⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-21 更新
Surface-SOS: Self-Supervised Object Segmentation via Neural Surface Representation
Authors:Xiaoyun Zheng, Liwei Liao, Jianbo Jiao, Feng Gao, Ronggang Wang
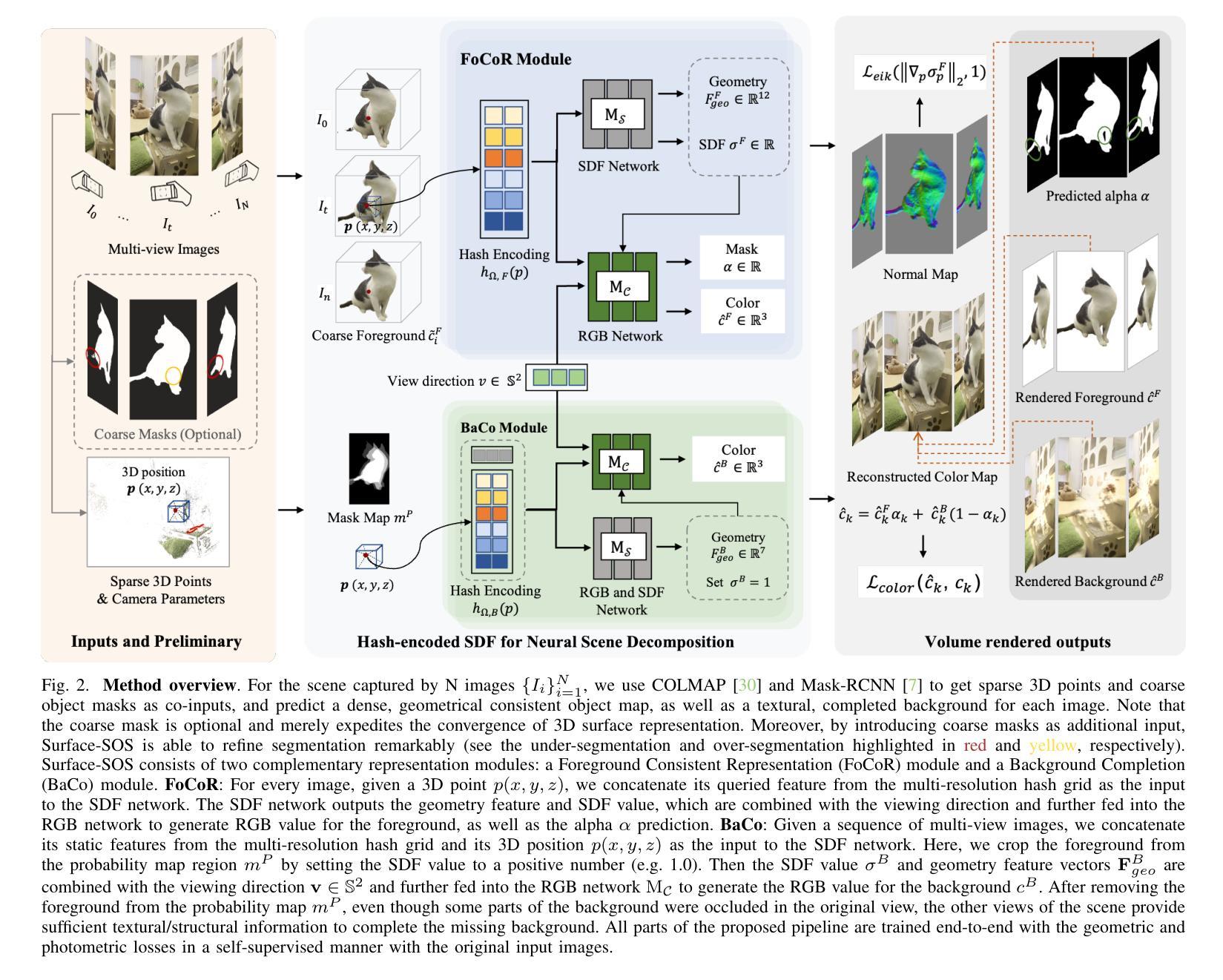
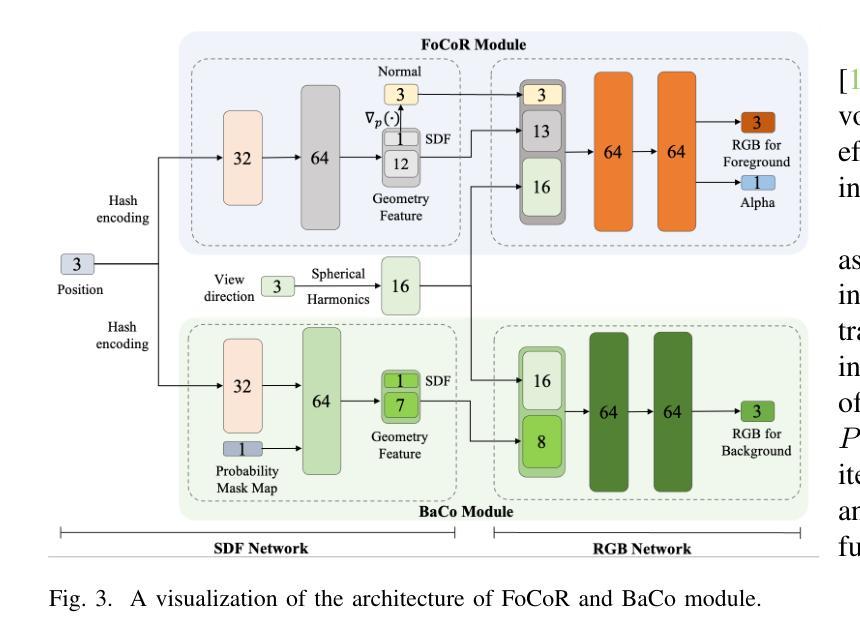
Self-supervised Object Segmentation (SOS) aims to segment objects without any annotations. Under conditions of multi-camera inputs, the structural, textural and geometrical consistency among each view can be leveraged to achieve fine-grained object segmentation. To make better use of the above information, we propose Surface representation based Self-supervised Object Segmentation (Surface-SOS), a new framework to segment objects for each view by 3D surface representation from multi-view images of a scene. To model high-quality geometry surfaces for complex scenes, we