⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-21 更新
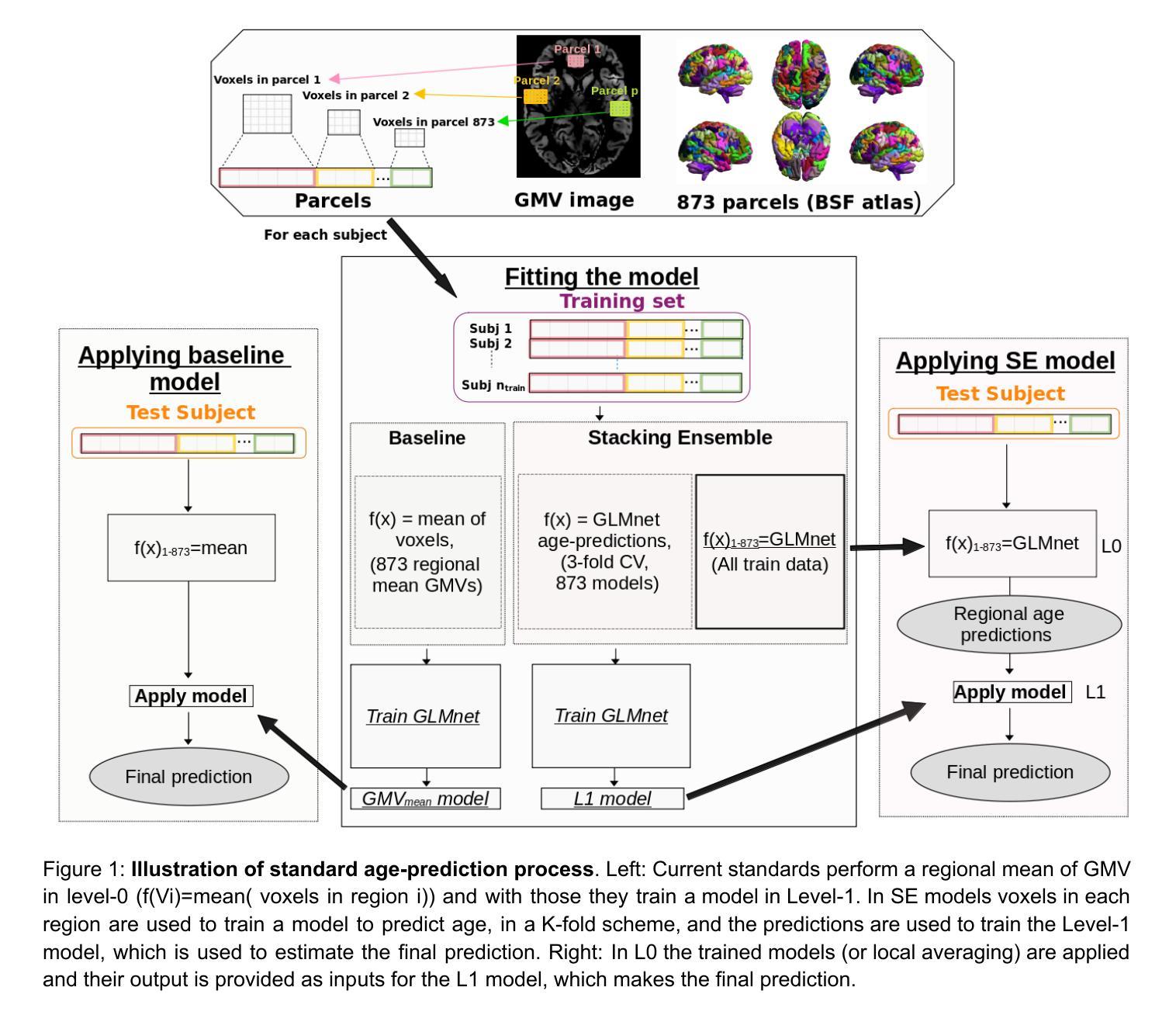
Region-wise stacking ensembles for estimating brain-age using MRI
Authors:Georgios Antonopoulos, Shammi More, Simon B. Eickhoff, Federico Raimondo, Kaustubh R. Patil
Predictive modeling using structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data is a prominent approach to study brain-aging. Machine learning algorithms and feature extraction methods have been employed to improve predictions and explore healthy and accelerated aging e.g. neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders. The high-dimensional MRI data pose challenges to building generalizable and interpretable models as well as for data privacy. Common practices are resampling or averaging voxels within predefined parcels, which reduces anatomical specificity and biological interpretability as voxels within a region may differently relate to aging. Effectively, naive fusion by averaging can result in information loss and reduced accuracy. We present a conceptually novel two-level stacking ensemble (SE) approach. The first level comprises regional models for predicting individuals’ age based on voxel-wise information, fused by a second-level model yielding final predictions. Eight data fusion scenarios were explored using as input Gray matter volume (GMV) estimates from four datasets covering the adult lifespan. Performance, measured using mean absolute error (MAE), R2, correlation and prediction bias, showed that SE outperformed the region-wise averages. The best performance was obtained when first-level regional predictions were obtained as out-of-sample predictions on the application site with second-level models trained on independent and site-specific data (MAE=4.75 vs baseline regional mean GMV MAE=5.68). Performance improved as more datasets were used for training. First-level predictions showed improved and more robust aging signal providing new biological insights and enhanced data privacy. Overall, the SE improves accuracy compared to the baseline while preserving or enhancing data privacy.
使用结构磁共振成像(MRI)数据进行预测建模是研究大脑衰老的一种突出方法。机器学习和特征提取方法已被用于提高预测能力,并探索健康和加速衰老,例如神经退行性疾病和精神疾病。高维MRI数据给构建通用和可解释的模型以及数据隐私带来了挑战。常见的做法是重新采样或在预定义的区域中对体素进行平均处理,这降低了解剖特异性和生物学解释性,因为在同一区域内的体素与衰老可能有不同的关联。实际上,通过平均进行简单的融合可能导致信息丢失和准确性降低。我们提出了一种概念上新颖的两级堆叠集成(SE)方法。第一级包括基于体素信息的预测个体年龄的局部模型,通过第二级模型融合得出最终预测结果。我们探索了八种数据融合情景,以灰质体积(GMV)估计值作为输入,这些估计值来自覆盖成人生命周期的四个数据集。通过平均绝对误差(MAE)、R2、相关系数和预测偏差来衡量性能,SE的表现超过了区域平均值。当第一级区域预测作为应用站点上的离样预测获得,而第二级模型在独立和特定站点数据上进行训练时,获得了最佳性能(MAE=4.75与基线区域平均GMV MAE=5.68)。随着用于训练的数据集数量的增加,性能得到了提高。第一级的预测显示出更加稳健的衰老信号,提供了新的生物学见解并增强了数据隐私。总体而言,SE在保持或提高数据隐私的同时,提高了准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF version1
Summary
本文介绍了利用结构磁共振成像(MRI)数据进行预测建模的方法,并指出了其在研究脑衰老中的重要作用。文章通过使用机器学习算法和特征提取方法,探索了健康及加速衰老(如神经退行性疾病和精神疾病)的预测。文章指出,高维MRI数据给建立通用和可解释的模型以及数据隐私带来了挑战。传统的做法是在预定义的区域内重采样或平均体素,这降低了解剖特异性和生物学解释性。本文提出了一种概念上新颖的两级堆叠集成(SE)方法,首先基于体素信息建立区域模型进行年龄预测,然后通过第二级模型融合得到最终预测结果。研究结果显示,SE方法优于区域平均方法,特别是在使用多个数据集进行训练时,性能更佳。SE方法不仅提高了预测准确性,而且保护数据隐私。
Key Takeaways
- 预测建模使用结构磁共振成像(MRI)数据是研究脑衰老的一种重要方法。
- 机器学习算法和特征提取方法用于改善预测,并探索健康和加速衰老。
- 高维MRI数据给建立通用和可解释的模型以及数据隐私带来挑战。
- 传统做法在重采样或平均体素时可能丢失信息并降低准确性。
- 提出了一种新的两级堆叠集成(SE)方法,通过两级模型融合提高预测性能。
- SE方法在第一级区域预测中表现出最佳性能,使用更多数据集进行训练可提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

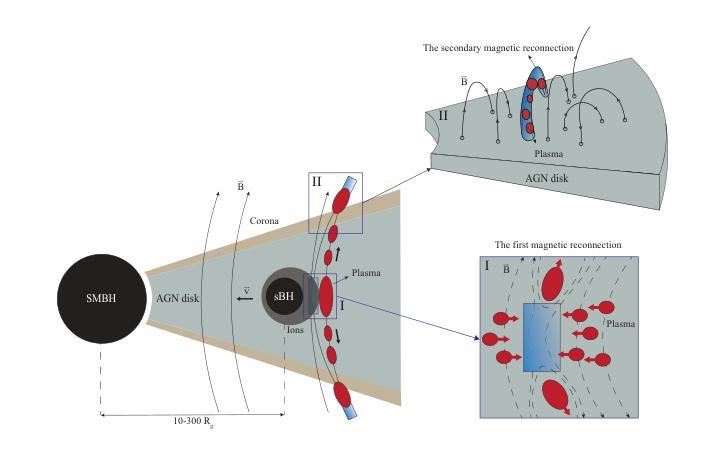
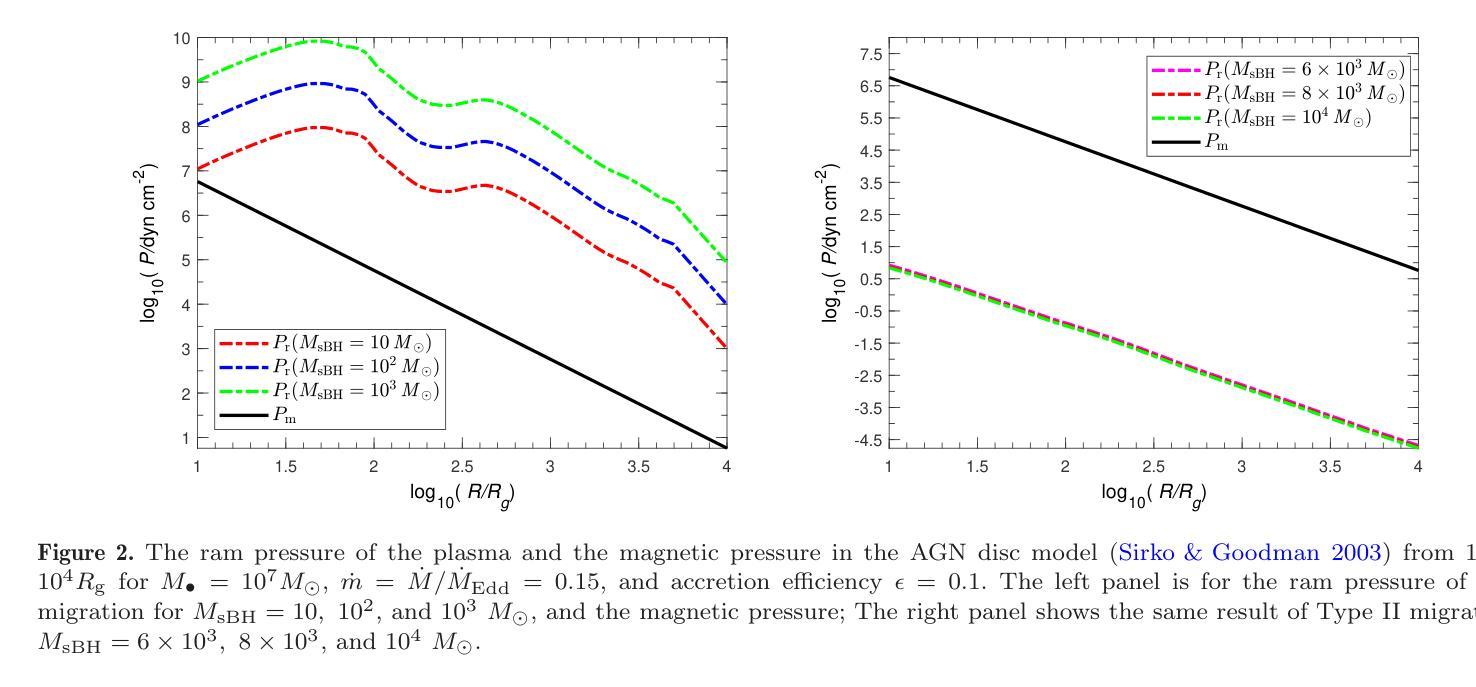
Variabilities driven by satellite black hole migration in AGN discs
Authors:Jing-Tong Xing, Tong Liu, Bao-Quan Huang, Mouyuan Sun
The physical origin of active galactic nucleus (AGN) variability remains unclear. Here we propose that the magnetic reconnection driven by the migration of satellite black holes (sBHs) in the AGN disc can be a new plausible mechanism for AGN short-term variability. During the sBH migration, the co-moving plasmas surrounding the sBH could influence the large-scale magnetic field of the AGN disk and trigger the magnetic reconnections to contribute to AGN UV/optical variability. Meanwhile, the plasma, which is accelerated by the magnetic reconnection, will successfully escape from the disc at Alfven velocity and cause a secondary magnetic reconnection in the corona. For a $\sim 10^{2}-10^{3}{M_\mathrm{\odot}}$ sBH (including its binding gas) in the inner regions of the disc surrounding a supermassive black hole with $\sim 10^{7}{M_\mathrm{\odot}}$, the reconnection process occurred in the space out of the disc can produce X-ray emission, which can last $\sim 10^4-10^6\rm s$ with the luminosity $\sim 10^{39}- 10^{43}\rm{erg ~s^{-1}}$.
