⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-16 更新
Code and Pixels: Multi-Modal Contrastive Pre-training for Enhanced Tabular Data Analysis
Authors:Kankana Roy, Lars Krämer, Sebastian Domaschke, Malik Haris, Roland Aydin, Fabian Isensee, Martin Held
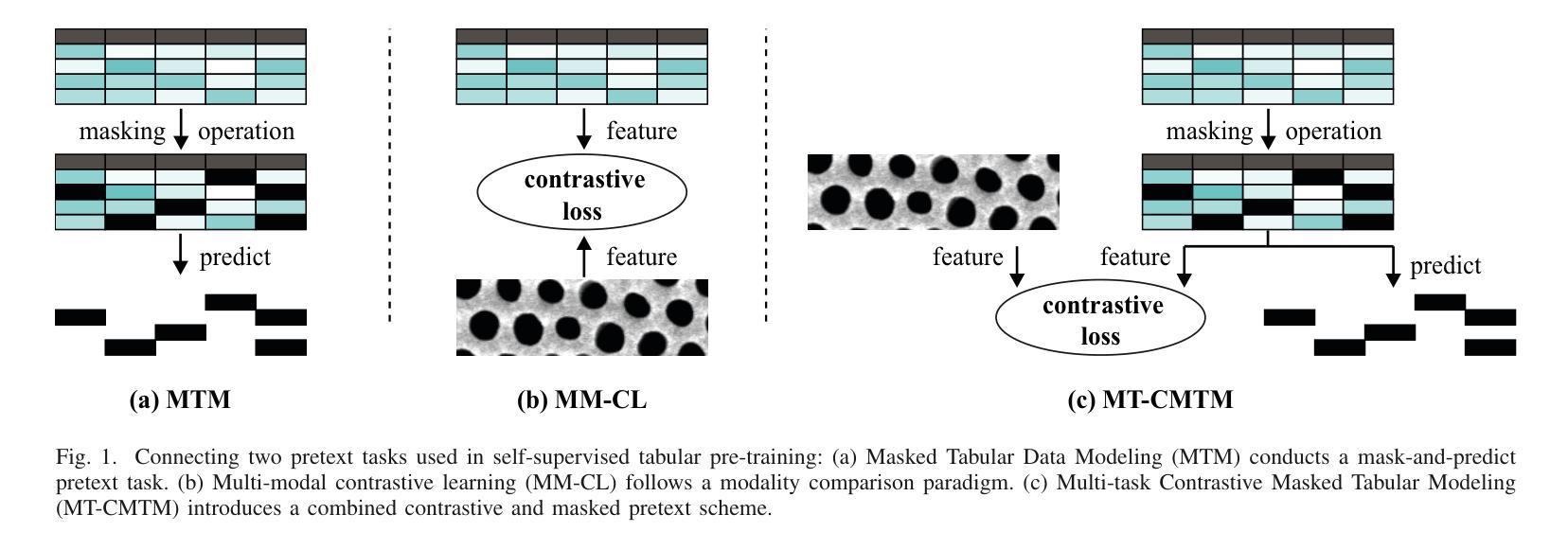
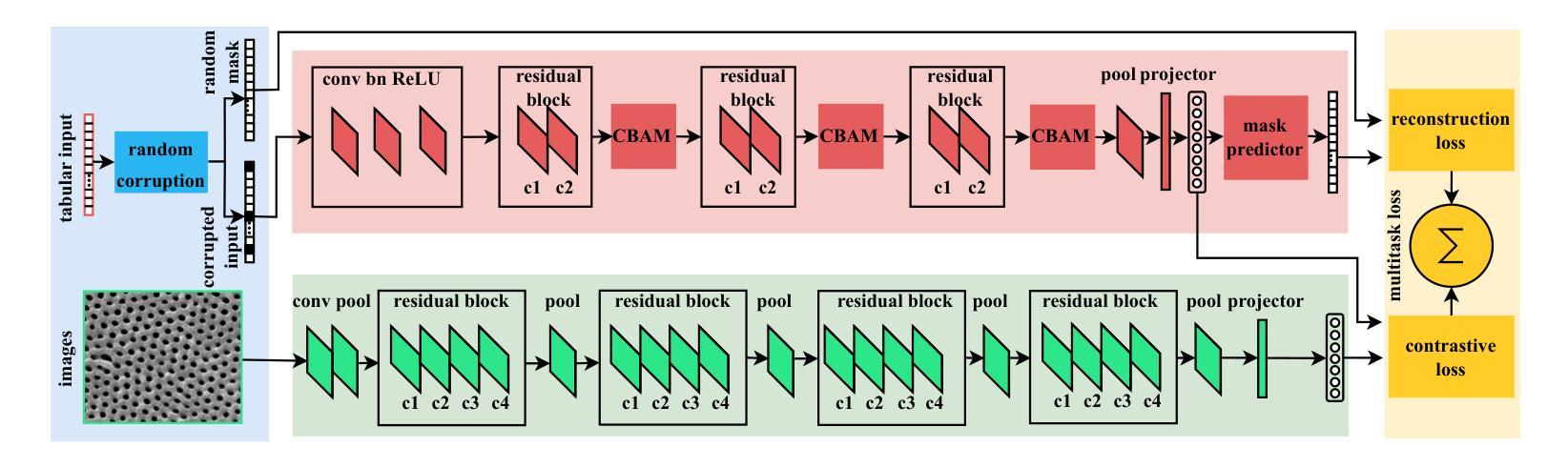
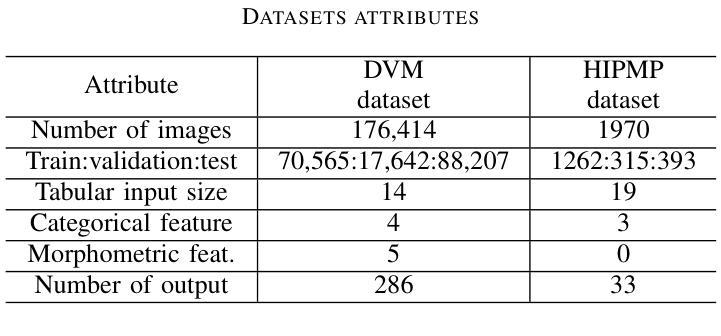
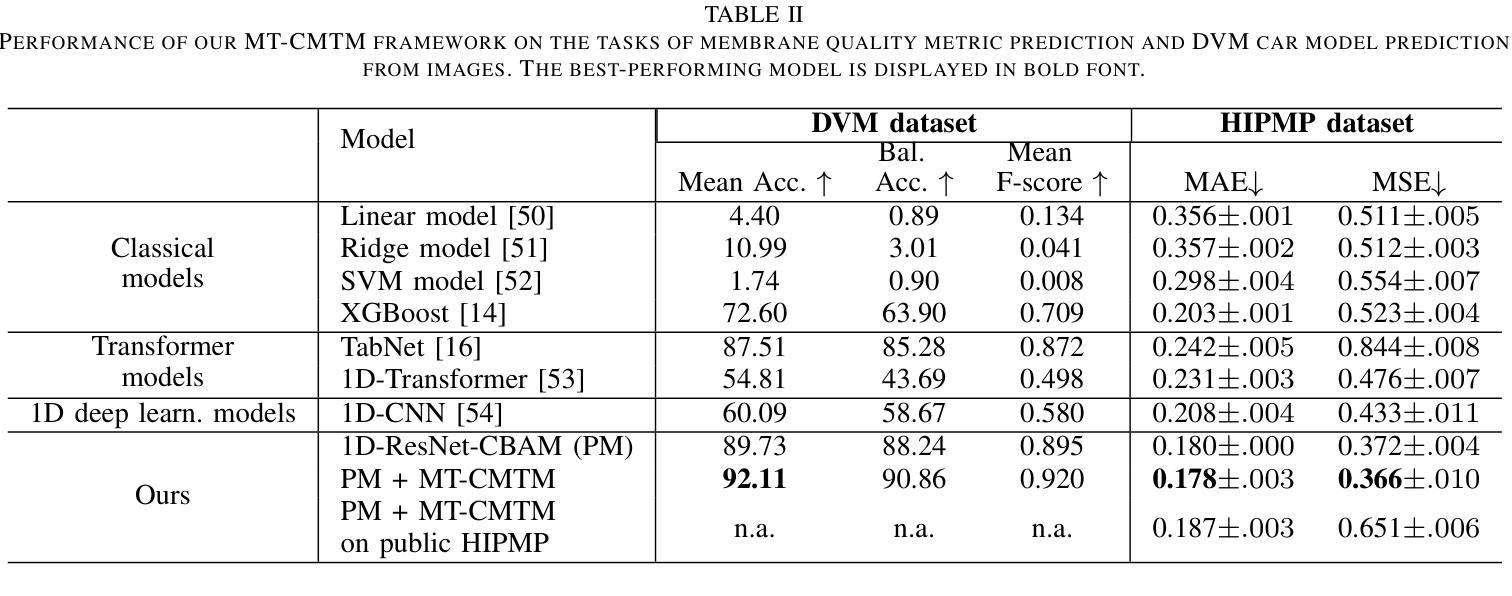
Learning from tabular data is of paramount importance, as it complements the conventional analysis of image and video data by providing a rich source of structured information that is often critical for comprehensive understanding and decision-making processes. We present Multi-task Contrastive Masked Tabular Modeling (MT-CMTM), a novel method aiming to enhance tabular models by leveraging the correlation between tabular data and corresponding images. MT-CMTM employs a dual strategy combining contrastive learning with masked tabular modeling, optimizing the synergy between these data modalities. Central to our approach is a 1D Convolutional Neural Network with residual connections and an attention mechanism (1D-ResNet-CBAM), designed to efficiently process tabular data without relying on images. This enables MT-CMTM to handle purely tabular data for downstream tasks, eliminating the need for potentially costly image acquisition and processing. We evaluated MT-CMTM on the DVM car dataset, which is uniquely suited for this particular scenario, and the newly developed HIPMP dataset, which connects membrane fabrication parameters with image data. Our MT-CMTM model outperforms the proposed tabular 1D-ResNet-CBAM, which is trained from scratch, achieving a relative 1.48% improvement in relative MSE on HIPMP and a 2.38% increase in absolute accuracy on DVM. These results demonstrate MT-CMTM’s robustness and its potential to advance the field of multi-modal learning.
