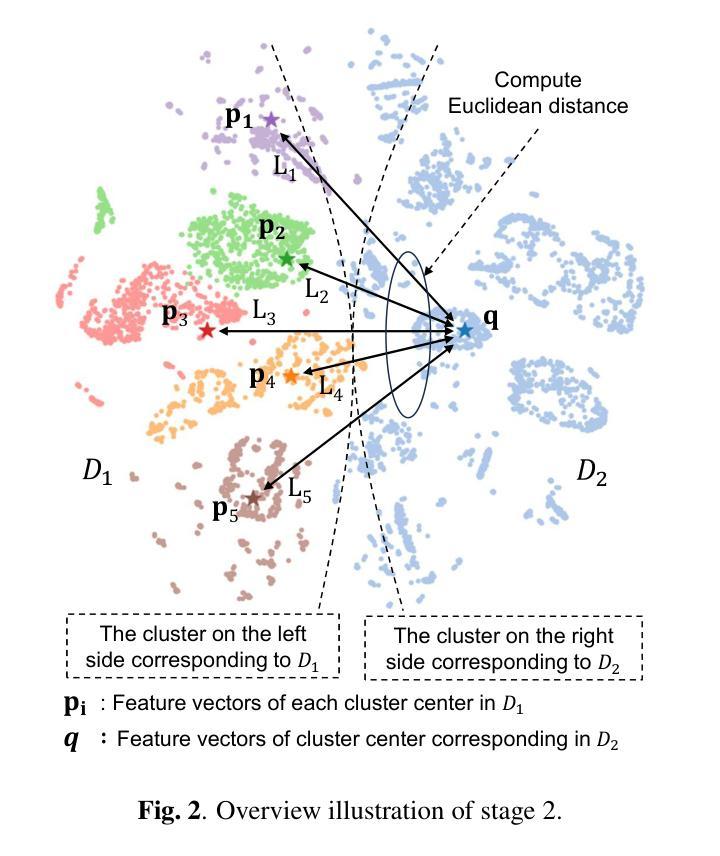
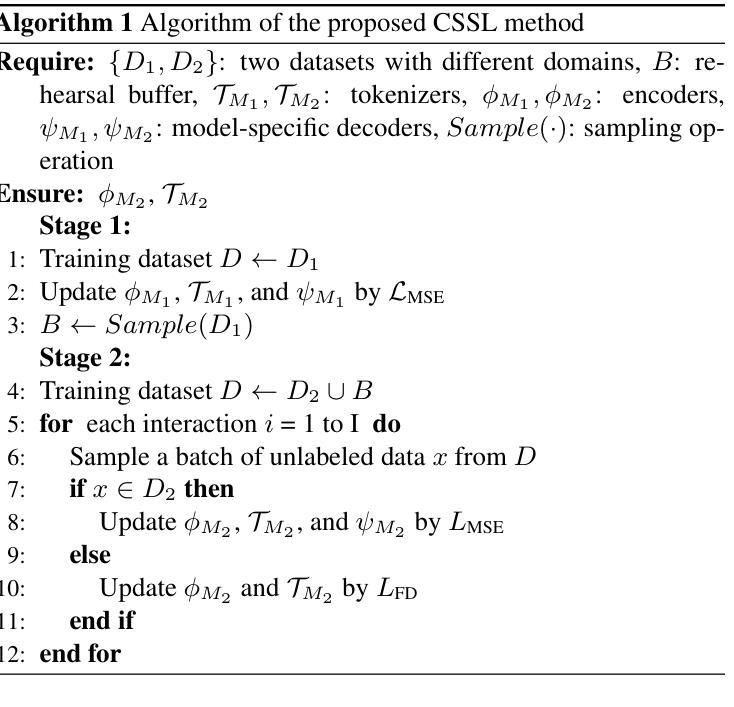
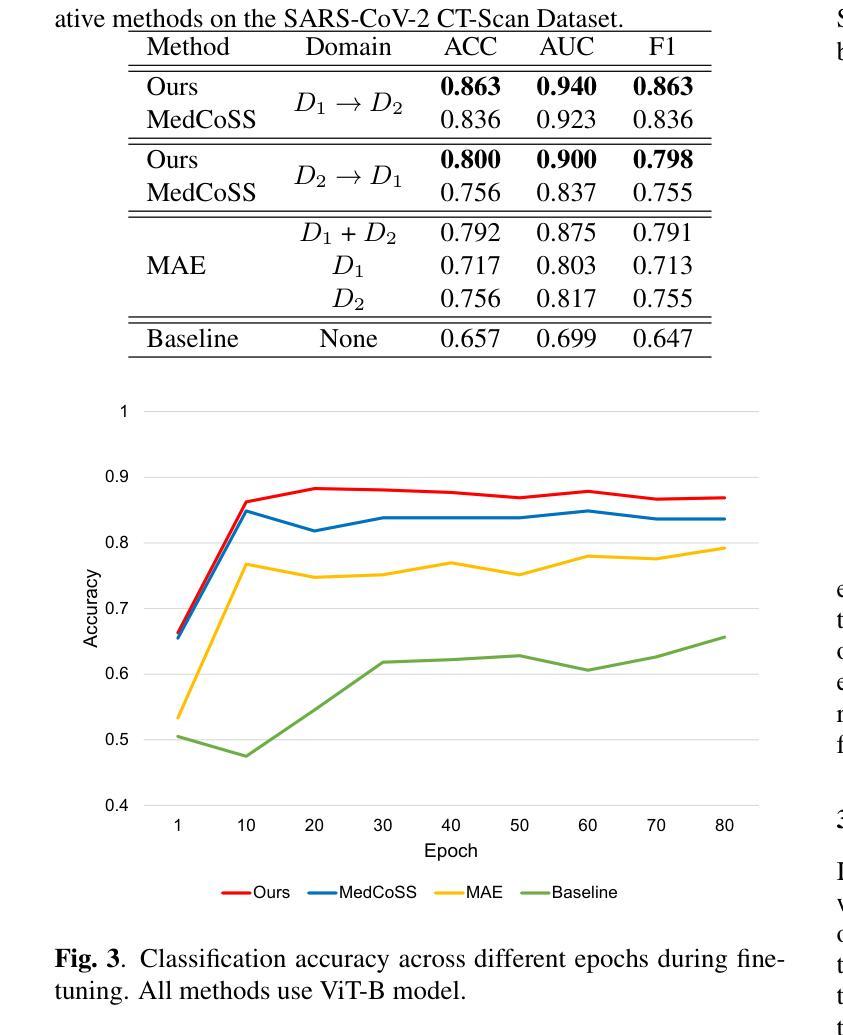
We propose a novel continual self-supervised learning method (CSSL) considering medical domain knowledge in chest CT images. Our approach addresses the challenge of sequential learning by effectively capturing the relationship between previously learned knowledge and new information at different stages. By incorporating an enhanced DER into CSSL and maintaining both diversity and representativeness within the rehearsal buffer of DER, the risk of data interference during pretraining is reduced, enabling the model to learn more richer and robust feature representations. In addition, we incorporate a mixup strategy and feature distillation to further enhance the model’s ability to learn meaningful representations. We validate our method using chest CT images obtained under two different imaging conditions, demonstrating superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
我们提出了一种新型的考虑医学领域知识的连续自监督学习方法(CSSL),应用于胸部CT图像。我们的方法通过有效捕捉不同阶段的先前学习知识和新信息之间的关系来解决顺序学习的挑战。通过将增强的DER融入CSSL并保持DER复习缓冲区内的多样性和代表性,降低了预训练过程中的数据干扰风险,使模型能够学习更丰富和稳健的特征表示。此外,我们结合了混合策略和特征蒸馏,进一步增强了模型学习有意义表示的能力。我们使用两种不同成像条件下获得的胸部CT图像验证了我们的方法,展现了相较于最新技术的前沿性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
摘要
本文提出了一种新型的考虑医学领域知识的持续自监督学习方法(CSSL),应用于胸部CT图像。该方法通过有效捕捉先前知识与新信息在不同阶段之间的关系,解决了顺序学习的挑战。通过将增强型DER融入CSSL,并在DER的演练缓冲区中保持多样性和代表性,降低了预训练过程中的数据干扰风险,使模型能够学习更丰富和稳健的特征表示。此外,我们采用了mixup策略和特征蒸馏,进一步增强了模型学习有意义表示的能力。使用两种不同成像条件下获得的胸部CT图像验证了我们的方法,表现优于最新技术方法。
要点
- 提出了结合医学领域知识的持续自监督学习方法(CSSL),专注于胸部CT图像。
- 通过有效捕捉先前知识与新信息的关系,解决顺序学习的挑战。
- 通过增强型DER和演练缓冲区内的多样性与代表性,降低数据干扰风险。
- 模型能够学习更丰富和稳健的特征表示。
- 采用了mixup策略和特征蒸馏,增强模型学习有意义表示的能力。
- 在两种不同成像条件下的胸部CT图像上验证了方法的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

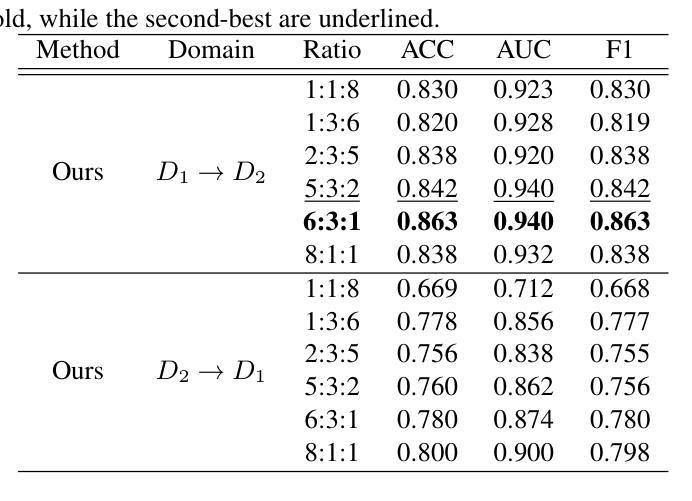
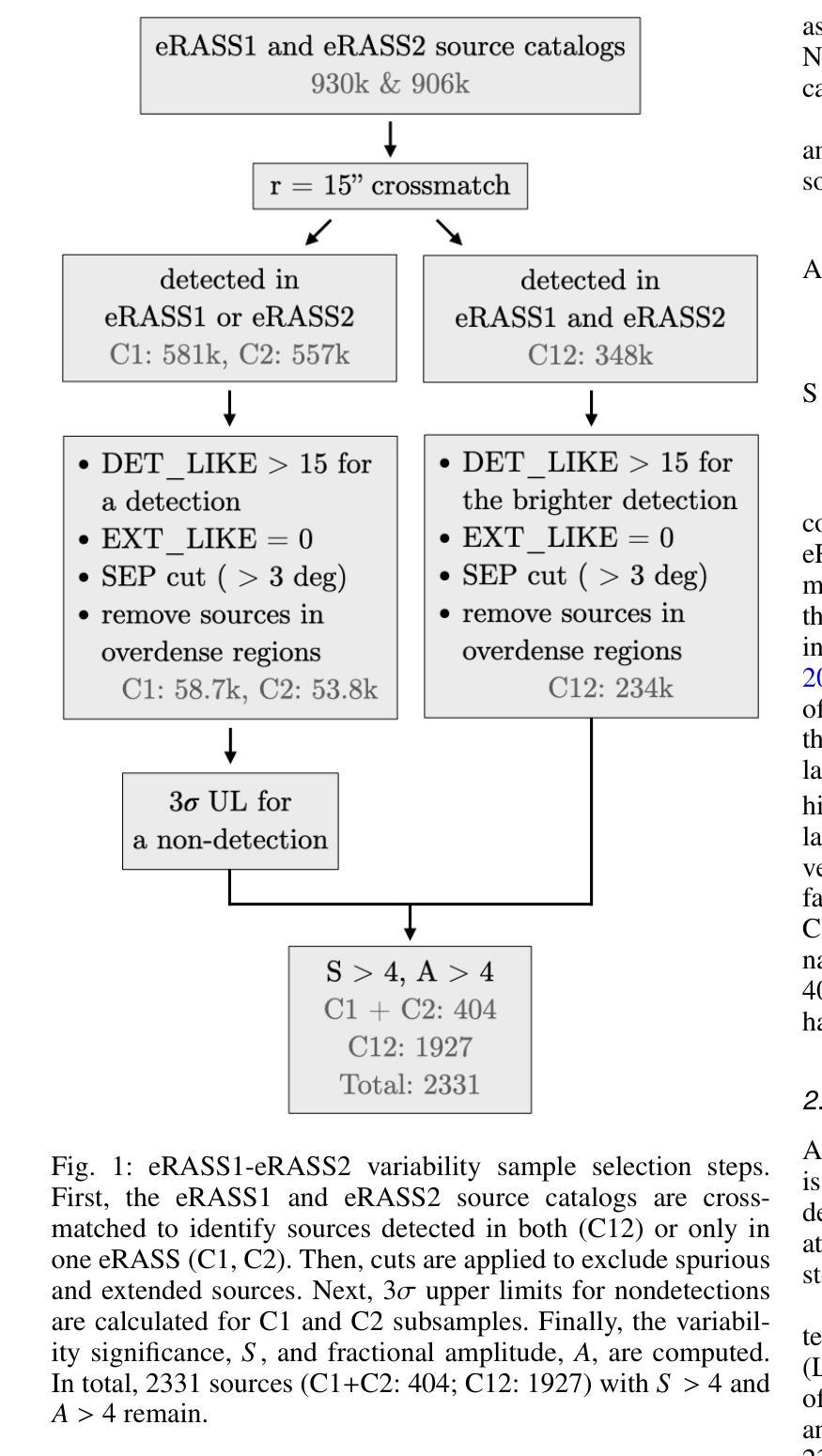
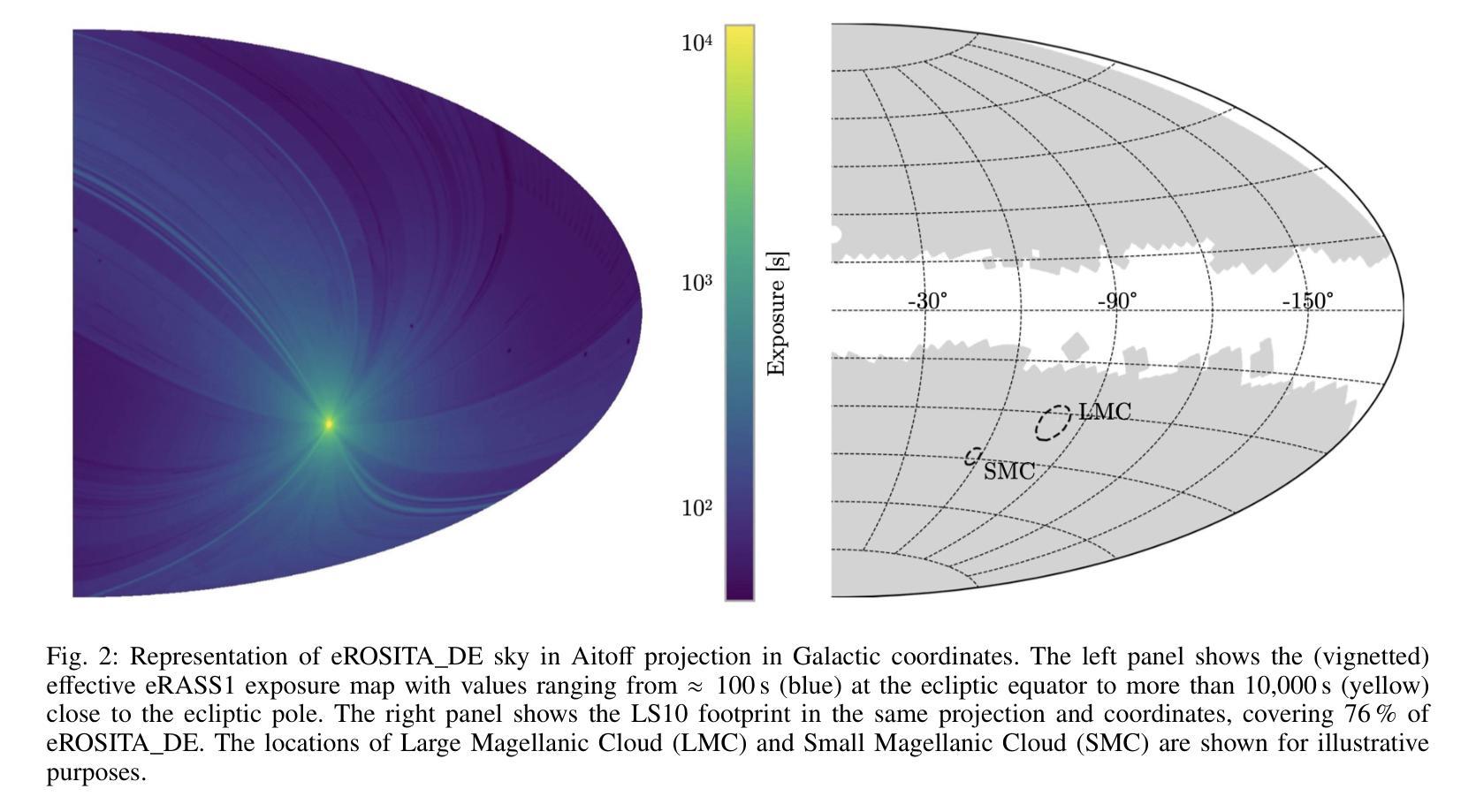
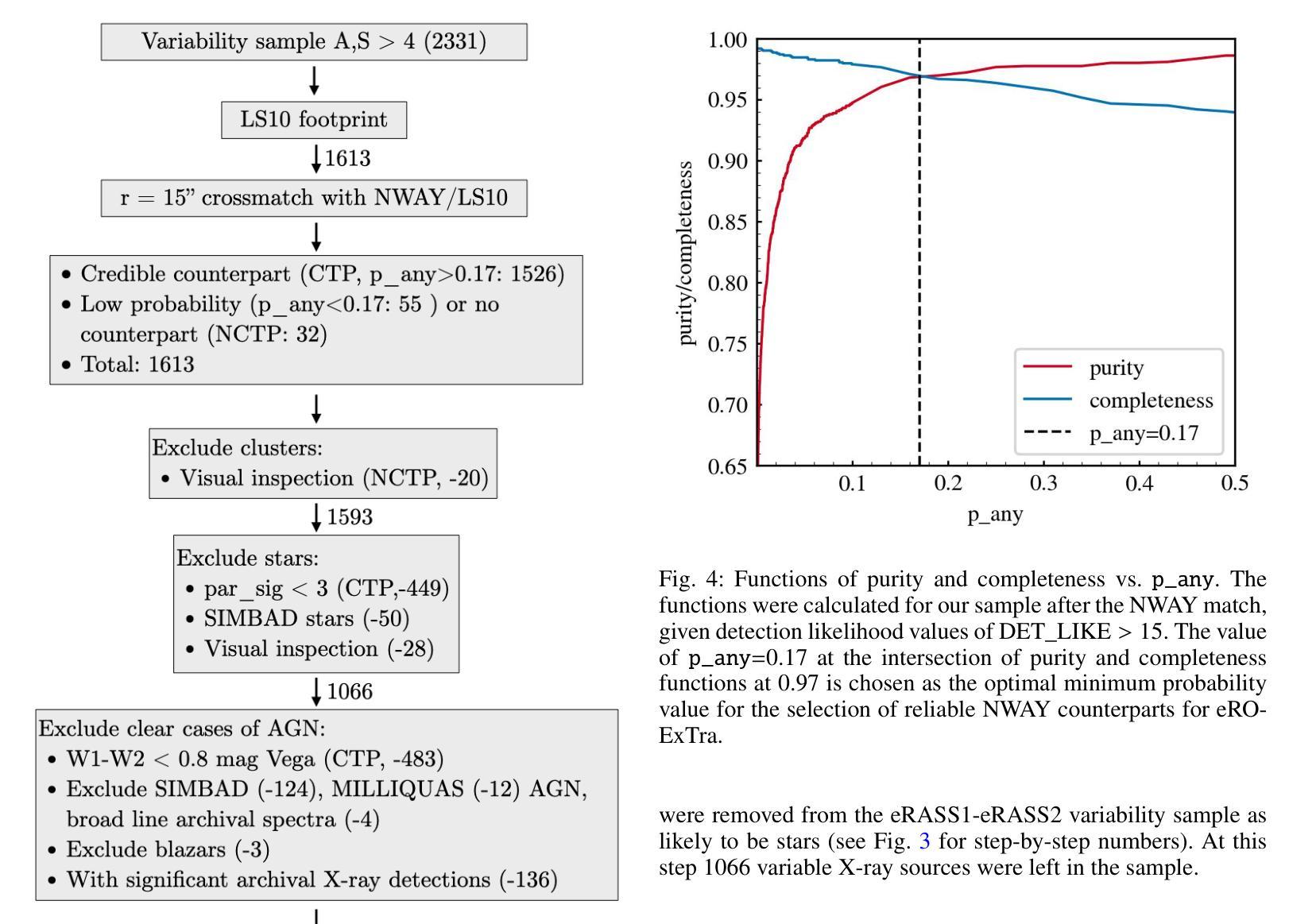
eRO-ExTra: eROSITA extragalactic non-AGN X-ray transients and variables in eRASS1 and eRASS2
Authors:Iuliia Grotova, Arne Rau, Mara Salvato, Johannes Buchner, Adelle J. Goodwin, Zhu Liu, Adam Malyali, Andrea Merloni, Dusán Tubín-Arenas, David Homan, Mirko Krumpe, Kirpal Nandra, Gemma E. Anderson, Riccardo Arcodia, Sabina Bahic, Pietro Baldini, David A. H. Buckley, Stefano Ciroi, Adela Kawka, Megan Masterson, James C. A. Miller-Jones, Francesco Di Mille
(Abridged) While previous X-ray studies showed the dominance of regular active galactic nuclei (AGN) variability, a small fraction of sources arise from more exotic phenomena such as tidal disruption events (TDEs), quasi-periodic eruptions, or other short-lived events associated with supermassive black hole accretion. This paper describes the systematic selection of X-ray extragalactic transients found in the first two eROSITA all-sky surveys (eRASS) that are not associated with known AGN prior to eROSITA observations. We generated a variability sample from eRASS1 and eRASS2 (Dec. 2019-Dec. 2020), which includes sources with a variability significance and a fractional amplitude larger than four, located in the Legacy Survey DR10 (LS10) footprint. The properties of LS10 counterparts were used to exclude stars and known AGN. The sample was additionally cleaned using pre-eROSITA classifications, archival optical spectra, and archival X-ray data. The final catalog eRO-ExTra includes 304 extragalactic eROSITA transients and variables not associated with known AGN. More than 90% of sources have reliable LS10 optical counterparts. For each source, we provide archival X-ray data from Swift, ROSAT, and XMM-Newton; the eROSITA long-term light curve (2-2.5 years) with a light curve classification; as well as the best power law fit spectral results at the peak eROSITA epoch. Reliable spectroscopic and photometric redshifts are provided for more than 80% of the sample. Several sources in the catalog are known TDE candidates discovered by eROSITA. In addition, 31 sources are radio detected. The eRO-ExTra transients constitute a relatively clean parent sample of non-AGN variability phenomena associated with massive black holes. More than 95% of eRO-ExTra sources were discovered in X-rays with eROSITA for the first time, which makes it a valuable resource for studying unique nuclear transients.
