⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-10 更新
InfiGUIAgent: A Multimodal Generalist GUI Agent with Native Reasoning and Reflection
Authors:Yuhang Liu, Pengxiang Li, Zishu Wei, Congkai Xie, Xueyu Hu, Xinchen Xu, Shengyu Zhang, Xiaotian Han, Hongxia Yang, Fei Wu
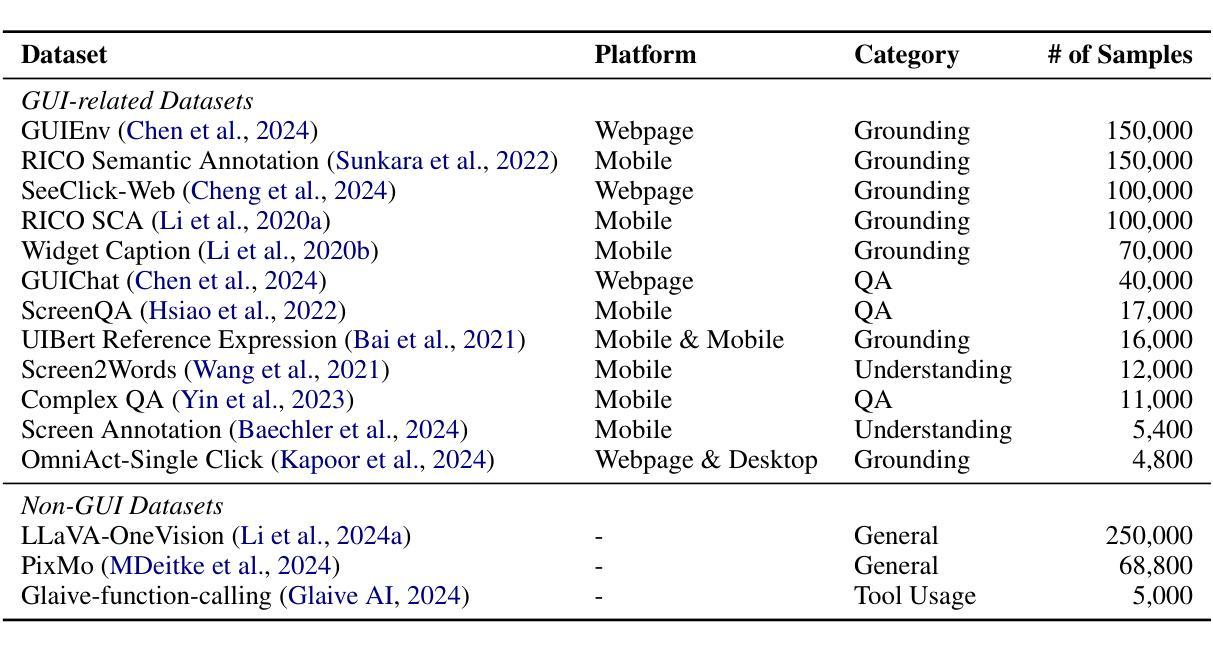
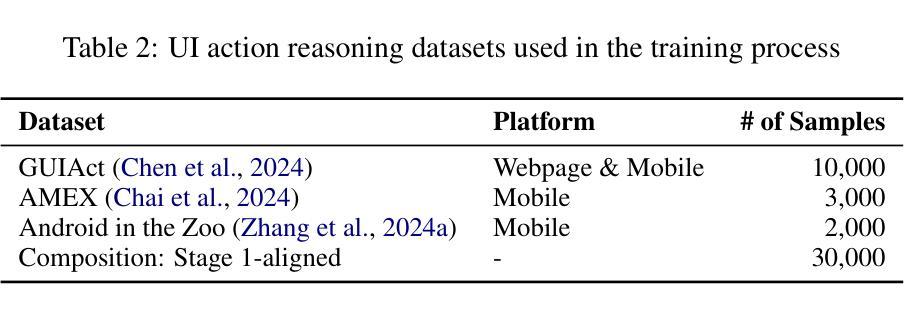
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Agents, powered by multimodal large language models (MLLMs), have shown great potential for task automation on computing devices such as computers and mobile phones. However, existing agents face challenges in multi-step reasoning and reliance on textual annotations, limiting their effectiveness. We introduce \textit{InfiGUIAgent}, an MLLM-based GUI Agent trained with a two-stage supervised fine-tuning pipeline. Stage 1 enhances fundamental skills such as GUI understanding and grounding, while Stage 2 integrates hierarchical reasoning and expectation-reflection reasoning skills using synthesized data to enable native reasoning abilities of the agents. \textit{InfiGUIAgent} achieves competitive performance on several GUI benchmarks, highlighting the impact of native reasoning skills in enhancing GUI interaction for automation tasks. Resources are available at \url{https://github.com/Reallm-Labs/InfiGUIAgent}.
图形用户界面(GUI)代理通过多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)赋能,显示出在计算机设备和手机等计算设备上实现任务自动化的巨大潜力。然而,现有代理面临多步推理和依赖文本注释的挑战,这限制了其有效性。我们引入了基于MLLM的GUI代理——InfiGUIAgent,它采用两阶段监督微调管道进行训练。第一阶段增强基础技能,如GUI理解和定位,而第二阶段利用合成数据集成层次推理和期望反思推理技能,以实现代理的内在推理能力。InfiGUIAgent在多个GUI基准测试中表现出色,凸显了内在推理技能在提高GUI交互自动化任务中的重要作用。资源可通过https://github.com/Reallm-Labs/InfiGUIAgent获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 7 figures, work in progress
Summary
基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的图形用户界面(GUI)代理在自动化计算设备任务方面显示出巨大潜力,如计算机和移动电话。然而,现有代理面临多步推理和依赖文本注释的挑战,限制了其有效性。我们引入InfiGUIAgent代理,采用两阶段监督微调管道进行训练。第一阶段增强基本能力,如GUI理解和接地能力;第二阶段使用合成数据集成层次推理和期望反思推理能力,实现代理的本土推理能力。InfiGUIAgent在多个GUI基准测试中表现优异,突显本土推理能力在增强GUI交互以执行自动化任务方面的作用。相关资源可通过链接访问:https://github.com/Reallm-Labs/InfiGUIAgent。
Key Takeaways
- GUI代理使用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)具有强大的任务自动化潜力。
- 现有GUI代理在多步推理和依赖文本注释方面存在挑战。
- InfiGUIAgent通过两阶段监督微调管道进行训练,增强GUI理解和接地能力。
- 第二阶段集成层次推理和期望反思推理能力,实现代理的本土推理。
- InfiGUIAgent在多个GUI基准测试中表现优异。
- 本地推理能力对增强GUI交互以执行自动化任务有重要影响。
点此查看论文截图

The importance of being discrete – An agent-based model for active nematics and more
Authors:Mathieu Dedenon, Carles Blanch-Mercader, Karsten Kruse, Jens Elgeti
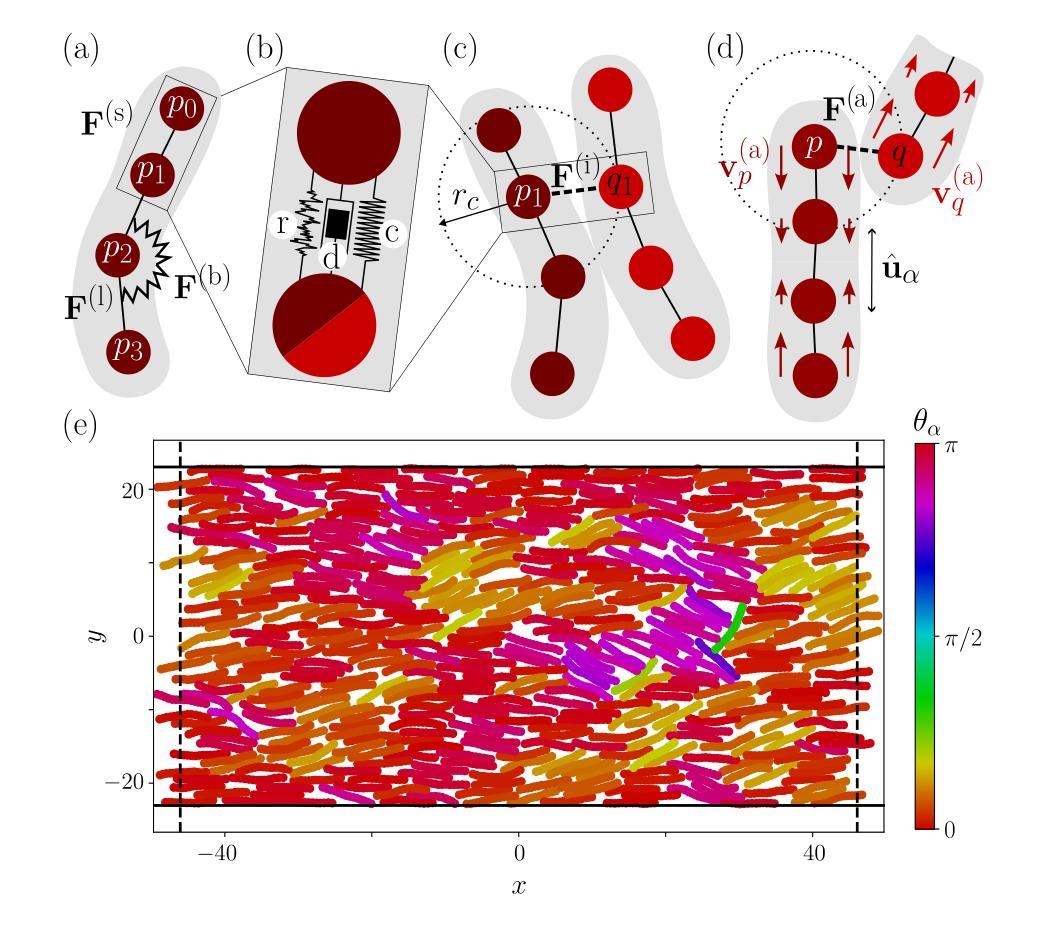
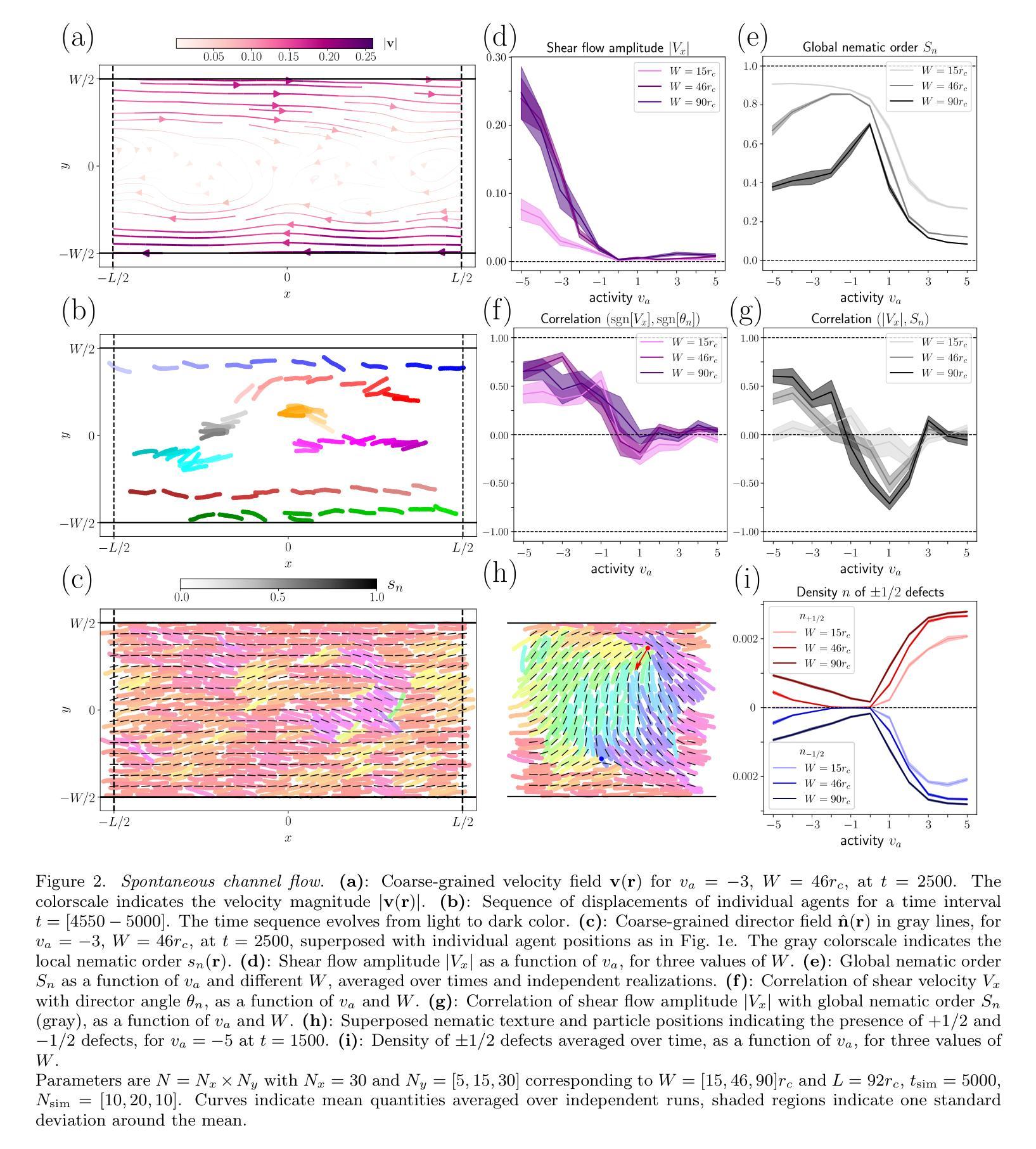
Living systems are composed of discrete units, assembled through a hierarchy of structures, and active, by locally extracting energy from their environment to produce mechanical work. Hydrodynamic theories have been successfully applied to describe the large scale dynamics of active materials. Yet, the hydrodynamic limit requires a separation of scales which is not necessarily fulfilled among living systems. In this work, we propose a novel agent-based model of flexible rods exchanging active force dipoles with nematic symmetry, allowing us to explore their behavior down to the sub-agent scale. We obtain spontaneous flows and self-propulsion of $+1/2$ topological defects, hallmarks of the