⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-10 更新
Listening and Seeing Again: Generative Error Correction for Audio-Visual Speech Recognition
Authors:Rui Liu, Hongyu Yuan, Haizhou Li
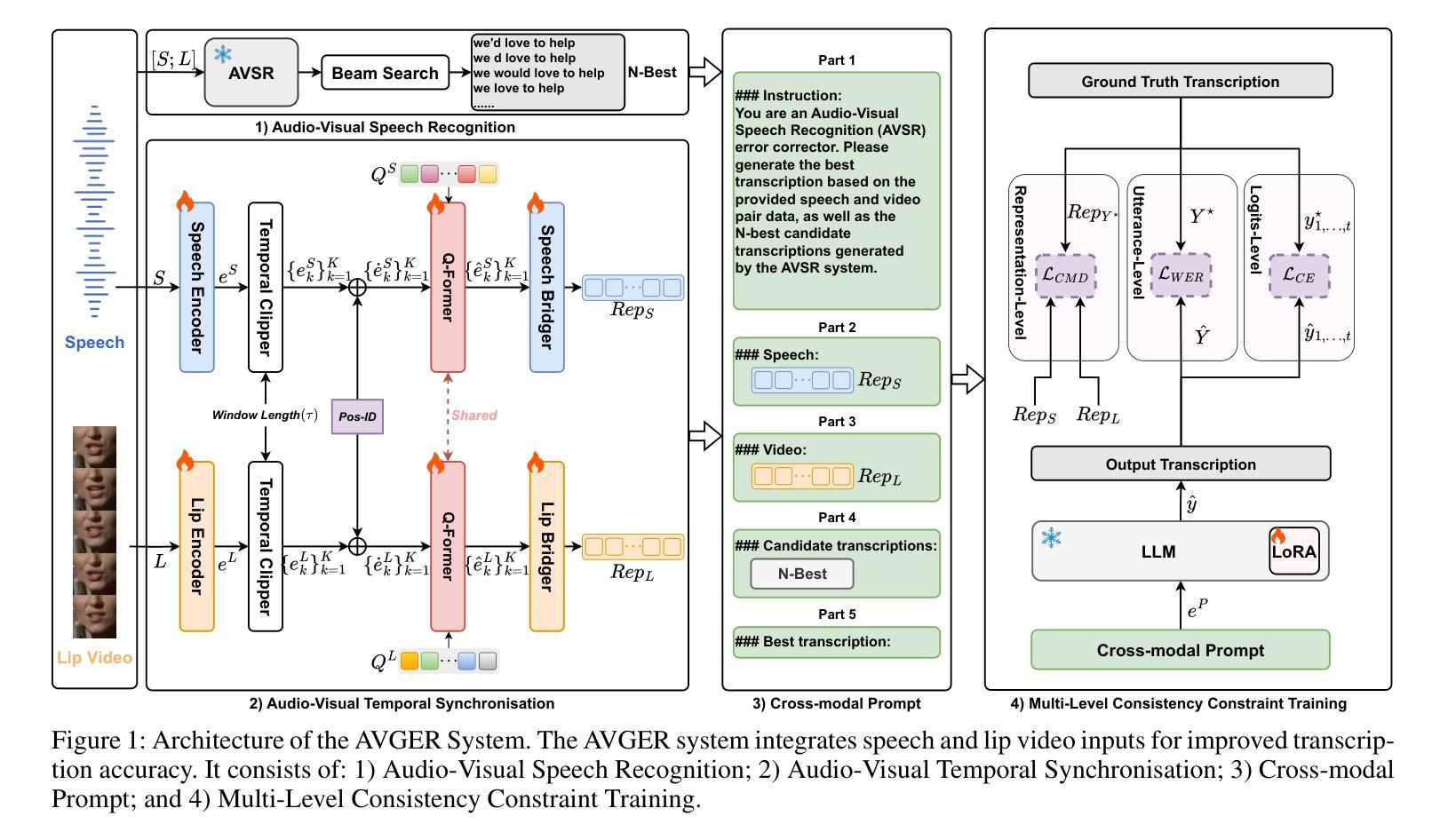
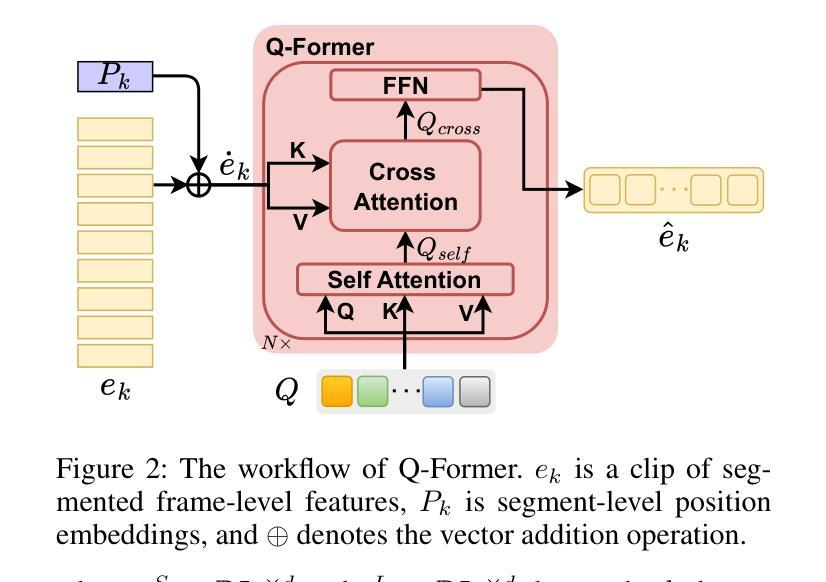
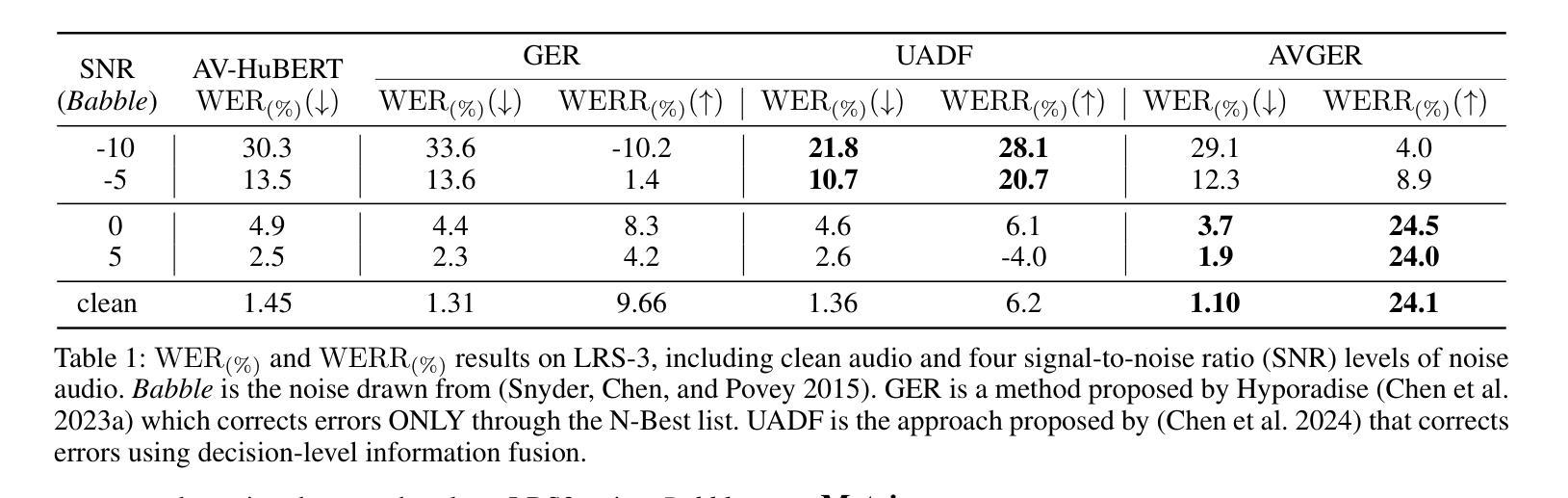
Unlike traditional Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (AVSR) takes audio and visual signals simultaneously to infer the transcription. Recent studies have shown that Large Language Models (LLMs) can be effectively used for Generative Error Correction (GER) in ASR by predicting the best transcription from ASR-generated N-best hypotheses. However, these LLMs lack the ability to simultaneously understand audio and visual, making the GER approach challenging to apply in AVSR. In this work, we propose a novel GER paradigm for AVSR, termed AVGER, that follows the concept of ``listening and seeing again’’. Specifically, we first use the powerful AVSR system to read the audio and visual signals to get the N-Best hypotheses, and then use the Q-former-based Multimodal Synchronous Encoder to read the audio and visual information again and convert them into an audio and video compression representation respectively that can be understood by LLM. Afterward, the audio-visual compression representation and the N-Best hypothesis together constitute a Cross-modal Prompt to guide the LLM in producing the best transcription. In addition, we also proposed a Multi-Level Consistency Constraint training criterion, including logits-level, utterance-level and representations-level, to improve the correction accuracy while enhancing the interpretability of audio and visual compression representations. The experimental results on the LRS3 dataset show that our method outperforms current mainstream AVSR systems. The proposed AVGER can reduce the Word Error Rate (WER) by 24% compared to them. Code and models can be found at: https://github.com/CircleRedRain/AVGER.
