⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-23 更新
Parameterised Quantum Circuits for Novel Representation Learning in Speech Emotion Recognition
Authors:Thejan Rajapakshe, Rajib Rana, Farina Riaz, Sara Khalifa, Björn W. Schuller
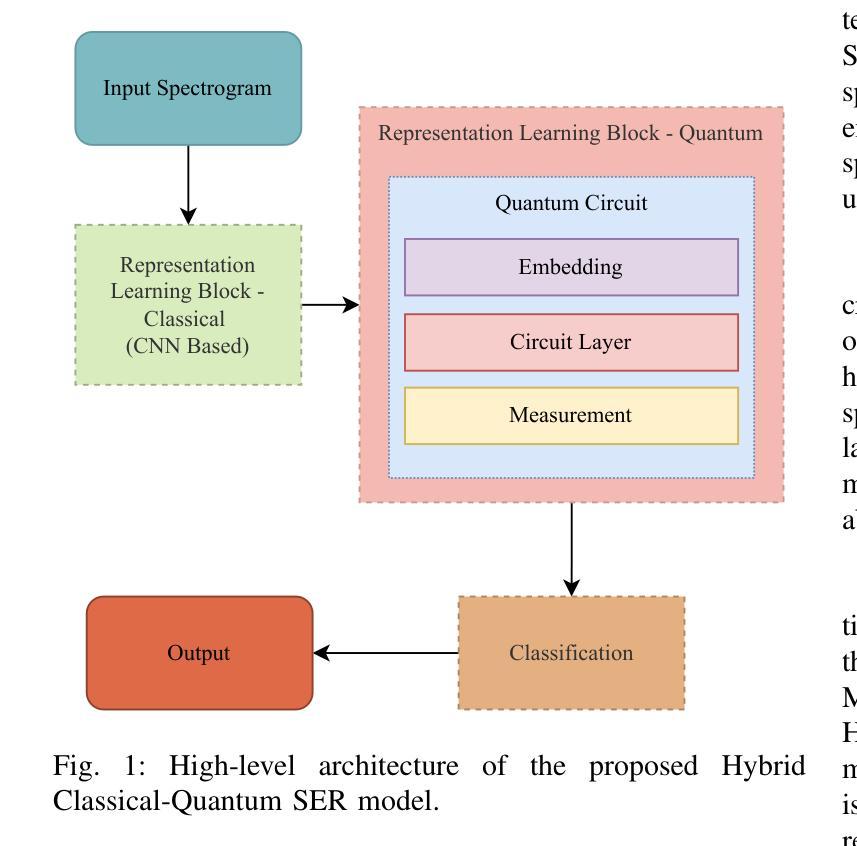
Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) is a complex and challenging task in human-computer interaction due to the intricate dependencies of features and the overlapping nature of emotional expressions conveyed through speech. Although traditional deep learning methods have shown effectiveness, they often struggle to capture subtle emotional variations and overlapping states. This paper introduces a hybrid classical-quantum framework that integrates Parameterised Quantum Circuits (PQCs) with conventional Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures. By leveraging quantum properties such as superposition and entanglement, the proposed model enhances feature representation and captures complex dependencies more effectively than classical methods. Experimental evaluations conducted on benchmark datasets, including IEMOCAP, RECOLA, and MSP-Improv, demonstrate that the hybrid model achieves higher accuracy in both binary and multi-class emotion classification while significantly reducing the number of trainable parameters. While a few existing studies have explored the feasibility of using Quantum Circuits to reduce model complexity, none have successfully shown how they can enhance accuracy. This study is the first to demonstrate that Quantum Circuits has the potential to improve the accuracy of SER. The findings highlight the promise of QML to transform SER, suggesting a promising direction for future research and practical applications in emotion-aware systems.
语音情感识别(SER)是人机交互中的一项复杂且具挑战性的任务,由于语音特征之间的复杂依赖性和情感表达的重叠性。尽管传统的深度学习方法已经显示出其有效性,但它们在捕捉微妙的情感变化和重叠状态方面往往遇到困难。本文介绍了一种混合的经典-量子框架,该框架将参数化量子电路(PQCs)与传统卷积神经网络(CNN)架构相结合。通过利用量子叠加和纠缠等特性,所提出的模型增强了特征表示,更有效地捕捉了复杂的依赖性,比经典方法表现更优。在IEMOCAP、RECOLA和MSP-Improv等基准数据集上进行的实验评估表明,混合模型在二元和多元情感分类中都实现了更高的精度,同时显著减少了可训练参数的数量。尽管已有一些现有研究探讨了使用量子电路减少模型复杂性的可行性,但没有研究成功表明它们如何提高准确性。本研究首次证明了量子电路在提高SER准确性方面的潜力。研究结果突出了量子机器学习(QML)在改变SER方面的前景,为未来的研究和情感感知系统的实际应用指明了有前景的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种融合传统深度学习与量子计算的新型情感识别模型。该模型利用参数化量子电路(PQC)与卷积神经网络(CNN)架构,通过量子计算的叠加和纠缠特性,提高特征表示能力,更有效地捕捉情感表达的复杂依赖关系。实验评估显示,该混合模型在二元和多类情感分类任务上实现更高的精度,同时显著减少训练参数数量。本研究首次证明了量子电路在提高语音识别准确率方面的潜力,并展望了量子机器学习在情感识别领域的未来发展。
Key Takeaways
- 情感识别(SER)是人工智能领域中的一项复杂任务,因特征间的复杂依赖性和情感表达的重叠性而具有挑战性。
- 传统深度学习方法在捕捉细微情感变化和重叠状态方面存在困难。
- 融合量子计算与深度学习的新型模型通过利用量子特性如叠加和纠缠,提高了特征表示能力。
- 实验评估显示,新型混合模型在多个基准数据集上实现了更高的情感分类精度。
- 与现有研究相比,该模型在减少训练参数数量的同时提高了准确性。
- 本研究首次证明了量子电路在提升语音识别准确率方面的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


