⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-14 更新
AgroGPT: Efficient Agricultural Vision-Language Model with Expert Tuning
Authors:Muhammad Awais, Ali Husain Salem Abdulla Alharthi, Amandeep Kumar, Hisham Cholakkal, Rao Muhammad Anwer
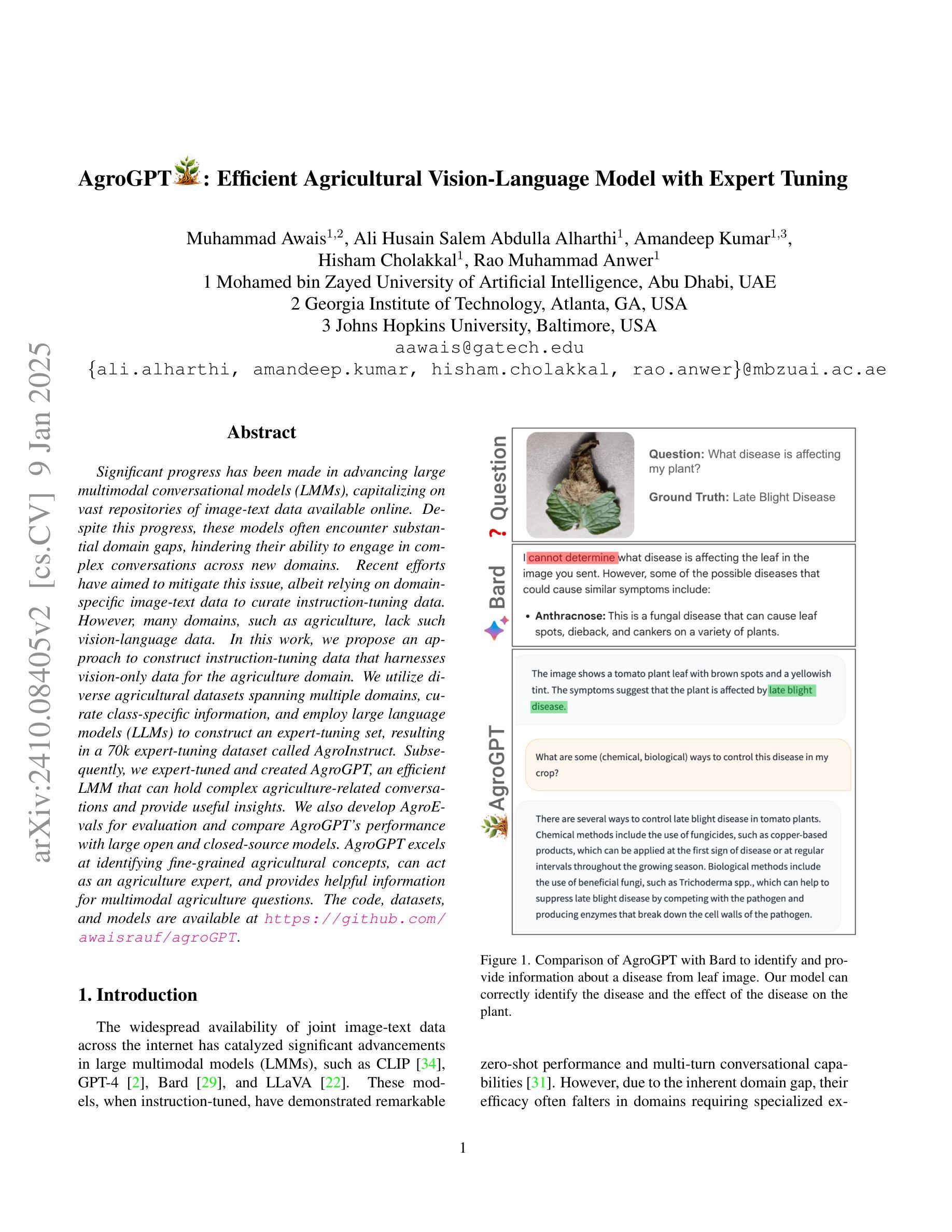
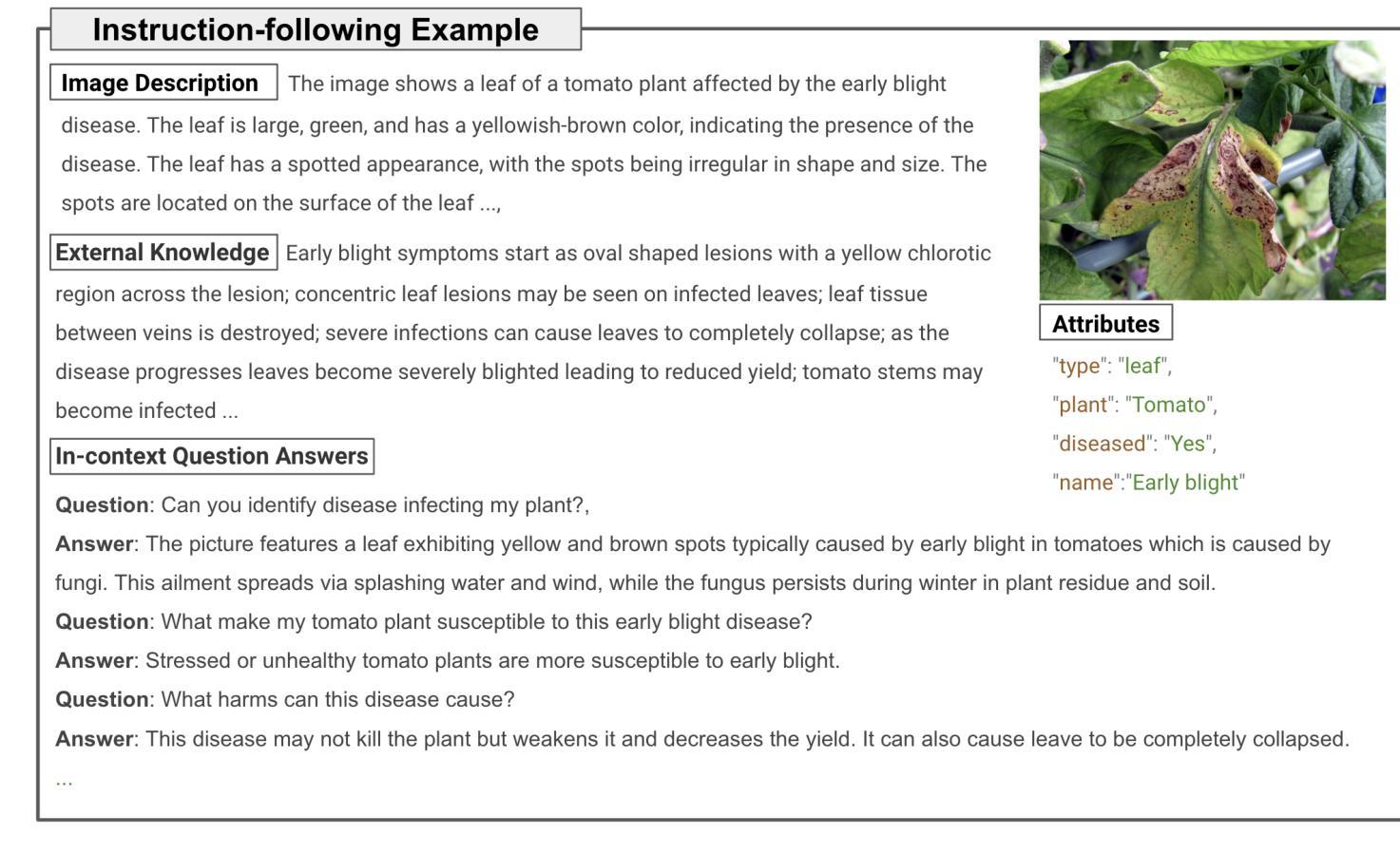
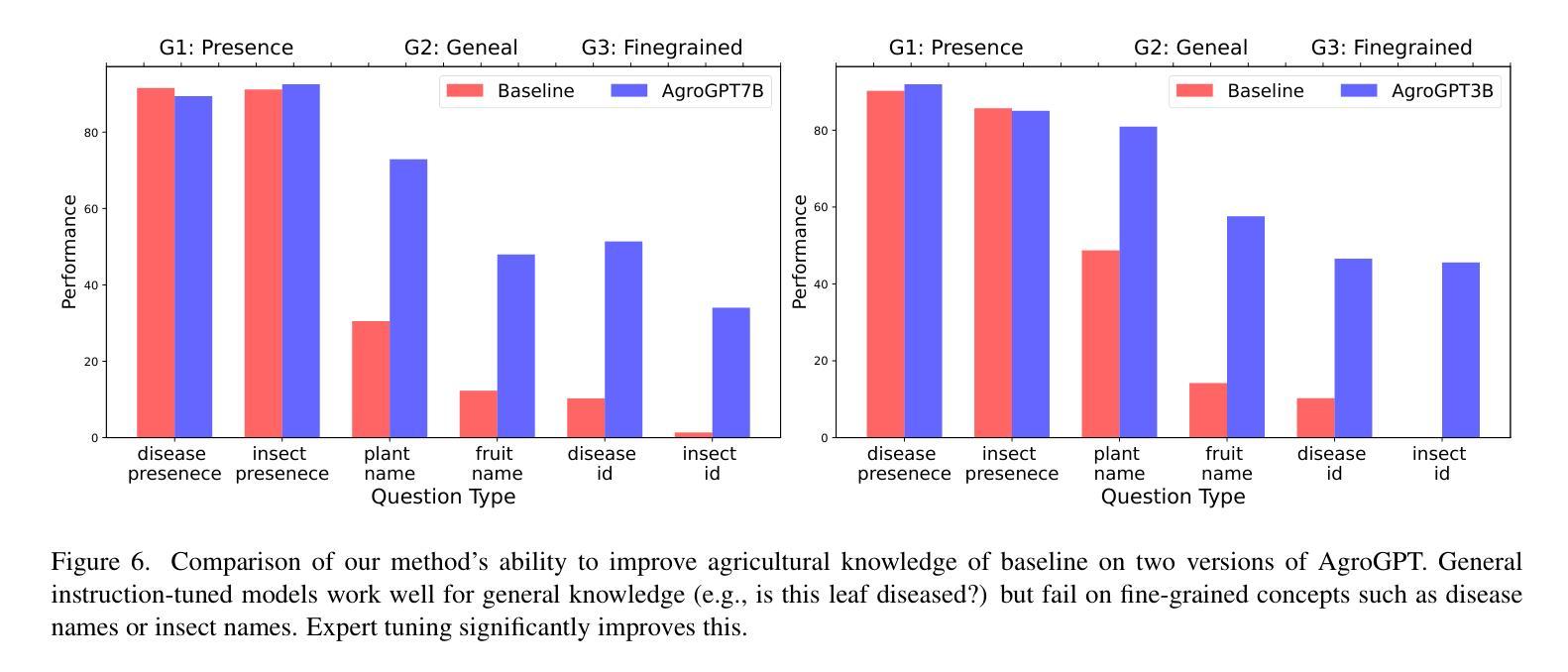
Significant progress has been made in advancing large multimodal conversational models (LMMs), capitalizing on vast repositories of image-text data available online. Despite this progress, these models often encounter substantial domain gaps, hindering their ability to engage in complex conversations across new domains. Recent efforts have aimed to mitigate this issue, albeit relying on domain-specific image-text data to curate instruction-tuning data. However, many domains, such as agriculture, lack such vision-language data. In this work, we propose an approach to construct instruction-tuning data that harnesses vision-only data for the agriculture domain. We utilize diverse agricultural datasets spanning multiple domains, curate class-specific information, and employ large language models (LLMs) to construct an expert-tuning set, resulting in a 70k expert-tuning dataset called AgroInstruct. Subsequently, we expert-tuned and created AgroGPT, an efficient LMM that can hold complex agriculture-related conversations and provide useful insights. We also develop AgroEvals for evaluation and compare {AgroGPT’s} performance with large open and closed-source models. {AgroGPT} excels at identifying fine-grained agricultural concepts, can act as an agriculture expert, and provides helpful information for multimodal agriculture questions. The code, datasets, and models are available at https://github.com/awaisrauf/agroGPT.
在推进大型多模态对话模型(LMMs)方面取得了重大进展,这得益于网络上可用的海量图像文本数据仓库。尽管取得了这些进展,但这些模型仍然经常遇到巨大的领域差距,阻碍了它们在新领域进行复杂对话的能力。最近的努力旨在缓解这个问题,尽管这依赖于特定领域的图像文本数据来策划指令微调数据。然而,许多领域,如农业,缺乏这样的视觉语言数据。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种构建指令微调数据的方法,该方法利用仅视觉数据针对农业领域。我们利用跨越多个领域的各种农业数据集,整理特定类别的信息,并采用大型语言模型(LLMs)来构建专家调整集,从而形成了名为AgroInstruct的70k专家调整数据集。随后,我们进行了专家调整并创建了AgrGPT,这是一个有效的LMM,可以进行复杂的农业相关对话并提供有用的见解。我们还开发了AgroEvals进行评估,并将AgrGPT的性能与大型开源和闭源模型进行比较。