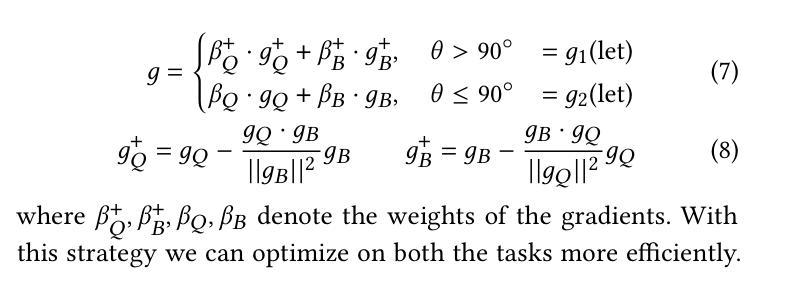⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-23 更新
InternVideo2.5: Empowering Video MLLMs with Long and Rich Context Modeling
Authors:Yi Wang, Xinhao Li, Ziang Yan, Yinan He, Jiashuo Yu, Xiangyu Zeng, Chenting Wang, Changlian Ma, Haian Huang, Jianfei Gao, Min Dou, Kai Chen, Wenhai Wang, Yu Qiao, Yali Wang, Limin Wang
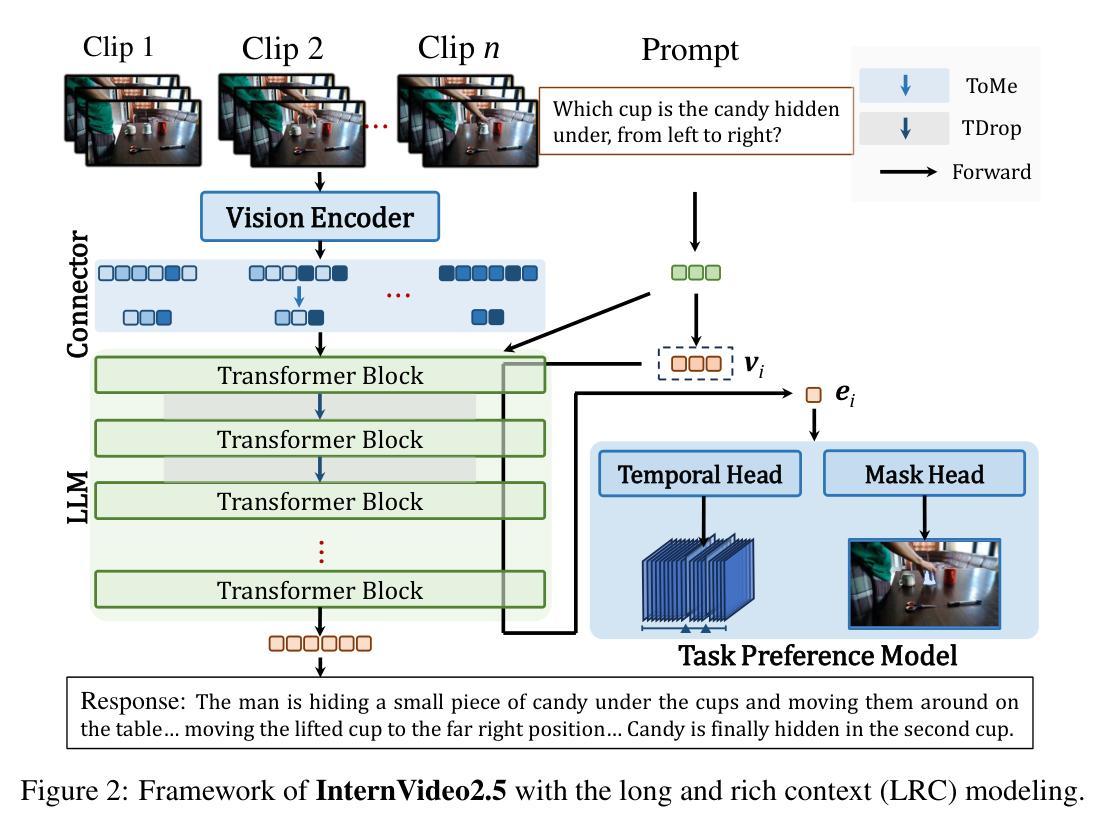
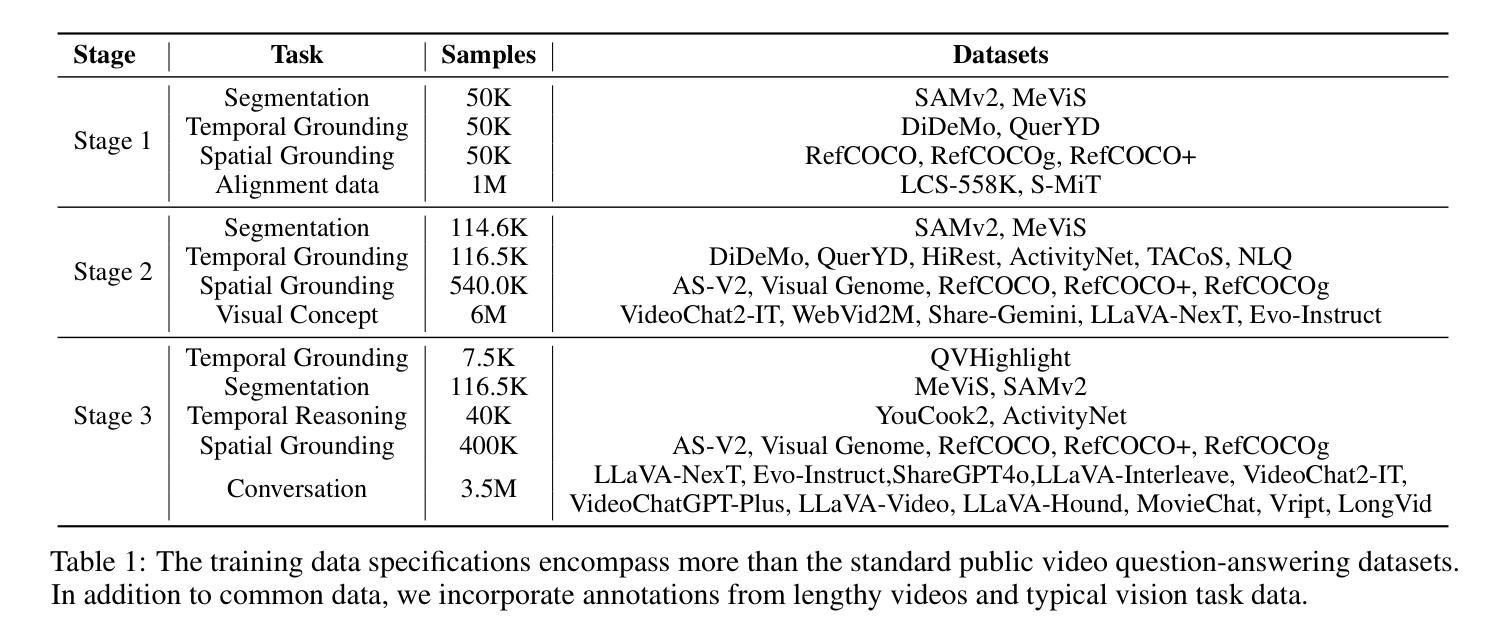
This paper aims to improve the performance of video multimodal large language models (MLLM) via long and rich context (LRC) modeling. As a result, we develop a new version of InternVideo2.5 with a focus on enhancing the original MLLMs’ ability to perceive fine-grained details and capture long-form temporal structure in videos. Specifically, our approach incorporates dense vision task annotations into MLLMs using direct preference optimization and develops compact spatiotemporal representations through adaptive hierarchical token compression. Experimental results demonstrate this unique design of LRC greatly improves the results of video MLLM in mainstream video understanding benchmarks (short & long), enabling the MLLM to memorize significantly longer video inputs (at least 6x longer than the original), and master specialized vision capabilities like object tracking and segmentation. Our work highlights the importance of multimodal context richness (length and fineness) in empowering MLLM’s innate abilites (focus and memory), providing new insights for future research on video MLLM. Code and models are available at https://github.com/OpenGVLab/InternVideo/tree/main/InternVideo2.5
本文旨在通过长丰富上下文(LRC)建模提高视频多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的性能。因此,我们开发了一个新的InternVideo2.5版本,重点增强原始MLLM感知细微细节的能力,并捕获视频中的长形式时间结构。具体来说,我们的方法通过直接偏好优化将密集视觉任务注释融入到MLLM中,并通过自适应分层令牌压缩开发紧凑的时空表示。实验结果表明,LRC的独特设计极大地提高了主流视频理解基准测试(短&长)中视频MLLM的结果,使MLLM能够记忆明显更长的视频输入(至少为原始版本的6倍),并掌握诸如对象跟踪和分割等专业视觉功能。我们的研究突出了多模态上下文丰富性(长度和精细度)在增强MLLM固有能力(焦点和记忆)方面的重要性,为未来视频MLLM的研究提供了新的见解。代码和模型可在https://github.com/OpenGVLab/InternVideo/tree/main/InternVideo2.5获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF technical report
摘要
MLLM在丰富且长时间的上下文下实现优化改进,以更深入地理解视频信息。推出新版本的InternVideo2.5模型,旨在增强原始MLLM捕捉视频精细细节和长期时间结构的能力。该研究采用直接偏好优化方法将密集视觉任务注释融入MLLM中,并通过自适应分层令牌压缩技术生成紧凑的时空表示。实验结果表明,LRC设计显著提高了主流视频理解基准测试中的视频MLLM结果,使MLLM能够处理显著更长的视频输入(至少是原始版本的六倍长),并掌握对象跟踪和分割等专业技能。本研究强调了多媒体上下文丰富性(长度和精细度)在增强MLLM固有能力(专注和记忆)中的重要性,为未来视频MLLM研究提供了新见解。代码和模型可在此处下载:链接[开放GV实验室网站](这是一个虚构的网站地址,供文本生成使用)。
关键见解
- 研究旨在通过引入丰富且长时间的上下文(LRC)来提高视频多媒体大型语言模型(MLLM)的性能。
- 新版InternVideo2.5模型强化了捕捉视频精细细节和长期时间结构的能力。
- 通过直接偏好优化融入密集视觉任务注释,并创建紧凑的时空表示。
- LRC设计显著提高了主流视频理解基准测试的结果。
- MLLM能够处理显著更长的视频输入。
- 新模型掌握对象跟踪和分割等专业技能。
点此查看论文截图

Expertise elevates AI usage: experimental evidence comparing laypeople and professional artists
Authors:Thomas F. Eisenmann, Andres Karjus, Mar Canet Sola, Levin Brinkmann, Bramantyo Ibrahim Supriyatno, Iyad Rahwan
Novel capacities of generative AI to analyze and generate cultural artifacts raise inevitable questions about the nature and value of artistic education and human expertise. Has AI already leveled the playing field between professional artists and laypeople, or do trained artistic expressive capacity, curation skills and experience instead enhance the ability to use these new tools? In this pre-registered study, we conduct experimental comparisons between 50 active artists and a demographically matched sample of laypeople. We designed two tasks to approximate artistic practice for testing their capabilities in both faithful and creative image creation: replicating a reference image, and moving as far away as possible from it. We developed a bespoke platform where participants used a modern text-to-image model to complete both tasks. We also collected and compared participants’ sentiments towards AI. On average, artists produced more faithful and creative outputs than their lay counterparts, although only by a small margin. While AI may ease content creation, professional expertise is still valuable - even within the confined space of generative AI itself. Finally, we also explored how well an exemplary vision-capable large language model (GPT-4o) would complete the same tasks, if given the role of an image generation agent, and found it performed on par in copying but outperformed even artists in the creative task. The very best results were still produced by humans in both tasks. These outcomes highlight the importance of integrating artistic skills with AI training to prepare artists and other visual professionals for a technologically evolving landscape. We see a potential in collaborative synergy with generative AI, which could reshape creative industries and education in the arts.
生成式人工智能分析和生成文化产品的新能力,不可避免地引发了关于艺术教育和人类专业知识性质与价值的疑问。人工智能是否已经使专业艺术家和业余爱好者处于同一竞争水平,或者专业的艺术表达技巧、策划技能和经验是否反而增强了使用这些新工具的能力?在这项预先注册的研究中,我们对50名活跃艺术家和与之人口学特征匹配的业余爱好者样本进行了实验对比。我们设计了两个任务来模拟艺术创作实践,测试他们在忠实和创造性图像创作方面的能力:复制参考图像,并尽可能远离它。我们开发了一个专用平台,参与者使用现代文本到图像模型来完成这两个任务。我们还收集了参与者对人工智能的看法并进行了比较。平均而言,艺术家比业余爱好者产出更忠实、更具创意的作品,但差距很小。虽然人工智能可能使内容创建变得更容易,但专业知识仍然很有价值,甚至在生成式人工智能本身的有限空间内也是如此。最后,我们还探索了一个典型的具备视觉功能的大型语言模型(GPT-4o)在扮演图像生成代理角色时完成相同的任务有多好,发现它在复制方面表现相当,但在创造性任务上甚至超过了艺术家。两个任务中最好的结果仍然是由人类产生的。这些结果强调了将艺术技能与人工智能培训相结合的重要性,为艺术家和其他视觉专业人士准备应对技术不断发展的环境。我们看到与生成式人工智能协同合作的潜力,这可能会重塑创意产业和艺术教育。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Eisenmann and Karjus contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
摘要
关于人工智能(AI)在文化产物分析与生成方面的新兴能力,对于艺术教育与人类专业知识本质及其价值提出了无可避免的问题。在AI介入下,专业艺术家与普通人之间的差距是否已经缩小?又或者,训练后的艺术表达力、策划能力及经验是否有助于更好地运用这些新工具?本研究对五十名活跃艺术家与相匹配的非艺术从业者进行对比实验,通过设计贴近艺术实践的任务比较二者能力,包括忠于原作的图像复制与创意图像创作任务。参与者使用文本生成图像模型完成任务,并收集他们对于AI的情感态度。结果表明,艺术家无论在忠实度还是创造性上表现均略高于非专业人士,但优势不大。AI虽有助于内容创作,但专业知识仍具价值,即使在生成式AI的局限空间内亦然。此外,我们也探究了大型语言模型GPT-4o作为图像生成代理完成相同任务的效果,发现其在复制任务中表现相当,而在创造性任务中甚至超越艺术家群体。然而无论结果如何,最优秀的作品仍由人类创作完成。结果强调了将艺术技能与AI培训相结合的重要性,为艺术家及其他视觉专业人士应对技术变革提供方向。我们期待人工智能与创造性产业和艺术教育的结合协作将带来变革性的潜力。
关键要点
- AI在分析和生成文化产品方面的能力对艺术教育和人类专业知识提出了质疑。
- 在特定任务中,艺术家表现稍优于非专业人士,但差距不大。
- AI使内容创作更为便捷,但专业知识在生成式AI领域仍具价值。
- 大型语言模型在创造性任务中表现卓越,但在忠实度方面仍需提升。
- 人类与AI的结合能创作出最优秀的作品,突显了技术与艺术结合培训的重要性。
点此查看论文截图


