⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-21 更新
Generalized Single-Image-Based Morphing Attack Detection Using Deep Representations from Vision Transformer
Authors:Haoyu Zhang, Raghavendra Ramachandra, Kiran Raja, Christoph Busch
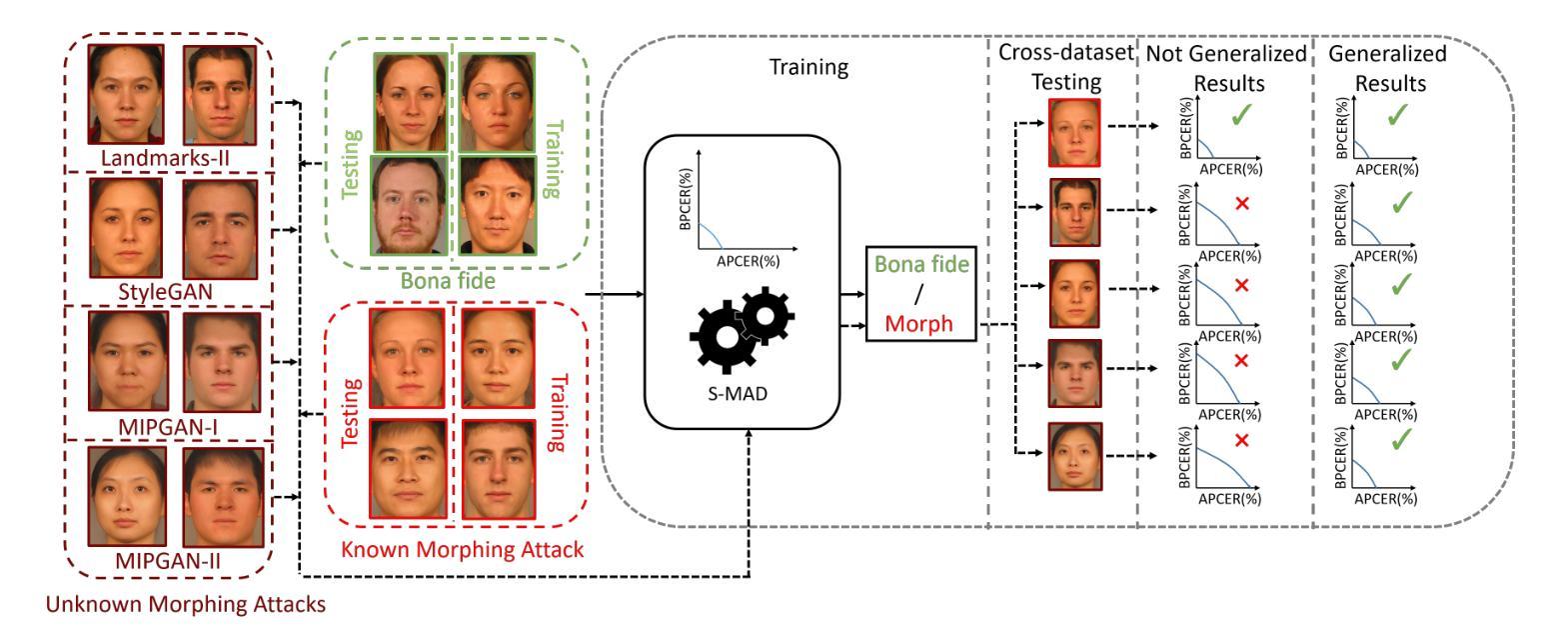
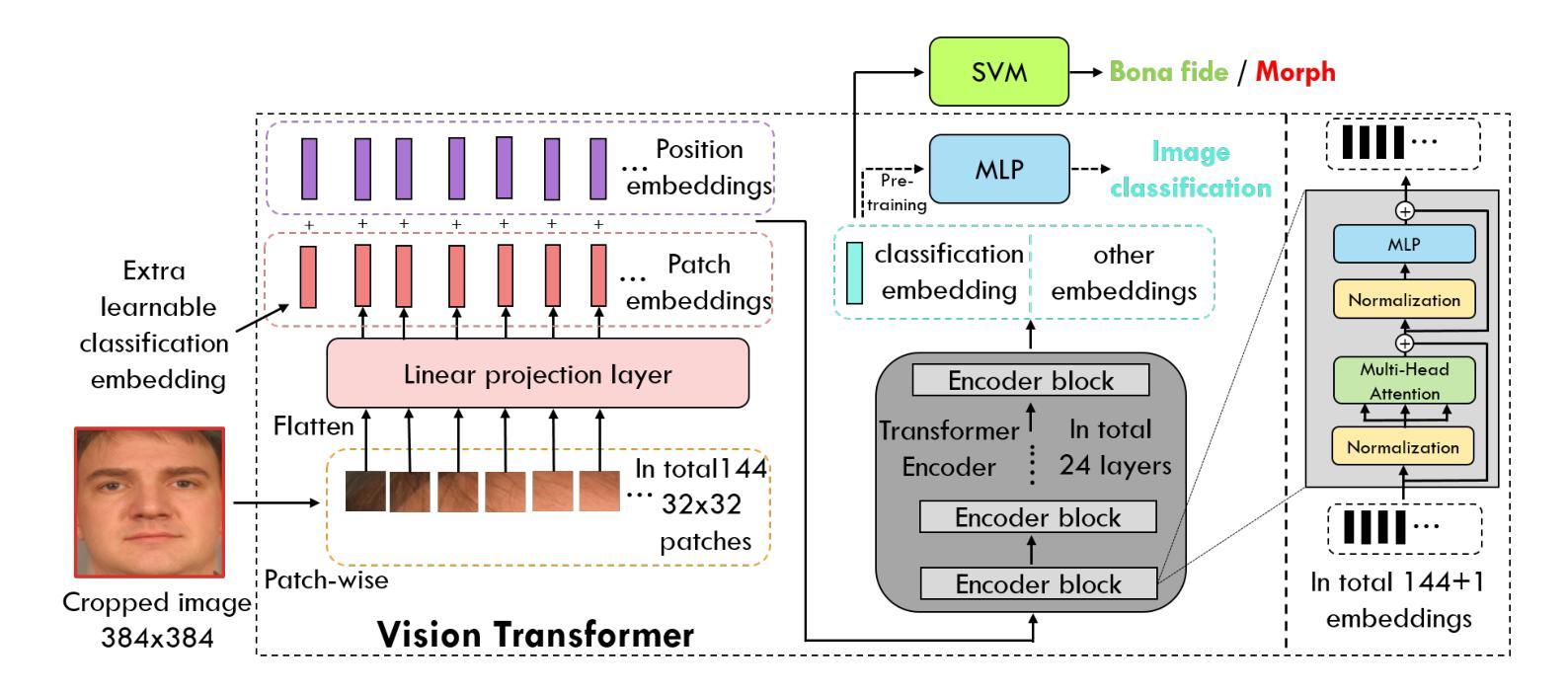
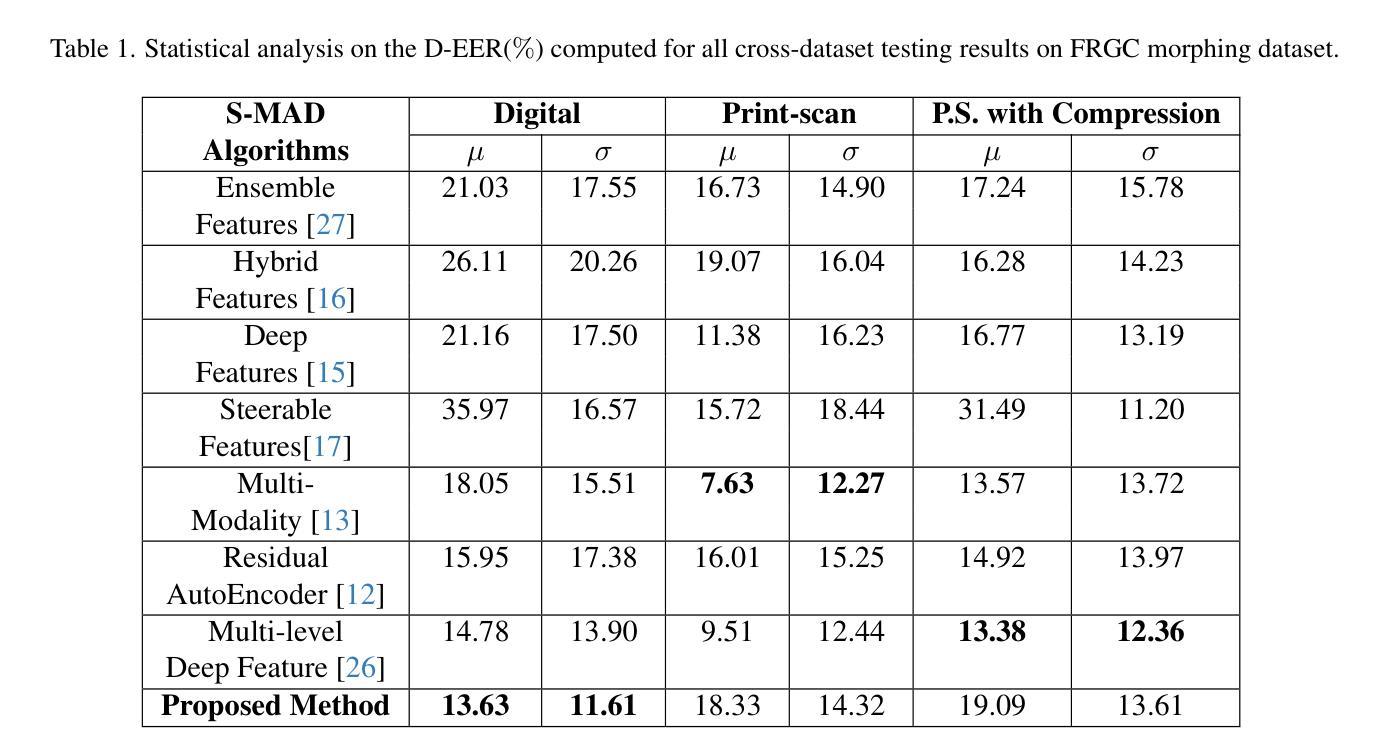
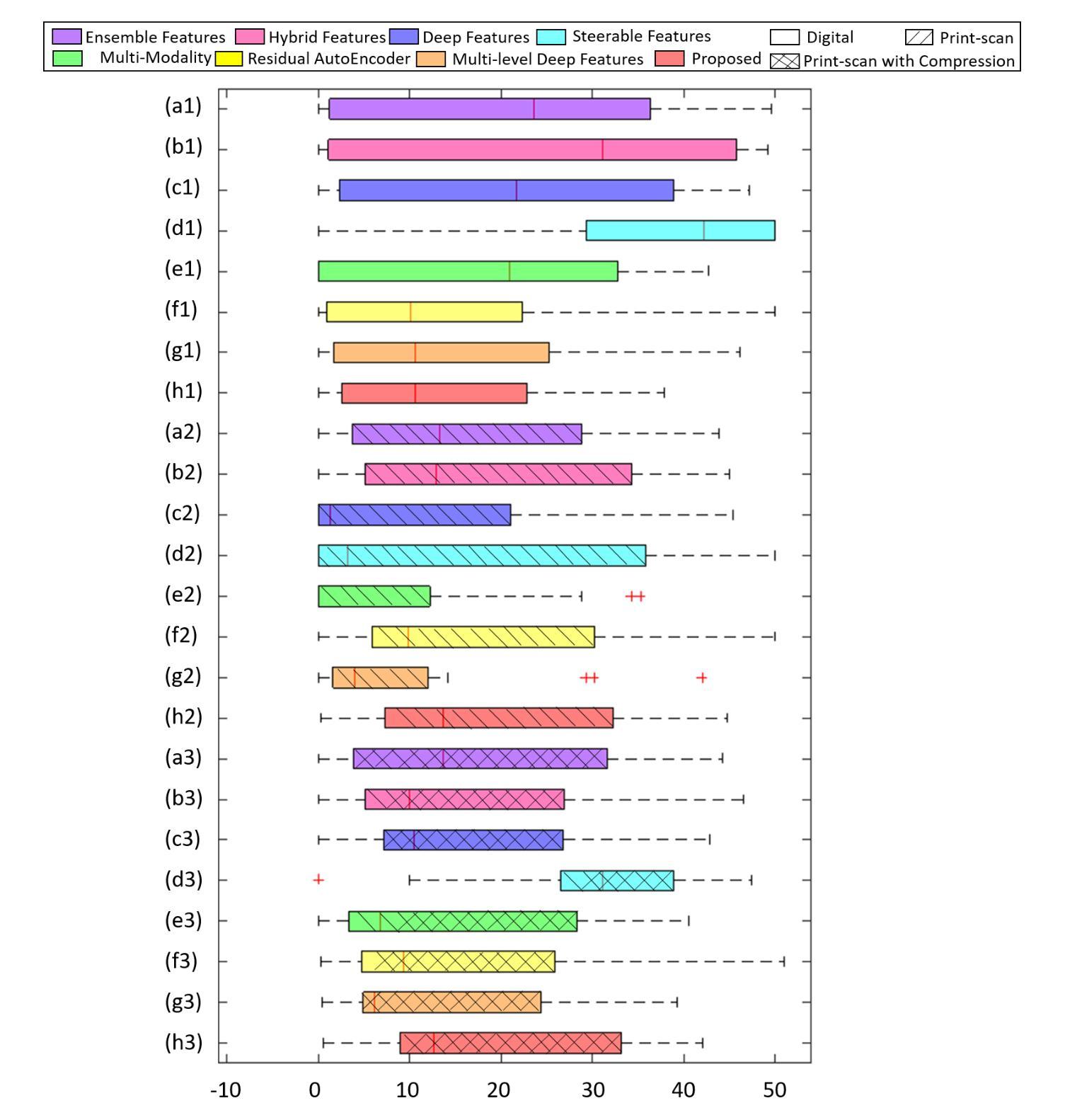
Face morphing attacks have posed severe threats to Face Recognition Systems (FRS), which are operated in border control and passport issuance use cases. Correspondingly, morphing attack detection algorithms (MAD) are needed to defend against such attacks. MAD approaches must be robust enough to handle unknown attacks in an open-set scenario where attacks can originate from various morphing generation algorithms, post-processing and the diversity of printers/scanners. The problem of generalization is further pronounced when the detection has to be made on a single suspected image. In this paper, we propose a generalized single-image-based MAD (S-MAD) algorithm by learning the encoding from Vision Transformer (ViT) architecture. Compared to CNN-based architectures, ViT model has the advantage on integrating local and