AgrGPT擅长识别农业中的细微概念,可以作为农业专家发挥作用,并为多模态农业问题提供有用的信息。代码、数据集和模型可在https://github.com/awaisrauf/agroGPT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at WACV, 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对农业领域的大型多模态对话模型(LMMs)的研究。研究团队利用仅有视觉数据构建了农业领域的指令调优数据集AgroInstruct,并以此为基础训练出能进行复杂农业相关对话并提供有用见解的专家级模型AgroGPT。该模型在农业领域的精细概念识别方面表现出色,可作为农业专家提供信息。
Key Takeaways
- 研究进展:大型多模态对话模型(LMMs)在利用丰富的在线图像文本数据方面取得了显著进展。
- 领域差距问题:尽管有这些进展,但模型在新领域进行复杂对话时仍会遇到显著的领域差距问题。
- 现有解决方案的不足:尽管有努力通过域特定的图像文本数据来减轻这个问题,但在诸如农业等领域,由于缺乏此类视觉语言数据,这一方法并不适用。
- 新方法介绍:提出了一种利用仅有视觉数据构建农业领域的指令调优数据集的方法,并命名为AgroInstruct。
- 专家级模型的训练:基于AgroInstruct数据集训练出了名为AgroGPT的专家级模型,能够进行复杂的农业相关对话并提供有用信息。
- 模型性能评估:开发了AgroEvals用于评估AgroGPT的性能,并与大型开源和闭源模型进行了比较。
点此查看论文截图




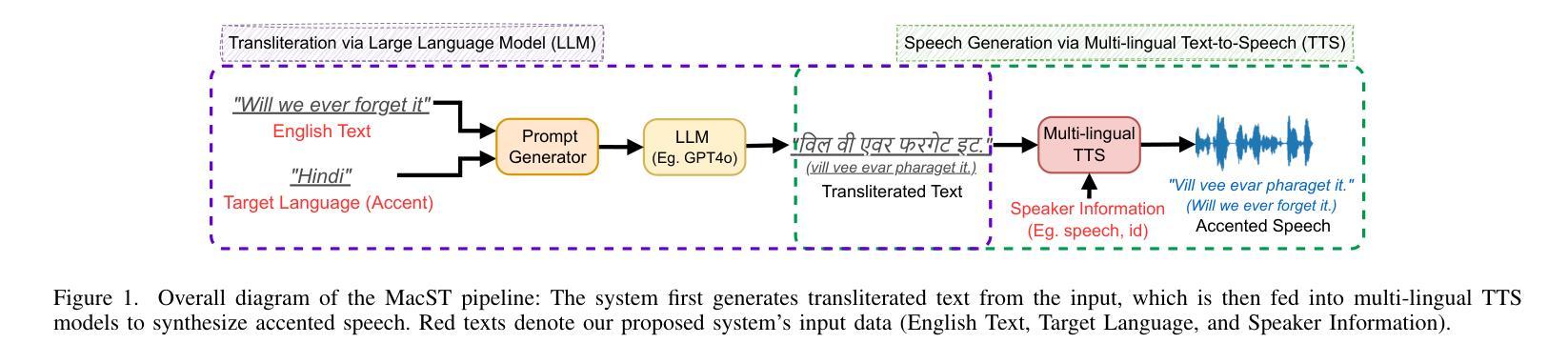
MacST: Multi-Accent Speech Synthesis via Text Transliteration for Accent Conversion
Authors:Sho Inoue, Shuai Wang, Wanxing Wang, Pengcheng Zhu, Mengxiao Bi, Haizhou Li
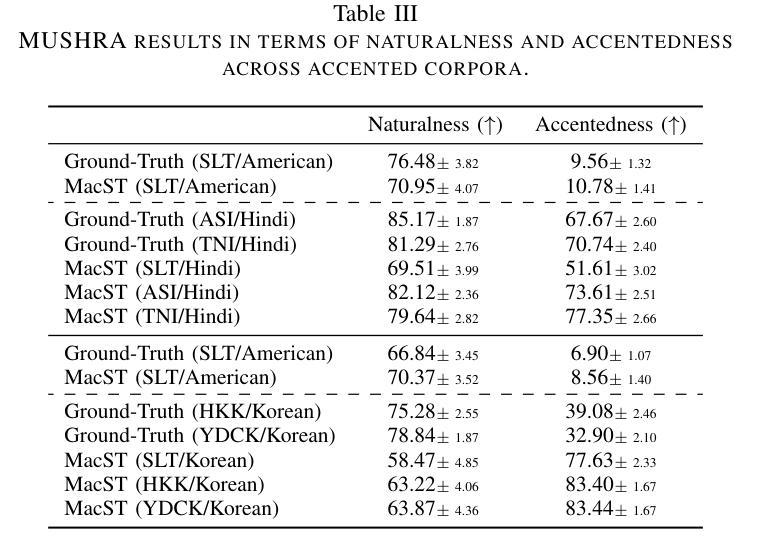
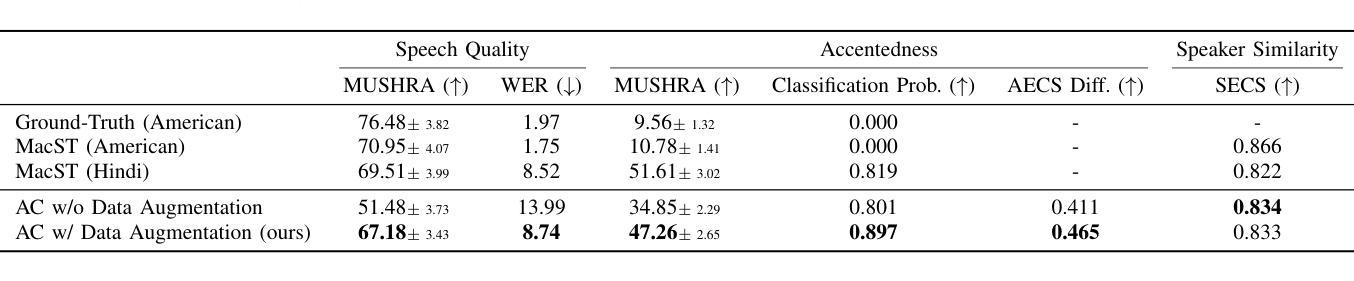
In accented voice conversion or accent conversion, we seek to convert the accent in speech from one another while preserving speaker identity and semantic content. In this study, we formulate a novel method for creating multi-accented speech samples, thus pairs of accented speech samples by the same speaker, through text transliteration for training accent conversion systems. We begin by generating transliterated text with Large Language Models (LLMs), which is then fed into multilingual TTS models to synthesize accented English speech. As a reference system, we built a sequence-to-sequence model on the synthetic parallel corpus for accent conversion. We validated the proposed method for both native and non-native English speakers. Subjective and objective evaluations further validate our dataset’s effectiveness in accent conversion studies.
在口音转换或语音转换中,我们旨在将语音中的口音进行转换,同时保留说话者的身份和语义内容。本研究中,我们提出了一种新的方法,通过文本转译来创建多口音语音样本,从而为口音转换系统训练提供同一说话人的带口音语音样本对。我们首先使用大型语言模型(LLM)生成转译文本,然后将其输入多语言TTS模型,合成带有口音的英语语音。作为参考系统,我们在合成平行语料库上建立了序列到序列的模型进行口音转换。我们验证了所提出的方法对于英语母语者和非母语者都有效。主观和客观评估进一步验证了我们的数据集在口音转换研究中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is accepted to IEEE ICASSP 2025; Project page with Speech Demo: https://github.com/shinshoji01/MacST-project-page