从表格数据进行学习至关重要,因为它通过提供丰富的结构化信息来源来补充对图像和视频数据的传统分析,这对于全面理解和决策过程经常至关重要。我们提出了多任务对比掩模表格建模(Multi-task Contrastive Masked Tabular Modeling,简称MT-CMTM),这是一种旨在利用表格数据与相应图像之间关联性的新方法,以增强表格模型。MT-CMTM采用了一种结合对比学习与掩模表格建模的双重策略,以优化这些数据模式之间的协同作用。我们的方法的核心是一维卷积神经网络,具有残差连接和注意力机制(1D-ResNet-CBAM),旨在有效处理表格数据而无需依赖图像。这使得MT-CMTM能够处理纯表格数据以进行下游任务,从而无需进行可能成本高昂的图像获取和处理。我们在DVM汽车数据集上评估了MT-CMTM,该数据集非常适合于此特定场景,以及新开发的HIPMP数据集,该数据集将膜制造参数与图像数据相关联。我们的MT-CMTM模型的表现优于从头开始训练的提议的表格数据1D-ResNet-CBAM模型,在HIPMP上相对MSE提高了1.48%,在DVM上绝对精度提高了2.38%。这些结果证明了MT-CMTM的稳健性以及其在多模式学习领域发展的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的多任务对比掩膜表格建模(MT-CMTM)方法,该方法旨在利用表格数据与对应图像之间的关联性来提高表格模型的性能。它结合了对比学习与掩膜表格建模的双重策略,优化了不同数据模式之间的协同作用。此外,该模型可以仅处理表格数据即可处理下游任务,而无需依赖于成本较高的图像采集和处理。在DVM汽车数据集和全新开发的HIPMP数据集上的实验结果表明,MT-CMTM模型的性能优于从头开始训练的1D-ResNet-CBAM模型,显示出其稳健性和在多模态学习领域的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- MT-CMTM是一种新型方法,旨在通过利用表格数据和对应图像之间的关联性提高表格模型的性能。
- 该方法结合了对比学习与掩膜表格建模的双重策略,以优化不同数据模式之间的协同作用。
- MT-CMTM使用一个具有残差连接和注意力机制的1D卷积神经网络(1D-ResNet-CBAM)来处理表格数据,无需依赖图像。
- 该模型在DVM汽车数据集和HIPMP数据集上进行了实验验证,显示出其稳健性和多模态学习潜力。
- MT-CMTM模型性能优于从头开始训练的1D-ResNet-CBAM模型。
- 在HIPMP数据集上,MT-CMTM模型相对于MSE的改进达到1.48%。
点此查看论文截图

Exploring the Use of Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training for Human Posture Classification: Insights from Yoga Pose Analysis
Authors:Andrzej D. Dobrzycki, Ana M. Bernardos, Luca Bergesio, Andrzej Pomirski, Daniel Sáez-Trigueros
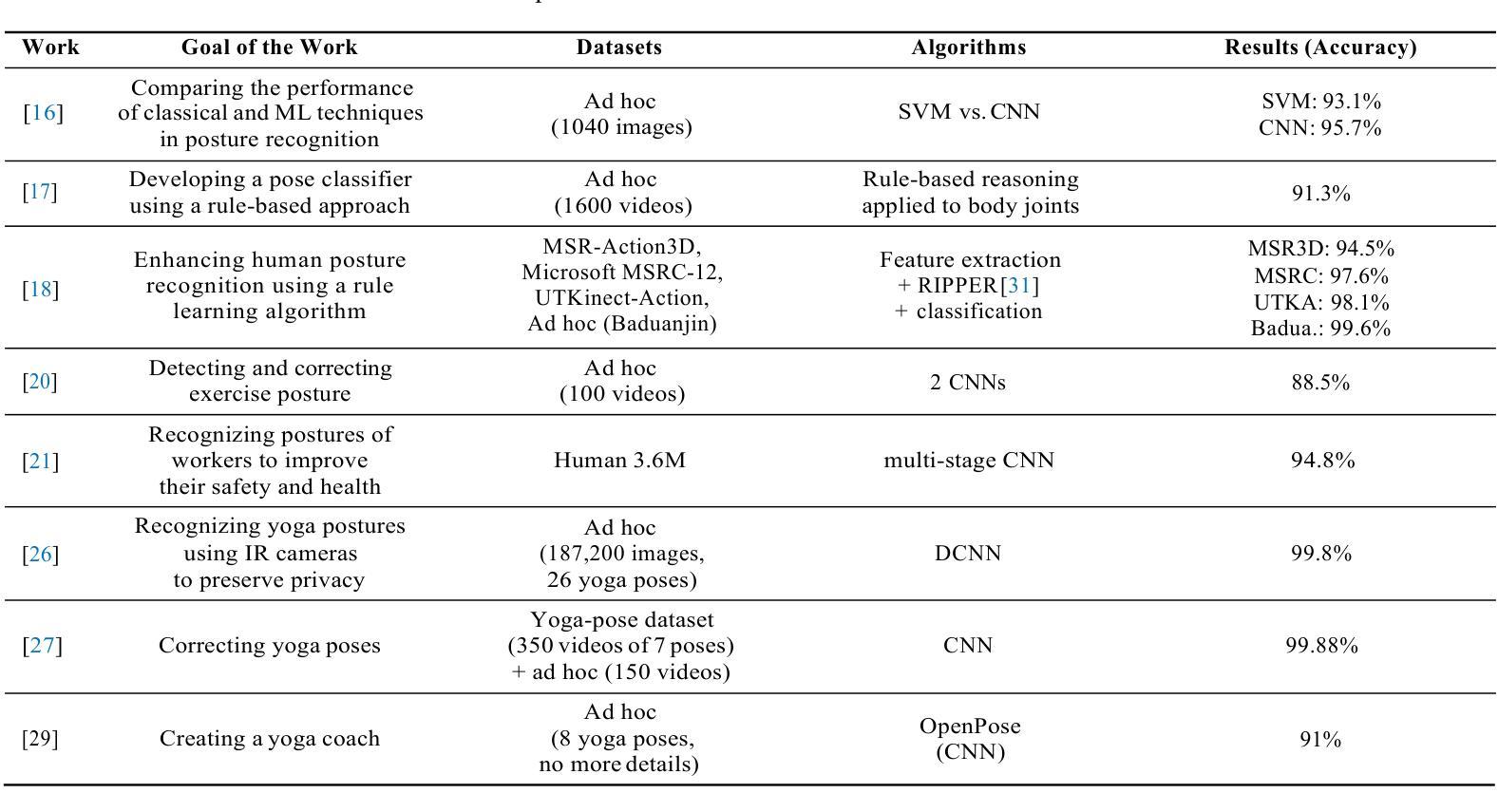
Accurate human posture classification in images and videos is crucial for automated applications across various fields, including work safety, physical rehabilitation, sports training, or daily assisted living. Recently, multimodal learning methods, such as Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP), have advanced significantly in jointly understanding images and text. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of CLIP in classifying human postures, focusing on its application in yoga. Despite the initial limitations of the zero-shot approach, applying transfer learning on 15,301 images (real and synthetic) with 82 classes has shown promising results. The article describes the full procedure for fine-tuning, including the choice