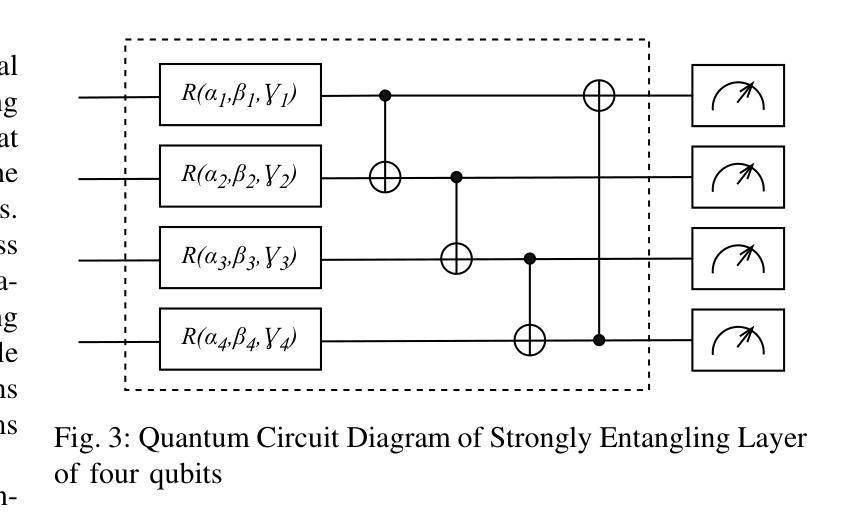
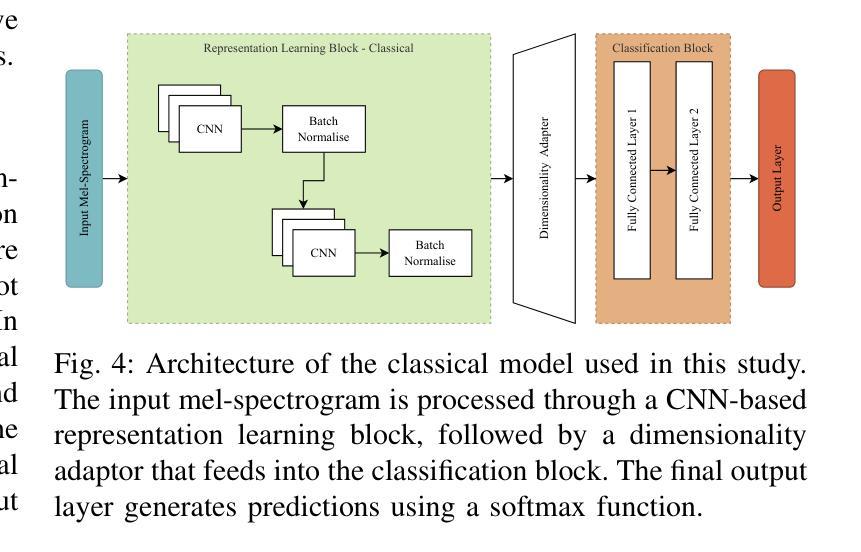
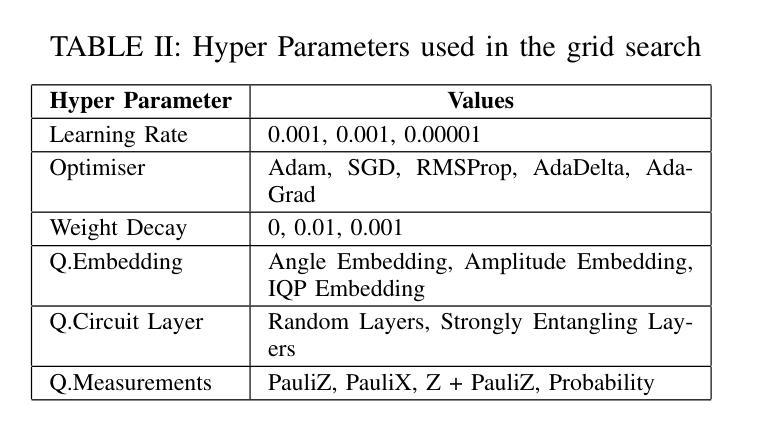
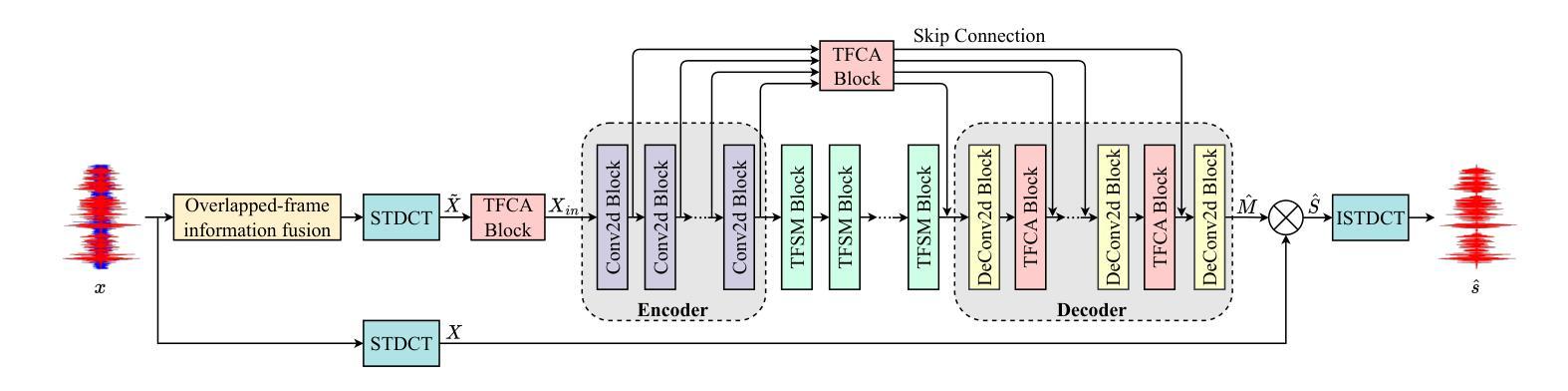
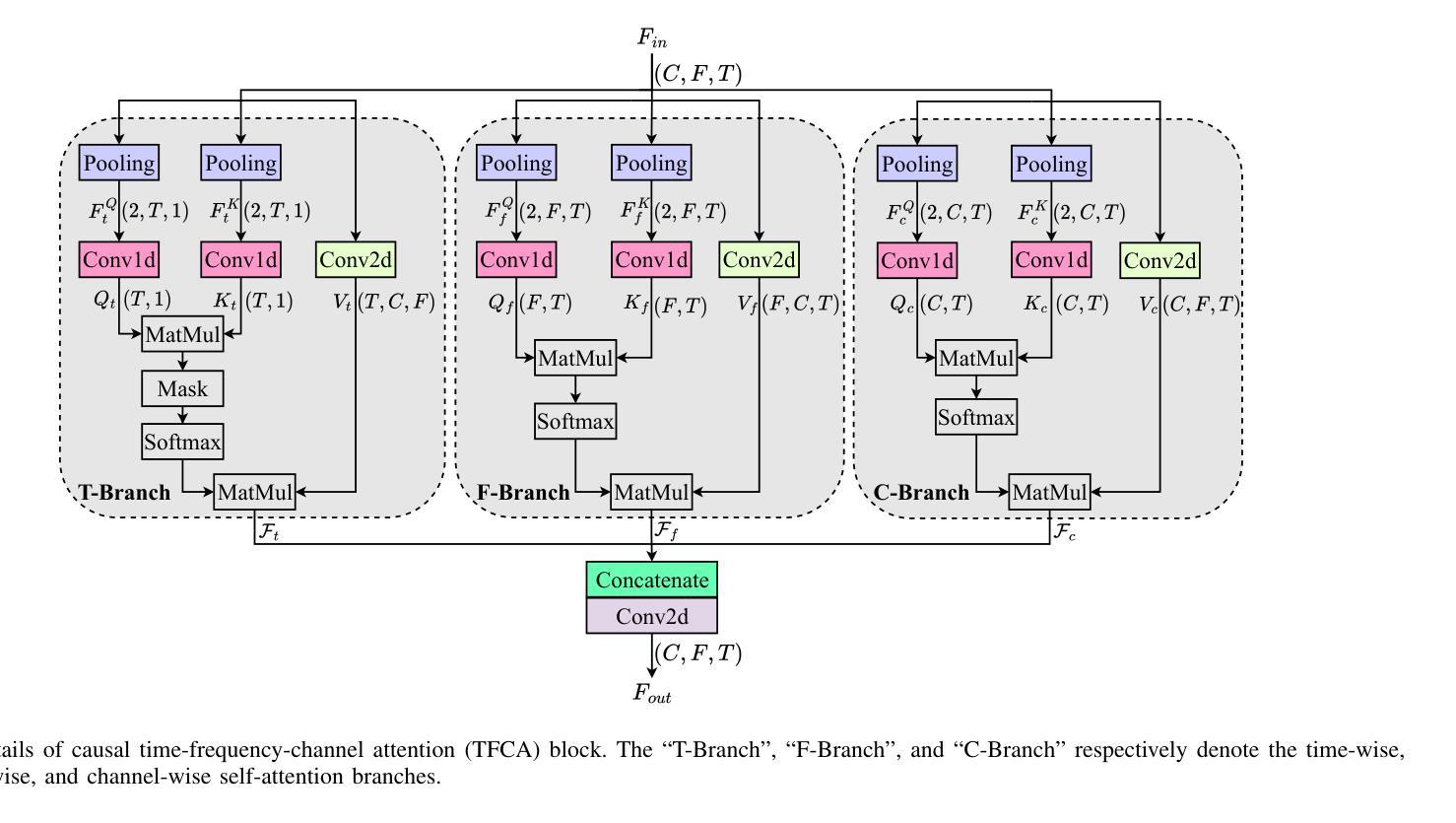
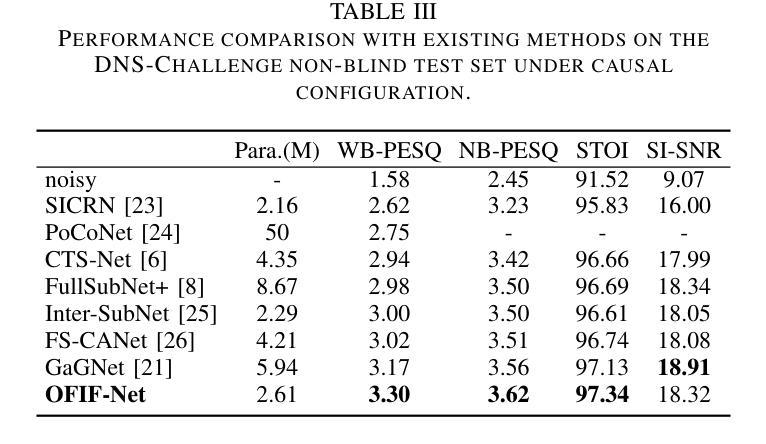
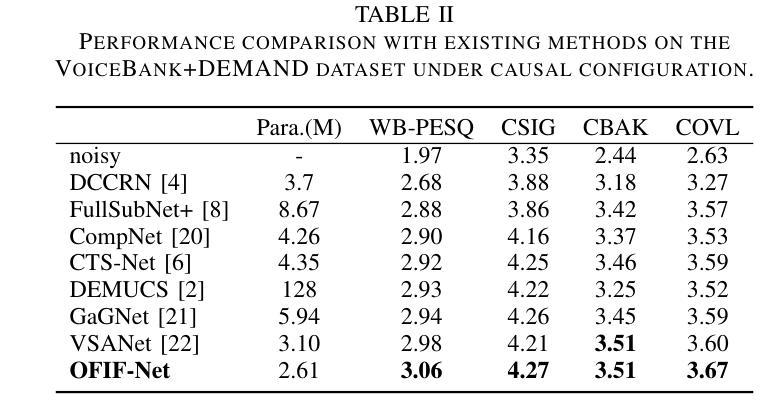
Speech Enhancement with Overlapped-Frame Information Fusion and Causal Self-Attention
Authors:Yuewei Zhang, Huanbin Zou, Jie Zhu
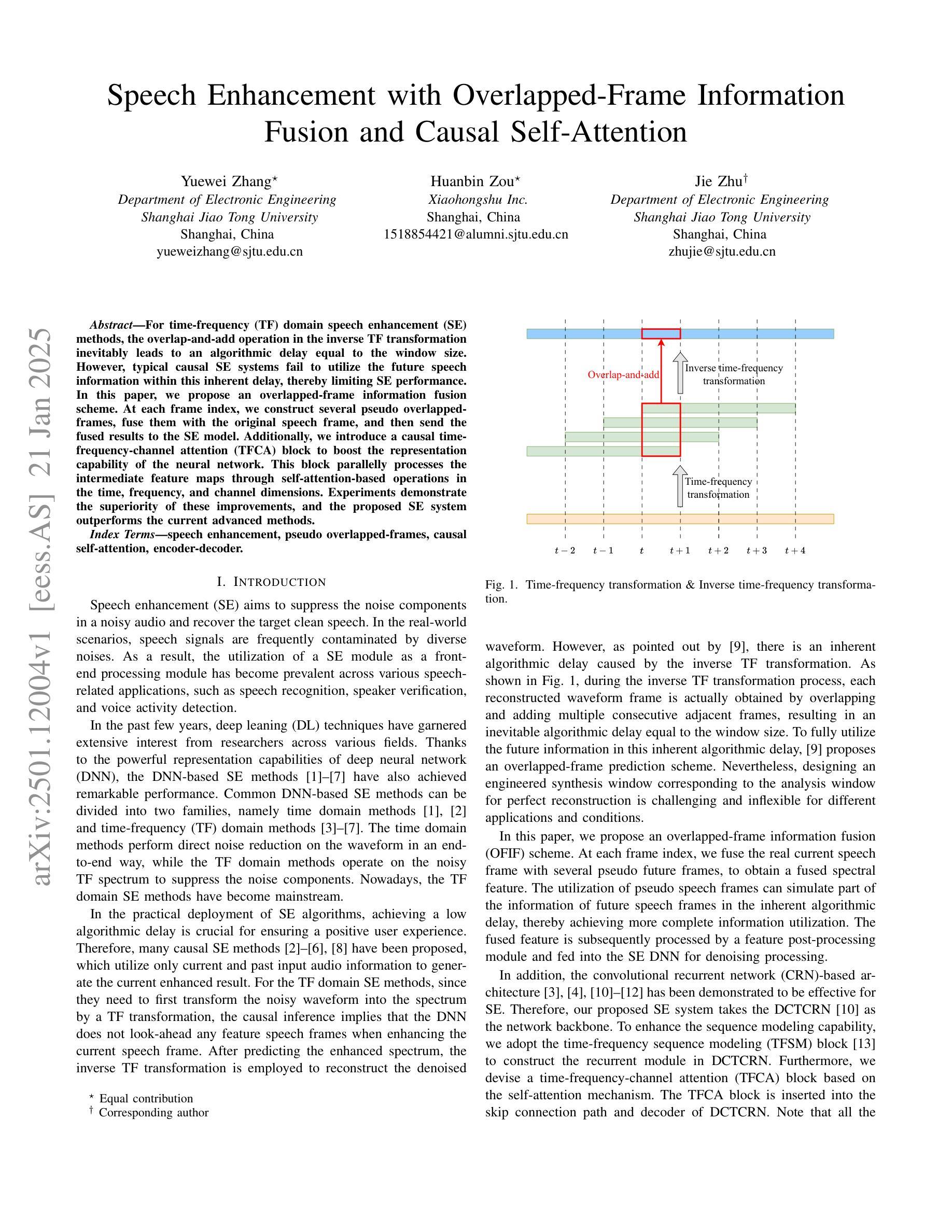
For time-frequency (TF) domain speech enhancement (SE) methods, the overlap-and-add operation in the inverse TF transformation inevitably leads to an algorithmic delay equal to the window size. However, typical causal SE systems fail to utilize the future speech information within this inherent delay, thereby limiting SE performance. In this paper, we propose an overlapped-frame information fusion scheme. At each frame index, we construct several pseudo overlapped-frames, fuse them with the original speech frame, and then send the fused results to the SE model. Additionally, we introduce a causal time-frequency-channel attention (TFCA) block to boost the representation capability of the neural network. This block parallelly processes the intermediate feature maps through self-attention-based operations in the time, frequency, and channel dimensions. Experiments demonstrate the superiority of these improvements, and the proposed SE system outperforms the current advanced methods.
对于时频域(TF)语音增强(SE)方法,逆TF变换中的叠加操作不可避免地会导致等于窗口大小的算法延迟。然而,典型的因果SE系统未能利用此固有延迟内的未来语音信息,从而限制了SE性能。在本文中,我们提出了一种重叠帧信息融合方案。在每个帧索引处,我们构建多个伪重叠帧,将它们与原始语音帧融合,然后将融合结果发送到SE模型。此外,我们引入了一个因果时频通道注意力(TFCA)块,以提高神经网络的表示能力。该块通过时间、频率和通道维度上的自注意力操作并行处理中间特征图。实验证明了这些改进的优势,并且所提出的SE系统优于当前的高级方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
本论文针对时频域语音增强方法中的重叠添加操作导致的算法延迟问题进行研究,并提出一种重叠帧信息融合方案。通过构建伪重叠帧并与原始语音帧融合,提高语音增强性能。同时,引入因果时频通道注意力机制,提升神经网络的表现能力。实验证明,所提方案优于当前先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 时频域语音增强方法中的重叠添加操作会导致算法延迟,限制性能。
- 提出重叠帧信息融合方案,利用伪重叠帧与原始语音帧融合,提高语音增强效果。
- 引入因果时频通道注意力机制,增强神经网络的表现能力。
- 注意力机制通过自我关注操作处理中间特征图,涉及时间、频率和通道维度。
- 实验证明所提方案优于当前先进方法。
- 重叠帧信息融合与注意力机制结合,有效改善语音增强性能。
点此查看论文截图
Rate-Aware Learned Speech Compression
Authors:Jun Xu, Zhengxue Cheng, Guangchuan Chi, Yuhan Liu, Yuelin Hu, Li Song
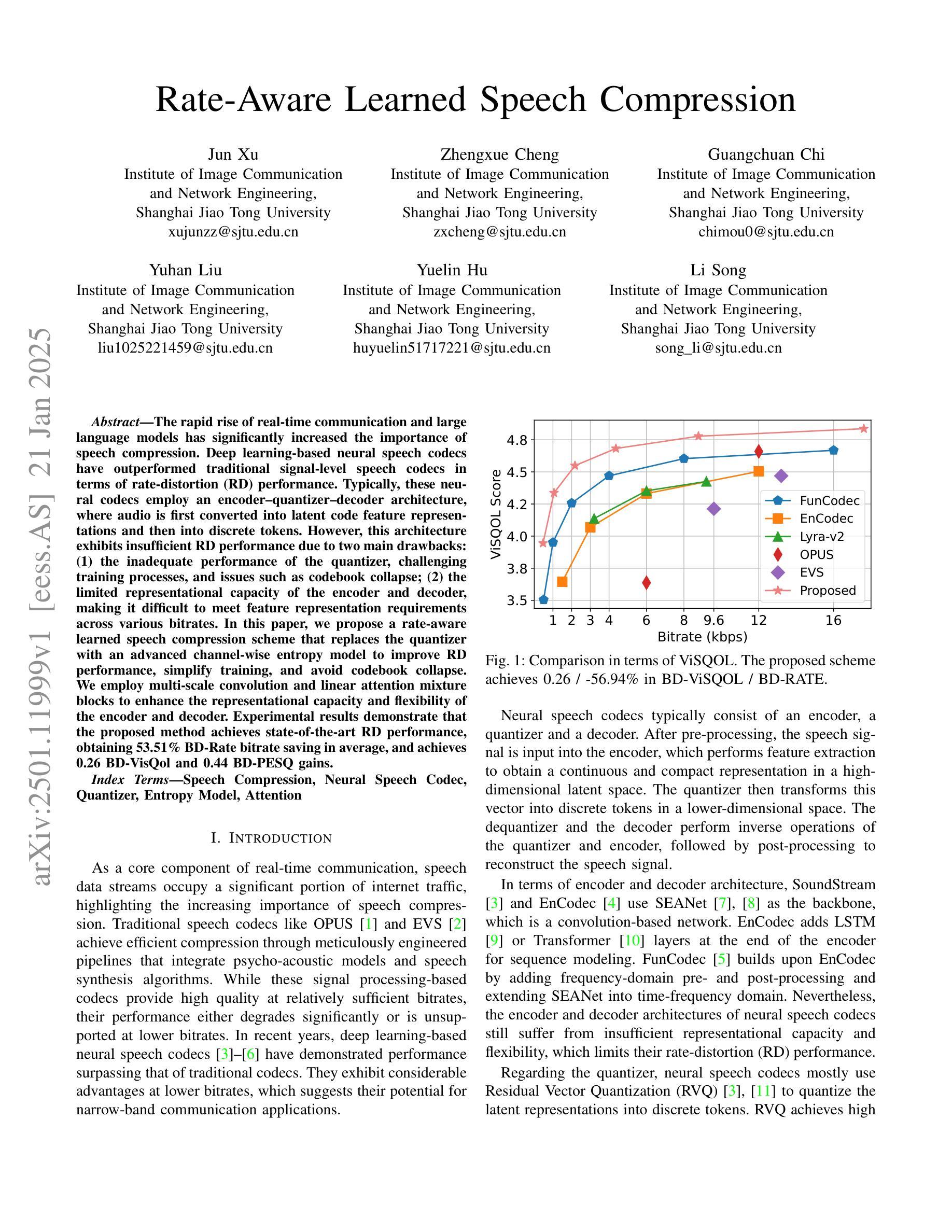
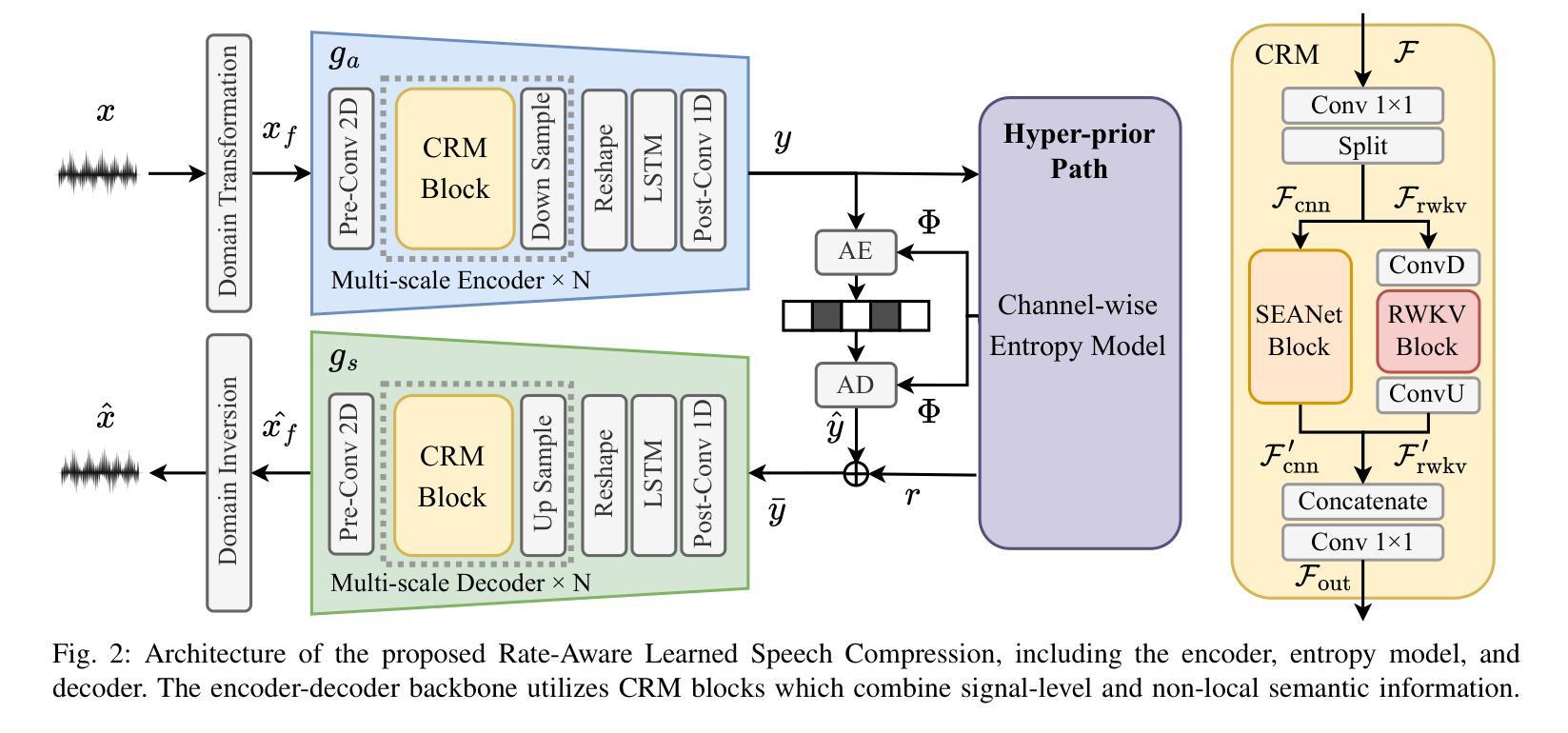
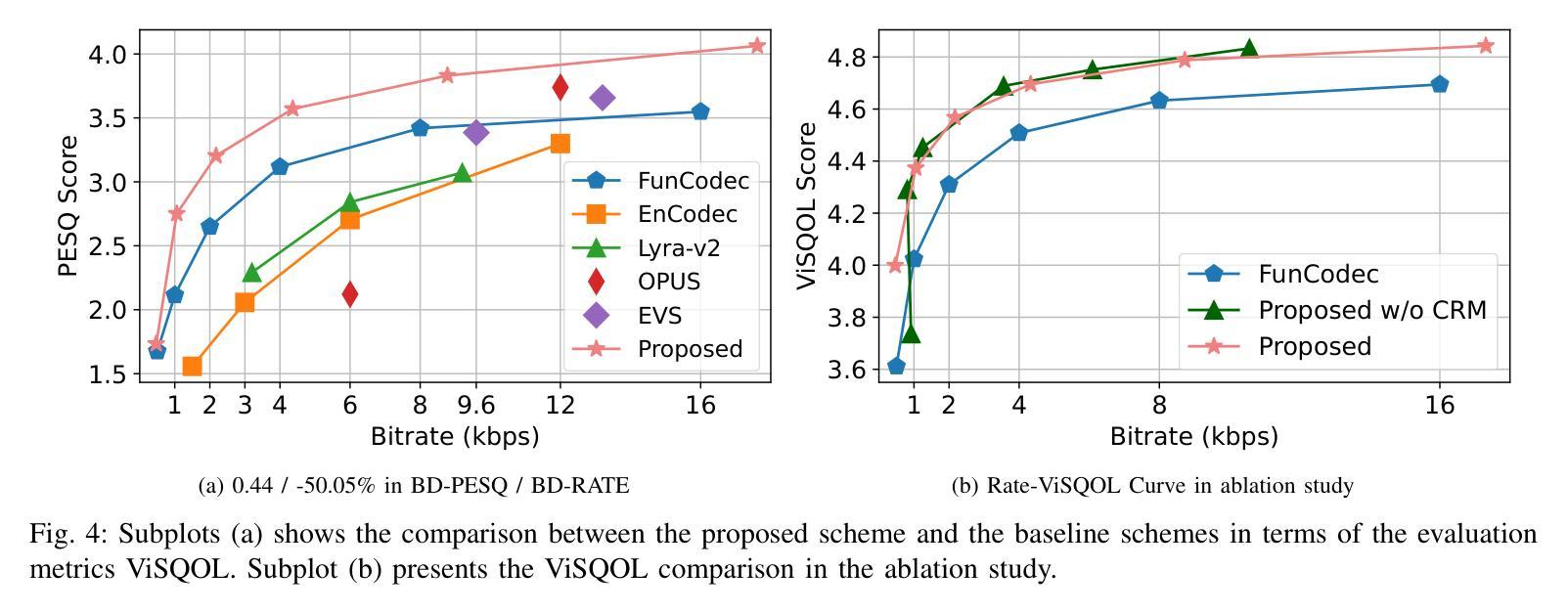
The rapid rise of real-time communication and large language models has significantly increased the importance of speech compression. Deep learning-based neural speech codecs have outperformed traditional signal-level speech codecs in terms of rate-distortion (RD) performance. Typically, these neural codecs employ an encoder-quantizer-decoder architecture, where audio is first converted into latent code feature representations and then into discrete tokens. However, this architecture exhibits insufficient RD performance due to two main drawbacks: (1) the inadequate performance of the quantizer, challenging training processes, and issues such as codebook collapse; (2) the limited representational capacity of the encoder and decoder, making it difficult to meet feature representation requirements across various bitrates. In this paper, we propose a rate-aware learned speech compression scheme that replaces the quantizer with an advanced channel-wise entropy model to improve RD performance, simplify training, and avoid codebook collapse. We employ multi-scale convolution and linear attention mixture blocks to enhance the representational capacity and flexibility of the encoder and decoder. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art RD performance, obtaining 53.51% BD-Rate bitrate saving in average, and achieves 0.26 BD-VisQol and 0.44 BD-PESQ gains.
实时通信和大型语言模型的迅速崛起,极大地提高了语音压缩的重要性。基于深度学习的神经网络语音编解码器在速率失真(RD)性能上已经超越了传统的信号级语音编解码器。这些神经网络编解码器通常采用编码器-量化器-解码器的架构,首先将音频转换为潜在代码特征表示,然后转换为离散令牌。然而,由于两个主要缺点,这种架构的RD性能表现不足:(1)量化器的性能不足,训练过程具有挑战性,以及诸如码本崩溃之类的问题;(2)编码器和解码器的表示能力有限,难以满足各种比特率下的特征表示要求。在本文中,我们提出了一种速率感知的语音压缩方案,该方案用先进的通道感知熵模型取代了量化器,以提高RD性能,简化训练并避免码本崩溃。我们采用多尺度卷积和线性注意力混合块来增强编码器和解码器的表示能力和灵活性。实验结果表明,该方法达到了最先进的RD性能,平均节省比特率53.51%的BD-Rate,实现了0.26的BD-VisQol和0.44的BD-PESQ增益。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络语音压缩技术提高了语音通信效率。新方案利用先进的通道感知熵模型替换量化器,增强编码器解码器性能,实现码率失真优化。实验证明该方法达到业界领先水平,平均节省比特率达53.51%,视觉质量和感知质量评价分别提升0.26和0.44。
Key Takeaways
- 实时通信和大型语言模型的快速发展增加了语音压缩的重要性。
- 深度学习神经网络语音编解码器在速率失真性能上超越了传统信号级语音编解码器。
- 当前神经网络编解码器存在量化器性能不足和编码器解码器代表性容量有限的两个主要问题。
- 新的语音压缩方案利用先进的通道感知熵模型替换量化器,改善速率失真性能,简化训练过程,避免码本崩溃。
- 该方案采用多尺度卷积和线性注意力混合块,增强编码器解码器的表现力和灵活性。
- 实验结果表明,新方案实现了业界领先的速率失真性能,平均节省比特率达53.51%。
点此查看论文截图
30+ Years of Source Separation Research: Achievements and Future Challenges
Authors:Shoko Araki, Nobutaka Ito, Reinhold Haeb-Umbach, Gordon Wichern, Zhong-Qiu Wang, Yuki Mitsufuji
Source separation (SS) of acoustic signals is a research field that emerged in the mid-1990s and has flourished ever since. On the occasion of ICASSP’s 50th anniversary, we review the major contributions and advancements in the past three decades in the speech, audio, and music SS research field. We will cover both single- and multi-channel SS approaches. We will also look back on key efforts to foster a culture of scientific evaluation in the research field, including challenges, performance metrics, and datasets. We will conclude by discussing current trends and future research directions.
音频信号的源分离(SS)是上世纪90年代中期出现并自此繁荣起来的研究领域。正值ICASSP成立五十周年之际,我们回顾了语音、音频和音乐SS研究领域过去三十年的主要贡献和进展。我们将介绍单通道和多通道SS方法。我们也回顾了在该领域推动科学评价文化的关键举措,包括挑战、性能指标和数据集。最后,我们将讨论当前趋势和未来研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE ICASSP 2025
Summary
声源分离(SS)是上世纪九十年代涌现并在之后蓬勃发展的一个研究领域。值此ICASSP五十周年之际,回顾过去三十年语音、音频和音乐SS研究领域的重大贡献和进展。本文将介绍单通道和多通道SS方法,并回顾推动该领域科学评估文化发展的关键工作,包括挑战、性能度和数据集。本文还将讨论当前趋势和未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 声源分离领域在九十年代涌现并迅速发展。
- 此领域涵盖了单通道和多通道声源分离方法。
- 在声源分离领域的发展过程中,关键努力之一是建立科学评估文化,包括制定挑战、性能指标和数据集。
- 声源分离在语音、音频和音乐领域都有广泛应用。
- 当前声源分离领域的趋势是不断发展和完善现有技术,同时探索新的应用方向。
- ICASSP在声源分离领域的研究中发挥了重要作用。
点此查看论文截图