global information and hence can be suitable to detect the morphing traces widely distributed among the face region. Extensive experiments are carried out on face morphing datasets generated using publicly available FRGC face datasets. Several state-of-the-art (SOTA) MAD algorithms, including representative ones that have been publicly evaluated, have been selected and benchmarked with our ViT-based approach. Obtained results demonstrate the improved detection performance of the proposed S-MAD method on inter-dataset testing (when different data is used for training and testing) and comparable performance on intra-dataset testing (when the same data is used for training and testing) experimental protocol.
人脸变形攻击已对面部识别系统(FRS)构成严重威胁,这些系统在边境控制和护照签发等场景中运行。因此,需要变形攻击检测算法(MAD)来防御此类攻击。MAD方法必须足够稳健,能够处理开放场景中的未知攻击,其中攻击可能来自各种人脸变形生成算法、后期处理以及打印机/扫描仪的多样性。当必须在单个可疑图像上进行检测时,泛化问题进一步突出。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于单图像的通用MAD(S-MAD)算法,通过从视觉转换器(ViT)架构中学习编码。与基于CNN的架构相比,ViT模型具有整合局部和全局信息的优势,因此适合检测人脸区域广泛分布的变形痕迹。在利用公开可用的FRGC人脸数据集生成的人脸变形数据集上进行了大量实验。我们选择并评估了若干最新先进(SOTA)的MAD算法,包括具有代表性的已公开评估的算法,并与我们的基于ViT的方法进行了基准测试。获得的结果表明,在跨数据集测试(使用不同数据进行训练和测试)时,所提出的S-MAD方法的检测性能有所提高,而在内部数据集测试(使用相同数据进行训练和测试)的实验协议上,其性能表现相当。