⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-10 更新
EditAR: Unified Conditional Generation with Autoregressive Models
Authors:Jiteng Mu, Nuno Vasconcelos, Xiaolong Wang
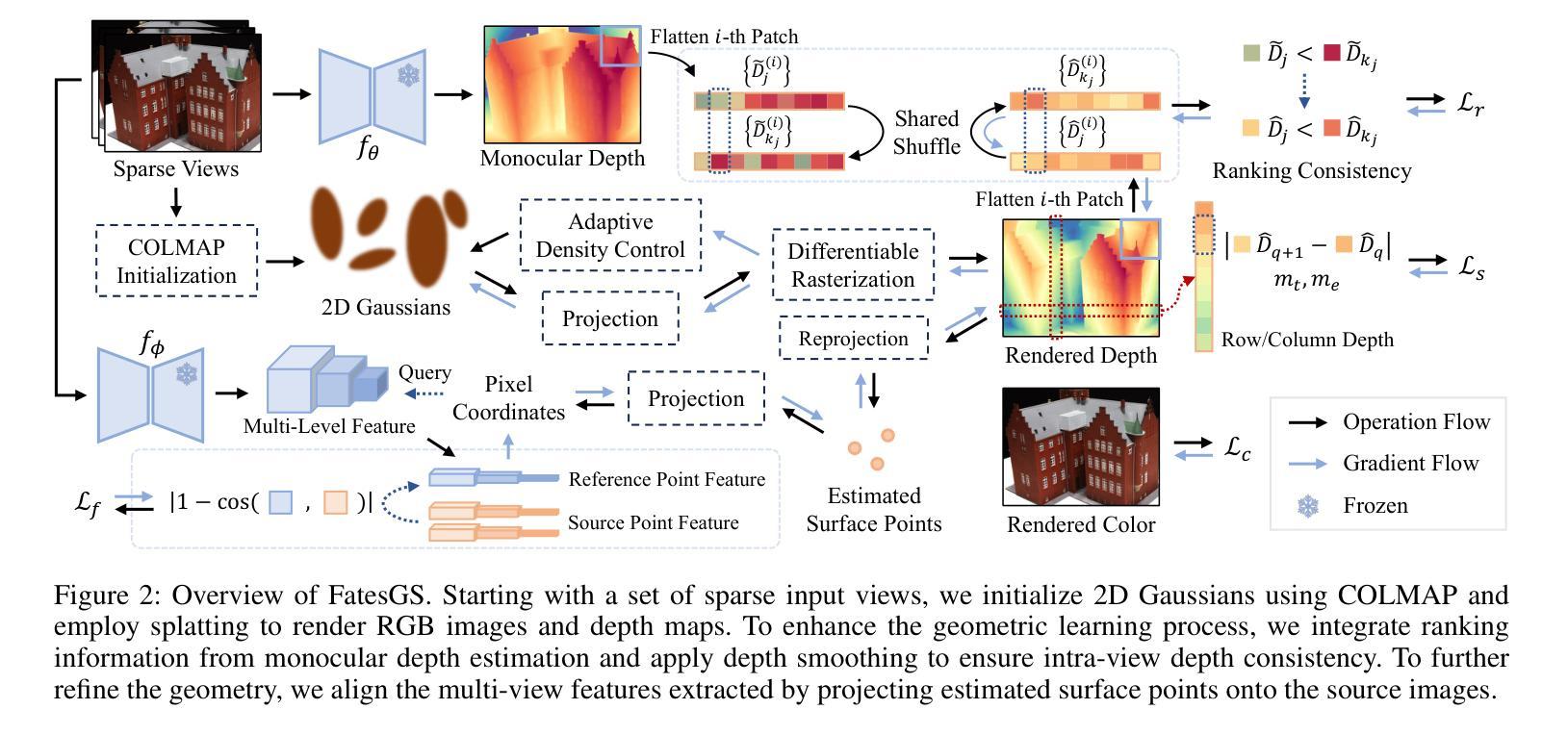
Recent progress in controllable image generation and editing is largely driven by diffusion-based methods. Although diffusion models perform exceptionally well in specific tasks with tailored designs, establishing a unified model is still challenging. In contrast, autoregressive models inherently feature a unified tokenized representation, which simplifies the creation of a single foundational model for various tasks. In this work, we propose EditAR, a single unified autoregressive framework for a variety of conditional image generation tasks, e.g., image editing, depth-to-image, edge-to-image, segmentation-to-image. The model takes both images and instructions as inputs, and predicts the edited images tokens in a vanilla next-token paradigm. To enhance the text-to-image alignment, we further propose to distill the knowledge from foundation models into the autoregressive modeling process. We evaluate its effectiveness across diverse tasks on established benchmarks, showing competitive performance to various state-of-the-art task-specific methods. Project page: https://jitengmu.github.io/EditAR/
近期可控图像生成和编辑的进展主要得益于基于扩散的方法。尽管扩散模型在特定任务中表现非常出色,但建立统一模型仍然具有挑战性。相比之下,自回归模型天生具有统一的令牌化表示,这简化了为各种任务创建单一基础模型的过程。在这项工作中,我们提出了EditAR,这是一个统一的自回归框架,可用于各种条件图像生成任务,例如图像编辑、深度到图像、边缘到图像、分割到图像。该模型同时接受图像和指令作为输入,并在标准的下一个令牌范式中预测编辑后的图像令牌。为了增强文本到图像的对应性,我们进一步提出将来自基础模型的知识蒸馏到自回归建模过程中。我们在既定的基准测试上对多种任务进行了有效性评估,显示出与各种最先进的任务特定方法相竞争的性能。项目页面:https://jitengmu.github.io/EditAR/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://jitengmu.github.io/EditAR/
Summary
扩散模型在可控图像生成和编辑方面取得了最新进展,表现出强大的能力。尽管扩散模型在特定任务上的表现卓越,但建立统一模型仍然具有挑战。与此相反,自回归模型具有内在的统一标记表示,简化了各种任务的基础模型的创建。在此工作中,我们提出了EditAR,这是一个统一的自回归框架,可用于多种条件图像生成任务,如图像编辑、深度图像、边缘图像、分割图像等。该模型接受图像和指令作为输入,并在标准的下一个令牌模式中预测编辑后的图像令牌。为了增强文本到图像的对应,我们进一步提出将知识从基础模型蒸馏到自回归建模过程中。我们在多个任务上的评估结果表明,其性能与各种最先进的任务特定方法相竞争。想了解更多关于此项目的信息,请访问:项目页面链接。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在可控图像生成和编辑方面取得显著进展。
- 自回归模型具有内在的统一标记表示,便于创建统一模型应对多种任务。
- EditAR框架是一个统一的自回归模型,适用于多种条件图像生成任务。
- EditAR接受图像和指令作为输入,预测编辑后的图像令牌。
- 通过蒸馏技术,增强了文本到图像的对应准确性。
- 在多个任务上的评估结果表明,EditAR性能与最先进的任务特定方法相竞争。
点此查看论文截图


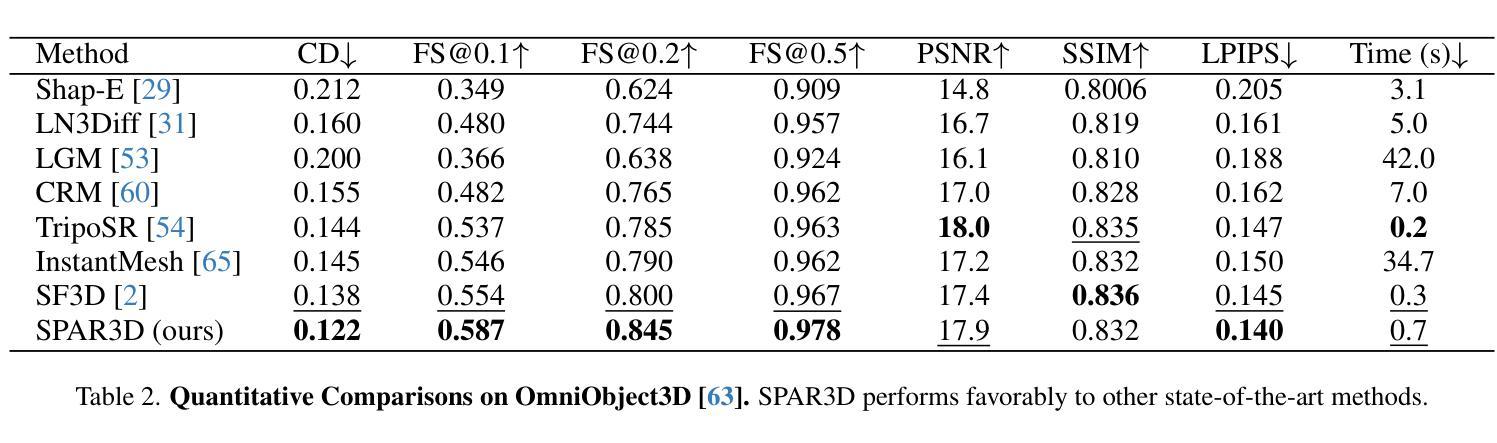
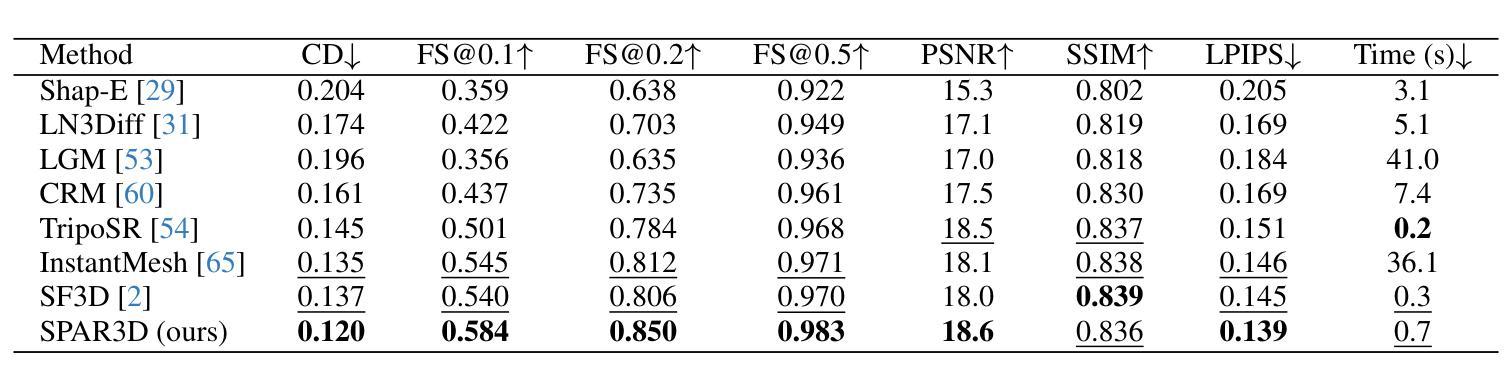
SPAR3D: Stable Point-Aware Reconstruction of 3D Objects from Single Images
Authors:Zixuan Huang, Mark Boss, Aaryaman Vasishta, James M. Rehg, Varun Jampani
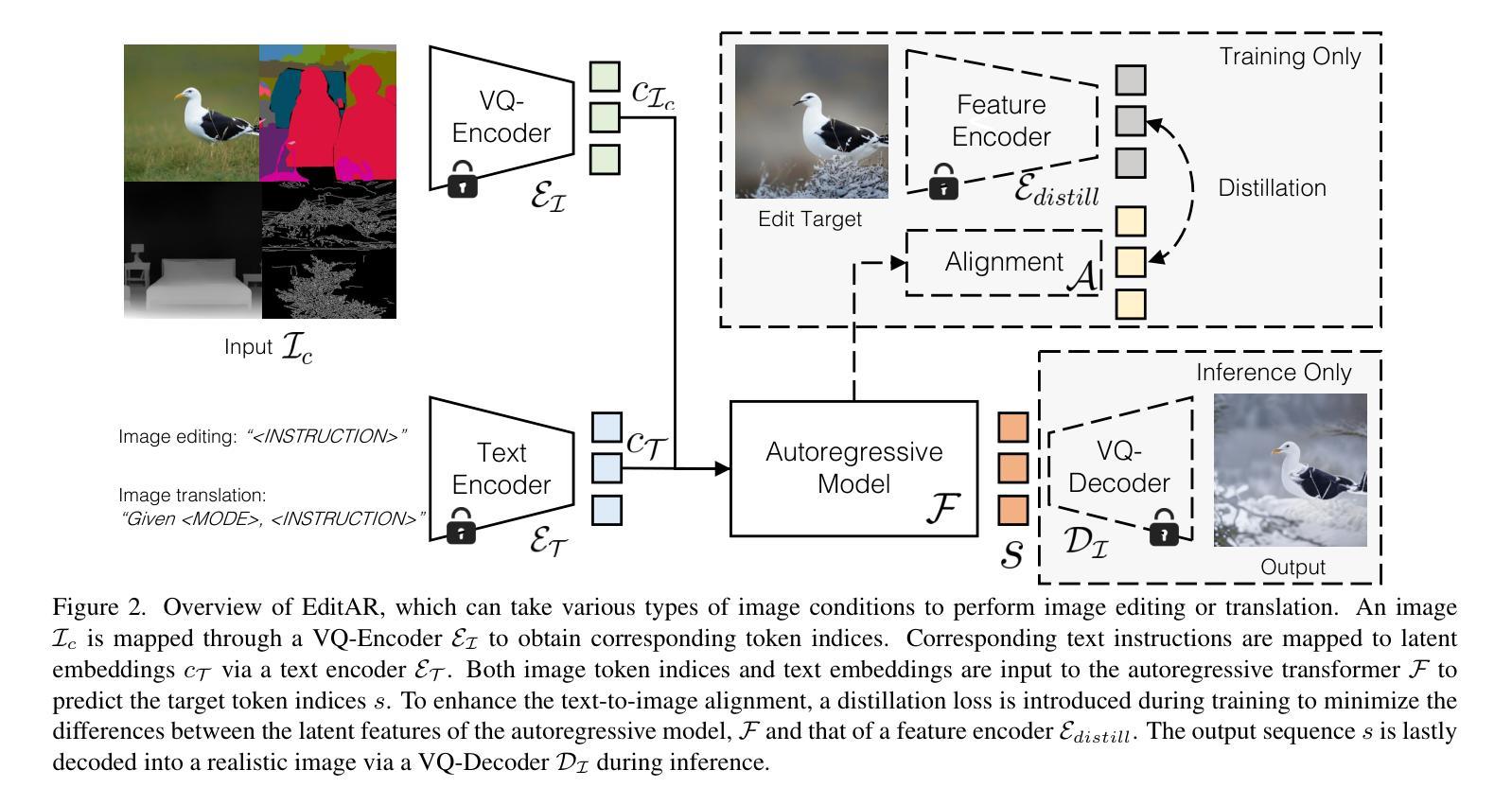
We study the problem of single-image 3D object reconstruction. Recent works have diverged into two directions: regression-based modeling and generative modeling. Regression methods efficiently infer visible surfaces, but struggle with occluded regions. Generative methods handle uncertain regions better by modeling distributions, but are computationally expensive and the generation is often misaligned with visible surfaces. In this paper, we present SPAR3D, a novel two-stage approach aiming to take the best of both directions. The first stage of SPAR3D generates sparse 3D point clouds using a lightweight point diffusion model, which has a fast sampling speed. The second