LLM supervised Pre-training for Multimodal Emotion Recognition in Conversations
Authors:Soumya Dutta, Sriram Ganapathy
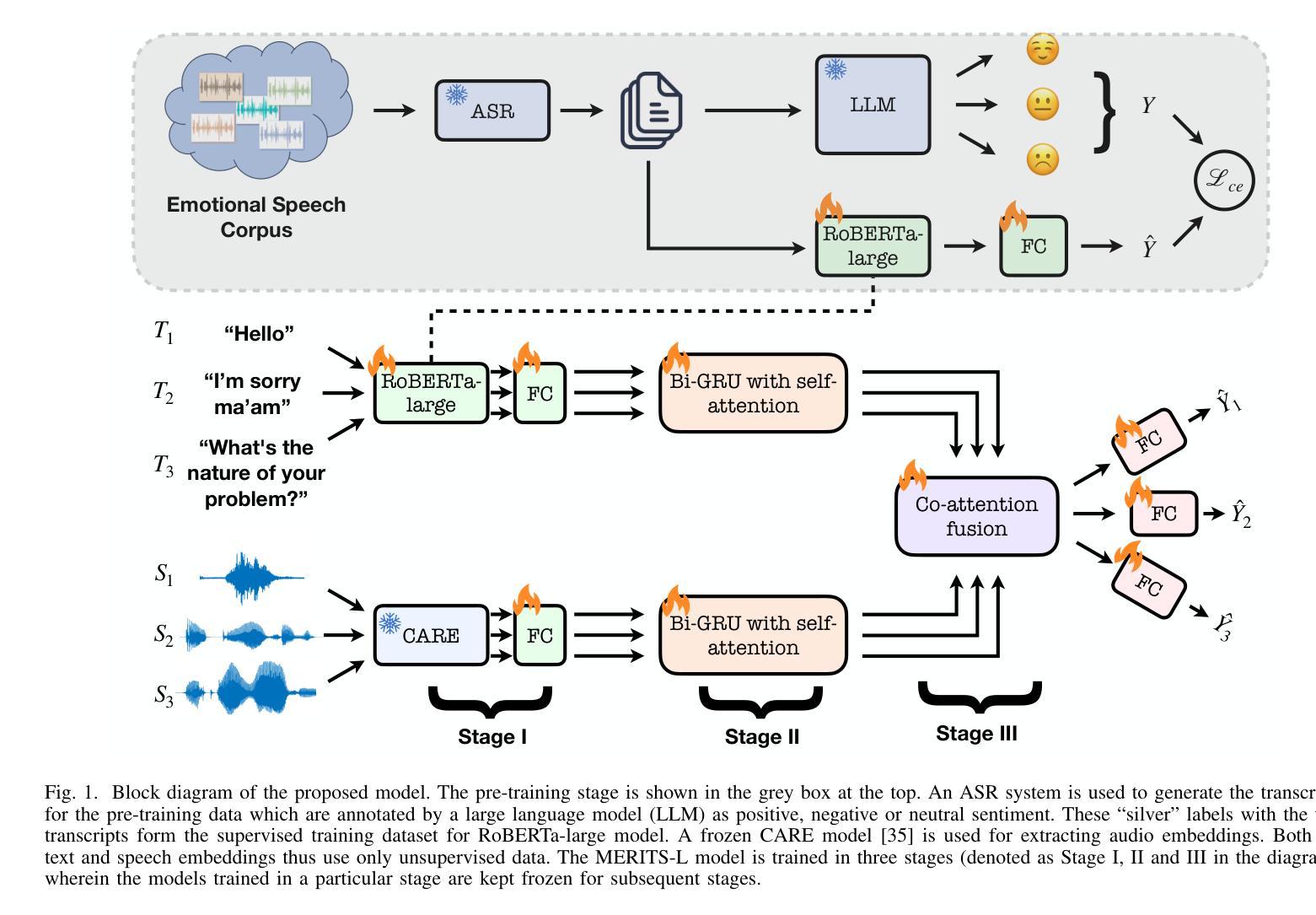
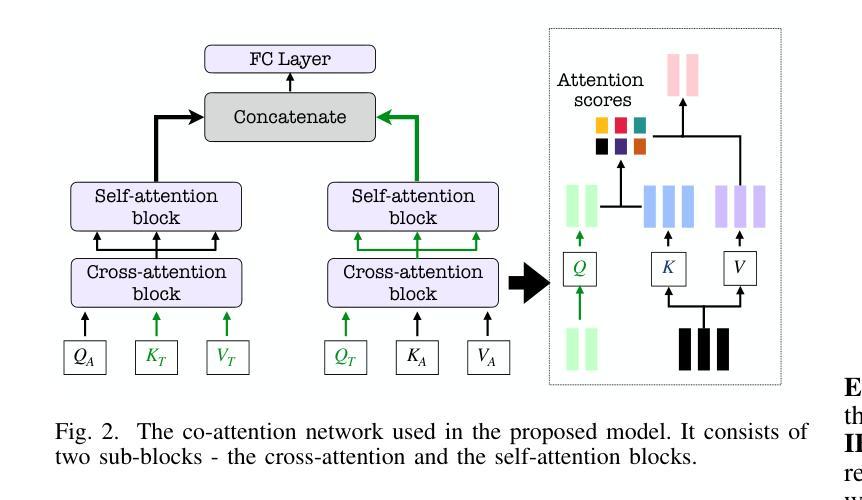
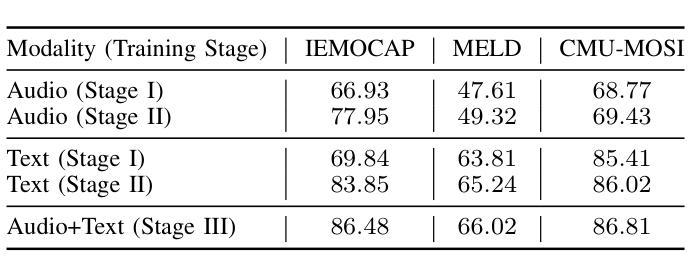
Emotion recognition in conversations (ERC) is challenging due to the multimodal nature of the emotion expression. In this paper, we propose to pretrain a text-based recognition model from unsupervised speech transcripts with LLM guidance. These transcriptions are obtained from a raw speech dataset with a pre-trained ASR system. A text LLM model is queried to provide pseudo-labels for these transcripts, and these pseudo-labeled transcripts are subsequently used for learning an utterance level text-based emotion recognition model. We use the utterance level text embeddings for emotion recognition in conversations along with speech embeddings obtained from a recently proposed pre-trained model. A hierarchical way of training the speech-text model is proposed, keeping in mind the conversational nature of the dataset. We perform experiments on three established datasets, namely, IEMOCAP, MELD, and CMU- MOSI, where we illustrate that the proposed model improves over other benchmarks and achieves state-of-the-art results on two out of these three datasets.
对话中的情绪识别(ERC)由于情绪表达的多模式性质而具有挑战性。在本文中,我们提出从带有LLM指导的无监督语音转录本中预训练基于文本的识别模型。这些转录本是由带有预训练自动语音识别系统的原始语音数据集获得的。文本LLM模型被查询以提供这些转录本的伪标签,随后这些伪标签转录本被用于学习基于文本的对话级情绪识别模型的发言权水平。我们使用对话中的发言级文本嵌入和从最近提出的预训练模型获得的语音嵌入来进行情绪识别。考虑到数据集的对话性质,提出了一种训练语音文本模型的分层方法。我们在三个建立的数据集IEMOCAP、MELD和CMU-MOSI上进行了实验,我们证明了所提出的模型在其他基准测试上的改进,并在其中两个数据集上达到了最新水平的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2025; 5 pages, 4 figures, 2 tables
摘要
基于对话的情感识别(ERC)是一项具有挑战性的任务,主要是因为情感表达的多媒体性质。本文提出了一种使用预训练的大型语言模型指导来训练文本情感识别模型的方法。这些文本转译通过带有预训练语音识别系统的原始语音数据集获得。我们向文本大型语言模型询问并获取这些转译的伪标签,然后将这些伪标签转译用于学习基于文本的情感识别模型的发言级别表达。我们将发言级别的文本嵌入与来自最近提出的预训练模型的语音嵌入相结合,用于对话中的情感识别。考虑到数据集的对话性质,我们提出了一种训练语音文本模型的分层方法。我们在三个已建立的数据集上进行实验,即IEMOCAP、MELD和CMU-MOSI。实验结果表明,该模型在多个基准测试中表现优异,并在其中两个数据集上达到了最新的技术水平。
关键见解
- 基于对话的情感识别(ERC)面临挑战,主要由于情感的多媒体性质。
- 使用预训练的大型语言模型指导进行文本情感识别模型的训练是一种有效方法。
- 通过预训练的语音识别系统获取原始语音数据集以生成文本转译。
- 大型语言模型用于获取文本转译的伪标签,进而用于学习发言级别的文本情感识别模型。
- 结合文本嵌入和语音嵌入进行情感识别,以应对对话中的复杂性。
- 提出了一种分层训练语音文本模型的策略,考虑了数据集的对话性质。
点此查看论文截图

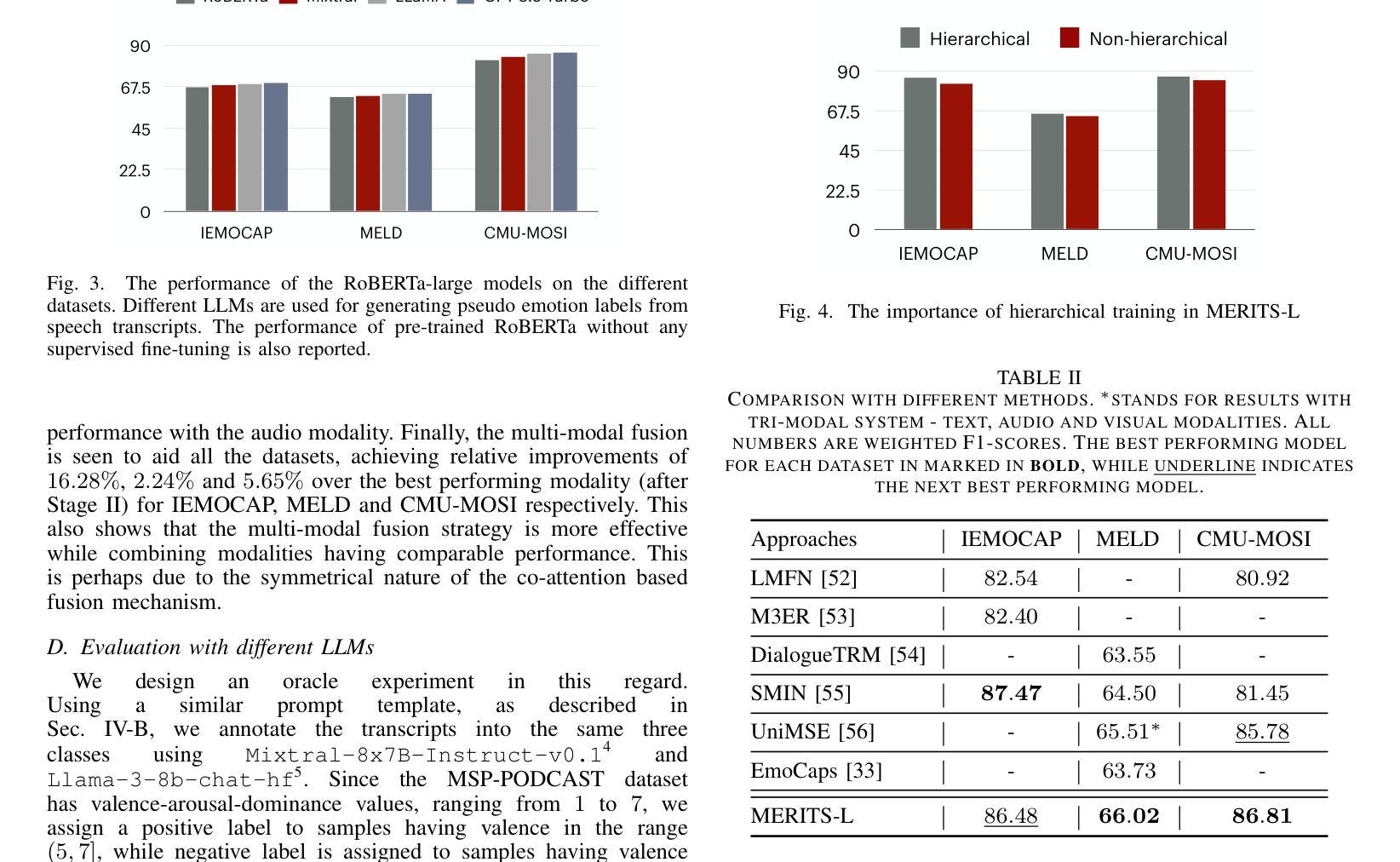
Investigation of Whisper ASR Hallucinations Induced by Non-Speech Audio
Authors:Mateusz Barański, Jan Jasiński, Julitta Bartolewska, Stanisław Kacprzak, Marcin Witkowski, Konrad Kowalczyk
Hallucinations of deep neural models are amongst key challenges in automatic speech recognition (ASR). In this paper, we investigate hallucinations of the Whisper ASR model induced by non-speech audio segments present during inference. By inducting hallucinations with various types of sounds, we show that there exists a set of hallucinations that appear frequently. We then study hallucinations caused by the augmentation of speech with such sounds. Finally, we describe the creation of a bag of hallucinations (BoH) that allows to remove the effect of hallucinations through the post-processing of text transcriptions. The results of our experiments show that such post-processing is capable of reducing word error rate (WER) and acts as a good safeguard against problematic hallucinations.
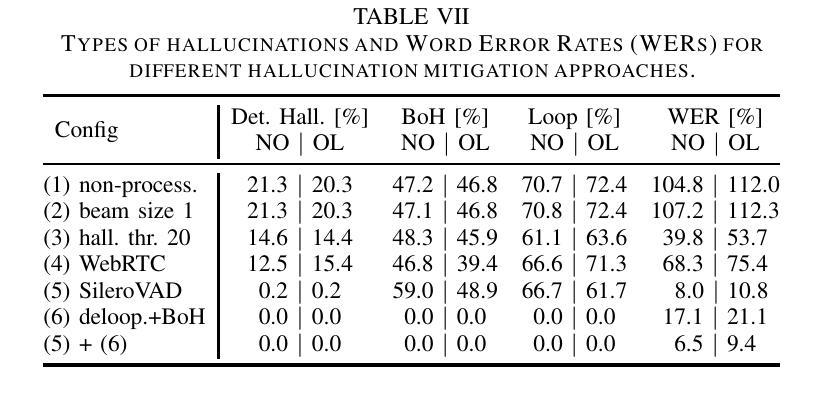
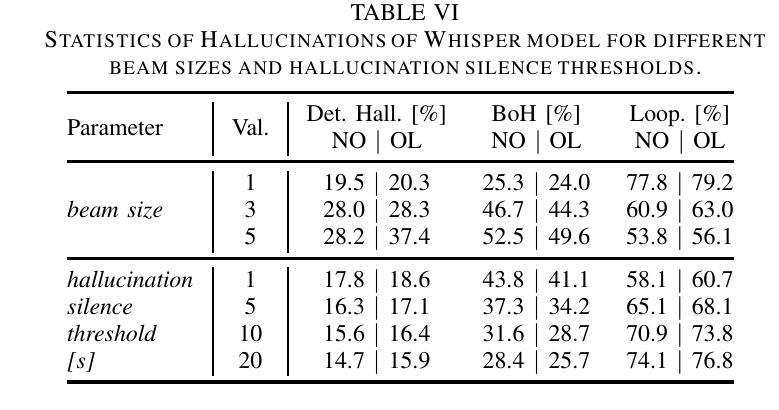
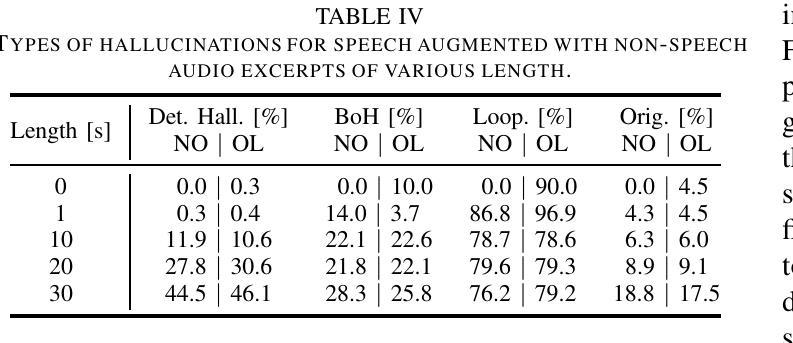
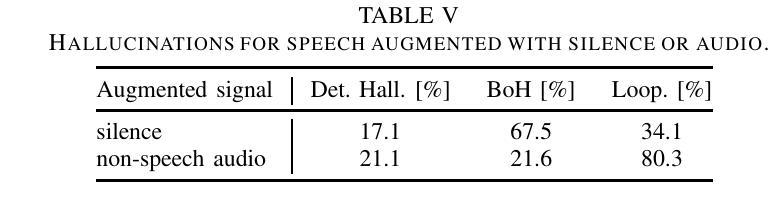
深度神经网络模型的幻觉是自动语音识别(ASR)中的关键挑战之一。在本文中,我们研究了在推理过程中由非语音音频片段引起的Whisper ASR模型的幻觉。通过用各种声音诱发幻觉,我们发现存在一系列经常出现的幻觉。然后,我们研究了通过用这些声音增强语音而产生的幻觉。最后,我们描述了幻觉包(BoH)的创建,该包可以通过文本转录的后处理来消除幻觉的影响。我们的实验结果表明,这种后处理能够降低词错误率(WER),并作为防止问题幻觉的良好保障。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for IEEE ICASSP 2025
Summary:
本文探讨了自动语音识别(ASR)中的深度神经网络模型产生的关键挑战之一——hallucination现象。研究发现在推理过程中存在的非语音音频片段会引发hallucination,存在频繁出现的hallucination类型。通过对语音增加这些声音的研究,提出了一种消除hallucination影响的“hallucination包(BoH)”的创建方法,通过文本转录的后处理来减少word error rate(WER),并作为对抗问题hallucination的良好保障。
Key Takeaways:
- 非语音音频片段在自动语音识别模型的推理过程中会引发hallucination现象。
- 存在一系列频繁出现的hallucination类型。
- 通过对语音增加特定声音,可以产生更多的hallucination。
- 提出了通过创建“hallucination包(BoH)”来消除hallucination影响的方法。
- 文本转录的后处理能够减少word error rate(WER)。
- 后处理作为一种保障措施,可以有效对抗问题hallucination。
点此查看论文截图

