⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-21 更新
TalkingEyes: Pluralistic Speech-Driven 3D Eye Gaze Animation
Authors:Yixiang Zhuang, Chunshan Ma, Yao Cheng, Xuan Cheng, Jing Liao, Juncong Lin
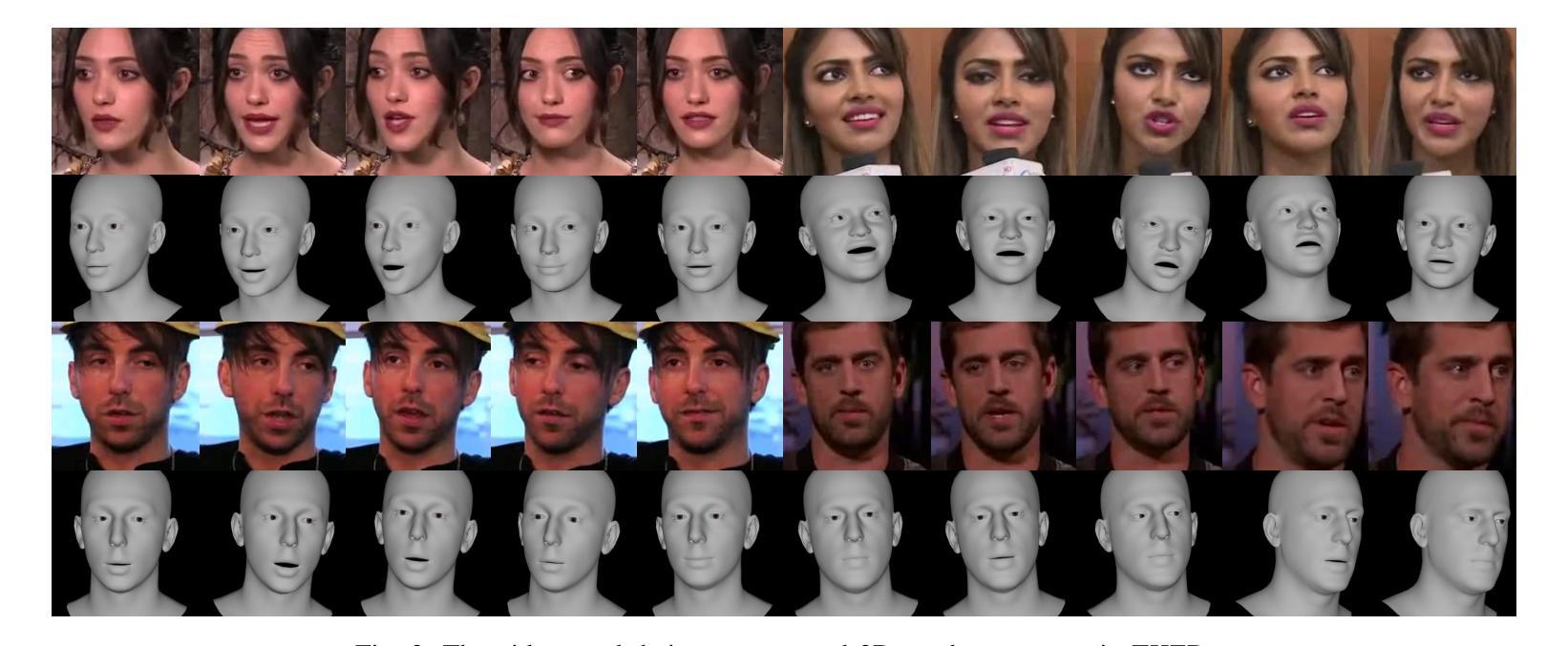
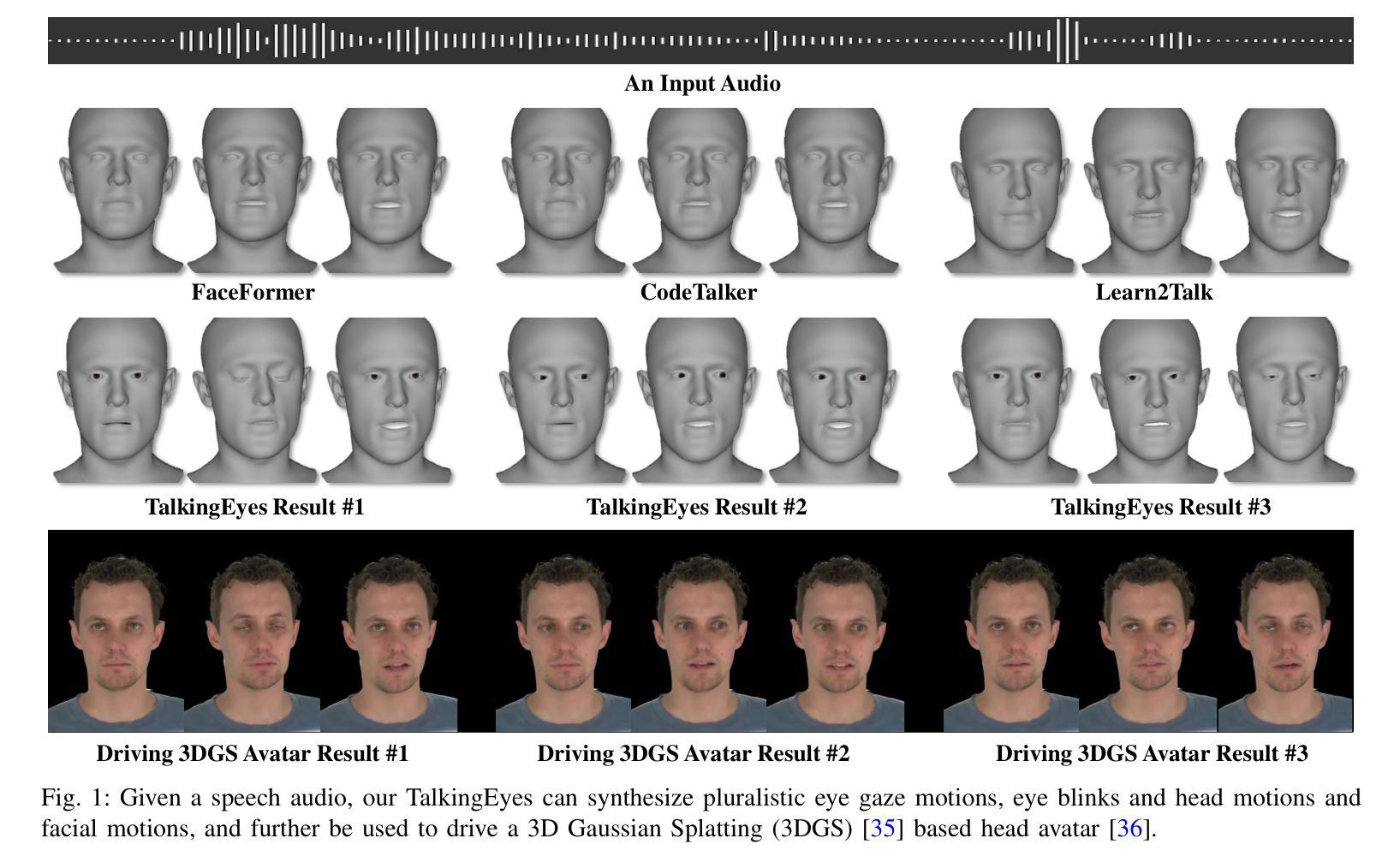
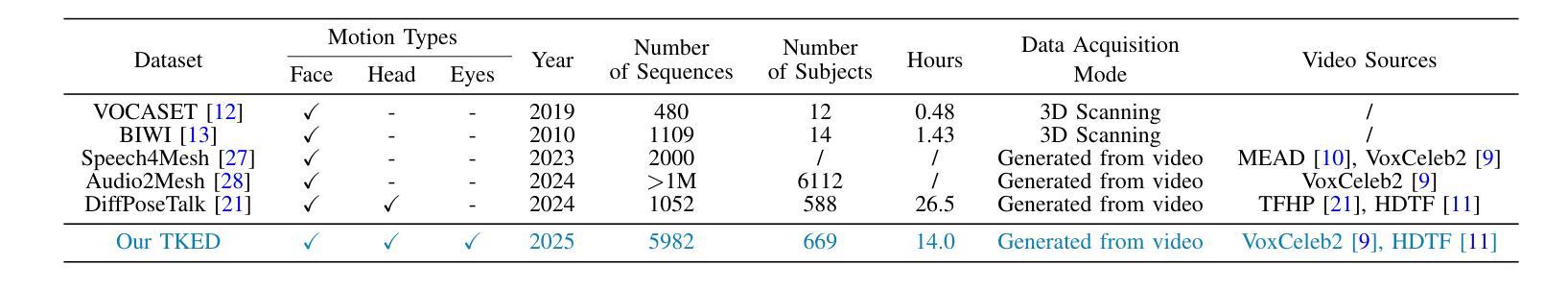
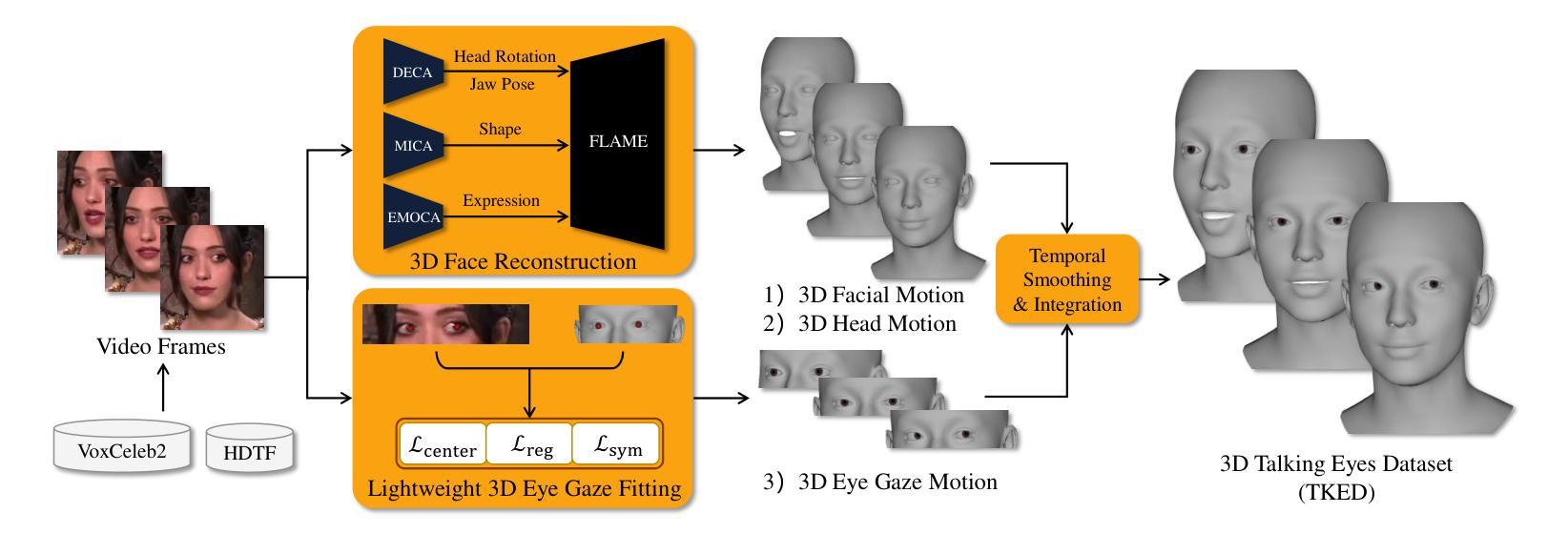
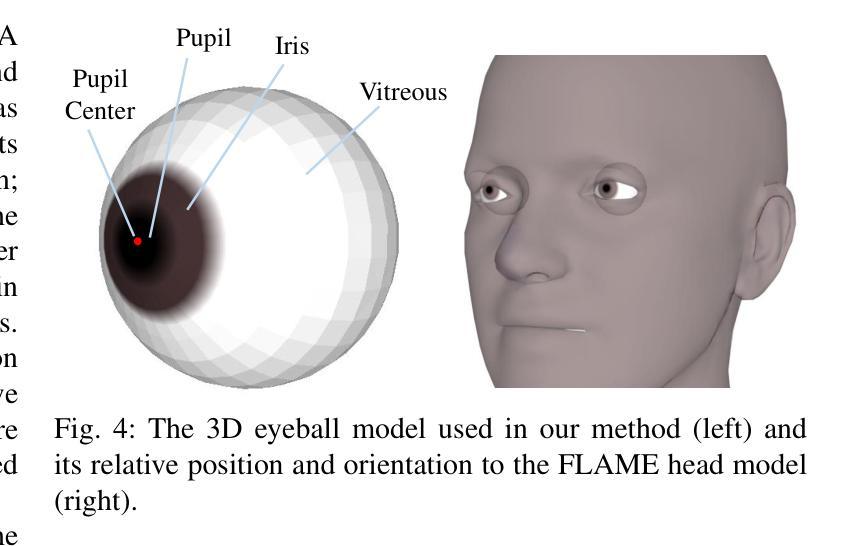
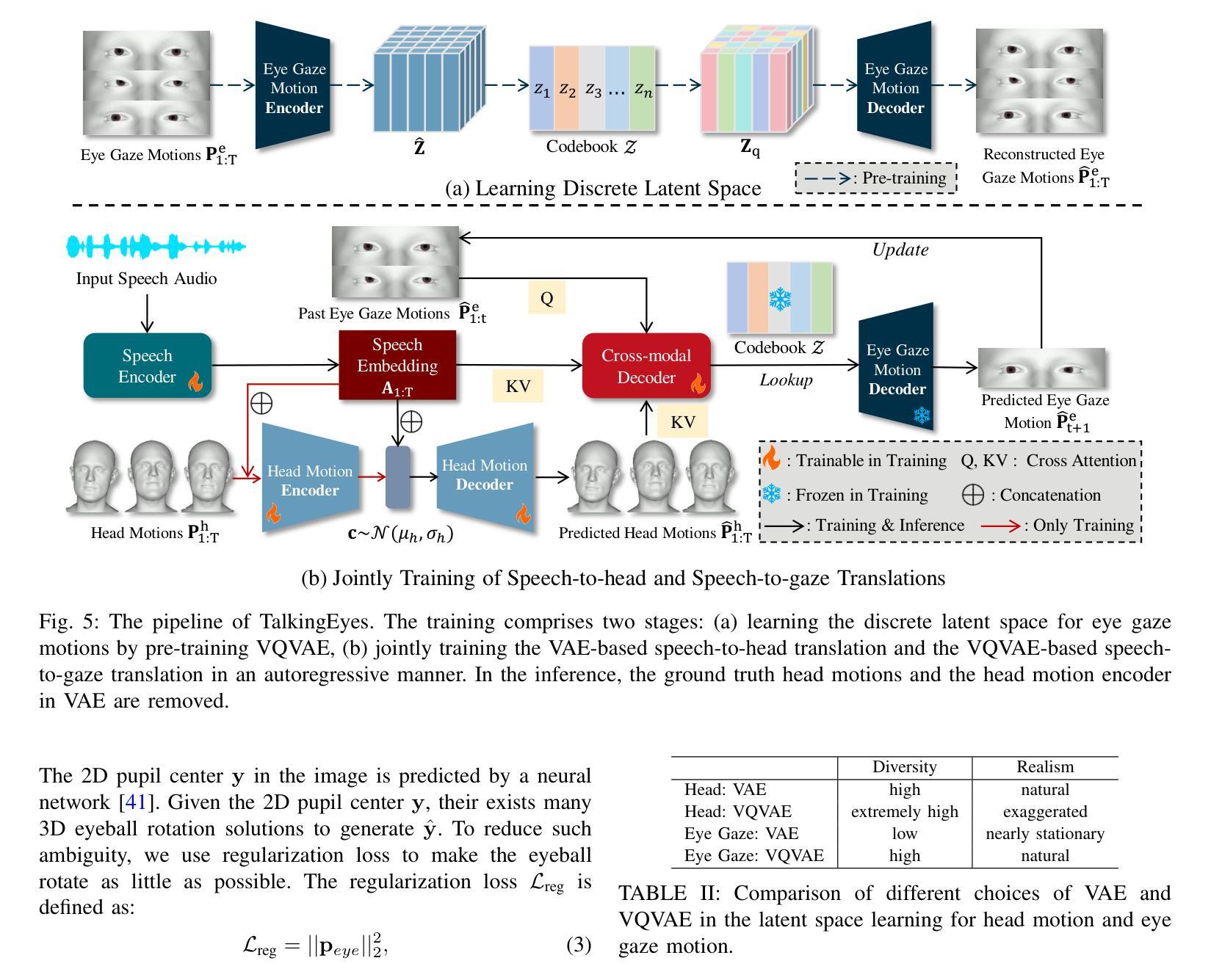
Although significant progress has been made in the field of speech-driven 3D facial animation recently, the speech-driven animation of an indispensable facial component, eye gaze, has been overlooked by recent research. This is primarily due to the weak correlation between speech and eye gaze, as well as the scarcity of audio-gaze data, making it very challenging to generate 