Summary
在口音转换研究中,本文提出了一种新型的多口音语音样本创建方法。通过大型语言模型(LLM)进行文本转译,生成口音样本对,用于训练口音转换系统。实验结果显示,该方法能有效实现口音转换,同时保留说话人身份和语义内容。对本地和非本地英语说话者均进行了验证。主观和客观评估进一步验证了数据集在口音转换研究中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了使用大型语言模型(LLM)生成文本转译来创建多口音语音样本的方法。
- 创建的口音样本对用于训练口音转换系统。
- 说话人的身份和语义内容在口音转换过程中得以保留。
- 该方法既适用于本地英语说话者也适用于非本地英语说话者。
- 主观和客观评估验证了数据集的有效性。
- 本文采用了一种序列到序列模型进行口音转换。
点此查看论文截图


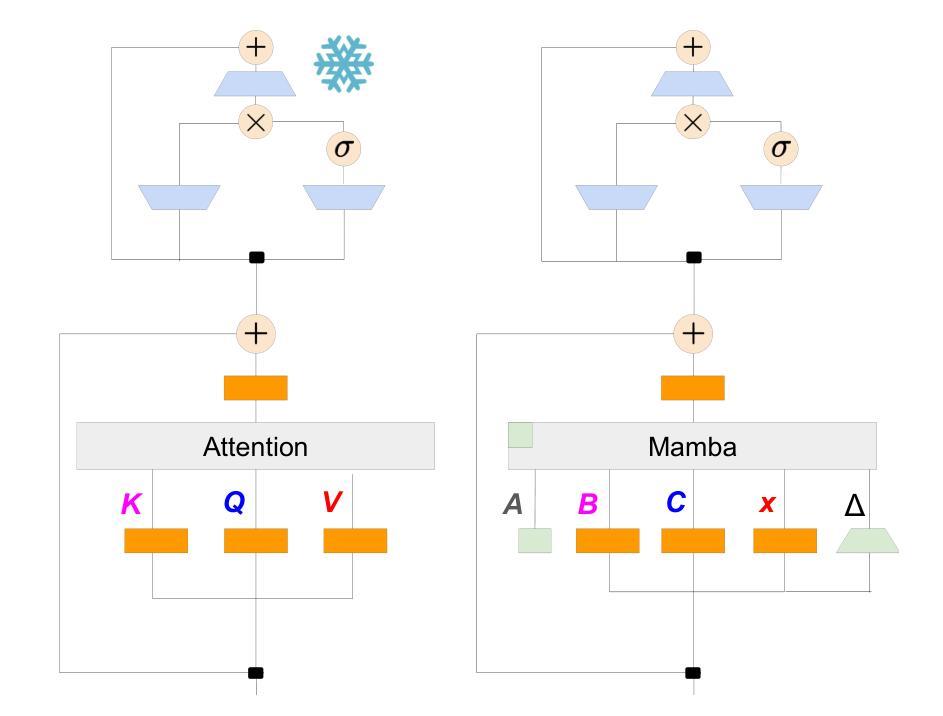
The Mamba in the Llama: Distilling and Accelerating Hybrid Models
Authors:Junxiong Wang, Daniele Paliotta, Avner May, Alexander M. Rush, Tri Dao
Linear RNN architectures, like Mamba, can be competitive with Transformer models in language modeling while having advantageous deployment characteristics. Given the focus on training large-scale Transformer models, we consider the challenge of converting these pretrained models for deployment. We demonstrate that it is feasible to distill large Transformers into linear RNNs by reusing the linear projection weights from attention layers with academic GPU resources. The resulting hybrid model, which incorporates a quarter of the attention layers, achieves performance comparable to the original Transformer in chat benchmarks and outperforms open-source hybrid Mamba models trained from scratch with trillions of tokens in both chat benchmarks and general benchmarks. Moreover, we introduce a hardware-aware speculative decoding algorithm that accelerates the inference speed of Mamba and hybrid models. Overall we show how, with limited computation resources, we can remove many of the original attention layers and generate from the resulting model more efficiently. Our top-performing model, distilled from Llama3-8B-Instruct, achieves a 29.61 length-controlled win rate on AlpacaEval 2 against GPT-4 and 7.35 on MT-Bench, surpassing the best 8B scale instruction-tuned linear RNN model. We also find that the distilled model has natural length extrapolation, showing almost perfect accuracy in the needle-in-a-haystack test at 20x the distillation length. Code and pre-trained checkpoints are open-sourced at https://github.com/jxiw/MambaInLlama and https://github.com/itsdaniele/speculative_mamba.