for image description syntax, models and hyperparameters adjustment. The fine-tuned CLIP model, tested on 3826 images, achieves an accuracy of over 85%, surpassing the current state-of-the-art of previous works on the same dataset by approximately 6%, its training time being 3.5 times lower than what is needed to fine-tune a YOLOv8-based model. For more application-oriented scenarios, with smaller datasets of six postures each, containing 1301 and 401 training images, the fine-tuned models attain an accuracy of 98.8% and 99.1%, respectively. Furthermore, our experiments indicate that training with as few as 20 images per pose can yield around 90% accuracy in a six-class dataset. This study demonstrates that this multimodal technique can be effectively used for yoga pose classification, and possibly for human posture classification, in general. Additionally, CLIP inference time (around 7 ms) supports that the model can be integrated into automated systems for posture evaluation, e.g., for developing a real-time personal yoga assistant for performance assessment.
在图像和视频中进行准确的人体姿势分类对于自动化应用在多个领域是至关重要的,包括工作安全、物理康复、体育训练或日常辅助生活。最近,如Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining(CLIP)等多模态学习方法在联合理解图像和文本方面取得了显著进展。本研究旨在评估CLIP在人体姿势分类方面的有效性,重点关注其在瑜伽中的应用。尽管零样本方法存在初始局限性,但在具有82类的15301张(真实和合成)图像上应用迁移学习已显示出令人鼓舞的结果。文章详细介绍了微调过程的完整步骤,包括图像描述语法、模型的选择和超参数的调整。经过精细调整的CLIP模型在3826张图像上进行了测试,准确率超过85%,较同一数据集上的先前最佳工作高出约6%,其训练时间是微调YOLOv8模型所需时间的3.5倍。对于面向应用的实际场景,使用每个姿势仅包含少量图像(例如六个姿势中的六个图像)的数据集进行训练时,精细调整后的模型在包含1301张和401张训练图像的数据集上分别达到了98.8%和99.1%的准确率。此外,我们的实验表明,每姿势仅使用少量图像(如每个六类数据集仅使用大约二十张图像)进行训练可以达到大约90%的准确率。本研究表明,这种多模态技术可有效用于瑜伽姿势分类,并可能适用于一般的人体姿势分类。此外,CLIP推理时间约为7毫秒,支持将该模型集成到姿势评估的自动化系统中,例如开发用于性能评估的实时个人瑜伽助理。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究利用对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)进行瑜伽姿势分类,通过对15,301张图像(真实和合成)进行迁移学习,在瑜伽姿势分类上取得了显著效果。精细调整的CLIP模型在测试集上准确率超过85%,显著优于先前在同一数据集上的最佳表现,同时训练时间减少了约三倍。此外,即使使用少量图像(每姿势仅20张),该模型在六类数据集中仍能达到约90%的准确率。研究证明该技术可有效地用于瑜伽姿势分类及一般人类姿势分类,并且CLIP的快速推理时间使其可集成到姿势评估的自动化系统中。
Key Takeaways
