⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-23 更新
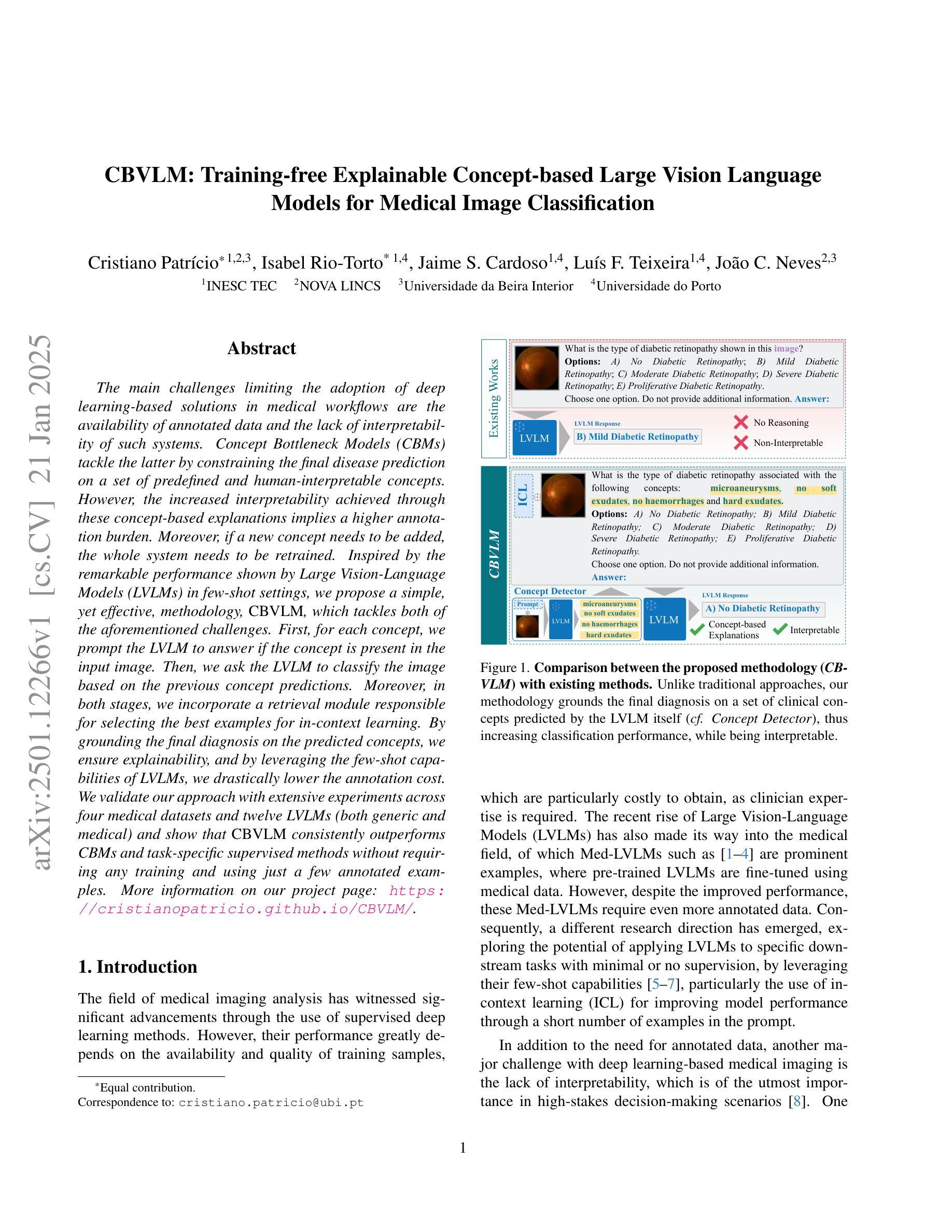
CBVLM: Training-free Explainable Concept-based Large Vision Language Models for Medical Image Classification
Authors:Cristiano Patrício, Isabel Rio-Torto, Jaime S. Cardoso, Luís F. Teixeira, João C. Neves
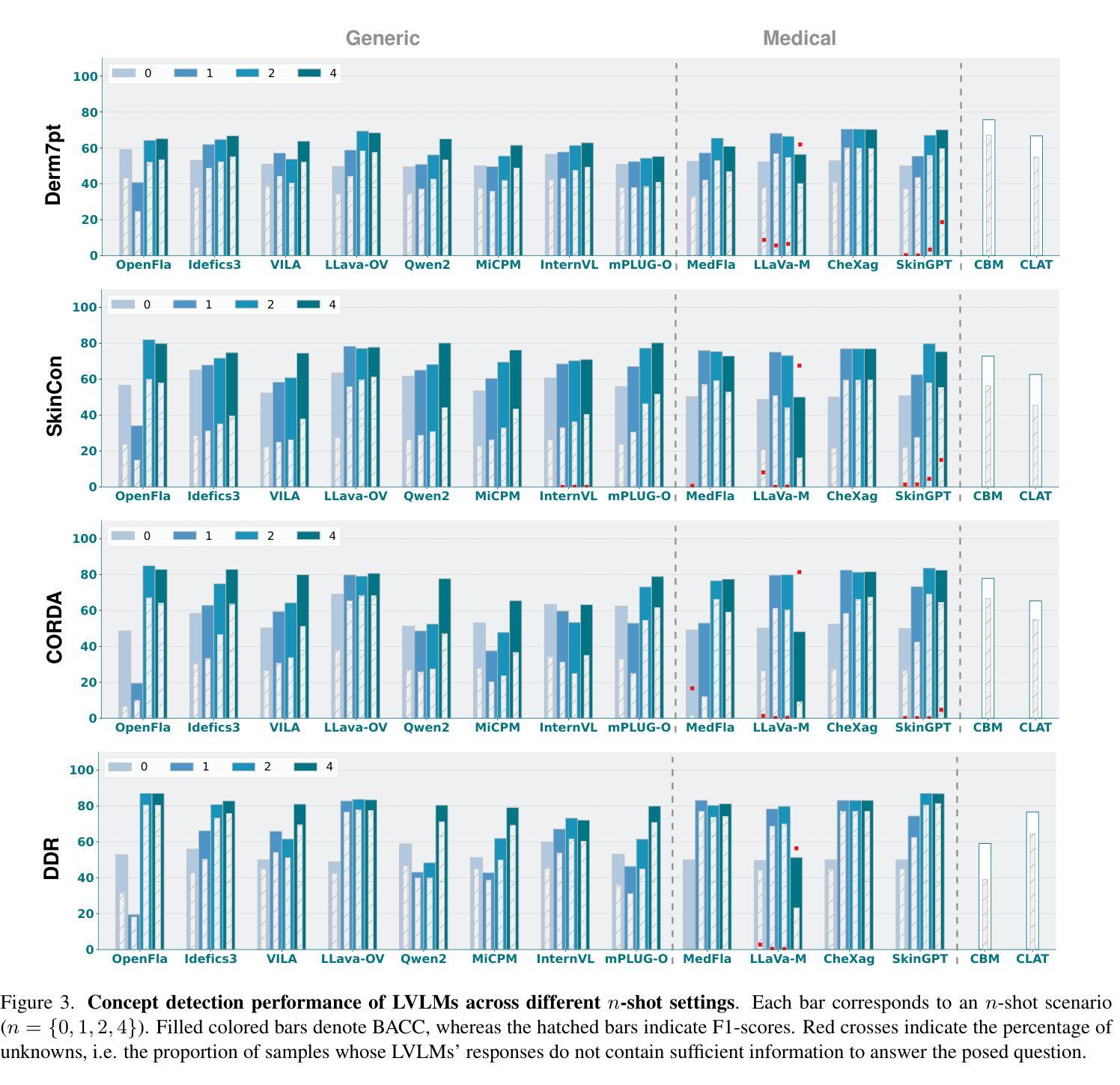
The main challenges limiting the adoption of deep learning-based solutions in medical workflows are the availability of annotated data and the lack of interpretability of such systems. Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) tackle the latter by constraining the final disease prediction on a set of predefined and human-interpretable concepts. However, the increased interpretability achieved through these concept-based explanations implies a higher annotation burden. Moreover, if a new concept needs to be added, the whole system needs to be retrained. Inspired by the remarkable performance shown by Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) in few-shot settings, we propose a simple, yet effective, methodology, CBVLM, which tackles both of the aforementioned challenges. First, for each concept, we prompt the LVLM to answer if the concept is present in the input image. Then, we ask the LVLM to classify the image based on the previous concept predictions. Moreover, in both stages, we incorporate a retrieval module responsible for selecting the best examples for in-context learning. By grounding the final diagnosis on the predicted concepts, we ensure explainability, and by leveraging the few-shot capabilities of LVLMs, we drastically lower the annotation cost. We validate our approach with extensive experiments across four medical datasets and twelve LVLMs (both generic and medical) and show that CBVLM consistently outperforms CBMs and task-specific supervised methods without requiring any training and using just a few annotated examples. More information on our project page: https://cristianopatricio.github.io/CBVLM/.
在医学工作流中采用基于深度学习的解决方案的主要挑战是标注数据的不易获取以及这些系统缺乏可解释性。概念瓶颈模型(CBMs)通过限制在预定义和可解释的概念集上的最终疾病预测来解决后者的问题。然而,通过基于概念的解释所提高的可解释性意味着更高的标注负担。而且,如果要添加新概念,整个系统都需要重新训练。受大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在少样本环境中的出色表现的启发,我们提出了一种简单而有效的方法,即CBVLM,可以解决上述两个挑战。首先,对于每个概念,我们提示LVLM回答概念是否出现在输入图像中。然后,我们要求LVLM基于先前的概念预测对图像进行分类。此外,在两个阶段中,我们都融入了一个检索模块,负责选择最佳样本进行上下文学习。通过将最终诊断基于预测的概念,我们确保了可解释性,并通过利用LVLMs的少样本能力,我们大大降低了标注成本。我们在四个医学数据集和十二个(通用和医学)LVLM上进行了广泛的实验,验证了我们的方法,并证明CBVLM在不需要任何训练和仅使用少量标注样本的情况下,始终优于CBMs和特定任务监督方法。更多关于我们项目的信息请访问:https://cristianopatricio.github.io/CBVLM/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
本文介绍了深度学习在医疗工作流程应用中的主要挑战,包括标注数据的可用性和系统解释性的缺失。概念瓶颈模型(CBMs)通过约束疾病预测在一组预先定义和可解释的概念上来解决后者的问题。然而,概念性解释带来的解释性的提升意味着更高的标注负担。因此,研究人员提出了一个新的方法CBVLM来解决这两个挑战。该方法利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在少量样本场景下的出色性能,通过预测概念并基于这些概念对图像进行分类来实现医疗诊断。通过选择最佳的上下文学习例子,CBVLM确保了诊断的解释性并降低了标注成本。实验证明,CBVLM在四个医疗数据集上的表现均优于CBMs和特定任务监督方法,且无需任何训练,只需使用少量标注样本即可。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医疗工作流中面临的主要挑战是标注数据的可用性和系统解释性的缺失。
- 概念瓶颈模型(CBMs)通过约束疾病预测在一组预先定义和可解释的概念上解决了解释性问题,但带来了更高的标注负担和需要重复训练的问题。
- CBVLM方法结合了大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的优异性能和概念预测来解决上述挑战。
- CBVLM通过利用LVLMs的少量样本能力来降低标注成本并实现医疗诊断。
- 实验结果显示,CBVLM在多个医疗数据集上的表现优于CBMs和其他特定任务监督方法。
- CBVLM无需额外训练,并能利用少量标注样本进行高效预测和分类。
点此查看论文截图