(摘要)虽然之前的X射线研究表明,规则活跃星系核(AGN)的变异性占主导地位,但一小部分源来自于潮汐撕裂事件(TDEs)、准周期喷发或其他与超大质量黑洞吸积相关的短暂事件等更奇特的现象。本文描述了eROSITA前两次全天空调查(eRASS)中发现的X射线外星暂态系统的选择过程,这些暂态与已知的AGN无关。我们从eRASS1和eRASS2(2019年12月至2020年12月)生成了一个变化样本,其中包括位于遗产调查DR10(LS10)足迹内的变异性显著且分数幅度大于四的源。使用LS10对应体的属性来排除恒星和已知AGN。还使用预eROSITA分类、档案光学光谱和档案X射线数据对样本进行了清理。最终的目录eRO-ExTra包含了304个与已知AGN无关的星外eROSITA暂态和变量。超过90%的源有可靠的LS10光学对应体。对于每个源,我们提供了来自Swift、ROSAT和XMM-Newton的档案X射线数据;eROSITA长期光变曲线(2-2.5年)及其光变曲线分类;以及在eROSITA峰值时期的最佳幂律拟合光谱结果。超过80%的样本提供了可靠的光谱和红移测定。目录中有几个源是eROSITA发现的已知TDE候选者。此外,有31个源被检测到无线电信号。eRO-ExTra暂态是与大规模黑洞相关的非AGN变现象相对干净的母体样本。超过95%的eRO-ExTra源是首次用eROSITA在X射线上发现的,这使得它成为研究独特核暂态的宝贵资源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 15 figures, published in A&A. To download the eRO-ExTra catalog, see https://cdsarc.cds.unistra.fr/viz-bin/cat/J/A+A/693/A62
Summary
eROSITA首次全天空调查中发现了一批新的非活跃星系核(非AGN)的可变源,包括潮汐撕裂事件(TDEs)等与超大质量黑洞相关的罕见现象。样本经过严格筛选,包含LS10光学对应体的超过九成来源具有可靠性。此研究提供了这些源的长期光变曲线、光谱结果及红移信息,为深入研究非活跃星系核可变现象提供了宝贵的资源。大部分来源尚未被罗西阿特尔成像和光波天文学研究所等机构探测到,故成为研究独特核瞬变现象的宝贵资源。这一发现在推动X射线研究领域的发展和进一步了解宇宙中不活跃核活动的多样性上具有重要地位。同时介绍了使用最理想的幂律拟合光谱方法处理谱数据和捕捉核心精华部分的案例分析过程及有效成果的梳理结果作为个案予以报告总结了相关成果和重要性。同时提供了关于样本的详细信息,包括分类和检测数据等。此外,本文还探讨了样本中某些已知潮汐撕裂事件候选源的特征和表现。总体来说,这是一个具有重要价值的发现和研究领域,为研究宇宙中独特现象提供了重要依据。这一研究将大大有助于推进对宇宙中的罕见事件和未知领域的探索。此项研究还发现样本中有多个已知潮汐撕裂事件候选源,这些源都是宝贵的科学研究资源。该项研究具有重要的科学意义和实践价值。随着进一步的研究,相信该领域将会带来更多的科学发现。此次调查涉及天文学中的罕见现象和超大规模黑洞的活动规律研究等多个方面。总体来看,该研究对于推动天文学领域的发展具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways:
- eROSITA首次发现数百个与已知活动星系核无关的新的可变外太阳系外星源样本被整理在目录eRO-ExTra中。
点此查看论文截图


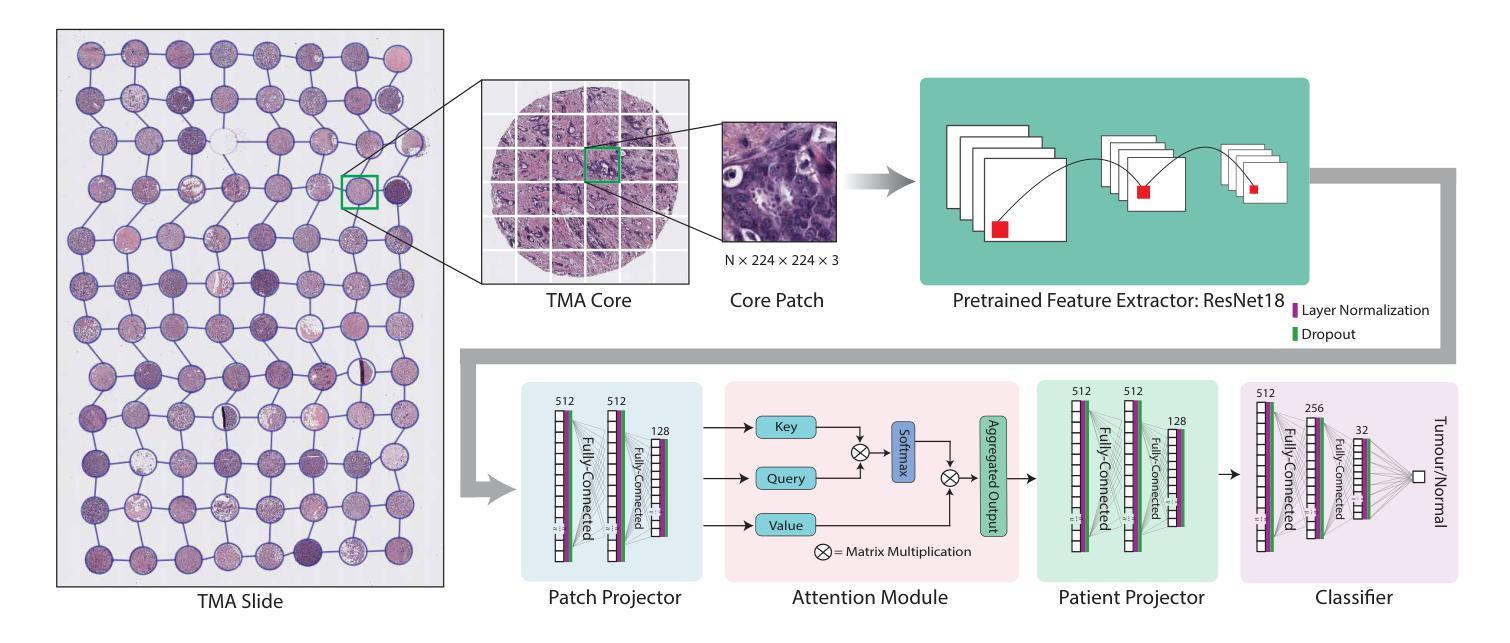
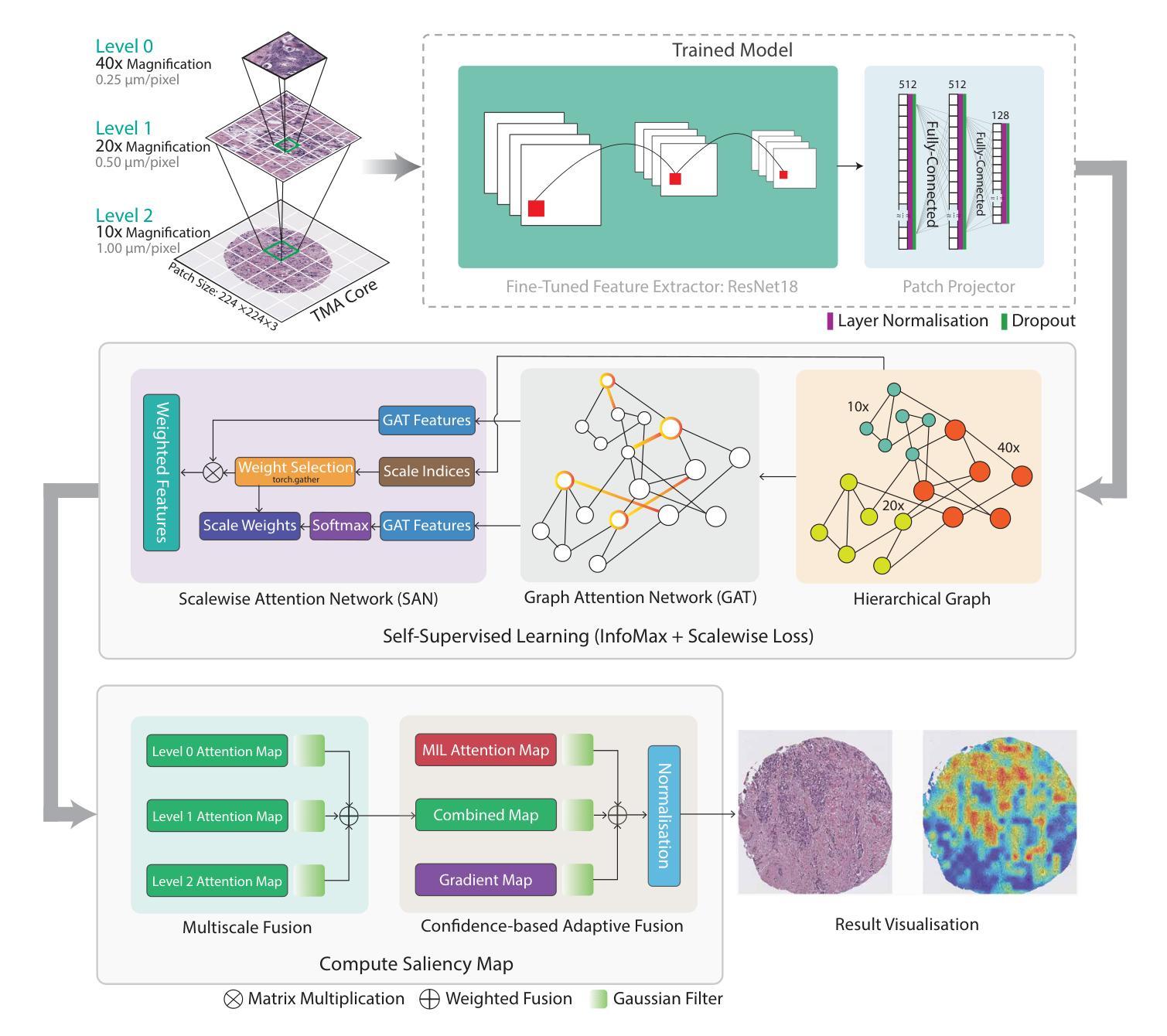
GRAPHITE: Graph-Based Interpretable Tissue Examination for Enhanced Explainability in Breast Cancer Histopathology
Authors:Raktim Kumar Mondol, Ewan K. A. Millar, Peter H. Graham, Lois Browne, Arcot Sowmya, Erik Meijering
Explainable AI (XAI) in medical histopathology is essential for enhancing the interpretability and clinical trustworthiness of deep learning models in cancer diagnosis. However, the black-box nature of these models often limits their clinical adoption. We introduce GRAPHITE (Graph-based Interpretable Tissue Examination), a post-hoc explainable framework designed for breast cancer tissue microarray (TMA) analysis. GRAPHITE employs a multiscale approach, extracting patches at various magnification levels, constructing an hierarchical graph, and utilising graph attention networks (GAT) with scalewise attention (SAN) to capture scale-dependent features. We trained the model on 140 tumour TMA cores and four benign whole slide images from which 140 benign samples were created, and tested it on 53 pathologist-annotated TMA samples. GRAPHITE outperformed traditional XAI methods, achieving a mean average precision (mAP) of 0.56, an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.94, and a threshold robustness (ThR) of 0.70, indicating that the model maintains high performance across a wide range of thresholds. In clinical utility, GRAPHITE achieved the highest area under the decision curve (AUDC) of 4.17e+5, indicating reliable decision support across thresholds. These results highlight GRAPHITE’s potential as a clinically valuable tool in computational pathology, providing interpretable visualisations that align with the pathologists’ diagnostic reasoning and support precision medicine.