活动星系核(AGN)变异的物理起源仍然不明确。在这里,我们提出一种新机制,即星系核盘中的卫星黑洞(sBHs)迁移所驱动的磁重联,可能是导致星系核短期变异的一种可行机制。在卫星黑洞迁移过程中,卫星黑洞周围共动的等离子体可能影响星系核盘的大规模磁场,并引发磁重联,从而导致星系核的紫外/光学变异。同时,被磁重联加速的等离子体将以阿尔芬速度成功逃离磁盘,并在冕区引起次级磁重联。对于位于超大质量黑洞周围盘内区域的约为$10^{2}-10^{3} {M_\mathrm{\odot}}$的卫星黑洞(包括其束缚气体),发生在磁盘外部空间的重联过程会产生X射线发射,持续时间约为$10^{4}-10^{6} \rm s$,光度约为$10^{39}- 10^{43} \rm{erg ~s^{-1}}$。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 2 figures, submitted
Summary
卫星黑洞(sBHs)在活跃星系核(AGN)盘中的迁移所驱动的磁重联可能是一个新机制,用于解释活跃星系核短期内的变化。sBH迁移过程中,周围的共动等离子体可能影响AGN盘的大规模磁场并触发磁重联,从而有助于解释AGNUV或光学波段的变化。此外,由磁重联加速的等离子体以阿尔文速度成功逃离圆盘并在冕中形成二次磁重联现象。这种新型重联机制可以产生X射线发射,持续时间约为数秒至数分钟不等,光度约为数十亿至数千亿尔格每秒。此研究对理解活跃星系核的短期变化提供了新的视角。
Key Takeaways
以下是从这段文字中提取出的关键见解:
- 研究提出了一种新的假设机制,解释了活跃星系核(AGNs)短期内的变化,该机制与卫星黑洞(sBHs)迁移驱动的磁重联有关。
- sBH迁移过程中伴随的等离子体可能通过影响大规模磁场触发磁重联反应,从而导致AGNUV或光学波段的变化。这一点是研究提出的核心观点之一。
- 由磁重联加速的等离子体能够逃离磁盘并在冕中引发二次磁重联现象。这是另一个重要的关键见解。这种逃逸的速度与某些条件下的现象产生密切相关。
点此查看论文截图

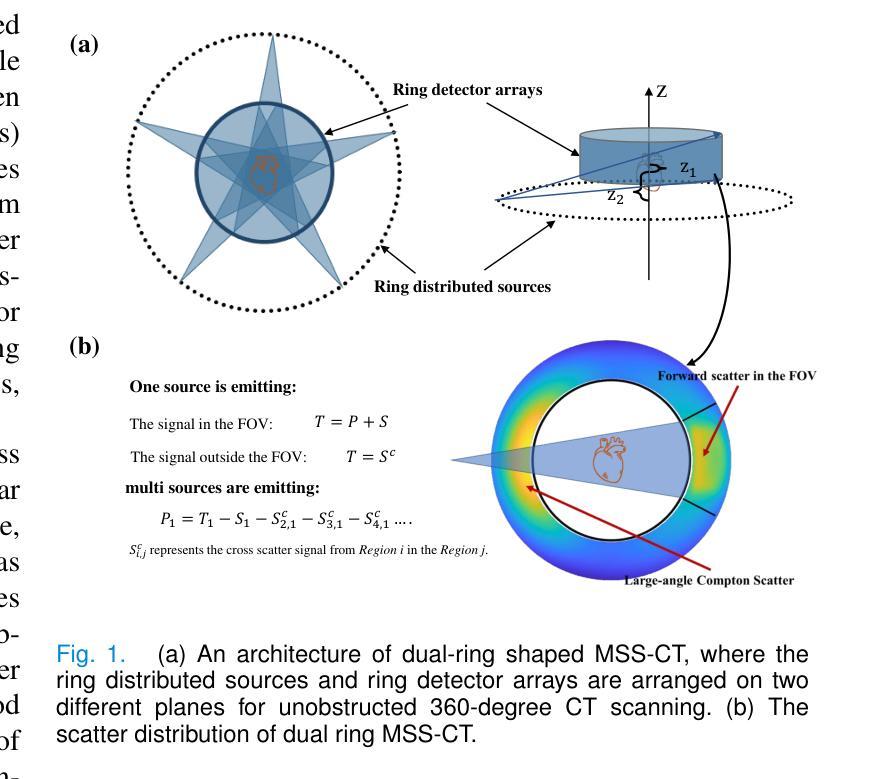
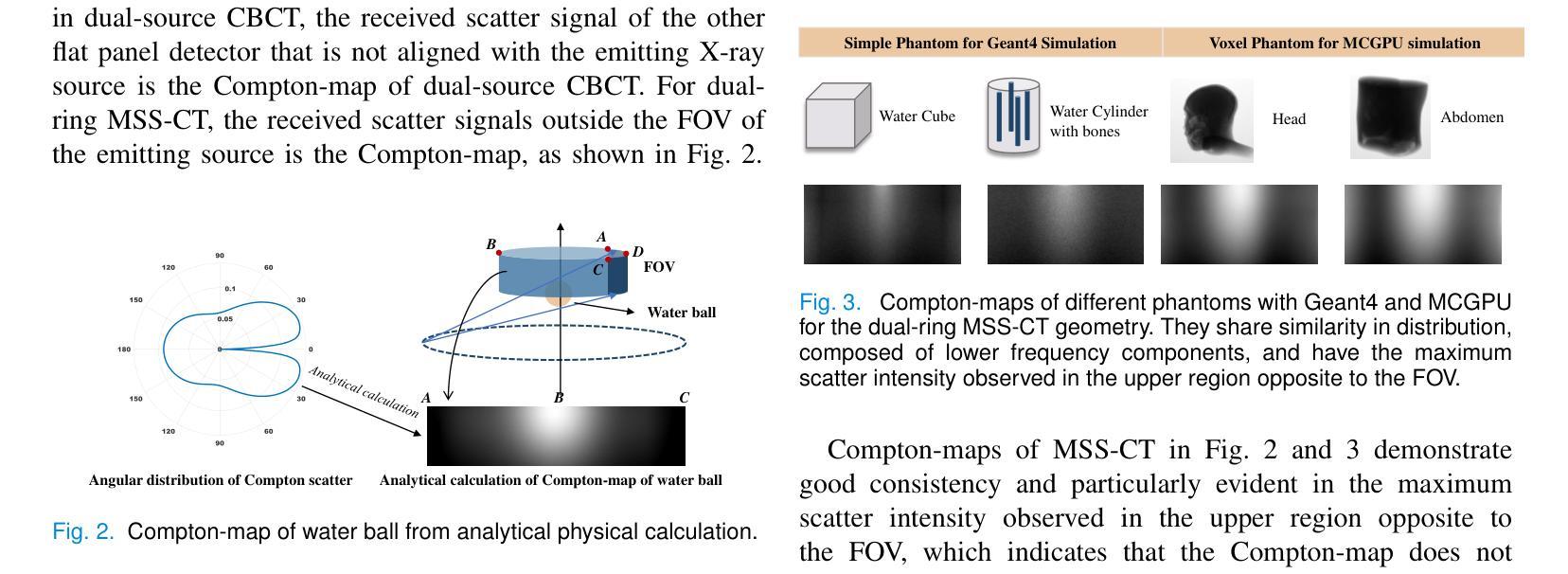
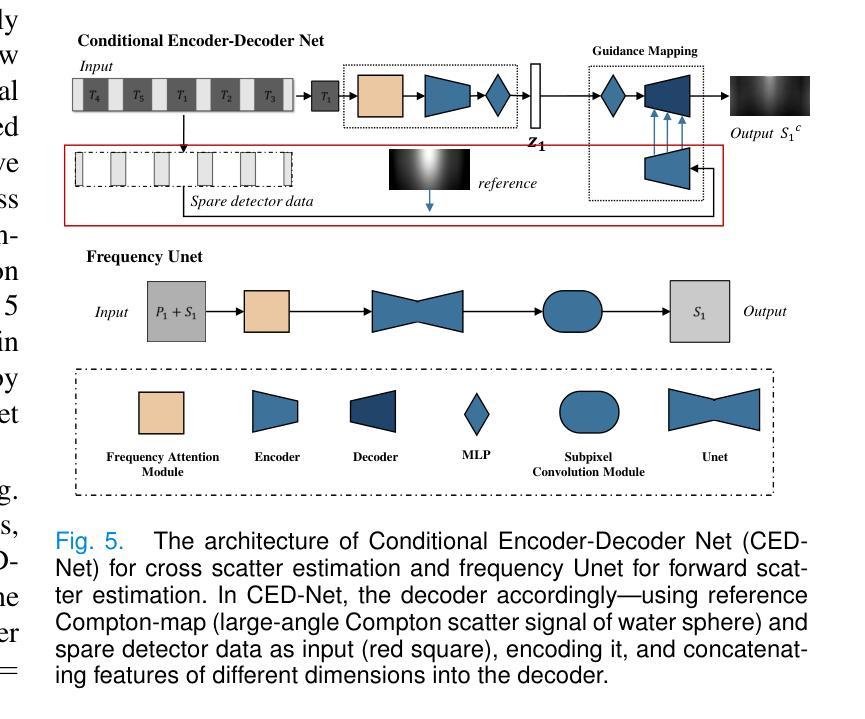
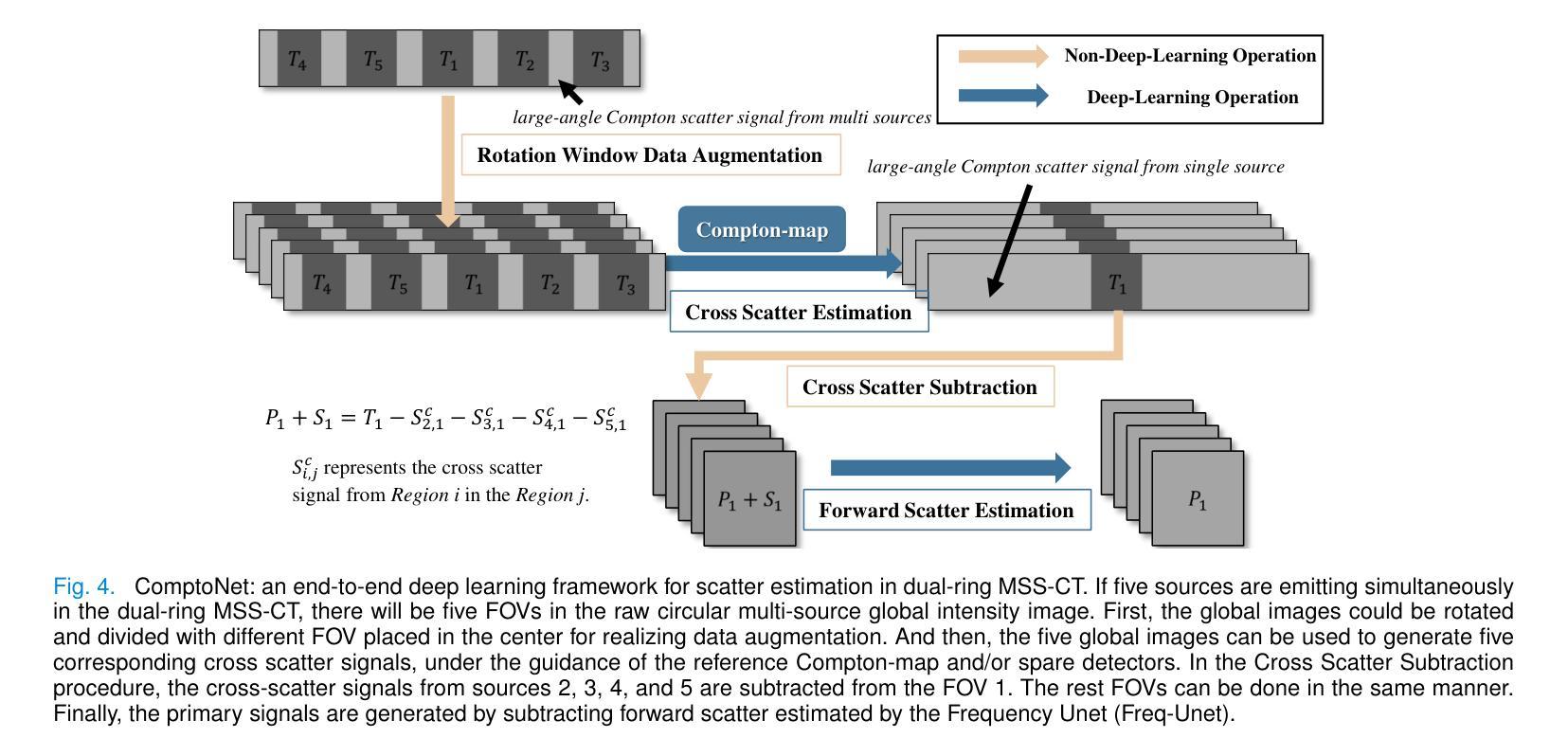
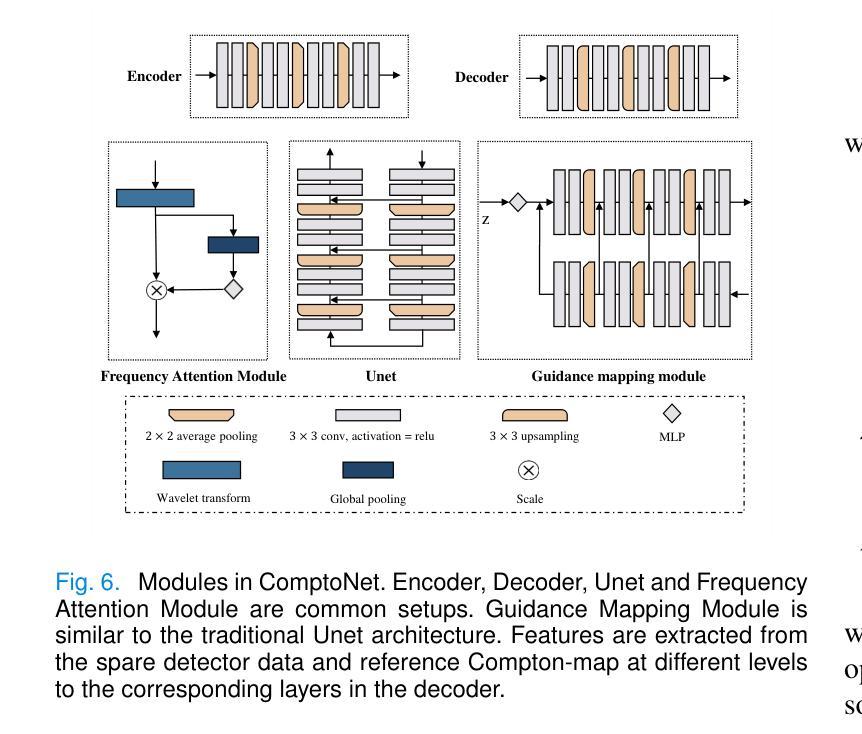
ComptoNet: An End-to-End Deep Learning Framework for Scatter Estimation in Multi-Source Stationary CT
Authors:Yingxian Xia, Zhiqiang Chen, Li Zhang, Yuxiang Xing, Hewei Gao
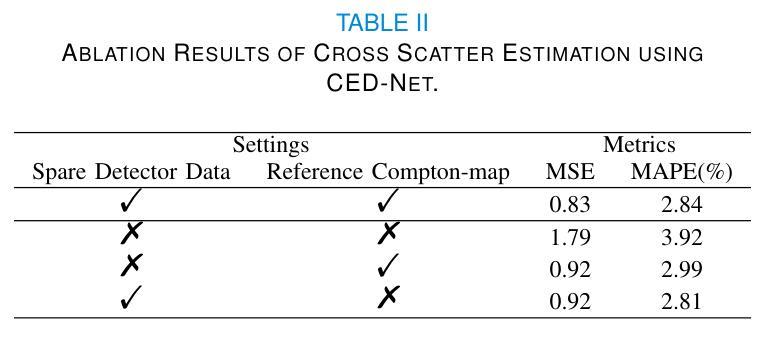
Multi-source stationary computed tomography (MSS-CT) offers significant advantages in medical and industrial applications due to its gantry-less scan architecture and/or capability of simultaneous multi-source emission. However, the lack of anti-scatter grid deployment in MSS-CT results in severe forward and/or cross scatter contamination, presenting a critical challenge that necessitates an accurate and efficient scatter correction. In this work, ComptoNet, an innovative end-to-end deep learning framework for scatter estimation in MSS-CT, is proposed, which integrates Compton-scattering physics with deep learning techniques to address the challenges of scatter estimation effectively. Central to ComptoNet is the Compton-map, a novel concept that captures the distribution of scatter signals outside the scan field of view, primarily consisting of large-angle Compton scatter. In ComptoNet, a reference Compton-map and/or spare detector data are used to guide the physics-driven deep estimation of scatter from simultaneous emissions by multiple sources. Additionally, a frequency attention module is employed for enhancing the low-frequency smoothness. Such a multi-source deep scatter estimation framework decouples the cross and forward scatter. It reduces network complexity and ensures a consistent low-frequency signature with different photon numbers of simulations, as evidenced by mean absolute percentage errors (MAPEs) that are less than $1.26%$. Conducted by using data generated from Monte Carlo simulations with various phantoms, experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of ComptoNet, with significant improvements in scatter estimation accuracy (a MAPE of $0.84%$). After scatter correction, nearly artifact-free CT images are obtained, further validating the capability of our proposed ComptoNet in mitigating scatter-induced errors.