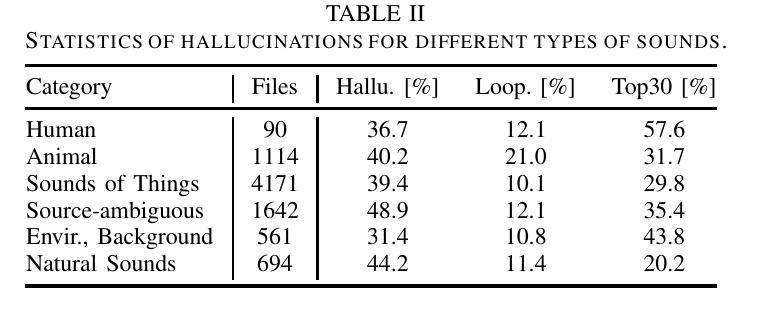
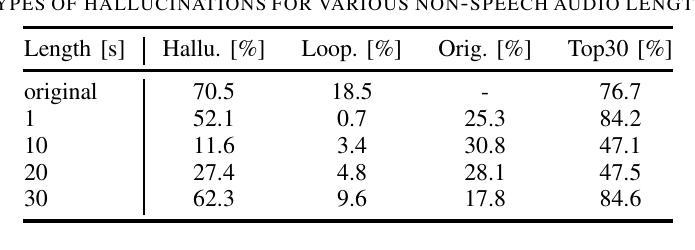
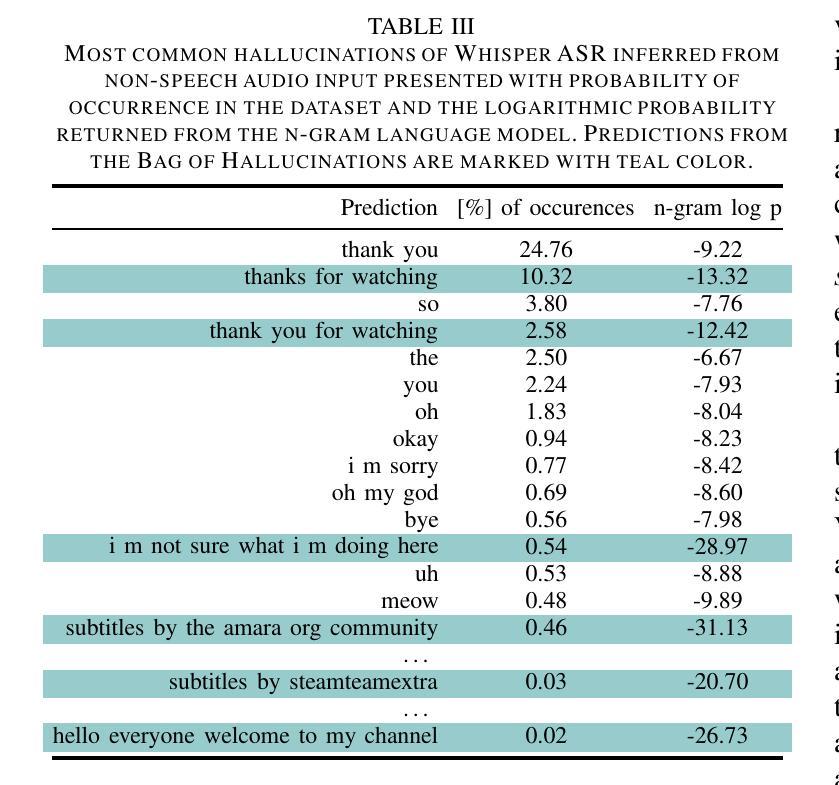
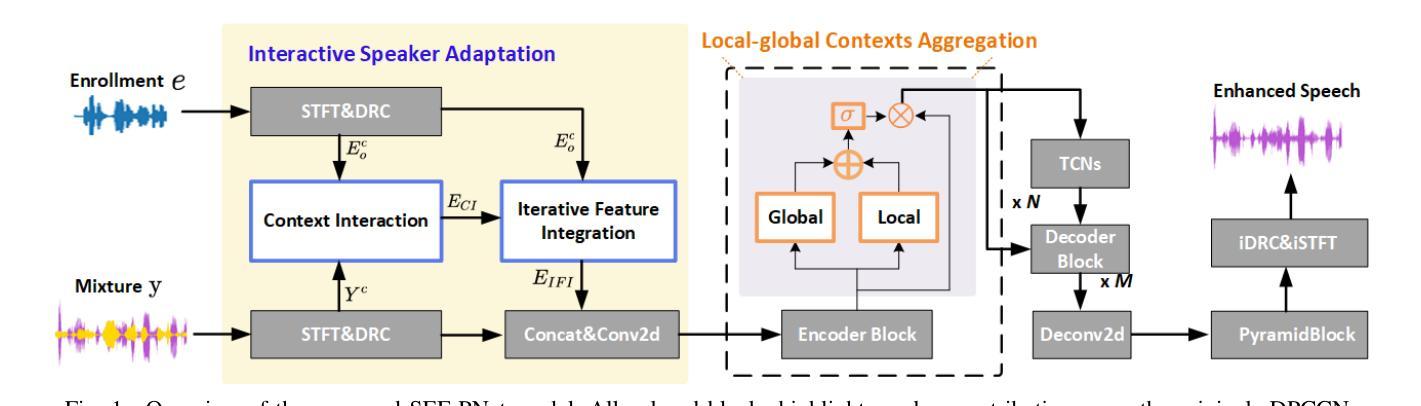
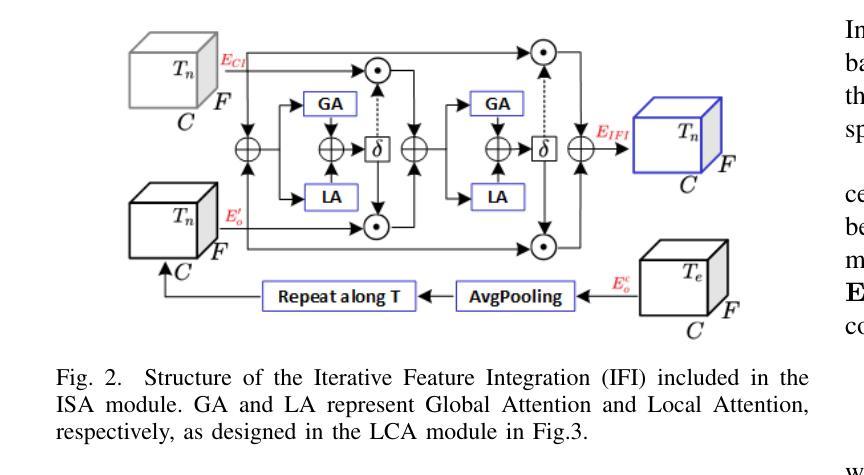
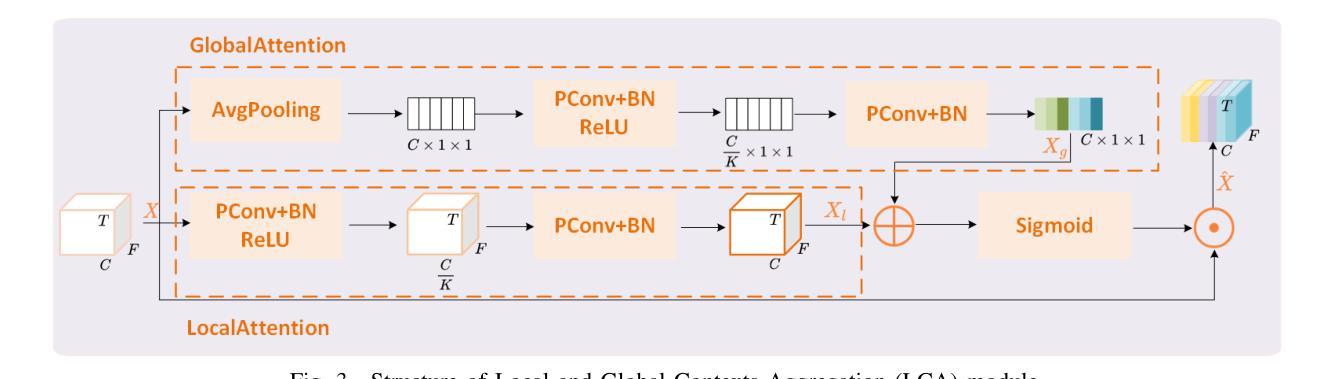
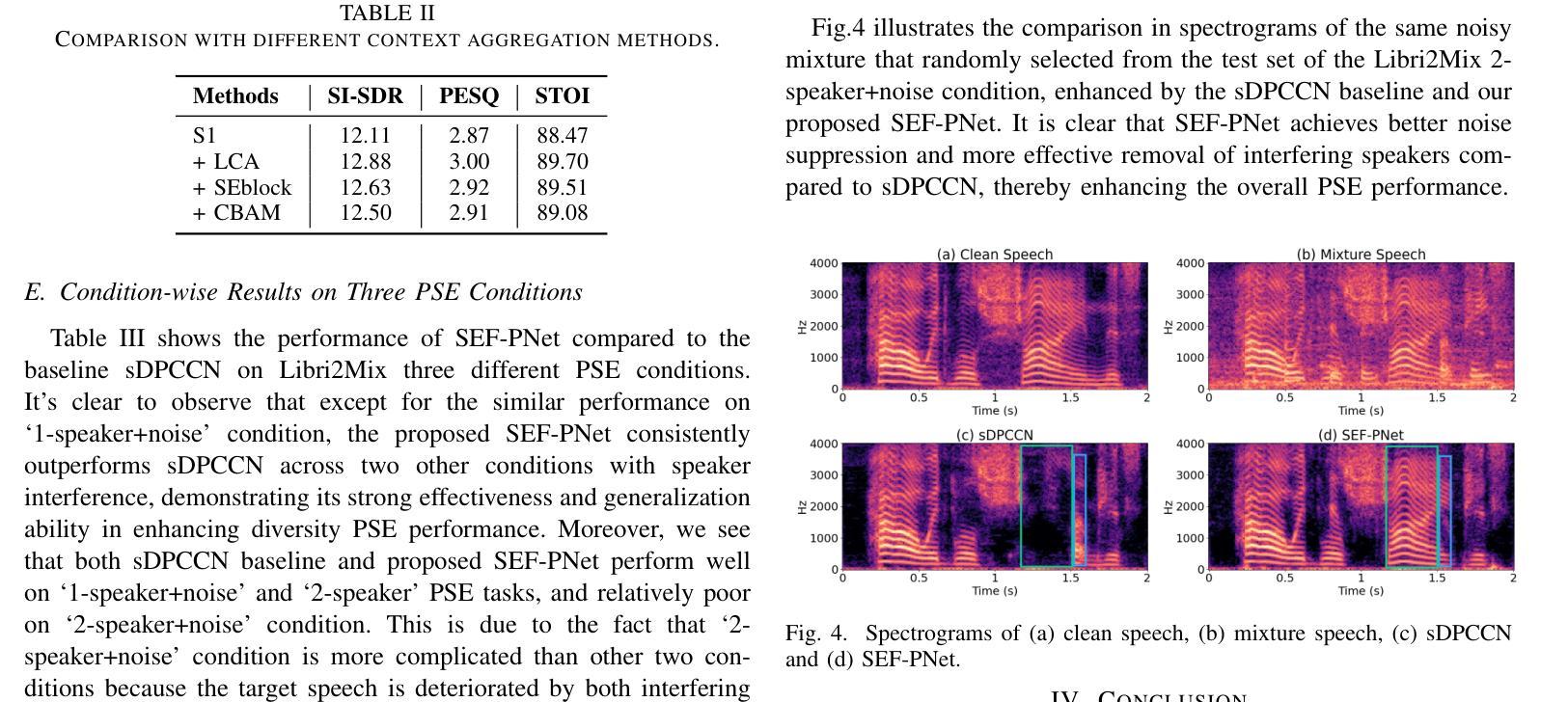
SEF-PNet: Speaker Encoder-Free Personalized Speech Enhancement with Local and Global Contexts Aggregation
Authors:Ziling Huang, Haixin Guan, Haoran Wei, Yanhua Long
Personalized speech enhancement (PSE) methods typically rely on pre-trained speaker verification models or self-designed speaker encoders to extract target speaker clues, guiding the PSE model in isolating the desired speech. However, these approaches suffer from significant model complexity and often underutilize enrollment speaker information, limiting the potential performance of the PSE model. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Speaker Encoder-Free PSE network, termed SEF-PNet, which fully exploits the information present in both the enrollment speech and noisy mixtures. SEF-PNet incorporates two key innovations: Interactive Speaker Adaptation (ISA) and Local-Global Context Aggregation (LCA). ISA dynamically modulates the interactions between enrollment and noisy signals to enhance the speaker adaptation, while LCA employs advanced channel attention within the PSE encoder to effectively integrate local and global contextual information, thus improving feature learning. Experiments on the Libri2Mix dataset demonstrate that SEF-PNet significantly outperforms baseline models, achieving state-of-the-art PSE performance.
个性化语音增强(PSE)方法通常依赖于预先训练的说话人验证模型或自行设计的说话人编码器来提取目标说话人的线索,指导PSE模型分离出所需的语音。然而,这些方法存在模型复杂度高、往往未能充分利用注册说话人的信息等问题,限制了PSE模型的潜在性能。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新型的无需说话人编码器的PSE网络,称为SEF-PNet,它充分利用了注册语音和噪声混合物中的信息。SEF-PNet有两个关键的创新点:交互式说话人适应(ISA)和局部-全局上下文聚合(LCA)。ISA动态调制注册语音和噪声信号之间的交互作用,以增强说话人适应,而LCA在PSE编码器内采用先进的通道注意力机制,有效地整合局部和全局上下文信息,从而改进特征学习。在Libri2Mix数据集上的实验表明,SEF-PNet显著优于基线模型,达到了最先进的PSE性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accpeted by ICASSP2025
摘要
本文提出了一种新型的无需Speaker Encoder的个性化语音增强网络(SEF-PNet),解决了现有方法模型复杂度高和未能充分利用注册语音信息的问题。SEF-PNet创新地引入交互式说话人适应(ISA)和局部全局上下文聚合(LCA)两大模块,分别动态调节注册语音与噪声信号的交互以增强说话人适应性,并在PSE编码器中使用先进的通道注意力机制来有效整合局部和全局上下文信息,从而改进特征学习。在Libri2Mix数据集上的实验表明,SEF-PNet显著优于基准模型,达到了先进的个性化语音增强性能。
要点分析
- SEF-PNet解决了个性化语音增强(PSE)方法中模型复杂度高的问题。
- 现有PSE方法通常依赖预训练的说话人验证模型或自设计的说话人编码器,而SEF-PNet无需这些。
- SEF-PNet通过引入交互式说话人适应(ISA)模块,动态调节注册语音与噪声信号的交互。
- SEF-PNet采用局部全局上下文聚合(LCA)模块,通过先进的通道注意力机制整合局部和全局上下文信息。
- 实验表明,SEF-PNet在Libri2Mix数据集上的性能显著优于基准模型。
- SEF-PNet充分利用了注册语音信息和噪声混合中的信息。
点此查看论文截图


A Benchmark of French ASR Systems Based on Error Severity
Authors:Antoine Tholly, Jane Wottawa, Mickael Rouvier, Richard Dufour
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) transcription errors are commonly assessed using metrics that compare them with a reference transcription, such as Word Error Rate (WER), which measures spelling deviations from the reference, or semantic score-based metrics. However, these approaches often overlook what is understandable to humans when interpreting transcription errors. To address this limitation, a new evaluation is proposed that categorizes errors into four levels of severity, further divided into subtypes, based on objective linguistic criteria, contextual patterns, and the use of content words as the unit of analysis. This metric is applied to a benchmark of 10 state-of-the-art ASR systems on French language, encompassing both HMM-based and end-to-end models. Our findings reveal the strengths and weaknesses of each system, identifying those that provide the most comfortable reading experience for users.
自动语音识别(ASR)的转录错误通常通过将其与参考转录进行比较的度量标准进行评估,例如字错误率(WER)衡量的是拼写与参考之间的差异,或者基于语义得分的度量标准。然而,这些方法在解释转录错误时往往忽略了人类的理解。为了解决这一局限性,提出了一种新的评估方法,该方法根据客观的语言标准、上下文模式以及以内容词作为分析单位,将错误分为四个严重程度类别,并进一步细分为各种亚型。该指标适用于法语中10个最新ASR系统的基准测试,包括基于隐马尔可夫模型(HMM)和端到端模型的系统。我们的研究揭示了每个系统的优点和缺点,并确定了哪些系统为用户提供了最舒适的阅读体验。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in COLING 2025 Proceedings
Summary
本文提出一种新型的自动语音识别(ASR)转录错误评估方法,该方法将误差分为四个严重程度级别并进一步划分亚型,基于客观语言标准、上下文模式以及以内容词作为分析单位进行评估。新方法应用于法语领域的十个前沿ASR系统基准测试,揭示了各系统的优缺点,特别是用户阅读体验方面的表现。
Key Takeaways
- ASR转录错误的评估常使用与参考转录对比的度量指标,如Word Error Rate(WER)和语义评分。
- 新提出的评估方法将误差分为四个严重程度级别并细分亚型,考虑客观语言标准、上下文模式。
- 新方法以内容词作为分析单位,更注重人类理解度。
- 研究对基于HMM和端到端模型的先进ASR系统在法语上进行了基准测试。
- 结果揭示了各ASR系统的优缺点。
- 新的评估方法能够识别出为用户提供最舒适阅读体验的ASR系统。
点此查看论文截图