hydrodynamic theory of active nematics, even on scales smaller than the individual agent! Moreover, our results go beyond the hydrodynamic framework, identifying novel correlations between orientation and flows or strong asymmetries between contractile and extensile activity. Finally, we show the versatility of our agent-based model by presenting spontaneous flows in three dimensions and nematic tissue growth. Because living systems like cell tissues often exhibit several sources of activity, our framework opens the way for more integrated descriptions of living materials.
生命系统由离散单元组成,这些单元通过结构层次进行组装,并从局部环境中提取能量以产生机械功,从而变得活跃。流体动力学理论已成功应用于描述活性材料的宏观动力学。然而,流体动力学极限需要尺度分离,这在生命系统中并不一定满足。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于杆状主体的新型模型,这些主体交换具有向列对称性的主动力偶极子,使我们能够探索其下至次主体级别的行为。我们获得了自发流动和$+1/2$拓扑缺陷的自推进,这是活性向列流体动力学理论的重要标志,甚至在比单个主体更小的尺度上也是如此!此外,我们的结果超越了流体动力学的框架,确定了方向流之间的新型关联,或收缩与扩展活动之间的强烈不对称性。最后,我们通过展示三维空间中的自发流动和向列组织生长,展示了基于主体的模型的通用性。由于像细胞组织这样的生命系统经常表现出多种活动来源,我们的框架为更综合地描述生命材料开辟了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出一种基于活性力偶极子的柔性杆模型,该模型具有向列对称性,能够在子代理尺度上探索活性材料的行为。研究结果显示,即使在个体代理尺度以下,也能产生自发流动和自推进等活性向列体的特征行为。此外,该研究还发现了方向流之间的新型关联以及收缩与扩展活动之间的强烈不对称性。最后,该研究展示了三维自发流动和向列组织生长的多功能模型,为更全面地描述生命材料提供了框架。
Key Takeaways
- 活性材料行为的模型:介绍了一种基于活性力偶极子的柔性杆模型,用于探索活性材料的行为。
- 尺度效应的挑战:尽管流体动力学理论已成功应用于描述活性材料的宏观动力学,但生活系统中的尺度分离并不总是满足流体动力学极限的要求。
- 子代理尺度上的自发流动和自推进:研究结果显示即使在个体代理尺度以下,也能观察到自发流动和自推进行为,这与流体动力学理论中的活性向列体特征相吻合。
- 方向和流动的关联:发现了方向流之间的新型关联,这是对该领域的新理解。
- 活动不对称性:研究还观察到收缩与扩展活动之间的强烈不对称性。
- 三维自发流动和生长模型:展示了一种能够在三维空间中模拟自发流动和向列组织生长的多功能模型。
点此查看论文截图

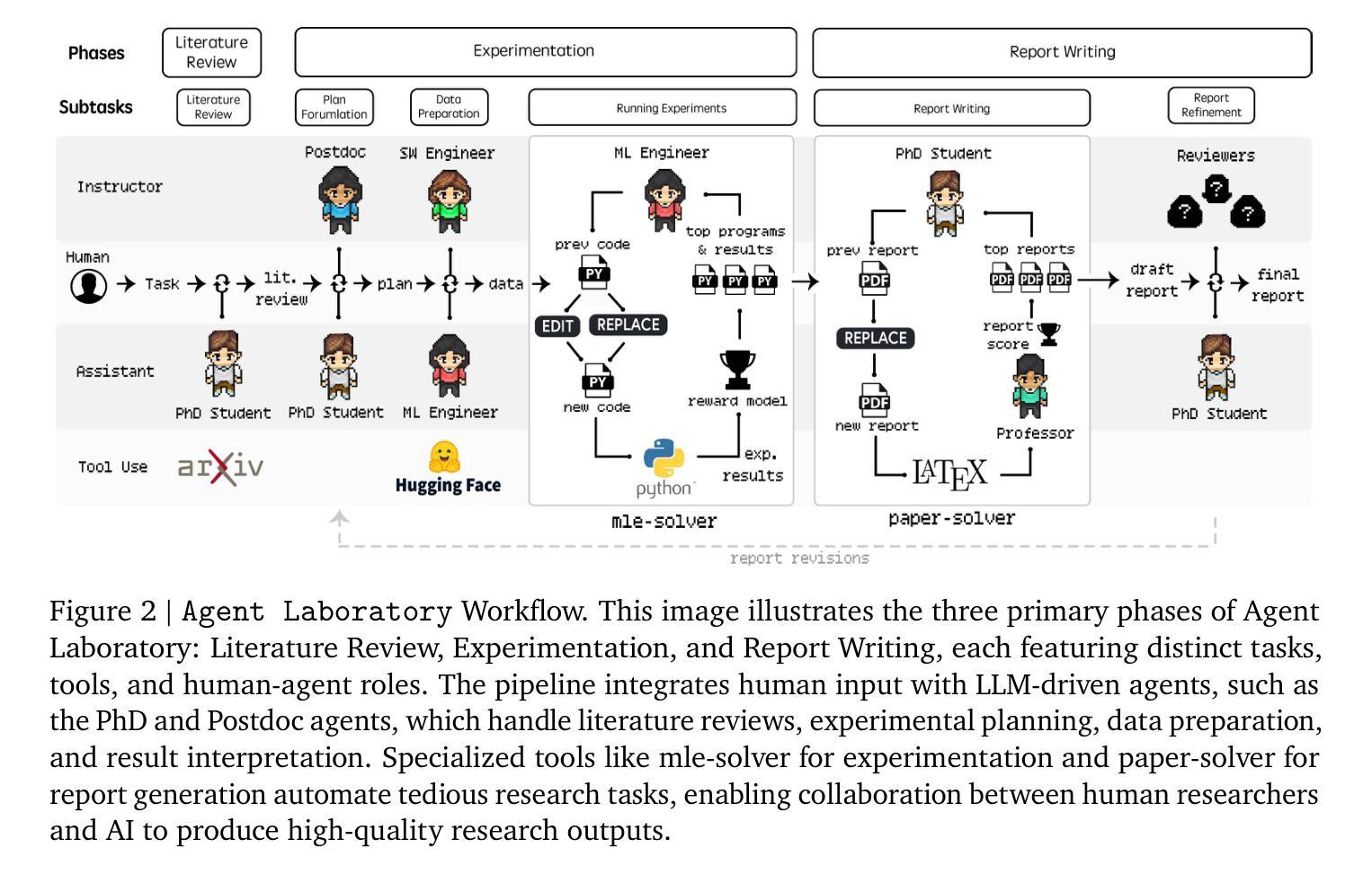
Agent Laboratory: Using LLM Agents as Research Assistants
Authors:Samuel Schmidgall, Yusheng Su, Ze Wang, Ximeng Sun, Jialian Wu, Xiaodong Yu, Jiang Liu, Zicheng Liu, Emad Barsoum
Historically, scientific discovery has been a lengthy and costly process, demanding substantial time and resources from initial conception to final results. To accelerate scientific discovery, reduce research costs, and improve research quality, we introduce Agent Laboratory, an autonomous LLM-based framework capable of completing the entire research process. This framework accepts a human-provided research idea and progresses through three stages–literature review, experimentation, and report writing to produce comprehensive research outputs, including a code repository and a research report, while enabling users to provide feedback and guidance at each stage. We deploy Agent Laboratory with various state-of-the-art LLMs and invite multiple researchers to assess its quality by participating in a survey, providing human feedback to guide the research process, and then evaluate the final paper. We found that: (1) Agent Laboratory driven by o1-preview generates the best research outcomes; (2) The generated machine learning code is able to achieve state-of-the-art performance compared to existing methods; (3) Human involvement, providing feedback at each stage, significantly improves the overall quality of research; (4) Agent Laboratory significantly reduces research expenses, achieving an 84% decrease compared to previous autonomous research methods. We hope Agent Laboratory enables researchers to allocate more effort toward creative ideation rather than low-level coding and writing, ultimately accelerating scientific discovery.