多源静止计算机断层扫描(MSS-CT)由于其无支架扫描架构和/或同时多源发射的能力,在医疗和工业应用中提供了显著的优势。然而,MSS-CT中缺乏防散射格栅的部署导致了严重的正向散射和/或交叉散射污染,呈现出一个关键挑战,需要进行准确高效的散射校正。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
康普顿网络(ComptoNet)是一个用于多源静态计算机断层扫描(MSS-CT)散射估计的端到端深度学习框架,它结合了康普顿散射物理与深度学习技术,有效应对散射估计的挑战。其核心在于康普顿图(Compton-map),用于捕捉扫描视野外的散射信号分布。此框架可提高散射估计的准确性,并减少网络复杂性,确保在不同光子数模拟下的低频频谱一致性。通过蒙特卡罗模拟与各种幻影数据实验验证,ComptoNet在散射估计准确性上有显著提升,经散射校正后获得几乎无伪影的CT图像。
Key Takeaways
- MSS-CT因无转塔扫描架构和/或多源同时发射能力,在医疗和工业应用中具有显著优势。
- MSS-CT中缺乏反散射网格部署导致严重的前向和/或交叉散射污染,需要准确高效的散射校正。
- ComptoNet是一个创新的深度学习框架,用于MSS-CT中的散射估计,结合了康普顿散射物理与深度学习技术。
- 康普顿图是ComptoNet的核心概念,用于捕捉扫描视野外的散射信号分布,主要包括大角度康普顿散射。
- ComptoNet使用参考康普顿图和/或备用检测器数据,指导由多个源同时发射的散射物理驱动的深度估计。
- ComptoNet采用频率注意力模块增强低频频谱平滑性,能减少网络复杂性并确保在不同光子数模拟下的低频频谱一致性。
点此查看论文截图

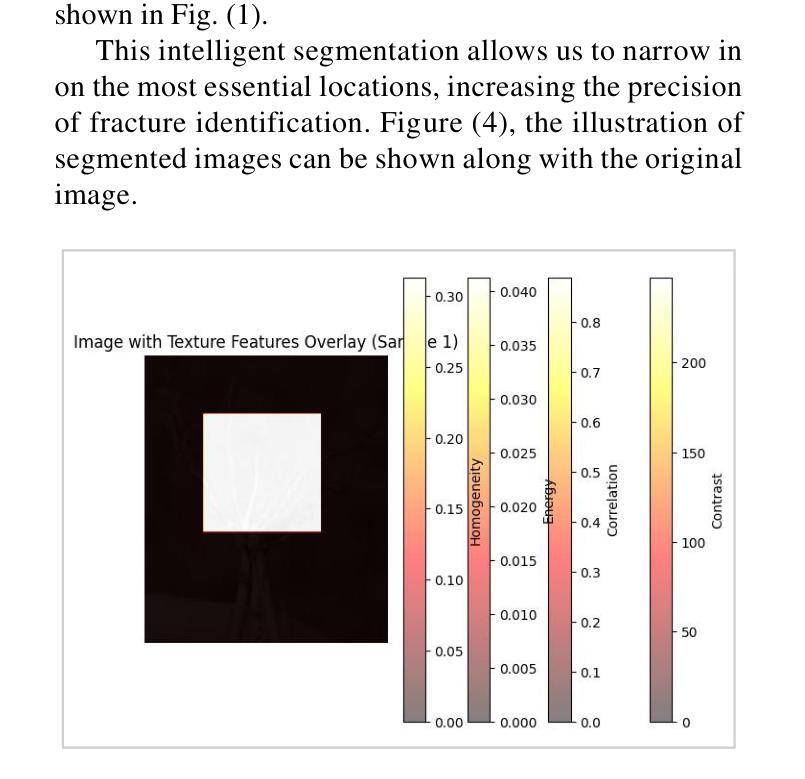
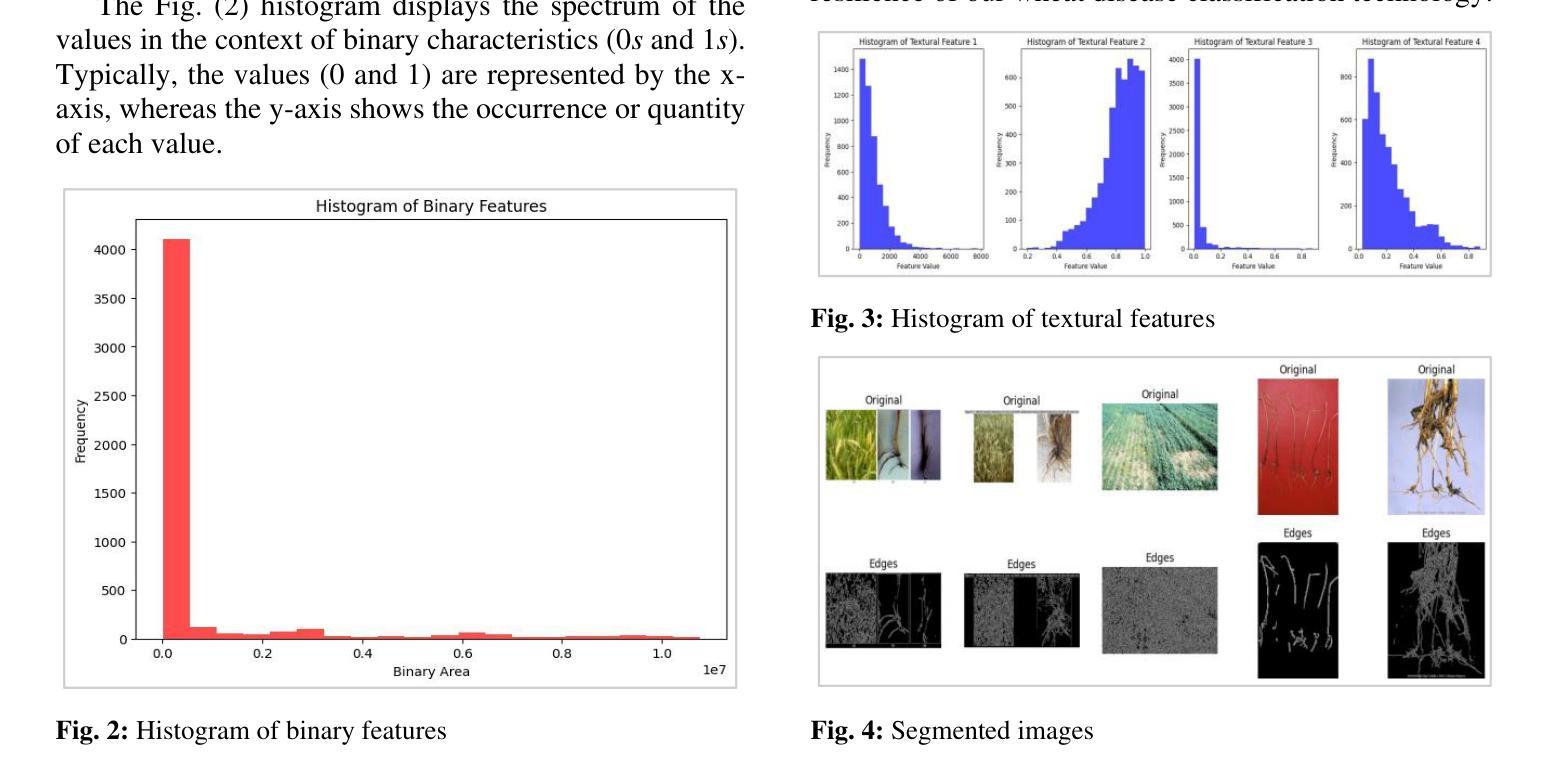
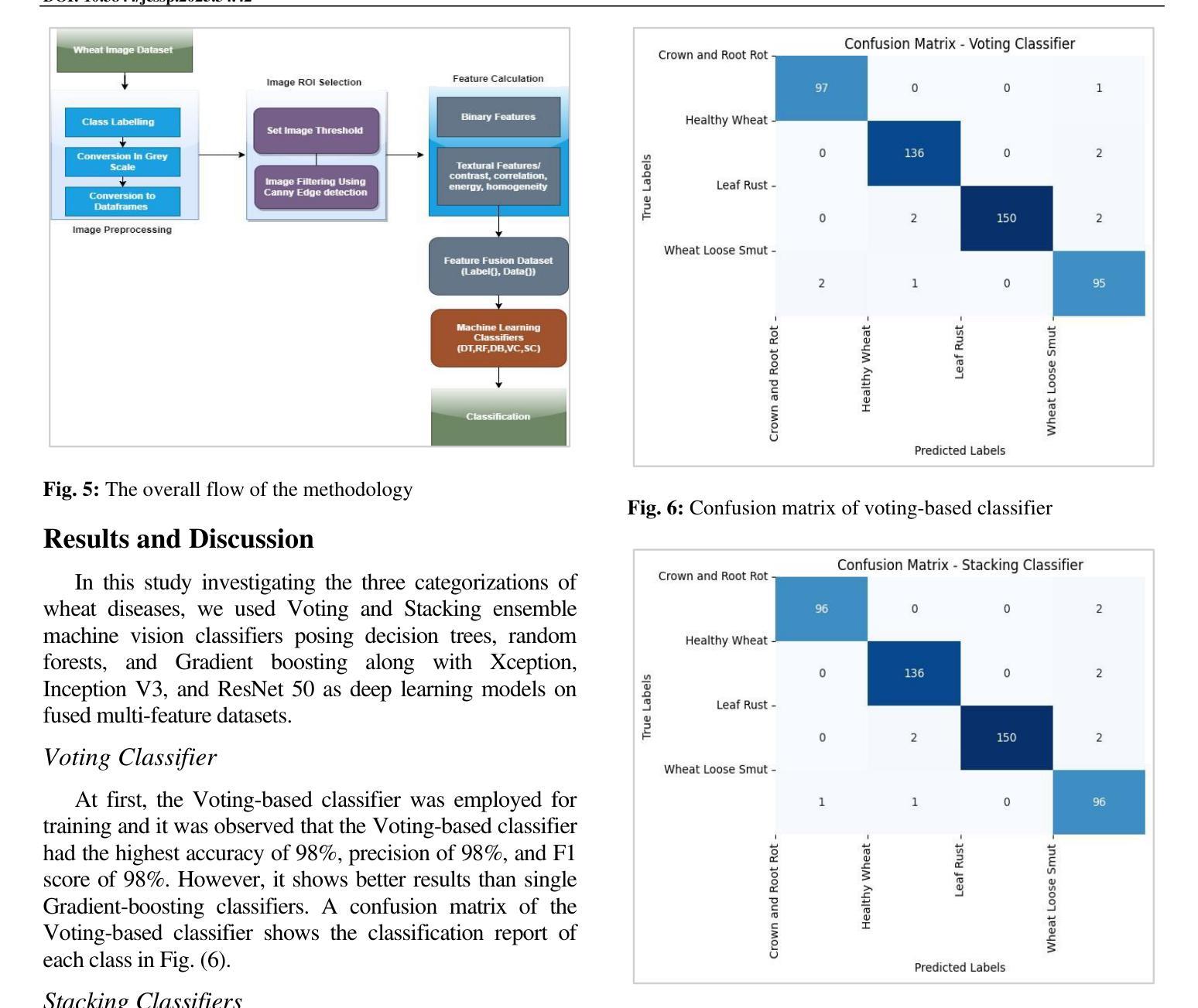
A Multi-Scale Feature Extraction and Fusion Deep Learning Method for Classification of Wheat Diseases
Authors:Sajjad Saleem, Adil Hussain, Nabila Majeed, Zahid Akhtar, Kamran Siddique
Wheat is an important source of dietary fiber and protein that is negatively impacted by a number of risks to its growth. The difficulty of identifying and classifying wheat diseases is discussed with an emphasis on wheat loose smut, leaf rust, and crown and root rot. Addressing conditions like crown and root rot, this study introduces an innovative approach that integrates multi-scale feature extraction with advanced image segmentation techniques to enhance classification accuracy. The proposed method uses neural network models Xception, Inception V3, and ResNet 50 to train on a large wheat disease classification dataset 2020 in conjunction with an ensemble of machine vision classifiers, including voting and stacking. The study shows that the suggested methodology has a superior accuracy of 99.75% in the classification of wheat diseases when compared to current state-of-the-art approaches. A deep learning ensemble model Xception showed the highest accuracy.
小麦是重要的膳食纤维和蛋白质来源,其生长受到多种风险的负面影响。本文重点讨论了小麦病害的识别与分类难点,特别是小麦腥黑穗病、叶锈病和冠根腐病等。针对冠根腐等问题,本研究引入了一种创新的方法,将多尺度特征提取与先进的图像分割技术相结合,以提高分类精度。所提出的方法使用神经网络模型Xception、Inception V3和ResNet 50,结合机器视觉分类器的集合(包括投票和堆叠),对2020年大规模小麦病害分类数据集进行训练。研究表明,与目前最先进的方法相比,所提出的方法在小麦病害分类方面的准确率高达99.75%,其中深度学习集成模型Xception的准确率最高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
小麦是重要的膳食纤维和蛋白质来源,其生长受到多种风险的威胁。本文介绍了小麦病害识别与分类的难点,并重点关注小麦松散大穗、叶锈病和冠根腐病等问题。为解决冠根腐病等难题,本研究提出了一种创新方法,结合多尺度特征提取与先进的图像分割技术,提高分类准确性。研究采用神经网络模型Xception、Inception V3和ResNet 50等,在大型小麦病害分类数据集上训练,并结合投票和堆叠等机器视觉分类器。研究表明,该方法在小麦病害分类方面的准确率达到了惊人的99.75%,优于当前最前沿的技术水平。其中,深度学习集成模型Xception的准确率最高。
Key Takeaways
- 小麦作为重要的膳食纤维和蛋白质来源,其生长受到多种风险的威胁。
- 识别与分类小麦病害存在困难,如松散大穗、叶锈病和冠根腐病等。
- 研究提出了一种结合多尺度特征提取与图像分割技术的创新方法来解决这些难题。
- 采用神经网络模型如Xception、Inception V3和ResNet 50等在大规模小麦病害分类数据集上进行训练。
- 结合了投票和堆叠等机器视觉分类器来提高分类准确率。
- 该方法的准确率达到了99.75%,优于当前最前沿的技术。
点此查看论文截图

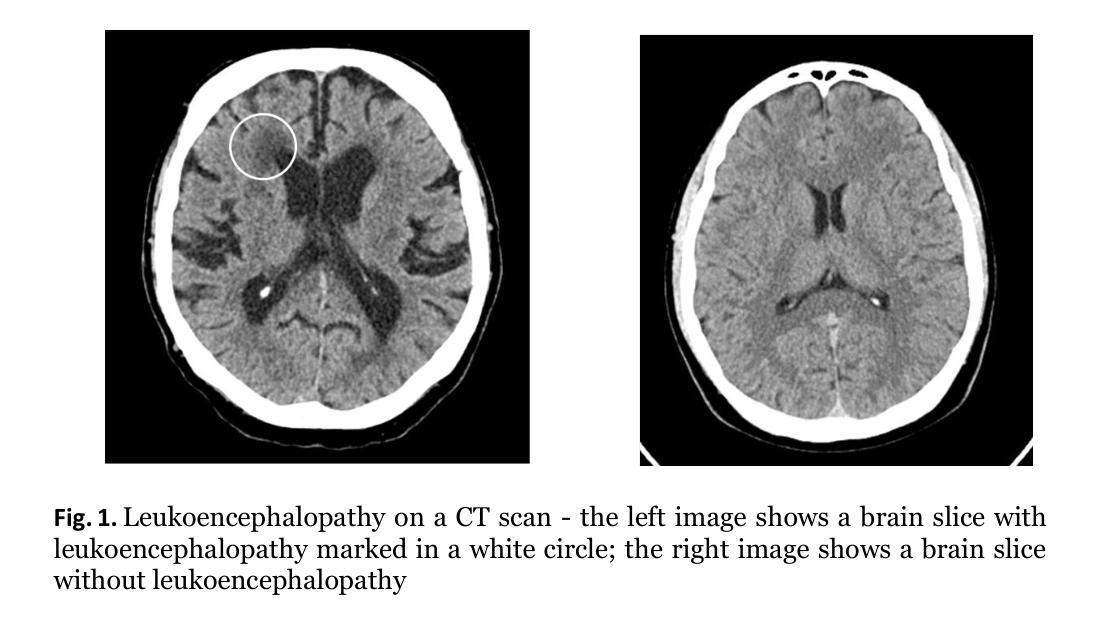
Detection of Vascular Leukoencephalopathy in CT Images
Authors:Z. Cernekova, V. Sisik, F. Jafari
Artificial intelligence (AI) has seen a significant surge in popularity, particularly in its application to medicine. This study explores AI’s role in diagnosing leukoencephalopathy, a small vessel disease of the brain, and a leading cause of vascular dementia and hemorrhagic strokes. We utilized a dataset of approximately 1200 patients with axial brain CT scans to train convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for binary disease classification. Addressing the challenge of varying scan dimensions due to different patient physiologies, we processed the data to a uniform size and applied three preprocessing methods to improve model accuracy. We compared four neural network architectures: ResNet50, ResNet50 3D, ConvNext, and Densenet. The ConvNext model achieved the highest accuracy of 98.5% without any preprocessing, outperforming models with 3D convolutions. To gain insights into model decision-making, we implemented Grad-CAM heatmaps, which highlighted the focus areas of the models on the scans. Our results demonstrate that AI, particularly the ConvNext architecture, can significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy for leukoencephalopathy. This study underscores AI’s potential in advancing diagnostic methodologies for brain diseases and highlights the effectiveness of CNNs in medical imaging applications.