与传统的自动语音识别(ASR)不同,视听语音识别(AVSR)同时采用音频和视觉信号来进行转录推断。近期研究表明,大型语言模型(LLM)可以通过预测ASR生成的N-best假设中的最佳转录,有效地用于自动语音识别中的生成错误校正(GER)。然而,这些LLM缺乏同时理解音频和视觉的能力,使得在AVSR中应用GER方法具有挑战性。在此工作中,我们提出了一种新型的AVSR的GER范式,称为AVGER,它遵循“再次聆听和观看”的概念。具体来说,我们首先使用强大的AVSR系统读取音频和视觉信号来获得N-best假设,然后使用基于Q-former的多模态同步编码器再次读取音频和视觉信息,并将它们转换成可以被LLM理解的音频和视觉压缩表示。之后,音频视觉压缩表示和N-best假设共同构成跨模态提示,引导LLM产生最佳转录。此外,我们还提出了一个多级别一致性约束训练准则,包括logits级别、话语级别和表示级别,以提高校正准确性,同时增强音频和视觉压缩表示的可解释性。在LRS3数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法优于当前主流AVSR系统。拟议的AVGER可以比它们降低24%的单词错误率(WER)。代码和模型可在https://github.com/CircleRedRain/AVGER找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出了一种新型的音视频语音识别的生成式错误校正方法(AVGER),它结合了音视频信号,使用强大的AVSR系统获取N-best假设,再通过Q-former基多模态同步编码器进行二次音视频信息读取并转换为可被大型语言模型理解的音视频压缩表示。同时,研究还提出了多级别一致性约束训练准则,旨在提高校正精度并增强音视频压缩表示的可解释性。实验结果显示,该方法在LRS3数据集上的表现优于主流AVSR系统,可降低24%的单词错误率。
Key Takeaways
- AVGER结合音视频信号进行语音识别,提升识别准确性。
- 利用强大的AVSR系统获取N-best假设,为后续的错误校正提供多种可能性。
- Q-former基多模态同步编码器用于二次读取音视频信息,并转换为可理解的压缩表示。
- 提出多级别一致性约束训练准则,包括logits级别、话语级别和表示级别,以提高校正精度和增强表示的可解释性。
- AVGER在LRS3数据集上的表现优于主流AVSR系统。
- AVGER可降低单词错误率(WER)达24%。
- 代码和模型可在https://github.com/CircleRedRain/AVGER找到。
点此查看论文截图

A Zero-Shot Open-Vocabulary Pipeline for Dialogue Understanding