- 对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在多模态学习中表现出色,用于瑜伽姿势分类。
- 通过迁移学习在大量图像数据上进行精细调整,实现了高准确率的人体位姿分类。
- CLIP模型在测试集上的准确率超过85%,显著优于先前的研究。
- 使用少量图像(每姿势仅20张)也能实现约90%的准确率。
- CLIP模型的训练时间比YOLOv8模型低约三倍。
- CLIP的快速推理时间支持集成到自动化系统中进行姿势评估。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Counterfactual and Contrastive Explainability and Transparency of DCNN Image Classifiers
Authors:Syed Ali Tariq, Tehseen Zia, Mubeen Ghafoor
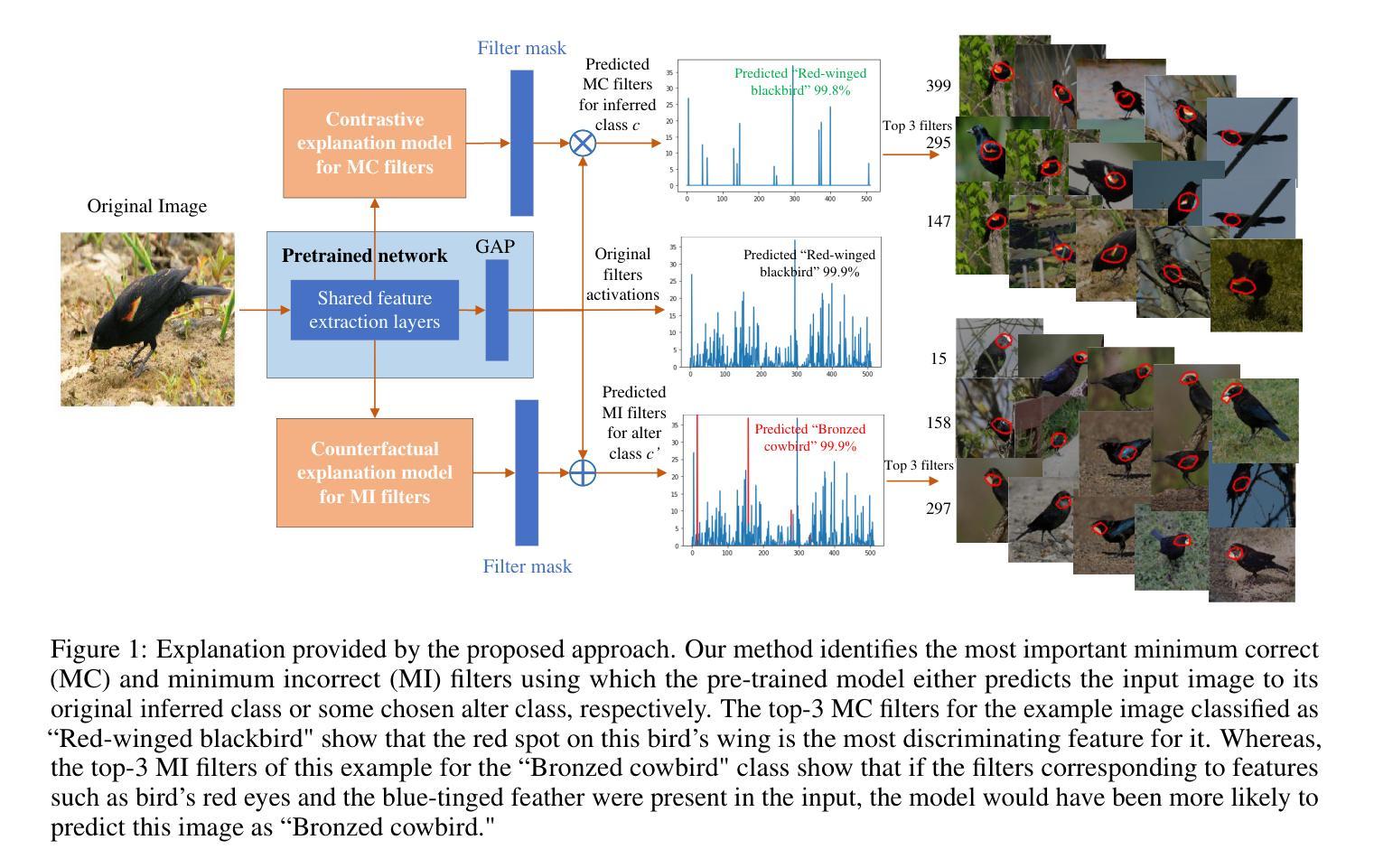
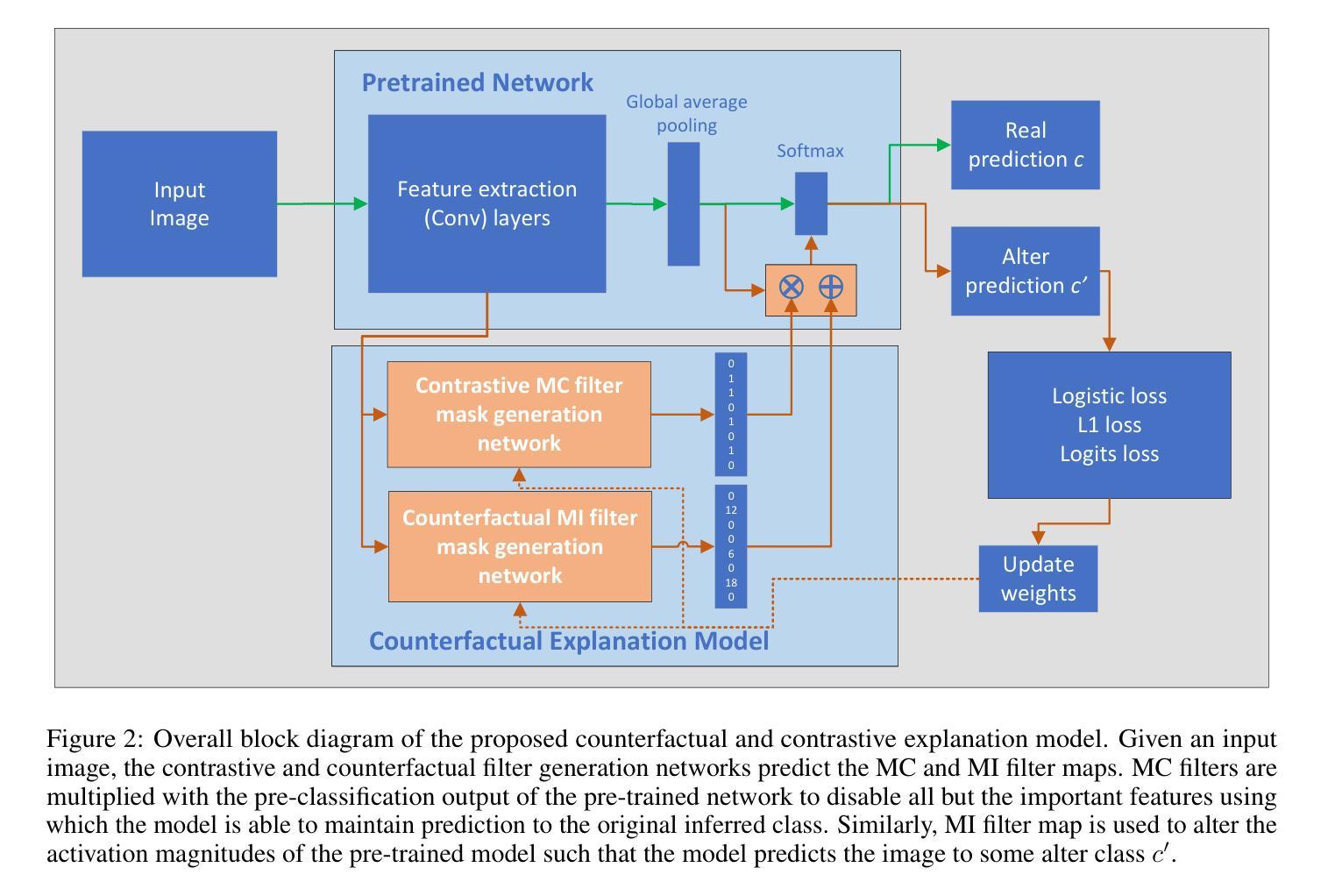
Explainability of deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) is an important research topic that tries to uncover the reasons behind a DCNN model’s decisions and improve their understanding and reliability in high-risk environments. In this regard, we propose a novel method for generating interpretable counterfactual and contrastive explanations for DCNN models. The proposed method is model intrusive that probes the internal workings of a DCNN instead of altering the input image to generate explanations. Given an input image, we provide contrastive explanations by identifying the most important filters in the DCNN representing features and concepts that separate the model’s decision between classifying the image to the original inferred class or some other specified alter class. On the other hand, we provide counterfactual explanations by specifying the minimal changes necessary in such filters so that a contrastive output is obtained. Using these identified filters and concepts, our method can provide contrastive and counterfactual reasons behind a model’s decisions and makes the model more transparent. One of the interesting applications of this method is misclassification analysis, where we compare the identified concepts from a particular input image and compare them with class-specific concepts to establish the validity of the model’s decisions. The proposed method is compared with state-of-the-art and evaluated on the Caltech-UCSD Birds (CUB) 2011 dataset to show the usefulness of the explanations provided.