历史上,科学发现是一个漫长而昂贵的进程,从最初的概念到最终的结果需要大量的时间和资源。为了加速科学发现,降低研究成本,提高研究质量,我们推出了Agent Laboratory,这是一个基于自主大型语言模型(LLM)的框架,能够完成整个研究过程。该框架接受人类提供的研究想法,并经过三个阶段——文献综述、实验和报告撰写,以产生全面的研究成果,包括代码仓库和研究报告,同时允许用户在每个阶段提供反馈和指导。我们通过使用各种先进的大型语言模型部署Agent Laboratory,并邀请多名研究人员参与评估其质量。通过参与调查提供人类反馈来指导研究过程,并对最终论文进行评估。我们发现:(1)由o1-preview驱动的Agent Laboratory产生最佳的研究成果;(2)生成的机器学习代码能够与传统方法相比实现最佳性能;(3)人类的参与,在每个阶段提供反馈,极大地提高了研究的整体质量;(4)Agent Laboratory显著降低了研究费用,与之前的自主研究方法相比减少了84%。我们希望Agent Laboratory能够帮助研究人员将更多精力投入到创意构思上,而非低级的编码和写作,从而最终加速科学发现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
引入Agent Laboratory框架,该框架基于大型语言模型(LLM),旨在加速科学发现过程,降低研究成本并提高研究质量。通过接受人类提供的研究想法,完成文献综述、实验和报告写作等阶段,产生包括代码仓库和研究报告的综合研究成果。研究结果表明,Agent Laboratory能够有效生成高质量的研究成果,降低研究成本并提高研究效率。期望Agent Laboratory能使研究人员更多地专注于创意构思,加速科学发现。
Key Takeaways:
- Agent Laboratory是一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自主研究框架,可完成整个研究过程。
- Agent Laboratory接受人类提供的研究想法,并经过文献综述、实验和报告写作三个阶段产生综合研究成果。
- Agent Laboratory能够生成高质量的研究成果,其中由o1-preview驱动的Agent Laboratory表现最佳。
- Agent Laboratory生成的机器学习代码能够实现最新性能水平,与现有方法相比具有优势。
- 人类在每个阶段的参与和反馈显著提高了研究的整体质量。
- Agent Laboratory显著降低了研究费用,与之前的自主研究方法相比实现了84%的减少。
点此查看论文截图

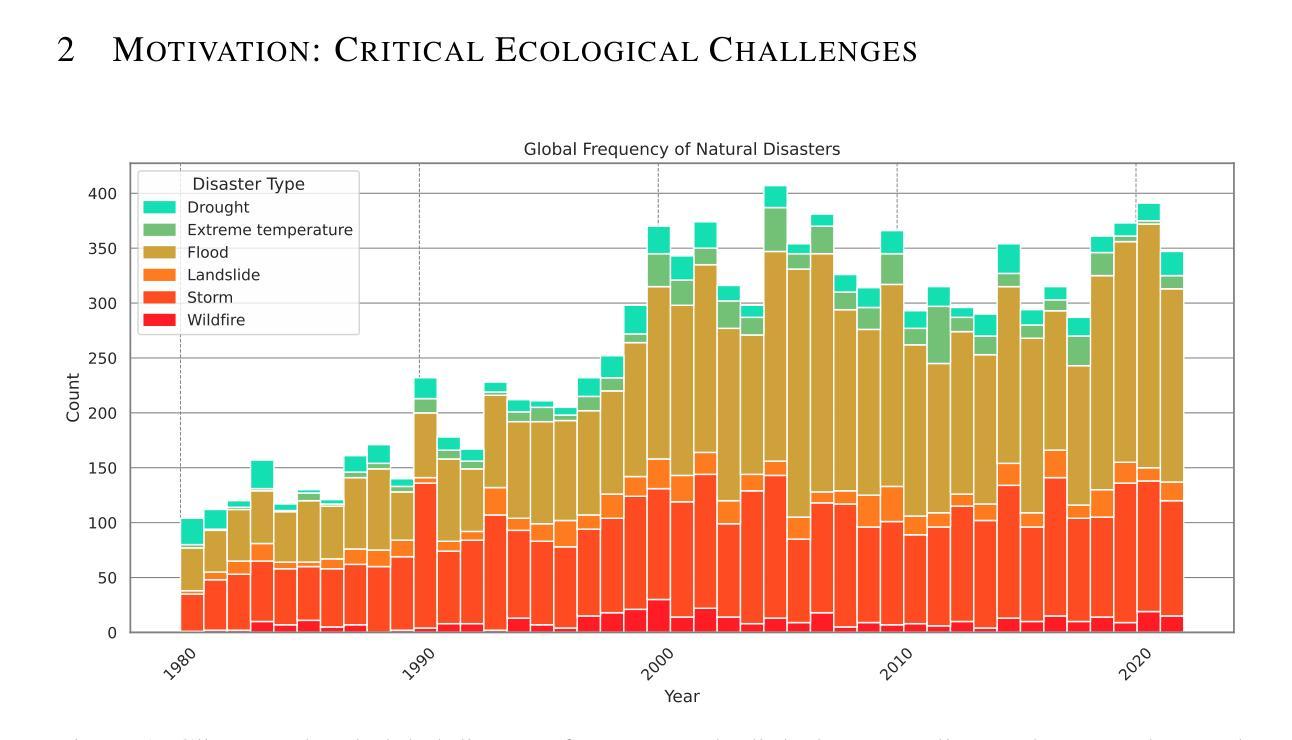
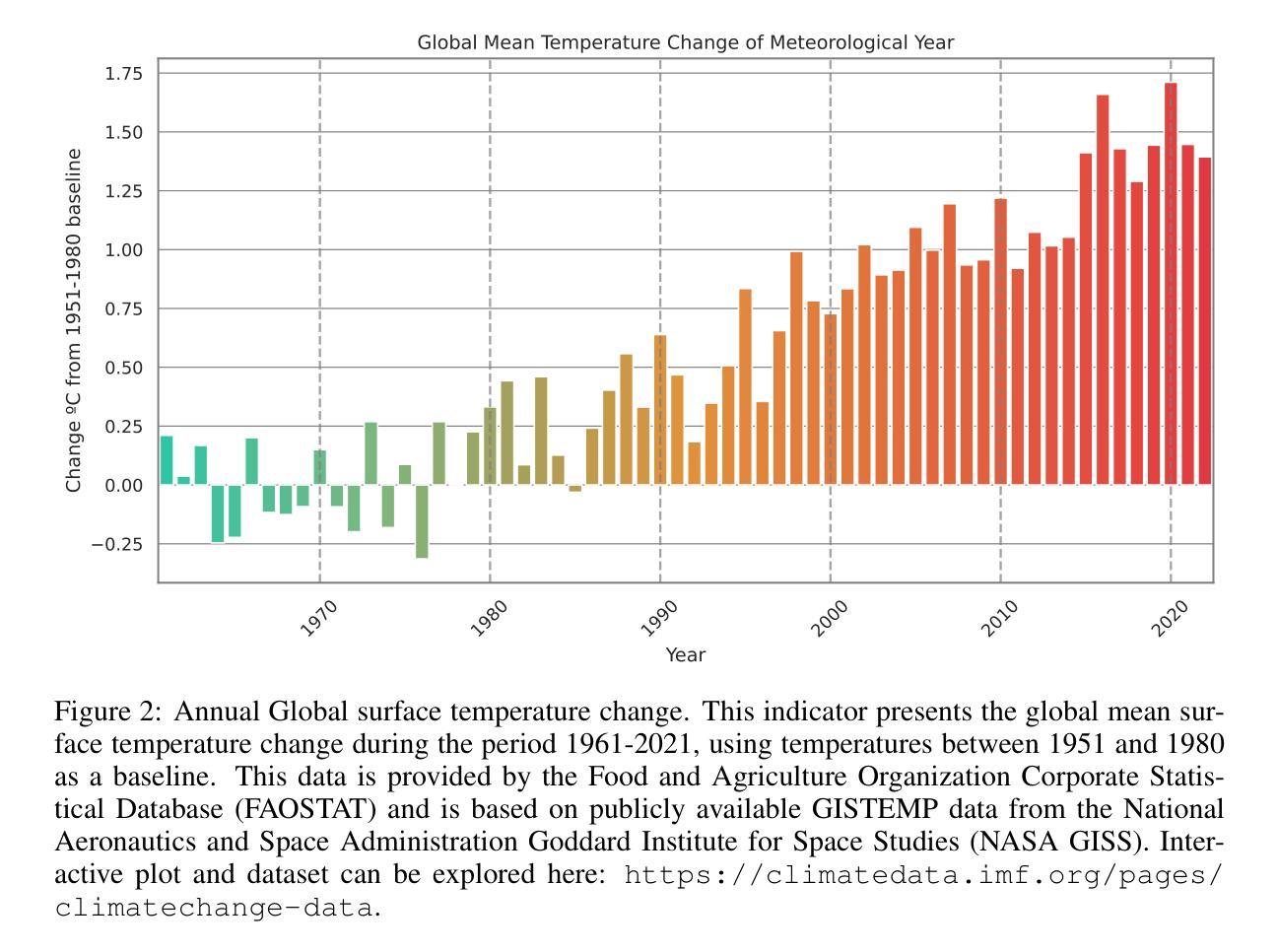
HIVEX: A High-Impact Environment Suite for Multi-Agent Research (extended version)
Authors:Philipp D. Siedler
Games have been vital test beds for the rapid development of Agent-based research. Remarkable progress has been achieved in the past, but it is unclear if the findings equip for real-world problems. While pressure grows, some of the most critical ecological challenges can find mitigation and prevention solutions through technology and its applications. Most real-world domains include multi-agent scenarios and require machine-machine and human-machine collaboration. Open-source environments have not advanced and are often toy scenarios, too abstract or not suitable for multi-agent research. By mimicking real-world problems and increasing the complexity of environments, we hope to advance state-of-the-art multi-agent research and inspire researchers to work on immediate real-world problems. Here, we present HIVEX, an environment suite to benchmark multi-agent research focusing on ecological challenges. HIVEX includes the following environments: Wind Farm Control, Wildfire Resource Management, Drone-Based Reforestation, Ocean Plastic Collection, and Aerial Wildfire Suppression. We provide environments, training examples, and baselines for the main and sub-tasks. All trained models resulting from the experiments of this work are hosted on Hugging Face. We also provide a leaderboard on Hugging Face and encourage the community to submit models trained on our environment suite.