Can open source large language models be used for tumor documentation in Germany? – An evaluation on urological doctors’ notes
Authors:Stefan Lenz, Arsenij Ustjanzew, Marco Jeray, Torsten Panholzer
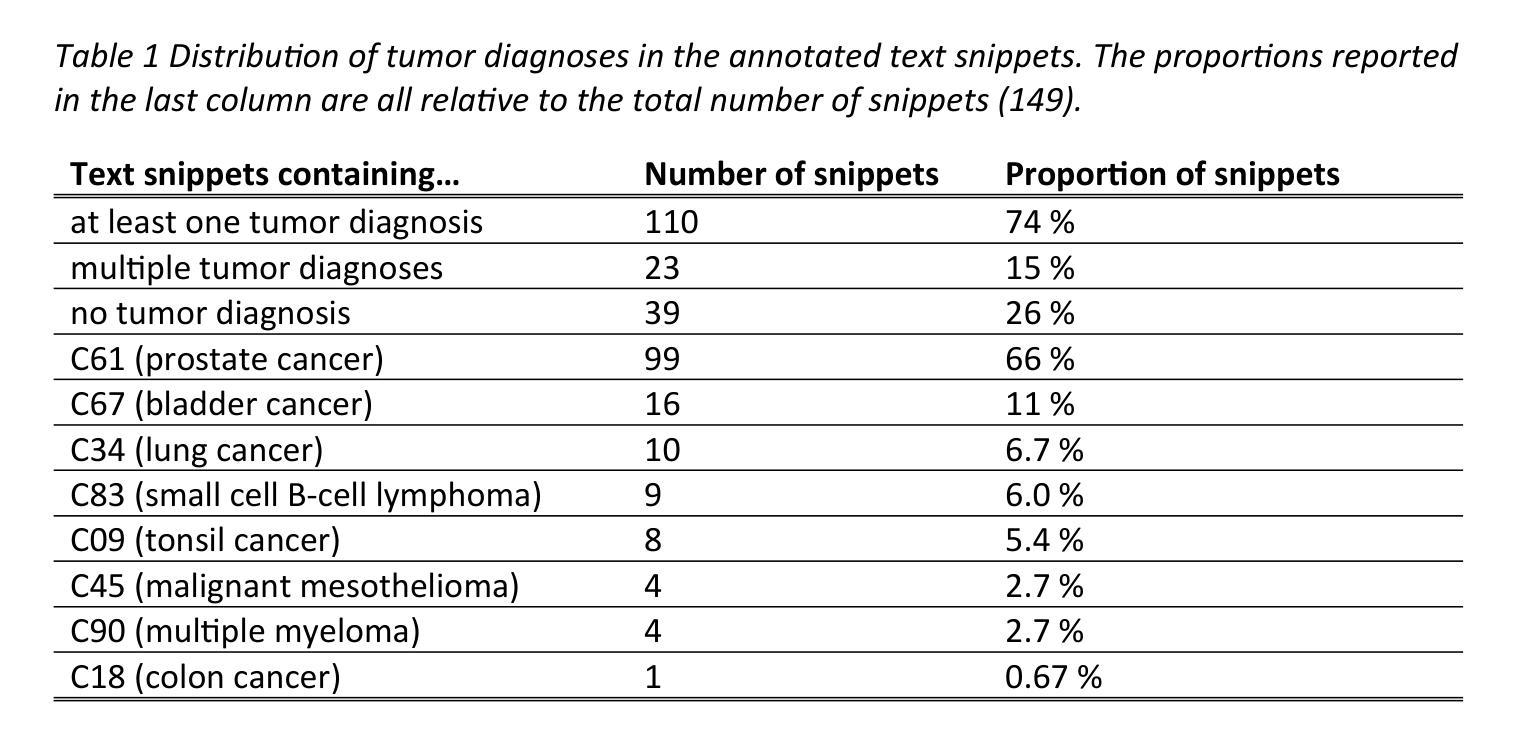
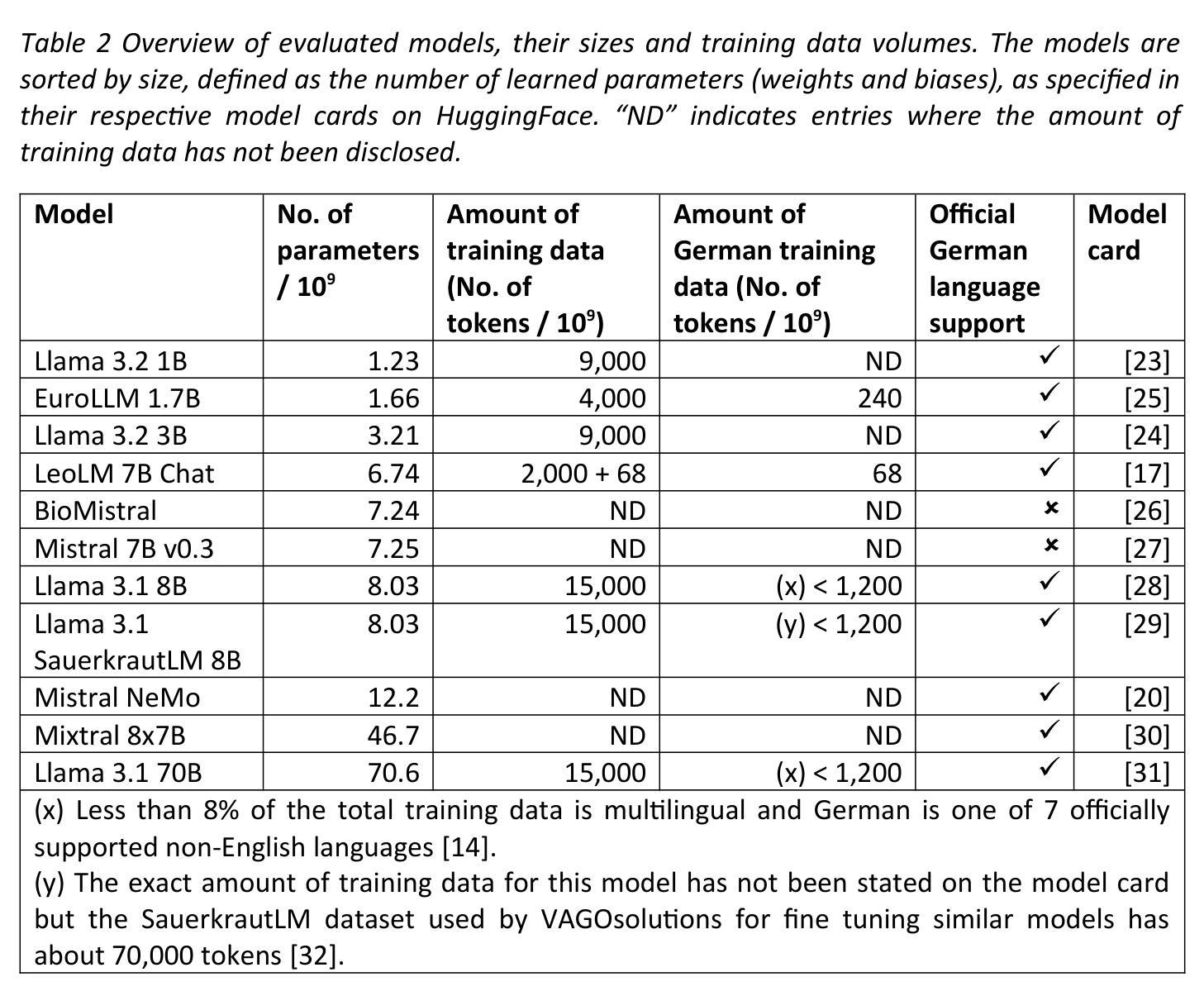
Tumor documentation in Germany is largely done manually, requiring reading patient records and entering data into structured databases. Large language models (LLMs) could potentially enhance this process by improving efficiency and reliability. This evaluation tests eleven different open source LLMs with sizes ranging from 1-70 billion model parameters on three basic tasks of the tumor documentation process: identifying tumor diagnoses, assigning ICD-10 codes, and extracting the date of first diagnosis. For evaluating the LLMs on these tasks, a dataset of annotated text snippets based on anonymized doctors’ notes from urology was prepared. Different prompting strategies were used to investigate the effect of the number of examples in few-shot prompting and to explore the capabilities of the LLMs in general. The models Llama 3.1 8B, Mistral 7B, and Mistral NeMo 12 B performed comparably well in the tasks. Models with less extensive training data or having fewer than 7 billion parameters showed notably lower performance, while larger models did not display performance gains. Examples from a different medical domain than urology could also improve the outcome in few-shot prompting, which demonstrates the ability of LLMs to handle tasks needed for tumor documentation. Open source LLMs show a strong potential for automating tumor documentation. Models from 7-12 billion parameters could offer an optimal balance between performance and resource efficiency. With tailored fine-tuning and well-designed prompting, these models might become important tools for clinical documentation in the future. The code for the evaluation is available from https://github.com/stefan-m-lenz/UroLlmEval. We also release the dataset as a new valuable resource that addresses the shortage of authentic and easily accessible benchmarks in German-language medical NLP.
在德国,肿瘤记录工作大多以手动方式进行,需要阅读患者病历并将数据录入结构化数据库。大型语言模型(LLM)有潜力通过提高效率和可靠性来增强这一流程。本次评估对三种肿瘤记录基本任务(识别肿瘤诊断、分配ICD-10代码和提取首次诊断日期)中,使用了11种不同开源的LLM,这些模型参数规模从1亿到70亿不等。为了评估这些模型在这些任务上的表现,我们准备了一份基于泌尿科匿名医生笔记的标注文本片段数据集。使用了不同的提示策略来研究少量示例提示中示例数量对模型的影响,并探索LLM的一般能力。Llama 3.1 8B、Mistral 7B和Mistral NeMo 12B等模型在这些任务中表现良好。具有较少训练数据或参数少于7亿的模型表现明显较差,而更大的模型并没有显示出性能提升。来自泌尿科以外的其他医学领域的例子也能在少量提示中改善结果,这证明了LLM处理肿瘤记录所需任务的能力。开源LLM在自动化肿瘤记录方面显示出巨大潜力。参数规模在7-12亿之间的模型可能在性能和资源效率之间达到最佳平衡。通过有针对性的微调和精心设计的提示,这些模型可能会成为未来临床记录的重要工具。评估的代码可从https://github.com/stefan-m-lenz/UroLlmEval获取。我们还公开了数据集,作为解决德语医学NLP领域中真实、易于访问的基准测试短缺问题的新有价值资源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 48 pages, 5 figures
Summary
在肿瘤记录过程中,使用大型语言模型(LLMs)能够提高效率和可靠性。本研究评估了不同规模的LLMs在三项基本任务上的表现,包括肿瘤诊断识别、ICD-10代码分配以及首次诊断日期提取。研究中公开的代码和数据集可供研究之用。研究发现规模为7至12亿参数的模型在性能和资源效率之间达到最佳平衡,有望在未来成为临床文档的重要工具。
Key Takeaways
- 在德国的肿瘤记录过程中,大型语言模型(LLMs)能够提高效率和可靠性。
- 研究评估了不同规模的LLMs在三项基本任务上的表现:肿瘤诊断识别、ICD-10代码分配和首次诊断日期提取。
- 在这项研究中,Llama 3.1 8B、Mistral 7B和Mistral NeMo 12B等模型在任务中表现良好。
- 模型规模较小的LLMs性能较低,而更大的模型并没有明显的性能提升。
- 不同医学领域的示例数据能够提高少样本提示的效果,证明LLMs有能力处理肿瘤记录所需的任务。
- 公开的代码和数据集有助于解决德国医疗NLP领域中真实和可访问的基准测试数据短缺的问题。
点此查看论文截图