线性RNN架构(如Mamba)在语言建模方面可以与Transformer模型竞争,同时拥有优势部署特性。鉴于目前主要关注训练大规模Transformer模型,我们面临将这些预训练模型进行部署的挑战。我们证明了通过利用GPU资源重复使用注意力层的线性投影权重,将大型Transformer蒸馏成线性RNN是可行的。所得混合模型结合了四分之一的注意力层,在聊天基准测试中实现了与原始Transformer相当的性能,并且在聊天基准测试和一般基准测试中表现优于从头开始训练的开源混合Mamba模型(这些模型训练时使用了万亿个令牌)。此外,我们引入了一种硬件感知的投机解码算法,该算法加速了Mamba和混合模型的推理速度。总体而言,我们展示了如何在有限的计算资源下删除许多原始注意力层并更高效地生成结果模型。我们的高性能模型从Llama3-8B-Instruct中提炼出来,在AlpacaEval 2上相对于GPT-4达到了29.61的长度控制胜率,并在MT-Bench上达到了7.35,超过了最佳8B规模指令调整线性RNN模型。我们还发现,提炼后的模型具有自然的长度扩展能力,在蒸馏长度提高20倍的情况下,几乎达到了完美的准确率在“海底捞针”测试中。代码和预先训练的模型检查点已开源分享至:https://github.com/jxiw/MambaInLlama和https://github.com/itsdaniele/speculative_mamba。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024. v3 updates: fix format errors
摘要
线性RNN架构如Mamba,在语言建模方面可与Transformer模型竞争,并具有优势部署特性。研究挑战在于将大型预训练Transformer模型进行部署转换。研究展示了用学术GPU资源通过复用注意力层的线性投影权重来蒸馏大型Transformer为线性RNN的可行性。得到的混合模型只使用了四分之一的注意力层,在聊天基准测试中表现与原始Transformer相当,并且在聊天基准测试和一般基准测试中表现优于从头开始训练的开源混合Mamba模型。此外,研究还引入了一种硬件感知的投机解码算法,提高了Mamba和混合模型的推理速度。总体上,研究展示了如何在有限的计算资源下减少许多原始注意力层并更高效地生成模型。最佳性能的模型是从Llama3-8B-Instruct中提炼出来的,在AlpacaEval 2上相对于GPT-4取得了29.61的长度控制胜率,在MT-Bench上取得了7.35的成绩,超过了最佳8B规模指令调整线性RNN模型。还发现提炼的模型具有自然长度外推能力,在蒸馏长度提高20倍的情况下,几乎达到了完美的准确率。代码和预先训练的模型检查点在GitHub上开源。
关键见解
- 线性RNN架构如Mamba在语言建模方面可与Transformer模型竞争,且具有优势部署特性。
- 通过复用注意力层的线性投影权重,可以将大型Transformer模型蒸馏为线性RNN模型。
- 混合模型使用四分之一的注意力层即可实现与原始Transformer相当的性能。
- 引入了一种硬件感知的投机解码算法,以提高模型推理速度。
- 最佳性能的模型是从大型预训练模型Llama3-8B-Instruct中提炼出来的。
- 提炼的模型在多个基准测试中表现出色,超过了其他类似规模的模型。
- 提炼的模型具有自然长度外推能力,表现出强大的性能。
点此查看论文截图



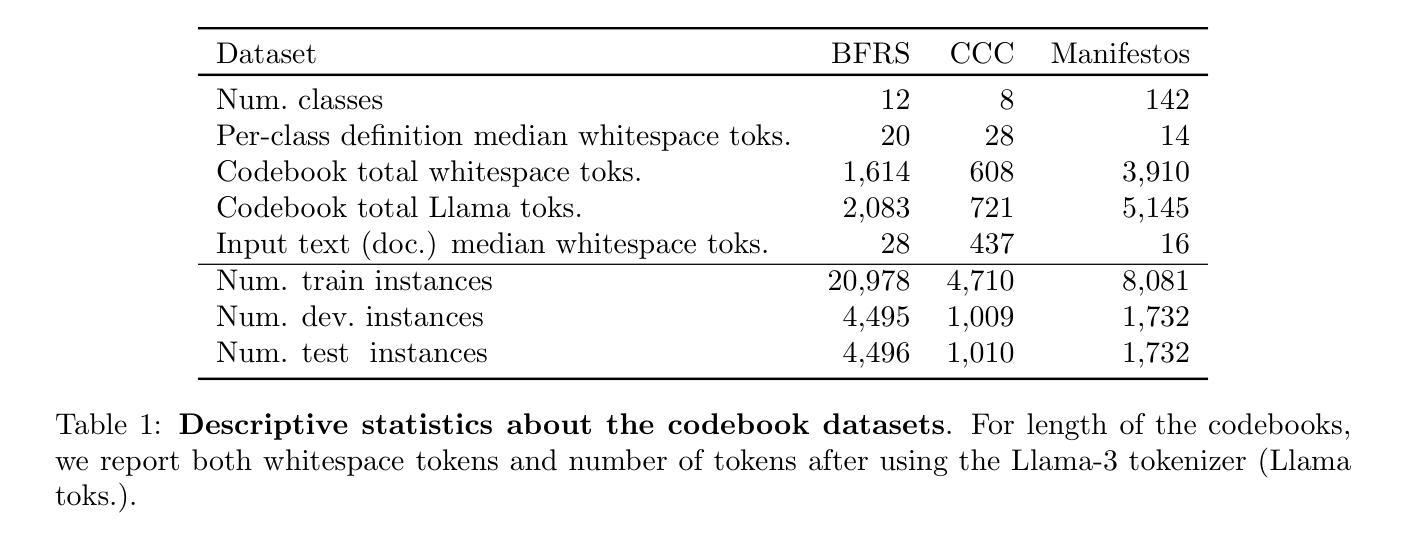
Codebook LLMs: Evaluating LLMs as Measurement Tools for Political Science Concepts
Authors:Andrew Halterman, Katherine A. Keith
Codebooks – documents that operationalize concepts and outline annotation procedures – are used almost universally by social scientists when coding political texts. To code these texts automatically, researchers are increasing turning to generative large language models (LLMs). However, there is limited empirical evidence on whether “off-the-shelf” LLMs faithfully follow real-world codebook operationalizations and measure complex political constructs with sufficient accuracy. To address this, we gather and curate three real-world political science codebooks – covering protest events, political violence and manifestos – along with their unstructured texts and human labels. We also propose a five-stage framework for codebook-LLM measurement: preparing a codebook for both humans and LLMs, testing LLMs’ basic capabilities on a codebook, evaluating zero-shot measurement accuracy (i.e. off-the-shelf performance), analyzing errors, and further (parameter-efficient) supervised training of LLMs. We provide an empirical demonstration of this framework using our three codebook datasets and several pretrained 7-12 billion open-weight LLMs. We find current open-weight LLMs have limitations in following codebooks zero-shot, but that supervised instruction tuning can substantially improve performance. Rather than suggesting the “best” LLM, our contribution lies in our codebook datasets, evaluation framework, and guidance for applied researchers who wish to implement their own codebook-LLM measurement projects.