stage uses both the sampled point cloud and the input image to create highly detailed meshes. Our two-stage design enables probabilistic modeling of the ill-posed single-image 3D task while maintaining high computational efficiency and great output fidelity. Using point clouds as an intermediate representation further allows for interactive user edits. Evaluated on diverse datasets, SPAR3D demonstrates superior performance over previous state-of-the-art methods, at an inference speed of 0.7 seconds. Project page with code and model: https://spar3d.github.io
我们研究了单图像3D对象重建的问题。近期的研究工作主要分为两个方向:基于回归的建模和生成式建模。回归方法能够有效地推断出可见表面,但在处理遮挡区域时遇到困难。生成式方法通过建模分布来处理不确定区域,但计算成本较高,且生成的结果往往与可见表面不匹配。在本文中,我们提出了SPAR3D,这是一种新颖的两阶段方法,旨在融合两个方向的优点。SPAR3D的第一阶段使用轻量级的点扩散模型生成稀疏的3D点云,具有快速的采样速度。第二阶段则使用采样得到的点云和输入图像来创建高度详细的网格。我们的两阶段设计能够在保持高计算效率和输出质量的同时,对不适定的单图像3D任务进行概率建模。以点云作为中间表示形式还可以进一步实现交互式用户编辑。在多种数据集上的评估表明,SPAR3D在推理速度为0.7秒的情况下,其性能优于以前的最先进方法。项目页面包含代码和模型:https://spar3d.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了单图像三维物体重建的问题。当前研究主要分两大方向:回归建模和生成建模。回归方法能高效推断可见表面,但难以处理遮挡区域。生成方法通过建模分布来处理不确定区域,但计算量大且生成结果常与可见表面不匹配。本研究提出SPAR3D,一种结合两者优点的新型两阶段方法。第一阶段利用轻量级点扩散模型生成稀疏三维点云,采样速度快;第二阶段结合采样点云和输入图像创建高精度网格。SPAR3D的两阶段设计实现了单图像三维任务的概率建模,同时保持高计算效率和出色的输出保真度。利用点云作为中间表示形式,还可实现用户交互编辑。在多个数据集上的评估显示,SPAR3D在推理速度达到0.7秒的情况下,性能优于之前的最先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 研究背景是关于单图像三维物体重建问题,该领域近期主要分为回归建模和生成建模两大方向。
- 回归方法能够高效推断可见表面,但在处理遮挡区域时遇到困难。
- 生成方法通过建模分布来处理不确定区域,但存在计算量大和生成结果与可见表面不匹配的问题。
- SPAR3D是一种新型的两阶段方法,旨在结合两者的优点。
- 第一阶段利用轻量级点扩散模型快速生成稀疏三维点云。
- 第二阶段结合采样点云和输入图像创建高精度网格,实现良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

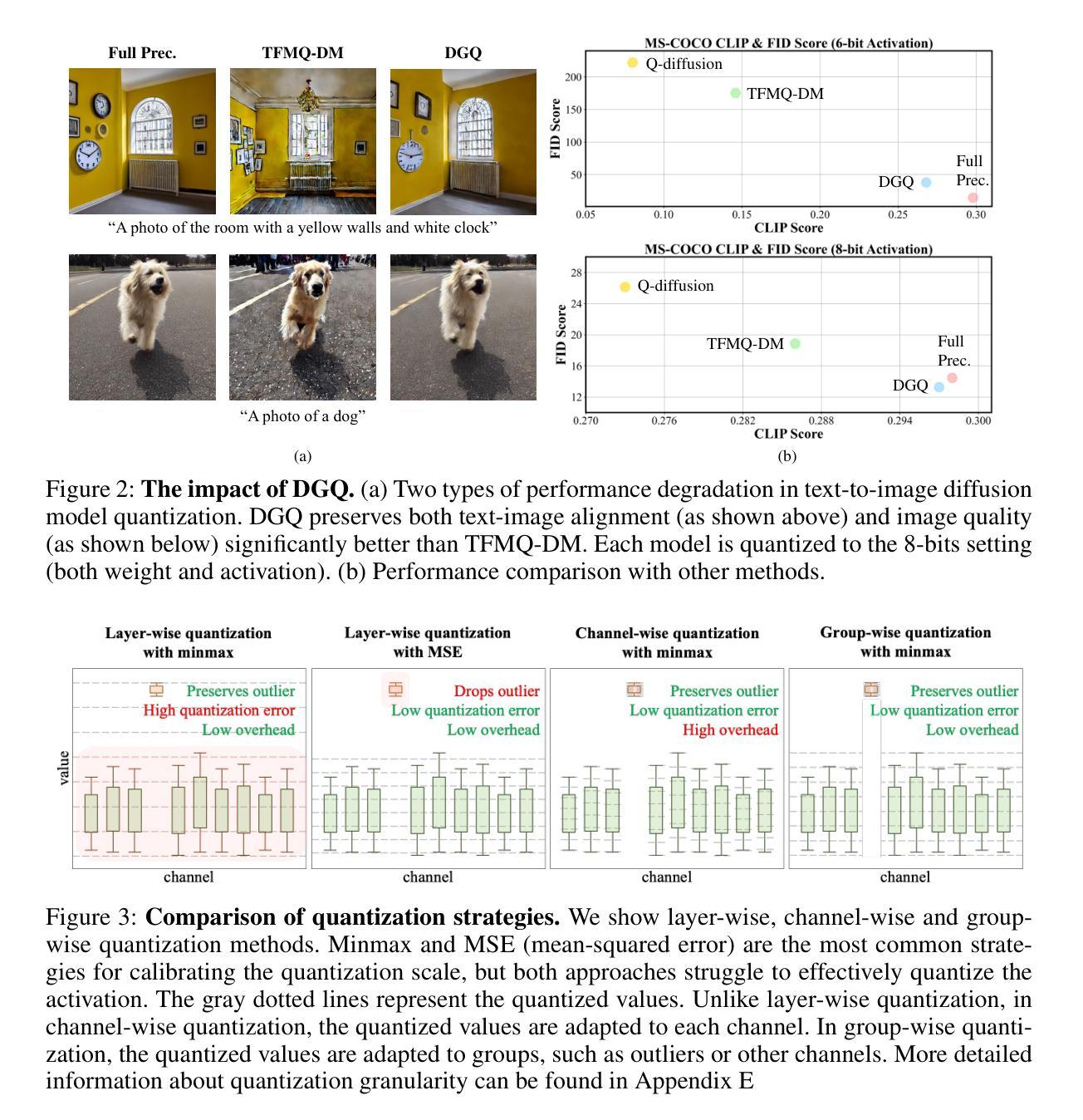
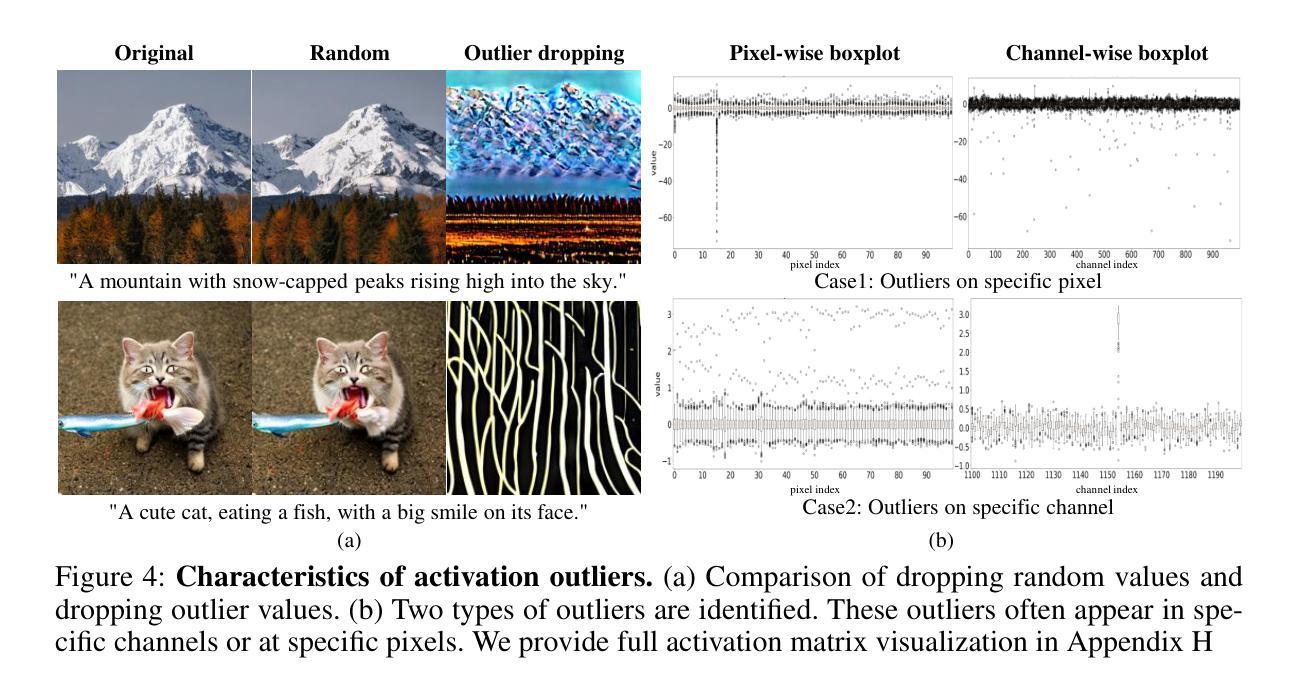
DGQ: Distribution-Aware Group Quantization for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Hyogon Ryu, NaHyeon Park, Hyunjung Shim
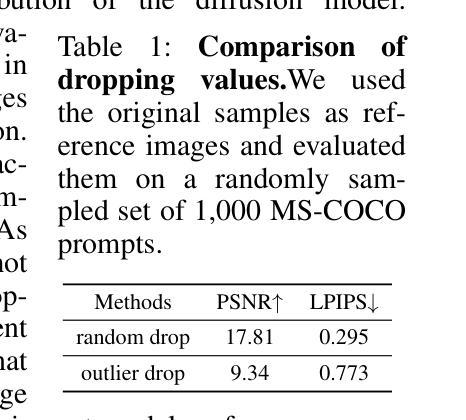
Despite the widespread use of text-to-image diffusion models across various tasks, their computational and memory demands limit practical applications. To mitigate this issue, quantization of diffusion models has been explored. It reduces memory usage and computational costs by compressing weights and activations into lower-bit formats. However, existing methods often struggle to preserve both image quality and text-image alignment, particularly in lower-bit($<$ 8bits) quantization. In this paper, we analyze the challenges associated with quantizing text-to-image diffusion models from a distributional perspective. Our analysis reveals that activation outliers play a crucial role in determining image quality. Additionally, we identify distinctive patterns in cross-attention scores, which significantly affects text-image alignment. To address these challenges, we propose Distribution-aware Group Quantization (DGQ), a method that identifies and adaptively handles pixel-wise and channel-wise outliers to preserve image quality. Furthermore, DGQ applies prompt-specific logarithmic quantization scales to maintain text-image alignment. Our method demonstrates remarkable performance on datasets such as MS-COCO and PartiPrompts. We are the first to successfully achieve low-bit quantization of text-to-image diffusion models without requiring additional fine-tuning of weight quantization parameters.
