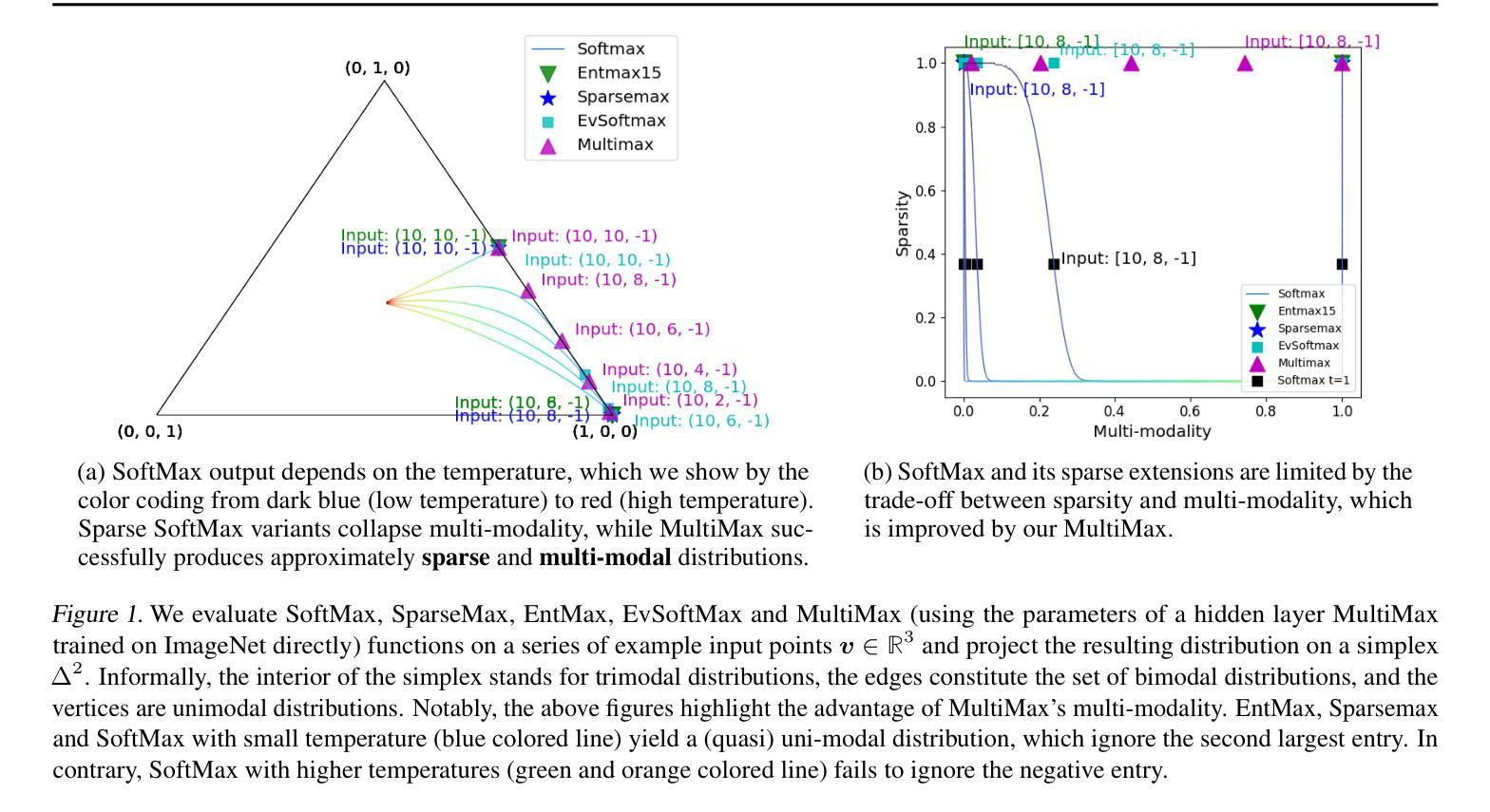
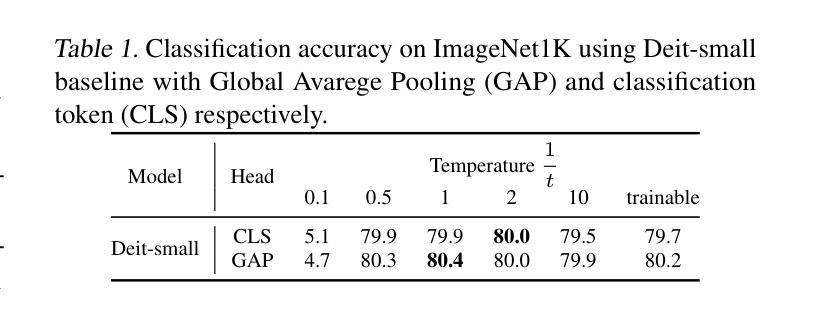
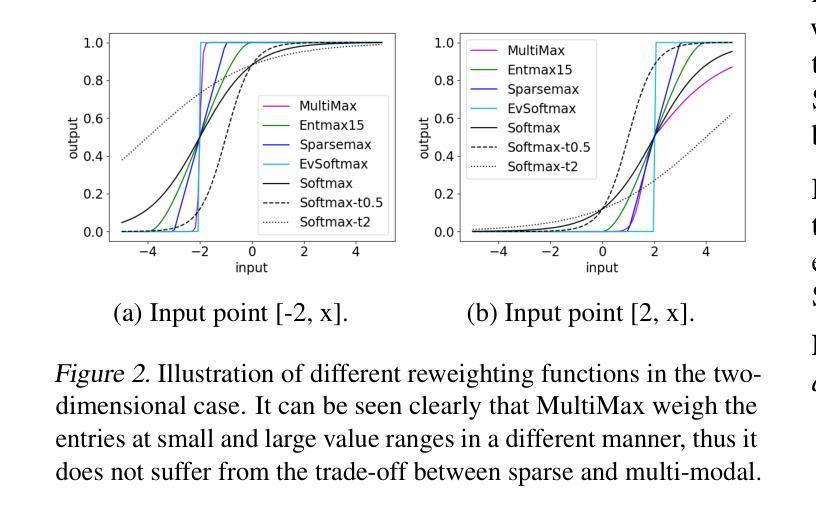
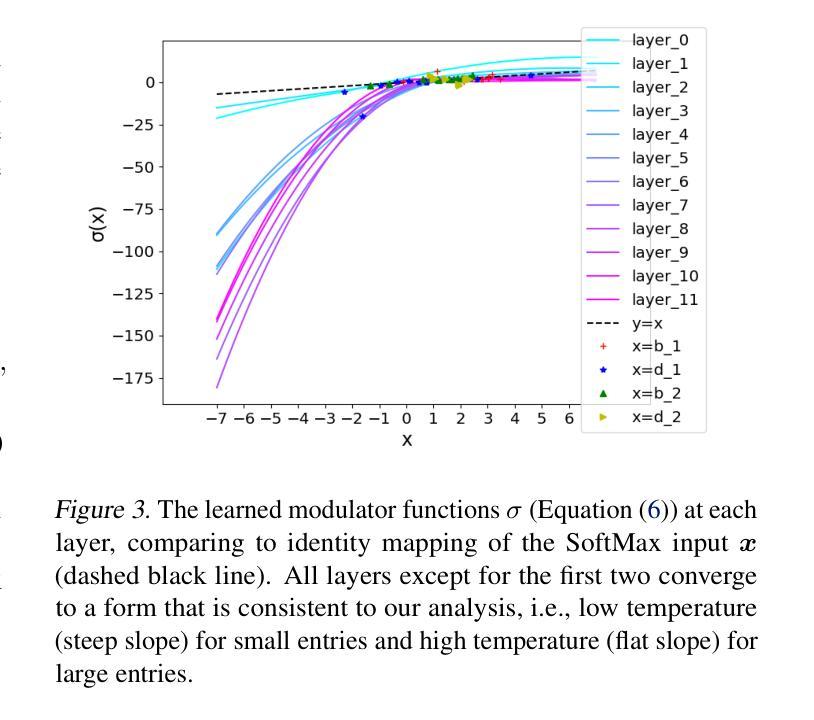
⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-10 更新
MultiMax: Sparse and Multi-Modal Attention Learning
Authors:Yuxuan Zhou, Mario Fritz, Margret Keuper
SoftMax is a ubiquitous ingredient of modern machine learning algorithms. It maps an input vector onto a probability simplex and reweights the input by concentrating the probability mass at large entries. Yet, as a smooth approximation to the Argmax function, a significant amount of probability mass is distributed to other, residual entries, leading to poor interpretability and noise. Although sparsity can be achieved by a family of SoftMax variants, they often require an alternative loss function and do not preserve