⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-18 更新
Efficient Few-Shot Medical Image Analysis via Hierarchical Contrastive Vision-Language Learning
Authors:Harrison Fuller, Fernando Gabriela Garcia, Victor Flores
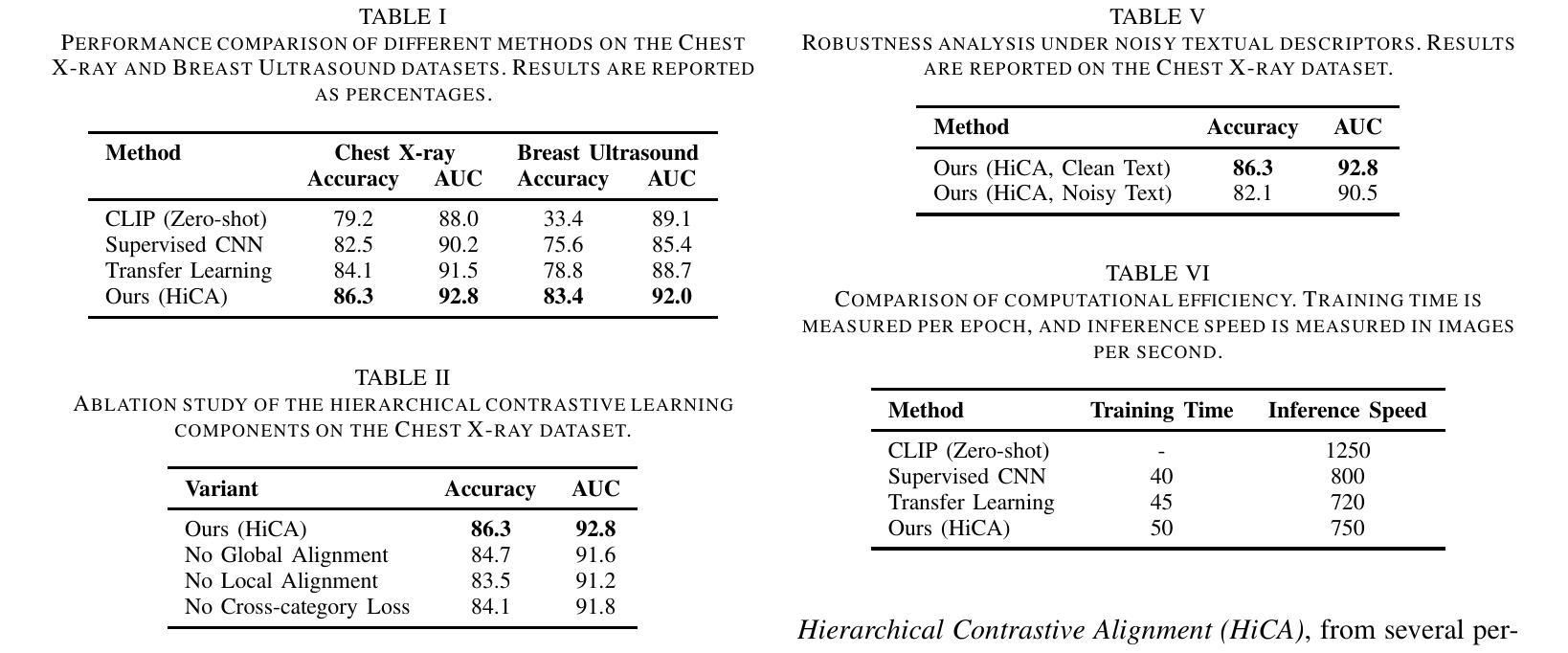
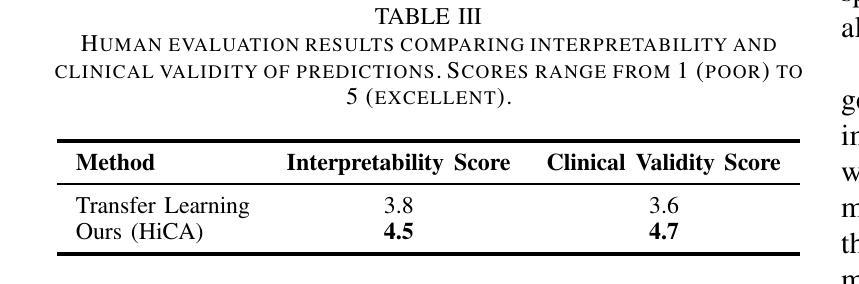
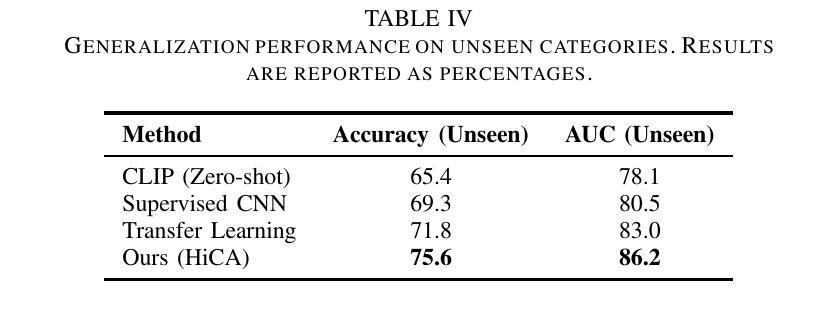
Few-shot learning in medical image classification presents a significant challenge due to the limited availability of annotated data and the complex nature of medical imagery. In this work, we propose Adaptive Vision-Language Fine-tuning with Hierarchical Contrastive Alignment (HiCA), a novel framework that leverages the capabilities of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) for medical image analysis. HiCA introduces a two-stage fine-tuning strategy, combining domain-specific pretraining and hierarchical contrastive learning to align visual and textual representations at multiple levels. We evaluate our approach on two benchmark datasets, Chest X-ray and Breast Ultrasound, achieving state-of-the-art performance in both few-shot and zero-shot settings. Further analyses demonstrate the robustness, generalizability, and interpretability of our method, with substantial improvements in performance compared to existing baselines. Our work highlights the potential of hierarchical contrastive strategies in adapting LVLMs to the unique challenges of medical imaging tasks.
