⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-14 更新
The ultraviolet luminosity function of star-forming galaxies between redshifts of 0.4 and 0.6
Authors:M. J. Page, T. Dwelly, I. McHardy, N. Seymour, K. O. Mason, M. Sharma, J. A. Kennea, T. P. Sasseen, A. A. Breeveld, A. E. Matthews
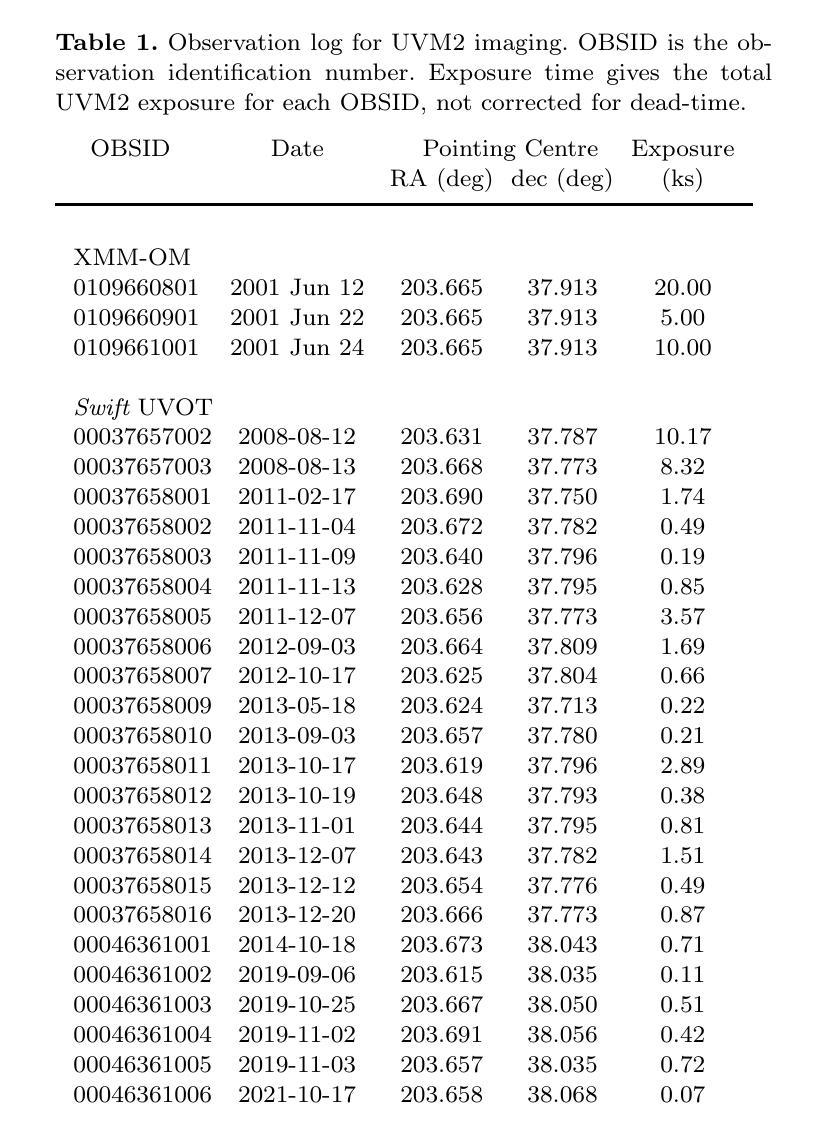
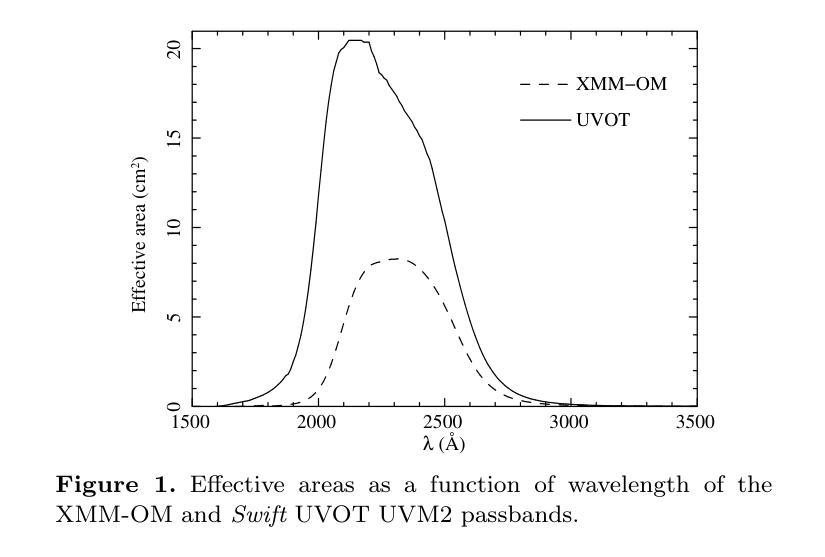
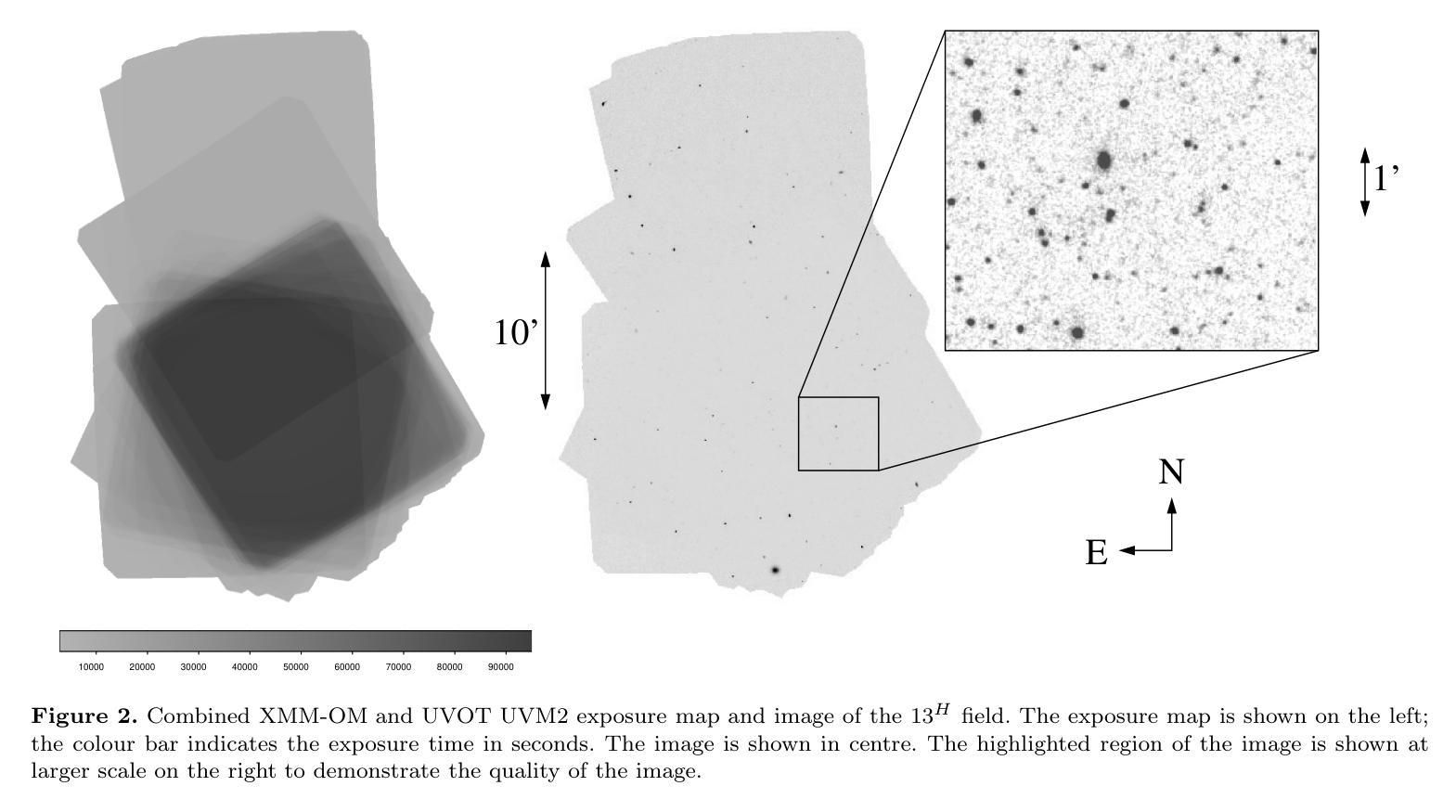
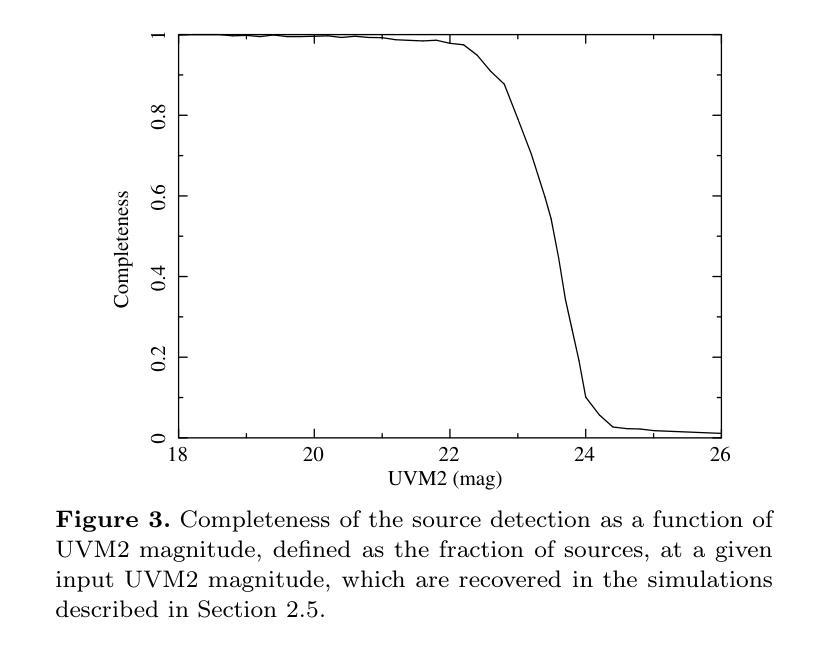
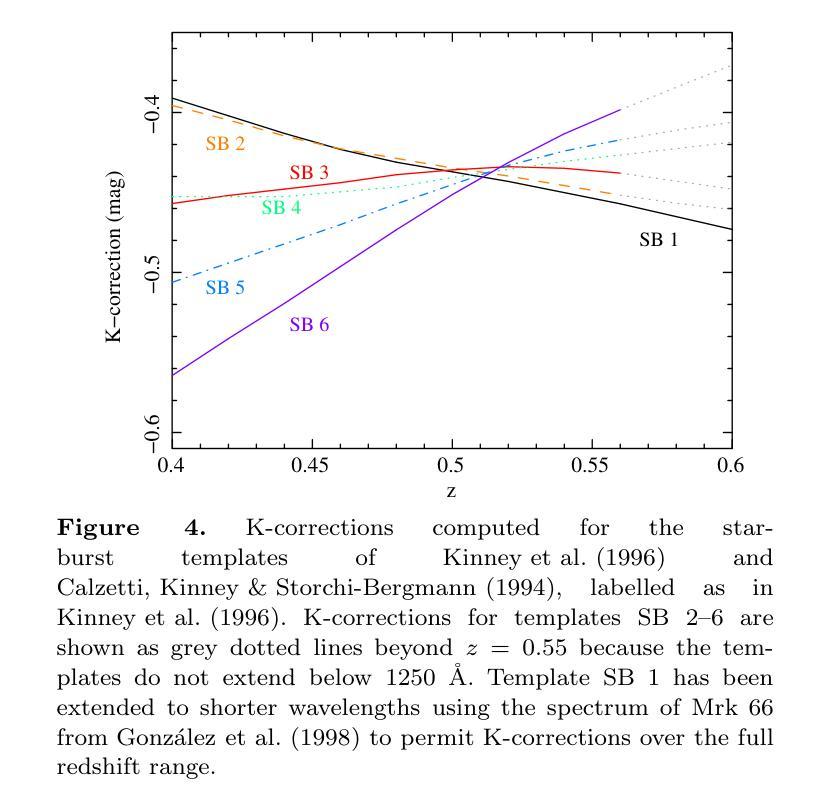
We combine ultraviolet imaging of the 13H survey field, taken with the XMM-Newton Optical Monitor telescope (XMM-OM) and the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory Ultraviolet and Optical Telescope (UVOT) in the UVM2 band, to measure rest-frame ultraviolet 1500A luminosity functions of star-forming galaxies with redshifts between 0.4 and 0.6. In total the UVM2 imaging covers a sky area of 641 square arcmin, and we detect 273 galaxies in the UVM2 image with 0.4<z<0.6. The luminosity function is fit by a Schechter function with best-fit values for the faint end slope alpha = -1.8 +0.4 -0.3 and characteristic absolute magnitude M* = -19.1 +0.3 -0.4. In common with XMM-OM based studies at higher redshifts, our best-fitting value for M* is fainter than previous measurements. We argue that the purging of active galactic nuclei from the sample, facilitated by the co-spatial X-ray survey carried out with XMM-Newton is important for the determination of M*. At the brightest absolute magnitudes (M1500<-18.5) the average UV colour of our galaxies is consistent with that of minimal-extinction local analogues, but the average UV colour is redder for galaxies at fainter absolute magnitudes, suggesting that higher levels of dust attenuation enter the sample at absolute magnitudes somewhat fainter than M*.
我们将结合了使用XMM-Newton光学监视望远镜(XMM-OM)和尼尔·格雷尔斯迅游天文台紫外光学望远镜(UVOT)在紫外光区带下的紫外线成像技术,对处于红移范围在0.4至0.6之间的星系形成恒星进行了紫外波段的光度函数测量。总的来说,UVM2成像覆盖了天空区域为641平方角分的区域,并在UVM2图像中检测到红移在0.4至0.6之间的星系共273个。光度函数通过谢克特函数拟合得出最佳值,其中暗端斜率α=-1.8±0.4±0.3,特征绝对星等M*= - 19.1 ± 0.3 ± 0.4。与高红移的基于XMM-OM的研究类似,我们确定的M星亮度低于以前的测量值。我们认为,由于通过与XMM-牛顿同时进行的X射线观测清除活跃中的银河系核心样本的存在有利于M的确定。在最亮的绝对星等(Muv绝对亮度高于约减波长变光,-亮度大约为8m长与以下的UV辐射),我们的星系平均紫外颜色与本地类似的最小减弱的星系相符,但对于更暗的绝对星等的星系来说,平均紫外颜色更为红亮,这表明在高绝对星等的样本中存在更高水平的尘埃衰减。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in MNRAS
Summary
本研究结合XMM-Newton光学监视器望远镜(XMM-OM)和尼尔·盖尔瑞斯·斯威夫特天文台紫外光学望远镜(UVOT)的紫外线成像数据,测量了红移范围在0.4至0.6之间的恒星形成星系在静止帧紫外波段下的光度函数。通过对谢克特函数进行拟合,得到了较为准确的结果。剔除活动星系核后样本的确重要,便于确定光度函数的特征绝对星等M()。在较亮的绝对星等条件下,星系平均紫外颜色与本地类似物一致,但在较暗的绝对星等条件下,平均紫外颜色更红,暗示着尘埃衰减的影响更大。
Key Takeaways
- 结合XMM-Newton光学监视器望远镜和UVOT的紫外线成像数据测量了特定红移范围内的恒星形成星系在静止帧紫外波段的光度函数。
- 通过谢克特函数拟合光度函数,得到最佳拟合值中的暗端斜率α和特征绝对星等M()。其中M()比之前的研究结果更暗。
- 剔除活动星系核对确定特征绝对星等M()的影响十分重要。这是因为这些核心会影响观测到的紫外光的强度分布。这一点对后续的研究也有重要指导意义。
点此查看论文截图