Is Long Context All You Need? Leveraging LLM’s Extended Context for NL2SQL
Authors:Yeounoh Chung, Gaurav T. Kakkar, Yu Gan, Brenton Milne, Fatma Ozcan
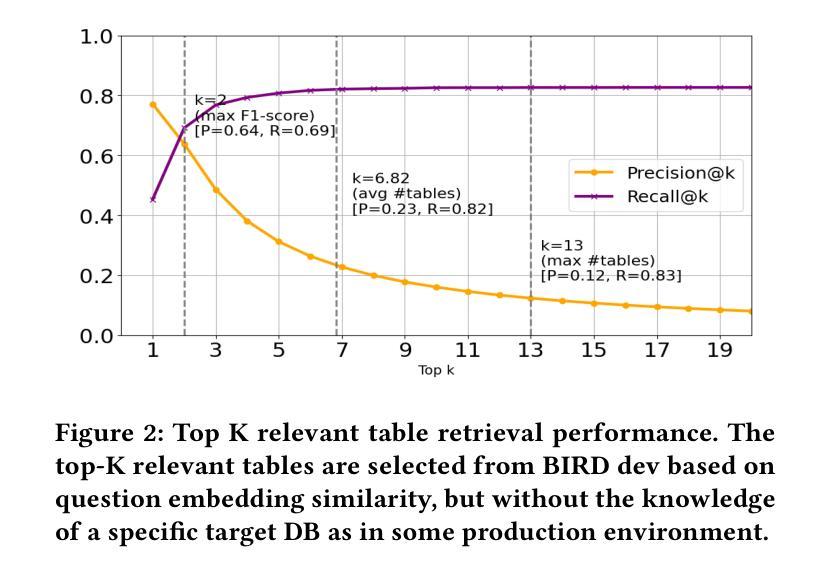
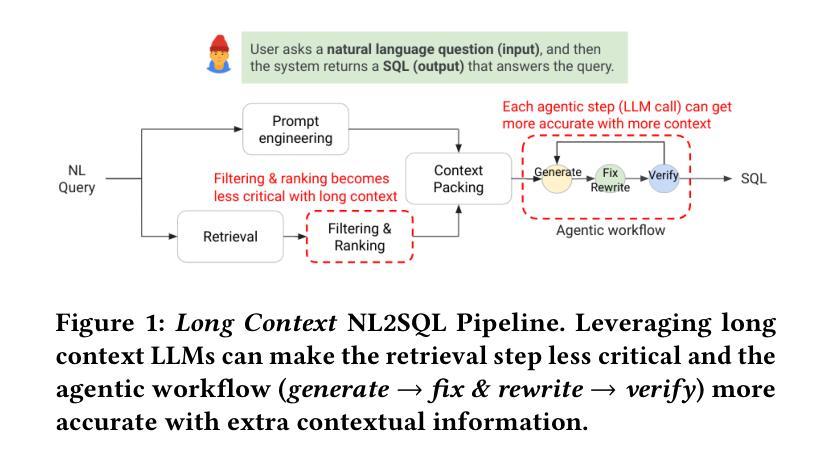
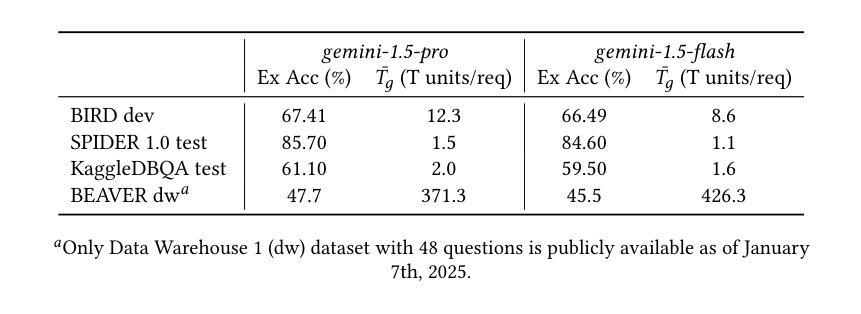
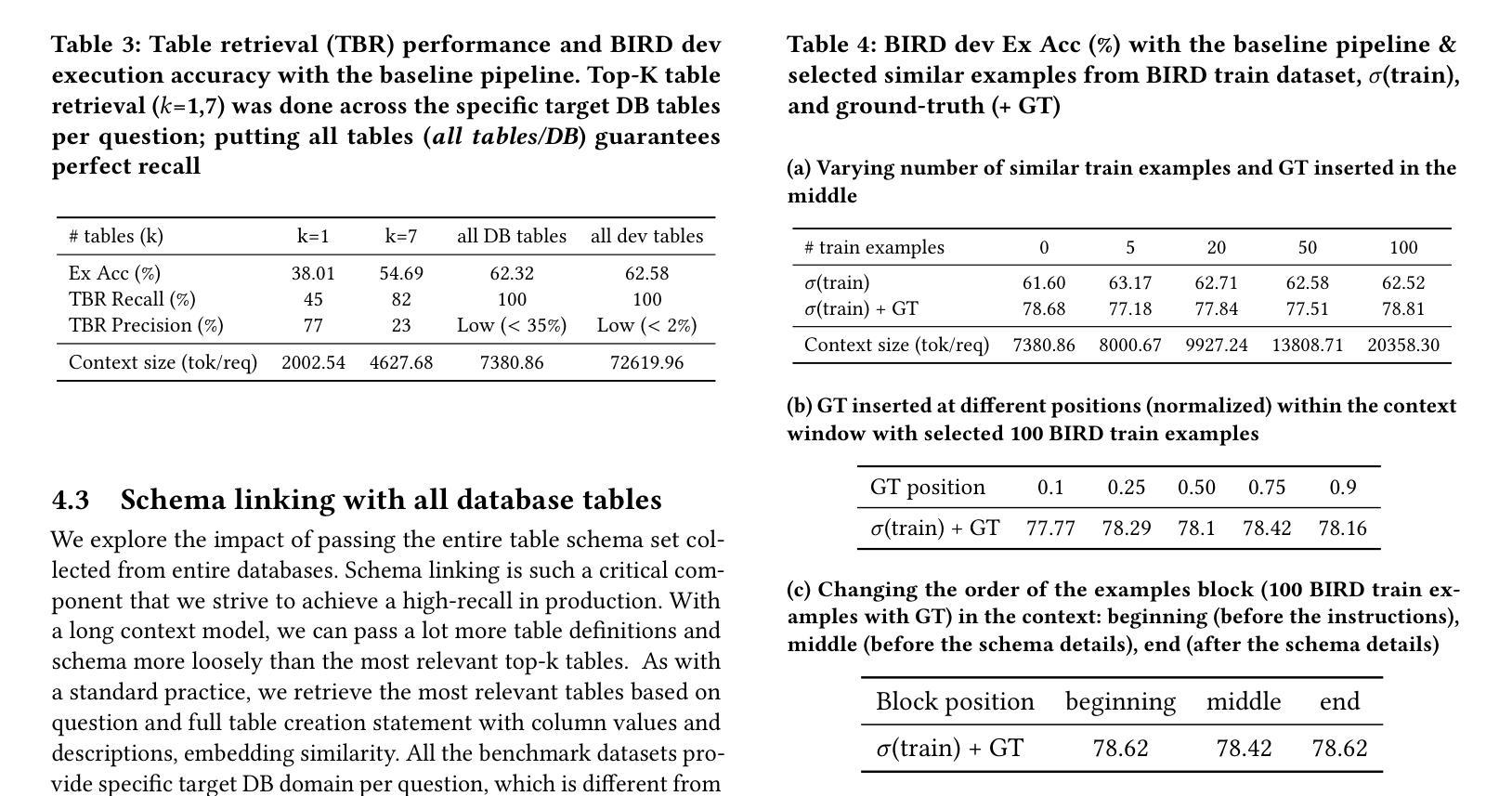
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across a range of natural language processing tasks. In particular, improvements in reasoning abilities and the expansion of context windows have opened new avenues for leveraging these powerful models. NL2SQL is challenging in that the natural language question is inherently ambiguous, while the SQL generation requires a precise understanding of complex data schema and semantics. One approach to this semantic ambiguous problem is to provide more and sufficient contextual information. In this work, we explore the performance and the latency trade-offs of the extended context window (a.k.a., long context) offered by Google’s state-of-the-art LLM (\textit{gemini-1.5-pro}). We study the impact of various contextual information, including column example values, question and SQL query pairs, user-provided hints, SQL documentation, and schema. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to study how the extended context window and extra contextual information can help NL2SQL generation with respect to both accuracy and latency cost. We show that long context LLMs are robust and do not get lost in the extended contextual information. Additionally, our long-context NL2SQL pipeline based on Google’s \textit{gemini-pro-1.5} achieve a strong performance with 67.41% on BIRD benchmark (dev) without finetuning and expensive self-consistency based techniques.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多种自然语言处理任务中表现出了令人印象深刻的能力。特别是推理能力的改进和上下文窗口的扩展,为利用这些强大模型开辟了新途径。NL2SQL的挑战在于自然语言问题本质上是模糊的,而SQL生成则需要精确理解复杂的数据结构和语义。解决这种语义模糊问题的一种方法是提供更多和足够的上下文信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 10 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理任务中展现出令人印象深刻的能力,特别是在推理能力和上下文窗口扩展方面。对于NL2SQL问题,由于其天然的语言歧义性和SQL生成的复杂性,提供足够的上下文信息是一种解决语义模糊问题的方法。本研究首次探讨了Google先进LLM(双子座-专业版)提供的扩展上下文窗口和额外上下文信息对NL2SQL生成的影响,包括列示例值、问答对、用户提示、SQL文档和模式等。实验表明,长上下文LLM具有稳健性,不会迷失在扩展的上下文信息中。基于Google的双子座专业版构建的长上下文NL2SQL管道在BIRD基准测试上取得了强大的性能,未经微调且未采用昂贵的自一致性技术即达到了67.41%的准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理任务中展现出强大的能力,特别是在推理和上下文窗口扩展方面。
- NL2SQL问题因其天然的语言歧义性而具有挑战性。
- 提供足够的上下文信息是解决NL2SQL语义模糊问题的一种方法。
- 本研究首次探讨了扩展上下文窗口和额外上下文信息对NL2SQL生成的影响。
- 实验表明,长上下文LLM具有处理复杂上下文信息的稳健性。
- 基于Google的双子座专业版构建的长上下文NL2SQL管道在BIRD基准测试上取得了强大的性能。
点此查看论文截图