design a novel scene representation scheme, which decomposes the scene into two complementary neural representation modules respectively with a Signed Distance Function (SDF). Moreover, Surface-SOS is able to refine single-view segmentation with multi-view unlabeled images, by introducing coarse segmentation masks as additional input. To the best of our knowledge, Surface-SOS is the first self-supervised approach that leverages neural surface representation to break the dependence on large amounts of annotated data and strong constraints. These constraints typically involve observing target objects against a static background or relying on temporal supervision in videos. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks including LLFF, CO3D, BlendedMVS, TUM and several real-world scenes show that Surface-SOS always yields finer object masks than its NeRF-based counterparts and surpasses supervised single-view baselines remarkably. Code is available at: https://github.com/zhengxyun/Surface-SOS.
自监督对象分割(SOS)旨在无需任何注释的情况下对对象进行分割。在多相机输入的情况下,可以利用每个视图的结构、纹理和几何一致性来实现精细粒度的对象分割。为了更好地利用上述信息,我们提出了基于表面表示的自监督对象分割(Surface-SOS),这是一种新的框架,通过场景的多视图图像的3D表面表示来对每个视图的对象进行分割。为了对复杂场景的高质量几何表面进行建模,我们设计了一种新的场景表示方案,该方案将场景分解为两个互补的神经表示模块,分别具有符号距离函数(SDF)。此外,Surface-SOS能够通过引入粗分割掩膜作为附加输入,来细化单视图分割,并利用多视图无标签图像。据我们所知,Surface-SOS是第一个利用神经表面表示的自监督方法,打破了大量注释数据和严格约束的依赖。这些约束通常包括在静态背景下观察目标对象或依赖视频中的时间监督。在包括LLFF、CO3D、BlendedMVS、TUM标准基准和几个真实场景的大量实验表明,Surface-SOS始终产生比其基于NeRF的同类产品更精细的对象掩膜,并显著超越了受监督的单视图基线。代码可用在:https://github.com/zhengxyun/Surface-SOS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TIP
Summary
本文介绍了基于表面表示的自监督物体分割(Surface-SOS)框架,该框架利用多视角图像的场景三维表面表示来实现物体分割,无需任何标注。通过引入符号距离函数(SDF)来分解场景,并设计了一种新的场景表示方案,以建立高质量几何表面模型。此外,Surface-SOS能利用粗分割掩膜作为附加输入来优化单视角分割结果。