3D eye gaze motion from speech alone. In this paper, we propose a novel data-driven method which can generate diverse 3D eye gaze motions in harmony with the speech. To achieve this, we firstly construct an audio-gaze dataset that contains about 14 hours of audio-mesh sequences featuring high-quality eye gaze motion, head motion and facial motion simultaneously. The motion data is acquired by performing lightweight eye gaze fitting and face reconstruction on videos from existing audio-visual datasets. We then tailor a novel speech-to-motion translation framework in which the head motions and eye gaze motions are jointly generated from speech but are modeled in two separate latent spaces. This design stems from the physiological knowledge that the rotation range of eyeballs is less than that of head. Through mapping the speech embedding into the two latent spaces, the difficulty in modeling the weak correlation between speech and non-verbal motion is thus attenuated. Finally, our TalkingEyes, integrated with a speech-driven 3D facial motion generator, can synthesize eye gaze motion, eye blinks, head motion and facial motion collectively from speech. Extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method in generating diverse and natural 3D eye gaze motions from speech. The project page of this paper is: https://lkjkjoiuiu.github.io/TalkingEyes_Home/
尽管最近在语音驱动的三维面部动画领域取得了重大进展,但最近的研究忽视了面部的重要组成部分——眼神的语音驱动动画。这主要是因为语音和眼神之间的弱相关性以及音频眼神数据的稀缺,使得仅从语音生成三维眼神运动具有极大的挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的数据驱动方法,可以生成与语音协调的多样化的三维眼神运动。为实现这一目标,我们首先构建了一个音频眼神数据集,其中包含约14小时的音频网格序列,同时具有高质量的眼神运动、头部运动和面部运动。