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Face Recognition Systems(FRS)在边境控制和护照签发等场景中的应用,面部变形攻击带来了严重威胁。因此,需要对抗变形攻击的算法(MAD)进行防御。MAD方法必须足够稳健,以应对开放场景中来自各种变形生成算法、后处理和打印机/扫描仪多样性的未知攻击。本文提出了一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)架构的通用单图像MAD(S-MAD)算法。相较于CNN架构,ViT模型在集成局部和全局信息方面具有优势,因此适合检测面部区域广泛分布的变形痕迹。实验在利用公开可用的FRGC面部数据集生成的面部变形数据集上进行,并与包括已公开评估的代表性MAD算法在内的几种先进算法进行了基准测试。结果证明,在跨数据集测试中(使用不同数据进行训练和测试),所提出S-MAD方法的检测性能有所提高,并在同一数据集测试中(使用相同数据进行训练和测试)展现出相当的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- Face morphing攻击对Face Recognition Systems构成严重威胁,特别是在边境控制和护照签发等场景。
- 需要MAD算法来防御此类攻击,且这些算法必须在开放场景中对抗未知攻击。
- 提出了基于Vision Transformer(ViT)架构的通用单图像MAD(S-MAD)算法。
- ViT模型能更有效地集成局部和全局信息,适合检测面部区域的变形痕迹。
- 与其他先进算法相比,S-MAD算法在跨数据集测试中的检测性能有所提高。
点此查看论文截图

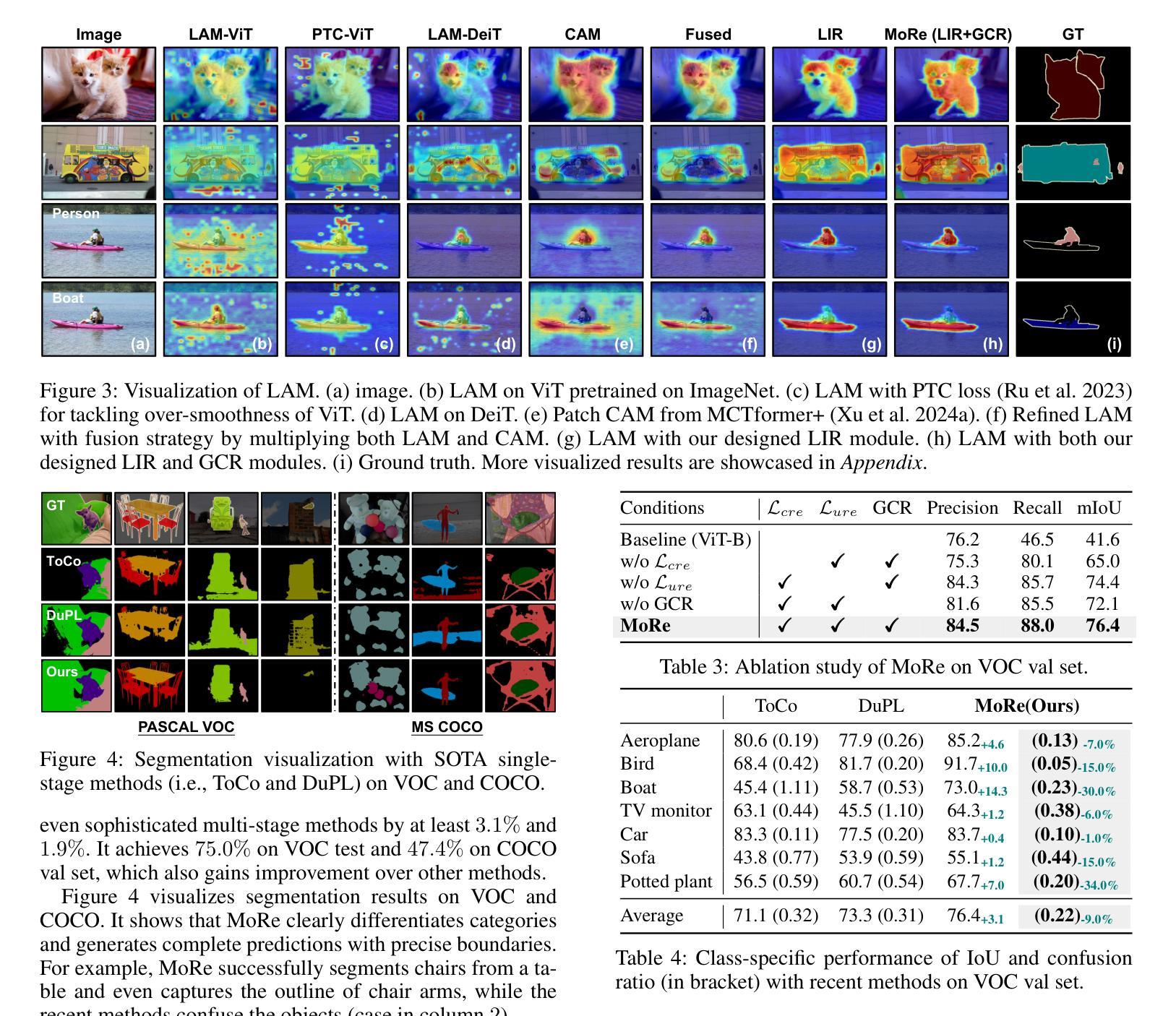
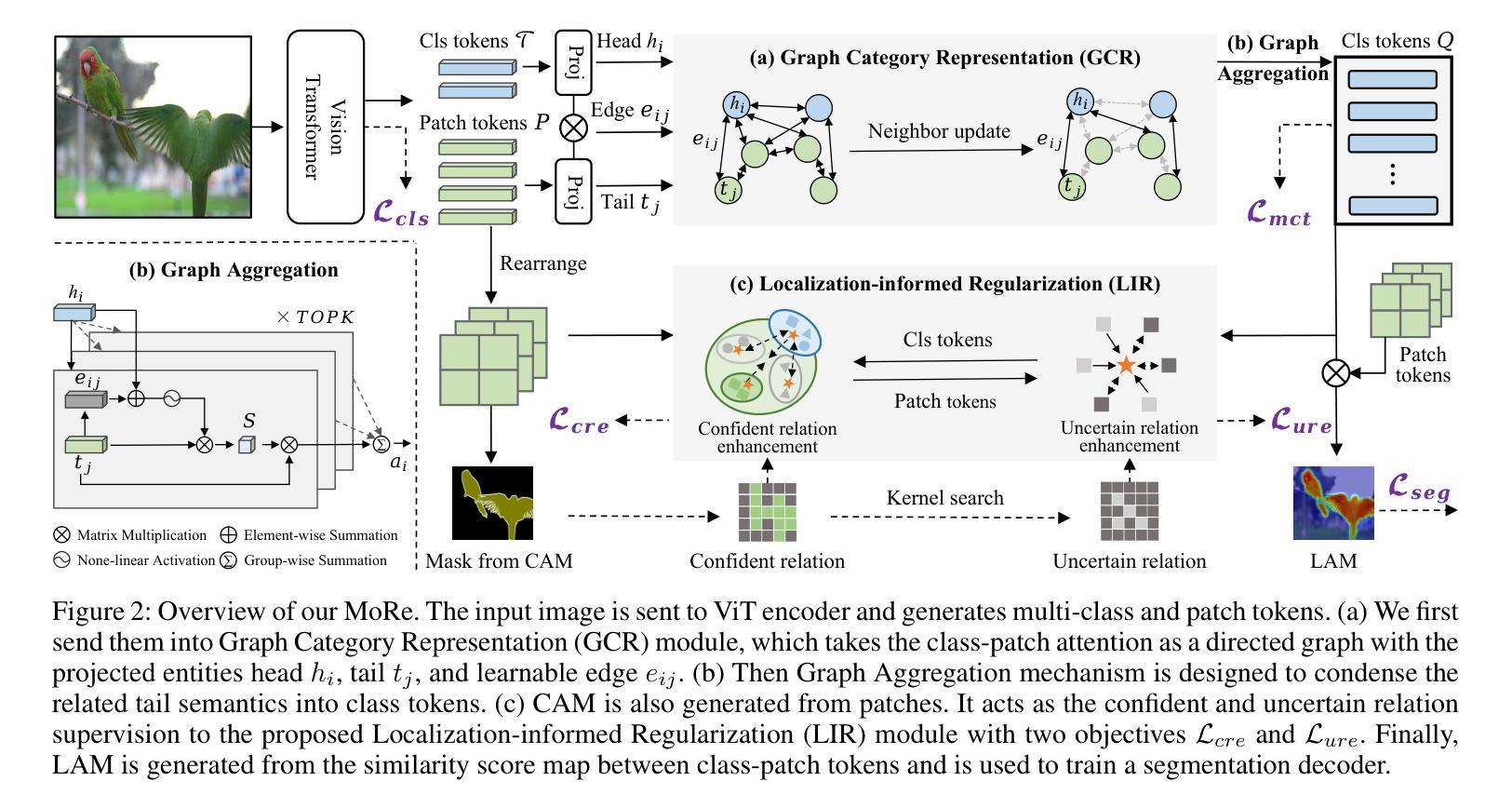
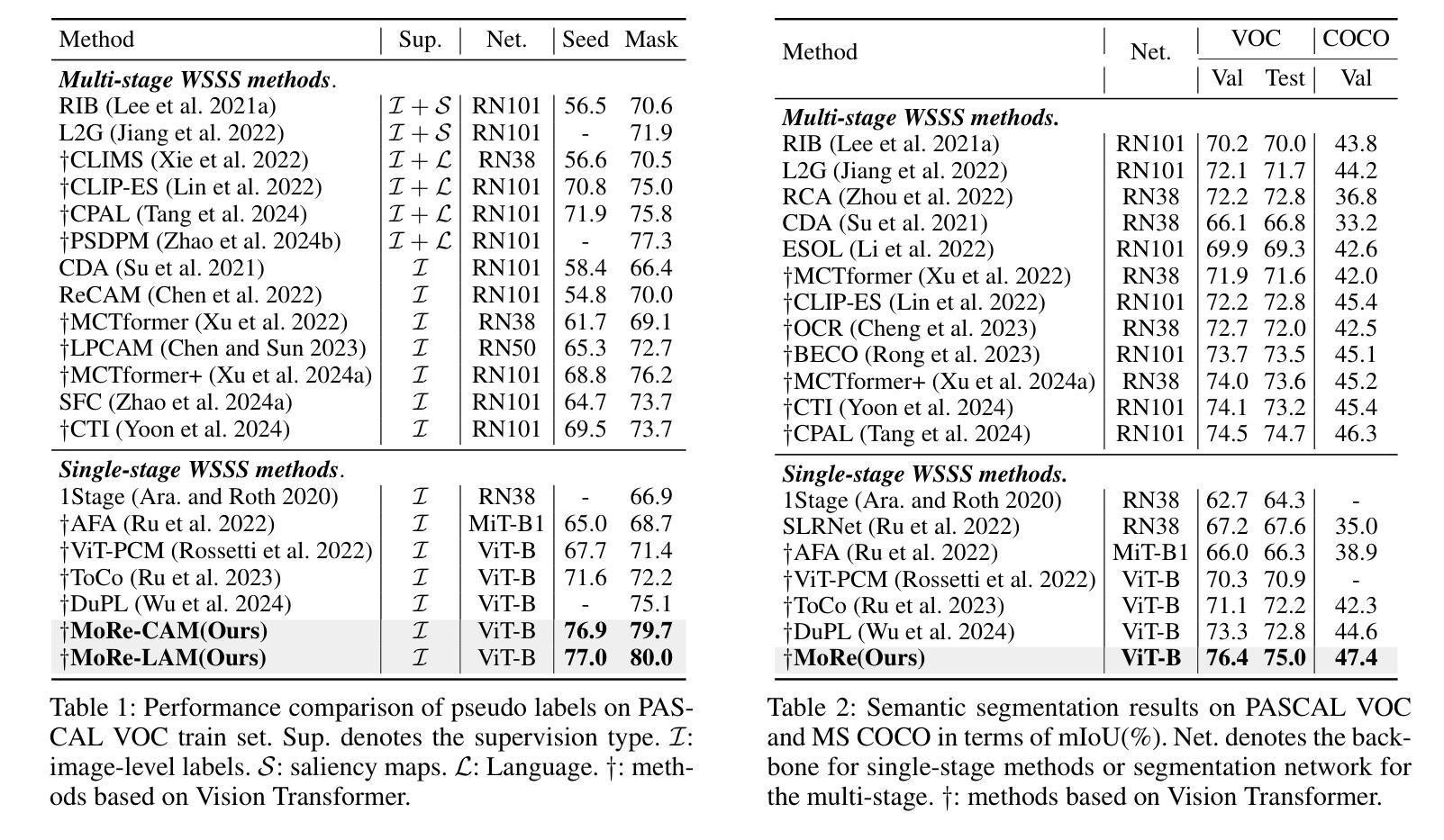
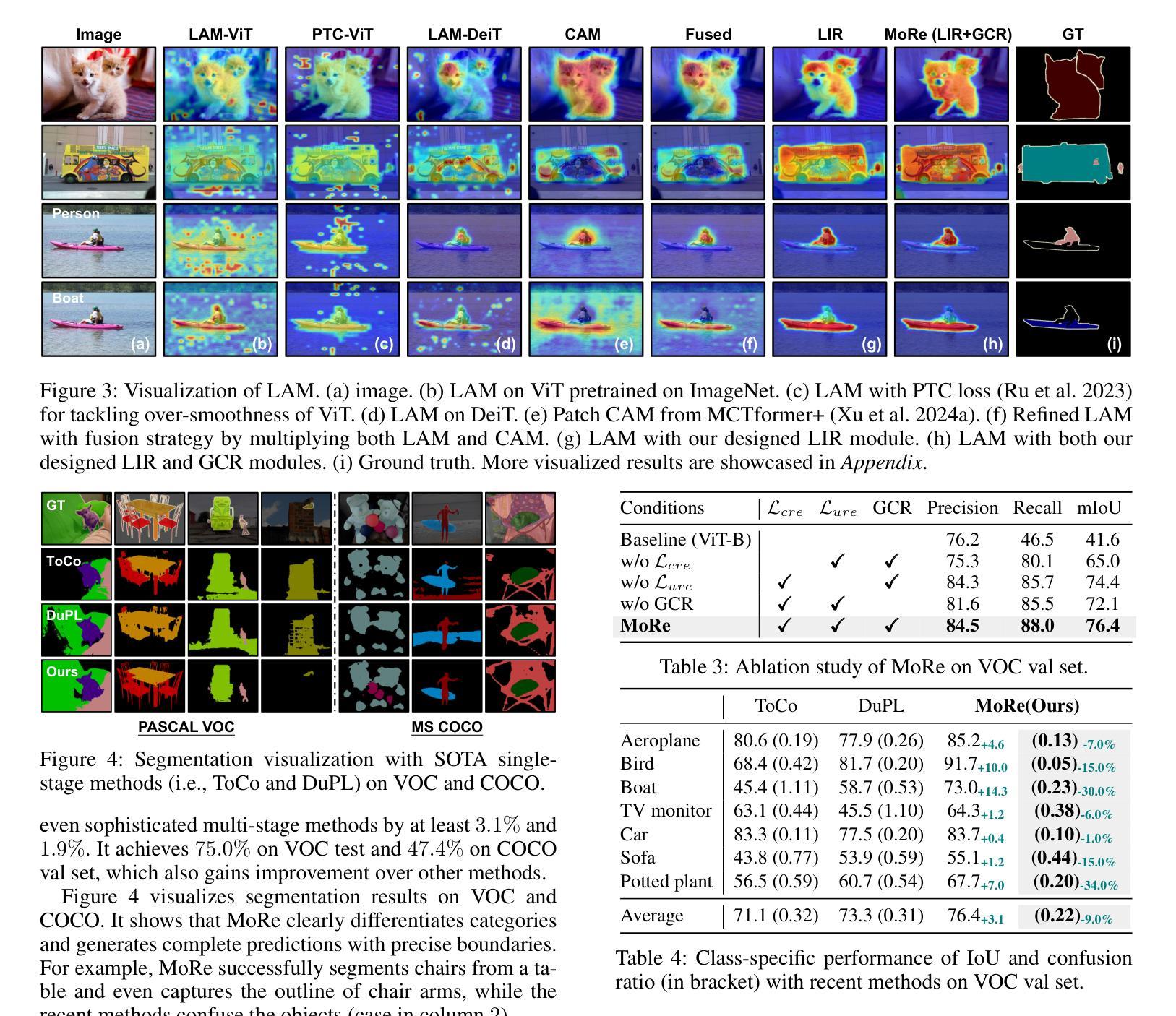
MoRe: Class Patch Attention Needs Regularization for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Zhiwei Yang, Yucong Meng, Kexue Fu, Shuo Wang, Zhijian Song
