⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-17 更新
CityLoc: 6 DoF Localization of Text Descriptions in Large-Scale Scenes with Gaussian Representation
Authors:Qi Ma, Runyi Yang, Bin Ren, Ender Konukoglu, Luc Van Gool, Danda Pani Paudel
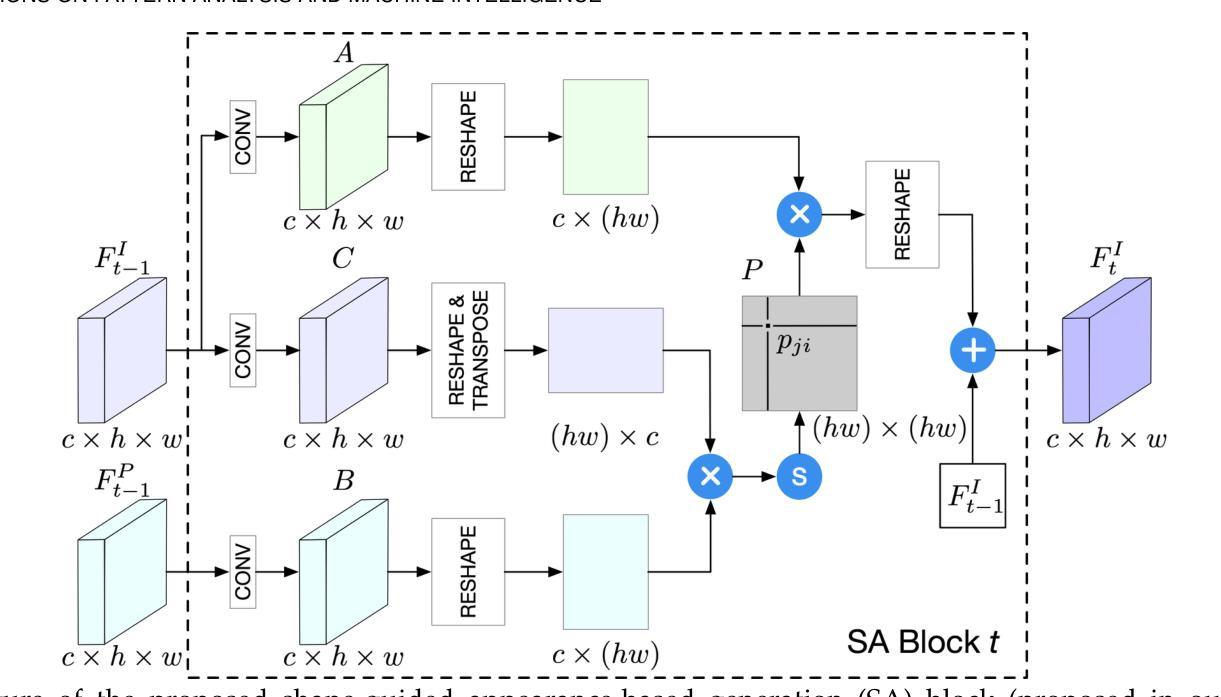
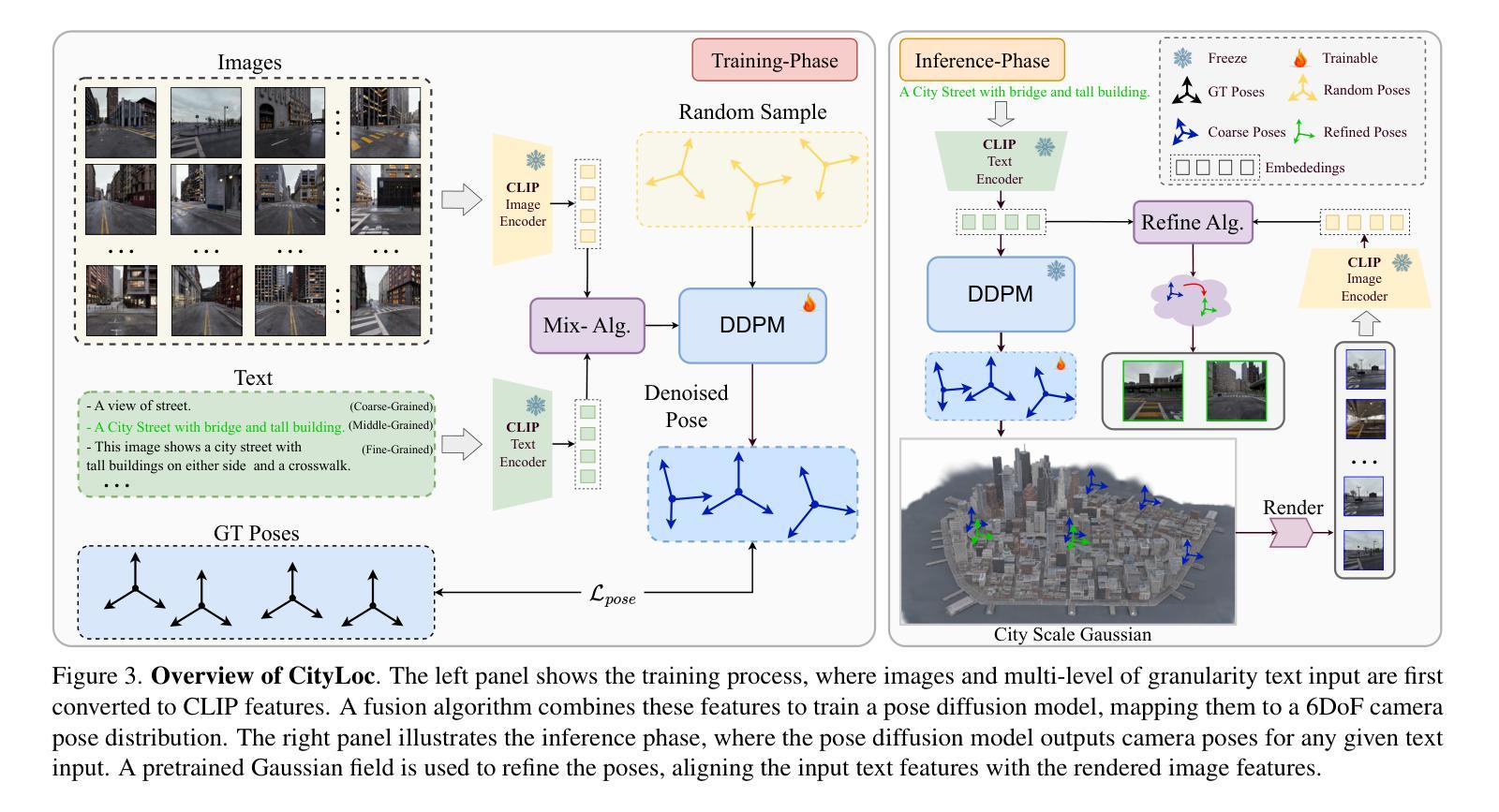
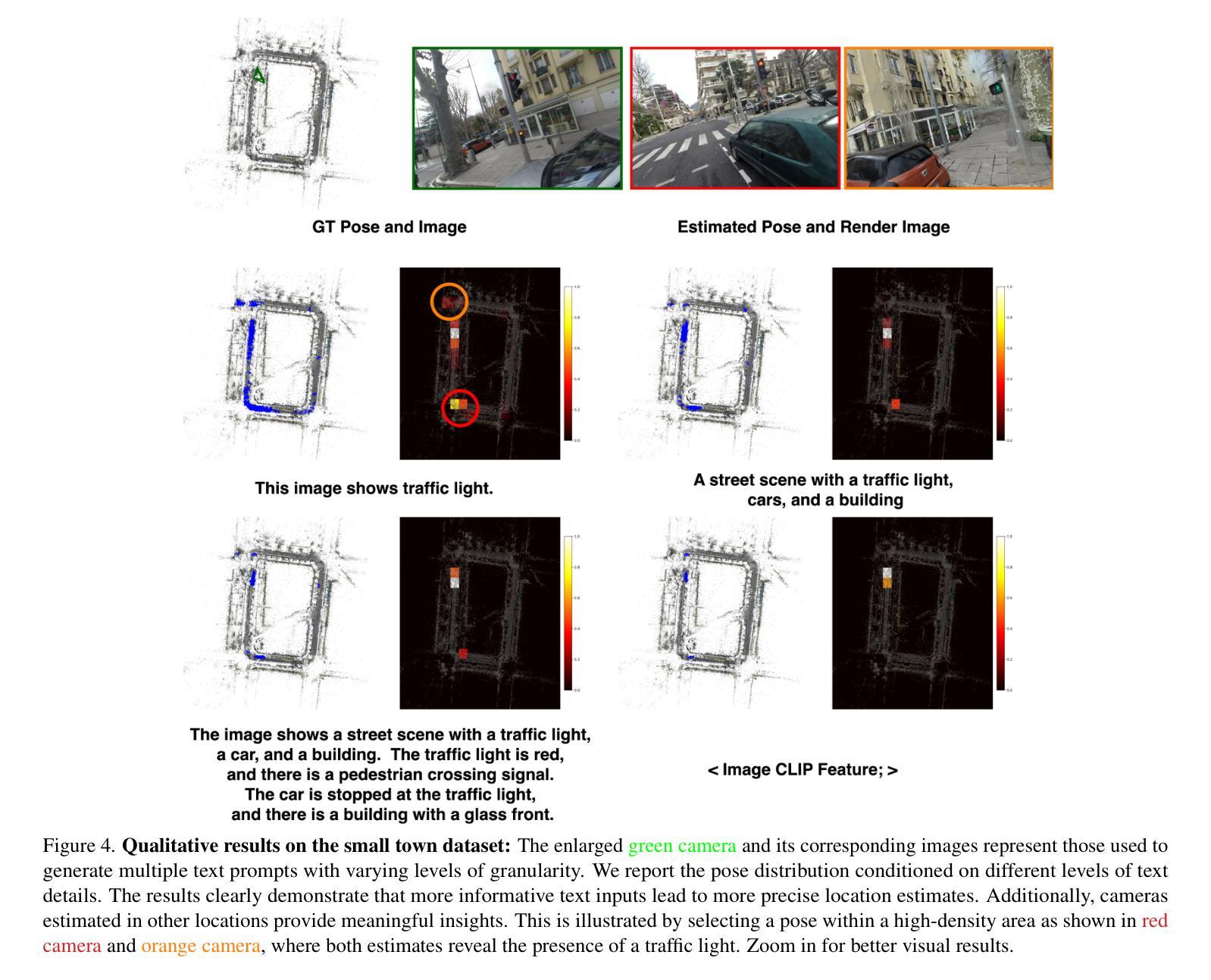
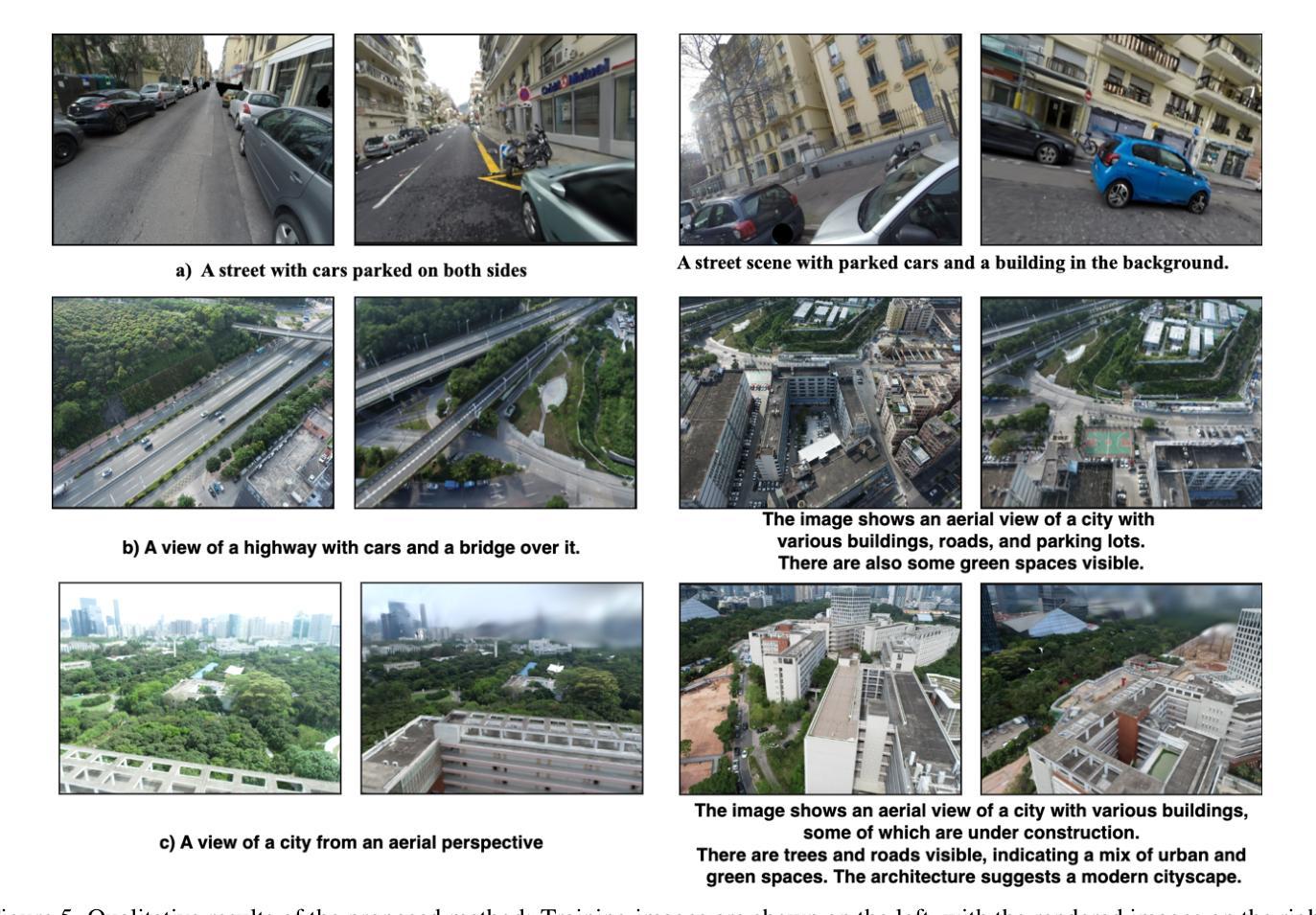
Localizing text descriptions in large-scale 3D scenes is inherently an ambiguous task. This nonetheless arises while describing general concepts, e.g. all traffic lights in a city. To facilitate reasoning based on such concepts, text localization in the form of distribution is required. In this paper, we generate the distribution of the camera poses conditioned upon the textual description. To facilitate such generation, we propose a diffusion-based architecture that conditionally diffuses the noisy 6DoF camera poses to their plausible locations. The conditional signals are derived from the text descriptions, using the pre-trained text encoders. The connection between text descriptions and pose distribution is established through pretrained Vision-Language-Model, i.e. CLIP. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the candidate poses for the distribution can be further refined by rendering potential poses using 3D Gaussian splatting, guiding incorrectly posed samples towards locations that better align with the textual description, through visual reasoning. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method by comparing it with both standard retrieval methods and learning-based approaches. Our proposed method consistently outperforms these baselines across all five large-scale datasets. Our source code and dataset will be made publicly available.
