⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-23 更新
HAC++: Towards 100X Compression of 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yihang Chen, Qianyi Wu, Weiyao Lin, Mehrtash Harandi, Jianfei Cai
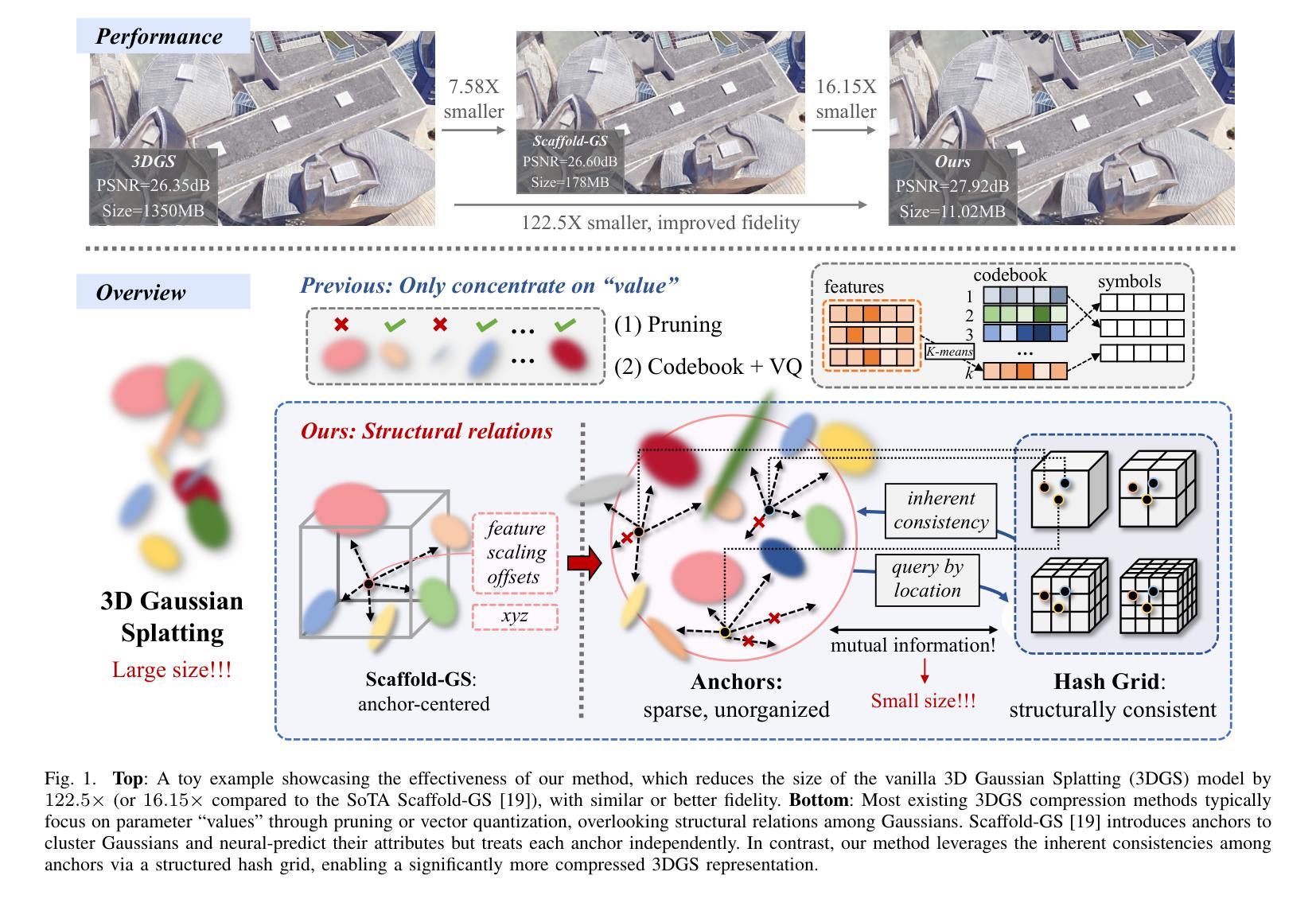
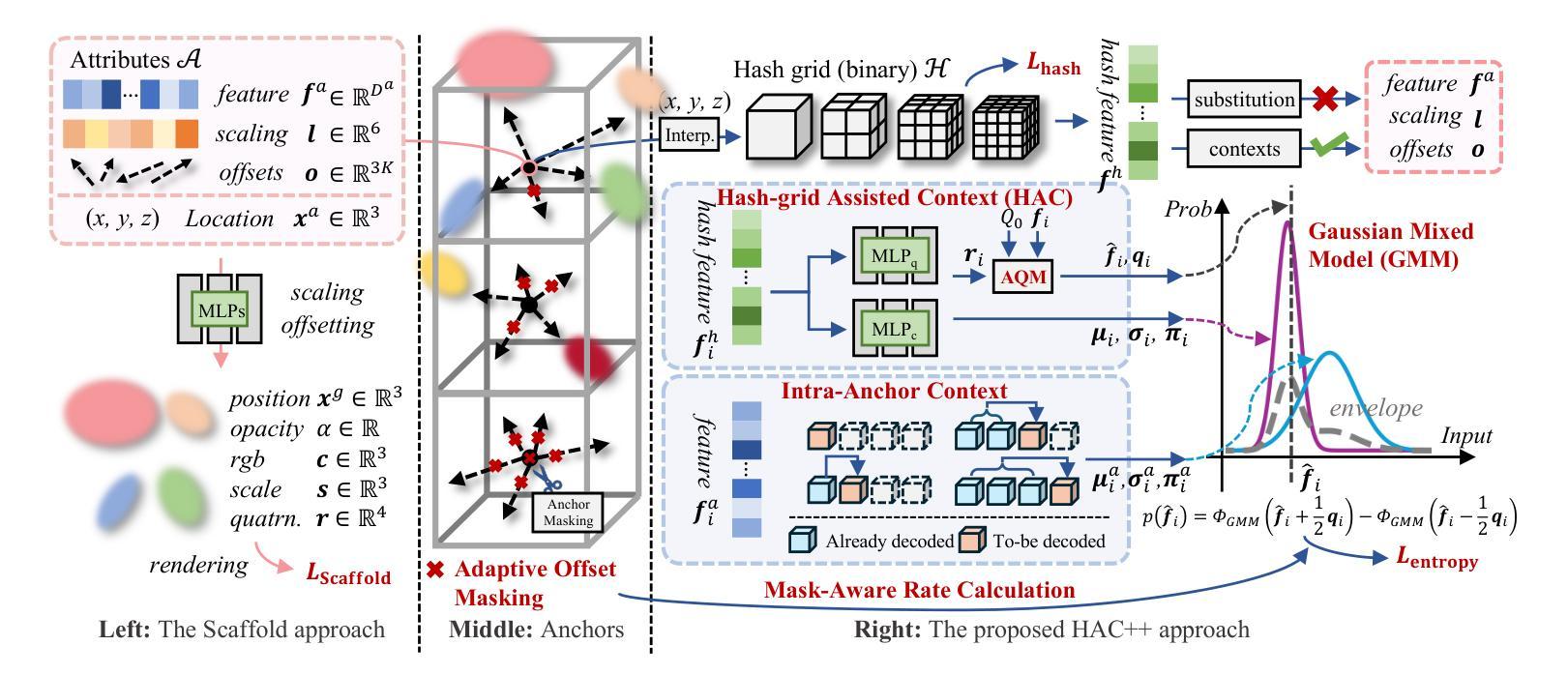
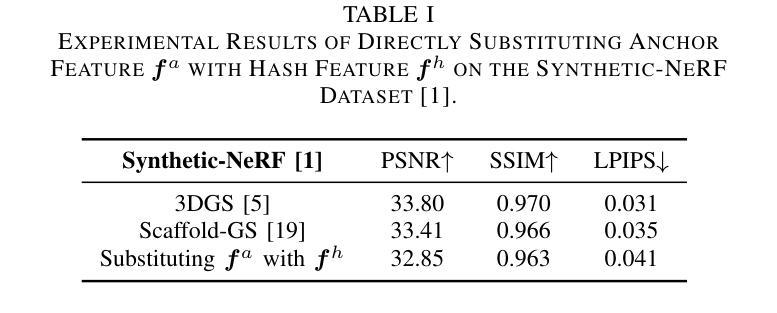
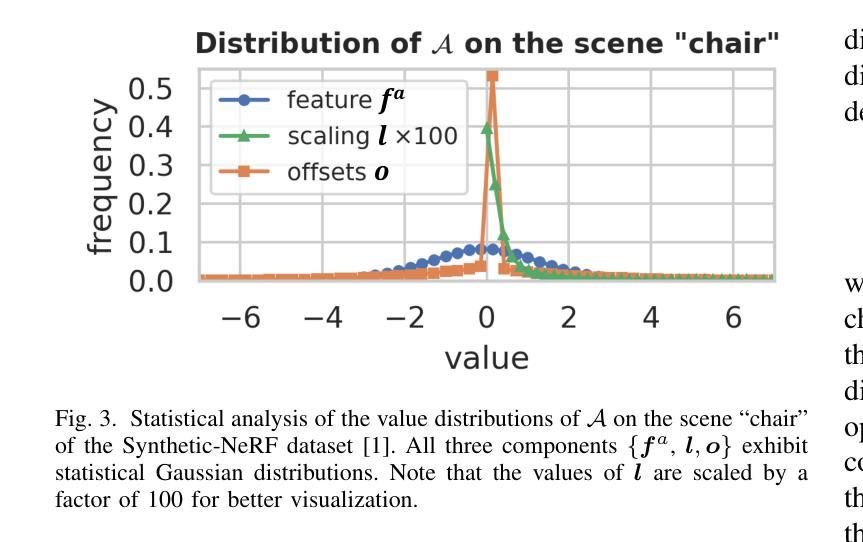
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a promising framework for novel view synthesis, boasting rapid rendering speed with high fidelity. However, the substantial Gaussians and their associated attributes necessitate effective compression techniques. Nevertheless, the sparse and unorganized nature of the point cloud of Gaussians (or anchors in our paper) presents challenges for compression. To achieve a compact size, we propose HAC++, which leverages the relationships between unorganized anchors and a structured hash grid, utilizing their mutual information for context modeling. Additionally, HAC++ captures intra-anchor contextual relationships to further enhance compression performance. To facilitate entropy coding, we utilize Gaussian distributions to precisely estimate the probability of each quantized attribute, where an adaptive quantization module is proposed to enable high-precision quantization of these attributes for improved fidelity restoration. Moreover, we incorporate an adaptive masking strategy to eliminate invalid Gaussians and anchors. Overall, HAC++ achieves a remarkable size reduction of over 100X compared to vanilla 3DGS when averaged on all datasets, while simultaneously improving fidelity. It also delivers more than 20X size reduction compared to Scaffold-GS. Our code is available at https://github.com/YihangChen-ee/HAC-plus.