它是首个利用神经表面表示进行自监督学习的物体分割方法,突破了依赖大量标注数据和严苛约束的限制。实验表明,Surface-SOS在多个标准基准测试上表现优越,显著优于基于NeRF的对比方法以及监督学习的单视角基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- Surface-SOS框架实现了基于多视角图像的自监督物体分割,无需任何标注。
- 引入符号距离函数(SDF)来分解场景并建立高质量几何表面模型。
- 利用粗分割掩膜优化单视角分割结果。
- Surface-SOS是首个利用神经表面表示进行自监督学习的物体分割方法。
- 该方法突破了依赖大量标注数据和严苛约束的限制。
- 在多个标准基准测试上,Surface-SOS表现优越,显著优于基于NeRF的对比方法。
点此查看论文截图

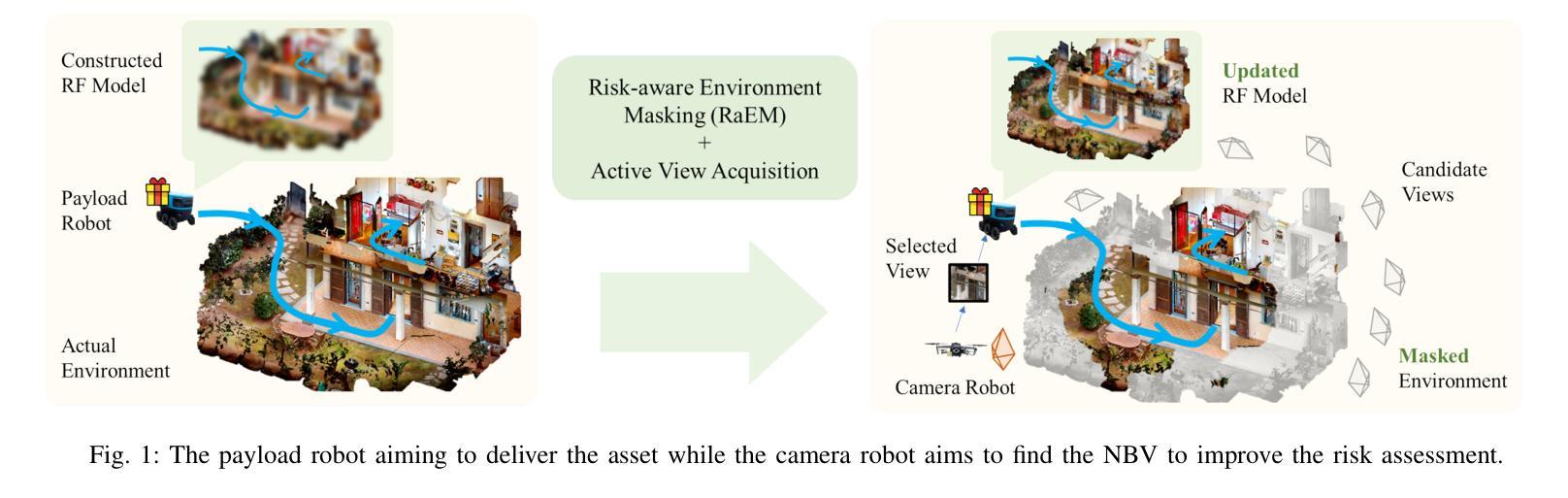
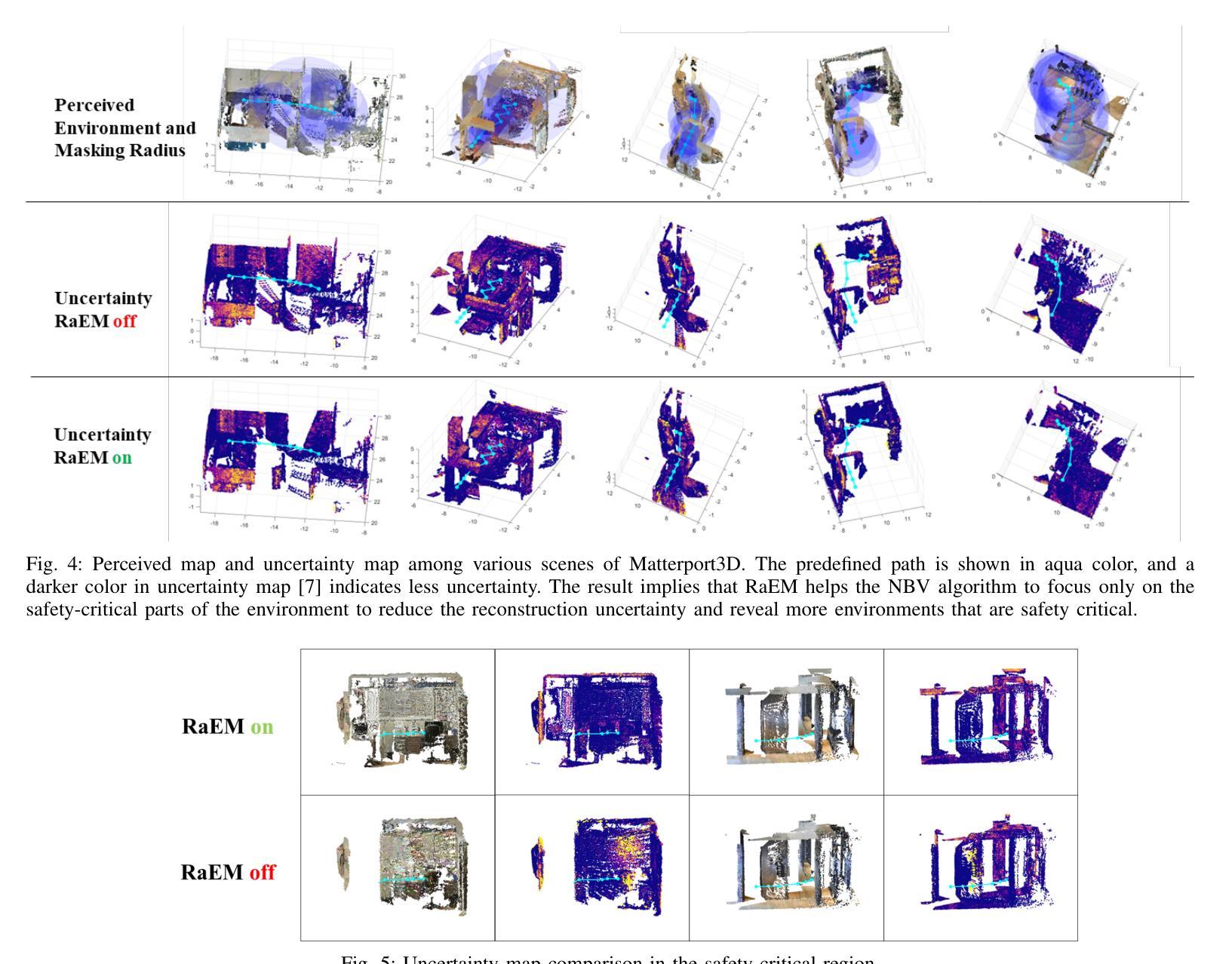
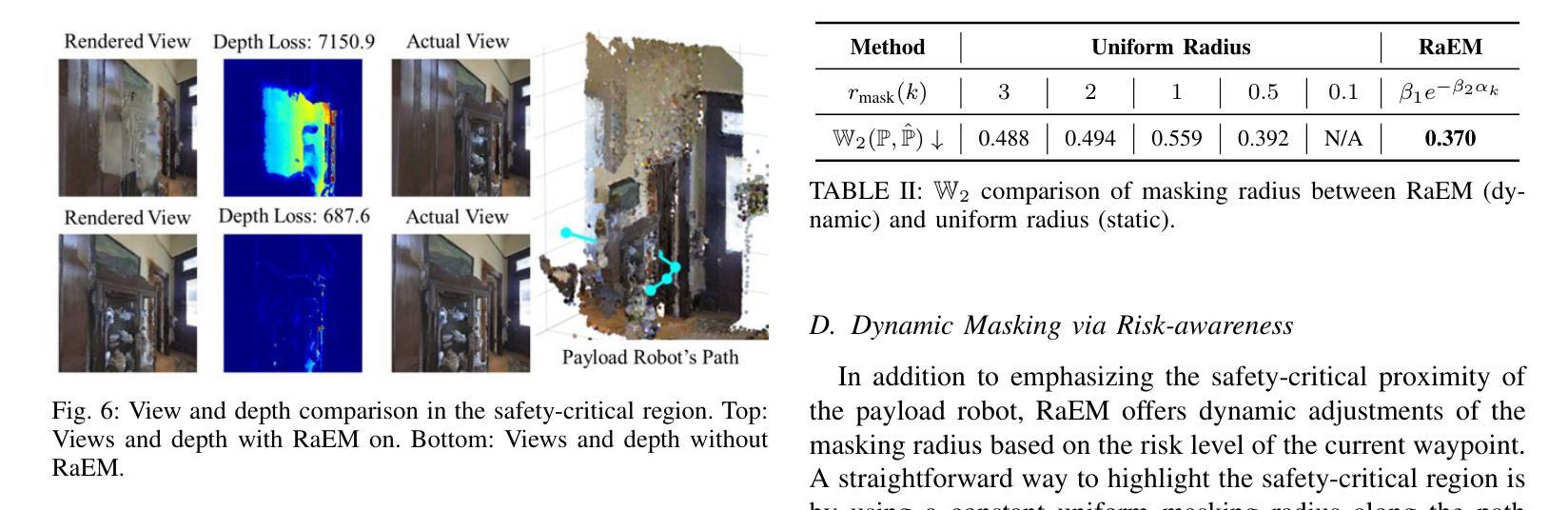
Beyond Uncertainty: Risk-Aware Active View Acquisition for Safe Robot Navigation and 3D Scene Understanding with FisherRF
Authors:Guangyi Liu, Wen Jiang, Boshu Lei, Vivek Pandey, Kostas Daniilidis, Nader Motee
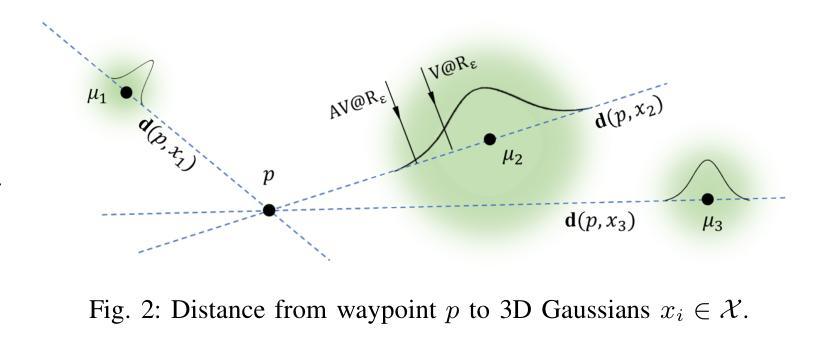
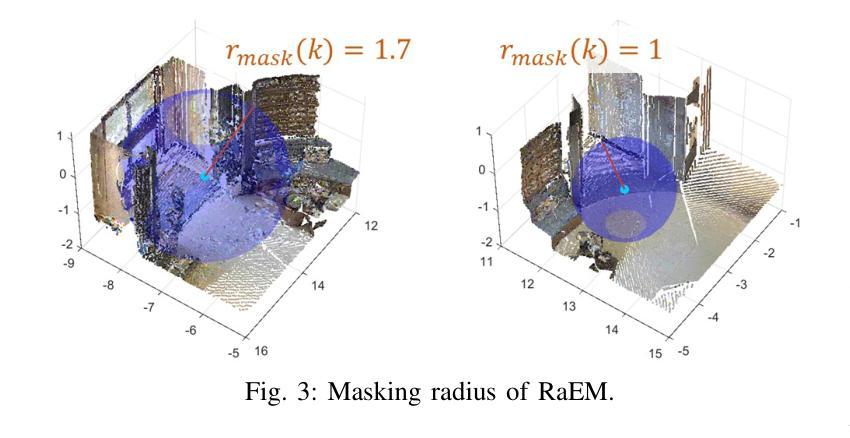
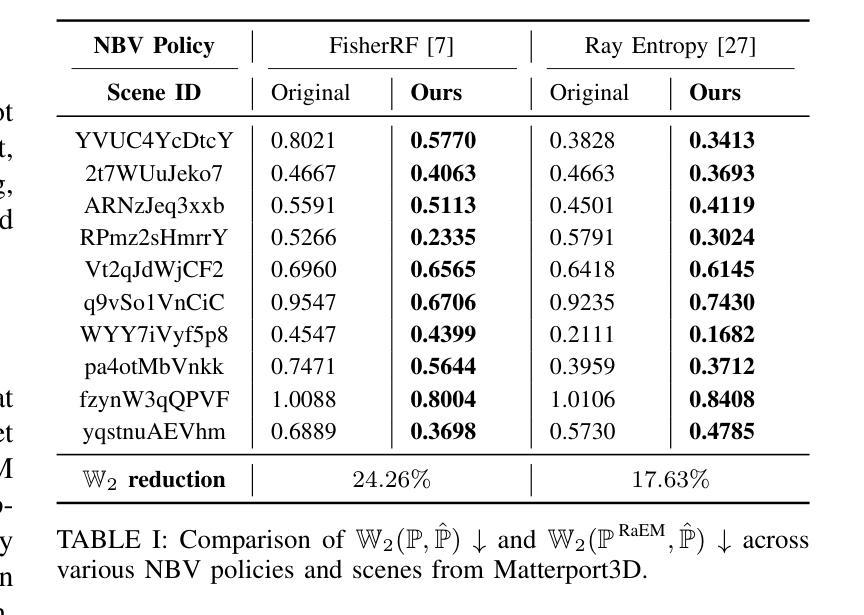