深度卷积神经网络(DCNNs)的解释性是一个重要的研究课题,旨在揭示DCNN模型决策背后的原因,并在高风险环境中提高对其理解和可靠性。在这方面,我们提出了一种为DCNN模型生成可解释的假设和对比解释的新方法。该方法具有模型侵入性,它通过探查DCNN的内部工作原理而不是改变输入图像来生成解释。给定一个输入图像,我们通过识别DCNN中最重要的过滤器来提供对比解释,这些过滤器代表特征和概念,能够区分模型将图像分类为原始推断类别或其他指定的替代类别之间的决策。另一方面,我们通过指定这些过滤器中所需的最小变化来提供反事实解释,以便获得对比输出。通过使用这些确定的过滤器和概念,我们的方法可以提供模型决策背后的对比和反事实原因,并使模型更加透明。该方法的有趣应用之一是误分类分析,我们比较特定输入图像中识别的概念并与特定类别的概念进行比较,以验证模型决策的合理性。该方法与当前先进技术进行了比较,并在Caltech-UCSD鸟类(CUB)2011数据集上进行了评估,以展示所提供解释的有用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习卷积神经网络(DCNN)的可解释性研究旨在揭示模型决策背后的原因,提高高风险环境下的理解和可靠性。为此,提出一种新型生成解释DCNN模型决策的可解释性方法,该方法采用模型侵入方式探查DCNN的内部工作方式,而不改变输入图像来生成解释。对于输入图像,通过识别代表特征和概念的DCNN中最重要过滤器来提供对比解释,这些特征和概念将模型对图像的分类与原始推断类别或其他特定替代类别区分开来。另一方面,通过指定这些过滤器所需的最小变化来提供反事实解释以获得对比输出。利用这些已识别的过滤器和概念,此方法提供了模型的决策背后的对比和反事实原因,使模型更加透明。该方法在Caltech-UCSD鸟类(CUB)数据集上进行了比较和评估,以展示所提供解释的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究重点:研究深度卷积神经网络(DCNN)的可解释性,以理解模型决策的机制和原理。
- 提出新型方法:开发了一种新颖的模型侵入性方法来解析DCNN模型的内部工作机制,提供了对模型决策的对比和反事实解释。
- 对比解释和反事实解释:对比解释通过识别区分模型决策的关键特征和概念来实现;反事实解释则通过确定过滤器所需的最小变化来获得对比输出。
- 应用领域:该技术在误分类分析中具有重要的应用潜力,可以通过对比特定输入图像的概念与类别特定概念来验证模型的决策有效性。
- 实验验证:在Caltech-UCSD鸟类数据集上对所提出的方法进行了评估,显示了所提供解释的有效性和实用性。
- 模型透明度提升:该方法增强了DCNN模型的透明度,使其决策过程更加易于理解和信任。
点此查看论文截图

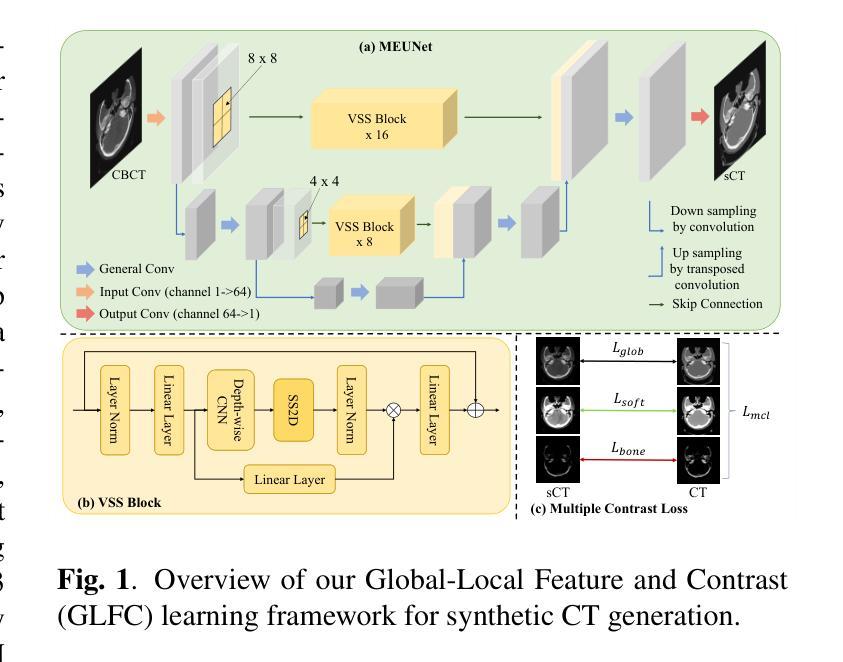
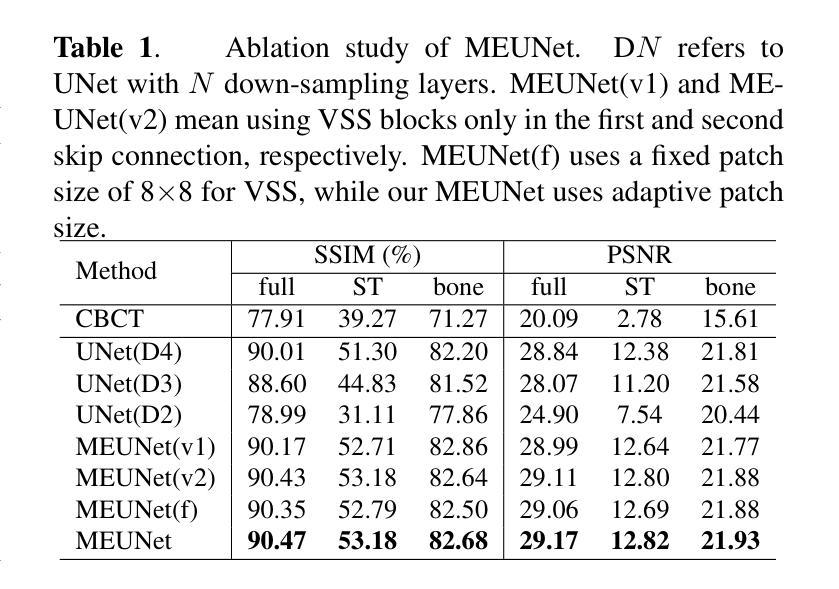
GLFC: Unified Global-Local Feature and Contrast Learning with Mamba-Enhanced UNet for Synthetic CT Generation from CBCT
Authors:Xianhao Zhou, Jianghao Wu, Huangxuan Zhao, Lei Chen, Shaoting Zhang, Guotai Wang
Generating synthetic Computed Tomography (CT) images from Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is desirable for improving the image quality of CBCT. Existing synthetic CT (sCT) generation methods using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Transformers often face difficulties in effectively capturing both global and local features and contrasts for high-quality sCT generation. In this work, we propose a Global-Local Feature and Contrast learning (GLFC) framework for sCT generation. First, a Mamba-Enhanced UNet (MEUNet) is introduced by integrating Mamba blocks into the skip connections of a high-resolution UNet for effective global and local feature learning. Second, we propose a Multiple Contrast Loss (MCL) that