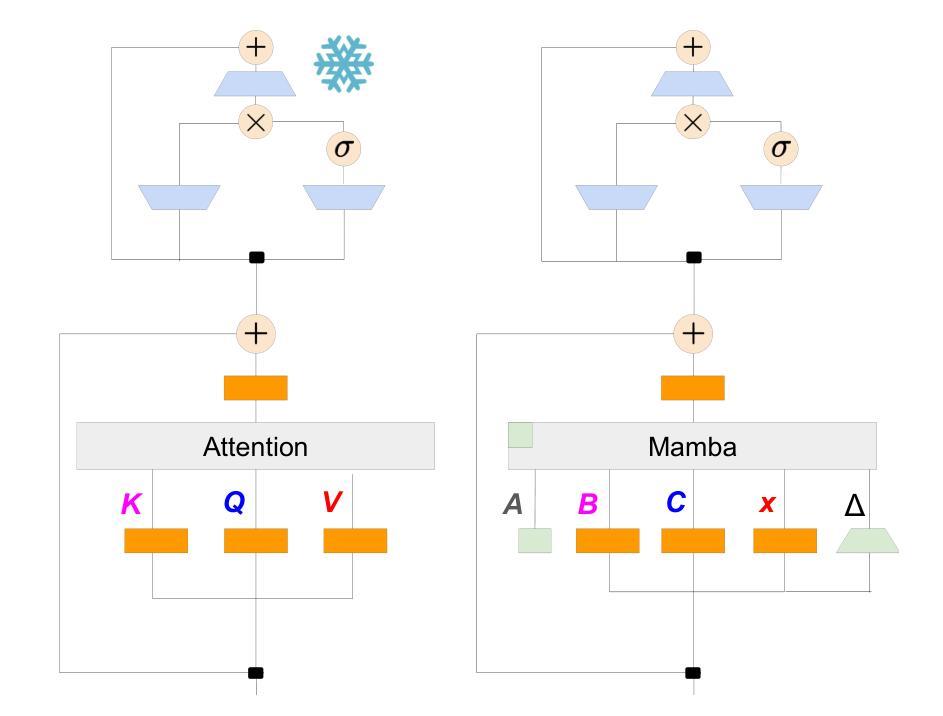
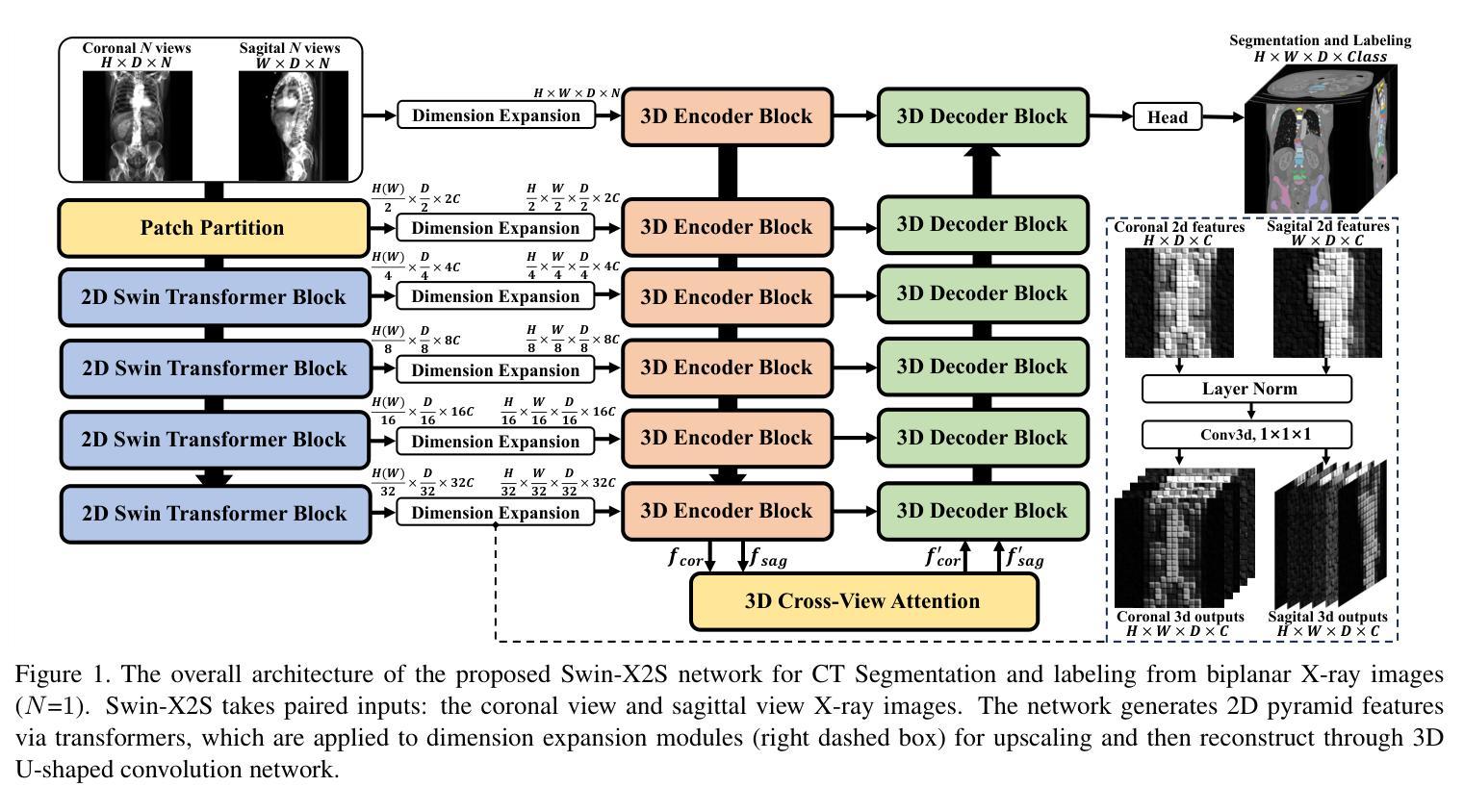
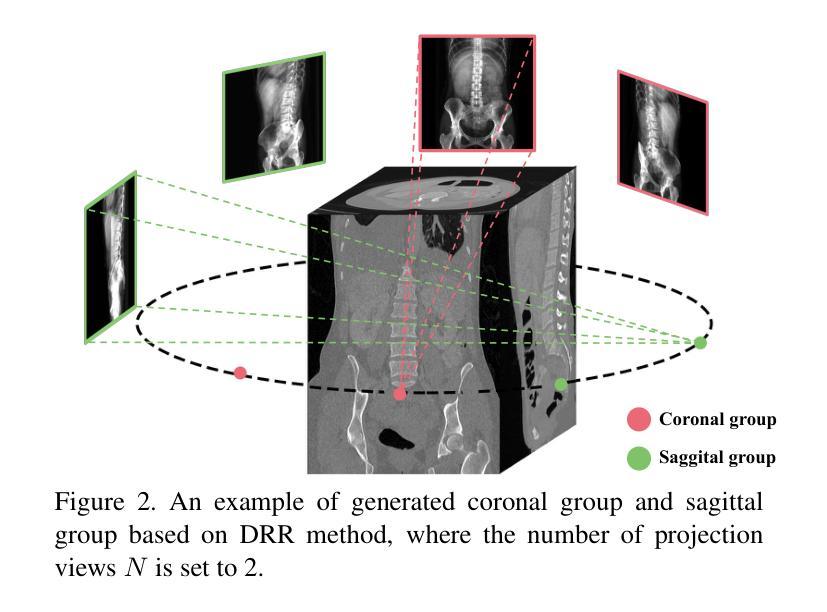
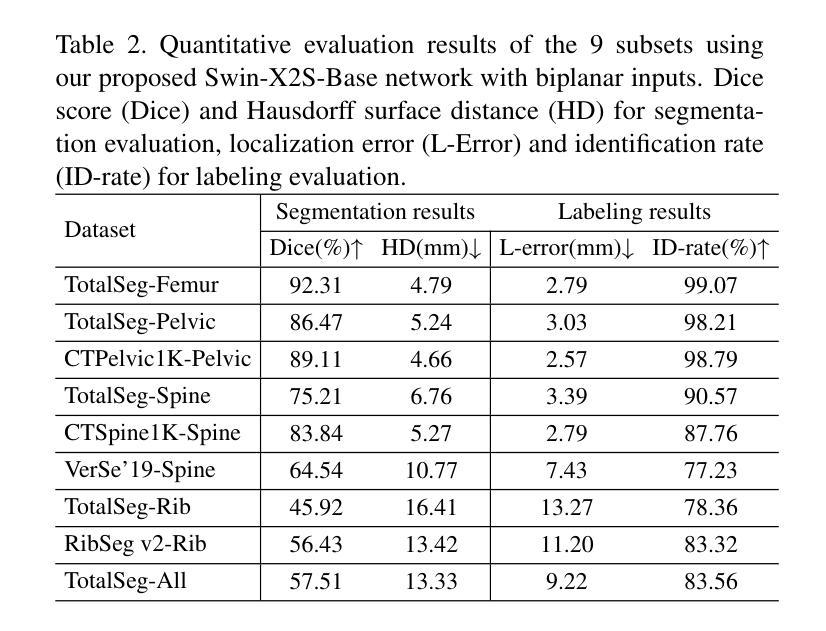
Swin-X2S: Reconstructing 3D Shape from 2D Biplanar X-ray with Swin Transformers
Authors:Kuan Liu, Zongyuan Ying, Jie Jin, Dongyan Li, Ping Huang, Wenjian Wu, Zhe Chen, Jin Qi, Yong Lu, Lianfu Deng, Bo Chen
The conversion from 2D X-ray to 3D shape holds significant potential for improving diagnostic efficiency and safety. However, existing reconstruction methods often rely on hand-crafted features, manual intervention, and prior knowledge, resulting in unstable shape errors and additional processing costs. In this paper, we introduce Swin-X2S, an end-to-end deep learning method for directly reconstructing 3D segmentation and labeling from 2D biplanar orthogonal X-ray images. Swin-X2S employs an encoder-decoder architecture: the encoder leverages 2D Swin Transformer for X-ray information extraction, while the decoder employs 3D convolution with cross-attention to integrate structural features from orthogonal views. A dimension-expanding module is introduced to bridge the encoder and decoder, ensuring a smooth conversion from 2D pixels to 3D voxels. We evaluate proposed method through extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments across nine publicly available datasets covering four anatomies (femur, hip, spine, and rib), with a total of 54 categories. Significant improvements over previous methods have been observed not only in the segmentation and labeling metrics but also in the clinically relevant parameters that are of primary concern in practical applications, which demonstrates the promise of Swin-X2S to provide an effective option for anatomical shape reconstruction in clinical scenarios. Code implementation is available at: \url{https://github.com/liukuan5625/Swin-X2S}.
从2D X光图像转换到3D形状在提升诊断效率和安全性方面具有巨大潜力。然而,现有的重建方法通常依赖于手工特征、人工干预和先验知识,导致形状误差不稳定并增加了处理成本。在本文中,我们介绍了Swin-X2S,这是一种端到端的深度学习方法,可直接从2D双平面正交X光图像重建3D分割和标记。Swin-X2S采用编码器-解码器架构:编码器利用2D Swin Transformer进行X光信息提取,而解码器则采用具有跨注意力的3D卷积,以整合来自正交视图的结构特征。引入了一个维度扩展模块,以连接编码器和解码器,确保从2D像素到3D体素的平滑转换。我们在九个公开数据集上进行了广泛的定性和定量实验,涵盖了四个部位(股骨、髋关节、脊椎和肋骨),共54个类别,对所提出的方法进行了评估。相较于以前的方法,不仅在分割和标记指标上观察到显著改进,而且在临床相关参数方面也表现出优异性能,这些参数是实际应用中的主要关注点。这证明了Swin-X2S在临床场景中为解剖形状重建提供有效选项的潜力。代码实现可访问于:\url{https://github.com/liukuan5625/Swin-X2S}。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习的Swin-X2S方法可直接从二维双正交X射线图像重建三维分割和标签,提高了诊断效率和安全性。相较于现有方法,该方法显著减少了手工特征、人工干预和先验知识的依赖,降低了形状误差和额外处理成本。代码实现已发布于GitHub。
Key Takeaways
- 从二维X射线转换到三维形态对提升诊断效率和安全性具有显著潜力。
- 当前重建方法依赖于手工特征、人工干预和先验知识,存在不稳定性和额外成本。
- Swin-X2S是一种基于深度学习的端到端方法,可直接从二维双正交X射线图像重建三维分割和标签。
- Swin-X2S使用编码-解码架构,编码阶段利用二维Swin Transformer提取X射线信息,解码阶段采用三维卷积与交叉注意力机制整合正交视图的结构特征。
- 引入维度扩展模块,确保从二维像素到三维体素的平滑转换。
- 在涵盖四个解剖部位(股骨、髋关节、脊椎和肋骨)的九个公开数据集上进行了广泛实验,相较于先前方法有明显改进。
点此查看论文截图


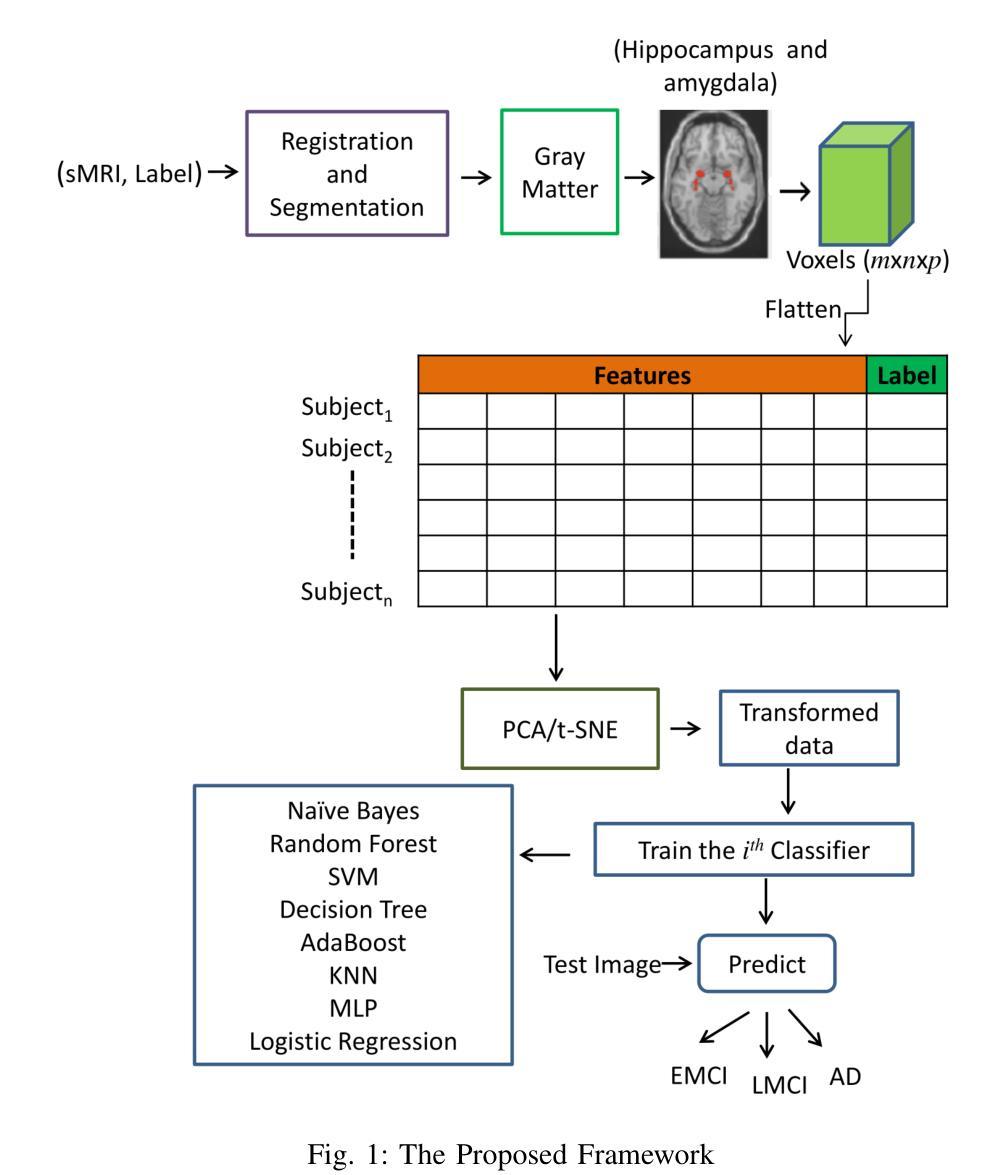
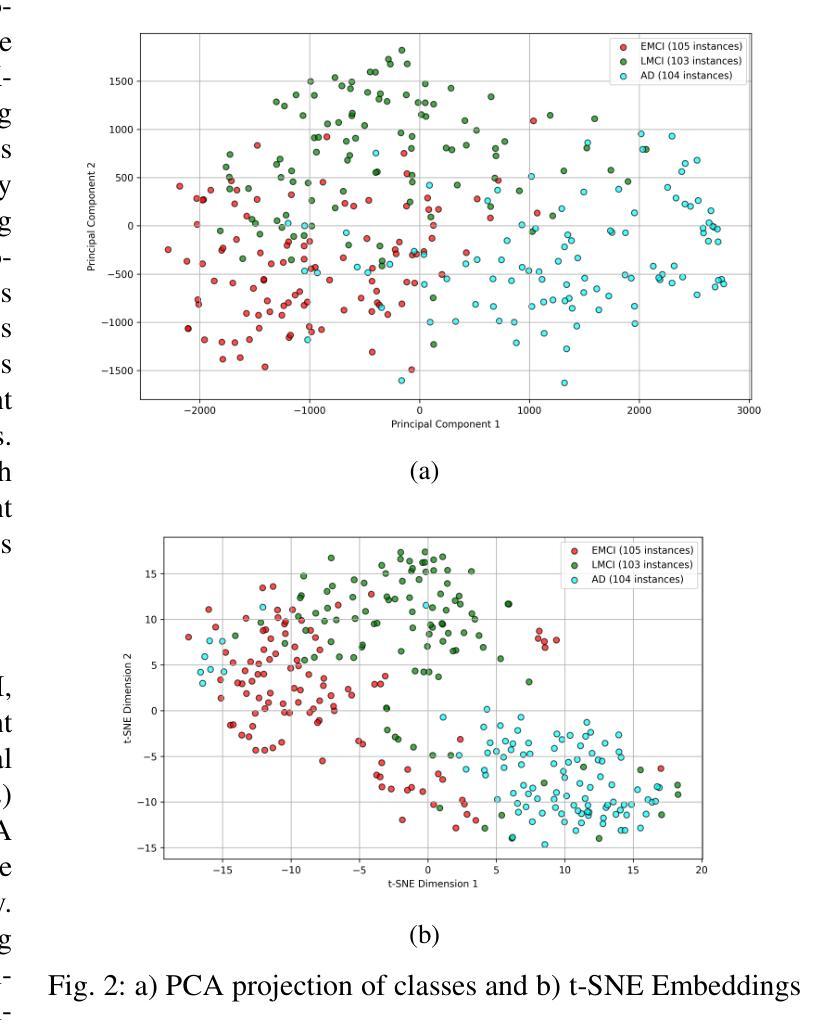
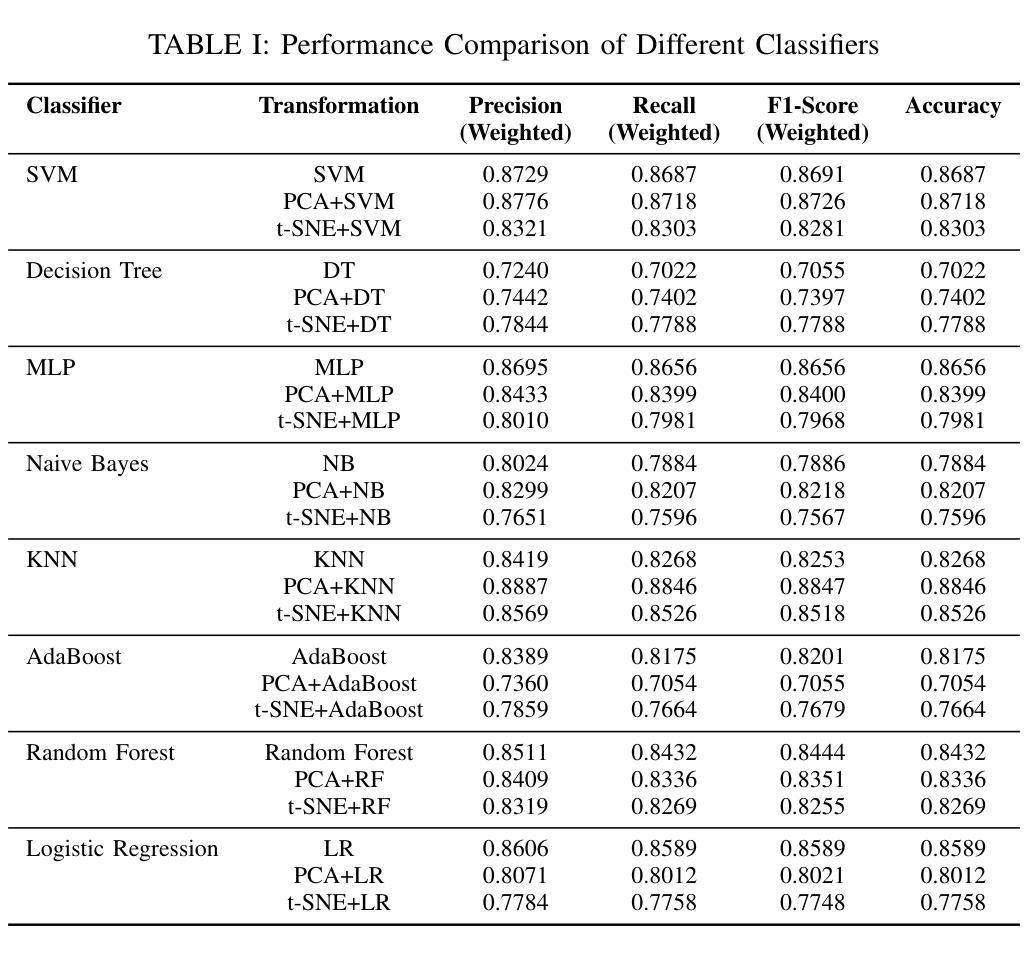
MRI Patterns of the Hippocampus and Amygdala for Predicting Stages of Alzheimer’s Progression: A Minimal Feature Machine Learning Framework
Authors:Aswini Kumar Patra, Soraisham Elizabeth Devi, Tejashwini Gajurel
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) progresses through distinct stages, from early mild cognitive impairment (EMCI) to late mild cognitive impairment (LMCI) and eventually to AD. Accurate identification of these stages, especially distinguishing LMCI from EMCI, is crucial for developing pre-dementia treatments but remains challenging due to subtle and overlapping imaging features. This study proposes a minimal-feature machine learning framework that leverages structural MRI data, focusing on the hippocampus and amygdala as regions of interest. The framework addresses the curse of dimensionality through feature selection, utilizes region-specific voxel information, and implements innovative data organization to enhance classification performance by reducing noise. The methodology integrates dimensionality reduction techniques such as PCA and t-SNE with state-of-the-art classifiers, achieving the highest accuracy of 88.46%. This framework demonstrates the potential for efficient and accurate staging of AD progression while providing valuable insights for clinical applications.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)进展经过不同的阶段,从早期轻度认知障碍(EMCI)到晚期轻度认知障碍(LMCI),最终发展到AD。准确识别这些阶段,特别是区分LMCI和EMCI,对于开发痴呆前治疗至关重要。然而,由于成像特征的细微和重叠,这仍然是一个挑战。本研究提出了一种基于结构MRI数据的机器学习框架,重点关注海马体和杏仁核作为感兴趣区域。该框架通过特征选择解决了维数诅咒问题,利用特定区域的体素信息,并通过创新的数据组织提高分类性能,减少噪声干扰。该方法结合了主成分分析和t-SNE等降维技术与最先进的分类器,取得了最高的88.46%准确率。该框架展示了在AD进展分期中高效准确的潜力,同时为临床应用提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于结构MRI数据的机器学习框架,用于准确识别阿尔茨海默病(AD)的不同阶段,特别是早期轻度认知障碍(EMCI)和晚期轻度认知障碍(LMCI)。该框架关注海马体和杏仁核这两个关键区域,通过特征选择解决维度灾难问题,利用区域特定体素信息,并采用创新的数据组织方式提高分类性能。结合PCA和t-SNE等降维技术与最先进的分类器,最高准确率可达88.46%,为AD进展的有效分期提供了潜力,并为临床应用提供了有价值的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 阿尔茨海默病(AD)的进展包括从早期轻度认知障碍(EMCI)到晚期轻度认知障碍(LMCI)再到AD的多个阶段。
- 准确识别这些阶段对于开发预痴呆治疗至关重要,但由于成像特征的细微和重叠,仍具有挑战性。
- 研究提出了一种基于结构MRI数据的机器学习框架,关注海马体和杏仁核这两个关键区域进行分类。
- 该框架通过特征选择解决维度灾难问题,提高分类性能。
- 框架结合了降维技术和最先进的分类器,实现最高准确率88.46%。
- 该研究为AD进展的有效分期提供了潜力。
点此查看论文截图