Directional Diffusion-Style Code Editing Pre-training
Authors:Qingyuan Liang, Zeyu Sun, Qihao Zhu, Junhao Hu, Yifan Zhao, Yizhou Chen, Mingxuan Zhu, Guoqing Wang, Lu Zhang
Code pre-trained models have shown promising effectiveness in various software engineering tasks. Among these tasks, many tasks are related to software evolution and/or code editing. However, existing code pre-trained models often overlook the real-world code editing data and the evolutionary nature of the editing process. In this paper, to simulate the step-by-step code editing process of human developers, we propose DivoT5, a pre-trained model based on directional diffusion at the data level. In DivoT5, we adopt two categories of pre-training tasks. The first category is mask and denoising tasks augmented with a diffusion direction representing code evolution. That is, we first apply a noising process to the code snippets before evolution, and then ask the pre-training process to restore the snippets with noise into the code snippets after evolution. The second category is tasks aiming to reinforce the evolutionary direction. That is, we first generate various intermediate versions for each pair of snippets before and after evolution, and then ask the pre-training process to transform the intermediate versions into the snippet after evolution for each pair. We evaluate DivoT5 for two code-editing scenarios and one non-editing scenario using five downstream tasks. Given each downstream task, we fine-tune the pre-trained DivoT5 to evaluate its effectiveness. Our experimental results show that DivoT5 achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on most tasks in comparison to models of the same scale (220M), large scale (770M) models in fine-tuning, and billion-scale (6.7B, 8B, ChatGPT) models in few-shot settings. For one code-editing task (i.e., automated code review), DivoT5 pre-trained on top of CodeT5-small (60M) can even outperform CodeT5-base (220M) and other pre-trained models with 220M parameters except for DivoT5 pre-trained on top of CodeT5-base (220M).
预训练代码模型在各种软件工程任务中表现出了良好的有效性。其中许多任务与软件演进和/或代码编辑相关。然而,现有的代码预训练模型往往忽略了现实世界的代码编辑数据和编辑过程的演化性质。在本文中,为了模拟人类开发者逐步的代码编辑过程,我们提出了基于数据级别方向扩散的预训练模型DivoT5。在DivoT5中,我们采用了两类预训练任务。第一类是通过带有代表代码演化的扩散方向的掩膜和去噪任务。也就是说,我们首先应用噪声过程对演化前的代码片段进行干扰,然后要求预训练过程将带有噪声的片段恢复为演化后的代码片段。第二类是旨在加强演化方向的任务。具体来说,我们首先为演化前后的每一对片段生成各种中间版本,然后要求预训练过程将这些中间版本转化为每一对的演化后片段。我们评估了DivoT5在两个代码编辑场景和一个非编辑场景中的性能,使用五个下游任务。对于每个下游任务,我们微调预训练的DivoT5以评估其有效性。实验结果表明,与相同规模(220M)、大规模(770M)模型的微调相比,DivoT5在大多数任务上达到了最先进的性能;在少样本设置下,与数十亿规模(6.7B、8B、ChatGPT)的模型相比也表现出色。对于一项代码编辑任务(即自动化代码审查),基于CodeT5-small(60M)的DivoT5预训练甚至超越了CodeT5-base(220M)和其他具有220M参数的预训练模型,除非是基于CodeT5-base(220M)的DivoT5进行预训练。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于数据层面方向扩散的预训练模型DivoT5,用于模拟人类开发者的逐步代码编辑过程。DivoT5采用两类预训练任务:一类是带有扩散方向代表代码演化的遮蔽和去噪任务;另一类是加强演化方向的任务。实验结果表明,DivoT5在大多数任务上实现了与相同规模模型相比的最佳性能,并且在微调方面,即使是基于CodeT5-small的预训练模型也能超越CodeT5-base和其他预训练模型,除非是基于CodeT5-base的DivoT5预训练模型。
Key Takeaways
- 代码预训练模型在软件工程任务中表现出良好效果,但忽略了真实世界的代码编辑数据和编辑过程的演化性质。
- 提出了基于数据层面方向扩散的预训练模型DivoT5,模拟人类开发者的逐步代码编辑过程。
- DivoT5采用两类预训练任务:遮蔽和去噪任务,以及加强演化方向的任务。
- DivoT5在大多数任务上实现了最佳性能,甚至在微调方面超越了一些规模更大的模型。
- 基于CodeT5-small的DivoT5预训练模型在自动化代码审查等代码编辑任务上表现出色,甚至超越了CodeT5-base和其他一些预训练模型。
- DivoT5的成功可能源于其考虑到了代码的演化过程和真实世界的代码编辑数据。
点此查看论文截图