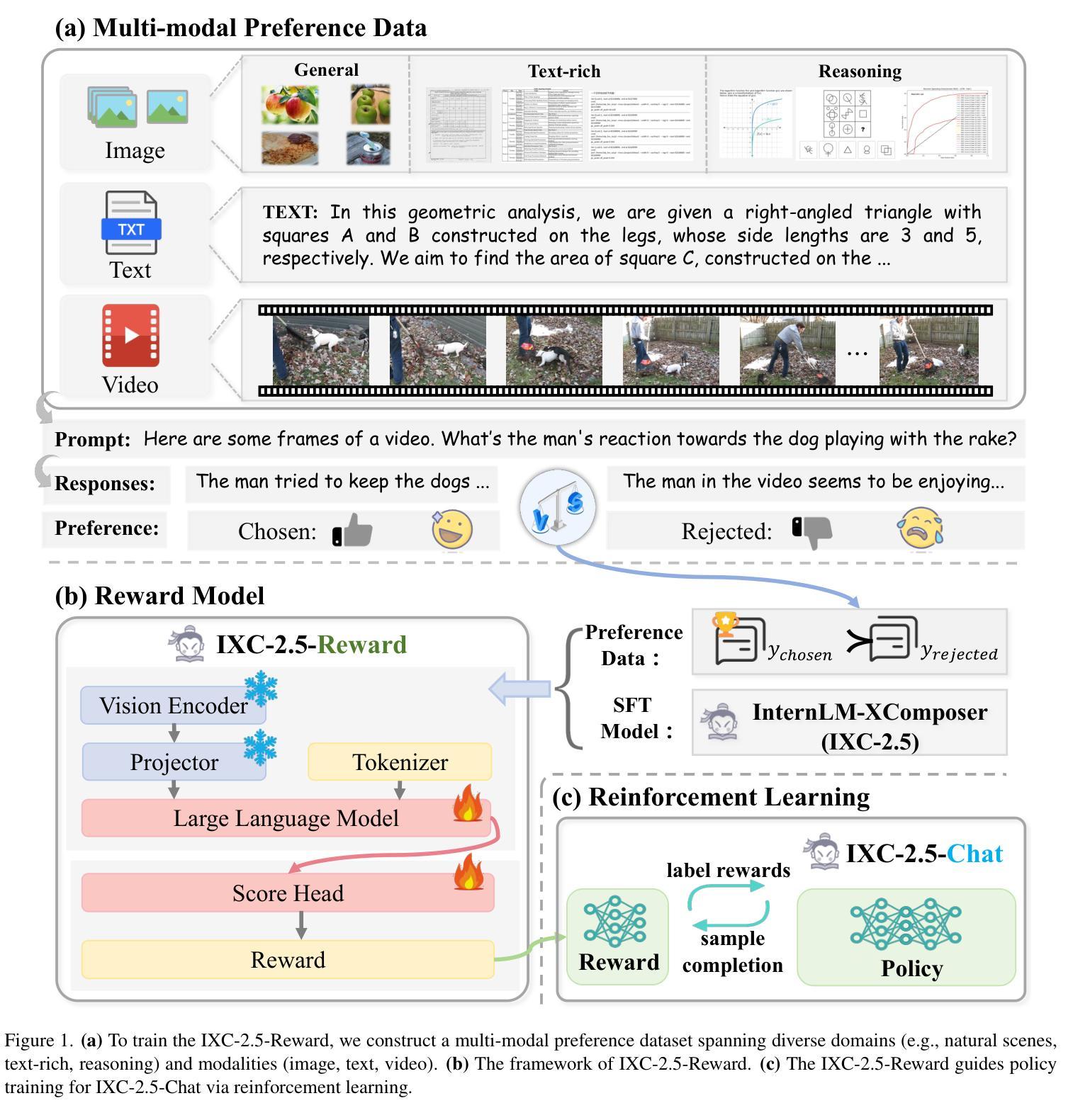
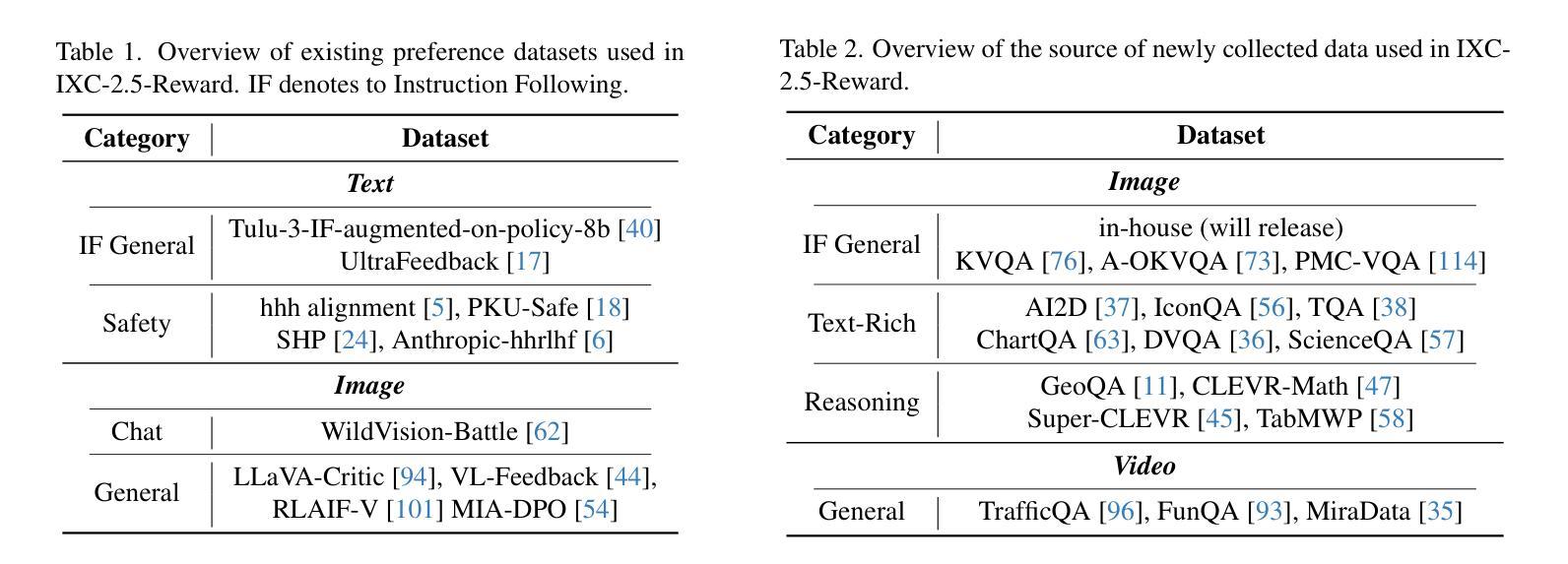
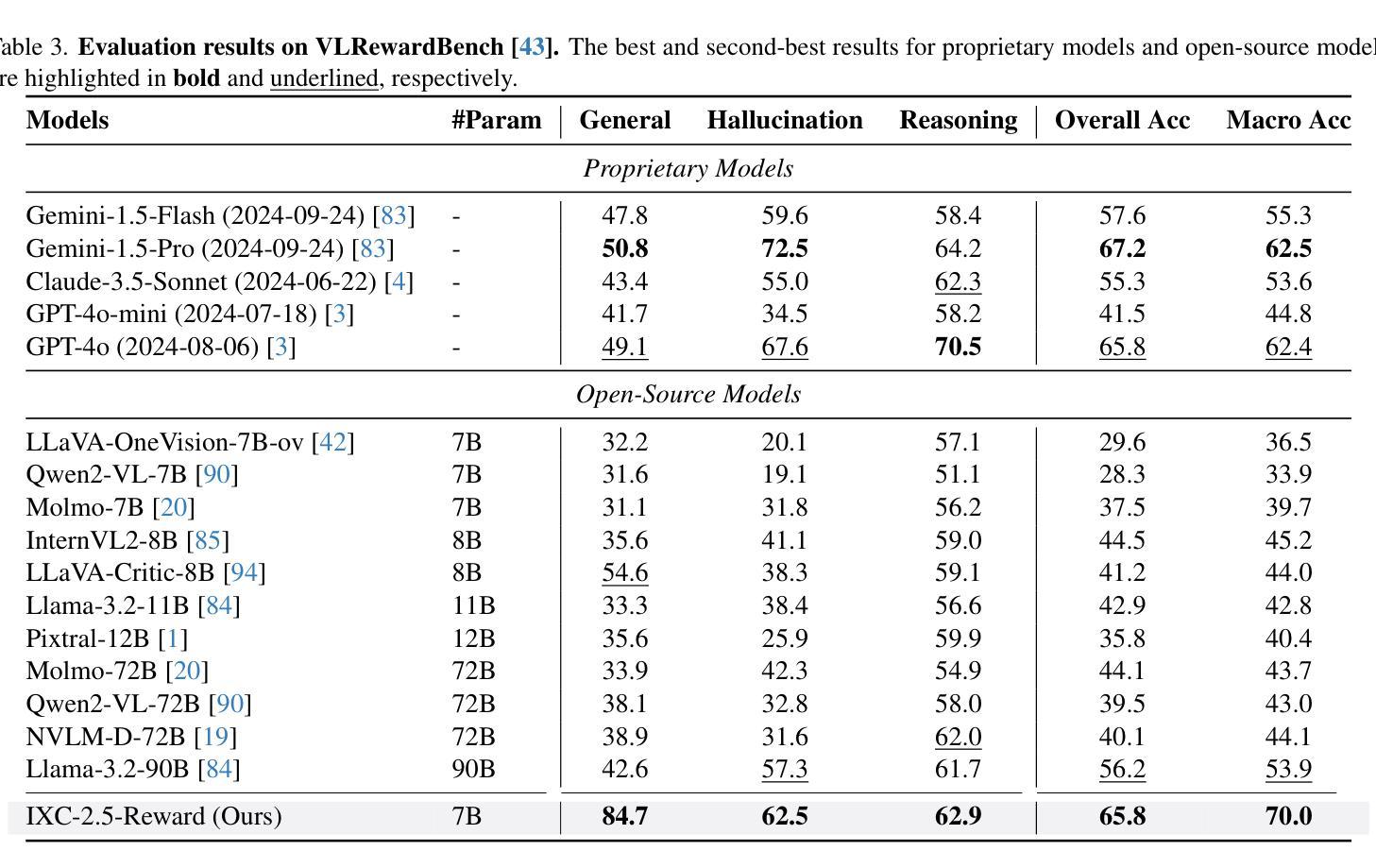
InternLM-XComposer2.5-Reward: A Simple Yet Effective Multi-Modal Reward Model
Authors:Yuhang Zang, Xiaoyi Dong, Pan Zhang, Yuhang Cao, Ziyu Liu, Shengyuan Ding, Shenxi Wu, Yubo Ma, Haodong Duan, Wenwei Zhang, Kai Chen, Dahua Lin, Jiaqi Wang
Despite the promising performance of Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) in visual understanding, they occasionally generate incorrect outputs. While reward models (RMs) with reinforcement learning or test-time scaling offer the potential for improving generation quality, a critical gap remains: publicly available multi-modal RMs for LVLMs are scarce, and the implementation details of proprietary models are often unclear. We bridge this gap with InternLM-XComposer2.5-Reward (IXC-2.5-Reward), a simple yet effective multi-modal reward model that aligns LVLMs with human preferences. To ensure the robustness and versatility of IXC-2.5-Reward, we set up a high-quality multi-modal preference corpus spanning text, image, and video inputs across diverse domains, such as instruction following, general understanding, text-rich documents, mathematical reasoning, and video understanding. IXC-2.5-Reward achieves excellent results on the latest multi-modal reward model benchmark and shows competitive performance on text-only reward model benchmarks. We further demonstrate three key applications of IXC-2.5-Reward: (1) Providing a supervisory signal for RL training. We integrate IXC-2.5-Reward with Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) yields IXC-2.5-Chat, which shows consistent improvements in instruction following and multi-modal open-ended dialogue; (2) Selecting the best response from candidate responses for test-time scaling; and (3) Filtering outlier or noisy samples from existing image and video instruction tuning training data. To ensure reproducibility and facilitate further research, we have open-sourced all model weights and training recipes at https://github.com/InternLM/InternLM-XComposer
尽管大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在视觉理解方面表现出良好的性能,但它们偶尔会产生错误的输出。虽然使用强化学习或测试时间缩放的奖励模型(RMs)有提高生成质量的潜力,但仍存在一个关键差距:针对LVLMs的公开可用多模式RMs很少见,专有模型的实现细节通常也不清楚。我们通过与InternLM-XComposer2.5-Reward(IXC-2.5-Reward)弥合这一鸿沟,这是一个简单而有效的多模式奖励模型,使LVLMs与人类偏好保持一致。为确保IXC-2.5-Reward的稳健性和通用性,我们建立了一个高质量的多模式偏好语料库,涵盖文本、图像和视频输入,涉及不同领域,如指令遵循、一般理解、文本丰富文档、数学推理和视频理解。IXC-2.5-Reward在最新的多模式奖励模型基准测试上取得了优异的结果,并在只有文本的奖励模型基准测试上表现出了竞争力。我们还展示了IXC-2.5-Reward的三个关键应用:(1)为强化学习训练提供监督信号。我们将IXC-2.5-Reward与近端策略优化(PPO)相结合,产生了IXC-2.5-Chat,在指令遵循和多模式开放式对话方面表现出持续改进;(2)在测试时间缩放时从候选响应中选择最佳响应;(3)从现有的图像和视频指令调整训练数据中过滤异常值或噪声样本。为确保可复制性并促进进一步研究,我们已在https://github.com/InternLM/InternLM-XComposer公开了所有模型权重和训练配方。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Tech Report
Summary
LVLMs在视觉理解方面表现出色,但有时会生成错误输出。为解决此问题,我们推出了InternLM-XComposer2.5-Reward模型,这是一个简单有效的多模态奖励模型,可将LVLMs与人类偏好对齐。我们建立了高质量的多模态偏好语料库,涵盖文本、图像和视频输入的不同领域,如指令遵循、通用理解、文本丰富文档、数学推理和视频理解等。该模型在最新多模态奖励模型基准测试上表现优异,并在文本奖励模型基准测试中展现出竞争力。此外,我们还展示了该模型在提供监督信号用于强化学习训练、从候选响应中选择最佳响应进行测试时间缩放以及过滤现有图像和视频指令调整训练数据中的异常值或噪声样本等三个关键应用。为确保可复制性和促进进一步研究,我们已在https://github.com/InternLM/InternLM-XComposer公开了所有模型权重和训练配方。
Key Takeaways
- InternLM-XComposer2.5-Reward是一个用于LVLMs的多模态奖励模型,与人类偏好对齐。
- 该模型通过高质量的多模态偏好语料库进行训练,涵盖多个领域。
- InternLM-XComposer2.5-Reward在多个基准测试中表现优异。
- 模型可用于强化学习训练的监督信号提供、从候选响应中选择最佳响应以及过滤训练数据中的异常值或噪声样本。
- 模型的应用场景包括指令遵循、通用理解、文本丰富文档、数学推理和视频理解等。
- 该模型已开源,所有模型权重和训练配方可在指定网站找到。
点此查看论文截图