文本描述定位在大型3D场景中的任务本质上是具有模糊性的。尽管如此,在描述一般概念(例如城市中的所有交通灯)时仍会出现这种情况。为了基于此类概念进行推理,需要以分布形式进行文本定位。在本文中,我们根据文本描述生成相机姿态的分布。为了促进这种生成,我们提出了一种基于扩散的架构,该架构将噪声6DoF相机姿态扩散到其可能的位置。条件信号来源于文本描述,并使用预训练的文本编码器进行推导。通过预训练的视觉语言模型(即CLIP)建立文本描述与姿态分布之间的联系。此外,我们通过使用3D高斯贴图渲染潜在姿态来进一步细化分布的候选姿态,通过视觉推理引导错误定位的样本朝向与文本描述更匹配的地点。我们通过将其与标准检索方法和基于学习的方法进行比较,证明了我们的方法的有效性。我们的方法在所有五个大型数据集上均优于这些基线方法。我们的源代码和数据集将公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本描述在大规模3D场景中的定位是一个具有固有模糊性的任务。本文生成了基于文本描述的相机姿态分布,并提出了一种基于扩散的架构,该架构将噪声6DoF相机姿态扩散到其可能的位置。条件信号来源于文本描述,并使用预训练的文本编码器进行推导。通过预训练的视觉语言模型CLIP建立了文本描述与姿态分布之间的联系。此外,通过3D高斯喷涂技术渲染潜在姿态,对分布候选姿态进行进一步优化,通过视觉推理引导错误姿态样本向与文本描述更匹配的地点靠近。通过与传统检索方法和基于学习的方法进行比较,本文提出的方法在五个大规模数据集上均表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 文本描述在3D场景中的定位是一个模糊的任务,需要基于概念进行推理。