Authors:Abdulfattah Safa, Gözde Gül Şahin
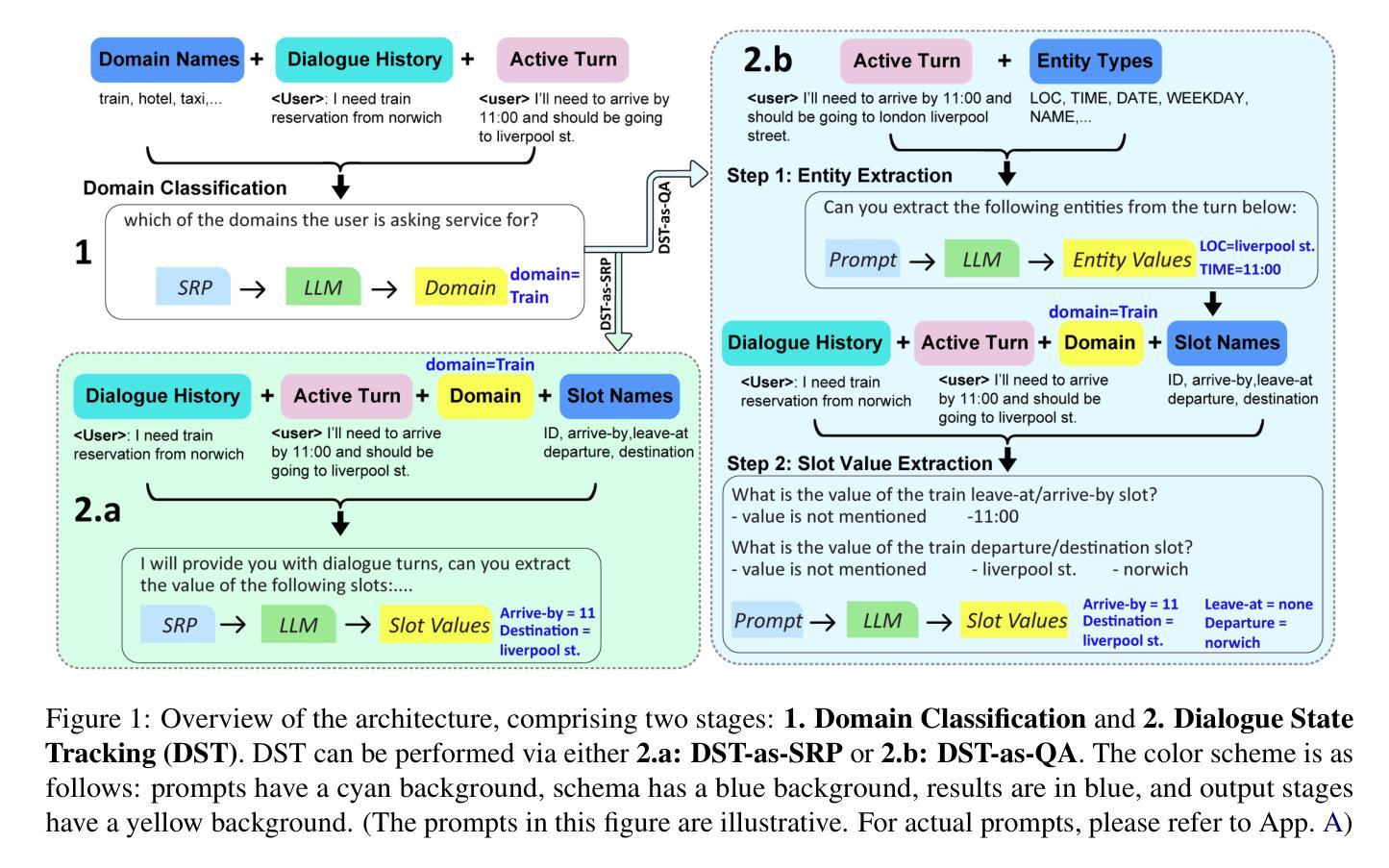
Dialogue State Tracking (DST) is crucial for understanding user needs and executing appropriate system actions in task-oriented dialogues. Majority of existing DST methods are designed to work within predefined ontologies and assume the availability of gold domain labels, struggling with adapting to new slots values. While Large Language Models (LLMs)-based systems show promising zero-shot DST performance, they either require extensive computational resources or they underperform existing fully-trained systems, limiting their practicality. To address these limitations, we propose a zero-shot, open-vocabulary system that integrates domain classification and DST in a single pipeline. Our approach includes reformulating DST as a question-answering task for less capable models and employing self-refining prompts for more adaptable ones. Our system does not rely on fixed slot values defined in the ontology allowing the system to adapt dynamically. We compare our approach with existing SOTA, and show that it provides up to 20% better Joint Goal Accuracy (JGA) over previous methods on datasets like Multi-WOZ 2.1, with up to 90% fewer requests to the LLM API.