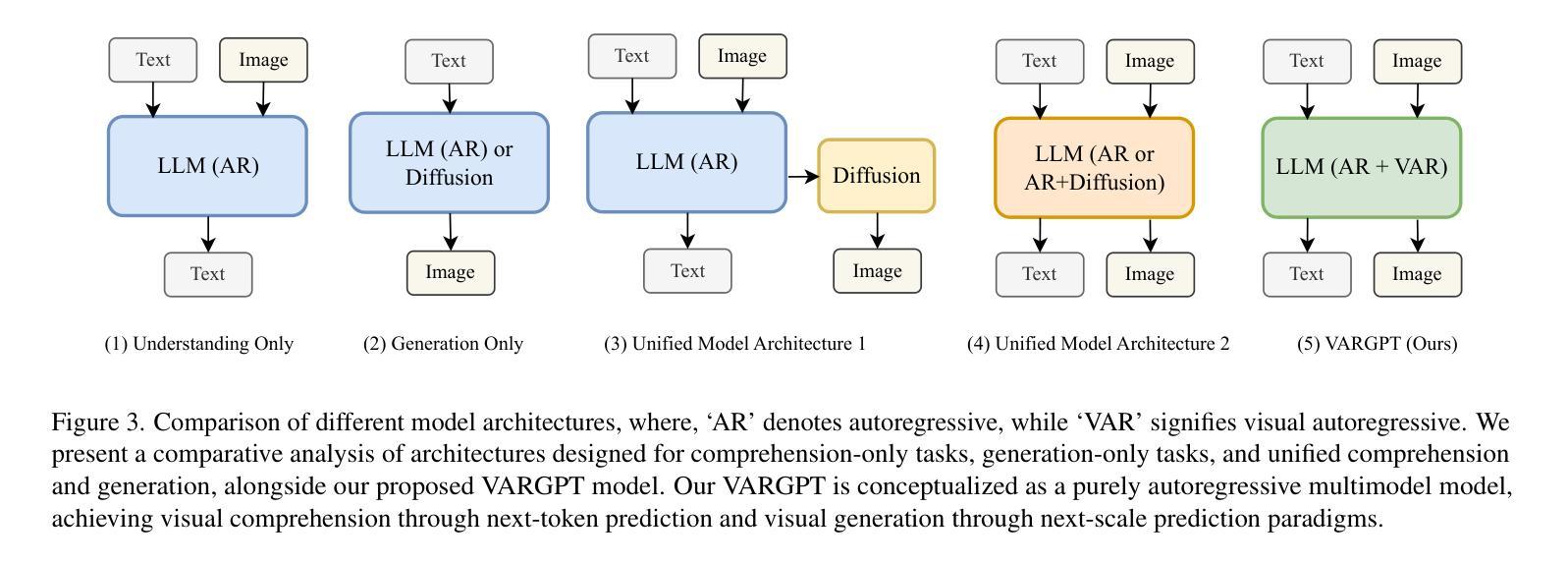
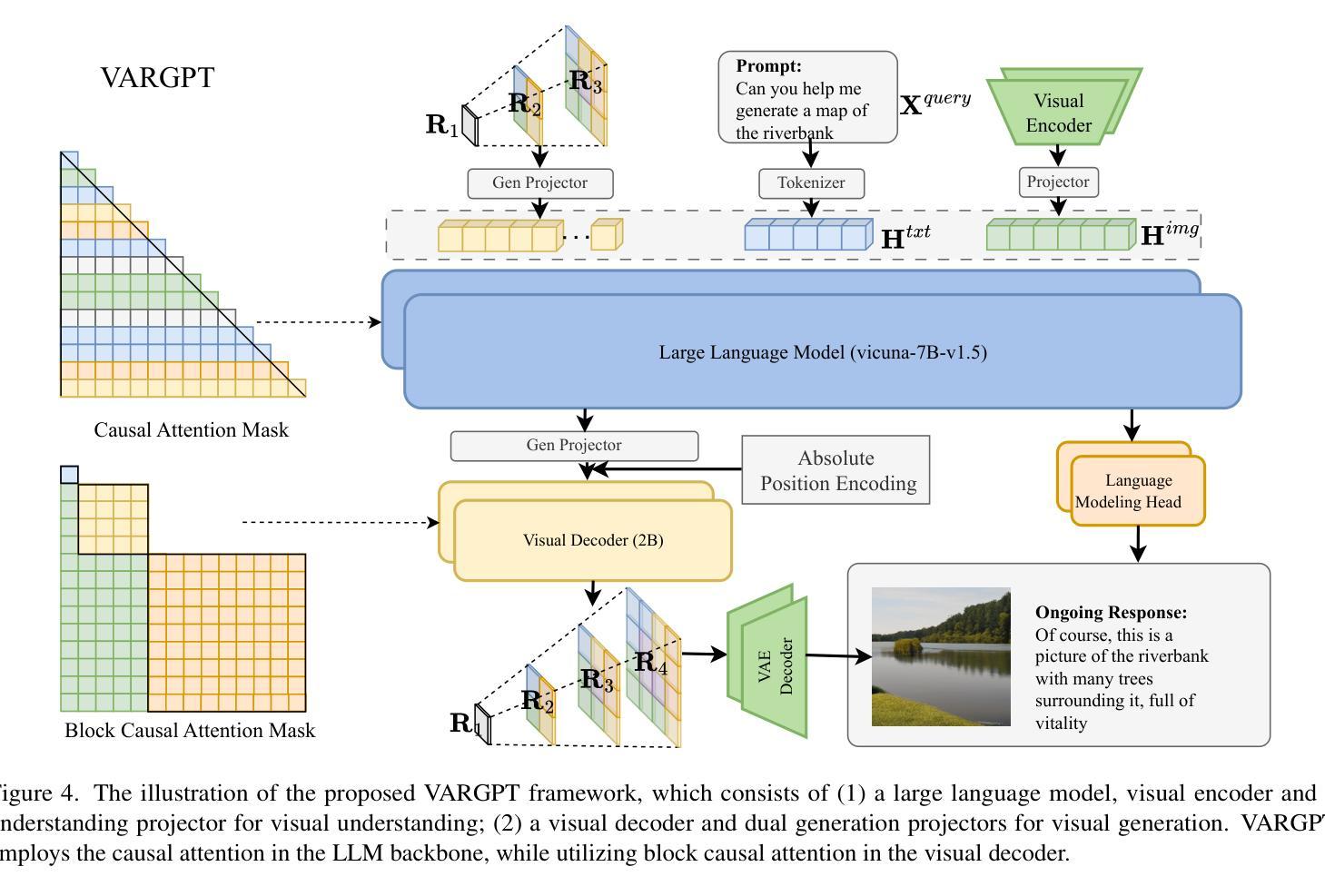
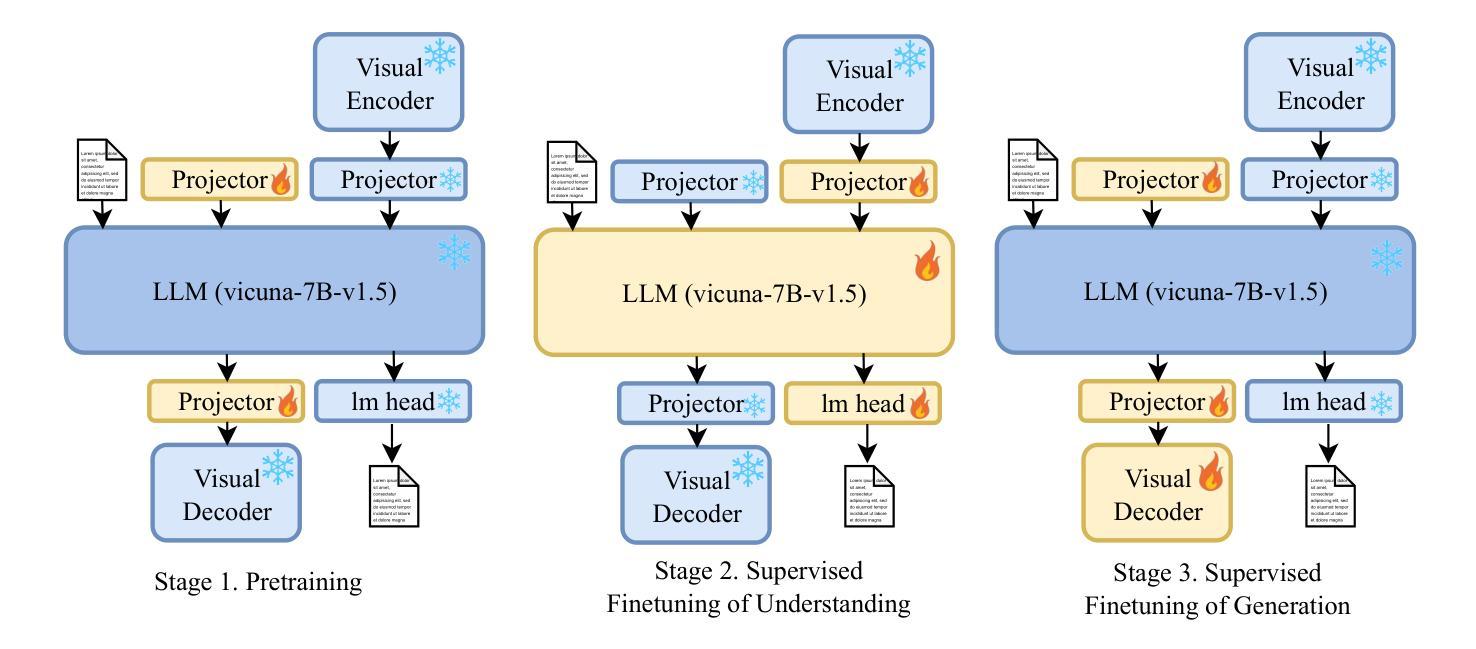
VARGPT: Unified Understanding and Generation in a Visual Autoregressive Multimodal Large Language Model
Authors:Xianwei Zhuang, Yuxin Xie, Yufan Deng, Liming Liang, Jinghan Ru, Yuguo Yin, Yuexian Zou
We present VARGPT, a novel multimodal large language model (MLLM) that unifies visual understanding and generation within a single autoregressive framework. VARGPT employs a next-token prediction paradigm for visual understanding and a next-scale prediction paradigm for visual autoregressive generation. VARGPT innovatively extends the LLaVA architecture, achieving efficient scale-wise autoregressive visual generation within MLLMs while seamlessly accommodating mixed-modal input and output within a single model framework. Our VARGPT undergoes a three-stage unified training process on specially curated datasets, comprising a pre-training phase and two mixed visual instruction-tuning phases. The unified training strategy are designed to achieve alignment between visual and textual features, enhance instruction following for both understanding and generation, and improve visual generation quality, respectively. Despite its LLAVA-based architecture for multimodel understanding, VARGPT significantly outperforms LLaVA-1.5 across various vision-centric benchmarks, such as visual question-answering and reasoning tasks. Notably, VARGPT naturally supports capabilities in autoregressive visual generation and instruction-to-image synthesis, showcasing its versatility in both visual understanding and generation tasks. Project page is at: \url{https://vargpt-1.github.io/}
我们提出了VARGPT,这是一种新型的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),它在一个单一的自回归框架内统一了视觉理解和生成。VARGPT采用下一个令牌预测范式进行视觉理解,并采用下一个尺度预测范式进行视觉自回归生成。VARGPT创新地扩展了LLaVA架构,在MLLMs中实现了高效的尺度自回归视觉生成,同时在一个模型框架中无缝地容纳了混合模态的输入和输出。我们的VARGPT在专门定制的数据集上经历了三阶段统一训练过程,包括预训练阶段和两个混合视觉指令调整阶段。统一训练策略旨在实现视觉和文本特征的对齐,增强理解和生成方面的指令遵循能力,以及提高视觉生成质量。尽管其基于LLAVA的架构用于多模态理解,但VARGPT在各种以视觉为中心的基准测试中,如视觉问答和推理任务中,都显著优于LLaVA-1.5。值得注意的是,VARGPT自然地支持自回归视觉生成和指令到图像合成的功能,展示了其在视觉理解和生成任务中的通用性。项目页面位于:[https://vargpt-1.github.io/]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
VARGPT是一种新型的多模态大语言模型,它将视觉理解和生成统一在一个单一的自回归框架内。它采用下一个令牌预测范式进行视觉理解,并采用下一个尺度预测范式进行视觉自回归生成。VARGPT创新地扩展了LLaVA架构,实现了MLLM内的有效尺度自回归视觉生成,同时在一个模型框架内无缝地容纳混合模态的输入和输出。VARGPT经历了在专门设计的数据集上的三阶段统一训练过程,包括预训练阶段和两个混合视觉指令调整阶段。其设计旨在实现视觉和文本特征的对齐,增强理解和生成方面的指令遵循能力,并提高视觉生成质量。与LLaVA-1.5相比,VARGPT在各种以视觉为中心的基准测试中表现出显著优势,如视觉问答和推理任务。此外,VARGPT自然地支持自回归视觉生成和指令到图像的合成能力,展示其在视觉理解和生成任务中的通用性。
Key Takeaways
- VARGPT是一个多模态大语言模型,结合了视觉理解和生成。
- 它采用下一令牌/尺度预测范式进行视觉理解和生成。
- VARGPT扩展了LLaVA架构,实现了在单一模型内的多模态输入和输出。
- VARGPT经历了三阶段的统一训练过程,包括预训练和两个混合视觉指令调整阶段。
- VARGPT实现了视觉和文本特征的对齐,增强了指令遵循能力,提高了视觉生成质量。
- 与LLaVA-1.5相比,VARGPT在视觉问答和推理等任务上表现更优秀。
点此查看论文截图