运动数据是通过对来自现有音频视觉数据集的视频进行轻量级眼神拟合和面部重建而获得的。然后,我们定制了一个新颖的语音到运动翻译框架,其中头部运动和眼神运动是从语音中联合生成的,但在两个单独的潜在空间中建模。这种设计源于生理知识,即眼球的旋转范围小于头部。通过将语音嵌入映射到这两个潜在空间,减轻了建模语音和非言语运动之间弱相关性的难度。最后,我们的TalkingEyes结合语音驱动的三维面部运动生成器,可以从语音中合成眼神运动、眨眼、头部运动和面部运动。大量的定量和定性评估证明,该方法在从语音生成多样化和自然的三维眼神运动方面具有优势。该项目页面的链接为:https://lkjkjoiuiu.github.io/TalkingEyes_Home/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种数据驱动的方法,用于生成与语音相协调的多样化的3D眼动。为建立此模型,作者建立了一个包含约14小时音频网格序列的音频-凝视数据集,其中包含高质量的眼睛凝视运动、头部运动和面部运动。然后作者设计了一个新型的语音到运动翻译框架,其中头部运动和眼睛凝视运动从语音共同生成,但在两个单独的潜在空间中建模。这种方法的设计源于生理知识,即眼球的旋转范围小于头部。最后,作者提出的TalkingEyes结合语音驱动的3D面部运动生成器,能够从语音中合成眼睛凝视运动、眨眼运动、头部运动和面部运动。该方法在生成多样化的自然3D眼动方面表现出优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究指出了在语音驱动的3D面部动画领域中,关于眼睛凝视运动的动画研究被忽视的问题。
- 提出了一个数据驱动的方法,旨在生成与语音相协调的多样化的3D眼动。
- 构建了一个包含高质量眼睛凝视运动、头部运动和面部运动的音频-凝视数据集。
- 设计了一个新型的语音到运动翻译框架,该框架在两个单独的潜在空间中建模头部和眼睛凝视运动。
- 通过轻量级眼睛凝视拟合和面部重建视频从现有音频视觉数据集中获取运动数据。
- 方法考虑了眼球旋转范围小于头部的生理知识。
- TalkingEyes能够集体从语音中合成眼睛凝视运动、眨眼运动、头部运动和面部运动。
点此查看论文截图


Checking Cheap Talk
Authors:Ian Ball, Xin Gao
We consider a sender–receiver game in which the state is multidimensional and the receiver’s action is binary. The sender always prefers the same action. The receiver can select one dimension of the state to verify. Despite the extreme conflict of interest, costless communication can be influential. We identify a class of symmetric equilibria in which the sender’s message reveals which dimensions of the state are highest, and the receiver selects one of these dimensions to check. Using this construction, we characterize whether the sender benefits from communication. Similar equilibria exist when the receiver can check multiple dimensions.