在医学病理学中,可解释性人工智能(XAI)对于提高癌症诊断中深度学习模型的解释性和临床可信度至关重要。然而,这些模型的“黑箱”性质常常限制了它们在临床上的采纳。我们引入了GRAPHITE(基于图的可解释组织检查),这是一种专为乳腺癌组织微阵列(TMA)分析设计的后验可解释框架。GRAPHITE采用多尺度方法,在不同放大级别提取斑块,构建分层图,并利用具有尺度注意(SAN)的图注意网络(GAT)来捕获尺度相关特征。我们在由肿瘤组织微阵列的140个核心和四个良性全幻灯片图像创建的140个良性样本上训练了模型,并在病理学家注释的53个TMA样本上进行了测试。与传统的XAI方法相比,GRAPHITE表现更好,达到了平均精度均值(mAP)为0.56,受试者工作特征曲线下的面积(AUROC)为0.94,阈值稳健性(ThR)为0.70的指标,这表明模型在广泛的阈值范围内都能保持高性能。在临床应用中,GRAPHITE的决策曲线下的面积(AUDC)最高达到了4.17e+5,表明其在不同阈值下都能提供可靠的决策支持。这些结果突出了GRAPHITE在临床病理学中的价值潜力,它能提供与病理医师诊断推理相符的可视化解释并支持精准医学。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 Pages, 9 Figures, 1 Tables
Summary
本文介绍了Explainable AI(XAI)在医学病理学中对于提高深度学习模型在癌症诊断中的可解释性和临床可靠性的重要性。为应对深度学习模型的黑箱特性在临床应用中的限制,提出了一种名为GRAPHITE的基于图的解释性框架,用于乳腺癌组织微阵列(TMA)分析。GRAPHITE采用多尺度方法,通过不同放大级别提取斑块、构建层次图,并利用带有尺度感知注意力(SAN)的图注意力网络(GAT)捕捉尺度相关特征。在140个肿瘤TMA芯和4个良性全幻灯片图像上进行训练,并在53个病理学家注释的TMA样本上进行测试。相较于传统XAI方法,GRAPHITE表现更佳,平均精度(mAP)达到0.56,受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUROC)为0.94,阈值稳健性(ThR)为0.70。在临床应用中,GRAPHITE决策曲线下面积(AUDC)最高,达到4.17e+5,为临床决策提供了可靠的辅助。
Key Takeaways
- Explainable AI (XAI)在医学病理学中对于深度学习模型的诊断应用至关重要。
- GRAPHITE是一个基于图的解释性框架,旨在提高深度学习模型在乳腺癌组织微阵列分析中的可解释性。
- GRAPHITE采用多尺度方法,在不同放大级别下提取特征,构建层次图。
- GRAPHITE使用图注意力网络(GAT)和尺度感知注意力(SAN)来捕捉尺度相关特征。
- GRAPHITE在实验中表现优于传统XAI方法,具有高的平均精度(mAP)、受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUROC)和阈值稳健性(ThR)。
- GRAPHITE在临床决策中提供了可靠的辅助,具有最高的决策曲线下面积(AUDC)。
点此查看论文截图

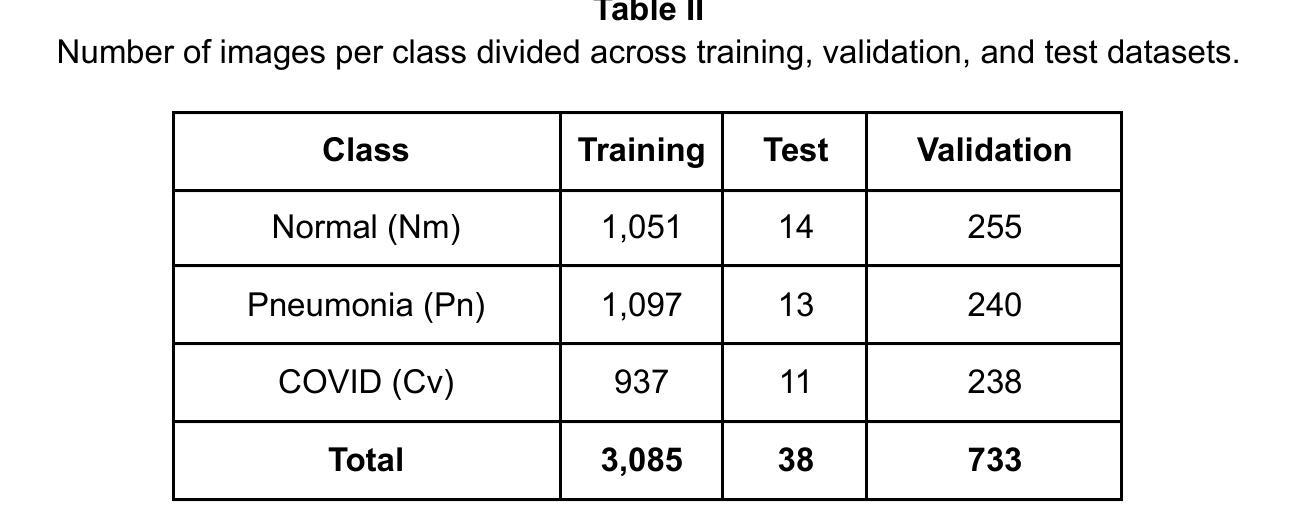
Comparison of Neural Models for X-ray Image Classification in COVID-19 Detection
Authors:Jimi Togni, Romis Attux
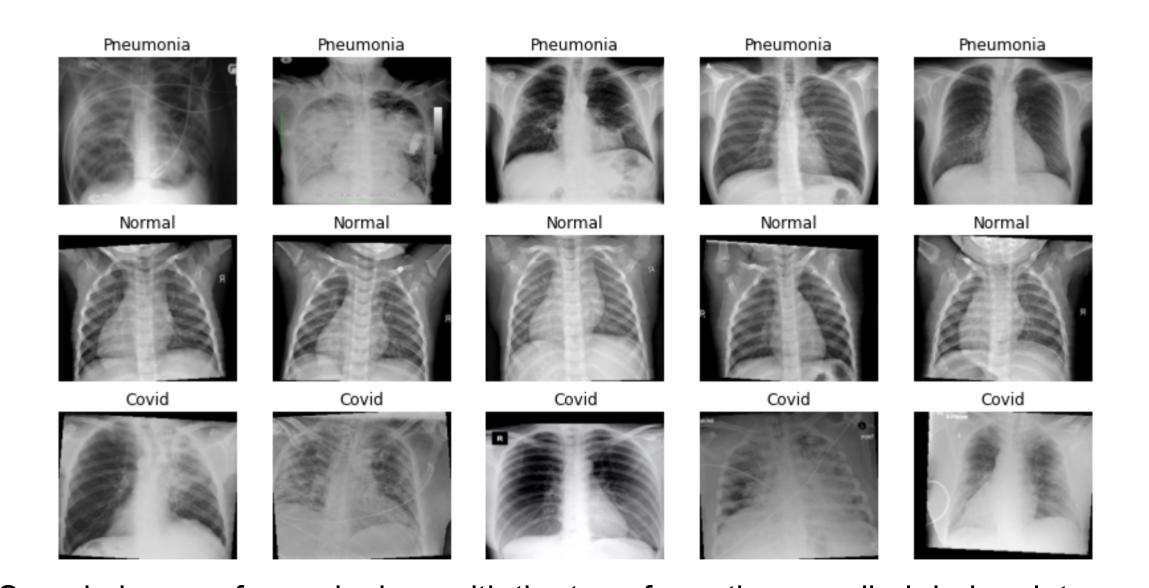
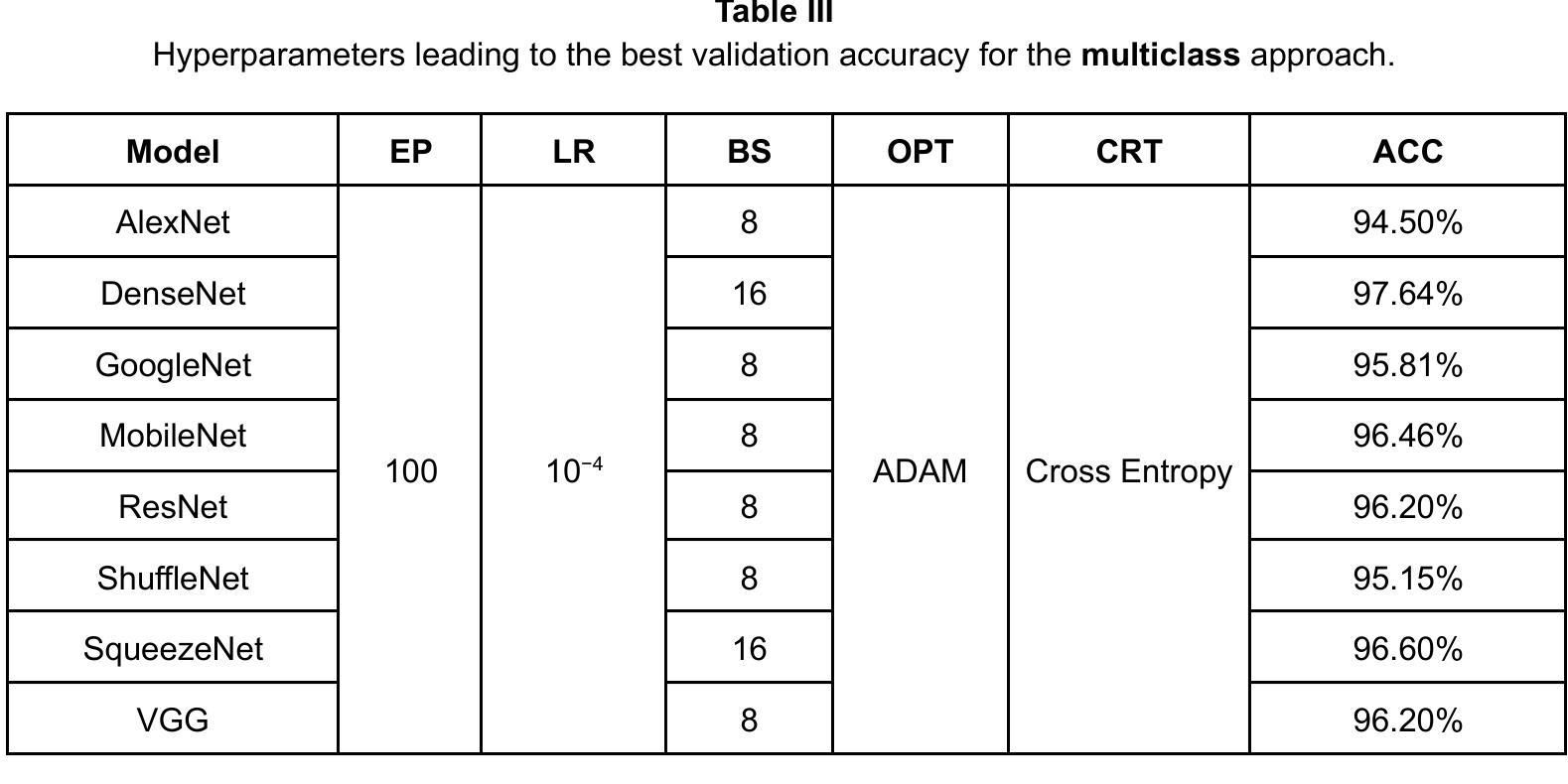
This study presents a comparative analysis of methods for detecting COVID-19 infection in radiographic images. The images, sourced from publicly available datasets, were categorized into three classes: ‘normal,’ ‘pneumonia,’ and ‘COVID.’ For the experiments, transfer learning was employed using eight pre-trained networks: SqueezeNet, DenseNet, ResNet, AlexNet, VGG, GoogleNet, ShuffleNet, and MobileNet. DenseNet achieved the highest accuracy of 97.64% using the ADAM optimization function in the multiclass approach. In the binary classification approach, the highest precision was 99.98%, obtained by the VGG, ResNet, and MobileNet networks. A comparative evaluation was also conducted using heat maps.