对话状态跟踪(DST)对于理解用户需求和在执行任务导向型对话中执行适当的系统操作至关重要。现有的大多数DST方法都是为在预定义的本体论内工作而设计的,并假设有黄金领域标签可用,但在适应新槽值方面遇到了困难。基于大型语言模型(LLM)的系统显示出有前景的零步DST性能,但它们要么需要大量的计算资源,要么它们的性能低于现有的完全训练的系统,从而限制了它们的实用性。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种零步开放词汇系统,它将领域分类和DST集成到一个单一流程中。我们的方法包括将DST重新表述为适合能力较低模型的问答任务,并为更灵活的模型使用自我提炼提示。我们的系统不依赖于本体论中定义的固定槽值,允许系统动态适应。我们将我们的方法与现有的最佳技术进行比较,并证明它在MultiWOZ 2.1等数据集的联合目标准确率(JGA)上比以前的方法高出高达20%,并且使用LLM API的请求减少了高达90%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该研究强调对话状态跟踪(DST)在任务导向对话中的重要性,并提出一种零样本、开放词汇的系统来解决现有DST方法对新槽值适应困难的问题。该研究将DST重新构建为问答任务,以应对能力较弱的模型,并利用自我修正提示来提高适应性。该系统不依赖于本体中定义的固定槽值,可动态适应。与现有先进技术相比,该研究方法在MultiWOZ 2.1等数据集上的联合目标准确率(JGA)提高了高达20%,且对大型语言模型API的请求减少了高达90%。
要点
- 对话状态跟踪(DST)在任务导向对话中的重要性。
- 现有DST方法对新槽值适应困难的问题。
- 提出一种零样本、开放词汇的系统来解决上述问题。
- 将DST重新构建为问答任务,以提高模型的适应能力。
- 系统不依赖本体中定义的固定槽值,具备动态适应性。
- 与现有先进技术相比,该方法的联合目标准确率(JGA)有所提高。
- 在数据集如MultiWOZ 2.1上的性能表现优越,且对大型语言模型API的请求减少。
点此查看论文截图

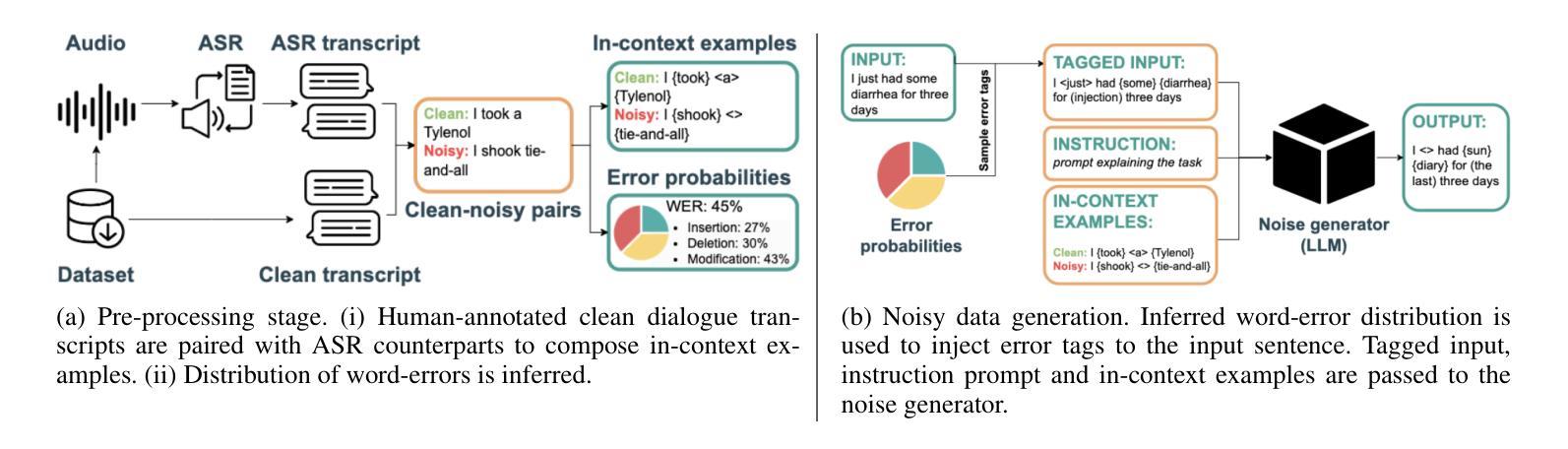
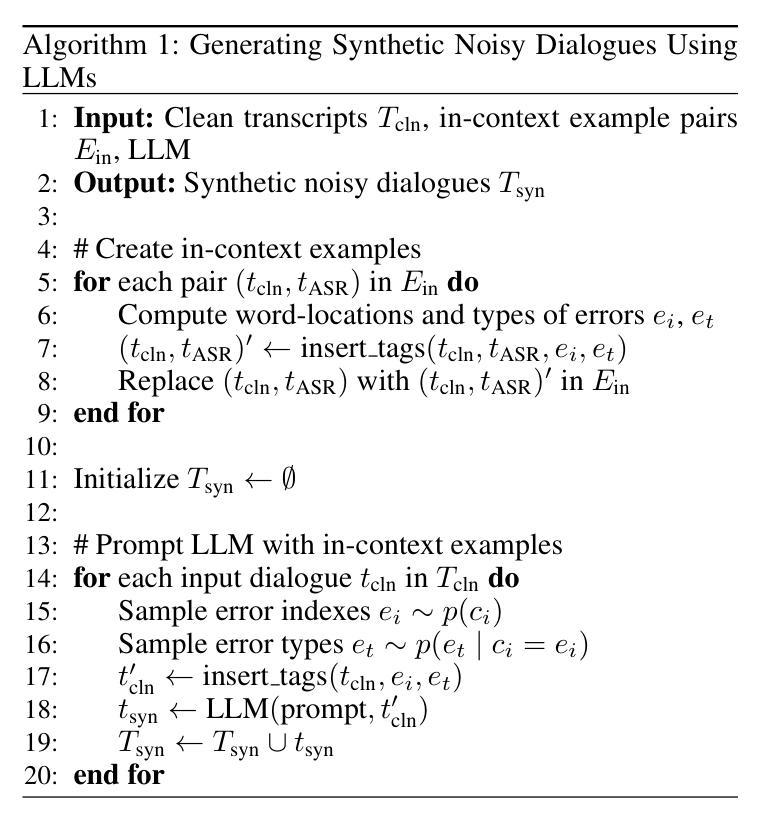