游戏对于基于代理研究的快速发展至关重要。过去取得了显著的进步,但尚不清楚这些发现是否能应对现实世界的问题。随着压力越来越大,一些最重要的生态挑战可以通过技术及其应用找到缓解和预防的解决方案。大多数现实世界领域都包括多代理场景,需要机器与机器以及人与机器的协作。然而,开源环境并未取得进展,往往是玩具场景,过于抽象或不适合多代理研究。通过模拟现实世界问题并增加环境复杂性,我们希望推动最前沿的多代理研究,并激励研究人员致力于解决紧迫的现实世界问题。在这里,我们推出了HIVEX,这是一个专注于生态挑战的多代理研究基准测试环境套件。HIVEX包括以下环境:风电场控制、野火资源管理、无人机为基础的植树造林、海洋塑料收集以及航空野火压制。我们提供了主要任务和子任务的环境、训练示例和基准测试。所有由此项工作实验训练出的模型都托管在Hugging Face上。我们还为Hugging Face提供了一个排行榜,鼓励社区提交在我们环境套件上训练的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多智能体技术在解决生态挑战方面有着巨大的潜力。文章提出了HIVEX环境套件,旨在推动多智能体研究的发展,解决现实问题,如风电场控制、野火资源管理、无人机造林、海洋塑料收集以及空中灭火等。文章提供了环境和任务训练示例及基准线,并鼓励社区提交在该环境套件上训练的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 游戏对于基于智能体的研究有着重要的推动作用。
- 在解决生态挑战方面,多智能体技术具有巨大的潜力。
- 当前开源环境对于多智能体研究的支持不足,需要更真实、复杂的环境来推动研究进步。
- HIVEX环境套件旨在解决现实问题,包括风电场控制、野火管理等任务。
- 文章提供了环境和任务训练示例及基准线,便于研究人员进行实验和比较。
- Hugging Face上提供了模型训练和结果展示的社区平台,鼓励社区参与。
点此查看论文截图

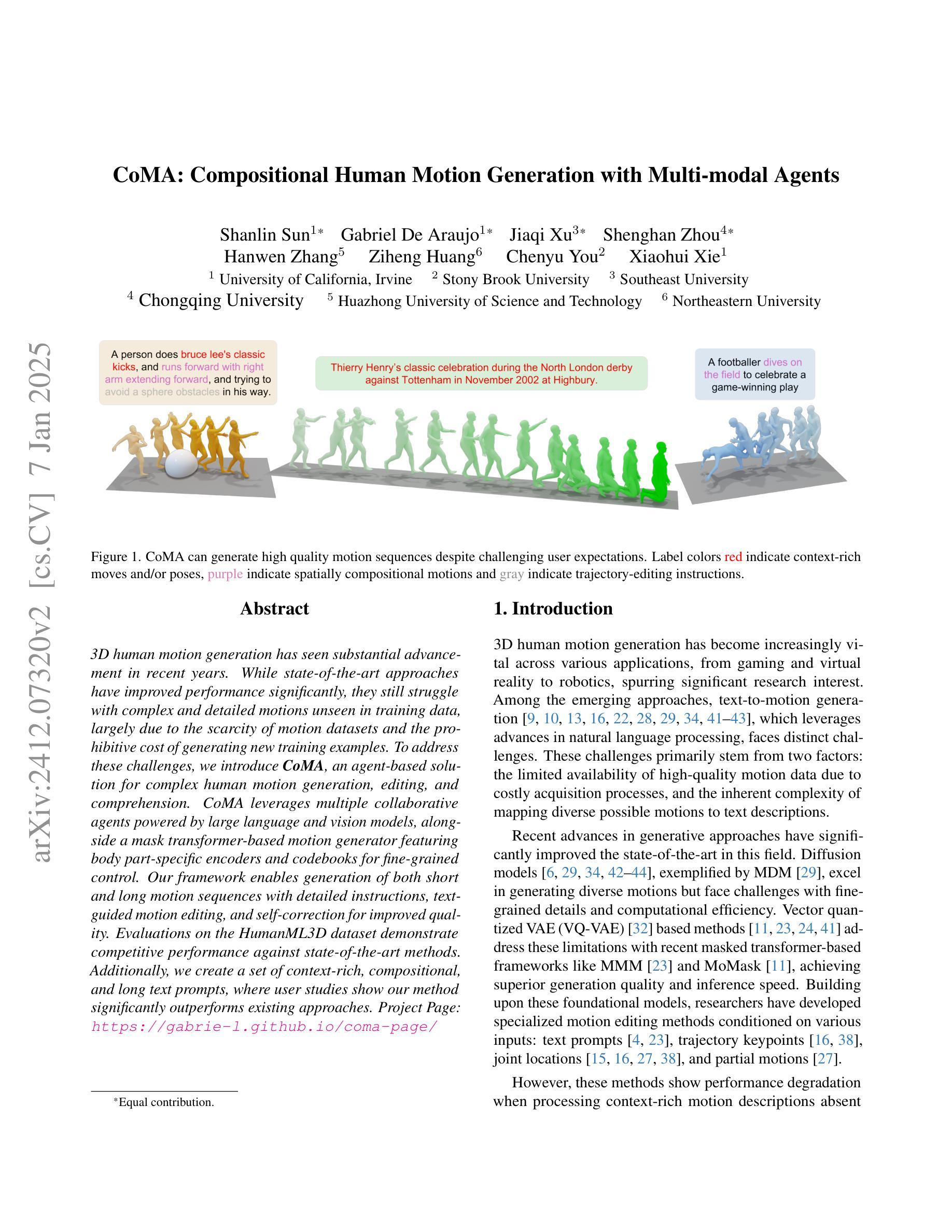
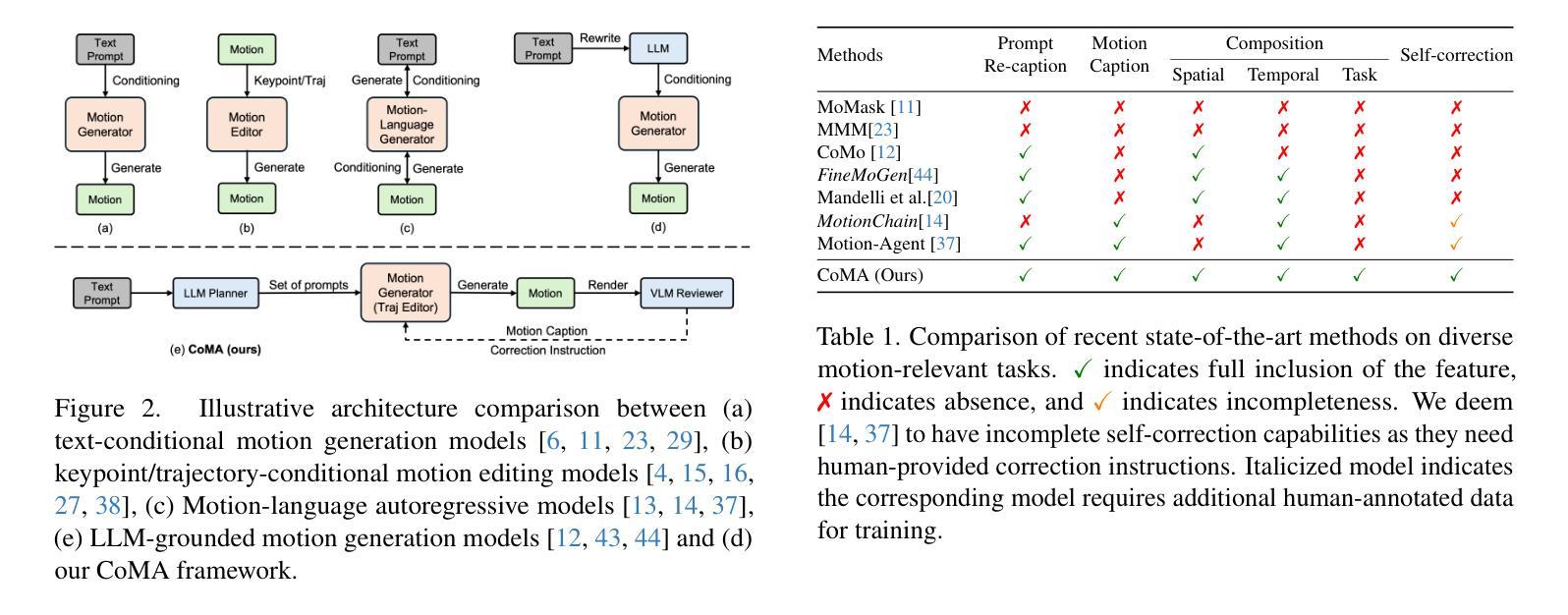
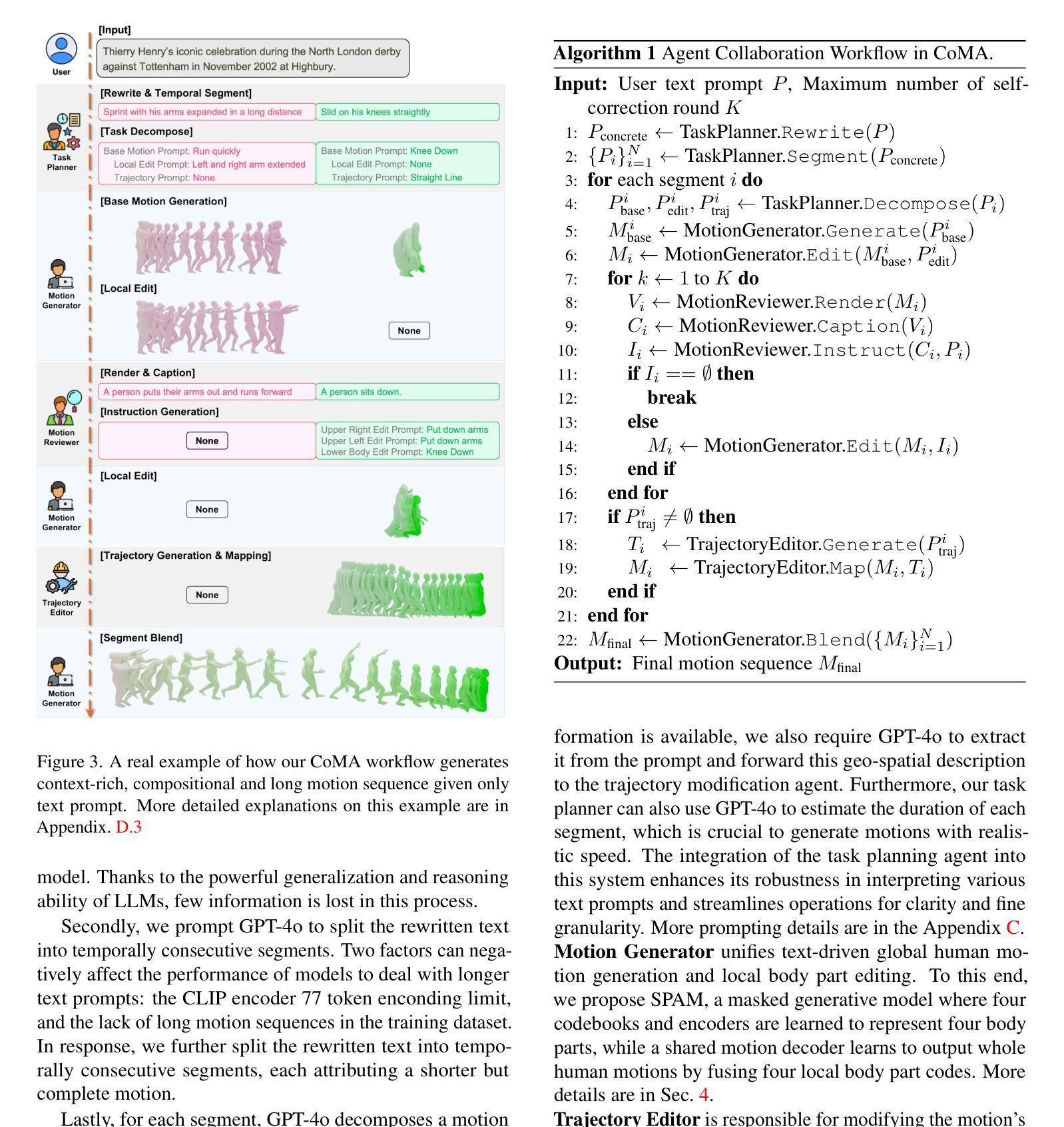
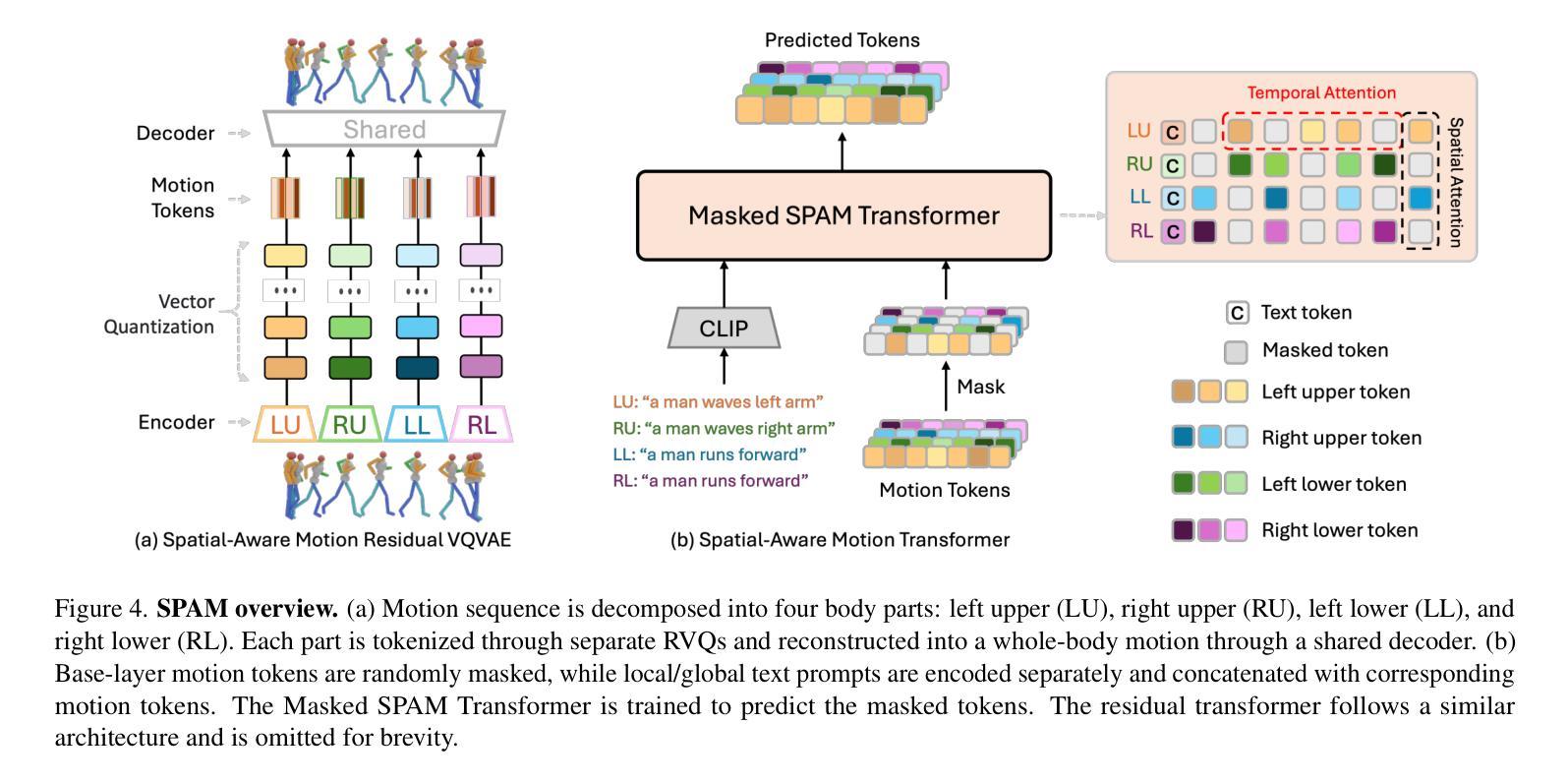
CoMA: Compositional Human Motion Generation with Multi-modal Agents
Authors:Shanlin Sun, Gabriel De Araujo, Jiaqi Xu, Shenghan Zhou, Hanwen Zhang, Ziheng Huang, Chenyu You, Xiaohui Xie
3D human motion generation has seen substantial advancement in recent years. While state-of-the-art approaches have improved performance significantly, they still struggle with complex and detailed motions unseen in training data, largely due to the scarcity of motion datasets and the prohibitive cost of generating new training examples. To address these challenges, we introduce CoMA, an agent-based solution for complex human motion generation, editing, and comprehension. CoMA leverages multiple collaborative agents powered by large language and vision models, alongside a mask transformer-based motion generator featuring body part-specific encoders and codebooks for fine-grained control. Our framework enables generation of both short and long motion sequences with detailed instructions, text-guided motion editing, and self-correction for improved quality. Evaluations on the HumanML3D dataset demonstrate competitive performance against state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, we create a set of context-rich, compositional, and long text prompts, where user studies show our method significantly outperforms existing approaches.