3D高斯点集(3DGS)作为新颖视角合成的有前途框架应运而生,它以快速渲染速度和高保真度而自豪。然而,大量的高斯及其相关属性需要进行有效的压缩技术处理。尽管如此,高斯点云(或我们论文中的锚点)的稀疏和无组织性质给压缩带来了挑战。为了达到紧凑的尺寸,我们提出了HAC++,它利用无序锚点之间的关系和一个结构化哈希网格,利用它们的互信息来进行上下文建模。此外,HAC++捕获了锚点内部上下文关系,以进一步增强压缩性能。为了促进熵编码,我们利用高斯分布来精确估计每个量化属性的概率,其中我们提出了一种自适应量化模块,以实现这些属性的高精度量化,以改善保真度恢复。此外,我们采用自适应掩码策略来消除无效的高斯和锚点。总体而言,与基础3DGS相比,HAC++在所有数据集上的平均压缩比例达到了惊人的超过100倍的大小减少,同时提高了保真度。与Scaffold-GS相比,其大小减少了超过20倍。我们的代码可在https://github.com/YihangChen-ee/HAC-plus找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE TPAMI Submission. This paper is an extension of HAC at arXiv:2403.14530 (ECCV 2024)
Summary
本文主要介绍了基于关系的点云高斯压缩方法HAC++。该方法利用未组织锚点间的关系和结构化哈希网格进行上下文建模,并采用高斯分布进行概率估计。它结合了自适应量化模块和自适应掩模策略,在保留精度的同时,实现了3DGS的大小缩减,并且在多个数据集上实现平均超过其他方法的表现。该论文的相关代码可在公开链接上获取。
Key Takeaways
以下是关于该文本的关键见解:
- 3DGS在新型视图合成领域具有前景,但其需要大量高斯数据,需要有效的压缩技术。
- HAC++方法利用未组织锚点间的关系进行上下文建模,并采用结构化哈希网格实现紧凑大小。
- HAC++引入了自适应量化模块,能精确地量化每个属性的精度以恢复更高的保真度。
- 采用自适应掩模策略可以消除无效的高斯数据和锚点。
点此查看论文截图

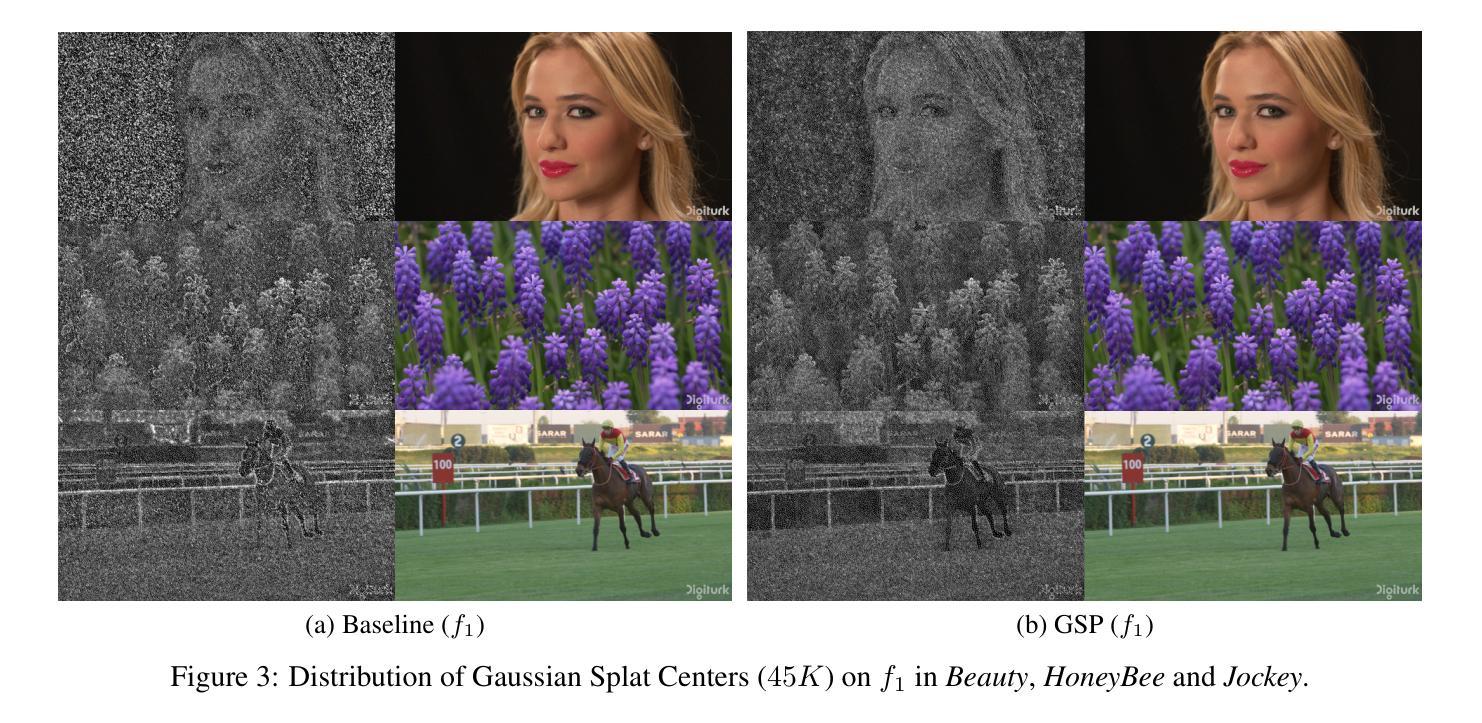
GaussianVideo: Efficient Video Representation Through 2D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Longan Wang, Yuang Shi, Wei Tsang Ooi
3D Gaussian splats have emerged as a revolutionary, effective, learned representation for static 3D scenes. In this work, we explore using 2D Gaussian splats as a new primitive for representing videos. We propose GaussianVideo, an approach to learning a set of 2D Gaussian splats that can effectively represent video frames. GaussianVideo incorporates the following techniques: (i) To exploit temporal redundancy among adjacent frames, which can speed up training and improve the compression efficiency, we predict the Gaussian splats of a frame based on its previous frame; (ii) To control the trade-offs between file size and quality, we remove Gaussian splats with low contribution to the video quality; (iii) To capture dynamics in videos, we randomly add Gaussian splats to fit content with large motion or newly-appeared objects; (iv) To handle significant changes in the scene, we detect key frames based on loss differences during the learning process. Experiment results show that GaussianVideo achieves good rate-distortion trade-offs, comparable to state-of-the-art video codecs such as AV1 and VVC, and a rendering speed of 1500 fps for a 1920x1080 video.