医疗图像分类中的小样本学习由于标注数据的有限性和医疗图像本身的复杂性,面临巨大挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了自适应视觉语言微调与分层对比对齐(HiCA)的新框架,该框架利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)进行医学图像分析。HiCA引入了两阶段微调策略,结合领域特定预训练和分层对比学习,在多个级别上对齐视觉和文本表示。我们在Chest X光片和乳腺超声两个基准数据集上评估了我们的方法,在少量样本和零样本设置中均达到了最先进的性能。进一步的分析表明,我们的方法在稳健性、通用性和可解释性方面都有出色的表现,相较于现有的基线有大幅的性能提升。我们的工作突出了分层对比策略在适应医疗成像任务的独特挑战时LVLMs的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在医疗图像分类的few-shot学习中,由于标注数据的有限性和医学图像本身的复杂性,构成了一项重大挑战。本研究提出一种新型框架——自适应视觉语言精细调整与分层对比对齐(HiCA),利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)进行医学图像分析。HiCA引入两阶段精细调整策略,结合领域特定预训练和分层对比学习,在多个层次上对齐视觉和文本表示。我们在Chest X-ray和Breast Ultrasound两个基准数据集上评估了我们的方法,在少样本和无样本设置下均达到了最先进的性能。进一步的分析表明,我们的方法在稳健性、通用性和可解释性方面表现出色,与现有基线相比,性能得到了显著提高。我们的研究突出了分层对比策略在适应医疗成像任务的独特挑战中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分类的few-shot学习面临挑战,因为标注数据有限且医学图像复杂。
