⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-21 更新
DPCL-Diff: The Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning Based on Graph Node Diffusion Model with Dual-Domain Periodic Contrastive Learning
Authors:Yukun Cao, Lisheng Wang, Luobin Huang
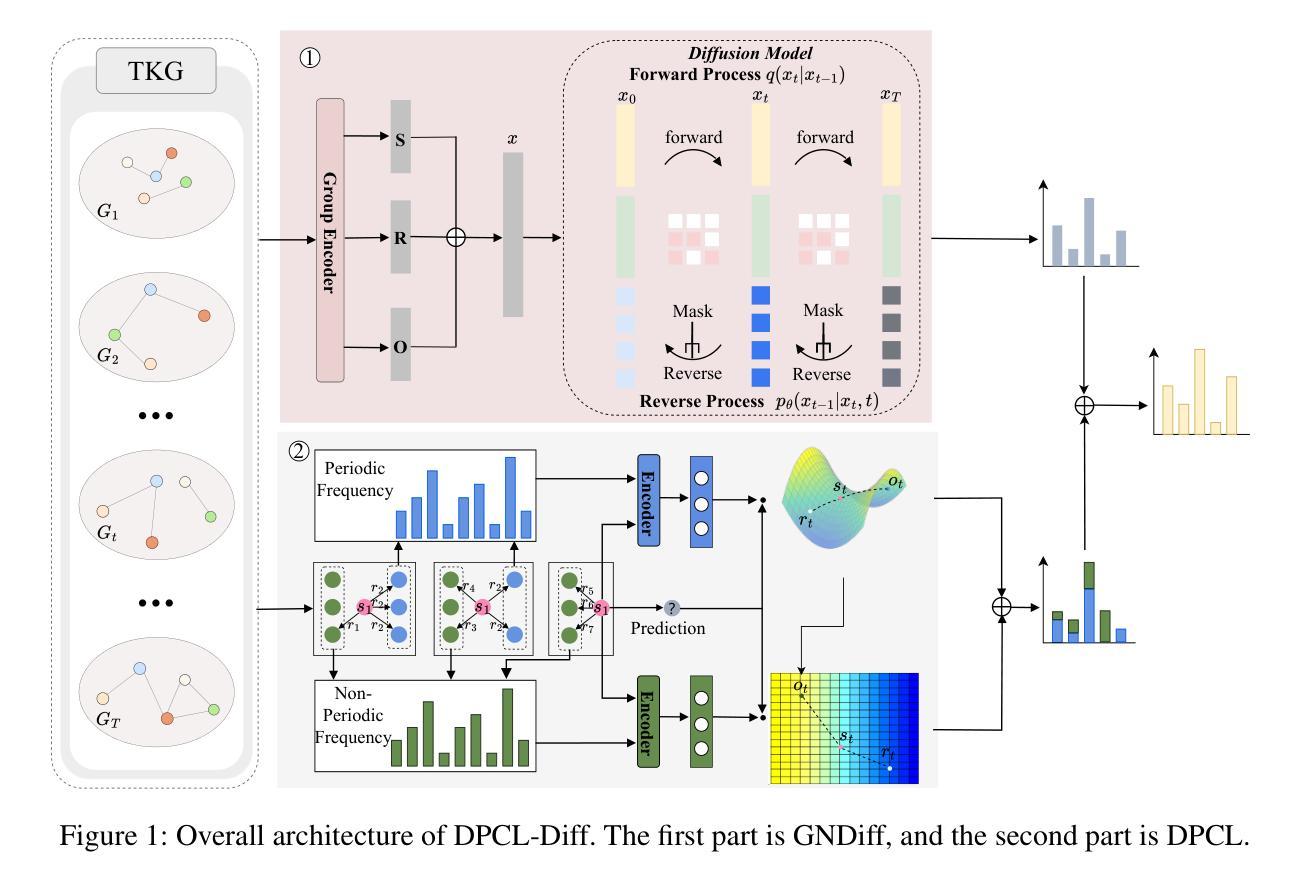
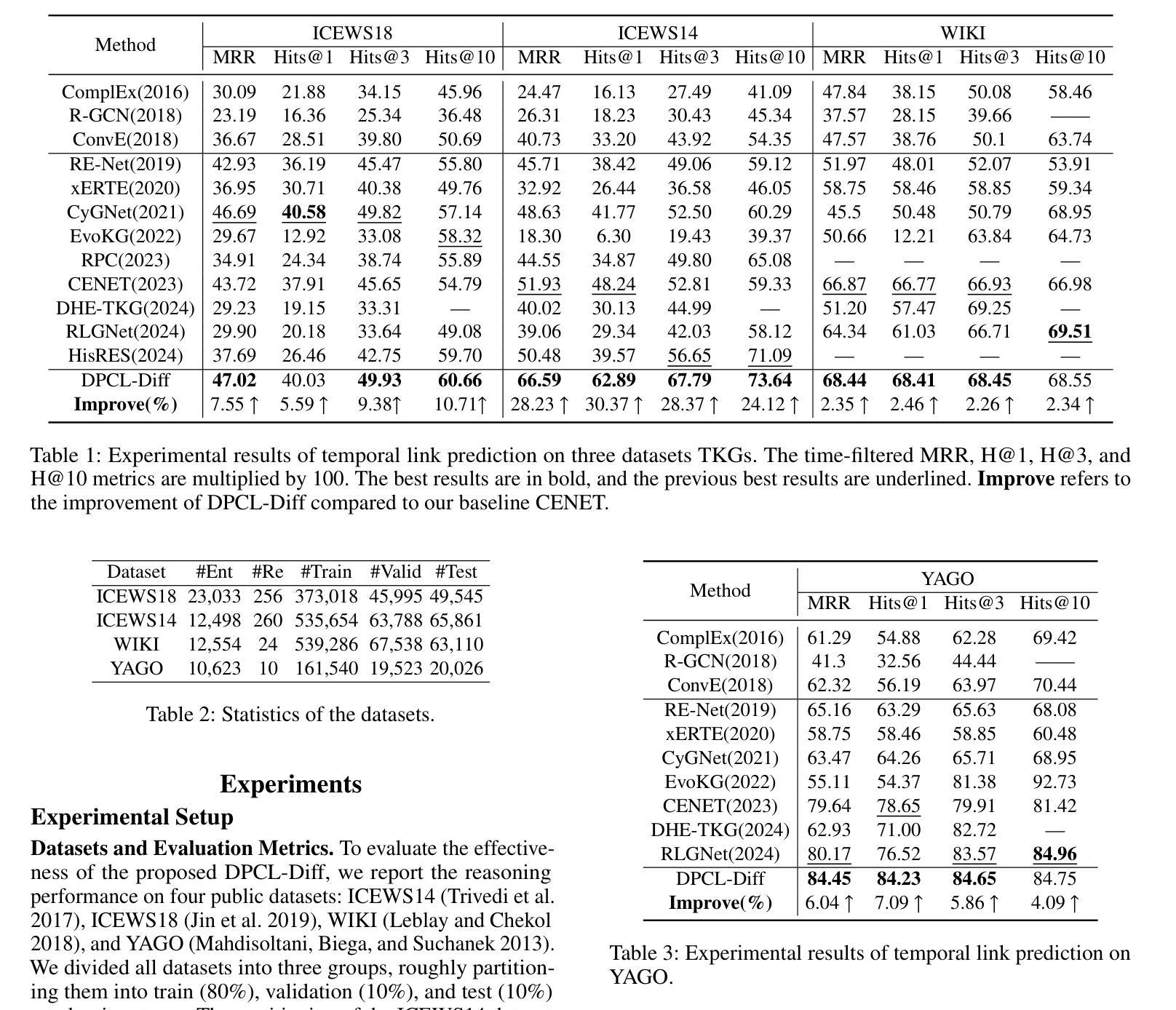
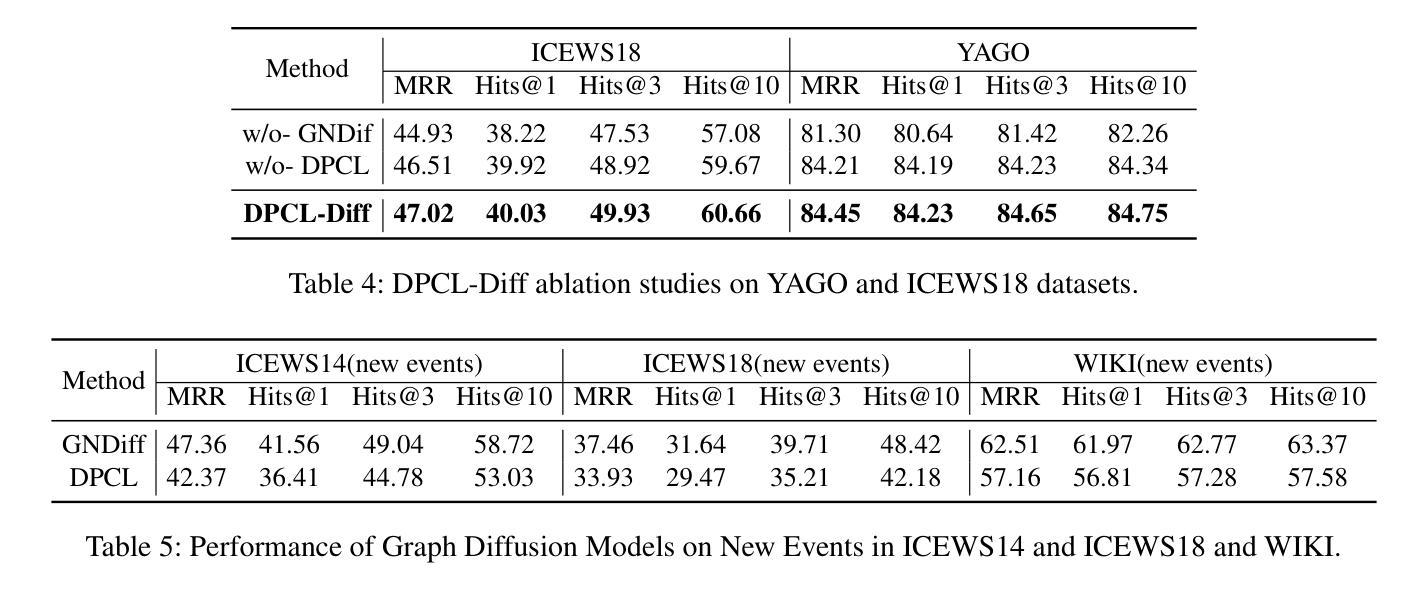
Temporal knowledge graph (TKG) reasoning that infers future missing facts is an essential and challenging task. Predicting future events typically relies on closely related historical facts, yielding more accurate results for repetitive or periodic events. However, for future events with sparse historical interactions, the effectiveness of this method, which focuses on leveraging high-frequency historical information, diminishes. Recently, the capabilities of diffusion models in image generation have opened new opportunities for TKG reasoning. Therefore, we