人工智能(AI)的普及率已经显著上升,特别是在医学领域的应用。本研究探讨了人工智能在诊断脑白质病(一种小血管疾病,血管性痴呆和出血性中风的主要原因)中的作用。我们使用了大约1200名患者的轴向脑部CT扫描数据集来训练用于二元疾病分类的卷积神经网络(CNN)。针对因患者生理差异导致的扫描维度不一的挑战,我们对数据进行了统一尺寸处理,并应用了三种预处理方法来提高模型精度。我们比较了四种神经网络架构:ResNet50、ResNet50 3D、ConvNext和Densenet。在没有预处理的情况下,ConvNext模型达到了最高的98.5%的准确率,优于使用3D卷积的模型。为了深入了解模型的决策过程,我们实施了Grad-CAM热图,突出了模型在扫描上的重点区域。我们的结果表明,人工智能,尤其是ConvNext架构,可以显著提高对脑白质病的诊断准确率。本研究强调了人工智能在推进脑部疾病诊断方法方面的潜力,并突出了卷积神经网络在医学成像应用中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究利用卷积神经网络(CNN)技术,针对白质脑病(一种小血管脑部疾病)进行人工智能诊断。通过处理大约1200名患者的脑部CT扫描数据,对四种神经网络架构进行比较,发现ConvNext模型在不经过预处理的情况下,准确率达到98.5%,表现出最佳性能。该研究突显了人工智能在推进脑部疾病诊断方法方面的潜力,以及卷积神经网络在医学成像应用中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 利用人工智能(AI)技术诊断白质脑病,通过卷积神经网络(CNN)进行分类。
- 使用包含约1200名患者的轴向脑CT扫描数据集进行训练。
- 面对因患者生理差异导致的扫描维度不一问题,对数据进行统一尺寸处理,并应用三种预处理方法来提高模型准确性。
- 对比了四种神经网络架构,发现ConvNext模型表现最佳,准确率达到98.5%。
- ConvNext模型在无需预处理的情况下便取得高准确性,优于采用3D卷积的模型。
- 利用Grad-CAM热图了解模型决策过程,突出模型在扫描上的关注区域。
点此查看论文截图

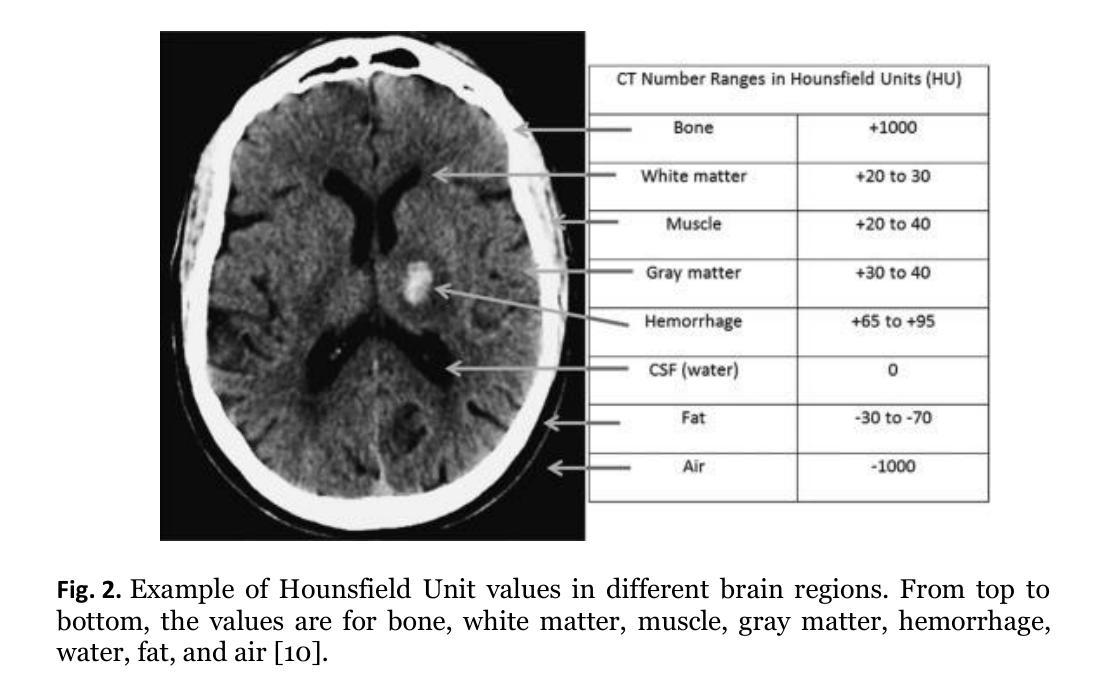
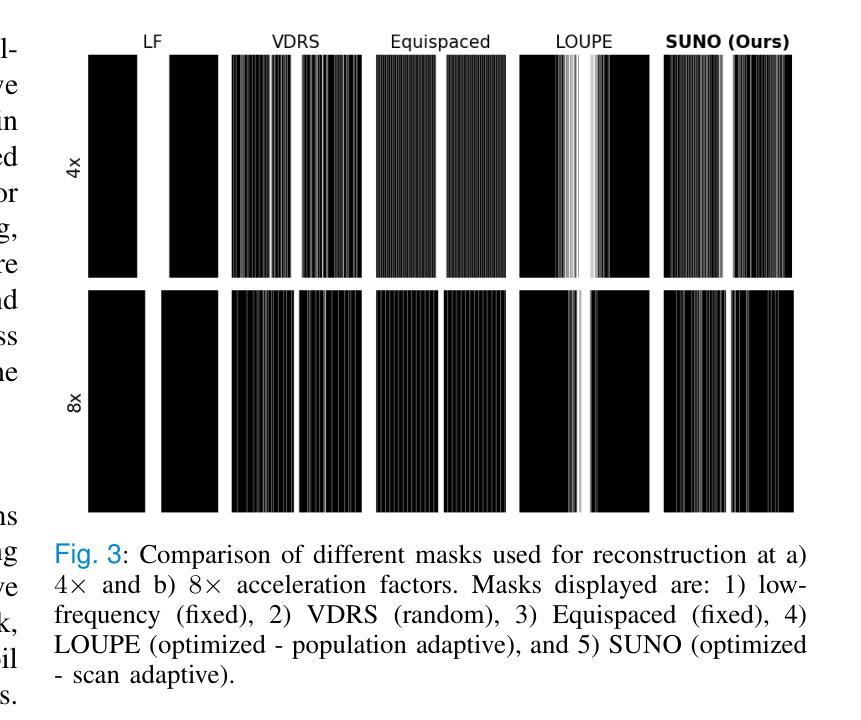
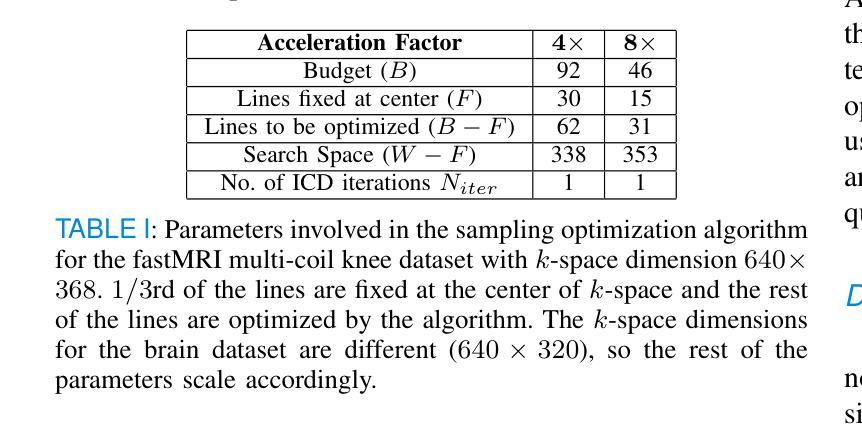
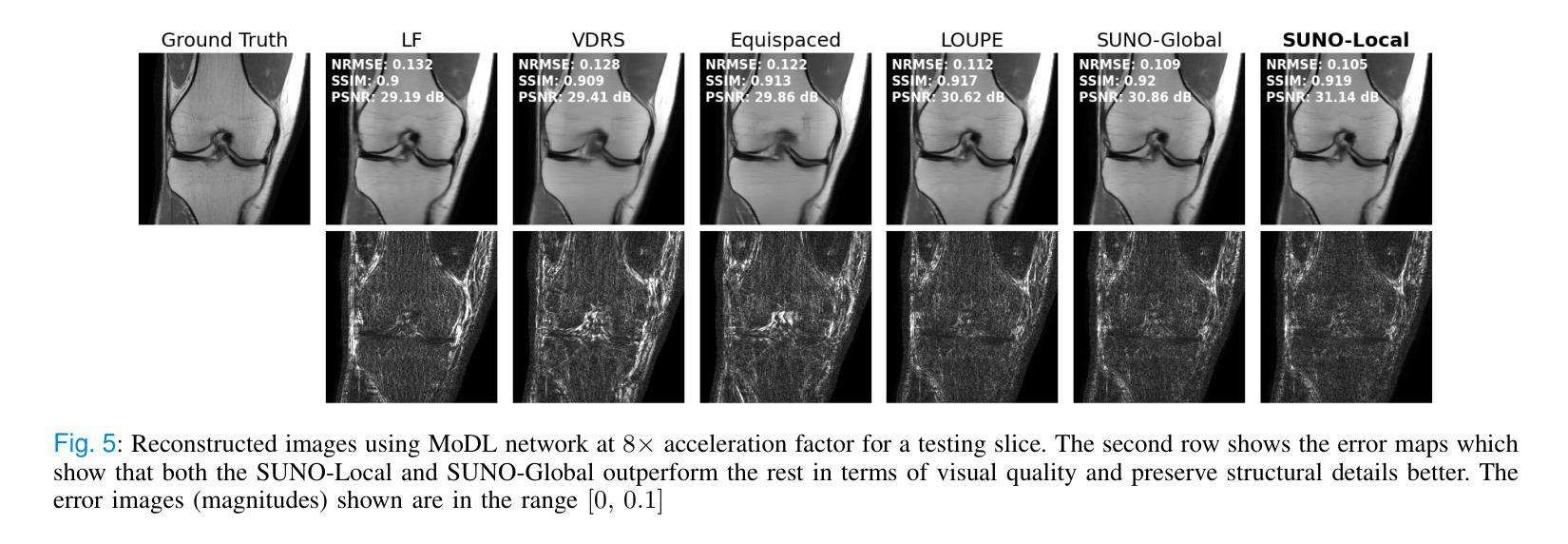
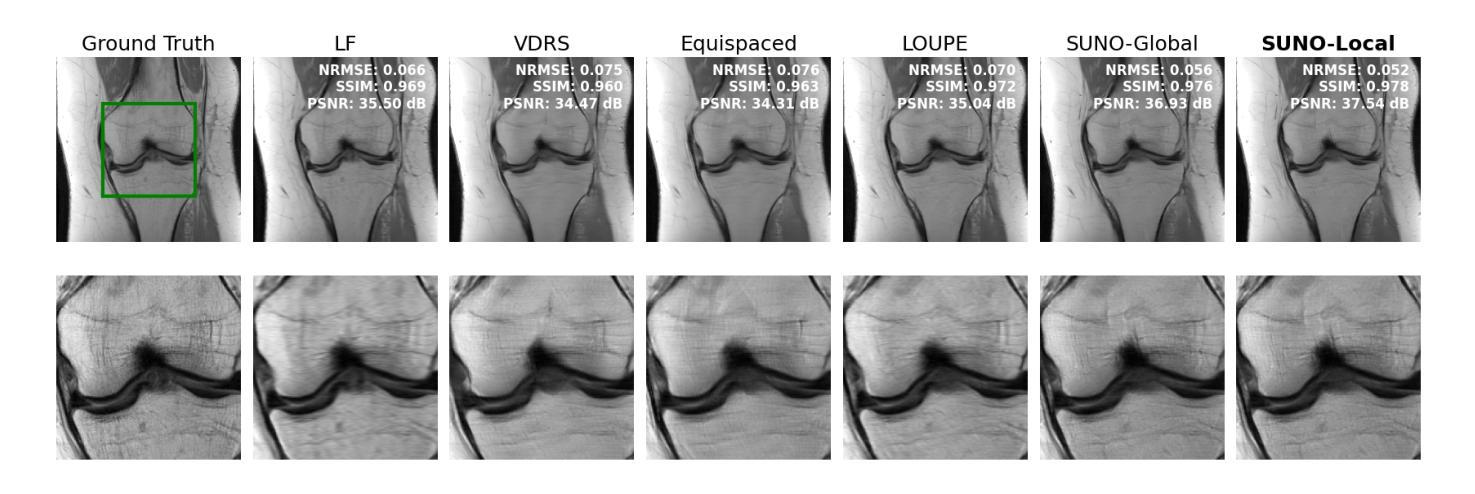
Scan-Adaptive MRI Undersampling Using Neighbor-based Optimization (SUNO)
Authors:Siddhant Gautam, Angqi Li, Nicole Seiberlich, Jeffrey A. Fessler, Saiprasad Ravishankar
Accelerated MRI involves collecting partial k-space measurements to reduce acquisition time, patient discomfort, and motion artifacts, and typically uses regular undersampling patterns or hand-designed schemes. Recent works have studied population-adaptive sampling patterns that are learned from a group of patients (or scans) based on population-specific metrics. However, such a general sampling pattern can be sub-optimal for any specific scan since it may lack scan or slice adaptive details. To overcome this issue, we propose a framework for jointly learning scan-adaptive Cartesian undersampling patterns and a corresponding reconstruction model from a training set. We use an alternating algorithm for learning the sampling patterns and reconstruction model where we use an iterative coordinate descent (ICD) based offline optimization of scan-adaptive k-space sampling patterns for each example in the training set. A nearest neighbor search is then used to select the scan-adaptive sampling pattern at test time from initially acquired low-frequency k-space information. We applied the proposed framework (dubbed SUNO) to the fastMRI multi-coil knee and brain datasets, demonstrating improved performance over currently used undersampling patterns at both 4x and 8x acceleration factors in terms of both visual quality and quantitative metrics. The code for the proposed framework is available at https://github.com/sidgautam95/adaptive-sampling-mri-suno.