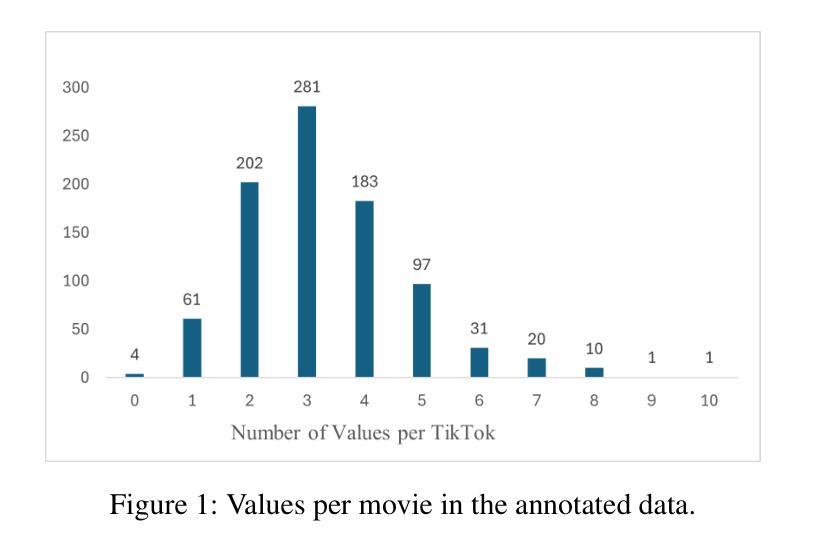
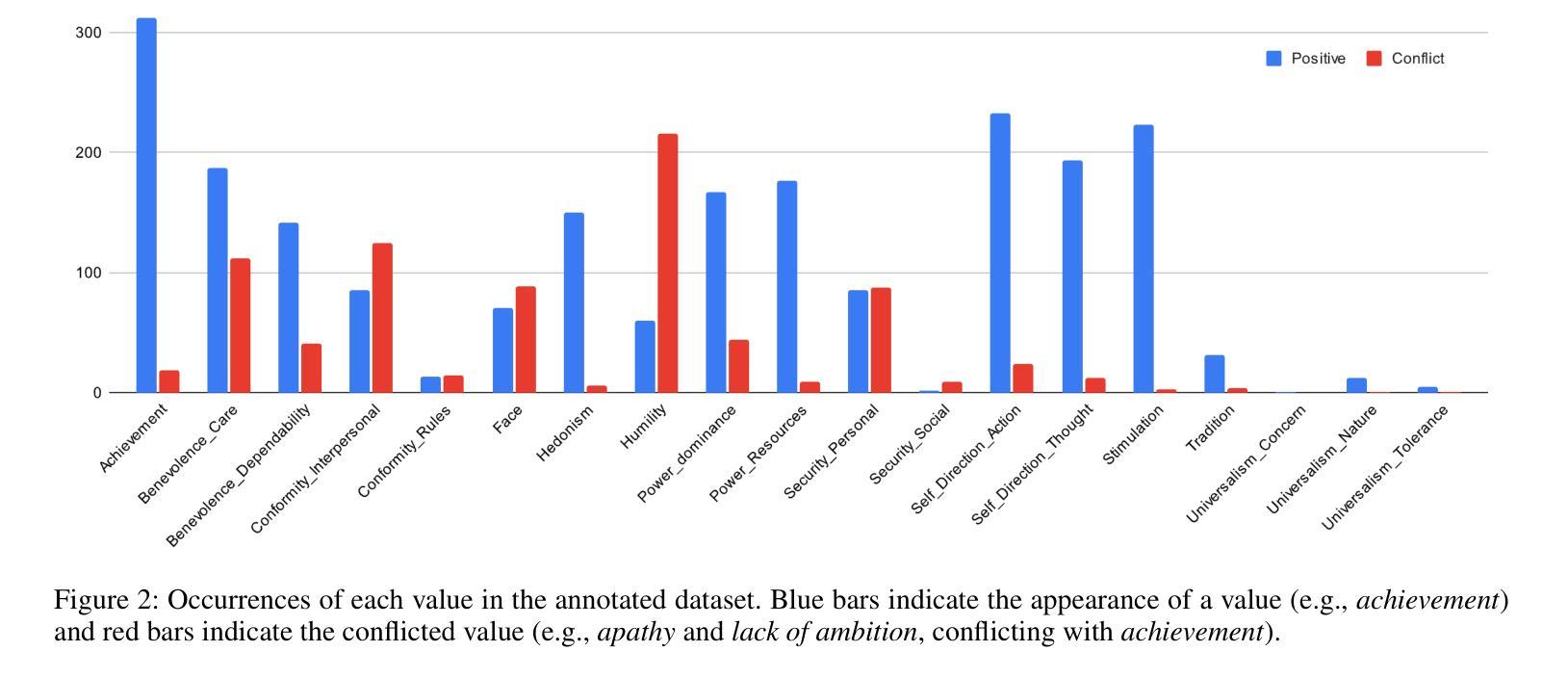
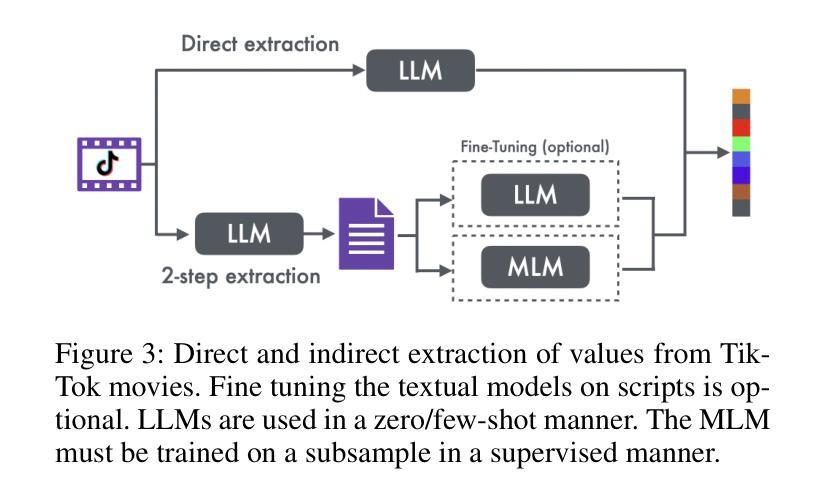
The Value of Nothing: Multimodal Extraction of Human Values Expressed by TikTok Influencers
Authors:Alina Starovolsky-Shitrit, Alon Neduva, Naama Appel Doron, Ella Daniel, Oren Tsur
Societal and personal values are transmitted to younger generations through interaction and exposure. Traditionally, children and adolescents learned values from parents, educators, or peers. Nowadays, social platforms serve as a significant channel through which youth (and adults) consume information, as the main medium of entertainment, and possibly the medium through which they learn different values. In this paper we extract implicit values from TikTok movies uploaded by online influencers targeting children and adolescents. We curated a dataset of hundreds of TikTok movies and annotated them according to the Schwartz Theory of Personal Values. We then experimented with an array of Masked and Large language model, exploring how values can be detected. Specifically, we considered two pipelines – direct extraction of values from video and a 2-step approach in which videos are first converted to elaborated scripts and then values are extracted. Achieving state-of-the-art results, we find that the 2-step approach performs significantly better than the direct approach and that using a trainable Masked Language Model as a second step significantly outperforms a few-shot application of a number of Large Language Models. We further discuss the impact of fine-tuning and compare the performance of the different models on identification of values present or contradicted in the TikTok. Finally, we share the first values-annotated dataset of TikTok videos. Our results pave the way to further research on influence and value transmission in video-based social platforms.
社会和个人价值观通过互动和接触传递给年轻一代。传统上,儿童和青少年从父母、教育工作者或同龄人那里学习价值观。如今,社交平台成为青年(和成年人)获取信息、主要娱乐媒介以及可能的学习不同价值观的渠道。在本文中,我们从针对儿童和青少年上传的TikTok电影中提取了隐含的价值观。我们整理了一个包含数百部TikTok电影的数据库,并根据施瓦茨个人价值观理论对它们进行了注释。然后,我们尝试了一系列遮罩和大语言模型,探索如何检测价值观。具体来说,我们考虑了两个流程——直接从视频中提取价值观和两步法(首先视频转换为详细的脚本,然后提取价值观)。通过获得最新结果,我们发现两步法明显优于直接法,使用可训练遮罩语言模型作为第二步明显优于多个大型语言模型的少数用例应用。我们进一步讨论了微调的影响,比较了不同模型在识别TikTok中存在的或相互矛盾的价值观方面的表现。最后,我们分享了第一个TikTok视频的价值观注释数据集。我们的研究结果为视频社交平台上的影响和价值观传递研究铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究社交媒体平台TikTok对儿童及青少年价值观的影响。通过对数百部TikTok视频的分析,并基于施瓦茨价值观理论进行标注,实验了两种价值观检测方法:直接从视频提取价值观和两步法(视频转化为剧本后再提取价值观)。研究结果显示两步法效果更佳,尤其是第二步使用可训练的掩码语言模型时,明显优于几种大型语言模型的几次应用。文章还讨论了微调的影响,并分享了首个TikTok视频的价值标注数据集。
Key Takeaways
- TikTok成为传递价值观给青少年甚至成人的重要渠道。
- 对TikTok视频的研究发现两步法检测价值观更为准确。
- 掩码语言模型在两步法中的第二步表现出卓越性能。
- 精细调整对模型性能有显著影响。
- 分享了一个标注了价值的TikTok视频数据集。
- 传统价值观传播方式(如父母、教育者、同龄人)正逐渐被社交媒体取代。
点此查看论文截图


ProKeR: A Kernel Perspective on Few-Shot Adaptation of Large Vision-Language Models
Authors:Yassir Bendou, Amine Ouasfi, Vincent Gripon, Adnane Boukhayma
The growing popularity of Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) has led to its widespread application in various visual downstream tasks. To enhance CLIP’s effectiveness and versatility, efficient few-shot adaptation techniques have been widely adopted. Among these approaches, training-free methods, particularly caching methods exemplified by Tip-Adapter, have gained attention for their lightweight adaptation without the need for additional fine-tuning. In this paper, we revisit Tip-Adapter from a kernel perspective, showing that caching methods function as local adapters and are connected to a well-established kernel literature. Drawing on this insight, we offer a theoretical understanding of how these methods operate and suggest multiple avenues for enhancing the Tip-Adapter baseline. Notably, our analysis shows the importance of incorporating global information in local adapters. Therefore, we subsequently propose a global method that learns a proximal regularizer in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS) using CLIP as a base learner. Our method, which we call ProKeR (Proximal Kernel ridge Regression), has a closed form solution and achieves state-of-the-art performances across 11 datasets in the standard few-shot adaptation benchmark.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)的日益普及已导致其在各种视觉下游任务中的广泛应用。为了提高CLIP的有效性和通用性,高效的少样本自适应技术已得到广泛采用。在这些方法中,无需训练的方法,特别是以Tip-Adapter为代表的缓存方法,因其无需额外微调即可实现轻量级自适应而备受关注。本文将从核心视角重新审视Tip-Adapter,展示缓存方法作为局部适配器与已建立的核心文献之间的联系。基于这一见解,我们提供了对这些方法如何运作的理论理解,并给出了增强Tip-Adapter基线性能的多种途径。值得注意的是,我们的分析表明在局部适配器中融入全局信息的重要性。因此,我们随后提出了一种全局方法,在再生核希尔伯特空间(RKHS)中学习近端正则化器,以CLIP为基础学习器。我们提出的方法被称为ProKeR(近端核岭回归),它具有封闭形式的解决方案,并在标准少样本自适应基准测试中实现了跨11个数据集的最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code available at https://ybendou.github.io/ProKeR
Summary
基于对比语言图像预训练模型(CLIP)的普及和其广泛应用于各种视觉下游任务的需求,本文研究了高效的CLIP少样本适应技术。特别关注了无训练方法中的缓存方法,如Tip-Adapter。本文从核心角度重新审视Tip-Adapter,将其与现有的内核文献联系起来,提供了其工作原理的理论理解,并建议改进基线Tip-Adapter的方法。文章提出结合全局信息对局部适配器进行改进的方法,提出了一种基于CLIP的再生核希尔伯特空间(RKHS)近端正则化的新方法ProKeR。该方法具有闭式解,在标准少样本适应基准测试中实现了跨11个数据集的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP的普及和在各种视觉下游任务中的广泛应用推动了对其高效少样本适应技术的研究。
- 无训练方法的缓存方法,如Tip-Adapter,由于其无需额外精细调整而受到了关注。
- Tip-Adapter与内核文献之间的联系得到了深入研究,并揭示了其工作原理的理论基础。
- 结合全局信息对局部适配器进行改进是必要的,以提高模型的性能。
- 提出了一种基于CLIP的新方法ProKeR,用于学习再生核希尔伯特空间中的近端正则化器。
- ProKeR实现了在标准少样本适应基准测试中跨多个数据集的最佳性能表现。这意味着这种方法在各种场景下均表现出了稳健而出色的效果。这可能为后续的研究提供新的思路或启示,并可能在实际应用中带来显著的提升。它也有助于我们更深入地理解CLIP模型在各种视觉任务中的潜力和局限性。因此,未来可能会有更多的研究关注于如何进一步改进和完善这一模型以取得更好的性能。该方法具备出色的通用性和适应性未来或将引发更多的探索和改进实践以增强其在各种视觉任务中的性能并扩展其应用范围该方法还具有巨大的潜力在未来为许多不同的应用领域带来创新和改进我们期待未来对此方法的更多研究和探索以实现更广泛的应用场景和提升效果。。这些方法也给我们提供了一个很好的视角来进一步理解和优化CLIP模型在各种视觉任务中的表现和应用范围。总的来说,这篇文章为我们提供了一个关于如何优化和改进CLIP模型在视觉任务中性能的重要视角和新的思路。这对于未来的研究和应用具有重要的意义和价值。 因此它的成功实现可能为机器学习领域的许多其他问题提供了新的解决方案和创新思路,。最后期待有更多对该方法和模型的探索和优化能够在不同场景下获得更为优秀的性能表现和广阔的应用前景被开发出此外对此主题的持续探索和研究将有助于推动计算机视觉和机器学习领域的进一步发展我们也期待未来看到更多相关的研究和应用案例出现以解决更多现实生活中的问题并为相关领域的发展做出更大的贡献,。也相信未来的研究将能够推动该领域取得更大的突破和进展为实际应用带来更多创新和价值同时推动整个机器学习领域的进步和发展因此对该主题的研究具有重要的价值和意义并有望在未来产生深远的影响。总的来说这篇文章提供了一个关于CLIP模型少样本适应技术的深入理解以及在未来研究的可能性提供了富有前景的研究方向这些洞见都将为我们打开进一步理解并掌握计算机视觉任务的关键机遇将我们推向了一个关于人工智能技术和计算机视觉的未来前沿随着人工智能的飞速发展以及研究的不断进步这一领域必将产生更多的创新和突破值得我们持续关注并投入研究以推动人工智能技术的整体进步和发展。
点此查看论文截图