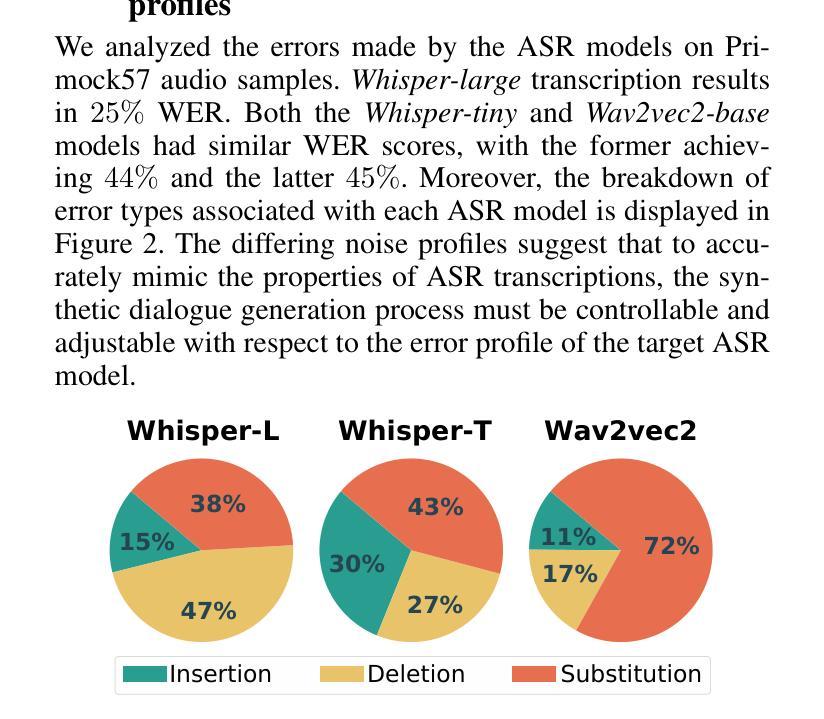
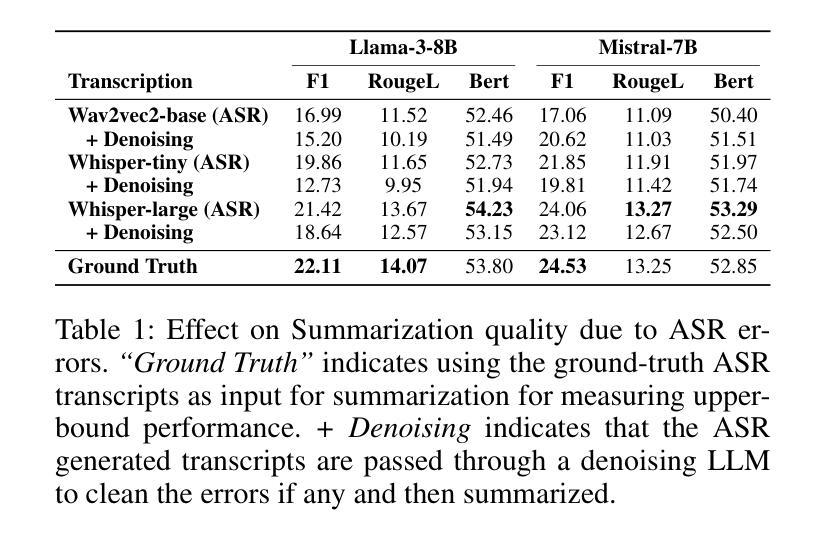
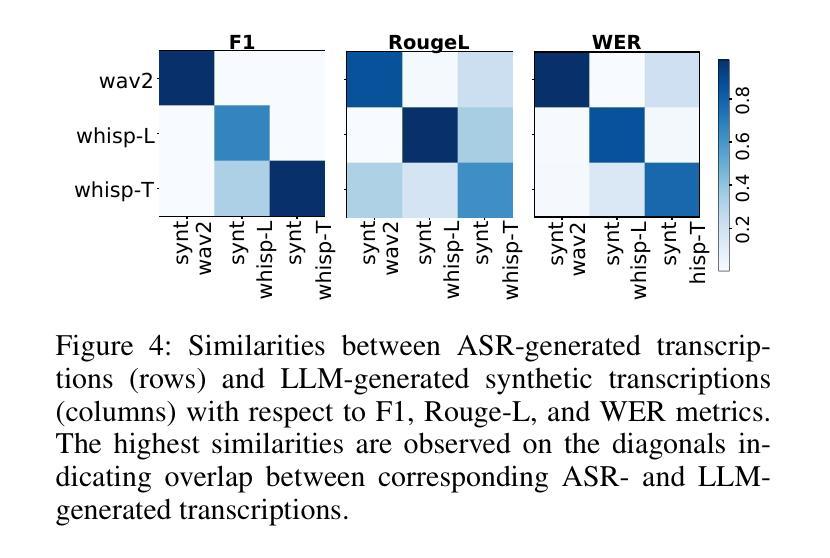
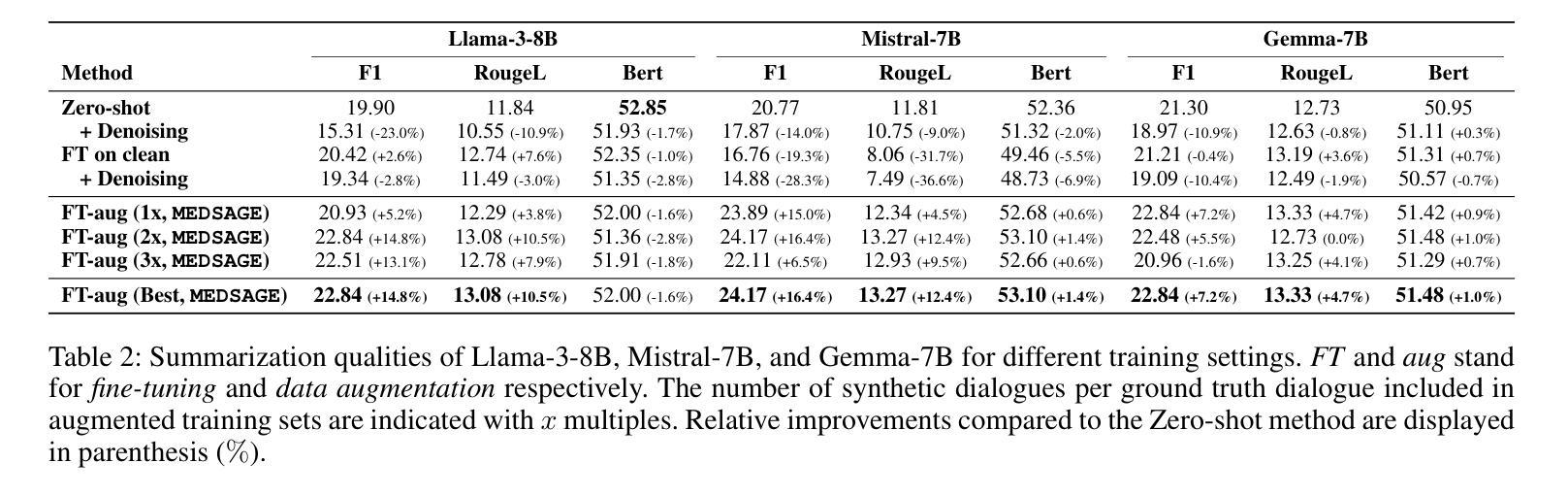
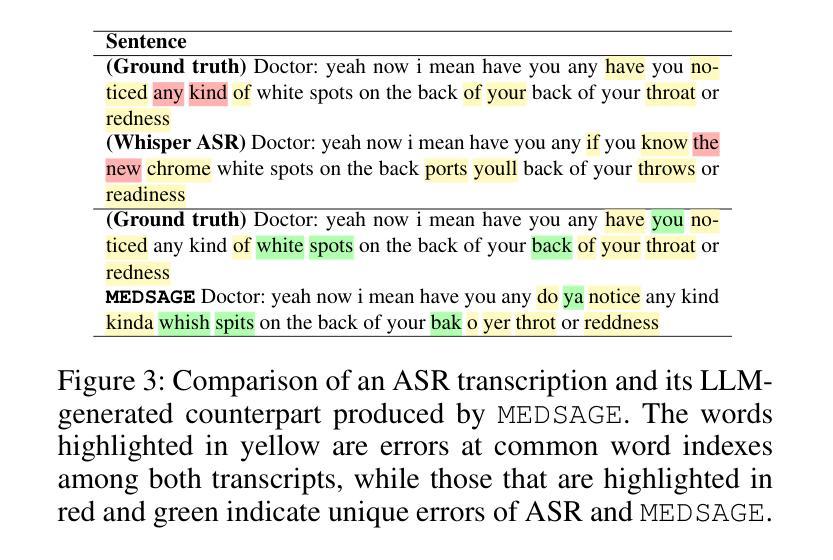
MEDSAGE: Enhancing Robustness of Medical Dialogue Summarization to ASR Errors with LLM-generated Synthetic Dialogues
Authors:Kuluhan Binici, Abhinav Ramesh Kashyap, Viktor Schlegel, Andy T. Liu, Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Thanh-Tung Nguyen, Xiaoxue Gao, Nancy F. Chen, Stefan Winkler
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems are pivotal in transcribing speech into text, yet the errors they introduce can significantly degrade the performance of downstream tasks like summarization. This issue is particularly pronounced in clinical dialogue summarization, a low-resource domain where supervised data for fine-tuning is scarce, necessitating the use of ASR models as black-box solutions. Employing conventional data augmentation for enhancing the