概念操作化文档和概述注释程序的手册几乎被社会科学家在分析政治文本编码时普遍使用。为了自动对这些文本进行编码,研究人员正越来越多地转向生成大型语言模型(LLM)。然而,关于“现成的”LLM是否能够忠实遵循现实世界的手册操作化,并以足够的准确性衡量复杂的政治结构,现有的实证证据有限。为了解决这一问题,我们收集并整理了三个现实世界的政治科学手册数据集,涵盖抗议事件、政治暴力和宣言等内容及其非结构化文本和人类标签。我们还提出了一个五阶段的手册-LLM测量框架:为人工和LLM准备手册,测试LLM在手册上的基本能力,评估零启动测量精度(即现成性能),分析错误,以及对LLM进行进一步的(参数高效)监督训练。我们使用这三个手册数据集和几个预训练的7-12亿开放式权重LLM来实证展示这个框架。我们发现现有的开放式权重LLM在零启动遵循手册方面存在局限性,但监督指令微调可以显著提高性能。我们的贡献不在于建议“最佳”LLM,而在于我们的手册数据集、评估框架以及希望对自家进行手册-LLM测量项目的应用研究者提供的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Version 2 (v1 Presented at PolMeth 2024)
Summary
本文探讨了社会科学家在进行政治文本编码时普遍使用的编码手册(codebooks)与大型语言模型(LLMs)的结合应用。针对现有研究中关于LLMs是否能忠实遵循现实编码手册操作并准确测量复杂政治概念的问题,作者收集并整理了三个真实世界的政治科学编码手册及其相关文本和人类标签。同时,作者提出了一个五阶段的编码手册-LLM测量框架,包括准备编码手册、测试LLM的基本能力、评估零样本测量精度、分析误差以及进一步对LLM进行参数有效的监督训练。通过实证演示,作者发现现有的大型语言模型在零样本遵循编码手册方面存在局限性,但通过监督指令微调可以显著提高性能。本文的贡献在于提供编码手册数据集、评估框架以及为希望实施自己的编码手册-LLM测量项目的应用研究者提供指导。
Key Takeaways
- 社会科学家普遍使用编码手册(codebooks)对政治文本进行编码。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)被越来越多地用于自动编码这些文本。
- 目前对于LLMs是否忠实遵循现实编码手册操作并准确测量复杂政治概念的研究证据有限。
- 作者提出了一个五阶段的编码手册-LLM测量框架,包括准备、测试、评估、分析和进一步训练LLM。
- 实证研究表明,现有LLMs在零样本遵循编码手册方面存在局限性。
- 通过监督指令微调可以显著提高LLMs的性能。
点此查看论文截图

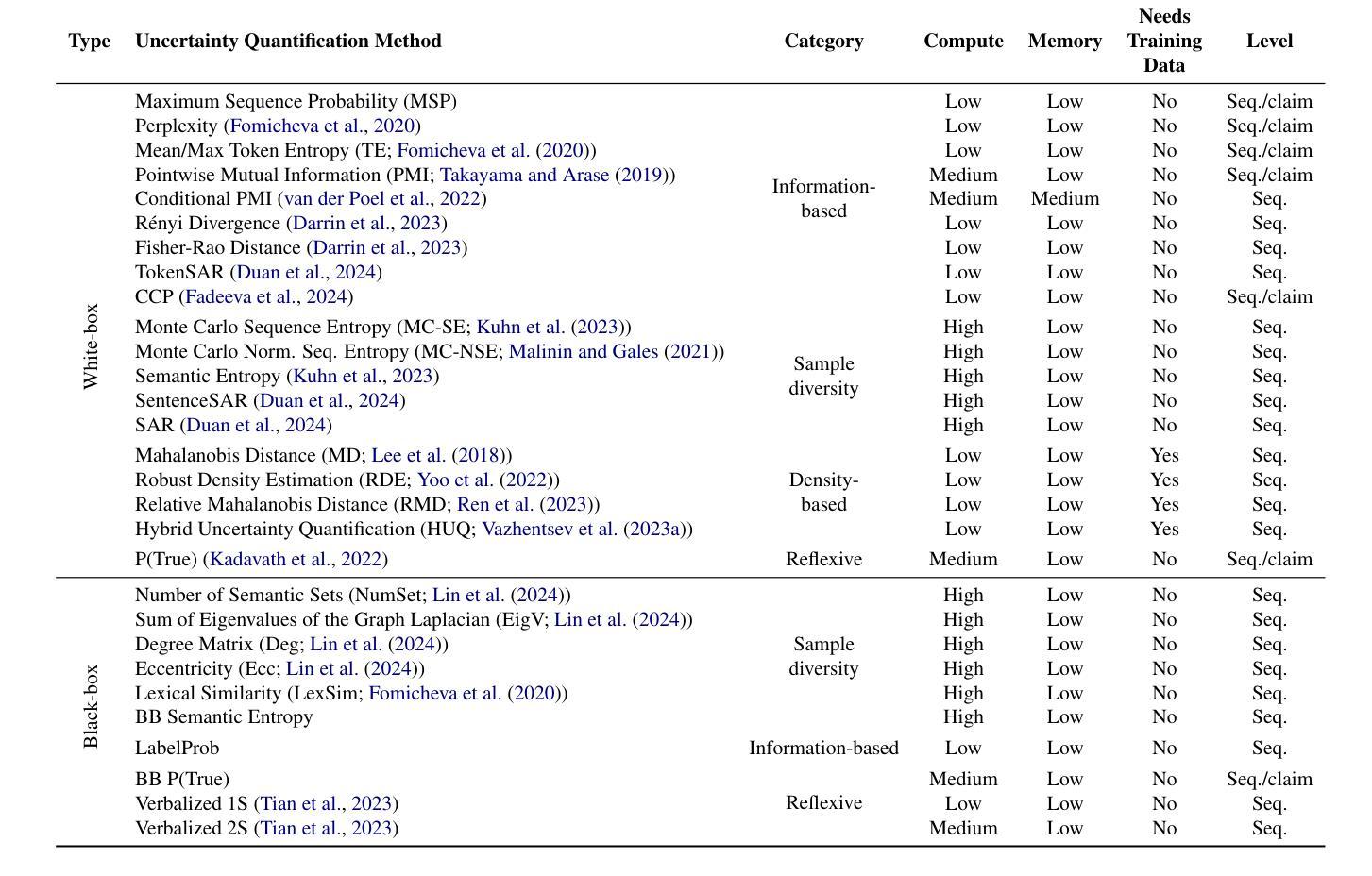
Benchmarking Uncertainty Quantification Methods for Large Language Models with LM-Polygraph
Authors:Roman Vashurin, Ekaterina Fadeeva, Artem Vazhentsev, Lyudmila Rvanova, Akim Tsvigun, Daniil Vasilev, Rui Xing, Abdelrahman Boda Sadallah, Kirill Grishchenkov, Sergey Petrakov, Alexander Panchenko, Timothy Baldwin, Preslav Nakov, Maxim Panov, Artem Shelmanov
The rapid proliferation of large language models (LLMs) has stimulated researchers to seek effective and efficient approaches to deal with LLM hallucinations and low-quality outputs. Uncertainty quantification (UQ) is a key element of machine learning applications in dealing with such challenges. However, research to date on UQ for LLMs has been fragmented in terms of techniques and evaluation methodologies. In this work, we address this issue by introducing a novel benchmark that implements a collection of state-of-the-art UQ baselines and offers an environment for controllable and consistent evaluation of novel UQ techniques over various text generation tasks. Our benchmark also supports the assessment of confidence normalization methods in terms of their ability to provide interpretable scores. Using our benchmark, we conduct a large-scale empirical investigation of UQ and normalization techniques across eleven tasks, identifying the most effective approaches. Code: https://github.com/IINemo/lm-polygraph Benchmark: https://huggingface.co/LM-Polygraph