Beyond Any-Shot Adaptation: Predicting Optimization Outcome for Robustness Gains without Extra Pay
Authors:Qi Cheems Wang, Zehao Xiao, Yixiu Mao, Yun Qu, Jiayi Shen, Yiqin Lv, Xiangyang Ji
The foundation model enables fast problem-solving without learning from scratch, and such a desirable adaptation property benefits from its adopted cross-task generalization paradigms, e.g., pretraining, meta-training, or finetuning. Recent trends have focused on the curation of task datasets during optimization, which includes task selection as an indispensable consideration for either adaptation robustness or sampling efficiency purposes. Despite some progress, selecting crucial task batches to optimize over iteration mostly exhausts massive task queries and requires intensive evaluation and computations to secure robust adaptation. This work underscores the criticality of both robustness and learning efficiency, especially in scenarios where tasks are risky to collect or costly to evaluate. To this end, we present Model Predictive Task Sampling (MPTS), a novel active task sampling framework to establish connections between the task space and adaptation risk landscape achieve robust adaptation. Technically, MPTS characterizes the task episodic information with a generative model and predicts optimization outcome after adaptation from posterior inference, i.e., forecasting task-specific adaptation risk values. The resulting risk learner amortizes expensive annotation, evaluation, or computation operations in task robust adaptation learning paradigms. Extensive experimental results show that MPTS can be seamlessly integrated into zero-shot, few-shot, and many-shot learning paradigms, increases adaptation robustness, and retains learning efficiency without affording extra cost. The code will be available at the project site https://github.com/thu-rllab/MPTS.
基础模型能够实现快速的问题解决,而无需从头开始学习,这种理想的适应性得益于其采用的跨任务泛化范式,例如预训练、元训练或微调。最近的趋势集中在优化过程中的任务数据集筛选上,任务选择成为适应稳健性或采样效率目的不可或缺的重要因素。尽管取得了一些进展,但选择关键任务批次进行优化在迭代过程中大多消耗了大量的任务查询,并需要大量评估和计算以确保稳健的适应。这项工作强调了稳健性和学习效率的重要性,特别是在任务收集风险大或评估成本高的场景中。为此,我们提出了模型预测任务采样(MPTS),这是一种新的主动任务采样框架,旨在建立任务空间和适应风险景观之间的联系,以实现稳健的适应。从技术上讲,MPTS使用生成模型对任务片段信息进行表征,并通过后验推断预测适应后的优化结果,即预测特定任务的适应风险值。所得的风险学习者在任务稳健适应学习范式中减少了昂贵的标注、评估或计算操作。大量实验结果表明,MPTS可以无缝地融入零样本、少样本和多样本学习范式中,提高适应的稳健性,同时保持学习效率且无需额外成本。代码将在项目网站https://github.com/thu-rllab/MPTS上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模型预训练、元训练或微调等跨任务泛化范式,使模型具备快速解决问题的能力,而无需从头开始学习。近期趋势聚焦于优化任务数据集的选择,考虑任务选择的适应稳健性或采样效率。本文强调在任务采集风险大或评估成本高的场景下,稳健性和学习效率的重要性。为此,提出了基于预测任务采样的模型预测任务采样(MPTS)框架,建立任务空间与适应风险景观之间的联系,实现稳健适应。MPTS利用生成模型对任务片段信息进行表征,通过后天推理预测优化结果,即预测任务特定的适应风险值。这降低了昂贵的标注、评估或计算操作成本,提高了任务稳健适应学习的效率。实验表明,MPTS可无缝融入零样本、少样本和多样本学习范式,提高适应性并保留学习效率,且不增加额外成本。
Key Takeaways
- 跨任务泛化范式(如预训练、元训练、微调)使模型具备快速解决问题的能力。
- 任务数据集的选择是优化中的一个重要考虑因素,特别是在适应稳健性和采样效率方面。
- 在任务采集风险大或评估成本高的场景下,需要强调稳健性和学习效率的重要性。
- 提出了一种新的主动任务采样框架——模型预测任务采样(MPTS),它通过预测任务特定的适应风险值来建立任务空间和适应风险景观之间的联系。
- MPTS框架降低了标注、评估和计算操作的成本,提高了任务稳健适应学习的效率。
- MPTS可广泛应用于零样本、少样本和多样本学习范式中。
点此查看论文截图




Few-shot Human Motion Recognition through Multi-Aspect mmWave FMCW Radar Data
Authors:Hao Fan, Lingfeng Chen, Chengbai Xu, Jiadong Zhou, Yongpeng Dai, Panhe HU
Radar human motion recognition methods based on deep learning models has been a heated spot of remote sensing in recent years, yet the existing methods are mostly radial-oriented. In practical application, the test data could be multi-aspect and the sample number of each motion could be very limited, causing model overfitting and reduced recognition accuracy. This paper proposed channel-DN4, a multi-aspect few-shot human motion recognition method. First, local descriptors are introduced for a precise classification metric. Moreover, episodic training strategy was adopted to reduce model overfitting. To utilize the invariant sematic information in multi-aspect conditions, we considered channel attention after the embedding network to obtain precise implicit high-dimensional representation of sematic information. We tested the performance of channel-DN4 and methods for comparison on measured mmWave FMCW radar data. The proposed channel-DN4 produced competitive and convincing results, reaching the highest 87.533% recognition accuracy in 3-way 10-shot condition while other methods suffer from overfitting. Codes are available at: https://github.com/MountainChenCad/channel-DN4
基于深度学习模型的雷达人体运动识别方法近年来已成为遥感领域的热点,但现有方法大多以径向为导向。在实际应用中,测试数据可能是多方面的,每种运动的样本数量可能非常有限,导致模型过拟合和识别精度降低。本文提出了channel-DN4,一种多方面的小样本人体运动识别方法。首先,引入局部描述符进行精确的分类度量。此外,采用周期训练策略以减少模型过拟合。为了利用多方面条件下的不变语义信息,我们在嵌入网络后考虑通道注意力,以获得精确的隐式高维语义信息表示。我们在测量的毫米波FMCW雷达数据上测试了channel-DN4及其对比方法的性能。所提出的channel-DN4表现优异,在3类10样本的条件下达到了最高的87.533%的识别精度,而其他方法则存在过拟合问题。代码可在https://github.com/MountainChenCad/channel-DN4找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习的雷达人体运动识别方法已成为遥感领域的热点。但现有方法多为径向方向,实际应用中测试数据可能具有多方面且每种运动的样本数量有限,导致模型过拟合和识别精度降低。本文提出channel-DN4,一种多方面的小样本人体运动识别方法。引入局部描述符进行精确分类度量,采用周期训练策略减轻模型过拟合。通过嵌入网络后的通道注意力利用多方面条件下的不变语义信息,获得精确的高维语义表示。在实测毫米波FMCW雷达数据上测试channel-DN4和其他对比方法,channel-DN4表现出竞争性和令人信服的结果,在3类10样本的条件下达到最高的87.533%识别精度。
Key Takeaways
- 雷达人体运动识别基于深度学习模型已成为遥感热点。
- 现有方法主要为径向方向,实际应用面临多方面和有限样本的挑战。
- channel-DN4方法引入局部描述符进行精确分类。
- 采用周期训练策略减轻模型过拟合问题。
- 通过通道注意力利用多方面条件下的不变语义信息。
- 在实测数据上测试,channel-DN4表现出高识别精度。
点此查看论文截图






Visual RAG: Expanding MLLM visual knowledge without fine-tuning
Authors:Mirco Bonomo, Simone Bianco
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved notable performance in computer vision tasks that require reasoning across visual and textual modalities, yet their capabilities are limited to their pre-trained data, requiring extensive fine-tuning for updates. Recent researches have explored the use of In-Context Learning (ICL) to overcome these challenges by providing a set of demonstrating examples as context to augment MLLMs performance in several tasks, showing that many-shot ICL leads to substantial improvements compared to few-shot ICL. However, the reliance on numerous demonstrating examples and the limited MLLMs context windows presents significant obstacles. This paper aims to address these challenges by introducing a novel approach, Visual RAG, that synergically combines the MLLMs capability to learn from the context, with a retrieval mechanism. The crux of this approach is to ensure to augment the MLLM knowledge by selecting only the most relevant demonstrating examples for the query, pushing it to learn by analogy. In this way, relying on the new information provided dynamically during inference time, the resulting system is not limited to the knowledge extracted from the training data, but can be updated rapidly and easily without fine-tuning. Furthermore, this greatly reduces the computational costs for improving the model image classification performance, and augments the model knowledge to new visual domains and tasks it was not trained for. Extensive experiments on eight different datasets in the state of the art spanning several domains and image classification tasks show that the proposed Visual RAG, compared to the most recent state of the art (i.e., many-shot ICL), is able to obtain an accuracy that is very close or even higher (approx. +2% improvement on average) while using a much smaller set of demonstrating examples (approx. only 23% on average).
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在计算机视觉任务中取得了引人注目的成果,这些任务需要在视觉和文本模态之间进行推理。然而,它们的能力仅限于预训练数据,需要进行广泛的微调才能更新。最近的研究探讨了使用上下文学习(ICL)来克服这些挑战,通过提供一系列演示例子作为上下文来增强MLLMs在多个任务中的性能,表明多示例ICL与少示例ICL相比,可以带来实质性的改进。然而,对大量演示例子的依赖以及MLLMs上下文窗口的限制构成了重大障碍。
本文旨在通过引入一种新方法来解决这些挑战,即Visual RAG。该方法协同结合了MLLMs从上下文中学习的能力与检索机制。该方法的核心是确保通过选择与查询最相关的演示例子来增强MLLM的知识,推动其通过类比进行学习。通过这种方式,依赖推理时动态提供的新信息,结果系统不限于从训练数据中提取的知识,但可以快速轻松地更新而无需微调。此外,这大大降低了提高模型图像分类性能的计算成本,并增强了模型对未训练的新视觉领域和任务的知识。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在计算机视觉任务中展现出强大的跨视觉和文本模态推理能力,但其受限于预训练数据,需大量微调更新。近期研究通过提供演示例子上下文来克服这些挑战,探索了语境学习(ICL)的潜力,多模态显示相比少模态显示出显著改善。然而依赖众多演示例子以及有限的MLLM语境窗口存在明显障碍。本文旨在通过引入一种新型方法Visual RAG来解决这些挑战,该方法结合了MLLM从语境中学习的能力与检索机制。该方法核心在于仅选择对查询最相关的演示例子来扩充MLLM的知识,推动其通过类比学习。通过这种方式,新信息在推理过程中动态提供,使得系统不再局限于从训练数据中提取的知识,可快速轻松更新而无需微调。此外,这大大降低了改进模型图像分类性能的计算成本,并扩充了模型知识到未训练的新视觉领域和任务。在涵盖多个领域和图像分类任务的八个不同数据集上的实验表明,与最新技术相比,提出的Visual RAG能获得相近或更高的准确率(平均提高约+2%),同时使用更少的演示例子(平均仅使用约23%)。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在计算机视觉任务中展现出强大的跨模态推理能力,但需大量微调更新。
- 语境学习(ICL)通过提供演示例子上下文来克服挑战,但依赖众多演示例子和有限的语境窗口存在障碍。
- Visual RAG方法结合了MLLM从语境中学习的能力与检索机制,通过选择最相关的演示例子来扩充知识。
- Visual RAG能够在不使用大量演示例子的情况下提高模型性能,降低计算成本并扩充模型知识到新的视觉领域和任务。
- 实验表明,Visual RAG相比最新技术获得相近或更高的准确率。
- Visual RAG动态利用新信息提高模型适应性,无需微调即可快速更新知识。
点此查看论文截图