我们考虑一个发送者-接收者的游戏,其中状态是多维的,接收者的行动是二进制的。发送者总是偏好相同的行动。接收者可以选择状态的一个维度来验证。尽管存在极端的利益冲突,但无成本沟通仍然可以产生影响。我们确定了一类对称均衡状态,其中发送者的信息揭示了状态哪些维度是最重要的,接收者会选择其中一个维度进行检查。通过这种构建,我们描述了沟通是否对发送者有益。当接收者可以检查多个维度时,也存在类似的均衡状态。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:在一个发送者-接收者的游戏中,状态是多维的,接收者的行动是二进制的。发送者总是偏好相同的行动。尽管存在利益冲突,但无成本沟通依然具有影响力。我们找到一类对称平衡,其中发送者的信息揭示了状态维度的优先级,接收者选择其中一个维度进行验证。通过此结构,我们确定了沟通是否对发送者有益。当接收者可以检查多个维度时,也存在类似的平衡。
Key Takeaways:
- 在发送者-接收者游戏中,即使存在极端的利益冲突,低成本或免费的沟通依然能产生重大影响。
- 对称平衡存在于游戏策略中,其中发送者通过信息透露哪些状态维度最为重要。
- 接收者会选择其中一个优先级最高的维度进行验证。
- 发送者可以通过沟通获得优势。
- 当接收者能够检查多个维度时,也存在类似的平衡状态。
- 沟通有助于解决信息不对称问题,从而提高决策效率和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

Audio-Driven Reinforcement Learning for Head-Orientation in Naturalistic Environments
Authors:Wessel Ledder, Yuzhen Qin, Kiki van der Heijden
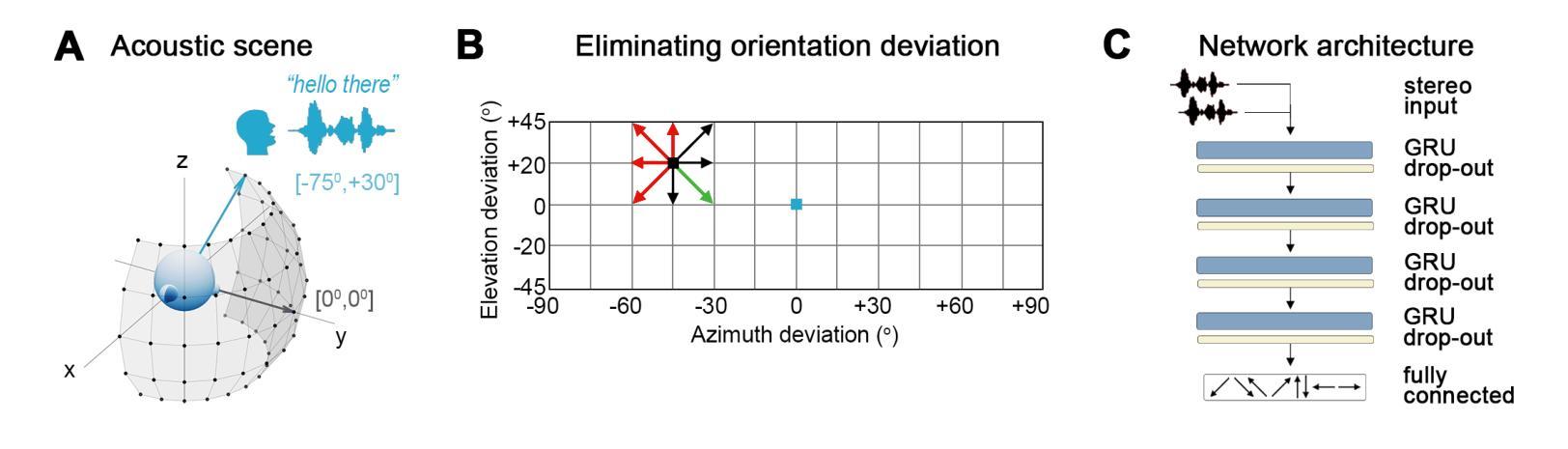
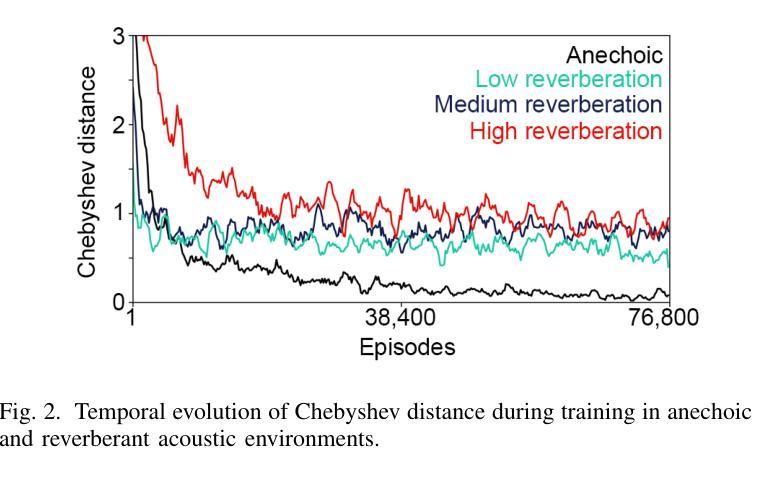
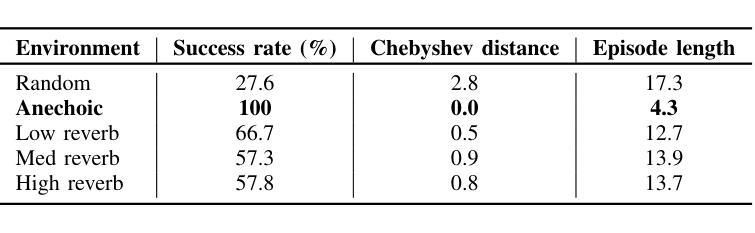
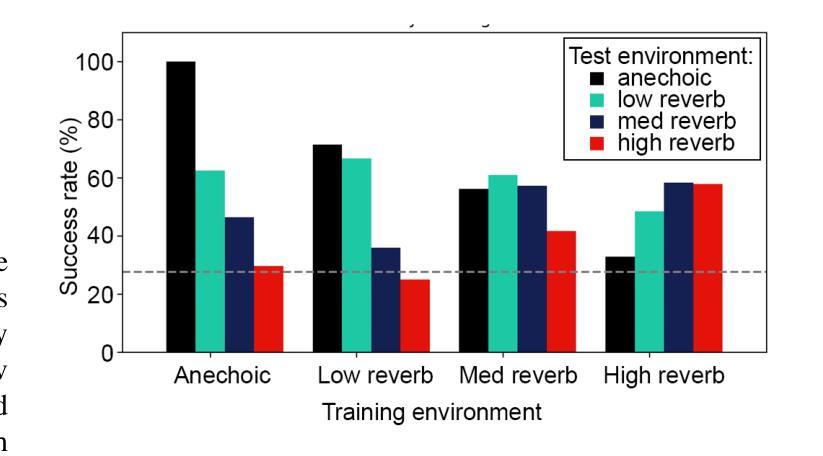
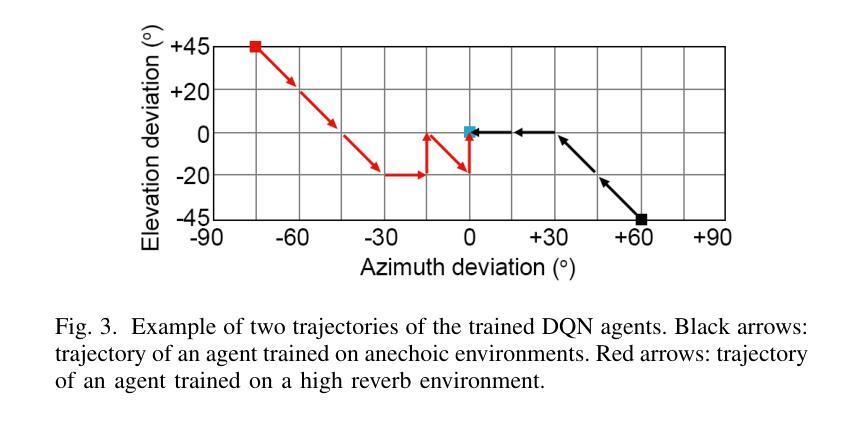
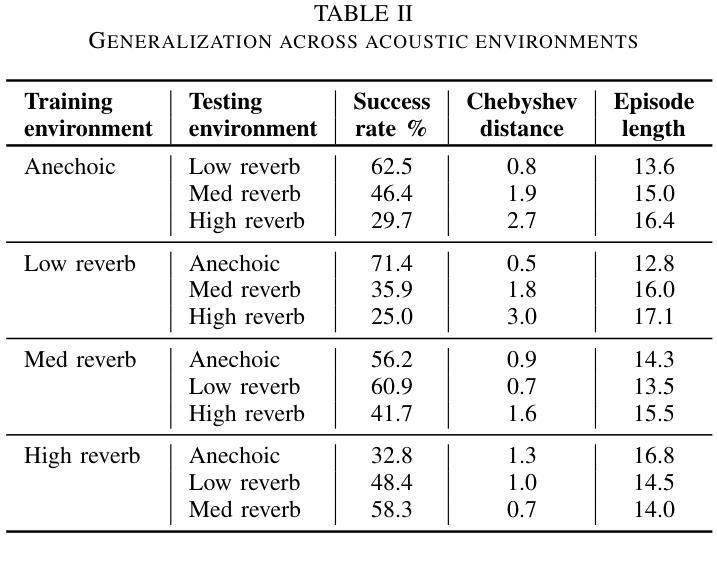