MoGERNN: An Inductive Traffic Predictor for Unobserved Locations in Dynamic Sensing Networks
Authors:Qishen Zhou, Yifan Zhang, Michail A. Makridis, Anastasios Kouvelas, Yibing Wang, Simon Hu
Given a partially observed road network, how can we predict the traffic state of unobserved locations? While deep learning approaches show exceptional performance in traffic prediction, most assume sensors at all locations of interest, which is impractical due to financial constraints. Furthermore, these methods typically require costly retraining when sensor configurations change. We propose MoGERNN, an inductive spatio-temporal graph representation model, to address these challenges. Inspired by the Mixture of Experts approach in Large Language Models, we introduce a Mixture of Graph Expert (MoGE) block to model complex spatial dependencies through multiple graph message aggregators and a sparse gating network. This block estimates initial states for unobserved locations, which are then processed by a GRU-based Encoder-Decoder that integrates a graph message aggregator to capture spatio-temporal dependencies and predict future states. Experiments on two real-world datasets show MoGERNN consistently outperforms baseline methods for both observed and unobserved locations. MoGERNN can accurately predict congestion evolution even in areas without sensors, offering valuable information for traffic management. Moreover, MoGERNN is adaptable to dynamic sensing networks, maintaining competitive performance even compared to its retrained counterpart. Tests with different numbers of available sensors confirm its consistent superiority, and ablation studies validate the effectiveness of its key modules.
对于部分观测的路网,我们如何预测未观测位置的交通状态?虽然深度学习方法在交通预测方面表现出卓越的性能,但大多数方法都假设所有感兴趣的位置都有传感器,这在财务上是不切实际的。此外,当传感器配置发生变化时,这些方法通常需要昂贵的重新训练。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了MoGERNN,这是一种归纳式时空图表示模型。受大型语言模型中专家混合方法的启发,我们引入了图专家混合(MoGE)块,通过多个图消息聚合器和稀疏门控网络来建模复杂的空间依赖性。该块估计未观测位置的初始状态,然后通过一个基于GRU的编码器-解码器进行处理,该编码器-解码器集成了图消息聚合器来捕捉时空依赖性并预测未来状态。在两个真实世界数据集上的实验表明,MoGERNN在观测和未观测位置上的表现均持续超越基准方法。MoGERNN即使在无传感器的地区也能准确预测拥堵演变,为交通管理提供了有价值的信息。此外,MoGERNN能够适应动态传感网络,即使在重新训练的情况下也保持了竞争力。不同可用传感器数量的测试证实了其始终出色的性能,而消融研究验证了其关键模块的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于部分观测的路网数据,如何预测未观测位置的交通状态?本文提出MoGERNN模型,采用归纳性时空图表示方法应对挑战。受大型语言模型中专家混合方法的启发,引入图专家混合(MoGE)模块建模复杂的空间依赖性,并结合稀疏门控网络进行初始状态估计。未观测位置的初始状态进一步由基于GRU的编码器解码器处理,结合图消息聚合器捕捉时空依赖性并进行未来状态预测。实验表明,MoGERNN在观测和未观测位置均优于基准方法,能准确预测无传感器区域的拥堵演变,对交通管理具有实用价值。此外,MoGERNN能够适应动态传感网络,即使与重新训练的模型相比也保持竞争力。不同传感器数量的测试验证了其持续优势,而消融研究也验证了其关键模块的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出MoGERNN模型,利用归纳性时空图表示方法预测交通状态。
- MoGE模块用于建模复杂的空间依赖性,结合稀疏门控网络进行初始状态估计。
- GRU-based Encoder-Decoder结合图消息聚合器捕捉时空依赖性并进行预测。
- MoGERNN在观测和未观测位置均表现出优于基准方法的性能。
- MoGERNN能准确预测无传感器区域的拥堵演变,对交通管理有实用价值。
- MoGERNN适应动态传感网络,性能稳定。
点此查看论文截图


InsTALL: Context-aware Instructional Task Assistance with Multi-modal Large Language Models
Authors:Pha Nguyen, Sailik Sengupta, Girik Malik, Arshit Gupta, Bonan Min
The improved competence of generative models can help building multi-modal virtual assistants that leverage modalities beyond language. By observing humans performing multi-step tasks, one can build assistants that have situational awareness of actions and tasks being performed, enabling them to cater assistance based on this understanding. In this paper, we develop a Context-aware Instructional Task Assistant with Multi-modal Large Language Models (InsTALL) that leverages an online visual stream (e.g. a user’s screen share or video recording) and responds in real-time to user queries related to the task at hand. To enable useful assistance, InsTALL 1) trains a multi-modal model on task videos and paired textual data, and 2) automatically extracts task graph from video data and leverages it at training and inference time. We show InsTALL achieves state-of-the-art performance across proposed sub-tasks considered for multimodal activity understanding – task recognition (TR), action recognition (AR), next action prediction (AP), and plan prediction (PP) – and outperforms existing baselines on two novel sub-tasks related to automatic error identification.
提高生成模型的竞争力有助于构建利用多种语言之外的模态的多模态虚拟助理。通过观察人类执行多任务,可以构建对正在执行的动作和任务有情境意识的助理,使它们能够根据这种理解提供协助。在本文中,我们开发了一种基于多模态大型语言模型的上下文感知任务助理(InsTALL)。它利用在线视频流(例如用户的屏幕共享或视频录制),实时响应用户与当前任务相关的查询。为了实现有用的帮助功能,InsTALL 1)在任务视频和配对文本数据上训练多模态模型;2)自动从视频数据中提取任务图,并在训练和推理时使用它。我们证明InsTALL在处理提议的多模态活动理解的子任务上取得了最先进的性能——任务识别(TR)、动作识别(AR)、下一步动作预测(AP)和计划预测(PP)——并且在两个与自动错误识别相关的两个新子任务上优于现有基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
改进后的生成模型有助于构建利用多种模态(超越语言)的多模态虚拟助理。通过观察人类执行多任务,可以构建具有情境意识的助理,了解正在执行的动作和任务,并根据这种理解提供协助。本文开发了利用在线视频流(如用户屏幕共享或视频录制)的基于多模态大语言模型的情境感知任务助理(InsTALL),并实时响应与当前任务相关的用户查询。为了实现有用的协助,InsTALL 1) 在任务视频和配对文本数据上训练多模态模型,2) 自动从视频数据中提取任务图并在训练和推理时使用。研究表明,InsTALL在多模态活动理解的相关子任务上实现了最先进的性能,包括任务识别(TR)、动作识别(AR)、下一个动作预测(AP)和计划预测(PP),并在两个新的子任务上的基线表现出色。能够在自动化错误识别方面提供卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型的改进有助于构建多模态虚拟助理,这些助理能够理解并响应多种模态的信息,而不仅仅是语言。
- 通过观察人类执行多任务,虚拟助理可以获得情境意识,从而更好地理解并响应人类的动作和任务需求。
- InsTALL系统利用在线视频流提供实时任务相关的虚拟助理服务。
- InsTALL系统通过训练多模态模型和在训练和推理时自动提取任务图来实现有效协助。
- InsTALL在多模态活动理解的多个子任务上实现了最先进的性能。
- InsTALL在自动错误识别方面的性能优异。
点此查看论文截图







CDW-CoT: Clustered Distance-Weighted Chain-of-Thoughts Reasoning
Authors:Yuanheng Fang, Guoqing Chao, Wenqiang Lei, Shaobo Li, Dianhui Chu
Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently achieved impressive results in complex reasoning tasks through Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting. However, most existing CoT methods rely on using the same prompts, whether manually designed or automatically generated, to handle the entire dataset. This one-size-fits-all approach may fail to meet the specific needs arising from the diversities within a single dataset. To solve this problem, we propose the Clustered Distance-Weighted Chain of Thought (CDW-CoT) method, which dynamically constructs prompts tailored to the characteristics of each data instance by integrating clustering and prompt optimization techniques. Our method employs clustering algorithms to categorize the dataset into distinct groups, from which a candidate pool of prompts is selected to reflect the inherent diversity within the dataset. For each cluster, CDW-CoT trains the optimal prompt probability distribution tailored to their specific characteristics. Finally, it dynamically constructs a unique prompt probability distribution for each test instance, based on its proximity to cluster centers, from which prompts are selected for reasoning. CDW-CoT consistently outperforms traditional CoT methods across six datasets, including commonsense, symbolic, and mathematical reasoning tasks. Specifically, when compared to manual CoT, CDW-CoT achieves an average accuracy improvement of 25.34% on LLaMA2 (13B) and 15.72% on LLaMA3 (8B).
大型语言模型(LLM)最近通过思维链(CoT)提示法在复杂的推理任务中取得了令人印象深刻的结果。然而,大多数现有的CoT方法都依赖于使用相同的提示,无论是手动设计还是自动生成的,来处理整个数据集。这种一刀切的方法可能无法满足由单一数据集内部多样性产生的特定需求。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了聚类距离加权思维链(CDW-CoT)方法,它通过集成聚类和提示优化技术,动态构建适应每个数据实例特性的提示。我们的方法使用聚类算法将数据集分成不同的组,从中选择候选提示池来反映数据集的固有多样性。对于每个集群,CDW-CoT训练与其特定特征相匹配的优化提示概率分布。最后,它基于测试实例与簇中心的接近程度,动态构建每个测试实例的唯一提示概率分布,并从中选择提示进行推理。在包括常识、符号和数学推理任务在内的六个数据集上,CDW-CoT始终优于传统CoT方法。具体来说,与手动CoT相比,CDW-CoT在LLaMA2(13B)上的平均准确率提高了25.34%,在LLaMA3(8B)上提高了15.72%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF aaai25(poster)
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过链式思维(CoT)提示在复杂推理任务中取得了显著成果。然而,现有的大多数CoT方法使用相同的手工设计或自动生成的提示来处理整个数据集,这种一刀切的方法可能无法满足单一数据集内部产生的特定需求。为解决此问题,我们提出了聚类距离加权链式思维(CDW-CoT)方法,它通过集成聚类和提示优化技术,根据每个数据实例的特性动态构建针对性的提示。CDW-CoT通过聚类算法将数据集分成不同的组,并从中选择提示候选池来反映数据集的内在多样性。针对每个集群,CDW-CoT训练与其特定特征相匹配的优化提示概率分布。最后,它基于测试实例与集群中心的接近程度,动态构建独特的提示概率分布,并从中选择提示进行推理。在六个数据集上,CDW-CoT持续优于传统CoT方法,特别是在常识、符号和数学推理任务中表现更出色。与手动CoT相比,CDW-CoT在LLaMA2(13B)和LLaMA3(8B)上的平均准确度分别提高了25.34%和15.72%。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs通过CoT提示在复杂推理任务中表现出色。
- 现有CoT方法使用固定提示处理整个数据集,可能无法满足特定需求。
- CDW-CoT方法通过聚类算法将数据集分成不同组,并针对每组特性构建提示。
- CDW-CoT根据测试实例与集群中心的接近程度动态选择提示。
- CDW-CoT在多个数据集上表现优于传统CoT方法,特别是在常识、符号和数学推理任务中。
- 与手动CoT相比,CDW-CoT在LLaMA2和LLaMA3上的平均准确度有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图