High order strong-coupling expansion for X-ray absorption on a dynamically screened impurity
Authors:Eva Paprotzki, Martin Eckstein
Time-resolved X-ray absorption can reveal the dynamical screening of the local Coulomb interaction in strongly correlated photo-excited materials. Here, we focus on the theoretical prediction of X-ray absorption in the presence of dynamical screening using the strong coupling expansion, i.e., an expansion around the isolated absorption site in terms of the retarded interaction. The evaluation of higher order diagrams is made numerically feasible by an approach based on the decomposition of the retarded interaction into complex exponentials. With this, we evaluate the strong coupling series to third order on an electron-boson model of Holstein type. We demonstrate that in relevant coupling regimes, even low orders of the strong coupling expansion can give a significant correction over the previously used lowest order approximation.
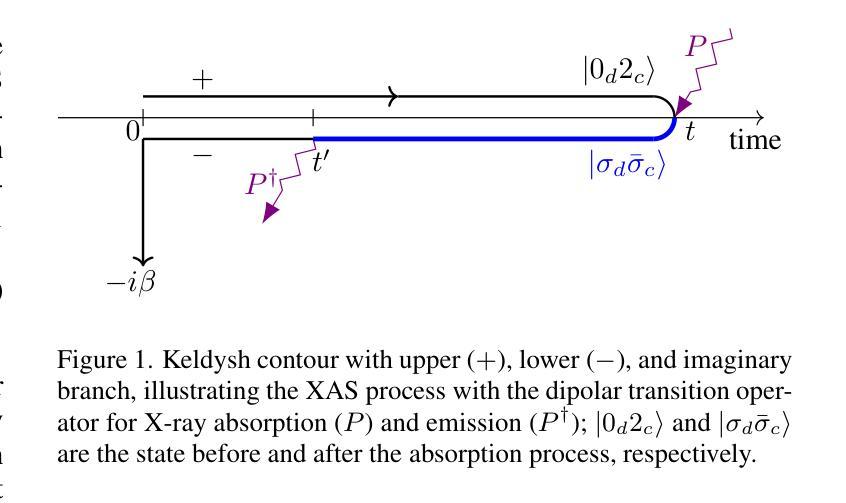
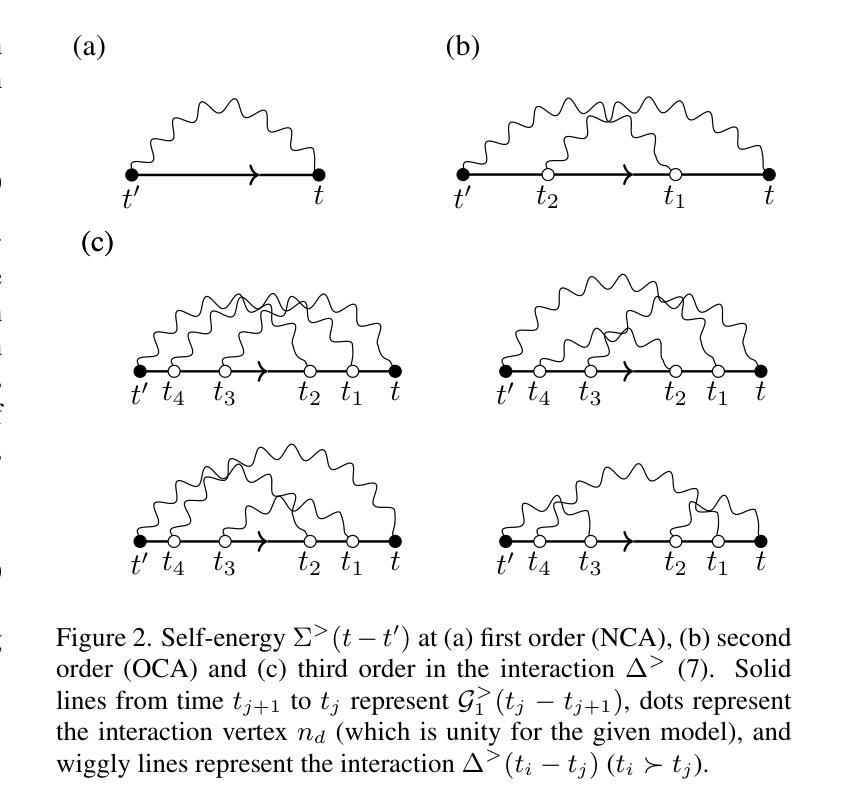
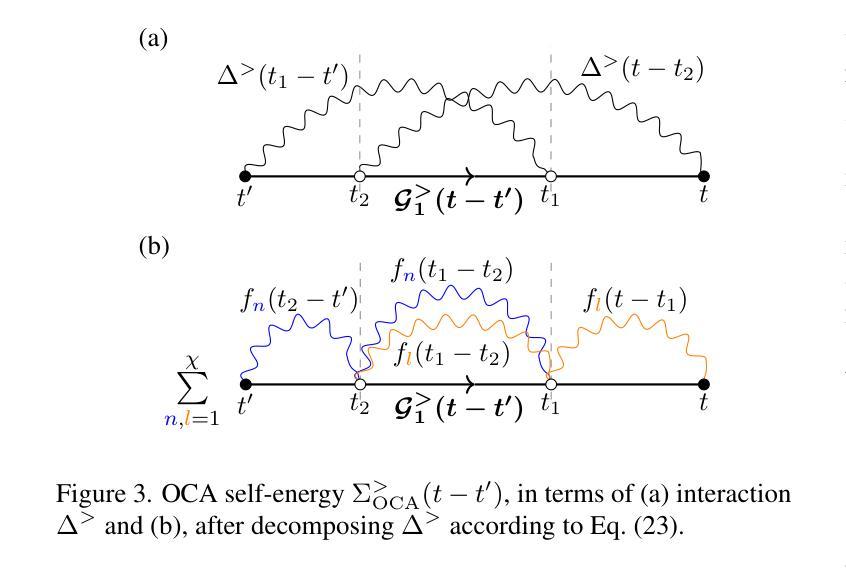
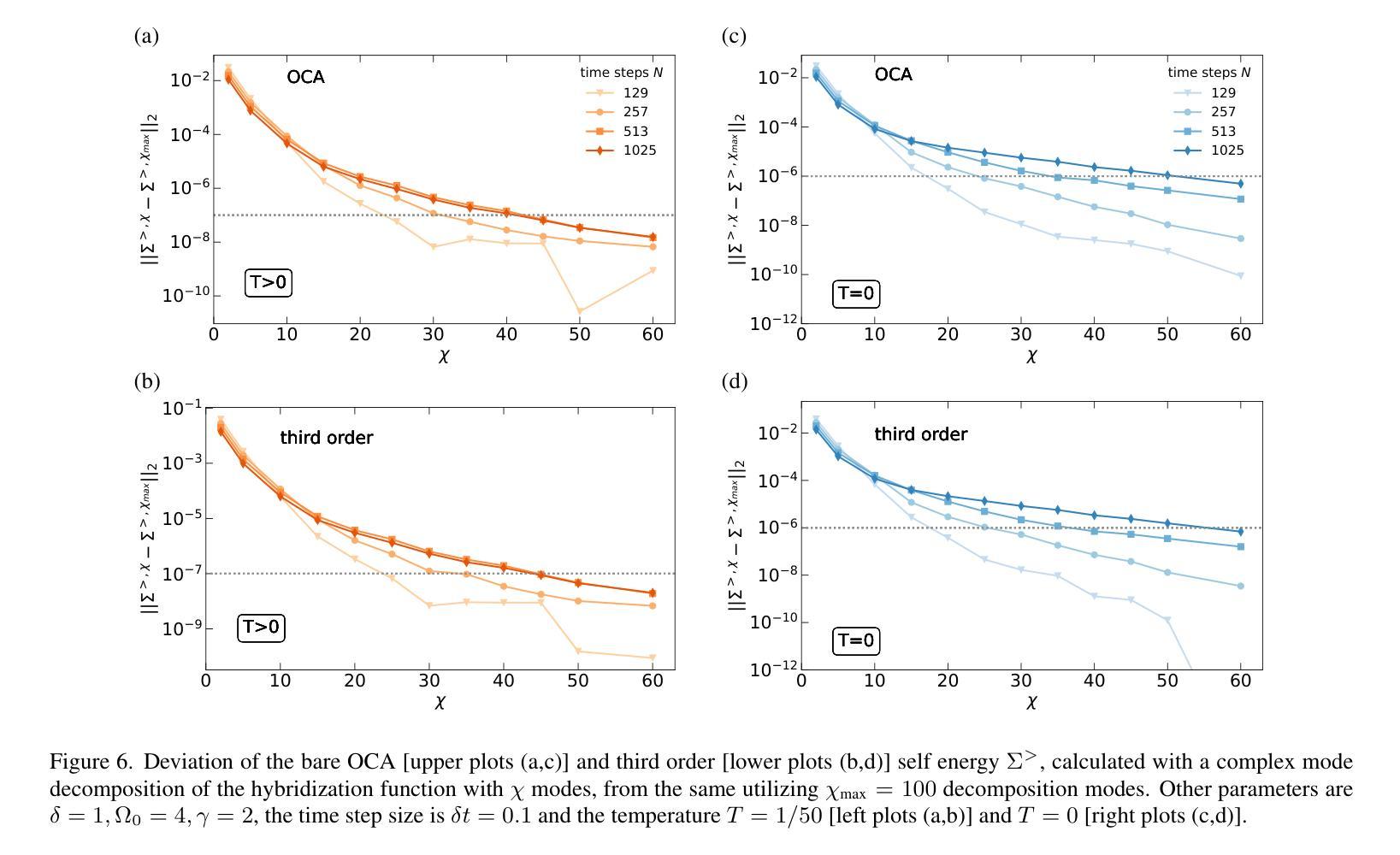
时间分辨的X射线吸收能够揭示强相关光激发材料中局部库仑相互作用的动力学筛选。在这里,我们重点关注在存在动力学筛选的情况下,使用强耦合展开法对X射线吸收的理论预测。这是一种围绕孤立吸收位点进行延迟相互作用展开的展开方法。通过将延迟相互作用分解为复数指数的方法,使得高阶图的评估在数值上是可行的。利用此方法,我们在Holstein型电子-玻色子模型上对强耦合系列进行了三阶评估。我们证明,在相关的耦合状态下,即使是强耦合展开的较低阶也可以对之前使用的最低阶近似进行重大修正。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文研究了基于时间解析的X射线吸收技术揭示强关联光激发材料中局部库仑相互作用的动力学筛选机制。文章重点关注了存在动力学筛选作用下的X射线吸收的理论预测,采用了强耦合展开法,围绕孤立吸收位点展开,用延迟相互作用表示。通过对高阶图进行数值分解的方法,实现了延迟相互作用的分解为复数指数形式的计算。通过评估霍尔斯坦电子-玻色模型的强耦合级数扩展至三阶来演示其在相关耦合环境下的应用价值。结果显示,在低阶近似的基础上引入高阶修正可以显著提高预测精度。
Key Takeaways
- 时间解析的X射线吸收技术可用于揭示强关联光激发材料中的动力学筛选机制。
- 采用强耦合展开法预测存在动力学筛选作用下的X射线吸收。
- 通过延迟相互作用将复杂模型数值化处理成为可能。
- 使用基于复杂指数形式的计算实现对高阶图的数值分解。
- 在霍尔斯坦电子-玻色模型中评估强耦合系列的扩展效果至三阶。
- 高阶修正可显著改进最低阶近似下的预测结果。
点此查看论文截图


Learned Discrepancy Reconstruction and Benchmark Dataset for Magnetic Particle Imaging
Authors:Meira Iske, Hannes Albers, Tobias Knopp, Tobias Kluth
Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) is an emerging imaging modality based on the magnetic response of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles to achieve high-resolution and real-time imaging without harmful radiation. One key challenge in the MPI image reconstruction task arises from its underlying noise model, which does not fulfill the implicit Gaussian assumptions that are made when applying traditional reconstruction approaches. To address this challenge, we introduce the Learned Discrepancy Approach, a novel learning-based reconstruction method for inverse problems that includes a learned discrepancy function. It enhances traditional techniques by incorporating an invertible neural network to explicitly model problem-specific noise distributions. This approach does not rely on implicit Gaussian noise assumptions, making it especially suited to handle the sophisticated noise model in MPI and also applicable to other inverse problems. To further advance MPI reconstruction techniques, we introduce the MPI-MNIST dataset - a large collection of simulated MPI measurements derived from the MNIST dataset of handwritten digits. The dataset includes noise-perturbed measurements generated from state-of-the-art model-based system matrices and measurements of a preclinical MPI scanner device. This provides a realistic and flexible environment for algorithm testing. Validated against the MPI-MNIST dataset, our method demonstrates significant improvements in reconstruction quality in terms of structural similarity when compared to classical reconstruction techniques.
磁共振颗粒成像(MPI)是一种新兴的成像技术,基于超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子的磁响应实现高分辨率和实时成像,无需有害辐射。MPI图像重建任务中的一个关键挑战在于其固有的噪声模型,它并不满足在应用传统重建方法时所做的隐含高斯假设。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了学习差异法(Learned Discrepancy Approach),这是一种针对逆问题的新型学习重建方法,包括一个学习到的差异函数。它通过融入可逆神经网络来显式建模特定问题的噪声分布,增强了传统技术。这种方法不依赖于隐含的高斯噪声假设,使其特别适合处理MPI中的复杂噪声模型,也可应用于其他逆问题。为了进一步推进MPI重建技术,我们推出了MPI-MNIST数据集——这是一个基于MNIST手写数字数据集模拟的大量MPI测量值的大型集合。该数据集包括由国家先进技术模型矩阵生成并经过噪声干扰的测量值以及来自临床前MPI扫描设备的测量值。这为算法测试提供了一个现实且灵活的环境。与MPI-MNIST数据集验证相比,我们的方法在结构相似性方面重建质量显著提高,与传统重建技术相比优势明显。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子的磁性响应,磁性粒子成像(MPI)是一种新兴的无辐射、实时、高分辨率成像技术。MPI图像重建任务面临的一个关键挑战在于其噪声模型不满足传统重建方法隐含的高斯假设。为解决这一挑战,我们提出了学习差异法,这是一种针对逆问题的新型学习重建方法,包括学习差异函数。它通过引入可逆神经网络来显式建模问题特定的噪声分布,增强传统技术。该方法不依赖于隐含的高斯噪声假设,特别适用于处理MPI中的复杂噪声模型,也可应用于其他逆问题。为进一步推进MPI重建技术,我们还推出了MPI-MNIST数据集——从MNIST手写数字数据集中模拟的MPI测量结果的集合。该数据集包含由最新模型系统矩阵生成的噪声干扰测量值和预临床MPI扫描设备的测量值,为算法测试提供了现实且灵活的环境。验证结果表明,与经典重建技术相比,该方法在结构相似性方面重建质量显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- MPI是一种新兴成像技术,基于超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子的磁性响应,可实现无辐射、实时、高分辨率成像。
- MPI图像重建面临的关键挑战在于其噪声模型不满足传统重建方法的高斯假设。
- 学习差异法是一种新型的针对逆问题的学习重建方法,通过引入可逆神经网络显式建模问题特定的噪声分布。
- 学习差异法不依赖隐含的高斯噪声假设,适用于处理MPI中的复杂噪声模型和其他逆问题。
- 推出了MPI-MNIST数据集,为MPI重建技术的算法测试提供了现实且灵活的环境。
点此查看论文截图

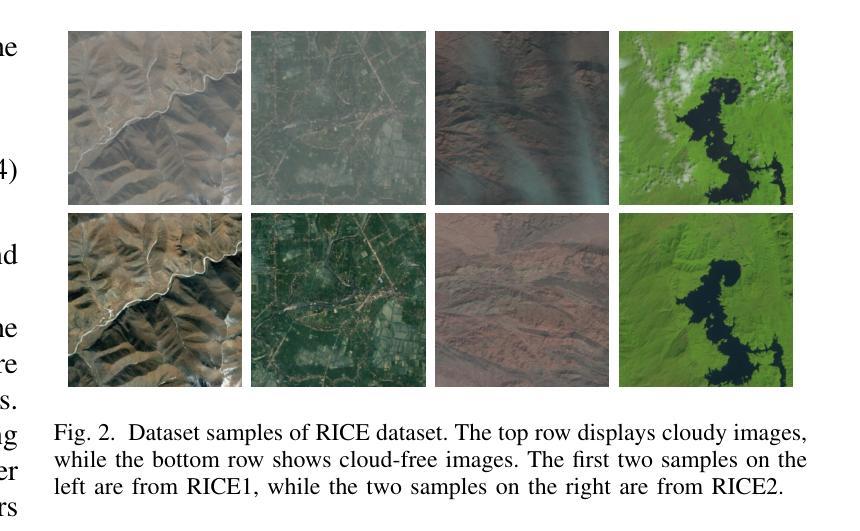
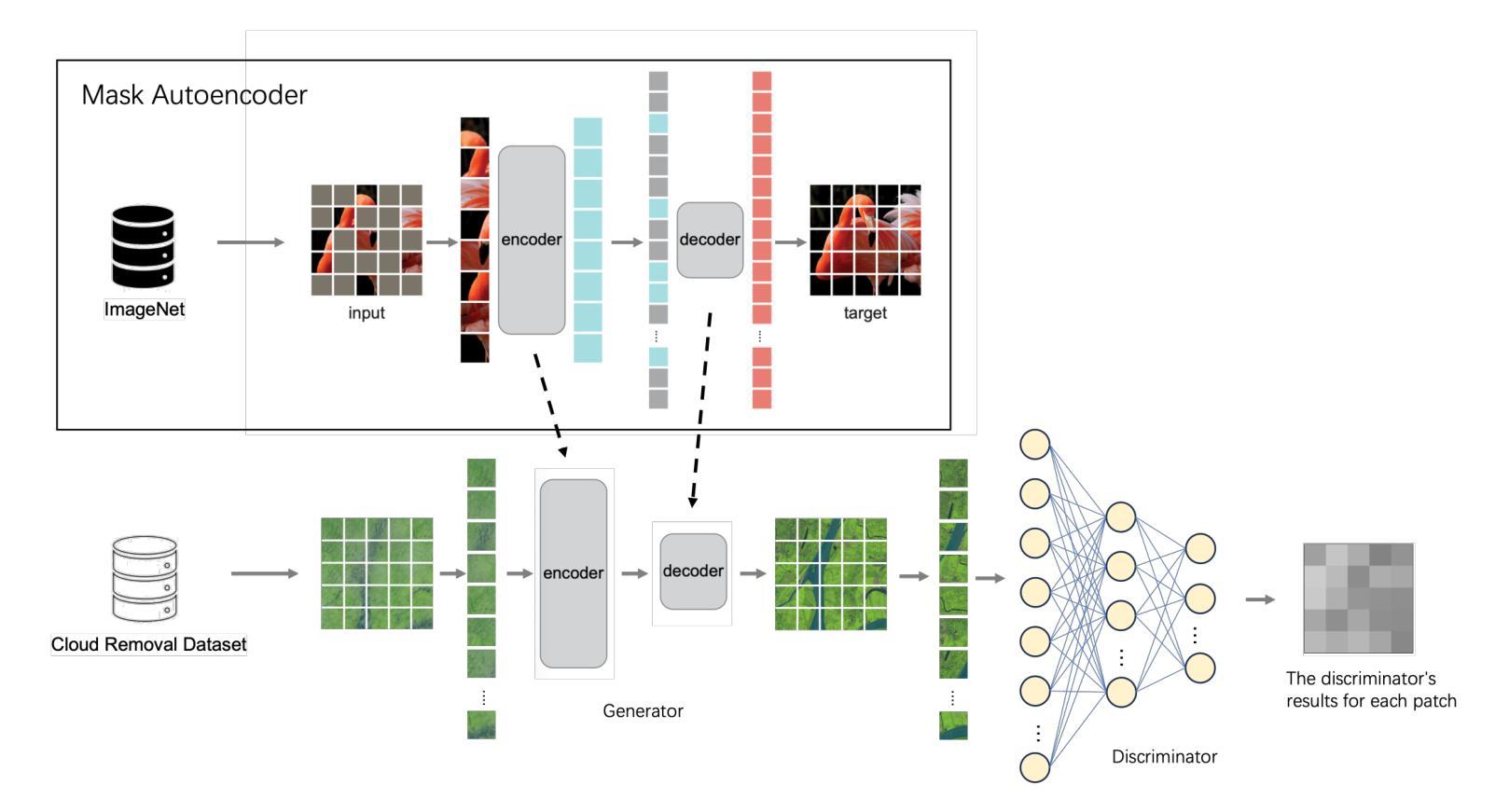
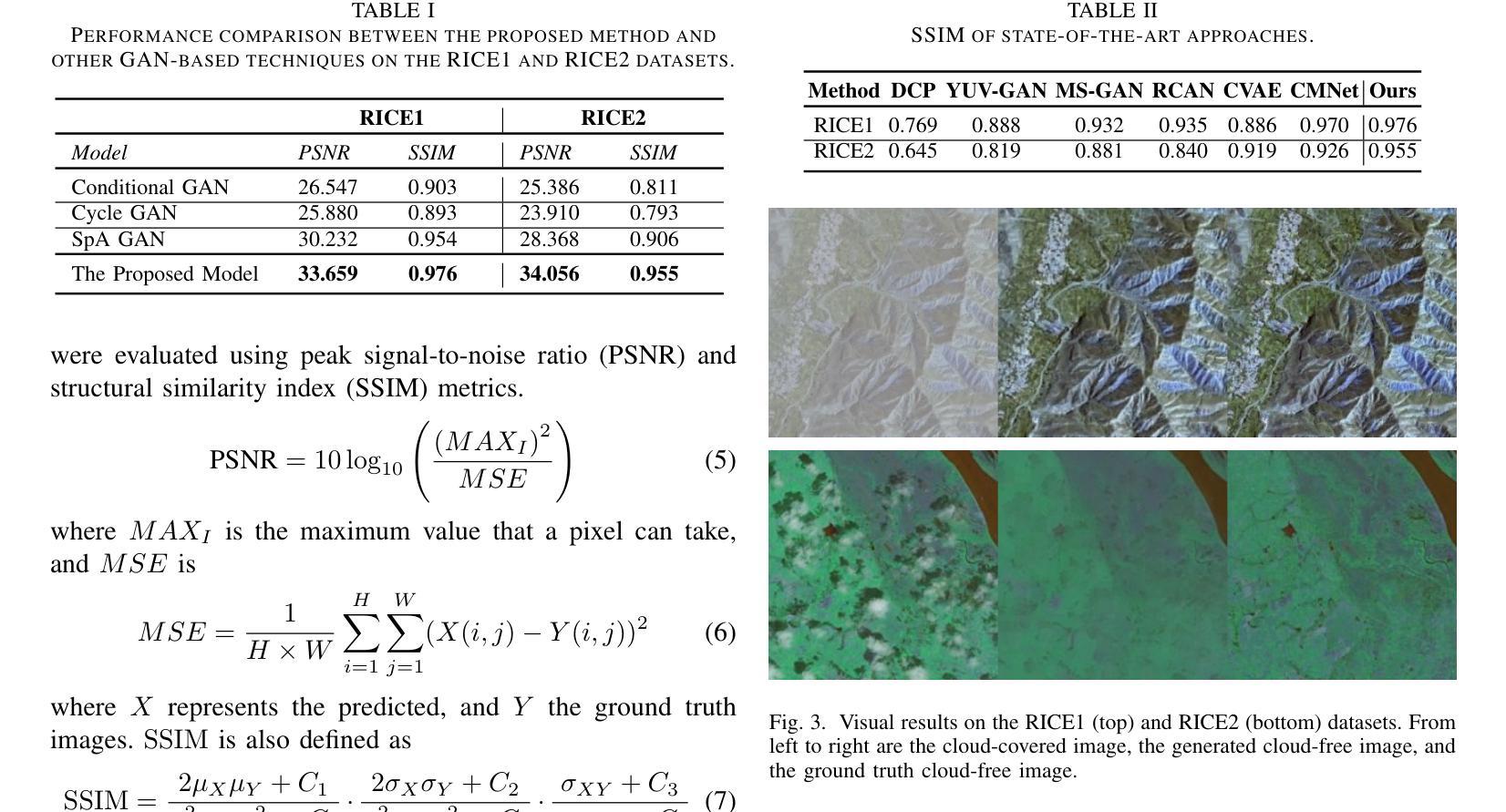
Patch-GAN Transfer Learning with Reconstructive Models for Cloud Removal
Authors:Wanli Ma, Oktay Karakus, Paul L. Rosin
Cloud removal plays a crucial role in enhancing remote sensing image analysis, yet accurately reconstructing cloud-obscured regions remains a significant challenge. Recent advancements in generative models have made the generation of realistic images increasingly accessible, offering new opportunities for this task. Given the conceptual alignment between image generation and cloud removal tasks, generative models present a promising approach for addressing cloud removal in remote sensing. In this work, we propose a deep transfer learning approach built on a generative adversarial network (GAN) framework to explore the potential of the novel masked autoencoder (MAE) image reconstruction model in cloud removal. Due to the complexity of remote sensing imagery, we further propose using a patch-wise discriminator to determine whether each patch of the image is real or not. The proposed reconstructive transfer learning approach demonstrates significant improvements in cloud removal performance compared to other GAN-based methods. Additionally, whilst direct comparisons with some of the state-of-the-art cloud removal techniques are limited due to unclear details regarding their train/test data splits, the proposed model achieves competitive results based on available benchmarks.
云去除在增强遥感图像分析方面起着至关重要的作用,然而,准确地重建被云层遮蔽的区域仍然是一个巨大的挑战。最近生成模型的发展使得生成真实图像变得越来越容易,这为这一任务提供了新的机会。鉴于图像生成和云去除任务之间的概念一致性,生成模型为解决遥感中的云去除问题提供了一种有前途的方法。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)框架的深度迁移学习方法,旨在探索新型掩码自动编码器(MAE)图像重建模型在云去除中的潜力。由于遥感图像的复杂性,我们进一步建议使用基于补丁的鉴别器来确定图像的每个补丁是否真实。所提出的重建迁移学习方法在云去除性能上显示出与其他基于GAN的方法相比的显著改善。此外,尽管由于对其训练/测试数据分割的细节不明确,无法直接与一些最先进的云去除技术进行比较,但基于现有基准测试,所提出模型取得了具有竞争力的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
云去除在增强遥感图像分析方面起着至关重要的作用,但准确重建云遮挡区域仍存在重大挑战。最近生成模型的进展使得生成真实图像变得更容易,为该任务提供了新的机会。鉴于图像生成和云去除任务之间的概念一致性,生成模型在解决遥感中的云去除方面呈现出充满希望的方法。本研究提出了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)框架的深度迁移学习方法,旨在探索新型掩码自动编码器(MAE)图像重建模型在云去除方面的潜力。由于遥感图像的复杂性,我们进一步提出使用基于补丁的鉴别器来判断图像中的每个补丁是否真实。所提出的重建迁移学习方法在云去除性能方面取得了显著的改进,与其他基于GAN的方法相比具有显著的优势。尽管由于对其训练/测试数据分割的细节不明确,无法与某些最先进的云去除技术直接进行比较,但基于可用的基准测试,所提出的模型取得了有竞争力的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 云去除在遥感图像分析中至关重要,但重建云遮挡区域具有挑战性。
- 生成模型的发展为云去除任务提供了新的机会。
- 本研究提出了一种基于GAN框架的深度迁移学习方法,利用新型掩码自动编码器(MAE)进行云去除。
- 为应对遥感图像的复杂性,引入了基于补丁的鉴别器。
- 所提出的重建迁移学习方法在云去除性能上取得了显著改进,相较于其他GAN方法具有优势。
- 模型在可用基准测试中表现出竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