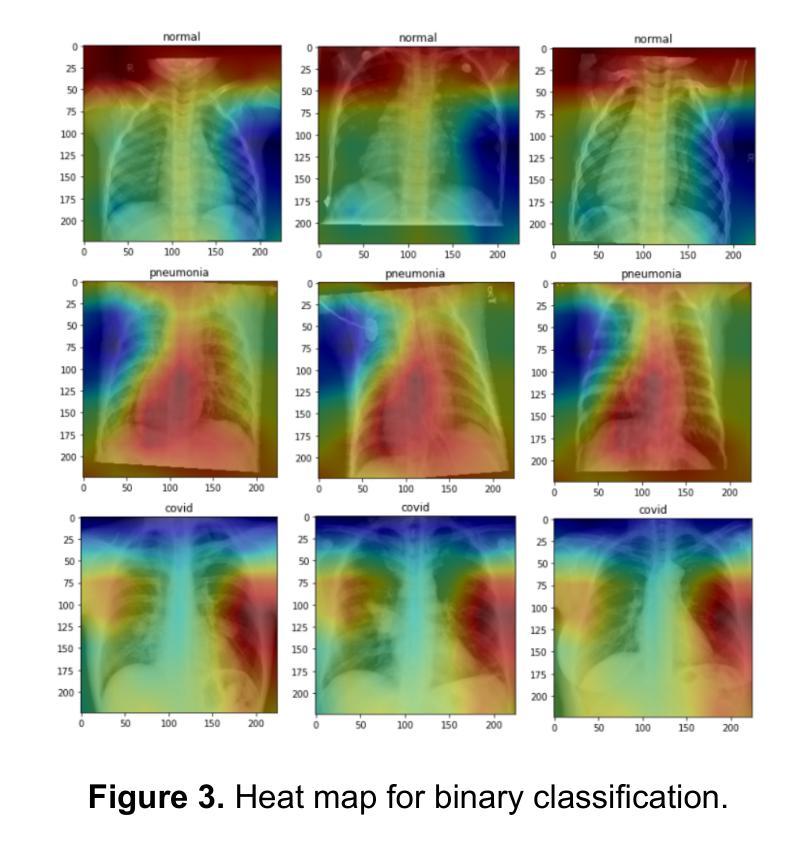
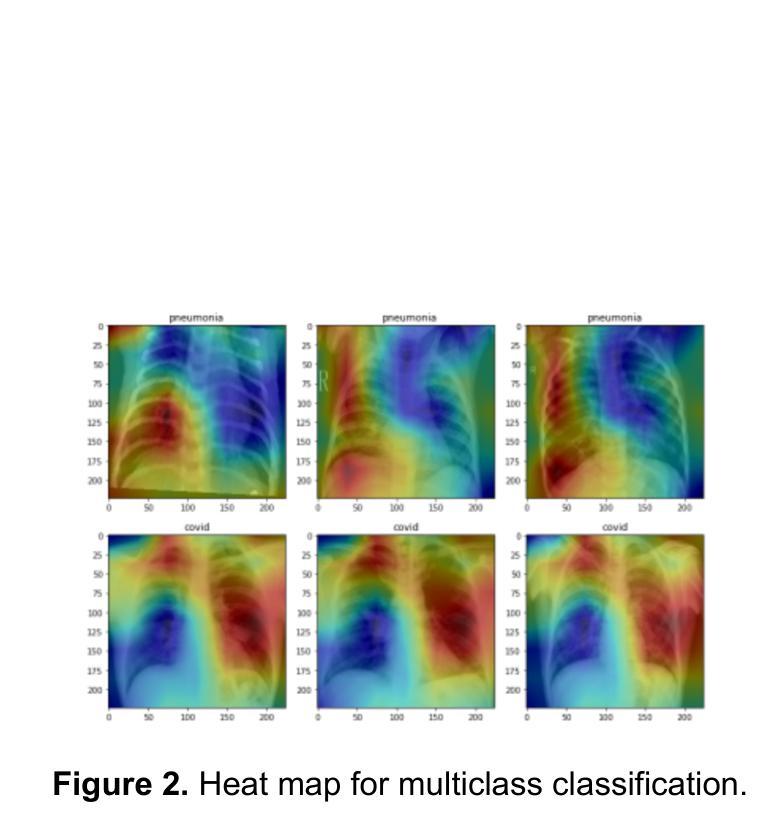
本研究对检测COVID-19感染在放射图像中的方法进行了比较分析。图像来源于公开数据集,分为三类:“正常”、“肺炎”和“COVID”。在实验中,采用迁移学习,使用8种预训练网络:SqueezeNet、DenseNet、ResNet、AlexNet、VGG、GoogleNet、ShuffleNet和MobileNet。在采用多类方法的策略中,DenseNet使用ADAM优化函数取得了最高准确率,为97.64%。在二元分类方法中,最高精度为99.98%,由VGG、ResNet和MobileNet网络获得。还利用热图进行了比较分析。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 7 tables, 5 figures. XXXIX SIMPOSIO BRASILEIRO DE TELECOMUNICACOES E PROCESSAMENTO DE SINAIS - SBrT 2021
Summary
本文比较分析了用于检测COVID-19感染的放射影像图像的方法。研究使用了从公开数据库中获取的图像,并将其分为三类:“正常”、“肺炎”和“COVID”。实验采用迁移学习,使用八种预训练网络,包括SqueezeNet、DenseNet、ResNet、AlexNet等。DenseNet在多类方法中利用ADAM优化函数达到了最高的准确性,即97.64%。在二元分类方法中,VGG、ResNet和MobileNet网络的精度最高,达到99.98%。此外,还通过热图进行了比较分析。
Key Takeaways
- 研究对检测COVID-19感染的放射影像图像方法进行了比较分析。
- 图像来源于公开数据库,分为“正常”、“肺炎”和“COVID”三类。
- 实验采用迁移学习,使用了八种预训练网络。
- DenseNet在多类方法中的准确性最高,达到97.64%。
- 在二元分类方法中,VGG、ResNet和MobileNet网络的精度最高,达到99.98%。
- 研究还通过热图进行了比较分析。
点此查看论文截图

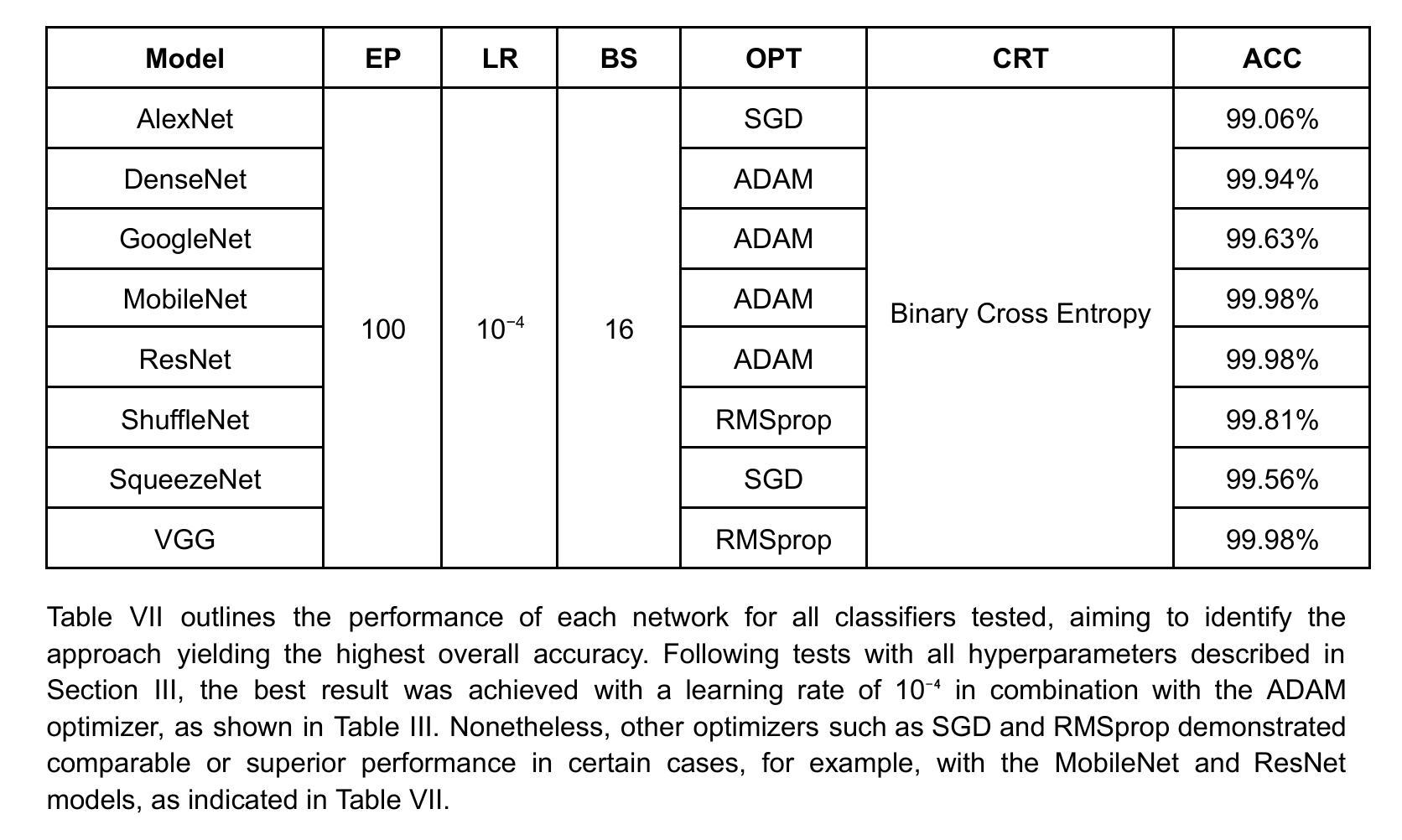
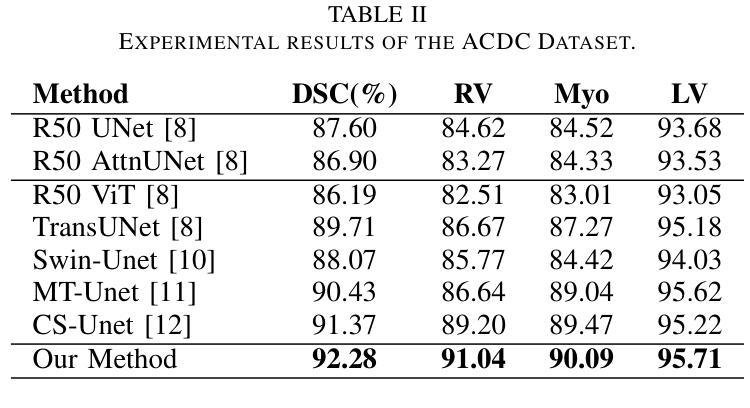
GLoG-CSUnet: Enhancing Vision Transformers with Adaptable Radiomic Features for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Niloufar Eghbali, Hassan Bagher-Ebadian, Tuka Alhanai, Mohammad M. Ghassemi
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown promise in medical image semantic segmentation (MISS) by capturing long-range correlations. However, ViTs often struggle to model local spatial information effectively, which is essential for accurately segmenting fine anatomical details, particularly when applied to small datasets without extensive pre-training. We introduce Gabor and Laplacian of Gaussian Convolutional Swin Network (GLoG-CSUnet), a novel architecture enhancing Transformer-based models by incorporating learnable radiomic features. This approach integrates dynamically adaptive Gabor and Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filters to capture texture, edge, and boundary information, enhancing the feature representation processed by the Transformer model. Our method uniquely combines the long-range dependency modeling of Transformers with the texture analysis capabilities of Gabor and LoG features. Evaluated on the Synapse multi-organ and ACDC cardiac segmentation datasets, GLoG-CSUnet demonstrates significant improvements over state-of-the-art models, achieving a 1.14% increase in Dice score for Synapse and 0.99% for ACDC, with minimal computational overhead (only 15 and 30 additional parameters, respectively). GLoG-CSUnet’s flexible design allows integration with various base models, offering a promising approach for incorporating radiomics-inspired feature extraction in Transformer architectures for medical image analysis. The code implementation is available on GitHub at: https://github.com/HAAIL/GLoG-CSUnet.