- 提出了一种新型框架Adaptive Vision-Language Fine-tuning with Hierarchical Contrastive Alignment (HiCA)。
- HiCA利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)进行医学图像分析。
- HiCA采用两阶段精细调整策略,结合领域特定预训练和分层对比学习。
- 在Chest X-ray和Breast Ultrasound数据集上评估,少样本和无样本设置下均表现优异。
- 分析显示,该方法在稳健性、通用性和可解释性方面表现出色。
点此查看论文截图

Benchmarking Robustness of Contrastive Learning Models for Medical Image-Report Retrieval
Authors:Demetrio Deanda, Yuktha Priya Masupalli, Jeong Yang, Young Lee, Zechun Cao, Gongbo Liang
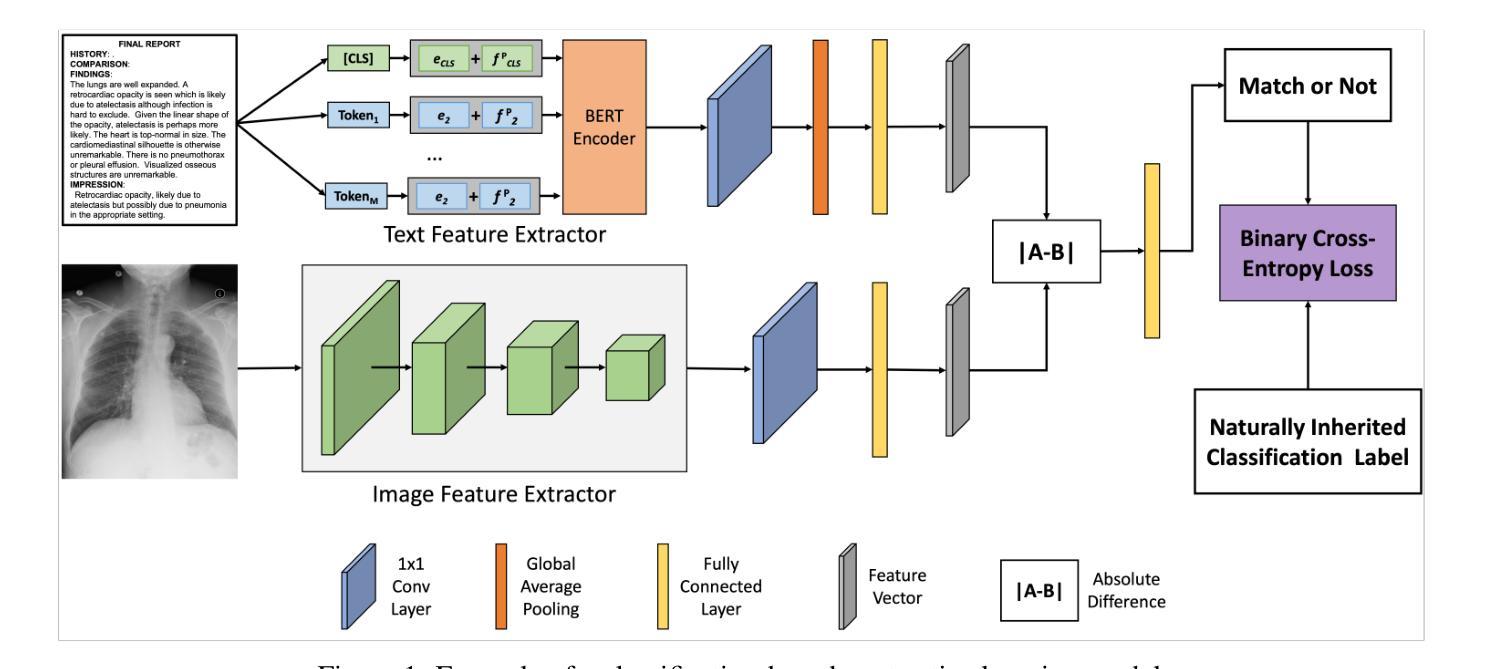
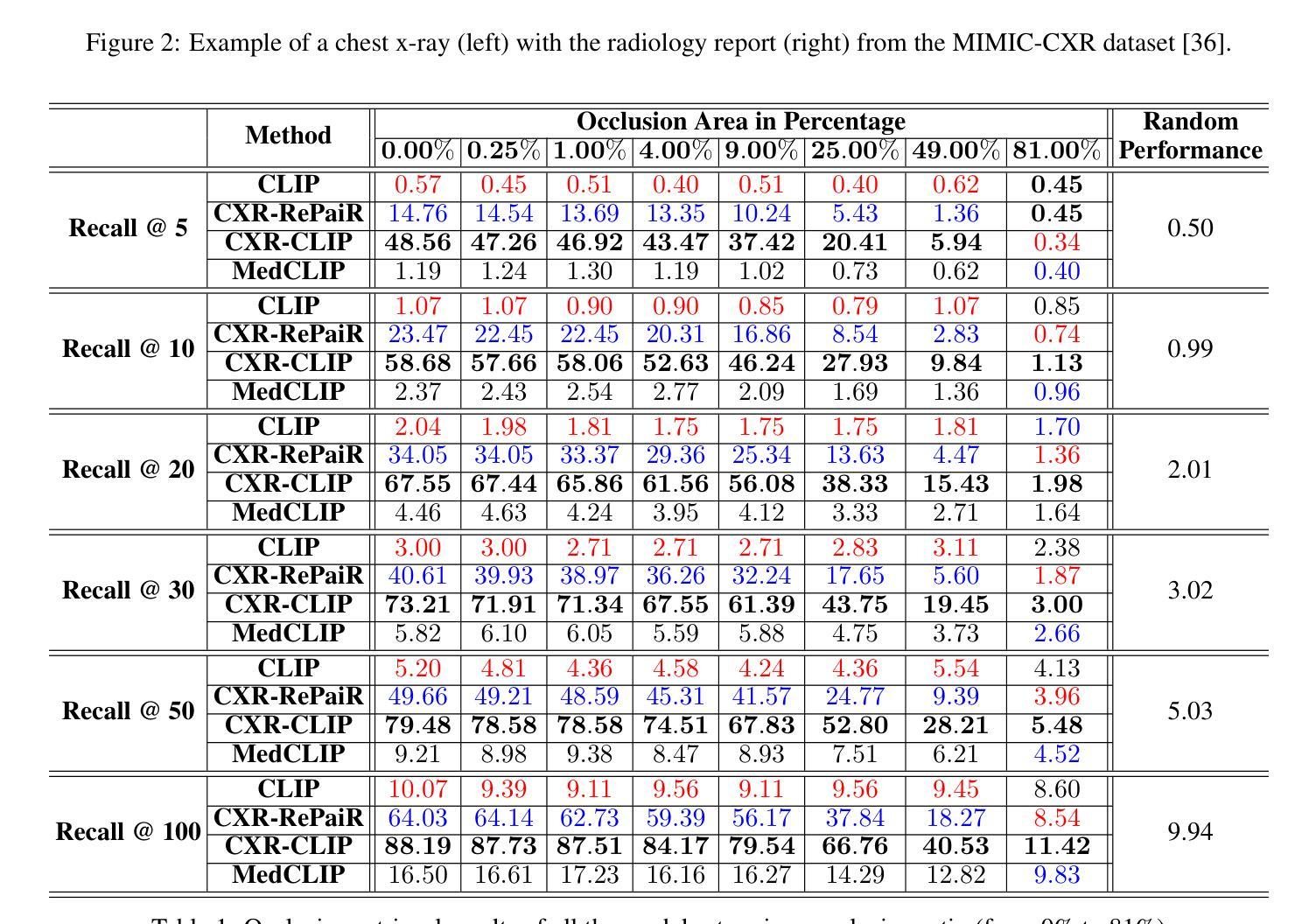
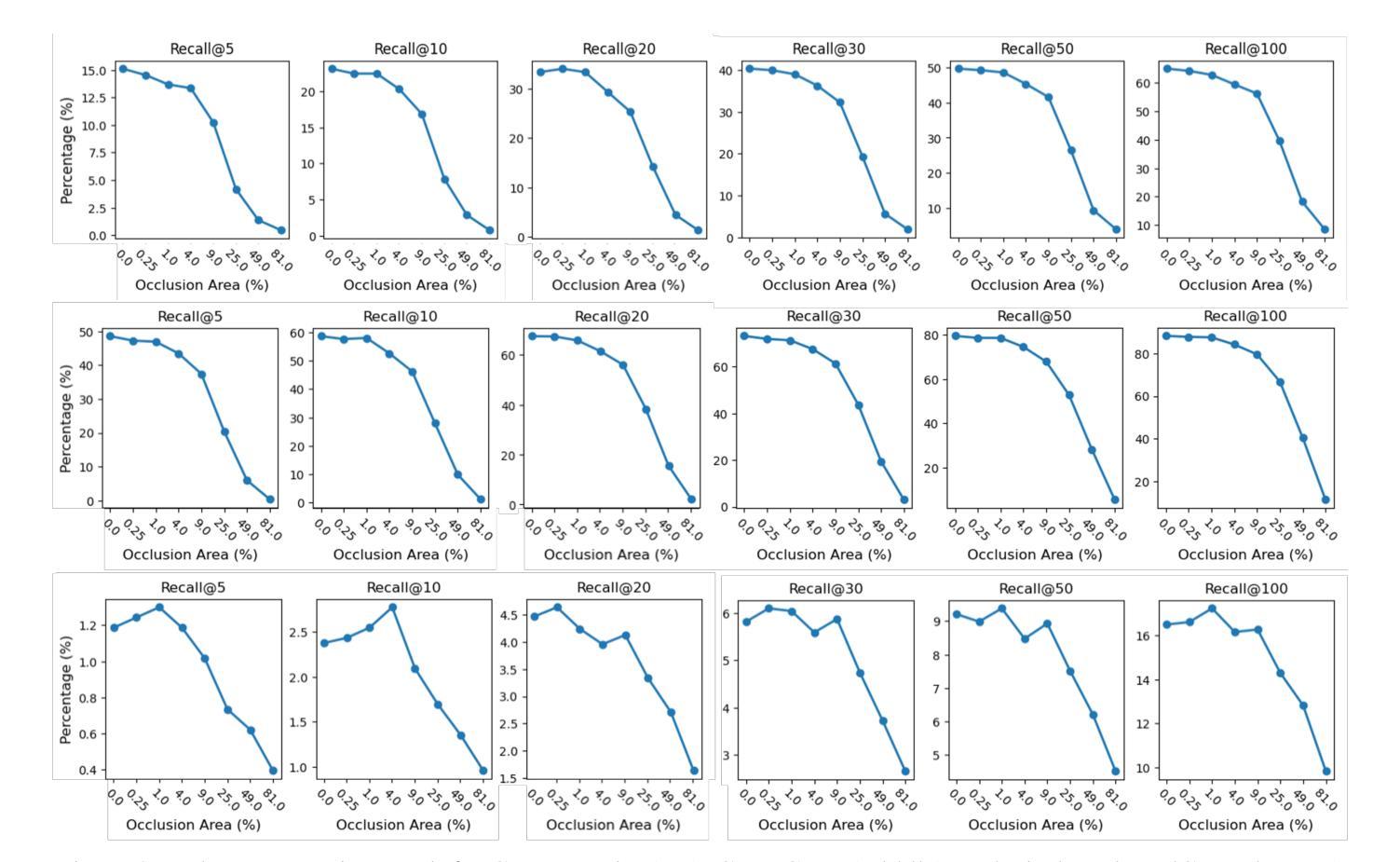
Medical images and reports offer invaluable insights into patient health. The heterogeneity and complexity of these data hinder effective analysis. To bridge this gap, we investigate contrastive learning models for cross-domain retrieval, which associates medical images with their corresponding clinical reports. This study benchmarks the robustness of four state-of-the-art contrastive learning models: CLIP, CXR-RePaiR, MedCLIP, and CXR-CLIP. We introduce an occlusion retrieval task to evaluate model performance under varying levels of image corruption. Our findings reveal that all evaluated models are highly sensitive to out-of-distribution data, as evidenced by the proportional decrease in performance with increasing occlusion levels. While MedCLIP exhibits slightly more robustness, its overall performance remains significantly behind CXR-CLIP and CXR-RePaiR. CLIP, trained on a general-purpose dataset, struggles with medical image-report retrieval, highlighting the importance of domain-specific training data. The evaluation of this work suggests that more effort needs to be spent on improving the robustness of these models. By addressing these limitations, we can develop more reliable cross-domain retrieval models for medical applications.