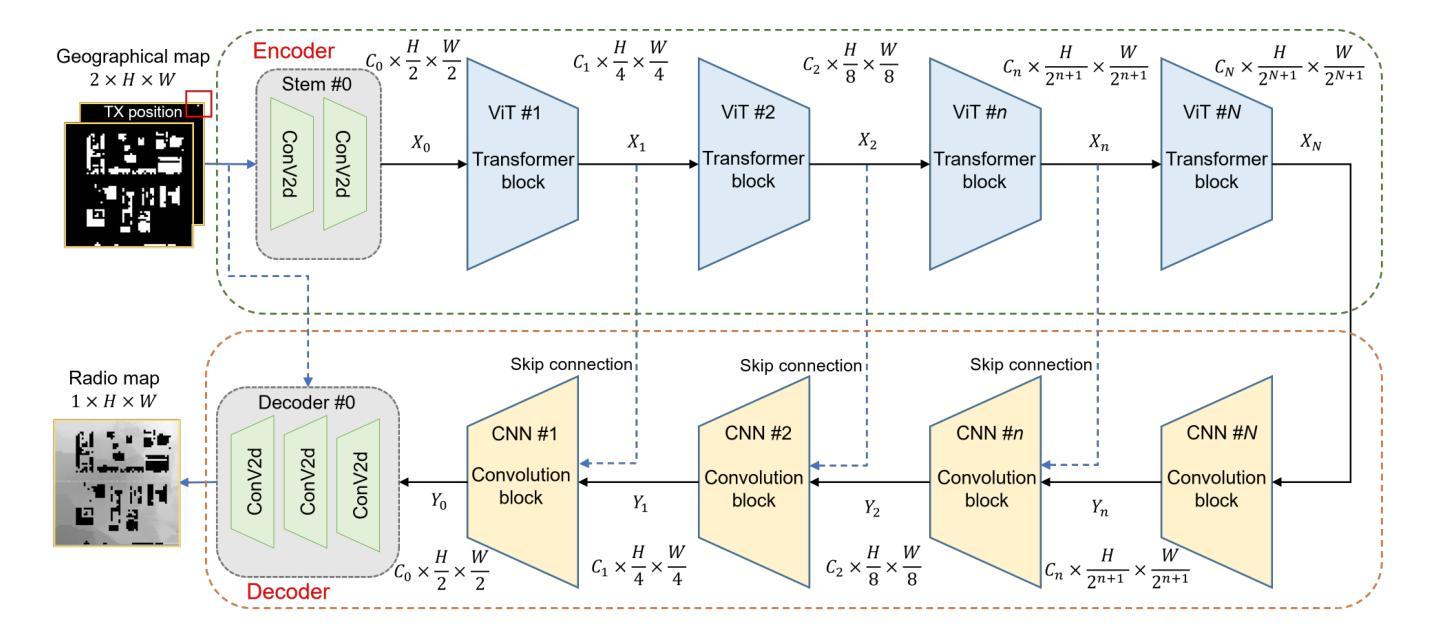
RadioTransformer: Accurate Radio Map Construction and Coverage Prediction
Authors:Yuxuan Li, Cheng Zhang, Wen Wang, Yongming Huang
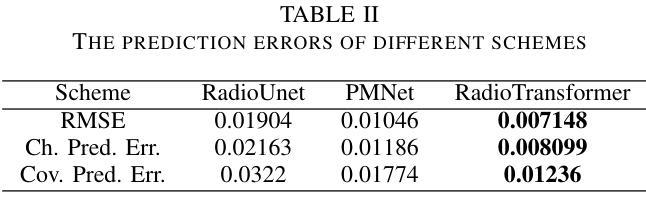
Radio map, or pathloss map prediction, is a crucial method for wireless network modeling and management. By leveraging deep learning to construct pathloss patterns from geographical maps, an accurate digital replica of the transmission environment could be established with less computational overhead and lower prediction error compared to traditional model-driven techniques. While existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods predominantly rely on convolutional architectures, this paper introduces a hybrid transformer-convolution model, termed RadioTransformer, to enhance the accuracy of radio map prediction. The proposed model features a multi-scale transformer-based encoder for efficient feature extraction and a convolution-based decoder for precise pixel-level image reconstruction. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed scheme significantly improves prediction accuracy, and over a 30% reduction in root mean square error (RMSE) is achieved compared to typical SOTA approaches.
无线电地图(或路径损耗地图预测)是无线网络建模和管理的重要方法。通过利用深度学习从地理地图构建路径损耗模式,可以建立一个具有较少计算开销和较低预测误差的传输环境的精确数字副本,与传统模型驱动技术相比。尽管现有的最新方法主要依赖于卷积架构,但本文引入了一种混合的Transformer卷积模型,称为RadioTransformer,以提高无线电地图预测的精度。所提出的模型具有基于多尺度Transformer的编码器,用于有效的特征提取和基于卷积的解码器,用于精确的像素级图像重建。仿真结果表明,该方案显著提高预测精度,与典型的最新方法相比,均方根误差(RMSE)降低了30%以上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE VTC 2025 Spring
总结
利用深度学习结合地理地图构建路径损耗模式,建立传输环境的精准数字副本,相较于传统模型驱动技术,此方法计算开销更小,预测误差更低。现有先进技术主要依赖卷积架构,而本文提出了一种混合Transformer卷积模型——RadioTransformer,以提高路径损耗地图预测的准确度。该模型具有基于多尺度Transformer的编码器进行高效特征提取和基于卷积的解码器进行精确的像素级图像重建。仿真结果表明,该方案显著提高预测精度,相较于典型先进技术,均方根误差降低了超过30%。
关键见解
- 无线电地图预测在无线网络建模和管理中是关键方法。
- 深度学习被用于从地理地图构建路径损耗模式,创建传输环境的数字副本。
- 与传统模型驱动技术相比,使用深度学习的方法计算开销更小,预测误差更低。
- 当前先进技术主要依赖卷积架构进行路径损耗地图预测。
- 本文提出了一种混合Transformer卷积模型——RadioTransformer。
- RadioTransformer模型包括基于多尺度Transformer的编码器和基于卷积的解码器。
点此查看论文截图


Improving the U-Net Configuration for Automated Delineation of Head and Neck Cancer on MRI
Authors:Andrei Iantsen
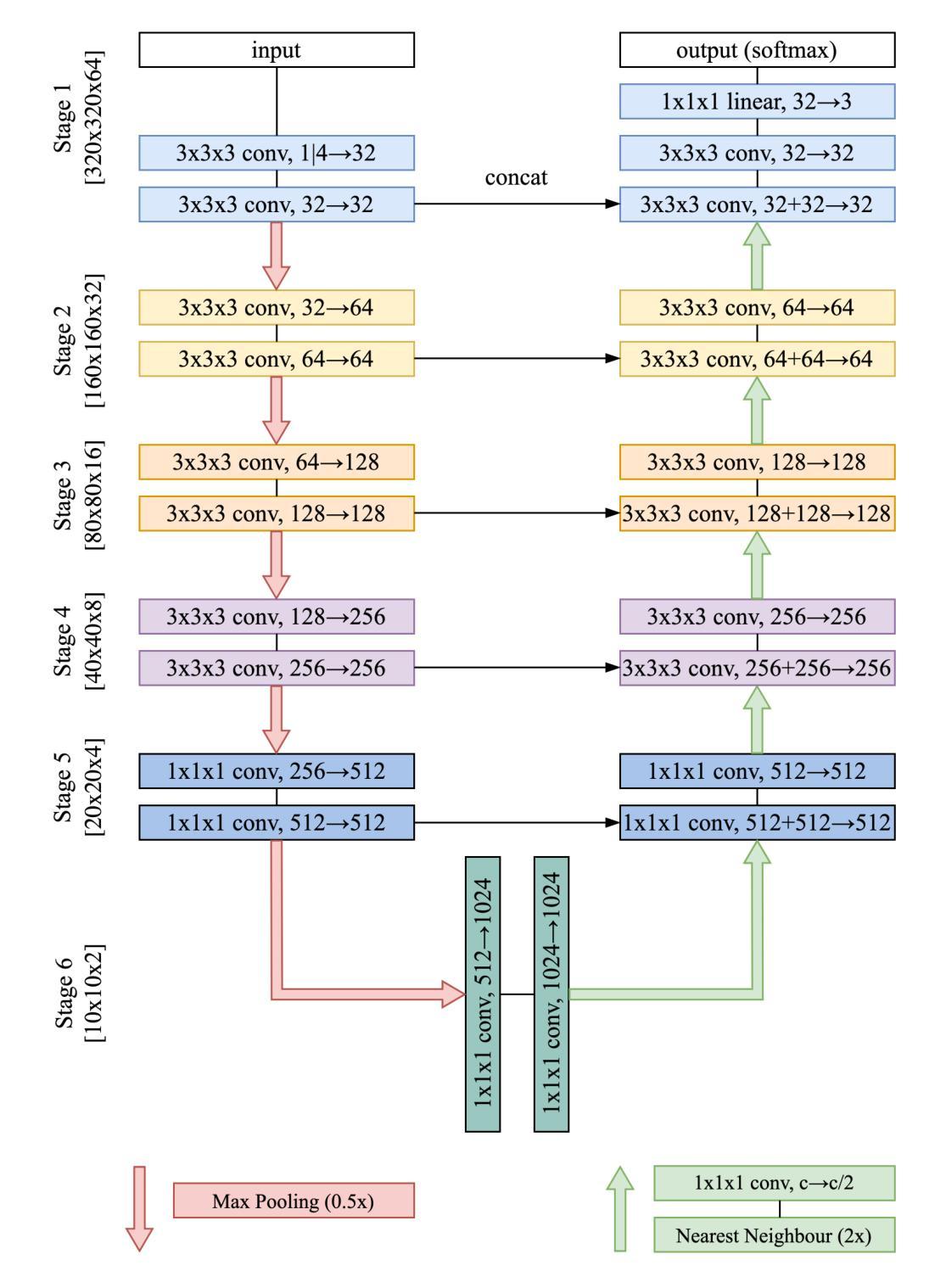
Tumor volume segmentation on MRI is a challenging and time-consuming process that is performed manually in typical clinical settings. This work presents an approach to automated delineation of head and neck tumors on MRI scans, developed in the context of the MICCAI Head and Neck Tumor Segmentation for MR-Guided Applications (HNTS-MRG) 2024 Challenge. Rather than designing a new, task-specific convolutional neural network, the focus of this research was to propose improvements to the configuration commonly used in medical segmentation tasks, relying solely on the traditional U-Net architecture. The empirical results presented in this article suggest the superiority of patch-wise normalization used for both training and sliding window inference. They also indicate that the performance of segmentation models can be enhanced by applying a scheduled data augmentation policy during training. Finally, it is shown that a small improvement in quality can be achieved by using Gaussian weighting to combine predictions for individual patches during sliding window inference. The model with the best configuration obtained an aggregated Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSCagg) of 0.749 in Task 1 and 0.710 in Task 2 on five cross-validation folds. The ensemble of five models (one best model per validation fold) showed consistent results on a private test set of 50 patients with an DSCagg of 0.752 in Task 1 and 0.718 in Task 2 (team name: andrei.iantsen). The source code and model weights are freely available at www.github.com/iantsen/hntsmrg.
肿瘤体积在MRI上的分割是一个具有挑战性和耗时的过程,通常在典型的临床环境中手动执行。本文介绍了一种在MRI扫描上自动描绘头部和颈部肿瘤的方法,该方法是在MICCAI头部和颈部肿瘤分割用于MR引导应用(HNTS-MRG)2024挑战赛的背景下开发的。本文的重点不是设计新的针对特定任务的卷积神经网络,而是对医学分割任务中通常使用的配置进行改进,仅依赖于传统的U-Net架构。本文的实证结果表明,用于训练和滑动窗口推断的块级归一化具有优越性。他们还表明,通过训练期间实施计划数据增强策略,可以提高分割模型的性能。最后,结果显示,在使用高斯权重合并滑动窗口推断期间个别补丁的预测时,可以实现质量的小幅提升。最佳配置模型在五个交叉验证折叠中的任务1和任务2上分别获得了0.749和0.710的Dice相似系数(DSCagg)。五个模型(每个验证折叠的最佳模型)在包含50名患者的私有测试集上的结果表现一致,任务1和任务2的DSCagg分别为0.752和0.718(团队名称:andrei.iantsen)。源代码和模型权重可在www.github.com/iantsen/hntsmrg免费获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对MRI扫描中头部和颈部肿瘤的自动分割方法,重点是对常用医学分割任务配置的改进,而非设计新的卷积神经网络。通过采用patch-wise归一化进行训练和滑动窗口推断,以及计划数据增强策略,提高了分割模型的性能。最佳配置的模型在五个交叉验证集上获得了较高的Dice相似系数。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究关注于改进常用于医学分割任务的配置,而非设计新的卷积神经网络。
- 采用patch-wise归一化进行训练和滑动窗口推断,提高了模型性能。
- 通过计划数据增强策略,增强了分割模型的性能。
- 最佳配置的模型在五个交叉验证集上的Dice相似系数表现优异。
- 模型在私人测试集上的结果也表现稳定。
- 源代码和模型权重已公开发布在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

D3RM: A Discrete Denoising Diffusion Refinement Model for Piano Transcription
Authors:Hounsu Kim, Taegyun Kwon, Juhan Nam
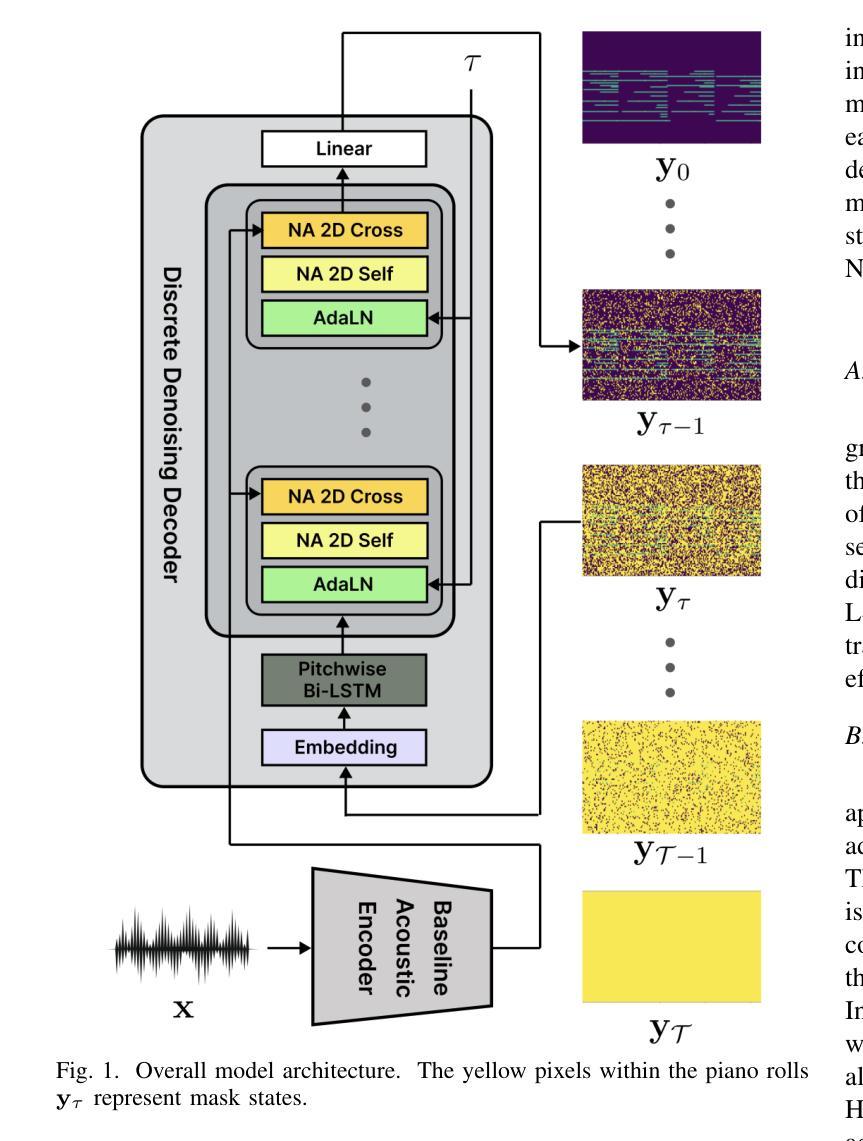
Diffusion models have been widely used in the generative domain due to their convincing performance in modeling complex data distributions. Moreover, they have shown competitive results on discriminative tasks, such as image segmentation. While diffusion models have also been explored for automatic music transcription, their performance has yet to reach a competitive level. In this paper, we focus on discrete diffusion model’s refinement capabilities and present a novel architecture for piano transcription. Our model utilizes Neighborhood Attention layers as the denoising module, gradually predicting the target high-resolution piano roll, conditioned on the finetuned features of a pretrained acoustic model. To further enhance refinement, we devise a novel strategy which applies distinct transition states during training and inference stage of discrete diffusion models. Experiments on the MAESTRO dataset show that our approach outperforms previous diffusion-based piano transcription models and the baseline model in terms of F1 score. Our code is available in https://github.com/hanshounsu/d3rm.
扩散模型由于其在对复杂数据分布进行建模时的出色表现,在生成领域得到了广泛应用。此外,它们在判别任务(如图像分割)上也取得了具有竞争力的结果。虽然扩散模型也已被探索用于自动音乐转录,但其性能尚未达到竞争水平。在本文中,我们重点关注离散扩散模型的精细化能力,并提出了一种用于钢琴转录的新型架构。我们的模型利用邻域注意力层作为去噪模块,基于预训练声学模型的微调特征,逐步预测目标高分辨率钢琴乐谱。为了进一步提高精细化程度,我们设计了一种新型策略,在离散扩散模型的训练和推理阶段应用不同的过渡状态。在MAESTRO数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法在F1分数方面优于之前的基于扩散的钢琴转录模型和基线模型。我们的代码位于https://github.com/hanshounsu/d3rm。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了离散扩散模型在钢琴音乐转录方面的应用。通过采用新颖的架构和策略,该模型在MAESTRO数据集上的表现超越了之前的扩散模型及基线模型,具有出色的精细化能力。具体采用了邻居注意力层作为去噪模块,逐步预测目标高分辨率钢琴谱卷,并在训练及推理阶段实施独特的过渡状态策略来提升模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- 离散扩散模型在钢琴音乐转录领域展现出潜力。
- 论文提出了一种新型架构用于钢琴转录的离散扩散模型。
- 模型使用邻居注意力层作为去噪模块以提高精细化能力。
- 模型采用独特的过渡状态策略,在训练和推理阶段表现优异。
- 实验结果表明该模型在MAESTRO数据集上的表现优于其他扩散模型及基线模型。
- 模型代码已公开在GitHub上供研究人员参考和使用。
点此查看论文截图