大型语言模型(LLM)的迅速增殖促使研究人员寻求有效且高效的方法来应对LLM幻觉和输出质量低的问题。不确定性量化(UQ)是机器学习应用中解决此类挑战的关键因素。然而,迄今为止关于LLM的不确定性量化的研究在技术和评估方法方面都是零碎的。在这项工作中,我们通过引入一个新型基准测试来解决这个问题,该测试实现了最先进的UQ基线技术的集合,并提供了对各种文本生成任务中新型UQ技术进行可控且一致评估的环境。我们的基准测试还支持对信心归一化方法的评估,以评估其提供可解释分数的能力。使用我们的基准测试,我们对UQ和归一化技术在十一个任务上进行了大规模实证研究,确定了最有效的方式。代码:https://github.com/IINemo/lm-polygraph 基准测试:https://huggingface.co/LM-Polygraph
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to TACL 2025, pre-MIT Press publication version. Roman Vashurin, Ekaterina Fadeeva, Artem Vazhentsev contributed equally
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展引发了研究人员对于处理LLM幻觉和低质量输出的有效和高效方法的探求。不确定性量化(UQ)是机器学习应用中应对这些挑战的关键因素。然而,迄今为止,针对LLM的不确定性量化研究在技术和评估方法上都是分散的。本研究通过引入新型基准测试来解决这一问题,该基准测试实现了先进的不确定性量化基准测试集合,并为各种文本生成任务上新型不确定性量化技术的可控和一致评估提供了环境。此外,该基准测试还支持对信心归一化方法的评估,以衡量其提供可解释分数能力的高低。借助我们的基准测试,我们对UQ和归一化技术在十一个任务上进行了大规模实证研究,并确定了最有效的途径。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展引发了对于处理其幻觉和低质量输出的关注。
- 不确定性量化(UQ)在应对LLM挑战中扮演重要角色。
- 目前针对LLM的不确定性量化研究在技术和评估方法上较为分散。
- 引入的新型基准测试集合实现了先进的不确定性量化基准测试。
- 该基准测试为各种文本生成任务上的新型不确定性量化技术提供了可控和一致的评估环境。
- 基准测试支持对信心归一化方法的评估,衡量其提供可解释分数的能力。
点此查看论文截图

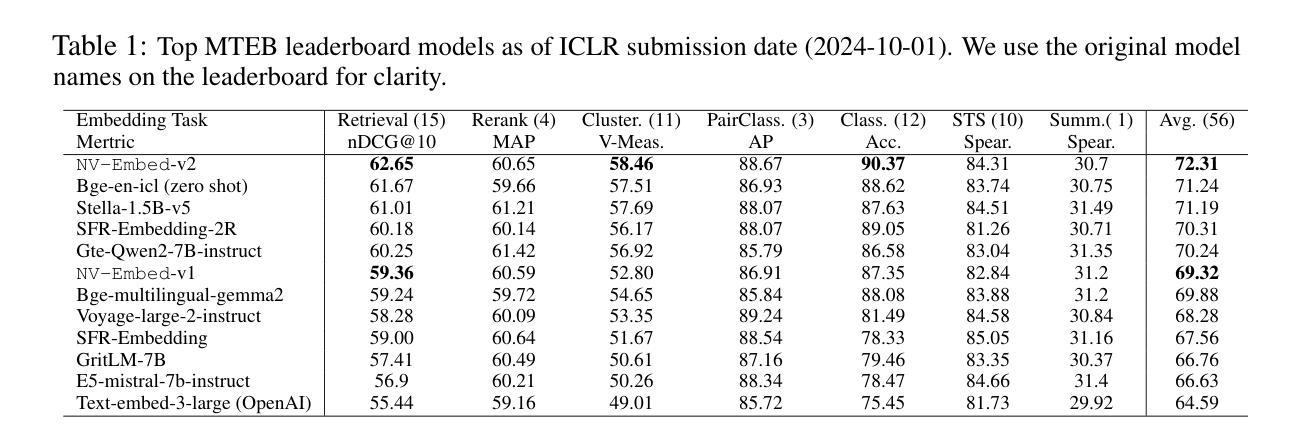
NV-Embed: Improved Techniques for Training LLMs as Generalist Embedding Models
Authors:Chankyu Lee, Rajarshi Roy, Mengyao Xu, Jonathan Raiman, Mohammad Shoeybi, Bryan Catanzaro, Wei Ping
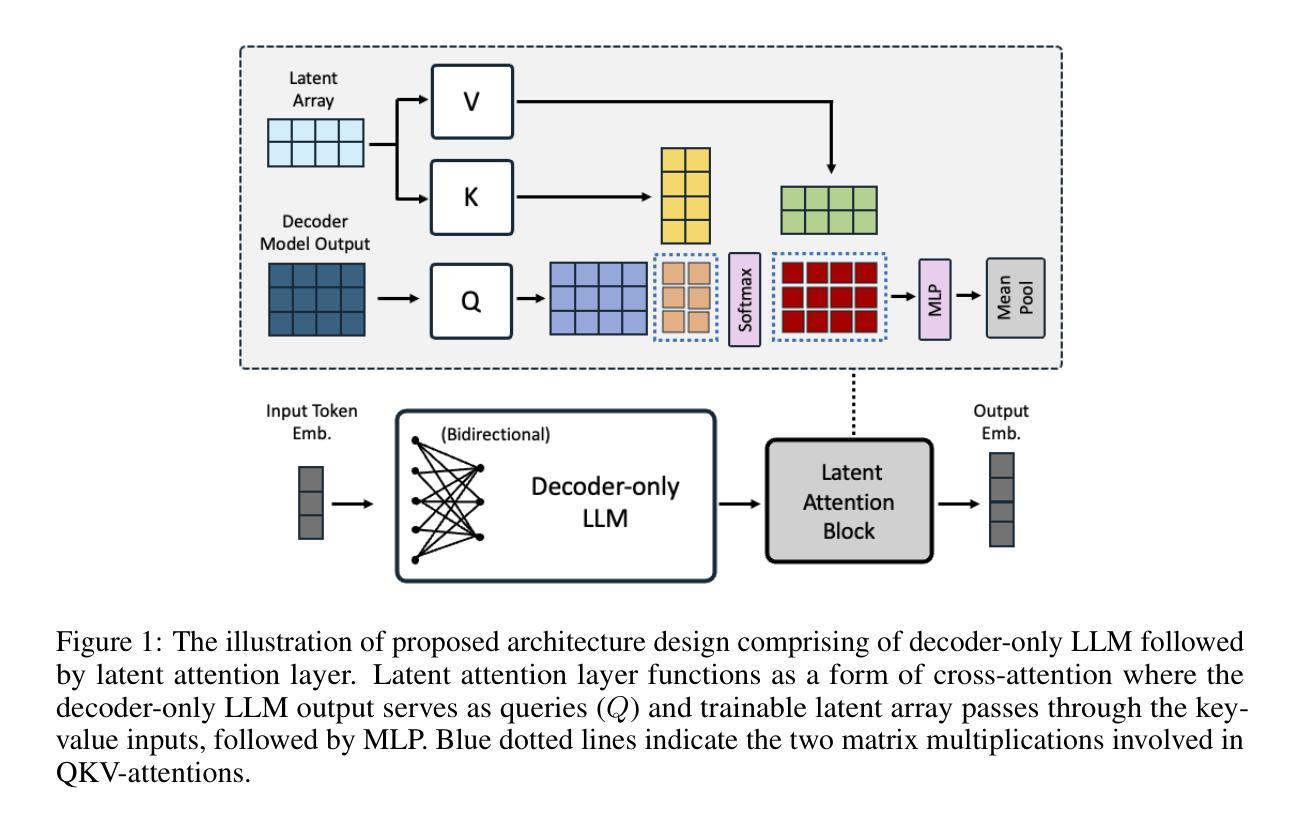
Decoder-only large language model (LLM)-based embedding models are beginning to outperform BERT or T5-based embedding models in general-purpose text embedding tasks, including dense vector-based retrieval. In this work, we introduce the NV-Embed model, incorporating architectural designs, training procedures, and curated datasets to significantly enhance the performance of LLM as a versatile embedding model, while maintaining its simplicity and reproducibility. For model architecture, we propose a latent attention layer to obtain pooled embeddings, which consistently improves retrieval and downstream task accuracy compared to mean pooling or using the last
基于解码器的大型语言模型(LLM)嵌入模型开始在通用文本嵌入任务中表现优于BERT或T5嵌入模型,包括基于密集向量的检索。在这项工作中,我们引入了NV-Embed模型,它结合了架构设计、训练程序和精选数据集,旨在显著增强LLM作为通用嵌入模型的表现,同时保持其简洁性和可重复性。在模型架构方面,我们提出了一种潜在注意力层来获得池化嵌入,与基于LLM的平均池化或使用最后一个