医疗图像和报告为患者健康状况提供了宝贵的见解。这些数据的异质性和复杂性阻碍了有效的分析。为了弥补这一差距,我们研究了对比学习模型在跨域检索中的应用,该模型将医疗图像与相应的临床报告相关联。本研究对四种最先进的对比学习模型进行了稳健性评估:CLIP、CXR-RePaiR、MedCLIP和CXR-CLIP。我们引入了一个遮挡检索任务来评估模型在不同程度的图像损坏下的性能。我们的研究发现,所有评估的模型对异常分布的数据高度敏感,随着遮挡程度的增加,性能呈比例下降。虽然MedCLIP表现出略微的稳健性,但其总体性能仍然远远落后于CXR-CLIP和CXR-RePaiR。CLIP在通用数据集上进行训练,因此在医疗图像报告检索方面表现挣扎,这突显了特定领域训练数据的重要性。对此工作的评估表明,还需要在改进这些模型的稳健性方面做出更多努力。通过解决这些局限性,我们可以为医疗应用开发更可靠的跨域检索模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work is accepted to AAAI 2025 Workshop – the 9th International Workshop on Health Intelligence
Summary
本文研究了基于对比学习模型的跨域检索在医疗图像和报告关联中的应用。实验对比了四种先进的对比学习模型(CLIP、CXR-RePaiR、MedCLIP和CXR-CLIP)的性能,并引入遮挡检索任务来评估模型在不同程度图像失真下的表现。研究发现,这些模型对异常数据的敏感性较高,在遮挡水平增加时性能有所下降。虽然MedCLIP展现出了一定的稳健性,但其总体性能显著落后于CXR-CLIP和CXR-RePaiR。CLIP在医疗图像报告检索方面的表现较差,突显出领域特定训练数据的重要性。研究评价表明,需要更多努力来提升这些模型的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 对比学习模型用于医疗图像和报告的跨域检索。
- 实验中评估了四种对比学习模型:CLIP、CXR-RePaiR、MedCLIP和CXR-CLIP。
- 引入遮挡检索任务来评估模型性能。
- 所有评估模型对异常数据敏感,性能随遮挡水平增加而下降。
- MedCLIP虽展现稳健性,但总体性能落后于CXR-CLIP和CXR-RePaiR。
- CLIP在医疗图像报告检索方面表现较差,突显领域特定训练数据的重要性。
点此查看论文截图


SHYI: Action Support for Contrastive Learning in High-Fidelity Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Tianxiang Xia, Lin Xiao, Yannick Montorfani, Francesco Pavia, Enis Simsar, Thomas Hofmann
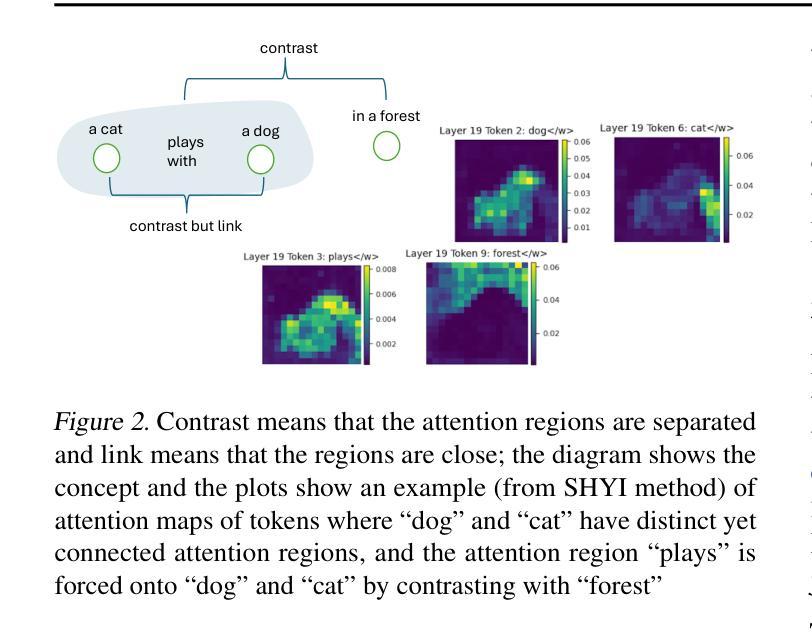
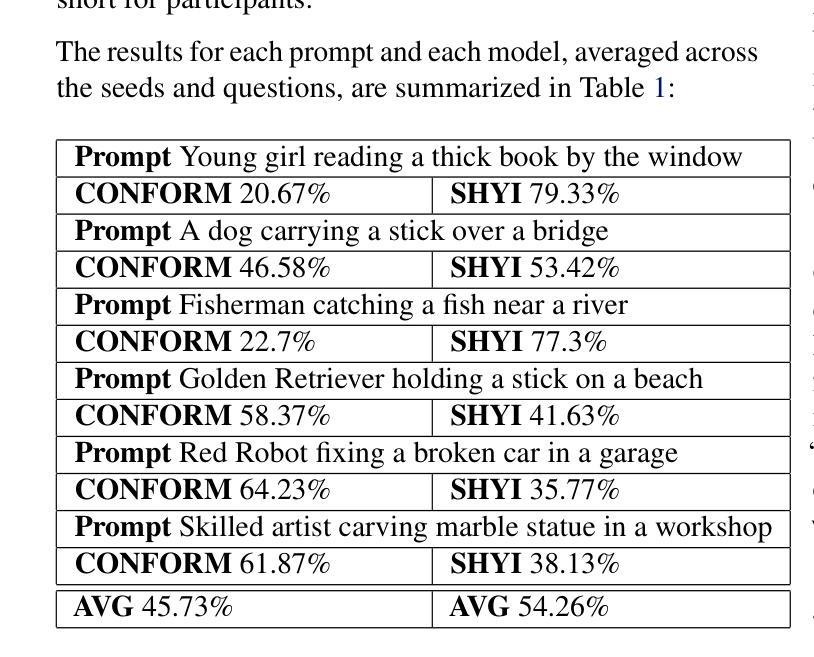
In this project, we address the issue of infidelity in text-to-image generation, particularly for actions involving multiple objects. For this we build on top of the CONFORM framework which uses Contrastive Learning to improve the accuracy of the generated image for multiple objects. However the depiction of actions which involves multiple different object has still large room for improvement. To improve, we employ semantically hypergraphic contrastive adjacency learning, a comprehension of enhanced contrastive structure and “contrast but link” technique. We further amend Stable Diffusion’s understanding of actions by InteractDiffusion. As evaluation metrics we use image-text similarity CLIP and TIFA. In addition, we conducted a user study. Our method shows promising results even with verbs that Stable Diffusion understands mediocrely. We then provide future directions by analyzing the results. Our codebase can be found on polybox under the link: https://polybox.ethz.ch/index.php/s/dJm3SWyRohUrFxn