近年来,3D人体运动生成技术已经取得了重大进展。虽然最新技术在性能上已经有了显著提高,但它们仍然难以处理训练和测试数据中未见过的复杂和详细运动,这主要是因为运动数据集稀缺且生成新训练样本的成本高昂。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了CoMA,这是一种基于代理的复杂人体运动生成、编辑和理解的解决方案。CoMA利用由大型语言和视觉模型驱动的多个协作代理,以及基于掩码变压器的人体部位特定编码器、编码簿和运动生成器,实现精细粒度控制。我们的框架能够生成具有详细指令的短和长运动序列,实现文本引导的运动编辑以及自我修正以提高质量。在HumanML3D数据集上的评估显示,其性能与最新技术相比具有竞争力。此外,我们还创建了一系列内容丰富、组合性强、文本提示长的场景,用户研究证明我们的方法显著优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://gabrie-l.github.io/coma-page/
Summary
复杂人体运动生成、编辑与理解的研究近年来取得了显著进展。然而,最先进的方法在面对训练和测试数据中未见过的复杂和精细运动时仍面临挑战,这主要是由于运动数据集稀缺且生成新训练样本的成本高昂。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了基于代理的解决方案CoMA,用于复杂人体运动生成、编辑和解析。CoMA利用大型语言和视觉模型驱动的多代理协作,结合基于掩膜转换器的运动生成器,具有针对身体部位的编码器和精细控制的书签。我们的框架可以生成带有详细指令的短长运动序列,文本指导的运动编辑和自我修正功能以提升质量。在人类ML3D数据集上的评估证明了我们方法的竞争力。此外,我们还创建了一系列上下文丰富、组合性强、文本提示长的场景,用户研究证明我们的方法明显优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 复杂人体运动生成领域近年来取得显著进展,但仍面临未见复杂和精细运动的挑战。
- 缺乏运动数据集和生成新训练样本的高成本是主要原因。
- CoMA是一个基于代理的解决方案,旨在解决这些问题,实现复杂人体运动的生成、编辑和解析。
- CoMA利用大型语言和视觉模型驱动的多代理协作。
- 基于掩膜转换器的运动生成器具有身体部位特定的编码器和精细控制的书签。
- CoMA框架可以生成带有详细指令的短长运动序列,支持文本指导的运动编辑和自我修正功能。
点此查看论文截图
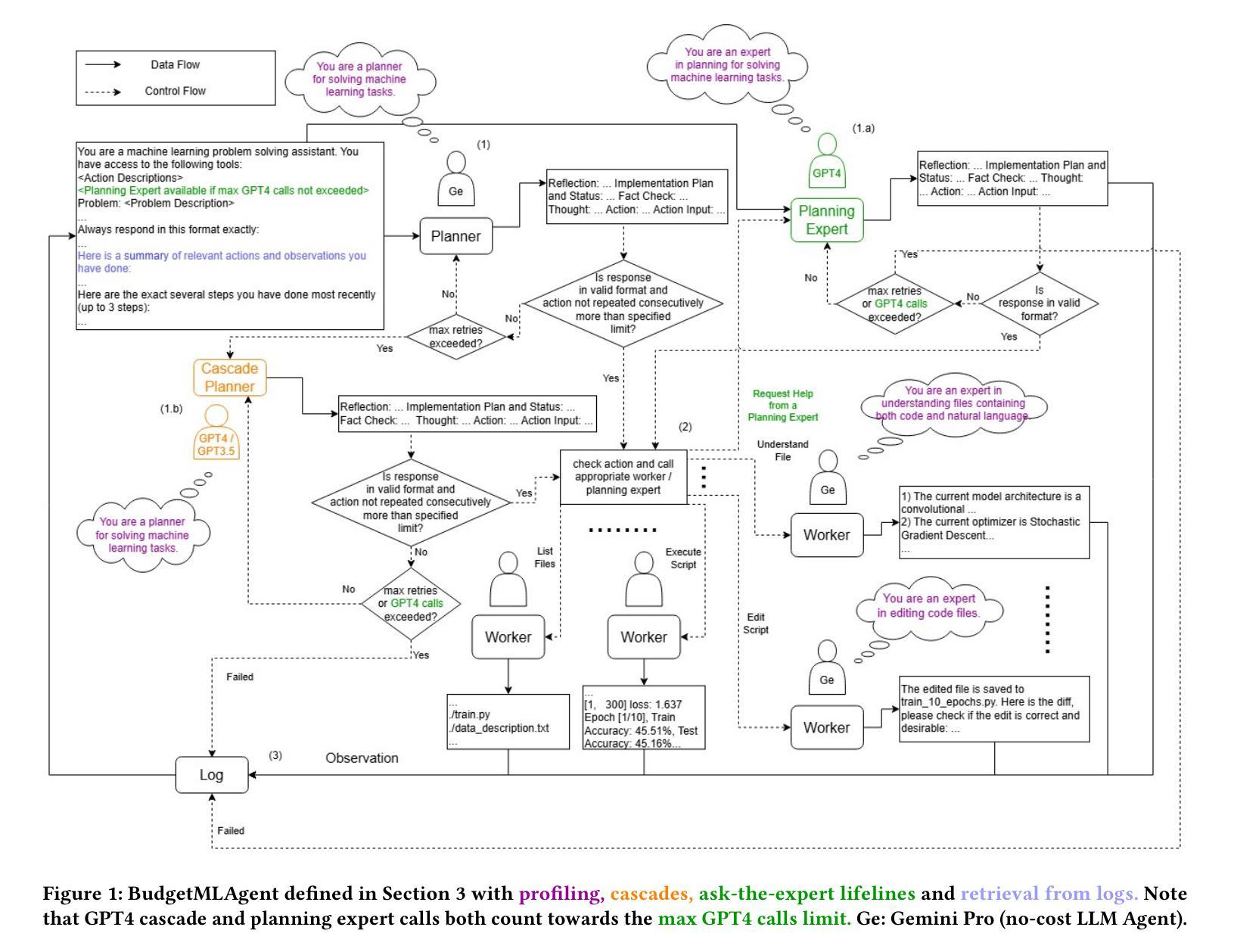
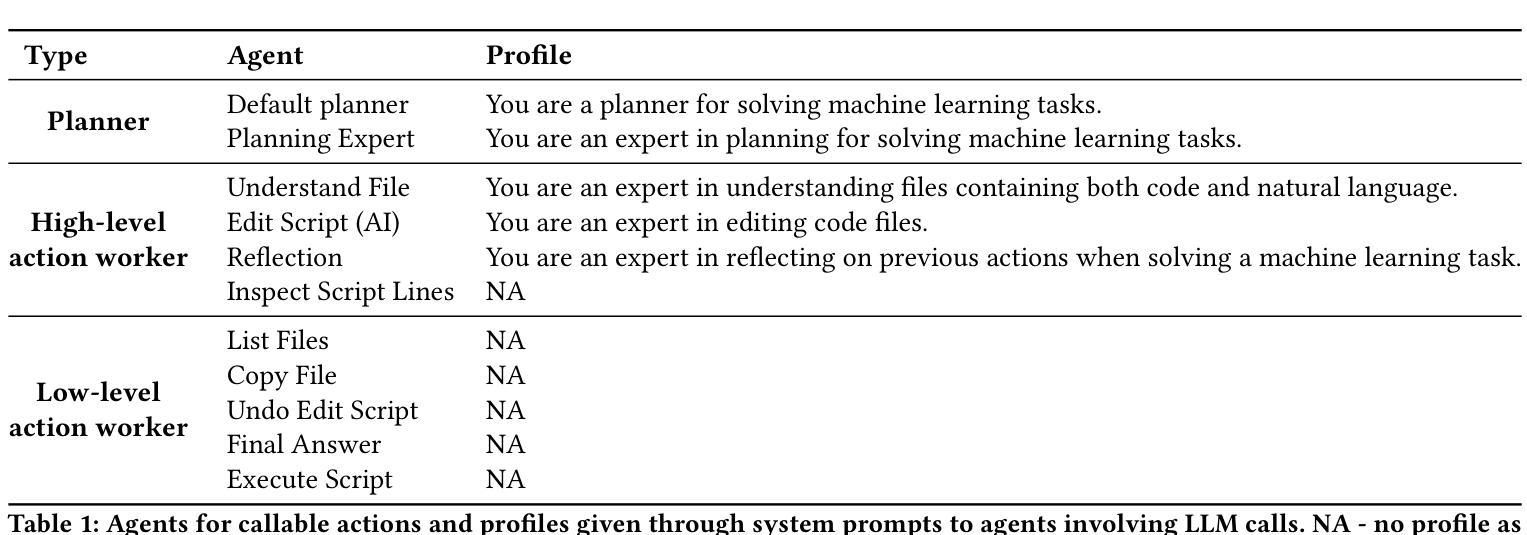
BudgetMLAgent: A Cost-Effective LLM Multi-Agent system for Automating Machine Learning Tasks
Authors:Shubham Gandhi, Manasi Patwardhan, Lovekesh Vig, Gautam Shroff
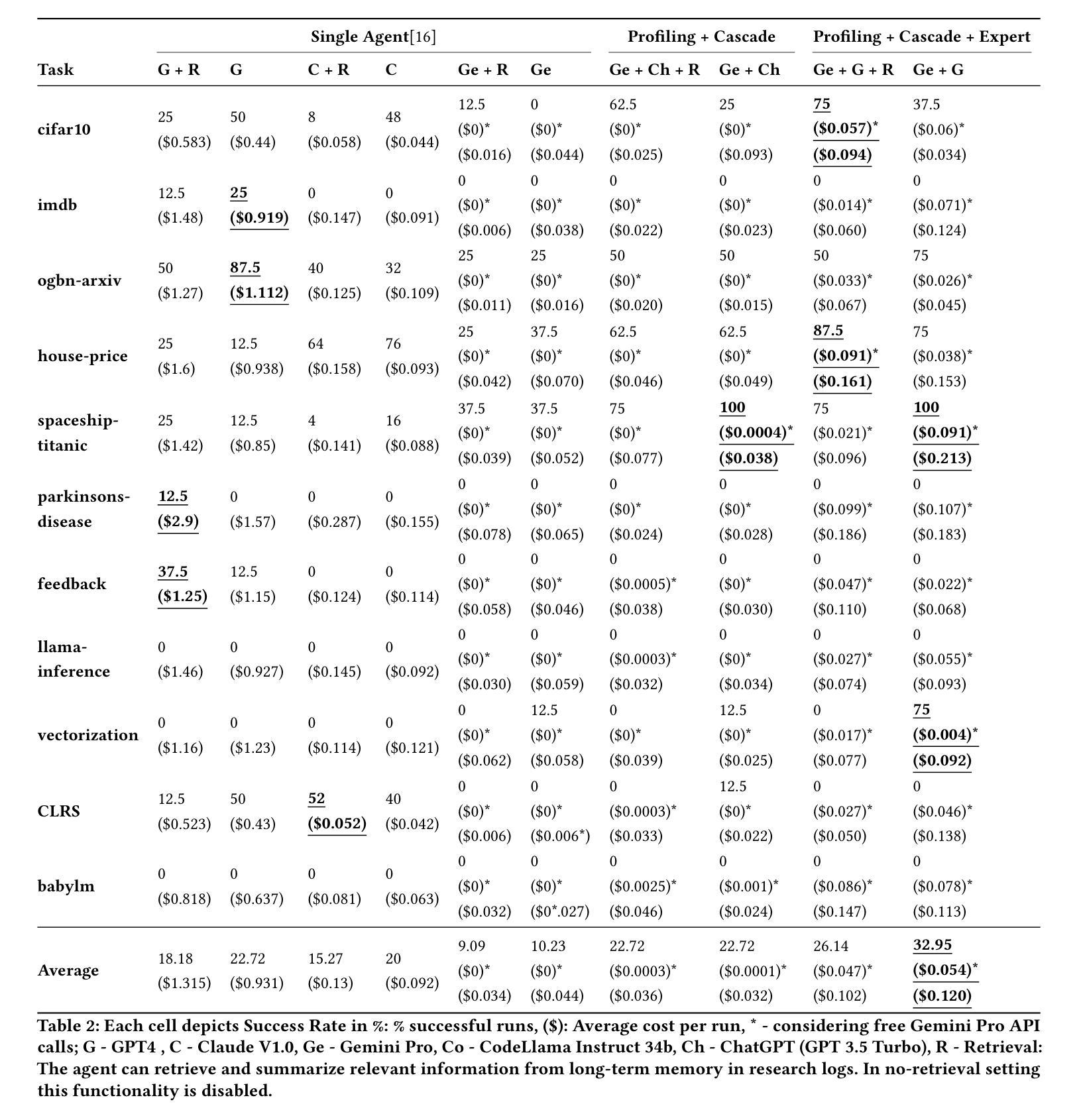
Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in diverse applications including generation of code snippets, but often struggle with generating code for complex Machine Learning (ML) tasks. Although existing LLM single-agent based systems give varying performance depending on the task complexity, they purely rely on larger and expensive models such as GPT-4. Our investigation reveals that no-cost and low-cost models such as Gemini-Pro, Mixtral and CodeLlama perform far worse than GPT-4 in a single-agent setting. With the motivation of developing a cost-efficient LLM based solution for solving ML tasks, we propose an LLM Multi-Agent based system which leverages combination of experts using profiling, efficient retrieval of past observations, LLM cascades, and ask-the-expert calls. Through empirical analysis on ML engineering tasks in the MLAgentBench benchmark, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our system, using no-cost models, namely Gemini as the base