视觉Transformer(ViTs)通过捕捉长程关联在医学图像语义分割(MISS)方面显示出潜力。然而,ViT通常在建模局部空间信息方面存在困难,这对于准确分割精细的解剖细节至关重要,尤其是在未进行广泛预训练的小数据集上应用时。我们引入了Gabor和Laplacian of Gaussian卷积Swin网络(GLoG-CSUnet),这是一种新型架构,通过融入可学习的放射学特征来增强基于Transformer的模型。该方法结合了动态自适应的Gabor和Laplacian of Gaussian(LoG)滤波器,以捕捉纹理、边缘和边界信息,增强Transformer模型处理的特征表示。我们的方法独特地结合了Transformer的长程依赖建模与Gabor和LoG特征的纹理分析能力。在Synapse多器官和ACDC心脏分割数据集上进行评估,GLoG-CSUnet在最新模型的基础上实现了显著改进,Synapse的Dice得分提高了1.14%,ACDC提高了0.99%,同时计算开销极小(仅分别增加了15和30个额外参数)。GLoG-CSUnet的灵活设计允许与各种基础模型集成,为在Transformer架构中融入放射学特征提取的医学图像分析提供了有前景的方法。代码实现可在GitHub上获得:https://github.com/HAAIL/GLoG-CSUnet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于ViT的模型在处理医学图像语义分割时虽然能捕捉长远相关关系,但其在处理精细解剖结构时往往难以有效建模局部空间信息。为解决这一问题,我们提出结合了可学习放射学特征的Gabor与Laplacian of Gaussian卷积网络(GLoG-CSUnet)。该模型通过动态自适应的Gabor和LoG滤波器捕捉纹理、边缘和边界信息,增强了Transformer模型的特性表示。在Synapse多器官和ACDC心脏分割数据集上的评估显示,GLoG-CSUnet相较于最先进的模型有明显改进,Dice得分提高了1.14%和0.99%,同时计算开销较小。其灵活的设计可与其他基础模型集成,为医学图像分析中融入放射学特征提取的Transformer架构提供了有前景的方法。相关代码已在GitHub上发布。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 在医学图像语义分割(MISS)中有潜力,但难以处理局部空间信息。
- GLoG-CSUnet是一种新型架构,结合了Transformer模型和可学习放射学特征,以改善ViT的不足。
- 通过使用动态自适应的Gabor和LoG滤波器,GLoG-CSUnet能够捕捉纹理、边缘和边界信息,增强特征表示。
- 在多个数据集上的评估显示,GLoG-CSUnet相较于其他模型表现更优,Dice得分显著提高。
- GLoG-CSUnet设计灵活,易于与其他基础模型集成。
- 该方法对于在医学图像分析中融入放射学特征提取的Transformer架构具有前景。
点此查看论文截图

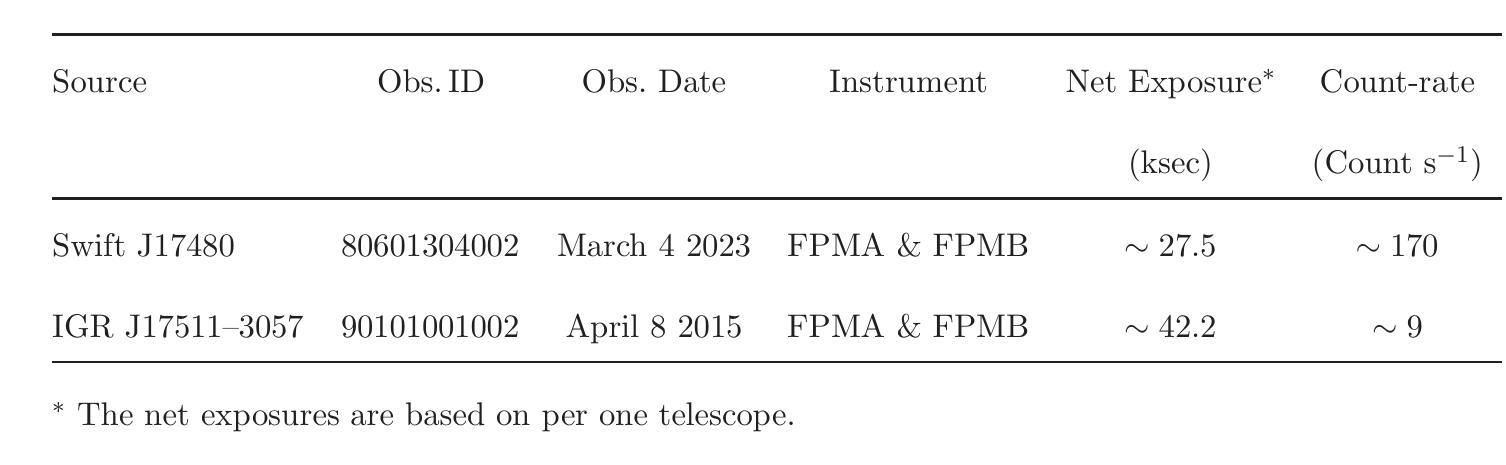
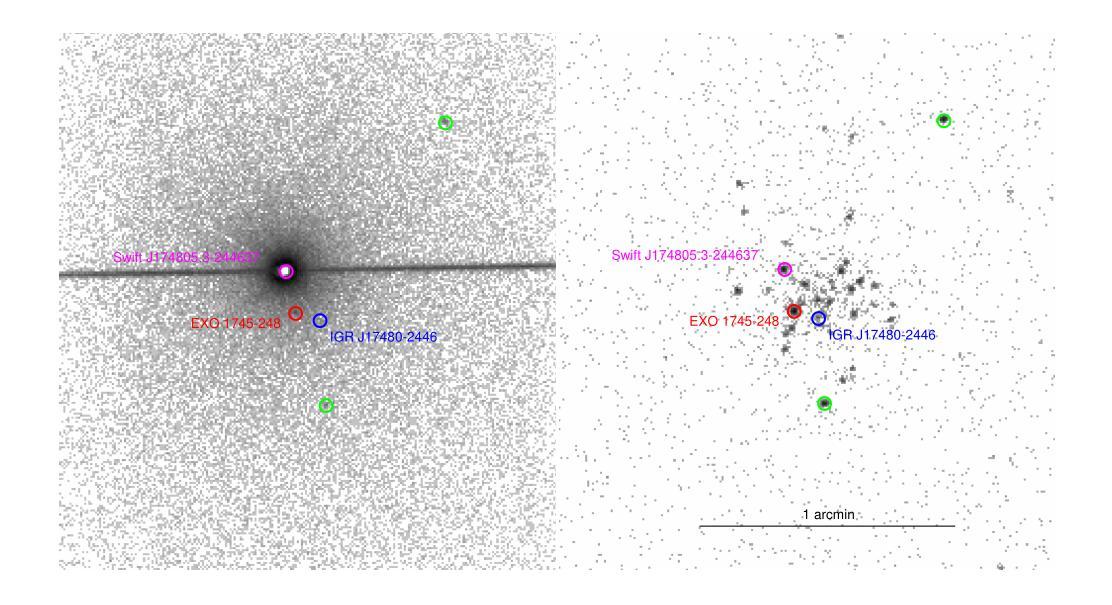
NuSTAR view of the X-ray transients Swift J174805.3-244637 and IGR J17511-3057
Authors:Aditya S. Mondal, Mahasweta Bhattacharya, Mayukh Pahari, Biplab Raychaudhuri, Rohit Ghosh, Gulab C. Dewangan
We report on the NuSTAR observations of the neutron star low-mass X-ray binary Swift J174805.3-244637 (hereafter SwiftJ17480) and the accreting millisecond X-ray pulsar IGRJ17511-3057 performed on March 4, 2023, and April 8, 2015, respectively. We describe the continuum emission of SwiftJ17480 with a combination of two soft thermal components and an additional hard X-ray emission described by a power-law. We suggest that the spectral properties of SwiftJ17480 are consistent with a soft spectral state. The source IGRJ17511-3057 exhibits a hard spectrum characterized by a Comptonized emission from the corona. The X-ray spectrum of both sources shows evidence of disc reflection. For the first time, we employ the self-consistent reflection models ({\tt relxill} and {\tt relxillNS}) to fit the reflection features in the \nustar{} spectrum. From the best-fit spectral model, we find an inner disc radius ($R_{in}$) is precisely constrained to $(1.99-2.68):R_{ISCO}$ and inclination to $30\pm 1\degree$ for SwiftJ17480. We determine an inner disc radius of $\lesssim 1.3;R_{ISCO}$ and inclination of $44\pm 3\degree$ for IGRJ17511-3057. A low inclination angle of the system is required for both sources. For the source IGRJ17511-3057, spinning at $4.1$ ms, the value of co-rotation radius ($R_{co}$) is estimated to be $\sim 42$ km ($3.6:R_{ISCO})$, consistent with the position of inner disc radius as $R_{in}\lesssim R_{co}$. We further place an upper limit on the magnetic field strength of the sources, considering the disc is truncated at the magnetospheric radius.
我们报告了NuSTAR对中子星低质量X射线双星Swift J174805.3-244637(以下简称Swift J17480)和增亮毫秒X射线脉冲星IGR J17511-3057于2023年3月4日和2015年4月8日的观测结果。我们采用两种软热成分和一个额外的幂律硬X射线发射来描述Swift J17480的连续发射。我们认为Swift J17480的光谱特性与软态光谱相符。源IGR J17511-3057表现出由日冕产生的康普顿化发射的硬光谱特征。两个源的X射线光谱都显示出盘反射的证据。我们首次采用自洽反射模型(relxill和relxillNS)来拟合NuSTAR光谱中的反射特征。根据最佳拟合光谱模型,我们发现Swift J17480的内盘半径(R_{in})精确约束在(1.99-2.68)× R_{ISCO},倾角为30±1°。我们确定IGR J17511-3057的内盘半径不大于约为(约为 \leq 转发字符所表示的意思)(发出文本“<=”) )并且其倾角为倾斜角度约为为在数据源符号)。在放射物质生成之前的给定或存在的高阶段我们发现其中核的物质已合并最终生成了脉冲星IGRJ在脉冲星IGRJ中我们发现其内盘半径小于等于协转半径并且估计协转半径约为大约半径约为并且我们进一步确定了磁场的上限,考虑了磁层半径处截断盘的情况。我们进一步确定了磁场的上限考虑了磁层截断的情况这将磁场的影响影响可能极大地降低从而使得一些效应使得光谱模型中可能出现更多的波动导致了脉压缩成为致光谱更加硬化的原因因此我们的研究对于理解这些源的物理性质以及未来的观测研究具有重要意义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 13 figures, 3 tables, Accepted for publication in Journal of High Energy Astrophysics (JHEAP)
摘要
本文对NuSTAR观察到的两个天体,即低质量X射线双星Swift J174805.3-244637(以下简称Swift~J17480)和毫秒X射线脉冲星IGR J17511-3057在2023年3月4日和2015年4月8日的观测结果进行了报告。Swift J17480的连续发射通过两个软热成分和一个额外的硬X射线发射(由幂律描述)的组合来描述。我们认为其谱特性与软谱状态一致。IGR J17511-3057表现出硬谱特性,具有来自日冕的康普顿发射。两个源的X射线光谱都显示出盘反射的证据。首次采用自洽反射模型(relxill和relxillNS)拟合反射特征,并得出了最佳的内部盘半径和内倾角的测量值。这两个源的倾斜角较小,且对于自转周期为4.1毫秒的IGR J17511-3057,其协转半径与内盘半径的估计值相符。此外,考虑了磁球半径处盘被截断的情况,对源磁场强度给出了上限。
要点归纳
一、报告了NuSTAR对两个天体Swift J17480和IGR J17511-3057的观测结果。
二、Swift J17480的连续发射包含两个软热成分和一个硬X射线发射,其谱特性与软谱状态一致。
三、IGR J17511-3057的硬谱特性表现出康普顿发射,来自其日冕。
四、两个源的X射线光谱都具有盘反射特征,首次使用自洽反射模型进行拟合。
五、Swift J17480的内盘半径精确约束在某个范围内,倾斜角为约$ 30°$ 。而对于IGR J17511-3057,其内盘半径小于协转半径,倾斜角为约$ 44°$ 。
六、两个源的倾斜角均较小。对于IGR J17511-3057,其协转半径与内盘半径的估计值相吻合。
点此查看论文截图

A Practical Guide to Transcranial Ultrasonic Stimulation from the IFCN-endorsed ITRUSST Consortium
Authors:Keith R Murphy, Tulika Nandi, Benjamin Kop, Takahiro Osada, W Apoutou N’Djin, Maximilian Lueckel, Kevin A Caulfield, Anton Fomenko, Hartwig R Siebner, Yoshikazu Ugawa, Lennart Verhagen, Sven Bestmann, Eleanor Martin, Kim Butts Pauly, Elsa Fouragnan, Til Ole Bergmann
Low-intensity Transcranial Ultrasonic Stimulation (TUS) is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique enabling cortical and deep brain targeting with unprecedented spatial accuracy. Given the high rate of adoption by new users with varying levels of expertise and interdisciplinary backgrounds, practical guidelines are needed to ensure state-of-the-art TUS application and reproducible outcomes. Therefore, the International Transcranial Ultrasonic Stimulation Safety and Standards (ITRUSST) consortium has formed a subcommittee, endorsed by the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology (IFCN), to develop recommendations for best practice in TUS applications in humans. The practical guide presented here provides a brief introduction into ultrasound physics and sonication parameters. It explains the requirements of TUS lab equipment and transducer selection and discusses experimental design and procedures alongside potential confounds and control conditions. Finally, the guide elaborates on essential steps of application planning for stimulation safety and efficacy, as well as considerations when combining TUS with neuroimaging, electrophysiology, or other brain stimulation techniques. We hope that this practical guide to TUS will assist both novice and experienced users in planning and conducting high-quality studies and provide a solid foundation for further advancements in this promising field.