Although deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approaches in audio signal processing have seen substantial progress in recent years, audio-driven DRL for tasks such as navigation, gaze control and head-orientation control in the context of human-robot interaction have received little attention. Here, we propose an audio-driven DRL framework in which we utilise deep Q-learning to develop an autonomous agent that orients towards a talker in the acoustic environment based on stereo speech recordings. Our results show that the agent learned to perform the task at a near perfect level when trained on speech segments in anechoic environments (that is, without reverberation). The presence of reverberation in naturalistic acoustic environments affected the agent’s performance, although the agent still substantially outperformed a baseline, randomly acting agent. Finally, we quantified the degree of generalization of the proposed DRL approach across naturalistic acoustic environments. Our experiments revealed that policies learned by agents trained on medium or high reverb environments generalized to low reverb environments, but policies learned by agents trained on anechoic or low reverb environments did not generalize to medium or high reverb environments. Taken together, this study demonstrates the potential of audio-driven DRL for tasks such as head-orientation control and highlights the need for training strategies that enable robust generalization across environments for real-world audio-driven DRL applications.
尽管深度强化学习(DRL)在音频信号处理方面近年来取得了重大进展,但在人机交互背景下的导航、目光控制和头部方向控制等任务方面,音频驱动的DRL受到的关注却很少。在这里,我们提出了一个音频驱动的DRL框架,利用深度Q学习来开发一个自主代理,该代理能够根据立体声语音记录来定位声环境中的说话者。我们的结果表明,当在消声环境中对语音片段进行训练时,代理几乎能够完美地完成任务(即,没有混响)。尽管在真实的声学环境中混响的存在影响了代理的性能,但它仍然显著优于随机行动的基线代理。最后,我们量化了所提议的DRL方法在自然声学环境中的泛化程度。我们的实验表明,在中等或高混响环境中训练的代理策略可以推广到低混响环境,但在消声或低混响环境中训练的代理策略并不能推广到中等或高混响环境。总的来说,本研究展示了音频驱动DRL在头部方向控制等任务上的潜力,并强调了需要训练策略来实现在各种环境中的稳健泛化,以便用于真实世界的音频驱动DRL应用程序。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文研究了基于深度强化学习(DRL)的音频驱动技术在人机交互中的导航、目光控制和头部方向控制任务的应用。实验结果显示,在无声学回声(anechoic)环境下训练的智能体可以近乎完美地完成任务。然而,在自然声学环境中的回声对智能体的性能产生影响,但仍优于随机行为的基线智能体。此外,研究发现,在中等或高回声环境下训练的智能体可以推广到低回声环境,但在无声学回声或低回声环境下训练的智能体则不能推广到中等或高回声环境。本研究展示了音频驱动DRL在头部方向控制等任务上的潜力,并强调了为现实世界应用开发能够在不同环境中稳健推广的训练策略的必要。
Key Takeaways
- DRL在音频信号处理方面取得显著进展,但在基于音频驱动的机器人交互任务(如导航、目光控制和头部方向控制)上的研究较少。
- 提出一种基于深度Q学习的音频驱动DRL框架,用于根据立体声语音录音使机器人朝向说话者。
- 在无声学回声环境下训练的智能体几乎可以完美完成任务。
- 自然声学环境中的回声会影响智能体的性能,但仍优于随机行为的基线智能体。
- 在中等或高回声环境下训练的智能体能推广到低回声环境,但反之则不能。
- 音频驱动DRL在头部方向控制等任务上具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图