尽管文本到图像扩散模型在各种任务中得到了广泛应用,但其计算和内存需求限制了实际应用的范围。为了缓解这个问题,已经探索了扩散模型的量化。通过压缩权重和激活值到低位格式,它可以减少内存使用量和计算成本。然而,现有方法往往难以在图像质量和文本-图像对齐方面取得平衡,特别是在低位(<8位)量化中。在本文中,我们从分布的角度分析了量化文本到图像扩散模型所面临的挑战。我们的分析表明,激活异常值在决定图像质量方面起着至关重要的作用。此外,我们还发现了跨注意力分数的独特模式,这显著影响了文本-图像对齐。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了分布感知组量化(DGQ)方法,该方法能够识别和自适应处理像素级和通道级的异常值,以保留图像质量。此外,DGQ应用提示特定的对数量化尺度以维持文本-图像对齐。我们的方法在MS-COCO和PartiPrompts等数据集上表现出了卓越的性能。我们是首批成功实现文本到图像扩散模型的低位量化的研究者,且无需对权重量化参数进行额外的微调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://ugonfor.kr/DGQ
Summary
本文探讨了文本到图像扩散模型的量化问题。由于扩散模型在各项任务中的广泛应用,其计算与内存需求限制了实际应用。为解决这一问题,研究者尝试对扩散模型进行量化,以降低内存使用和计算成本。然而,现有方法难以在保持图像质量和文本-图像对齐方面达到平衡,特别是在低位(<8位)量化中尤为明显。本文从分布角度出发,分析了量化文本到图像扩散模型的挑战,并提出一种名为分布感知组量化(DGQ)的方法,该方法能够自适应处理像素级和通道级的异常值,以保留图像质量,并应用提示特定对数量化尺度来维持文本-图像对齐。DGQ方法在MS-COCO和PartiPrompts等数据集上表现出卓越性能,并且是首个成功实现低位量化的文本到图像扩散模型方法,无需对权重量化参数进行额外微调。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型在计算和内存需求方面存在挑战,限制了其实际应用。
- 量化是降低扩散模型内存使用和计算成本的一种方法。
- 现有量化方法在保持图像质量和文本-图像对齐方面存在困难,特别是在低位量化中。
- 本文从分布角度分析了文本到图像扩散模型的量化挑战。
- 激活异常值对图像质量至关重要。
- 交叉注意力得分对文本-图像对齐有重要影响。
点此查看论文截图

Adapting Image-to-Video Diffusion Models for Large-Motion Frame Interpolation
Authors:Luoxu Jin, Hiroshi Watanabe
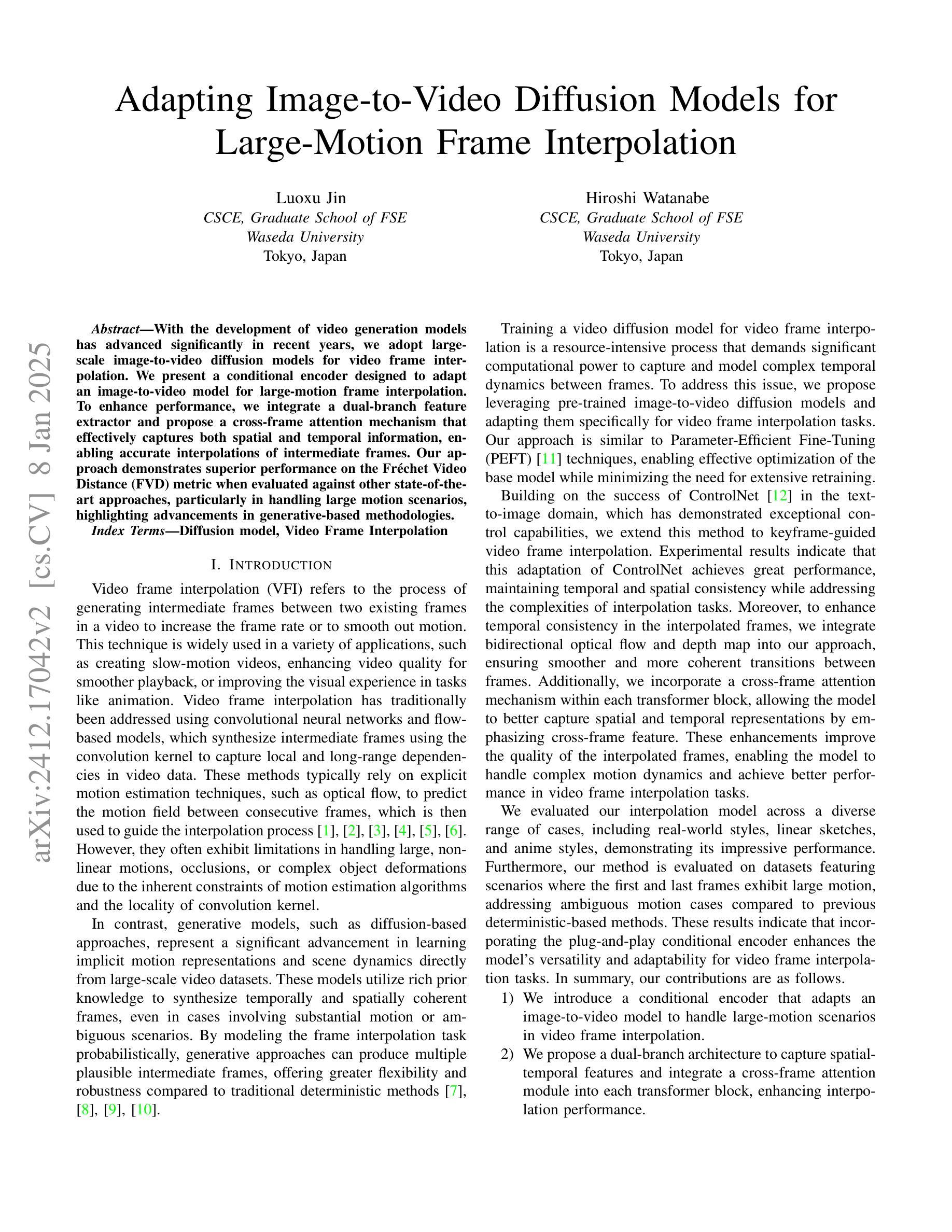
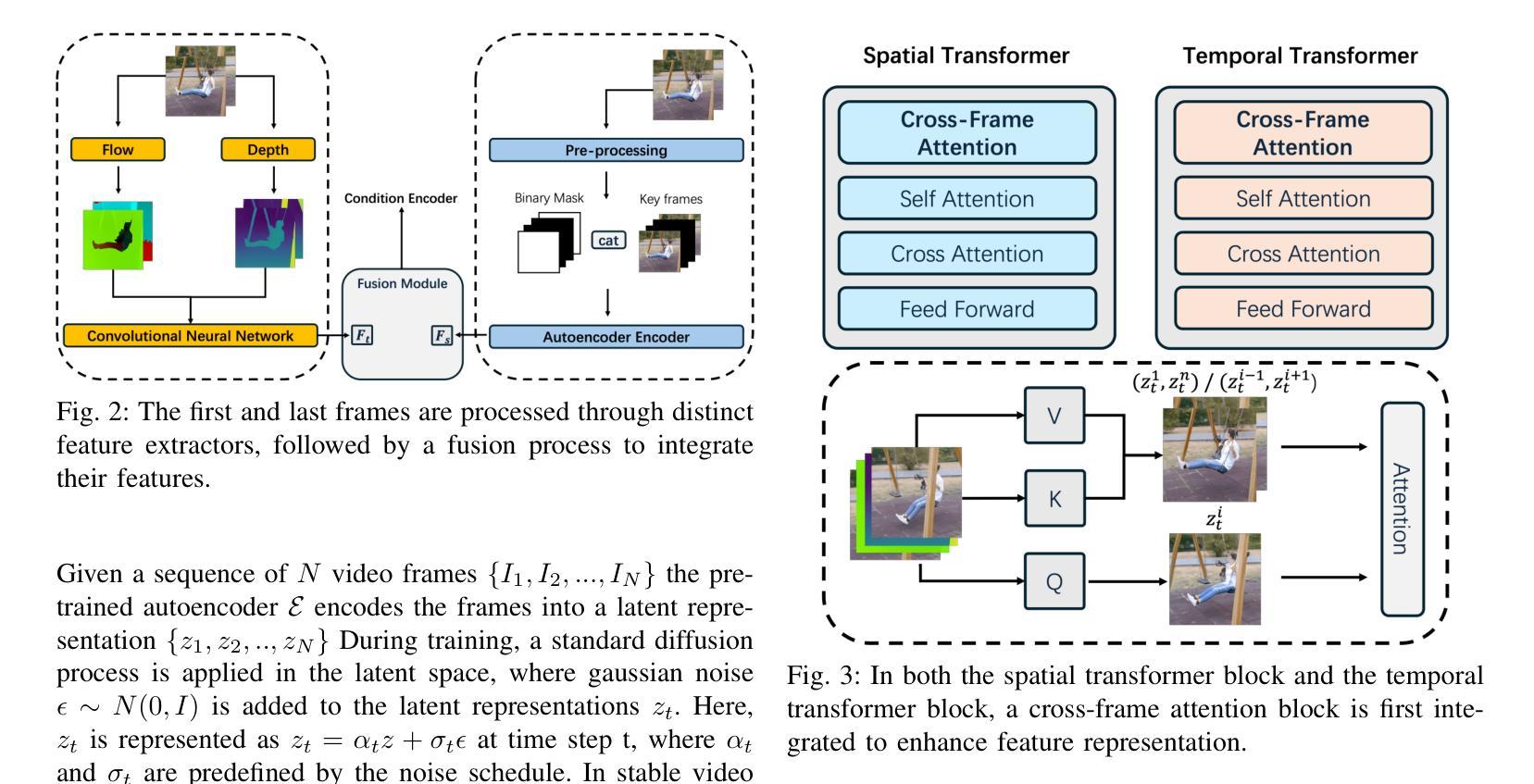
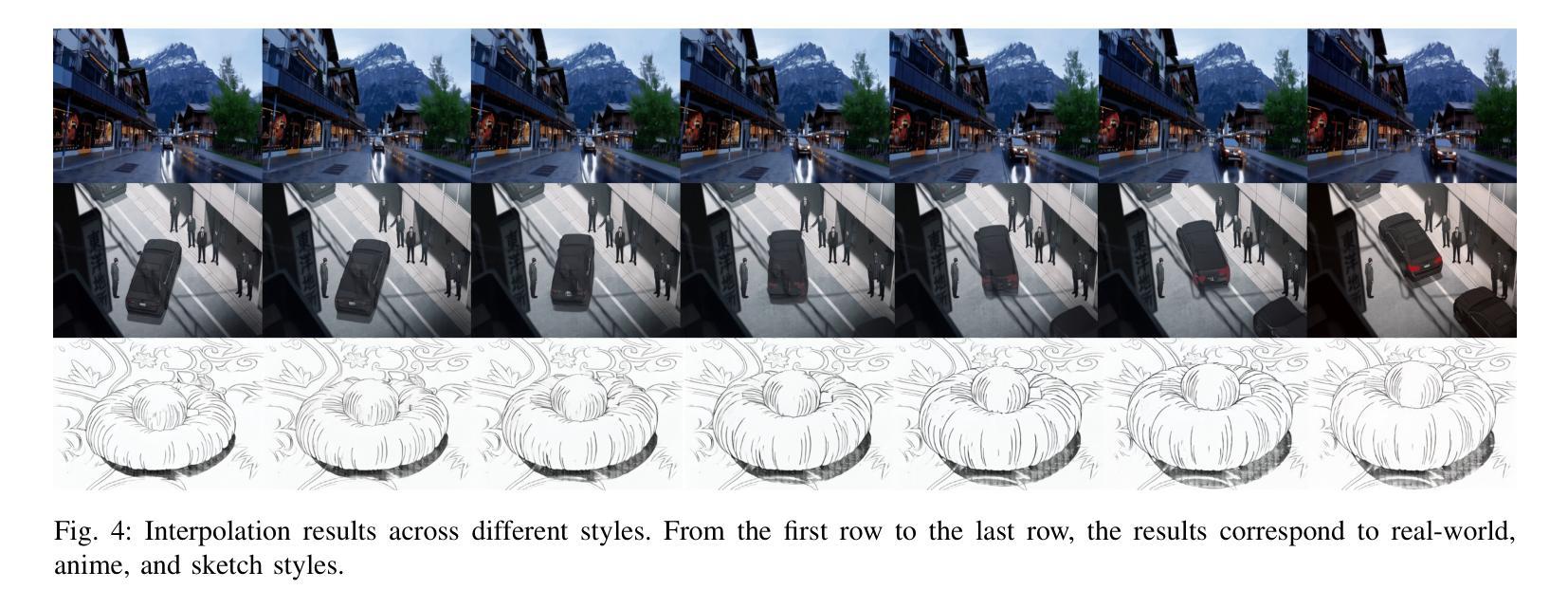
With the development of video generation models has advanced significantly in recent years, we adopt large-scale image-to-video diffusion models for video frame interpolation. We present a conditional encoder designed to adapt an image-to-video model for large-motion frame interpolation. To enhance performance, we integrate a dual-branch feature extractor and propose a cross-frame attention mechanism that effectively captures both spatial and temporal information, enabling accurate interpolations of intermediate frames. Our approach demonstrates superior performance on the Fr'echet Video Distance (FVD) metric when evaluated against other state-of-the-art approaches, particularly in handling large motion scenarios, highlighting advancements in generative-based methodologies.