在这个项目中,我们解决了文本到图像生成中的不忠问题,尤其是涉及多个对象的操作。为此,我们在CONFORM框架的基础上构建,该框架使用对比学习来提高对多个对象的生成图像的准确性。然而,涉及多个不同对象的动作描述仍然有很大的改进空间。为了改进这一点,我们采用了语义超图对比邻接学习、增强对比结构理解和“对比但链接”技术。我们通过交互扩散(InteractDiffusion)进一步改进了Stable Diffusion对动作的理解。作为评价指标,我们使用了图像文本相似性CLIP和TIFA。此外,我们还进行了用户研究。即使对于Stable Diffusion理解平庸的动词,我们的方法也显示出有前景的结果。然后通过分析结果提供未来研究方向。我们的代码库可以在polybox上找到,链接为:https://polybox.ethz.ch/index.php/s/dJm3SWyRohUrFxn。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Main content 4 pages
Summary
该项目针对文本到图像生成中的不忠问题进行研究,特别是在涉及多个对象的动作方面。项目基于使用对比学习提高生成图像准确性的CONFORM框架进行构建。为改善涉及多个不同对象的动作描绘,我们采用语义超图对比邻接学习,理解增强对比结构,并运用“对比但链接”技术。通过InteractDiffusion改进Stable Diffusion对动作的理解。我们使用CLIP和TIFA作为图像文本相似度评估指标,并进行了用户研究。该方法在Stable Diffusion理解一般的动词方面也表现出有前途的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 项目关注文本到图像生成中的不忠问题,特别是在涉及多个对象的动作描绘方面。
- 项目基于CONFORM框架,运用对比学习提高图像生成的准确性。
- 采用语义超图对比邻接学习、增强对比结构和“对比但链接”技术来改善多对象动作的描绘。
- 通过InteractDiffusion改进Stable Diffusion对动作的理解。
- 使用CLIP和TIFA作为图像文本相似度评估指标,并进行用户研究来评估方法的有效性。
- 该方法在涉及Stable Diffusion理解一般的动词方面表现出前景。
点此查看论文截图





TCMM: Token Constraint and Multi-Scale Memory Bank of Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Person Re-identification
Authors:Zheng-An Zhu, Hsin-Che Chien, Chen-Kuo Chiang
This paper proposes the ViT Token Constraint and Multi-scale Memory bank (TCMM) method to address the patch noises and feature inconsistency in unsupervised person re-identification works. Many excellent methods use ViT features to obtain pseudo labels and clustering prototypes, then train the model with contrastive learning. However, ViT processes images by performing patch embedding, which inevitably introduces noise in patches and may compromise the performance of the re-identification model. On the other hand, previous memory bank based contrastive methods may lead data inconsistency due to the limitation of batch size. Furthermore, existing pseudo label methods often discard outlier samples that are difficult to cluster. It sacrifices the potential value of outlier samples, leading to limited model diversity and robustness. This paper introduces the ViT Token Constraint to mitigate the damage caused by patch noises to the ViT architecture. The proposed Multi-scale Memory enhances the exploration of outlier samples and maintains feature consistency. Experimental results demonstrate that our system achieves state-of-the-art performance on common benchmarks. The project is available at \href{https://github.com/andy412510/TCMM}{https://github.com/andy412510/TCMM}.