加速MRI通过收集部分k空间测量值来减少采集时间、患者不适和运动伪影,通常使用常规欠采样模式或手工设计方案。近期的研究工作研究了基于人群特定指标的群体自适应采样模式,该模式是从一组患者(或扫描)中学习得到的。然而,对于任何特定扫描,这种通用采样模式可能是次优的,因为它可能缺乏扫描或切片自适应细节。为了克服这一问题,我们提出了一种从训练集中联合学习扫描自适应笛卡尔欠采样模式和相关重建模型的框架。我们使用交替算法来学习采样模式和重建模型,其中我们使用基于迭代坐标下降(ICD)的离线优化,针对训练集中的每个示例,对扫描自适应k空间采样模式进行优化。在测试时,使用最近邻搜索从最初获取的低频k空间信息中选择扫描自适应采样模式。我们将所提出的框架(称为SUNO)应用于fastMRI的多线圈膝关节和大脑数据集,在4倍和8倍的加速因子下,无论是在视觉质量还是定量指标方面,都展示了相较于当前使用的欠采样模式有所改善的性能。所提出框架的代码可在https://github.com/sidgautam95/adaptive-sampling-mri-suno上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种联合学习扫描自适应笛卡尔欠采样模式和相应重建模型的框架。该框架通过迭代坐标下降法优化扫描自适应k空间采样模式,并在测试时通过最近邻搜索选择采样模式。应用于fastMRI的多线圈膝关节和脑数据集,该框架在4倍和8倍加速因子下,在视觉质量和定量指标方面均表现出优于现有采样模式的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文本介绍了加速MRI中通过采集部分k空间测量值以减少采集时间、患者不适和运动伪影的方法。
- 现有方法使用常规欠采样模式或手工设计方案,可能存在对特定扫描或切片适应性不足的问题。
- 文本提出了一种联合学习扫描自适应笛卡尔欠采样模式和重建模型的框架。
- 该框架使用迭代坐标下降法优化扫描自适应k空间采样模式,针对训练集中的每个示例进行离线优化。
- 在测试时,通过最近邻搜索选择扫描自适应采样模式。
- 该框架在fastMRI的多线圈膝关节和脑数据集上进行了验证,在视觉质量和定量指标方面均表现出优异性能。
点此查看论文截图

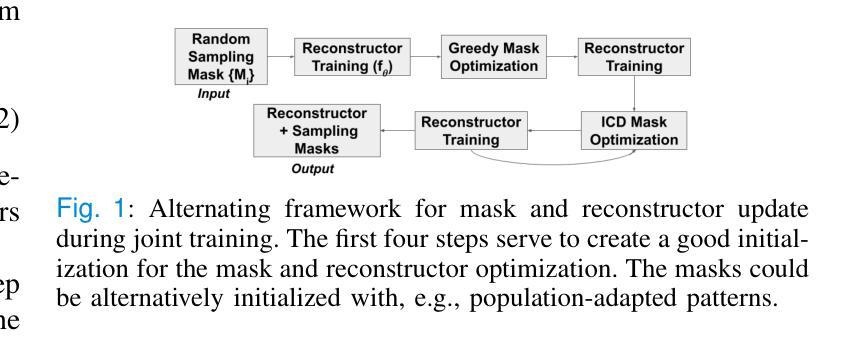
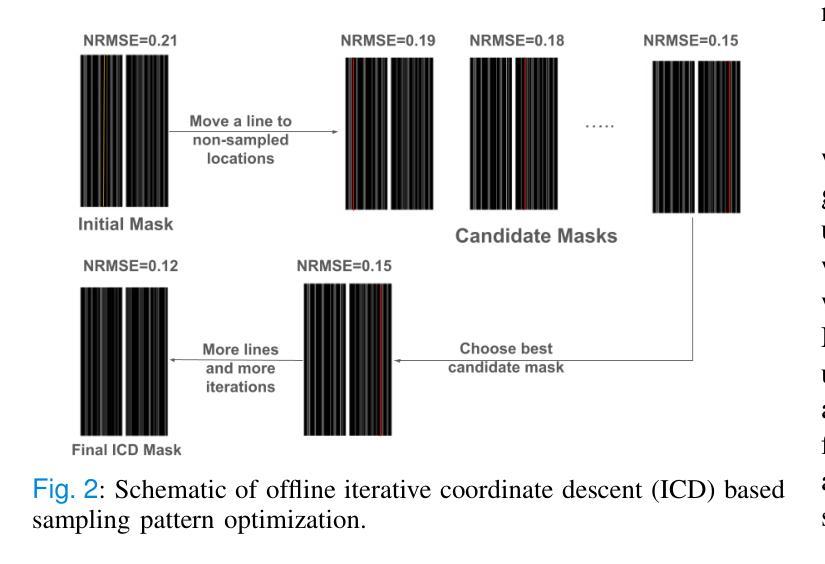
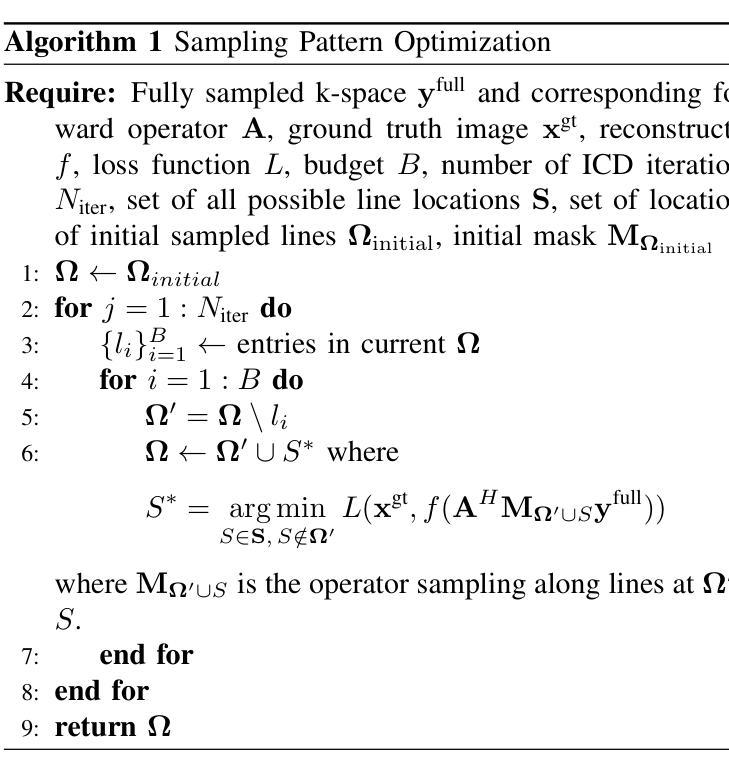
Cyclical accretion regime change in the slow X-ray pulsar 4U 0114+65 observed with Chandra
Authors:Graciela Sanjurjo-Ferrín, Jose Miguel Torrejón, Konstantin Postnov, Michael Nowak, Jose Joaquín Rodes-Roca, Lida Oskinova, Jessica Planelles-Villalva, Norbert Schulz
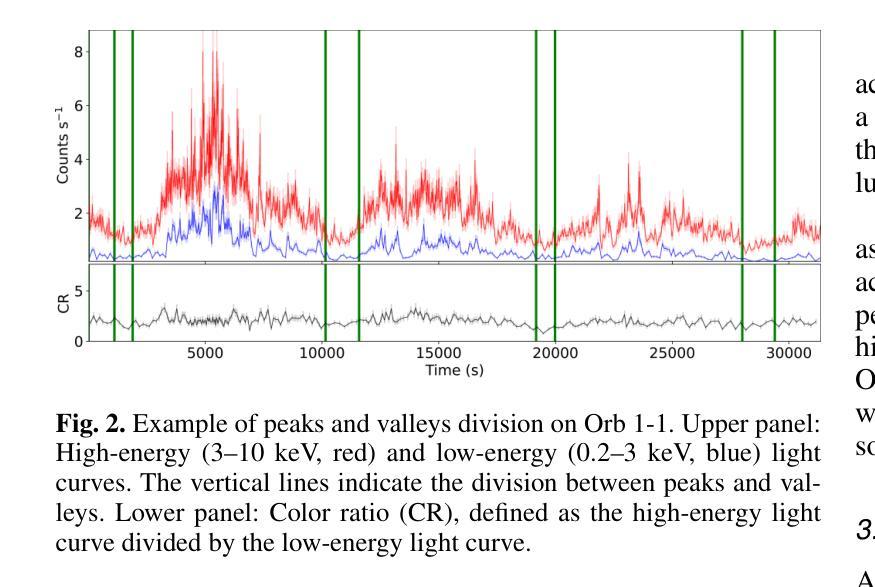
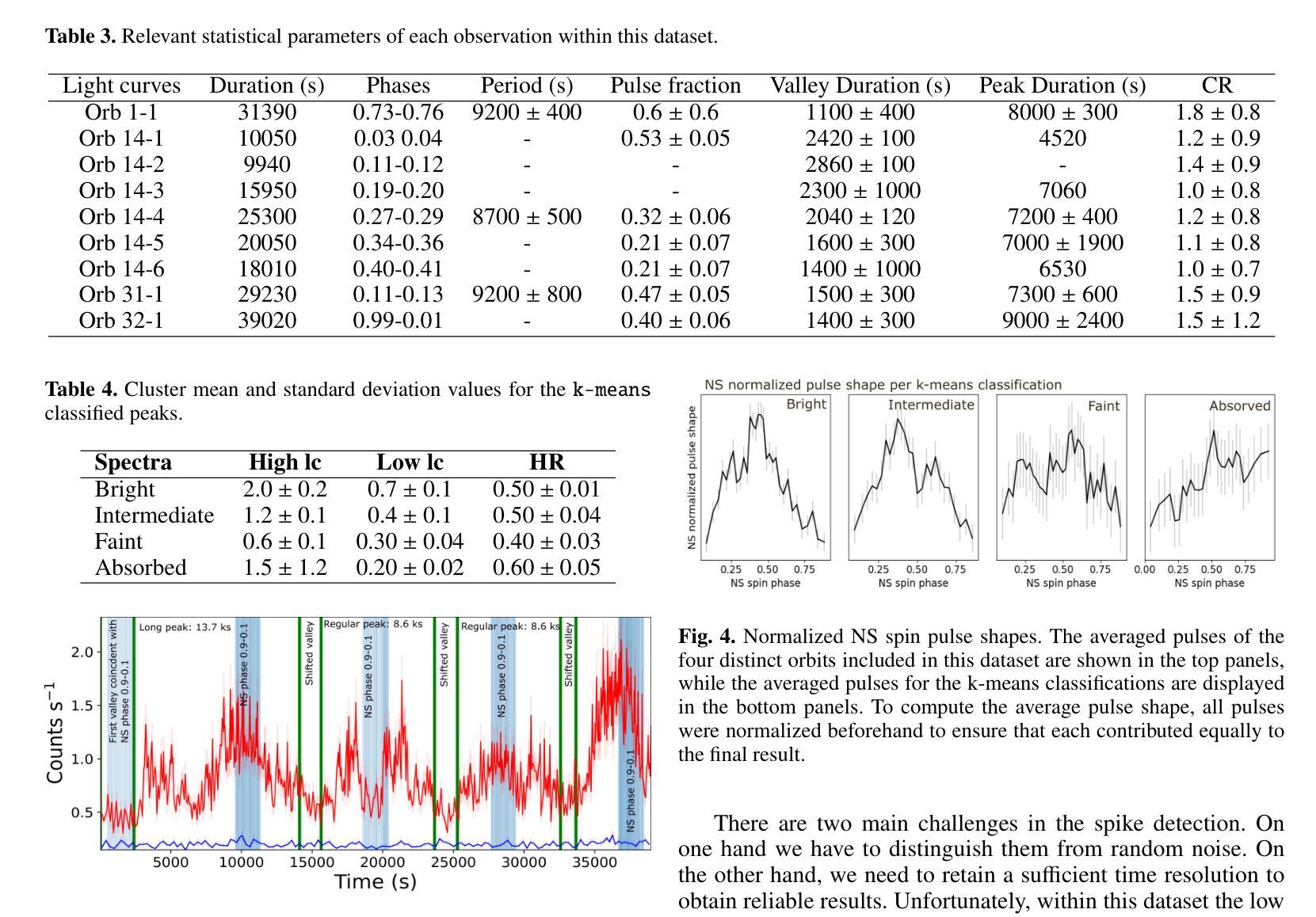
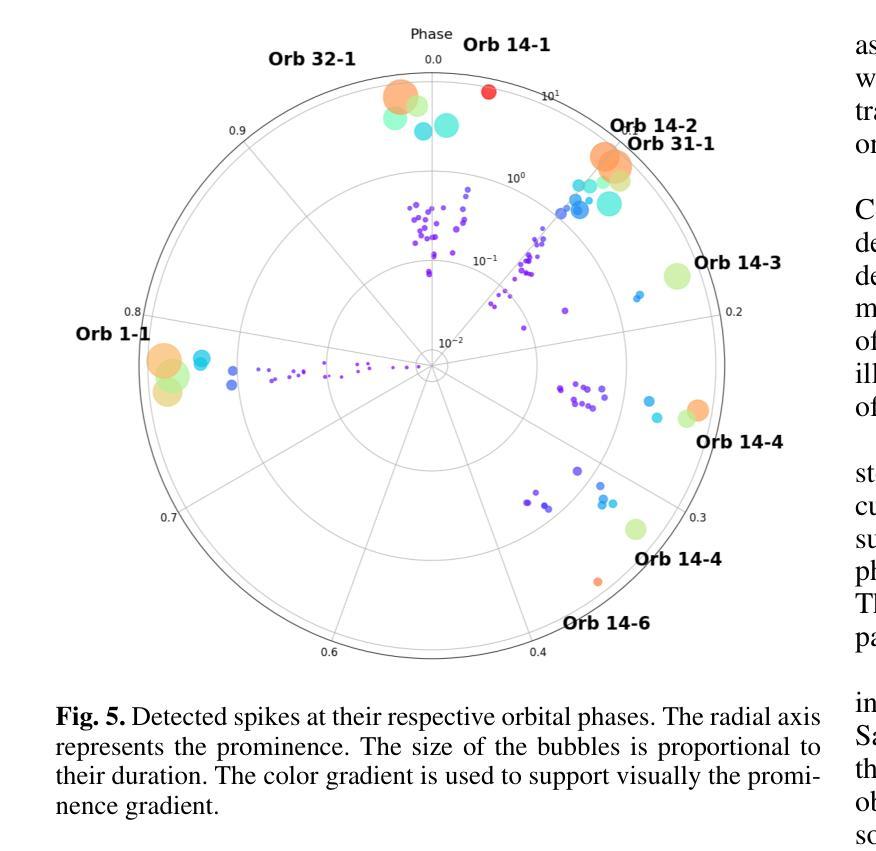
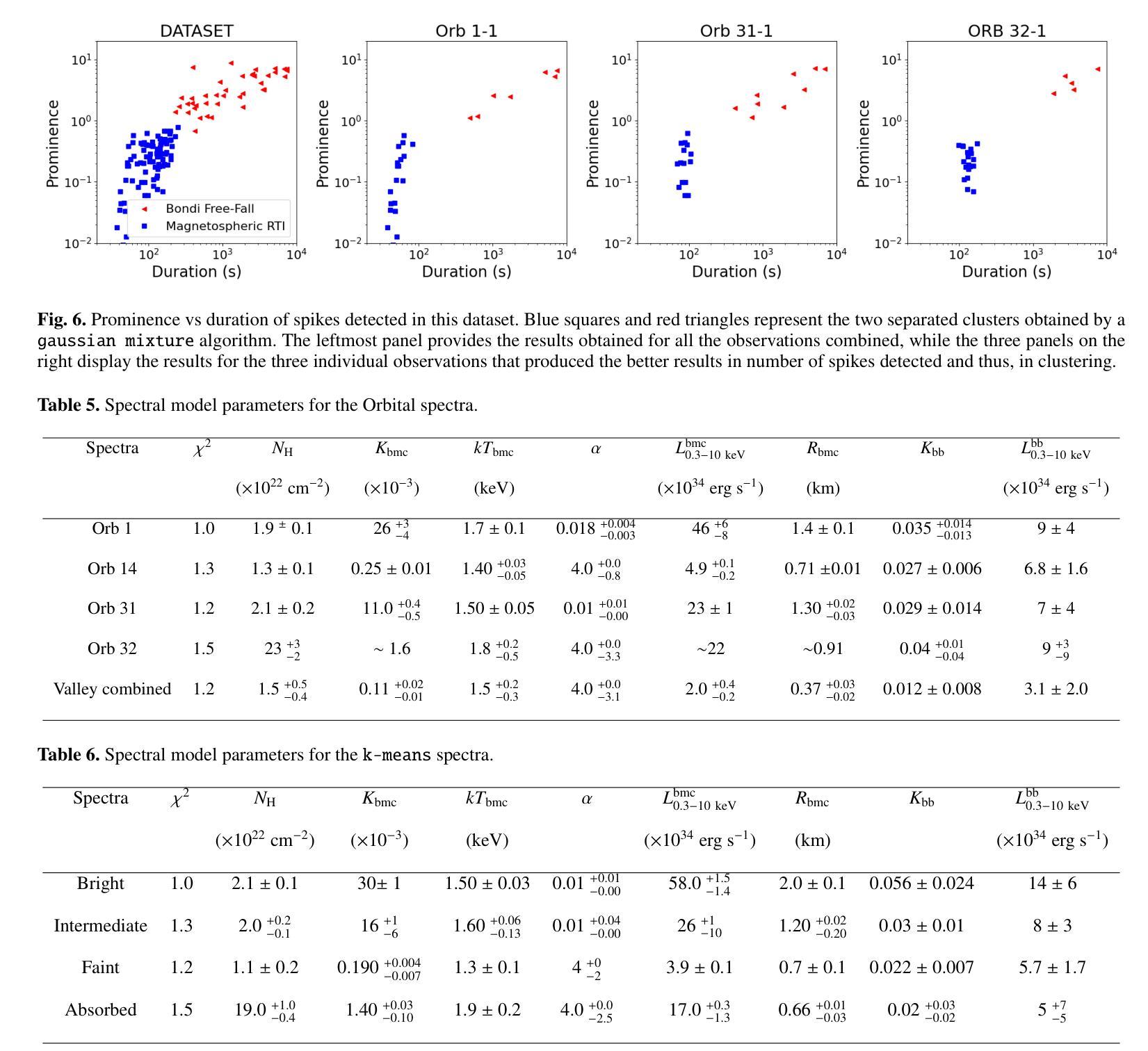
4U 0114+65 is a high-mass X-ray binary system formed by the luminous supergiant B1Ia, known as V{*} V662 Cas, and one of the slowest rotating neutron stars (NS) with a spin period of about 2.6 hours. This fact provides a rare opportunity to study interesting details of the accretion within each individual pulse of the compact object. In this paper, we analyze 200 ks of Chandra grating data, divided into 9 uninterrupted observations around the orbit. The changes in the circumstellar absorption column through the orbit suggest an orbital inclination of $\sim$ $40^{\circ}$ with respect to the observer and a companion mass-loss rate of $\sim$ 8.6 10$^{-7}$ solar masses yr$^{-1}$. The peaks of the NS pulse show a large pulse-to-pulse variability. Three of them show an evolution from a brighter regime to a weaker one. We propose that the efficiency of Compton cooling in this source fluctuates throughout an accumulation cycle. After significant depletion of matter within the magnetosphere, since the settling velocity is $\sim \times$ 2 times lower than the free-fall velocity, the source gradually accumulates matter until the density exceeds a critical threshold. This increase in density triggers a transition to a more efficient Compton cooling regime, leading to a higher mass accretion rate and consequently to an increased brightness.