随着视频生成模型近年来显著发展,我们采用大规模图像到视频的扩散模型进行视频帧插值。我们提出了一种条件编码器,旨在适应图像到视频模型进行大运动帧插值。为了提高性能,我们集成了双分支特征提取器,并提出了一种跨帧注意力机制,该机制可以有效地捕获空间和时间信息,从而实现中间帧的准确插值。与其他最先进的方法相比,我们的方法在Fréchet视频距离(FVD)指标上表现出卓越的性能,特别是在处理大运动场景时,凸显了基于生成的方法的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于大规模图像到视频的扩散模型的视频帧插值技术。采用条件编码器设计,以适应图像到视频模型的插值处理。为提高性能,结合了双分支特征提取器,并提出跨帧注意力机制,能有效捕捉空间和时间信息,实现了准确的中间帧插值。相较于其他前沿方法,特别是在处理大运动场景时,本文方法在Fréchet视频距离(FVD)指标上表现出卓越性能,突显了生成式方法的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 采用大规模图像到视频的扩散模型进行视频帧插值。
- 设计了条件编码器以适应图像到视频模型的插值处理。
- 结合双分支特征提取器提高性能。
- 提出跨帧注意力机制,捕捉空间和时间信息。
- 实现了准确的中间帧插值。
- 在Fréchet视频距离(FVD)指标上表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

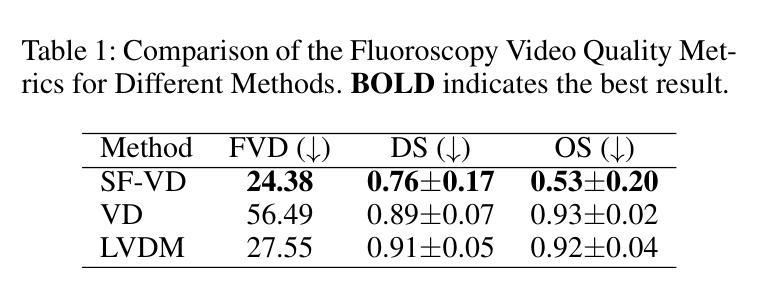
Label-Efficient Data Augmentation with Video Diffusion Models for Guidewire Segmentation in Cardiac Fluoroscopy
Authors:Shaoyan Pan, Yikang Liu, Lin Zhao, Eric Z. Chen, Xiao Chen, Terrence Chen, Shanhui Sun
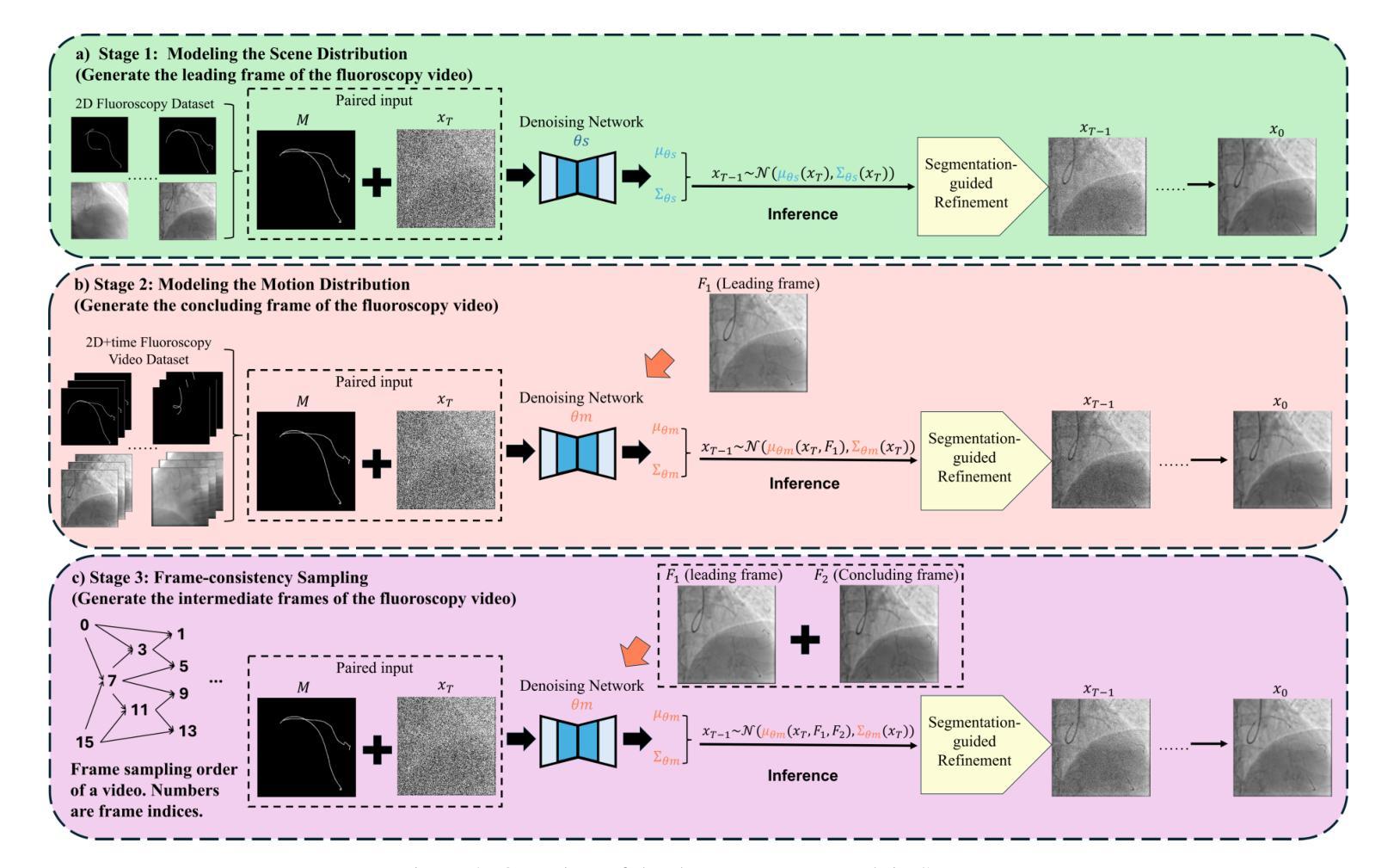
The accurate segmentation of guidewires in interventional cardiac fluoroscopy videos is crucial for computer-aided navigation tasks. Although deep learning methods have demonstrated high accuracy and robustness in wire segmentation, they require substantial annotated datasets for generalizability, underscoring the need for extensive labeled data to enhance model performance. To address this challenge, we propose the Segmentation-guided Frame-consistency Video Diffusion Model (SF-VD) to generate large collections of labeled fluoroscopy videos, augmenting the training data for wire segmentation networks. SF-VD leverages videos with limited annotations by independently modeling scene distribution and motion distribution. It first samples the scene distribution by generating 2D fluoroscopy images with wires positioned according to a specified input mask, and then samples the motion distribution by progressively generating subsequent frames, ensuring frame-to-frame coherence through a frame-consistency strategy. A segmentation-guided mechanism further refines the process by adjusting wire contrast, ensuring a diverse range of visibility in the synthesized image. Evaluation on a fluoroscopy dataset confirms the superior quality of the generated videos and shows significant improvements in guidewire segmentation.
在心脏介入手术的荧光透视视频中,对导线进行准确的分割对于计算机辅助导航任务至关重要。虽然深度学习的方法在导线分割方面已经表现出了高准确性和稳健性,但它们需要大量的标注数据集来实现泛化,这突显了对丰富标注数据的需要,以提高模型的性能。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了分割引导的帧一致性视频扩散模型(SF-VD),以生成大量的标注荧光透视视频,增强导线分割网络的训练数据。SF-VD通过独立建模场景分布和运动分布来利用标注较少的视频。它通过根据指定的输入掩码生成带有导线的二维荧光透视图像来采样场景分布,然后通过逐步生成后续帧来采样运动分布,通过帧一致性策略确保帧到帧的一致性。分割引导机制进一步通过调整导线对比度来完善这一过程,确保合成图像的可见性范围广泛。在荧光透视数据集上的评估证实了所生成视频的高质量,并显示出导线分割的显著改善。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
在心脏介入荧光视频中的导线准确分割对于计算机辅助导航任务至关重要。针对现有深度学习模型需要大量标注数据以提高性能的问题,我们提出了基于分割引导的帧一致性视频扩散模型(SF-VD)。该模型通过独立建模场景分布和运动分布,生成大量标注的荧光视频,增强导线分割网络的训练数据。SF-VD首先根据指定的输入掩膜生成二维荧光图像来采样场景分布,然后通过逐步生成后续帧来采样运动分布,确保帧间一致性。分割引导机制进一步调整导线的对比度,确保合成图像的可见性多样。在荧光数据集上的评估证实了生成视频的高质量,并在导线分割方面取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 准确分割心脏介入荧光视频中的导线对计算机辅助导航至关重要。
- 深度学习模型在导线分割中表现出高准确性和稳健性,但需要大量标注数据以提高性能。
- 提出了一种新的模型SF-VD来解决标注数据不足的问题。
- SF-VD通过独立建模场景分布和运动分布来生成大量标注的荧光视频。
- SF-VD利用帧一致性策略确保生成的视频帧间连贯性。
- 分割引导机制用于调整导线的对比度,增加合成图像的可见性多样性。
点此查看论文截图


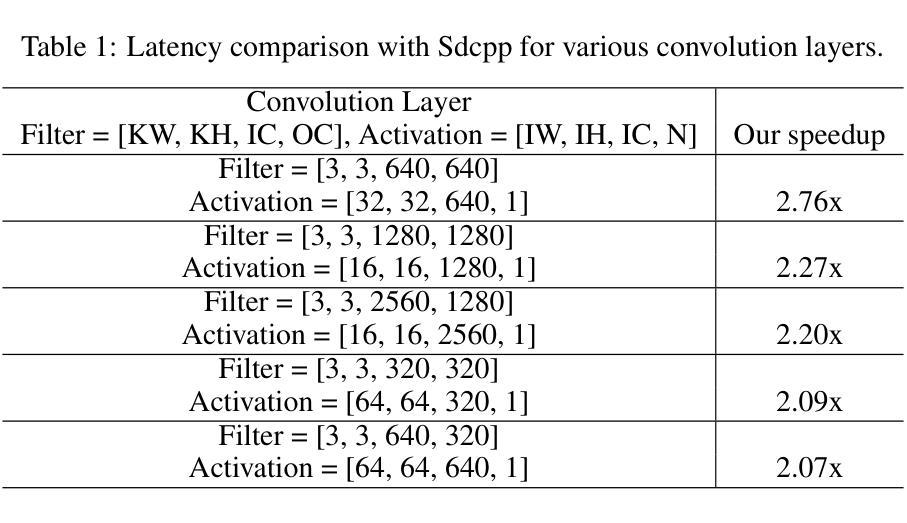
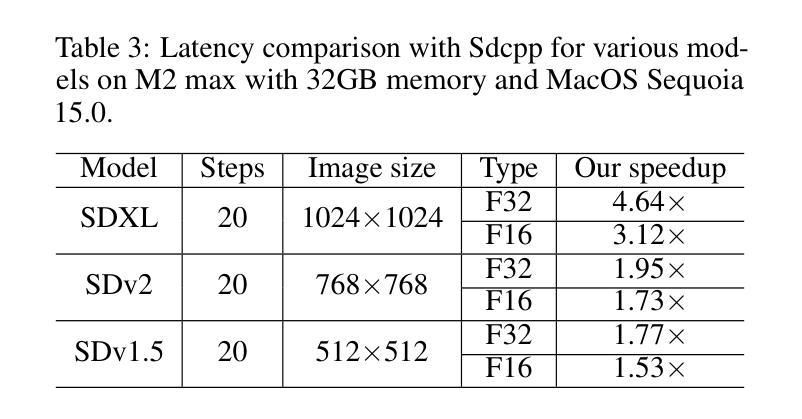
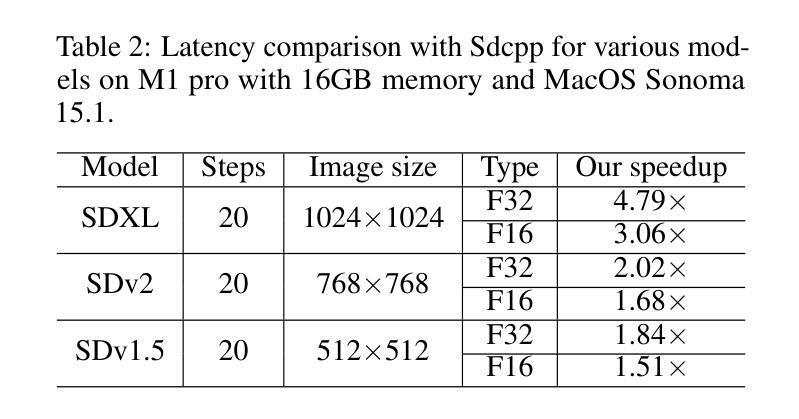