multi-modality. We show that this trade-off between multi-modality and sparsity limits the expressivity of SoftMax as well as its variants. We provide a solution to this tension between objectives by proposing a piece-wise differentiable function, termed MultiMax, which adaptively modulates the output distribution according to input entry range. Through comprehensive analysis and evaluation, we show that MultiMax successfully produces a distribution that supresses irrelevant entries while preserving multimodality, with benefits in image classification, language modeling and machine translation. The code is available at https://github.com/ZhouYuxuanYX/MultiMax.
SoftMax是现代机器学习算法中普遍存在的成分。它将输入向量映射到概率单纯形上,并通过在较大条目上集中概率质量来重新加权输入。然而,作为Argmax函数的平滑近似,相当一部分概率质量会分布到其他残留条目上,导致解释性差和噪声。尽管可以通过一系列SoftMax变体实现稀疏性,但它们通常需要替代损失函数并且无法保留多峰性。我们表明,多峰性和稀疏性之间的权衡限制了SoftMax及其变体的表现力。我们通过提出一种分段可微函数,称为MultiMax,根据输入条目范围自适应地调制输出分布,解决了目标之间的紧张关系。通过全面分析和评估,我们证明MultiMax成功地产生了一种分布,该分布在抑制不相关条目的同时保留了多峰性,在图像分类、语言建模和机器翻译中都有益处。代码可在https://github.com/ZhouYuxuanYX/MultiMax找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2024
Summary
SoftMax是现代机器学习算法中的常见成分,它能将输入向量映射到概率单纯形上,并通过在较大条目上集中概率质量来重新加权输入。然而,作为Argmax函数的平滑近似,SoftMax会将相当多的概率质量分配给其他残留条目,导致解释性差和噪声。虽然一系列SoftMax变体可以实现稀疏性,但它们通常需要替代损失函数,并且不能保持多峰性。研究指出,这种多峰性和稀疏性之间的权衡限制了SoftMax及其变体的表现力。为解决这一矛盾,提出了一种分段可微函数MultiMax,它可根据输入条目的范围自适应调节输出分布。综合分析和评估表明,MultiMax成功生成了一种既能抑制无关条目又能保持多峰性的分布,在图像分类、语言建模和机器翻译中均有优势。
Key Takeaways
- SoftMax是机器学习中的关键成分,能将输入向量转化为概率分布。
- SoftMax存在解释性不足和噪声问题,因为概率质量不仅集中在大型条目上,还分布在其他条目上。
- 尽管存在多种SoftMax变体以实现稀疏性,但它们往往牺牲了多峰性。
- SoftMax及其变体在表达力上受到限制,因为多峰性和稀疏性之间的权衡。
- 提出了一种新的方法MultiMax,通过分段可微函数自适应调节输出分布。
- MultiMax能在抑制无关条目的同时保持多峰性,提高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图