3D高斯样条已经作为静态3D场景的一种革命性、有效的学习表示方法而出现。在这项工作中,我们探索使用2D高斯样条作为表示视频的新原始形式。我们提出了GaussianVideo,这是一种学习一组能够有效代表视频帧的2D高斯样条的方法。GaussianVideo结合了以下技术:(i)为了利用相邻帧之间的时间冗余,这可以加快训练并提高压缩效率,我们根据前一帧预测帧的高斯样条;(ii)为了控制文件大小和质量的权衡,我们删除对视频质量贡献较小的高斯样条;(iii)为了捕捉视频中的动态,我们随机添加高斯样条以适应具有大运动或新出现对象的内容;(iv)为了处理场景中的重大变化,我们基于学习过程中的损失差异检测关键帧。实验结果表明,GaussianVideo具有良好的速率失真权衡,与先进的视频编码技术如AV1和VVC相当,并且对1920x1080视频的渲染速度达到1500帧/秒。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文探讨了使用二维高斯斑点作为视频表示的新原始形式的方法。提出了一种名为GaussianVideo的方法,通过学习和利用一系列二维高斯斑点来有效地表示视频帧。该方法利用时间冗余性预测帧的高斯斑点,移除对视频质量贡献较低的高斯斑点以控制文件大小与质量的权衡,随机添加高斯斑点以捕捉视频中的动态内容,并基于学习过程中的损失差异检测关键帧。实验结果表明,GaussianVideo具有良好的率失真权衡,与AV1和VVC等先进视频编码器的性能相当,对1920x1080视频的渲染速度可达1500帧/秒。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出使用二维高斯斑点作为新的视频表示方法。
- GaussianVideo方法通过学习和利用一系列二维高斯斑点有效地表示视频帧。
- 利用时间冗余性预测帧的高斯斑点以提高训练速度和压缩效率。
- 通过移除对视频质量贡献较低的高斯斑点来控制文件大小与质量的平衡。
- 随机添加高斯斑点以捕捉视频中的动态内容和新出现的对象。
- 通过检测关键帧来处理场景中的重要变化。
点此查看论文截图
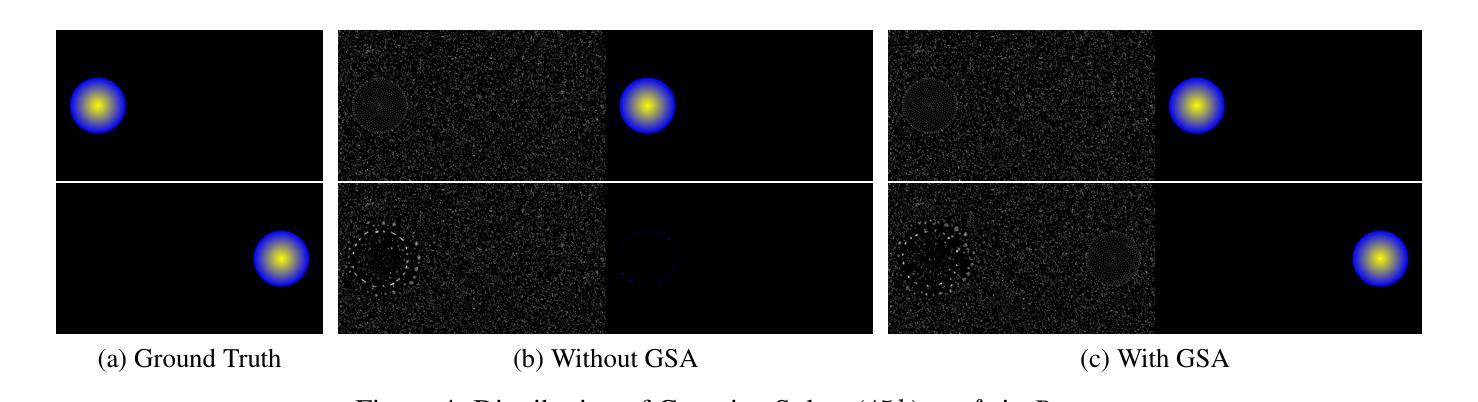





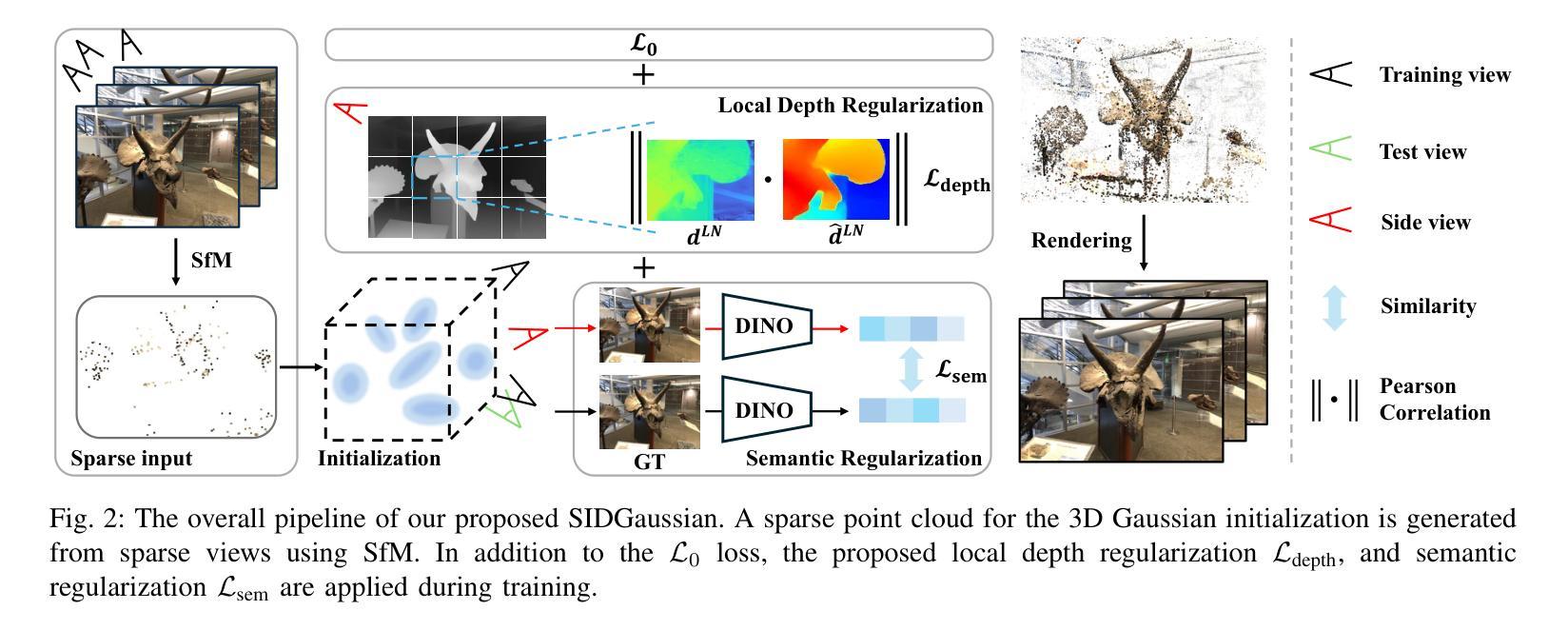
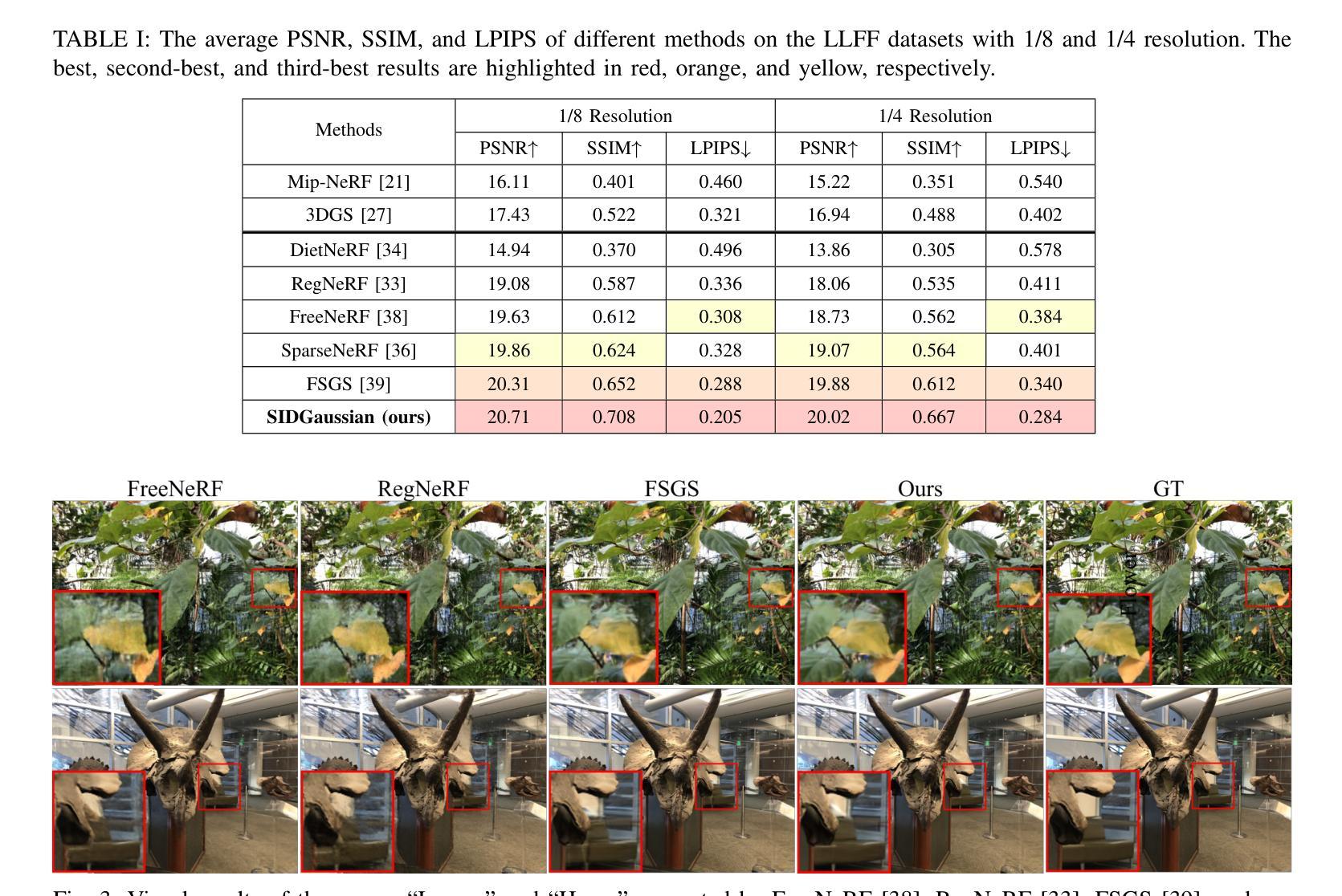
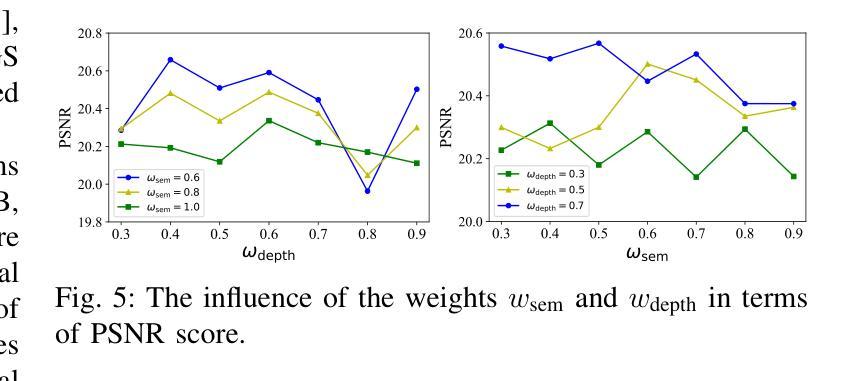
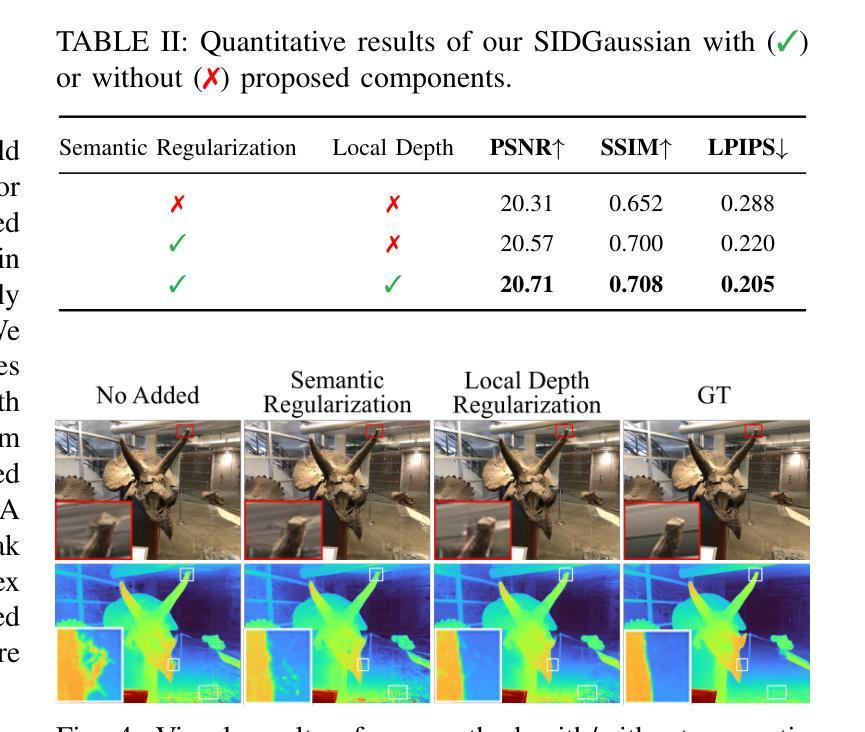
See In Detail: Enhancing Sparse-view 3D Gaussian Splatting with Local Depth and Semantic Regularization
Authors:Zongqi He, Zhe Xiao, Kin-Chung Chan, Yushen Zuo, Jun Xiao, Kin-Man Lam
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has shown remarkable performance in novel view synthesis. However, its rendering quality deteriorates with sparse inphut views, leading to distorted content and reduced details. This limitation hinders its practical application. To address this issue, we propose a sparse-view 3DGS method. Given the inherently ill-posed nature of sparse-view rendering, incorporating prior information is crucial. We propose a semantic regularization technique, using features extracted from the pretrained DINO-ViT model, to ensure multi-view semantic consistency. Additionally, we propose local depth regularization, which constrains depth values to improve generalization on unseen views. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art novel view synthesis approaches, achieving up to 0.4dB improvement in terms of PSNR on the LLFF dataset, with reduced distortion and enhanced visual quality.