Open-Source Acceleration of Stable-Diffusion.cpp Deployable on All Devices
Authors:Jingxu Ng, Cheng Lv, Pu Zhao, Wei Niu, Juyi Lin, Minzhou Pan, Yun Liang, Yanzhi Wang
Stable diffusion plays a crucial role in generating high-quality images. However, image generation is time-consuming and memory-intensive. To address this, stable-diffusion.cpp (Sdcpp) emerges as an efficient inference framework to accelerate the diffusion models. Although it is lightweight, the current implementation of ggml_conv_2d operator in Sdcpp is suboptimal, exhibiting both high inference latency and massive memory usage. To address this, in this work, we present an optimized version of Sdcpp leveraging the Winograd algorithm to accelerate 2D convolution operations, which is the primary bottleneck in the pipeline. By analyzing both dependent and independent computation graphs, we exploit the device’s locality and parallelism to achieve substantial performance improvements. Our framework delivers correct end-to-end results across various stable diffusion models, including SDv1.4, v1.5, v2.1, SDXL, and SDXL-Turbo. Our evaluation results demonstrate a speedup up to 2.76x for individual convolutional layers and an inference speedup up to 4.79x for the overall image generation process, compared with the original Sdcpp on M1 pro. Homepage: https://github.com/SealAILab/stable-diffusion-cpp
稳定扩散在生成高质量图像中起着至关重要的作用。然而,图像生成是耗时的且需要大量内存。为了解决这一问题,stable-diffusion.cpp(Sdcpp)作为一个高效的推理框架应运而生,以加速扩散模型的运行。虽然它很轻便,但Sdcpp中ggml_conv_2d算子的当前实现并不理想,存在推理延迟高和内存使用量大的问题。针对这一问题,我们在本工作中推出了一个优化版的Sdcpp,利用Winograd算法加速2D卷积操作,这是管道中的主要瓶颈。通过分析有依赖和无依赖的计算图,我们利用设备的局部性和并行性实现了显著的性能提升。我们的框架在各种稳定的扩散模型中都能提供正确的端到端结果,包括SDv1.4、v1.5、v2.1、SDXL和SDXL-Turbo。我们的评估结果表明,与原始Sdcpp在M1 pro上的表现相比,单个卷积层的速度提高了2.76倍,整个图像生成过程的推理速度提高了4.79倍。更多信息请访问:https://github.com/SealAILab/stable-diffusion-cpp
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
稳定扩散在生成高质量图像中起到关键作用,但图像生成耗时且占用过多的内存资源。为了解决这个问题,stable-diffusion.cpp(Sdcpp)作为一个高效的推理框架应运而生,以加速扩散模型的运行。然而,Sdcpp中ggml_conv_2d算子的当前实现并不理想,存在推理延迟高和内存使用量大等问题。为解决这些问题,本研究提出了一种利用Winograd算法优化Sdcpp的版本,以加速2D卷积操作,这是管道中的主要瓶颈。通过分析有依赖和无依赖的计算图,我们充分利用设备的局部性和并行性,实现了显著的性能提升。我们的框架适用于各种稳定扩散模型,包括SDv1.4、v1.5、v2.1、SDXL和SDXL-Turbo。评估结果显示,相对于原始Sdcpp在M1 pro上的表现,我们的框架对单个卷积层的加速最高可达2.76倍,对整个图像生成过程的推理速度提高最高可达4.79倍。
Key Takeaways
- 稳定扩散在生成高质量图像中扮演重要角色,但存在时间消耗和内存占用的问题。
- stable-diffusion.cpp(Sdcpp)作为推理框架旨在优化扩散模型的运行效率。
- Sdcpp中的ggml_conv_2d算子当前实现存在缺陷,导致高推理延迟和大量内存使用。
- 利用Winograd算法优化Sdcpp,加速2D卷积操作,解决主要瓶颈问题。
- 通过分析计算图,充分利用设备局部性和并行性,实现显著性能提升。
- 优化的框架适用于多种稳定扩散模型,包括SDv1.4、v1.5、v2.1、SDXL和SDXL-Turbo。
- 评估结果显示,相对于原始Sdcpp,优化后的框架在多个层面实现了显著的性能加速。
点此查看论文截图


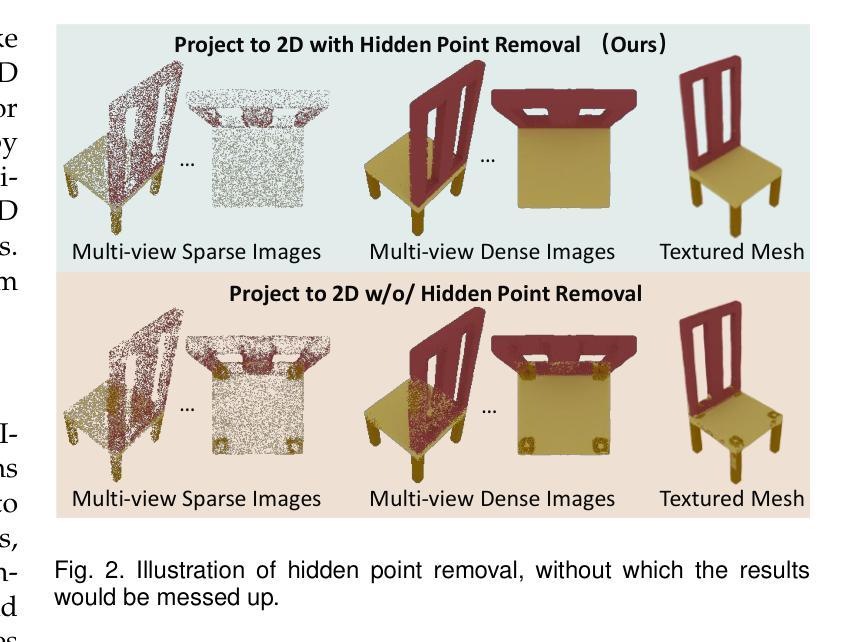
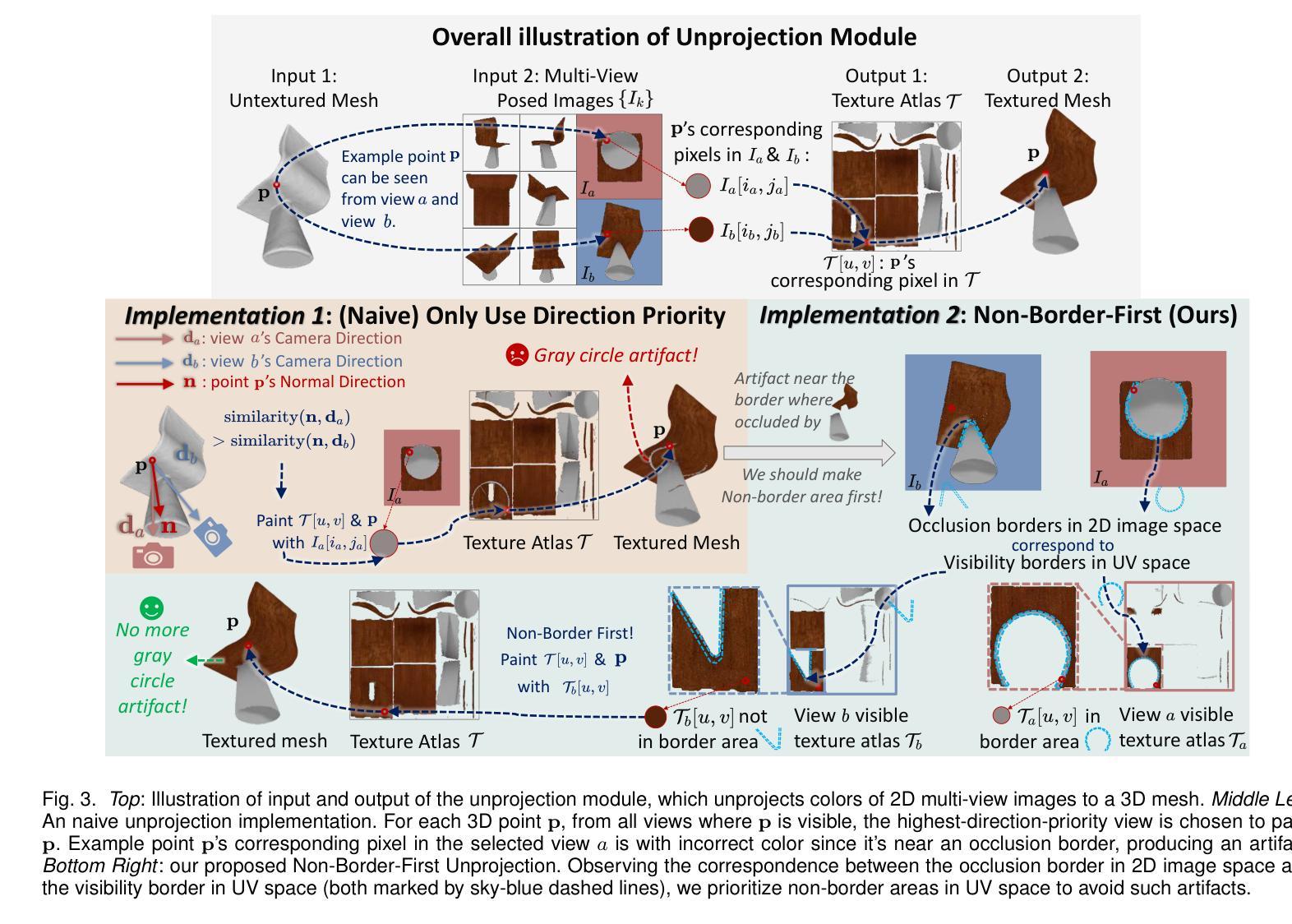
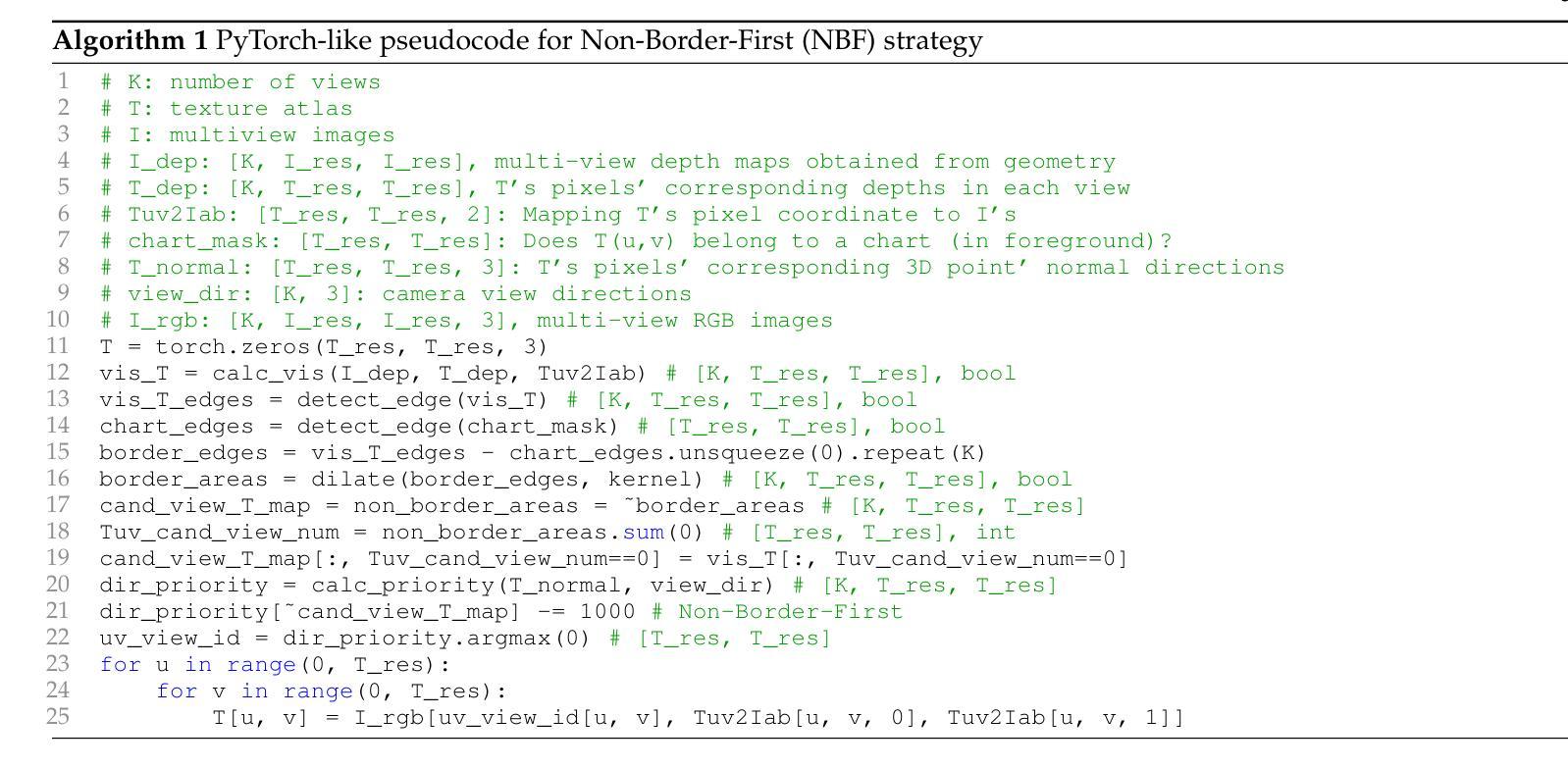
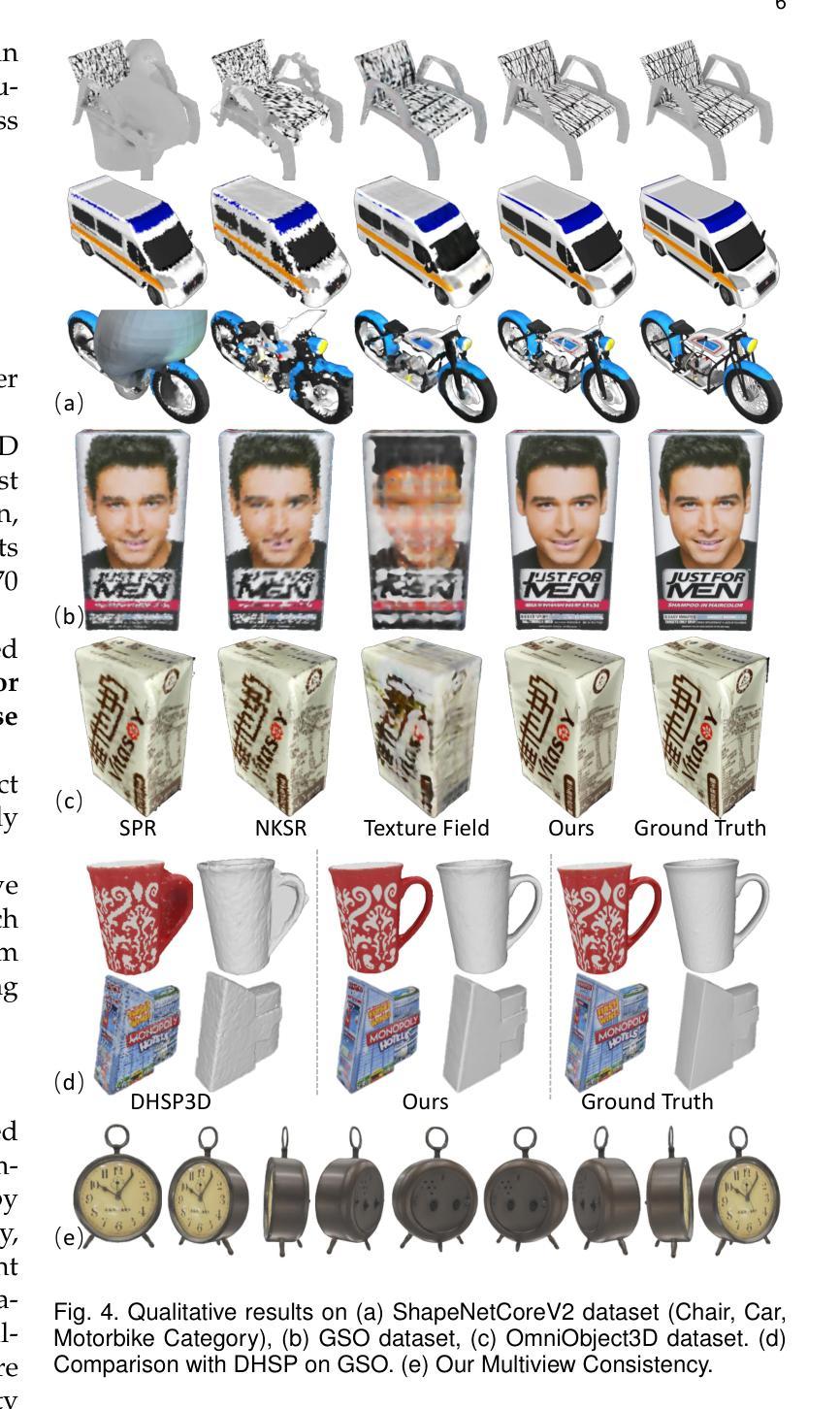
PointDreamer: Zero-shot 3D Textured Mesh Reconstruction from Colored Point Cloud
Authors:Qiao Yu, Xianzhi Li, Yuan Tang, Xu Han, Jinfeng Xu, Long Hu, Min Chen