Leveraging Large Language Models for Realizing Truly Intelligent User Interfaces
Authors:Allard Oelen, Sören Auer
The number of published scholarly articles is growing at a significant rate, making scholarly knowledge organization increasingly important. Various approaches have been proposed to organize scholarly information, including describing scholarly knowledge semantically leveraging knowledge graphs. Transforming unstructured knowledge, presented within articles, to structured and semantically represented knowledge generally requires human intelligence and labor since natural language processing methods alone typically do not render sufficient precision and recall for many applications. With the recent developments of Large Language Models (LLMs), it becomes increasingly possible to provide truly intelligent user interfaces guiding humans in the transformation process. We present an approach to integrate non-intrusive LLMs guidance into existing user interfaces. More specifically, we integrate LLM-supported user interface components into an existing scholarly knowledge infrastructure. Additionally, we provide our experiences with LLM integration, detailing best practices and obstacles. Finally, we evaluate the approach using a small-scale user evaluation with domain experts.
学术论文的发表数量正在以显著的速度增长,这使得学术知识组织变得越来越重要。为组织学术信息,已经提出了各种方法,包括利用知识图谱进行语义描述。将文章中的非结构化知识转化为结构和语义表示的知识通常需要人类智慧和劳动,因为单靠自然语言处理方法通常不能为许多应用提供足够的精度和召回率。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的最近发展,提供真正智能的用户界面指导人们完成转化过程变得越来越有可能。我们提出了一种将非侵入式LLM指导集成到现有用户界面中的方法。更具体地说,我们将LLM支持的用户界面组件集成到现有的学术知识基础设施中。此外,我们还分享了LLM集成的经验,并详细介绍了最佳实践和障碍。最后,我们通过小规模的用户评价专家评估了这种方法的效果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着学术文章数量的快速增长,学术知识组织变得越来越重要。本文提出一种利用大型语言模型(LLMs)来指导用户界面的方法,将非侵入式的LLMs指导集成到现有的学术知识基础设施中,以实现对学术信息的语义描述和组织。通过小型用户评价验证了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 学术文章数量增长迅速,学术知识组织变得重要。
- 知识图谱可用于语义描述学术知识。
- 将无结构的学术知识转化为结构和语义表示需要人类智能和劳动。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)为学术知识的转化过程提供了智能用户界面的可能性。
- 提出一种将LLMs指导集成到现有学术知识基础设施中的方法。
- LLMs集成提供了实践经验,并详细说明了最佳实践和障碍。
点此查看论文截图





You Can’t Eat Your Cake and Have It Too: The Performance Degradation of LLMs with Jailbreak Defense
Authors:Wuyuao Mai, Geng Hong, Pei Chen, Xudong Pan, Baojun Liu, Yuan Zhang, Haixin Duan, Min Yang
With the rise of generative large language models (LLMs) like LLaMA and ChatGPT, these models have significantly transformed daily life and work by providing advanced insights. However, as jailbreak attacks continue to circumvent built-in safety mechanisms, exploiting carefully crafted scenarios or tokens, the safety risks of LLMs have come into focus. While numerous defense strategies–such as prompt detection, modification, and model fine-tuning–have been proposed to counter these attacks, a critical question arises: do these defenses compromise the utility and usability of LLMs for legitimate users? Existing research predominantly focuses on the effectiveness of defense strategies without thoroughly examining their impact on performance, leaving a gap in understanding the trade-offs between LLM safety and performance. Our research addresses this gap by conducting a comprehensive study on the utility degradation, safety elevation, and exaggerated-safety escalation of LLMs with jailbreak defense strategies. We propose USEBench, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate these aspects, along with USEIndex, a comprehensive metric for assessing overall model performance. Through experiments on seven state-of-the-art LLMs, we found that mainstream jailbreak defenses fail to ensure both safety and performance simultaneously. Although model-finetuning performs the best overall, their effectiveness varies across LLMs. Furthermore, vertical comparisons reveal that developers commonly prioritize performance over safety when iterating or fine-tuning their LLMs.
随着类似LLaMA和ChatGPT的生成式大型语言模型(LLM)的兴起,这些模型通过提供高级洞察显著地改变了日常生活和工作。然而,随着越狱攻击继续绕过内置的安全机制,利用精心策划的场景或令牌,LLM的安全风险已成为关注的焦点。虽然提出了许多防御策略,如提示检测、修改和模型微调,来应对这些攻击,但一个问题出现了:这些防御措施是否损害LLM对合法用户的实用性和可用性?现有研究主要集中在防御策略的有效性上,而没有彻底研究它们对性能的影响,因此在对LLM安全与性能之间的权衡方面存在理解上的空白。我们的研究通过一项综合研究来填补这一空白,包括研究实用程序降级、安全提升和具有越狱防御策略的LLM的过度安全升级。我们提出了USEBench,这是一个用于评估这些方面的新型基准测试,以及USEIndex,这是一个用于评估模型总体性能的全面指标。通过对七款最先进的LLM进行实验,我们发现主流的越狱防御无法保证同时实现安全和性能。尽管模型微调总体上表现最佳,但它们在LLM之间的效果各不相同。此外,垂直对比表明,开发人员在迭代或微调其LLM时通常会优先考虑性能而非安全。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着生成式大型语言模型(LLM)如LLaMA和ChatGPT的兴起,这些模型为日常生活和工作提供了深刻的见解,但安全漏洞问题也逐渐凸显。尽管已有许多防御策略如提示检测、修改和模型微调等被提出以应对攻击,但防御措施是否会影响模型的实用性和用户友好性成为关键问题。我们的研究旨在填补这一缺口,探讨防御措施导致的语言模型效用下降、安全性提升和夸大安全性的问题。通过在一系列先进的LLM上进行实验,我们发现主流的安全防护措施无法在保障安全性和性能之间取得平衡。模型微调整体表现最佳,但不同语言模型之间存在差异。垂直对比表明,在迭代或微调LLM时,开发人员通常优先考虑性能而非安全性。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式大型语言模型(LLM)如LLaMA和ChatGPT为日常生活和工作提供了先进的见解。
- LLM的安全漏洞问题逐渐凸显,存在被精心设计的场景或令牌利用的风险。
- 目前有许多防御策略来应对LLM的安全攻击,但对防御策略的实施对模型性能和实用性的影响的研究存在空白。
- 我们的研究旨在探讨防御措施导致的语言模型效用下降、安全性提升和夸大安全性的问题。
- 主流的安全防护措施无法在保障安全性和性能之间取得平衡。
- 模型微调是表现最佳的防御策略之一,但不同语言模型之间存在差异。
点此查看论文截图





AdaServe: SLO-Customized LLM Serving with Fine-Grained Speculative Decoding
Authors:Zikun Li, Zhuofu Chen, Remi Delacourt, Gabriele Oliaro, Zeyu Wang, Qinghan Chen, Shuhuai Lin, April Yang, Zhihao Zhang, Zhuoming Chen, Sean Lai, Xupeng Miao, Zhihao Jia
This paper introduces AdaServe, the first LLM serving system to support SLO customization through fine-grained speculative decoding. AdaServe leverages the logits of a draft model to predict the speculative accuracy of tokens and employs a theoretically optimal algorithm to construct token trees for verification. To accommodate diverse SLO requirements without compromising throughput, AdaServe employs a speculation-and-selection scheme that first constructs candidate token trees for each request and then dynamically selects tokens to meet individual SLO constraints while optimizing throughput. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that AdaServe achieves up to 73% higher SLO attainment and 74% higher goodput compared to state-of-the-art systems. These results underscore AdaServe’s potential to enhance the efficiency and adaptability of LLM deployments across varied application scenarios.
本文介绍了AdaServe,它是第一个支持通过精细粒度的推测解码进行SLO定制的大型语言模型服务系统。AdaServe利用草案模型的logits来预测符号的推测准确性,并采用理论上的最优算法构建符号树进行验证。为了适应各种SLO要求而不影响吞吐量,AdaServe采用了一种推测和选择方案,该方案首先为每个请求构建候选符号树,然后动态选择符号以满足个别的SLO约束,同时优化吞吐量。综合评估表明,与最新系统相比,AdaServe的SLO达成度提高了高达73%,goodput提高了74%。这些结果强调了AdaServe在不同应用场景中提高大型语言模型部署效率和适应性的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了AdaServe系统,它是首个支持SLO定制的大语言模型服务系统,通过精细的推测解码提供服务。AdaServe利用模型草案的logits预测标记的推测准确性,并采用理论上的最佳算法构建用于验证的标记树。为了满足不同的SLO要求而不影响吞吐量,AdaServe采用推测和选择方案,为每个请求构建候选标记树,然后动态选择标记以满足单独的SLO约束,同时优化吞吐量。综合评估表明,AdaServe的SLO达成度比现有系统高出高达73%,goodput高出74%。这突显了AdaServe在不同应用场景中提高LLM部署效率和适应性的潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- AdaServe是首个支持SLO定制的大语言模型服务系统。
- AdaServe通过精细的推测解码提供服务,利用模型草案的logits预测标记的推测准确性。
- AdaServe采用理论上的最佳算法构建用于验证的标记树。
- AdaServe通过构建候选标记树并动态选择标记以满足SLO约束和吞吐量优化来满足不同SLO要求。
- AdaServe与现有系统相比,SLO达成度提高了高达73%,goodput提高了74%。
- AdaServe提高了大语言模型部署的效率和适应性。
点此查看论文截图




Improving Influence-based Instruction Tuning Data Selection for Balanced Learning of Diverse Capabilities
Authors:Qirun Dai, Dylan Zhang, Jiaqi W. Ma, Hao Peng
Selecting appropriate training data is crucial for effective instruction fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs), which aims to (1) elicit strong capabilities, and (2) achieve balanced performance across a diverse range of tasks. Influence-based methods show promise in achieving (1) by estimating the contribution of each training example to the model’s predictions, but often struggle with (2). Our systematic investigation reveals that this underperformance can be attributed to an inherent bias where certain tasks intrinsically have greater influence than others. As a result, data selection is often biased towards these tasks, not only hurting the model’s performance on others but also, counterintuitively, harms performance on these high-influence tasks themselves. As a remedy, we propose BIDS, a Balanced and Influential Data Selection algorithm. BIDS first normalizes influence scores of the training data, and then iteratively balances data selection by choosing the training example with the highest influence on the most underrepresented task. Experiments with both Llama-3 and Mistral-v0.3 on seven benchmarks spanning five diverse capabilities show that BIDS consistently outperforms both state-of-the-art influence-based algorithms and other non-influence-based selection frameworks. Surprisingly, training on a 15% subset selected by BIDS can even outperform full-dataset training with a much more balanced performance. Our analysis further highlights the importance of both instance-level normalization and iterative optimization of selected data for balanced learning of diverse capabilities.
选择适当的训练数据对于大型语言模型(LLM)的有效指令微调至关重要,其旨在(1)激发强大的能力,以及(2)在多种任务上实现平衡的性能。基于影响的方法在通过估计每个训练样本对模型预测的贡献来实现(1)方面显示出希望,但往往难以应对(2)。我们的系统调查表明,这种性能不佳可归因于一种固有偏见,即某些任务天生比其他任务具有更大的影响力。因此,数据选择往往偏向于这些任务,这不仅会损害模型在其他任务上的表现,而且出人意料的是,还会损害这些高影响力任务本身的性能。作为一种补救措施,我们提出了BIDS(平衡和影响数据选择算法)。BIDS首先标准化训练数据的影响分数,然后通过选择对最不具代表性的任务具有最高影响的训练样本来迭代平衡数据选择。在七个基准测试上的Llama-3和Mistral-v0.3实验,涵盖了五种不同的能力,表明BIDS始终优于最新的基于影响力和其他非影响力选择框架的算法。令人惊讶的是,通过BIDS选择的15%子集进行训练甚至可以超越全数据集训练的性能,且表现更为平衡。我们的分析进一步强调了实例级标准化和迭代优化所选数据在平衡学习多种能力方面的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
训练数据的选择对于大型语言模型(LLM)的有效指令微调至关重要,旨在(1)激发强大的能力,并(2)在多种任务上实现平衡性能。基于影响的方法在实现(1)方面显示出希望,通过估计每个训练样本对模型预测的贡献,但往往难以兼顾(2)。我们的系统调查表明,这种性能不佳可归因于固有偏见,某些任务的影响天生较大。因此,数据选择往往偏向于这些任务,这不仅会损害模型在其他任务上的表现,而且会出乎意料地损害这些高影响力任务本身的表现。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了BIDS算法,这是一种平衡和有影响力的数据选择算法。BIDS首先标准化训练数据的影响力分数,然后通过选择对最代表性不足的任务具有最高影响力的训练样本来进行迭代平衡数据选择。在Llama-3和Mistral-v0.3上的七个基准测试,涵盖五种不同能力的实验表明,BIDS始终优于最新影响算法和其他非影响选择框架。令人惊讶的是,通过BIDS选择的子集仅占整体的15%,但其训练效果甚至可以超越全数据集训练,且性能更为平衡。我们的分析进一步强调了实例级标准化以及优化选定数据的迭代选择对于平衡学习不同能力的重要性。
关键见解
- 训练数据的选择对于大型语言模型的指令微调至关重要。
- 基于影响的方法在评估训练样本对模型预测的贡献方面显示出潜力,但在实现跨任务平衡性能时遇到困难。
- 某些任务在数据选择中可能存在固有偏见,影响数据选择的平衡性。
- BIDS算法通过标准化影响力分数和迭代平衡数据选择来解决这一问题。
- BIDS算法在多个基准测试上表现出优异的性能,甚至在小规模数据子集上也能超越全数据集训练。
- 实例级标准化对平衡学习不同能力至关重要。
点此查看论文截图