LLM, paired with GPT-4 in cascade and expert to serve occasional ask-the-expert calls for planning. With 94.2% reduction in the cost (from $0.931 per run cost averaged over all tasks for GPT-4 single agent system to $0.054), our system is able to yield better average success rate of 32.95% as compared to GPT-4 single-agent system yielding 22.72% success rate averaged over all the tasks of MLAgentBench.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在多种应用中都表现出色,包括生成代码片段,但在生成用于复杂机器学习(ML)任务的代码时常常遇到困难。尽管现有的基于单一LLM的系统的性能取决于任务的复杂性,但它们纯粹依赖于像GPT-4这样的大而昂贵的模型。我们的调查发现,在单一代理设置中,无成本和低成本的模型,如Gemini-Pro、Mixtral和CodeLlama的表现远远低于GPT-4。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented at AIMLSystems ‘24
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在生成代码片段等多样化应用中表现出色,但在生成用于复杂机器学习(ML)任务的代码时常常遇到困难。现有LLM单代理系统依赖大型且昂贵的模型(如GPT-4),但低成本或无成本模型(如Gemini-Pro、Mixtral和CodeLlama)在单代理环境中的表现较差。为此,我们提出了一种基于LLM的多代理系统,该系统通过结合专家使用分析,有效检索过往观察结果,利用LLM级联和专家咨询等方式。在MLAgentBench基准的机器学习工程任务上进行实证分析显示,我们的系统以低成本模型Gemini为基础,结合GPT-4进行级联和专业支持,在降低成本的同时提高了成功率。相较于GPT-4单代理系统的平均运行成本从每次运行的0.931美元降至0.054美元,我们的系统实现了成本降低94.2%,并且在所有任务上的平均成功率提高至32.95%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在生成代码片段等领域表现优秀,但在复杂机器学习(ML)任务中生成代码存在挑战。
- 现有LLM单代理系统主要依赖大型且昂贵的模型,如GPT-4。
- 低成本或无成本模型在单代理环境中的表现不佳。
- 提出了一种基于LLM的多代理系统,结合专家使用分析、有效检索过往观察结果、LLM级联和专家咨询等方法。
- 实证分析显示,新系统在降低成本的同时提高了成功率,与GPT-4单代理系统相比,成本大幅降低,并且平均成功率也有所提高。
- 系统以低成本模型为基础,结合更高级模型进行特定任务级联和专业支持。
点此查看论文截图
Multi-Agent Training for Pommerman: Curriculum Learning and Population-based Self-Play Approach
Authors:Nhat-Minh Huynh, Hoang-Giang Cao, I-Chen Wu
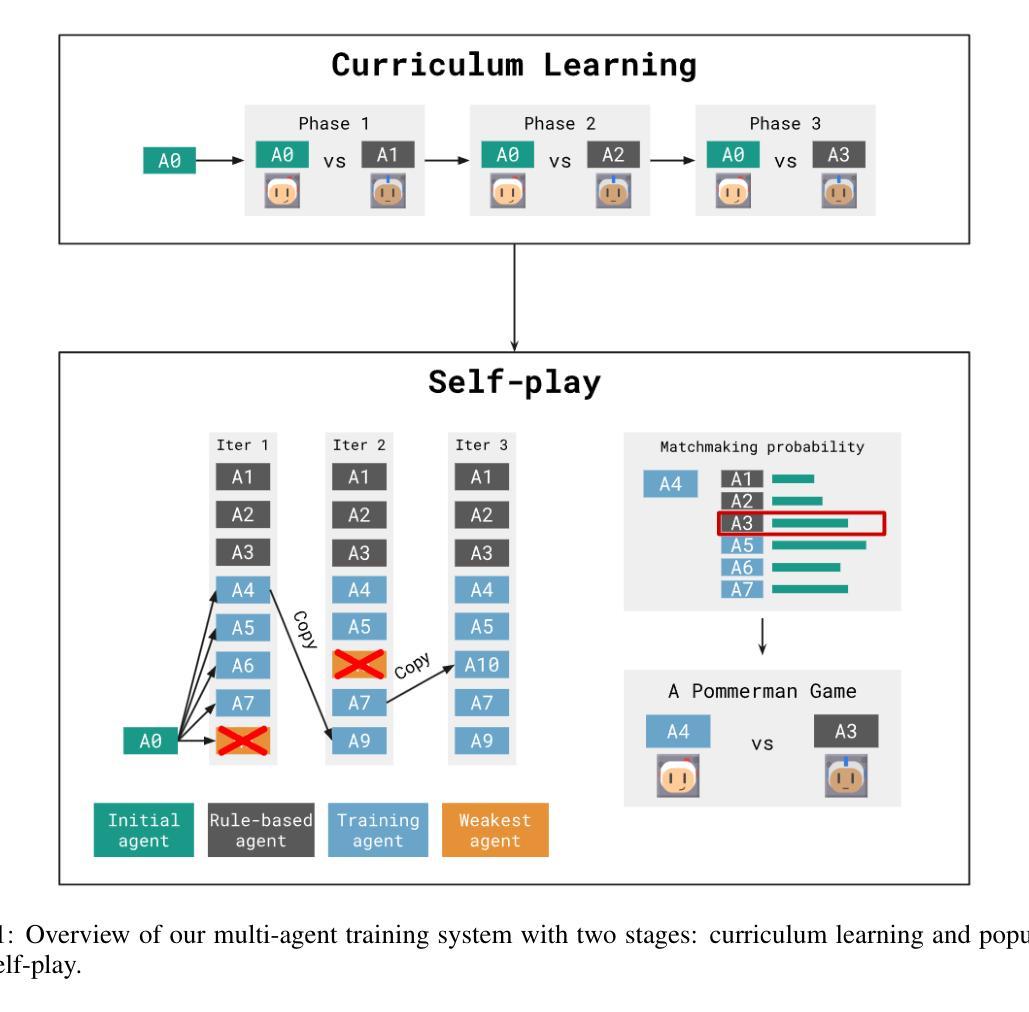
Pommerman is a multi-agent environment that has received considerable attention from researchers in recent years. This environment is an ideal benchmark for multi-agent training, providing a battleground for two teams with communication capabilities among allied agents. Pommerman presents significant challenges for model-free reinforcement learning due to delayed action effects, sparse rewards, and false positives, where opponent players can lose due to their own mistakes. This study introduces a system designed to train multi-agent systems to play Pommerman using a combination of curriculum learning and population-based self-play. We also tackle two challenging problems when deploying the multi-agent training system for competitive games: sparse reward