Reconstructing textured meshes from colored point clouds is an important but challenging task. Most existing methods yield blurry-looking textures or rely on 3D training data that are hard to acquire. Regarding this, we propose PointDreamer, a novel framework for textured mesh reconstruction from colored point cloud via diffusion-based 2D inpainting. Specifically, we first reconstruct an untextured mesh. Next, we project the input point cloud into 2D space to generate sparse multi-view images, and then inpaint empty pixels utilizing a pre-trained 2D diffusion model. After that, we unproject the colors of the inpainted dense images onto the untextured mesh, thus obtaining the final textured mesh. This project-inpaint-unproject pipeline bridges the gap between 3D point clouds and 2D diffusion models for the first time. Thanks to the powerful 2D diffusion model pre-trained on extensive 2D data, PointDreamer reconstructs clear, high-quality textures with high robustness to sparse or noisy input. Also, it’s zero-shot requiring no extra training. In addition, we design Non-Border-First unprojection strategy to address the border-area inconsistency issue, which is less explored but commonly-occurred in methods that generate 3D textures from multiview images. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments on various synthetic and real-scanned datasets show the SoTA performance of PointDreamer, by significantly outperforming baseline methods with 30% improvement in LPIPS score (from 0.118 to 0.068). Code at: https://github.com/YuQiao0303/PointDreamer.
从彩色点云重建纹理网格是一项重要且具有挑战性的任务。大多数现有方法产生的纹理模糊,或者依赖于难以获取的3D训练数据。针对这一问题,我们提出了PointDreamer,这是一种新的从彩色点云重建纹理网格的方法,基于扩散的2D图像修复技术。具体来说,我们首先重建一个无纹理的网格。然后,我们将输入的点云投影到2D空间,生成稀疏的多视角图像,并利用预训练的2D扩散模型填充空白像素。之后,我们将填充后的密集图像的颜色反投影到无纹理的网格上,从而获得最终的纹理网格。这种投影-修复-反投影的管道首次填补了3D点云和2D扩散模型之间的空白。由于预训练的强大的2D扩散模型在大量的2D数据上进行了训练,PointDreamer能够重建清晰、高质量的纹理,对稀疏或嘈杂的输入具有高度的鲁棒性。此外,它是零次射击,不需要额外的训练。另外,我们设计了非边界优先的反投影策略,以解决从多视角图像生成3D纹理时较少探索但常发生的边界区域不一致问题。在各种合成和真实扫描数据集上的大量定性和定量实验表明,PointDreamer的性能处于领先水平,相较于基线方法在LPIPS得分上有30%的改进(从0.118提高到0.068)。代码地址:https://github.com/YuQiao0303/PointDreamer。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
PointDreamer是一个基于扩散模型的框架,可从彩色点云中重建纹理网格。它采用投影-修复-反投影的流程,利用预训练的二维扩散模型填充稀疏像素,从而得到清晰的、高质量的纹理。该框架无需额外训练,对稀疏或噪声输入具有鲁棒性。此外,还设计了解决边界区域不一致问题的非边界优先反投影策略。在多个合成和真实扫描数据集上的实验表明,PointDreamer性能优于基线方法,在LPIPS得分上有30%的改进。
关键见解
- PointDreamer是一个用于从彩色点云中重建纹理网格的新框架。
- 该框架采用投影-修复-反投影流程,结合三维点云和二维扩散模型。
- 利用预训练的二维扩散模型,PointDreamer能够生成清晰、高质量的纹理。
- 该框架对稀疏或噪声输入具有鲁棒性,且无需额外训练。
- 引入非边界优先反投影策略,解决从多视角图像生成三维纹理时常见的边界区域不一致问题。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,PointDreamer在性能上优于基线方法。
- PointDreamer的代码已公开,可供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图

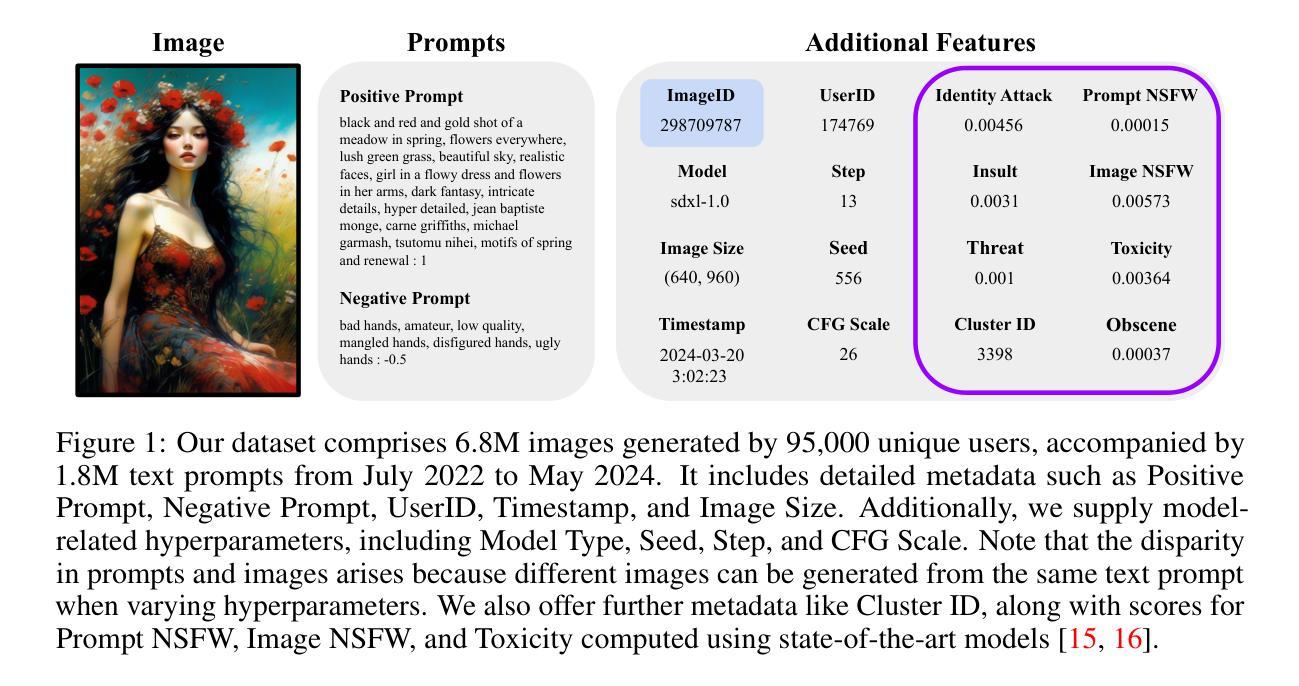
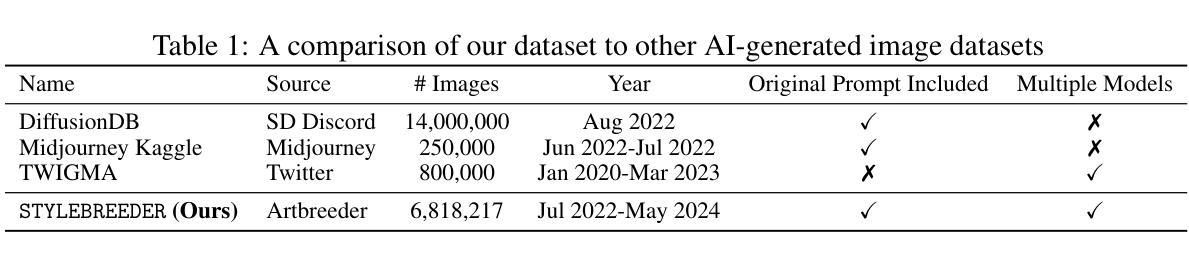
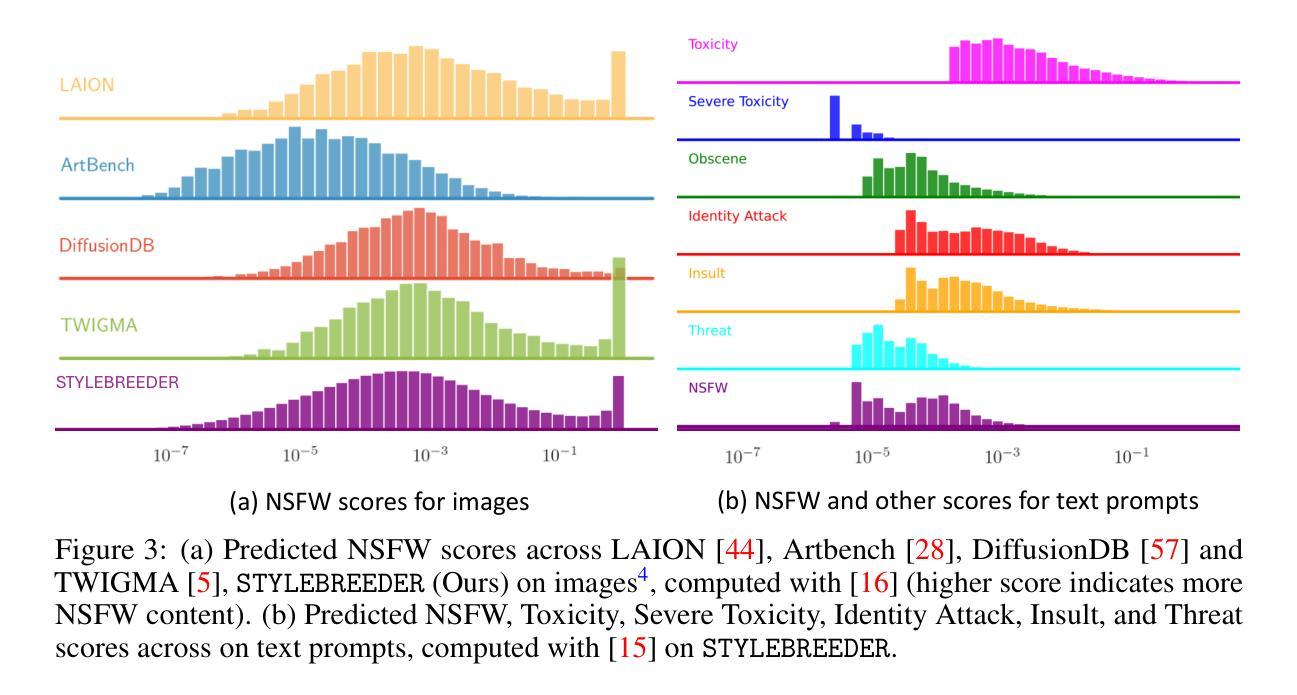
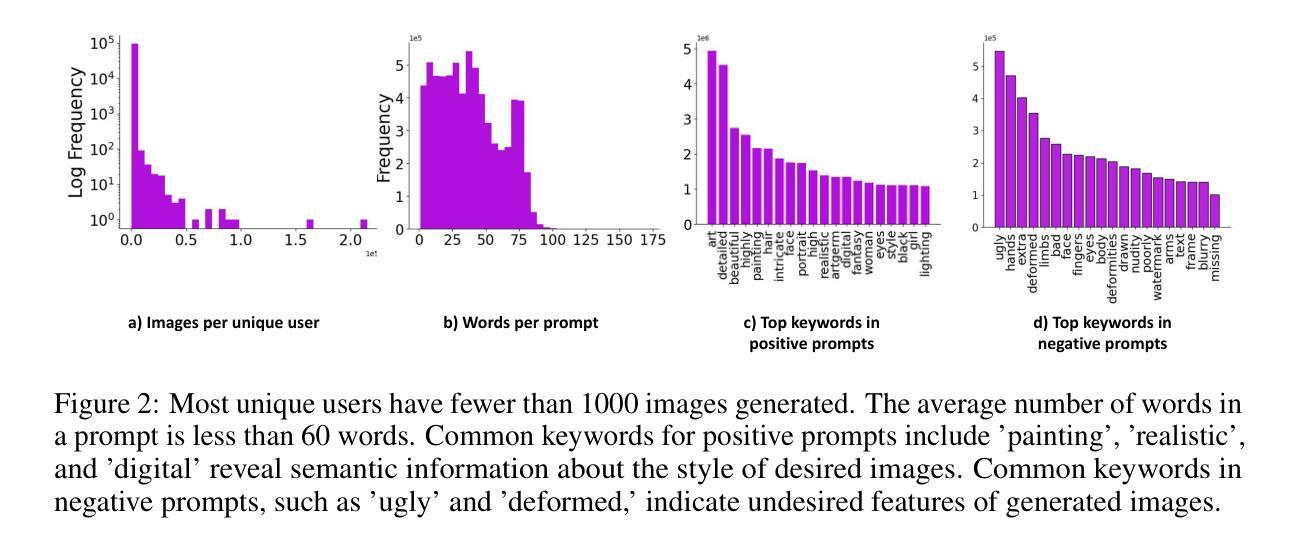
Stylebreeder: Exploring and Democratizing Artistic Styles through Text-to-Image Models
Authors:Matthew Zheng, Enis Simsar, Hidir Yesiltepe, Federico Tombari, Joel Simon, Pinar Yanardag
Text-to-image models are becoming increasingly popular, revolutionizing the landscape of digital art creation by enabling highly detailed and creative visual content generation. These models have been widely employed across various domains, particularly in art generation, where they facilitate a broad spectrum of creative expression and democratize access to artistic creation. In this paper, we introduce \texttt{STYLEBREEDER}, a comprehensive dataset of 6.8M images and 1.8M prompts generated by 95K users on Artbreeder, a platform that has emerged as a significant hub for creative exploration with over 13M users. We introduce a series of tasks with this dataset aimed at identifying diverse artistic styles, generating personalized content, and recommending styles