- 相机姿态分布生成是文本定位的核心部分。
- 提出了一种基于扩散的架构来扩散噪声相机姿态到可能的位置。
- 条件信号来源于文本描述,并使用预训练的文本编码器进行处理。
- 通过预训练的视觉语言模型CLIP建立文本描述与姿态分布之间的联系。
- 使用3D高斯喷涂技术优化候选姿态,通过视觉推理引导错误姿态样本向正确方向靠近。
点此查看论文截图


3D Gaussian Splatting with Normal Information for Mesh Extraction and Improved Rendering
Authors:Meenakshi Krishnan, Liam Fowl, Ramani Duraiswami
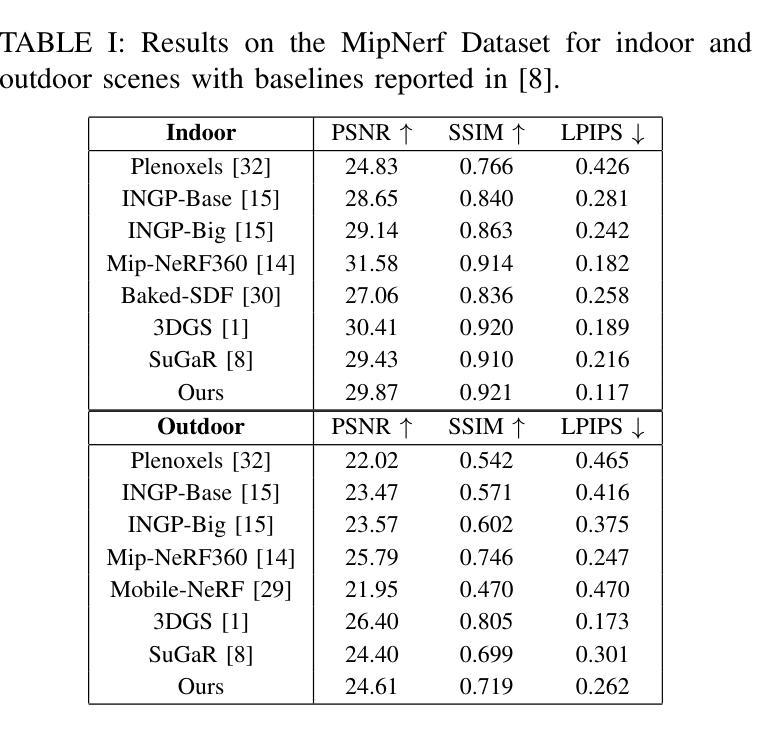
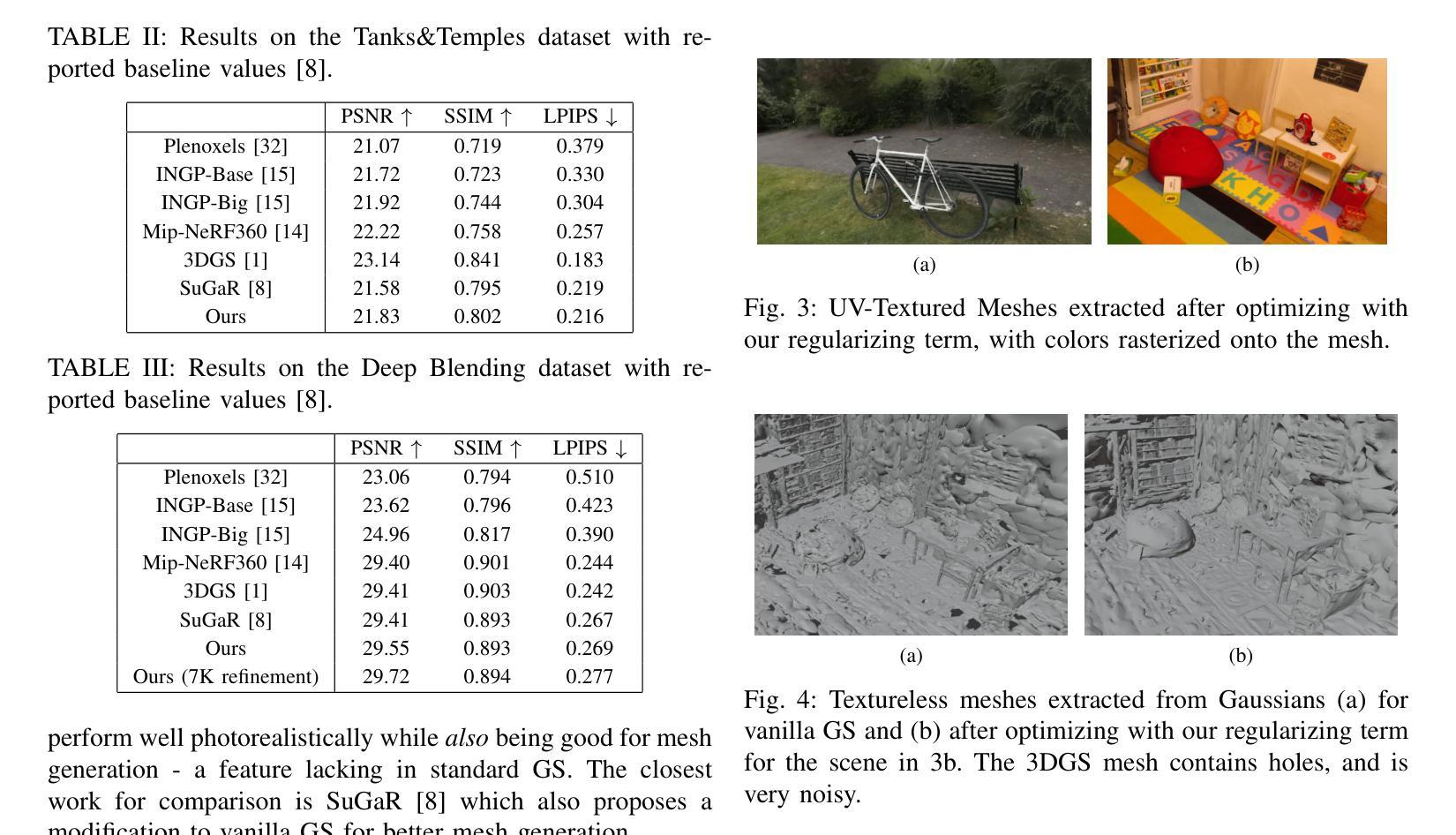
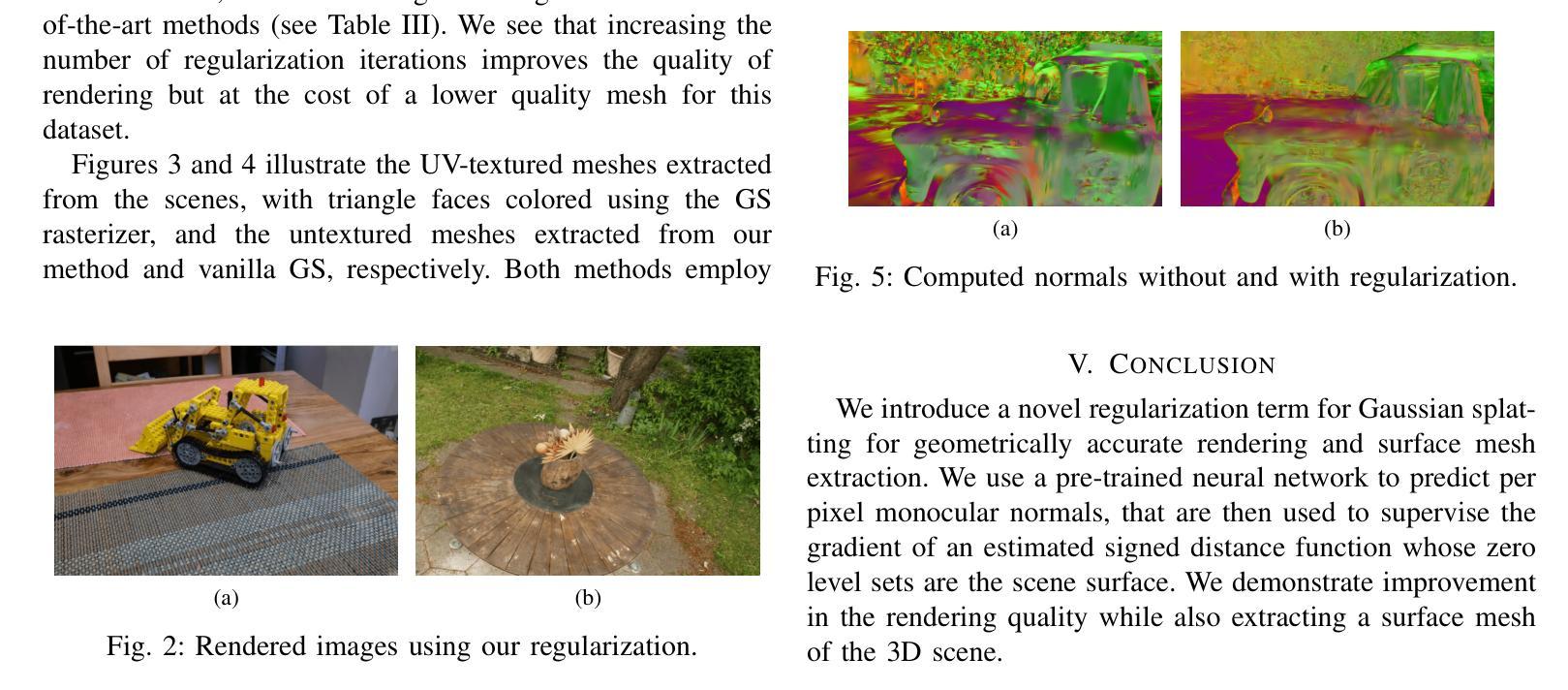
Differentiable 3D Gaussian splatting has emerged as an efficient and flexible rendering technique for representing complex scenes from a collection of 2D views and enabling high-quality real-time novel-view synthesis. However, its reliance on photometric losses can lead to imprecisely reconstructed geometry and extracted meshes, especially in regions with high curvature or fine detail. We propose a novel regularization method using the gradients of a signed distance function estimated from the Gaussians, to improve the quality of rendering while also extracting a surface mesh. The regularizing normal supervision facilitates better rendering and mesh reconstruction, which is crucial for downstream applications in video generation, animation, AR-VR and gaming. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on datasets such as Mip-NeRF360, Tanks and Temples, and Deep-Blending. Our method scores higher on photorealism metrics compared to other mesh extracting rendering methods without compromising mesh quality.