3D高斯混合技术(3DGS)在新型视图合成领域表现出卓越的性能。然而,当输入视图稀疏时,其渲染质量会下降,导致内容失真和细节减少。这一局限性阻碍了其实际应用。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种稀疏视图的3DGS方法。考虑到稀疏视图渲染的本质不适定性,融入先验信息至关重要。我们提出了一种语义正则化技术,利用从预训练的DINO-ViT模型中提取的特征,以确保多视图语义一致性。此外,我们还提出了局部深度正则化,通过约束深度值来提高未见视图的泛化能力。我们的方法在新型视图合成方面超越了现有技术,在LLFF数据集上,峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高了高达0.4dB,降低了失真,提高了视觉质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 5 figures, has been accepted by the ICASSP 2025
Summary
3DGS在新型视角合成中表现出卓越性能,但在稀疏视角输入下渲染质量下降,导致内容失真和细节缺失。为解决此问题,提出一种稀疏视角的3DGS方法,并结合先验信息,采用预训练的DINO-ViT模型提取特征,确保多视角语义一致性。此外,还提出局部深度正则化,约束深度值以提高未见视角的泛化能力。该方法优于现有新型视角合成方法,在LLFF数据集上的PSNR提高达0.4dB,降低了失真并提高了视觉质量。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在新型视角合成中表现优秀,但在稀疏视角输入时存在渲染质量下降的问题。
- 为解决渲染质量问题,提出一种稀疏视角的3DGS方法。
- 结合先验信息,采用预训练的DINO-ViT模型提取特征,确保多视角语义一致性。
- 引入局部深度正则化,约束深度值以提高未见视角的泛化能力。
- 该方法在新型视角合成方面优于其他方法。
- 在LLFF数据集上,该方法相比其他方法PSNR提高了0.4dB。
点此查看论文截图

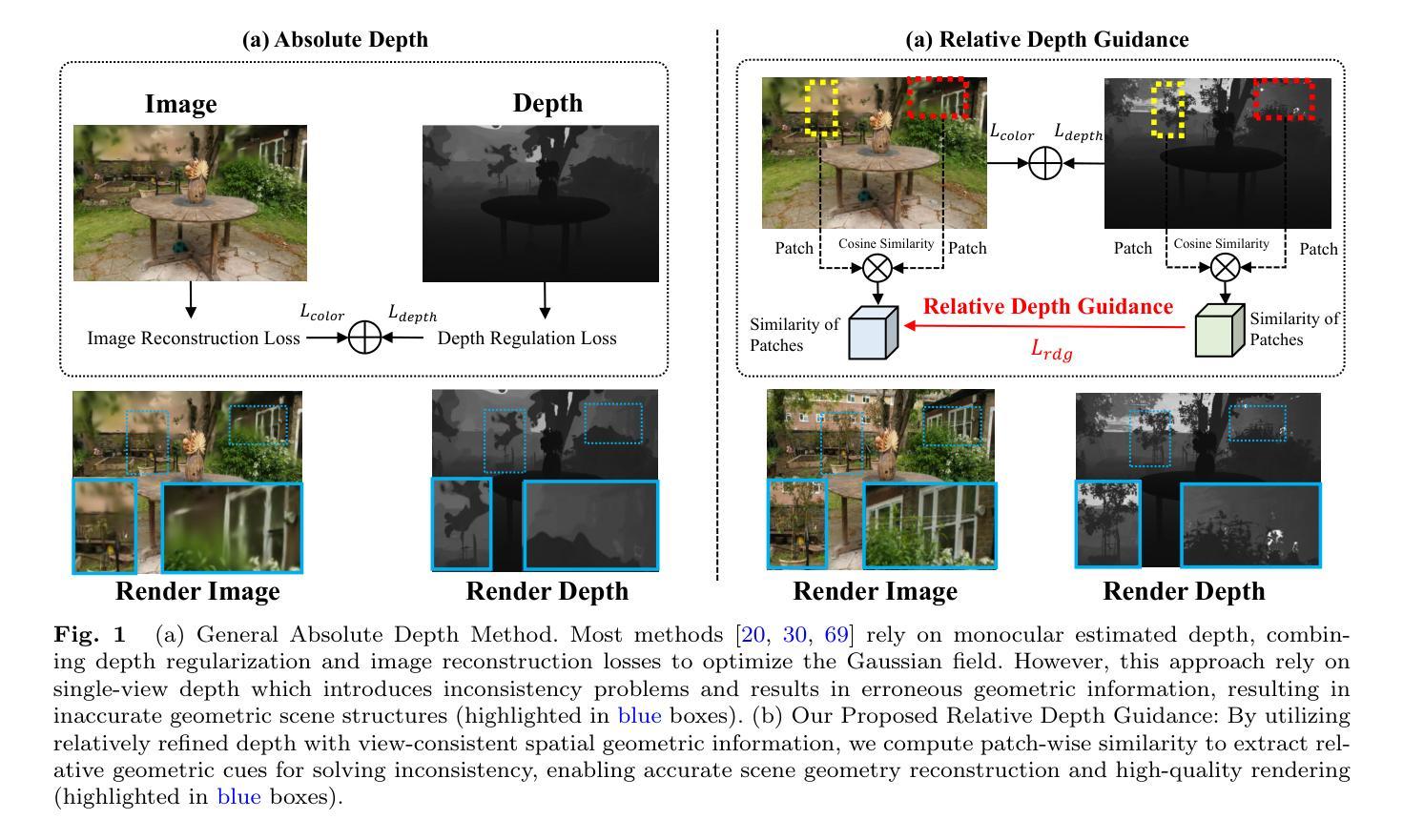
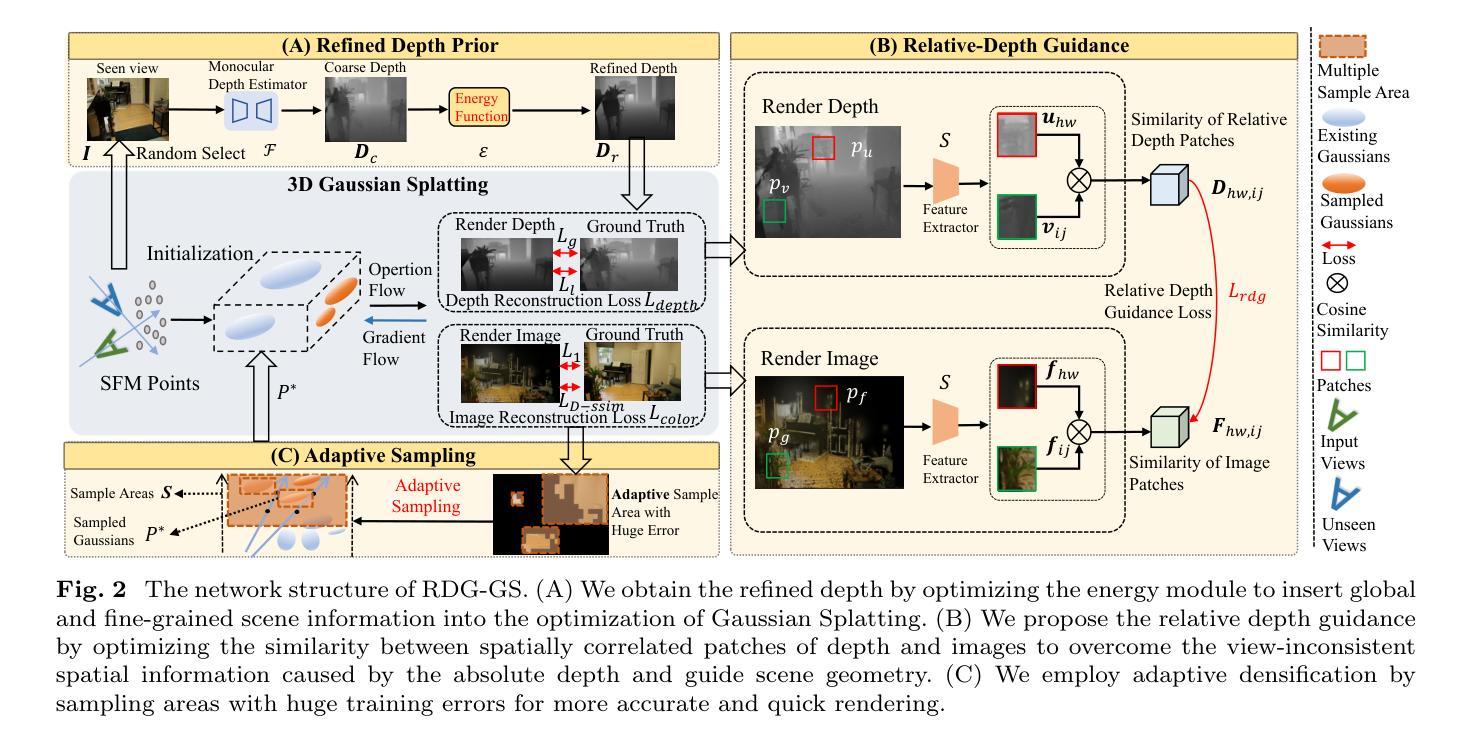
RDG-GS: Relative Depth Guidance with Gaussian Splatting for Real-time Sparse-View 3D Rendering
Authors:Chenlu Zhan, Yufei Zhang, Yu Lin, Gaoang Wang, Hongwei Wang
Efficiently synthesizing novel views from sparse inputs while maintaining accuracy remains a critical challenge in 3D reconstruction. While advanced techniques like radiance fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting achieve rendering quality and impressive efficiency with dense view inputs, they suffer from significant geometric reconstruction errors when applied to sparse input views. Moreover, although recent methods leverage monocular depth estimation to enhance geometric learning, their dependence on single-view estimated depth often leads to view inconsistency issues across different viewpoints. Consequently, this reliance on absolute depth can introduce inaccuracies in geometric information, ultimately compromising the quality of scene reconstruction with Gaussian splats. In this paper, we present RDG-GS, a novel sparse-view 3D rendering framework with Relative Depth Guidance based on 3D Gaussian Splatting. The core innovation lies in utilizing relative depth guidance to refine the Gaussian field, steering it towards view-consistent spatial geometric representations, thereby enabling the reconstruction of accurate geometric structures and capturing intricate textures. First, we devise refined depth priors to rectify the coarse estimated depth and insert global and fine-grained scene information to regular Gaussians. Building on this, to address spatial geometric inaccuracies from absolute depth, we propose relative depth guidance by optimizing the similarity between spatially correlated patches of depth and images. Additionally, we also directly deal with the sparse areas challenging to converge by the adaptive sampling for quick densification. Across extensive experiments on Mip-NeRF360, LLFF, DTU, and Blender, RDG-GS demonstrates state-of-the-art rendering quality and efficiency, making a significant advancement for real-world application.