based on user interests. By documenting unique, user-generated styles that transcend conventional categories like ‘cyberpunk’ or ‘Picasso,’ we explore the potential for unique, crowd-sourced styles that could provide deep insights into the collective creative psyche of users worldwide. We also evaluate different personalization methods to enhance artistic expression and introduce a style atlas, making these models available in LoRA format for public use. Our research demonstrates the potential of text-to-image diffusion models to uncover and promote unique artistic expressions, further democratizing AI in art and fostering a more diverse and inclusive artistic community. The dataset, code and models are available at https://stylebreeder.github.io under a Public Domain (CC0) license.
文本转图像模型正日益受到欢迎,它通过生成高度详细和创造性的视觉内容,彻底改变了数字艺术创作的格局。这些模型已被广泛应用于各个领域,特别是在艺术生成领域,它们促进了广泛的创意表达,并使艺术创作变得民主化。在本文中,我们介绍了
STYLEBREEDER数据集,该数据集包含由Artbreeder平台上9.5万名用户生成的680万张图像和180万个提示,Artbreeder平台已成为拥有超过13百万用户的创意探索重要中心。我们利用这个数据集进行了一系列任务,旨在识别不同的艺术风格、生成个性化内容以及根据用户兴趣推荐风格。通过记录超越传统类别(如“赛博朋克”或“毕加索”)的独特用户生成风格,我们探索了独特的大众源风格的潜力,这些风格可能深入洞察全球用户的集体创意心理。我们还评估了不同的个性化方法来增强艺术表现力,并引入了一个风格图谱,以LoRA格式提供这些模型供公众使用。我们的研究表明,文本转图像扩散模型具有揭示和促进独特艺术表达方式的潜力,进一步使人工智能在艺术创作中民主化,并促进一个更加多样化和包容性的艺术社区。数据集、代码和模型可在https://stylebreeder.github.io上以公共领域(CC0)许可证使用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at NeurIPS 2024 D&B Track, Project page: https://stylebreeder.github.io HuggingFace DB Page: https://huggingface.co/datasets/stylebreeder/stylebreeder
Summary:
文本到图像模型正日益普及,它们通过促进高度详细和创造性的视觉内容生成,革命性地改变了数字艺术创作的格局。本文介绍了与Artbreeder平台相关的数据集“STYLEBREEDER”,该平台包含超过1.3亿用户生成的图像和提示,已成为创意探索的重要中心。研究通过一系列任务探索了独特、用户生成的艺术风格,并评估了个性化方法以增强艺术表现力。此外,该研究还推出了风格图谱,以LoRA格式提供这些模型供公众使用。研究表明文本到图像扩散模型具有促进独特艺术表达和创新艺术社区的潜力。数据集、代码和模型均可在https://stylebreeder.github.io网站上免费访问。
Key Takeaways:
- 文本到图像模型在数字艺术领域越来越受欢迎,可生成高度详细和创造性的视觉内容。
- “STYLEBREEDER”数据集由超过680万张图像和数百万个提示组成,反映了用户的集体创造力。
- 该研究探索了用户生成的艺术风格,超越了传统的艺术风格分类,如科幻朋克或毕加索风格等。
- 研究评估了个性化方法来增强艺术表现力,并引入了风格图谱来展示这些模型的应用。
- 这些模型和工具旨在进一步推动艺术的民主化,促进更多多样化的艺术社区的发展。
点此查看论文截图


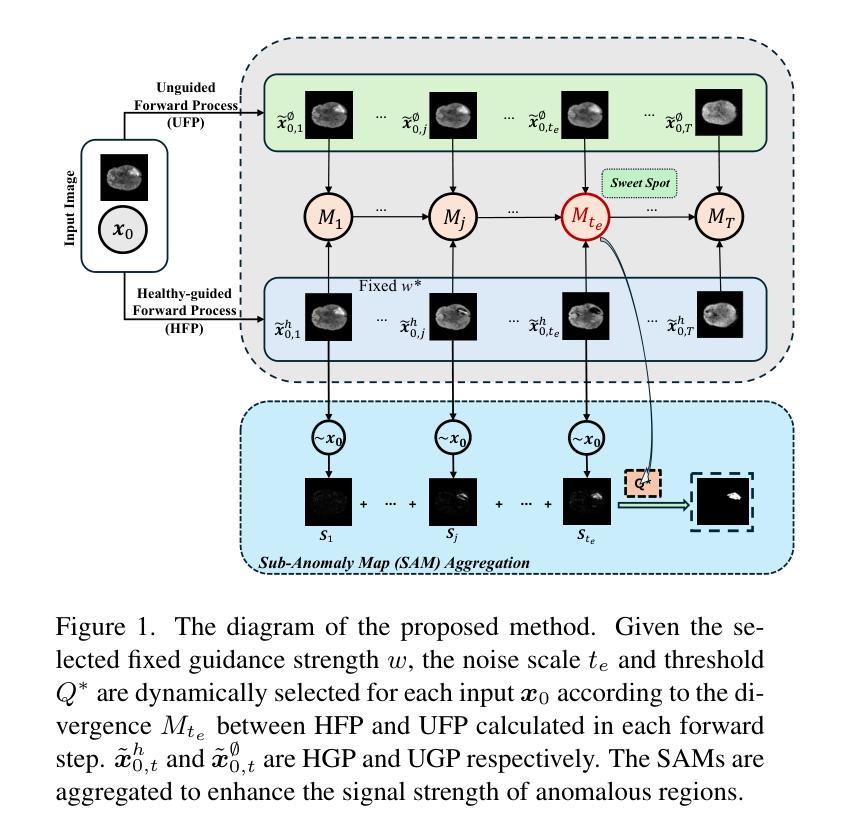
AnoFPDM: Anomaly Segmentation with Forward Process of Diffusion Models for Brain MRI
Authors:Yiming Che, Fazle Rafsani, Jay Shah, Md Mahfuzur Rahman Siddiquee, Teresa Wu
Weakly-supervised diffusion models (DMs) in anomaly segmentation, leveraging image-level labels, have attracted significant attention for their superior performance compared to unsupervised methods. It eliminates the need for pixel-level labels in training, offering a more cost-effective alternative to supervised methods. However, existing methods are not fully weakly-supervised because they heavily rely on costly pixel-level labels for hyperparameter tuning in inference. To tackle this challenge, we introduce Anomaly Segmentation with Forward Process of Diffusion Models (AnoFPDM), a fully weakly-supervised framework that operates without the need of pixel-level labels. Leveraging the unguided forward process as a reference for the guided forward process, we select hyperparameters such as the noise scale, the threshold for segmentation and the guidance strength. We aggregate anomaly maps from guided forward process, enhancing the signal strength of anomalous regions. Remarkably, our proposed method outperforms recent state-of-the-art weakly-supervised approaches, even without utilizing pixel-level labels.