A CT Image Classification Network Framework for Lung Tumors Based on Pre-trained MobileNetV2 Model and Transfer learning, And Its Application and Market Analysis in the Medical field
Authors:Ziyang Gao, Yong Tian, Shih-Chi Lin, Junghua Lin
In the medical field, accurate diagnosis of lung cancer is crucial for treatment. Traditional manual analysis methods have significant limitations in terms of accuracy and efficiency. To address this issue, this paper proposes a deep learning network framework based on the pre-trained MobileNetV2 model, initialized with weights from the ImageNet-1K dataset (version 2). The last layer of the model (the fully connected layer) is replaced with a new fully connected layer, and a softmax activation function is added to efficiently classify three types of lung cancer CT scan images. Experimental results show that the model achieves an accuracy of 99.6% on the test set, with significant improvements in feature extraction compared to traditional models.With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technologies, deep learning applications in medical image processing are bringing revolutionary changes to the healthcare industry. AI-based lung cancer detection systems can significantly improve diagnostic efficiency, reduce the workload of doctors, and occupy an important position in the global healthcare market. The potential of AI to improve diagnostic accuracy, reduce medical costs, and promote precision medicine will have a profound impact on the future development of the healthcare industry.
在医学领域,肺癌的准确诊断对治疗至关重要。传统的分析方法在准确性和效率方面存在重大局限性。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种基于预训练MobileNetV2模型的深度学习网络框架,该框架使用ImageNet-1K数据集(第二版)的权重进行初始化。该模型的最后一层(全连接层)被替换为新的全连接层,并添加了一个softmax激活函数,以有效地对三种肺癌CT扫描图像进行分类。实验结果表明,该模型在测试集上达到了99.6%的准确率,在特征提取方面相比传统模型有了显著改进。随着人工智能技术的快速发展,深度学习在医学图像处理中的应用给医疗保健行业带来了革命性的变化。基于人工智能的肺癌检测系统可以显著提高诊断效率,减轻医生的工作量,在全球医疗市场中占据重要地位。人工智能提高诊断准确率、降低医疗成本、促进精准医疗的潜力将对医疗卫生行业的未来发展产生深远影响。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习网络框架的肺癌诊断研究采用预训练的MobileNetV2模型,利用ImageNet-1K数据集进行权重初始化,提出新方法以提升模型在CT扫描图像上的肺癌分类准确性。模型在测试集上准确率高达99.6%,显示出巨大的潜力改变医疗行业的诊断效率和精度。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用深度学习网络框架,基于预训练的MobileNetV2模型进行肺癌诊断。
- 使用ImageNet-1K数据集进行权重初始化,以提高模型的准确性。
- 模型通过替换原有全连接层并添加softmax激活函数,实现对三种肺癌CT扫描图像的高效分类。
- 实验结果显示模型在测试集上的准确率高达99.6%。
- 与传统模型相比,该模型在特征提取方面表现出显著改进。
- AI在医疗图像处理方面的应用为医疗行业带来革命性变化。
- AI肺癌检测系统能显著提高诊断效率,减轻医生工作量。
点此查看论文截图

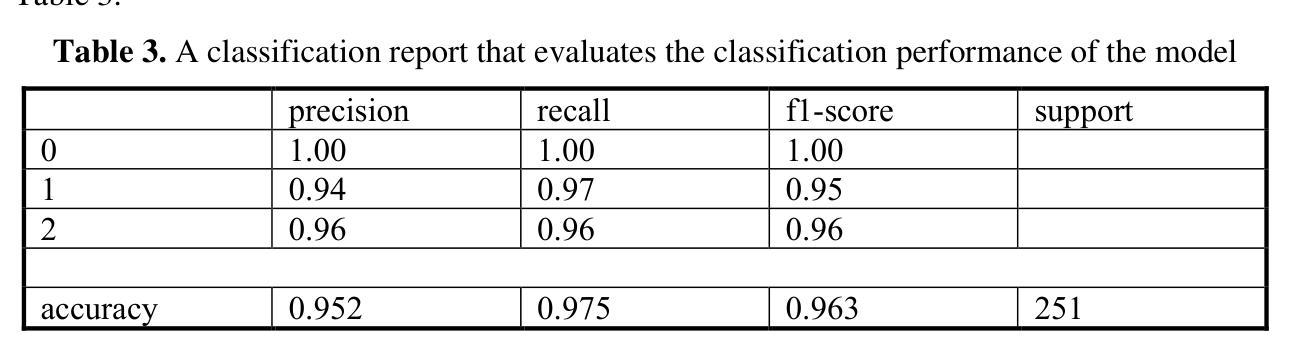
A Steerable Deep Network for Model-Free Diffusion MRI Registration
Authors:Gianfranco Cortes, Xiaoda Qu, Baba C. Vemuri
Nonrigid registration is vital to medical image analysis but remains challenging for diffusion MRI (dMRI) due to its high-dimensional, orientation-dependent nature. While classical methods are accurate, they are computationally demanding, and deep neural networks, though efficient, have been underexplored for nonrigid dMRI registration compared to structural imaging. We present a novel, deep learning framework for model-free, nonrigid registration of raw diffusion MRI data that does not require explicit reorientation. Unlike previous methods relying on derived representations such as diffusion tensors or fiber orientation distribution functions, in our approach, we formulate the registration as an equivariant diffeomorphism of position-and-orientation space. Central to our method is an $\mathsf{SE}(3)$-equivariant UNet that generates velocity fields while preserving the geometric properties of a raw dMRI’s domain. We introduce a new loss function based on the maximum mean discrepancy in Fourier space, implicitly matching ensemble average propagators across images. Experimental results on Human Connectome Project dMRI data demonstrate competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art approaches, with the added advantage of bypassing the overhead for estimating derived representations. This work establishes a foundation for data-driven, geometry-aware dMRI registration directly in the acquisition space.
非刚性配准对医学图像分析至关重要,但由于扩散磁共振成像(dMRI)的高维、方向依赖特性,它仍然是一个挑战。虽然经典方法准确,但计算量大,而深度神经网络虽然效率高,但与结构成像相比,在非刚性dMRI配准方面的探索较少。我们提出了一种新型的深度学习框架,用于无模型非刚性配准原始扩散MRI数据,无需明确调整方向。不同于依赖衍生表示(如扩散张量或纤维方向分布函数)的先前方法,我们的方法将配准公式化为位置和方向的等距同构空间。我们的方法的核心是一个SE(3)等距UNet,它生成速度场的同时保留了原始dMRI域的几何属性。我们引入了一个新的损失函数,基于傅里叶空间中的最大均值差异,隐式匹配图像之间的整体平均传播器。在人类连接组项目dMRI数据上的实验结果表明,与最新方法相比,我们的方法具有竞争性能,并额外避免了估计衍生表示的开销。这项工作为直接在采集空间中进行数据驱动、几何感知的dMRI配准奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Coauthor was inadvertently left out. This is now corrected
Summary
该摘要提出了一种新型的深度学习框架,用于对原始扩散磁共振成像(dMRI)数据进行非刚性注册,无需明确调整方向。该框架采用SE(3)等价性UNet生成速度场,同时保留原始dMRI域的几何特性。实验结果表明,该方法在Human Connectome Project dMRI数据上的性能与最新方法相当,且具有无需估计派生表示的额外优势。这为直接在采集空间进行数据驱动、几何感知的dMRI注册奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 非刚性注册对医学图像分析至关重要,但对于高维、方向依赖的扩散磁共振成像(dMRI)具有挑战性。
- 经典方法虽然准确但计算量大,而深度神经网络虽然效率高但在非刚性dMRI注册方面的应用相较于结构成像被探索得较少。
- 提出了一种新型的深度学习框架,用于对原始dMRI数据进行非刚性注册,无需明确调整方向。
- 采用SE(3)-equivariant UNet生成速度场,同时保留原始dMRI域的几何特性。
- 引入了一种基于傅里叶空间中最大均值差异的新损失函数,隐式匹配图像间的整体平均传播器。
- 在Human Connectome Project dMRI数据上的实验结果表明该方法具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

Rethinking domain generalization in medical image segmentation: One image as one domain
Authors:Jin Hong, Bo Liu, Guoli Long
Domain shifts in medical image segmentation, particularly when data comes from different centers, pose significant challenges. Intra-center variability, such as differences in scanner models or imaging protocols, can cause domain shifts as large as, or even larger than, those between centers. To address this, we propose the “one image as one domain” (OIOD) hypothesis, which treats each image as a unique domain, enabling flexible and robust domain generalization. Based on this hypothesis, we develop a unified disentanglement-based domain generalization (UniDDG) framework, which simultaneously handles both multi-source and single-source domain generalization without requiring explicit domain labels. This approach simplifies training with a fixed architecture, independent of the number of source domains, reducing complexity and enhancing scalability. We decouple each input image into content representation and style code, then exchange and combine these within the batch for segmentation, reconstruction, and further disentanglement. By maintaining distinct style codes for each image, our model ensures thorough decoupling of content representations and style codes, improving domain invariance of the content representations. Additionally, we enhance generalization with expansion mask attention (EMA) for boundary preservation and style augmentation (SA) to simulate diverse image styles, improving robustness to domain shifts. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves Dice scores of 84.43% and 88.91% for multi-source to single-center and single-center generalization in optic disc and optic cup segmentation, respectively, and 86.96% and 88.56% for prostate segmentation, outperforming current state-of-the-art domain generalization methods, offering superior performance and adaptability across clinical settings.
医学图像分割中的领域漂移,特别是当数据来自不同中心时,会带来重大挑战。来自同一中心的内部差异性,如扫描仪型号或成像协议的不同,可能会导致与跨中心领域漂移一样甚至更大的领域漂移。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了“一图一个领域”(OIOD)假设,该假设将每张图像视为一个独特的领域,以实现灵活和稳健的领域泛化。基于这一假设,我们开发了一个统一的基于分离理论的领域泛化(UniDDG)框架,该框架可以同时处理多源和单源领域泛化,无需明确的领域标签。这种方法简化了固定架构的训练过程,无论源领域的数量如何都是如一的。我们通过将每个输入图像解耦为内容表示和风格代码,然后在批次内进行交换和组合以进行分割、重建和进一步的解耦。通过为每个图像保留独特的风格代码,我们的模型确保了内容表示和风格代码的彻底解耦,提高了内容表示的领域不变性。此外,我们通过扩展掩膜注意力(EMA)保持边界,模拟各种图像风格以增强风格扩充(SA),提高了对领域漂移的稳健性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视盘和视杯分割的多源到单一中心和单一中心泛化中分别实现了84.43%和88.91%的Dice得分,在前列腺分割中分别实现了86.96%和88.56%,超越了当前最先进的领域泛化方法,在临床环境中提供了卓越的性能和适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对医学图像分割中的跨中心数据领域漂移问题,提出“一图一域”(OIOD)假设和统一解耦的域泛化(UniDDG)框架。该框架无需明确的域标签即可同时处理多源和单源域泛化问题,简化了固定架构的训练,增强了模型的扩展性。通过维护每个图像特有的风格代码,模型确保内容和风格代码的彻底解耦,提高内容表示的域不变性。此外,通过扩展掩膜注意力(EMA)和风格增强(SA)提高模型的泛化能力。实验表明,该方法在光学圆盘、光学杯和前列腺分割中均取得了优于当前最先进的域泛化方法的结果。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割中的跨中心和跨仪器差异造成了领域漂移的挑战。
- 提出“一图一域”(OIOD)假设,将每幅图像视为独特的域,促进灵活和稳健的域泛化。
- 发展了统一解耦的域泛化(UniDDG)框架,无需明确的域标签即可处理多源和单源域泛化问题。
- 通过解耦输入图像为内容表示和风格代码,增强了模型的域不变性。
- 通过扩展掩膜注意力(EMA)和风格增强(SA)提高了模型的边界保留能力和对各种图像风格的稳健性。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在多种医学图像分割任务上均取得了优异性能。
点此查看论文截图

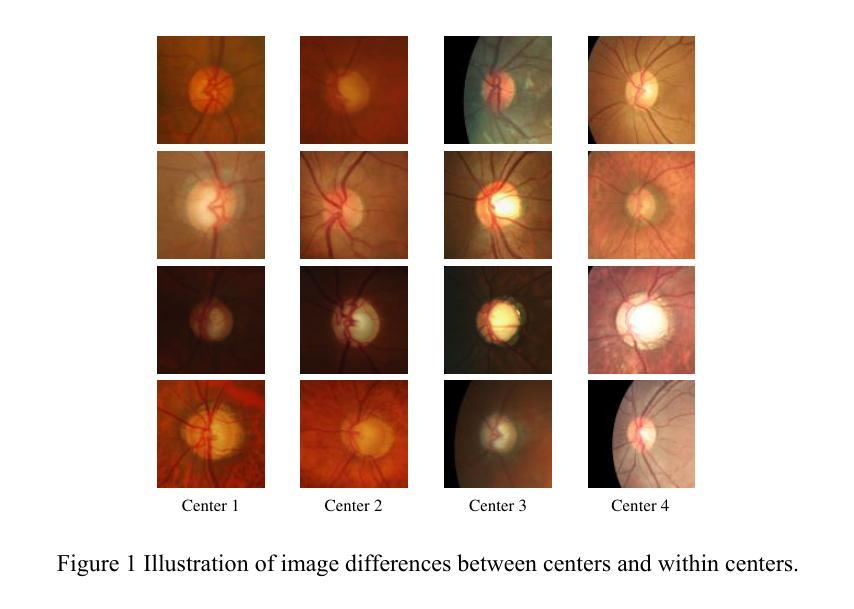
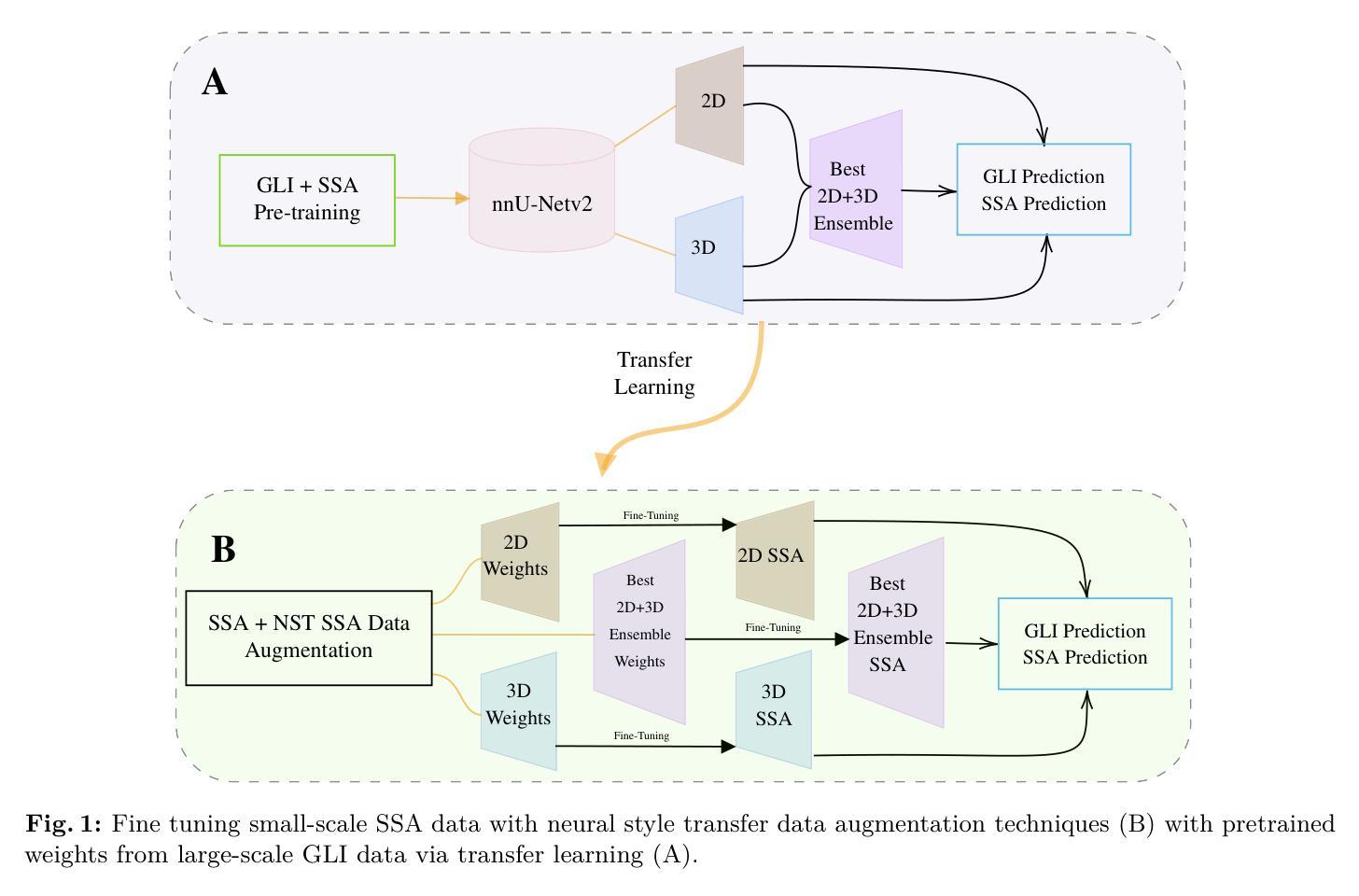
Generative Style Transfer for MRI Image Segmentation: A Case of Glioma Segmentation in Sub-Saharan Africa
Authors:Rancy Chepchirchir, Jill Sunday, Raymond Confidence, Dong Zhang, Talha Chaudhry, Udunna C. Anazodo, Kendi Muchungi, Yujing Zou
In Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), the utilization of lower-quality Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) technology raises questions about the applicability of machine learning methods for clinical tasks. This study aims to provide a robust deep learning-based brain tumor segmentation (BraTS) method tailored for the SSA population using a threefold approach. Firstly, the impact of domain shift from the SSA training data on model efficacy was examined, revealing no significant effect. Secondly, a comparative analysis of 3D and 2D full-resolution models using the nnU-Net framework indicates similar performance of both the models trained for 300 epochs achieving a five-fold cross-validation score of 0.93. Lastly, addressing the performance gap observed in SSA validation as opposed to the relatively larger BraTS glioma (GLI) validation set, two strategies are proposed: fine-tuning SSA cases using the GLI+SSA best-pretrained 2D fullres model at 300 epochs, and introducing a novel neural style transfer-based data augmentation technique for the SSA cases. This investigation underscores the potential of enhancing brain tumor prediction within SSA’s unique healthcare landscape.
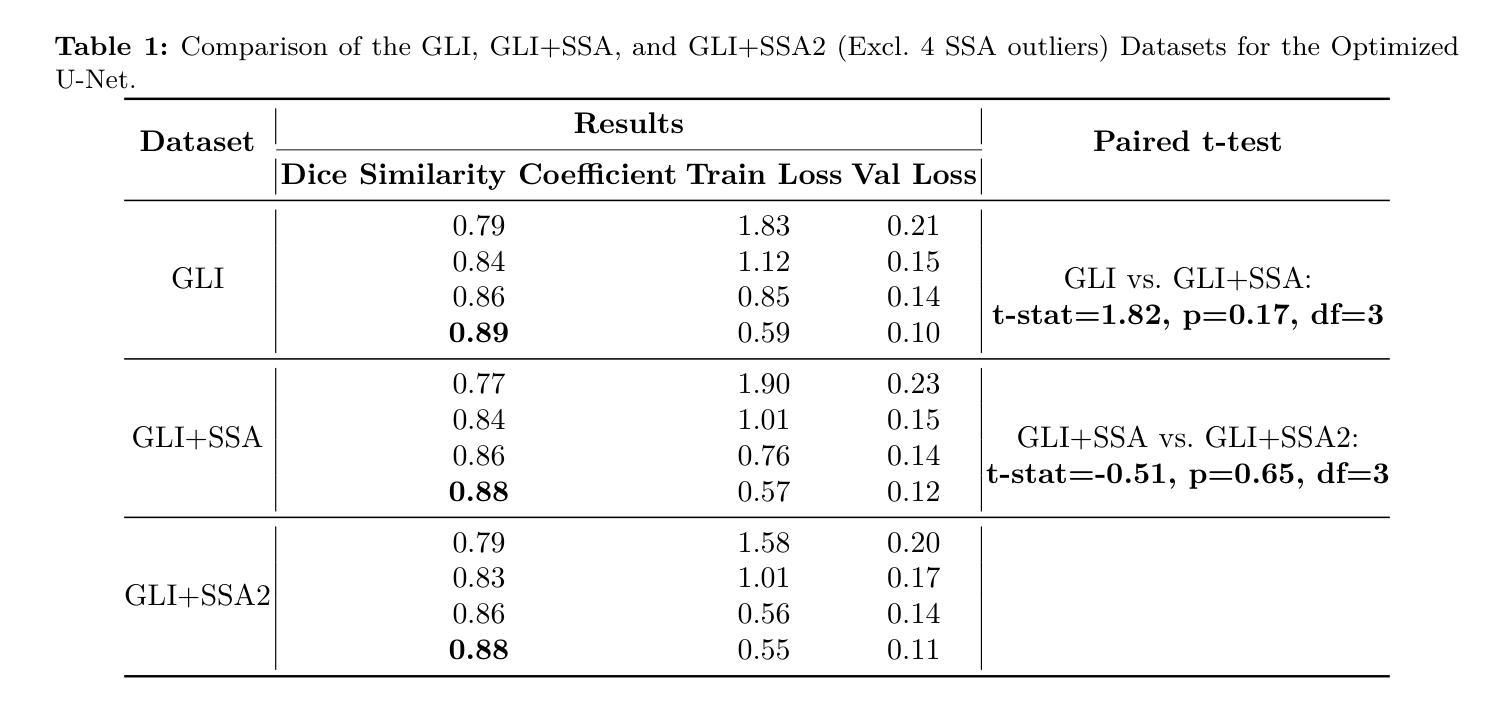
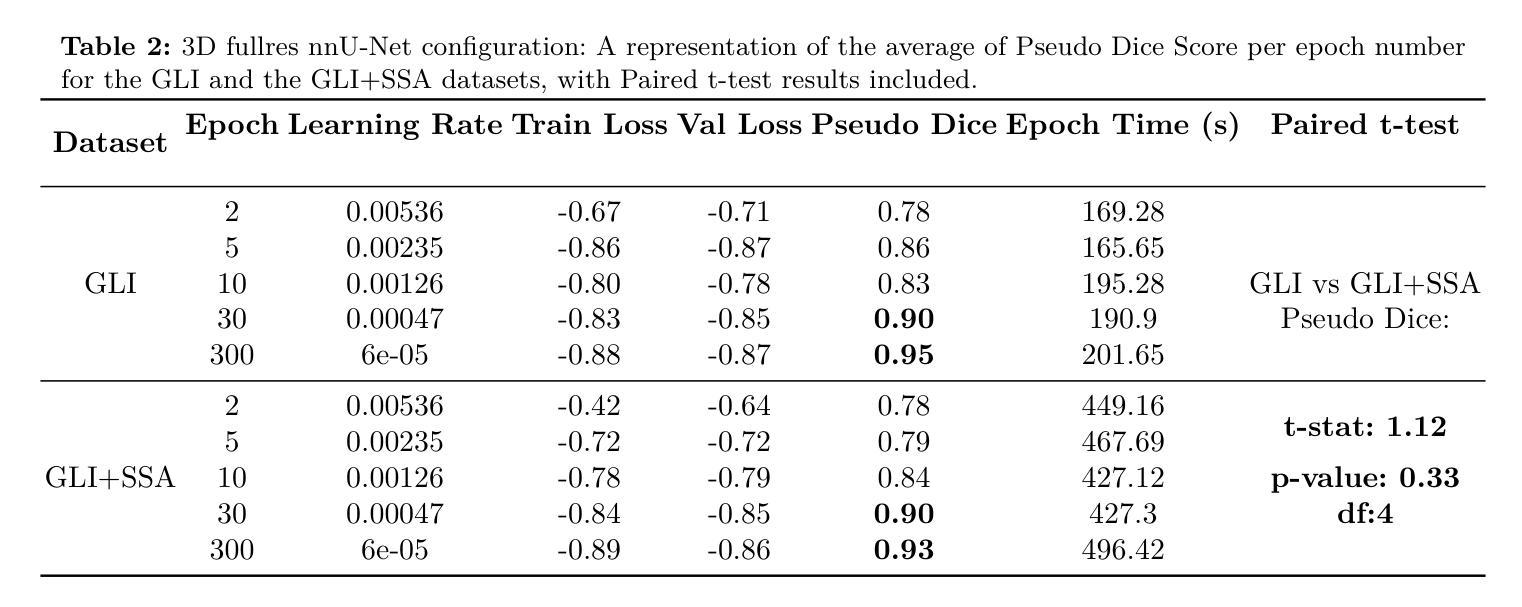
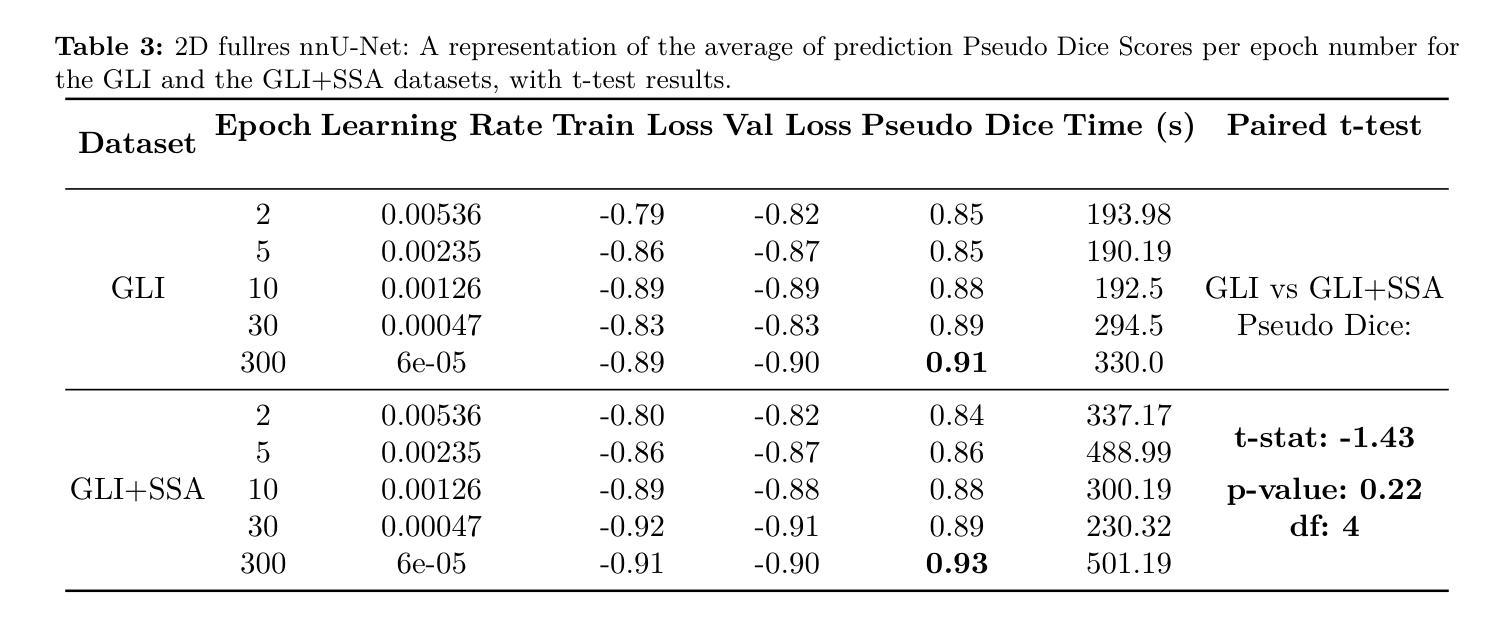
在撒哈拉以南非洲(SSA),由于使用质量较低的磁共振成像(MRI)技术,机器学习在临床任务中的适用性引发了质疑。本研究旨在采用三重方法,为SSA人群提供一种稳健的深度学习的脑肿瘤分割(BraTS)方法。首先,研究了SSA训练数据对模型功效的域偏移影响,结果显示无显著影响。其次,利用nnU-Net框架对3D和2D全分辨率模型进行的比较分析表明,两者性能相似,经过300轮训练的模型在五倍交叉验证中得分达到0.93。最后,针对在SSA验证集中观察到的性能差距与相对较大的BraTS胶质瘤(GLI)验证集之间的对比,提出了两种策略:使用GLI+SSA最佳预训练的2D全分辨率模型对SSA病例进行微调(训练周期为300轮),并为SSA病例引入一种新型的基于神经风格转移的数据增强技术。本研究强调了提高SSA独特医疗环境下脑肿瘤预测潜力的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究旨在利用深度学习技术为撒哈拉以南非洲(SSA)地区开发一种稳健的脑肿瘤分割(BraTS)方法。研究通过三方面展开:首先,研究了SSA训练数据对模型有效性的影响,发现无明显影响;其次,对比分析了基于nnU-Net框架的3D和2D全分辨率模型,二者性能相似,训练模型达到五倍交叉验证得分0.93;最后,针对SSA验证集与较大的BraTS胶质瘤(GLI)验证集之间的性能差距,提出了两种策略:使用最佳预训练的2D fullres模型对SSA案例进行微调,并引入一种新型的基于神经风格转移的数据增强技术。研究突出了提高SSA地区脑肿瘤预测潜力的可能性。
要点掌握
- SSA地区使用低质量MRI技术引发对机器学习方法临床适用性的质疑。
- 研究通过三方面为SSA地区开发了一种稳健的脑肿瘤分割(BraTS)方法。
- SSA训练数据对模型有效性的影响研究未发现显著效果。
- 3D和2D全分辨率模型的性能对比分析显示二者相似,且均表现良好。
- 针对SSA验证集与GLI验证集间的性能差距,提出了两种策略来提高预测准确性。
- 使用预训练的2D fullres模型对SSA案例进行微调是一种有效的策略。
点此查看论文截图