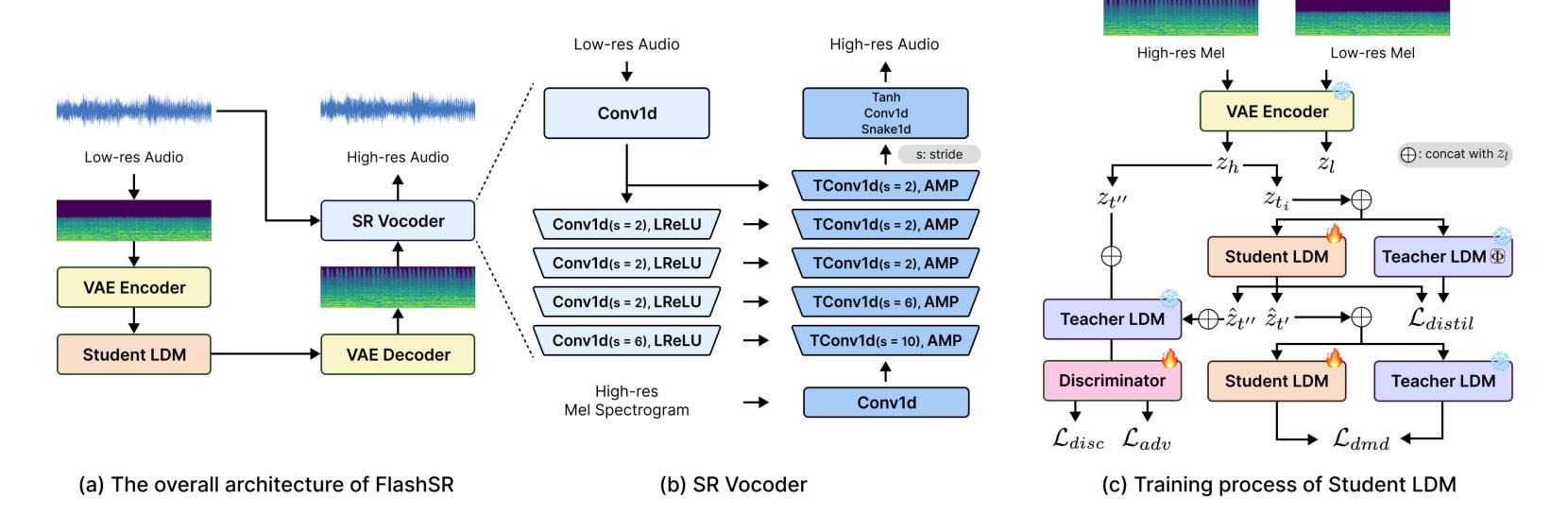
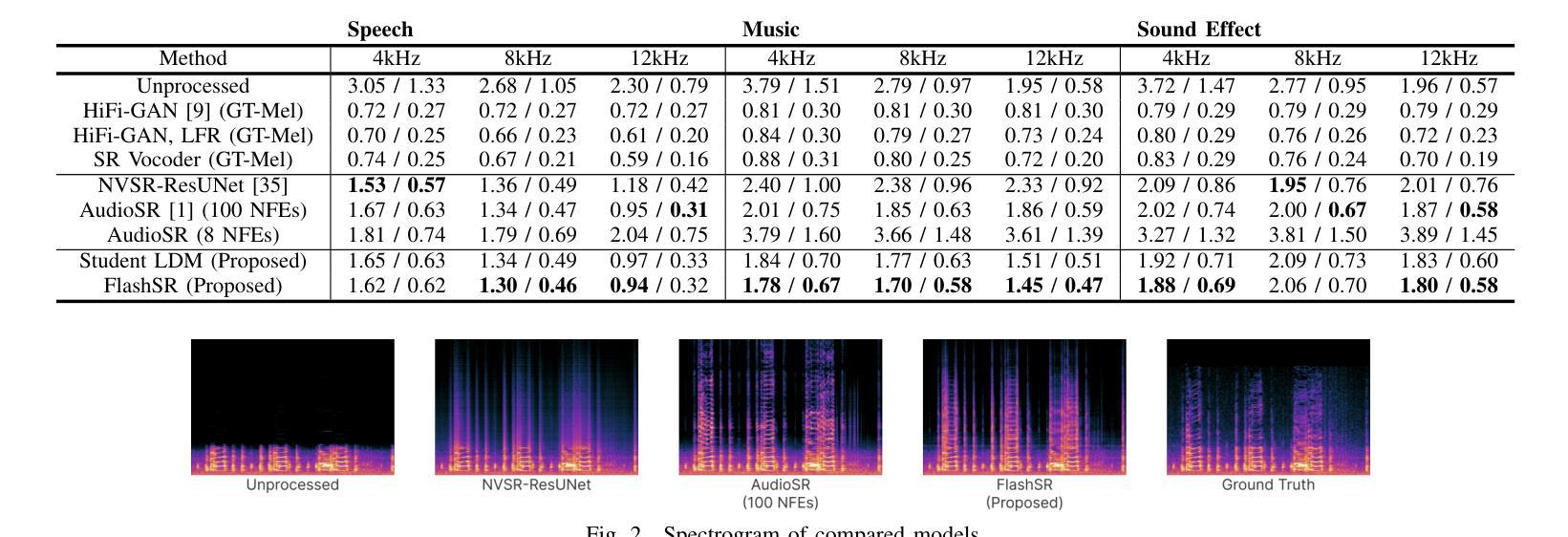
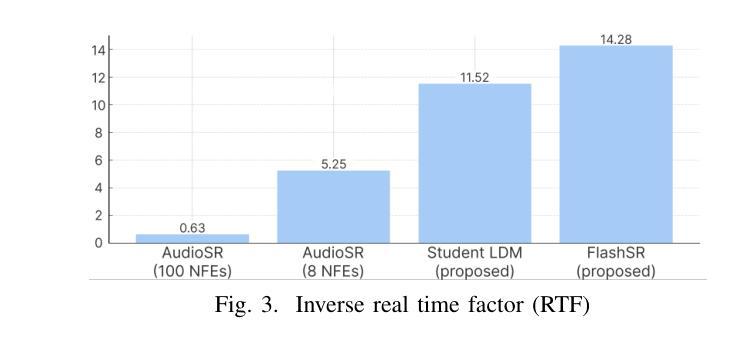
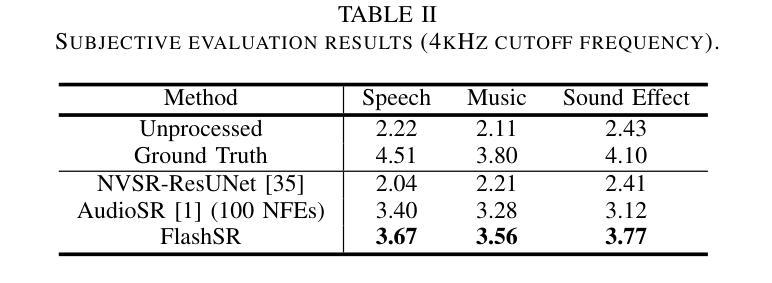
FlashSR: One-step Versatile Audio Super-resolution via Diffusion Distillation
Authors:Jaekwon Im, Juhan Nam
Versatile audio super-resolution (SR) is the challenging task of restoring high-frequency components from low-resolution audio with sampling rates between 4kHz and 32kHz in various domains such as music, speech, and sound effects. Previous diffusion-based SR methods suffer from slow inference due to the need for a large number of sampling steps. In this paper, we introduce FlashSR, a single-step diffusion model for versatile audio super-resolution aimed at producing 48kHz audio. FlashSR achieves fast inference by utilizing diffusion distillation with three objectives: distillation loss, adversarial loss, and distribution-matching distillation loss. We further enhance performance by proposing the SR Vocoder, which is specifically designed for SR models operating on mel-spectrograms. FlashSR demonstrates competitive performance with the current state-of-the-art model in both objective and subjective evaluations while being approximately 22 times faster.
多功能音频超分辨率(SR)是一项具有挑战性的任务,即从采样率为4kHz至32kHz的低分辨率音频中恢复各种领域(如音乐、语音和音效)的高频成分。之前的基于扩散的SR方法由于需要大量的采样步骤,导致推理速度较慢。在本文中,我们介绍了FlashSR,这是一种用于多功能音频超分辨率的单步扩散模型,旨在生成48kHz音频。FlashSR通过利用扩散蒸馏的三个目标来实现快速推理,包括蒸馏损失、对抗损失和分布匹配蒸馏损失。我们进一步通过提出专门用于操作梅尔频谱图的SR Vocoder来提高性能。FlashSR在客观和主观评估中均表现出与当前最先进的模型相当的竞争力,同时速度大约快22倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为FlashSR的单步扩散模型,用于通用音频超分辨率,旨在生成48kHz音频。它通过利用扩散蒸馏技术实现快速推理,并实现了三个目标:蒸馏损失、对抗损失和分布匹配蒸馏损失。此外,还提出了专门为梅尔频谱图设计的SR Vocoder,以提高性能。FlashSR在客观和主观评估中都表现出与当前最先进的模型相当的竞争力,并且速度提高了约22倍。
Key Takeaways
- FlashSR是一种用于音频超分辨率的单步扩散模型,可生成高质量48kHz音频。
- 通过扩散蒸馏技术实现快速推理,提高计算效率。
- 实现三个目标:蒸馏损失、对抗损失和分布匹配蒸馏损失,以提高模型性能。
- 引入SR Vocoder,专门为梅尔频谱图设计的工具,进一步提升模型性能。
- FlashSR在客观和主观评估中表现优异,与当前最先进的模型相当。
- FlashSR模型推理速度大幅提高,约是现有方法的22倍。
点此查看论文截图


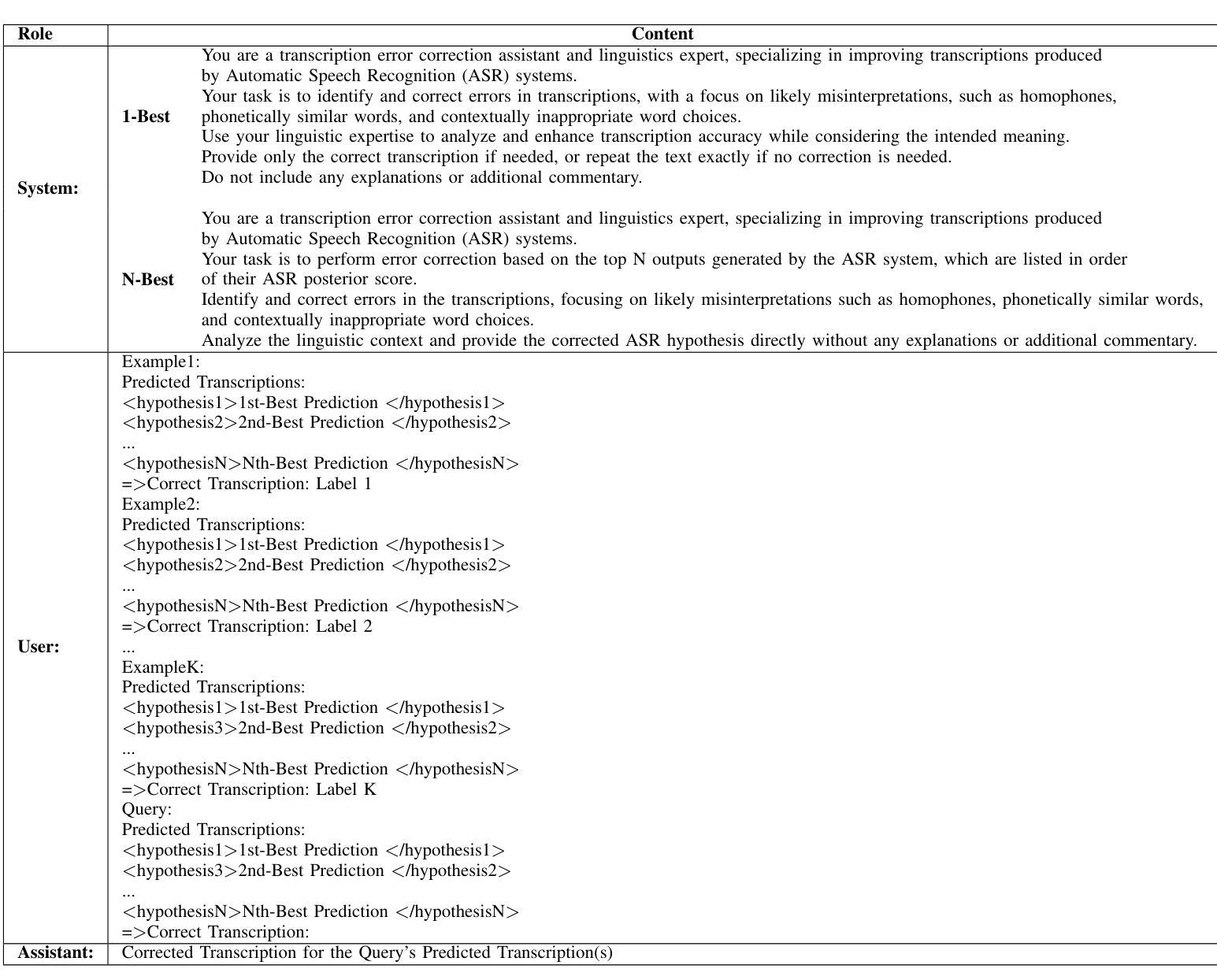
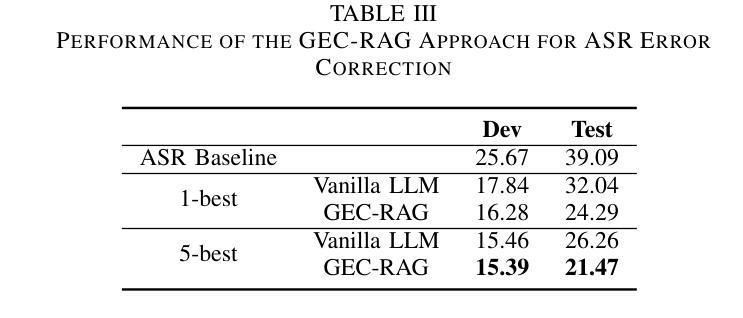
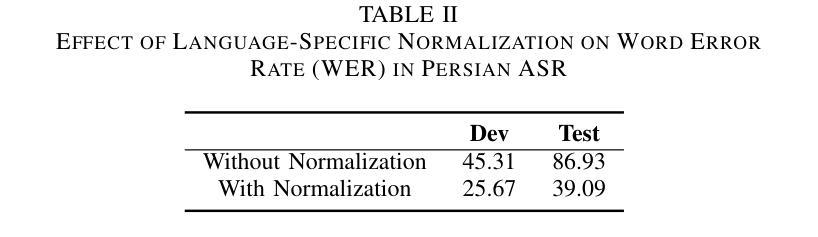
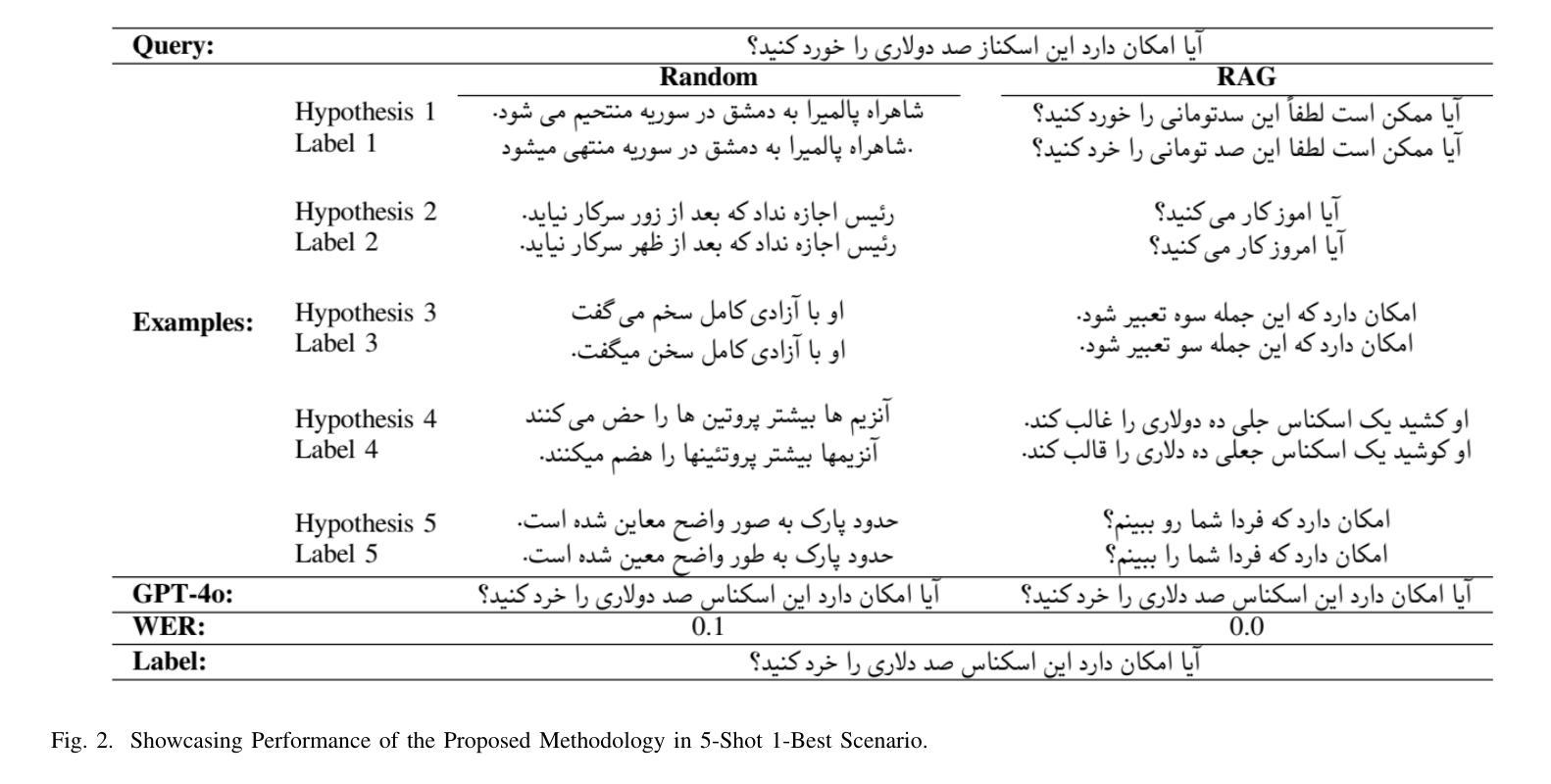
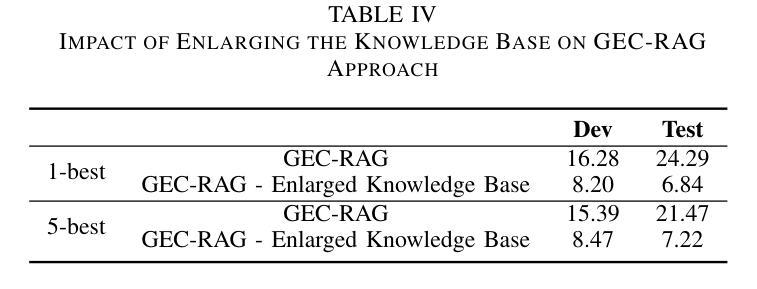
GEC-RAG: Improving Generative Error Correction via Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Automatic Speech Recognition Systems
Authors:Amin Robatian, Mohammad Hajipour, Mohammad Reza Peyghan, Fatemeh Rajabi, Sajjad Amini, Shahrokh Ghaemmaghami, Iman Gholampour
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems have demonstrated remarkable performance across various applications. However, limited data and the unique language features of specific domains, such as low-resource languages, significantly degrade their performance and lead to higher Word Error Rates (WER). In this study, we propose Generative Error Correction via Retrieval-Augmented Generation (GEC-RAG), a novel approach designed to improve ASR accuracy for low-resource domains, like Persian. Our approach treats the ASR system as a black-box, a common practice in cloud-based services, and proposes a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) approach within the In-Context Learning (ICL) scheme to enhance the quality of ASR predictions. By constructing a knowledge base that pairs ASR predictions (1-best and 5-best hypotheses) with their corresponding ground truths, GEC-RAG retrieves lexically similar examples to the ASR transcription using the Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) measure. This process provides relevant error patterns of the system alongside the ASR transcription to the Generative Large Language Model (LLM), enabling targeted corrections. Our results demonstrate that this strategy significantly reduces WER in Persian and highlights a potential for domain adaptation and low-resource scenarios. This research underscores the effectiveness of using RAG in enhancing ASR systems without requiring direct model modification or fine-tuning, making it adaptable to any domain by simply updating the transcription knowledge base with domain-specific data.
自动语音识别(ASR)系统在各种应用中表现出了卓越的性能。然而,特定领域的有限数据和独特语言特征,如低资源语言,会显著地降低其性能,导致更高的词错误率(WER)。在这项研究中,我们提出了通过检索增强生成(RAG)进行生成错误校正(GEC-RAG)的新方法,旨在提高低资源领域(如波斯语)的ASR准确性。我们的方法将ASR系统视为一个黑盒,这是云服务中的常见做法,并提出了在上下文学习(ICL)方案内使用检索增强生成(RAG)的方法,以提高ASR预测的质量。通过构建配对ASR预测(最佳假设和前五个假设)与其相应真实值的知识库,GEC-RAG使用词频-逆文档频率(TF-IDF)度量来检索与ASR转录词汇上相似的例子。这个过程为系统相关的错误模式以及ASR转录提供了生成式大型语言模型(LLM),从而实现有针对性的校正。我们的结果表明,该策略在波斯语中显著降低了WER,并突出了领域适应和低资源场景的潜力。这项研究强调了使用RAG在增强ASR系统效果上的有效性,且无需进行直接的模型修改或微调,通过简单地更新转录知识库并引入特定领域的数据,即可适应任何领域。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages
Summary
本研究针对自动语音识别(ASR)系统在低资源领域如波斯语中的性能问题,提出了一种基于检索增强生成(RAG)的生成误差校正(GEC-RAG)新方法。该方法将ASR系统视为黑盒,通过构建与ASR预测及其对应真实值相匹配的知识库,使用TF-IDF度量标准检索与ASR转录词汇相似的例子。这种方法能有效减少系统错误模式,针对生成式大型语言模型(LLM)进行针对性校正,显著提高波斯语的ASR准确性。此方法无需对模型进行直接修改或微调,仅通过更新转录知识库即可适应任何领域。
Key Takeaways
- ASR系统在低资源领域如波斯语中面临性能挑战,导致较高的单词错误率(WER)。
- 提出了一种新的方法GEC-RAG,旨在提高ASR系统的准确性。
- GEC-RAG采用黑盒方式处理ASR系统,适应云服务的常见实践。
- 通过构建知识库和采用检索增强生成(RAG)方法,在上下文学习(ICL)框架下提高ASR预测质量。
- 使用TF-IDF度量标准检索与ASR转录词汇相似的例子,以获取系统的相关错误模式。
- GEC-RAG能显著减少波斯语的WER,并展示在领域适应和低资源场景下的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