and suitable matchmaking mechanism. Specifically, we propose an adaptive annealing factor based on agents’ performance to adjust the dense exploration reward during training dynamically. Additionally, we implement a matchmaking mechanism utilizing the Elo rating system to pair agents effectively. Our experimental results demonstrate that our trained agent can outperform top learning agents without requiring communication among allied agents.
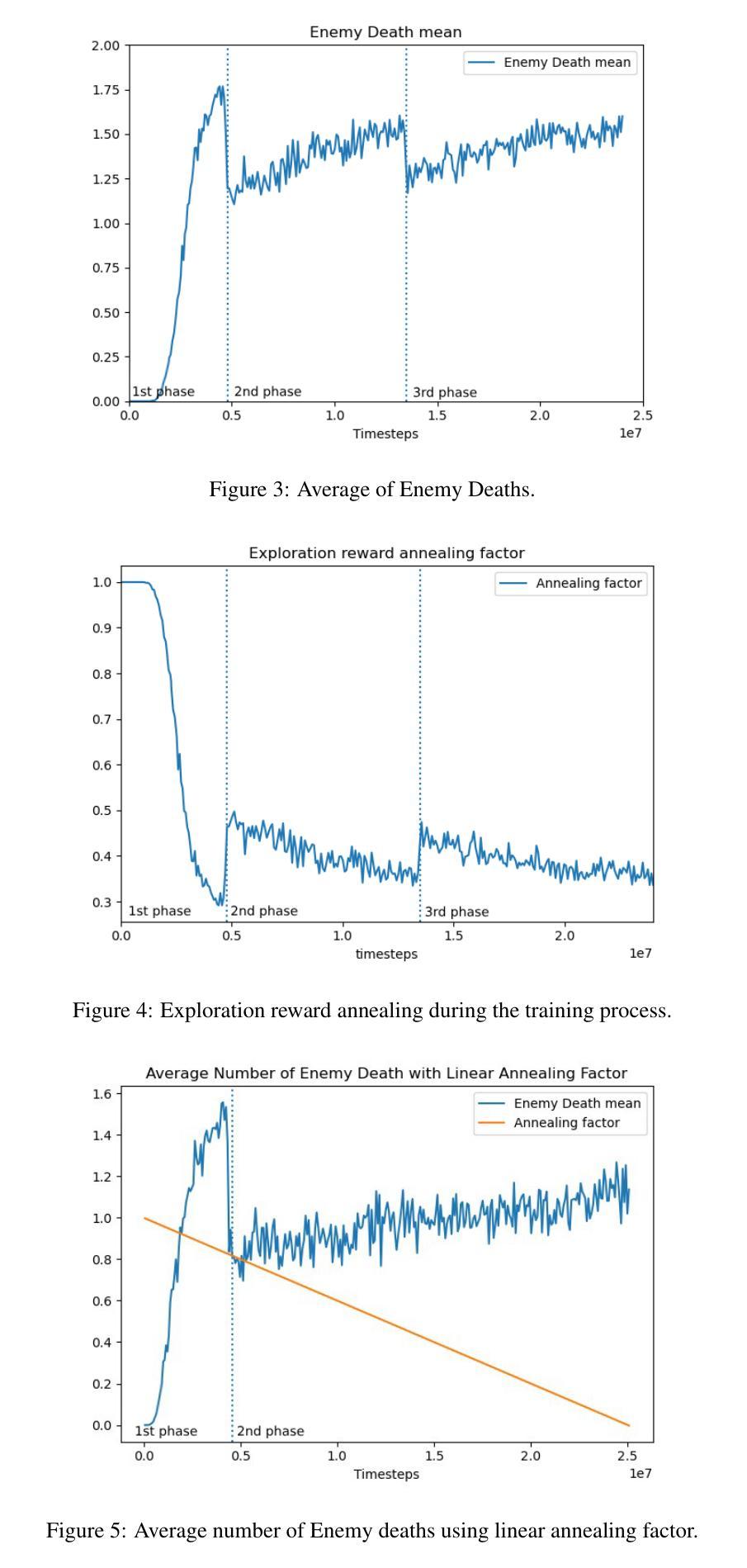
Pommerman是一个多智能体环境,近年来受到了研究人员的广泛关注。该环境是评估多智能体训练的理想基准测试,为拥有通讯能力的两个团队的智能体提供了一个战场。由于动作的延迟效果、奖励稀疏和误判(对手玩家可能因自身失误而失败),Pommerman给无模型强化学习带来了重大挑战。本研究引入了一个系统,旨在结合课程学习和基于群体的自学习来训练能在Pommerman中游戏的智能体系统。我们还解决了部署多智能体训练系统用于竞技游戏时面临的两个挑战问题:奖励稀疏和合适的配对机制。具体来说,我们提出了一个基于智能体性能的自适应退火因子,以动态调整训练过程中的密集探索奖励。此外,我们实现了利用Elo评级系统进行配对的有效机制。实验结果表明,我们训练出的智能体能够超越顶级学习智能体的表现,而无需在盟军智能体之间进行通信。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at The First Workshop on Game AI Algorithms and Multi-Agent Learning - IJCAI 2024
Summary
Pommerman是一款多智能体环境,适合作为多智能体训练的基准测试平台。本研究提出了一种结合课程学习和基于种群自玩的系统来训练Pommerman游戏的多智能体系统,解决了其中的稀疏奖励和匹配机制问题。通过动态调整基于智能体性能的退火因子来调整密集探索奖励,并采用基于Elo评级系统的匹配机制来有效配对智能体。实验结果表明,训练出的智能体能够超越顶级学习智能体,无需盟军智能体间的通信。
Key Takeaways
- Pommerman是一个多智能体环境,适合作为多智能体训练的基准测试平台。
- 研究提出了一种结合课程学习和基于种群自玩的系统来训练Pommerman游戏的多智能体系统。
- 解决的主要挑战包括稀疏奖励和匹配机制问题。
- 通过动态调整退火因子来调整密集探索奖励,以提高智能体的性能。
- 采用基于Elo评级系统的匹配机制来有效配对智能体。
- 训练出的智能体能够超越顶级学习智能体。
点此查看论文截图

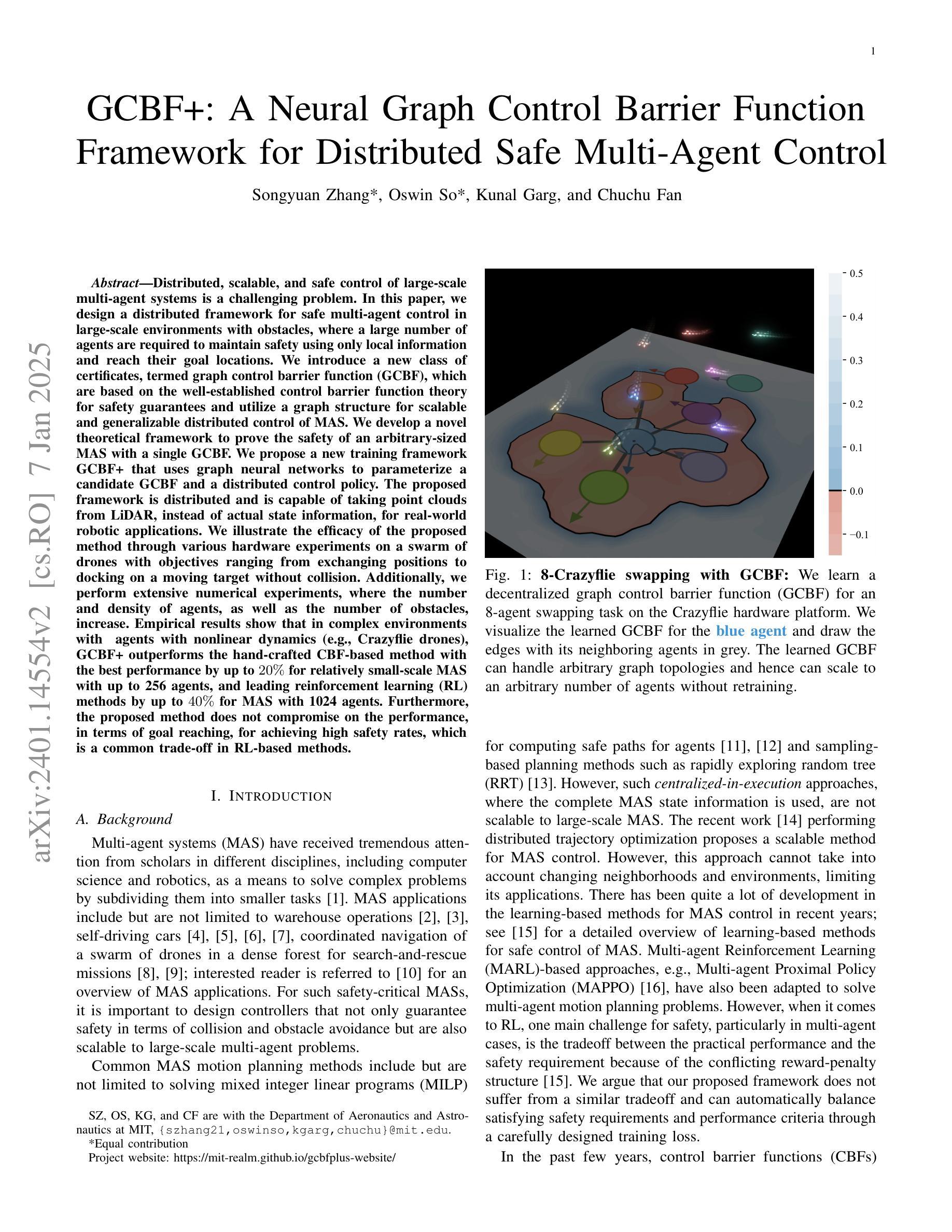
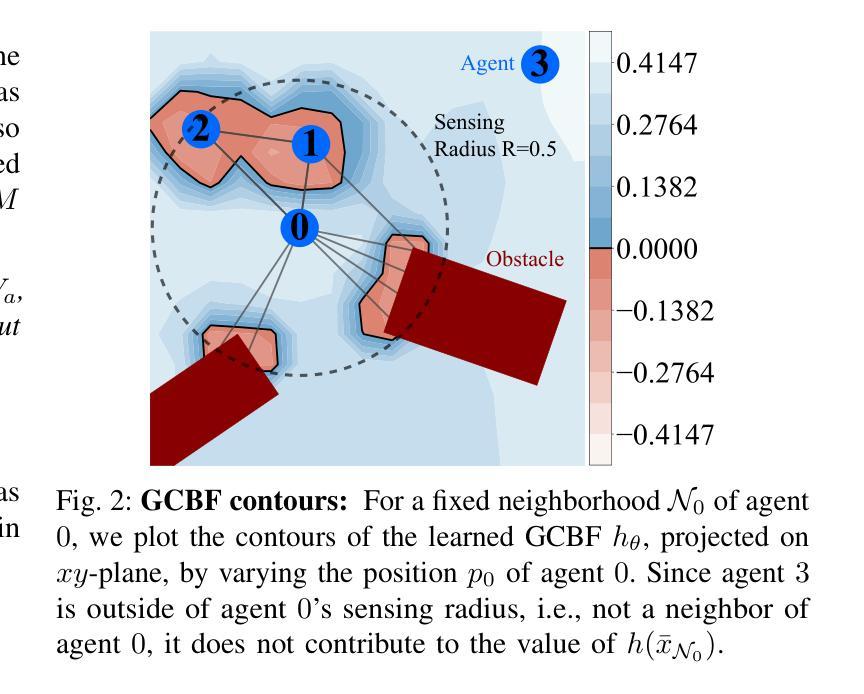
GCBF+: A Neural Graph Control Barrier Function Framework for Distributed Safe Multi-Agent Control
Authors:Songyuan Zhang, Oswin So, Kunal Garg, Chuchu Fan
Distributed, scalable, and safe control of large-scale multi-agent systems is a challenging problem. In this paper, we design a distributed framework for safe multi-agent control in large-scale environments with obstacles, where a large number of agents are required to maintain safety using only local information and reach their goal locations. We introduce a new class of certificates, termed graph control barrier function (GCBF), which are based on the well-established control barrier function theory for safety guarantees and utilize a graph structure for scalable and generalizable distributed control of MAS. We develop a novel theoretical framework to prove the safety of an arbitrary-sized MAS with a single GCBF. We propose a new training