Class Incremental Fault Diagnosis under Limited Fault Data via Supervised Contrastive Knowledge Distillation
Authors:Hanrong Zhang, Yifei Yao, Zixuan Wang, Jiayuan Su, Mengxuan Li, Peng Peng, Hongwei Wang
Class-incremental fault diagnosis requires a model to adapt to new fault classes while retaining previous knowledge. However, limited research exists for imbalanced and long-tailed data. Extracting discriminative features from few-shot fault data is challenging, and adding new fault classes often demands costly model retraining. Moreover, incremental training of existing methods risks catastrophic forgetting, and severe class imbalance can bias the model’s decisions toward normal classes. To tackle these issues, we introduce a Supervised Contrastive knowledge distiLlation for class Incremental Fault Diagnosis (SCLIFD) framework proposing supervised contrastive knowledge distillation for improved representation learning capability and less forgetting, a novel prioritized exemplar selection method for sample replay to alleviate catastrophic forgetting, and the Random Forest Classifier to address the class imbalance. Extensive experimentation on simulated and real-world industrial datasets across various imbalance ratios demonstrates the superiority of SCLIFD over existing approaches. Our code can be found at https://github.com/Zhang-Henry/SCLIFD_TII.
类增量故障诊断需要模型在适应新故障类的同时保留先前知识。然而,对于不平衡和长尾数据的研究有限。从少量故障数据中提取判别特征具有挑战性,添加新故障类通常需要昂贵的模型重新训练。此外,现有方法的增量训练存在灾难性遗忘的风险,严重的类别不平衡可能使模型决策偏向正常类别。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了用于类增量故障诊断的监督对比知识蒸馏(SCLIFD)框架,该框架提出监督对比知识蒸馏,以提高表示学习能力并减少遗忘,一种用于样本回放的新型优先级示例选择方法,以缓解灾难性遗忘,以及随机森林分类器来解决类别不平衡问题。在模拟和真实工业数据集上进行的各种不平衡比率的大量实验表明,SCLIFD优于现有方法。我们的代码位于:https://github.com/Zhang-Henry/SCLIFD_TII。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对类增量故障诊断的问题,提出一种名为SCLIFD的框架,通过监督对比知识蒸馏提高表示学习能力并减少遗忘,采用新型优先示例选择方法进行样本回放以缓解灾难性遗忘问题,并使用随机森林分类器解决类别不平衡问题。实验证明,SCLIFD在模拟和真实工业数据集上,在不同不平衡比率下均表现出优于现有方法的效果。
Key Takeaways
- SCLIFD框架被提出用于解决类增量故障诊断中的问题,该框架能够适应新故障类并保留先前知识。
- 在面临不平衡和长尾数据的问题时,提取少数故障数据的判别特征具有挑战性。
- 增量训练现有方法存在灾难性遗忘的风险。
- SCLIFD采用监督对比知识蒸馏,提高表示学习能力并减少遗忘。
- 引入了一种新型的优先示例选择方法,用于样本回放,以减轻灾难性遗忘。
- 使用随机森林分类器来解决类别不平衡问题,以更准确地识别故障类。
点此查看论文截图









IDEA: Image Description Enhanced CLIP-Adapter
Authors:Zhipeng Ye, Feng Jiang, Qiufeng Wang, Kaizhu Huang, Jiaqi Huang
CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training) has attained great success in pattern recognition and computer vision. Transferring CLIP to downstream tasks (e.g. zero- or few-shot classification) is a hot topic in multimodal learning. However, current studies primarily focus on either prompt learning for text or adapter tuning for vision, without fully exploiting the complementary information and correlations among image-text pairs. In this paper, we propose an Image Description Enhanced CLIP-Adapter (IDEA) method to adapt CLIP to few-shot image classification tasks. This method captures fine-grained features by leveraging both visual features and textual descriptions of images. IDEA is a training-free method for CLIP, and it can be comparable to or even exceeds state-of-the-art models on multiple tasks. Furthermore, we introduce Trainable-IDEA (T-IDEA), which extends IDEA by adding two lightweight learnable components (i.e., a projector and a learnable latent space), further enhancing the model’s performance and achieving SOTA results on 11 datasets. As one important contribution, we employ the Llama model and design a comprehensive pipeline to generate textual descriptions for images of 11 datasets, resulting in a total of 1,637,795 image-text pairs, named “IMD-11”. Our code and data are released at https://github.com/FourierAI/IDEA.
CLIP(对比语言-图像预训练)在模式识别和计算机视觉领域取得了巨大成功。将CLIP迁移到下游任务(例如零样本或少样本分类)是多模态学习的热门话题。然而,当前的研究主要集中于文本提示学习或视觉适配器调整,而没有充分利用图像-文本对之间的互补信息和关联。在本文中,我们提出了一种图像描述增强CLIP适配器(IDEA)方法,将CLIP适应于小样本图像分类任务。该方法通过利用图像的视觉特征和文本描述来捕获精细特征。IDEA是一种无需训练的CLIP方法,它在多个任务上的性能可以与最先进的模型相当,甚至超过它们。此外,我们引入了可训练的IDEA(T-IDEA),它通过添加两个轻量级的可学习组件(即投影器和可学习潜在空间)来扩展IDEA,进一步提高了模型的性能,并在11个数据集上实现了最新结果。作为重要贡献之一,我们采用了Llama模型,并设计了一个全面的流程来生成这11个数据集的图像文本描述,共生成了1,637,795个图像-文本对,名为“IMD-11”。我们的代码和数据已在https://github.com/FourierAI/IDEA上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CLIP在多模态学习中取得显著成功,但在下游任务如零样本或少样本分类上的转移应用仍是研究热点。本文提出一种基于图像描述增强的CLIP适配器(IDEA)方法,用于适应少样本图像分类任务。该方法利用视觉特征和图像文本描述,捕获精细特征。此外,还介绍了可训练的IDEA(T-IDEA),通过添加两个轻量级的学习组件,进一步提高模型性能,并在11个数据集上达到最新结果。该研究使用Llama模型生成图像文本描述,构建了一个大规模图像文本对数据库IMD-11。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP在模式识别和计算机视觉领域取得了很大成功。
- 将CLIP转移到下游任务(如零样本或少样本分类)是当前的热门话题。
- IDEA方法通过结合视觉特征和图像文本描述,适应少样本图像分类任务。
- IDEA是一种针对CLIP的无训练方法,在某些任务上的性能可与或超过现有最新模型。
- T-IDEA通过添加学习组件进一步提高了模型性能,并在多个数据集上实现了最新结果。
- 研究人员使用Llama模型生成了大规模的图像文本对数据库IMD-11。
点此查看论文截图


ValuesRAG: Enhancing Cultural Alignment Through Retrieval-Augmented Contextual Learning
Authors:Wonduk Seo, Zonghao Yuan, Yi Bu
Cultural values alignment in Large Language Models (LLMs) is a critical challenge due to their tendency to embed Western-centric biases from training data, leading to misrepresentations and fairness issues in cross-cultural contexts. Recent approaches, such as role-assignment and few-shot learning, often struggle with reliable cultural alignment as they heavily rely on pre-trained knowledge, lack scalability, and fail to capture nuanced cultural values effectively. To address these issues, we propose ValuesRAG, a novel and effective framework that applies Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with In-Context Learning (ICL) to integrate cultural and demographic knowledge dynamically during text generation. Leveraging the World Values Survey (WVS) dataset, ValuesRAG first generates summaries of values for each individual. Subsequently, we curate several representative regional datasets to serve as test datasets and retrieve relevant summaries of values based on demographic features, followed by a reranking step to select the top-k relevant summaries. ValuesRAG consistently outperforms baseline methods, both in the main experiment and in the ablation study where only the values summary was provided. Notably, ValuesRAG demonstrates an accuracy of 21% improvement over other baseline methods, highlighting its potential to foster culturally aligned AI systems and enhance the inclusivity of AI-driven applications.
大型语言模型(LLM)中的文化价值观对齐是一个关键挑战,因为它们往往嵌入从训练数据中获得的西方中心偏见,导致跨文化背景下的误表征和公平性问题。最近的方法,如角色分配和少样本学习,通常难以可靠地进行文化对齐,因为它们严重依赖于预训练知识,缺乏可扩展性,并且未能有效地捕捉微妙的文化价值观。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了ValuesRAG,这是一个新颖有效的框架,它应用检索增强生成(RAG)与上下文学习(ICL)来在文本生成过程中动态整合文化和人口统计数据知识。借助世界价值观调查(WVS)数据集,ValuesRAG首先为每个人生成价值观摘要。随后,我们策划了几个具有代表性的区域数据集作为测试数据集,并基于人口统计特征检索相关的价值观摘要,然后进行重新排序步骤以选择前k个相关摘要。ValuesRAG在主实验和仅提供价值观摘要的消融研究中均优于基准方法。值得注意的是,ValuesRAG的准确率较其他基准方法提高了21%,这凸显了其在促进文化对齐的AI系统和提高AI驱动应用的包容性方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在文化价值观对齐方面面临挑战,因训练数据中的西方中心偏见导致跨文化背景下的误表示和公平问题。ValuesRAG框架采用检索增强生成(RAG)与上下文学习(ICL)结合,动态整合文化和人口统计知识来进行文本生成,解决这一问题。ValuesRAG利用世界价值观调查(WVS)数据集,首先为个人生成价值观摘要,然后基于人口统计特征检索相关价值观摘要,并进行重新排序。ValuesRAG在主要实验和仅提供价值观摘要的消融研究中均表现优于基线方法,准确率提高21%,显示出其在促进文化对齐的AI系统和提高AI应用程序的包容性方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在文化价值观对齐方面具有挑战,因训练数据中的西方中心偏见导致问题。
- ValuesRAG框架通过结合检索增强生成(RAG)和上下文学习(ICL),动态整合文化和人口统计知识来进行文本生成。
- ValuesRAG利用世界价值观调查(WVS)数据集生成个人价值观摘要。
- ValuesRAG基于人口统计特征检索相关价值观摘要,并进行重新排序。
- ValuesRAG在实验中表现优于其他基线方法,准确率提高21%。
- ValuesRAG有助于促进文化对齐的AI系统的发展。
点此查看论文截图