低强度经颅超声刺激(TUS)是一种非侵入性的脑刺激技术,能够以前所未有的空间精度实现大脑皮质和深层的定位。考虑到不同专业和跨学科背景的新用户采用率较高,为确保最先进的TUS应用和可重复的结果,需要实用指南。因此,国际经颅超声刺激安全与标准(ITRUSST)联盟在国际临床神经生理学联合会(IFCN)的支持下,成立了一个专门委员会,旨在为人类TUS应用提供最佳实践建议。本文提供的实用指南简要介绍了超声物理学和超声参数。它解释了TUS实验室设备和换能器的要求,并讨论了实验设计和程序以及潜在的干扰和控制条件。最后,本指南详细阐述了刺激安全性和有效性的应用规划的必要步骤,以及将TUS与神经成像、电生理学或其他脑刺激技术相结合时的注意事项。我们希望这本TUS实用指南能帮助初学者和经验丰富的用户进行高质量的研究规划,并为这一充满希望领域的进一步发展提供坚实的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 67 pages, 23 Figures, 2 Tables, 5 Supplementary Tables
Summary
本文主要介绍了跨颅超声刺激(TUS)的实践指南,包括超声物理学和声音参数、实验室设备和换能器选择的要求,以及实验设计和程序、潜在干扰和控制条件,以及应用规划的刺激安全和功效的必要步骤。该指南旨在为新手和经验丰富的用户提供帮助,规划并进行高质量研究,并为这个充满希望的领域的进一步发展提供坚实的基础。
希望通过这份指南能为新手和经验丰富的用户提供帮助,共同推动跨颅超声刺激领域的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 低强度跨颅超声刺激(TUS)是一种非侵入性的脑刺激技术,可实现前所未有的空间准确性的大脑皮质和深层大脑定位。
- 国际跨颅超声刺激安全与标准联盟(ITRUSST)为在人类应用TUS开发最佳实践建议设立了专门委员会。
- 该指南简要介绍了超声物理学和声音参数,解释了TUS实验室设备和换能器的选择要求。
- 讨论了实验设计、潜在干扰和控制条件以及应用规划的刺激安全和功效的关键步骤。
- 该指南旨在为跨颅超声刺激领域的新手和经验丰富的用户提供帮助,进行高质量的研究。
- 该指南为跨颅超声刺激的进一步发展提供了坚实的基础。
点此查看论文截图


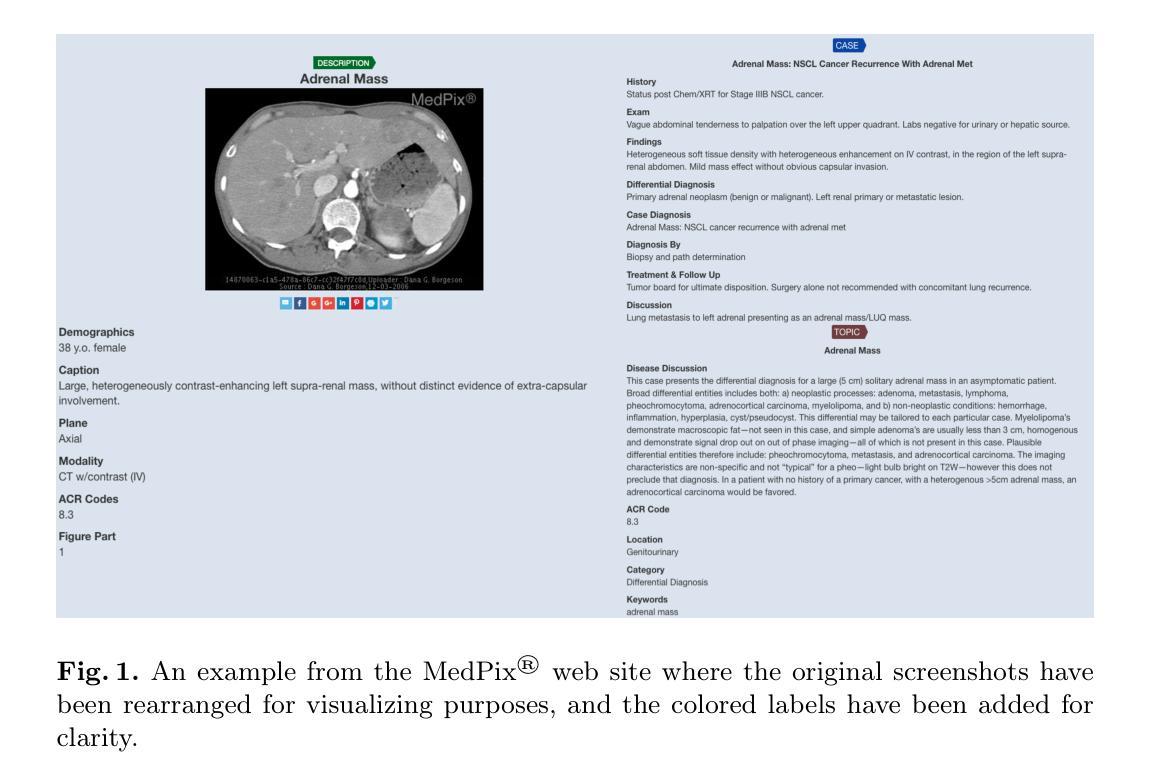
MedPix 2.0: A Comprehensive Multimodal Biomedical Data set for Advanced AI Applications with Retrieval Augmented Generation and Knowledge Graphs
Authors:Irene Siragusa, Salvatore Contino, Massimo La Ciura, Rosario Alicata, Roberto Pirrone
The increasing interest in developing Artificial Intelligence applications in the medical domain, suffers from the lack of high-quality data set, mainly due to privacy-related issues. In addition, the recent increase in large multimodal models (LMM) leads to the need for multimodal medical data sets, where clinical reports and findings are attached to the corresponding CT or MRI scans. This paper illustrates the entire workflow for building the MedPix 2.0 data set. Starting with the well-known multimodal data set MedPix\textsuperscript{\textregistered}, mainly used by physicians, nurses, and healthcare students for Continuing Medical Education purposes, a semi-automatic pipeline was developed to extract visual and textual data followed by a manual curing procedure in which noisy samples were removed, thus creating a MongoDB database. Along with the data set, we developed a GUI aimed at navigating efficiently the MongoDB instance and obtaining the raw data that can be easily used for training and/or fine-tuning LMMs. To enforce this point, in this work, we first recall DR-Minerva, a RAG-based LMM trained using MedPix 2.0. DR-Minerva predicts the body part and the modality used to scan its input image. We also propose the extension of DR-Minerva with a Knowledge Graph that uses Llama 3.1 Instruct 8B, and leverages MedPix 2.0. The resulting architecture can be queried in a end-to-end manner, as a medical decision support system. MedPix 2.0 is available on GitHub. \url{https://github.com/CHILab1/MedPix-2.0}
随着医疗领域对开发人工智能应用的日益关注,由于缺乏高质量的数据集,尤其是隐私相关问题,造成了很大的困扰。此外,最近大型多模态模型(LMM)的增加导致了对多模态医疗数据集的需求增加,这些医疗数据集中附带了临床报告和检查结果以及与CT或MRI扫描结果相对应的图像。本文阐述了构建MedPix 2.0数据集的整个工作流程。以著名的多模态数据集MedPix®开始,该数据集主要用于医生、护士和医疗保健学生继续医学教育的目的,我们开发了一个半自动管道来提取视觉和文本数据,随后进行手动清理程序,去除噪声样本,从而创建了MongoDB数据库。除了数据集之外,我们还开发了一个GUI,旨在高效浏览MongoDB实例并获得可用于训练和/或微调LMM的原始数据。为了强化这一点,在这项工作中,我们首先回顾了DR-Minerva,这是一种基于RAG的LMM,使用MedPix 2.0进行训练。DR-Minerva可以预测身体部位以及用于扫描其输入图像的模态。我们还提出了DR-Minerva的扩展版本,该版本使用Llama 3.1 Instruct 8B并借助MedPix 2.0构建知识图谱。最终架构可以以端到端的方式进行查询,作为医疗决策支持系统。MedPix 2.0已在GitHub上提供。\url{https://github.com/CHILab1/MedPix-2.0}
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
构建MedPix 2.0数据集的工作流程涉及从已知的多模态数据集MedPix®中提取视觉和文本数据,通过半自动管道进行处理,并经过手动净化以创建MongoDB数据库。此外,还开发了用于高效浏览MongoDB实例的GUI,便于获取可用于训练和/或微调大型多模态模型(LMM)的原始数据。本工作回顾了使用MedPix 2.0训练的基于RAG的LMM——DR-Minerva,并提议将其扩展为知识图谱,利用Llama 3.1 Instruct 8B并依托MedPix 2.0。MedPix 2.0数据集已在GitHub上发布。
Key Takeaways
- 缺乏高质量数据集是人工智能在医疗领域应用面临的挑战之一,主要原因是隐私相关问题。
- 大型多模态模型(LMM)的需要增长推动了多模态医疗数据集的需求,临床报告和发现需要与CT或MRI扫描相对应。
- MedPix 2.0数据集构建于现有的MedPix®数据集之上,经过半自动管道处理并手动净化数据,存储在MongoDB数据库中。
- 提供了一个图形用户界面(GUI),以高效浏览MongoDB实例并获取可用于训练和/或微调LMM的原始数据。
- DR-Minerva是一个基于RAG的LMM,使用MedPix 2.0数据集进行训练,能够预测图像的身体部位和扫描方式。
- DR-Minerva通过与知识图谱的结合扩展,利用Llama 3.1 Instruct 8B并依赖MedPix 2.0作为其核心资源。
点此查看论文截图

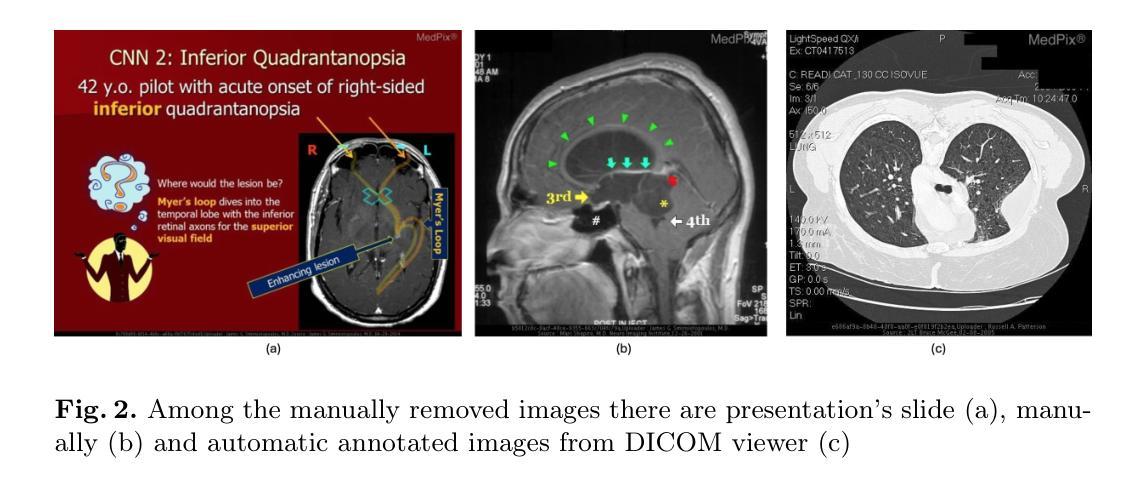
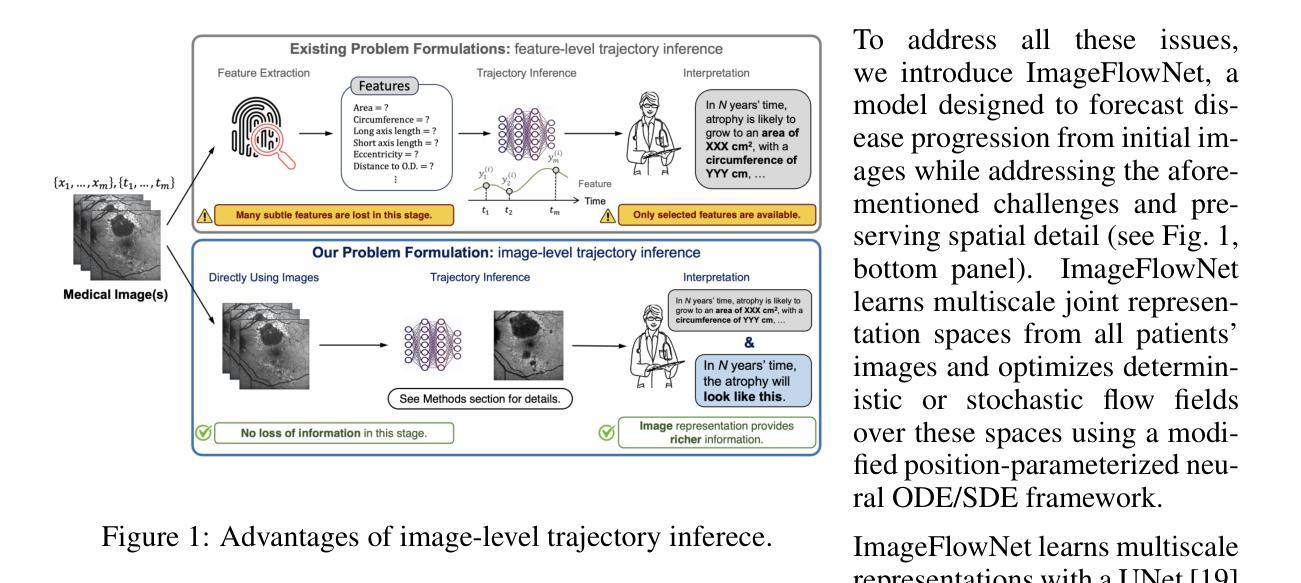
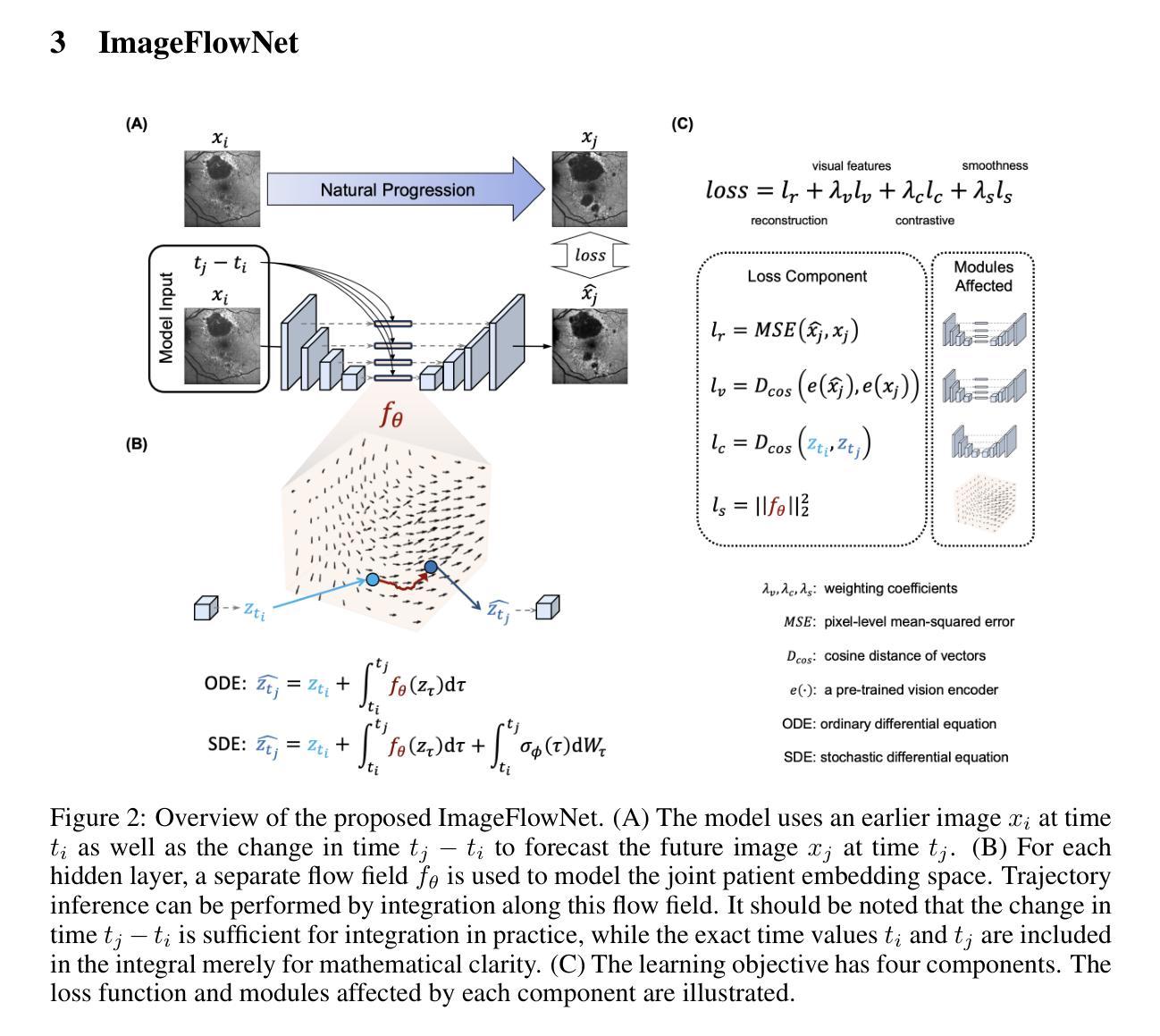
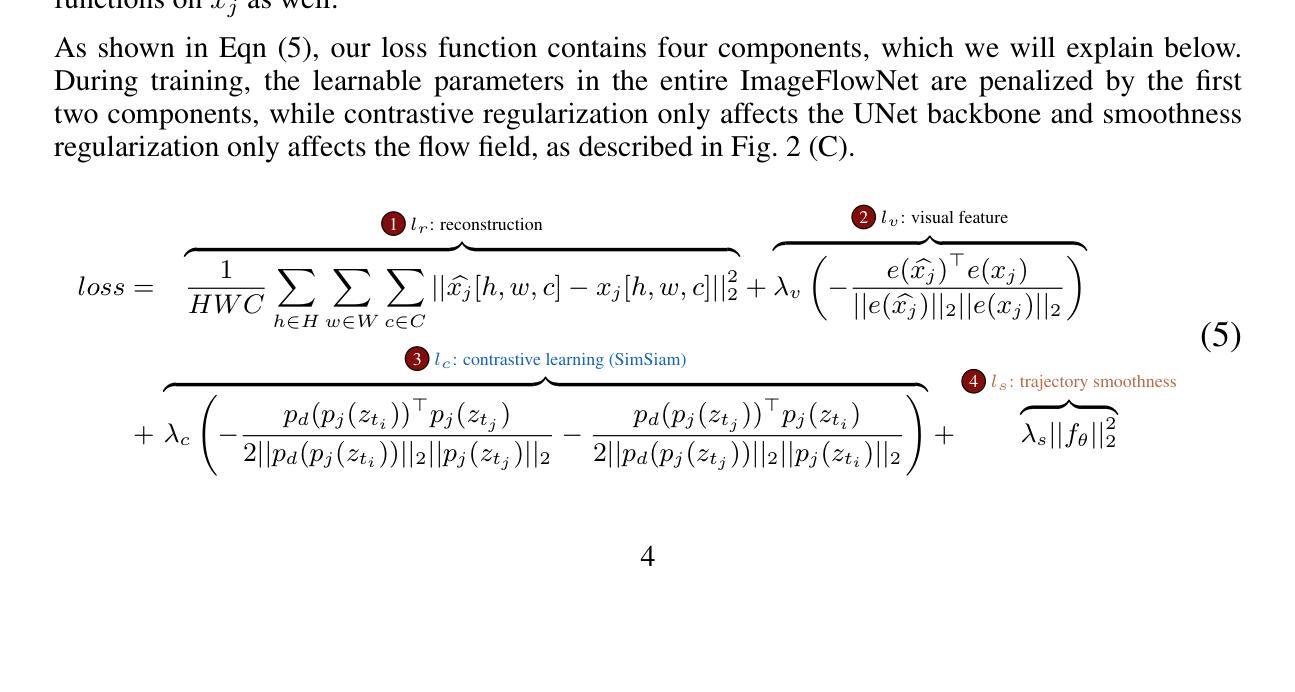
ImageFlowNet: Forecasting Multiscale Image-Level Trajectories of Disease Progression with Irregularly-Sampled Longitudinal Medical Images
Authors:Chen Liu, Ke Xu, Liangbo L. Shen, Guillaume Huguet, Zilong Wang, Alexander Tong, Danilo Bzdok, Jay Stewart, Jay C. Wang, Lucian V. Del Priore, Smita Krishnaswamy
Advances in medical imaging technologies have enabled the collection of longitudinal images, which involve repeated scanning of the same patients over time, to monitor disease progression. However, predictive modeling of such data remains challenging due to high dimensionality, irregular sampling, and data sparsity. To address these issues, we propose ImageFlowNet, a novel model designed to forecast disease trajectories from initial images while preserving spatial details. ImageFlowNet first learns multiscale joint representation spaces across patients and time points, then optimizes deterministic or stochastic flow fields within these spaces using a position-parameterized neural ODE/SDE framework. The model leverages a UNet architecture to create robust multiscale representations and mitigates data scarcity by combining knowledge from all patients. We provide theoretical insights that support our formulation of ODEs, and motivate our regularizations involving high-level visual features, latent space organization, and trajectory smoothness. We validate ImageFlowNet on three longitudinal medical image datasets depicting progression in geographic atrophy, multiple sclerosis, and glioblastoma, demonstrating its ability to effectively forecast disease progression and outperform existing methods. Our contributions include the development of ImageFlowNet, its theoretical underpinnings, and empirical validation on real-world datasets. The official implementation is available at https://github.com/KrishnaswamyLab/ImageFlowNet.