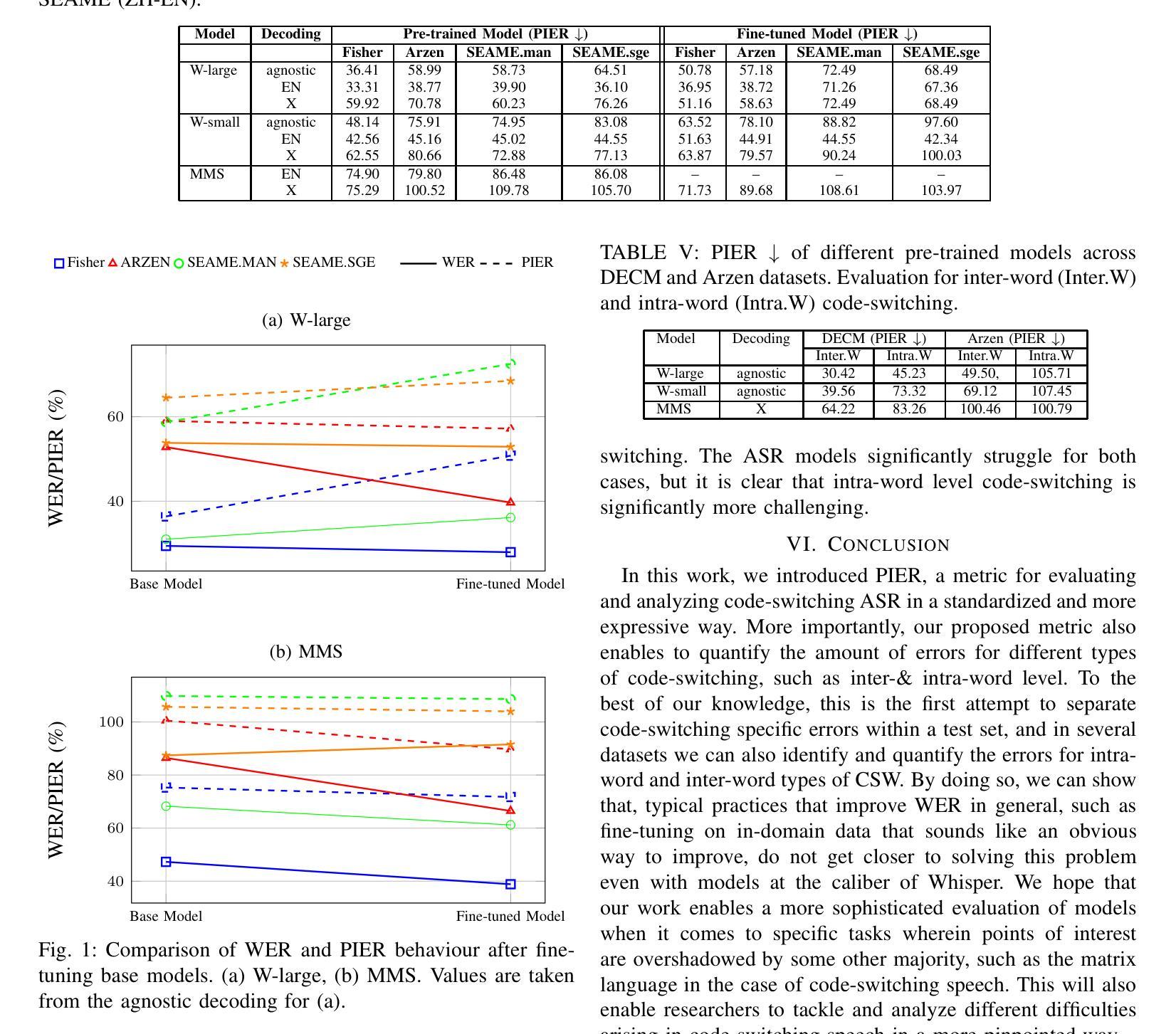
PIER: A Novel Metric for Evaluating What Matters in Code-Switching
Authors:Enes Yavuz Ugan, Ngoc-Quan Pham, Leonard Bärmann, Alex Waibel
Code-switching, the alternation of languages within a single discourse, presents a significant challenge for Automatic Speech Recognition. Despite the unique nature of the task, performance is commonly measured with established metrics such as Word-Error-Rate (WER). However, in this paper, we question whether these general metrics accurately assess performance on code-switching. Specifically, using both Connectionist-Temporal-Classification and Encoder-Decoder models, we show fine-tuning on non-code-switched data from both matrix and embedded language improves classical metrics on code-switching test sets, although actual code-switched words worsen (as expected). Therefore, we propose Point-of-Interest Error Rate (PIER), a variant of WER that focuses only on specific words of interest. We instantiate PIER on code-switched utterances and show that this more accurately describes the code-switching performance, showing huge room for improvement in future work. This focused evaluation allows for a more precise assessment of model performance, particularly in challenging aspects such as inter-word and intra-word code-switching.
语言转换(code-switching)指的是在同一语境中交替使用不同的语言,这对自动语音识别(ASR)构成了一大挑战。尽管这项任务具有独特性,但其性能通常使用既定的指标(如单词错误率(WER))来衡量。然而,在这篇论文中,我们质疑这些通用指标是否准确评估了语言转换的性能。具体来说,我们利用连接时序分类和编码器-解码器模型,展示了通过对来自矩阵和嵌入式语言的非代码转换数据进行微调,可以在代码转换测试集上提高经典指标的性能,尽管实际的代码转换单词有所恶化(符合预期)。因此,我们提出了兴趣点错误率(PIER),它是WER的一种变体,只关注特定的兴趣词汇。我们在代码转换的片段中实例化PIER,并证明它能更准确地描述代码转换的性能,显示出未来工作中有很大的改进空间。这种有针对性的评估允许对模型性能进行更精确的评估,特别是在词间和词内代码转换等具有挑战性的方面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文探讨了代码切换(不同语言在单一语境中的交替使用)对自动语音识别(ASR)带来的挑战。现有评估指标如字错误率(WER)未能准确衡量ASR在代码切换任务上的性能。研究通过采用连接时序分类和编码器解码器模型发现,在非代码切换数据上进行微调虽能提高经典指标在代码切换测试集上的表现,但实际的代码切换词汇表现仍会下降。因此,提出一种新的评估指标——兴趣点错误率(PIER),这是一种关注特定兴趣词汇的WER变体。在代码切换的语音片段中实施PIER,能更准确地描述代码切换性能,显示出未来改进的巨大空间。这种有针对性的评估方法能更精确地评估模型性能,特别是在跨词和词内代码切换等挑战方面。
Key Takeaways
- 代码切换对自动语音识别(ASR)构成挑战,需要特定的评估指标。
- 现有评估指标如字错误率(WER)未能准确衡量ASR在代码切换任务上的性能。
- 非代码切换数据的微调能提高经典指标在代码切换测试集上的表现,但实际应用中代码切换词汇的表现仍然不佳。
- 提出新的评估指标——兴趣点错误率(PIER),专注于特定词汇的评估,更能准确反映代码切换的性能。
- PIER在代码切换的语音片段中实施,显示出未来改进的巨大空间。
- 针对性的评估方法能更精确地评估模型性能,特别是在跨词和词内代码切换等挑战方面。
点此查看论文截图

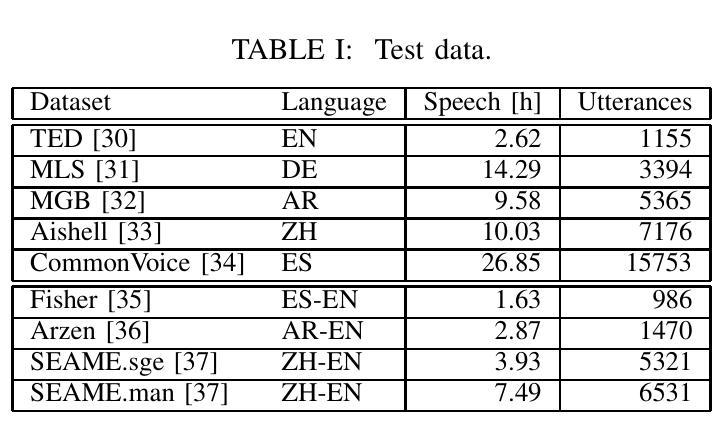
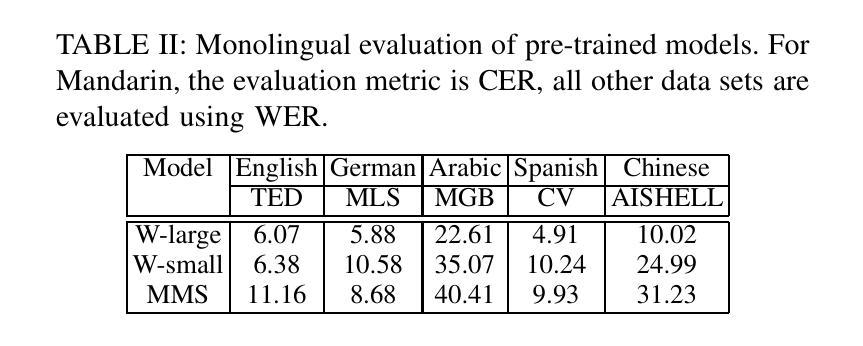
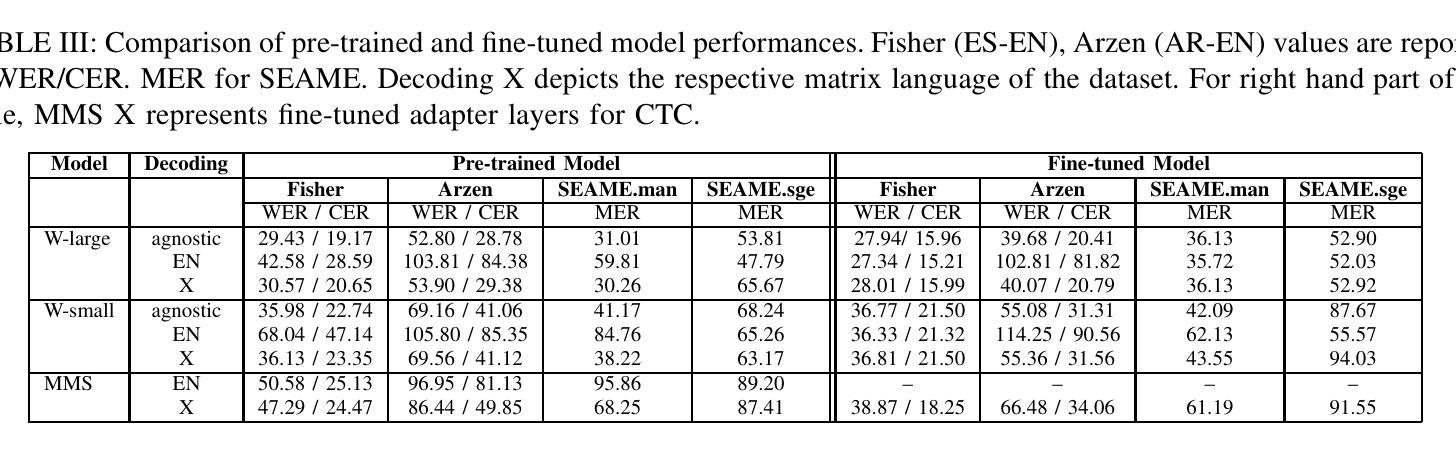
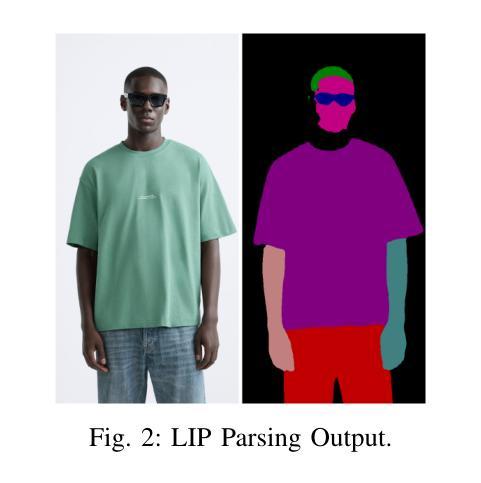
Multimodal Marvels of Deep Learning in Medical Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Review of COVID-19 Detection
Authors:Md Shofiqul Islam, Khondokar Fida Hasan, Hasibul Hossain Shajeeb, Humayan Kabir Rana, Md Saifur Rahmand, Md Munirul Hasan, AKM Azad, Ibrahim Abdullah, Mohammad Ali Moni
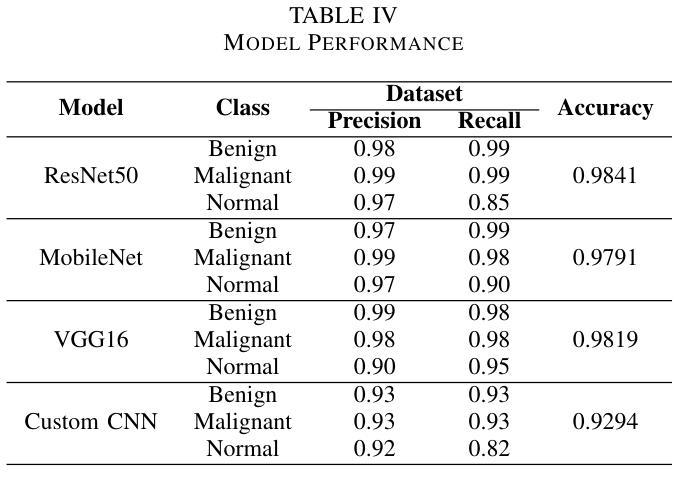
This study presents a comprehensive review of the potential of multimodal deep learning (DL) in medical diagnosis, using COVID-19 as a case example. Motivated by the success of artificial intelligence applications during the COVID-19 pandemic, this research aims to uncover the capabilities of DL in disease screening, prediction, and classification, and to derive insights that enhance the resilience, sustainability, and inclusiveness of science, technology, and innovation systems. Adopting a systematic approach, we investigate the fundamental methodologies, data sources, preprocessing steps, and challenges encountered in various studies and implementations. We explore the architecture of deep learning models, emphasising their data-specific structures and underlying algorithms. Subsequently, we compare different deep learning strategies utilised in COVID-19 analysis, evaluating them based on methodology, data, performance, and prerequisites for future research. By examining diverse data types and diagnostic modalities, this research contributes to scientific understanding and knowledge of the multimodal application of DL and its effectiveness in diagnosis. We have implemented and analysed 11 deep learning models using COVID-19 image, text, and speech (ie, cough) data. Our analysis revealed that the MobileNet model achieved the highest accuracy of 99.97% for COVID-19 image data and 93.73% for speech data (i.e., cough). However, the BiGRU model demonstrated superior performance in COVID-19 text classification with an accuracy of 99.89%. The broader implications of this research suggest potential benefits for other domains and disciplines that could leverage deep learning techniques for image, text, and speech analysis.
本研究全面回顾了多模态深度学习(DL)在医学诊断中的潜力,并以COVID-19作为案例进行说明。本研究受COVID-19疫情期间人工智能应用成功的启发,旨在揭示深度学习在疾病筛查、预测和分类方面的能力,并借此获得能够增强科学、技术和创新系统韧性、可持续性和包容性的见解。我们采用系统方法,研究各种研究和实践中的基本方法、数据来源、预处理步骤和遇到的挑战。我们探讨深度学习模型的架构,重点介绍其数据特定结构和基础算法。然后,我们对COVID-19分析中使用的不同深度学习策略进行比较,根据方法、数据、性能和未来研究的前提条件进行评估。本研究通过检查多种数据类型和诊断模式,有助于理解和认识深度学习多模态应用的科学知识及其诊断的有效性。我们使用和分析了11种深度学习模型,使用COVID-19图像、文本和语音(即咳嗽声)数据。分析结果显示,MobileNet模型对COVID-19图像数据的准确率最高,达99.97%,对语音数据的准确率为93.73%(即咳嗽声识别)。然而,BiGRU模型在COVID-19文本分类方面表现出卓越的性能,准确率为99.89%。这项研究的更广泛意义表明,其他领域和学科也有可能受益于深度学习技术在图像、文本和语音分析中的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 43 pages
摘要
本文全面综述了多模态深度学习在医学诊断中的潜力,以COVID-19为例。该研究旨在揭示深度学习在疾病筛查、预测和分类方面的能力,并从科学、技术和创新系统的韧性、可持续性和包容性中汲取见解。文章采用系统方法,探讨了各种研究和实践中的基本方法、数据来源、预处理步骤和遇到的挑战。文章探讨了深度学习模型的架构,强调其数据特定结构和基础算法。通过对COVID-19分析中使用的不同深度学习策略进行比较,本文评估了它们在方法、数据、性能和未来研究需求方面的表现。通过对多种数据类型和诊断方式的研究,本文为深度学习在多模态应用中的科学理解和有效性诊断做出了贡献。研究发现,MobileNet模型在COVID-19图像和语音数据上的准确率最高,分别为99.97%和93.73%(即咳嗽声)。然而,BiGRU模型在COVID-19文本分类中表现出卓越的性能,准确率为99.89%。该研究的更广泛影响表明,其他领域和学科也可能从深度学习中受益,用于图像、文本和语音分析。
关键见解
- 多模态深度学习在医学诊断中具有巨大潜力,特别是在COVID-19等疾病的筛查、预测和分类方面。
- 研究对比了多种深度学习模型在COVID-19图像、文本和语音数据上的表现,发现MobileNet模型在图像和语音数据上表现最佳,而BiGRU模型在文本分类中表现优秀。
- 该研究强调深度学习模型的数据特定结构和基础算法的重要性。
- 研究指出了多模态深度学习应用中的挑战,包括数据类型多样性和诊断方式的复杂性。
- 深度学习技术能够提高科学、技术和创新系统的韧性、可持续性和包容性。
- 该研究的发现不仅限于医学领域,对其他需要图像、文本和语音分析的领域也有潜在应用价值。
点此查看论文截图



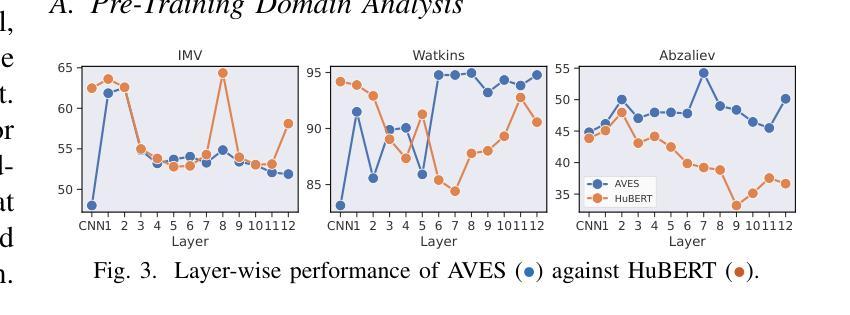
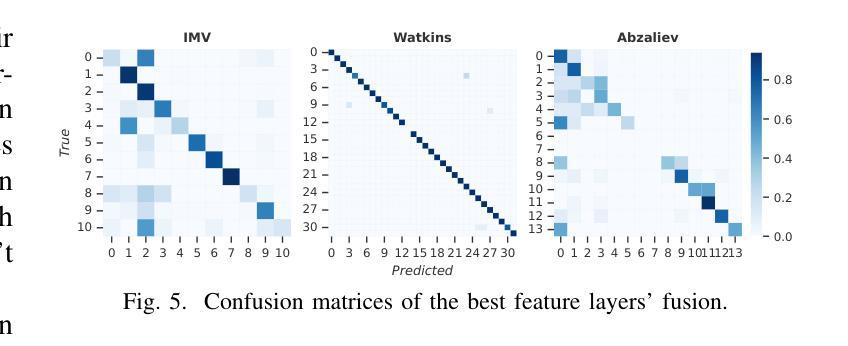
Comparing Self-Supervised Learning Models Pre-Trained on Human Speech and Animal Vocalizations for Bioacoustics Processing
Authors:Eklavya Sarkar, Mathew Magimai. -Doss
Self-supervised learning (SSL) foundation models have emerged as powerful, domain-agnostic, general-purpose feature extractors applicable to a wide range of tasks. Such models pre-trained on human speech have demonstrated high transferability for bioacoustic processing. This paper investigates (i) whether SSL models pre-trained directly on animal vocalizations offer a significant advantage over those pre-trained on speech, and (ii) whether fine-tuning speech-pretrained models on automatic speech recognition (ASR) tasks can enhance bioacoustic classification. We conduct a comparative analysis using three diverse bioacoustic datasets and two different bioacoustic tasks. Results indicate that pre-training on bioacoustic data provides only marginal improvements over speech-pretrained models, with comparable performance in most scenarios. Fine-tuning on ASR tasks yields mixed outcomes, suggesting that the general-purpose representations learned during SSL pre-training are already well-suited for bioacoustic tasks. These findings highlight the robustness of speech-pretrained SSL models for bioacoustics and imply that extensive fine-tuning may not be necessary for optimal performance.
自监督学习(SSL)基础模型已经作为强大、领域无关、通用的特征提取器出现,适用于各种任务。这种在人类语音上预训练的模型已经显示出在生物声音处理上的高可迁移性。本文旨在研究(i)直接对动物鸣叫声进行预训练的自监督学习模型是否相对于在语音上预训练的模型具有显著优势;(ii)在自动语音识别(ASR)任务上对语音预训练模型进行微调是否能提高生物声音分类能力。我们使用三个不同的生物声音数据集和两个不同的生物声音任务进行了对比分析。结果表明,在生物声音数据上进行预训练只在对语音预训练模型的基础上有微小的改进,并且在大多数情况下性能相当。在ASR任务上进行微调会产生混合的结果,这表明在SSL预训练期间学习的通用表示已经非常适合生物声音任务。这些发现突出了语音预训练SSL模型在生物声学方面的稳健性,并且暗示可能不需要大量微调就能达到最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
总结
本研究探讨了自我监督学习(SSL)模型在动物发声和语音上的预训练对生物声学处理的优越性,并研究了在语音识别任务上微调语音预训练模型对生物声学分类的增强效果。实验使用三个不同的生物声学数据集和两个任务进行比较分析,结果表明,在生物声学数据上进行预训练只带来了微小的改进,在大多数场景中性能相当。对语音识别任务进行微调产生了混合的结果,这表明在SSL预训练期间学习的通用表示已经适合生物声学任务。这些发现突显了语音预训练SSL模型在生物声学中的稳健性,并暗示对于最佳性能可能不需要大量微调。
关键见解
- 自我监督学习(SSL)模型已成为强大的、领域无关的、通用的特征提取器,适用于各种任务。
- SSL模型在动物发声上的预训练相较于语音预训练只带来微小优势。
- 在大多数场景中,基于语音预训练的SSL模型与基于动物发声预训练的模型性能相当。
- 对语音识别(ASR)任务进行微调在生物声学分类中的效果不一,这表明通用表示已适合生物声学任务。
- 语音预训练的SSL模型在生物声学领域具有稳健性。
- 对于最佳性能,可能不需要大量的微调。
- 研究结果有助于更深入地理解SSL模型在生物声学及其他领域的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图