可微分的三维高斯融合技术已成为一种高效且灵活的可视化技术,能够从多个二维视角中展示复杂的场景,并实现高质量实时新视角合成。然而,它依赖于光度损失,可能导致重建的几何形状和提取的网格不准确,特别是在高曲率或精细细节的区域。我们提出了一种新的正则化方法,利用从高斯估计的符号距离函数的梯度来提高渲染质量,同时提取表面网格。正则化的法线监督有助于更好的渲染和网格重建,这对于下游应用如视频生成、动画、增强现实虚拟现实和游戏至关重要。我们在Mip-NeRF360、坦克与寺庙以及深度融合等数据集上展示了我们的方法的有效性。与其他网格提取渲染方法相比,我们的方法在照片逼真度指标上得分更高,且不影响网格质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2025: Workshop on Generative Data Augmentation for Real-World Signal Processing Applications
摘要
高效灵活的差分渲染技术可以支持从多个二维视角呈现复杂场景并实现高质量实时新视角合成。然而,其对光度损失的依赖可能导致重建几何和提取网格的不精确,特别是在高曲率或精细细节区域。本文提出一种使用基于高斯估计的符号距离函数梯度的新型正则化方法,以提高渲染质量并提取表面网格。正则化法向监督有助于更好的渲染和网格重建,对于下游的视频生成、动画、增强现实虚拟现实和游戏应用至关重要。我们在Mip-NeRF360、Tanks和Temples以及Deep-Blending等数据集中验证了方法的有效性。相较于其他网格提取渲染方法,本方法具有更高的逼真度得分,且未对网格质量造成影响。
关键见解
- 可微分的三维高斯映射已成为一种高效的渲染技术,可以从多个二维视角呈现复杂场景并支持高质量实时新视角合成。
- 基于光度损失的依赖可能导致重建几何和提取网格的不精确问题,特别是在具有高曲率或精细细节的区域中尤为明显。
- 提出了一种新的正则化方法,该方法使用基于高斯估计的符号距离函数梯度来改善渲染质量并优化网格提取。
- 正则化法向监督有助于提高渲染和网格重建的质量,对于视频生成、动画、增强现实虚拟现实和游戏等下游应用至关重要。
- 方法在多种数据集上进行了验证,包括Mip-NeRF360、Tanks and Temples以及Deep-Blending等。
- 与其他网格提取渲染方法相比,该方法在逼真度得分上表现更佳,同时并未影响网格质量。
点此查看论文截图


SplatMAP: Online Dense Monocular SLAM with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yue Hu, Rong Liu, Meida Chen, Peter Beerel, Andrew Feng
Achieving high-fidelity 3D reconstruction from monocular video remains challenging due to the inherent limitations of traditional methods like Structure-from-Motion (SfM) and monocular SLAM in accurately capturing scene details. While differentiable rendering techniques such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) address some of these challenges, their high computational costs make them unsuitable for real-time applications. Additionally, existing 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) methods often focus on photometric consistency, neglecting geometric accuracy and failing to exploit SLAM’s dynamic depth and pose updates for scene refinement. We propose a framework integrating dense SLAM with 3DGS for real-time, high-fidelity dense reconstruction. Our approach introduces SLAM-Informed Adaptive Densification, which dynamically updates and densifies the Gaussian model by leveraging dense point clouds from SLAM. Additionally, we incorporate Geometry-Guided Optimization, which combines edge-aware geometric constraints and photometric consistency to jointly optimize the appearance and geometry of the 3DGS scene representation, enabling detailed and accurate SLAM mapping reconstruction. Experiments on the Replica and TUM-RGBD datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving state-of-the-art results among monocular systems. Specifically, our method achieves a PSNR of 36.864, SSIM of 0.985, and LPIPS of 0.040 on Replica, representing improvements of 10.7%, 6.4%, and 49.4%, respectively, over the previous SOTA. On TUM-RGBD, our method outperforms the closest baseline by 10.2%, 6.6%, and 34.7% in the same metrics. These results highlight the potential of our framework in bridging the gap between photometric and geometric dense 3D scene representations, paving the way for practical and efficient monocular dense reconstruction.
从单目视频中实现高保真3D重建仍然是一个挑战,这主要是由于传统方法(如结构从运动(SfM)和单目SLAM)在准确捕捉场景细节方面的固有局限性。虽然像神经辐射场(NeRF)这样的可微分渲染技术解决了一些这些挑战,但它们的高计算成本使它们不适合实时应用。此外,现有的3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)方法通常侧重于光度一致性,忽略了几何精度,并且未能利用SLAM的动态深度和姿态更新来进行场景细化。我们提出了一个整合密集SLAM与3DGS的框架,用于实时高保真密集重建。我们的方法引入了SLAM信息自适应密集化,利用SLAM的密集点云来动态更新和密集化高斯模型。此外,我们结合了几何引导优化,它结合了边缘感知几何约束和光度一致性,以联合优化3DGS场景表示的外观和几何形状,从而实现详细而准确的SLAM映射重建。在Replica和TUM-RGBD数据集上的实验证明了我们的方法的有效性,在单目系统中达到了最新水平的结果。具体来说,我们的方法在Replica上的峰值信噪比(PSNR)达到36.864,结构相似性(SSIM)达到0.985,学习感知图像空间相似性度量(LPIPS)为0.040,分别比先前的最佳技术水平提高了10.7%,6.4%和49.4%。在TUM-RGBD上,我们的方法在相同的指标上比最接近的基线高出10.2%,6.6%和34.7%。这些结果突显了我们框架在连接光度表示和几何密集3D场景表示方面的潜力,为实用和高效的单目密集重建铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个融合密集SLAM与3DGS的方法,旨在实现实时高保真密集重建。方法引入了SLAM信息自适应精细化技术,通过利用SLAM的密集点云动态更新和精细化高斯模型,并结合几何引导优化技术,联合优化场景表示的几何和外观,实现详细的精确SLAM映射重建。在Replica和TUM-RGBD数据集上的实验证明了该方法的有效性,相较于其他单目系统,达到了先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- 传统方法如SfM和单目SLAM在捕捉场景细节时存在局限性。