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) with image-level labels typically uses Class Activation Maps (CAM) to achieve dense predictions. Recently, Vision Transformer (ViT) has provided an alternative to generate localization maps from class-patch attention. However, due to insufficient constraints on modeling such attention, we observe that the Localization Attention Maps (LAM) often struggle with the artifact issue, i.e., patch regions with minimal semantic relevance are falsely activated by class tokens. In this work, we propose MoRe to address this issue and further explore the potential of LAM. Our findings suggest that imposing additional regularization on class-patch attention is necessary. To this end, we first view the attention as a novel directed graph and propose the Graph Category Representation module to implicitly regularize the interaction among class-patch entities. It ensures that class tokens dynamically condense the related patch information and suppress unrelated artifacts at a graph level. Second, motivated by the observation that CAM from classification weights maintains smooth localization of objects, we devise the Localization-informed Regularization module to explicitly regularize the class-patch attention. It directly mines the token relations from CAM and further supervises the consistency between class and patch tokens in a learnable manner. Extensive experiments are conducted on PASCAL VOC and MS COCO, validating that MoRe effectively addresses the artifact issue and achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing recent single-stage and even multi-stage methods. Code is available at https://github.com/zwyang6/MoRe.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)通常使用图像级别的标签和类激活图(CAM)来实现密集预测。最近,视觉转换器(ViT)提供了一种生成定位图的替代方案,来源于类补丁注意力。然而,由于对这类注意力的建模约束不足,我们观察到定位注意力图(LAM)经常面临伪影问题,即语义相关性极小的补丁区域会被类令牌错误激活。在这项工作中,我们提出MoRe来解决这个问题,并进一步研究LAM的潜力。我们的研究结果表明,对类补丁注意力施加额外的正则化是必要的。为此,我们首先将注意力视为一种新型的有向图,并提出图类别表示模块来隐式地正则化类补丁实体之间的交互。它确保类令牌能够动态地凝聚相关的补丁信息,并在图级别上抑制不相关的伪影。其次,受分类权重CAM能维持对象定位平滑的启发,我们设计了定位信息正则化模块来显式地正则化类补丁注意力。它从CAM中提取令牌关系,并以可学习的方式进一步监督类令牌和补丁令牌之间的一致性。在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO上进行了大量实验,验证了MoRe有效地解决了伪影问题,并实现了最先进的性能,超越了最新的单阶段甚至多阶段方法。代码可在https://github.com/zwyang6/MoRe找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
在给定文本中,讨论了使用图像级标签的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)通常使用类激活图(CAM)来实现密集预测的问题。虽然Vision Transformer(ViT)提供了从类补丁注意力生成定位图(LAM)的替代方案,但由于对这类注意力的建模约束不足,LAM经常出现伪激活问题,即语义相关性极小的补丁区域被类标记错误激活。本文提出了MoRe来解决这个问题,并探索LAM的潜力。研究结果表明,对类补丁注意力施加额外的正则化是必要的。为了动态凝聚相关补丁信息并抑制无关伪迹,提出了基于图类别的表示模块来隐式正则化类补丁实体间的交互。