noise robustness of summarization models is not feasible either due to the unavailability of sufficient medical dialogue audio recordings and corresponding ASR transcripts. To address this challenge, we propose MEDSAGE, an approach for generating synthetic samples for data augmentation using Large Language Models (LLMs). Specifically, we leverage the in-context learning capabilities of LLMs and instruct them to generate ASR-like errors based on a few available medical dialogue examples with audio recordings. Experimental results show that LLMs can effectively model ASR noise, and incorporating this noisy data into the training process significantly improves the robustness and accuracy of medical dialogue summarization systems. This approach addresses the challenges of noisy ASR outputs in critical applications, offering a robust solution to enhance the reliability of clinical dialogue summarization.
自动语音识别(ASR)系统在将语音转录为文本方面起着关键作用,但它们引入的错误会显著地降低下游任务(如摘要)的性能。这一问题在临床对话摘要中尤为突出,这是一个资源匮乏的领域,缺乏用于微调的数据,因而需要使用ASR模型作为黑匣子解决方案。由于缺少足够的医疗对话音频记录和相应的ASR转录,因此采用传统数据增强方法来提高摘要模型的抗噪声性能并不可行。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了MEDSAGE方法,这是一种利用大型语言模型(LLM)生成合成样本进行数据增强的方法。具体来说,我们利用LLM的上下文学习能力,以少量带有音频记录的医疗对话示例为基础,指导它们生成类似ASR的错误。实验结果表明,LLM可以有效地模拟ASR噪声,将这种带噪声的数据纳入训练过程,可以显著提高医疗对话摘要系统的鲁棒性和准确性。该方法解决了关键应用中噪声ASR输出所面临的挑战,为提高临床对话摘要的可靠性提供了稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the Thirty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-25)
Summary
ASR系统在语音识别领域扮演重要角色,但其产生的错误会影响下游任务如摘要的性能。临床对话摘要是一个资源匮乏的领域,缺乏精细调整所需的监督数据,因此需使用黑箱解决方案中的ASR模型。因缺少医疗对话音频录音及相应ASR译文,无法采用传统数据增强方法来提高摘要模型的抗噪性。为解决此挑战,我们提出MEDSAGE方法,利用大型语言模型生成合成样本进行数据增强。实验结果表明,大型语言模型能有效模拟ASR噪声,将此类噪声数据融入训练过程,可显著提高医疗对话摘要系统的稳健性和准确性。此方法解决了关键应用中ASR输出噪声的问题,为提高临床对话摘要的可靠性提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- ASR系统在语音识别中扮演重要角色,但错误会影响下游任务性能。
- 临床对话摘要是一个资源匮乏的领域,需使用黑箱解决方案中的ASR模型。
- 传统数据增强方法因缺乏医疗对话音频录音及相应ASR译文而不适用。
- MEDSAGE方法利用大型语言模型生成合成样本进行数据增强。
- 大型语言模型能有效模拟ASR噪声。
- 将噪声数据融入训练过程可显著提高医疗对话摘要系统的稳健性和准确性。
点此查看论文截图