4U 0114+65是一个高质量X射线双星系统,由明亮的超巨星B1Ia(也称为V{*} V662 Cas)和自转周期约为2.6小时的中子星(NS)组成。这一事实提供了一个难得的机会,可以研究紧凑天体每个脉冲内的吸积过程的有趣细节。在本文中,我们分析了长达20万秒的Chandra光谱数据,这些数据被分成围绕轨道进行的9次不间断观测。恒星周围吸收柱在轨道上的变化表明轨道倾角约为相对于观察者约40°,以及伴随恒星的质量损失率约为每年损失约太阳能质量的8.6乘以十的负七次方。中子星脉冲峰值显示出很大的脉冲间变化。其中三个脉冲峰值从一个较亮的区域逐渐变为一个较弱的区域。我们提出,该源的康普顿冷却效率在一个积累周期内会发生波动。由于磁层内的物质显著减少,且由于沉降速度约为自由落体速度的2倍低,因此物质逐渐积累,直到密度超过临界阈值。密度的增加会引发过渡到更有效的康普顿冷却状态,从而导致更高的物质吸积率,进而导致亮度增加。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
这篇论文针对高质X射线双星系4U 0114+65进行了研究,该系统由巨大超巨星B1Ia(也被称为V*{*} V662 Cas)和旋转速度最慢的中子星(NS)组成,NS自转周期约为2.6小时。分析该双星系统的钱德拉拉塔望远镜获取的为期连续观测了总共长达二十万秒的精细数据后揭示了许多令人振奋的现象和独特现象的研究机遇。研究中通过围绕轨道分成不间断观察的九次观察结果显示轨道公转期间的星际物质变化线索揭示出了近观轨道倾角约四十度以及伴随恒星质量损失率约为每秒损失约太阳质量损失率的负七次方量级的信息。中子星脉冲峰值在脉动中展现出显著的差异波动现象。三个脉冲峰值相继显示一个逐渐暗淡到较弱的过程,推测可能是该源中康普顿冷却效率的波动变化所致。当磁层内的物质被大量消耗后,由于沉降速度大约是自由落体速度的两倍,该源会逐渐积累物质直至密度超过临界阈值,随后引发向更高效的康普顿冷却状态的转变,进而提高了物质积聚率并相应地提高了亮度。这个分析提供了深入理解双星系统中中子星状态转变过程的契机。此外还给出了其独特的轨道特征和物质转移机制的新见解。
关键见解
点此查看论文截图


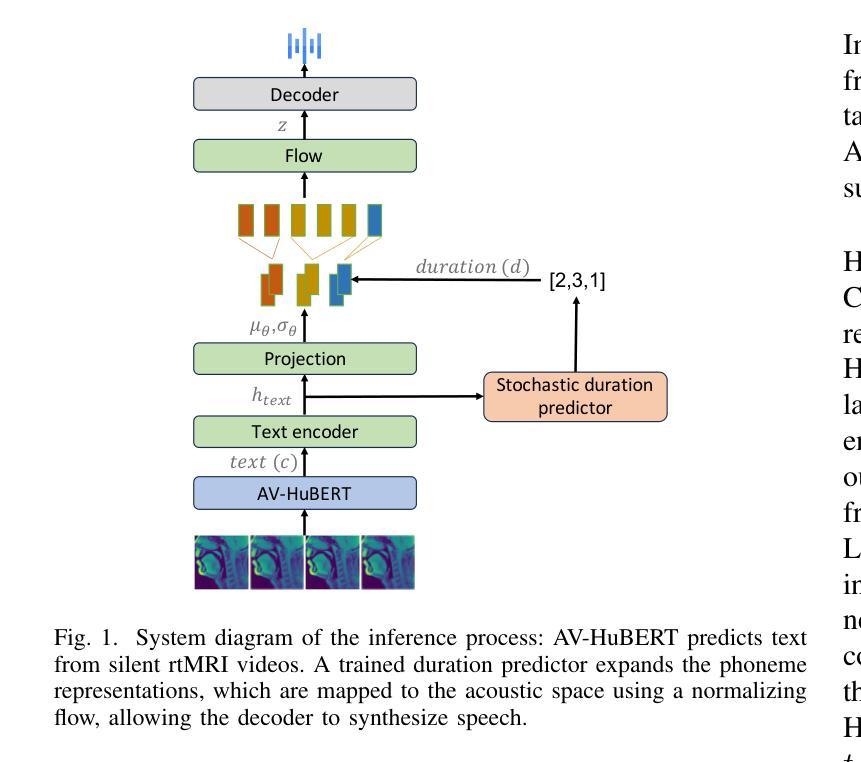
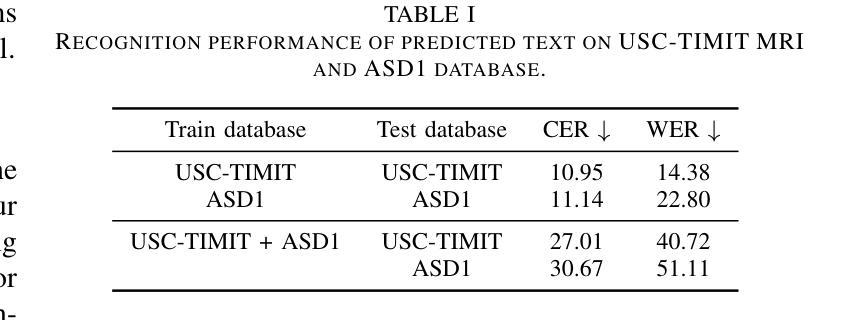
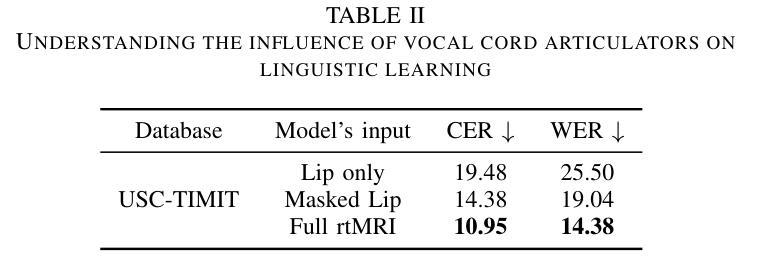
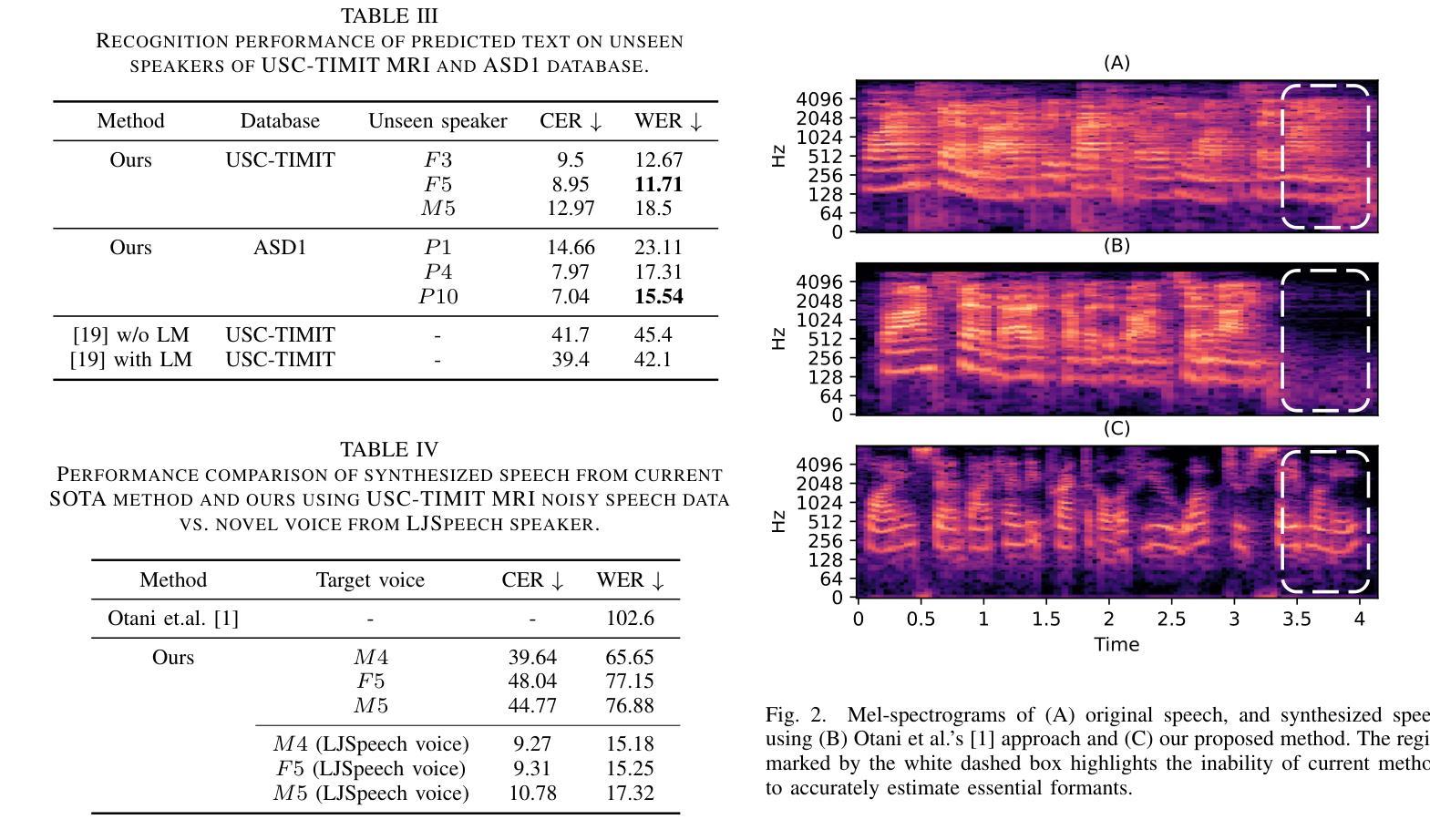
MRI2Speech: Speech Synthesis from Articulatory Movements Recorded by Real-time MRI
Authors:Neil Shah, Ayan Kashyap, Shirish Karande, Vineet Gandhi
Previous real-time MRI (rtMRI)-based speech synthesis models depend heavily on noisy ground-truth speech. Applying loss directly over ground truth mel-spectrograms entangles speech content with MRI noise, resulting in poor intelligibility. We introduce a novel approach that adapts the multi-modal self-supervised AV-HuBERT model for text prediction from rtMRI and incorporates a new flow-based duration predictor for speaker-specific alignment. The predicted text and durations are then used by a speech decoder to synthesize aligned speech in any novel voice. We conduct thorough experiments on two datasets and demonstrate our method’s generalization ability to unseen speakers. We assess our framework’s performance by masking parts of the rtMRI video to evaluate the impact of different articulators on text prediction. Our method achieves a $15.18%$ Word Error Rate (WER) on the USC-TIMIT MRI corpus, marking a huge improvement over the current state-of-the-art. Speech samples are available at https://mri2speech.github.io/MRI2Speech/
先前基于实时磁共振成像(rtMRI)的语音合成模型在很大程度上依赖于嘈杂的地面真实语音。直接在地面真实梅尔频谱图上应用损失会使语音内容与磁共振成像噪声纠缠在一起,导致可理解性较差。我们引入了一种新方法,该方法适应了多模态自监督AV-HuBERT模型,用于从rtMRI进行文本预测,并融入了一个新的基于流的持续时间预测器,以实现针对特定发言者的对齐。预测的文本和持续时间随后被语音解码器用于合成任何新颖声音的对齐语音。我们在两个数据集上进行了全面的实验,证明了我们方法对于未见过的发言者的泛化能力。我们通过遮挡rtMRI视频的部分内容来评估我们框架的性能,以评估不同发音器官对文本预测的影响。我们的方法在USC-TIMIT MRI语料库上实现了15.18%的单词错误率(WER),标志着与当前先进技术相比的巨大改进。语音样本可在https://mri2speech.github.io/MRI2Speech/上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的基于实时磁共振成像(rtMRI)的语音合成方法,该方法采用多模态自监督AV-HuBERT模型进行文本预测,并引入基于流的持续时间预测器以实现说话人特定的对齐。通过合成与真实语音对齐的文本和持续时间,然后使用语音解码器生成任意新声音的语音。实验表明,该方法在未见过的说话人上具有良好的泛化能力,且在USC-TIMIT MRI语料库上的词错误率(WER)达到15.18%,较现有技术有显著改善。
Key Takeaways
- 引入新型方法,结合实时磁共振成像(rtMRI)和多模态自监督AV-HuBERT模型进行语音合成。
- 采用基于流的持续时间预测器,实现说话人特定的文本对齐。
- 方法能够在未见过的说话人上良好泛化。
- 通过遮挡rtMRI视频的部分内容,评估不同发音器官对文本预测的影响。
- 在USC-TIMIT MRI语料库上实现较低的词错误率(WER),达到15.18%。
- 提供语音样本以供评估。
点此查看论文截图

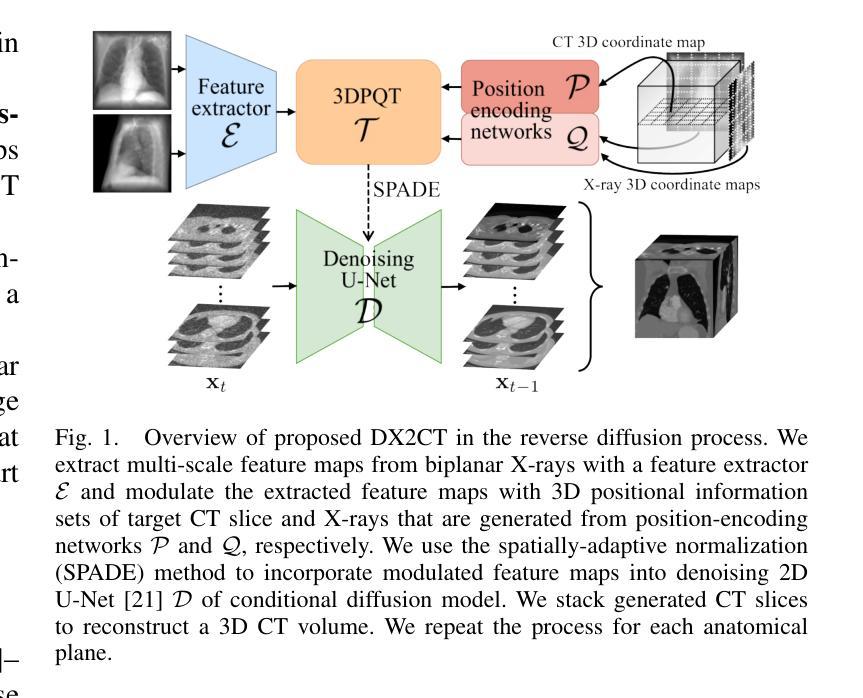
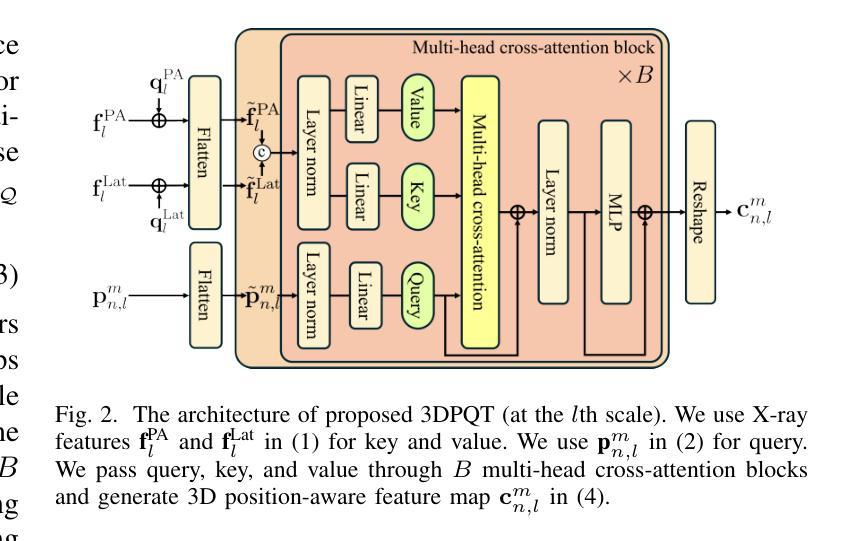
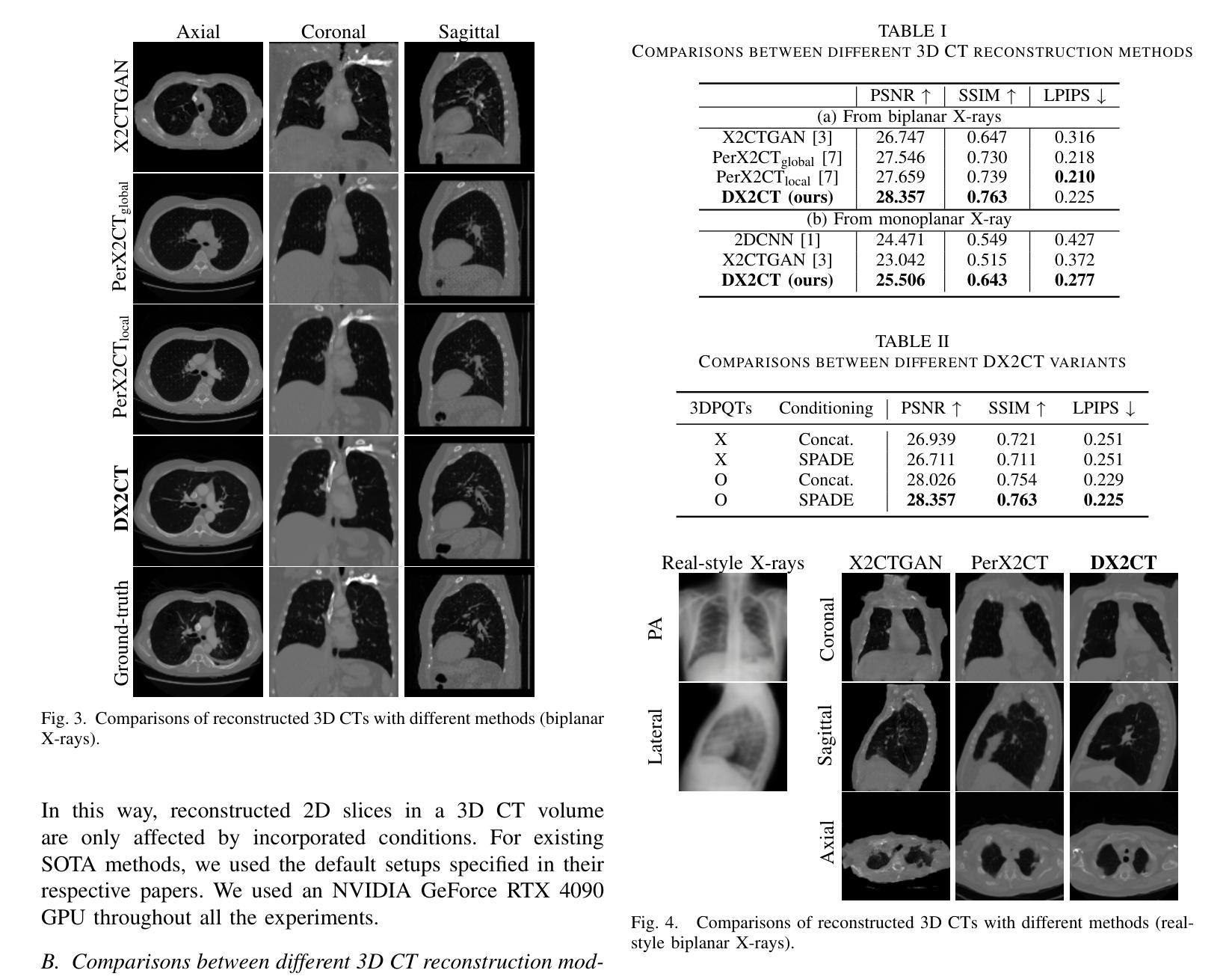
DX2CT: Diffusion Model for 3D CT Reconstruction from Bi or Mono-planar 2D X-ray(s)
Authors:Yun Su Jeong, Hye Bin Yoo, Il Yong Chun
Computational tomography (CT) provides high-resolution medical imaging, but it can expose patients to high radiation. X-ray scanners have low radiation exposure, but their resolutions are low. This paper proposes a new conditional diffusion model, DX2CT, that reconstructs three-dimensional (3D) CT volumes from bi or mono-planar X-ray image(s). Proposed DX2CT consists of two key components: 1) modulating feature maps extracted from two-dimensional (2D) X-ray(s) with 3D positions of CT volume using a new transformer and 2) effectively using the modulated 3D position-aware feature maps as conditions of DX2CT. In particular, the proposed transformer can provide conditions with rich information of a target CT slice to the conditional diffusion model, enabling high-quality CT reconstruction. Our experiments with the bi or mono-planar X-ray(s) benchmark datasets show that proposed DX2CT outperforms several state-of-the-art methods. Our codes and model will be available at: https://www.github.com/intyeger/DX2CT.