医学成像技术的进展使得能够收集纵向图像,这些图像涉及对同一患者的重复扫描,以监测疾病的进展。然而,由于数据的高维性、不规则采样和数据稀疏性,此类数据的预测建模仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了ImageFlowNet这一新型模型,旨在从初始图像预测疾病轨迹,同时保留空间细节。ImageFlowNet首先学习患者和时间点之间的多尺度联合表示空间,然后利用位置参数化的神经ODE/SDE框架优化这些空间内的确定性或随机流场。该模型利用UNet架构创建稳健的多尺度表示,并通过结合所有患者的知识来缓解数据稀缺问题。我们提供了支持我们制定ODE的理论见解,并激发了我们涉及高级视觉特征、潜在空间组织和轨迹平滑性的正则化。我们在三个描绘地理萎缩、多发性硬化症和胶质母细胞瘤进展的纵向医学图像数据集上验证了ImageFlowNet,证明了其有效预测疾病进展并优于现有方法的能力。我们的贡献包括ImageFlowNet的开发、其理论基础以及在真实数据集上的实证验证。官方实现可访问于:https://github.com/KrishnaswamyLab/ImageFlowNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
医疗影像技术的进展使得纵向影像数据的收集成为可能,为疾病进展监测提供了有力支持。针对此类数据预测模型面临的高维性、不规则采样和数据稀疏等问题,提出了ImageFlowNet模型。该模型通过联合学习跨患者和时间点的多尺度表示空间,并利用神经常微分方程/随机微分方程框架优化确定性或随机流场,以从初始图像预测疾病轨迹并保留空间细节。在三个描绘地理萎缩、多发性硬化症和胶质母细胞瘤进展的纵向医学图像数据集上验证了ImageFlowNet的有效性,展示其优于现有方法的预测能力。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗成像技术现在能够收集纵向图像数据,用于监测疾病进展。
- ImageFlowNet模型被提出来解决高维性、不规则采样和数据稀疏等预测挑战。
- ImageFlowNet通过联合学习跨患者和时间点的多尺度表示空间进行预测。
- 使用神经常微分方程/随机微分方程框架优化确定性或随机流场。
- ImageFlowNet利用UNet架构创建稳健的多尺度表示,并通过结合所有患者的知识来缓解数据稀缺问题。
- 在三个不同的纵向医学图像数据集上验证了ImageFlowNet的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

AnoFPDM: Anomaly Segmentation with Forward Process of Diffusion Models for Brain MRI
Authors:Yiming Che, Fazle Rafsani, Jay Shah, Md Mahfuzur Rahman Siddiquee, Teresa Wu
Weakly-supervised diffusion models (DMs) in anomaly segmentation, leveraging image-level labels, have attracted significant attention for their superior performance compared to unsupervised methods. It eliminates the need for pixel-level labels in training, offering a more cost-effective alternative to supervised methods. However, existing methods are not fully weakly-supervised because they heavily rely on costly pixel-level labels for hyperparameter tuning in inference. To tackle this challenge, we introduce Anomaly Segmentation with Forward Process of Diffusion Models (AnoFPDM), a fully weakly-supervised framework that operates without the need of pixel-level labels. Leveraging the unguided forward process as a reference for the guided forward process, we select hyperparameters such as the noise scale, the threshold for segmentation and the guidance strength. We aggregate anomaly maps from guided forward process, enhancing the signal strength of anomalous regions. Remarkably, our proposed method outperforms recent state-of-the-art weakly-supervised approaches, even without utilizing pixel-level labels.
弱监督扩散模型(DMs)在异常分割中的应用已经引起了广泛关注,因为它利用图像级别的标签,其性能优于无监督方法。它消除了对训练过程中的像素级别标签的需求,为监督方法提供了更具成本效益的替代方案。然而,现有方法并不是完全的弱监督,因为它们严重依赖于推理过程中的超参数调整所需的昂贵像素级标签。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了基于扩散模型前向过程的异常分割(AnoFPDM),这是一个完全弱监督的框架,无需像素级标签即可运行。我们以非引导前向过程作为引导前向过程的参考,选择超参数,如噪声规模、分割阈值和引导强度。我们从引导前向过程中聚合异常图,增强异常区域的信号强度。值得注意的是,我们提出的方法甚至在不需要像素级标签的情况下,也优于最新的弱监督前沿方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF v4: added appendices and fixed some typos
Summary
本文介绍了弱监督扩散模型(DMs)在异常分割中的应用,其利用图像级标签相较于无监督方法具有优越的性能。该模型不需要像素级标签进行训练,相较于监督学习方法成本更低。但现有方法并未实现完全的弱监督,因为它们依赖昂贵的像素级标签进行超参数调整。为解决此问题,我们提出了Anomaly Segmentation with Forward Process of Diffusion Models (AnoFPDM)这一完全弱监督的框架,无需像素级标签即可操作。我们利用无导向的前向过程作为有导向前向过程的参考,选择噪声规模、分割阈值和指导强度等超参数,并聚集异常映射,增强异常区域的信号强度。所提方法在不使用像素级标签的情况下,性能优于最新的弱监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督扩散模型在异常分割中应用广泛,因其仅依赖图像级标签而表现优越。
- 现有方法虽宣称弱监督,但仍依赖像素级标签进行超参数调整,成本较高。
- 提出了一种全新的弱监督框架——Anomaly Segmentation with Forward Process of Diffusion Models (AnoFPDM)。
- AnoFPDM利用无导向前向过程作为参考,选择超参数,完全无需像素级标签。
- 通过聚集异常映射,增强了异常区域的信号强度。
- 所提方法性能优于现有弱监督方法。
点此查看论文截图

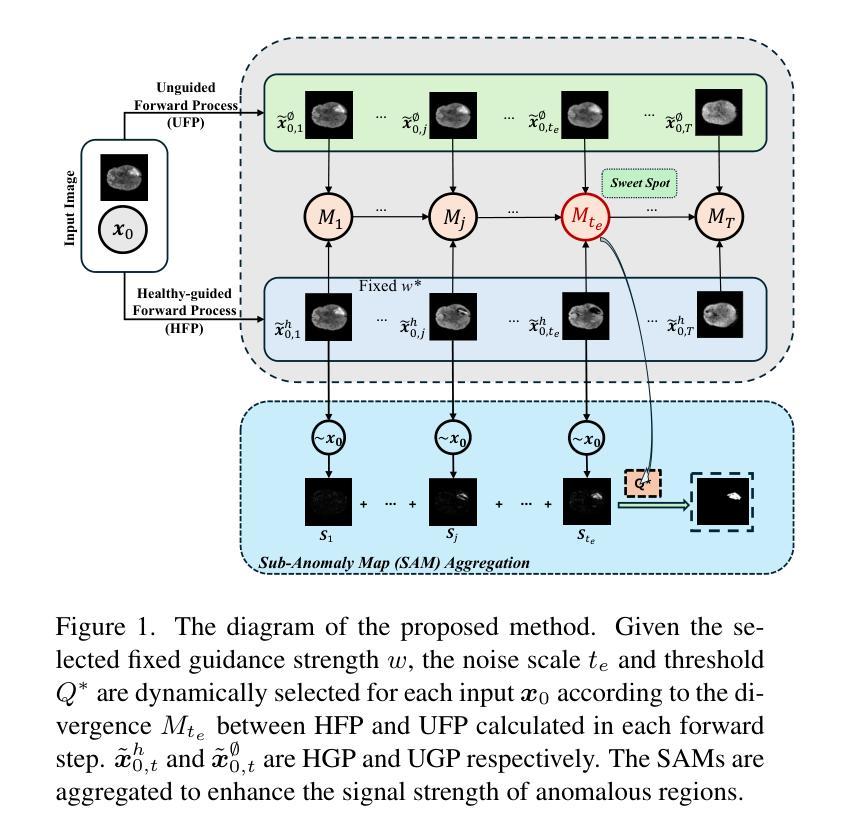
Deep Unfolding Network with Spatial Alignment for multi-modal MRI reconstruction
Authors:Hao Zhang, Qi Wang, Jun Shi, Shihui Ying, Zhijie Wen
Multi-modal Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) offers complementary diagnostic information, but some modalities are limited by the long scanning time. To accelerate the whole acquisition process, MRI reconstruction of one modality from highly undersampled k-space data with another fully-sampled reference modality is an efficient solution. However, the misalignment between modalities, which is common in clinic practice, can negatively affect reconstruction quality. Existing deep learning-based methods that account for inter-modality misalignment perform better, but still share two main common limitations: (1) The spatial alignment task is not adaptively integrated with the reconstruction process, resulting in insufficient complementarity between the two tasks; (2) the entire framework has weak interpretability. In this paper, we construct a novel Deep Unfolding Network with Spatial Alignment, termed DUN-SA, to appropriately embed the spatial alignment task into the reconstruction process. Concretely, we derive a novel joint alignment-reconstruction model with a specially designed cross-modal spatial alignment term. By relaxing the model into cross-modal spatial alignment and multi-modal reconstruction tasks, we propose an effective algorithm to solve this model alternatively. Then, we unfold the iterative steps of the proposed algorithm and design corresponding network modules to build DUN-SA with interpretability. Through end-to-end training, we effectively compensate for spatial misalignment using only reconstruction loss, and utilize the progressively aligned reference modality to provide inter-modality prior to improve the reconstruction of the target modality. Comprehensive experiments on three real datasets demonstrate that our method exhibits superior reconstruction performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