calculates synthetic loss at different intensity windows to improve quality for both soft tissues and bone regions. Experiments on the SynthRAD2023 dataset demonstrate that GLFC improved the SSIM of sCT from 77.91% to 91.50% compared with the original CBCT, and significantly outperformed several existing methods for sCT generation. The code is available at https://github.com/HiLab-git/GLFC
从锥束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)生成合成计算机断层扫描(CT)图像是提高CBCT图像质量的理想方法。现有使用卷积神经网络(CNN)和Transformer的合成CT(sCT)生成方法,在有效捕获全局和局部特征以及对比以实现高质量sCT生成方面经常面临困难。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于sCT生成的全球-局部特征和对比学习(GLFC)框架。首先,通过在高分辨率UNet的跳跃连接中集成Mamba块,引入了一种Mamba增强UNet(MEUNet),以实现有效的全局和局部特征学习。其次,我们提出了一种多对比度损失(MCL),该损失在不同的强度窗口上计算合成损失,以提高软组织和骨区域的图像质量。在SynthRAD2023数据集上的实验表明,与原始CBCT相比,GLFC将sCT的SSIM从77.91%提高到91.50%,并且在sCT生成方面显著优于几种现有方法。代码可用在:https://github.com/HiLab-git/GLFC。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ISBI2025
Summary
本摘要提出了一种基于全局-局部特征与对比度学习(GLFC)的框架,用于生成合成计算机断层扫描(sCT)图像。通过集成Mamba块到高分辨率UNet的跳过连接中,引入Mamba增强UNet(MEUNet)以有效学习全局和局部特征。同时,提出多重对比度损失(MCL),通过在不同强度窗口计算合成损失,提高软组织和骨区域的图像质量。在SynthRAD2023数据集上的实验表明,GLFC方法提高了sCT的SSIM指数,从77.91%提升至91.50%,显著优于其他现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的合成计算机断层扫描(sCT)图像生成方法——全局-局部特征与对比度学习(GLFC)框架。
- 通过集成Mamba块到UNet中,形成Mamba增强UNet(MEUNet),有效学习全局和局部特征。
- 引入了多重对比度损失(MCL),以提高软组织和骨区域的图像质量。
- 在SynthRAD2023数据集上的实验验证了GLFC方法的优越性,sCT图像的SSIM指数得到显著提升。
- 该方法显著优于其他现有方法,为改善CBCT图像质量提供了新的途径。
- 公开了代码,便于后续研究使用。
- 该方法有望应用于医学图像分析、诊断及治疗等领域。
点此查看论文截图

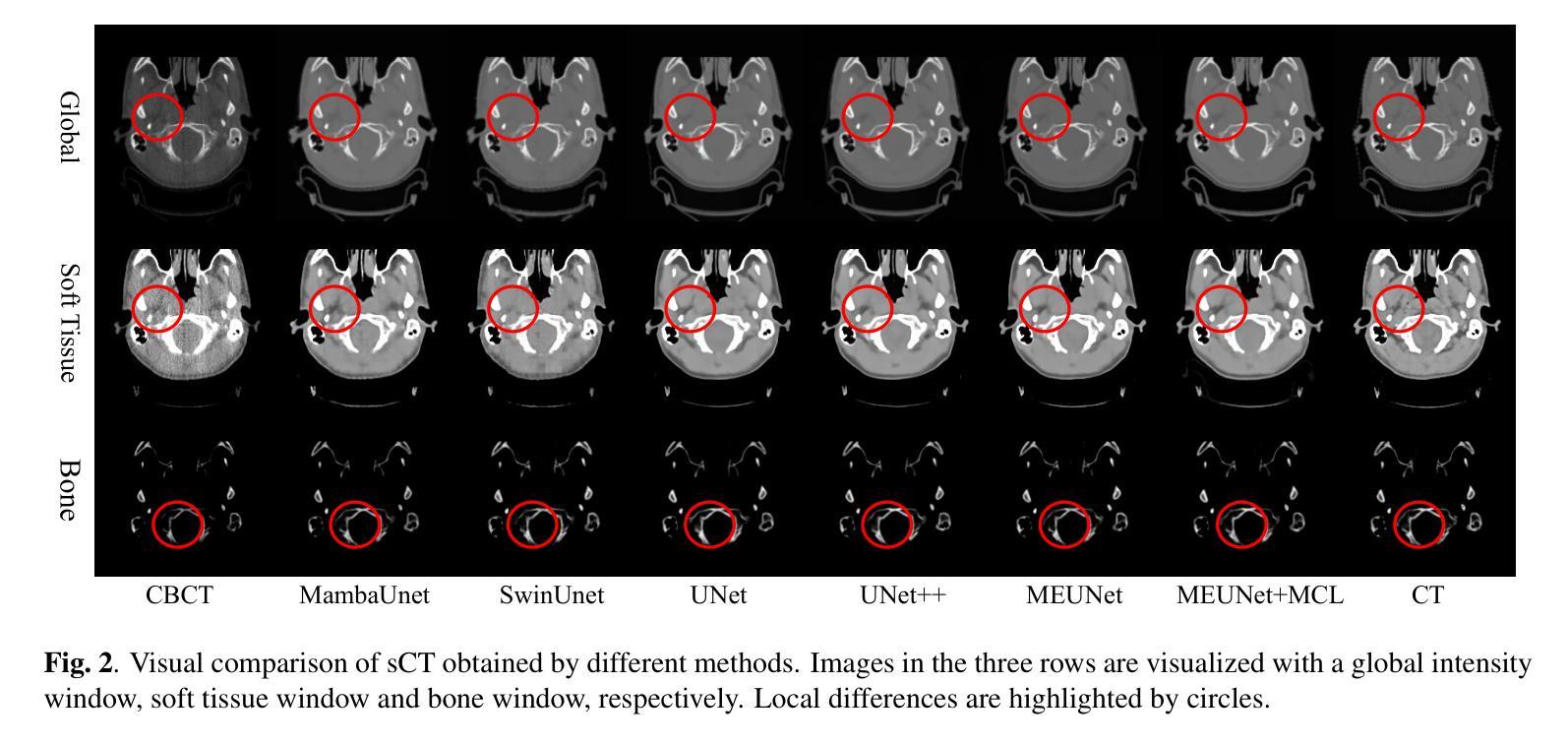

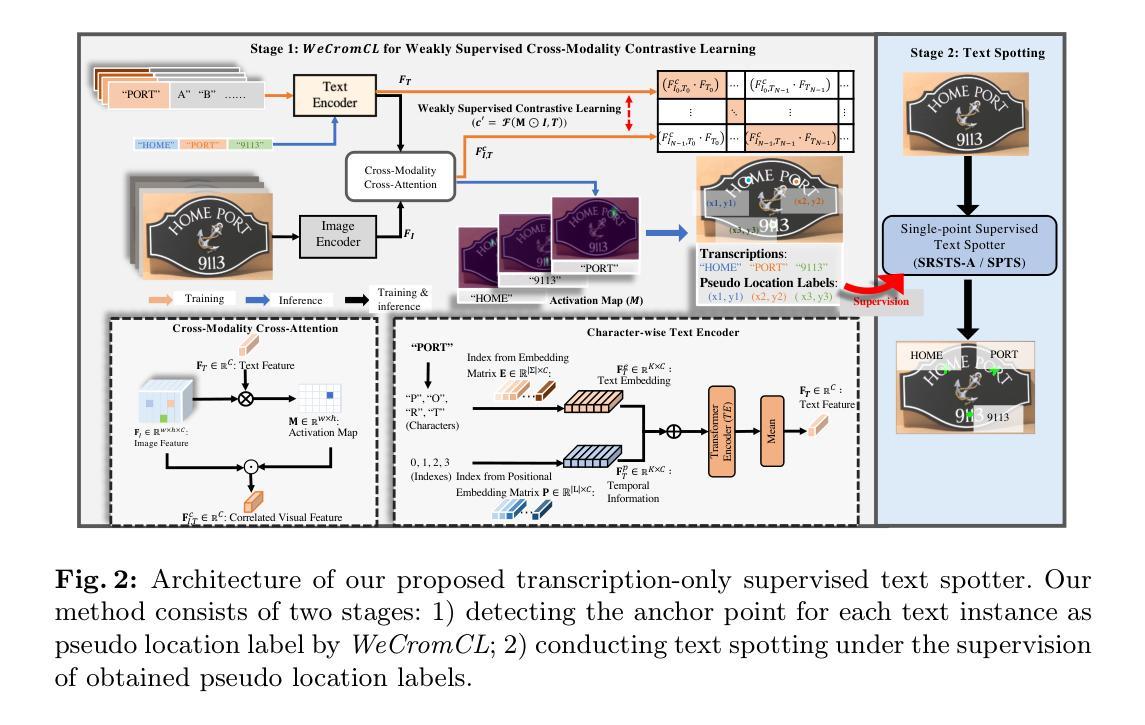
WeCromCL: Weakly Supervised Cross-Modality Contrastive Learning for Transcription-only Supervised Text Spotting
Authors:Jingjing Wu, Zhengyao Fang, Pengyuan Lyu, Chengquan Zhang, Fanglin Chen, Guangming Lu, Wenjie Pei
Transcription-only Supervised Text Spotting aims to learn text spotters relying only on transcriptions but no text boundaries for supervision, thus eliminating expensive boundary annotation. The crux of this task lies in locating each transcription in scene text images without location annotations. In this work, we formulate this challenging problem as a Weakly Supervised Cross-modality Contrastive Learning problem, and