计算机断层扫描(CT)提供高分辨率医学成像,但可能会使患者暴露在较高的辐射之下。X射线扫描仪的辐射暴露较低,但其分辨率较低。本文提出了一种新的条件扩散模型DX2CT,可从二维或单平面X射线图像重建三维(3D)CT体积。提出的DX2CT由两个关键组件组成:1)使用新型变压器将二维(2D)X射线特征图与CT体积的三维(3D)位置进行调制;2)有效地利用调制后的三维定位特征图作为DX2CT的条件。特别是,所提出的变压器能够提供目标CT切片丰富的信息给条件扩散模型,从而实现高质量的CT重建。我们在二维或单平面X射线基准数据集上的实验表明,提出的DX2CT优于几种最新方法。我们的代码和模型将在https://www.github.com/intyeger/DX2CT上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的条件扩散模型DX2CT,可从二维X射线图像重建出三维CT体积,降低患者辐射暴露。DX2CT包括两个关键组件:使用新变压器调制特征图,并使用调制后的三维位置感知特征图作为条件。实验表明,DX2CT在二维X射线基准数据集上的表现优于其他最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- DX2CT是一种新的条件扩散模型,能够从二维X射线图像重建出高质量的三维CT体积。
- DX2CT包含两个核心组件:使用新变压器调制特征图,并使用三维位置感知特征图作为条件。
- 提出的变压器能够为目标CT切片提供丰富的信息,以支持条件扩散模型。
- DX2CT在二维X射线基准数据集上的表现优于其他最先进的方法。
- DX2CT有助于降低患者接受的高辐射暴露风险。
- 该模型的代码和模型将在指定链接上公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

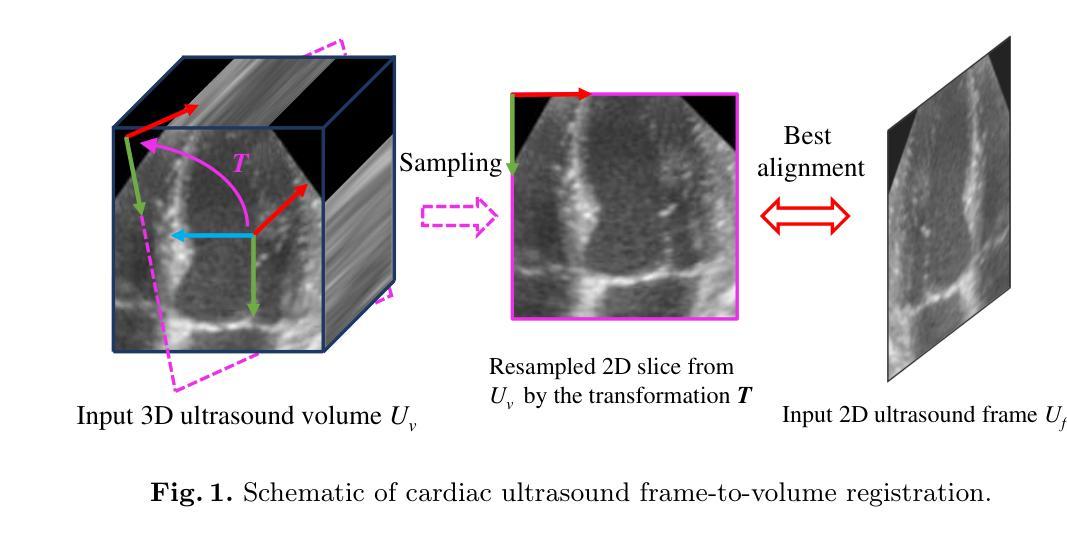
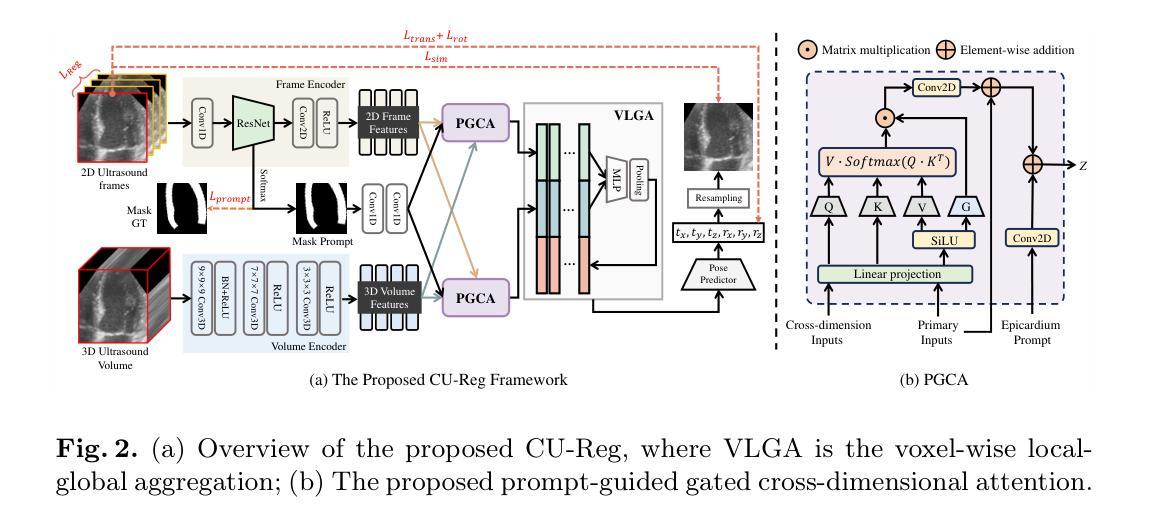
Epicardium Prompt-guided Real-time Cardiac Ultrasound Frame-to-volume Registration
Authors:Long Lei, Jun Zhou, Jialun Pei, Baoliang Zhao, Yueming Jin, Yuen-Chun Jeremy Teoh, Jing Qin, Pheng-Ann Heng
A comprehensive guidance view for cardiac interventional surgery can be provided by the real-time fusion of the intraoperative 2D images and preoperative 3D volume based on the ultrasound frame-to-volume registration. However, cardiac ultrasound images are characterized by a low signal-to-noise ratio and small differences between adjacent frames, coupled with significant dimension variations between 2D frames and 3D volumes to be registered, resulting in real-time and accurate cardiac ultrasound frame-to-volume registration being a very challenging task. This paper introduces a lightweight end-to-end Cardiac Ultrasound frame-to-volume Registration network, termed CU-Reg. Specifically, the proposed model leverages epicardium prompt-guided anatomical clues to reinforce the interaction of 2D sparse and 3D dense features, followed by a voxel-wise local-global aggregation of enhanced features, thereby boosting the cross-dimensional matching effectiveness of low-quality ultrasound modalities. We further embed an inter-frame discriminative regularization term within the hybrid supervised learning to increase the distinction between adjacent slices in the same ultrasound volume to ensure registration stability. Experimental results on the reprocessed CAMUS dataset demonstrate that our CU-Reg surpasses existing methods in terms of registration accuracy and efficiency, meeting the guidance requirements of clinical cardiac interventional surgery.
通过基于超声帧到体积注册的术中2D图像和术前3D体积的实时融合,可以为心脏介入手术提供全面的指导视图。然而,心脏超声图像的特点是信噪比低,相邻帧之间的差异小,以及要注册的2D帧和3D体积之间尺寸变化的显著差异,导致实时和准确的心脏超声帧到体积注册是一项具有挑战性的任务。本文介绍了一种轻量级的端到端心脏超声帧到体积注册网络,称为CU-Reg。具体而言,所提出的模型利用心包提示引导解剖线索来加强2D稀疏和3D密集特征的交互,然后对增强特征进行像素级的局部-全局聚合,从而提高低质量超声模态的跨维度匹配效果。我们进一步在混合监督学习中嵌入帧间判别正则化项,以增加同一超声体积内相邻切片之间的区分度,以确保注册的稳定性。在重新处理的CAMUS数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的CU-Reg在注册准确性和效率方面超过了现有方法,满足了临床心脏介入手术的指导要求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by MICCAI 2024
Summary
实时融合术中二维图像和术前三维体积数据,基于超声帧到体积注册技术,为心脏介入手术提供全面指导。心脏超声图像存在信号噪声比低、相邻帧差异小、二维帧与待注册三维体积尺寸变化显著等问题,使得实时准确的心脏超声帧到体积注册具有挑战性。本文引入了一种轻量级的端到端心脏超声帧到体积注册网络CU-Reg,利用心包引导的解剖线索加强二维稀疏和三维密集特征的交互,通过增强特征的像素级局部全局聚合,提高低质量超声模态的跨维度匹配效果。此外,本文还在混合监督学习中嵌入帧间判别正则化项,增加同一超声体积内相邻切片的区分度,确保注册稳定性。在重新处理的CAMUS数据集上的实验结果表明,CU-Reg在注册精度和效率方面超越了现有方法,符合临床心脏介入手术的指导要求。
Key Takeaways
- 实时融合术中二维图像和术前三维体积数据,为心脏介入手术提供指导。
- 心脏超声图像存在低信号噪声比和尺寸变化大的挑战。
- 引入轻量级端到端心脏超声帧到体积注册网络CU-Reg。
- CU-Reg利用心包引导的解剖线索强化特征交互。
- 通过像素级局部全局聚合增强特征,提高低质量超声模态的匹配效果。
- 在混合监督学习中嵌入帧间判别正则化项,提高注册稳定性。
点此查看论文截图

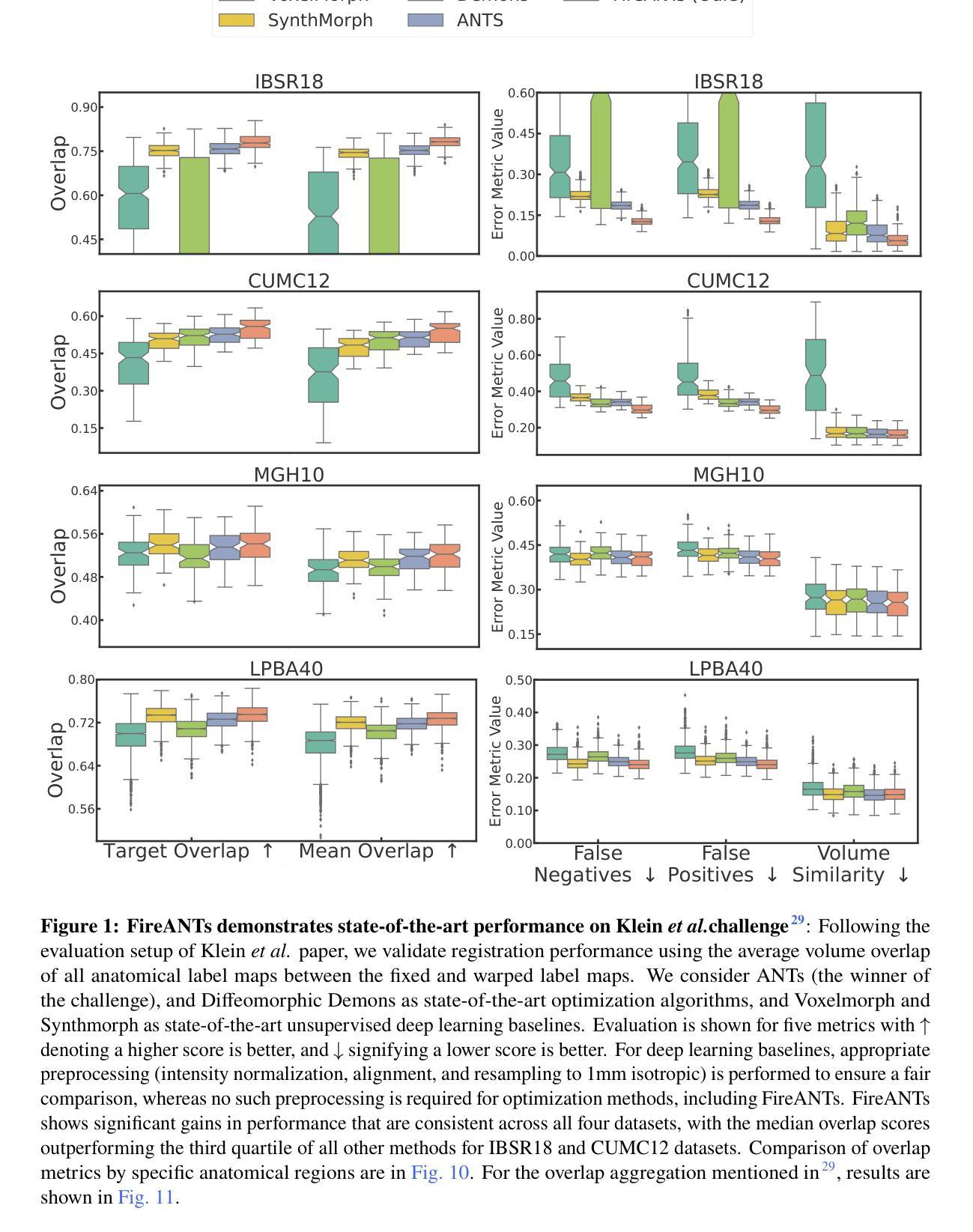
FireANTs: Adaptive Riemannian Optimization for Multi-Scale Diffeomorphic Matching
Authors:Rohit Jena, Pratik Chaudhari, James C. Gee
The paper proposes FireANTs, the first multi-scale Adaptive Riemannian Optimization algorithm for dense diffeomorphic image matching. One of the most critical and understudied aspects of diffeomorphic image matching algorithms are its highly ill-conditioned nature. We quantitatively capture the extent of ill-conditioning in a typical MRI matching task, motivating the need for an adaptive optimization algorithm for diffeomorphic matching. To this end, FireANTs generalizes the concept of momentum and adaptive estimates of the Hessian to mitigate this ill-conditioning in the non-Euclidean space of diffeomorphisms. Unlike common non-Euclidean manifolds, we also formalize considerations for multi-scale optimization of diffeomorphisms. Our rigorous mathematical results and operational contributions lead to a state-of-the-art dense matching algorithm that can be applied to generic image data with remarkable accuracy and robustness. We demonstrate consistent improvements in image matching performance across a spectrum of community-standard medical and biological correspondence matching challenges spanning a wide variety of image modalities, anatomies, resolutions, acquisition protocols, and preprocessing pipelines. This improvement is supplemented by from 300x up to 3200x speedup over existing state-of-the-art algorithms. For the first time, we perform diffeomorphic matching of sub-micron mouse cortex volumes at native resolution. Our fast implementation also enables hyperparameter studies that were intractable with existing correspondence matching algorithms.