多模态磁共振成像(MRI)提供了互补的诊断信息,但某些模态受到长时间扫描的限制。为了加速整个采集过程,从高度欠采样的k空间数据中重建一种模态,并使用另一种完全采样的参考模态作为参考,是一种有效的解决方案。然而,临床实践中常见的模态间的不对准会直接影响重建质量。虽然现有的基于深度学习的方法考虑了跨模态的不对准问题,并表现更好,但它们仍然具有两个主要的常见局限性:(1)空间对准任务没有与重建过程自适应地集成,导致两个任务之间的互补性不足;(2)整个框架的可解释性较弱。在本文中,我们构建了一种新型的具有空间对准功能的深度展开网络,称为DUN-SA,以适当地将空间对准任务嵌入到重建过程中。具体来说,我们推导出了一个新型的联合对准-重建模型,并特别设计了一个跨模态空间对准项。通过将模型放松为跨模态空间对准和多模态重建任务,我们提出了一种有效的交替求解算法。然后,我们展开了所提出算法的迭代步骤,并设计了相应的网络模块来构建具有可解释性的DUN-SA。通过端到端的训练,我们仅使用重建损失来有效地补偿空间不对准,并利用逐步对齐的参考模态为目标模态的重建提供跨模态先验。在三个真实数据集上的综合实验表明,我们的方法相较于最先进的方法展现出更高的重建性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于深度学习的多模态MRI重建方法,通过构建名为DUN-SA的展开网络,将空间对齐任务适当地嵌入到重建过程中。通过设计跨模态空间对齐项,形成联合对齐重建模型。通过交替求解模型,实现有效算法。最终,利用重建损失补偿空间失配,利用逐步对齐的参考模态提供跨模态先验,提高目标模态的重建效果。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态MRI能够提供互补的诊断信息,但扫描时间过长是其限制之一。
- 从高度欠采样的k空间数据中重建一种模态,同时使用另一种完全采样的参考模态作为参考,可以加速整个采集过程。
- 跨模态空间失配是影响重建质量的一个重要问题。
- 现有基于深度学习的解决跨模态空间失配的方法存在两个主要局限性:空间对齐任务与重建过程缺乏适应性融合,以及整个框架的可解释性较弱。
- 本文提出了一种新型Deep Unfolding Network with Spatial Alignment(DUN-SA),将空间对齐任务适当地嵌入到重建过程中。
- 通过设计跨模态空间对齐项,形成了联合对齐-重建模型,并通过有效算法交替求解该模型。
点此查看论文截图

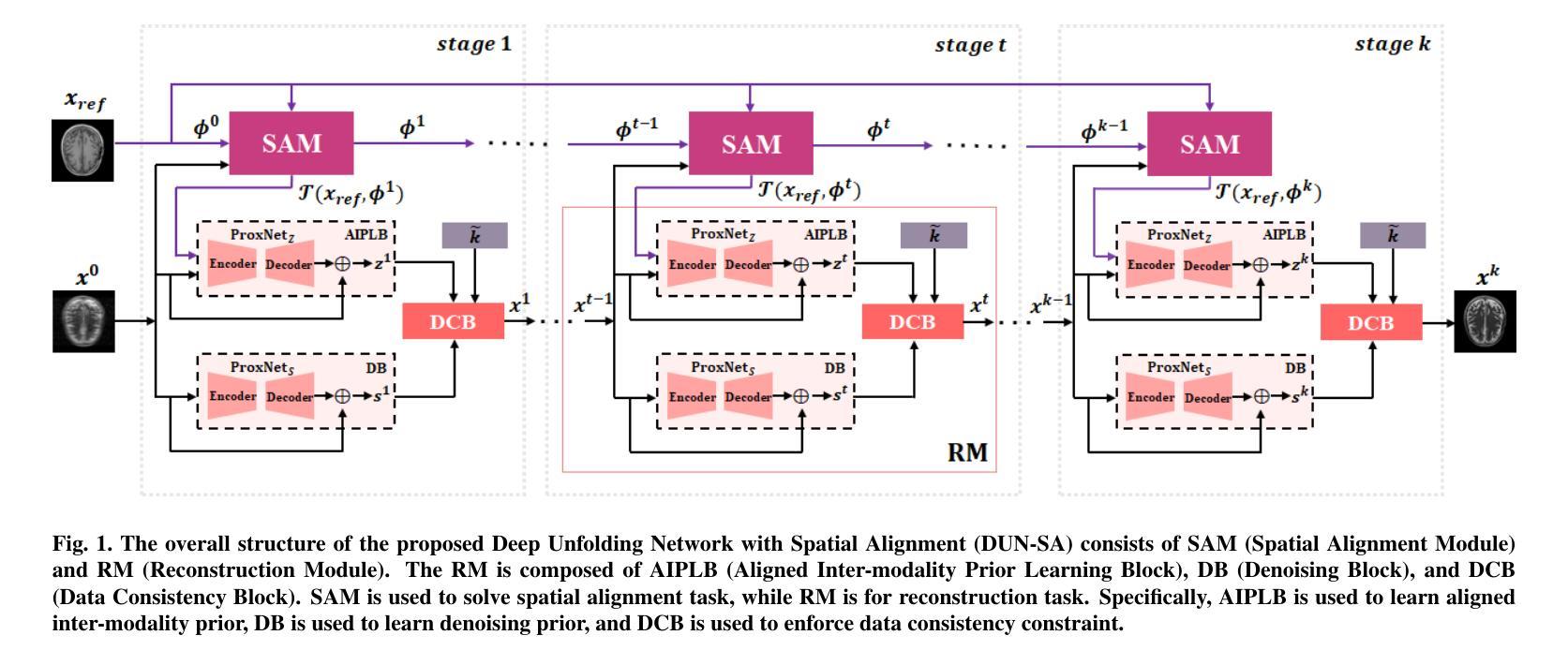
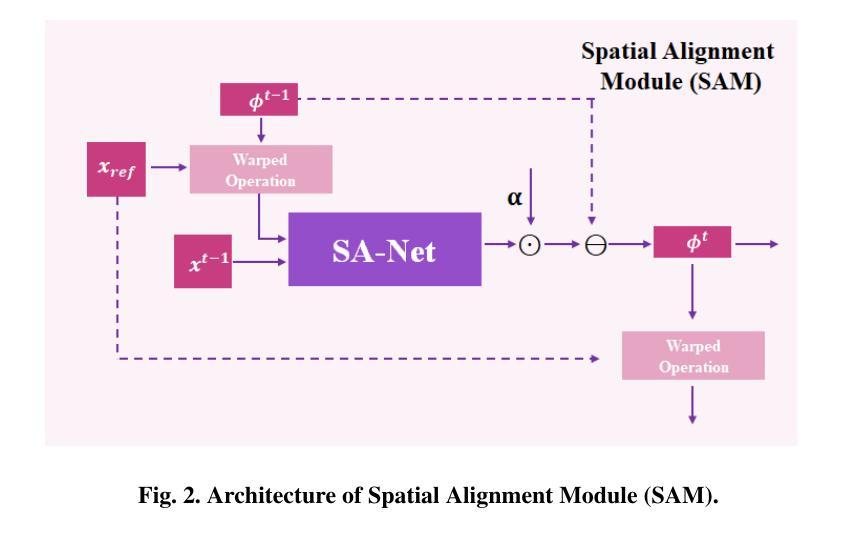
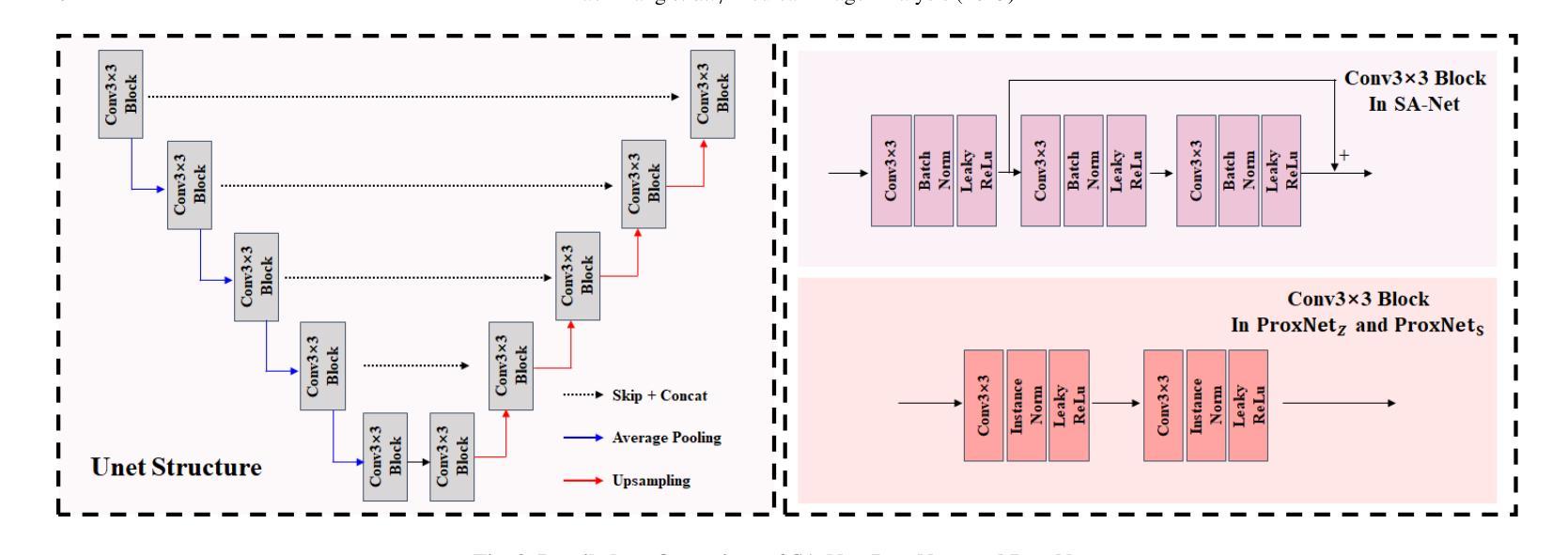
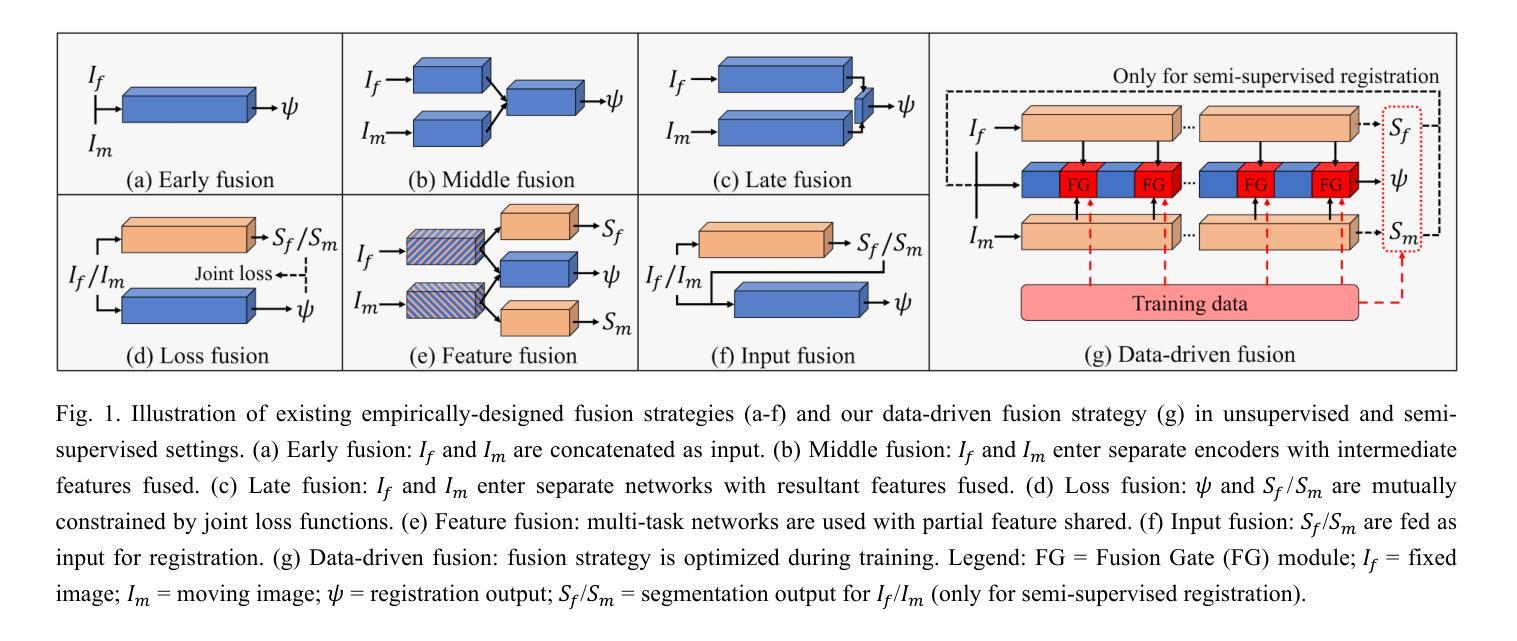
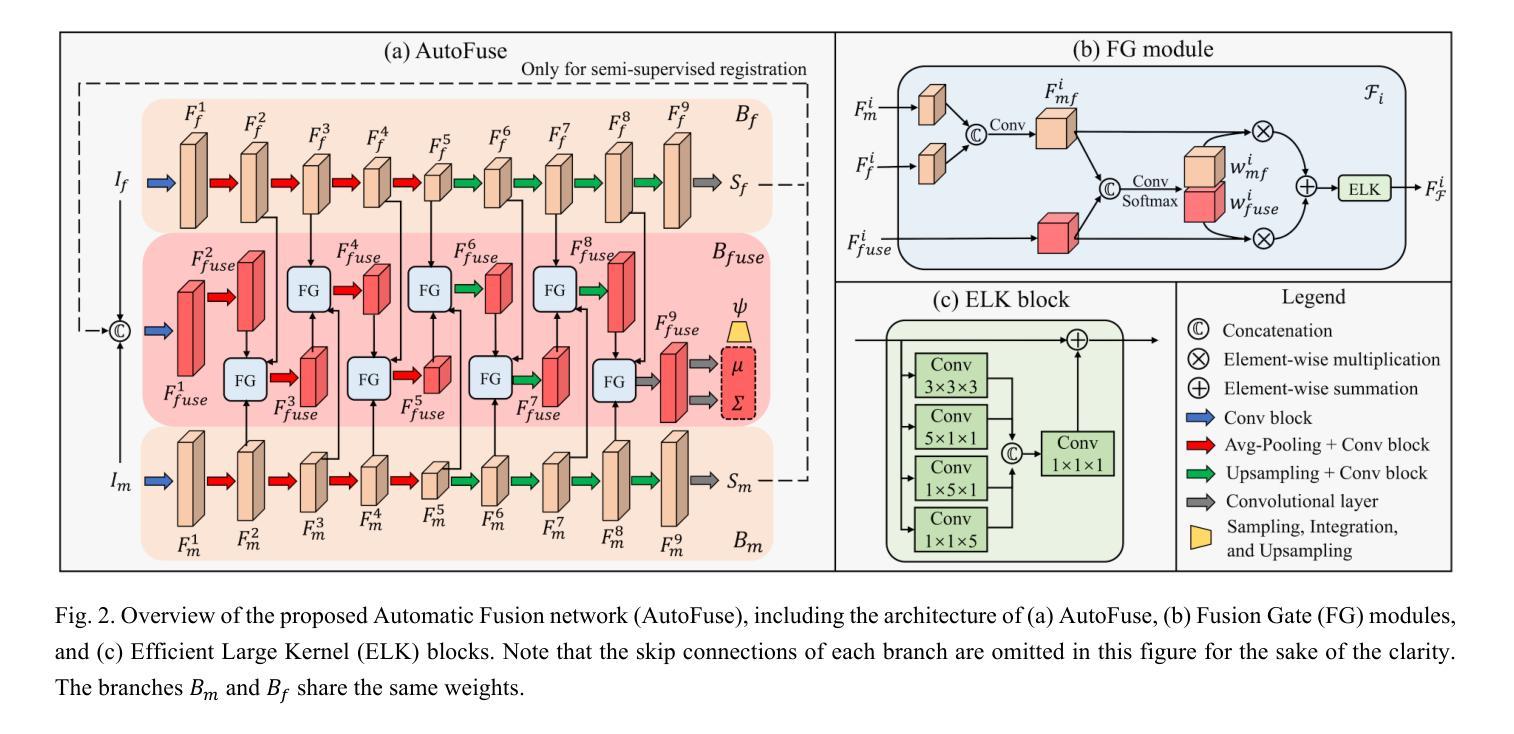
AutoFuse: Automatic Fusion Networks for Deformable Medical Image Registration
Authors:Mingyuan Meng, Michael Fulham, Dagan Feng, Lei Bi, Jinman Kim
Deformable image registration aims to find a dense non-linear spatial correspondence between a pair of images, which is a crucial step for many medical tasks such as tumor growth monitoring and population analysis. Recently, Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have been widely recognized for their ability to perform fast end-to-end registration. However, DNN-based registration needs to explore the spatial information of each image and fuse this information to characterize spatial correspondence. This raises an essential question: what is the optimal fusion strategy to characterize spatial correspondence? Existing fusion strategies (e.g., early fusion, late fusion) were empirically designed to fuse information by manually defined prior knowledge, which inevitably constrains the registration performance within the limits of empirical designs. In this study, we depart from existing empirically-designed fusion strategies and develop a data-driven fusion strategy for deformable image registration. To achieve this, we propose an Automatic Fusion network (AutoFuse) that provides flexibility to fuse information at many potential locations within the network. A Fusion Gate (FG) module is also proposed to control how to fuse information at each potential network location based on training data. Our AutoFuse can automatically optimize its fusion strategy during training and can be generalizable to both unsupervised registration (without any labels) and semi-supervised registration (with weak labels provided for partial training data). Extensive experiments on two well-benchmarked medical registration tasks (inter- and intra-patient registration) with eight public datasets show that our AutoFuse outperforms state-of-the-art unsupervised and semi-supervised registration methods.
可变图像配准旨在寻找一对图像之间的密集非线性空间对应关系,这是许多医学任务(如肿瘤生长监测和人口分析)中的关键步骤。最近,深度神经网络(DNN)因其能够执行快速端到端配准的能力而得到广泛认可。然而,基于DNN的配准需要探索每个图像的空间信息并将这些信息融合以表征空间对应关系。这引发了一个关键问题:表征空间对应关系的最佳融合策略是什么?现有的融合策略(例如,早期融合、后期融合)是经验设计,通过手动定义的先验知识来融合信息,这不可避免地使配准性能受到经验设计的限制。在本研究中,我们摒弃了现有的经验设计融合策略,并开发了一种用于可变图像配准的数据驱动融合策略。为实现这一目标,我们提出了一种自动融合网络(AutoFuse),该网络可以在网络的许多潜在位置灵活地融合信息。还提出了一种融合门(FG)模块,用于根据训练数据控制每个潜在网络位置的融合方式。我们的AutoFuse可以在训练过程中自动优化其融合策略,并可推广应用于无监督配准(无需任何标签)和半监督配准(仅部分训练数据提供弱标签)。在两种经过良好评估的医疗配准任务(患者间和患者内部配准)上的八个公开数据集进行的广泛实验表明,我们的AutoFuse优于最先进的无监督和半监督配准方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at Pattern Recognition
Summary
变形图像配准旨在寻找一对图像间的密集非线性空间对应关系,对于肿瘤生长监测和人口分析等多种医疗任务至关重要。本研究提出了基于数据驱动的信息融合策略优化配准方法,设计了一个能够灵活地在网络多个潜在位置进行信息融合的自动融合网络(AutoFuse)。此外,还提出了融合门(FG)模块,能够根据训练数据控制每个潜在网络位置的信息融合方式。实验表明,AutoFuse在无需任何标签的无监督配准和仅部分训练数据有弱标签的半监督配准中,均表现出超越现有主流方法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 变形图像配准在医疗领域具有重要的应用价值,如肿瘤生长监测和人口分析。
- 本研究提出一种新的基于数据驱动的融合策略优化配准方法。
- 引入了自动融合网络(AutoFuse),能在网络的多个潜在位置进行信息融合。
- 设计了融合门(FG)模块以控制不同网络位置的信息融合方式。
- 实验证明了AutoFuse在无监督配准和半监督配准中的优越性。
- AutoFuse方法具有广泛的应用前景,可以应用于不同的医学图像配准任务。
点此查看论文截图