design a simple yet effective model dubbed WeCromCL that is able to detect each transcription in a scene image in a weakly supervised manner. Unlike typical methods for cross-modality contrastive learning that focus on modeling the holistic semantic correlation between an entire image and a text description, our WeCromCL conducts atomistic contrastive learning to model the character-wise appearance consistency between a text transcription and its correlated region in a scene image to detect an anchor point for the transcription in a weakly supervised manner. The detected anchor points by WeCromCL are further used as pseudo location labels to guide the learning of text spotting. Extensive experiments on four challenging benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance of our model over other methods. Code will be released.
仅转录监督文本点识别旨在仅依靠转录学习文本识别器,而无需文本边界进行监管,从而消除了昂贵的边界注释。这项任务的关键在于在没有位置注释的场景文本图像中找到每个转录。在这项工作中,我们将这个具有挑战性的问题制定为弱监督跨模态对比学习问题,并设计了一个简单有效的模型,称为WeCromCL,该模型能够以弱监督的方式在场景图像中检测每个转录。与典型的跨模态对比学习方法不同,这些方法侧重于建模整个图像和文本描述之间的整体语义相关性,我们的WeCromCL进行原子对比学习,以建模文本转录与其在场景图像中的相关区域之间的字符级外观一致性,以弱监督的方式检测转录的锚点。WeCromCL检测到的锚点进一步作为伪位置标签,用于指导文本识别的学习。在四个具有挑战性的基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的模型优于其他方法。代码将发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ECCV 2024
Summary
文本提出了一种仅依赖转录进行文本识别的方法,无需文本边界进行标注。该方法的核心在于在没有位置标注的情况下,在场景文本图像中定位每个转录。为此,该任务被归纳为弱监督跨模态对比学习问题,并提出了一种简单有效的模型WeCromCL。与传统的图像和文本描述的跨模态对比学习不同,WeCromCL模型字符级别的外观一致性来检测转录中的锚点。这些锚点进一步作为伪位置标签来指导文本识别的学习。在四个具有挑战性的基准测试上进行的实验证明了该模型的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 该方法旨在通过仅依赖转录进行文本识别,无需昂贵的边界标注。
- 核心在于在没有位置标注的场景文本图像中定位每个转录。
- 将此任务归纳为弱监督跨模态对比学习问题。
- 提出了一种简单有效的模型WeCromCL进行弱监督检测。
- WeCromCL模型通过字符级别的外观一致性来检测转录中的锚点。
- 检测到的锚点作为伪位置标签来指导文本识别的学习。
点此查看论文截图

XVertNet: Unsupervised Contrast Enhancement of Vertebral Structures with Dynamic Self-Tuning Guidance and Multi-Stage Analysis
Authors:Ella Eidlin, Assaf Hoogi, Hila Rozen, Mohammad Badarne, Nathan S. Netanyahu
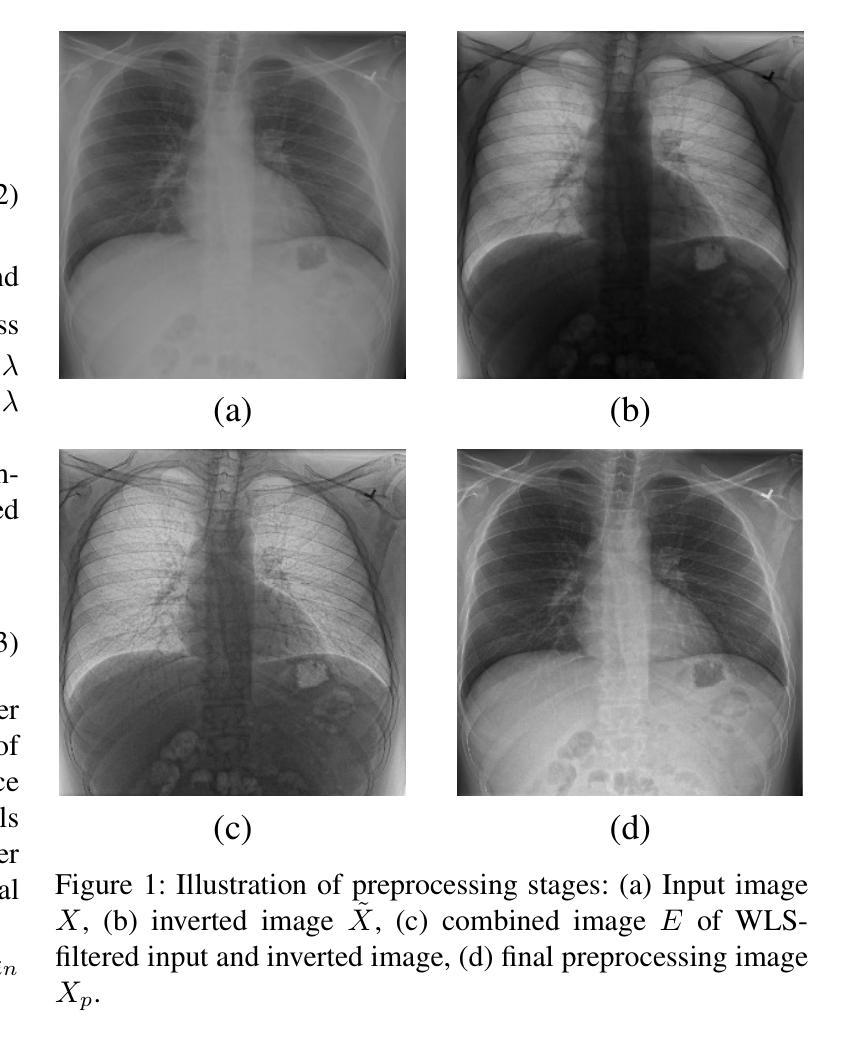
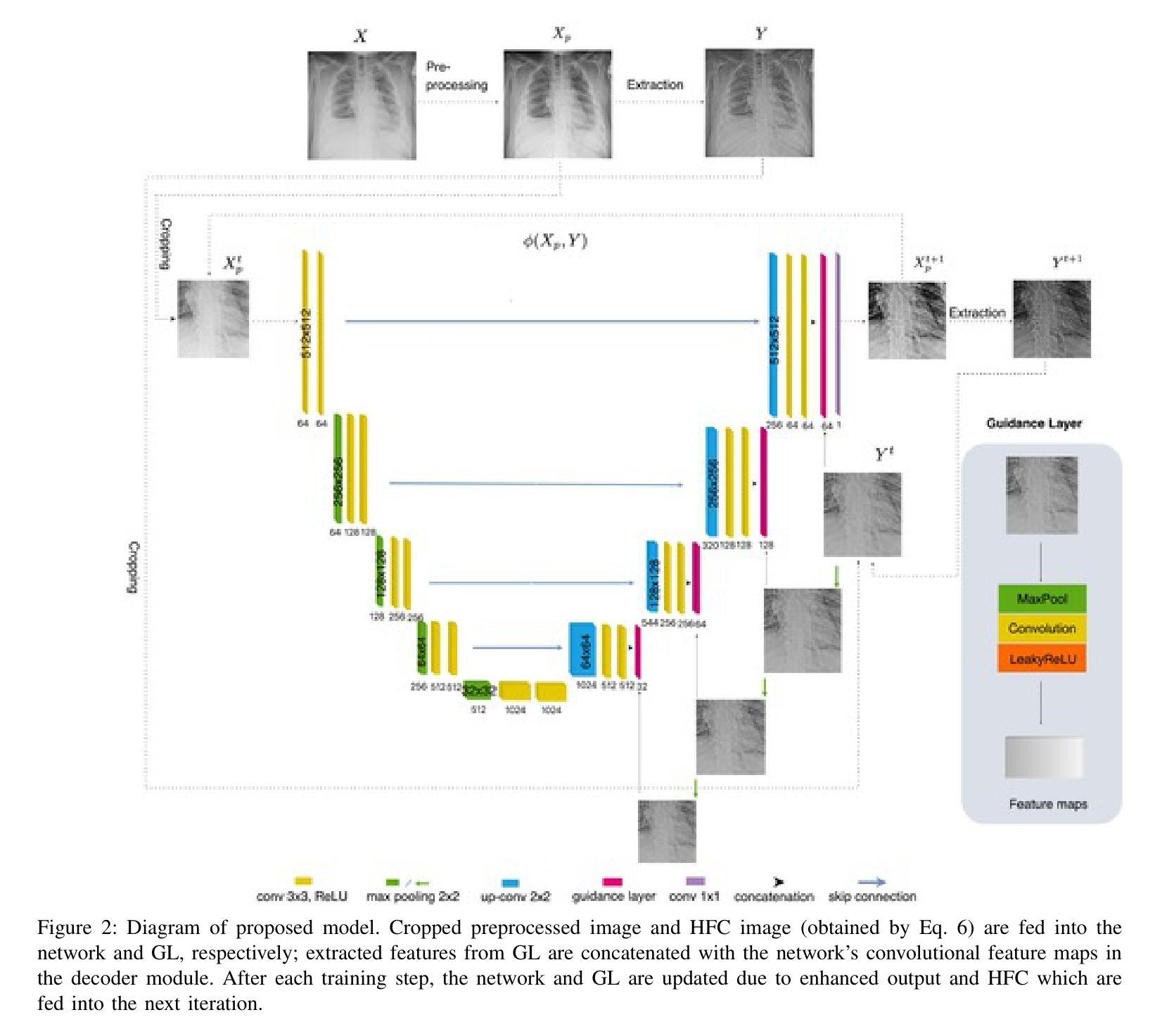