同时,为了维护对象定位的平滑性并直接挖掘CAM中的令牌关系,设计了一个定位信息正则化模块来显式地正则化类补丁注意力。通过PASCAL VOC和MS COCO的大量实验验证,MoRe有效地解决了伪激活问题,实现了卓越的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- WSSS利用CAM实现密集预测,但ViT生成的LAM存在伪激活问题。
- MoRe旨在解决LAM中的伪激活问题并探索其潜力。
- 对类补丁注意力施加额外的正则化是必要的。
- 提出了基于图类别的表示模块来隐式正则化类补丁实体间的交互。
- 设计了定位信息正则化模块来显式地正则化类补丁注意力并维护对象定位的平滑性。
- MoRe在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO上实现了卓越性能表现,超越了近期单阶段和多阶段方法。
点此查看论文截图

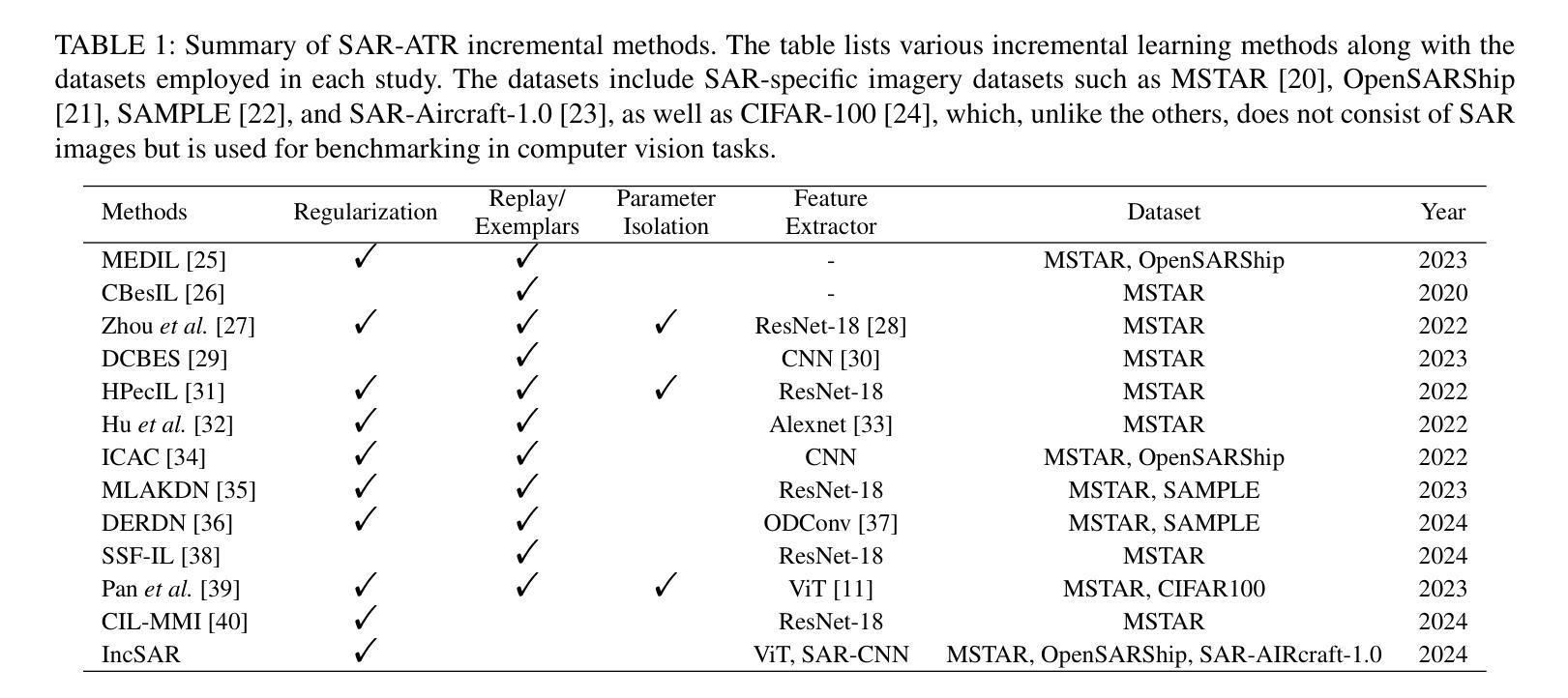
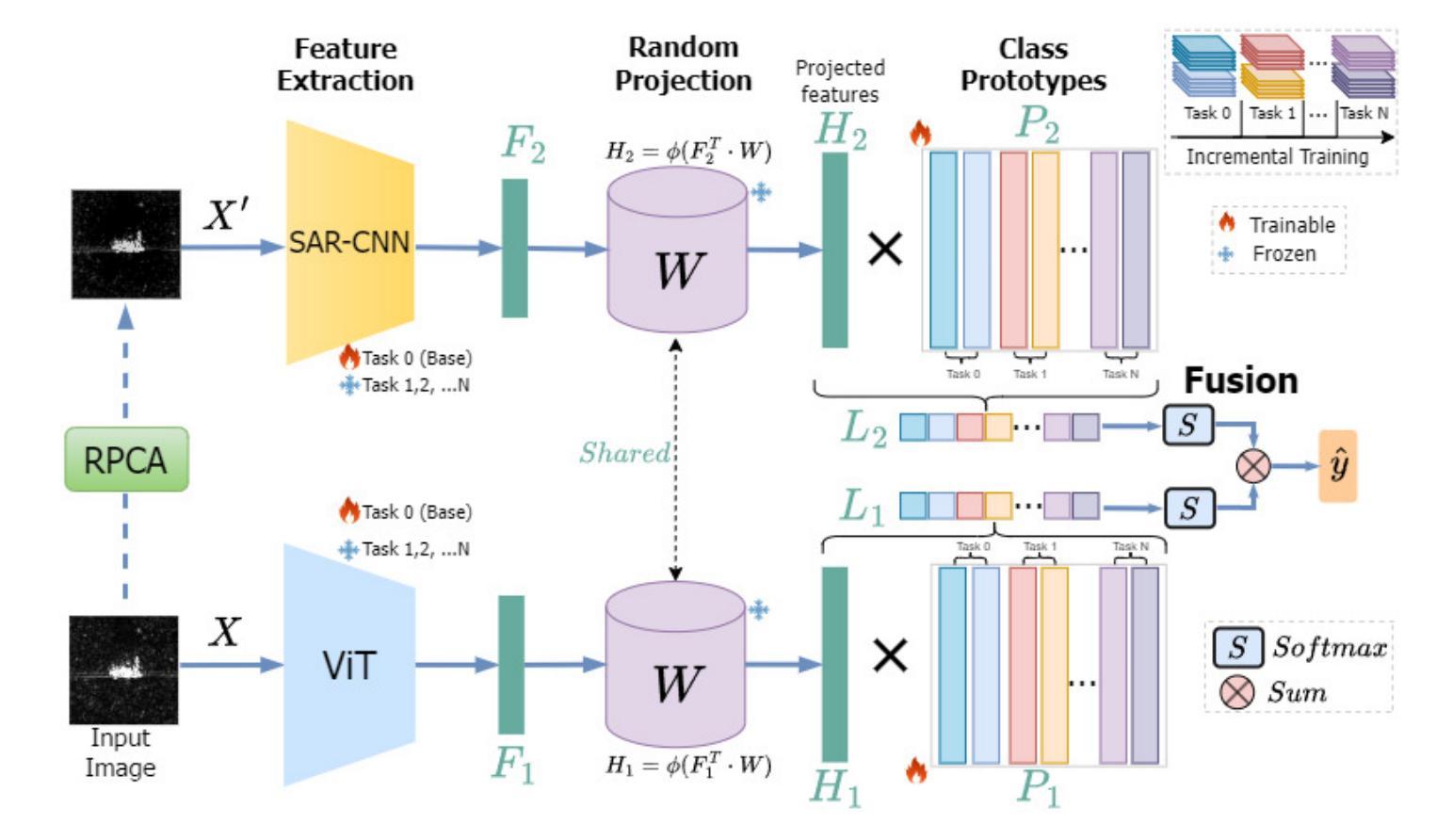
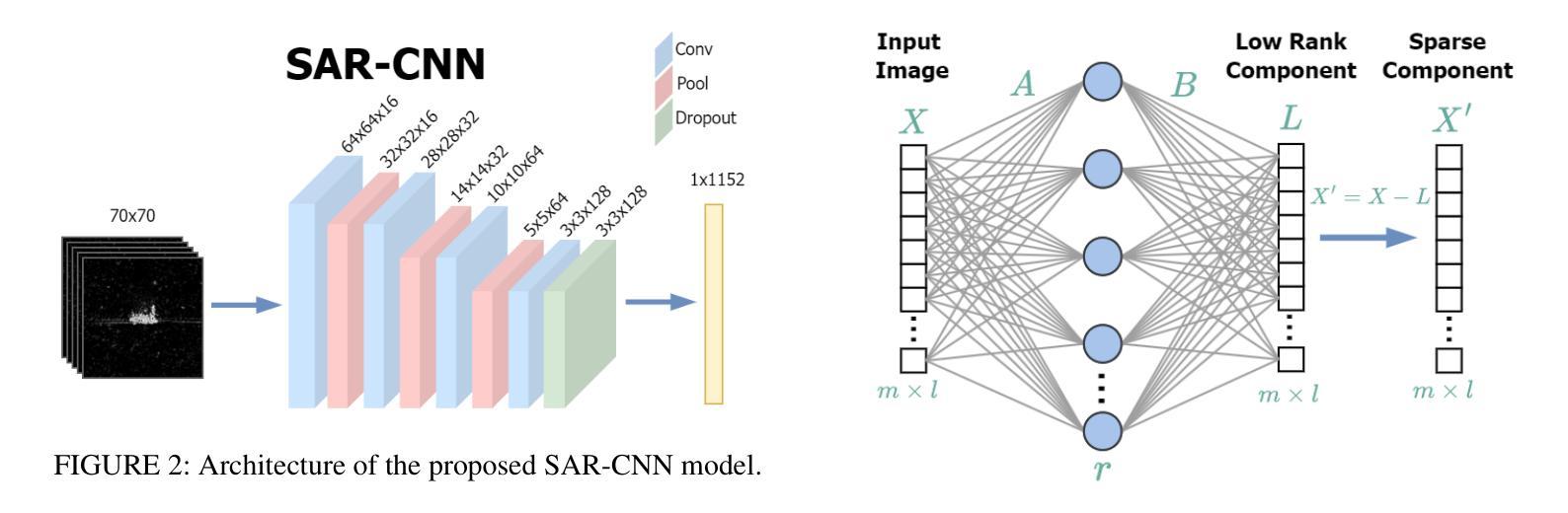
IncSAR: A Dual Fusion Incremental Learning Framework for SAR Target Recognition
Authors:George Karantaidis, Athanasios Pantsios, Ioannis Kompatsiaris, Symeon Papadopoulos
Deep learning techniques have achieved significant success in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) target recognition using predefined datasets in static scenarios. However, real-world applications demand that models incrementally learn new information without forgetting previously acquired knowledge. The challenge of catastrophic forgetting, where models lose past knowledge when adapting to new tasks, remains a critical issue. In this paper, we introduce IncSAR, an incremental