弱监督扩散模型(DMs)在异常分割中的应用已经引起了广泛关注,它利用图像级标签,相较于无监督方法表现出卓越的性能。它消除了对训练过程中像素级标签的需求,为监督方法提供了更具成本效益的替代方案。然而,现有方法并非完全弱监督,因为它们严重依赖于推理过程中的超参数调整所需的昂贵像素级标签。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了基于扩散模型正向过程的异常分割(AnoFPDM),这是一个完全弱监督的框架,无需像素级标签即可运行。我们以非引导正向过程作为引导正向过程的参考,选择超参数,如噪声规模、分割阈值和引导强度。我们从引导的正向过程中聚合异常图,增强异常区域的信号强度。值得注意的是,我们提出的方法即使在不需要像素级标签的情况下,也优于最新的弱监督方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF v4: added appendices and fixed some typos
Summary
基于图像级标签的弱监督扩散模型在异常分割中受到广泛关注,其性能优于无监督方法。它消除了对像素级标签训练的需求,提供了更经济替代监督方法。然而,现有方法并非完全弱监督,因为它们依赖于昂贵的像素级标签进行推理阶段的超参数调整。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了基于扩散模型的异常分割正向过程(AnomFPDM),这是一个完全弱监督的框架,无需像素级标签即可运行。利用未引导的正向过程作为引导正向过程的参考,我们选择超参数,如噪声规模、分割阈值和引导强度。我们从引导正向过程中聚合异常图,增强异常区域的信号强度。值得注意的是,我们提出的方法在无像素级标签的情况下,甚至超越了最新的弱监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督扩散模型在异常分割中受到关注,其性能优于无监督方法。
- 现有方法仍依赖像素级标签进行超参数调整,成本较高。
- 提出了一种全新的弱监督框架AnomFPDM,无需像素级标签。
- AnomFPDM利用未引导的正向过程作为引导正向过程的参考,选择关键超参数。
- 通过聚合来自引导正向过程的异常图,增强了异常区域的信号强度。
- AnomFPDM超越了最新的弱监督方法,即使在没有像素级标签的情况下。
点此查看论文截图

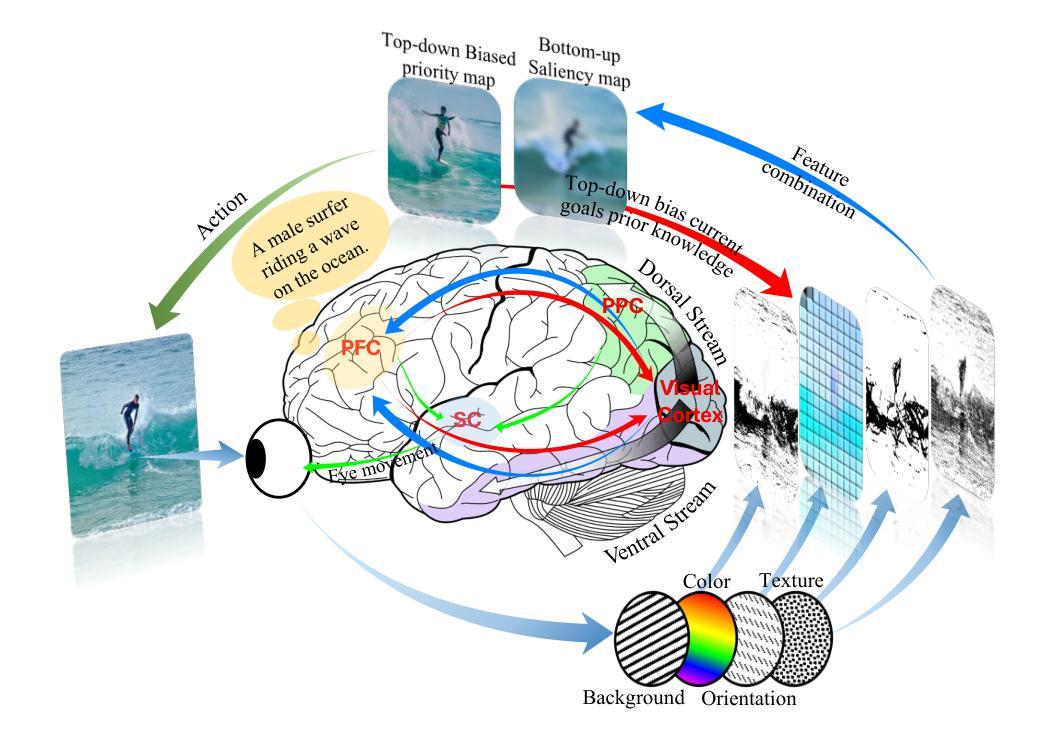
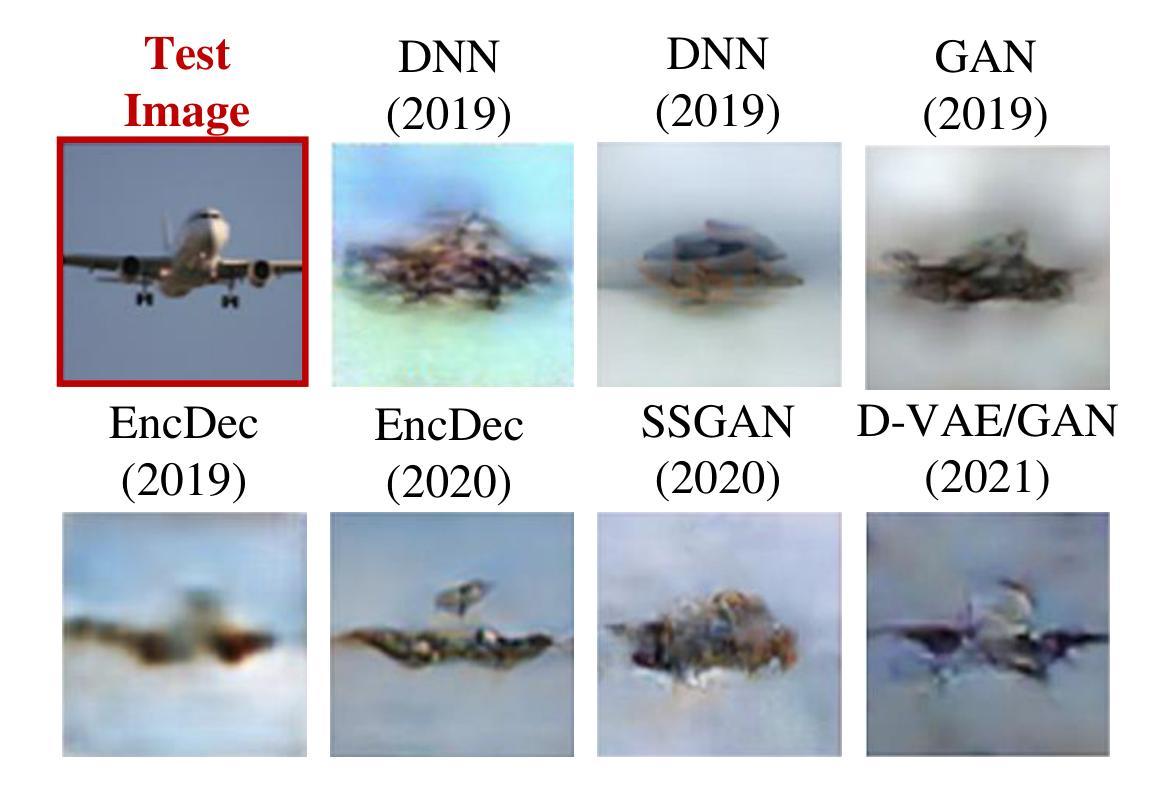
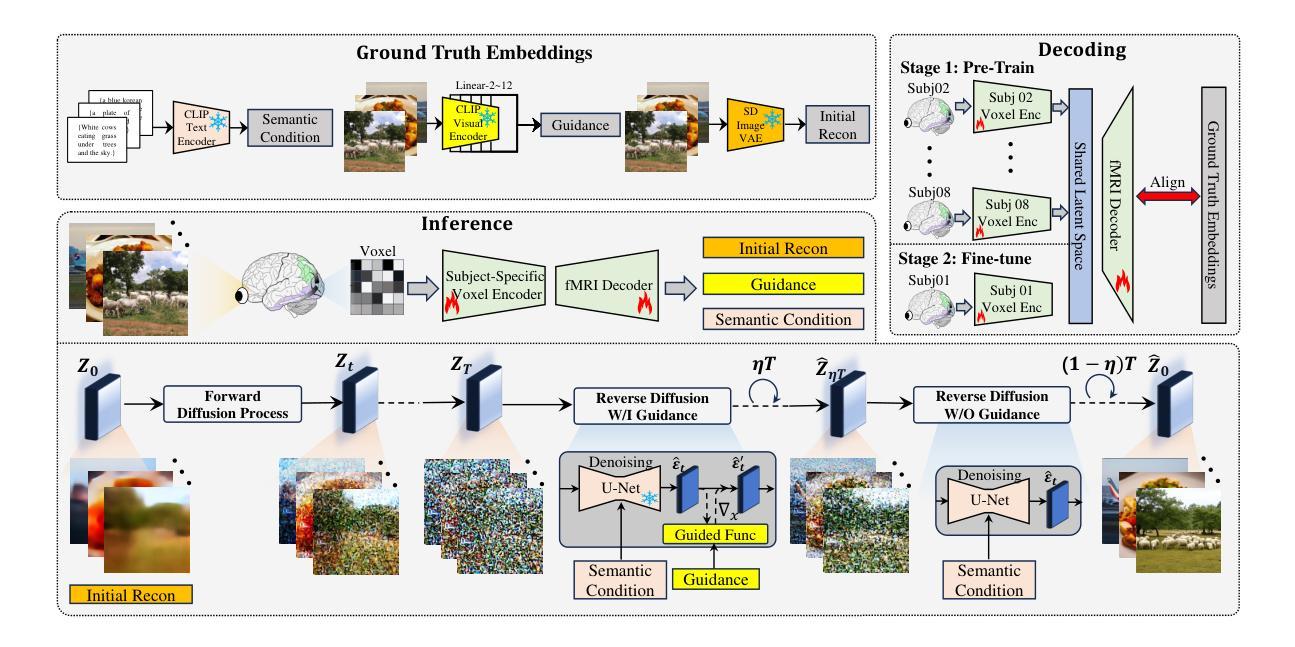
NeuralDiffuser: Neuroscience-inspired Diffusion Guidance for fMRI Visual Reconstruction
Authors:Haoyu Li, Hao Wu, Badong Chen
Reconstructing visual stimuli from functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging fMRI enables fine-grained retrieval of brain activity. However, the accurate reconstruction of diverse details, including structure, background, texture, color, and more, remains challenging. The stable diffusion models inevitably result in the variability of reconstructed images, even under identical conditions. To address this challenge, we first uncover the neuroscientific perspective of diffusion methods, which primarily involve top-down creation using pre-trained knowledge from extensive image datasets, but tend to lack detail-driven bottom-up perception, leading to a loss of faithful details. In this paper, we propose NeuralDiffuser, which incorporates primary visual feature guidance to provide detailed cues in the form of gradients. This extension of the bottom-up process for diffusion models achieves both semantic coherence and detail fidelity when reconstructing visual stimuli. Furthermore, we have developed a novel guidance strategy for reconstruction tasks that ensures the consistency of repeated outputs with original images rather than with various outputs. Extensive experimental results on the Natural Senses Dataset (NSD) qualitatively and quantitatively demonstrate the advancement of NeuralDiffuser by comparing it against baseline and state-of-the-art methods horizontally, as well as conducting longitudinal ablation studies.
从功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)重建视觉刺激能够实现精细的大脑活动检索。然而,准确重建包括结构、背景、纹理、颜色等在内的各种细节仍然具有挑战性。稳定的扩散模型即使在相同条件下也不可避免地导致重建图像的变化。为了解决这一挑战,我们首先揭示了扩散方法在神经科学方面的视角,其主要涉及使用来自大量图像数据集的预训练知识进行自上而下的创建,但往往缺乏细节驱动的自下而上的感知,导致丢失忠实细节。在本文中,我们提出了NeuralDiffuser,它结合了主要视觉特征指导,以梯度形式提供详细线索。这种扩散模型的自下而上过程的扩展在重建视觉刺激时实现了语义连贯性和细节保真度。此外,我们还为重建任务开发了一种新的指导策略,确保重复输出与原始图像的一致性,而不是与各种输出的一致。在自然人感数据集(NSD)上的大量实验结果定性和定量地证明了NeuralDiffuser的先进性,通过与基准和最新技术方法进行横向比较,并进行纵向消融研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了基于功能磁共振成像(fMRI)的视觉刺激重建问题,指出重建过程中结构、背景、纹理、色彩等细节准确重建的挑战。针对扩散模型在重建过程中的固有变异性问题,文章从神经科学角度分析了扩散方法的特点,并提出了NeuralDiffuser方案。该方案通过引入主要视觉特征引导,以梯度形式提供细节线索,实现了扩散模型的自下而上过程扩展,在重建视觉刺激时既保证了语义连贯性又保持了细节真实性。此外,还开发了一种新的重建任务引导策略,确保重复输出的一致性,与原始图像相比,避免了输出多样性。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉刺激从功能磁共振成像(fMRI)的重建对于精细的大脑活动恢复具有重要意义,但准确重建多样细节仍具有挑战性。
- 扩散模型在视觉刺激重建中存在稳定性和输出变异性问题。
- 扩散模型缺乏细节驱动的自下而上感知,导致丢失忠实细节。
- NeuralDiffuser方案通过引入视觉特征引导,以梯度形式提供细节线索,实现语义连贯性和细节真实性的平衡。
- NeuralDiffuser采用新的引导策略,确保重复输出的一致性,避免输出多样性。
- 广泛实验结果表明,NeuralDiffuser在横向和纵向评估中均表现出优越性。
- 研究结果对理解大脑活动和推动视觉刺激重建技术的发展具有重要影响。
点此查看论文截图