Chest X-rays remain the primary diagnostic tool in emergency medicine, yet their limited ability to capture fine anatomical details can result in missed or delayed diagnoses. To address this, we introduce XVertNet, a novel deep-learning framework designed to enhance vertebral structure visualization in X-ray images significantly. Our framework introduces two key innovations: (1) An unsupervised learning architecture that eliminates reliance on manually labeled training data a persistent bottleneck in medical imaging, and (2) a dynamic self-tuned internal guidance mechanism featuring an adaptive feedback loop for real-time image optimization. Extensive validation across four major public datasets revealed that XVertNet outperforms state-of-the-art enhancement methods, as demonstrated by improvements in entropy scores, Tenengrad criterion values, the local phase coherence sharpness index (LPC-SI), and thetone mapped image quality index (TMQI). Furthermore, clinical validation conducted with two board-certified radiologists confirmed that the enhanced images enabled more sensitive detection of subtle vertebral fractures and degenerative changes. The unsupervised nature of XVertNet facilitates immediate clinical deployment without requiring additional training overhead. This innovation represents a transformative advancement in emergency radiology, providing a scalable and time-efficient solution to enhance diagnostic accuracy in high-pressure clinical environments.
胸部X光片仍然是急诊医学中的主要诊断工具,然而,其捕捉精细解剖结构的能力有限,可能导致诊断遗漏或延迟。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了XVertNet,这是一个新的深度学习框架,旨在显著提高X光片中椎骨结构的可视化效果。我们的框架引入了两个关键的创新点:(1)一种无需监督的学习架构,消除了对手动标记训练数据的依赖,这是医学影像中的一个持续瓶颈;(2)一种动态自调整的内部引导机制,具有自适应反馈循环,用于实时图像优化。在四个主要公共数据集上的广泛验证表明,XVertNet优于最新增强方法,体现在熵分数、Tenengrad准则值、局部相位相干度锐度指数(LPC-SI)和色调映射图像质量指数(TMQI)的改进上。此外,由两位认证放射科医生进行的临床验证证实,增强图像能够更敏感地检测到细微的椎体骨折和退行性变化。XVertNet的无监督性质促进了其立即在临床中部署,而无需额外的训练开销。这项创新代表了急诊放射学中的一项突破性进展,为高压临床环境中提高诊断准确性提供了可伸缩和时间效率高的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages
Summary
XVertNet是一种新型的深度学习框架,旨在提高X光片中椎体结构的可视化效果。它引入了两个关键创新点:一是采用无监督学习架构,消除了对手动标注训练数据的依赖;二是具备动态自我调整的内部引导机制,具有自适应反馈回路,用于实时图像优化。该框架在多个公共数据集上的表现均超越了现有增强方法,经临床验证可有效提高诊断准确性。
Key Takeaways
- XVertNet是一种深度学习框架,旨在提高X光片中椎体结构的可视化。
- 引入无监督学习架构,减少对手动标注训练数据的依赖。
- 具备动态自我调整的内部引导机制,具有自适应反馈回路,实现实时图像优化。
- 在多个公共数据集上的表现优于其他增强方法。
- 通过熵分数、Tenengrad标准值、局部相位相干锐度指数(LPC-SI)和色调映射图像质量指数(TMQI)等指标评估性能。
- 临床验证显示,该框架能提高对细微椎体骨折和退行性变化的检测敏感性。
点此查看论文截图