3DGS-CD: 3D Gaussian Splatting-based Change Detection for Physical Object Rearrangement
Authors:Ziqi Lu, Jianbo Ye, John Leonard
We present 3DGS-CD, the first 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)-based method for detecting physical object rearrangements in 3D scenes. Our approach estimates 3D object-level changes by comparing two sets of unaligned images taken at different times. Leveraging 3DGS’s novel view rendering and EfficientSAM’s zero-shot segmentation capabilities, we detect 2D object-level changes, which are then associated and fused across views to estimate 3D change masks and object transformations. Our method can accurately identify changes in cluttered environments using sparse (as few as one) post-change images within as little as 18s. It does not rely on depth input, user instructions, pre-defined object classes, or object models – An object is recognized simply if it has been re-arranged. Our approach is evaluated on both public and self-collected real-world datasets, achieving up to 14% higher accuracy and three orders of magnitude faster performance compared to the state-of-the-art radiance-field-based change detection method. This significant performance boost enables a broad range of downstream applications, where we highlight three key use cases: object reconstruction, robot workspace reset, and 3DGS model update. Our code and data will be made available at https://github.com/520xyxyzq/3DGS-CD.
我们提出了3DGS-CD方法,这是第一个基于三维高斯插值(3DGS)的物理对象重排检测的三维场景方法。我们的方法通过比较在不同时间拍摄的不对齐的两组图像来估计三维物体级别的变化。我们利用3DGS的新型视图渲染和EfficientSAM的零样本分割能力,检测二维物体级别的变化,然后在不同视图中关联和融合这些变化,以估计三维变化掩膜和物体变换。我们的方法可以在杂乱的环境中准确地识别变化,仅使用少数(一张)变化后的图像在短短18秒内即可完成。它不依赖于深度输入、用户指令、预定义的对象类别或对象模型——只要对象被重新排列,它就能被识别。我们的方法在公共和自行收集的真实世界数据集上进行了评估,与最新的基于辐射场的变化检测方法相比,我们的方法提高了高达14%的准确性和三个数量级的性能。这一显著的性能提升为下游应用提供了广泛的可能性,我们重点介绍了三个关键用例:对象重建、机器人工作空间重置和3DGS模型更新。我们的代码和数据将在https://github.com/520xyxyzq/3DGS-CD上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种基于3D高斯渲染(3DGS)的方法,用于检测三维场景中的物体重新排列。该方法通过比较不同时间拍摄的两组未对齐图像来估计三维物体级别的变化。利用3DGS的新型视图渲染和EfficientSAM的零样本分割能力,检测二维物体级别的变化,并在不同视图中关联和融合这些变化,以估计三维变化掩膜和物体变换。该方法能够在杂乱的环境中准确识别物体变化,仅使用少数几张(甚至一张)变化后的图像在短短18秒内完成。它不依赖于深度输入、用户指令、预定义物体类别或物体模型,只要物体被重新排列即可识别。在公共和自行收集的真实世界数据集上的评估表明,与基于辐射场的变化检测方法相比,该方法准确性提高高达14%,性能提升三个数量级。显著的性能提升使得下游应用广泛,本文突出了三个关键应用场景:物体重建、机器人工作空间重置和3DGS模型更新。
关键见解
- 提出首个基于3D高斯渲染(3DGS)的方法,用于检测三维场景中的物体重新排列。
- 通过比较不同时间的未对齐图像集来估计三维物体级别的变化。
- 利用3DGS的新型视图渲染和EfficientSAM的零样本分割能力,检测二维物体级别的变化。
- 方法能在杂乱环境中准确工作,仅使用少量或一张变化后的图像。
- 不依赖于深度输入、用户指令等,具有灵活性。
- 与现有方法相比,具有更高的准确性和显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图







Few-Shot Domain Adaptation for Learned Image Compression
Authors:Tianyu Zhang, Haotian Zhang, Yuqi Li, Li Li, Dong Liu
Learned image compression (LIC) has achieved state-of-the-art rate-distortion performance, deemed promising for next-generation image compression techniques. However, pre-trained LIC models usually suffer from significant performance degradation when applied to out-of-training-domain images, implying their poor generalization capabilities. To tackle this problem, we propose a few-shot domain adaptation method for LIC by integrating plug-and-play adapters into pre-trained models. Drawing inspiration from the analogy between latent channels and frequency components, we examine domain gaps in LIC and observe that out-of-training-domain images disrupt pre-trained channel-wise decomposition. Consequently, we introduce a method for channel-wise re-allocation using convolution-based adapters and low-rank adapters, which are lightweight and compatible to mainstream LIC schemes. Extensive experiments across multiple domains and multiple representative LIC schemes demonstrate that our method significantly enhances pre-trained models, achieving comparable performance to H.266/VVC intra coding with merely 25 target-domain samples. Additionally, our method matches the performance of full-model finetune while transmitting fewer than $2%$ of the parameters.
学习图像压缩(LIC)已经达到了最先进的速率失真性能,被认为是下一代图像压缩技术的有力候选者。然而,预训练的LIC模型在应用于训练域外的图像时通常会出现显著的性能下降,这表明它们的泛化能力较差。为了解决这一问题,我们通过将即插即用适配器集成到预训练模型中,为LIC提出了一种小样本域适应方法。我们从潜在通道和频率成分之间的类比中汲取灵感,研究LIC中的域差距,并观察到训练域外的图像会破坏预训练的通道分解。因此,我们引入了一种基于卷积适配器和低秩适配器的通道重新分配方法,它们既轻便又兼容主流LIC方案。在多个领域和多个代表性LIC方案的大量实验表明,我们的方法显著增强了预训练模型,仅使用25个目标域样本即可实现与H.266/VVC帧内编码相当的性能。此外,我们的方法在传输少于2%的参数时,就能达到与全模型微调相匹配的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练图像压缩(LIC)模型在应用于训练域外图像时性能显著下降,缺乏泛化能力。为此,我们提出了一种基于卷积适配器和低秩适配器的少量域适应方法用于LIC模型,实现通道级重新分配,提高了模型的泛化能力。实验证明,该方法仅需使用少量目标域样本即可显著提高预训练模型的性能,达到与H.266/VVC帧内编码相近的效果。此外,此方法能在仅传输少量参数的情况下匹配全模型微调的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练图像压缩(LIC)模型在应用于训练域外图像时存在性能下降的问题。
- 提出了基于卷积适配器和低秩适配器的少量域适应方法来解决这个问题。
- 通过实现通道级重新分配,提高了LIC模型的泛化能力。
- 该方法仅需使用少量目标域样本即可显著提高预训练模型的性能。
- 方法达到与H.266/VVC帧内编码相近的效果。
- 该方法在仅传输少量参数的情况下匹配全模型微调的性能。
点此查看论文截图







VLM Agents Generate Their Own Memories: Distilling Experience into Embodied Programs of Thought
Authors:Gabriel Sarch, Lawrence Jang, Michael J. Tarr, William W. Cohen, Kenneth Marino, Katerina Fragkiadaki
Large-scale LLMs and VLMs excel at few-shot learning but require high-quality examples. We introduce In-Context Abstraction Learning (ICAL), which iteratively refines suboptimal trajectories into high-quality data with optimized actions and detailed reasoning. Given an inefficient demonstration, a VLM corrects actions and annotates causal relationships, object states, subgoals, and task-relevant visuals, forming “programs of thought.” With human feedback, these programs are improved as the agent executes them in a similar environment. The resulting examples, used as prompt context or fine-tuning data, significantly boost decision-making while reducing human feedback needs. ICAL surpasses state-of-the-art in TEACh (dialogue-based instruction following), VisualWebArena (multimodal web agents), and Ego4D (egocentric video action anticipation). In TEACh, combining fine-tuning and retrieval on ICAL examples outperforms raw human demonstrations and expert examples, achieving a 17.5% increase in goal-condition success. In VisualWebArena, retrieval-augmented GPT-4V with ICAL improves task success rate 1.6x over GPT-4V, while fine-tuning Qwen2-VL achieves a 2.8x improvement. In Ego4D, ICAL outperforms few-shot GPT-4V and remains competitive with supervised models. Overall, ICAL scales 2x better than raw human demonstrations and reduces manual prompt engineering.
大规模的语言模型和视觉语言模型在少量样本学习上表现出色,但需要高质量的例子。我们引入了上下文抽象学习(ICAL),它能够迭代地优化次优轨迹,形成具有优化动作和详细推理的高质量数据。对于低效的演示,视觉语言模型会纠正动作,并注释因果关系、对象状态、子目标和任务相关视觉,形成“思维程序”。随着代理在类似环境中执行这些程序,这些程序会随着人类反馈而不断改进。这些结果示例被用作提示上下文或微调数据,可显著提高决策能力,同时减少人类反馈的需求。ICAL超越了TEACh(基于对话的指令遵循)、VisualWebArena(多模式网络代理)和Ego4D(以自我为中心的视频动作预测)的最新水平。在TEACh中,结合微调与在ICAL示例上的检索优于原始人类演示和专家示例,目标条件成功率提高了17.5%。在VisualWebArena中,使用ICAL增强的GPT-4V检索提高了任务成功率1.6倍,而使用Qwen2-VL的微调则实现了2.8倍的改进。在Ego4D中,ICAL表现优于少量的GPT-4V,并与监督模型保持竞争力。总的来说,ICAL的表现比原始人类演示高出两倍,并减少了手动提示工程的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project website: https://ical-learning.github.io/
Summary
大模型在少样本学习方面表现出色,但需要高质量样本。本文提出一种名为In-Context Abstraction Learning(ICAL)的方法,该方法通过优化动作和详细推理,将不佳的轨迹转化为高质量数据。VLM能够在执行过程中修正动作并标注因果关系、物体状态、子目标和任务相关视觉,形成“思维程序”。通过人类反馈,这些程序可以在类似环境中改善代理执行效果。使用ICAL生成的例子作为提示上下文或微调数据,能显著提高决策能力并减少人类反馈需求。在TEACh、VisualWebArena和Ego4D等任务上,ICAL超越了现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模语言模型和视觉语言模型在少样本学习上表现优异,但需高质量样本。
- 引入In-Context Abstraction Learning(ICAL)方法,能将不佳的轨迹转化为高质量数据。
- VLM能够标注因果关系、物体状态、子目标和任务相关视觉,形成“思维程序”。
- 通过人类反馈,这些“思维程序”可以在类似环境中改善代理执行效果。
- ICAL在TEACh、VisualWebArena和Ego4D等任务上超越现有技术。
- 相较于原始人类示范,ICAL能提高决策能力并减少人类反馈需求。
点此查看论文截图