在3D重建中,从稀疏输入高效地合成新型视图的同时保持准确性仍然是一个关键挑战。虽然像辐射场和3D高斯泼溅这样的先进技术可以实现高质量的渲染和高效的性能,但当应用于稀疏输入视图时,它们会存在显著的几何重建误差。此外,尽管最近的方法利用单眼深度估计来增强几何学习,但它们对单视图估计深度的依赖往往导致不同视点之间的视图不一致问题。因此,这种对绝对深度的依赖可能会引入几何信息的不准确,最终损害高斯喷溅场景重建的质量。在本文中,我们提出了基于3D高斯泼溅的相对深度指导的稀疏视图3D渲染框架RDG-GS。核心创新之处在于利用相对深度指导来优化高斯场,使其朝向一致的视图空间几何表示,从而能够实现准确的几何结构重建并捕捉精细纹理。首先,我们设计了精细的深度先验来纠正粗略估计的深度,并将全局和精细场景信息插入高斯函数中。在此基础上,为了解决由绝对深度引起的空间几何误差,我们通过优化深度和图像空间相关斑块之间的相似性来提出相对深度指导。此外,我们还通过自适应采样直接处理稀疏区域,以快速实现密集化,应对挑战。在Mip-NeRF360、LLFF、DTU和Blender的大量实验表明,RDG-GS具有最先进的渲染质量和效率,为实际应用取得了重大进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 12 figures
Summary
在稀疏输入下进行高效的视角合成仍然是保持精确性的一个难题。先进的渲染技术如光线辐射场和3D高斯平板印刷可以在密集视图输入下实现高质量的渲染和高效的效率,但当应用于稀疏视图输入时,它们会面临重大的几何重建误差问题。尽管最近的方法利用单眼深度估计增强几何学习,但它们依赖于单视图估计的深度,这往往导致不同视角之间的视图不一致问题。因此,对绝对深度的依赖可能会导致几何信息的不准确,从而最终损害场景的重建质量。本文提出了一种基于相对深度指导的稀疏视图3D渲染框架RDG-GS。核心创新在于利用相对深度指导优化高斯场,使其朝一致的空间几何表示方向移动,从而实现准确的几何结构重建和精细纹理捕捉。通过广泛的实验验证,RDG-GS在Mip-NeRF360、LLFF、DTU和Blender等多个数据集上展现出最佳的渲染质量和效率,为实际应用提供了显著的进步。
Key Takeaways
- 稀疏输入下的视角合成是维持精确性的关键挑战。当前技术在几何重建中易出错,尤其是处理稀疏视角时。
点此查看论文截图

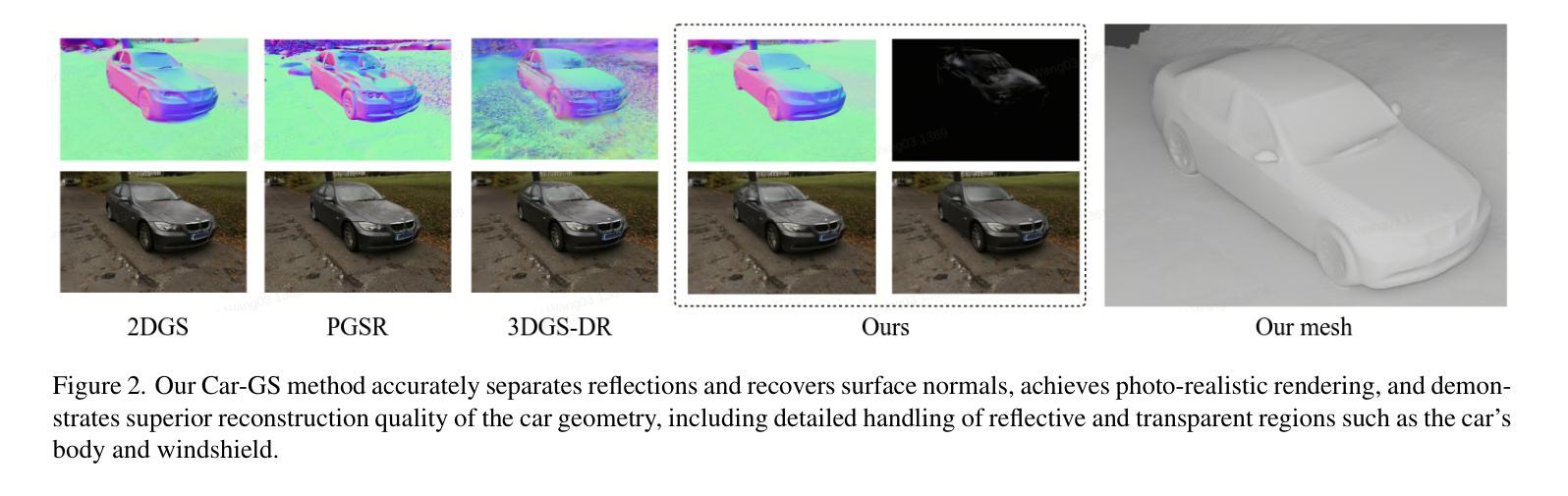
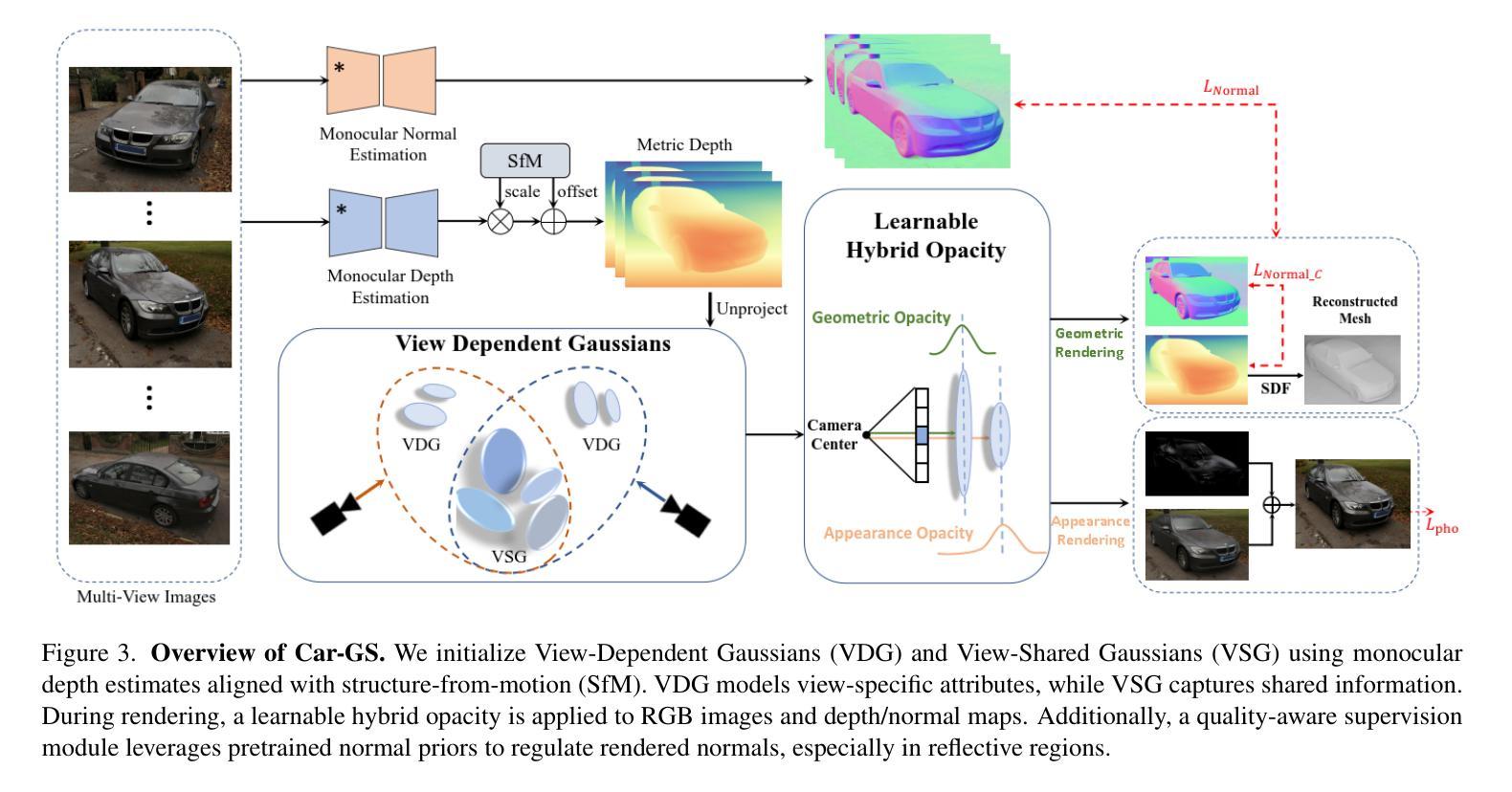
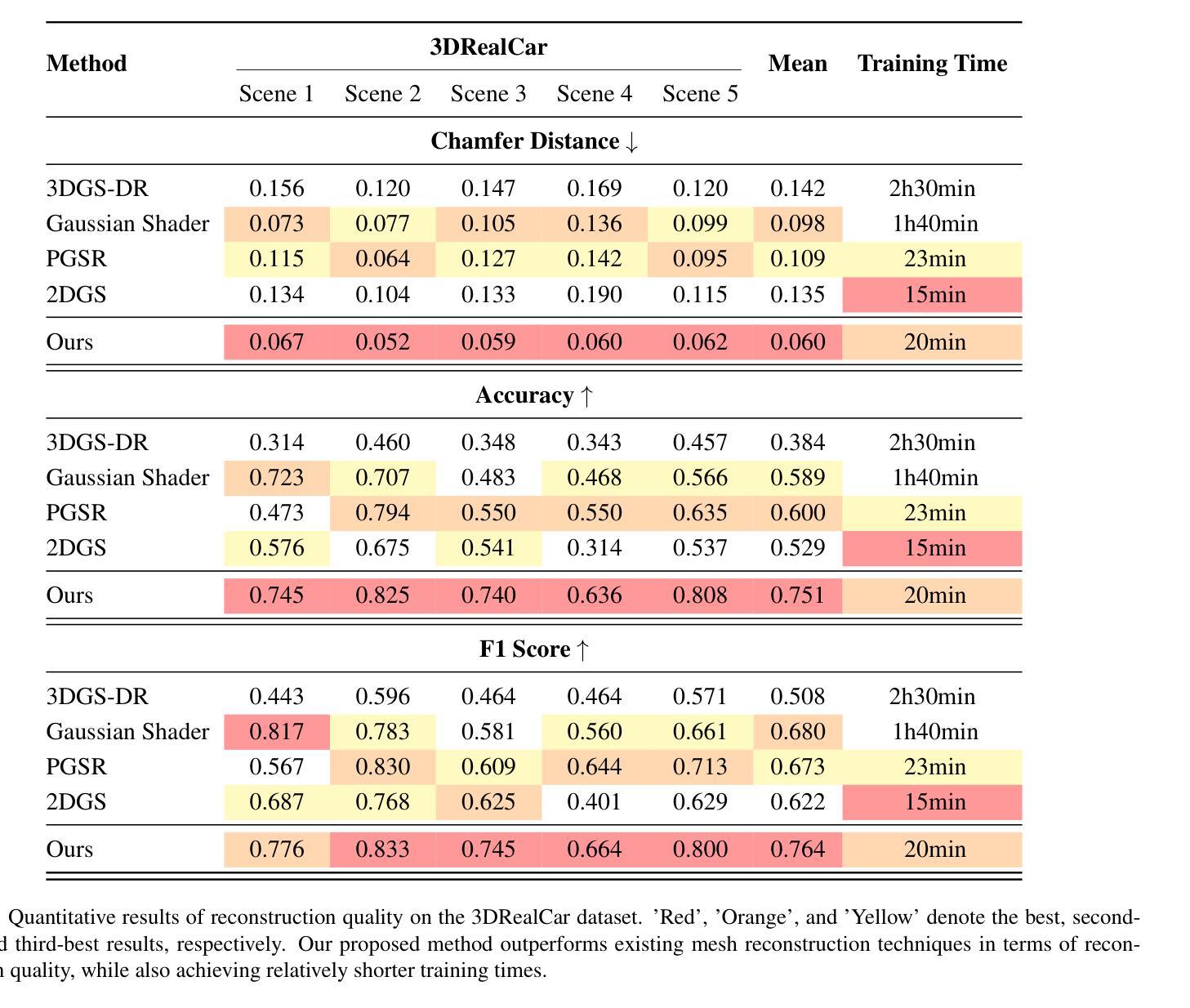
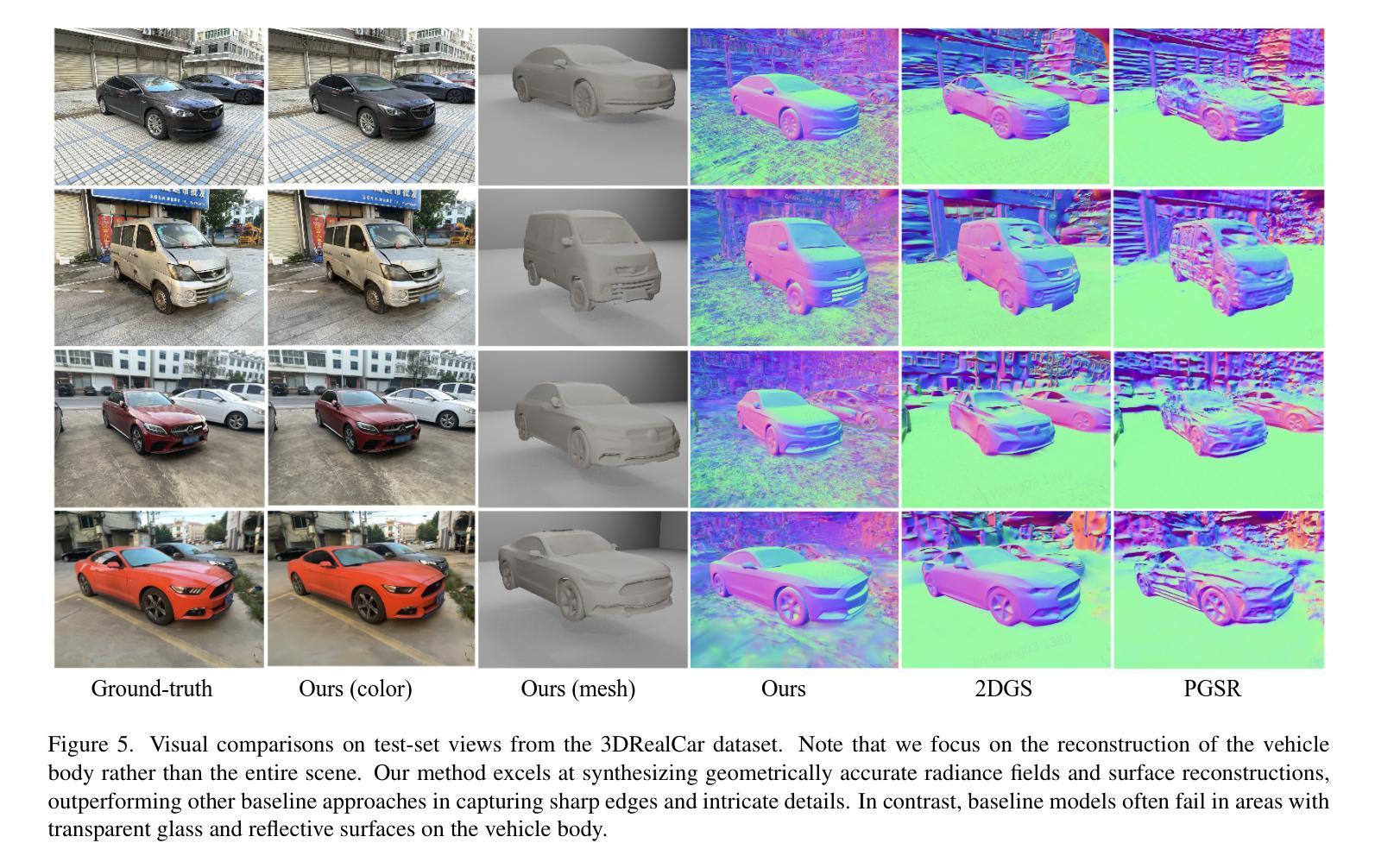
Car-GS: Addressing Reflective and Transparent Surface Challenges in 3D Car Reconstruction
Authors:Congcong Li, Jin Wang, Xiaomeng Wang, Xingchen Zhou, Wei Wu, Yuzhi Zhang, Tongyi Cao
3D car modeling is crucial for applications in autonomous driving systems, virtual and augmented reality, and gaming. However, due to the distinctive properties of cars, such as highly reflective and transparent surface materials, existing methods often struggle to achieve accurate 3D car reconstruction.To address these limitations, we propose Car-GS, a novel approach designed to mitigate the effects of specular highlights and the coupling of RGB and geometry in 3D geometric and shading reconstruction (3DGS). Our method incorporates three key innovations: First, we introduce view-dependent Gaussian primitives to effectively model surface reflections. Second, we identify the limitations of using a shared opacity parameter for both image rendering and geometric attributes when modeling transparent objects. To overcome this, we assign a learnable geometry-specific opacity to each 2D Gaussian primitive, dedicated solely to rendering depth and normals. Third, we observe that reconstruction errors are most prominent when the camera view is nearly orthogonal to glass surfaces. To address this issue, we develop a quality-aware supervision module that adaptively leverages normal priors from a pre-trained large-scale normal model.Experimental results demonstrate that Car-GS achieves precise reconstruction of car surfaces and significantly outperforms prior methods. The project page is available at https://lcc815.github.io/Car-GS.
3D车辆建模在自动驾驶系统、虚拟和增强现实以及游戏等领域具有广泛的应用。然而,由于汽车的独特属性,如高反射和透明表面材料,现有方法往往难以进行准确的3D车辆重建。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了Car-GS这一新方法,旨在缓解镜面高光和RGB与几何形状在三维几何和着色重建(3DGS)中的耦合效应的影响。我们的方法结合了三项关键创新:首先,我们引入视相关的高斯基本元素来有效地模拟表面反射。其次,我们发现使用共享的透明度参数对图像渲染和几何属性进行建模时存在局限性,尤其是在模拟透明物体时。为了克服这一问题,我们为每个二维高斯基本元素分配了一个可学习的几何特定透明度,专门用于渲染深度和法线。最后,我们观察到当相机视角几乎垂直于玻璃表面时,重建误差最为明显。为了解决这个问题,我们开发了一个质量感知的监督模块,该模块自适应地利用预训练的大规模法线模型的法线先验信息。实验结果表明,Car-GS实现了汽车表面的精确重建,并显著优于以前的方法。项目页面可在https://lcc815.github.io/Car-GS访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出Car-GS方法来解决在自主驾驶系统、虚拟与增强现实和游戏中应用的车辆三维建模问题。针对车辆特有的反射和透明表面材质特性,Car-GS通过引入视图相关的高斯基本形状、可学习的几何特定遮光度以及质量感知监督模块等技术创新解决了现有方法的局限性,实现了精确的车辆表面重建。