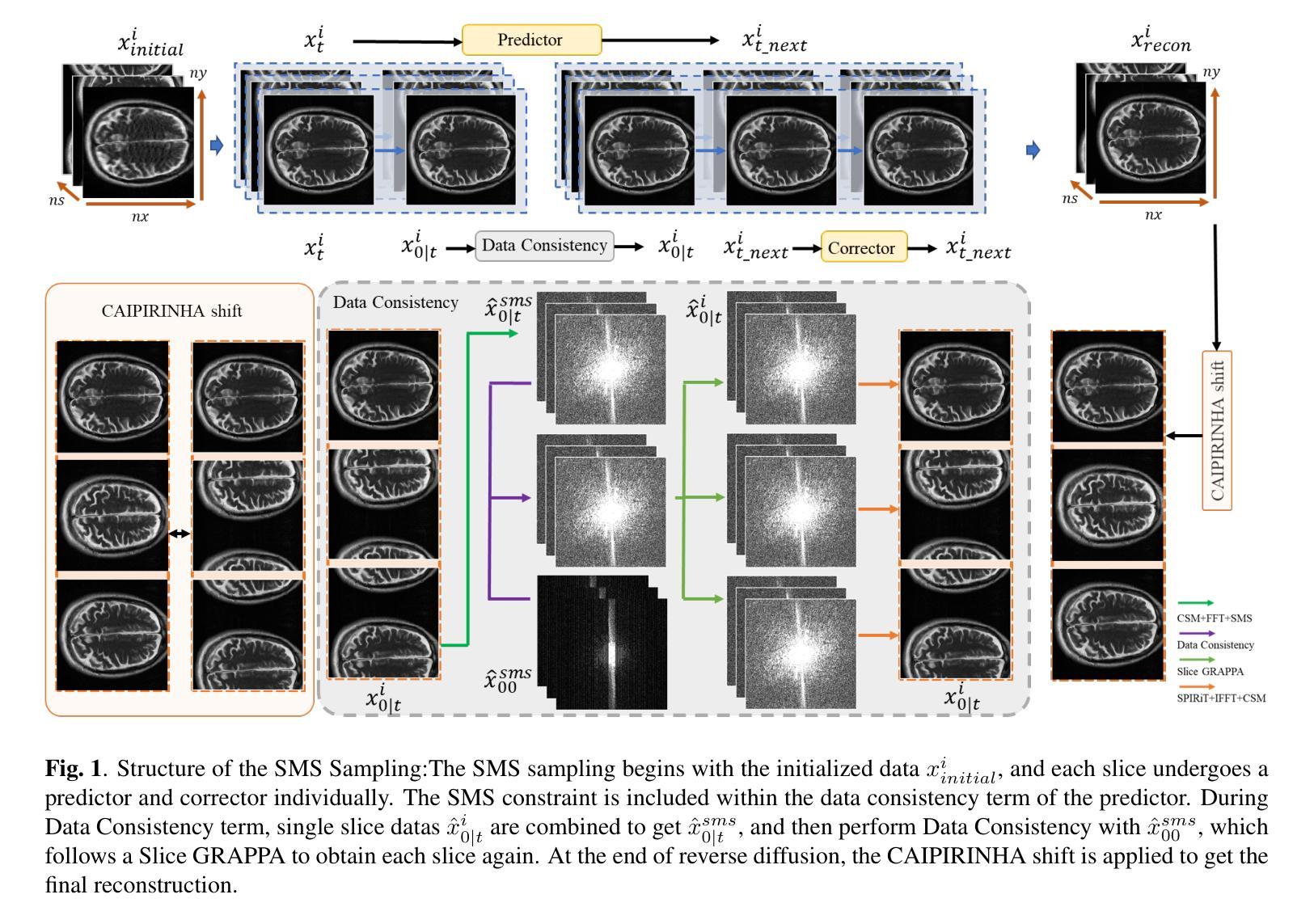
K-space Diffusion Model Based MR Reconstruction Method for Simultaneous Multislice Imaging
Authors:Ting Zhao, Zhuoxu Cui, Congcong Liu, Xingyang Wu, Yihang Zhou, Dong Liang, Haifeng Wang
Simultaneous Multi-Slice(SMS) is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique which excites several slices concurrently using multiband radiofrequency pulses to reduce scanning time. However, due to its variable data structure and difficulty in acquisition, it is challenging to integrate SMS data as training data into deep learning frameworks.This study proposed a novel k-space diffusion model of SMS reconstruction that does not utilize SMS data for training. Instead, it incorporates Slice GRAPPA during the sampling process to reconstruct SMS data from different acquisition modes.Our results demonstrated that this method outperforms traditional SMS reconstruction methods and can achieve higher acceleration factors without in-plane aliasing.
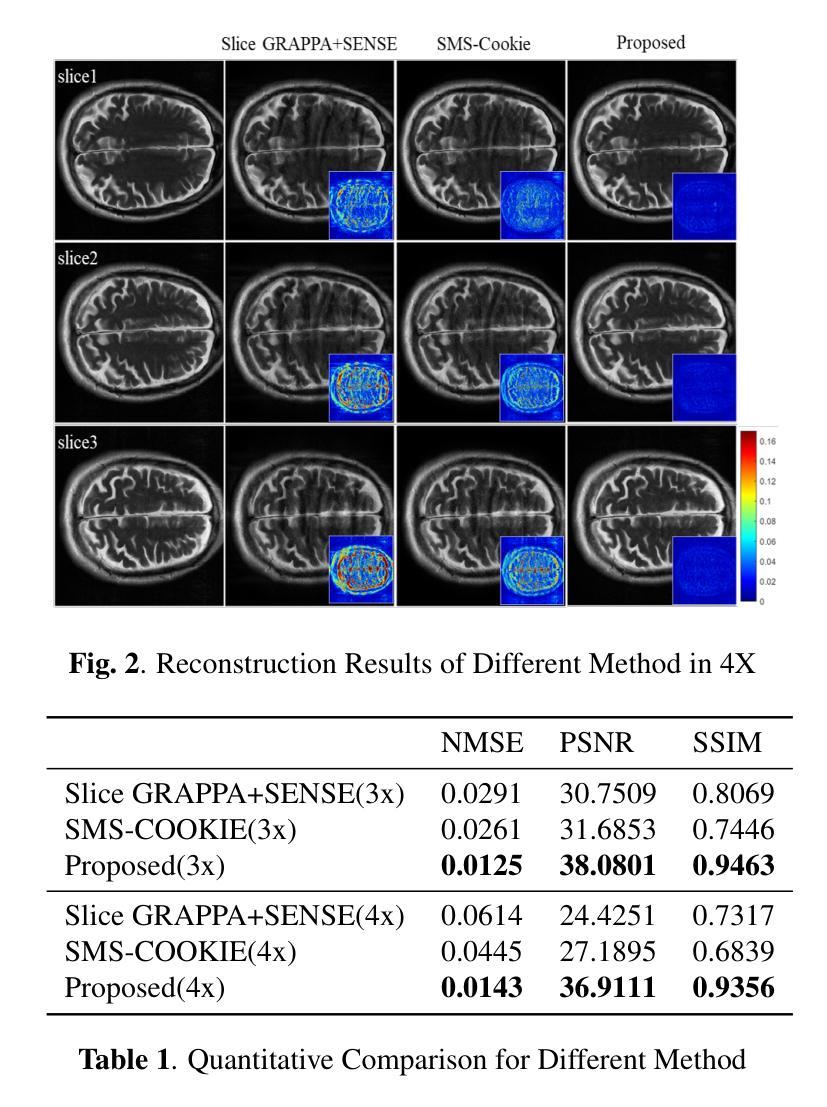
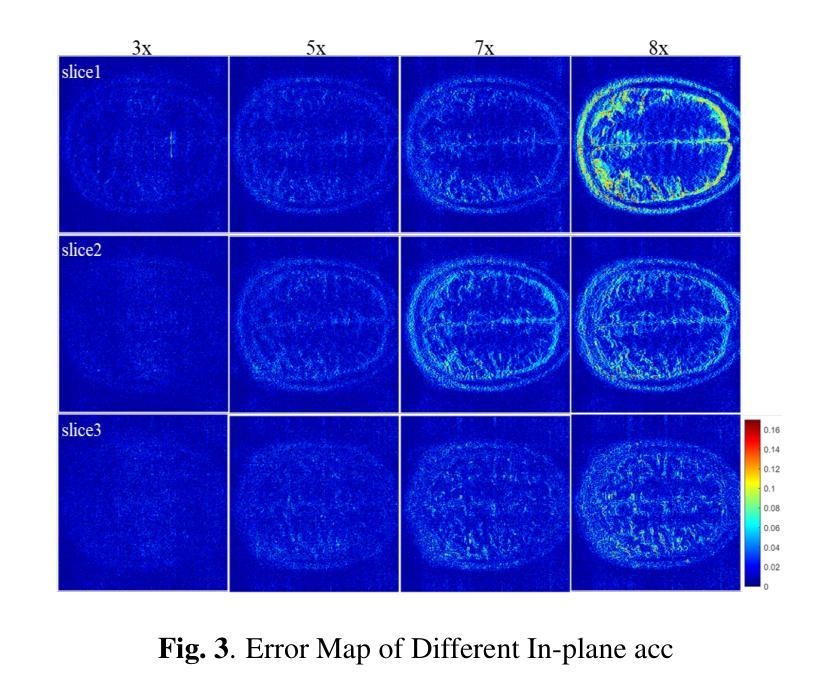
同步多层(Simultaneous Multi-Slice,简称SMS)是一种磁共振成像(MRI)技术。它通过多频带射频脉冲同时激发多个层面,从而减少扫描时间。然而,由于其数据结构多变且采集难度高,将SMS数据作为训练数据集成到深度学习框架中是一项挑战。本研究提出了一种新型的SMS重建k空间扩散模型,该模型不使用SMS数据进行训练。相反,它在采样过程中结合了Slice GRAPPA,从不同采集模式重建SMS数据。我们的结果表明,该方法优于传统SMS重建方法,且在不出现平面混叠的情况下,可实现更高的加速因子。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 2025 IEEE 22nd International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI)
Summary
该文本介绍了Simultaneous Multi-Slice(SMS)磁共振成像技术及其在深度学习框架中的集成挑战。研究提出了一种新型的k空间扩散模型用于SMS重建,该模型不利用SMS数据进行训练,而是在采样过程中融入Slice GRAPPA技术,从不同采集模式重建SMS数据。此方法优于传统SMS重建方法,可以实现更高的加速因子且没有平面混叠问题。
Key Takeaways
- SMS是一种磁共振成像技术,可并行激发多个切片以减少扫描时间。
- SMS数据由于其数据结构的变化和采集难度,难以作为训练数据集成到深度学习框架中。
- 研究提出了一种新型的k空间扩散模型用于SMS重建,该模型不需要使用SMS数据进行训练。
- 此模型通过融入Slice GRAPPA技术,能够在采样过程中重建不同采集模式的SMS数据。
- 研究结果表明,该方法优于传统SMS重建方法。
- 该方法可以实现更高的加速因子,提高成像效率。
点此查看论文截图