The active view acquisition problem has been extensively studied in the context of robot navigation using NeRF and 3D Gaussian Splatting. To enhance scene reconstruction efficiency and ensure robot safety, we propose the Risk-aware Environment Masking (RaEM) framework. RaEM leverages coherent risk measures to dynamically prioritize safety-critical regions of the unknown environment, guiding active view acquisition algorithms toward identifying the next-best-view (NBV). Integrated with FisherRF, which selects the NBV by maximizing expected information gain, our framework achieves a dual objective: improving robot safety and increasing efficiency in risk-aware 3D scene reconstruction and understanding. Extensive high-fidelity experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating its ability to establish a robust and safety-focused framework for active robot exploration and 3D scene understanding.
在NeRF和3D高斯溅射技术的背景下,主动视图采集问题在机器人导航中得到了广泛的研究。为了提升场景重建效率并确保机器人安全,我们提出了风险感知环境掩蔽(RaEM)框架。RaEM利用连贯的风险度量来动态地优先处理未知环境中对安全至关重要的区域,指导主动视图采集算法确定最佳的下一个视图(NBV)。该框架与FisherRF相结合,通过最大化预期信息增益来选择NBV,实现了双重目标:提高机器人安全性和风险感知的三维场景重建与理解的效率。大量高保真实验验证了我们的方法的有效性,展示了一个稳健且专注于安全的主动机器人探索和三维场景理解框架的建立能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对基于NeRF和3D高斯展布技术的机器人导航中的主动视图获取问题,我们提出了风险感知环境掩蔽(RaEM)框架。该框架利用连贯的风险度量来动态优先处理未知环境中的安全关键区域,引导主动视图获取算法识别最佳下一个视图(NBV)。结合FisherRF,通过最大化预期信息增益选择NBV,我们的框架实现了双重目标:提高机器人安全性和风险感知下的三维场景重建和理解的效率。高保真实验验证了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了风险感知环境掩蔽(RaEM)框架,用于机器人导航中的主动视图获取问题。
- RaEM框架利用连贯的风险度量来优先处理未知环境中的安全关键区域。
- 结合FisherRF,RaEM框架实现了机器人安全性和风险感知下的三维场景重建效率的提升。
- 通过最大化预期信息增益来选择最佳下一个视图(NBV),以指导主动视图获取算法。
- 框架通过动态指导机器人探索,促进了风险感知下的三维场景理解。
- 进行了广泛的高保真实验,验证了RaEM框架的有效性和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图