令牌嵌入相比,它始终提高了检索和下游任务的准确性。为了增强表示学习,我们在对比训练期间移除了LLM的因果注意力掩码。在训练算法方面,我们引入了一种两阶段的对比指令微调方法。它首先在检索数据集上应用带有指令的对比训练,利用批处理内的负样本和精选的硬负样本。在第二阶段,它将各种非检索任务融入指令微调中,这不仅提高了非检索任务准确性,还提高了检索性能。对于训练数据,我们利用硬负样本挖掘、合成数据生成和现有公共可用数据集来提升嵌入模型的性能。通过结合这些技术,我们的NV-Embed-v1和NV-Embed-v2模型在56个嵌入任务上获得了大规模文本嵌入基准测试(MTEB)的第一名(截至2024年5月24日和2024年8月30日),证明了所提出方法随时间推移的持续有效性。此外,它在AIR基准测试的Long Doc部分获得最高分,在QA部分获得第二名,涵盖了MTEB以外的广泛跨域信息检索主题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We open-source the model at: https://huggingface.co/nvidia/NV-Embed-v2
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的解码器嵌入模型在通用文本嵌入任务中开始表现出优于BERT或T5的嵌入模型性能,包括基于密集向量的检索任务。本研究介绍了NV-Embed模型,通过设计架构、训练程序和定制数据集来显著提高LLM作为通用嵌入模型的性能,同时保持其简单性和可复现性。NV-Embed模型通过使用潜在意图层进行池化嵌入来改善检索和下游任务准确性,并去除LLM中的因果注意力掩码进行对比训练。此外,还介绍了两阶段对比指令微调方法,并利用硬负样本挖掘、合成数据生成等现有公开数据集提升嵌入模型的性能。NV-Embed模型在大量文本嵌入基准测试(MTEB)中获得第一名,在长期和短期评价中都展示了方法的有效性,并在AIR基准测试中取得了优异成绩。
Key Takeaways
- LLM的解码器嵌入模型在通用文本嵌入任务中表现出优越性能。
- NV-Embed模型通过特定架构、训练程序和定制数据集显著提高了LLM的嵌入性能。
- 潜在意图层用于池化嵌入改善了检索和下游任务准确性。
- 去除LLM的因果注意力掩码进行对比训练增强了表示学习。
- 两阶段对比指令微调方法提高了非检索任务准确性和检索性能。
- 利用硬负样本挖掘、合成数据生成等策略提升了嵌入模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Attention Mechanisms Don’t Learn Additive Models: Rethinking Feature Importance for Transformers
Authors:Tobias Leemann, Alina Fastowski, Felix Pfeiffer, Gjergji Kasneci
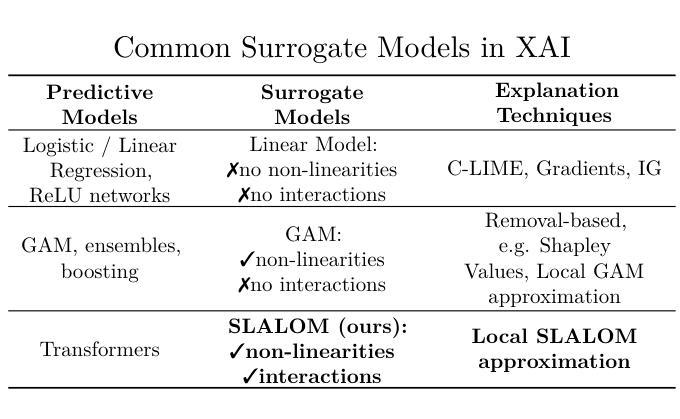
We address the critical challenge of applying feature attribution methods to the transformer architecture, which dominates current applications in natural language processing and beyond. Traditional attribution methods to explainable AI (XAI) explicitly or implicitly rely on linear or additive surrogate models to quantify the impact of input features on a model’s output. In this work, we formally prove an alarming incompatibility: transformers are structurally incapable of representing linear or additive surrogate models used for feature attribution, undermining the grounding of these conventional explanation methodologies. To address this discrepancy, we introduce the Softmax-Linked Additive Log Odds Model (SLALOM), a novel surrogate model specifically designed to align with the transformer framework. SLALOM demonstrates the capacity to deliver a range of insightful explanations with both synthetic and real-world datasets. We highlight SLALOM’s unique efficiency-quality curve by showing that SLALOM can produce explanations with substantially higher fidelity than competing surrogate models or provide explanations of comparable quality at a fraction of their computational costs. We release code for SLALOM as an open-source project online at https://github.com/tleemann/slalom_explanations.