Harnessing Generative Pre-Trained Transformer for Datacenter Packet Trace Generation
Authors:Chen Griner
Today, the rapid growth of applications reliant on datacenters calls for new advancements to meet the increasing traffic and computational demands. Traffic traces from datacenters are essential for further development and optimization of future datacenters. However, traces are rarely released to the public. Researchers often use simplified mathematical models that lack the depth needed to recreate intricate traffic patterns and, thus, miss optimization opportunities found in realistic traffic. In this preliminary work, we introduce DTG-GPT, a packet-level Datacenter Traffic Generator (DTG), based on the generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) architecture used by many state-of-the-art large language models. We train our model on a small set of available traffic traces from different domains and offer a simple methodology to evaluate the fidelity of the generated traces to their original counterparts. We show that DTG-GPT can synthesize novel traces that mimic the spatiotemporal patterns found in real traffic traces. We further demonstrate that DTG-GPT can generate traces for networks of different scales while maintaining fidelity. Our findings indicate the potential that, in the future, similar models to DTG-GPT will allow datacenter operators to release traffic information to the research community via trained GPT models.
当今,依赖于数据中心的应用程序的快速增长要求新的进展以满足日益增长的流量和计算需求。数据中心的流量跟踪对于未来数据中心的进一步发展和优化至关重要。然而,这些跟踪很少公开发布。研究人员通常使用简化的数学模型,这些模型缺乏所需的深度,无法重现复杂的流量模式,从而错过了现实流量中发现的优化机会。在这项初步工作中,我们介绍了基于生成预训练转换器(GPT)架构的数据中心流量生成器(DTG-GPT),该架构被许多最先进的大型语言模型所采用。我们对不同领域可用的少量流量跟踪数据进行训练模型,并提供了一种简单的方法来评估生成跟踪与其原始对应物的保真度。我们表明,DTG-GPT可以合成模仿真实流量跟踪中时空模式的新型跟踪。我们进一步证明,DTG-GPT可以在保持保真度的同时,为不同规模的网络生成跟踪。我们的研究结果表明,未来类似DTG-GPT的模型将允许数据中心运营商通过训练的GPT模型向研究社区发布流量信息。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据中心的应用快速发展,产生了巨大的流量和计算需求。研究人员通常依赖简化的数学模型,无法重现真实流量模式中的机会,需要进行进一步的发展和优化。本工作介绍了基于GPT架构的数据中心流量生成器DTG-GPT,可以合成模拟真实流量模式的流量轨迹,并展示其在不同规模网络中的适用性。
Key Takeaways
- 数据中心应用的快速发展导致对流量和计算需求的增加。
- 流量轨迹对于数据中心的发展和优化至关重要。
- 现有的流量轨迹很少公开,研究人员通常使用简化的数学模型,这限制了优化机会。
- DTG-GPT是一种基于GPT架构的数据中心流量生成器,能够生成模拟真实流量模式的流量轨迹。
- DTG-GPT提供了一种简单的方法论来评估生成轨迹与原始轨迹的保真度。
- DTG-GPT能够在不同规模的网络中生成流量轨迹,并保持较高的保真度。
点此查看论文截图




Trustformer: A Trusted Federated Transformer
Authors:Ali Abbasi Tadi, Dima Alhadidi, Luis Rueda
Transformers, a cornerstone of deep-learning architectures for sequential data, have achieved state-of-the-art results in tasks like Natural Language Processing (NLP). Models such as BERT and GPT-3 exemplify their success and have driven the rise of large language models (LLMs). However, a critical challenge persists: safeguarding the privacy of data used in LLM training. Privacy-preserving techniques like Federated Learning (FL) offer potential solutions, but practical limitations hinder their effectiveness for Transformer training. Two primary issues are (I) the risk of sensitive information leakage due to aggregation methods like FedAvg or FedSGD, and (II) the high communication overhead caused by the large size of Transformer models. This paper introduces a novel FL method that reduces communication overhead while maintaining competitive utility. Our approach avoids sharing full model weights by simulating a global model locally. We apply k-means clustering to each Transformer layer, compute centroids locally, and transmit only these centroids to the server instead of full weights or gradients. To enhance security, we leverage Intel SGX for secure transmission of centroids. Evaluated on a translation task, our method achieves utility comparable to state-of-the-art baselines while significantly reducing communication costs. This provides a more efficient and privacy-preserving FL solution for Transformer models.
Transformer是序列数据深度学习架构的基石,在自然语言处理(NLP)等任务中取得了最新技术成果。BERT和GPT-3等模型体现了其成功,并推动了大型语言模型(LLM)的崛起。然而,仍存在一项关键挑战:保护用于LLM训练的数据隐私。联邦学习(FL)等隐私保护技术提供了潜在的解决方案,但实际应用中的限制阻碍了其在Transformer训练中的有效性。两个问题主要是(I)由于FedAvg或FedSGD等聚合方法导致的敏感信息泄露风险,(II)由于Transformer模型规模较大导致的通信开销较高。本文介绍了一种新型的FL方法,该方法在保持竞争力的同时减少了通信开销。我们的方法通过在本地模拟全局模型,避免共享完整的模型权重。我们对每个Transformer层应用k-means聚类,本地计算质心,并将这些质心而不是完整的权重或梯度传输到服务器。为了提高安全性,我们利用Intel SGX进行质心的安全传输。在翻译任务上评估,我们的方法达到了与最新技术基线相当的效果,同时显著降低了通信成本。这为Transformer模型的联邦学习提供了更高效、更保护隐私的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型联邦学习(Federated Learning,FL)方法,旨在减少训练Transformer模型时的通信开销并保护数据隐私。该方法通过模拟全局模型进行本地训练,利用k-means聚类计算各Transformer层的质心,仅传输这些质心到服务器,同时采用Intel SGX技术保障安全传输。在翻译任务上的评估显示,该方法在保证性能的同时显著降低了通信成本,为Transformer模型提供高效且隐私保护的联邦学习解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer模型在自然语言处理任务中取得了卓越的性能,但数据隐私保护仍是其面临的关键挑战。
- 传统的隐私保护技术如联邦学习在Transformer训练中存在局限性,面临着信息泄露和通信开销问题。
- 本文提出了一种新型的联邦学习方法,通过模拟全局模型进行本地训练来减少通信开销。
- 该方法利用k-means聚类计算Transformer各层的质心,并仅传输这些质心到服务器,降低了通信成本。
- 为了增强安全性,该方法采用Intel SGX技术保障质心的安全传输。
- 在翻译任务上的评估显示,该方法在保证性能的同时显著降低了通信成本。
点此查看论文截图




Question-to-Question Retrieval for Hallucination-Free Knowledge Access: An Approach for Wikipedia and Wikidata Question Answering
Authors:Santhosh Thottingal
This paper introduces an approach to question answering over knowledge bases like Wikipedia and Wikidata by performing “question-to-question” matching and retrieval from a dense vector embedding store. Instead of embedding document content, we generate a comprehensive set of questions for each logical content unit using an instruction-tuned LLM. These questions are vector-embedded and stored, mapping to the corresponding content. Vector embedding of user queries are then matched against this question vector store. The highest similarity score leads to direct retrieval of the associated article content, eliminating the need for answer generation. Our method achieves high cosine similarity ( > 0.9 ) for relevant question pairs, enabling highly precise retrieval. This approach offers several advantages including computational efficiency, rapid response times, and increased scalability. We demonstrate its effectiveness on Wikipedia and Wikidata, including multimedia content through structured fact retrieval from Wikidata, opening up new pathways for multimodal question answering.
本文介绍了一种在知识库(如Wikipedia和Wikidata)上进行问答的方法,通过执行“问题到问题”的匹配和从密集向量嵌入存储库中进行检索来实现。我们不是嵌入文档内容,而是使用指令调整的大型语言模型(LLM)为每个逻辑内容单元生成一组全面的问题。这些问题被向量嵌入并存储,映射到相应的内容。然后,将用户查询的向量嵌入与此问题向量存储库进行匹配。最高相似度得分直接导致直接检索相关的文章内容,无需生成答案。我们的方法实现了相关问题对的高余弦相似度(> 0.9),能够实现高度精确的检索。这种方法提供了几个优点,包括计算效率高、响应速度快和可扩展性强。我们在Wikipedia和Wikidata上展示了其有效性,包括通过从Wikidata进行结构化事实检索来包含多媒体内容,为多媒体问答开辟了新途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
论文介绍了一种通过执行“问题到问题”匹配和从密集向量嵌入存储中进行检索,实现基于知识库(如Wikipedia和Wikidata)的问题回答的方法。该方法不嵌入文档内容,而是为逻辑内容单元生成一组问题并使用大型语言模型(LLM)调整指令。这些问题进行向量嵌入并存储,映射到对应的内容。然后匹配用户查询的向量嵌入与问题向量存储。最高相似度得分可直接检索相关文章内容,无需生成答案。该方法实现了高余弦相似性(> 0.9),为Wikipedia和Wikidata等多媒体内容提供了高效、快速响应和高度可扩展的精准检索方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 该方法通过执行“问题到问题”匹配和从密集向量嵌入存储中检索,实现了基于知识库的问题回答。
- 方法不嵌入文档内容,而是为逻辑内容单元生成一组问题并使用LLM调整指令。
- 通过匹配用户查询与问题向量存储,实现直接检索相关文章内容。
- 该方法实现了高余弦相似性(> 0.9),提高了检索的精准度。
- 方法具有计算效率高、响应速度快和可扩展性强的优点。
- 该方法在Wikipedia和Wikidata等多媒体内容上展示了有效性。
点此查看论文截图





Robust Hybrid Classical-Quantum Transfer Learning Model for Text Classification Using GPT-Neo 125M with LoRA & SMOTE Enhancement
Authors:Santanam Wishal
This research introduces a hybrid classical-quantum framework for text classification, integrating GPT-Neo 125M with Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) using quantum computing backends. While the GPT-Neo 125M baseline remains the best-performing model, the implementation of LoRA and SMOTE enhances the hybrid model, resulting in improved accuracy, faster convergence, and better generalization. Experiments on IBM’s 127-qubit quantum backend and Pennylane’s 32-qubit simulation demonstrate the viability of combining classical neural networks with quantum circuits. This framework underscores the potential of hybrid architectures for advancing natural language processing applications.
本研究引入了一种用于文本分类的混合经典-量子框架,该框架结合了GPT-Neo 125M与低秩适应(LoRA)和合成少数过采样技术(SMOTE),并使用量子计算后端。虽然GPT-Neo 125M基线仍然是表现最好的模型,但LoRA和SMOTE的实施增强了混合模型,提高了准确性、更快的收敛速度和更好的泛化能力。在IBM的127量子比特后端和Pennylane的32量子比特模拟上进行的实验证明了将经典神经网络与量子电路相结合是可行的。该框架强调了混合架构在推进自然语言处理应用方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 11 figures
Summary
基于量子计算后端技术的支持,本研究提出了一个融合经典与量子计算的文本分类框架。它结合了GPT-Neo 125M模型、低秩适应(LoRA)技术以及合成少数类过采样技术(SMOTE)。其中GPT-Neo 125M表现最优,结合了LoRA和SMOTE技术的混合模型在准确性、收敛速度以及泛化能力上有所提升。在IBM的127量子比特后端和Pennylane的32量子比特模拟器上进行的实验验证了结合经典神经网络与量子电路的有效性,突显了混合架构在自然语言处理应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一个融合经典与量子计算的文本分类框架。
- 该框架结合了GPT-Neo 125M模型、低秩适应(LoRA)和合成少数类过采样技术(SMOTE)。
- GPT-Neo 125M表现最优,但结合LoRA和SMOTE技术后,混合模型的性能有所提升。
- 混合模型在准确性、收敛速度和泛化能力上有所改进。
- 在IBM的量子后端和Pennylane模拟器上进行的实验验证了框架的有效性。
- 该研究突显了混合架构在自然语言处理应用中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