Key Takeaways
- 3D car modeling在自主驾驶系统、虚拟与增强现实和游戏中具有关键作用。但车辆特有的反射和透明材质给建模带来挑战。
- 现有方法在车辆建模中面临准确重建的挑战。为此,提出了Car-GS方法来解决这些问题。
- Car-GS引入视图相关的高斯基本形状,有效模拟表面反射。
- Car-GS识别了为透明物体建模时共享遮光度参数的局限性,并对其进行改进。为每个二维高斯基本形状分配一个仅用于渲染深度和法线的几何特定遮光度。
- 当相机视角几乎垂直于玻璃表面时,重建误差最为明显。为此,Car-GS开发了一个质量感知监督模块,自适应利用预训练的大规模法线模型的法线先验信息。
点此查看论文截图


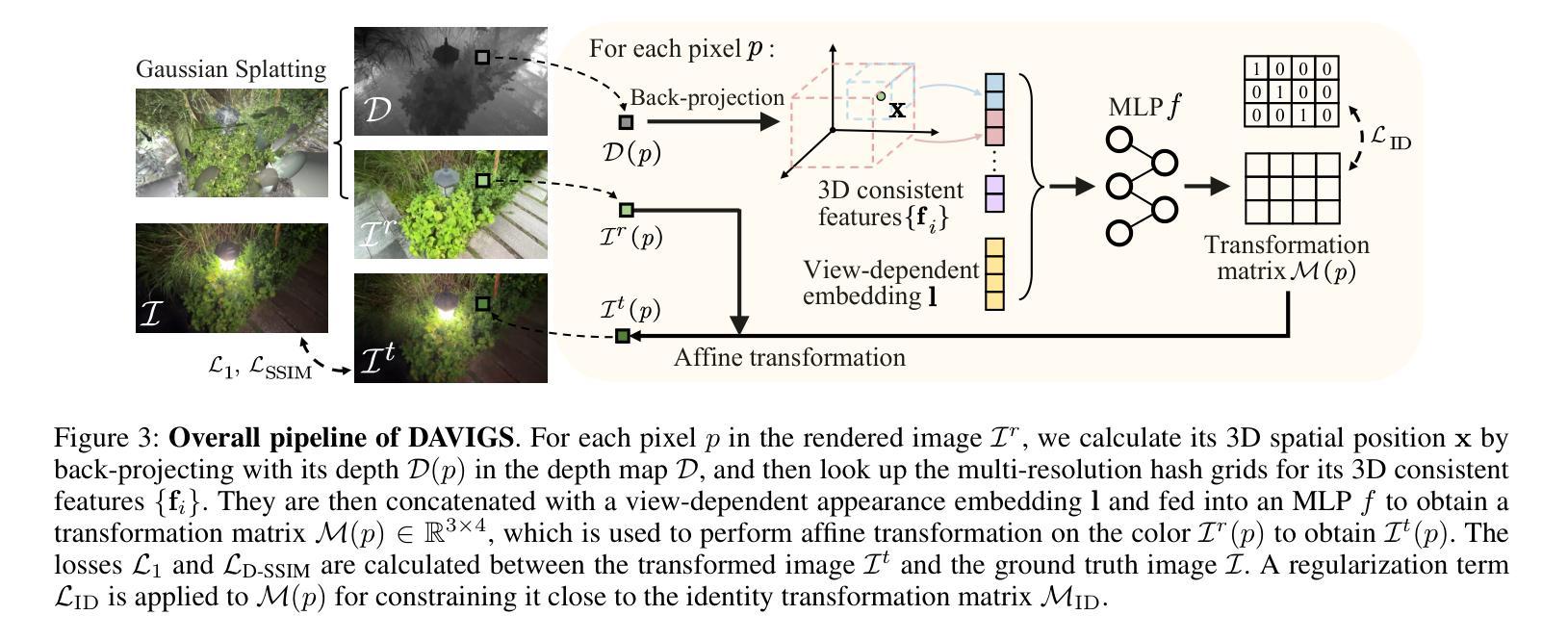
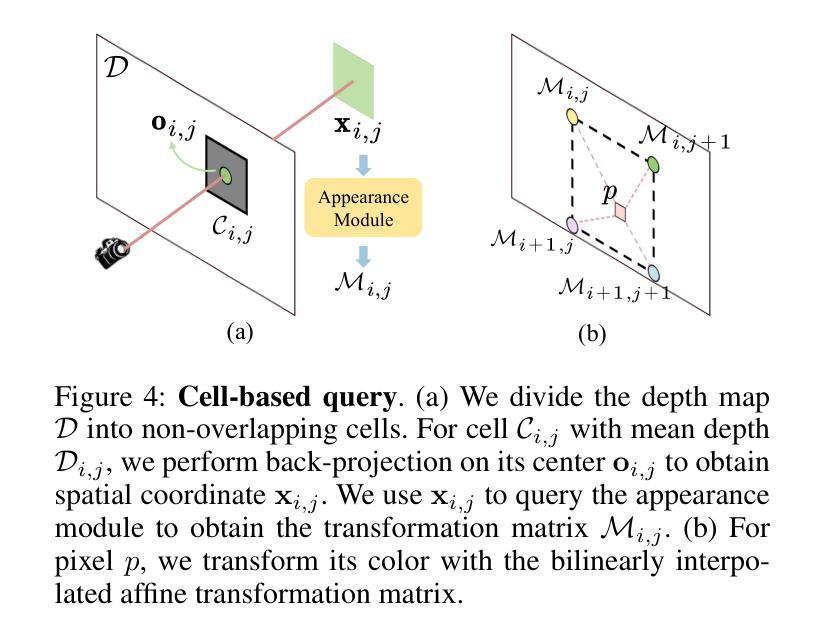
Decoupling Appearance Variations with 3D Consistent Features in Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jiaqi Lin, Zhihao Li, Binxiao Huang, Xiao Tang, Jianzhuang Liu, Shiyong Liu, Xiaofei Wu, Fenglong Song, Wenming Yang
Gaussian Splatting has emerged as a prominent 3D representation in novel view synthesis, but it still suffers from appearance variations, which are caused by various factors, such as modern camera ISPs, different time of day, weather conditions, and local light changes. These variations can lead to floaters and color distortions in the rendered images/videos. Recent appearance modeling approaches in Gaussian Splatting are either tightly coupled with the rendering process, hindering real-time rendering, or they only account for mild global variations, performing poorly in scenes with local light changes. In this paper, we propose DAVIGS, a method that decouples appearance variations in a plug-and-play and efficient manner. By transforming the rendering results at the image level instead of the Gaussian level, our approach can model appearance variations with minimal optimization time and memory overhead. Furthermore, our method gathers appearance-related information in 3D space to transform the rendered images, thus building 3D consistency across views implicitly. We validate our method on several appearance-variant scenes, and demonstrate that it achieves state-of-the-art rendering quality with minimal training time and memory usage, without compromising rendering speeds. Additionally, it provides performance improvements for different Gaussian Splatting baselines in a plug-and-play manner.
高斯平铺技术已成为新型视图合成中的突出3D表示方法,但它仍然受到外观变化的影响,这些变化是由现代相机ISP、一天中的不同时间、天气条件和局部光照变化等各种因素造成的。这些变化可能导致渲染的图像/视频中浮现浮光与色彩失真。高斯平铺技术中最近的外观建模方法要么与渲染过程紧密耦合,阻碍实时渲染,要么只考虑轻微的全局变化,在局部光照变化的场景中表现不佳。在本文中,我们提出了DAVIGS方法,该方法能够以即插即用和高效的方式解耦外观变化。我们的方法通过在图像层面而非高斯层面转换渲染结果,能够以最短的优化时间和内存开销对外观变化进行建模。此外,我们的方法还能够在3D空间中收集与外观相关的信息以转换渲染的图像,从而隐式地建立跨视图的3D一致性。我们在多个外观变化的场景上验证了我们的方法,并证明它在训练时间和内存使用最少的情况下实现了最先进的渲染质量,同时不牺牲渲染速度。此外,它还以即插即用方式提高了不同高斯平铺基准的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AAAI 2025. Project website: https://davi-gaussian.github.io
Summary
高斯描影技术已成为新型视角合成中的主流3D表示方法,但仍有外观变化问题。论文提出DAVIGS方法,以高效的方式解决外观变化问题,提升渲染图像质量。该方法在图像层面进行渲染结果转换,而非高斯层面,能模拟外观变化且优化时间和内存开销最小。DAVIGS还能在3D空间中收集外观相关信息来转换渲染图像,从而建立视图之间的隐式3D一致性。
Key Takeaways
- Gaussian Splatting是主流3D表示方法,但仍存在外观变化问题。
- 外观变化可能来源于现代相机ISP、时间、天气和局部光照变化。
- 现有方法要么与渲染过程紧密耦合,影响实时渲染速度,要么仅适用于轻微全局变化。
- DAVIGS方法能在图像层面进行渲染结果转换,模拟外观变化,优化时间和内存开销最小。
- DAVIGS在建立视图之间的隐式3D一致性方面表现出优势。
- 该方法在多个场景下的验证证明了其优秀渲染质量,并且具有快速的训练时间和较低的内存使用。
点此查看论文截图




GSTAR: Gaussian Surface Tracking and Reconstruction
Authors:Chengwei Zheng, Lixin Xue, Juan Zarate, Jie Song