我们面临将特征归因方法应用于主导当前自然语言处理及其他领域应用的变压器架构的关键挑战。传统的归因方法明确地或隐含地依赖于线性或附加替代模型来量化输入特征对模型输出的影响,以实现可解释人工智能(XAI)。在这项工作中,我们正式证明了一个令人警觉的矛盾:从结构上来说,变压器无法代表用于特征归因的线性或附加替代模型,这破坏了这些传统解释方法的基础。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了Softmax-Linked Additive Log Odds Model(SLALOM),这是一种专门设计来与变压器框架对齐的新型替代模型。SLALOM展示了在合成和真实世界数据集上提供一系列深刻解释的能力。我们通过展示SLALOM能够产生比竞争替代模型更高保真度的解释,或者提供同等质量的解释但计算成本较低,来突出SLALOM独特的效率-质量曲线。我们在https://github.com/tleemann/slalom_explanations上发布了SLALOM的开源项目代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF TMLR Camera-Ready version
Summary
本文解决了将特征归因方法应用于自然语言处理及其他领域广泛应用的transformer架构的关键挑战。传统的人工智能解释(XAI)归因方法直接或间接依赖于线性或附加代理模型来衡量输入特征对模型输出的影响。然而,本文正式证明了一个令人担忧的不兼容性:transformer的结构无法代表用于特征归因的线性或附加代理模型,这使得这些传统解释方法的根基动摇。为解决这一问题,我们提出了名为SLALOM的新型代理模型,该模型专门设计以与transformer框架对齐。SLALOM能够在合成和真实数据集上提供一系列深入的解释。我们强调SLALOM的高效性与其质量之间的独特关系曲线,表明SLALOM可以在提供更高保真度的解释的同时,相较于其他代理模型大幅降低计算成本。我们已将SLALOM的代码作为开源项目在线发布在[链接地址](请根据实际情况替换)。
Key Takeaways
- 传统特征归因方法依赖于线性或附加代理模型,但在transformer架构中存在不兼容性问题。
- 引入新型代理模型SLALOM,专为transformer架构设计,以解决传统解释方法的不兼容问题。
- SLALOM在合成和真实数据集上展现出强大的解释能力。
- SLALOM与现有代理模型相比具有较高的保真度和计算效率优势。
- 通过公开代码实现,便于研究者和开发者使用SLALOM进行进一步研究和应用。
- SLALOM对于理解和解释transformer架构的工作原理具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

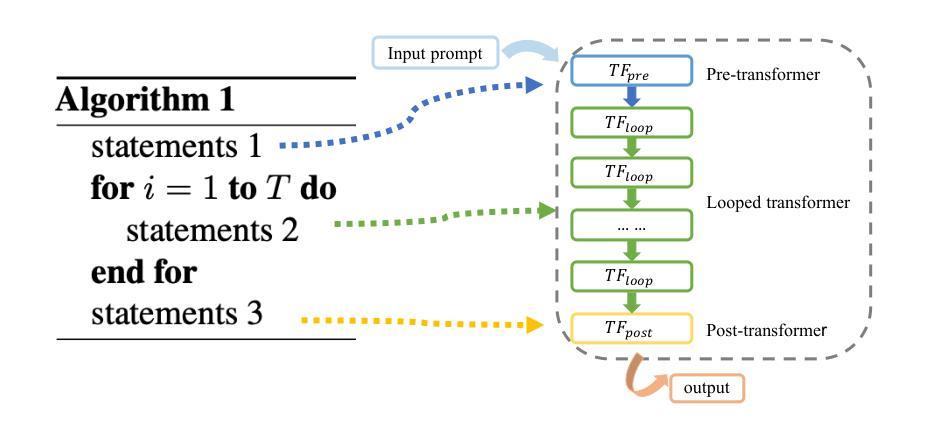
AlgoFormer: An Efficient Transformer Framework with Algorithmic Structures
Authors:Yihang Gao, Chuanyang Zheng, Enze Xie, Han Shi, Tianyang Hu, Yu Li, Michael K. Ng, Zhenguo Li, Zhaoqiang Liu
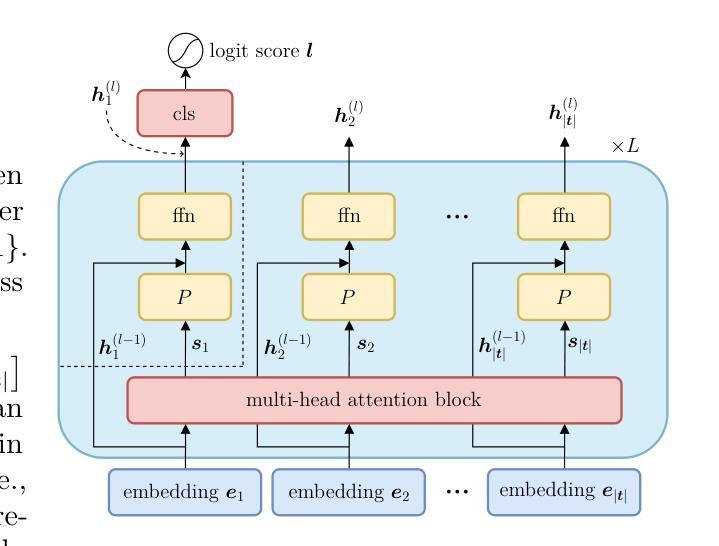
Besides natural language processing, transformers exhibit extraordinary performance in solving broader applications, including scientific computing and computer vision. Previous works try to explain this from the expressive power and capability perspectives that standard transformers are capable of performing some algorithms. To empower transformers with algorithmic capabilities and motivated by the recently proposed looped transformer, we design a novel transformer framework, dubbed Algorithm Transformer (abbreviated as AlgoFormer). We provide an insight that efficient transformer architectures can be designed by leveraging prior knowledge of tasks and the underlying structure of potential algorithms. Compared with the standard transformer and vanilla looped transformer, the proposed AlgoFormer can perform efficiently in algorithm representation in some specific tasks. In particular, inspired by the structure of human-designed learning algorithms, our transformer framework consists of a pre-transformer that is responsible for task preprocessing, a looped transformer for iterative optimization algorithms, and a post-transformer for producing the desired results after post-processing. We provide theoretical evidence of the expressive power of the AlgoFormer in solving some challenging problems, mirroring human-designed algorithms. Furthermore, some theoretical and empirical results are presented to show that the designed transformer has the potential to perform algorithm representation and learning. Experimental results demonstrate the empirical superiority of the proposed transformer in that it outperforms the standard transformer and vanilla looped transformer in some specific tasks. An extensive experiment on real language tasks (e.g., neural machine translation of German and English, and text classification) further validates the expressiveness and effectiveness of AlgoFormer.
除了自然语言处理外,变压器(transformer)在解决更广泛的应用方面表现出卓越的性能,包括科学计算和计算机视觉。之前的研究工作试图从表现力和能力角度解释这一点,即标准变压器能够执行某些算法。为了赋予变压器算法能力,并受到最近提出的循环变压器的启发,我们设计了一种新型变压器框架,称为算法变压器(Algorithm Transformer,简称AlgoFormer)。我们提供了一种见解,即通过利用任务的先验知识和潜在算法的基本结构,可以有效地设计变压器架构。与标准变压器和基本的循环变压器相比,所提出的AlgoFormer在某些特定任务的算法表示方面能够高效执行。特别是,受到人类设计的学习算法的结构的启发,我们的变压器框架包括一个负责任务预处理的预变压器、一个用于迭代优化算法的循环变压器、以及一个用于后处理的后变压器,以产生所需的结果。我们提供了AlgoFormer在解决一些具有挑战性的问题时的表现力的理论证据,反映人类设计的算法。此外,我们还提供了一些理论和实证结果,以展示所设计的变压器在算法表示和学习方面的潜力。实验结果表明,所提出的变压器在某些特定任务上优于标准变压器和基本的循环变压器。在真实语言任务(例如德语和英语的神经机器翻译和文本分类)上的大量实验进一步验证了AlgoFormer的表达力和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR). The paper provides insight that the Transformer architectures can mimic the algorithm structures in (in-context) algorithm learning and representation. The incorporated algorithmic structure in Algoformer shows its potential in (deep learning for) scientific computing, besides the real language tasks
Summary
本文介绍了除自然语言处理外,变压器在更广泛的应用中的卓越性能,包括科学计算和计算机视觉。为赋能变压器具有算法能力,并受循环变压器的启发,设计了一种新型变压器框架——Algorithm Transformer(简称AlgoFormer)。通过利用任务先验知识和潜在算法的底层结构,可以设计有效的变压器架构。与标准变压器和循环变压器相比,所提出的AlgoFormer在某些特定任务中的算法表示效率更高。该框架包括负责任务预处理的预变压器、负责迭代优化算法的循环变压器以及负责后处理的后变压器。理论证据表明AlgoFormer在解决某些挑战性问题时具有表现力,可模拟人类设计的算法。实验结果表明,该变压器在特定任务上的表现优于标准和循环变压器。在真实语言任务上的广泛实验进一步验证了AlgoFormer的表达力和有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 变压器在自然语言处理以外的领域,如科学计算和计算机视觉,也有卓越性能。
- 提出了一种新型变压器框架Algorithm Transformer(AlgoFormer),融合了预变压器、循环变压器和后变压器的设计。
- AlgoFormer利用任务的先验知识和潜在算法的底层结构来提高算法表示的效率。
- AlgoFormer在某些特定任务上的表现优于标准变压器和循环变压器。
- AlgoFormer具有解决某些挑战性问题的理论依据,可模拟人类设计的算法。
- 实验结果证明了AlgoFormer的有效性和优越性。
点此查看论文截图