VITA-1.5: Towards GPT-4o Level Real-Time Vision and Speech Interaction
Authors:Chaoyou Fu, Haojia Lin, Xiong Wang, Yi-Fan Zhang, Yunhang Shen, Xiaoyu Liu, Haoyu Cao, Zuwei Long, Heting Gao, Ke Li, Long Ma, Xiawu Zheng, Rongrong Ji, Xing Sun, Caifeng Shan, Ran He
Recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have typically focused on integrating visual and textual modalities, with less emphasis placed on the role of speech in enhancing interaction. However, speech plays a crucial role in multimodal dialogue systems, and implementing high-performance in both vision and speech tasks remains a significant challenge due to the fundamental modality differences. In this paper, we propose a carefully designed multi-stage training methodology that progressively trains LLM to understand both visual and speech information, ultimately enabling fluent vision and speech interaction. Our approach not only preserves strong vision-language capacity, but also enables efficient speech-to-speech dialogue capabilities without separate ASR and TTS modules, significantly accelerating multimodal end-to-end response speed. By comparing our method against state-of-the-art counterparts across benchmarks for image, video, and speech tasks, we demonstrate that our model is equipped with both strong visual and speech capabilities, making near real-time vision and speech interaction.
最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)主要聚焦于整合视觉和文本模态,较少强调语音在增强交互中的作用。然而,语音在多模态对话系统中起着至关重要的作用。由于基本模态差异,在视觉和语音任务中实现高性能仍然是一个重大挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种精心设计的多阶段训练方法论,逐步训练LLM理解视觉和语音信息,最终使流畅的视觉和语音交互成为可能。我们的方法不仅保留了强大的视觉语言功能,还实现了高效的语音对话功能,无需使用单独的自动语音识别(ASR)和文本转语音(TTS)模块,从而大大加快了多模态端到端的响应速度。通过与图像、视频和语音任务的最新先进模型进行比较,我们证明了我们的模型具有强大的视觉和语音功能,可实现近乎实时的视觉和语音交互。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/VITA-MLLM/VITA (2K+ Stars by now)
Summary:
近期多模态大型语言模型主要融合视觉和文本模态,较少关注语音在增强交互中的作用。本文提出一种精心设计的多阶段训练策略,逐步训练大型语言模型理解视觉和语音信息,实现流畅的视听交互。该方法不仅保持强大的视觉语言处理能力,还能实现高效的语音对话能力,无需额外的语音识别和文本转语音模块,显著提高多模态端到端的响应速度。与前沿技术对比实验表明,该模型具备强大的视觉和语音功能,实现近乎实时的视听交互。
Key Takeaways:
- 近期多模态大型语言模型主要关注视觉和文本模态的融合。
- 语音在多模态对话系统中扮演重要角色,同时处理视觉和语音任务具有挑战性。
- 提出一种多阶段训练策略,使大型语言模型逐步理解视觉和语音信息。
- 训练策略实现流畅的视听交互,并具备强大的视觉语言处理能力。
- 模型具备高效的语音对话能力,无需额外的语音识别和文本转语音模块。
- 模型显著提高多模态端到端的响应速度。
点此查看论文截图





Bridging the Training-Inference Gap in LLMs by Leveraging Self-Generated Tokens
Authors:Zhepeng Cen, Yao Liu, Siliang Zeng, Pratik Chaudhari, Huzefa Rangwala, George Karypis, Rasool Fakoor
Language models are often trained to maximize the likelihood of the next token given past tokens in the training dataset. However, during inference time, they are utilized differently, generating text sequentially and auto-regressively by using previously generated tokens as input to predict the next one. Marginal differences in predictions at each step can cascade over successive steps, resulting in different distributions from what the models were trained for and potentially leading to unpredictable behavior. This paper proposes two simple approaches based on model own generation to address this discrepancy between the training and inference time. Our first approach is Batch-Scheduled Sampling, where, during training, we stochastically choose between the ground-truth token from the dataset and the model’s own generated token as input to predict the next token. This is done in an offline manner, modifying the context window by interleaving ground-truth tokens with those generated by the model. Our second approach is Reference-Answer-based Correction, where we explicitly incorporate a self-correction capability into the model during training. This enables the model to effectively self-correct the gaps between the generated sequences and the ground truth data without relying on an external oracle model. By incorporating our proposed strategies during training, we have observed an overall improvement in performance compared to baseline methods, as demonstrated by our extensive experiments using summarization, general question-answering, and math question-answering tasks.
语言模型通常经过训练,以最大化在给定的训练数据集中过去标记下一个标记的可能性。但在推理过程中,它们的使用方式不同。通过先前生成的标记来预测下一个标记,以自回归的方式连续生成文本。每一步预测中的微小差异可能会在后续步骤中累积,导致与模型训练时的分布不同,并可能导致不可预测的行为。本文针对训练和推理时间之间的差异提出了两种简单的方法来解决这一问题。第一种方法是批调度采样(Batch-Scheduled Sampling),在训练过程中,我们随机选择数据集的真实标记和模型自身生成的标记作为输入来预测下一个标记。这是离线完成的,通过交替真实标记和模型生成的标记来修改上下文窗口。第二种方法是基于参考答案的校正(Reference-Answer-based Correction),我们在训练过程中显式地将自我校正能力融入模型。这使模型能够有效地自我校正生成序列和真实数据之间的差距,而不依赖外部标准模型。通过训练过程中融入我们提出的策略,相较于基线方法,我们观察到整体性能有所提升,这在我们使用摘要、通用问答和数学问答任务进行的广泛实验中得到了验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in TMLR
Summary:
本文探讨了语言模型在训练和推理时间之间的差异,并提出了两种简单的方法来解决这一问题。第一种方法是Batch-Scheduled Sampling,它在训练过程中随机选择真实或模型生成的token作为输入进行预测。第二种方法是Reference-Answer-based Correction,它在训练过程中为模型增加自我纠错能力,从而提高生成的序列与真实数据之间的匹配度。实验表明,这两种方法均能提高语言模型的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 语言模型在训练和推理时间存在差异,可能导致不可预测的行为。
- Batch-Scheduled Sampling方法通过随机选择真实或模型生成的token进行训练,缩小了训练和推理之间的差距。
- Reference-Answer-based Correction方法训练模型时增加了自我纠错能力。
- 通过这两种方法,可以提高语言模型的性能。
- 提出的策略在总结、通用问答和数学问答任务中均表现出良好的效果。
- Batch-Scheduled Sampling是通过离线方式修改上下文窗口来实现的。
点此查看论文截图



FLARE: Faithful Logic-Aided Reasoning and Exploration
Authors:Erik Arakelyan, Pasquale Minervini, Pat Verga, Patrick Lewis, Isabelle Augenstein
Modern Question Answering (QA) and Reasoning approaches based on Large Language Models (LLMs) commonly use prompting techniques, such as Chain-of-Thought (CoT), assuming the resulting generation will have a more granular exploration and reasoning over the question space and scope. However, such methods struggle with generating outputs that are faithful to the intermediate chain of reasoning produced by the model. On the other end of the spectrum, neuro-symbolic methods such as Faithful CoT (F-CoT) propose to combine LLMs with external symbolic solvers. While such approaches boast a high degree of faithfulness, they usually require a model trained for code generation and struggle with tasks that are ambiguous or hard to formalise strictly. We introduce $\textbf{F}$aithful $\textbf{L}$ogic-$\textbf{A}$ided $\textbf{R}$easoning and $\textbf{E}$xploration ($\textbf{FLARE}$), a novel interpretable approach for traversing the problem space using task decompositions. We use the LLM to plan a solution, soft-formalise the query into facts and predicates using a logic programming code and simulate that code execution using an exhaustive multi-hop search over the defined space. Our method allows us to compute the faithfulness of the reasoning process w.r.t. the generated code and analyse the steps of the multi-hop search without relying on external solvers. Our methods achieve SOTA results on $\mathbf{7}$ out of $\mathbf{9}$ diverse reasoning benchmarks. We also show that model faithfulness positively correlates with overall performance and further demonstrate that $\textbf{FLARE}$ allows pinpointing the decisive factors sufficient for and leading to the correct answer with optimal reasoning during the multi-hop search.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的现代问答(QA)和推理方法通常使用提示技术,如思维链(CoT),假设生成的答案将对问题空间和范围进行更详细的探索和理解。然而,这些方法在生成忠实于模型产生的中间推理链的输出方面遇到了困难。另一方面,神经符号方法,如忠实思维链(F-CoT),提议将LLM与外部符号求解器相结合。虽然这种方法具有很高的忠实度,但它们通常需要经过代码生成的模型训练,并且在处理模糊或难以严格形式化的任务时遇到困难。我们引入了“忠实逻辑辅助推理与探索”(FLARE)这一全新的可解释方法,通过任务分解来遍历问题空间。我们使用LLM来规划解决方案,将查询软形式化为事实和谓词,并使用逻辑编程代码模拟代码执行,在定义的空间上进行详尽的多跳搜索。我们的方法允许我们计算推理过程相对于生成代码的忠实度,并分析了多跳搜索的步骤,而无需依赖外部求解器。我们的方法在九个不同推理基准测试中的七个上取得了最先进的成果。我们还表明模型的忠实度与整体性能呈正相关,并进一步证明FLARE能够识别出在多跳搜索过程中得出正确答案的决定性关键因素,并在推理过程中实现最优选择。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大语言模型的现代问答和推理方法通常采用链式思维等提示技术,假设生成的结果会在问题的空间和范围内进行更细致的探索和推理。然而,这些方法在生成与模型产生的中间推理链相符的输出方面存在困难。另一方面,神经符号方法如忠实链式思维结合了语言模型和外部符号求解器,虽然具有很高的忠实度,但它们通常需要针对代码生成进行训练的模型,并且在任务模糊或难以严格形式化时表现不佳。本文介绍了一种新的可解释方法——忠实逻辑辅助推理与探索(FLARE),通过任务分解来遍历问题空间。我们使用语言模型来规划解决方案,将查询软形式化为事实和谓词,并使用逻辑编程代码模拟代码执行,在定义的空间上进行详尽的多跳搜索。我们的方法允许我们计算推理过程相对于生成代码的忠实性,并分析了多跳搜索的步骤,无需依赖外部求解器。我们的方法在九个推理基准测试中的七个上达到了最先进的成果。我们还表明,模型的忠实性与总体性能呈正相关,并进一步证明FLARE能够确定多跳搜索过程中得出正确答案的关键因素。
Key Takeaways
- 现代问答和推理方法基于大语言模型,常用链式思维等提示技术,但在生成与中间推理链相符的输出方面存在挑战。
- 神经符号方法如忠实链式思维结合了语言模型和外部符号求解器,虽高忠实度但面临特定挑战。
- 引入了一种新的可解释方法——忠实逻辑辅助推理与探索(FLARE),通过任务分解遍历问题空间,结合语言模型和逻辑编程。
- FLARE允许计算推理过程的忠实性,分析多跳搜索步骤,不依赖外部求解器。
- FLARE在多个推理基准测试上达到最先进水平。
- 模型忠实性与总体性能正相关。
点此查看论文截图





Does GPT Really Get It? A Hierarchical Scale to Quantify Human vs AI’s Understanding of Algorithms
Authors:Mirabel Reid, Santosh S. Vempala
As Large Language Models (LLMs) perform (and sometimes excel at) more and more complex cognitive tasks, a natural question is whether AI really understands. The study of understanding in LLMs is in its infancy, and the community has yet to incorporate well-trodden research in philosophy, psychology, and education. We initiate this, specifically focusing on understanding algorithms, and propose a hierarchy of levels of understanding. We use the hierarchy to design and conduct a study with human subjects (undergraduate and graduate students) as well as large language models (generations of GPT), revealing interesting similarities and differences. We expect that our rigorous criteria will be useful to keep track of AI’s progress in such cognitive domains.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在越来越多复杂的认知任务中表现出色,一个自然的问题是人工智能是否真的理解。关于LLM的理解研究还处于起步阶段,尚未充分融入哲学、心理学和教育领域的成熟研究。我们以此为重点,特别是理解算法,并提出了理解层次结构。我们使用层次结构设计和开展了一项研究,研究对象包括本科生和研究生以及大型语言模型(GPT各代),揭示了有趣的相似性和差异性。我们预计我们严格的评价标准将用于跟踪AI在认知领域的进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 10 figures. To be published at AAAI 2025
Summary
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在越来越多复杂认知任务上的表现(有时甚至表现出色),关于人工智能是否真的理解的问题自然产生。对于LLM的理解研究尚处于起步阶段,尚未充分融入哲学、心理学和教育等领域的成熟研究。本研究专注于理解算法,并提出了理解层次结构。我们利用这一层次结构,设计并开展了一项涉及人类受试者(本科生和研究生)以及大型语言模型(各代GPT)的研究,揭示了有趣的一致性和差异性。我们预计,我们严格的评估标准将有助于跟踪AI在认知领域的进展。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂认知任务上的表现日益突出,引发关于AI是否真正理解的疑问。
- LLM的理解研究尚处于起步阶段,需借鉴哲学、心理学和教育的成熟研究。
- 研究聚焦于理解算法,并提出理解层次结构。
- 通过人类受试者(本科生和研究生)及大型语言模型(各代GPT)的研究,发现有趣的一致性和差异性。
- 提出的严格评估标准有助于跟踪AI在认知领域的进展。
- 通过此研究,强调了将不同领域研究成果结合以推动AI理解发展的重要性。
点此查看论文截图