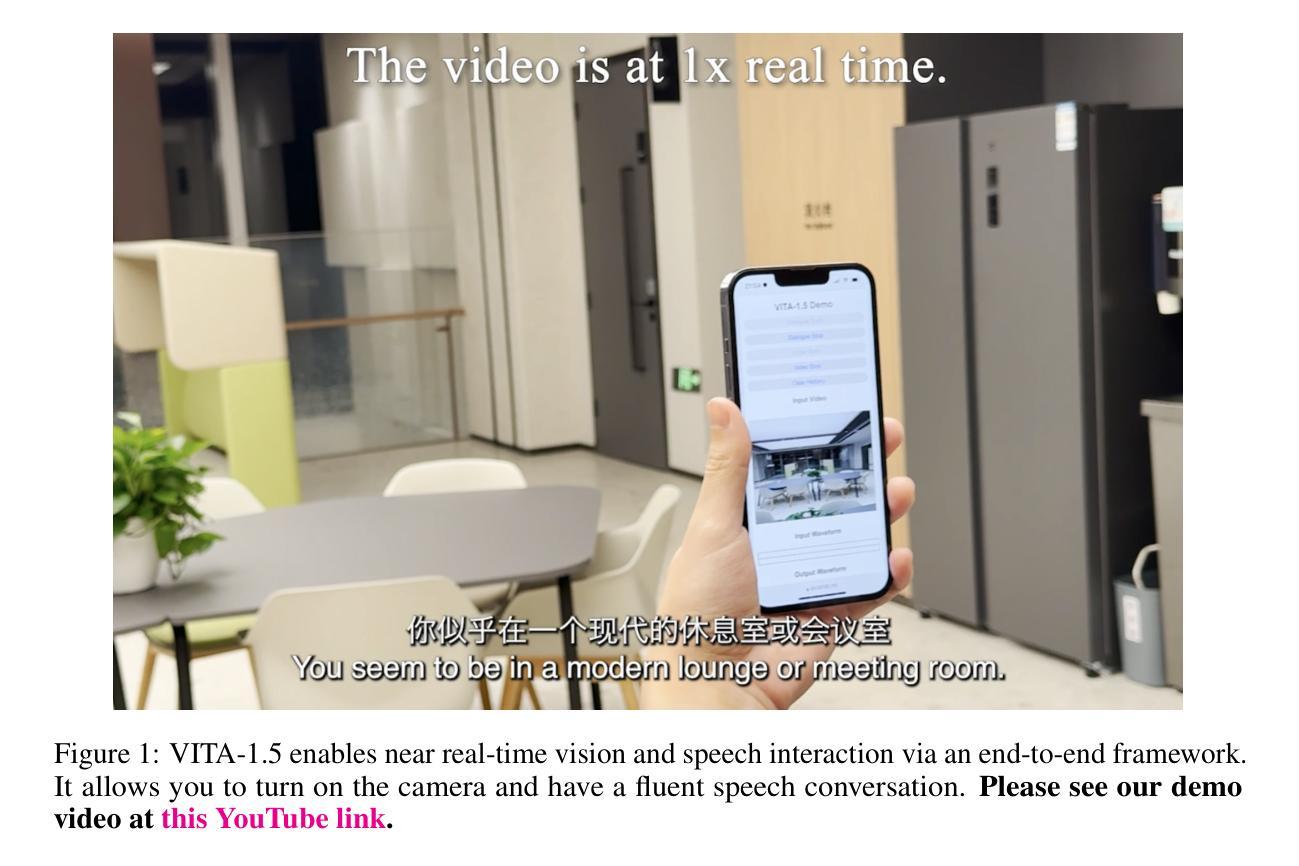
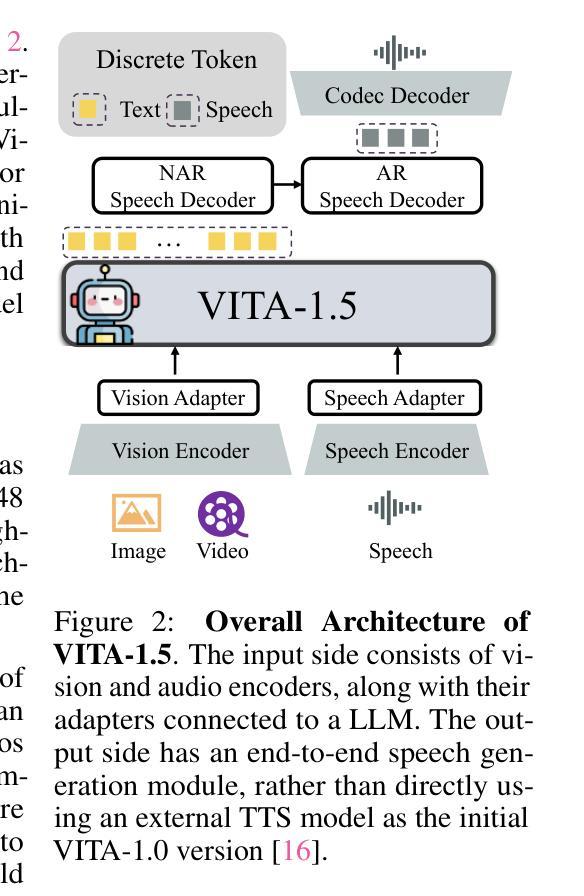
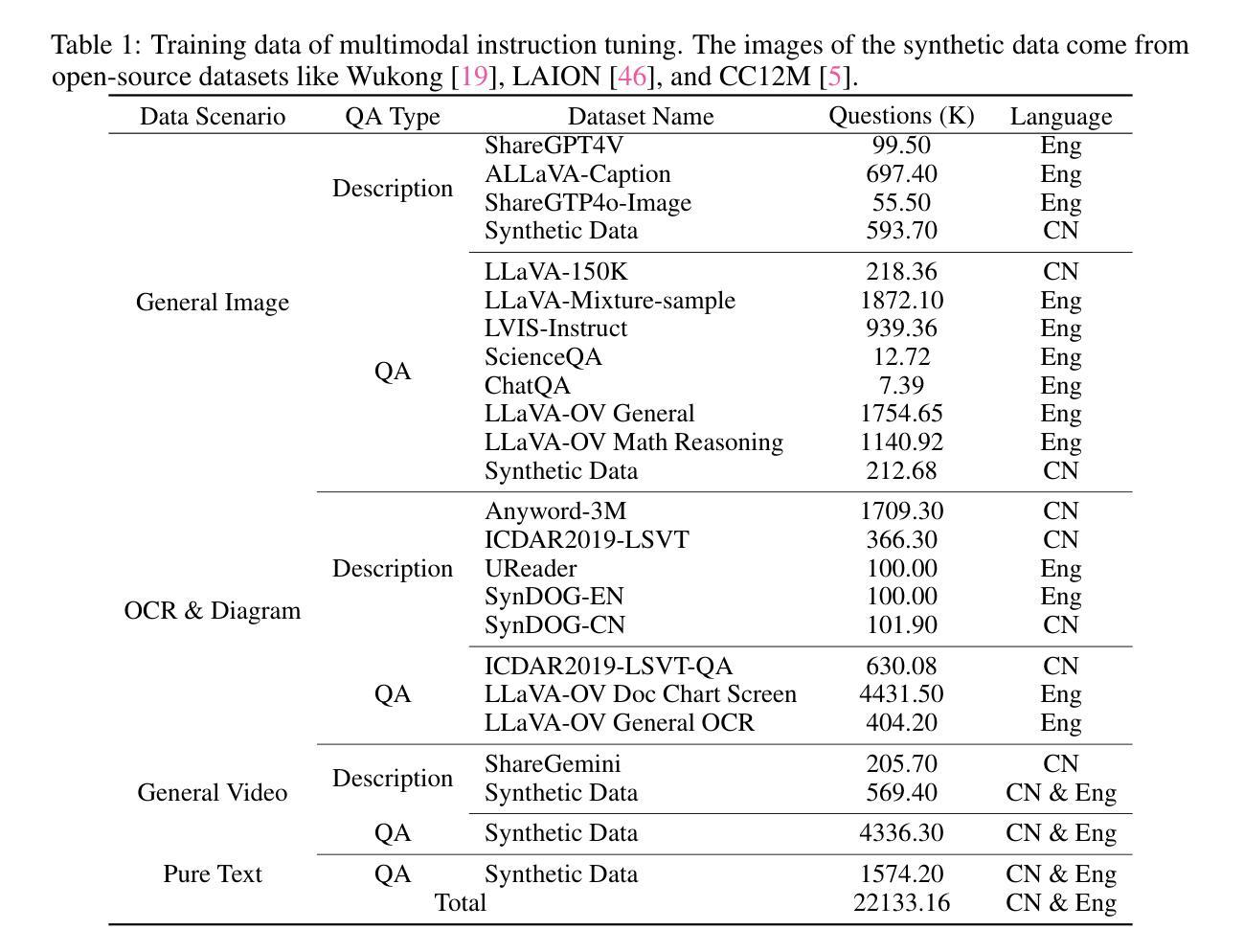
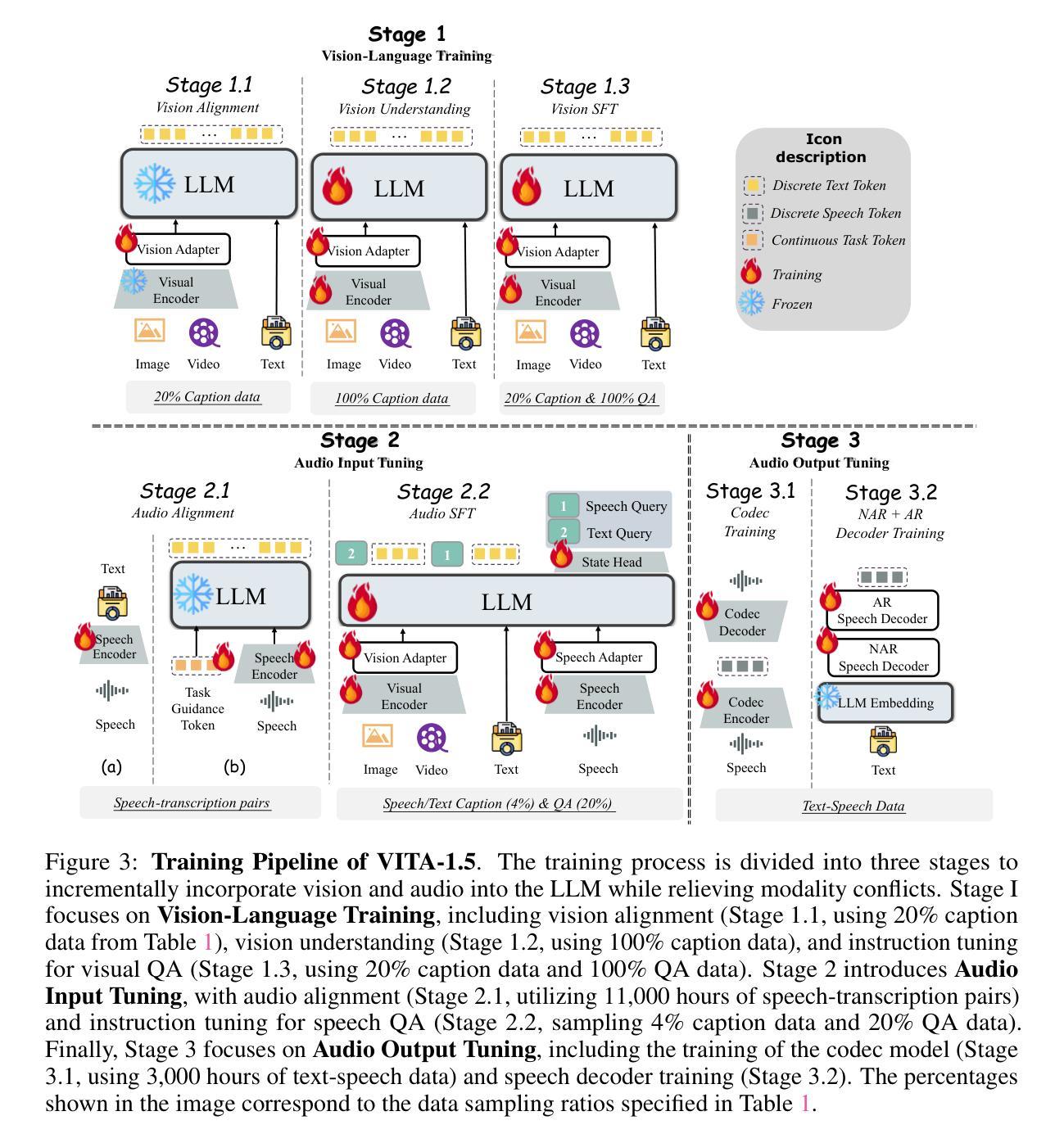
VITA-1.5: Towards GPT-4o Level Real-Time Vision and Speech Interaction
Authors:Chaoyou Fu, Haojia Lin, Xiong Wang, Yi-Fan Zhang, Yunhang Shen, Xiaoyu Liu, Haoyu Cao, Zuwei Long, Heting Gao, Ke Li, Long Ma, Xiawu Zheng, Rongrong Ji, Xing Sun, Caifeng Shan, Ran He
Recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have typically focused on integrating visual and textual modalities, with less emphasis placed on the role of speech in enhancing interaction. However, speech plays a crucial role in multimodal dialogue systems, and implementing high-performance in both vision and speech tasks remains a significant challenge due to the fundamental modality differences. In this paper, we propose a carefully designed multi-stage training methodology that progressively trains LLM to understand both visual and speech information, ultimately enabling fluent vision and speech interaction. Our approach not only preserves strong vision-language capacity, but also enables efficient speech-to-speech dialogue capabilities without separate ASR and TTS modules, significantly accelerating multimodal end-to-end response speed. By comparing our method against state-of-the-art counterparts across benchmarks for image, video, and speech tasks, we demonstrate that our model is equipped with both strong visual and speech capabilities, making near real-time vision and speech interaction.
最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)主要关注视觉和文本模态的融合,对语音在增强交互中的作用重视不足。然而,语音在多模态对话系统中起着至关重要的作用,由于在视觉和语音任务之间存在基本模式差异,因此在两者上实现高性能仍然是一个巨大的挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种精心设计的多阶段训练方法论,逐步训练大型语言模型以理解视觉和语音信息,最终使流畅的视觉和语音交互成为可能。我们的方法不仅保留了强大的视觉语言功能,还能够在没有单独的语音识别和文本转语音模块的情况下实现高效的语音对话功能,从而显著加快多模态端到端的响应速度。通过与图像、视频和语音任务的最新先进模型进行比较,我们证明了我们的模型具有强大的视觉和语音功能,能够实现近乎实时的视觉和语音交互。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/VITA-MLLM/VITA (2K+ Stars by now)
Summary
本文提出一种分阶段训练方法,让大型语言模型同时理解视觉和语音信息,实现流畅的视觉和语音交互。该方法不仅保留了强大的视觉语言能力,还能实现高效的语音对话能力,无需额外的语音识别和文本转语音模块,显著加速了多模态端到端的响应速度。实验证明,该模型在图像、视频和语音任务上均表现出优异性能,实现了近实时的视觉和语音交互能力。
Key Takeaways
- 近期多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)更多地关注视觉和文本模态的融合,忽略了语音在增强交互中的作用。
- 语音在多模态对话系统中扮演关键角色,同时在视觉和语音任务中实现高性能是一个挑战。
- 论文提出了一种多阶段训练策略,使LLM能够理解视觉和语音信息,实现流畅的多模态交互。
- 该方法保留了强大的视觉语言能力,同时增强了模型的语音对话能力,无需额外的语音识别和文本转语音模块。
- 模型在多模态端到端的响应速度上有所突破,显著提高了实时性能。
- 实验结果表明,该模型在图像、视频和语音任务上均表现出优异性能。
点此查看论文截图