本文提出了ViT令牌约束和多尺度存储库(TCMM)方法,以解决无监督行人再识别工作中的补丁噪声和特征不一致问题。许多优秀的方法使用ViT特征来获取伪标签和聚类原型,然后使用对比学习训练模型。然而,ViT通过执行补丁嵌入来处理图像,这不可避免地会在补丁中引入噪声,并可能损害再识别模型的性能。另一方面,基于先前存储库的对比方法可能会由于批次大小的限制而导致数据不一致。此外,现有的伪标签方法通常会丢弃难以聚类的异常值样本。这牺牲了异常值样本的潜在价值,导致模型多样性和稳健性的有限。本文引入了ViT令牌约束,以减轻补丁噪声对ViT架构造成的损害。所提出的多尺度存储库增强了异常值样本的探索并保持特征一致性。实验结果表明,我们的系统在常用基准测试上达到了最先进的性能。项目可在[https://github.com/andy412510/TCMM]上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了ViT令牌约束和多尺度内存银行(TCMM)方法,以解决无监督行人再识别工作中出现的补丁噪声和特征不一致问题。文章利用ViT特征获取伪标签和聚类原型,采用对比学习方法进行模型训练。然而,ViT通过执行补丁嵌入来处理图像,这不可避免地引入了补丁噪声,并可能影响再识别模型的性能。为解决这一问题,文章引入了ViT令牌约束,减轻了补丁噪声对ViT架构的损害。同时,提出的多尺度内存提高了对异常样本的探索并保持特征一致性。实验结果表明,该系统在常用基准测试上达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 论文针对无监督行人再识别中的补丁噪声和特征不一致问题,提出了ViT令牌约束和多尺度内存银行(TCMM)方法。
- ViT特征被用于获取伪标签和聚类原型,并采用对比学习方法训练模型。
- ViT处理图像通过补丁嵌入,可能引入补丁噪声,影响再识别模型的性能。
- ViT令牌约束用于减轻补丁噪声对ViT架构的影响。
- 多尺度内存设计旨在提高异常样本的探索并保持特征一致性。
- 实验结果表明,该系统在常用基准测试上表现优秀。
点此查看论文截图

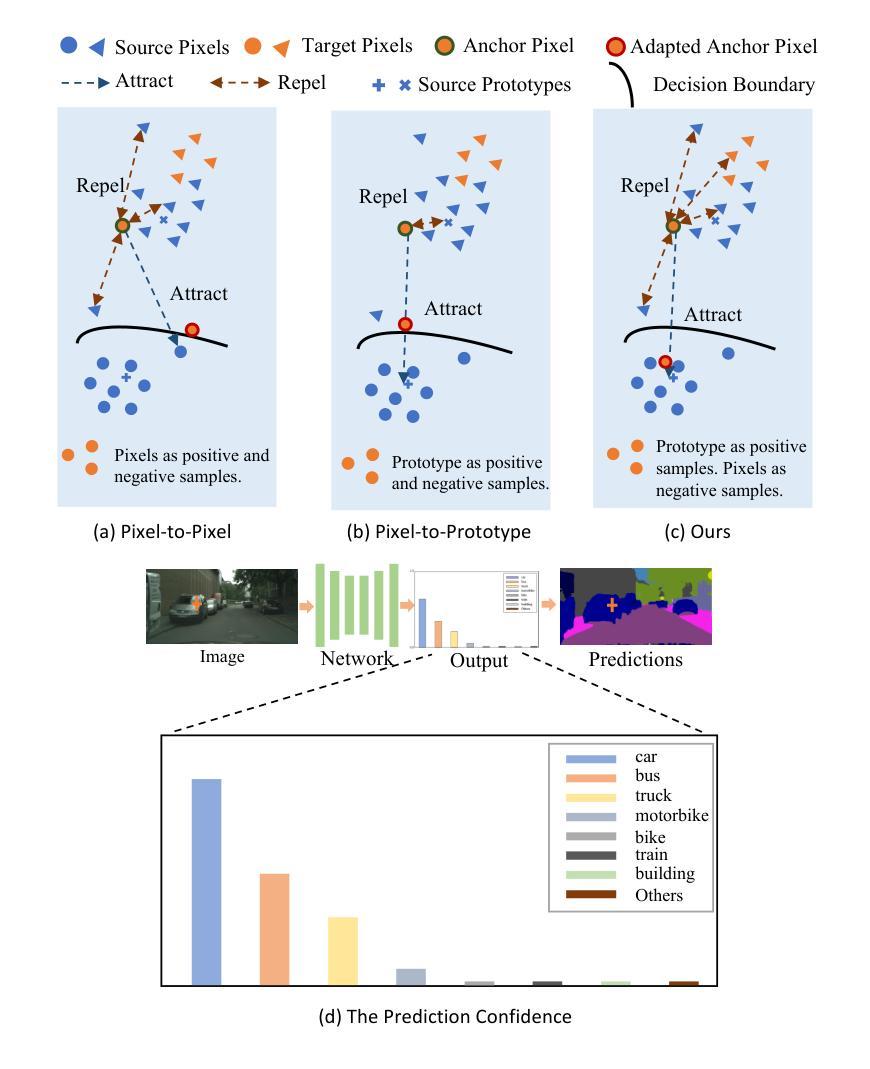
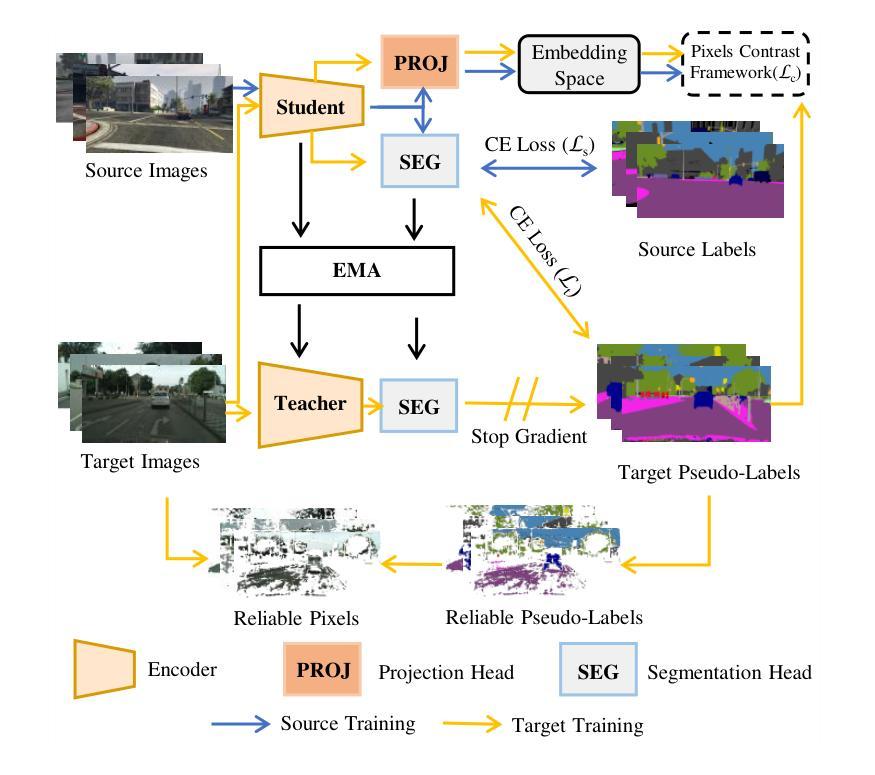
Pseudolabel guided pixels contrast for domain adaptive semantic segmentation
Authors:Jianzi Xiang, Cailu Wan, Zhu Cao
Semantic segmentation is essential for comprehending images, but the process necessitates a substantial amount of detailed annotations at the pixel level. Acquiring such annotations can be costly in the real-world. Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) for semantic segmentation is a technique that uses virtual data with labels to train a model and adapts it to real data without labels. Some recent works use contrastive learning, which is a powerful method for self-supervised learning, to help with this technique. However, these works do not take into account the diversity of features within each class when using contrastive learning, which leads to errors in class