3D Gaussian Splatting techniques have enabled efficient photo-realistic rendering of static scenes. Recent works have extended these approaches to support surface reconstruction and tracking. However, tracking dynamic surfaces with 3D Gaussians remains challenging due to complex topology changes, such as surfaces appearing, disappearing, or splitting. To address these challenges, we propose GSTAR, a novel method that achieves photo-realistic rendering, accurate surface reconstruction, and reliable 3D tracking for general dynamic scenes with changing topology. Given multi-view captures as input, GSTAR binds Gaussians to mesh faces to represent dynamic objects. For surfaces with consistent topology, GSTAR maintains the mesh topology and tracks the meshes using Gaussians. In regions where topology changes, GSTAR adaptively unbinds Gaussians from the mesh, enabling accurate registration and the generation of new surfaces based on these optimized Gaussians. Additionally, we introduce a surface-based scene flow method that provides robust initialization for tracking between frames. Experiments demonstrate that our method effectively tracks and reconstructs dynamic surfaces, enabling a range of applications. Our project page with the code release is available at https://eth-ait.github.io/GSTAR/.
三维高斯扩展技术已经实现了静态场景的光照现实渲染。近期的研究已经将这些方法扩展到支持表面重建和跟踪。然而,使用三维高斯跟踪动态表面仍然具有挑战性,这是由于复杂的拓扑变化,例如表面出现、消失或分裂。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了GSTAR,这是一种实现光照现实渲染、精确表面重建和可靠的三维跟踪的新方法,适用于具有拓扑变化的通用动态场景。给定多视图捕获作为输入,GSTAR将高斯绑定到网格面以表示动态对象。对于具有一致拓扑的表面,GSTAR保持网格拓扑并使用高斯进行网格跟踪。在拓扑变化区域,GSTAR自适应地从网格解绑高斯,从而实现准确注册和基于优化高斯生成新的表面。此外,我们引入了一种基于表面的场景流方法,为帧间跟踪提供稳健的初始化。实验表明,我们的方法可以有效地跟踪和重建动态表面,从而支持一系列应用。我们的项目页面及代码发布可在https://eth-ait.github.io/GSTAR/查看。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为GSTAR的新方法,该方法实现了动态场景的光照真实渲染、精确表面重建和可靠的3D跟踪。它通过将高斯绑定到网格表面来表示动态对象,自适应地处理拓扑变化,实现表面准确注册和新表面生成。同时引入基于表面的场景流方法,为帧间跟踪提供稳健初始化。此方法在动态表面跟踪和重建方面表现出色,可应用于多种领域。
Key Takeaways
- GSTAR实现了动态场景的光照真实渲染、表面重建和3D跟踪。
- GSTAR通过将高斯绑定到网格表面来表示动态对象。
- 对于拓扑一致的表面,GSTAR保持网格拓扑并使用高斯进行追踪。
- 在拓扑变化区域,GSTAR能够自适应地解绑高斯,实现准确注册和新表面生成。
- GSTAR引入了一种基于表面的场景流方法,为帧间跟踪提供稳健初始化。
- 实验表明,GSTAR在动态表面跟踪和重建方面效果显著。
- GSTAR方法可应用于多种领域。
点此查看论文截图




F3D-Gaus: Feed-forward 3D-aware Generation on ImageNet with Cycle-Consistent Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yuxin Wang, Qianyi Wu, Dan Xu
This paper tackles the problem of generalizable 3D-aware generation from monocular datasets, e.g., ImageNet. The key challenge of this task is learning a robust 3D-aware representation without multi-view or dynamic data, while ensuring consistent texture and geometry across different viewpoints. Although some baseline methods are capable of 3D-aware generation, the quality of the generated images still lags behind state-of-the-art 2D generation approaches, which excel in producing high-quality, detailed images. To address this severe limitation, we propose a novel feed-forward pipeline based on pixel-aligned Gaussian Splatting, coined as F3D-Gaus, which can produce more realistic and reliable 3D renderings from monocular inputs. In addition, we introduce a self-supervised cycle-consistent constraint to enforce cross-view consistency in the learned 3D representation. This training strategy naturally allows aggregation of multiple aligned Gaussian primitives and significantly alleviates the interpolation limitations inherent in single-view pixel-aligned Gaussian Splatting. Furthermore, we incorporate video model priors to perform geometry-aware refinement, enhancing the generation of fine details in wide-viewpoint scenarios and improving the model’s capability to capture intricate 3D textures. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach not only achieves high-quality, multi-view consistent 3D-aware generation from monocular datasets, but also significantly improves training and inference efficiency.