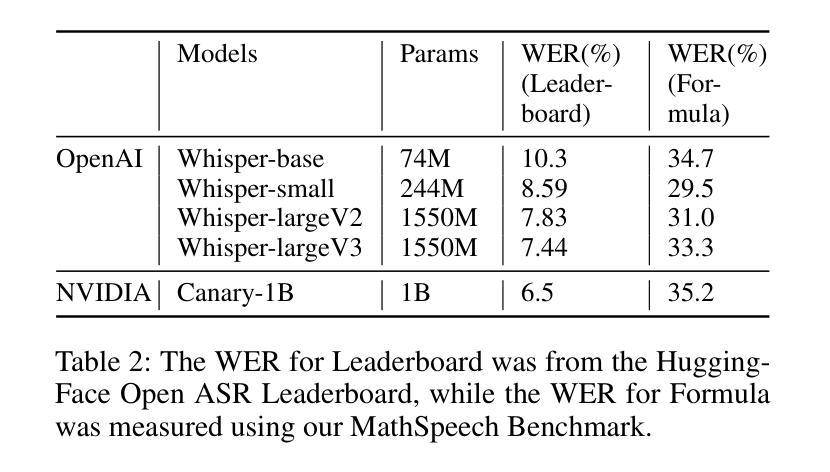
MathSpeech: Leveraging Small LMs for Accurate Conversion in Mathematical Speech-to-Formula
Authors:Sieun Hyeon, Kyudan Jung, Jaehee Won, Nam-Joon Kim, Hyun Gon Ryu, Hyuk-Jae Lee, Jaeyoung Do
In various academic and professional settings, such as mathematics lectures or research presentations, it is often necessary to convey mathematical expressions orally. However, reading mathematical expressions aloud without accompanying visuals can significantly hinder comprehension, especially for those who are hearing-impaired or rely on subtitles due to language barriers. For instance, when a presenter reads Euler’s Formula, current Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models often produce a verbose and error-prone textual description (e.g., e to the power of i x equals cosine of x plus i $\textit{side}$ of x), instead of the concise $\LaTeX{}$ format (i.e., $ e^{ix} = \cos(x) + i\sin(x) $), which hampers clear understanding and communication. To address this issue, we introduce MathSpeech, a novel pipeline that integrates ASR models with small Language Models (sLMs) to correct errors in mathematical expressions and accurately convert spoken expressions into structured $\LaTeX{}$ representations. Evaluated on a new dataset derived from lecture recordings, MathSpeech demonstrates $\LaTeX{}$ generation capabilities comparable to leading commercial Large Language Models (LLMs), while leveraging fine-tuned small language models of only 120M parameters. Specifically, in terms of CER, BLEU, and ROUGE scores for $\LaTeX{}$ translation, MathSpeech demonstrated significantly superior capabilities compared to GPT-4o. We observed a decrease in CER from 0.390 to 0.298, and higher ROUGE/BLEU scores compared to GPT-4o.
在各种学术和专业场合,如数学讲座或研究报告会中,传达数学表达式是常有的需求。然而,在没有视觉辅助的情况下大声阅读数学表达式可能会极大地阻碍理解,特别是对于听力受损或由于语言障碍而依赖字幕的人来说。例如,当演讲者朗读欧拉公式时,当前的自动语音识别(ASR)模型往往会生成冗长和易出错的文本描述(例如,“e的i乘以x次方等于x的余弦值加上i倍的x正弦值”),而不是简洁的LaTeX格式(即,$ e^{ix} = \cos(x) + i\sin(x) $)。这阻碍了清晰的理解和沟通。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了MathSpeech,这是一种新型管道,它将ASR模型与小语言模型(sLMs)结合起来,以纠正数学表达式中的错误,并将口头表达准确转换为结构化的LaTeX表示。在新的数据集上评估发现该数据集来自讲座录音,MathSpeech表现出可与领先商业大型语言模型(LLMs)相媲美的LaTeX生成能力,同时利用仅包含1.2亿参数的微调小型语言模型。具体来说,在LaTeX翻译的CER、BLEU和ROUGE分数方面,MathSpeech相对于GPT-4o展现出显著优越的能力。我们观察到CER从0.390降至0.298,并且与GPT-4o相比具有更高的ROUGE/BLEU分数。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAAI 2025
Summary
数学表达式在学术和专业场合的口头传达至关重要,但无视觉辅助时存在理解障碍。为解决现有自动语音识别模型在处理数学表达时的冗长和误差问题,引入MathSpeech管道。它整合了小语言模型,能纠正数学表达中的错误,准确将口语转化为结构化LaTeX表示。新数据集上的评估显示,MathSpeech在LaTeX生成能力上表现卓越,且仅需微调12亿参数的小型语言模型即可实现。相较于GPT-4o,MathSpeech在CER、BLEU和ROUGE得分上表现更优。
Key Takeaways
- 口头传达数学表达在学术和专业场合很重要,但缺乏视觉辅助会增加理解难度。
- 现有自动语音识别模型在处理数学表达时存在冗长和误差问题。
- MathSpeech是一个整合了小语言模型的管道,旨在解决这些问题并提高准确性。
- MathSpeech能够纠正数学表达中的错误并转化为结构化的LaTeX表示。
- MathSpeech在新数据集上的评估表现出卓越的LaTeX生成能力。
- MathSpeech与大型语言模型相比具有显著优势,尤其在参数规模较小的模型上。
点此查看论文截图

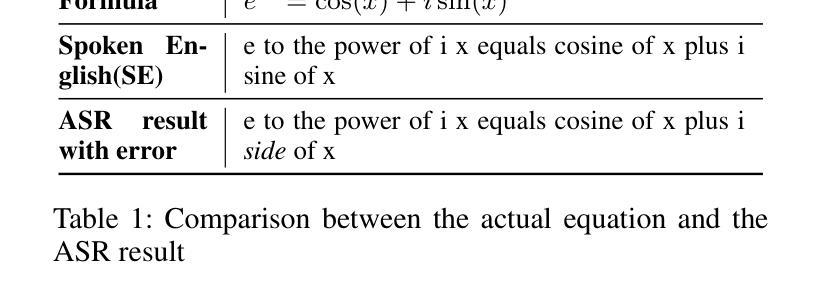




Recent Advances in Speech Language Models: A Survey
Authors:Wenqian Cui, Dianzhi Yu, Xiaoqi Jiao, Ziqiao Meng, Guangyan Zhang, Qichao Wang, Yiwen Guo, Irwin King
Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently garnered significant attention, primarily for their capabilities in text-based interactions. However, natural human interaction often relies on speech, necessitating a shift towards voice-based models. A straightforward approach to achieve this involves a pipeline of ``Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) + LLM + Text-to-Speech (TTS)”, where input speech is transcribed to text, processed by an LLM, and then converted back to speech. Despite being straightforward, this method suffers from inherent limitations, such as information loss during modality conversion, significant latency due to the complex pipeline, and error accumulation across the three stages. To address these issues, Speech Language Models (SpeechLMs) – end-to-end models that generate speech without converting from text – have emerged as a promising alternative. This survey paper provides the first comprehensive overview of recent methodologies for constructing SpeechLMs, detailing the key components of their architecture and the various training recipes integral to their development. Additionally, we systematically survey the various capabilities of SpeechLMs, categorize their evaluation metrics, and discuss the challenges and future research directions in this rapidly evolving field. The GitHub repository is available at https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey
大型语言模型(LLM)近期引起了广泛关注,主要因其基于文本的交互能力。然而,自然人类互动通常依赖于语音,因此需要向基于语音的模型转变。实现这一目标的一种直接方法涉及“自动语音识别(ASR)+ LLM +文本到语音(TTS)”的管道,其中输入语音被转录为文本,由LLM处理,然后转回语音。尽管这种方法很直接,但它存在固有的局限性,例如在模态转换过程中的信息损失、由于复杂管道导致的显著延迟以及三个阶段的错误累积。为了解决这些问题,语音语言模型(SpeechLM)——一种无需从文本转换即可生成语音的端到端模型——作为有前途的替代品应运而生。这篇综述论文首次全面概述了构建SpeechLM的最新方法,详细描述了其架构的关键组件以及对其发展至关重要的各种培训配方。此外,我们还系统地调查了SpeechLM的各种功能,对其评估指标进行分类,并讨论了这一快速演变领域面临的挑战和未来研究方向。GitHub仓库可通过以下链接访问:[https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey。](注:该链接为虚构链接,实际访问可能无法打开)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary:
近期,大型语言模型(LLMs)在文本交互中备受关注。然而,自然人类交互通常依赖于语音,因此需要转向语音模型。一种实现这一目标的直接方法是采用“自动语音识别(ASR)+大型语言模型(LLM)+文本到语音(TTS)”的管道,将输入语音转录为文本,由LLM处理后再转回语音。尽管这种方法看似简单直接,但它存在固有的局限性,如模态转换中的信息损失、复杂的管道导致的延迟以及三个阶段中的误差累积。为解决这些问题,语音语言模型(SpeechLMs)应运而生,这是一种无需从文本转换即可生成语音的端到端模型。这篇综述论文首次全面概述了构建SpeechLMs的最新方法,详细介绍了其架构的关键组件以及开发过程中不可或缺的各种训练配方。此外,系统地对SpeechLMs的各项功能进行了概述,分类了评估指标,并讨论了这一快速演变领域的挑战和未来研究方向。GitHub仓库地址:https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在文本交互中受到关注,但自然交互更多依赖语音,需要发展语音模型。
- 现有的“ASR+LLM+TTS”方法在模态转换、延迟和误差累积方面存在局限性。
- 语音语言模型(SpeechLMs)作为无需文本转换的端到端模型,为解决上述问题提供了有前景的替代方案。
- 综述论文首次全面概述了SpeechLMs的构建方法、架构组件、训练配方及功能特点。
- SpeechLMs的能力得到系统概述,评估指标被分类讨论。
- 该领域面临挑战,包括需要进一步提高性能、解决实际应用中的复杂性等。
点此查看论文截图







Investigating Training Objectives for Generative Speech Enhancement
Authors:Julius Richter, Danilo de Oliveira, Timo Gerkmann
Generative speech enhancement has recently shown promising advancements in improving speech quality in noisy environments. Multiple diffusion-based frameworks exist, each employing distinct training objectives and learning techniques. This paper aims to explain the differences between these frameworks by focusing our investigation on score-based generative models and the Schr"odinger bridge. We conduct a series of comprehensive experiments to compare their performance and highlight differing training behaviors. Furthermore, we propose a novel perceptual loss function tailored for the Schr"odinger bridge framework, demonstrating enhanced performance and improved perceptual quality of the enhanced speech signals. All experimental code and pre-trained models are publicly available to facilitate further research and development in this domain.
生成式语音增强在改善噪声环境中的语音质量方面最近显示出有希望的进展。存在多个基于扩散的框架,每个框架采用不同的训练目标和学习技术。本文旨在通过重点研究基于评分的生成模型和薛定谔桥来解释这些框架之间的差异。我们进行了一系列全面的实验来比较它们的性能并突出不同的训练行为。此外,我们针对薛定谔桥框架量身定制了一种新型感知损失函数,展示了其增强的性能和改善的感知语音信号质量。所有实验代码和预训练模型均公开提供,以促进该领域的进一步研究和开发。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
总结
本文探讨了生成性语音增强技术在噪声环境下的语音质量提升方面的最新进展。文章主要聚焦于基于评分的生成模型和Schrödinger bridge框架的差异,通过一系列实验比较了它们的性能和不同的训练行为。此外,还提出了一种针对Schrödinger bridge框架的新型感知损失函数,展示了其提升语音信号增强性能和感知质量的潜力。文章的实验代码和预训练模型已公开,有助于该领域的进一步研究和开发。
关键见解
- 生成性语音增强技术在噪声环境下提升语音质量方面展现出巨大潜力。
- 基于评分的生成模型和Schrödinger bridge框架在生成性语音增强领域中各具特色。
- 文章通过全面实验比较了不同扩散框架的性能和训练行为差异。
- 针对Schrödinger bridge框架,提出了一种新型感知损失函数。
- 此新型感知损失函数增强了语音信号增强的性能并提高了感知质量。
- 文章的实验代码和预训练模型已公开发布,为相关研究提供便利。
点此查看论文截图




A Study on Zero-shot Non-intrusive Speech Assessment using Large Language Models
Authors:Ryandhimas E. Zezario, Sabato M. Siniscalchi, Hsin-Min Wang, Yu Tsao
This work investigates two strategies for zero-shot non-intrusive speech assessment leveraging large language models. First, we explore the audio analysis capabilities of GPT-4o. Second, we propose GPT-Whisper, which uses Whisper as an audio-to-text module and evaluates the naturalness of text via targeted prompt engineering. We evaluate the assessment metrics predicted by GPT-4o and GPT-Whisper, examining their correlation with human-based quality and intelligibility assessments and the character error rate (CER) of automatic speech recognition. Experimental results show that GPT-4o alone is less effective for audio analysis, while GPT-Whisper achieves higher prediction accuracy, has moderate correlation with speech quality and intelligibility, and has higher correlation with CER. Compared to SpeechLMScore and DNSMOS, GPT-Whisper excels in intelligibility metrics, but performs slightly worse than SpeechLMScore in quality estimation. Furthermore, GPT-Whisper outperforms supervised non-intrusive models MOS-SSL and MTI-Net in Spearman’s rank correlation for CER of Whisper. These findings validate GPT-Whisper’s potential for zero-shot speech assessment without requiring additional training data.
本文研究了两种利用大型语言模型进行零样本非侵入性语音评估的策略。首先,我们探索了GPT-4o的音频分析功能。其次,我们提出了GPT-Whisper,它使用Whisper作为音频到文本的模块,并通过有针对性的提示工程评估文本的自然度。我们评估了GPT-4o和GPT-Whisper的评估指标,检查它们与人类基于的质量和可理解性评估以及自动语音识别字符错误率(CER)的相关性。实验结果表明,GPT-4o单独进行音频分析的效果较差,而GPT-Whisper的预测精度更高,与语音质量和可理解性的相关性适中,与CER的相关性更高。与SpeechLMScore和DNSMOS相比,GPT-Whisper在可理解性指标上表现优异,但在质量估计方面略逊于SpeechLMScore。此外,在Whisper的CER的斯皮尔曼等级相关性方面,GPT-Whisper表现优于监督非侵入性模型MOS-SSL和MTI-Net。这些发现验证了GPT-Whisper在不需要额外训练数据的零样本语音评估中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文研究了两种利用大型语言模型进行零样本非侵入式语音评估的策略。首先,探索了GPT-4o的音频分析功能;其次,提出了GPT-Whisper,它使用Whisper作为音频转文本模块,并通过有针对性的提示工程评估文本的自然性。实验结果表明,GPT-Whisper在预测准确性、语音质量和可理解性相关性以及字符错误率(CER)方面表现较好,与其他评估方法相比具有优势。
Key Takeaways
- GPT-4o在音频分析方面的能力有限。
- GPT-Whisper结合了音频转文本模块Whisper和有针对性的提示工程,提高了预测准确性。
- GPT-Whisper在语音质量和可理解性方面与人类评估有中等相关性。
- GPT-Whisper与字符错误率(CER)有较高的相关性。
- GPT-Whisper在可理解性指标上优于SpeechLMScore,但在质量评估上略逊于SpeechLMScore。
- GPT-Whisper在Spearman等级相关性方面优于其他非侵入式模型,如MOS-SSL和MTI-Net。
点此查看论文截图




ASR Error Correction using Large Language Models
Authors:Rao Ma, Mengjie Qian, Mark Gales, Kate Knill
Error correction (EC) models play a crucial role in refining Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) transcriptions, enhancing the readability and quality of transcriptions. Without requiring access to the underlying code or model weights, EC can improve performance and provide domain adaptation for black-box ASR systems. This work investigates the use of large language models (LLMs) for error correction across diverse scenarios. 1-best ASR hypotheses are commonly used as the input to EC models. We propose building high-performance EC models using ASR N-best lists which should provide more contextual information for the correction process. Additionally, the generation process of a standard EC model is unrestricted in the sense that any output sequence can be generated. For some scenarios, such as unseen domains, this flexibility may impact performance. To address this, we introduce a constrained decoding approach based on the N-best list or an ASR lattice. Finally, most EC models are trained for a specific ASR system requiring retraining whenever the underlying ASR system is changed. This paper explores the ability of EC models to operate on the output of different ASR systems. This concept is further extended to zero-shot error correction using LLMs, such as ChatGPT. Experiments on three standard datasets demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed methods for both Transducer and attention-based encoder-decoder ASR systems. In addition, the proposed method can serve as an effective method for model ensembling.
错误修正(EC)模型在优化自动语音识别(ASR)转录、提高转录的清晰度和质量方面扮演着至关重要的角色。无需访问底层代码或模型权重,EC就能提高性能并为黑盒ASR系统进行领域适应。本研究探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)在多种场景中的错误修正应用。通常使用ASR的1-best假设作为EC模型的输入。我们建议使用ASR的N-best列表构建高性能EC模型,这能为修正过程提供更多上下文信息。此外,标准EC模型的生成过程是无限制的,即可以生成任何输出序列。对于某些场景(如未见领域),这种灵活性可能会影响性能。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种基于N-best列表或ASR晶格的约束解码方法。最后,大多数EC模型是为特定ASR系统训练的,每当底层ASR系统发生变化时都需要重新训练。本文探讨了EC模型对不同的ASR系统输出的处理能力。这一概念进一步扩展到了使用LLM的零样本错误修正,如ChatGPT。在三个标准数据集上的实验证明了我们提出的方法对于转换器和基于注意力的编码器-解码器ASR系统的有效性。此外,该方法可以作为模型集成的一种有效方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
本文主要探讨了错误修正(EC)模型在自动语音识别(ASR)转录中的重要性。研究利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行跨场景的错误修正,提出使用ASR N-best列表构建高性能EC模型,以提供更多上下文信息用于修正过程。为解决在某些场景(如未见领域)中标准EC模型的灵活性可能影响性能的问题,引入基于N-best列表或ASR晶格的约束解码方法。此外,本文还探讨了EC模型在不同ASR系统输出上的操作能力,并扩展到零样本错误修正的LLM,如ChatGPT。实验结果表明,本文提出的方法对转换器(Transducer)和基于注意力的编码器解码器ASR系统均有效,并且可以作为有效的模型集成方法。
Key Takeaways
- 错误修正(EC)模型在自动语音识别(ASR)中起关键作用,能提高转录质量和可读性。
- 使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行错误修正,适用于多种场景。
- 提出利用ASR N-best列表构建高性能EC模型,以提供上下文信息用于修正。
- 针对某些场景(如未见领域),引入基于N-best或ASR晶格的约束解码来解决灵活性问题。
- EC模型能在不同ASR系统输出上操作,具有跨系统适应性。
- 扩展到零样本错误修正,利用LLM如ChatGPT。
点此查看论文截图







NEST: Self-supervised Fast Conformer as All-purpose Seasoning to Speech Processing Tasks
Authors:He Huang, Taejin Park, Kunal Dhawan, Ivan Medennikov, Krishna C. Puvvada, Nithin Rao Koluguri, Weiqing Wang, Jagadeesh Balam, Boris Ginsburg
Self-supervised learning has been proved to benefit a wide range of speech processing tasks, such as speech recognition/translation, speaker verification and diarization, etc. However, most of current approaches are computationally expensive. In this paper, we propose a simplified and more efficient self-supervised learning framework termed as NeMo Encoder for Speech Tasks (NEST). Specifically, we adopt the FastConformer architecture with 8x sub-sampling rate, which is faster than Transformer or Conformer architectures. Instead of clustering-based quantization, we use fixed random projection for its simplicity and effectiveness. We also implement a generalized noisy speech augmentation that teaches the model to disentangle the main speaker from noise or other speakers. Experiments show that \model improves over existing self-supervised models and achieves new state-of-the-art performance on a variety of speech processing tasks, such as speech recognition/translation, speaker diarization, spoken language understanding, etc. Code and checkpoints are publicly available via NVIDIA NeMo framework.
自监督学习已被证明对多种语音处理任务(如语音识别/翻译、说话人验证和音频转文字等)都有益处。然而,当前大多数方法的计算成本都很高。在本文中,我们提出了一种简化且更高效的自监督学习框架,名为用于语音任务的NeMo编码器(NEST)。具体来说,我们采用了具有8倍子采样率的FastConformer架构,其速度比Transformer或Conformer架构更快。我们没有使用基于聚类的量化方法,而是采用简单的固定随机投影法。我们还实现了一种通用的噪声语音增强技术,使模型学会从噪声或其他说话者中分离主要说话者。实验表明,我们的模型在多种语音处理任务上的性能超过了现有的自监督模型,并达到了新的领先水平,包括语音识别/翻译、说话人音频转文字、语音理解等任务。模型和检查点可通过NVIDIA NeMo框架公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种简化且高效的自监督学习框架,名为NeMo Encoder for Speech Tasks (NEST)。采用FastConformer架构,具有更快的计算速度。使用固定随机投影进行量化,并实现了通用的噪声语音增强技术。实验表明,该模型在多种语音处理任务上超过了现有自监督模型,并达到了最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种新的自监督学习框架NEST,用于语音处理任务。
- NEST采用FastConformer架构,具有更高的计算效率。
- 量化方法采用固定随机投影,既简单又有效。
- 实现了通用的噪声语音增强技术,使模型能够在嘈杂环境中更好地识别主要说话人。
- NEST在多种语音处理任务上表现出优异性能,如语音识别、翻译、说话人分化和口语理解等。
- 该模型通过NVIDIA NeMo框架公开可用。
点此查看论文截图