framework GCBF+ that uses graph neural networks to parameterize a candidate GCBF and a distributed control policy. The proposed framework is distributed and is capable of taking point clouds from LiDAR, instead of actual state information, for real-world robotic applications. We illustrate the efficacy of the proposed method through various hardware experiments on a swarm of drones with objectives ranging from exchanging positions to docking on a moving target without collision. Additionally, we perform extensive numerical experiments, where the number and density of agents, as well as the number of obstacles, increase. Empirical results show that in complex environments with agents with nonlinear dynamics (e.g., Crazyflie drones), GCBF+ outperforms the hand-crafted CBF-based method with the best performance by up to 20% for relatively small-scale MAS with up to 256 agents, and leading reinforcement learning (RL) methods by up to 40% for MAS with 1024 agents. Furthermore, the proposed method does not compromise on the performance, in terms of goal reaching, for achieving high safety rates, which is a common trade-off in RL-based methods.
在大规模多智能体系统中,实现分布式、可伸缩和安全的控制是一个具有挑战性的问题。在本论文中,我们设计了一个用于在充满障碍的大规模环境中进行安全多智能体控制的分布式框架。在该环境中,需要大量智能体仅使用局部信息来保持安全并到达其目标位置。我们引入了一种新的证书类别,称为图控制障碍函数(GCBF),它基于成熟的控制障碍函数理论来保证安全,并利用图结构来实现MAS的可扩展和可通用的分布式控制。我们开发了一个新型理论框架,以证明具有单个GCBF的任意规模MAS的安全性。我们提出了一个新的训练框架GCBF+,该框架使用图神经网络来参数化候选GCBF和分布式控制策略。所提出框架是分布式的,能够从激光雷达获取点云,而不是实际状态信息,适用于实际机器人应用。我们通过各种无人机集群的硬件实验验证了所提方法的有效性,实验目标包括交换位置、在移动目标上停靠且不发生碰撞等。此外,我们还进行了大量的数值实验,增加了智能体和障碍物的数量和密度。实证结果表明,在具有非线性动力学特性的复杂环境中(例如Crazyflie无人机),GCBF+相对于手工制作的CBF方法性能最佳时高出高达20%,适用于相对较小规模的MAS(最多包含256个智能体),并且相对于领先的强化学习方法高出高达40%,适用于包含1024个智能体的MAS。此外,所提出的方法在达到高安全率的同时并不牺牲目标达成的性能,这在基于RL的方法中是一种常见的权衡。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 15 figures; Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Robotics (T-RO)
Summary
本文设计了一种分布式框架,用于在大型障碍环境中实现安全的多智能体控制。引入了一种新的证书——图控制屏障函数(GCBF),基于已建立的屏障函数理论确保安全,并利用图结构实现智能体的分布式可控性。开发了一种理论框架,证明任意规模的智能体系统使用单一GCBF的安全性。提出了使用图神经网络参数化候选GCBF和分布式控制策略的新训练框架GCBF+。该方法适用于真实世界机器人应用,可从激光雷达获取点云而非实际状态信息。实验证明,该方法在无人机群等多智能体系统中表现出优异性能,且在复杂环境中具有显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 分布式框架用于大型障碍环境中的安全多智能体控制。
- 引入图控制屏障函数(GCBF)确保智能体在复杂环境中的安全性。
- 理论框架证明任意规模智能体系统的安全性。
- GCBF+训练框架使用图神经网络参数化候选GCBF和分布式控制策略。
- 该方法适用于真实世界机器人应用,可从激光雷达获取点云信息。
- 实验证明GCBF+在多智能体系统控制中性能优异,特别是在复杂环境中。
点此查看论文截图