One size doesn’t fit all: Predicting the Number of Examples for In-Context Learning
Authors:Manish Chandra, Debasis Ganguly, Iadh Ounis
In-context learning (ICL) refers to the process of adding a small number of localized examples from a training set of labelled data to an LLM’s prompt with an objective to effectively control the generative process seeking to improve the downstream task performance. Existing ICL approaches use an identical number of examples (a pre-configured hyper-parameter) for each data instance. Our work alleviates the limitations of this ‘one fits all’ approach by dynamically predicting the number of examples for each data instance to be used in few-shot inference with LLMs. In particular, we employ a multi-label classifier, the parameters of which are fitted using a training set, where the label for each instance in this training set indicates if using a specific value of k (number of most similar examples from 0 up to a maximum value) leads to correct k-shot downstream predictions. Our experiments on a number of text classification benchmarks show that AICL substantially outperforms standard ICL by up to 17%.
上下文学习(ICL)指的是在LLM提示中添加少量来自标注数据训练集的本地化示例,旨在有效控制生成过程,以提高下游任务性能的过程。现有的ICL方法为每个数据实例使用相同数量的示例(一个预先配置的超参数)。我们的工作通过动态预测每个数据实例在少样本推断中使用LLM的示例数量来缓解这种“一刀切”方法的局限性。具体来说,我们采用多标签分类器,其参数使用训练集进行拟合,该训练集中每个实例的标签表示使用特定的k值(从最接近的最多k个示例数开始到最大值)是否能导致正确的k次下游预测。我们在多个文本分类基准测试上的实验表明,AICL显著优于标准ICL,最高提升了约17%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
适应型实例学习(AICL)针对少样本推断提出了一个解决方案,该方案通过动态预测每个数据实例在LLM中使用示例的数量来改进现有实例学习(ICL)的局限性。具体来说,它采用多标签分类器,并使用训练集拟合参数,该训练集的标签表示使用特定数量的示例是否导致正确的下游预测。实验表明,AICL在多个文本分类基准测试中显著优于标准ICL。
Key Takeaways
- 实例学习(ICL)旨在通过向LLM提示中添加少量局部示例来改善下游任务性能。
- 现有ICL方法为每个数据实例使用相同数量的示例,而AICL则动态预测每个实例所需的示例数量。
- AICL采用多标签分类器并使用训练集拟合参数。
- 训练集的标签表示使用特定数量的示例是否导致正确的下游预测。
点此查看论文截图



UniGraph: Learning a Unified Cross-Domain Foundation Model for Text-Attributed Graphs
Authors:Yufei He, Yuan Sui, Xiaoxin He, Bryan Hooi
Foundation models like ChatGPT and GPT-4 have revolutionized artificial intelligence, exhibiting remarkable abilities to generalize across a wide array of tasks and applications beyond their initial training objectives. However, graph learning has predominantly focused on single-graph models, tailored to specific tasks or datasets, lacking the ability to transfer learned knowledge to different domains. This limitation stems from the inherent complexity and diversity of graph structures, along with the different feature and label spaces specific to graph data. In this paper, we recognize text as an effective unifying medium and employ Text-Attributed Graphs (TAGs) to leverage this potential. We present our UniGraph framework, designed to learn a foundation model for TAGs, which is capable of generalizing to unseen graphs and tasks across diverse domains. Unlike single-graph models that use pre-computed node features of varying dimensions as input, our approach leverages textual features for unifying node representations, even for graphs such as molecular graphs that do not naturally have textual features. We propose a novel cascaded architecture of Language Models (LMs) and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) as backbone networks. Additionally, we propose the first pre-training algorithm specifically designed for large-scale self-supervised learning on TAGs, based on Masked Graph Modeling. We introduce graph instruction tuning using Large Language Models (LLMs) to enable zero-shot prediction ability. Our comprehensive experiments across various graph learning tasks and domains demonstrate the model’s effectiveness in self-supervised representation learning on unseen graphs, few-shot in-context transfer, and zero-shot transfer, even surpassing or matching the performance of GNNs that have undergone supervised training on target datasets.
ChatGPT和GPT-4等基础模型已经彻底改变了人工智能领域,展现出了令人瞩目的能力,能够在广泛的任务和应用中泛化,超出其初始训练目标范围。然而,图学习主要集中在针对特定任务或数据集的单一图模型上,缺乏将所学知识迁移到不同领域的能力。这一局限性源于图结构固有的复杂性和多样性,以及图数据特定的特征和标签空间。在本文中,我们认识到文本是一种有效的统一媒介,并采用文本属性图(TAGs)来利用这一潜力。我们提出了UniGraph框架,旨在学习文本属性图的基准模型,能够泛化到不同领域的未见图和任务。与那些使用预计算节点特征作为输入的单一图模型不同,我们的方法利用文本特征来统一节点表示,即使对于没有自然文本特征的图形(如分子图形)也是如此。我们提出了一种新颖的级联架构,将语言模型(LMs)和图神经网络(GNNs)作为主干网络。此外,我们提出了第一个专门为TAG上的大规模自监督学习设计的预训练算法,基于掩码图建模。我们引入大型语言模型(LLMs)进行指令微调,以实现零样本预测能力。我们在各种图学习任务和领域进行的全面实验表明,该模型在未见图的自监督表示学习、少量上下文迁移和零样本迁移方面的有效性,甚至超越或匹配了在目标数据集上进行监督训练的GNN的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF KDD 2025
Summary
本文介绍了UniGraph框架,这是一个用于Text-Attributed Graphs(TAGs)的基础模型。该框架能够泛化到未见过的图和跨域任务。它采用文本特征来统一节点表示,并提出了一种新的级联架构,包括语言模型和图神经网络。此外,本文还提出了针对TAGs的大规模自监督学习的预训练算法,以及利用大型语言模型进行图形指令调整的方法,以实现零射击预测能力。实验表明,该模型在未见过的图的自监督表示学习、少样本上下文迁移和零样本迁移方面表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- UniGraph框架引入Text-Attributed Graphs(TAGs)概念,实现了跨不同领域的泛化能力。
- 该框架通过结合语言模型和图神经网络,采用文本特征来统一节点表示。
- 提出了针对TAGs的大规模自监督学习的预训练算法。
- 通过利用大型语言模型进行图形指令调整,实现了零射击预测能力。
- UniGraph框架在未见过的图的自监督表示学习方面表现出色。
- 该框架支持少样本上下文迁移和零样本迁移。
点此查看论文截图




AutoMix: Automatically Mixing Language Models
Authors:Pranjal Aggarwal, Aman Madaan, Ankit Anand, Srividya Pranavi Potharaju, Swaroop Mishra, Pei Zhou, Aditya Gupta, Dheeraj Rajagopal, Karthik Kappaganthu, Yiming Yang, Shyam Upadhyay, Manaal Faruqui, Mausam
Large language models (LLMs) are now available from cloud API providers in various sizes and configurations. While this diversity offers a broad spectrum of choices, effectively leveraging the options to optimize computational cost and performance remains challenging. In this work, we present Automix, an approach that strategically routes queries to larger LMs, based on the approximate correctness of outputs from a smaller LM. Central to Automix are two key technical contributions. First, it has a few-shot self-verification mechanism, which estimates the reliability of its own outputs without requiring extensive training. Second, given that self-verification can be noisy, it employs a POMDP based router that can effectively select an appropriately sized model, based on answer confidence. Experiments across five language models and five challenging datasets show that Automix consistently surpasses strong baselines, reducing computational cost by over 50% for comparable performance.
大规模语言模型(LLM)现在可以从云API提供商处获得各种规模和配置。虽然这种多样性提供了广泛的选择,但有效利用这些选项来优化计算成本和性能仍然具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们提出了Automix方法,它根据较小LM的输出近似正确性来战略性地将查询路由到较大的LM。Automix的两个关键技术贡献是核心。首先,它拥有一种小样本自我验证机制,可以在不需要大量训练的情况下估计自身输出的可靠性。其次,由于自我验证可能带有噪声,它采用基于POMDP的路由器,可以有效地根据答案置信度选择适当大小的模型。在五个语言模型和五个具有挑战性的数据集上的实验表明,Automix始终超过强大的基准线,在可比性能的情况下将计算成本降低超过50%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 38th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2024). The first two authors contributed equally. Work started and partly done during Aman’s internship at Google. This version adds results on additional models and datasets
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)从云API提供商处获得,种类和配置多样。如何有效利用这些模型以优化计算成本和性能是一大挑战。本研究提出Automix方法,根据小型LM的输出近似正确性来战略性地将查询导向大型LM。Automix有两个关键技术贡献:一是具有少样本自我验证机制,无需大量训练即可估计输出可靠性;二是采用基于POMDP的路由器,在答案置信度的基础上有效地选择适当大小的模型。实验表明,Automix在五个语言模型和五个挑战性数据集上的表现一直优于强基线,计算成本降低了50%以上,性能相当。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的多样性和配置选择带来了有效利用的挑战。
- Automix方法根据小型LM的输出近似正确性来指导查询到大型LM。
- Automix具有少样本自我验证机制,无需大量训练即可评估输出可靠性。
- Automix采用基于POMDP的路由器,有效选择适当大小的模型以优化性能。
- 实验表明Automix在多个语言模型和数据集上的表现优于基线。
- Automix能够降低计算成本,达到超过50%的节省。
点此查看论文截图