learning framework designed to tackle catastrophic forgetting in SAR target recognition. IncSAR combines the power of a Vision Transformer (ViT) and a custom-designed Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) in a dual-branch architecture, integrated via a late-fusion strategy. Additionally, we explore the use of TinyViT to reduce computational complexity and propose an attention mechanism to dynamically enhance feature representation. To mitigate the speckle noise inherent in SAR images, we employ a denoising module based on a neural network approximation of Robust Principal Component Analysis (RPCA), leveraging a simple neural network for efficient noise reduction in SAR imagery. Moreover, a random projection layer improves the linear separability of features, and a variant of Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) decorrelates extracted class prototypes for better generalization. Extensive experiments on the MSTAR, SAR-AIRcraft-1.0, and OpenSARShip benchmark datasets demonstrate that IncSAR significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving a 99.63% average accuracy and a 0.33% performance drop, representing an 89% improvement in retention compared to existing techniques. The source code is available at https://github.com/geokarant/IncSAR.
深度学习技术在合成孔径雷达(SAR)目标识别方面,在静态场景中使用预定数据集取得了显著的成功。然而,现实世界的应用要求模型能够增量学习新信息,同时不忘掉之前获得的知识。模型适应新任务时遗忘过去知识的问题仍然是一个关键问题,我们称之为灾难性遗忘。在本文中,我们介绍了IncSAR,一个旨在解决SAR目标识别中灾难性遗忘问题的增量学习框架。IncSAR结合视觉转换器(ViT)和自定义设计的卷积神经网络(CNN)的力量,采用双分支架构,通过后期融合策略进行集成。此外,我们还探索了使用TinyViT来降低计算复杂性,并提出了一种注意力机制来动态增强特征表示。为了减轻SAR图像固有的斑点噪声,我们采用了一种基于神经网络逼近的稳健主成分分析(RPCA)的降噪模块,利用一个简单的神经网络实现SAR图像的高效降噪。此外,随机投影层提高了特征的线性可分性,线性判别分析(LDA)的变体对提取的类别原型进行去相关,以实现更好的泛化。在MSTAR、SAR-AIRcraft-1.0和OpenSARShip基准数据集上的大量实验表明,IncSAR显著优于最新方法,平均准确度达到99.63%,性能下降率为0.33%,与现有技术相比,保留性能提高了89%。源代码可在https://github.com/geokarant/IncSAR找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文针对合成孔径雷达(SAR)目标识别中的灾难性遗忘问题,提出了IncSAR增量学习框架。它结合Vision Transformer(ViT)和定制卷积神经网络(CNN)进行SAR目标识别,并采用晚期融合策略。同时,利用TinyViT降低计算复杂性,并引入注意力机制改善特征表示。为消除SAR图像的斑点噪声,采用了基于稳健主成分分析(RPCA)神经网络近似值的去噪模块。实验在MSTAR、SAR-AIRcraft-1.0和OpenSARShip数据集上验证了IncSAR的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- IncSAR框架解决了SAR目标识别中的灾难性遗忘问题。
- IncSAR结合了Vision Transformer和定制卷积神经网络进行SAR目标识别。
- TinyViT用于降低计算复杂性。
- 引入注意力机制改善特征表示。
- 采用基于RPCA神经网络近似值的去噪模块消除SAR图像的斑点噪声。
- IncSAR在MSTAR、SAR-AIRcraft-1.0和OpenSARShip数据集上的表现优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图