本文解决了从单目数据集(例如ImageNet)中进行可泛化的3D感知生成的问题。此任务的关键挑战在于,如何在没有多视角或动态数据的情况下学习稳健的3D感知表示,同时确保不同视角下的纹理和几何一致性。尽管一些基线方法能够进行3D感知生成,但所生成图像的质量仍然落后于最先进的2D生成方法,后者在生成高质量、详细的图像方面表现出色。为了解决这一严重限制,我们提出了一种基于像素对齐高斯拼贴的新型前馈管道,称为F3D-Gaus,它可以从单目输入中产生更真实和可靠的3D渲染。此外,我们引入了一种自监督循环一致性约束,以强制执行学习到的3D表示中的跨视图一致性。这种训练策略自然地允许多个对齐的高斯基元聚集,并大大减轻了单视图像素对齐高斯拼贴所固有的插值限制。此外,我们结合了视频模型先验知识来进行几何感知细化,提高了宽视角场景中的细节生成,并提高了模型捕捉复杂3D纹理的能力。大量实验表明,我们的方法不仅实现了从单目数据集的高质量、多视角一致的3D感知生成,还大大提高了训练和推理效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://w-ted.github.io/publications/F3D-Gaus
Summary
本文解决的是从单目数据集(如ImageNet)中进行通用化3D感知生成的问题。文章提出了一个基于像素对齐高斯摊铺的新的前馈管道(F3D-Gaus),用于从单目输入生成更真实、可靠的3D渲染。此外,还引入了一种自监督循环一致性约束来强制执行学习到的3D表示中的跨视图一致性。通过融入视频模型先验,进行几何感知细化,提高了宽视角场景中的细节生成能力,并提高了模型捕捉复杂3D纹理的能力。实验表明,该方法不仅实现了高质量的、多视角一致的3D感知生成,还大大提高了训练和推理的效率。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文解决了从单目数据集进行3D感知生成的问题,旨在学习一个不需要多视角或动态数据的稳健的3D表示。
- 提出了一种新的前馈管道F3D-Gaus,基于像素对齐高斯摊铺,能够生成更真实、可靠的3D渲染。
- 引入了自监督循环一致性约束,以确保学习到的3D表示在不同视角之间的一致性。
- 通过融入视频模型先验,提高了在宽视角场景中的细节生成能力,并增强了模型捕捉复杂3D纹理的能力。
- 该方法实现了高质量的、多视角一致的3D感知生成,同时提高了训练和推理的效率。
- F3D-Gaus方法能够有效缓解单一视角像素对齐高斯摊铺的插值限制,通过聚合多个对齐的高斯原始数据来实现。
点此查看论文截图





DehazeGS: Seeing Through Fog with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jinze Yu, Yiqun Wang, Zhengda Lu, Jianwei Guo, Yong Li, Hongxing Qin, Xiaopeng Zhang
Current novel view synthesis tasks primarily rely on high-quality and clear images. However, in foggy scenes, scattering and attenuation can significantly degrade the reconstruction and rendering quality. Although NeRF-based dehazing reconstruction algorithms have been developed, their use of deep fully connected neural networks and per-ray sampling strategies leads to high computational costs. Moreover, NeRF’s implicit representation struggles to recover fine details from hazy scenes. In contrast, recent advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting achieve high-quality 3D scene reconstruction by explicitly modeling point clouds into 3D Gaussians. In this paper, we propose leveraging the explicit Gaussian representation to explain the foggy image formation process through a physically accurate forward rendering process. We introduce DehazeGS, a method capable of decomposing and rendering a fog-free background from participating media using only muti-view foggy images as input. We model the transmission within each Gaussian distribution to simulate the formation of fog. During this process, we jointly learn the atmospheric light and scattering coefficient while optimizing the Gaussian representation of the hazy scene. In the inference stage, we eliminate the effects of scattering and attenuation on the Gaussians and directly project them onto a 2D plane to obtain a clear view. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world foggy datasets demonstrate that DehazeGS achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of both rendering quality and computational efficiency. visualizations are available at https://dehazegs.github.io/
当前的新型视图合成任务主要依赖于高质量、清晰的图像。然而在雾天场景中,散射和衰减会显著地降低重建和渲染质量。尽管已经开发了基于NeRF的去雾重建算法,但它们使用深度全连接神经网络和每射线采样策略,导致计算成本高昂。此外,NeRF的隐式表示很难从雾蒙蒙的场景中恢复细节。相比之下,3D高斯拼贴技术的最新进展通过显式地对面云进行建模来实现高质量的三维场景重建为三维高斯分布。在本文中,我们提出利用显式的高斯表示法,通过物理准确的正向渲染过程来解释雾蒙蒙图像的形成过程。我们介绍了DehazeGS方法,该方法能够从参与介质中分解并渲染无雾背景,仅使用多视角雾蒙蒙图像作为输入。我们模拟了高斯分布内的传输以模拟雾的形成。在此过程中,我们联合学习大气光和散射系数,同时优化雾蒙蒙场景的高斯表示。在推理阶段,我们消除了散射和衰减对高斯分布的影响,并将其直接投影到二维平面上以获得清晰视图。在合成和真实世界的雾天数据集上的实验表明,DehazeGS在渲染质量和计算效率方面都达到了最先进的性能。可视化效果请访问:[https://dehazegs.github.io/](《https://dehazegs.github.io》网站)查阅。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages,4 figures. visualizations are available at https://dehazegs.github.io/
Summary
本文提出一种基于3D高斯展布(Gaussian Splatting)的去雾方法,称为DehazeGS。该方法利用显式高斯表示来模拟雾天图像形成过程,通过多视角雾天图像输入,分解并渲染出无雾背景。该方法模拟高斯分布中的传输过程,联合学习大气光和散射系数,优化雾场景的Gaussian表示,并在推理阶段消除散射和衰减对高斯的影响,直接投影到2D平面以获得清晰视图。实验表明,DehazeGS在渲染质量和计算效率方面达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 当前视图合成任务主要依赖高质量清晰图像,但在雾天场景,散射和衰减会严重影响重建和渲染质量。
- NeRF的隐式表示在雾天场景难以恢复细节,而3D高斯展布可实现高质量3D场景重建。
- DehazeGS方法利用显式高斯表示模拟雾天图像形成过程,通过多视角雾天图像进行去雾处理。
- 方法中模拟高斯分布中的传输过程,联合学习大气光和散射系数。
- DehazeGS在推理阶段消除散射和衰减影响,直接将高斯投影到2D平面获得清晰视图。
- 实验证明DehazeGS在渲染质量和计算效率方面达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图



3DGS-CD: 3D Gaussian Splatting-based Change Detection for Physical Object Rearrangement
Authors:Ziqi Lu, Jianbo Ye, John Leonard
We present 3DGS-CD, the first 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)-based method for detecting physical object rearrangements in 3D scenes. Our approach estimates 3D object-level changes by comparing two sets of unaligned images taken at different times. Leveraging 3DGS’s novel view rendering and EfficientSAM’s zero-shot segmentation capabilities, we detect 2D object-level changes, which are then associated and fused across views to estimate 3D change masks and object transformations. Our method can accurately identify changes in cluttered environments using sparse (as few as one) post-change images within as little as 18s. It does not rely on depth input, user instructions, pre-defined object classes, or object models – An object is recognized simply if it has been re-arranged. Our approach is evaluated on both public and self-collected real-world datasets, achieving up to 14% higher accuracy and three orders of magnitude faster performance compared to the state-of-the-art radiance-field-based change detection method. This significant performance boost enables a broad range of downstream applications, where we highlight three key use cases: object reconstruction, robot workspace reset, and 3DGS model update. Our code and data will be made available at https://github.com/520xyxyzq/3DGS-CD.
我们提出了基于三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)的变化检测新方法,名为3DGS-CD,它是首个用于检测三维场景中物理对象重组的方法。我们的方法通过比较两个在不同时间拍摄的不对齐的图像集来估计三维对象级别的变化。我们利用3DGS的新型视图渲染和EfficientSAM的零样本分割能力,检测二维对象级别的变化,然后将这些变化在不同视图中关联和融合,以估计三维变化掩膜和对象变换。我们的方法能够在杂乱的环境中准确地识别变化,仅使用少量(至少一张)变化后的图像在短短18秒内即可完成。它不依赖于深度输入、用户指令、预定义的对象类别或对象模型——只要对象被重新排列即可识别。我们的方法在公共和自我收集的真实世界数据集上进行了评估,与基于辐射场的变化检测方法相比,我们的方法提高了高达14%的准确性和三个数量级的性能。这一显著的性能提升为多种下游应用提供了可能,我们重点介绍了三个关键用例:对象重建、机器人工作空间重置和3DGS模型更新。我们的代码和数据将在https://github.com/520xyxyzq/3DGS-CD上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于3D高斯拼接技术的新型物理对象重排检测方法。该方法通过对比不同时间点的未对齐图像,实现对物理对象的实时跟踪。该方法充分利用高效无照点的零视图分割能力与不同视图的组合信息,有效检测出复杂的对象变化和立体转换掩码。其特点是可在短期内精确捕捉移动、重塑的物体而不依赖于深度图像信息、用户预设的操作、特定的类别模型和预定目标的指向动作,拓展了广泛应用的可能性,包括物体重建、机器人重置空间和模型更新等。Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种基于3D高斯拼接技术的新型方法——3DGS-CD,用于检测三维场景中的物理对象重排。
- 方法通过比较两组不同时间的图像进行估算对象的三维变化。
- 结合高效SAM的无视无照点分割能力,准确检测二维对象变化,并跨视图关联融合生成三维变化掩码和对象转换。
- 该方法能够在短时间内准确识别出重组后的物体,仅使用少数几张改变后的图像。
- 不依赖于深度输入、用户指令、预定义对象类别或对象模型,能够识别任何被重新排列的对象。
- 在公共和自行收集的真实世界数据集上进行了评估,与当前主流的基于辐射场的变化检测方法相比,准确性提高了高达14%,性能提高了三个数量级。
点此查看论文截图