propose a graph node diffusion model with dual-domain periodic contrastive learning (DPCL-Diff). Graph node diffusion model (GNDiff) introduces noise into sparsely related events to simulate new events, generating high-quality data that better conforms to the actual distribution. This generative mechanism significantly enhances the model’s ability to reason about new events. Additionally, the dual-domain periodic contrastive learning (DPCL) maps periodic and non-periodic event entities to Poincar'e and Euclidean spaces, leveraging their characteristics to distinguish similar periodic events effectively. Experimental results on four public datasets demonstrate that DPCL-Diff significantly outperforms state-of-the-art TKG models in event prediction, demonstrating our approach’s effectiveness. This study also investigates the combined effectiveness of GNDiff and DPCL in TKG tasks.
时间知识图谱(TKG)推理,即推断未来缺失事实,是一项基本且具挑战性的任务。预测未来事件通常依赖于紧密相关的历史事实,对于重复或周期事件,这种依赖能够带来更准确的结果。然而,对于未来事件(具有稀疏历史交互的事件),这种方法的效果会降低,因为它侧重于利用高频历史信息。最近,扩散模型在图像生成方面的能力为TKG推理带来了新的机会。因此,我们提出了一种具有双域周期性对比学习(DPCL-Diff)的图节点扩散模型。图节点扩散模型(GNDiff)通过引入噪声来模拟稀疏相关事件,生成高质量数据,更好地符合实际分布。这种生成机制显著提高了模型对新事件的推理能力。此外,双域周期性对比学习(DPCL)将周期性事件实体和非周期性事件实体映射到庞加莱空间和欧几里得空间,利用其特性有效地区分相似的周期性事件。在四个公共数据集上的实验结果表明,DPCL-Diff在事件预测方面显著优于最先进的TKG模型,证明了我们的方法的有效性。本研究还探讨了GNDiff和DPCL在时间知识图谱任务中的组合效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文探讨了时间知识图谱(TKG)推理中预测未来缺失事实的挑战。针对稀疏历史交互的未来事件,提出一种结合图节点扩散模型和双域周期性对比学习(DPCL-Diff)的方法。图节点扩散模型(GNDiff)通过引入噪声模拟新事件,生成高质量数据,提高对新事件的推理能力。双域周期性对比学习(DPCL)则能将周期性和非周期性事件实体映射到不同的数学空间,从而有效区分相似周期性事件。在四个公开数据集上的实验结果表明,DPCL-Diff在事件预测方面显著优于现有TKG模型,验证了方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- TKG推理对于预测未来缺失事实至关重要,且面临挑战。
- 对于稀疏历史交互的未来事件,传统依赖高频历史信息的预测方法效果减弱。
- 引入图节点扩散模型(GNDiff),通过模拟新事件生成高质量数据,提高推理能力。
- 双域周期性对比学习(DPCL)能有效区分周期性事件和非周期性事件实体。
- DPCL-Diff方法结合了GNDiff和DPCL,提高了TKG任务的效果。
- 在四个公开数据集上的实验验证了DPCL-Diff在事件预测方面的优越性。
点此查看论文截图