- 可微渲染技术如NeRF虽能解决部分挑战,但计算成本高,不适合实时应用。
- 现有3DGS方法常侧重于光度一致性,忽视几何精度,未能利用SLAM的动态深度和姿态更新进行场景优化。
- 提出融合密集SLAM与3DGS的框架,实现实时高保真密集重建。
- 引入SLAM信息自适应精细化技术,利用SLAM的密集点云动态更新和精细化高斯模型。
- 结合几何引导优化技术,联合优化场景表示的几何和外观。
- 在Replica和TUM-RGBD数据集上的实验表现优异,相较于其他单目系统达到先进水平。
点此查看论文截图



RF-3DGS: Wireless Channel Modeling with Radio Radiance Field and 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Lihao Zhang, Haijian Sun, Samuel Berweger, Camillo Gentile, Rose Qingyang Hu
Precisely modeling radio propagation in complex environments has been a significant challenge, especially with the advent of 5G and beyond networks, where managing massive antenna arrays demands more detailed information. Traditional methods, such as empirical models and ray tracing, often fall short, either due to insufficient details or because of challenges for real-time applications. Inspired by the newly proposed 3D Gaussian Splatting method in the computer vision domain, which outperforms other methods in reconstructing optical radiance fields, we propose RF-3DGS, a novel approach that enables precise site-specific reconstruction of radio radiance fields from sparse samples. RF-3DGS can render radio spatial spectra at arbitrary positions within 2 ms following a brief 3-minute training period, effectively identifying dominant propagation paths. Furthermore, RF-3DGS can provide fine-grained Spatial Channel State Information (Spatial-CSI) of these paths, including the channel gain, the delay, the angle of arrival (AoA), and the angle of departure (AoD). Our experiments, calibrated through real-world measurements, demonstrate that RF-3DGS not only significantly improves reconstruction quality, training efficiency, and rendering speed compared to state-of-the-art methods, but also holds great potential for supporting wireless communication and advanced applications such as Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC). Code and dataset will be available at https://github.com/SunLab-UGA/RF-3DGS.
对复杂环境中的无线电传播进行精确建模一直是一个巨大的挑战,尤其是随着5G及以后网络的出现,管理大规模天线阵列需要更详细的信息。传统的方法,如经验模型和射线追踪,通常因为细节不足或实时应用中的挑战而表现不佳。我们受到计算机视觉领域新提出的3D高斯Splatting方法的启发,该方法在重建光学辐射场方面表现出比其他方法更好的性能,因此我们提出了RF-3DGS,这是一种能够从稀疏样本中进行精确的现场特定无线电辐射场重建的新方法。RF-3DGS可以在短暂的3分钟训练期后,在2毫秒内渲染任意位置的无线电频谱,有效地识别主要的传播路径。此外,RF-3DGS还可以提供这些路径的精细空间信道状态信息(Spatial-CSI),包括信道增益、延迟、到达角(AoA)和离开角(AoD)。我们的实验通过真实世界的测量进行了校准,证明RF-3DGS不仅显著提高了重建质量、训练效率和渲染速度,与最先进的方法相比,还大力支持无线通信和集成传感与通信(ISAC)等高级应用。代码和数据集将在https://github.com/SunLab-UGA/RF-3DGS上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF in submission to IEEE journals
Summary
针对复杂环境中的电波传播精确建模一直是重大挑战,尤其随着5G及以后网络的发展,管理大规模天线阵列需要更详细的信息。受计算机视觉领域新提出的3D高斯喷绘方法启发,该方法在重建光学辐射场方面优于其他方法,我们提出RF-3DGS,一种能从稀疏样本中精确重建特定站点的无线电辐射场的新方法。RF-3DGS可在短暂的3分钟训练后,在2毫秒内渲染任意位置的无线电频谱,有效识别主要的传播路径。此外,RF-3DGS还能提供这些路径的精细空间信道状态信息(Spatial-CSI),包括信道增益、延迟、到达角(AoA)和离开角(AoD)。经过真实世界测量的校准实验表明,RF-3DGS不仅显著提高了重建质量、训练效率和渲染速度,与最新方法相比,还大力支持无线通信和集成传感与通信(ISAC)等高级应用。
Key Takeaways
- RF-3DGS是一种利用3D高斯喷绘方法灵感,针对无线电辐射场的精确建模的新方法。
- RF-3DGS能够从稀疏样本中重建特定站点的无线电辐射场。
- RF-3DGS能迅速渲染无线电频谱,提供实时的电波传播路径信息。
- RF-3DGS提供精细的空间信道状态信息(Spatial-CSI),包括信道增益、延迟和角度等关键参数。
- 与现有方法相比,RF-3DGS在重建质量、训练效率和渲染速度方面表现出显著优势。
- RF-3DGS具有广泛的应用前景,可支持无线通信和集成传感与通信(ISAC)等高级应用。
点此查看论文截图