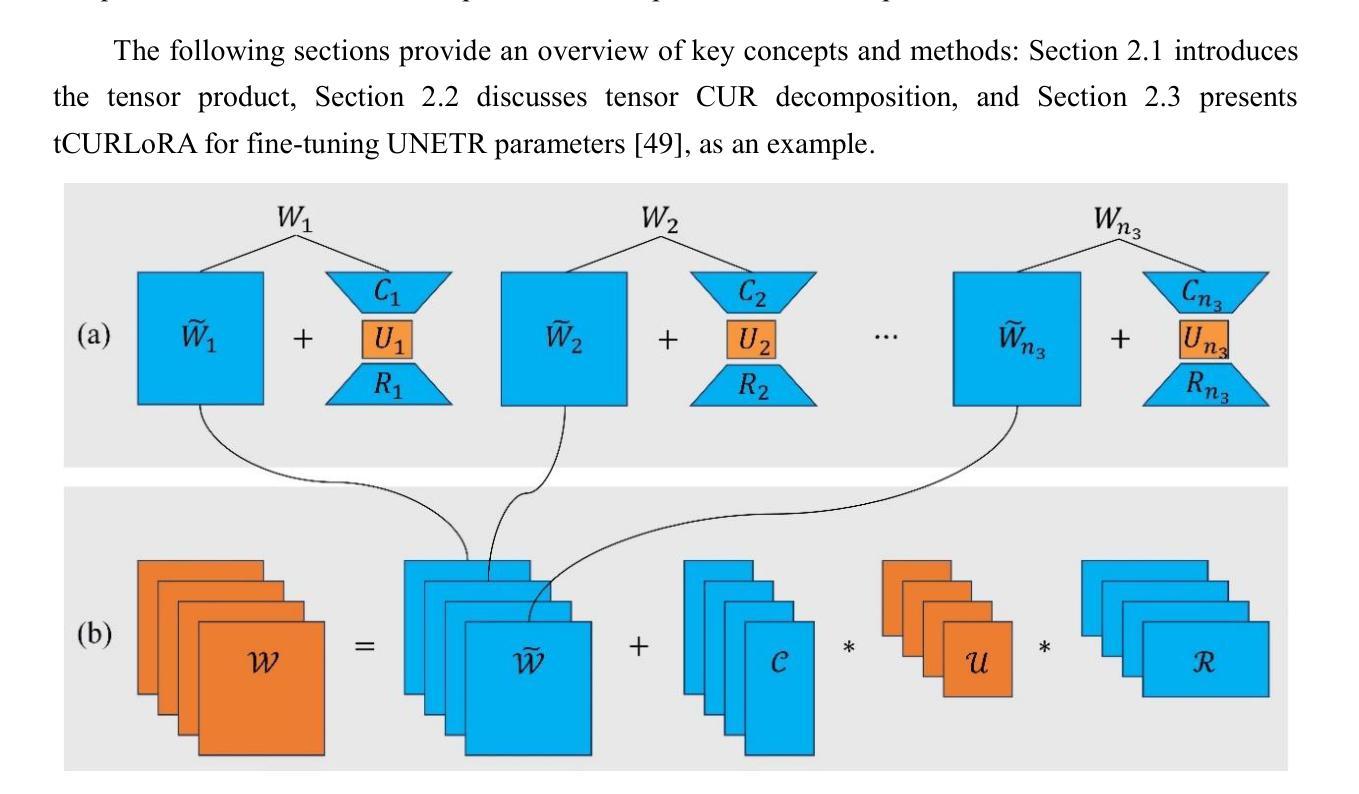
tCURLoRA: Tensor CUR Decomposition Based Low-Rank Parameter Adaptation and Its Application in Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Guanghua He, Wangang Cheng, Hancan Zhu, Xiaohao Cai, Gaohang Yu
Transfer learning, by leveraging knowledge from pre-trained models, has significantly enhanced the performance of target tasks. However, as deep neural networks scale up, full fine-tuning introduces substantial computational and storage challenges in resource-constrained environments, limiting its widespread adoption. To address this, parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods have been developed to reduce computational complexity and storage requirements by minimizing the number of updated parameters. While matrix decomposition-based PEFT methods, such as LoRA, show promise, they struggle to fully capture the high-dimensional structural characteristics of model weights. In contrast, high-dimensional tensors offer a more natural representation of neural network weights, allowing for a more comprehensive capture of higher-order features and multi-dimensional interactions. In this paper, we propose tCURLoRA, a novel fine-tuning method based on tensor CUR decomposition. By concatenating pre-trained weight matrices into a three-dimensional tensor and applying tensor CUR decomposition, we update only the lower-order tensor components during fine-tuning, effectively reducing computational and storage overhead. Experimental results demonstrate that tCURLoRA outperforms existing PEFT methods in medical image segmentation tasks.
利用预训练模型的知识进行迁移学习已显著提高目标任务的性能。然而,随着深度神经网络规模的扩大,完全微调在资源受限环境中带来了大量的计算和存储挑战,限制了其广泛采用。为解决这一问题,开发了参数高效的微调(PEFT)方法,通过最小化更新的参数数量来降低计算复杂性和存储要求。虽然基于矩阵分解的PEFT方法(如LoRA)显示出潜力,但它们难以完全捕获模型权重的高维结构特征。相比之下,高维张量提供了神经网络权重的更自然表示,能够更全面地捕获高阶特征和多维交互。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于张量CUR分解的新型微调方法tCURLoRA。我们将预训练的权重矩阵合并成一个三维张量,并应用张量CUR分解,在微调过程中只更新低阶张量组件,有效降低计算和存储开销。实验结果表明,在医学图像分割任务中,tCURLoRA优于现有的PEFT方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用预训练模型知识进行的迁移学习已显著提升目标任务性能。然而,随着深度神经网络规模的扩大,完全微调在资源受限环境中带来巨大计算和存储挑战,限制了其广泛应用。为解决这个问题,开发了参数高效微调(PEFT)方法,以减少计算和存储需求,最小化更新参数数量。虽然基于矩阵分解的PEFT方法(如LoRA)展现出潜力,但它们难以完全捕捉模型权重的高维结构特征。相反,高维张量提供更自然的神经网络权重表示,能更全面地捕获高阶特征和多维交互。本文提出基于张量CUR分解的新型微调方法tCURLoRA。通过将预训练权重矩阵拼接成三维张量并应用张量CUR分解,仅在微调时更新低阶张量组件,有效减少计算和存储开销。实验结果证明tCURLoRA在医学图像分割任务中表现优于现有PEFT方法。
Key Takeaways
- 迁移学习借助预训练模型知识提升了目标任务性能。
- 深度神经网络规模扩大导致完全微调面临计算和存储挑战。
- 参数高效微调(PEFT)方法旨在减少计算和存储需求。
- 现有矩阵分解方法如LoRA难以捕捉模型权重的高维结构特征。
- 高维张量为神经网络权重提供更自然的表示,有助于捕获高阶特征和多维交互。
- tCURLoRA方法基于张量CUR分解,仅在微调时更新低阶张量组件。
点此查看论文截图

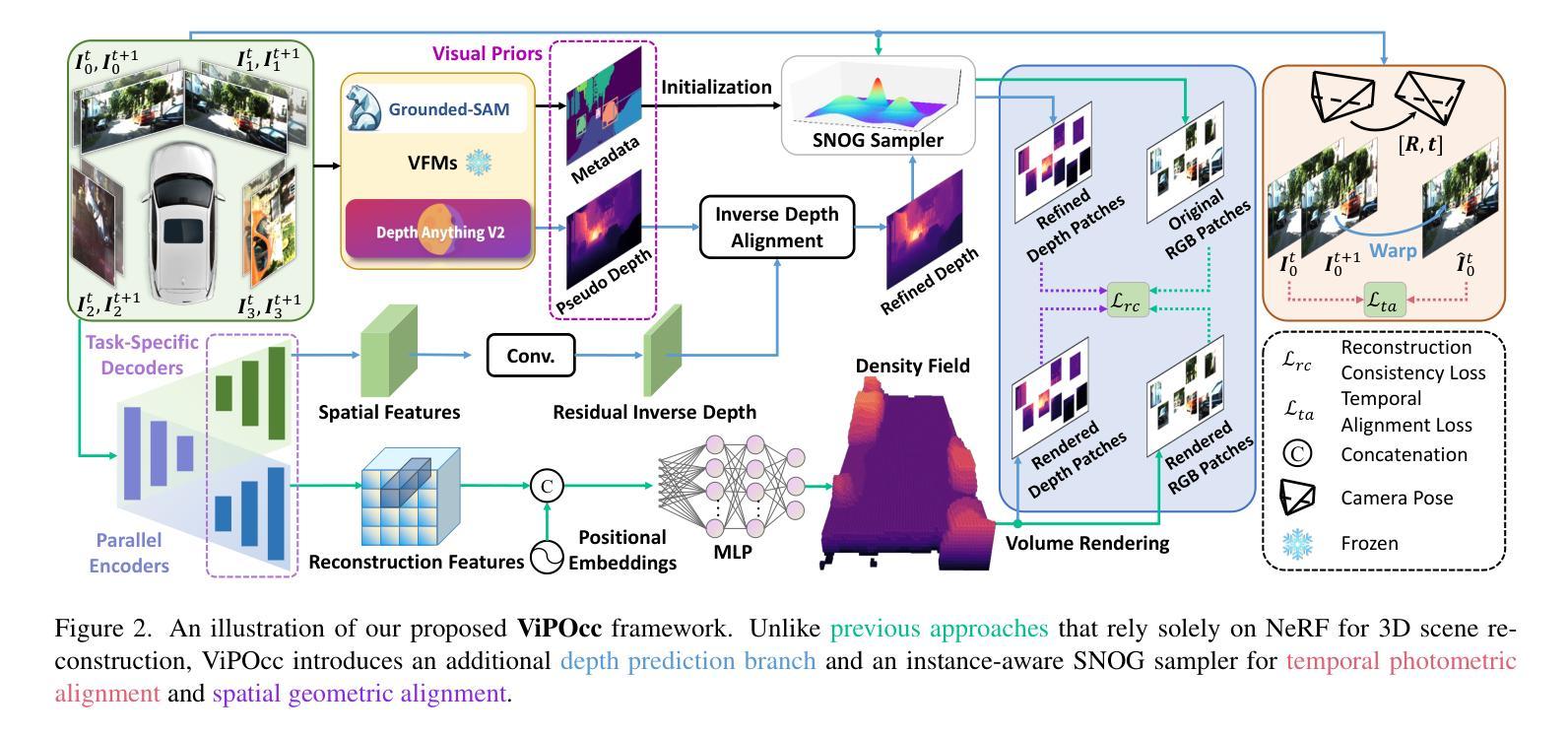
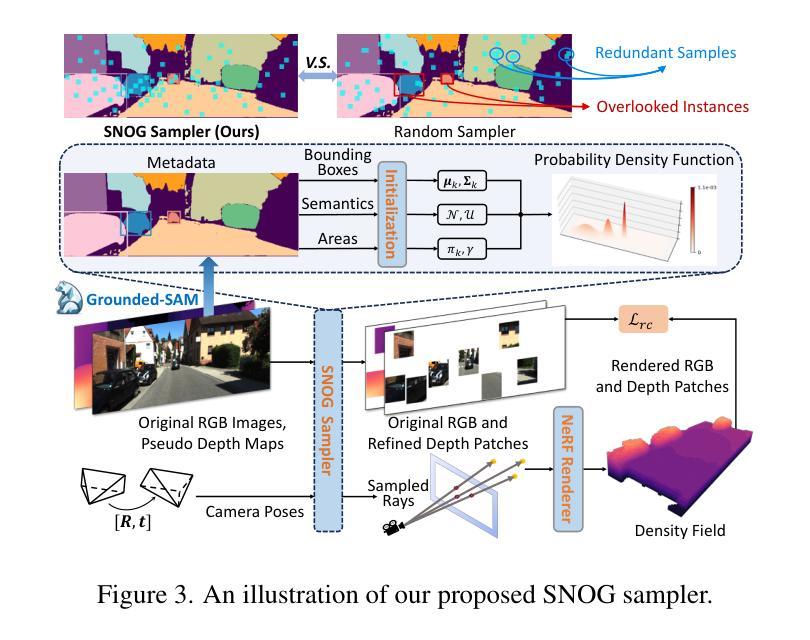
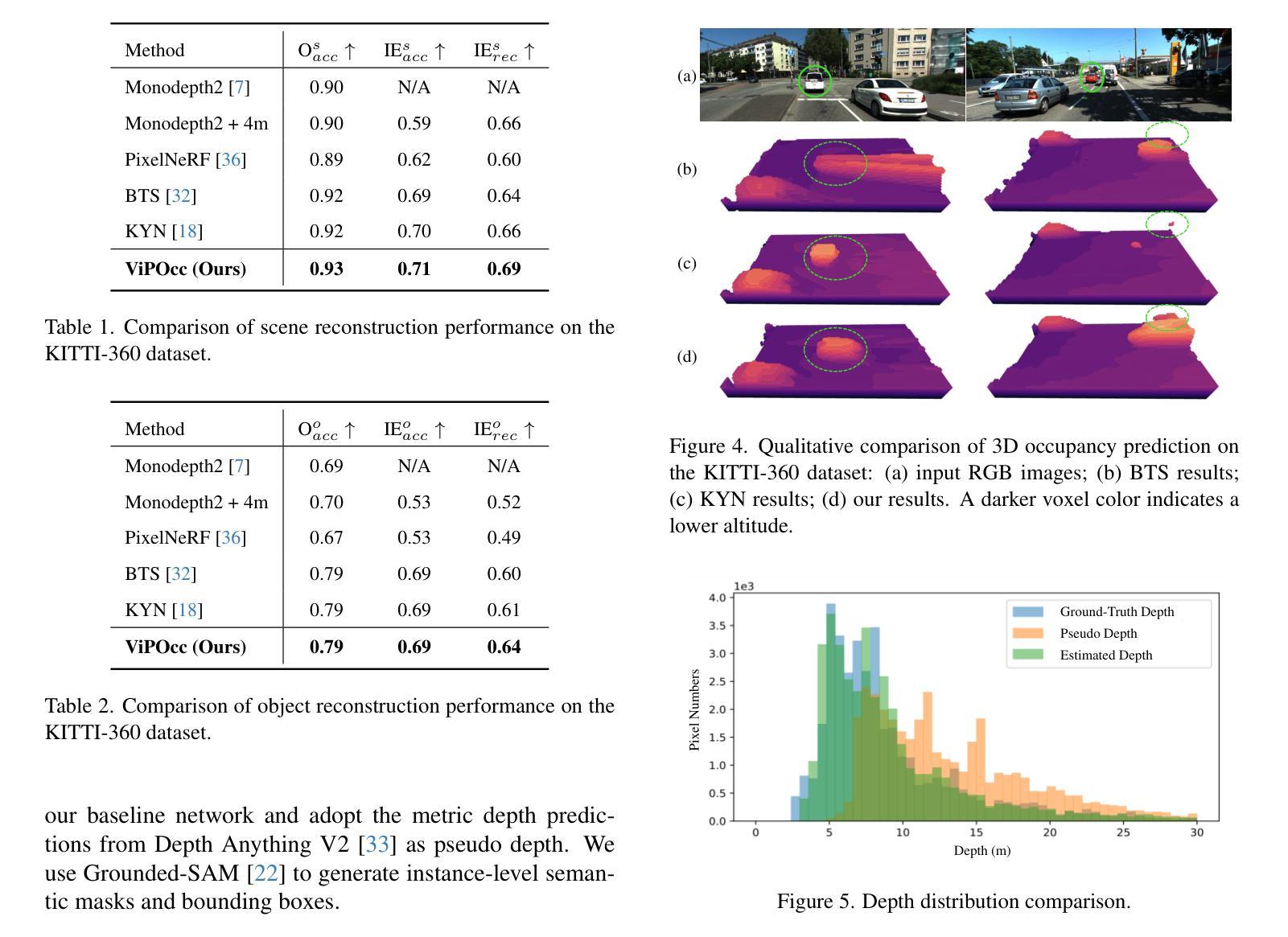
ViPOcc: Leveraging Visual Priors from Vision Foundation Models for Single-View 3D Occupancy Prediction
Authors:Yi Feng, Yu Han, Xijing Zhang, Tanghui Li, Yanting Zhang, Rui Fan
Inferring the 3D structure of a scene from a single image is an ill-posed and challenging problem in the field of vision-centric autonomous driving. Existing methods usually employ neural radiance fields to produce voxelized 3D occupancy, lacking instance-level semantic reasoning and temporal photometric consistency. In this paper, we propose ViPOcc, which leverages the visual priors from vision foundation models (VFMs) for fine-grained 3D occupancy prediction. Unlike previous works that solely employ volume rendering for RGB and depth image reconstruction, we introduce a metric depth estimation branch, in which an inverse depth alignment module is proposed to bridge the domain gap in depth distribution between VFM predictions and the ground truth. The recovered metric depth is then utilized in temporal photometric alignment and spatial geometric alignment to ensure accurate and consistent 3D occupancy prediction. Additionally, we also propose a semantic-guided non-overlapping Gaussian mixture sampler for efficient, instance-aware ray sampling, which addresses the redundant and imbalanced sampling issue that still exists in previous state-of-the-art methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of ViPOcc in both 3D occupancy prediction and depth estimation tasks on the KITTI-360 and KITTI Raw datasets. Our code is available at: \url{https://mias.group/ViPOcc}.
从单幅图像推断场景的三维结构是视觉自主驾驶领域中一个不适定且具有挑战性的问题。现有方法通常采用神经辐射场来生成体素化的三维占用信息,但缺乏实例级别的语义推理和暂时光度一致性。在本文中,我们提出了ViPOcc,它利用视觉先验知识,通过视觉基础模型(VFMs)进行精细的三维占用预测。不同于之前仅使用体积渲染进行RGB和深度图像重建的工作,我们引入了一个度量深度估计分支,并提出一个逆深度对齐模块,以缩小VFM预测和真实值之间深度分布的域差距。然后,恢复的度量深度被用于暂时光度对齐和空间几何对齐,以确保准确且一致的三维占用预测。此外,我们还提出了一种语义引导的非重叠高斯混合采样器,用于高效、实例感知的射线采样,解决了先前最先进方法中仍然存在的冗余和不平衡的采样问题。大量实验表明,ViPOcc在KITTI-360和KITTI Raw数据集上的三维占用预测和深度估计任务中都表现出卓越的性能。我们的代码可在:[https://mias.group/ViPOcc]获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted to AAAI25
Summary
本文提出一种基于视觉先验的精细粒度三维占用预测方法ViPOcc,解决了单一图像推断三维场景结构的问题。该方法引入视觉基础模型(VFMs)来提高深度估计的准确性,通过引入逆深度对齐模块来缩小VFM预测与真实深度之间的域差距。此外,还提出了语义引导的非重叠高斯混合采样器,解决了之前的冗余和不平衡采样问题。在KITTI-360和KITTI Raw数据集上的实验表明,ViPOcc在三维占用预测和深度估计任务上的性能优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- ViPOcc解决了从单一图像推断三维场景结构的挑战性问题。
- 方法利用视觉基础模型(VFMs)提高深度估计的准确性。
- 引入逆深度对齐模块来缩小VFM预测与真实深度之间的域差距。
- 提出了语义引导的非重叠高斯混合采样器,解决冗余和不平衡采样问题。
- ViPOcc在KITTI-360和KITTI Raw数据集上的实验表现出优异性能。
- 方法确保了准确且一致的三维占用预测。
点此查看论文截图

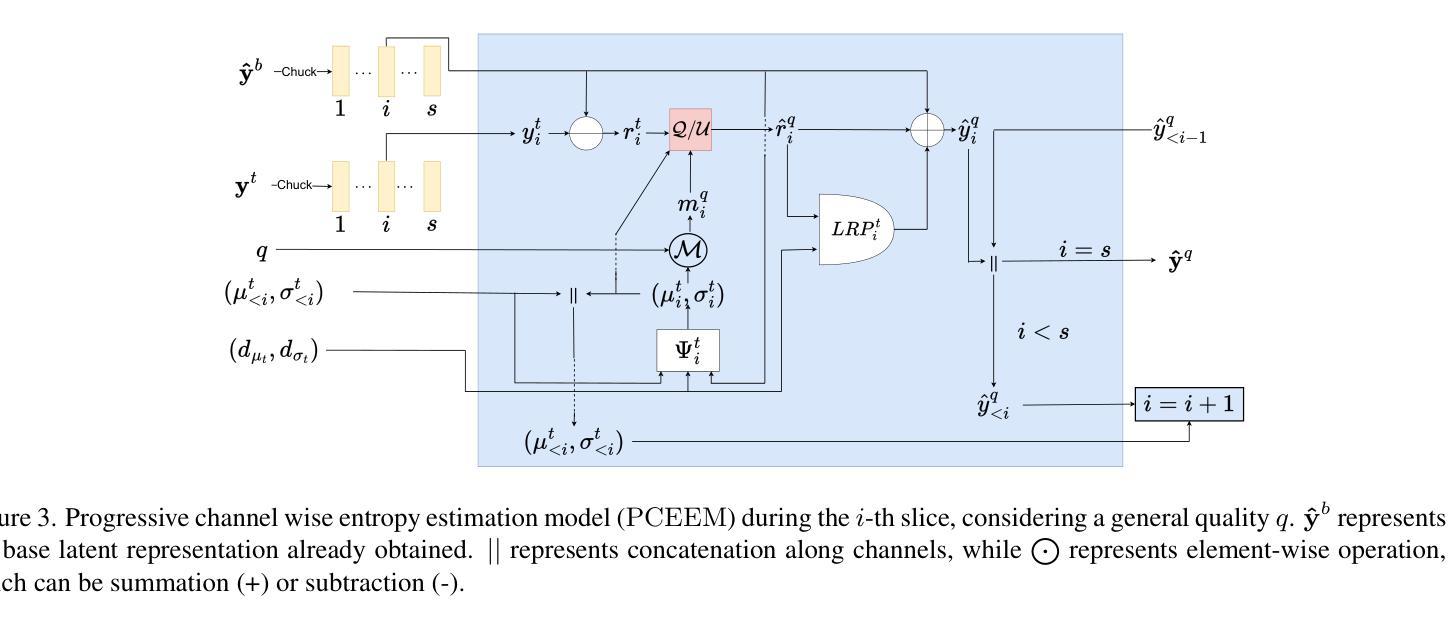
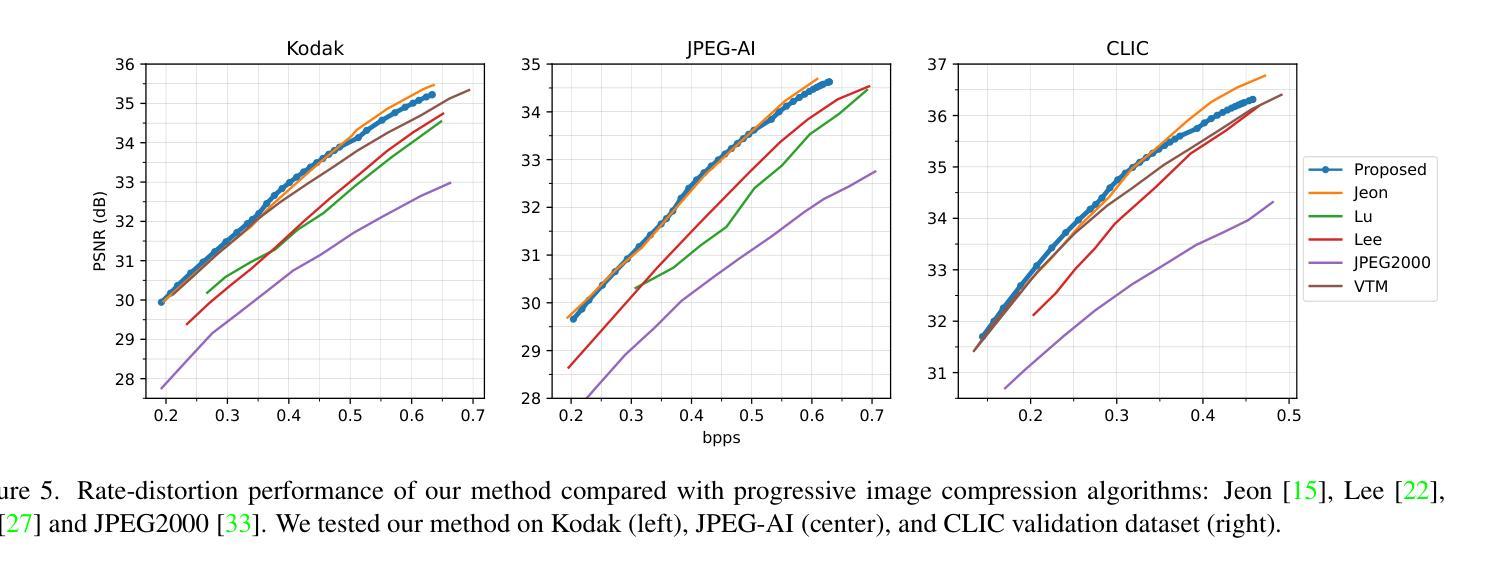
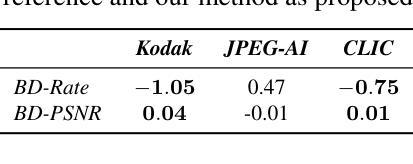
Efficient Progressive Image Compression with Variance-aware Masking
Authors:Alberto Presta, Enzo Tartaglione, Attilio Fiandrotti, Marco Grangetto, Pamela Cosman
Learned progressive image compression is gaining momentum as it allows improved image reconstruction as more bits are decoded at the receiver. We propose a progressive image compression method in which an image is first represented as a pair of base-quality and top-quality latent representations. Next, a residual latent representation is encoded as the element-wise difference between the top and base representations. Our scheme enables progressive image compression with element-wise granularity by introducing a masking system that ranks each element of the residual latent representation from most to least important, dividing it into complementary components, which can be transmitted separately to the decoder in order to obtain different reconstruction quality. The masking system does not add further parameters nor complexity. At the receiver, any elements of the top latent representation excluded from the transmitted components can be independently replaced with the mean predicted by the hyperprior architecture, ensuring reliable reconstructions at any intermediate quality level. We also introduced Rate Enhancement Modules (REMs), which refine the estimation of entropy parameters using already decoded components. We obtain results competitive with state-of-the-art competitors, while significantly reducing computational complexity, decoding time, and number of parameters.
渐进式医学图像压缩技术正逐渐受到关注,因为它在接收端解码更多位时,能够实现更好的图像重建。我们提出了一种渐进式图像压缩方法,首先,将图像表示为一对基础质量和顶级质量的潜在表示。然后,将残差潜在表示编码为顶级和基础表示之间的元素差异。通过引入一个对残差潜在表示中的每个元素进行重要性排序的掩码系统,我们的方案实现了具有元素级粒度的渐进式图像压缩。掩码系统分为不同的补充组件进行传输,这些组件可以单独传输到解码器以获得不同的重建质量。掩码系统不会增加额外的参数或复杂性。在接收端,顶级潜在表示中被排除的任何元素都可以独立替换为超先验架构预测的均值,确保在任何中间质量水平下都能实现可靠的重建。我们还引入了速率增强模块(REM),它使用已解码的组件来改进熵参数的估计。我们的结果与现代竞争对手相当,同时显著降低了计算复杂度、解码时间和参数数量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages. Accepted at WACV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种渐进式图像压缩方法,该方法将图像表示为基础质量层和顶级质量层的潜在表示,并编码剩余潜在表示为两者之间的差异。引入了一个掩码系统,按重要性对剩余潜在表示中的每个元素进行排名,将其分解为可单独传输的互补组件,以获得不同的重建质量。该方法通过引入率增强模块(REMs)改进了熵参数的估计,获得了与最新竞争对手相当的结果,同时显著降低了计算复杂度、解码时间和参数数量。
Key Takeaways
- 渐进式图像压缩方法允许在接收端解码更多位时改进图像重建。
- 图像被表示为基础质量层和顶级质量层的潜在表示,剩余潜在表示被编码为两者之间的差异。
- 引入掩码系统,按重要性对剩余潜在表示中的元素进行排名,并分解为可单独传输的互补组件。
- 掩码系统不会增加额外的参数或复杂性。
- 使用超先验架构预测的均值独立替换顶级潜在表示中未传输的组件元素,确保任何中间质量水平的可靠重建。
- 引入率增强模块(REMs)改进了熵参数的估计。
点此查看论文截图