prediction. We analyze the limitations of these works and propose a novel framework called Pseudo-label Guided Pixel Contrast (PGPC), which overcomes the disadvantages of previous methods. We also investigate how to use more information from target images without adding noise from pseudo-labels. We test our method on two standard UDA benchmarks and show that it outperforms existing methods. Specifically, we achieve relative improvements of 5.1% mIoU and 4.6% mIoU on the Grand Theft Auto V (GTA5) to Cityscapes and SYNTHIA to Cityscapes tasks based on DAFormer, respectively. Furthermore, our approach can enhance the performance of other UDA approaches without increasing model complexity. Code is available at https://github.com/embar111/pgpc
语义分割对于理解图像至关重要,但这一过程需要在像素级别进行大量的详细标注。在现实世界中获得这样的标注可能成本高昂。无监督域自适应(UDA)语义分割是一种使用带标签的虚拟数据来训练模型,并将其适应无标签的真实数据的技术。最近的一些作品采用对比学习这一强大的自监督学习方法来辅助该技术。然而,这些作品在使用对比学习时并未考虑到每一类别内特征的多样性,从而导致类别预测错误。我们分析了这些作品的局限性,并提出了一种名为伪标签引导像素对比(PGPC)的新型框架,克服了以往方法的缺点。我们还探讨了如何从目标图像中获取更多信息,同时避免伪标签带来的噪声。我们的方法在两个标准的UDA基准测试集上进行了测试,并证明了其优于现有方法。具体而言,我们在基于DAFormer的Grand Theft Auto V(GTA5)到Cityscapes以及SYNTHIA到Cityscapes任务上,分别实现了相对改进5.1%和4.6%的mIoU。此外,我们的方法还可以提高其他UDA方法的性能,且不增加模型复杂度。代码可在https://github.com/embar111/pgpc找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 5 figures. Code: https://github.com/embar111/pgpc
Summary
本文探讨了语义分割中的无监督域自适应(UDA)技术。由于获取像素级别的详细标注成本高昂,研究者开始使用虚拟数据训练模型并适应真实无标签数据。文章分析了现有工作中使用对比学习时的局限性,并提出了一个新的框架——伪标签引导像素对比(PGPC),以提高类内特征多样性的考虑,改善类预测错误问题。经过在两个标准UDA基准测试上的验证,该方法相较于现有技术取得了相对改进,并展示了其与其他UDA方法的兼容性。
Key Takeaways
- 无监督域自适应(UDA)在语义分割中用于训练模型并适应真实无标签数据。
- 对比学习在无监督学习中表现出强大的自学习能力,但在语义分割的UDA中未充分考虑到类内特征多样性。
- 提出新的框架——伪标签引导像素对比(PGPC),以改善类预测错误问题。
- PGPC能够在两个标准UDA基准测试中实现优于现有方法的效果。
- 与其他UDA方法兼容,不增加模型复杂性。
- 提供了实验验证,包括在Grand Theft Auto V到Cityscapes和SYNTHIA到Cityscapes任务上的相对改进数据。
点此查看论文截图