本文提出了FireANTs,这是首个多尺度的自适应黎曼优化算法,用于密集的同胚图像匹配。同胚图像匹配算法中最重要的且尚未得到充分研究的一个方面是其高度病态性质。我们定量捕获了典型MRI匹配任务中的病态程度,从而强调了需要自适应优化算法进行同胚匹配。为此,FireANTs推广了动量的概念以及海森矩阵的自适应估计,以缓解在非欧几里得同胚空间中的病态问题。与常见的非欧几里得流形不同,我们还正式考虑了同胚的多尺度优化。我们严谨的数学结果和操作贡献导致最先进的密集匹配算法,可以非常准确和稳健地应用于通用图像数据。我们在一系列社区标准的医学和生物对应匹配挑战中证明了图像匹配性能的持续提高,这些挑战涵盖了各种图像模式、解剖学、分辨率、采集协议和预处理流程。这种改进还辅以现有最先进的算法的300倍至高达3200倍的速度提升。我们首次以原始分辨率对亚微米小鼠皮层体积进行同胚匹配。我们的快速实现还使得以前难以处理的超参数研究成为可能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为FireANTs的多尺度自适应黎曼优化算法,用于密集微分同胚图像匹配。该算法解决了微分同胚图像匹配算法中高度病态的问题,通过引入动量和Hessian的自适应估计来适应非欧几里得空间中的微分同胚。此外,本文还正式考虑了微分同胚的多尺度优化,提出了一种最先进的密集匹配算法。该算法可应用于通用图像数据,具有较高的准确性和鲁棒性,并且在跨多种图像模态、解剖学、分辨率、采集协议和预处理管道的医学和生物对应匹配挑战中表现出一致的性能改进。相较于现有算法,该算法实现了从300倍到3200倍的加速。此外,本文首次实现了在原始分辨率下的微米级小鼠皮层体积的微分同胚匹配。
Key Takeaways
- FireANTs是一种多尺度自适应黎曼优化算法,用于密集微分同胚图像匹配。
- 该算法解决了微分同胚图像匹配中的高度病态问题。
- 通过引入动量和Hessian的自适应估计,FireANTs适应了非欧几里得空间中的微分同胚。
- 相比其他算法,FireANTs实现了显著的性能提升和加速。
- 该算法在多种医学和生物对应匹配挑战中表现优异,适用于多种图像模态和数据特点。
- FireANTs首次实现了在原始分辨率下的微米级小鼠皮层体积的微分同胚匹配。
点此查看论文截图

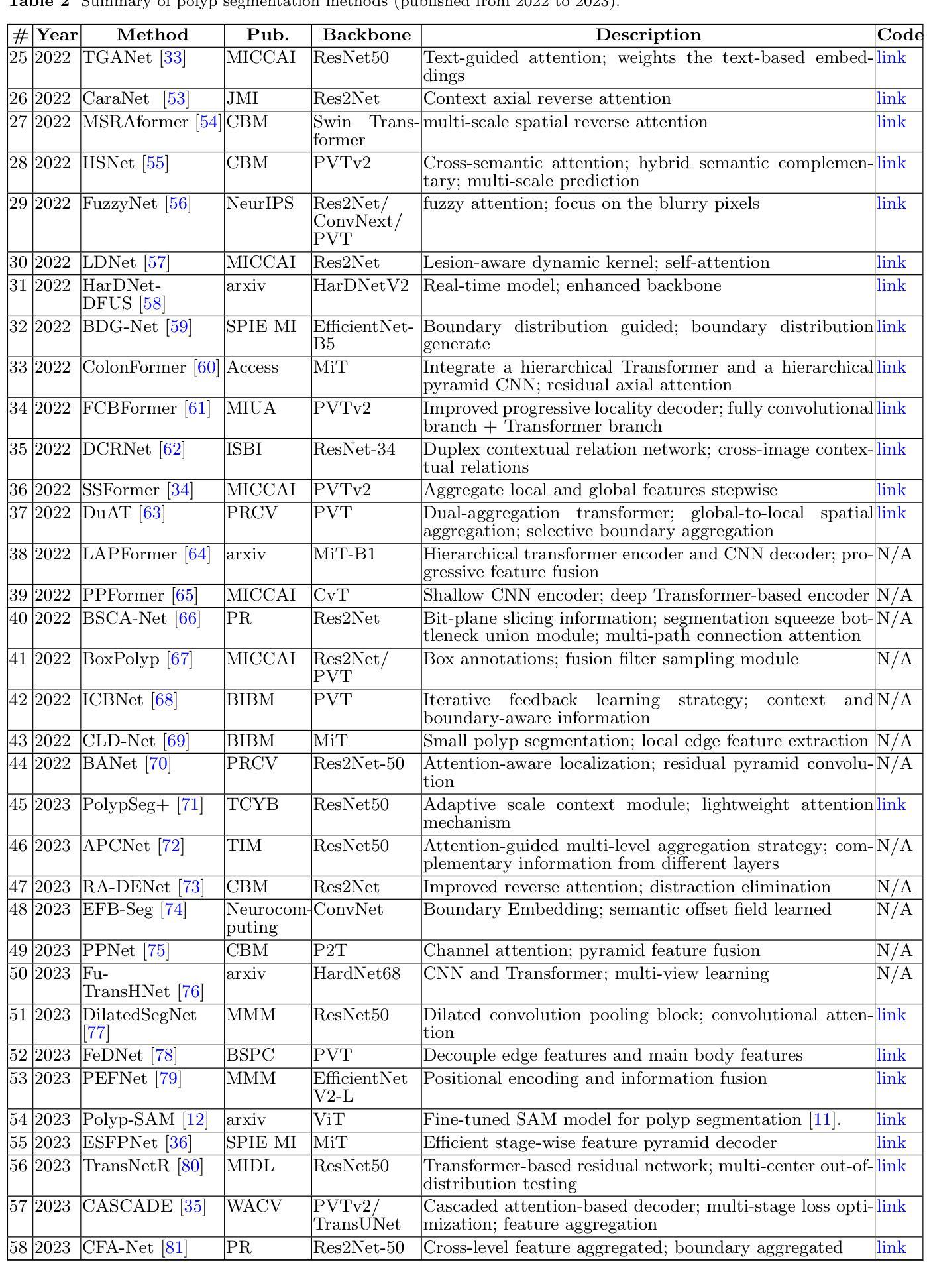
A Survey on Deep Learning for Polyp Segmentation: Techniques, Challenges and Future Trends
Authors:Jiaxin Mei, Tao Zhou, Kaiwen Huang, Yizhe Zhang, Yi Zhou, Ye Wu, Huazhu Fu
Early detection and assessment of polyps play a crucial role in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC). Polyp segmentation provides an effective solution to assist clinicians in accurately locating and segmenting polyp regions. In the past, people often relied on manually extracted lower-level features such as color, texture, and shape, which often had issues capturing global context and lacked robustness to complex scenarios. With the advent of deep learning, more and more outstanding medical image segmentation algorithms based on deep learning networks have emerged, making significant progress in this field. This paper provides a comprehensive review of polyp segmentation algorithms. We first review some traditional algorithms based on manually extracted features and deep segmentation algorithms, then detail benchmark datasets related to the topic. Specifically, we carry out a comprehensive evaluation of recent deep learning models and results based on polyp sizes, considering the pain points of research topics and differences in network structures. Finally, we discuss the challenges of polyp segmentation and future trends in this field. The models, benchmark datasets, and source code links we collected are all published at https://github.com/taozh2017/Awesome-Polyp-Segmentation.
早期检测和评估息肉在结直肠癌(CRC)的预防和治疗中起着至关重要的作用。息肉分割为临床医生准确定位和分割息肉区域提供了有效的解决方案。过去,人们通常依赖手动提取的低级特征,如颜色、纹理和形状,这些特征往往难以捕捉全局上下文,并且对复杂场景缺乏鲁棒性。随着深度学习的出现,基于深度学习网络的出色医学图像分割算法不断涌现,在这一领域取得了显著进展。本文对息肉分割算法进行了全面综述。我们首先回顾了一些基于手动提取特征和深度分割算法的传统算法,然后详细介绍了与此主题相关的基准数据集。具体来说,我们对最近的深度学习模型进行了全面的评估,并基于息肉大小给出了结果,同时考虑了研究主题的痛点和网络结构的差异。最后,我们讨论了息肉分割的挑战和该领域的未来趋势。我们收集的模型、基准数据集和源代码链接均已发布在https://github.com/taozh2017/Awesome-Polyp-Segmentation。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Have been published in Visual Intelligence
Summary
本文综述了息肉分割算法在结直肠癌预防和诊疗中的重要性,从传统算法到基于深度学习的算法进行了全面评价。文章详细介绍了与息肉分割相关的基准数据集,并对近期深度学习模型在息肉大小方面的表现进行了全面评估,同时探讨了息肉分割的挑战和未来趋势。
Key Takeaways
- 早期发现和评估息肉对结直肠癌的预防和诊疗至关重要。
- 息肉分割有助于临床医生准确定位和分割息肉区域。
- 传统算法主要依赖手动提取的低层次特征,存在捕捉全局上下文不足和复杂场景鲁棒性不足的问题。
- 深度学习在医学图像分割领域取得了显著进展,出现了许多出色的基于深度学习的息肉分割算法。
- 文章全面评价了息肉分割算法,包括对传统算法和深度分割算法的回顾。
- 文章详细介绍了与息肉分割相关的基准数据集,并对不同网络结构的深度学习模型在息肉大小方面的表现进行了评估。
点此查看论文截图

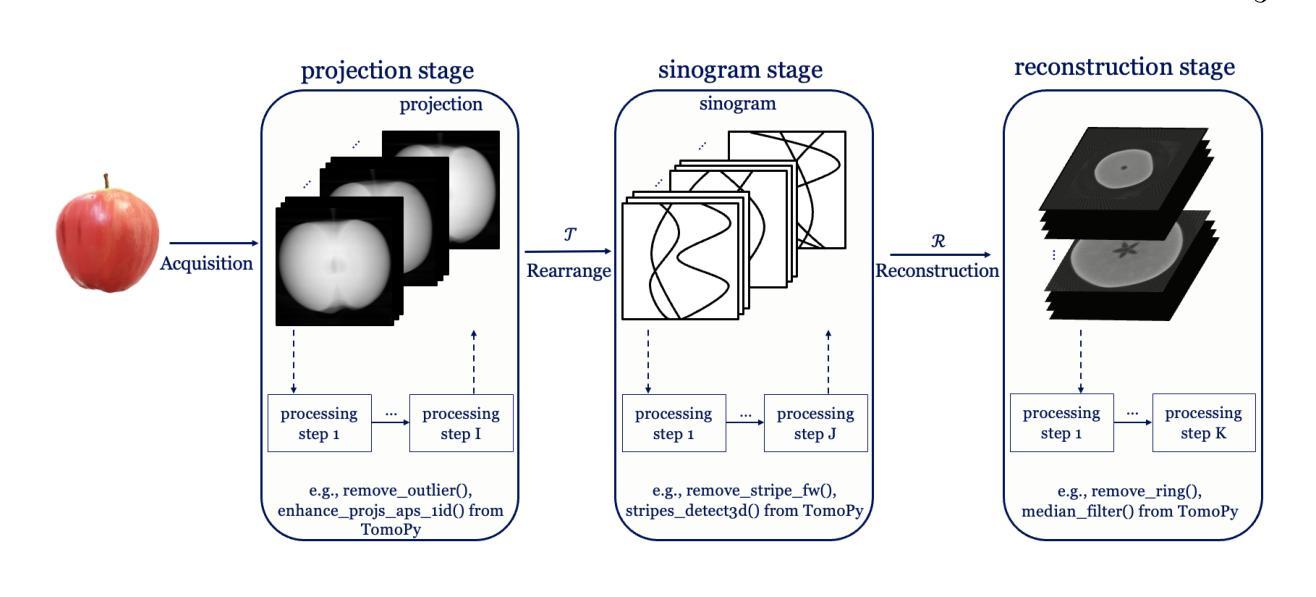
Multi-stage Deep Learning Artifact Reduction for Pallel-beam Computed Tomography
Authors:Jiayang Shi, Daniel M. Pelt, K. Joost Batenburg
Computed Tomography (CT) using synchrotron radiation is a powerful technique that, compared to lab-CT techniques, boosts high spatial and temporal resolution while also providing access to a range of contrast-formation mechanisms. The acquired projection data is typically processed by a computational pipeline composed of multiple stages. Artifacts introduced during data acquisition can propagate through the pipeline, and degrade image quality in the reconstructed images. Recently, deep learning has shown significant promise in enhancing image quality for images representing scientific data. This success has driven increasing adoption of deep learning techniques in CT imaging. Various approaches have been proposed to incorporate deep learning into computational pipelines, but each has limitations in addressing artifacts effectively and efficiently in synchrotron CT, either in properly addressing the specific artifacts, or in computational efficiency. Recognizing these challenges, we introduce a novel method that incorporates separate deep learning models at each stage of the tomography pipeline-projection, sinogram, and reconstruction-to address specific artifacts locally in a data-driven way. Our approach includes bypass connections that feed both the outputs from previous stages and raw data to subsequent stages, minimizing the risk of error propagation. Extensive evaluations on both simulated and real-world datasets illustrate that our approach effectively reduces artifacts and outperforms comparison methods.
使用同步辐射的计算机断层扫描(CT)是一种强大的技术,与实验室CT技术相比,它提高了空间和时间分辨率,同时提供了多种对比剂形成机制。所获得的投影数据通常通过由多个阶段组成的计算流程进行处理。在数据采集过程中引入的伪影可以通过流水线传播,并降低重建图像的图像质量。最近,深度学习在提高科学图像图像质量方面显示出巨大潜力。这一成功推动了深度学习技术在CT成像中的不断采用。虽然已提出将深度学习纳入计算流程的各种方法,但每种方法在有效和高效地解决同步加速器CT中的伪影方面都存在局限性,要么是无法适当处理特定伪影,要么是计算效率低下。认识到这些挑战,我们引入了一种新方法,在层析成像流程的每个阶段(投影、辛氏图和重建)都融入单独的深度学习模型,以数据驱动的方式局部解决特定伪影问题。我们的方法包括旁路连接,将前一阶段的输出和原始数据传递给后续阶段,最小化错误传播的风险。对模拟和现实数据集的广泛评估表明,我们的方法有效地减少了伪影,并优于比较方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
同步辐射计算机断层扫描(CT)技术相比实验室CT技术具有更高的空间和时间分辨率,并提供多种对比剂形成机制。获取的数据通常通过多个阶段组成的计算流程进行处理。深度学习在增强科学图像质量方面表现出巨大潜力,因此在CT成像中得到了广泛应用。为改善同步辐射CT中的伪影问题,我们提出一种新方法,在断层扫描管道的每个阶段(投影、辛格尔姆和重建)引入单独的深度学习模型,以数据驱动的方式局部解决特定伪影问题。该方法包括旁路连接,将前一阶段的输出和原始数据提供给后续阶段,最小化误差传播的风险。在模拟和真实数据集上的广泛评估表明,该方法有效地减少了伪影,并优于其他比较方法。
Key Takeaways
- 同步辐射CT技术相较于实验室CT具有更高的空间和时间分辨率。
- 深度学习在增强科学图像质量方面表现出巨大潜力,已被广泛应用于CT成像。
- 现有方法在处理同步辐射CT中的伪影时存在局限性。
- 提出一种新型方法,在断层扫描管道的各个阶段引入深度学习模型,以处理特定伪影。
- 该方法通过旁路连接,将前一阶段的输出和原始数据提供给后续阶段,降低误差传播风险。
- 在模拟和真实数据集上的评估证明,该方法有效减少伪影并优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图