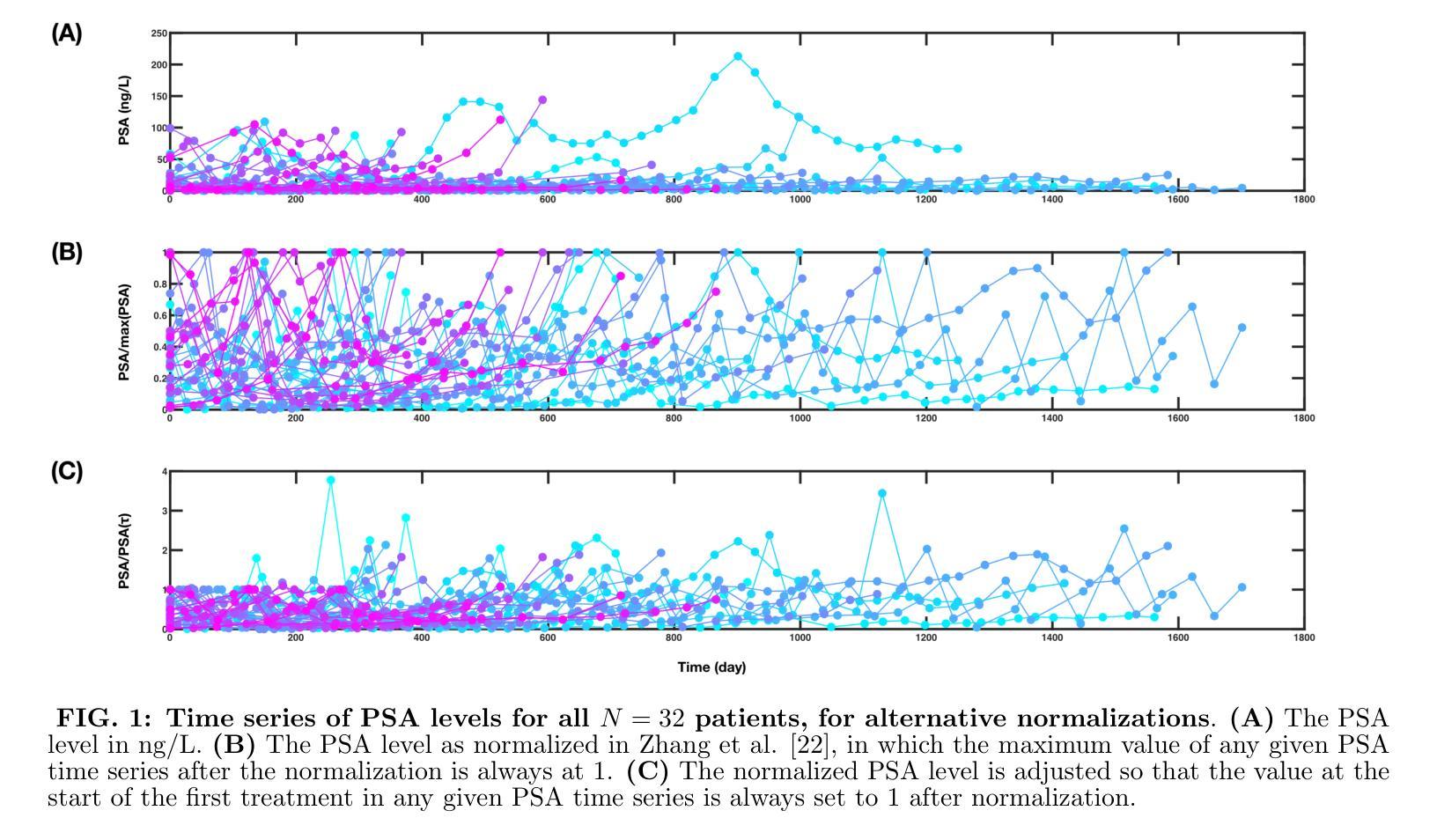
Foundations of Adaptive High-Level Tight Control of Prostate Cancer: A Path from From Terminal Disease to Chronic Condition
Authors:Trung V. Phan, Shengkai Li, Benjamin Howe, Sarah R. Amend, Kenneth J. Pienta, Joel S. Brown, Robert A. Gatenby, Constantine Frangakis, Robert H. Austin, Ioannis G. Keverkidis
Metastatic prostate cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related morbidity and mortality worldwide. It is characterized by a high mortality rate and a poor prognosis. In this work, we explore how a clinical oncologist can apply a Stackelberg game-theoretic framework to prolong metastatic prostate cancer survival, or even make it chronic in duration. We utilize a Bayesian optimization approach to identify the optimal adaptive chemotherapeutic treatment policy for a single drug (Abiraterone) to maximize the time before the patient begins to show symptoms. We show that, with precise adaptive optimization of drug delivery, it is possible to significantly prolong the cancer suppression period, potentially converting metastatic prostate cancer from a terminal disease to a chronic disease for most patients, as supported by clinical and analytical evidence. We suggest that clinicians might explore the possibility of implementing a high-level tight control (HLTC) treatment, in which the trigger signals (i.e. biomarker levels) for drug administration and cessation are both high and close together, typically yield the best outcomes, as demonstrated through both computation and theoretical analysis. This simple insight could serve as a valuable guide for improving current adaptive chemotherapy treatments in other hormone-sensitive cancers.
转移性前列腺癌是全球范围内导致癌症相关发病率和死亡率的主要原因之一。其特点是死亡率高,预后不良。在这项工作中,我们探讨了临床肿瘤科医生如何运用斯塔克尔伯格博弈理论框架来延长转移性前列腺癌患者的生存期,甚至使其转变为慢性病。我们采用贝叶斯优化方法来确定针对单一药物(阿比特龙)的最佳自适应化疗治疗方案,以最大程度地延长患者开始表现出症状之前的时间。我们表明,通过精确的自适应药物优化,可以显著延长癌症抑制期,从而将大多数患者的转移性前列腺癌从一种致命疾病转变为一种慢性疾病,这得到了临床和分析证据的支持。我们建议临床医生可能探索实施高级紧密控制(HLTC)治疗的可能性,其中药物治疗和停药的触发信号(即生物标志物水平)既高又紧密相关,通常会产生最佳效果,这已通过计算和理论分析得到证明。这一简单见解可以为改进其他激素敏感癌症的当前自适应化疗治疗提供有价值的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了临床肿瘤学家如何运用斯塔克尔伯格博弈理论框架来延长转移性前列腺癌患者的生存期,甚至使其成为一种慢性病。研究采用贝叶斯优化方法,针对单一药物阿比特龙(Abiraterone)制定最佳适应性化疗方案,以延长患者无症状期时间。研究表明,通过精确的药物输送适应性优化,可以显著延长癌症抑制期,将转移性前列腺癌从致命疾病转变为大多数患者的慢性疾病。建议临床医师考虑实施高级紧密控制(HLTC)治疗,其中药物给药和停药的触发信号接近,通常能取得最佳效果。
Key Takeaways
- 转移性前列腺癌是全球癌症发病率和死亡率的主要原因之一,具有高度的致死率和不良的预后。
- 研究采用斯塔克尔伯格博弈理论框架和贝叶斯优化方法,探索如何延长转移性前列腺癌患者的生存期。
- 通过精确的药物输送适应性优化,使用单一药物阿比特龙(Abiraterone)可以显著延长癌症抑制期。
- 将转移性前列腺癌从致命疾病转变为慢性疾病是可能的。
- 实施高级紧密控制(HLTC)治疗可能取得最佳治疗效果,其中药物给药和停药的触发信号接近。
- 这种治疗方法可能对其他激素敏感的癌症的适应性化疗治疗有改进价值。
点此查看论文截图

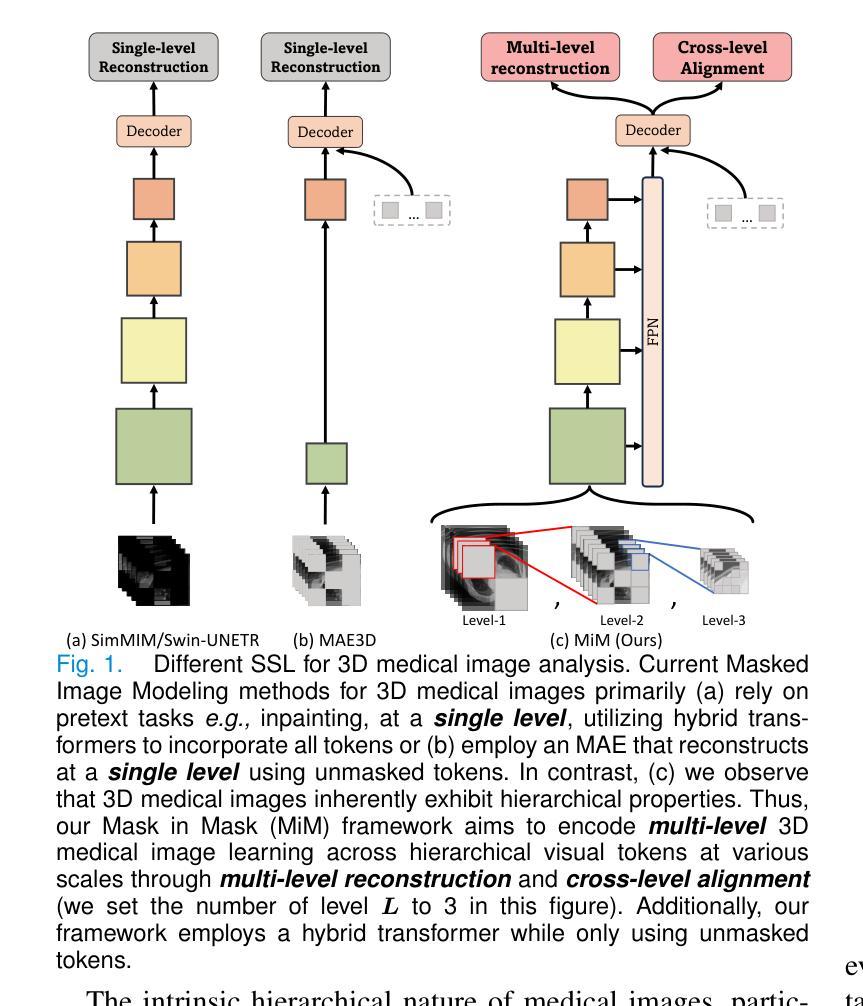
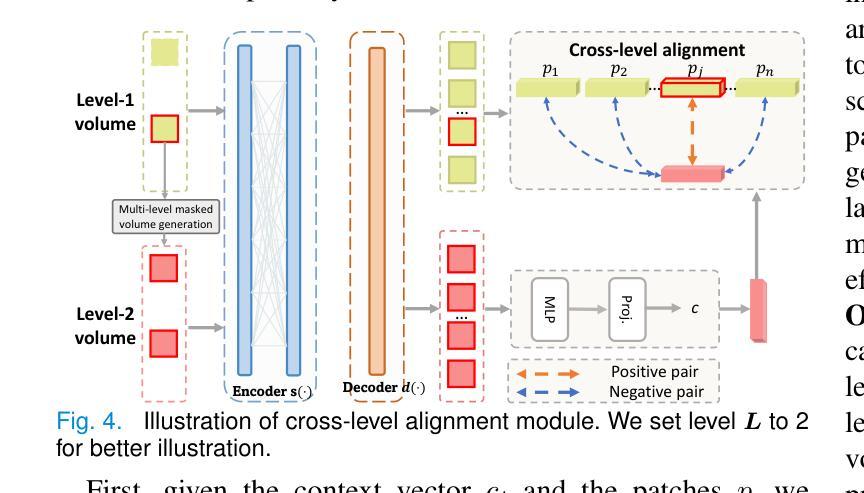
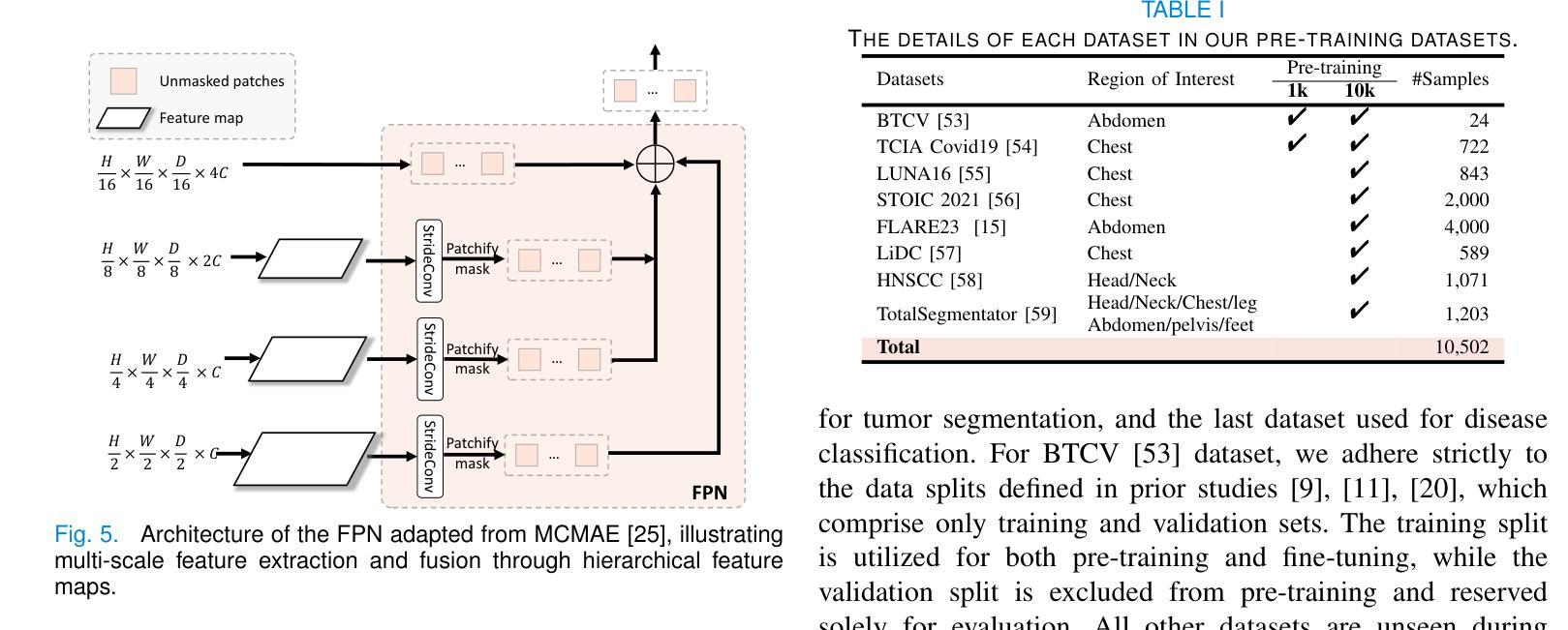
MiM: Mask in Mask Self-Supervised Pre-Training for 3D Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Jiaxin Zhuang, Linshan Wu, Qiong Wang, Peng Fei, Varut Vardhanabhuti, Lin Luo, Hao Chen
The Vision Transformer (ViT) has demonstrated remarkable performance in Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) for 3D medical image analysis. Masked AutoEncoder (MAE) for feature pre-training can further unleash the potential of ViT on various medical vision tasks. However, due to large spatial sizes with much higher dimensions of 3D medical images, the lack of hierarchical design for MAE may hinder the performance of downstream tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel \textit{Mask in Mask (MiM)} pre-training framework for 3D medical images, which aims to advance MAE by learning discriminative representation from hierarchical visual tokens across varying scales. We introduce multiple levels of granularity for masked inputs from the volume, which are then reconstructed simultaneously ranging at both fine and coarse levels. Additionally, a cross-level alignment mechanism is applied to adjacent level volumes to enforce anatomical similarity hierarchically. Furthermore, we adopt a hybrid backbone to enhance the hierarchical representation learning efficiently during the pre-training. MiM was pre-trained on a large scale of available 3D volumetric images, \textit{i.e.,} Computed Tomography (CT) images containing various body parts. Extensive experiments on thirteen public datasets demonstrate the superiority of MiM over other SSL methods in organ/lesion/tumor segmentation and disease classification. We further scale up the MiM to large pre-training datasets with more than 10k volumes, showing that large-scale pre-training can further enhance the performance of downstream tasks. The improvement also concluded that the research community should pay more attention to the scale of the pre-training dataset towards the healthcare foundation model for 3D medical images.
Vision Transformer(ViT)在用于3D医学图像分析的Self-Supervised Learning(SSL)中表现出了卓越的性能。使用Masked AutoEncoder(MAE)进行特征预训练可以进一步释放ViT在各种医学视觉任务上的潜力。然而,由于3D医学图像具有较大的空间尺寸和更高的维度,MAE缺乏层次设计可能会阻碍下游任务的性能。在本文中,我们针对3D医学图像提出了一种新型的\textit{Mask in Mask(MiM)预训练框架},旨在通过从各种尺度的分层视觉标记中学习判别表示来改进MAE。我们从体积中引入了多个粒度的遮挡输入,然后在精细和粗略级别上同时进行重建。此外,还应用了跨级对齐机制来对相邻级别体积进行分层解剖相似性强制。此外,我们采用混合骨干网在预训练期间有效地增强分层表示学习。MiM在大量可用的3D体积图像上进行了预训练,即包含各种身体部位的计算机断层扫描(CT)图像。在十三个公共数据集上的大量实验表明,MiM在器官/病灶/肿瘤分割和疾病分类方面优于其他SSL方法。我们进一步将MiM扩展到具有超过10k体积的大规模预训练数据集,结果表明大规模预训练可以进一步提高下游任务的性能。改进结果也表明,研究界应更加关注预训练数据集规模对于构建面向3D医学图像的卫生健康基础模型的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to a journal, updated v2
Summary
本文介绍了针对3D医学图像自监督学习(SSL)的Mask in Mask(MiM)预训练框架。该框架旨在通过从多层次视觉标记中学习判别表示来改进Mask AutoEncoder(MAE)在多种医学视觉任务上的性能。MiM引入多个级别的粒度对体积进行掩码输入,并在精细和粗略级别上进行同时重建。此外,还应用了跨级别对齐机制来增强相邻级别体积的解剖相似性。MiM在大量可用的3D体积图像上进行预训练,并在器官/病变/肿瘤分割和疾病分类等十三个公共数据集上表现出优于其他SSL方法的性能。大规模预训练可进一步提高下游任务的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer (ViT)在自监督学习(SSL)中展现出对3D医学图像分析的出色性能。
- Masked AutoEncoder (MAE)能够进一步释放ViT在各种医学视觉任务上的潜力。
- 由于3D医学图像的空间尺寸大且维度高,MAE缺乏层次设计可能阻碍下游任务的性能。
- 提出了Mask in Mask (MiM)预训练框架,旨在通过从多层次视觉标记中学习来提高MAE的性能。
- MiM引入多个级别的粒度对体积进行掩码输入,并在精细和粗略级别上进行重建。
- MiM采用跨级别对齐机制来增强相邻级别体积的解剖相似性。
点此查看论文截图